This article is about the player. For an overview of the platform, see Adobe Flash.
«Shockwave Flash» redirects here. Not to be confused with Adobe Shockwave. For the file format sometimes referred to as «Shockwave Flash», see SWF.
 |
||||||||||||||||
| Original author(s) | FutureWave Macromedia |
|||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Developer(s) | Adobe Inc. Zhongcheng Harman |
|||||||||||||||
| Initial release | January 1, 1996; 27 years ago | |||||||||||||||
| Stable release(s) [±] | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| Preview release(s) [±] | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| Written in | ActionScript | |||||||||||||||
| Operating system | Windows, macOS, Linux, ChromeOS, Solaris, BlackBerry Tablet OS, Android, Pocket PC | |||||||||||||||
| Platform | Web browsers and ActiveX-based software | |||||||||||||||
| Available in | Chinese Simplified, Chinese Traditional, English, French, German, Italian, Japanese, Polish, Russian, Portuguese, Spanish, Korean, Turkish, Xhosa, Telugu, Vietnamese, Afrikaans, Yiddish, Zulu, and Arabic[9] | |||||||||||||||
| Type | Runtime system and browser extension | |||||||||||||||
| License | Freeware | |||||||||||||||
| Website | Adobe Flash Player End of Life (EOL, original global variants) Adobe Flash Player Harman official website (active, Harman enterprise variant) Adobe Flash Player China official website (active, China-specific variant) |
Adobe Flash Player (known in Internet Explorer, Firefox, and Google Chrome as Shockwave Flash)[10] is computer software for viewing multimedia contents, executing rich Internet applications, and streaming audio and video content created on the Adobe Flash platform. It can run from a web browser as a browser plug-in or independently on supported devices. Originally created by FutureWave under the name FutureSplash Player, it was renamed to Macromedia Flash Player after Macromedia acquired FutureWave in 1996. It was then developed and distributed by Adobe Systems as Flash Player after Adobe acquired Macromedia in 2005. It is currently developed and distributed by Zhongcheng for users in China, and by Harman International for enterprise users outside of China, in collaboration with Adobe.
Flash Player runs SWF files that can be created by Adobe Flash Professional, Adobe Flash Builder or by third-party tools such as FlashDevelop. Flash Player supports vector graphics, 3D graphics, embedded audio, video and raster graphics, and a scripting language called ActionScript, which is based on ECMAScript (similar to JavaScript) and supports object-oriented code. Internet Explorer 11 and Microsoft Edge Legacy, in Windows 8 and later, along with Google Chrome on all versions of Windows, came bundled with a sandboxed Adobe Flash plug-in.[11][12][13][14][15]
Flash Player once had a large user base, and was a common format for web games, animations, and graphical user interface (GUI) elements embedded in web pages. Adobe stated in 2013 that more than 400 million out of over 1 billion connected desktops updated to new versions of Flash Player within six weeks of release.[16] However, Flash Player became increasingly criticized for its performance, consumption of battery on mobile devices, the number of security vulnerabilities that had been discovered in the software, and its closed platform nature. Apple co-founder Steve Jobs was highly critical of Flash Player, having published an open letter detailing Apple’s reasoning for not supporting Flash on its iOS device family. Its usage also waned because of modern web standards that allow some of Flash’s use cases to be fulfilled without third-party plugins.[17][18][19] This led to the eventual deprecation of the platform by Adobe. Flash Player was officially discontinued on 31 December 2020, and its download page was removed two days later. Since 12 January 2021, Flash Player (original global variants) versions newer than 32.0.0.371, released in May 2020, refuse to play Flash content and instead display a static warning message.[20] The software remains supported in mainland China and in some enterprise variants.[21]
Features[edit]
Adobe Flash Player is a runtime that executes and displays content from a provided SWF file, although it has no in-built features to modify the SWF file at runtime. It can execute software written in the ActionScript programming language which enables the runtime manipulation of text, data, vector graphics, raster graphics, sound, and video. The player can also access certain connected hardware devices, including the web cameras and microphones, after permission for the same has been granted by the user.
Flash Player was used internally by the Adobe Integrated Runtime (AIR), to provide a cross-platform runtime environment for desktop applications and mobile applications. AIR supports installable applications on Windows, Linux, macOS, and some mobile operating systems such as iOS and Android. Flash applications must specifically be built for the AIR runtime to use additional features provided, such as file system integration, native client extensions, native window/screen integration, taskbar/dock integration, and hardware integration with connected Accelerometer and GPS devices.[22]
Data formats[edit]
Flash Player included native support for many data formats, some of which can only be accessed through the ActionScript scripting interface.
- XML: Flash Player has included native support for XML parsing and generation since version 8. XML data is held in memory as an XML Document Object Model, and can be manipulated using ActionScript. ActionScript 3 also supports ECMAScript for XML (E4X), which allows XML data to be manipulated more easily.
- JSON: Flash Player 11 includes native support for importing and exporting data in the JavaScript Object Notation (JSON) format, which allows interoperability with web services and JavaScript programs.
- AMF: Flash Player allows application data to be stored on users computers, in the form of Local Shared Objects, the Flash equivalent to browser cookies.[23] Flash Player can also natively read and write files in the Action Message Format, the default data format for Local Shared Objects. Since the AMF format specification is published, data can be transferred to and from Flash applications using AMF datasets instead of JSON or XML, reducing the need for parsing and validating such data.
- SWF: The specification for the SWF file format was published by Adobe, enabling the development of the SWX Format project, which used the SWF file format and AMF as a means for Flash applications to exchange data with server side applications.[24][25] The SWX system stores data as standard SWF bytecode which is automatically interpreted by Flash Player.[26] Another open-source project, SWXml allows Flash applications to load XML files as native ActionScript objects without any client-side XML parsing, by converting XML files to SWF/AMF on the server.[27][28]
Multimedia formats[edit]
Flash Player is primarily a graphics and multimedia platform, and has supported raster graphics and vector graphics since its earliest version. It supports the following different multimedia formats which it can natively decode and play back.
- MP3: Support for decoding and playback of streaming MPEG-2 Audio Layer III (MP3) audio was introduced in Flash Player 4. MP3 files can be accessed and played back from a server via HTTP, or embedded inside an SWF file, which is also a streaming format.
- FLV: Support for decoding and playing back video and audio inside Flash Video (FLV and F4V) files, a format developed by Adobe Systems and Macromedia. Flash Video is only a container format and supports multiple different video codecs, such as Sorenson Spark, VP6, and more recently H.264.[29] Flash Player uses hardware acceleration to display video where present, using technologies such as DirectX Video Acceleration and OpenGL to do so. Flash Video is used by YouTube,[30] Hulu,[31] Yahoo! Video, BBC Online,[32] and other news providers. FLV files can be played back from a server using HTTP progressive download, and can also be embedded inside an SWF file. Flash Video can also be streamed via RTMP using the Adobe Flash Media Server or other such server-side software.
- PNG: Support for decoding and rendering Portable Network Graphics (PNG) images, in both its 24-bit (opaque) and 32-bit (semi-transparent) variants. Flash Player 11 can also encode a PNG bitmap via ActionScript.
- JPEG: Support for decoding and rendering compressed JPEG images. Flash Player 10 added support for the JPEG-XR advanced image compression standard developed by Microsoft Corporation, which results in better compression and quality than JPEG. JPEG-XR enables lossy and lossless compression with or without alpha channel transparency. Flash Player 11 can also encode a JPEG or JPEG-XR bitmap via ActionScript.
- GIF: Support for decoding and rendering compressed Graphics Interchange Format (GIF) images, in its single-frame variants only. Loading a multi-frame GIF will display only the first image frame.
Streaming protocols[edit]
- HTTP: Support for communicating with web servers using HTTP requests and POST data.[33] However, only websites that explicitly allow Flash to connect to them can be accessed via HTTP or sockets, to prevent Flash being used as a tool for cross-site request forgery,[34] cross-site scripting, DNS rebinding,[35] and denial-of-service attacks. Websites must host a certain XML file termed a cross domain policy,[35] allowing or denying Flash content from specific websites to connect to them. Certain websites, such as Digg, Flickr, and Photobucket already host a cross domain policy that permits Flash content to access their website via HTTP.[36]
- RTMP: Support for live audio and video streaming using the Real Time Messaging Protocol (RTMP) developed by Macromedia. RTMP supports a non-encrypted version over the Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) or an encrypted version over a secure Transport Layer Security (SSL) connection. RTMPT can also be encapsulated within HTTP requests to traverse firewalls that only allow HTTP traffic.
- TCP: Support for Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) Internet socket communication to communicate with any type of server, using stream sockets. Sockets can be used only via ActionScript, and can transfer plain text, XML, or binary data (ActionScript 3.0 and later).[37][38] To prevent security issues, web servers that permit Flash content to communicate with them using sockets must host an XML-based cross domain policy file, served on Port 843.[39] Sockets enable AS3 programs to interface with any kind of server software, such as MySQL.[40]
Performance[edit]
Hardware acceleration[edit]
Until version 10 of the Flash player, there was no support for GPU acceleration. Version 10 added a limited form of support for shaders on materials in the form of the Pixel Bender API, but still did not have GPU-accelerated 3D vertex processing.[41] A significant change came in version 11, which added a new low-level API called Stage3D (initially codenamed Molehill), which provides full GPU acceleration, similar to WebGL.[42][43] (The partial support for GPU acceleration in Pixel Bender was completely removed in Flash 11.8, resulting in the disruption of some projects like MIT’s Scratch, which lacked the manpower to recode their applications quickly enough.[44][45])
Current versions of Flash Player are optimized to use hardware acceleration for video playback and 3D graphics rendering on many devices, including desktop computers. Performance is similar to HTML5 video playback.[46][47] Also, Flash Player has been used on multiple mobile devices as a primary user interface renderer.[48]
Compilation[edit]
Although code written in ActionScript 3 executes up to 10 times faster than the prior ActionScript 2,[49] the Adobe ActionScript 3 compiler is a non-optimizing compiler, and produces inefficient bytecode in the resulting SWF, when compared to toolkits such as CrossBridge.[50][51][52][53][54]
CrossBridge, a toolkit that targets C++ code to run within the Flash Player, uses the LLVM compiler to produce bytecode that runs up to 10 times faster than code the ActionScript 3 compiler produces, only because the LLVM compiler uses more aggressive optimization.[52][53][54]
Adobe has released ActionScript Compiler 2 (ASC2) in Flex 4.7 and onwards, which improves compilation times and optimizes the generated bytecode and supports method inlining, improving its performance at runtime.[55]
As of 2012, the Haxe multiplatform language can build programs for Flash Player that perform faster than the same application built with the Adobe Flex SDK compiler.[56][unreliable source?]
Development methods[edit]
Flash Player applications and games can be built in two significantly different methods:
- «Flex» applications: The Adobe Flex Framework is an integrated collection of stylable Graphical User Interface, data manipulation and networking components, and applications built upon it are termed «Flex» applications. Startup time is reduced since the Flex framework must be downloaded before the application begins, and weighs in at approximately 500KB. Editors include Adobe Flash Builder and FlashDevelop.
- «Pure ActionScript» applications: Applications built without the Flex framework allow greater flexibility and performance.[57][58][59] Video games built for Flash Player are typically pure-Actionscript projects. Various open-source component frameworks are available for pure ActionScript projects, such as MadComponents, that provide UI Components at significantly smaller SWF file sizes.[60][61]
In both methods, developers can access the full Flash Player set of functions, including text, vector graphics, bitmap graphics, video, audio, camera, microphone, and others. AIR also includes added features such as file system integration, native extensions, native desktop integration, and hardware integration with connected devices.
Development tools[edit]
Adobe provides five ways of developing applications for Flash Player:
- Adobe Animate: graphic design, animation and scripting toolset
- Adobe Flash Builder: enterprise application development and debugging
- Adobe Scout: visual profiler for performance optimization
- Apache Flex: a free SDK to compile Flash and Adobe AIR applications from source code; developed by Adobe and donated to the Apache Foundation[62]
- CrossBridge: a free SDK to cross-compile C++ code to run in Flash Player
Third-party development environments are also available:
- FlashDevelop: an open-source Flash ActionScript IDE, which includes a debugger for AIR applications
- Powerflasher FDT: a commercial ActionScript IDE
- CodeDrive: an extension to Microsoft Visual Studio 2010 for ActionScript 3 development and debugging
- MTASC: a compiler
- Haxe: a multi-platform language[63]
Game development[edit]
Adobe Gaming SDK 1.0 logo
Adobe offers the free Adobe Gaming SDK, consisting (as of August 2014) of several open-source AS3 libraries built on the Flash Player Stage3D APIs for GPU-accelerated graphics:[64]
- Away3D: GPU-accelerated 3D graphics and animation engine
- Starling: GPU-accelerated 2D graphics that mimics the Flash display list API
- Feathers: GPU-accelerated skinnable GUI library built on top of Starling
- Dragon Bones: GPU-accelerated 2D skeletal animation library
A few commercial game engines target Flash Player (Stage3D) as run-time environment, such as Unity 3D[65] and Unreal Engine 3.[65][66] Before the introduction of Stage3D, a number of older 2D engines or isometric engines like Flixel saw their heyday.[67]
Adobe also developed the CrossBridge toolkit which cross-compiles C/C++ code to run within the Flash Player, using LLVM and GCC as compiler backends, and high-performance memory-access opcodes in the Flash Player (termed «Domain Memory») to work with in-memory data quickly.[68] CrossBridge is targeted toward the game development industry, and includes tools for building, testing, and debugging C/C++ projects in Flash Player.
Notable online video games developed in Flash include Angry Birds, FarmVille, and AdventureQuest (started in 2002, and still active as of 2020).[69]
Availability[edit]
Desktop platforms[edit]
Adobe Flash Player is available in two major flavors:
- The plugin version for use in various web browsers
- The «projector» version is a standalone player that can open SWF files directly.[70][71]
On February 22, 2012, Adobe announced that it would no longer release new versions of NPAPI Flash plugins for Linux, although Flash Player 11.2 would continue to receive security updates.[72][73][74] In August 2016 Adobe announced that, beginning with version 24, it will resume offering of Flash Player for Linux for other browsers.[75]
The Extended Support Release (ESR) of Flash Player on macOS and Windows was a version of Flash Player kept up to date with security updates, but none of the new features or bug fixes available in later versions. In August 2016, Adobe discontinued the ESR branch and instead focused solely on the standard release.[76]
| Operating system | First version | Latest version | Support status | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Windows | XP SP2–11 | 1 | 34.0.0.277 (China-specific)[77] 50.x (Harman enterprise)[78] 32.0.0.465 (last public update, excluding China)[79] |
2017–present 2021–present 2001–2020 |
| 2000 and XP RTM–SP1 | 11.1.102.55 and 10.3.183.90[80] | 1999–2013 | ||
| 98, ME and 2000 RTM–SP2 | 9.0.289.0[80] | 1998–2011 | ||
| 95 and NT 4 (IA-32) | 7.0.14.0[80] | 1997–2005 | ||
| 3.1 | 3[81] | 1997–1998 | ||
| macOS | 10.12 and later | 5.0.41.0[82] | 34.0.0.277 (China-specific)[77] | 2017–present |
| 10.10 and later | 50.x (Harman enterprise)[78] 32.0.0.465 (last public update, excluding China)[79] |
2021–present 2014–2020 |
||
| 10.9 | 29.0.0.171[80] | 2013–2018 | ||
| 10.6–10.8 (IA-32, x64) | 22.0.0.209[80] | 2009–2016 | ||
| 10.5 (IA-32,x64) | 10.3.183.90[80] | 2007–2013 | ||
| 10.4 (IA-32,PPC)–10.5 (PPC) | 10.1.102.64[80] | 2005–2011 | ||
| 10.1–10.3 | 9.0.289.0[80] | 2001–2011 | ||
| Classic Mac OS | 7.6.1–9.2.2 (PowerPC) | 1 | 7.0.14.0[80] | 1997–2005 |
| 7.6.1–8.1 (68k) | 3[81] | 1997–1998 | ||
| Linux desktops | 4.0r12[83][84] | 50.x (Harman enterprise)[78] 34.0.0.137 (last public update, China-specific)[85] 32.0.0.465 (last public update, excluding China)[79] |
2021–present 2017–2021[86] 1999–2020 |
|
| Solaris and OpenSolaris | 4.0r12[83] | 11.2.202.223 and 10.3.183.90[80] | 2004–2013 | |
| IRIX | 4.0r12[83][87] | 4.0.r12[88] | 1999 |
Version 10 can be run under Windows 98/Me using KernelEx. HP offered Version 6 of the player for HP-UX,[89] while Innotek GmbH offered versions 4 and 5 for OS/2.[90] Other versions of the player have been available at some point for BeOS.[citation needed]
Mobile platforms[edit]
In 2011, Flash Player had emerged as the de facto standard for online video publishing on the desktop, with adaptive bitrate video streaming, DRM, and fullscreen support.[30][31] On mobile devices, however, after Apple refused to allow the Flash Player within the inbuilt iOS web browser, Adobe changed strategy, enabling Flash content to be delivered as native mobile applications using the Adobe Integrated Runtime.
Up until 2012, Flash Player 11 was available for the Android (ARM Cortex-A8 and above),[91] although in June 2012, Google announced that Android 4.1 (codenamed Jelly Bean) would not support Flash by default. In August 2012, Adobe stopped updating Flash for Android.[92]
Flash Player was supported on a select range of mobile and tablet devices, from Acer, BlackBerry 10, Dell, HTC, Lenovo, Logitech, LG, Motorola, Samsung, Sharp, SoftBank, Sony (and Sony Ericsson), and Toshiba.[93][94][95] As of 2012, Adobe has stopped browser-based Flash Player development for mobile browsers in favor of HTML5,[96][97] however, Adobe continues to support Flash content on mobile devices with the Adobe Integrated Runtime, which allows developers to publish content that runs as native applications on certain supported mobile phone platforms.
