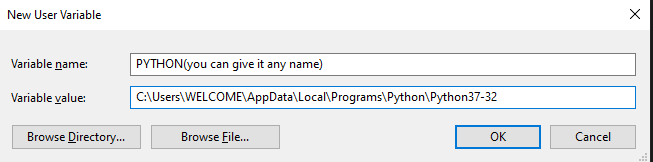
This question needs a proper answer:
Just use the standard package site, which was made for this job!
and here is how (plagiating my own answer to my own question on the very same topic):
- Open a Python prompt and type
>>> import site
>>> site.USER_SITE
'C:\Users\ojdo\AppData\Roaming\Python\Python37\site-packages'
...
(Alternatively, call python -m site --user-site for the same effect.)
- Create this folder if it does not exist yet:
...
>>> import os
>>> os.makedirs(site.USER_SITE)
...
(Or, in Bash, your preferred variant of makedirs -p $(python -m site --user-site).)
- Create a file
sitecustomize.py(with exactly this filename, or it won’t work) in this folder containing the content ofFIND_MY_PACKAGES, either manually or using something like the following code. Of course, you have to changeC:My_Projectsto the correct path to your custom import location.
...
>>> FIND_MY_PACKAGES = """
import site
site.addsitedir(r'C:My_Projects')
"""
>>> filename = os.path.join(site.USER_SITE, 'sitecustomize.py')
>>> with open(filename, 'w') as outfile:
... print(FIND_MY_PACKAGES, file=outfile)
And the next time you start Python, C:My_Projects is present in your sys.path, without having to touch system-wide settings. Bonus: the above steps work on Linux, too!
Why does this work?
From the documentation of standard library package site:
[Then] an attempt is made to import a module named
sitecustomize, which can perform arbitrary site-specific customizations. […].
So if you create a module named sitecustomize anywhere in PYTHONPATH, package site will execute it at Python startup. And by calling site.addsitedir, the sys.path can be safely extended to your liking.
Python is a great language! However, it doesn’t come pre-installed with Windows. Hence we download it to interpret the Python code which we write. But wait, windows don’t know where you have installed the Python so when trying to any Python code, you will get an error.
We will be using Windows10 and python3 for this article. (Most of the part is same for any other version of either windows or python)
Add Python to Windows Path
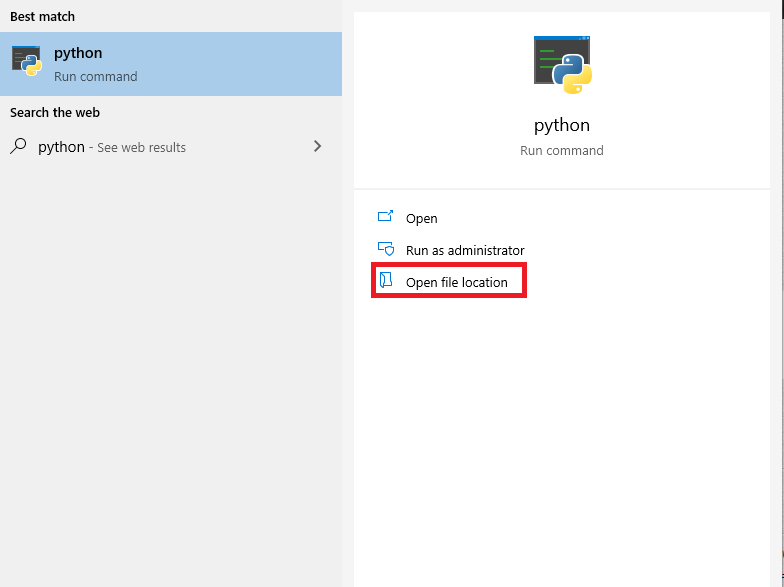
First, we need to locate where the python is being installed after downloading it. Press WINDOWS key and search for “Python”, you will get something like this:
If no results appear then Python is not installed on your machine, download it before proceeding further. Click on open file location and you will be in a location where Python is installed, Copy the location path from the top by clicking over it.
