I am trying to add C:xamppphp to my system PATH environment variable in Windows.
I have already added it using the Environment Variables dialog box.
But when I type into my console:
C:>path
it doesn’t show the new C:xamppphp directory:
PATH=D:Program FilesAutodeskMaya2008bin;C:Ruby192bin;C:WINDOWSsystem32;C:WINDOWS;
C:WINDOWSSystem32Wbem;C:PROGRA~1DISKEE~2DISKEE~1;c:Program FilesMicrosoft SQL
Server90Toolsbinn;C:Program FilesQuickTimeQTSystem;D:Program FilesTortoiseSVNbin
;D:Program FilesBazaar;C:Program FilesAndroidandroid-sdktools;D:Program Files
Microsoft Visual StudioCommonToolsWinNT;D:Program FilesMicrosoft Visual StudioCommon
MSDev98Bin;D:Program FilesMicrosoft Visual StudioCommonTools;D:Program Files
Microsoft Visual StudioVC98bin
I have two questions:
- Why did this happen? Is there something I did wrong?
- Also, how do I add directories to my
PATHvariable using the console (and programmatically, with a batch file)?
asked Mar 3, 2012 at 12:58
8
Option 1
After you change PATH with the GUI, close and reopen the console window.
This works because only programs started after the change will see the new PATH.
Option 2
This option only affects your current shell session, not the whole system. Execute this command in the command window you have open:
set PATH=%PATH%;C:yourpathhere
This command appends C:yourpathhere to the current PATH. If your path includes spaces, you do not need to include quote marks.
Breaking it down:
set– A command that changes cmd’s environment variables only for the current cmd session; other programs and the system are unaffected.PATH=– Signifies thatPATHis the environment variable to be temporarily changed.%PATH%;C:yourpathhere– The%PATH%part expands to the current value ofPATH, and;C:yourpathhereis then concatenated to it. This becomes the newPATH.
answered Mar 3, 2012 at 13:03
JimRJimR
15.1k2 gold badges20 silver badges26 bronze badges
12
WARNING: This solution may be destructive to your PATH, and the stability of your system. As a side effect, it will merge your user and system PATH, and truncate PATH to 1024 characters. The effect of this command is irreversible. Make a backup of PATH first. See the comments for more information.
Don’t blindly copy-and-paste this. Use with caution.
You can permanently add a path to PATH with the setx command:
setx /M path "%path%;C:yourpathhere"
Remove the /M flag if you want to set the user PATH instead of the system PATH.
Notes:
- The
setxcommand is only available in Windows 7 and later. -
You should run this command from an elevated command prompt.
-
If you only want to change it for the current session, use set.
StayOnTarget
10.9k10 gold badges49 silver badges75 bronze badges
answered Feb 28, 2015 at 5:12
NafscriptNafscript
4,9572 gold badges16 silver badges15 bronze badges
15
This only modifies the registry. An existing process won’t use these values. A new process will do so if it is started after this change and doesn’t inherit the old environment from its parent.
You didn’t specify how you started the console session. The best way to ensure this is to exit the command shell and run it again. It should then inherit the updated PATH environment variable.
answered Mar 3, 2012 at 13:23
Hans PassantHans Passant
912k145 gold badges1670 silver badges2507 bronze badges
6
You don’t need any set or setx command. Simply open the terminal and type:
PATH
This shows the current value of PATH variable. Now you want to add directory to it? Simply type:
PATH %PATH%;C:xamppphp
If for any reason you want to clear the PATH variable (no paths at all or delete all paths in it), type:
PATH ;
Update
Like Danial Wilson noted in comment below, it sets the path only in the current session. To set the path permanently, use setx but be aware, although that sets the path permanently, but not in the current session, so you have to start a new command line to see the changes. More information is here.
To check if an environmental variable exist or see its value, use the ECHO command:
echo %YOUR_ENV_VARIABLE%
answered Jul 1, 2015 at 15:11
zarzar
10.9k13 gold badges90 silver badges171 bronze badges
6
I would use PowerShell instead!
To add a directory to PATH using PowerShell, do the following:
$PATH = [Environment]::GetEnvironmentVariable("PATH")
$xampp_path = "C:xamppphp"
[Environment]::SetEnvironmentVariable("PATH", "$PATH;$xampp_path")
To set the variable for all users, machine-wide, the last line should be like:
[Environment]::SetEnvironmentVariable("PATH", "$PATH;$xampp_path", "Machine")
In a PowerShell script, you might want to check for the presence of your C:xamppphp before adding to PATH (in case it has been previously added). You can wrap it in an if conditional.
So putting it all together:
$PATH = [Environment]::GetEnvironmentVariable("PATH", "Machine")
$xampp_path = "C:xamppphp"
if( $PATH -notlike "*"+$xampp_path+"*" ){
[Environment]::SetEnvironmentVariable("PATH", "$PATH;$xampp_path", "Machine")
}
Better still, one could create a generic function. Just supply the directory you wish to add:
function AddTo-Path{
param(
[string]$Dir
)
if( !(Test-Path $Dir) ){
Write-warning "Supplied directory was not found!"
return
}
$PATH = [Environment]::GetEnvironmentVariable("PATH", "Machine")
if( $PATH -notlike "*"+$Dir+"*" ){
[Environment]::SetEnvironmentVariable("PATH", "$PATH;$Dir", "Machine")
}
}
You could make things better by doing some polishing. For example, using Test-Path to confirm that your directory actually exists.
answered Mar 17, 2015 at 20:24
Ifedi OkonkwoIfedi Okonkwo
3,3064 gold badges31 silver badges45 bronze badges
4
Safer SETX
Nod to all the comments on the @Nafscript’s initial SETX answer.
SETXby default will update your user path.SETX ... /Mwill update your system path.%PATH%contains the system path with the user path appended
Warnings
- Backup your
PATH—SETXwill truncate your junk longer than 1024 characters - Don’t call
SETX %PATH%;xxx— adds the system path into the user path - Don’t call
SETX %PATH%;xxx /M— adds the user path into the system path - Excessive batch file use can cause blindness1
The ss64 SETX page has some very good examples. Importantly it points to where the registry keys are for SETX vs SETX /M
User Variables:
HKCUEnvironmentSystem Variables:
HKLMSYSTEMCurrentControlSetControlSession ManagerEnvironment
Usage instructions
Append to User PATH
append_user_path.cmd
@ECHO OFF
REM usage: append_user_path "path"
SET Key="HKCUEnvironment"
FOR /F "usebackq tokens=2*" %%A IN (`REG QUERY %Key% /v PATH`) DO Set CurrPath=%%B
ECHO %CurrPath% > user_path_bak.txt
SETX PATH "%CurrPath%";%1
Append to System PATH
append_system_path.cmd. Must be run as administrator.
(It’s basically the same except with a different Key and the SETX /M modifier.)
@ECHO OFF
REM usage: append_system_path "path"
SET Key="HKLMSYSTEMCurrentControlSetControlSession ManagerEnvironment"
FOR /F "usebackq tokens=2*" %%A IN (`REG QUERY %Key% /v PATH`) DO Set CurrPath=%%B
ECHO %CurrPath% > system_path_bak.txt
SETX PATH "%CurrPath%";%1 /M
Alternatives
Finally there’s potentially an improved version called SETENV recommended by the ss64 SETX page that splits out setting the user or system environment variables.