Adobe said it will optimize Flash for use on ARM architecture (ARMv7 and ARMv6 architectures used in the Cortex-A series of processors and in the ARM11 family) and release it in the second half of 2009. The company also stated it wants to enable Flash on NVIDIA Tegra, Texas Instruments OMAP 3, and Samsung ARMs.[98][99] Beginning 2009, it was announced that Adobe would be bringing Flash to TV sets via Intel Media Processor CE 3100 before mid-2009.[100] ARM Holdings later said it welcomes the move of Flash, because «it will transform mobile applications and it removes the claim that the desktop controls the Internet.»[101] However, as of May 2009, the expected ARM/Linux netbook devices had poor support for Web video and fragmented software base.[102]
Among other devices, LeapFrog Enterprises provides Flash Player with their Leapster Multimedia Learning System and extended the Flash Player with touch-screen support.[103] Version 9 was the most recent version available for the Linux/ARM-based Nokia 770/N800/N810 Internet tablets running Maemo OS2008.[89] Other versions of the player have been available at some point for Symbian OS and Palm OS.[104] The Kodak Easyshare One includes Flash Player.[105]
The following table documents historical support for Flash Player on mobile operating systems:
| Platform | Final version |
|---|---|
| Android 4.0, ARM Cortex-A8+[91] | Flash Player 11.1.115.81[80] |
| Android 2.2–3.x, ARM Cortex-A8+[106][91] | Flash Player 11.1.111.73[80] |
| Dreamcast | Flash Player 4.0[citation needed] |
| Maemo | Flash Player 9.4[107] |
| PlayStation 3 with Firmware 2.50, NetFront 2.81 | Flash Player 9.1 (update 3)[108] |
| PSP with Firmware 2.70 | Flash Player 6[109] |
| Pocket PC 2003[110] | Flash Player 7[111][112] |
| webOS (Palm and HP) | Flash Player 10[citation needed] |
| Windows Mobile 5[110] | Flash Player 7[111] |
Other hardware[edit]
Some CPU emulators have been created for Flash Player, including Chip8,[113] Commodore 64,[114] ZX Spectrum,[115] and the Nintendo Entertainment System.[116] They enable video games created for such platforms to run within Flash Player.
End of life[edit]
Adobe announced on July 25, 2017, that it would end support for the normal/global variant of Flash Player on January 1, 2021, and encouraged developers to use HTML5 standards in place of Flash.[117][118] The announcement was coordinated with Apple,[119] Facebook,[120] Google,[121] Microsoft,[122] and Mozilla.[123] Adobe announced that all major web browsers planned to officially remove the Adobe Flash Player component on December 31, 2020, and Microsoft removed it from the Windows OS in January 2021 via Windows Update. In a move to further reduce the number of Flash Player installations, Adobe added a «time bomb» to Flash to disable existing installations after January 12, 2021.[124] In mid-2020, Flash Player started prompting users to uninstall itself.[125] Adobe removed all existing download links for Flash installers.[126] After January 26, 2021, all major web browsers including Apple Safari, Google Chrome, Microsoft Edge, and Mozilla Firefox have already permanently removed Flash support.[127] However, Flash content continues to be accessible on the web through emulators such as Ruffle, with varying degrees of compatibility and performance, although this is not endorsed by Adobe.
Web browsers[edit]
Google Chrome[edit]
Starting from Chrome 76, Flash is disabled by default without any prompts to activate Flash content.[128] Users who wanted to play Flash content had to manually set a browser to prompt for Flash content, and then during each browser session enable Flash plugin for every site individually. Microsoft Edge, which is based on Chromium, followed the same plan as Google Chrome.[129]
Google Chrome blocked the Flash plugin as «out of date» in January 2021, and fully removed it from the browser with Chrome version 88, released on January 20, 2021.[130][131]
Mozilla Firefox[edit]
Starting with Firefox 85,[128] Flash is disabled by default without any prompts to activate Flash content. To play Flash content, users had to manually set a browser to prompt for Flash content, and then during each browser session enable Flash plugin for every site individually. Firefox 85, released on January 26, 2021, completely removed support for the Flash plugin.[127] Firefox ESR dropped support on November 2, 2021 (Firefox 78 ESR was the last version with support).[132]
Microsoft Windows[edit]
On October 27, 2020, Microsoft released an update (named KB4577586) for Windows 10 and 8.1 which removes the embedded Adobe Flash Player component from IE11 and Edge Legacy. In July 2021, this update was automatically installed as a security patch.[133][134] However, an ActiveX Flash Player plugin may still be used with IE after this update is applied.[135][136]
Apple Safari[edit]
Apple dropped Flash Player support from Safari 14 alongside the release of macOS Big Sur.[137][138]
Fallout[edit]
Despite the years of notice, several websites still were using Flash following December 31, 2020, including the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission. Many of these were resolved in the weeks after the deadline. However, many educational institutions still relied on Flash for educational material and did not have a path forward for replacement.[139]
Post-EOL support[edit]
Mainland China[edit]
The China-specific variant of Flash will be supported beyond 2020, by a company known as Zhongcheng.[140][141] The Projector (standalone) versions of this variant also work outside of China and do not include the «Flash Helper Service»; however, some tracking code still seems to be present. They are available on a somewhat hidden «Debug» page.[142] In addition, as the global variant of the plugin was discontinued, some users have figured how to modify and repack the China-specific variant to bring it more in line with the global variant. This includes removing the «Flash Helper Service» and removing the China only installation restriction, along with all other geo-restrictions and tracking code. A «time bomb», similar to the one found in later versions of the global variant, is also present in the unmodified China variant; this is also removed in most repacks. In theory, these repacks should provide users outside of China with the latest security updates to Flash Player, without having to deal with invasive advertisements or worry about privacy risks.[143] One such project, «Clean Flash Installer», was served a DMCA takedown from Adobe in October 2021.[144]
Enterprise[edit]
Adobe has partnered with Harman to support enterprise Flash Player users until at least 2023.[145][146] The Harman Flash player variant is labeled as version 50.x, to avoid confusion with other variants.[78]
Web browsers[edit]
Internet Explorer 11, along with IE mode in Edge,[78] will continue with ActiveX support, and by extension Flash Player support.[136] Firefox forks that plan to continue NPAPI support, and by extension Flash Player support, include Waterfox, Basilisk, Pale Moon, and K-Meleon. Various Chromium-based Chinese browsers will also continue to support Flash Player in PPAPI and/or NPAPI form, including, but not limited to, 360 Secure Browser.[135]
Shortly after Flash EOL, South African Revenue Service (SARS) released a custom version of Chromium browser with the Adobe Flash Player «time bomb» removed. This browser can access only a small set of SARS online pages containing Flash-based forms required for filing financial reports.[147]
Adobe Flash Player Projector[edit]
Although no longer available directly from Adobe, all versions of Adobe Flash Player Projector (also known as Adobe Flash Player Standalone) lack the «time bomb» present in the newer plug-in variants, and thus continue to be able to play all supported Flash file formats, including SWF files, without modification.[148][71][142]
Content preservation projects[edit]
The Internet Archive hosts some Flash content and makes it playable in modern browsers via emulators, Ruffle and Emularity.[149] Other emulators, such as CheerpX, also exist as options for Flash Player emulation on other websites.[150] BlueMaxima’s Flashpoint project claims to have collected more than 38,000 Adobe Flash Player games and animations and made them available for download.[151]
Open source[edit]
Adobe has released some components of Adobe Flash products as open source software via Open Screen Project or donated them to open source organizations. As of 2021, most of these technologies are considered obsolete. This includes: ActionScript Virtual Machine 2 (AVM2) which implements ActionScript 3 (donated as open-source to Mozilla Foundation), Adobe Flex Framework (donated as open-source to the Apache Software Foundation and rebranded as Apache Flex,[62] superseded by Apache Royale), CrossBridge C++ cross-compilation toolset (released on GitHub).[152][153]
Criticism[edit]
Accessibility and usability[edit]
In some browsers, prior Flash versions have had to be uninstalled before an updated version could be installed.[154][155] However, as of version 11.2 for Windows, there are now automatic updater options.[156] Linux is partially supported, as Adobe is cooperating with Google to implement it via Chrome web browser on all Linux platforms.[157]
Mixing Flash applications with HTML leads to inconsistent input handling leading to poor user experience with the site (keyboard and mouse not working as they would in an HTML-only document).[citation needed]
Privacy[edit]
Flash Player supports persistent local storage of data (also referred to as Local Shared Objects), which can be used similarly to HTTP cookies or Web Storage in web applications. Local storage in Flash Player allows websites to store non-executable data on a user’s computer, such as authentication information, game high scores or web browser games, server-based session identifiers, site preferences, saved work, or temporary files. Flash Player will only allow content originating from exactly the same website domain to access data saved in local storage.[158]
Because local storage can be used to save information on a computer that is later retrieved by the same site, a site can use it to gather user statistics, similar to how HTTP cookies and Web Storage can be used. With such technologies, the possibility of building a profile based on user statistics is considered by some a potential privacy concern. Users can disable or restrict use of local storage in Flash Player through a «Settings Manager» page.[159][160] These settings can be accessed from the Adobe website or by right-clicking on Flash-based content and selecting «Global Settings».
Local storage can be disabled entirely or on a site-by-site basis. Disabling local storage will block any content from saving local user information using Flash Player, but this may disable or reduce the functionality of some websites, such as saved preferences or high scores and saved progress in games.
Flash Player 10.1 and upward honor the privacy mode settings in the latest versions of the Chrome, Firefox, Internet Explorer, and Safari web browsers, such that no local storage data is saved when the browser’s privacy mode is in use.[161]
Security[edit]
Adobe security bulletins and advisories announce security updates, but Adobe Flash Player release notes do not disclose the security issues addressed when a release closes security holes, making it difficult to evaluate the urgency of a particular update. A version test page allows the user to check if the latest version is installed, and uninstallers may be used to ensure that old-version plugins have been uninstalled from all installed browsers.
In February 2010, Adobe officially apologized[162] for not fixing a known vulnerability for over a year. In June 2010 Adobe announced a «critical vulnerability» in recent versions, saying there are reports that this vulnerability is being actively exploited in the wild against both Adobe Flash Player, and Adobe Reader and Acrobat.[163][164] Later, in October 2010, Adobe announced[165] another critical vulnerability, this time also affecting Android-based mobile devices. Android users have been recommended to disable Flash or make it only on demand.[166] Subsequent security vulnerabilities also exposed Android users, such as the two critical vulnerabilities published in February 2013[167] or the four critical vulnerabilities published in March 2013,[168] all of which could lead to arbitrary code execution.
Symantec’s Internet Security Threat Report[169] states that a remote code execution in Adobe Reader and Flash Player[170] was the second most attacked vulnerability in 2009. The same report also recommended using browser extensions to disable Flash Player usage on untrusted websites. McAfee predicted that Adobe software, especially Reader and Flash, would be primary target for attacks in 2010.[171] Adobe applications had become, at least at some point, the most popular client-software targets for attackers during the last quarter of 2009.[172] The Kaspersky Security Network published statistics for the third quarter of 2012 showing that 47.5% of its users were affected by one or more critical vulnerabilities.[173] The report also highlighted that «Flash Player vulnerabilities enable cybercriminals to bypass security systems integrated into the application.»[173]
Steve Jobs criticized the security of Flash Player, noting that «Symantec recently highlighted Flash for having one of the worst security records in 2009».[174] Adobe responded by pointing out that «the Symantec Global Internet Threat Report for 2009, found that Flash Player had the second lowest number of vulnerabilities of all Internet technologies listed (which included both web plug-ins and browsers).»[175][176]
On April 7, 2016, Adobe released a Flash Player patch for a zero-day memory corruption vulnerability CVE-2016-1019 that could be used to deliver malware via the Magnitude exploit kit. The vulnerability could be exploited for remote code execution.[177][178]
Vendor lock-in[edit]
Flash Player 11.2 does not play certain kinds of content unless it has been digitally signed by Adobe, following a license obtained by the publisher directly from Adobe.[179]
This move by Adobe, together with the abandonment of Flex to Apache was criticized as a way to lock out independent tool developers, in favor of Adobe’s commercial tools.[180][181][182]
This has been resolved as of January 2013, after Adobe no longer requires a license or royalty from the developer. All premium features are now classified as general availability, and can be freely used by Flash applications.[183]
Apple controversy[edit]
In April 2010, Steve Jobs, at the time CEO of Apple Inc. published an open letter explaining why Apple would not support Flash on the iPhone, iPod Touch, and iPad.[174] In the letter he blamed problems with the «openness», stability, security, performance, and touchscreen integration of the Flash Player as reasons for refusing to support it. He also claimed that when one of Apple’s Macintosh computers crashes, «more often than not» the cause can be attributed to Flash, and described Flash as «buggy».[184] Adobe’s CEO Shantanu Narayen responded by saying, «If Flash [is] the number one reason that Macs crash, which I’m not aware of, it has as much to do with the Apple operating system.»[185]
Steve Jobs also claimed that a large percentage of the video on the Internet is supported on iOS, since many popular video sharing websites such as YouTube have published video content in an HTML5 compatible format, enabling videos to playback in mobile web browsers even without Flash Player.[186]
Mainland China-specific variant[edit]
Starting with version 30, Adobe stopped distributing Flash Player directly to users from mainland China. Instead, they selected 2144.cn as a partner and released a special variant of Flash Player on a specific website,[187] which contains a non-closable process, known as the «Flash Helper Service», that collects private information and pops up advertisement window contents,[188] by receiving and running encrypted programs from a remote server.[189] The partnership started in about 2017, but in version 30, Adobe disabled the usage of vanilla (global) variant of Flash Player in mainland China,[190] forcing users to use that specific variant, which may pose a risk to its users due to Internet censorship by Chinese Communist Party (CCP).[191] This only affected Chinese Chromium based browser users, Firefox users, and Internet Explorer users using Windows 7 and below, as Microsoft still directly distributed Flash Player for Internet Explorer and Microsoft Edge through Windows Update in Windows 8 and upward at the time. Starting in 2021, however, this variant is the only publicly supported version of Flash Player.
Release history[edit]
See also[edit]
- Adobe Flash
- Adobe AIR
- Adobe Shockwave
- Apache Flex
- Microsoft Silverlight
References[edit]
- ^ «Adobe — Flash Player». flash.cn (in Simplified Chinese). Zhongcheng Network Technology Co., Ltd. Retrieved July 14, 2021.
- ^ a b «_flash_install_packages_». flash.cn. Zhongcheng Network Technology Co., Ltd. Retrieved July 13, 2021.
- ^ «ADOBE® FLASH® PLAYER ENTERPRISE SUPPORT». harman.com. Harman International. Retrieved November 21, 2021.
- ^ «Flash Player官方下载中心». Flash (in Simplified Chinese). Flash.cn. Retrieved June 12, 2021.
- ^ «关于Linux操作系统下Flash Player个人版停用的公告». Flash (in Simplified Chinese). Flash.cn. May 10, 2021. Retrieved June 12, 2021.
- ^ a b «Adobe — Flash Player». Adobe.com. Adobe Systems. Retrieved December 8, 2020.
- ^ a b c d e «Archived Flash Player versions». Adobe.com. Adobe Systems. Retrieved October 20, 2015.
- ^ «Download Flash Player 32 Beta». labs.adobe.com. Adobe Systems. Retrieved May 19, 2020.
- ^ «Adobe Flash Player Download». Adobe Systems. Archived from the original on August 9, 2016. Retrieved August 10, 2016.
- ^ «Why You Should Ditch Adobe Shockwave». Krebs on Security. May 14, 2014. Archived from the original on May 25, 2014. Retrieved February 21, 2015.
- ^ Integrated Adobe Flash Player Plug-in Archived January 31, 2013, at the Wayback Machine, Chrome team blog
- ^ Porting Flash to sandboxed PPAPI platform Archived July 25, 2018, at the Wayback Machine, Official Chromium Blog
- ^ «Flash Player issues | Windows 8». Adobe Systems. Archived from the original on December 20, 2016. Retrieved December 15, 2016.
- ^ «Flash Player Issues | Windows 10 | Internet Explorer». Adobe Systems. Archived from the original on December 20, 2016. Retrieved December 15, 2016.
- ^ «Flash Player issues | Windows 10 | Microsoft Edge». Adobe Systems. Archived from the original on December 20, 2016. Retrieved December 15, 2016.
- ^ «Adobe Flash Runtimes Statistics». Adobe Systems Incorporated. Archived from the original on January 6, 2013. Retrieved January 2, 2013.
- ^ Barrett, Brian (July 15, 2015). «Flash. Must. Die». Wired.com. Condé Nast. Archived from the original on May 16, 2017. Retrieved May 9, 2017.
- ^ Vaughan-Nichols, Steven J. (June 16, 2016). «How to really fix the latest Adobe Flash security hole». ZDNet. CBS Interactive. Archived from the original on May 23, 2017. Retrieved May 9, 2017.
- ^ Collins, Katie (March 11, 2016). «Adobe rushes out emergency update for ‘critical’ Flash security flaw». CNET. Archived from the original on March 25, 2017. Retrieved May 9, 2017.
- ^ Cimpanu, Catalin (December 9, 2020). «Adobe to block Flash content from running on January 12, 2021». ZDNet. Red Ventures. Retrieved January 21, 2021.
- ^ «重橙网络» [Flash Center]. www.flash.cn. Retrieved October 8, 2021.
the exclusive and official distributor of Adobe Flash Player
- ^ AIR 3 Archived August 21, 2014, at the Wayback Machine, Adobe
- ^ «What are local shared objects?». Security and privacy. Adobe Systems. Archived from the original on May 29, 2010. Retrieved December 5, 2007.
- ^ SWX: SWF Data Format Archived August 17, 2012, at the Wayback Machine, official website
- ^ swxjava – SWX RPC implementation in Java Archived June 7, 2014, at the Wayback Machine, Google Code
- ^ swx-format – Data Format Archived August 3, 2014, at the Wayback Machine, Google Code
- ^ SWX Contest Winners Archived August 18, 2012, at the Wayback Machine, SWX Format Website
- ^ Introducing SWXml Archived November 12, 2007, at the Wayback Machine, Aral Balkan
- ^ «Flash H.264». MainConcept. Archived from the original on November 18, 2010. Retrieved September 24, 2010.
- ^ a b Flash and the HTML5 <video> tag Archived August 7, 2012, at the Wayback Machine, YouTube Blog
- ^ a b Pardon Our Dust Archived May 31, 2015, at the Wayback Machine, Hulu Blog
- ^ Future Media Standards & Guidelines – AV Addendum v1.5 Archived September 30, 2013, at the Wayback Machine BBC
- ^ Protocols: HTTP vs. RTMP> Beginner’s Guide to Distributing Flash Video Archived March 13, 2013, at the Wayback Machine, Adobe Press
- ^ Cross-domain policy file usage recommendations for Flash Player Archived August 13, 2014, at the Wayback Machine, Adobe
- ^ a b Policy file changes in Flash Player 9 and Flash Player 10 Archived August 18, 2014, at the Wayback Machine, Adobe
- ^ «Sites which support crossdomain.xml to allow Flash and Silverlight access». Retrieved March 25, 2017.