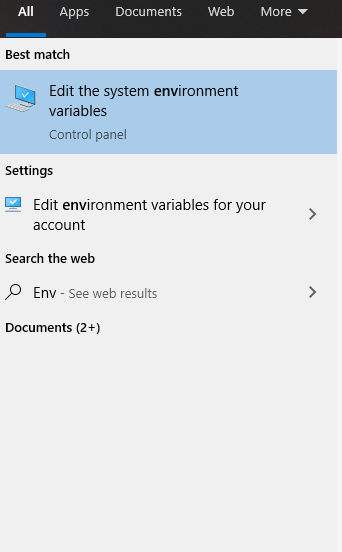
Now, we have to add the above-copied path as a variable so that windows can recognize. Search for “Environmental Variables”, you will see something like this:
Click on that
Now click the “Environmental Variables” button
There will be two categories namely “User” and “System”, we have to add it in Users, click on New button in the User section. Now, add a Variable Name and Path which we copied previously and click OK. That’s it, DONE!
Check if the Environment variable is set or not
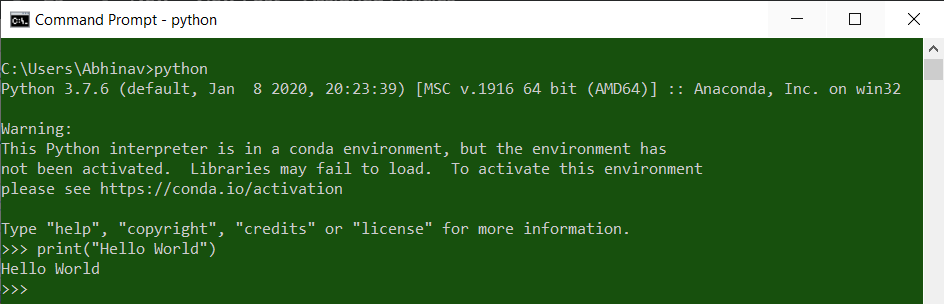
Now, after adding the Python to the Environment variable, let’s check if the Python is running anywhere in the windows or not. To do this open CMD and type Python. If the environment variable is set then the Python command will run otherwise not.
There are few ways to add Python to Windows PATH. In this guide, you’ll see two methods to add Python to Windows path:
- Via the installation of a recent version of Python
- Manual entry of the paths
Method 1: Install a Recent Version of Python
You can easily add Python to Windows path by downloading a recent version of Python, and then checking the box to Add Python to PATH at the bottom of the setup screen:
Add Python to PATH
Finish the installation, and you should be good to go.
Alternatively, you may manually add the paths into the Environment variables.
Method 2: Manually add Python to Windows Path
If you wish to stick with the previous version of Python, you may apply the steps below to manually add Python to Windows path.
First, navigate to the Windows Environment Variables screen (where you can add/edit your paths):
- Press the Windows Key + R on your keyboard in order to open the Run dialog box
- Type sysdm.cpl to open the System Properties
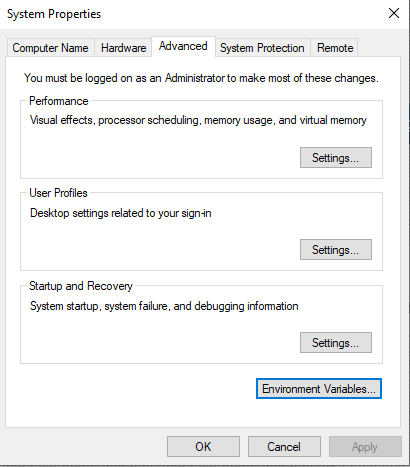
- Go to the Advanced tab and then click on the ‘Environment Variables…‘
That should take you to the Environment Variables screen, where you can add/edit your paths.