Example
Here’s a full example that works on Windows 7 to set the PATH environment variable system wide. The example detects if the software has already been added to the PATH before attempting to change the value. There are a number of minor technical differences from the examples given above:
@echo off
set OWNPATH=%~dp0
set PLATFORM=mswin
if defined ProgramFiles(x86) set PLATFORM=win64
if "%PROCESSOR_ARCHITECTURE%"=="AMD64" set PLATFORM=win64
if exist "%OWNPATH%textexmf-mswinbincontext.exe" set PLATFORM=mswin
if exist "%OWNPATH%textexmf-win64bincontext.exe" set PLATFORM=win64
rem Check if the PATH was updated previously
echo %PATH% | findstr "texmf-%PLATFORM%" > nul
rem Only update the PATH if not previously updated
if ERRORLEVEL 1 (
set Key="HKLMSYSTEMCurrentControlSetControlSession ManagerEnvironment"
for /F "USEBACKQ tokens=2*" %%A in (`reg query %%Key%% /v PATH`) do (
if not "%%~B" == "" (
rem Preserve the existing PATH
echo %%B > currpath.txt
rem Update the current session
set PATH=%PATH%;%OWNPATH%textexmf-%PLATFORM%bin
rem Persist the PATH environment variable
setx PATH "%%B;%OWNPATH%textexmf-%PLATFORM%bin" /M
)
)
)
1. Not strictly true
Dave Jarvis
29.9k39 gold badges177 silver badges310 bronze badges
answered Dec 29, 2016 at 12:04
icc97icc97
10.6k8 gold badges68 silver badges88 bronze badges
0
Handy if you are already in the directory you want to add to PATH:
set PATH=%PATH%;%CD%
It works with the standard Windows cmd, but not in PowerShell.
For PowerShell, the %CD% equivalent is [System.Environment]::CurrentDirectory.
answered Mar 18, 2016 at 16:09
nclordnclord
1,2271 gold badge16 silver badges17 bronze badges
2
Aside from all the answers, if you want a nice GUI tool to edit your Windows environment variables you can use Rapid Environment Editor.
Try it! It’s safe to use and is awesome!
answered Feb 17, 2016 at 4:10
NetoricaNetorica
18.1k17 gold badges72 silver badges108 bronze badges
1
- Command line changes will not be permanent and will be lost when the console closes.
- The path works like first comes first served.
- You may want to override other already included executables. For instance, if you already have another version on your path and you want to add different version without making a permanent change on path, you should put the directory at the beginning of the command.
To override already included executables;
set PATH=C:xamppphp;%PATH%;
answered Sep 6, 2016 at 14:37
hevihevi
2,3501 gold badge32 silver badges51 bronze badges
Use pathed from gtools.
It does things in an intuitive way. For example:
pathed /REMOVE "c:myfolder"
pathed /APPEND "c:myfolder"
It shows results without the need to spawn a new cmd!
answered Mar 19, 2019 at 9:37
womdwomd
2,97325 silver badges19 bronze badges
1
Regarding point 2, I’m using a simple batch file that is populating PATH or other environment variables for me. Therefore, there isn’t any pollution of environment variables by default. This batch file is accessible from everywhere so I can type:
mybatchfile
Output:
-- Here all environment variables are available
And:
php file.php
answered Oct 30, 2015 at 14:22
3
Checking the above suggestions on Windows 10 LTSB, and with a glimpse on the «help» outlines (that can be viewed when typing ‘command /?’ on the cmd), brought me to the conclusion that the PATH command changes the system environment variable Path values only for the current session, but after reboot all the values reset to their default- just as they were prior to using the PATH command.
On the other hand using the SETX command with administrative privileges is way more powerful. It changes those values for good (or at least until the next time this command is used or until next time those values are manually GUI manipulated… ).
The best SETX syntax usage that worked for me:
SETX PATH "%PATH%;C:pathtowherethecommandresides"
where any equal sign ‘=’ should be avoided, and don’t you worry about spaces! There isn’t any need to insert any more quotation marks for a path that contains spaces inside it — the split sign ‘;’ does the job.
The PATH keyword that follows the SETX defines which set of values should be changed among the System Environment Variables possible values, and the %PATH% (the word PATH surrounded by the percent sign) inside the quotation marks, tells the OS to leave the existing PATH values as they are and add the following path (the one that follows the split sign ‘;’) to the existing values.
answered Nov 22, 2016 at 20:34
1
If you run the command cmd, it will update all system variables for that command window.
answered Oct 17, 2018 at 2:06
1
In a command prompt you tell Cmd to use Windows Explorer’s command line by prefacing it with start.
So start Yourbatchname.
Note you have to register as if its name is batchfile.exe.
Programs and documents can be added to the registry so typing their name without their path in the Start — Run dialog box or shortcut enables Windows to find them.
This is a generic reg file. Copy the lines below to a new Text Document and save it as anyname.reg. Edit it with your programs or documents.
In paths, use \ to separate folder names in key paths as regedit uses a single to separate its key names. All reg files start with REGEDIT4. A semicolon turns a line into a comment. The @ symbol means to assign the value to the key rather than a named value.
The file doesn’t have to exist. This can be used to set Word.exe to open Winword.exe.
Typing start batchfile will start iexplore.exe.
REGEDIT4
;The bolded name below is the name of the document or program, <filename>.<file extension>
[HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINESoftwareMicrosoftWindowsCurrentVersionApp PathsBatchfile.exe]
; The @ means the path to the file is assigned to the default value for the key.
; The whole path in enclosed in a quotation mark ".
@=""C:\Program Files\Internet Explorer\iexplore.exe""
; Optional Parameters. The semicolon means don't process the line. Remove it if you want to put it in the registry
; Informs the shell that the program accepts URLs.
;"useURL"="1"
; Sets the path that a program will use as its' default directory. This is commented out.
;"Path"="C:\Program Files\Microsoft Office\Office\"
You’ve already been told about path in another answer. Also see doskey /? for cmd macros (they only work when typing).
You can run startup commands for CMD. From Windows Resource Kit Technical Reference
AutoRun
HKCUSoftwareMicrosoftCommand Processor
Data type Range Default value
REG_SZ list of commands There is no default value for this entry.
Description
Contains commands which are executed each time you start Cmd.exe.
answered Dec 21, 2016 at 1:08
A better alternative to Control Panel is to use this freeware program from SourceForge called Pathenator.
However, it only works for a system that has .NET 4.0 or greater such as Windows 7, Windows 8, or Windows 10.
answered Aug 28, 2017 at 1:24
BimoBimo
5,5972 gold badges35 silver badges57 bronze badges
0
As trivial as it may be, I had to restart Windows when faced with this problem.
I am running Windows 7 x64. I did a manual update to the system PATH variable. This worked okay if I ran cmd.exe from the stat menu. But if I type «cmd» in the Windows Explorer address bar, it seems to load the PATH from elsewhere, which doesn’t have my manual changes.