- ^ Socket Archived October 11, 2012, at the Wayback Machine, Adobe ActionScript 3 API Reference
- ^ Sockets Archived October 20, 2012, at the Wayback Machine, ActionScript 3.0 Developer’s Guide
- ^ Setting up a socket policy file server Archived August 3, 2014, at the Wayback Machine, Adobe
- ^ AsSQL – MySQL Driver for AS3 Archived May 25, 2013, at the Wayback Machine, Google Code
- ^ Remi Arnaud (2011). «3D in a Web Browser». In Eric Lengyel (ed.). Game Engine Gems 2. CRC Press. pp. 208–212. ISBN 978-1-56881-437-7. Archived from the original on January 10, 2016. Retrieved November 28, 2015.
- ^ Christer Kaitila (2011). Adobe Flash 11 Stage3D (Molehill) Game Programming Beginner’s Guide. Packt Publishing Ltd. p. 9. ISBN 978-1-84969-169-7.
- ^ «Stage3D vs WebGL Performance — Airtight Interactive». Airtightinteractive.com. October 28, 2011. Archived from the original on July 31, 2014. Retrieved August 4, 2014.
- ^ «Stage3D». scratch.mit.edu. Archived from the original on August 10, 2014. Retrieved August 5, 2014.
- ^ «Adobe Flash Player 11.8 – Bug 3591185: Pixel Bender shader performance drastically degraded in FP11.8. Closed as «NeverFix»«. Archived from the original on April 22, 2014.
- ^ Comparing Flash, HTML5 Performance Archived October 26, 2011, at the Wayback Machine, OS News
- ^ Battery Performance with Flash Player 10.1 on Nexus One Archived October 16, 2011, at the Wayback Machine, Flash Mobile Blog
- ^ Reference Designs and Demos Archived October 11, 2011, at the Wayback Machine, QNX
- ^ ActionScript 3.0 overview, «ActionScript 3.0 code executes up to 10 times faster than legacy ActionScript code.» Archived July 18, 2014, at the Wayback Machine, Adobe
- ^ «Alchemy:FAQ». Archived from the original on May 5, 2012. Retrieved May 5, 2012., Adobe Labs, «ASC performs few optimizations at this time»
- ^ Zotov, Peter (May 6, 2012). «Reaching the Limits of Adobe Stupidity – whitespace». Whitequark.org. Archived from the original on October 15, 2012. Retrieved October 27, 2012.
- ^ a b Alchemy:FAQ Archived May 5, 2012, at the Wayback Machine, Adobe Labs
- ^ a b Optimizing ActionScript Bytecode using LLVM Archived May 11, 2012, at the Wayback Machine, Adobe
- ^ a b Adobe Alchemy, is it ActionScript heresy? Archived August 19, 2012, at the Wayback Machine, Unit Zero One
- ^ Introducing ASC 2.0 Archived March 15, 2013, at the Wayback Machine, Thibault Imbert, ByteArray.com
- ^ AS3 vs haXe performance, SplashDust website Archived January 5, 2013, at the Wayback Machine
- ^ Optimizing performance of applications for connected TVs Archived August 22, 2016, at the Wayback Machine, Adobe Developer Connection
- ^ Top 10 Performance Killers in your AIR Application Archived October 15, 2014, at the Wayback Machine, FlexWiz
- ^ Flex versus ActionScript – the debate gets new life Archived December 9, 2014, at the Wayback Machine, Greg’s Ramblings
- ^ Pure ActionScript + MadComponents vs. Flash Builder 4.5 Archived December 22, 2014, at the Wayback Machine, MobileAppDev
- ^ Flex 4.5 vs Pure AS3 Archived October 21, 2011, at the Wayback Machine, Michael Crosby
- ^ a b «Adobe donates Flex to Apache». Techworld. Archived from the original on November 18, 2011. Retrieved November 17, 2011.
- ^ Response to «Thoughts on Flash» Archived November 12, 2011, at the Wayback Machine, True Gryc Blog
- ^ «Adobe Gaming SDK». creative.adobe.com. Adobe. Archived from the original on August 8, 2014. Retrieved August 4, 2014.
- ^ a b Wagner James Au (2012). Game Design Secrets. John Wiley & Sons. p. 130. ISBN 978-1-118-46391-8.
- ^ «Adobe Flash 11 adopts Unreal Engine 3 for better browser games | The Verge». theverge.com. October 7, 2011. Archived from the original on July 6, 2017. Retrieved August 4, 2014.
- ^ «List of Flash Gaming Engines». FlashRealtime.com. April 23, 2011. Archived from the original on April 6, 2013. Retrieved February 21, 2015.
- ^ CrossBridge for Flash Player Archived September 20, 2017, at the Wayback Machine, GitHub
- ^ Remi Arnaud (2011). «3D in a Web Browser». In Eric Lengyel (ed.). Game Engine Gems 2. CRC Press. p. 205. ISBN 978-1-56881-437-7. Archived from the original on January 10, 2016. Retrieved November 28, 2015.
- ^ «Downloads». Adobe Flash Player Support Center. Archived from the original on October 22, 2011. Retrieved October 29, 2011.
- ^ a b «Adobe Flash Player — Debug Downloads». Adobe Inc. Archived from the original on April 1, 2022. Retrieved April 15, 2022.
- ^ «Adobe and Google Partnering for Flash Player on Linux». Archived from the original on May 19, 2019. Retrieved November 25, 2012.
- ^ Noyes, Katherine (April 6, 2012). «For Flash on Linux, Chrome Will Be Users’ Only Choice | PCWorld Business Center». Pcworld.com. Archived from the original on October 20, 2012. Retrieved April 10, 2012.
- ^ «Adobe Releases Last Linux Version of Flash Player – Slashdot». Linux.slashdot.org. Archived from the original on March 31, 2012. Retrieved April 10, 2012.
- ^ «Beta News – Flash Player NPAPI for Linux». Adobe AIR and Adobe Flash Player Team Blog. August 31, 2016. Archived from the original on November 18, 2016. Retrieved November 17, 2016.
- ^ Campbell, Chris (August 23, 2016). «Where can I find the «Extended Support Release» of Flash Player for Windows or Macintosh?». forums.adobe.com. Adobe Systems. Archived from the original on July 5, 2016. Retrieved September 25, 2016.
- ^ a b «Adobe Flash Player (China Variant)». flash.cn. Zhongcheng Network Technology Co., Ltd. Retrieved March 9, 2021.
- ^ a b c d e «Adobe® Flash® Player Enterprise Support». harman.com. Harman International. Retrieved November 20, 2021.
- ^ a b c Adobe Flash Player Versions Archived January 1, 2019, at the Wayback Machine, Adobe.com
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p q «Archived Flash Player versions». Adobe. Archived from the original on February 15, 2014. Retrieved February 18, 2014.
- ^ a b «Flash Player 3 Archive». Archived from the original on July 18, 2020.
- ^ «Flash Player 5 Archive». Archived from the original on July 18, 2020.
- ^ a b c «MACROMEDIA INTRODUCES FREE FLASH PLAYERS FOR LINUX, SOLARIS, IRIX USERS. | Technology > Software Services & Applications from AllBusiness.com». Archived from the original on May 20, 2007. Retrieved May 20, 2011.
- ^ «Macromedia Flash Player download center (Linux)». Archived from the original on June 9, 2000.
- ^ «Flash Player官方下载中心». Flash (in Simplified Chinese). Flash.cn. Retrieved June 12, 2021.
- ^ «关于Linux操作系统下Flash Player个人版停用的公告». Flash (in Simplified Chinese). Flash.cn. May 10, 2021. Retrieved June 12, 2021.
- ^ «Macromedia Flash Player download center (IRIX)». Archived from the original on January 5, 2001.
- ^ «Macromedia — Macromedia Web Players: Alternates». Archived from the original on August 2, 2001.
- ^ a b Web Players Archived August 21, 2014, at the Wayback Machine. Adobe. Retrieved on March 11, 2011.
- ^ «InnoTek Systemberatung GmbH». Archived from the original on September 17, 2001.
- ^ a b c «Flash Player 10.1 – Installations and updates». Archived from the original on October 8, 2010. Retrieved November 19, 2010.
- ^ Arthur, Charles (June 29, 2012). «Flash Player for Android: Adobe calls time, declares it dead». The Guardian. Archived from the original on March 5, 2014. Retrieved June 30, 2012.
- ^ Flash Platform Certified Devices Archived June 22, 2012, at the Wayback Machine, Adobe
- ^ Flash Platform Certified Devices: Smartphones Archived July 8, 2012, at the Wayback Machine, Adobe
- ^ Flash Platform Certified Devices: Tablets Archived July 8, 2012, at the Wayback Machine, Adobe
- ^ Adobe abandons Flash Player on mobile browsers for HTML5 Archived November 14, 2011, at the Wayback Machine, CBS News
- ^ Adobe abandons Flash for mobile devices Archived July 9, 2016, at the Wayback Machine; The Telegraph
- ^ Press Room: For immediate release Archived August 5, 2014, at the Wayback Machine. Adobe. Retrieved on March 11, 2011.
- ^ Adobe Flash 10 to be ARM-optimized in 2009 Archived January 8, 2009, at the Wayback Machine. Electronista (November 17, 2008). Retrieved on March 11, 2011.
- ^ Press Room: For immediate release Archived August 16, 2014, at the Wayback Machine. Adobe. Retrieved on March 11, 2011.
- ^ ARM welcomes Adobe’s mobile Flash move – 5/2/2008 Archived February 20, 2009, at the Wayback Machine. Electronics Weekly (May 2, 2008). Retrieved on March 11, 2011.
- ^ ARM netbooks struggle with video, apps Archived July 12, 2012, at the Wayback Machine. Eetimes.com (April 14, 2009). Retrieved on March 11, 2011.
- ^ Adobe Success Story: LeapFrog Enterprises Archived October 14, 2007, at the Wayback Machine (Taken July 7, 2006).
- ^ Max, Jose. «Adobe Activation». Adobe Activator. Zii.
- ^ Macromedia – Flash Player SDK Archived July 18, 2006, at the Wayback Machine (Taken July 7, 2006).
- ^ Adobe Flash Player Archived October 13, 2011, at the Wayback Machine, Android Market
- ^ Maemo software | Nokia › Maemo Browser Archived December 29, 2009, at the Wayback Machine. Maemo.nokia.com. Retrieved on March 11, 2011.
- ^ «New info on the firmware updates for PS3 and PSP». ThreeSpeech. October 14, 2008. Archived from the original on October 15, 2008. Retrieved October 14, 2008.
- ^ Mobile and Devices Developer Center: Sony PSP Archived May 25, 2010, at the Wayback Machine. Adobe (July 16, 2007). Retrieved on March 11, 2011.
- ^ a b Download Macromedia Flash Player 7 for Pocket PC Archived February 7, 2014, at the Wayback Machine, Adobe
- ^ a b Flash Player 7 For Pocket PC Archived January 19, 2014, at the Wayback Machine. Adobe (July 14, 2009). Retrieved on March 11, 2011.
- ^ rich Internet applications | Adobe Flash Platform runtimes Archived May 30, 2010, at the Wayback Machine. Adobe.com (July 14, 2009). Retrieved on March 11, 2011.
- ^ «Flip8 – the World’s First Flash Emulator — v0.9». Newsdee.com. Archived from the original on January 27, 2010. Retrieved September 12, 2009.
- ^ Claus Wahlers. «FC64 – Flash Commodore 64 Emulator — Demo — c么deazur brasil lab». Codeazur.com.br. Archived from the original on October 5, 2009. Retrieved September 12, 2009.
- ^ «FlashZXSpectrum48k, Sinclair ZX Spectrum Emulator written in Flash». Jorin.com. Archived from the original on February 3, 2008. Retrieved September 12, 2009.
- ^ «aminnes – Project Hosting on Google Code». www.aminlab.com/. May 17, 2010. Archived from the original on September 19, 2014.
- ^ Lardinois, Frederic (July 25, 2017). «Get ready to finally say goodbye to Flash — in 2020». TechCrunch. Archived from the original on July 25, 2017. Retrieved July 25, 2017.
- ^ Warren, Tom (July 25, 2017). «Adobe will finally kill Flash in 2020». The Verge. Archived from the original on July 25, 2017. Retrieved July 25, 2017.
- ^ «Adobe Announces Flash Distribution and Updates to End». July 25, 2017. Archived from the original on July 26, 2017. Retrieved July 26, 2017.
- ^ Pudełek, Jakub (July 25, 2017). «Migrating Games from Flash to Open Web Standards on Facebook». Archived from the original on August 1, 2017. Retrieved July 26, 2017.
- ^ Laforge, Anthony (July 25, 2017). «Saying goodbye to Flash in Chrome». Archived from the original on July 25, 2017. Retrieved July 26, 2017.
- ^ «The End of an Era – Next Steps for Adobe Flash». July 25, 2017. Archived from the original on July 26, 2017. Retrieved July 26, 2017.
- ^ Smedberg, Benjamin (July 25, 2017). «Firefox Roadmap for Flash End-of-Life». Archived from the original on September 12, 2019. Retrieved August 21, 2019.
- ^ Tung, Liam (January 12, 2021). «Adobe Flash is finally gone: The end arrives as Adobe starts blocking Flash content». ZDNet. Retrieved January 14, 2021.
- ^ Cimpanu, Catalin. «Adobe wants users to uninstall Flash Player by the end of the year». ZDNet. Retrieved June 22, 2020.
- ^ Stahie, Silviu (June 24, 2020). «Adobe to Remove Flash Download Links, Recommends People Uninstall It Now». Security Boulevard. Retrieved February 18, 2021.
- ^ a b «Firefox 85.0, See All New Features, Updates and Fixes». Mozilla. Retrieved January 26, 2021.
- ^ a b «End of support for Adobe Flash | Firefox Help». support.mozilla.org. Retrieved November 25, 2020.
- ^ Venkat (June 16, 2019). «After Chrome 76, Mozilla Firefox 69 disables Flash by Default». Techdows. Retrieved June 16, 2019.
- ^ «Flash Roadmap — The Chromium Projects». www.chromium.org. Retrieved June 16, 2019.
- ^ Warren, Tom (January 20, 2021). «Google’s new Chrome 88 update improves dark mode, removes FTP and Adobe Flash». The Verge. Retrieved January 20, 2021.
- ^ «Firefox for Enterprise 93 — Release notes | Firefox for Enterprise Help». support.mozilla.org. Retrieved October 8, 2021.
- ^ «Update on Adobe Flash Player End of Support». Windows Blogs. September 4, 2020. Retrieved October 4, 2020.
- ^ «You can now uninstall Flash on Windows 10 and 8.1 using KB4577586». gHacks Tech News. October 28, 2020. Retrieved October 28, 2020.
- ^ a b «Adobe — Flash Player». Adobe.com. Adobe Systems. Retrieved February 5, 2021.
- ^ a b «_flash_install_packages_». flash.cn. Zhongcheng Network Technology Co., Ltd. Retrieved February 5, 2021.
- ^ «Flash Player on Adobe Support Community». community.adobe.com. Retrieved October 3, 2020.
- ^ Cimpanu, Catalin (June 24, 2020). «Safari 14 removes Flash, gets support for breach alerts, HTTP/3, and WebP». ZDNet. Retrieved July 27, 2020.
- ^ Debre, Elena (February 5, 2021). «These Places Were Not Ready for Flash to Die». Slate. Retrieved February 7, 2021.
- ^ «Release Notes — Flash Player 33». Adobe.com. Adobe Systems. Retrieved January 17, 2021.
- ^ «关于大连车务段使用Flash出现问题的声明公告». flash.cn (in Simplified Chinese). Zhongcheng Network Technology Co., Ltd. Retrieved January 25, 2021.
- ^ a b «Flash Player Debug Downloads (China-specific)». flash.cn (in Simplified Chinese). Zhongcheng Network Technology Co., Ltd. Retrieved April 1, 2021.
- ^ «Chinese repacks». msfn.com. Retrieved April 1, 2021.
- ^ Maxwell, Andy (October 12, 2021). «Adobe Uses DMCA to Nuke Project That Keeps Flash Alive, Secure & Adware Free». TorrentFreak. Retrieved October 13, 2021.
- ^ «Adobe Flash Player EOL Enterprise Information Page». Adobe.com. Adobe Systems. Retrieved January 17, 2021.
- ^ «Harman’s support program for Adobe Flash Player». harman.com. Harman International. Retrieved January 17, 2021.
- ^ Cimpanu, Catalin. «South African government releases its own browser just to re-enable Flash support». ZDNet. Retrieved February 3, 2021.
- ^ «Flash Projectors after 2020». community.adobe.com. July 22, 2020. Retrieved October 15, 2021.
- ^ Scott, Jason (November 22, 2020). «Flash Back! Further Thoughts on Flash at the Internet Archive». Retrieved January 3, 2021.
- ^ «CheerpX For Flash». Leaning Technologies. Retrieved November 20, 2021.
- ^ «Every Flash game disappears forever in 2020 – but this project has preserved 38,000 of them». PCGamesN. Retrieved February 15, 2021.
- ^ Open Source Flash C++ Compiler, CrossBridge Archived March 25, 2014, at the Wayback Machine, Adobe Blogs, June 25, 2013
- ^ CrossBridge Archived September 20, 2017, at the Wayback Machine, Adobe Gaming GitHub Website
- ^ «Flash Player Help / Installation problems». Archived from the original on March 16, 2012. Retrieved April 4, 2012.
- ^ «Help / Uninstall (old-version) Flash Player (if installation is unsuccessful)». Archived from the original on August 28, 2012. Retrieved August 31, 2012.
- ^ a b «Patch for Adobe Flash». The H. March 29, 2012. Archived from the original on February 22, 2014. Retrieved February 18, 2014.
- ^ «Adobe roadmap for the Flash Player». Adobe. Archived from the original on January 12, 2013. Retrieved January 14, 2013.
- ^ «What Is a Local Shared Object?». Adobe Systems. Archived from the original on May 29, 2010. Retrieved July 1, 2010.
- ^ «Adobe Flash Player Settings Manager». Adobe Systems. Archived from the original on June 20, 2010. Retrieved July 1, 2010.
- ^ «Web Storage Settings Panel». Adobe Systems. Archived from the original on April 4, 2012. Retrieved April 4, 2012.
- ^ «Private browsing in Flash Player 10». Adobe Systems. Archived from the original on May 28, 2010. Retrieved July 1, 2010.
- ^ «Flash Bug Report». February 6, 2010. Archived from the original on February 10, 2010. Retrieved March 27, 2010.
- ^ «Security Advisory for Flash Player, Adobe Reader and Acrobat». Adobe Systems. Archived from the original on June 8, 2010. Retrieved June 8, 2010.
- ^ «Adobe acknowledges critical security flaw in software». BBC News. June 7, 2010.
- ^ «Security Advisory for Adobe Flash Player, Adobe Reader and Acrobat». Adobe Systems. Archived from the original on October 31, 2010. Retrieved October 31, 2010.
- ^ «Flash vulnerability revealed for Android, fix coming November 9th». MobileCrunch. Archived from the original on October 31, 2010. Retrieved October 31, 2010.