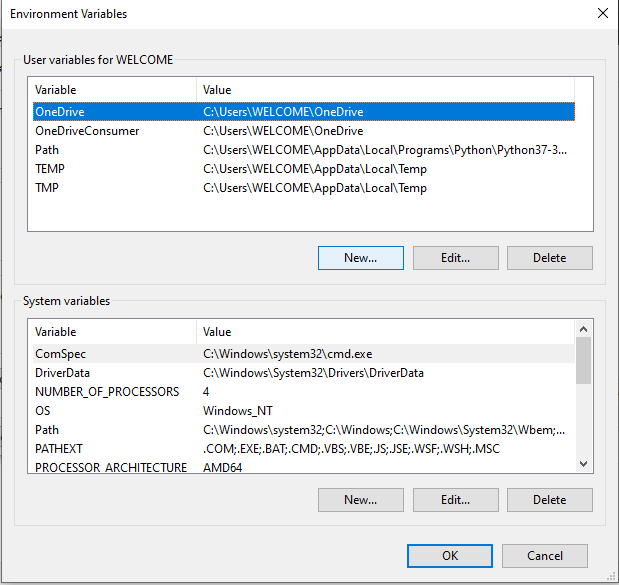
Under the User variables box, click on ‘New…‘ to add the ‘Path’ variable (note that if your ‘Path’ variable already exists, then click on ‘Edit…’ instead):
User variables
OneDrive
TEMP
TMP
New… Edit…
You should then see the New User Variable box, where you may add/edit variables:
Variable name:
Variable value:
Before you type any values, you’ll need to locate the relevant Python paths. The paths that you’ll need to get are:
(1) The Python application path, which is the folder where you originally installed Python. You can find the Python application path by following these steps:
- Type “Python” in the Windows Search Bar
- Right-click on the Python App, and then select “Open file location“
- Right-click again on the Python shortcut, and then select “Open file location“
Here is an example of a Python application path:
C:UsersRonAppDataLocalProgramsPythonPython39
(2) The Python Scripts path. The Scripts folder should be located within the Python application path. Example:
C:UsersRonAppDataLocalProgramsPythonPython39scripts
After you obtained the paths, fill the New User Variable box that you saw earlier:
- For the Variable name, type ‘Path‘
- For the Variable value, copy the full Python application path, then use semicolon (as highlighted in yellow below), and finally copy the Python Scripts path.
For our example:
Variable name: Path
Variable value: C:UsersRonAppDataLocalProgramsPythonPython39;C:UsersRonAppDataLocalProgramsPythonPython39Scripts
Press ‘OK’ and you would then see your new Python Path under the ‘User variables‘ section. Don’t forget to press ‘OK‘ again so that the changes will get implemented.
User variables
OneDrive
Path C:UsersRonAppDataLocalProgramsPythonPython39;C:Users…
TEMP
TMP
New… Edit…
System variables
…
…
…
OK Cancel
You just added Python to the Windows Path.
You should be able to install Python packages easily, by opening the Windows Command Prompt and then typing:
pip install package_name
For example, to install the Pandas package, simply type ‘pip install pandas‘ and then press ENTER:
pip install pandas
Similarly, you may upgrade PIP by typing the following command:
python -m pip install --upgrade pip
This article will put forth a very simple ye and important concept that is how to add Python to path and follow it up with a detailed practical demonstration. Following pointers will be covered in this article,
- Add Python To Path
- Installing Python
- Setting up Path
- How to add Python Path to Windows?
- Setting Path in Unix or Linux
- Environmental Variables
So let us get started then,
Add Python To Path
Today there is an application for whichever problem you can imagine. Be it in the form of a web application or one that runs on your smartphone, the world of applications is literally an endless pit of opportunities, thus making Python an obvious choice for many developers across the world. The reason for Python being such a popular choice is the plethora of features, the platform comes with.