(To avoid doubt — yes, I did close and rerun cmd a couple of times before I restarted and it didn’t help.)
answered Oct 20, 2019 at 18:03
svinecsvinec
6298 silver badges9 bronze badges
3
The below solution worked perfectly.
Try the below command in your Windows terminal.
setx PATH "C:myfolder;%PATH%"
SUCCESS: Specified value was saved.
You can refer to more on here.
answered Jun 5, 2021 at 13:42
Use these commands in the Bash shell on Windows to append a new location to the PATH variable
PATH=$PATH:/path/to/mydir
Or prepend this location
PATH=/path/to/mydir:$PATH
In your case, for instance, do
PATH=$PATH:C:xamppphp
You can echo $PATH to see the PATH variable in the shell.
answered Sep 1, 2021 at 6:48
kiriloffkiriloff
25.2k36 gold badges143 silver badges222 bronze badges
1
-
I have installed PHP that time. I extracted php-7***.zip into C:php</i>
-
Back up my current PATH environment variable: run
cmd, and execute command:path >C:path-backup.txt -
Get my current path value into C:path.txt file (the same way)
-
Modify path.txt (sure, my path length is more than 1024 characters, and Windows is running few years)
- I have removed duplicates paths in there, like ‘C:Windows; or C:WindowsSystem32; or C:WindowsSystem32Wbem; — I’ve got twice.
- Remove uninstalled programs paths as well. Example: C:Program FilesNonExistSoftware;
- This way, my path string length < 1024 :)))
- at the end of the path string, add
;C:php - Copy path value only into buffer with framed double quotes! Example: «C:Windows;****;C:php» No PATH= should be there!!!
-
Open Windows PowerShell as Administrator (e.g., Win + X).
-
Run command:
setx path "Here you should insert string from buffer (new path value)" -
Rerun your terminal (I use «Far Manager») and check:
php -v
answered Oct 24, 2018 at 20:50
SerbSerb
214 bronze badges
How to open the Environment Variables window from cmd.exe/Run… dialog
SystemPropertiesAdvancedand click «Environment Variables», no UACrundll32 sysdm.cpl,EditEnvironmentVariablesdirect, might trigger UAC
Via Can the environment variables tool in Windows be launched directly? on Server Fault.
How to open the Environment Variables window from Explorer
- right-click on «This PC»
- Click on «Properties»
- On the left panel of the window that pops up, click on «Advanced System Settings»
- Click on the «Advanced» tab
- Click on «Environment Variables» button at the bottom of the window
You can also search for Variables in the Start menu search.
Reference images how the Environment Variables window looks like:
Windows 10

via
Windows 7

via
Windows XP

via
On Windows 10, I was able to search for set path environment variable and got these instructions:
- From the desktop, right-click the very bottom-left corner of the screen to get the Power User Task Menu.
- From the Power User Task Menu, click System.
- In the Settings window, scroll down to the Related settings section and click the System info link.
- In the System window, click the Advanced system settings link in the left navigation panel.
- In the System Properties window, click the Advanced tab, then click the Environment Variables button near the bottom of that tab.
- In the Environment Variables window (pictured below), highlight the Path variable in the System variables section and click the Edit button. Add or modify the path lines with the paths you want the computer to access. Each different directory is separated with a semicolon, as shown below:
C:Program Files;C:Winnt;C:WinntSystem32
The first time I searched for it, it immediately popped up the System Properties Window. After that, I found the above instructions.
answered Nov 12, 2020 at 1:38
JaninJanin
2721 gold badge2 silver badges7 bronze badges
PATH is an environment variable that specifies a set of directories, separated with semicolons (;), where executable programs are located.
In this note i am showing how to print the contents of Windows PATH environment variable from the Windows command prompt.
I am also showing how to add a directory to Windows PATH permanently or for the current session only.
Cool Tip: List environment variables in Windows! Read More →
Print the contents of the Windows PATH variable from cmd:
C:> path
– or –
C:> echo %PATH%
The above commands return all directories in Windows PATH environment variable on a single line separated with semicolons (;) that is not very readable.
To print each entry of Windows PATH variable on a new line, execute:
C:> echo %PATH:;=&echo.%
Cool Tip: Set environment variables in Windows! Read More →
Add To Windows PATH
Warning! This solution may be destructive as Windows truncates PATH to 1024 characters. Make a backup of PATH before any modifications.
Save the contents of the Windows PATH environment variable to C:path-backup.txt file:
C:> echo %PATH% > C:path-backup.txt
Set Windows PATH For The Current Session
Set Windows PATH variable for the current session:
C:> set PATH="%PATH%;C:pathtodirectory"
Set Windows PATH Permanently
Run as Administrator: The setx command is only available starting from Windows 7 and requires elevated command prompt.
Permanently add a directory to the user PATH variable:
C:> setx path "%PATH%;C:pathtodirectory"
Permanently add a directory to the system PATH variable (for all users):
C:> setx /M path "%PATH%;C:pathtodirectory"
Info: To see the changes after running setx – open a new command prompt.
Users can run an executable from windows command prompt either by giving the absolute path of the file or just by the executable file name. In the latter case, Windows searches for the executable in a list of folders which is configured in environment variables. These environment variables are as below.
1. System path
2. User path
The values of these variables can be checked in system properties( Run sysdm.cpl from Run or computer properties). Initially user specific path environment variable will be empty. Users can add paths of the directories having executables to this variable. Administrators can modify the system path environment variable also.
How to set path from command line?
In Vista, Windows 7 and Windows 8 we can set path from command line using ‘setx’ command.
setx path "%path%;c:directoryPath"
For example, to add c:dir1dir2 to the path variable, we can run the below command.
setx path "%path%;c:dir1dir2"
Alternative way is to use Windows resource kit tools ‘pathman.exe‘. Using this command we can even remove a directory from path variable. See download windows resource kit tools. This works for Windows 7 also.
Add directory to system path environment variable:
Open administrator command prompt
Run the below command
pathman /as directoryPath
Remove path from system path environment variable:
Run the below command from elevated command prompt
pathman /rs directoryPath
Setting user path environment variable
For user environment varlables, admin privileges are not required. We can run the below command to add a directory to user path environment variable.
pathman /au directoryPath
To remove a directory from user path, you can run the below command.
pathman /ru directoryPath
Default option is not allowed more than ‘2’ time(s)
You get this error if you have not enclosed ‘path’ in double quotes. See the below example for setting the path of firefox.
C:Users>setx path %path%;"c:Program Files (x86)Mozilla Firefox" ERROR: Invalid syntax. Default option is not allowed more than '2' time(s). Type "SETX /?" for usage.
Now if you move %path% to be in the double quotes
C:Users>setx path "%path%;c:Program Files (x86)Mozilla Firefox" SUCCESS: Specified value was saved. C:Users>
Download Article
A simple guide to adding a directory to the Windows 10/11 path variable
Download Article
- Windows 7–11
- Windows XP
- Warnings
|
|
The PATH environment variable specifies in which directories the Windows command line looks for executable binaries. The process for changing it is not obvious, but it’s not too hard. Read on to learn how to change PATH.
Things You Should Know
- Adding a directory to your path makes it possible to run programs from the command line without typing the full path.
- To access your path settings, open Settings, type «path,» then click «Edit the System Environment Details.»