- ^ «Security updates available for Adobe Flash Player». Adobe Systems. February 7, 2013. Archived from the original on July 9, 2013. Retrieved July 7, 2013.
- ^ «Security updates available for Adobe Flash Player». Adobe Systems. March 12, 2013. Archived from the original on July 9, 2013. Retrieved July 7, 2013.
- ^ «Internet Security Threat Report: Volume XV: April 2010». Symantec. April 2010. pp. 37, 40, 42. Archived from the original on April 25, 2010. Retrieved May 9, 2010.
- ^ «Adobe Acrobat, Reader, and Flash Player Remote Code Execution Vulnerability». October 15, 2009. Archived from the original on April 24, 2011. Retrieved May 9, 2010.
- ^ «2010 Threat Predictions» (PDF). McAfee Labs. December 2009. p. 2. Archived from the original (PDF) on June 2, 2010. Retrieved May 9, 2010.
- ^ «McAfee Threats Report: Fourth quarter 2009» (PDF). McAfee Avert Labs. February 2010. p. 16. Archived from the original (PDF) on February 15, 2010. Retrieved May 9, 2010.
- ^ a b «IT Threat Evolution: Q3 2012». Kaspersky Lab ZAO. November 1, 2012. Archived from the original on November 5, 2012. Retrieved November 2, 2012.
- ^ a b Steve Jobs (April 29, 2010). «Thoughts on Flash». Apple. Archived from the original on May 1, 2010. Retrieved May 9, 2010.
- ^ future of Flash Archived November 17, 2011, at the Wayback Machine. Adobe (July 14, 2009). Retrieved on March 11, 2011.
- ^ Symantec Global Internet Threat Report for 2009 Archived August 4, 2010, at the Wayback Machine, page 40, «In 2009, Symantec documented 321 vulnerabilities affecting plug-ins for Web browsers (figure 9). ActiveX technologies were affected by 134 vulnerabilities, which was the highest among the plug-in technologies examined. Of the remaining technologies, Java SE had 84 vulnerabilities, Adobe Reader had 49 vulnerabilities, QuickTime had 27 vulnerabilities, and Adobe Flash Player was subject to 23 vulnerabilities. The remaining four vulnerabilities affected extensions for Firefox.»
- ^ «Adobe Patches Flash Zero-Day Exploited by Magnitude EK». April 7, 2016. Archived from the original on April 11, 2016. Retrieved April 25, 2016.
- ^ «Security Advisory for Adobe Flash Player». April 5, 2016. Archived from the original on June 4, 2016. Retrieved April 25, 2016.
- ^ Update: Premium Features for Flash Player Archived July 19, 2014, at the Wayback Machine, Adobe AIR and FP Blog
- ^ «Why will Premium Flash Player Features Kill Flash?». ASVGuy. March 10, 2012. Archived from the original on February 5, 2015. Retrieved February 21, 2015.
- ^ Shankland, Stephen (March 28, 2014). «Adobe to charge Flash coders to use ‘premium’ features». CNET. Archived from the original on January 19, 2015. Retrieved February 21, 2015.
- ^ «And Then Premium Features Arrived…». ASVGuy. April 5, 2012. Archived from the original on February 5, 2015. Retrieved February 21, 2015.
- ^ Adobe Premium Features for Flash Player Archived August 21, 2014, at the Wayback Machine, Flash Player Dev Center, Adobe
- ^ Cassella, Dena (February 1, 2010). «Steve Jobs Unleashes His Fury During Town Hall Meeting». Archived from the original on February 6, 2010. Retrieved February 22, 2010.
- ^ Richmond, Shane. (April 30, 2010) Adobe hits back at Apple’s ‘smokescreen’ – Telegraph Blogs Archived May 3, 2010, at the Wayback Machine. Blogs.telegraph.co.uk. Retrieved on March 11, 2011.
- ^ YouTube Mobile gets a kick start Archived January 7, 2012, at the Wayback Machine, Official YouTube Blog
- ^ «Flash Player官方下载-Flash中国官网». Flash.cn. Archived from the original on July 22, 2018. Retrieved July 22, 2018.
- ^ «Adobe update on 6/12/18 include 2144 game cente… | Adobe Community». forums.adobe.com. Archived from the original on March 30, 2019. Retrieved July 22, 2018.; «Adobe’s ‘Partner’ 2144 in China has suspicious … | Adobe Community». forums.adobe.com. June 26, 2018. Archived from the original on July 22, 2018. Retrieved July 22, 2018.; «Uninstall 2144 Game Center | Adobe Community». forums.adobe.com. Archived from the original on July 22, 2018. Retrieved July 22, 2018.
- ^ Roter, Tom (February 10, 2021). «The Curious Case of FlashHelperService — Updated». Minerva Labs.
- ^ «Flashplayer Is Incompatible With Your Area | Adobe Community». forums.adobe.com. June 14, 2018. Archived from the original on July 22, 2018. Retrieved July 22, 2018.
- ^ «IT之家 | 中国特供版Flash被曝向有关部门搜集用户隐私 – 中国数字时代». chinadigitaltimes.net (in Chinese (China)). Archived from the original on July 22, 2018. Retrieved July 22, 2018.
- ^ «FutureSplash Player 1.1». FutureWave Software, Inc. Archived from the original on November 5, 1996. Retrieved December 2, 2021.
- ^ Macromedia, Inc. (March 4, 2002) Macromedia and Sorenson Media bring video to Macromedia Flash content and applications, Retrieved on August 9, 2009
- ^ «Adobe Completes Acquisition of Macromedia». Adobe Systems. December 5, 2005. Archived from the original on June 2, 2007. Retrieved June 18, 2007.
- ^ Huang, Emmy (November 15, 2006). «Flash Player 9 Update (9.0.28.0) release now available for Windows and Macintosh». Archived from the original on June 25, 2007. Retrieved January 23, 2014.
- ^ «Exploring full-screen mode in Flash Player 9». Adobe Developer Center. December 3, 2007. Archived from the original on April 4, 2012. Retrieved April 10, 2012.
- ^ Melanson, Mike (December 4, 2007). «Flash Player 9 Update 3 (Final)». Archived from the original on September 7, 2010. Retrieved January 23, 2014.
- ^ «Adobe Delivers Flash Player 9 with H.264 Video Support». adobe.com (Press release). December 4, 2007. Archived from the original on December 12, 2007.
- ^ Adobe Systems Incorporated (December 3, 2007) List of codecs supported by Adobe Flash Player Archived August 19, 2009, at the Wayback Machine, Retrieved on August 5, 2009
- ^ Halfast, Todd. «Flash Player 10.1 Now Available for Windows, Mac, and Linux » Adobe AIR and Adobe Flash Player Team Blog». Blogs.adobe.com. Archived from the original on May 11, 2011. Retrieved April 10, 2012.
- ^ «features Flash Player 10.3 Release Notes». Kb2.adobe.com. Archived from the original on April 30, 2012. Retrieved April 10, 2012.
- ^ Tareq Aljaber (May 17, 2013). «Extended Support Release Updated to Flash Player 11.7». Adobe AIR and Adobe Flash Player Team Blog. Adobe. Archived from the original on October 2, 2015. Retrieved February 15, 2014.
- ^ «Flash Player 11 and AIR 3 Release Notes: 10/04/11». Kb2.adobe.com. Archived from the original on April 30, 2012. Retrieved April 10, 2012.
- ^ Introducing Molehill: 3D APIs for Adobe Flash Player and Adobe AIR Archived July 8, 2012, at the Wayback Machine, Adobe Edge
- ^ Extending AIR Archived July 24, 2014, at the Wayback Machine, Adobe Devnet
- ^ «Flash Player 11.1 and AIR 3.1 User Release Notes: 11/09/11». Kb2.adobe.com. Archived from the original on April 30, 2012. Retrieved April 10, 2012.
- ^ «Adobe Introduces Premium Features for Gaming with Flash Player 11.2; Announces Collaboration with Unity Technologies». adobe.com. Archived from the original on May 14, 2012. Retrieved May 18, 2012.
- ^ a b c d e «Flash Player and Adobe AIR feature list». adobe.com. Archived from the original on May 14, 2013. Retrieved May 9, 2013.
- ^ a b «Upcoming changes to Flash Player’s extended support release». Adobe. March 5, 2014. Archived from the original on October 1, 2015. Retrieved December 17, 2014.
- ^ «Flash Player 12.0.0.3». Adobe Systems. November 14, 2013. Archived from the original on December 24, 2013. Retrieved December 22, 2013.
- ^ «Adobe Labs Downloads». Adobe. April 22, 2015. Archived from the original on April 25, 2015. Retrieved April 25, 2015.
- ^ «Flash Player 13.0.0.80». Adobe Systems. January 28, 2014. Archived from the original on February 22, 2014. Retrieved February 18, 2014.
- ^ «8/12/2014 – Release – Flash Player 14». Adobe Systems. August 12, 2014. Archived from the original on November 11, 2014. Retrieved January 12, 2015.
- ^ «11/11/2014 – Release – Flash Player 15». Adobe Systems. November 11, 2014. Archived from the original on November 11, 2014. Retrieved January 12, 2015.
- ^ «12/9/2014 – Release – Flash Player 16». Adobe Systems. December 9, 2014. Archived from the original on December 15, 2014. Retrieved January 12, 2015.
- ^ «12/3/2015 – Release – Flash Player 17». Adobe Systems. March 12, 2014. Archived from the original on March 22, 2015. Retrieved March 13, 2015.
- ^ «Adobe Security Bulletin». Archived from the original on March 29, 2017. Retrieved March 25, 2017.
Further reading[edit]
- Understanding Flash Player with Adobe Scout – an article discussing the internals of the player and the Adobe Scout profiling tool
External links[edit]
- Official website
- Final global variant version of the standalone projector. at the Wayback Machine (archived April 1, 2022)
- Archived Adobe Flash Player versions at the Wayback Machine (archived July 18, 2020)
- Flash Tester Archived June 12, 2018, at the Wayback Machine (explains official old working version check)
This article is about the player. For an overview of the platform, see Adobe Flash.
«Shockwave Flash» redirects here. Not to be confused with Adobe Shockwave. For the file format sometimes referred to as «Shockwave Flash», see SWF.
 |
||||||||||||||||
| Original author(s) | FutureWave Macromedia |
|||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Developer(s) | Adobe Inc. Zhongcheng Harman |
|||||||||||||||
| Initial release | January 1, 1996; 27 years ago | |||||||||||||||
| Stable release(s) [±] | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| Preview release(s) [±] | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| Written in | ActionScript | |||||||||||||||
| Operating system | Windows, macOS, Linux, ChromeOS, Solaris, BlackBerry Tablet OS, Android, Pocket PC | |||||||||||||||
| Platform | Web browsers and ActiveX-based software | |||||||||||||||
| Available in | Chinese Simplified, Chinese Traditional, English, French, German, Italian, Japanese, Polish, Russian, Portuguese, Spanish, Korean, Turkish, Xhosa, Telugu, Vietnamese, Afrikaans, Yiddish, Zulu, and Arabic[9] | |||||||||||||||
| Type | Runtime system and browser extension | |||||||||||||||
| License | Freeware | |||||||||||||||
| Website | Adobe Flash Player End of Life (EOL, original global variants) Adobe Flash Player Harman official website (active, Harman enterprise variant) Adobe Flash Player China official website (active, China-specific variant) |
Adobe Flash Player (known in Internet Explorer, Firefox, and Google Chrome as Shockwave Flash)[10] is computer software for viewing multimedia contents, executing rich Internet applications, and streaming audio and video content created on the Adobe Flash platform. It can run from a web browser as a browser plug-in or independently on supported devices. Originally created by FutureWave under the name FutureSplash Player, it was renamed to Macromedia Flash Player after Macromedia acquired FutureWave in 1996. It was then developed and distributed by Adobe Systems as Flash Player after Adobe acquired Macromedia in 2005. It is currently developed and distributed by Zhongcheng for users in China, and by Harman International for enterprise users outside of China, in collaboration with Adobe.
Flash Player runs SWF files that can be created by Adobe Flash Professional, Adobe Flash Builder or by third-party tools such as FlashDevelop. Flash Player supports vector graphics, 3D graphics, embedded audio, video and raster graphics, and a scripting language called ActionScript, which is based on ECMAScript (similar to JavaScript) and supports object-oriented code. Internet Explorer 11 and Microsoft Edge Legacy, in Windows 8 and later, along with Google Chrome on all versions of Windows, came bundled with a sandboxed Adobe Flash plug-in.[11][12][13][14][15]
Flash Player once had a large user base, and was a common format for web games, animations, and graphical user interface (GUI) elements embedded in web pages. Adobe stated in 2013 that more than 400 million out of over 1 billion connected desktops updated to new versions of Flash Player within six weeks of release.[16] However, Flash Player became increasingly criticized for its performance, consumption of battery on mobile devices, the number of security vulnerabilities that had been discovered in the software, and its closed platform nature. Apple co-founder Steve Jobs was highly critical of Flash Player, having published an open letter detailing Apple’s reasoning for not supporting Flash on its iOS device family. Its usage also waned because of modern web standards that allow some of Flash’s use cases to be fulfilled without third-party plugins.[17][18][19] This led to the eventual deprecation of the platform by Adobe. Flash Player was officially discontinued on 31 December 2020, and its download page was removed two days later. Since 12 January 2021, Flash Player (original global variants) versions newer than 32.0.0.371, released in May 2020, refuse to play Flash content and instead display a static warning message.[20] The software remains supported in mainland China and in some enterprise variants.[21]
Features[edit]
Adobe Flash Player is a runtime that executes and displays content from a provided SWF file, although it has no in-built features to modify the SWF file at runtime. It can execute software written in the ActionScript programming language which enables the runtime manipulation of text, data, vector graphics, raster graphics, sound, and video. The player can also access certain connected hardware devices, including the web cameras and microphones, after permission for the same has been granted by the user.
Flash Player was used internally by the Adobe Integrated Runtime (AIR), to provide a cross-platform runtime environment for desktop applications and mobile applications. AIR supports installable applications on Windows, Linux, macOS, and some mobile operating systems such as iOS and Android. Flash applications must specifically be built for the AIR runtime to use additional features provided, such as file system integration, native client extensions, native window/screen integration, taskbar/dock integration, and hardware integration with connected Accelerometer and GPS devices.[22]
Data formats[edit]
Flash Player included native support for many data formats, some of which can only be accessed through the ActionScript scripting interface.
- XML: Flash Player has included native support for XML parsing and generation since version 8. XML data is held in memory as an XML Document Object Model, and can be manipulated using ActionScript. ActionScript 3 also supports ECMAScript for XML (E4X), which allows XML data to be manipulated more easily.
- JSON: Flash Player 11 includes native support for importing and exporting data in the JavaScript Object Notation (JSON) format, which allows interoperability with web services and JavaScript programs.
- AMF: Flash Player allows application data to be stored on users computers, in the form of Local Shared Objects, the Flash equivalent to browser cookies.[23] Flash Player can also natively read and write files in the Action Message Format, the default data format for Local Shared Objects. Since the AMF format specification is published, data can be transferred to and from Flash applications using AMF datasets instead of JSON or XML, reducing the need for parsing and validating such data.
- SWF: The specification for the SWF file format was published by Adobe, enabling the development of the SWX Format project, which used the SWF file format and AMF as a means for Flash applications to exchange data with server side applications.[24][25] The SWX system stores data as standard SWF bytecode which is automatically interpreted by Flash Player.[26] Another open-source project, SWXml allows Flash applications to load XML files as native ActionScript objects without any client-side XML parsing, by converting XML files to SWF/AMF on the server.[27][28]
Multimedia formats[edit]
Flash Player is primarily a graphics and multimedia platform, and has supported raster graphics and vector graphics since its earliest version. It supports the following different multimedia formats which it can natively decode and play back.
- MP3: Support for decoding and playback of streaming MPEG-2 Audio Layer III (MP3) audio was introduced in Flash Player 4. MP3 files can be accessed and played back from a server via HTTP, or embedded inside an SWF file, which is also a streaming format.
- FLV: Support for decoding and playing back video and audio inside Flash Video (FLV and F4V) files, a format developed by Adobe Systems and Macromedia. Flash Video is only a container format and supports multiple different video codecs, such as Sorenson Spark, VP6, and more recently H.264.[29] Flash Player uses hardware acceleration to display video where present, using technologies such as DirectX Video Acceleration and OpenGL to do so. Flash Video is used by YouTube,[30] Hulu,[31] Yahoo! Video, BBC Online,[32] and other news providers. FLV files can be played back from a server using HTTP progressive download, and can also be embedded inside an SWF file. Flash Video can also be streamed via RTMP using the Adobe Flash Media Server or other such server-side software.
- PNG: Support for decoding and rendering Portable Network Graphics (PNG) images, in both its 24-bit (opaque) and 32-bit (semi-transparent) variants. Flash Player 11 can also encode a PNG bitmap via ActionScript.
- JPEG: Support for decoding and rendering compressed JPEG images. Flash Player 10 added support for the JPEG-XR advanced image compression standard developed by Microsoft Corporation, which results in better compression and quality than JPEG. JPEG-XR enables lossy and lossless compression with or without alpha channel transparency. Flash Player 11 can also encode a JPEG or JPEG-XR bitmap via ActionScript.
- GIF: Support for decoding and rendering compressed Graphics Interchange Format (GIF) images, in its single-frame variants only. Loading a multi-frame GIF will display only the first image frame.
Streaming protocols[edit]
- HTTP: Support for communicating with web servers using HTTP requests and POST data.[33] However, only websites that explicitly allow Flash to connect to them can be accessed via HTTP or sockets, to prevent Flash being used as a tool for cross-site request forgery,[34] cross-site scripting, DNS rebinding,[35] and denial-of-service attacks. Websites must host a certain XML file termed a cross domain policy,[35] allowing or denying Flash content from specific websites to connect to them. Certain websites, such as Digg, Flickr, and Photobucket already host a cross domain policy that permits Flash content to access their website via HTTP.[36]
- RTMP: Support for live audio and video streaming using the Real Time Messaging Protocol (RTMP) developed by Macromedia. RTMP supports a non-encrypted version over the Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) or an encrypted version over a secure Transport Layer Security (SSL) connection. RTMPT can also be encapsulated within HTTP requests to traverse firewalls that only allow HTTP traffic.