For developers who are just beginning to learn Python, one might mistakenly install Python in Windows without fulfilling the prerequisites first. One of the most common problems that we hear from developers is how to add path in Python and in this article, we will talk about just that.
But first let’s get the basics out of the way.
Moving on with this article on How To Add Python To Path,
Flavors of Python
Similar to other programming platforms available on the market, Python too is supported by all the operating systems that are currently in existence, most prominently, Linux, Mac OS and Windows.
Installing Python
The most up to date version of Python that is available for download is pretty easy to install. You just need to download the binary code that is applicable for your operating system and install the same. If you find that the binary code is not available for the operating system you are using, you need to make use of a C compiler to compile the source code manually.
One of the most significant advantages of compiling your source code manually is that you will get more flexibility in terms of features that you might need during the installation process.
Moving on with this article on How To Add Python To Path,
Setting up Path
Once you have installed Python on your system, now comes the tricky part of setting path so that you can easily access the python.exe file. Depending on the operating system you are currently using, the process of setting up path varies greatly. Mentioned below are the steps to set up Path for Windows, Mac and Linux simultaneously.
Adding Python Path to Windows
If you have installed Python in Windows like most other developers by just following online tutorials, in most cases there is a chance that the Python executable file wasn’t added to the Windows Path Variable. While this might sound like a small thing at the beginning, when you start using Python full-fledged this will cause a problem. The Python executable file is responsible for listing the directories that will be executed when you type in a command in the command prompt of your Python window. Once you have added the Python executable file in the Windows directory, you will be able to access the python.exe file simply by typing the python keyword. One of the main advantages of adding this feature is that, every time you need to access the python.exe file, you don’t need to specify the full path to the program.
Now let us consider a case, where the Python executable file has not been added to the Windows Path. In such a scenario, when you enter a Python command in the command prompt, you will be greeted by an iteration of the following message.
C:>python
‘python’ is not recognized as an internal or external command,
operable program or batch file.
This message clearly indicates that the python.exe file has not been added to the Windows Path and therefore you won’t be able to access it. In such a scenario, if you want to access the python.exe file you need to specific the full address of the file. It will look something like this,
C:>C:Python34python –version
Python 3.4.3
As you can see from this example, this process is definitely more complicated than what meets the eye and therefore it is always advisable that you add the python executable file to the Windows Path at the very beginning of the installation process.
Moving on with this article on How To Add Python To Path,
How to add Python Path to Windows?
Now that we are aware of the effects of not adding Python Path to Windows, here is a simple method of adding it.
- Start the Run function on your Windows computer, by using the shortcuts ctrl+R.
- Once the Run prompt is up and running, type in sysdm.cpl
- Press Enter and you will be redirected to System Properties. In this section, locate the Advanced Tab and click on the button that reads Environment Variables.
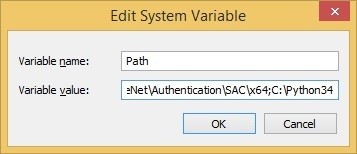
- Under Environment Variables, find System Variables and locate the Path.
- Click on Edit and locate the option which says Variable Value. In this section add the path at the end of the phrase that is already present. One of the most important things to note here is that, before you add the Path you need to include a semicolon (;) so that both can be differentiated easily.
- In our example above, we have added the Path which reads ;C:Python34.
Once this is done, press OK and the path will be added to the specific location. Save all your actions and reboot your system for more effective performance.
Moving on with this article on How To Add Python To Path,
Setting Path in Unix or Linux
The steps for adding Path in Unix or Linux are fairly straight forward, just follow the steps outlined below.
- In the csh shell, type the following sentence: PATH “$PATH:/usr/local/bin/python” and press Enter.
- If you are using the standard flavour of Linux, open up the bash shell and type the following phrase, export PATH=”$PATH:/usr/local/bin/python” and press Enter.