- While adding directories to the path is simple, don’t remove any existing path directories.
-
1
Open the «settings» application. This can be done by pressing the Windows key and clicking the gear icon in the «Start» menu. You can also search «settings» in Cortana or in the «Start» menu.
-
2
Search «path» in the settings menu.
Advertisement
-
3
Select Edit the System Environment Details. This option should be below Show Full Path in Title Bar and above Edit the Environment Details for your Account. A menu titled «System Properties» should pop up.
-
4
Click Environment Variables. This should be on the right-hand side of the menu below the Startup and Recovery section.
-
5
Select Path. You should not have to scroll down to find this option. It is in between two options titled OS and PATHEXT.
-
6
Click Edit, and proceed to edit the PATH environment variable.
Warning! Unless you want to potentially destroy your PC’s system, DO NOT edit this variable unless you know what you’re doing.
-
7
Select OK once you’re done editing. This will save any changes you may have made.
Advertisement
-
1
Create a shortcut to «My Computer». Click on «Start», mouse over «My Computer», right-click on it, and select «Show on Desktop».
-
2
Right-click on the shortcut and select Properties. A window will open.
-
3
Switch to the Advanced tab. In that tab, click on Environment Variables. Another window will open.
-
4
Scroll down until you see «Path». Select it and click on Edit. A third window will open.
-
5
Edit the PATH environment variable. Unless you really know what you’re doing, don’t remove what’s already there, only append to it. For example, you could add another directory by appending: ;C:pathtodirectory, with «pathtodirectory» being the actual path to the directory.
-
6
Click on OK. When the window closes, there should be a short delay because the environment variable is being updated. After that, you can press OK to close the other two windows, too.
-
7
Check that the environment variable changed. Open the command line by pressing ⊞ Win+R, entering cmd, and pressing ↵ Enter. Type: echo %PATH%. The output should be your updated PATH environment variable.
Advertisement
Ask a Question
200 characters left
Include your email address to get a message when this question is answered.
Submit
Advertisement
Thanks for submitting a tip for review!
-
Changing the PATH environment variable wrongly can cause your system to stop working correctly. You should have a basic understanding of what you’re doing before changing PATH.
Advertisement
About This Article
Thanks to all authors for creating a page that has been read 34,889 times.
Is this article up to date?
| Введение | |
| Для чего используется | |
| Пример | |
| Добавить директорию в PATH | |
| Изучить содержимое PATH | |
| Ошибки | |
| Postgesql | |
| Похожие статьи |
Введение
Если Вам нужно настроить PATH в Linux — перейдите
сюда
Для чего используется
Когда Вы выполняете какую-либо команду в консоли, система ищет соответствие
между названием этой команды и программой, которую можно выполнить.
Искать по всему жёсткому диску было бы слишком долго, поэтому поиск
осуществляется только по некоторым директориям.
Список этих особых директорий хранится в системной переменной PATH.
Пример
Предположим, что возникла необходимость запускать какую-то программу, например
Firefox
, непосредственно из командной строки.
Без предварительной подготовки ввод Firefox в консоль выдаст ошибку.
C:Usersa>firefox
‘firefox’ is not recognized as an internal or external command, operable program or batch file.
Чтобы решить эту проблему нужно добавить директорию с испоняемым файлом firefox в PATH
Добавить директорию в PATH
Быстрый способ перейти к редактированию PATH — нажать клавишу Win и ввести в поиск env
Пошаговый способ:
Правый клик на Этот Компьютер (This PC) → Свойства (Properties)
Дополнительные параметры системы (Advanced system settings)
Дополнительно (Advanced) → Переменные среды (Environment Variables)
Если хотите менять для всей системы, то в окошке «Переменные среды»
(System Variables)
найдите строку PATH в блоке
«Системные переменные» (System variables)
выделите кликом и нажмите кнопку «Изменить…» (Edit…)
Если хотите менять только для своего пользователя, то делайте это в блоке
«Переменные среды пользователя %USERNAME%» (User variables for %USERNAME%)
Создайте новый путь (New)
Введите адрес директории в которой лежит нужная программа. В нашем случае это
C:Program Files (x86)Mozilla Firefox
Перезапустите консоль или открываем новую и пишем там firefox.
C:Usersa>firefox
Браузер должен запуститься.
Изучить содержимое PATH
В
PowerShell
достаточно выполнить
echo $Env:Path
C:Windowssystem32;C:Windows;C:WindowsSystem32Wbem;C:WindowsSystem32WindowsPowerShellv1.0;
Или
Get-ChildItem Env:Path
Name Value
—- ——
Path C:Windowssystem32;C:Windows;C:WindowsSystem32Wbem;C:WindowsSystem32WindowsPo…
В cmd.exe посмотреть список переменных
окружения можно выполнив команду
set
без параметров.
set
Выдача содержит системные переменные и переменные пользователя
а также дополнительную информацию. Содержимое PATH выделено зелёным.
Ошибки
-bash: syntax error near unexpected token `(‘
Скорее всего Вы пытаетесь добавить в unix PATH адрес из Windows, c пробелами, скобками и так далее.
Например:
andrey@olegovich-10:/usr/share$ export PATH=/mnt/c/Program Files (x86)/Common Files/Oracle/Java/javapath_target_1128437:$PATH
-bash: syntax error near unexpected token `(‘
Для решения этой проблемы Вам нужно экранировать пробелы и скобки. Если импортируется много путей и ввод очень длинный —
немного проще записать PATH=$PATH:/путь , если Вам подходит запись в конец.
Также нужно помнить, что все лишние пробелы сломают импорт — для проверки можно сделать весь скрипт в одну строку
в текстовом редакторе.
Также стоит помнить, что если Вы работаете в
bash под Windows
,
то переменные окружения нужно задавать через Windows.
andrey@olegovich-10:/usr/share$ export PATH=$PATH:/mnt/c/Program Files (x86)/Common Files/Oracle/Java/javapath_target_1128437
Postgesql
Приведу пример для использования psql из
bash под Windows
— это может пригодиться если Вы хотите временно добавить
путь к psql в PATH чтобы запустить
Postrgres
скрипт.
В моём случае
psql.exe
находится в папке C:Program FilesPostgreSQL12bin
PATH=$PATH:/mnt/c/Program Files/PostgreSQL/12/bin
| Windows | |
| Loudness Equalization | |
| PowerShell | |
| Посмотреть конец файла в PowerShell (аналог tail) | |
| Создать новый файл в PowerShell (аналог touch) | |
| Проверить контрольную сумму файла в PowerShell (аналог md5sum) | |
| Windows Firewall | |
| Remote Desktop Protocol | |
| Драйверы в Windows | |
| Режим разработчика в Windows 10 | |
| BASH в Windows 10 | |
| Telnet в Windows 10 | |
| Системная переменная PATH | |
| Установка Windows на gpt диск | |
| batch file | |
| pstools | |
| Удалённый рабочий стол | |
| Горячие клавиши |
Привет, посетитель сайта ZametkiNaPolyah.ru! Продолжим разбираться с командами и системными утилитами в операционной системе Windows 10, на этот раз будет разговор о переменной PATH в Windows. Всё дело в том, что системная переменная PATH дает нам возможность расширить список команд командной строки Windows, как это сделать, вы узнаете из этой публикации. Здесь мы с вами поговорим о назначении системной переменной PATH, а также разберемся с вопросом: как добавить путь к исполняемому файлу в системную переменную PATH в операционных системах Windows 10, Windows 8 и Windows 7. Этой публикацией можно пользоваться как простой инструкцией по добавлению значений в переменную PATH для Windows.