- TCP: Support for Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) Internet socket communication to communicate with any type of server, using stream sockets. Sockets can be used only via ActionScript, and can transfer plain text, XML, or binary data (ActionScript 3.0 and later).[37][38] To prevent security issues, web servers that permit Flash content to communicate with them using sockets must host an XML-based cross domain policy file, served on Port 843.[39] Sockets enable AS3 programs to interface with any kind of server software, such as MySQL.[40]
Performance[edit]
Hardware acceleration[edit]
Until version 10 of the Flash player, there was no support for GPU acceleration. Version 10 added a limited form of support for shaders on materials in the form of the Pixel Bender API, but still did not have GPU-accelerated 3D vertex processing.[41] A significant change came in version 11, which added a new low-level API called Stage3D (initially codenamed Molehill), which provides full GPU acceleration, similar to WebGL.[42][43] (The partial support for GPU acceleration in Pixel Bender was completely removed in Flash 11.8, resulting in the disruption of some projects like MIT’s Scratch, which lacked the manpower to recode their applications quickly enough.[44][45])
Current versions of Flash Player are optimized to use hardware acceleration for video playback and 3D graphics rendering on many devices, including desktop computers. Performance is similar to HTML5 video playback.[46][47] Also, Flash Player has been used on multiple mobile devices as a primary user interface renderer.[48]
Compilation[edit]
Although code written in ActionScript 3 executes up to 10 times faster than the prior ActionScript 2,[49] the Adobe ActionScript 3 compiler is a non-optimizing compiler, and produces inefficient bytecode in the resulting SWF, when compared to toolkits such as CrossBridge.[50][51][52][53][54]
CrossBridge, a toolkit that targets C++ code to run within the Flash Player, uses the LLVM compiler to produce bytecode that runs up to 10 times faster than code the ActionScript 3 compiler produces, only because the LLVM compiler uses more aggressive optimization.[52][53][54]
Adobe has released ActionScript Compiler 2 (ASC2) in Flex 4.7 and onwards, which improves compilation times and optimizes the generated bytecode and supports method inlining, improving its performance at runtime.[55]
As of 2012, the Haxe multiplatform language can build programs for Flash Player that perform faster than the same application built with the Adobe Flex SDK compiler.[56][unreliable source?]
Development methods[edit]
Flash Player applications and games can be built in two significantly different methods:
- «Flex» applications: The Adobe Flex Framework is an integrated collection of stylable Graphical User Interface, data manipulation and networking components, and applications built upon it are termed «Flex» applications. Startup time is reduced since the Flex framework must be downloaded before the application begins, and weighs in at approximately 500KB. Editors include Adobe Flash Builder and FlashDevelop.
- «Pure ActionScript» applications: Applications built without the Flex framework allow greater flexibility and performance.[57][58][59] Video games built for Flash Player are typically pure-Actionscript projects. Various open-source component frameworks are available for pure ActionScript projects, such as MadComponents, that provide UI Components at significantly smaller SWF file sizes.[60][61]
In both methods, developers can access the full Flash Player set of functions, including text, vector graphics, bitmap graphics, video, audio, camera, microphone, and others. AIR also includes added features such as file system integration, native extensions, native desktop integration, and hardware integration with connected devices.
Development tools[edit]
Adobe provides five ways of developing applications for Flash Player:
- Adobe Animate: graphic design, animation and scripting toolset
- Adobe Flash Builder: enterprise application development and debugging
- Adobe Scout: visual profiler for performance optimization
- Apache Flex: a free SDK to compile Flash and Adobe AIR applications from source code; developed by Adobe and donated to the Apache Foundation[62]
- CrossBridge: a free SDK to cross-compile C++ code to run in Flash Player
Third-party development environments are also available:
- FlashDevelop: an open-source Flash ActionScript IDE, which includes a debugger for AIR applications
- Powerflasher FDT: a commercial ActionScript IDE
- CodeDrive: an extension to Microsoft Visual Studio 2010 for ActionScript 3 development and debugging
- MTASC: a compiler
- Haxe: a multi-platform language[63]
Game development[edit]
Adobe Gaming SDK 1.0 logo
Adobe offers the free Adobe Gaming SDK, consisting (as of August 2014) of several open-source AS3 libraries built on the Flash Player Stage3D APIs for GPU-accelerated graphics:[64]
- Away3D: GPU-accelerated 3D graphics and animation engine
- Starling: GPU-accelerated 2D graphics that mimics the Flash display list API
- Feathers: GPU-accelerated skinnable GUI library built on top of Starling
- Dragon Bones: GPU-accelerated 2D skeletal animation library
A few commercial game engines target Flash Player (Stage3D) as run-time environment, such as Unity 3D[65] and Unreal Engine 3.[65][66] Before the introduction of Stage3D, a number of older 2D engines or isometric engines like Flixel saw their heyday.[67]
Adobe also developed the CrossBridge toolkit which cross-compiles C/C++ code to run within the Flash Player, using LLVM and GCC as compiler backends, and high-performance memory-access opcodes in the Flash Player (termed «Domain Memory») to work with in-memory data quickly.[68] CrossBridge is targeted toward the game development industry, and includes tools for building, testing, and debugging C/C++ projects in Flash Player.
Notable online video games developed in Flash include Angry Birds, FarmVille, and AdventureQuest (started in 2002, and still active as of 2020).[69]
Availability[edit]
Desktop platforms[edit]
Adobe Flash Player is available in two major flavors:
- The plugin version for use in various web browsers
- The «projector» version is a standalone player that can open SWF files directly.[70][71]
On February 22, 2012, Adobe announced that it would no longer release new versions of NPAPI Flash plugins for Linux, although Flash Player 11.2 would continue to receive security updates.[72][73][74] In August 2016 Adobe announced that, beginning with version 24, it will resume offering of Flash Player for Linux for other browsers.[75]
The Extended Support Release (ESR) of Flash Player on macOS and Windows was a version of Flash Player kept up to date with security updates, but none of the new features or bug fixes available in later versions. In August 2016, Adobe discontinued the ESR branch and instead focused solely on the standard release.[76]
| Operating system | First version | Latest version | Support status | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Windows | XP SP2–11 | 1 | 34.0.0.277 (China-specific)[77] 50.x (Harman enterprise)[78] 32.0.0.465 (last public update, excluding China)[79] |
2017–present 2021–present 2001–2020 |
| 2000 and XP RTM–SP1 | 11.1.102.55 and 10.3.183.90[80] | 1999–2013 | ||
| 98, ME and 2000 RTM–SP2 | 9.0.289.0[80] | 1998–2011 | ||
| 95 and NT 4 (IA-32) | 7.0.14.0[80] | 1997–2005 | ||
| 3.1 | 3[81] | 1997–1998 | ||
| macOS | 10.12 and later | 5.0.41.0[82] | 34.0.0.277 (China-specific)[77] | 2017–present |
| 10.10 and later | 50.x (Harman enterprise)[78] 32.0.0.465 (last public update, excluding China)[79] |
2021–present 2014–2020 |
||
| 10.9 | 29.0.0.171[80] | 2013–2018 | ||
| 10.6–10.8 (IA-32, x64) | 22.0.0.209[80] | 2009–2016 | ||
| 10.5 (IA-32,x64) | 10.3.183.90[80] | 2007–2013 | ||
| 10.4 (IA-32,PPC)–10.5 (PPC) | 10.1.102.64[80] | 2005–2011 | ||
| 10.1–10.3 | 9.0.289.0[80] | 2001–2011 | ||
| Classic Mac OS | 7.6.1–9.2.2 (PowerPC) | 1 | 7.0.14.0[80] | 1997–2005 |
| 7.6.1–8.1 (68k) | 3[81] | 1997–1998 | ||
| Linux desktops | 4.0r12[83][84] | 50.x (Harman enterprise)[78] 34.0.0.137 (last public update, China-specific)[85] 32.0.0.465 (last public update, excluding China)[79] |
2021–present 2017–2021[86] 1999–2020 |
|
| Solaris and OpenSolaris | 4.0r12[83] | 11.2.202.223 and 10.3.183.90[80] | 2004–2013 | |
| IRIX | 4.0r12[83][87] | 4.0.r12[88] | 1999 |
Version 10 can be run under Windows 98/Me using KernelEx. HP offered Version 6 of the player for HP-UX,[89] while Innotek GmbH offered versions 4 and 5 for OS/2.[90] Other versions of the player have been available at some point for BeOS.[citation needed]
Mobile platforms[edit]
In 2011, Flash Player had emerged as the de facto standard for online video publishing on the desktop, with adaptive bitrate video streaming, DRM, and fullscreen support.[30][31] On mobile devices, however, after Apple refused to allow the Flash Player within the inbuilt iOS web browser, Adobe changed strategy, enabling Flash content to be delivered as native mobile applications using the Adobe Integrated Runtime.
Up until 2012, Flash Player 11 was available for the Android (ARM Cortex-A8 and above),[91] although in June 2012, Google announced that Android 4.1 (codenamed Jelly Bean) would not support Flash by default. In August 2012, Adobe stopped updating Flash for Android.[92]
Flash Player was supported on a select range of mobile and tablet devices, from Acer, BlackBerry 10, Dell, HTC, Lenovo, Logitech, LG, Motorola, Samsung, Sharp, SoftBank, Sony (and Sony Ericsson), and Toshiba.[93][94][95] As of 2012, Adobe has stopped browser-based Flash Player development for mobile browsers in favor of HTML5,[96][97] however, Adobe continues to support Flash content on mobile devices with the Adobe Integrated Runtime, which allows developers to publish content that runs as native applications on certain supported mobile phone platforms.
Adobe said it will optimize Flash for use on ARM architecture (ARMv7 and ARMv6 architectures used in the Cortex-A series of processors and in the ARM11 family) and release it in the second half of 2009. The company also stated it wants to enable Flash on NVIDIA Tegra, Texas Instruments OMAP 3, and Samsung ARMs.[98][99] Beginning 2009, it was announced that Adobe would be bringing Flash to TV sets via Intel Media Processor CE 3100 before mid-2009.[100] ARM Holdings later said it welcomes the move of Flash, because «it will transform mobile applications and it removes the claim that the desktop controls the Internet.»[101] However, as of May 2009, the expected ARM/Linux netbook devices had poor support for Web video and fragmented software base.[102]
Among other devices, LeapFrog Enterprises provides Flash Player with their Leapster Multimedia Learning System and extended the Flash Player with touch-screen support.[103] Version 9 was the most recent version available for the Linux/ARM-based Nokia 770/N800/N810 Internet tablets running Maemo OS2008.[89] Other versions of the player have been available at some point for Symbian OS and Palm OS.[104] The Kodak Easyshare One includes Flash Player.[105]
The following table documents historical support for Flash Player on mobile operating systems:
| Platform | Final version |
|---|---|
| Android 4.0, ARM Cortex-A8+[91] | Flash Player 11.1.115.81[80] |
| Android 2.2–3.x, ARM Cortex-A8+[106][91] | Flash Player 11.1.111.73[80] |
| Dreamcast | Flash Player 4.0[citation needed] |
| Maemo | Flash Player 9.4[107] |
| PlayStation 3 with Firmware 2.50, NetFront 2.81 | Flash Player 9.1 (update 3)[108] |
| PSP with Firmware 2.70 | Flash Player 6[109] |
| Pocket PC 2003[110] | Flash Player 7[111][112] |
| webOS (Palm and HP) | Flash Player 10[citation needed] |
| Windows Mobile 5[110] | Flash Player 7[111] |
Other hardware[edit]
Some CPU emulators have been created for Flash Player, including Chip8,[113] Commodore 64,[114] ZX Spectrum,[115] and the Nintendo Entertainment System.[116] They enable video games created for such platforms to run within Flash Player.
End of life[edit]
Adobe announced on July 25, 2017, that it would end support for the normal/global variant of Flash Player on January 1, 2021, and encouraged developers to use HTML5 standards in place of Flash.[117][118] The announcement was coordinated with Apple,[119] Facebook,[120] Google,[121] Microsoft,[122] and Mozilla.[123] Adobe announced that all major web browsers planned to officially remove the Adobe Flash Player component on December 31, 2020, and Microsoft removed it from the Windows OS in January 2021 via Windows Update. In a move to further reduce the number of Flash Player installations, Adobe added a «time bomb» to Flash to disable existing installations after January 12, 2021.[124] In mid-2020, Flash Player started prompting users to uninstall itself.[125] Adobe removed all existing download links for Flash installers.[126] After January 26, 2021, all major web browsers including Apple Safari, Google Chrome, Microsoft Edge, and Mozilla Firefox have already permanently removed Flash support.[127] However, Flash content continues to be accessible on the web through emulators such as Ruffle, with varying degrees of compatibility and performance, although this is not endorsed by Adobe.
Web browsers[edit]
Google Chrome[edit]
Starting from Chrome 76, Flash is disabled by default without any prompts to activate Flash content.[128] Users who wanted to play Flash content had to manually set a browser to prompt for Flash content, and then during each browser session enable Flash plugin for every site individually. Microsoft Edge, which is based on Chromium, followed the same plan as Google Chrome.[129]
Google Chrome blocked the Flash plugin as «out of date» in January 2021, and fully removed it from the browser with Chrome version 88, released on January 20, 2021.[130][131]
Mozilla Firefox[edit]
Starting with Firefox 85,[128] Flash is disabled by default without any prompts to activate Flash content. To play Flash content, users had to manually set a browser to prompt for Flash content, and then during each browser session enable Flash plugin for every site individually. Firefox 85, released on January 26, 2021, completely removed support for the Flash plugin.[127] Firefox ESR dropped support on November 2, 2021 (Firefox 78 ESR was the last version with support).[132]
Microsoft Windows[edit]
On October 27, 2020, Microsoft released an update (named KB4577586) for Windows 10 and 8.1 which removes the embedded Adobe Flash Player component from IE11 and Edge Legacy. In July 2021, this update was automatically installed as a security patch.[133][134] However, an ActiveX Flash Player plugin may still be used with IE after this update is applied.[135][136]
Apple Safari[edit]
Apple dropped Flash Player support from Safari 14 alongside the release of macOS Big Sur.[137][138]
Fallout[edit]
Despite the years of notice, several websites still were using Flash following December 31, 2020, including the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission. Many of these were resolved in the weeks after the deadline. However, many educational institutions still relied on Flash for educational material and did not have a path forward for replacement.[139]
Post-EOL support[edit]
Mainland China[edit]
The China-specific variant of Flash will be supported beyond 2020, by a company known as Zhongcheng.[140][141] The Projector (standalone) versions of this variant also work outside of China and do not include the «Flash Helper Service»; however, some tracking code still seems to be present. They are available on a somewhat hidden «Debug» page.[142] In addition, as the global variant of the plugin was discontinued, some users have figured how to modify and repack the China-specific variant to bring it more in line with the global variant. This includes removing the «Flash Helper Service» and removing the China only installation restriction, along with all other geo-restrictions and tracking code. A «time bomb», similar to the one found in later versions of the global variant, is also present in the unmodified China variant; this is also removed in most repacks. In theory, these repacks should provide users outside of China with the latest security updates to Flash Player, without having to deal with invasive advertisements or worry about privacy risks.[143] One such project, «Clean Flash Installer», was served a DMCA takedown from Adobe in October 2021.[144]
Enterprise[edit]
Adobe has partnered with Harman to support enterprise Flash Player users until at least 2023.[145][146] The Harman Flash player variant is labeled as version 50.x, to avoid confusion with other variants.[78]
Web browsers[edit]
Internet Explorer 11, along with IE mode in Edge,[78] will continue with ActiveX support, and by extension Flash Player support.[136] Firefox forks that plan to continue NPAPI support, and by extension Flash Player support, include Waterfox, Basilisk, Pale Moon, and K-Meleon. Various Chromium-based Chinese browsers will also continue to support Flash Player in PPAPI and/or NPAPI form, including, but not limited to, 360 Secure Browser.[135]
Shortly after Flash EOL, South African Revenue Service (SARS) released a custom version of Chromium browser with the Adobe Flash Player «time bomb» removed. This browser can access only a small set of SARS online pages containing Flash-based forms required for filing financial reports.[147]
Adobe Flash Player Projector[edit]
Although no longer available directly from Adobe, all versions of Adobe Flash Player Projector (also known as Adobe Flash Player Standalone) lack the «time bomb» present in the newer plug-in variants, and thus continue to be able to play all supported Flash file formats, including SWF files, without modification.[148][71][142]
Content preservation projects[edit]
The Internet Archive hosts some Flash content and makes it playable in modern browsers via emulators, Ruffle and Emularity.[149] Other emulators, such as CheerpX, also exist as options for Flash Player emulation on other websites.[150] BlueMaxima’s Flashpoint project claims to have collected more than 38,000 Adobe Flash Player games and animations and made them available for download.[151]
Open source[edit]
Adobe has released some components of Adobe Flash products as open source software via Open Screen Project or donated them to open source organizations. As of 2021, most of these technologies are considered obsolete. This includes: ActionScript Virtual Machine 2 (AVM2) which implements ActionScript 3 (donated as open-source to Mozilla Foundation), Adobe Flex Framework (donated as open-source to the Apache Software Foundation and rebranded as Apache Flex,[62] superseded by Apache Royale), CrossBridge C++ cross-compilation toolset (released on GitHub).[152][153]
Criticism[edit]
Accessibility and usability[edit]
In some browsers, prior Flash versions have had to be uninstalled before an updated version could be installed.[154][155] However, as of version 11.2 for Windows, there are now automatic updater options.[156] Linux is partially supported, as Adobe is cooperating with Google to implement it via Chrome web browser on all Linux platforms.[157]
Mixing Flash applications with HTML leads to inconsistent input handling leading to poor user experience with the site (keyboard and mouse not working as they would in an HTML-only document).[citation needed]
Privacy[edit]
Flash Player supports persistent local storage of data (also referred to as Local Shared Objects), which can be used similarly to HTTP cookies or Web Storage in web applications. Local storage in Flash Player allows websites to store non-executable data on a user’s computer, such as authentication information, game high scores or web browser games, server-based session identifiers, site preferences, saved work, or temporary files. Flash Player will only allow content originating from exactly the same website domain to access data saved in local storage.[158]
Because local storage can be used to save information on a computer that is later retrieved by the same site, a site can use it to gather user statistics, similar to how HTTP cookies and Web Storage can be used. With such technologies, the possibility of building a profile based on user statistics is considered by some a potential privacy concern. Users can disable or restrict use of local storage in Flash Player through a «Settings Manager» page.[159][160] These settings can be accessed from the Adobe website or by right-clicking on Flash-based content and selecting «Global Settings».
Local storage can be disabled entirely or on a site-by-site basis. Disabling local storage will block any content from saving local user information using Flash Player, but this may disable or reduce the functionality of some websites, such as saved preferences or high scores and saved progress in games.