- If you have access to either sh or ksh shell, then open up the terminal and type the following, PATH=”$PATH:/usr/local/bin/python” and press Enter.
One of the most important things to note when you are adding Path to Python in Unix or Linux is that, /usr/local/bin/python is the default path of the Python directory.
Moving on with this article on How To Add Python To Path,
Environmental Variables
Now that you have successfully added Path to Python, here are some of the most significant Environmental Variables that Python recognizes.
-
PYTHONPATH: This is one of the most common Environmental Variables that Python recognizes and it has a role that is similar to the original Path. The use of this variable tells Python where to locate the module files and how to import them into a program. While using this function, be sure to include Python source library directory and also the directories that contain the Python source code. In some instances, PYTHONPATH is already preset in the Python directory.
-
PYTHONSTARTUP: The use of this file contains the path of an initialization file which contains the Python source code. This function is executed every time you start the interpreter in Python. In Unix or Linux, this is named as pythonrc.py and using this command loads the utilities that modify PYTHONPATH.
-
PYTHONCASEOK: This is an Environmental Variable that is specific to Windows. When you use this variable, Python will find the first case insensitive match in an import statement. In order to activate this variable, you can set it to any value of your choice.
-
PYTHONHOME: This is an alternative to module search path that can be used in Python. In most scenarios this is embedded into the PYTHONSTARTUP or PYTHONPATH in order to make switching modules between libraries fairly easy.
This brings us to the end of this article on How To Add Python To Path?
To get in-depth knowledge on Python along with its various applications, you can enroll now for live Python course training with 24/7 support and lifetime access.
Got a question for us? Mention them in the comments section of “Python Tutorial” and we will get back to you.
I want to be able to run Python commands from the Windows CMD. However, if I don’t specify Python’s full path for each command, I get an error saying «Python is not recognized as an internal or external command, operable program or batch file.«
How do I add Python to the Windows PATH permanently?
Stevoisiak
13k36 gold badges96 silver badges150 bronze badges
asked May 19, 2010 at 21:54
For Windows 10/8/7:
- Open
System Properties(Right clickComputerin the start menu, or use the keyboard shortcut Win+Pause) - Click
Advanced system settingsin the sidebar. - Click
Environment Variables... - Select
PATHin theSystem variablessection - Click
Edit -
Add Python’s path to the end of the list (the paths are separated by semicolons). For example:
C:Windows;C:WindowsSystem32;C:Python27
For Windows XP:
- Open
System Properties(Type it in the start menu, or use the keyboard shortcut Win+Pause) - Switch to the
Advancedtab - Click
Environment Variables... - Select
PATHin theSystem variablessection - Click
Edit -
Add Python’s path to the end of the list (the paths are separated by semicolons). For example:
C:Windows;C:WindowsSystem32;C:Python27 -
Test on a new terminal window or if using an integrated terminal within a
text editor, close and restart your editor or the changes won’t be applied.
Run5k
15.6k24 gold badges49 silver badges63 bronze badges
answered May 19, 2010 at 21:58
Michael MrozekMichael Mrozek
1,8751 gold badge13 silver badges14 bronze badges
6
For anyone trying to achieve this with Python 3.3+, the Windows installer now includes an option to add python.exe to the system search path. Read more in the docs.
answered Nov 4, 2013 at 9:01
1
- Click on the windows button to start a search
- type in «system env» and click on the «edit system environment variables»
- Now click on the advanced tab on the top
- At the bottom click the button that says «environment variables»
- Now on the «user variables’your user name'» box at the top of the windows click on path then edit
- This should lead to another window where you want to click «new» and type in the commands: «C:Python27» and «C:Python27scripts»
- Python should now work on command prompt
answered Feb 12, 2018 at 20:00
3
As seen in the Python documentation:
Windows has a built-in dialog for
changing environment variables
(following guide applies to XP
classical view): Right-click the icon
for your machine (usually located on
your Desktop and called “My Computer”)
and choose Properties there. Then,
open the Advanced tab and click the
Environment Variables button.In short, your path is:
My Computer ‣ Properties ‣ Advanced ‣
Environment Variables In this dialog,
you can add or modify User and System
variables. To change System variables,
you need non-restricted access to your
machine (i.e. Administrator rights).