Если вам интересна тема компьютерных сетей, то в блоге уже практически закончена первая часть курса по основам компьютерных сетей, можете ознакомиться с ее содержимым. И вот здесь можно получить немного информации о самом курсе.
Что такое переменная Path и зачем она нужна в Windows. Зачем нужно добавлять путь?
Содержание статьи:
- Что такое переменная Path и зачем она нужна в Windows. Зачем нужно добавлять путь?
- Как добавить путь к программе в системную переменную Path в Windows 10 и Windows 8
- Как настроить переменную Path в Windows 7
- Выводы
PATH – это системная переменная окружения Unix-подобных (например, Linux Mint) операционных систем, а также операционных систем семейства Windows. В переменной PATH нет ничего сложно и хитрого, это обыкновенный список папок и каталогов, в которых лежат исполняемые файлы (программы). Программы, путь к исполняемым файлом которых задан в системной переменной PATH, могут быть исполнены (запущены) непосредственно из командной строки Windows и из любого места вашей файловой системы (в Linux тоже есть командная строка, но ее лучше называть эмулятор терминала).
Давайте лучше посмотрим на примере зачем нужна переменная PATH в операционных системах семейства Windows (как, впрочем, и в других семействах). Смотреть будем на примере сторонней утилиты командной строки Windows tracetcp.exe. Она у меня установлена по следующему пути: c:Program Filestracetcp. Запустим командую строку Windows и попробуем выполнить команду tracetcp.
Пробуем запустить стороннюю утилиту командной строки Windows
Обратите внимание на то, что командная строка не смогла выполнить команду tracetcp, хотя приложение и установлено на мой компьютер, проблема заключается в том, что командная строка не смогла найти исполняемый файл tracetcp.exe. Но где командная строка его искала? Она искала этот файл в текущем каталоге, то есть в данном случае в каталоге: c:UsersDell, там этого файла не оказалось, затем командная строка обратилась к переменной PATH, там она не обнаружила пути к исполняемому файлу tracetcp.exe, но обнаружила путь к папке System32, проверила, что в этой папке также нет файла tracetcp.exe и выдала нам предупреждение: «»tracetcp» не является внутренней или внешней командой, исполняемой программой или пакетным файлом.».
Поскольку мы находились в папке, отличной от той, где находится файл tracetcp.exe, а пути в переменной PATH к этому файлу не оказалось, командная строка просто не смогла его найти, чтобы исполнить, давайте всё-таки его запустим, для этого нужно будет перейти в папку c:Program Filestracetcp при помощи команды cd (в операционных системах Linux тоже есть команда cd и работает она аналогично), а затем запустить утилиту.
Запуск исполняемого файла в командной строке Windows
Теперь командная строка Windows смогла запустить нашу утилиту, поскольку смогла найти исполняемый файл tracetcp.exe, но каждый раз переходить в папку, где лежит исполняемый файл или каждый раз указывать абсолютный путь к исполняемому файлу — это очень неудобно, будет гораздо лучше, если мы укажем путь к исполняемому файлу в переменной PATH, тогда командная строка будет самостоятельно его находить в любое время и в любом месте.
Исполняемый файл был запущен, поскольку путь до него был добавлен в системную переменную Path
На рисунке выше показано, что командная строка смогла запустить приложение из домашней папки пользователя, но это лишь благодаря тому, что я добавил путь исполняемому файлу в переменную PATH, теперь команда tracetcp будет работать из любой другой папки. Утилита tracetcp довольно простое приложение, представляющее собой один исполняемый файл — tracetcp.exe, можно было бы не прописывать путь в переменную PATH, а просто скопировать этот файл в папку System32, но устанавливать сторонние и непроверенные приложения, не требующие наличия файлов в System32, не самая хорошая и безопасная затея. В Windows лучше потратить немного времени на то, чтобы добавить путь к файлу в переменную PATH, о том как это сделать мы и поговорим ниже, рассмотрев этот процесс для операционных систем Windows 10, Windows 8 и Windows 7.
Как добавить путь к программе в системную переменную Path в Windows 10 и Windows 8
Добавление пути к программе в системную переменную PATH в операционных системах Windows 10 и Windows 8 делается по одному алгоритму, показывать я буду на примере Windows 10, так как восьмерки под рукой нет. Ранее мы уже видели, что небольшая утилита tracetcp запускалась из командной строки Windows только в том случае, если мы переходили в ту папку, в которую она установлена. Но это легко исправить, просто добавив полный путь к исполняемому файлу tracetcp.exe в системную переменную PATH. Давайте это и сделаем. Описывать процесс добавления значения в переменную PATH буду буквально по шагам и с демонстрацией скриншотов окон в Windows 10. Хотя сперва я напишу сам алгоритм, если его не хватит, то обратитесь к скриншотам ниже:
- Открываем поиск и пишем: «Система» или «Панель управления».
- Появится окно, в левом верхнем углу которого есть небольшое меню и пункт «Дополнительные параметры системы».
- Появится окно поменьше, в нижнем правом углу есть кнопка «Переменные среды…».
- Откроется окно управления переменными средами в Windows 10.
- Нас интересует переменная PATH, которая находится в разделе «Системные переменные», нажимаем на нее два раза.
- Появится окно для редактирования значений переменной PATH, чтобы добавить новое значение воспользуйтесь кнопкой «Создать».
- Подтвердите добавление нового значения в переменную PATH нажатием кнопки «Ок» и закройте все остальные окна.
- Если во время редактирования переменной PATH у вас была запущена командная строка Windows, то закройте ее и откройте заново, чтобы cmd.exe прочитала новое значение переменной PATH.
Открываем поиск Windows и в форму пишем: «Система» или «Панель управления». В результате вы должны увидеть примерно такой результат, как показано на рисунке ниже.
Используем поиск Windows, ищем по ключевому слову Система
После того, как вы нажмете на кнопку «Система», у вас появится окно, в левой части которого есть небольшое меню, самым нижним пунктом этого меню будет «Дополнительные параметры системы».
Чтобы добавить значение в переменную PATH переходим во вкладку Дополнительные параметры системы
После перехода у вас появится окно поменьше, в этом окне нас интересует вкладка «Дополнительно». В правом нижнем углу есть кнопка «Переменные среды…», на нее и нажимаем.
Нажимаем на кнопку Переменные среды
Появится еще одно окно, которое позволяет управлять системными переменными Windows 10. Обратите внимание: в это окно разделено на две части, в верхней части происходит управление переменными среды для текущего пользователя, в нижней части расположены системные переменные.
В разделе Системные перемененные ищем переменную PATH
В данном случае нас будет интересовать переменная Path, которая находится в разделе «Системные переменные», кликаем на нее два раза, у нас появляется окно, которое позволяет удалять, добавлять и редактировать значения системной переменной Path в Windows 10 и Windows 8. Нам осталось выполнить два действия: нажать на кнопку создать, в появившуюся активную форму вписать путь к файлу tracetcp.exe и подтвердить свои действия нажатием клавиши «Ок».