Flash Player 10.1 and upward honor the privacy mode settings in the latest versions of the Chrome, Firefox, Internet Explorer, and Safari web browsers, such that no local storage data is saved when the browser’s privacy mode is in use.[161]
Security[edit]
Adobe security bulletins and advisories announce security updates, but Adobe Flash Player release notes do not disclose the security issues addressed when a release closes security holes, making it difficult to evaluate the urgency of a particular update. A version test page allows the user to check if the latest version is installed, and uninstallers may be used to ensure that old-version plugins have been uninstalled from all installed browsers.
In February 2010, Adobe officially apologized[162] for not fixing a known vulnerability for over a year. In June 2010 Adobe announced a «critical vulnerability» in recent versions, saying there are reports that this vulnerability is being actively exploited in the wild against both Adobe Flash Player, and Adobe Reader and Acrobat.[163][164] Later, in October 2010, Adobe announced[165] another critical vulnerability, this time also affecting Android-based mobile devices. Android users have been recommended to disable Flash or make it only on demand.[166] Subsequent security vulnerabilities also exposed Android users, such as the two critical vulnerabilities published in February 2013[167] or the four critical vulnerabilities published in March 2013,[168] all of which could lead to arbitrary code execution.
Symantec’s Internet Security Threat Report[169] states that a remote code execution in Adobe Reader and Flash Player[170] was the second most attacked vulnerability in 2009. The same report also recommended using browser extensions to disable Flash Player usage on untrusted websites. McAfee predicted that Adobe software, especially Reader and Flash, would be primary target for attacks in 2010.[171] Adobe applications had become, at least at some point, the most popular client-software targets for attackers during the last quarter of 2009.[172] The Kaspersky Security Network published statistics for the third quarter of 2012 showing that 47.5% of its users were affected by one or more critical vulnerabilities.[173] The report also highlighted that «Flash Player vulnerabilities enable cybercriminals to bypass security systems integrated into the application.»[173]
Steve Jobs criticized the security of Flash Player, noting that «Symantec recently highlighted Flash for having one of the worst security records in 2009».[174] Adobe responded by pointing out that «the Symantec Global Internet Threat Report for 2009, found that Flash Player had the second lowest number of vulnerabilities of all Internet technologies listed (which included both web plug-ins and browsers).»[175][176]
On April 7, 2016, Adobe released a Flash Player patch for a zero-day memory corruption vulnerability CVE-2016-1019 that could be used to deliver malware via the Magnitude exploit kit. The vulnerability could be exploited for remote code execution.[177][178]
Vendor lock-in[edit]
Flash Player 11.2 does not play certain kinds of content unless it has been digitally signed by Adobe, following a license obtained by the publisher directly from Adobe.[179]
This move by Adobe, together with the abandonment of Flex to Apache was criticized as a way to lock out independent tool developers, in favor of Adobe’s commercial tools.[180][181][182]
This has been resolved as of January 2013, after Adobe no longer requires a license or royalty from the developer. All premium features are now classified as general availability, and can be freely used by Flash applications.[183]
Apple controversy[edit]
In April 2010, Steve Jobs, at the time CEO of Apple Inc. published an open letter explaining why Apple would not support Flash on the iPhone, iPod Touch, and iPad.[174] In the letter he blamed problems with the «openness», stability, security, performance, and touchscreen integration of the Flash Player as reasons for refusing to support it. He also claimed that when one of Apple’s Macintosh computers crashes, «more often than not» the cause can be attributed to Flash, and described Flash as «buggy».[184] Adobe’s CEO Shantanu Narayen responded by saying, «If Flash [is] the number one reason that Macs crash, which I’m not aware of, it has as much to do with the Apple operating system.»[185]
Steve Jobs also claimed that a large percentage of the video on the Internet is supported on iOS, since many popular video sharing websites such as YouTube have published video content in an HTML5 compatible format, enabling videos to playback in mobile web browsers even without Flash Player.[186]
Mainland China-specific variant[edit]
Starting with version 30, Adobe stopped distributing Flash Player directly to users from mainland China. Instead, they selected 2144.cn as a partner and released a special variant of Flash Player on a specific website,[187] which contains a non-closable process, known as the «Flash Helper Service», that collects private information and pops up advertisement window contents,[188] by receiving and running encrypted programs from a remote server.[189] The partnership started in about 2017, but in version 30, Adobe disabled the usage of vanilla (global) variant of Flash Player in mainland China,[190] forcing users to use that specific variant, which may pose a risk to its users due to Internet censorship by Chinese Communist Party (CCP).[191] This only affected Chinese Chromium based browser users, Firefox users, and Internet Explorer users using Windows 7 and below, as Microsoft still directly distributed Flash Player for Internet Explorer and Microsoft Edge through Windows Update in Windows 8 and upward at the time. Starting in 2021, however, this variant is the only publicly supported version of Flash Player.
Release history[edit]
See also[edit]
- Adobe Flash
- Adobe AIR
- Adobe Shockwave
- Apache Flex
- Microsoft Silverlight
References[edit]
- ^ «Adobe — Flash Player». flash.cn (in Simplified Chinese). Zhongcheng Network Technology Co., Ltd. Retrieved July 14, 2021.
- ^ a b «_flash_install_packages_». flash.cn. Zhongcheng Network Technology Co., Ltd. Retrieved July 13, 2021.
- ^ «ADOBE® FLASH® PLAYER ENTERPRISE SUPPORT». harman.com. Harman International. Retrieved November 21, 2021.
- ^ «Flash Player官方下载中心». Flash (in Simplified Chinese). Flash.cn. Retrieved June 12, 2021.
- ^ «关于Linux操作系统下Flash Player个人版停用的公告». Flash (in Simplified Chinese). Flash.cn. May 10, 2021. Retrieved June 12, 2021.
- ^ a b «Adobe — Flash Player». Adobe.com. Adobe Systems. Retrieved December 8, 2020.
- ^ a b c d e «Archived Flash Player versions». Adobe.com. Adobe Systems. Retrieved October 20, 2015.
- ^ «Download Flash Player 32 Beta». labs.adobe.com. Adobe Systems. Retrieved May 19, 2020.
- ^ «Adobe Flash Player Download». Adobe Systems. Archived from the original on August 9, 2016. Retrieved August 10, 2016.
- ^ «Why You Should Ditch Adobe Shockwave». Krebs on Security. May 14, 2014. Archived from the original on May 25, 2014. Retrieved February 21, 2015.
- ^ Integrated Adobe Flash Player Plug-in Archived January 31, 2013, at the Wayback Machine, Chrome team blog
- ^ Porting Flash to sandboxed PPAPI platform Archived July 25, 2018, at the Wayback Machine, Official Chromium Blog
- ^ «Flash Player issues | Windows 8». Adobe Systems. Archived from the original on December 20, 2016. Retrieved December 15, 2016.
- ^ «Flash Player Issues | Windows 10 | Internet Explorer». Adobe Systems. Archived from the original on December 20, 2016. Retrieved December 15, 2016.
- ^ «Flash Player issues | Windows 10 | Microsoft Edge». Adobe Systems. Archived from the original on December 20, 2016. Retrieved December 15, 2016.
- ^ «Adobe Flash Runtimes Statistics». Adobe Systems Incorporated. Archived from the original on January 6, 2013. Retrieved January 2, 2013.
- ^ Barrett, Brian (July 15, 2015). «Flash. Must. Die». Wired.com. Condé Nast. Archived from the original on May 16, 2017. Retrieved May 9, 2017.
- ^ Vaughan-Nichols, Steven J. (June 16, 2016). «How to really fix the latest Adobe Flash security hole». ZDNet. CBS Interactive. Archived from the original on May 23, 2017. Retrieved May 9, 2017.
- ^ Collins, Katie (March 11, 2016). «Adobe rushes out emergency update for ‘critical’ Flash security flaw». CNET. Archived from the original on March 25, 2017. Retrieved May 9, 2017.
- ^ Cimpanu, Catalin (December 9, 2020). «Adobe to block Flash content from running on January 12, 2021». ZDNet. Red Ventures. Retrieved January 21, 2021.
- ^ «重橙网络» [Flash Center]. www.flash.cn. Retrieved October 8, 2021.
the exclusive and official distributor of Adobe Flash Player
- ^ AIR 3 Archived August 21, 2014, at the Wayback Machine, Adobe
- ^ «What are local shared objects?». Security and privacy. Adobe Systems. Archived from the original on May 29, 2010. Retrieved December 5, 2007.
- ^ SWX: SWF Data Format Archived August 17, 2012, at the Wayback Machine, official website
- ^ swxjava – SWX RPC implementation in Java Archived June 7, 2014, at the Wayback Machine, Google Code
- ^ swx-format – Data Format Archived August 3, 2014, at the Wayback Machine, Google Code
- ^ SWX Contest Winners Archived August 18, 2012, at the Wayback Machine, SWX Format Website
- ^ Introducing SWXml Archived November 12, 2007, at the Wayback Machine, Aral Balkan
- ^ «Flash H.264». MainConcept. Archived from the original on November 18, 2010. Retrieved September 24, 2010.
- ^ a b Flash and the HTML5 <video> tag Archived August 7, 2012, at the Wayback Machine, YouTube Blog
- ^ a b Pardon Our Dust Archived May 31, 2015, at the Wayback Machine, Hulu Blog
- ^ Future Media Standards & Guidelines – AV Addendum v1.5 Archived September 30, 2013, at the Wayback Machine BBC
- ^ Protocols: HTTP vs. RTMP> Beginner’s Guide to Distributing Flash Video Archived March 13, 2013, at the Wayback Machine, Adobe Press
- ^ Cross-domain policy file usage recommendations for Flash Player Archived August 13, 2014, at the Wayback Machine, Adobe
- ^ a b Policy file changes in Flash Player 9 and Flash Player 10 Archived August 18, 2014, at the Wayback Machine, Adobe
- ^ «Sites which support crossdomain.xml to allow Flash and Silverlight access». Retrieved March 25, 2017.
- ^ Socket Archived October 11, 2012, at the Wayback Machine, Adobe ActionScript 3 API Reference
- ^ Sockets Archived October 20, 2012, at the Wayback Machine, ActionScript 3.0 Developer’s Guide
- ^ Setting up a socket policy file server Archived August 3, 2014, at the Wayback Machine, Adobe
- ^ AsSQL – MySQL Driver for AS3 Archived May 25, 2013, at the Wayback Machine, Google Code
- ^ Remi Arnaud (2011). «3D in a Web Browser». In Eric Lengyel (ed.). Game Engine Gems 2. CRC Press. pp. 208–212. ISBN 978-1-56881-437-7. Archived from the original on January 10, 2016. Retrieved November 28, 2015.
- ^ Christer Kaitila (2011). Adobe Flash 11 Stage3D (Molehill) Game Programming Beginner’s Guide. Packt Publishing Ltd. p. 9. ISBN 978-1-84969-169-7.
- ^ «Stage3D vs WebGL Performance — Airtight Interactive». Airtightinteractive.com. October 28, 2011. Archived from the original on July 31, 2014. Retrieved August 4, 2014.
- ^ «Stage3D». scratch.mit.edu. Archived from the original on August 10, 2014. Retrieved August 5, 2014.
- ^ «Adobe Flash Player 11.8 – Bug 3591185: Pixel Bender shader performance drastically degraded in FP11.8. Closed as «NeverFix»«. Archived from the original on April 22, 2014.
- ^ Comparing Flash, HTML5 Performance Archived October 26, 2011, at the Wayback Machine, OS News
- ^ Battery Performance with Flash Player 10.1 on Nexus One Archived October 16, 2011, at the Wayback Machine, Flash Mobile Blog
- ^ Reference Designs and Demos Archived October 11, 2011, at the Wayback Machine, QNX
- ^ ActionScript 3.0 overview, «ActionScript 3.0 code executes up to 10 times faster than legacy ActionScript code.» Archived July 18, 2014, at the Wayback Machine, Adobe
- ^ «Alchemy:FAQ». Archived from the original on May 5, 2012. Retrieved May 5, 2012., Adobe Labs, «ASC performs few optimizations at this time»
- ^ Zotov, Peter (May 6, 2012). «Reaching the Limits of Adobe Stupidity – whitespace». Whitequark.org. Archived from the original on October 15, 2012. Retrieved October 27, 2012.
- ^ a b Alchemy:FAQ Archived May 5, 2012, at the Wayback Machine, Adobe Labs
- ^ a b Optimizing ActionScript Bytecode using LLVM Archived May 11, 2012, at the Wayback Machine, Adobe
- ^ a b Adobe Alchemy, is it ActionScript heresy? Archived August 19, 2012, at the Wayback Machine, Unit Zero One
- ^ Introducing ASC 2.0 Archived March 15, 2013, at the Wayback Machine, Thibault Imbert, ByteArray.com
- ^ AS3 vs haXe performance, SplashDust website Archived January 5, 2013, at the Wayback Machine
- ^ Optimizing performance of applications for connected TVs Archived August 22, 2016, at the Wayback Machine, Adobe Developer Connection
- ^ Top 10 Performance Killers in your AIR Application Archived October 15, 2014, at the Wayback Machine, FlexWiz
- ^ Flex versus ActionScript – the debate gets new life Archived December 9, 2014, at the Wayback Machine, Greg’s Ramblings
- ^ Pure ActionScript + MadComponents vs. Flash Builder 4.5 Archived December 22, 2014, at the Wayback Machine, MobileAppDev
- ^ Flex 4.5 vs Pure AS3 Archived October 21, 2011, at the Wayback Machine, Michael Crosby
- ^ a b «Adobe donates Flex to Apache». Techworld. Archived from the original on November 18, 2011. Retrieved November 17, 2011.
- ^ Response to «Thoughts on Flash» Archived November 12, 2011, at the Wayback Machine, True Gryc Blog
- ^ «Adobe Gaming SDK». creative.adobe.com. Adobe. Archived from the original on August 8, 2014. Retrieved August 4, 2014.
- ^ a b Wagner James Au (2012). Game Design Secrets. John Wiley & Sons. p. 130. ISBN 978-1-118-46391-8.
- ^ «Adobe Flash 11 adopts Unreal Engine 3 for better browser games | The Verge». theverge.com. October 7, 2011. Archived from the original on July 6, 2017. Retrieved August 4, 2014.
- ^ «List of Flash Gaming Engines». FlashRealtime.com. April 23, 2011. Archived from the original on April 6, 2013. Retrieved February 21, 2015.
- ^ CrossBridge for Flash Player Archived September 20, 2017, at the Wayback Machine, GitHub
- ^ Remi Arnaud (2011). «3D in a Web Browser». In Eric Lengyel (ed.). Game Engine Gems 2. CRC Press. p. 205. ISBN 978-1-56881-437-7. Archived from the original on January 10, 2016. Retrieved November 28, 2015.
- ^ «Downloads». Adobe Flash Player Support Center. Archived from the original on October 22, 2011. Retrieved October 29, 2011.
- ^ a b «Adobe Flash Player — Debug Downloads». Adobe Inc. Archived from the original on April 1, 2022. Retrieved April 15, 2022.
- ^ «Adobe and Google Partnering for Flash Player on Linux». Archived from the original on May 19, 2019. Retrieved November 25, 2012.
- ^ Noyes, Katherine (April 6, 2012). «For Flash on Linux, Chrome Will Be Users’ Only Choice | PCWorld Business Center». Pcworld.com. Archived from the original on October 20, 2012. Retrieved April 10, 2012.
- ^ «Adobe Releases Last Linux Version of Flash Player – Slashdot». Linux.slashdot.org. Archived from the original on March 31, 2012. Retrieved April 10, 2012.
- ^ «Beta News – Flash Player NPAPI for Linux». Adobe AIR and Adobe Flash Player Team Blog. August 31, 2016. Archived from the original on November 18, 2016. Retrieved November 17, 2016.
- ^ Campbell, Chris (August 23, 2016). «Where can I find the «Extended Support Release» of Flash Player for Windows or Macintosh?». forums.adobe.com. Adobe Systems. Archived from the original on July 5, 2016. Retrieved September 25, 2016.
- ^ a b «Adobe Flash Player (China Variant)». flash.cn. Zhongcheng Network Technology Co., Ltd. Retrieved March 9, 2021.
- ^ a b c d e «Adobe® Flash® Player Enterprise Support». harman.com. Harman International. Retrieved November 20, 2021.
- ^ a b c Adobe Flash Player Versions Archived January 1, 2019, at the Wayback Machine, Adobe.com
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p q «Archived Flash Player versions». Adobe. Archived from the original on February 15, 2014. Retrieved February 18, 2014.
- ^ a b «Flash Player 3 Archive». Archived from the original on July 18, 2020.
- ^ «Flash Player 5 Archive». Archived from the original on July 18, 2020.
- ^ a b c «MACROMEDIA INTRODUCES FREE FLASH PLAYERS FOR LINUX, SOLARIS, IRIX USERS. | Technology > Software Services & Applications from AllBusiness.com». Archived from the original on May 20, 2007. Retrieved May 20, 2011.
- ^ «Macromedia Flash Player download center (Linux)». Archived from the original on June 9, 2000.
- ^ «Flash Player官方下载中心». Flash (in Simplified Chinese). Flash.cn. Retrieved June 12, 2021.
- ^ «关于Linux操作系统下Flash Player个人版停用的公告». Flash (in Simplified Chinese). Flash.cn. May 10, 2021. Retrieved June 12, 2021.
- ^ «Macromedia Flash Player download center (IRIX)». Archived from the original on January 5, 2001.
- ^ «Macromedia — Macromedia Web Players: Alternates». Archived from the original on August 2, 2001.
- ^ a b Web Players Archived August 21, 2014, at the Wayback Machine. Adobe. Retrieved on March 11, 2011.
- ^ «InnoTek Systemberatung GmbH». Archived from the original on September 17, 2001.
- ^ a b c «Flash Player 10.1 – Installations and updates». Archived from the original on October 8, 2010. Retrieved November 19, 2010.
- ^ Arthur, Charles (June 29, 2012). «Flash Player for Android: Adobe calls time, declares it dead». The Guardian. Archived from the original on March 5, 2014. Retrieved June 30, 2012.
- ^ Flash Platform Certified Devices Archived June 22, 2012, at the Wayback Machine, Adobe
- ^ Flash Platform Certified Devices: Smartphones Archived July 8, 2012, at the Wayback Machine, Adobe
- ^ Flash Platform Certified Devices: Tablets Archived July 8, 2012, at the Wayback Machine, Adobe
- ^ Adobe abandons Flash Player on mobile browsers for HTML5 Archived November 14, 2011, at the Wayback Machine, CBS News
- ^ Adobe abandons Flash for mobile devices Archived July 9, 2016, at the Wayback Machine; The Telegraph
- ^ Press Room: For immediate release Archived August 5, 2014, at the Wayback Machine. Adobe. Retrieved on March 11, 2011.
- ^ Adobe Flash 10 to be ARM-optimized in 2009 Archived January 8, 2009, at the Wayback Machine. Electronista (November 17, 2008). Retrieved on March 11, 2011.