Stevoisiak
13k36 gold badges96 silver badges150 bronze badges
answered May 19, 2010 at 21:59
1
Right-click on My Computer, choose Properties. Then find the Environment Variables button (on Win7, it’s under the Advanced tab; I forget where it is on other versions of Windows). Click that, and under System variables, edit the Path one.
answered May 19, 2010 at 21:57
AmberAmber
6015 silver badges4 bronze badges
Running Python from the terminal is often unavoidable. However, if you just installed Python on Windows 10 for the first time, running it via the Windows Terminal is only possible if it’s added to the Windows PATH environment variable.
It can seem tricky to do, but it’s nothing to fear. To help you overcome the twists involved in adding Python to the Windows PATH after installing it, let’s take a look at the options and the few steps involved.
Why Add Python to Windows PATH?
If you fail to add Python to the PATH on your Windows OS, you can’t run the Python interpreter, start a virtual programming environment, or run commands like pip install from the terminal.
That’s because, when you run any non-default program from the command line, the machine looks for an executable in the current folder, or in the Windows PATH.
If it’s not in the PATH variable, the terminal returns a «command not found» error. Adding to the PATH is powerful, even if you’re executing a command from a created or default batch file, adding its parent execution file to the PATH variable makes it callable from the terminal as well.
How to Manually Add Python to the Windows PATH
First off, if you’ve not installed Python on your machine, go to the python.org website to download and install your preferred version.
Once Python is successfully installed on your PC, check if it’s already added to the Windows PATH. Open up your terminal and type python, then hit the Enter key. The command might return an error that says «‘python’ is not recognized as an internal or external command, operable program or batch file,» indicating that Python isn’t added to your machine’s PATH variable yet.
To execute Python programs from your command line, follow the steps highlighted below.
Find Python’s Installation Path on Your PC
To add Python to your Windows PATH, you need to get its installation path. To do that, open up the Windows search bar and type python.exe (don’t hit the Enter key). Then right-click on Python.exe that pops up in the resulting menu and select the Open file location option.
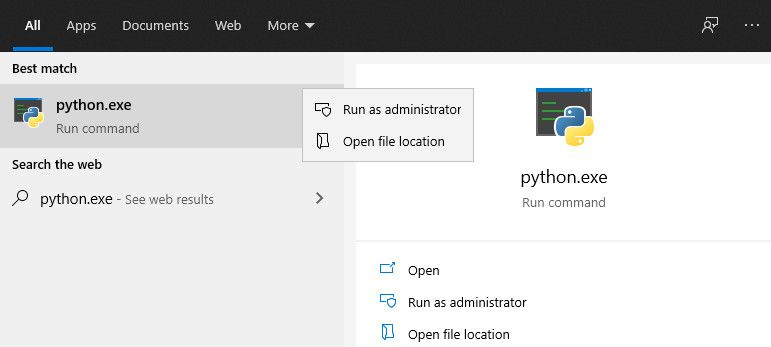
In the Explorer windows that opens, click on the long directory bar to the left of the search bar. Highlight and copy the entire path text to your clipboard with Ctrl + c. Then continue with the next steps below.