Дбовляем путь к исполняемому файлу в системную переменную PATH в Windows 10
Закройте все остальные окна. Если у вас была открыта командная строка, вы можете убедиться в том, что она не увидела новое значение переменной PATH, попробуйте выполнить tracetcp из корня диска C, ничего не сработает. Когда вы добавляете новый путь в переменную PATH, программе cmd.exe нужно перечитать значения этой переменной, самый простой способ заключается в том, чтобы закрыть и заново открыть командую строку. Теперь команда tracetcp работает из любой папки, аналогично можно поступать и с другими программами командной строки, которые вы устанавливаете в Windows.
Как настроить переменную Path в Windows 7
К сожалению, у меня не осталось скриншотов, на которых можно было бы продемонстрировать добавление пути в системную переменную PATH на Windows 7, поэтому здесь будет только пошаговый алгоритм добавления значения в переменную PATH:
- На вашем рабочем столе есть икнока с названием «Компьютер» или «Мой компьютер», нажмите на нее правой кнопкой мыши.
- Появится контекстное меню, в самом низу которого есть пункт «Свойства», выберете его.
- Перед вам развернется окно, в котором есть пункт меню «Дополнительные параметры системы», его и выбираем.
- В этом окне будет кнопка «Переменные среды», жмем на нее.
- У нас появляется окно управления системными переменными в Windows 7, внизу которого есть список переменных, среди которого нужно найти переменную PATH.
- Если такой переменной нет, то ее нужно создать, воспользовавшись кнопкой создать: у вас появится окно, в котором нужно будет вписать имя новой переменной, в нашем случае это Path.
- Если переменная PATH есть, то ее нужно выделить левой кнопкой мыши и нажать на кнопку изменить: появится небольшое окошко с двумя формами для ввода: верхняя форма содержит имя переменной — это Path. В нижней форме указаны абсолютные пути до исполняемых файлов различных программ, выглядет это примерно так: d:Program Filesapplication1;d:Program Filesapplication2;d:Program Filesaplication3; и так далее, чтобы добавить еще одно значение переместитесь в конец строки, убедитесь, что последним символом является «;» (именно этот символ является разделителем), впишите путь к исполняемому файлу (в моем случае он выглядел бы так: с:Program Filestracetcp) и в конце добавьте точку с запятой.
- Подтвердите свои действия нажатием кнопки «Ок» и закройте другие окна.
Как видите, настроить переменную PATH в Windows 7 не так уж и сложно.
Выводы
Вы этой статье мы разобрались с назначение системной переменной PATH и отметили, что в каждой операционной системе оно одинаковое и заключается в том, что переменная PATH является списком каталогов, в котором хранятся исполняемые файлы, если путь к исполняемому файлу есть в переменной PATH, то он может быть исполнен из командной строки операционной системы. Также мы разобрались с тем, как прописать путь к исполняемому файлу в операционных системах Windows 10, 8, 7.
Environment variables are name-value pairs for various programs or processes on an operating system. On Windows, the environment variables store all sorts of information about the operating system environment, such as its path, location of system programs and processes, and other essential data required by other system programs.
Of the different kinds of Windows environment variables, one that plays an important role—and impacts the way programs and commands get executed—is the PATH environment variable.
If you’re wondering why you’d want to set the PATH variable and how to do it, here’s a guide explaining the same in detail.
Why Would You Want to Set the PATH Variable?
PATH is an essential environment variable on all Windows operating systems. It determines the way a system executes a program or command on your computer.
Typically, when you have to launch a program or execute a command, you have two options. Either you can navigate to the directory where the program/command is stored and execute it from there. Or, you can use the absolute path for that program/command in the file system to run it from anywhere.
While both approaches let you execute programs or commands via the CLI (Command Prompt or PowerShell), they aren’t very efficient. A better solution here is to set the PATH variable for those programs or commands in the environment variable so you can access them from anywhere on the file system hierarchy.
For example, with Python installation, unless the installer gives you an option to set the PATH automatically, you have to do it explicitly to use Python within any directory on your system. Although this is an optional step, it’s highly recommended that you do so to alleviate the need for using absolute (full) paths while running Python scripts.
PATH variables can be specified via both GUI and CLI methods, and the steps involved are mostly the same for all Windows versions. The following is a breakdown of these steps to guide you in the process.
Setting the PATH Variable Using GUI
Using the graphical interface is the easiest way to set the PATH variable in Windows. To do this, first, open the Windows Run prompt by hitting the Windows + R key shortcut.
Next, in the field beside Open, type in sysdm.cpl and press Enter or click OK to open System Properties.
In System Properties, go to the Advanced tab and click on the Environment Variables button at the bottom.
On the Environment Variables window, you’ll see two sections: one for user variables and the other for system variables. System variables are accessible to all system users, whereas User variables are specific to only the current user. So depending on which variable type you want to modify, you need to click on Path in the appropriate section.
Now, open File Explorer and head to the installation directory of the program you want to add to PATH. Press and hold the Shift key, right-click on the folder, and select Copy as Path.
In the Environment Variables window, click on the Path variable name from either section and hit the Edit button. On Windows 7 and Windows 8, add a semi-colon at the end of the line, and without leaving a space, paste the program’s path you just copied into the Path field.
If you’re on Windows 10, hit the New button and paste the copied path on the new line. Alternatively, hit the Edit text, add a semi-colon to the end of the field for Variable value, and paste the program’s path.
Hit OK.
Setting the PATH Variable Using CLI
While the GUI method is easier to follow and sets the PATH variable permanently, it involves several steps. So if you want to save yourself the hassle of clicking through various menu windows, you can set PATH via the command line using the PATH command.
For this, first, fire up Command Prompt with administrator privileges. To do this, hit the Windows + X shortcut key to open the Power User Menu and select Command Prompt (Admin) from the available options. Hit Yes in the User Account Control. If you’re on Windows 7 or Windows 8, hit the Windows key, search Command Prompt, and hit the Ctrl + Shift + Enter shortcut to open it with administrator rights.
In the command window, enter your command using the following command syntax to set a variable:
set PATH=”value”
…where value is the path of the program in the file system you want to add.
Eg:
set PATH=”C:Program FilesAndroidPlatform-Tools”
However, this command sets PATH temporarily (only for the current session) and resets it to the default PATH entries upon system reboot.
So, if you’d like to set PATH for a program permanently—such that it persists even after rebooting the PC—you need to use the setx command.
Following is the syntax to use it:
setx PATH "value;%PATH%"
Eg:
setx PATH "C:Program FilesAndroidPlatform-Tools;%PATH%"
Do note that this will set the PATH variable for the local environment (the current user). If you’d like to do this system-wide, you need to use the /m parameter. For this, in an elevated Command Prompt, run the following command:
setx /m PATH "C:WindowsSystem32;%PATH%"
Once done, restart CMD.
Lastly, to verify if your PATH has been added successfully, run the following command in CMD:
echo %PATH%
How to Unset the PATH Variable
For some reason, if, after you’ve set the PATH variable, you want to unset it, you can do so using the following steps.