- ^ Press Room: For immediate release Archived August 16, 2014, at the Wayback Machine. Adobe. Retrieved on March 11, 2011.
- ^ ARM welcomes Adobe’s mobile Flash move – 5/2/2008 Archived February 20, 2009, at the Wayback Machine. Electronics Weekly (May 2, 2008). Retrieved on March 11, 2011.
- ^ ARM netbooks struggle with video, apps Archived July 12, 2012, at the Wayback Machine. Eetimes.com (April 14, 2009). Retrieved on March 11, 2011.
- ^ Adobe Success Story: LeapFrog Enterprises Archived October 14, 2007, at the Wayback Machine (Taken July 7, 2006).
- ^ Max, Jose. «Adobe Activation». Adobe Activator. Zii.
- ^ Macromedia – Flash Player SDK Archived July 18, 2006, at the Wayback Machine (Taken July 7, 2006).
- ^ Adobe Flash Player Archived October 13, 2011, at the Wayback Machine, Android Market
- ^ Maemo software | Nokia › Maemo Browser Archived December 29, 2009, at the Wayback Machine. Maemo.nokia.com. Retrieved on March 11, 2011.
- ^ «New info on the firmware updates for PS3 and PSP». ThreeSpeech. October 14, 2008. Archived from the original on October 15, 2008. Retrieved October 14, 2008.
- ^ Mobile and Devices Developer Center: Sony PSP Archived May 25, 2010, at the Wayback Machine. Adobe (July 16, 2007). Retrieved on March 11, 2011.
- ^ a b Download Macromedia Flash Player 7 for Pocket PC Archived February 7, 2014, at the Wayback Machine, Adobe
- ^ a b Flash Player 7 For Pocket PC Archived January 19, 2014, at the Wayback Machine. Adobe (July 14, 2009). Retrieved on March 11, 2011.
- ^ rich Internet applications | Adobe Flash Platform runtimes Archived May 30, 2010, at the Wayback Machine. Adobe.com (July 14, 2009). Retrieved on March 11, 2011.
- ^ «Flip8 – the World’s First Flash Emulator — v0.9». Newsdee.com. Archived from the original on January 27, 2010. Retrieved September 12, 2009.
- ^ Claus Wahlers. «FC64 – Flash Commodore 64 Emulator — Demo — c么deazur brasil lab». Codeazur.com.br. Archived from the original on October 5, 2009. Retrieved September 12, 2009.
- ^ «FlashZXSpectrum48k, Sinclair ZX Spectrum Emulator written in Flash». Jorin.com. Archived from the original on February 3, 2008. Retrieved September 12, 2009.
- ^ «aminnes – Project Hosting on Google Code». www.aminlab.com/. May 17, 2010. Archived from the original on September 19, 2014.
- ^ Lardinois, Frederic (July 25, 2017). «Get ready to finally say goodbye to Flash — in 2020». TechCrunch. Archived from the original on July 25, 2017. Retrieved July 25, 2017.
- ^ Warren, Tom (July 25, 2017). «Adobe will finally kill Flash in 2020». The Verge. Archived from the original on July 25, 2017. Retrieved July 25, 2017.
- ^ «Adobe Announces Flash Distribution and Updates to End». July 25, 2017. Archived from the original on July 26, 2017. Retrieved July 26, 2017.
- ^ Pudełek, Jakub (July 25, 2017). «Migrating Games from Flash to Open Web Standards on Facebook». Archived from the original on August 1, 2017. Retrieved July 26, 2017.
- ^ Laforge, Anthony (July 25, 2017). «Saying goodbye to Flash in Chrome». Archived from the original on July 25, 2017. Retrieved July 26, 2017.
- ^ «The End of an Era – Next Steps for Adobe Flash». July 25, 2017. Archived from the original on July 26, 2017. Retrieved July 26, 2017.
- ^ Smedberg, Benjamin (July 25, 2017). «Firefox Roadmap for Flash End-of-Life». Archived from the original on September 12, 2019. Retrieved August 21, 2019.
- ^ Tung, Liam (January 12, 2021). «Adobe Flash is finally gone: The end arrives as Adobe starts blocking Flash content». ZDNet. Retrieved January 14, 2021.
- ^ Cimpanu, Catalin. «Adobe wants users to uninstall Flash Player by the end of the year». ZDNet. Retrieved June 22, 2020.
- ^ Stahie, Silviu (June 24, 2020). «Adobe to Remove Flash Download Links, Recommends People Uninstall It Now». Security Boulevard. Retrieved February 18, 2021.
- ^ a b «Firefox 85.0, See All New Features, Updates and Fixes». Mozilla. Retrieved January 26, 2021.
- ^ a b «End of support for Adobe Flash | Firefox Help». support.mozilla.org. Retrieved November 25, 2020.
- ^ Venkat (June 16, 2019). «After Chrome 76, Mozilla Firefox 69 disables Flash by Default». Techdows. Retrieved June 16, 2019.
- ^ «Flash Roadmap — The Chromium Projects». www.chromium.org. Retrieved June 16, 2019.
- ^ Warren, Tom (January 20, 2021). «Google’s new Chrome 88 update improves dark mode, removes FTP and Adobe Flash». The Verge. Retrieved January 20, 2021.
- ^ «Firefox for Enterprise 93 — Release notes | Firefox for Enterprise Help». support.mozilla.org. Retrieved October 8, 2021.
- ^ «Update on Adobe Flash Player End of Support». Windows Blogs. September 4, 2020. Retrieved October 4, 2020.
- ^ «You can now uninstall Flash on Windows 10 and 8.1 using KB4577586». gHacks Tech News. October 28, 2020. Retrieved October 28, 2020.
- ^ a b «Adobe — Flash Player». Adobe.com. Adobe Systems. Retrieved February 5, 2021.
- ^ a b «_flash_install_packages_». flash.cn. Zhongcheng Network Technology Co., Ltd. Retrieved February 5, 2021.
- ^ «Flash Player on Adobe Support Community». community.adobe.com. Retrieved October 3, 2020.
- ^ Cimpanu, Catalin (June 24, 2020). «Safari 14 removes Flash, gets support for breach alerts, HTTP/3, and WebP». ZDNet. Retrieved July 27, 2020.
- ^ Debre, Elena (February 5, 2021). «These Places Were Not Ready for Flash to Die». Slate. Retrieved February 7, 2021.
- ^ «Release Notes — Flash Player 33». Adobe.com. Adobe Systems. Retrieved January 17, 2021.
- ^ «关于大连车务段使用Flash出现问题的声明公告». flash.cn (in Simplified Chinese). Zhongcheng Network Technology Co., Ltd. Retrieved January 25, 2021.
- ^ a b «Flash Player Debug Downloads (China-specific)». flash.cn (in Simplified Chinese). Zhongcheng Network Technology Co., Ltd. Retrieved April 1, 2021.
- ^ «Chinese repacks». msfn.com. Retrieved April 1, 2021.
- ^ Maxwell, Andy (October 12, 2021). «Adobe Uses DMCA to Nuke Project That Keeps Flash Alive, Secure & Adware Free». TorrentFreak. Retrieved October 13, 2021.
- ^ «Adobe Flash Player EOL Enterprise Information Page». Adobe.com. Adobe Systems. Retrieved January 17, 2021.
- ^ «Harman’s support program for Adobe Flash Player». harman.com. Harman International. Retrieved January 17, 2021.
- ^ Cimpanu, Catalin. «South African government releases its own browser just to re-enable Flash support». ZDNet. Retrieved February 3, 2021.
- ^ «Flash Projectors after 2020». community.adobe.com. July 22, 2020. Retrieved October 15, 2021.
- ^ Scott, Jason (November 22, 2020). «Flash Back! Further Thoughts on Flash at the Internet Archive». Retrieved January 3, 2021.
- ^ «CheerpX For Flash». Leaning Technologies. Retrieved November 20, 2021.
- ^ «Every Flash game disappears forever in 2020 – but this project has preserved 38,000 of them». PCGamesN. Retrieved February 15, 2021.
- ^ Open Source Flash C++ Compiler, CrossBridge Archived March 25, 2014, at the Wayback Machine, Adobe Blogs, June 25, 2013
- ^ CrossBridge Archived September 20, 2017, at the Wayback Machine, Adobe Gaming GitHub Website
- ^ «Flash Player Help / Installation problems». Archived from the original on March 16, 2012. Retrieved April 4, 2012.
- ^ «Help / Uninstall (old-version) Flash Player (if installation is unsuccessful)». Archived from the original on August 28, 2012. Retrieved August 31, 2012.
- ^ a b «Patch for Adobe Flash». The H. March 29, 2012. Archived from the original on February 22, 2014. Retrieved February 18, 2014.
- ^ «Adobe roadmap for the Flash Player». Adobe. Archived from the original on January 12, 2013. Retrieved January 14, 2013.
- ^ «What Is a Local Shared Object?». Adobe Systems. Archived from the original on May 29, 2010. Retrieved July 1, 2010.
- ^ «Adobe Flash Player Settings Manager». Adobe Systems. Archived from the original on June 20, 2010. Retrieved July 1, 2010.
- ^ «Web Storage Settings Panel». Adobe Systems. Archived from the original on April 4, 2012. Retrieved April 4, 2012.
- ^ «Private browsing in Flash Player 10». Adobe Systems. Archived from the original on May 28, 2010. Retrieved July 1, 2010.
- ^ «Flash Bug Report». February 6, 2010. Archived from the original on February 10, 2010. Retrieved March 27, 2010.
- ^ «Security Advisory for Flash Player, Adobe Reader and Acrobat». Adobe Systems. Archived from the original on June 8, 2010. Retrieved June 8, 2010.
- ^ «Adobe acknowledges critical security flaw in software». BBC News. June 7, 2010.
- ^ «Security Advisory for Adobe Flash Player, Adobe Reader and Acrobat». Adobe Systems. Archived from the original on October 31, 2010. Retrieved October 31, 2010.
- ^ «Flash vulnerability revealed for Android, fix coming November 9th». MobileCrunch. Archived from the original on October 31, 2010. Retrieved October 31, 2010.
- ^ «Security updates available for Adobe Flash Player». Adobe Systems. February 7, 2013. Archived from the original on July 9, 2013. Retrieved July 7, 2013.
- ^ «Security updates available for Adobe Flash Player». Adobe Systems. March 12, 2013. Archived from the original on July 9, 2013. Retrieved July 7, 2013.
- ^ «Internet Security Threat Report: Volume XV: April 2010». Symantec. April 2010. pp. 37, 40, 42. Archived from the original on April 25, 2010. Retrieved May 9, 2010.
- ^ «Adobe Acrobat, Reader, and Flash Player Remote Code Execution Vulnerability». October 15, 2009. Archived from the original on April 24, 2011. Retrieved May 9, 2010.
- ^ «2010 Threat Predictions» (PDF). McAfee Labs. December 2009. p. 2. Archived from the original (PDF) on June 2, 2010. Retrieved May 9, 2010.
- ^ «McAfee Threats Report: Fourth quarter 2009» (PDF). McAfee Avert Labs. February 2010. p. 16. Archived from the original (PDF) on February 15, 2010. Retrieved May 9, 2010.
- ^ a b «IT Threat Evolution: Q3 2012». Kaspersky Lab ZAO. November 1, 2012. Archived from the original on November 5, 2012. Retrieved November 2, 2012.
- ^ a b Steve Jobs (April 29, 2010). «Thoughts on Flash». Apple. Archived from the original on May 1, 2010. Retrieved May 9, 2010.
- ^ future of Flash Archived November 17, 2011, at the Wayback Machine. Adobe (July 14, 2009). Retrieved on March 11, 2011.
- ^ Symantec Global Internet Threat Report for 2009 Archived August 4, 2010, at the Wayback Machine, page 40, «In 2009, Symantec documented 321 vulnerabilities affecting plug-ins for Web browsers (figure 9). ActiveX technologies were affected by 134 vulnerabilities, which was the highest among the plug-in technologies examined. Of the remaining technologies, Java SE had 84 vulnerabilities, Adobe Reader had 49 vulnerabilities, QuickTime had 27 vulnerabilities, and Adobe Flash Player was subject to 23 vulnerabilities. The remaining four vulnerabilities affected extensions for Firefox.»
- ^ «Adobe Patches Flash Zero-Day Exploited by Magnitude EK». April 7, 2016. Archived from the original on April 11, 2016. Retrieved April 25, 2016.
- ^ «Security Advisory for Adobe Flash Player». April 5, 2016. Archived from the original on June 4, 2016. Retrieved April 25, 2016.
- ^ Update: Premium Features for Flash Player Archived July 19, 2014, at the Wayback Machine, Adobe AIR and FP Blog
- ^ «Why will Premium Flash Player Features Kill Flash?». ASVGuy. March 10, 2012. Archived from the original on February 5, 2015. Retrieved February 21, 2015.
- ^ Shankland, Stephen (March 28, 2014). «Adobe to charge Flash coders to use ‘premium’ features». CNET. Archived from the original on January 19, 2015. Retrieved February 21, 2015.
- ^ «And Then Premium Features Arrived…». ASVGuy. April 5, 2012. Archived from the original on February 5, 2015. Retrieved February 21, 2015.
- ^ Adobe Premium Features for Flash Player Archived August 21, 2014, at the Wayback Machine, Flash Player Dev Center, Adobe
- ^ Cassella, Dena (February 1, 2010). «Steve Jobs Unleashes His Fury During Town Hall Meeting». Archived from the original on February 6, 2010. Retrieved February 22, 2010.
- ^ Richmond, Shane. (April 30, 2010) Adobe hits back at Apple’s ‘smokescreen’ – Telegraph Blogs Archived May 3, 2010, at the Wayback Machine. Blogs.telegraph.co.uk. Retrieved on March 11, 2011.
- ^ YouTube Mobile gets a kick start Archived January 7, 2012, at the Wayback Machine, Official YouTube Blog
- ^ «Flash Player官方下载-Flash中国官网». Flash.cn. Archived from the original on July 22, 2018. Retrieved July 22, 2018.
- ^ «Adobe update on 6/12/18 include 2144 game cente… | Adobe Community». forums.adobe.com. Archived from the original on March 30, 2019. Retrieved July 22, 2018.; «Adobe’s ‘Partner’ 2144 in China has suspicious … | Adobe Community». forums.adobe.com. June 26, 2018. Archived from the original on July 22, 2018. Retrieved July 22, 2018.; «Uninstall 2144 Game Center | Adobe Community». forums.adobe.com. Archived from the original on July 22, 2018. Retrieved July 22, 2018.
- ^ Roter, Tom (February 10, 2021). «The Curious Case of FlashHelperService — Updated». Minerva Labs.
- ^ «Flashplayer Is Incompatible With Your Area | Adobe Community». forums.adobe.com. June 14, 2018. Archived from the original on July 22, 2018. Retrieved July 22, 2018.
- ^ «IT之家 | 中国特供版Flash被曝向有关部门搜集用户隐私 – 中国数字时代». chinadigitaltimes.net (in Chinese (China)). Archived from the original on July 22, 2018. Retrieved July 22, 2018.
- ^ «FutureSplash Player 1.1». FutureWave Software, Inc. Archived from the original on November 5, 1996. Retrieved December 2, 2021.
- ^ Macromedia, Inc. (March 4, 2002) Macromedia and Sorenson Media bring video to Macromedia Flash content and applications, Retrieved on August 9, 2009
- ^ «Adobe Completes Acquisition of Macromedia». Adobe Systems. December 5, 2005. Archived from the original on June 2, 2007. Retrieved June 18, 2007.
- ^ Huang, Emmy (November 15, 2006). «Flash Player 9 Update (9.0.28.0) release now available for Windows and Macintosh». Archived from the original on June 25, 2007. Retrieved January 23, 2014.
- ^ «Exploring full-screen mode in Flash Player 9». Adobe Developer Center. December 3, 2007. Archived from the original on April 4, 2012. Retrieved April 10, 2012.
- ^ Melanson, Mike (December 4, 2007). «Flash Player 9 Update 3 (Final)». Archived from the original on September 7, 2010. Retrieved January 23, 2014.
- ^ «Adobe Delivers Flash Player 9 with H.264 Video Support». adobe.com (Press release). December 4, 2007. Archived from the original on December 12, 2007.
- ^ Adobe Systems Incorporated (December 3, 2007) List of codecs supported by Adobe Flash Player Archived August 19, 2009, at the Wayback Machine, Retrieved on August 5, 2009
- ^ Halfast, Todd. «Flash Player 10.1 Now Available for Windows, Mac, and Linux » Adobe AIR and Adobe Flash Player Team Blog». Blogs.adobe.com. Archived from the original on May 11, 2011. Retrieved April 10, 2012.
- ^ «features Flash Player 10.3 Release Notes». Kb2.adobe.com. Archived from the original on April 30, 2012. Retrieved April 10, 2012.
- ^ Tareq Aljaber (May 17, 2013). «Extended Support Release Updated to Flash Player 11.7». Adobe AIR and Adobe Flash Player Team Blog. Adobe. Archived from the original on October 2, 2015. Retrieved February 15, 2014.
- ^ «Flash Player 11 and AIR 3 Release Notes: 10/04/11». Kb2.adobe.com. Archived from the original on April 30, 2012. Retrieved April 10, 2012.
- ^ Introducing Molehill: 3D APIs for Adobe Flash Player and Adobe AIR Archived July 8, 2012, at the Wayback Machine, Adobe Edge
- ^ Extending AIR Archived July 24, 2014, at the Wayback Machine, Adobe Devnet
- ^ «Flash Player 11.1 and AIR 3.1 User Release Notes: 11/09/11». Kb2.adobe.com. Archived from the original on April 30, 2012. Retrieved April 10, 2012.
- ^ «Adobe Introduces Premium Features for Gaming with Flash Player 11.2; Announces Collaboration with Unity Technologies». adobe.com. Archived from the original on May 14, 2012. Retrieved May 18, 2012.
- ^ a b c d e «Flash Player and Adobe AIR feature list». adobe.com. Archived from the original on May 14, 2013. Retrieved May 9, 2013.
- ^ a b «Upcoming changes to Flash Player’s extended support release». Adobe. March 5, 2014. Archived from the original on October 1, 2015. Retrieved December 17, 2014.
- ^ «Flash Player 12.0.0.3». Adobe Systems. November 14, 2013. Archived from the original on December 24, 2013. Retrieved December 22, 2013.
- ^ «Adobe Labs Downloads». Adobe. April 22, 2015. Archived from the original on April 25, 2015. Retrieved April 25, 2015.
- ^ «Flash Player 13.0.0.80». Adobe Systems. January 28, 2014. Archived from the original on February 22, 2014. Retrieved February 18, 2014.