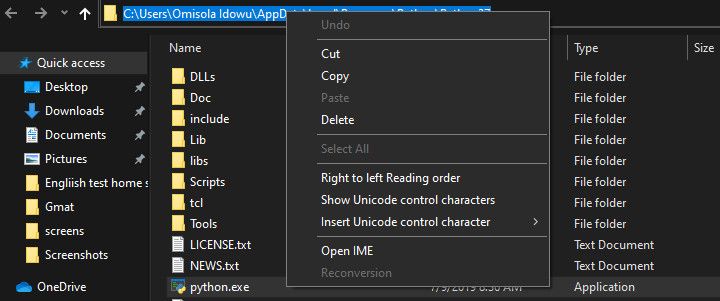
Next: Add Python to PATH in User Variables
To add Python to the PATH in User variables, right-click on This PC, and select Properties. Once in the properties menu, click on the Advanced system settings option. In the next window, select the Advanced tab, and select Environment Variables.
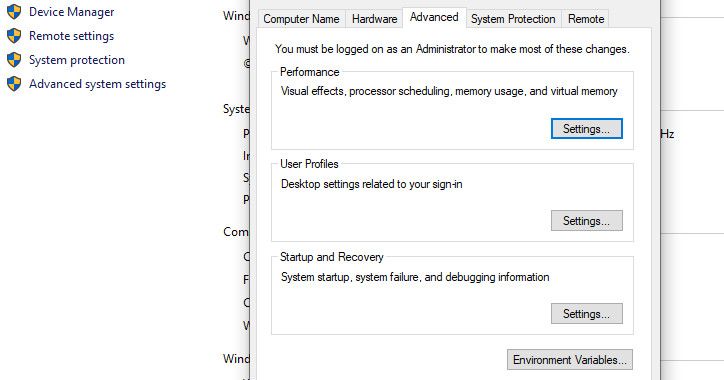
The Environment Variables menu has two distinct parts: an upper part called User variables, and a lower part named System variables. However, our focus is on the User variables in this case.
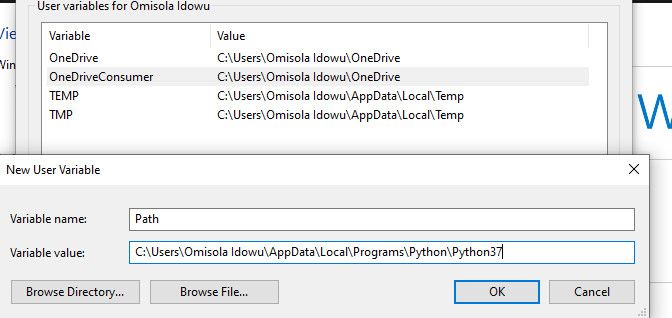
Within the User variables menu, locate a variable called Path. Then paste the path you copied earlier in the Variable value option using Ctrl + v and click Ok.
However, if you can’t find that variable, you might need to create it. To do that, click on New. Next, in the Variable name form, type Path, and paste your Python path in the Variable value field.
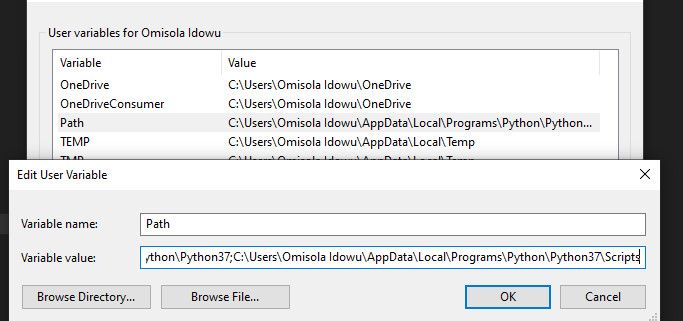
Go back to your Python installation path folder and double-click on Scripts to open that directory. Next, copy its path from the path bar at the upper part of the windows (besides the search bar), just like you did earlier for the Python installation path.
Once you’ve copied the Scripts path, head back to the Environment Variables. Next, select the Path variable and click on Edit. Type a semi-colon after your Python executable path and paste the Scripts path you just copied after it. Then click Ok.