Open Run and enter:
sysdm.cpl
In System Properties, tap on the Advanced tab and click the Environment Variables button at the bottom. Next, click on the Path entry from either section in the Environment Variables window—depending on whether you set the PATH temporarily or permanently—and hit the Edit button.
Tap on the entry you want to remove to select it and hit the Delete button on the right. On older versions of Windows, you can click the Edit text button and delete the recent PATH entry for the Variable value text field.
Hit OK to save the changes.
Running Programs/Commands From Anywhere With the CLI
Once you’ve set the PATH variable on your computer to include the path (or directory) of the program or command you want to execute from any directory, you can easily run it from Command Prompt or PowerShell without ever having to specify its absolute path.
FAQs About Setting the PATH Variable in Windows
1. How do I set the PATH variable in Windows 10?
On Windows 10, you can set the PATH variable either using the GUI or CLI. With GUI, you need to go into the Environment Variables settings and set/modify the PATH variable from there, whereas in the CLI approach, all you need to do is run a couple of commands in the CMD prompt, and you’ll have the PATH variable for your desired program set.
So depending on which method you find easier to follow, follow the steps listed earlier in the guide to set the PATH variable on your Windows 10 PC.
2. Does Windows have a PATH variable?
All Windows operating systems have the PATH variable as part of the environment variables, and by setting it for your most frequently used programs or commands, you can launch them from any directory in the file system without having to specify their absolute path.
3. How do I permanently set a PATH variable?
Permanently setting a PATH variable is possible via both GUI and CLI methods. With the GUI method, you’ll have to go into the Environment Variables setting and set the PATH for your program or command there. On the other hand, the CLI method simplifies this process and only involves using a command (setx) in the Command Prompt, which saves you the hassle of clicking through various menus.
4. How do I find my PATH in CMD?
To find the PATH variable on your Windows PC, open the Command Prompt with administrator privileges and run echo %PATH%.
Was this article helpful?
YesNo
TechPP is supported by our audience. We may earn affiliate commissions from buying links on this site.
The most efficient way to get most things done on Windows is via the graphical interface. Every now and then, though, you have to turn to the command line for troubleshooting, programming, or just working on your nerd cred.
But if you’re trying to run something that’s not natively part of Windows, you’ll need to add it to your PATH variable. That tells your system where to look for executables when you ask for them.
Environment variables store data about a system’s environment so the system knows where to look for certain information. The PATH variable is one of the most well-known environment variables since it exists on Windows, Mac, and Linux machines and does a fairly user-facing job on all. Its actual form is just a text string containing a list of directory paths that the system will search every time you request a program.

This is a bit like adding a desktop shortcut to your command line. Instead of entering “C:UsersusernameAppDataLocalProgramsPythonPython38-32python.exe” to launch Python, you can add the folder containing the file to the PATH variable and just type “python” to launch it in the future. Do that for any program you like, whether it launches a GUI (like Notepad) or works in the command line interface (like Python).

On Windows, PATH (capitalized by convention only, since Windows’ NTFS file system is not case-sensitive) points by default to the “C:Windows” and “C:Windowssystem32” directories.
If you type charmap into the command line, you’ll get a massive list of Unicode characters you can copy and use, for example. “notepad” runs Notepad, “msinfo32” gets you a list of your computer’s specs, and so on.
These programs can also be launched with the GUI. But if you’re already working in the command line, launching programs just by typing their names is a lot easier. This is especially true if you’re trying to launch a program that will open and run inside the command line interface, like Python or Node.js.
How do I edit the PATH variable?
The Windows GUI is pretty straightforward, so it’s probably the best way for most people to edit PATH.
Using the Windows GUI
1. Open “System Properties” and go to the “Advanced” tab. The easiest way to do this is by typing environment variable into your Windows Search bar and clicking “Edit the system environment variables.”

Alternatively, you can go to “Control Panel -> System and Security -> System” and click “Advanced system settings;” type sysdm.cpl into the Run command; or right-click “This PC,” select “Properties,” and click “Advanced system settings.” They all go to the same place.
2. Once you’re in the “Advanced” tab, click “Environment Variables … ”

3. The top box contains user variables, meaning any edits will only apply to your account. If you have multiple accounts on one machine and want the changes to affect everyone, edit the bottom box containing system variables instead.

4. Select the user or system Path variable (don’t let the title-case throw you; PATH and Path are the same in Windows) you want to edit and click the “Edit … ” button below the box.

5. If you already have the path to the folder you want to add, just click “New” and paste in the full path (not directly to the executable, just to the folder containing it). I’m pasting in the path to my NodeJS directory so I can use JavaScript in the command line.

6. If you’d rather browse to the folder and select it manually, use the “Browse” button to navigate to the folder where your executable is located and hit the “OK” button when you’re there.

7. If you want your program to launch slightly faster, you can use the “Move Up” and “Move Down” buttons to put its folder closer to the top so it’ll pop up more quickly in the directory search.
8. Open a new command-prompt window and test your program by typing in the name of the executable you want to launch. It won’t work in the current window since it’s still using the old PATH variable.
Edit PATH Variables Using Command Prompt
The Windows 10 GUI is very usable and should meet most peoples’ needs, but if you need to use the command line to set PATH and environment variables, you can do that too.
1. Open the command prompt as administrator, then enter the command set.
2. Scroll through the list of paths, then find the variable you want to edit. The variable name is the part before the ‘=’ sign, the variable value is the part after, which you will rename to the directory you want it point to.

3. With that in mind, to edit the PATH, enter the following command:
setx variable name "variable value"

You can use the following code to set your System PATH from the Command Prompt. (Run as administrator.) To use it to set your User PATH , just remove the /M.
setx /M PATH "%PATH%;<path-to-executable-folder>"
If you have problems, it’s a good idea to read through the known issues with and fixes for the setx command truncating the variable to 1024 characters or otherwise altering the variables. Definitely back up both your user and your system path variables first.
Frequent Asked Questions
1. Why would I need to edit PATH?
Chances are, if you’re reading this, you’ve run into something that requires you to add it to the PATH variable, so that’s probably what you should do. If you just want to add something to your PATH for easier access, though, that’s also fine. Just make sure it doesn’t interfere with the higher-priority programs.
2. Is there a Windows PATH length limit?
Yes, there is. So PATH-changing enthusiasts beware that the limit is 260 characters.
3. Can I disable the Windows PATH length limit?
Yes you can! Go to the Registry Editor, then within that navigate to:
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINESYSTEMCurrentControlSetControlFileSystem
In the right-side pane, double-click the entry called “LongPathsEnabled”, then change the “Value data” value from 0 to 1. Click OK, and you’re good to go.

Ready to keep digging beneath the Windows bonnet? Then head over to our favorite Windows registry hacks. Or for something a little lighter, check out our list of the best Windows 10 themes.
Robert Zak
Content Manager at Make Tech Easier. Enjoys Android, Windows, and tinkering with retro console emulation to breaking point.
Subscribe to our newsletter!
Our latest tutorials delivered straight to your inbox
Download PC Repair Tool to quickly find & fix Windows errors automatically
Environment Variables are responsible for storing information about the OS’s environment. Different apps and programs require different configurations and it is the job of Windows to ensure that each of them has the environment best suitable for them. Simply speaking, these Environment Variables are data storing facilities. A PATH variable is one of the most useful of the kind and helps you to run any executable found within Paths without having to give the full path to the executable. In this article, we will be discussing how you can manually add or edit existing PATH environment variables on Windows 11 or Windows 10.
An Environment variable is useful in the sense that it influences how software processes take place. The data stored in them play an important role in the process. Our tutorial will help you set up PATH variables so that you can run executables from your custom directories. These PATH variables store shortcuts, so you can create them for the programs of your choice. A prerequisite to push PATH variables through is to grant administrative privileges, so make sure you have them enabled. If you want a more detailed explanation of what System & User Environment Variables are, you can read the linked post.
How to set PATH variables manually on Windows 11/10
Without further ado, let’s see how you can add or edit a PATH Environment Variable in Windows 11/10:
- Click on the Search menu on the Taskbar and open the Windows Settings
- From the Settings panel, click on the System option from the left menu pane
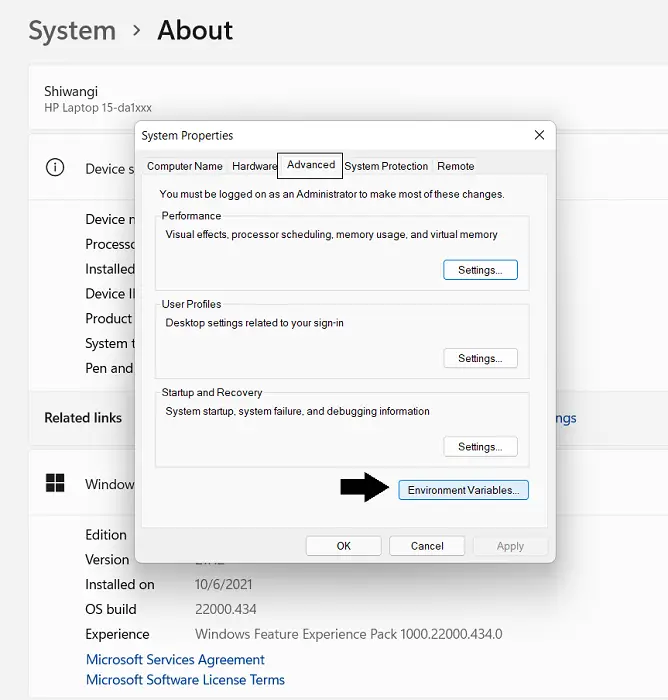
- Go to About and further click on Advanced System Settings. This will open a dialog box named System Properties
- Here, click on the Advanced tab and further click on the Environment Variables button on the bottom-right
- This will open the Environment Variables panel. Here, variables will be divided into two categories: System and User Variables. The former is applicable for system-wide changes while the latter is used to make modifications to the environment of a particular user. Make a decision based on the purpose of creating or editing a PATH variable and select PATH from a section
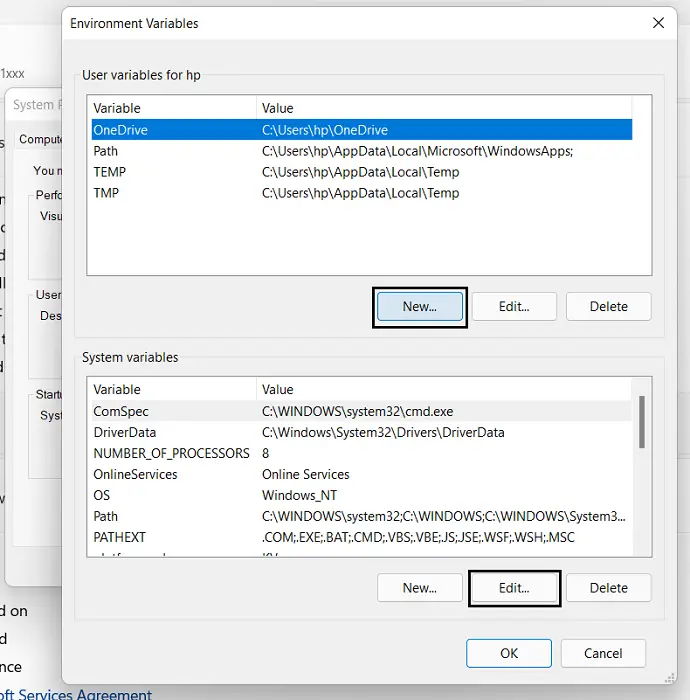
- Follow this by clicking on the Edit button
You can now modify the existing route lines with the ones you want your computer to access. This stuff may seem overwhelming to some of you and has very deep implications for some important PC processes, so you’re advised to express utmost caution.
In order to add a new route, you can click on the ‘New’ button. You can delete a Path the same way. Here, you can just paste the Path of your choice, and if you’re unsure of it, then you can use the Surf option to go about searching for it. Once you’re done, click on Ok and a new PATH variable will now exist.
Our guide here explains how you can add Environment Variables to your Windows Context Menu.
Read: How to see Names and Values of Environment Variables in Windows
How do I change Environment Variables without admin rights?
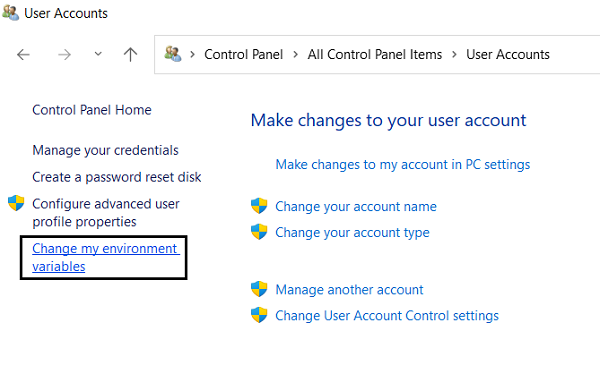
Granting administrative rights may not be as easy when the PC isn’t yours, but you can still make changes to your environment variables. Via the Control Panel, you can modify the environment variables on a user account, but not System variables. Here’s how you can do that:
- Open the Control Panel
- Select to view them as ‘Small icons’ and click on User Accounts
- Here, you’ll see an option to your left named ‘Change my environment variables’
- This will open the same Environment Variables dialog box as before, except now the System Variables aren’t accessible and you can only make changes to User variables
TIP: Rapid Environment Editor is a powerful free Environment Variables Editor for Windows.
How do I change the Path in Windows Command Prompt?
A command line on your Windows Terminal (Command Prompt) can help you add a Path to your Path environment variable. The changes that we have discussed above can be implemented via the Command Prompt as well, but again, are limited to the User’s environment only. Here’s how:
- Search ‘CMD’ on the Taskbar search menu and select to run it as the administrator
- Enter the command ‘Pathman /au’ and follow it by the Path to the directory you want to append.
- Similarly, you can use a ‘Pathman/ru’ command to delete an existing Path to a directory
We hope that this post was helpful for you and that you can now take care of your Path environment variables with ease.
Shiwangi loves to dabble with and write about computers. Creating a System Restore Point first before installing new software, and being careful about any third-party offers while installing freeware is recommended.