Adding Python to the PATH With the System Variables Option
You can add Python to the System Variables PATH as well. Although this is just an alternative, and it’s not necessary if you’ve added it in the Users variables already.
To use the System Variables option, follow the steps highlighted above for copying the Python path and its Scripts path. Then head back into the Environment Variables. Then, inside the System Variables segment, locate a variable called Path. Click on that variable and click on Edit.
In the next window that comes up, click on New and paste the path you copied earlier in the opened space. Repeat that process for the Scripts path as well. Next, click Ok and close the Environment Variables window.
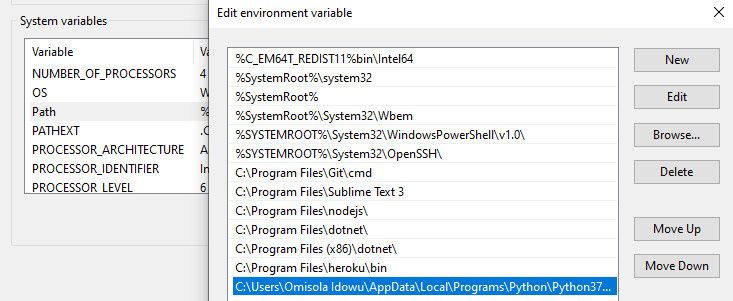
Add Python to Windows PATH Automatically
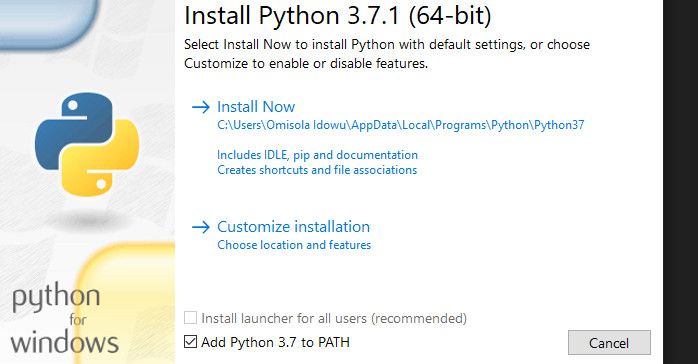
You can add Python to the Windows PATH automatically during installation as well. Although using this method doesn’t work in all cases, you can still give it a try.
To do that, click on your installation file and check the Add Python 3.7 to PATH box. The version number will change when installing different versions of Python.
Checking that box adds Python to your Windows PATH automatically. That means you can start running Python commands via the command line immediately after installation.
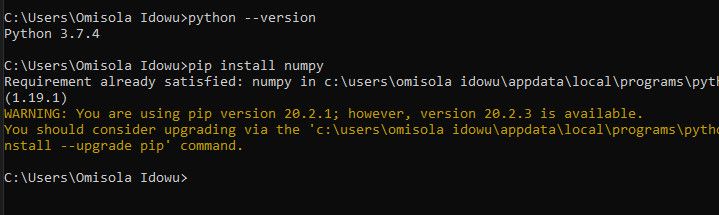
Confirm That Python Is Added to Windows PATH
To see if Python is already added to the Windows PATH, open the terminal and type python —version, then hit the Enter key. If the command returns the currently installed version of Python, it means you’ve successfully added it to the Windows PATH.
However, to check if you’ve added the Scripts directory to the Windows PATH, try to run pip install package on the terminal, replacing «package» with your preferred library. If you’ve installed Python 2.7.9 and above, the command installs the named package, indicating that you’ve successfully added Python’s Scripts to the path as well.
Other Program You Should Consider Adding to the Windows Path
In addition to adding Python to the Windows PATH, you can add text editors, Integrated Development Environments (IDEs), Git, Node, Anaconda, and many other programs.
For instance, managing a project with Sublime Text is easy when you open the terminal to the directory of your project folder and run the subl . command. This opens the editor in your current folder and displays it in the sidebar, another time-saving shortcut for working productively with Sublime Text.