- ^ «8/12/2014 – Release – Flash Player 14». Adobe Systems. August 12, 2014. Archived from the original on November 11, 2014. Retrieved January 12, 2015.
- ^ «11/11/2014 – Release – Flash Player 15». Adobe Systems. November 11, 2014. Archived from the original on November 11, 2014. Retrieved January 12, 2015.
- ^ «12/9/2014 – Release – Flash Player 16». Adobe Systems. December 9, 2014. Archived from the original on December 15, 2014. Retrieved January 12, 2015.
- ^ «12/3/2015 – Release – Flash Player 17». Adobe Systems. March 12, 2014. Archived from the original on March 22, 2015. Retrieved March 13, 2015.
- ^ «Adobe Security Bulletin». Archived from the original on March 29, 2017. Retrieved March 25, 2017.
Further reading[edit]
- Understanding Flash Player with Adobe Scout – an article discussing the internals of the player and the Adobe Scout profiling tool
External links[edit]
- Official website
- Final global variant version of the standalone projector. at the Wayback Machine (archived April 1, 2022)
- Archived Adobe Flash Player versions at the Wayback Machine (archived July 18, 2020)
- Flash Tester Archived June 12, 2018, at the Wayback Machine (explains official old working version check)
На чтение 5 мин Просмотров 10.6к. Опубликовано 20/02/2021 Обновлено 20/02/2021
3 года назад Adobe решила не развивать мобильную версию плагина для проигрывателя Flash Player. Тогда сообщалось, что благодаря такому шагу разработчики сосредоточатся на развитии технологий HTML5 для мобильных гаджетов. Недавно стало известно, что из-за проблем с безопасностью Adobe перестанет его поддерживать с 01.01.2021. Нужно понять, стоит ли удалять Flash Player и как это сделать.
Содержание
- Общая информация о программе Adobe Flash Player
- Предназначение
- Основные возможности Flash Player
- Нужно ли удалять с компьютера после завершения поддержки
- Причины для совершения процедуры
- Деинсталляция: алгоритм действий
- Стандартными средствами Windows
- С помощью Uninstaller
- Можно ли не удалять Adobe Flash Player
Ее устанавливают в качестве дополнения для браузера. С ее помощью можно смотреть видеоролики в интернете.
Предназначение
Flash Player — специальный проигрыватель, необходимый для того, чтобы пользовательский браузер, установленный на ПК, корректно показывал Flash-контент, который размещен на разных сайтах. Его также можно сравнить с виртуальной машиной, на которой воспроизводится загруженный из интернета код подобных программ.
Все версии приложения для любого устройства распространяются бесплатно. Весь интерфейс русифицированный. Доступно множество других языков.
Основные возможности Flash Player
- умеет создавать баннерные профили на сайте;
- дает возможность делать промоблоки и проморазделы;
- обладает небольшим размером выходных файлов, поэтому они быстро загружаются;
- позволяет воспроизводить аудио- и видеоролики;
- создает интерактивные формы на сайте;
- дает возможность строить графики и диаграммы;
- генерирует удобные сервисы закачки информации на сервер;
- допускает разработку развлекательных игр.
Кроме того, доступен режим приватного просмотра. Локальная информация пользователя не кэшируется, активность не сохраняется.
Нужно ли удалять с компьютера после завершения поддержки
Пользоваться плеером никто не запрещает. Но, начиная с 2021 г., контент на основе Flash станет блокироваться при запуске в браузерах. Для исправления этого — скачайте Adobe Flash Player с нашего сайта.
Поэтому важно понять, стоит ли удалять плеер.
Причины для совершения процедуры
Flash в настольных браузерах остается неуклюжим. Для отображения содержания HTML5 им нужно обрабатывать такой тип контента вместо использования одного кода через плагин Adobe. Однако это плохо, т.к. в плеере была обнаружена большая дыра безопасности. Через нее каждому хакеру получится легко получить доступ к системе.
За ближайшие недели проблему исправить нельзя, поэтому специалисты советуют удалять программу. Просить отсрочку у руководства Adobe не имеет смысла, деинсталляцией можно заняться уже сейчас. Сделать это несложно.
Кроме того, избавляться от флеш-плеера рекомендуется и из-за ряда других недостатков.
К ним относятся:
- Перегрузка центрального процессора на компьютере. На слабых ПК из-за этого возникают существенные проблемы.
- Недостаточный контроль ошибок. Приложения по этой причине часто отказывают.
- Плохая индексация текстовой информации.
- Невозможность увеличивать размер шрифта. Из-за этого посетители быстро переходят на другой сайт.
- Необходимость убирать весь Flash-модуль, если вносятся даже минимальные изменения.
- Отсутствие возможности соединить страницы.
- Запрет на отключение графических элементов.
- Сложное обновление сайтов.
- Невозможность копировать тексты, размещенные на Flash-странице портала.
- Несовместимость с иными языками программирования.
- Недоступность конвертации векторных изображений в другие форматы, если флеш-плеер используется в качестве редактора.
- Невозможность использовать правую кнопку мыши в старых версиях приложения.
Деинсталляция: алгоритм действий
Удалить плеер от компании Adobe получится 2 способами. Нужно разобрать каждый из вариантов.
Стандартными средствами Windows
Если нет желания пользоваться сторонним софтом, то подойдут универсальные средства удаления программ Windows.
Когда установлена «Виндовс 10», выполните следующее:
- Зайдите в раздел с параметрами.
- Перейдите во вкладку «Система», а из нее — в «Приложения и возможности».
- Найдите здесь Player, нажмите по нему и кликните «Удалить».
Если установлены другие версии Windows:
- Зайдите в «Панель управления».
- Из нее перейдите в раздел «Установка и удаление программ».
- Найдите здесь флеш-плеер, нажмите по нему и кликните «Удалить».
С помощью Uninstaller
Revo Uninstaller (RU) — это утилита, которая заменяет стандартный набор по удалению программ в Windows. Выпускаются бесплатная и платная версии. Помимо очищения системы, RU умеет делать то же с историей браузеров и безвозвратно удалять папки и файлы.
Последовательность действий:
- Скачайте программу Revo Uninstaller с официального сайта и запустите ее. Во вкладке «Деинсталлятор» появится список установленных программ. В нем вы увидите Flash Player.
- Кликните правой кнопкой мыши по нему и выберите «Удалить». Программа создаст точку восстановления Windows. С ее помощью получится откатить работу системы, если возникнут какие-либо проблемы.
- После создания резервной копии и запуска деинсталляции программы нажмите на кнопку «Удаление».
- Вернитесь в окошко Revo Uninstaller и проведите сканирование, чтобы найти оставшиеся файлы, если они есть. Лучше поставить режим «Продвинутый»: тогда система ничего не пропустит.
- После выделения всех ключей нажмите кнопки «Удалить» — «Далее».
- После появления списка оставшихся файлов нажмите «Выделить все», а затем «Удалить».
Останется только кликнуть «Готово».
Можно ли не удалять Adobe Flash Player
Да, это допускается. Если играете в игры на этой технологии или используете какие-то другие сервисы, то можете оставить программу у себя.
Разработчики планируют удалить все ссылки для загрузки плеера с собственного сайта.
Это сделано для того, чтобы люди не смогли скачать и установить неподдерживаемую версию ПО. Ссылки на загрузку останутся на нашем сайте. Adobe продолжит разработку Adobe Animate.
Adobe Flash Player
для Windows

Adobe Flash Player — кроссплатформенный модуль, который представляет собой незаменимый инструмент для воспроизведения мультимедийного интерактивного Flash-контента (файлы FLV, SWF) в различных браузерах и операционных системах.
Наличие установленного проигрывателя позволяет пользователю без всяких ограничений просматривать веб-сайты, содержащие на своих страницах видеоматериалы, анимацию, игры, приложения и др. Благодаря реализации программного интерфейса API Stage 3D, Adobe Flash Player обладает аппаратным ускорением рендеринга 2D/3D-графики.
Разработчики рекомендуют, во избежание конфликтов, перед инсталляцией Flash Player удалить старую версию плагина с помощью фирменной утилиты Adobe Flash Player Uninstaller.
Поддержка Adobe Flash Player завершилась 31 декабря 2020 года.
Компания Adobe заявила, что начиная с 12 января 2021 года Flash-контент будет блокироваться для воспроизведения в плеере и рекомендует пользователям удалить Adobe Flash Player.
- Adobe Flash Player Uninstaller — утилита удаления Adobe Flash Player
ТОП-сегодня раздела «Flash»

Macromedia Flash Player — Данная программа представляет собой перевод на русский язык последней версии всемирно известного проигрывателя Flash-роликов (SWF-файлов)…

Flash Movie Player — Программа для проигрывания Flash-файлов. Воспроизводит Flash-файлы форматов SWF, EXE и FMP…

FlashCore — программа для просмотра мультимедийных файлов с расширением swf (Flash ролики, игры и т.п.)….
Отзывы о программе Adobe Flash Player
Владимир про Adobe Flash Player 32.0.0.465 [24-04-2021]
Пишет, что версия для 7 и младше виндовс. Хотя в описании версии указаны все.
20 | 32 | Ответить
46Николай64 про Adobe Flash Player 32.0.0.468 [06-01-2021]
ПОДСКАЖИТЕ АДОБ НАЧНЕТ ПРИНУДИТЕЛЬНО БЛОКИРОВАТЬ ФЛЭШ С 12 ЯНВАРЯ (СООБЩЕНИЕ НА САЙТЕ). РАНЬШЕ МОЖНО БЫЛО СНИМАТЬ ФАЙЛ С ТРАНСЛЯЦИИ ПО ФЛЭШ. КАК ТЕПЕРЬ ДЕЛАТЬ ? ЕСТЬ ГДЕ НИБУДЬ ИНСТРУКЦИИ ? ПОДСКАЖИТЕ. ОЧЕНЬ НУЖНО
50 | 74 | Ответить
Владимир Владимирович про Adobe Flash Player 32.0.0.403 [15-07-2020]
Спасибо авторам сайта за возможность выразить личное мнение не только супер-позитивное, но и нейтральное или негативное! Я уже говорил что Adobe Flash Player — недоделанная программа, много проблем с ней, много времени отнимает и оперативной памяти. Как и ряд других «современных» программ. Сплошной спам, реклама и постоянные бесконечные обновления и с годами всё хуже. У меня несколько программ конца 90-х годов — до сих пор работают без проблем, но эти типа Adobe Flash Player — никак на 21 век не тянут. На других сайтах-отзовиках этот текст не опубликовали бы кстати с пометкой «ненормативная лексика», собрав у меня перед этим всё вплоть до №телефона, ФИО, почты и т.д. А между прочим я уже больше 20 лет в IT и не каждый год отозваться хочется.
46 | 40 | Ответить
Andrey в ответ Владимир Владимирович про Adobe Flash Player 32.0.0.465 [23-03-2022]
Ну вот и доделали! Просто сделали её платной.
7 | 11 | Ответить
Сергей про Adobe Flash Player 32.0.0.363 [03-05-2020]
абсолютно бесполезная паразитическая программа ваш Adobe Flash Player, стыдно должно быть тем кто такую рухлядь создаёт
50 | 35 | Ответить
Дмитрий в ответ Сергей про Adobe Flash Player 32.0.0.465 [01-02-2021]
Сергей как тебе не стыдно без него ты даже в браузерную игру сыграть не сможешь или загрузить файл во вконтакте!!!
29 | 21 | Ответить
A.C. про Adobe Flash Player 32.0.0.363 [18-04-2020]
Всё отлично работает. Спасибо разработчикам.У меня без Adobe фильмы тормозят.Пробовал через яндекс-это гавно засоряющий комп.
51 | 30 | Ответить
Обратите внимание! 01.01.2021 поддержка Adobe Flash Player была полностью прекращена. Так как об этом сообщалось заранее, еще в 2017 году, сторонние разработчики, в основе продуктов которых лежал Flash, должны были адаптировать свой контент под современные, поддерживаемые и развивающиеся технологии. В первую очередь, это работающий во всех браузерах по умолчанию HTML5, а также WebGL и WebAssembly. И если за 3 года кто-то не успел или не захотел этого сделать, значит, дальнейшее развитие продуктов и пользовательская аудитория таких разработчиков не волнует.
Никакой прямой замены Флеш Плееру нет, созданный на его основе контент, если он не был адаптирован, попросту не будет работать, от его использования придется отказаться! Любые предлагаемые кем-либо и на каких-либо сторонних (неофициальных) ресурсах альтернативы – небезопасны!
Сами же Adobe, как и многие эксперты по безопасности, настоятельно рекомендуют пользователям удалить Flash Player, так как в настоящий момент он имеет множество уязвимостей, подвержен атакам со стороны злоумышленников, и со временем этот риск будет только повышаться.
Подробнее: Как полностью удалить Adobe Flash Player с компьютера
Наверняка вы слышали о таком проигрывателе, как Adobe Flash Player, мнение о котором достаточно неоднозначно: одни считают, что это одно из наиболее важных ПО, которое должно быть установлено на каждом компьютере, другие же уверяют, что Flash Player – вещь весьма небезопасная. Сегодня мы подробнее рассмотрим, для чего нужен Adobe Flash Player.
Мы, как пользователи интернета, уже привыкли к тому, что в сети можно смотреть онлайн-видео, прослушивать музыку, играть в игры прямо в окне браузера, не задумываясь о том, что в большинстве случаев именно технология Flash позволяет осуществлять данную задачу.
Adobe Flash представляет собой технологию, позволяющую создавать мультимедийный контент, т.е. информацию, содержащую видео, аудио, анимацию, игры и прочее. После того, как данный контент будет размещен на сайтах, пользователь получает доступ к его воспроизведению, однако, он имеет собственный формат файлов (как правило, это SWF, FLV и F4V), для воспроизведения которых, как в случае и с любым другим форматом файлов, требуется свое программное обеспечение.
Что такое Adobe Flash Player?
И вот мы плавно подошли к главному вопросу – что же такое Flash Player. Как правило, браузеры по умолчанию не умеют воспроизводить Flash-содержимое, однако, их можно этому научить, если интегрировать в них специальное программное обеспечение.
В данном случае речь идет о Adobe Flash Player, который представляет собой мультимедийный проигрыватель, направленный на воспроизведение Flash-соержимого, которое, как правило, размещается в интернете.
На просторах интернета и по сей день достаточно часто встречается Flash-содержимое, однако, от него стараются отказаться в пользу технологии HTML5, поскольку сам проигрыватель Flash Player имеет ряд недостатков:
1. Flash-контент дает серьезную нагрузку на компьютер. Если открыть сайт, на котором размещено, например, Flash-видео, поставить его на воспроизведение, а затем перейти в «Диспетчер задач», то вы отметите, насколько браузер стал больше потреблять ресурсов системы. Старые и слабые компьютеры в данном случае особенно страдают.
2. Некорректная работа Flash Player. В процессе использования Flash Player часто возникают ошибки в работе плагина, которые могут привести к полному закрытию браузера.
3. Высокий уровень уязвимости. Пожалуй, наиболее значимая причина всемирного отказа от Flash Player, т.к. именно этот плагин становится главной мишенью злоумышленников за счет наличия огромного количества уязвимостей, которые позволяют легко проникать вирусам на компьютеры пользователей.
Именно по этой причине многие популярные браузеры, такие как Google Chrome, Opera и Mozilla Firefox, в ближайшем будущем собираются полностью отказаться от поддержки Flash Player, что позволит закрыть одну из главных уязвимостей браузеров.
Стоит ли устанавливать Flash Player?
Если вы посещаете веб-ресурсы, для воспроизведения контента на которых браузер требует установки Flash Player – данное программное обеспечение можно установить на компьютер, но загружать дистрибутив проигрывателя следует исключительно с официального сайта разработчика.
Читайте также: Как установить Adobe Flash Player на компьютер
В связи с тем, что все больше ресурсов отказывается от размещения на своих страницах Flash-контента, в процессе веб-серфинга вы и вовсе можете не столкнуться с сообщением о том, что для воспроизведения содержимого требуется плагин Flash Player, а значит, и смысла в установке для вас практически никакого нет.
Надеемся, данная статья помогла вам разобраться с вопросом, что такое Флеш Плеер.
На чтение 4 мин Просмотров 90 Опубликовано 23.07.2019

Содержание
- Что такое Adobe Flash Player?
- Особенности технологии
- Скачивание и установка
- Видеоинструкция
- Заключение
Что такое Adobe Flash Player?
Итак, начнем с основного назначения данного плагина. Несмотря на то, что в названии присутствует слово Player, средство используется для воспроизведения встроенных мультимедийных материалов, с которыми пользователь сталкивается в браузере и флеш-играх. Flash-содержимое присутствует на многих сайтах, которые вы посещаете каждый день. Если данный плагин отсутствует, то вместо контента вы увидите соответствующее уведомление и предложение об установке или включении.
Современные ресурсы постепенно отказываются от flash-технологии в пользу HTML5, однако до сих пор плагин от Adobe желателен для установки, чтобы вы могли просматривать большую часть контента.
У flash-материалов имеются собственные форматы – SWF, FLV, F4V. По умолчанию ни один браузер не способен воспроизводить данные расширения, поэтому вам предстоит установить компонент Adobe на ПК.
Особенности технологии
Несмотря на повсеместное распространения флеш-проигрывателя, многие пользователи и специалисты нелестно о нем отзываются. Это связано со спорными качествами, которые делают Flash Player не лучшей платформой для мультимедийного контента:
- Во-первых, Flash-материалы сильно нагружают компьютер. Особенно это проявляется при воспроизведении одновременно нескольких элементов. В основном, с такой ситуацией пользователи сталкиваются при просмотре с «тяжелыми» сайтами.
- Во-вторых, Adobe Flash Player известен частыми ошибками при воспроизведении. После них нужно перезагружать плагин. С технической стороны данная поломка является не критичной, но пользователям не нравится каждый раз перезапускать расширение.
- В-третьих, высокая уязвимость. Это является основной причиной, по которой разработчики стараются уходить от использования Flash Player.
Скачивание и установка
Поскольку вы так или иначе сталкиваетесь с флеш-контентом при использовании браузера, вам необходимо обязательно установить Adobe Flash Player. Просто следуйте представленному руководству:
- Сначала откройте ссылку на официальный ресурс разработчиков.
- Сайт определит версию Windows и ее разрядность.
- Если вы не хотите загружать компьютер дополнительным ПО, то снимите две галочки в центральном блоке, где говорится об утилитах от McAfee.
- Затем кликните на «Установить сейчас».
После этого на компьютер загрузится инсталлятор. Запустите файл в формате EXE и следуйте инструкции. Сначала нужно выбрать вариант обновления. Чтобы не возвращаться к данной процедуре позже, рекомендуется выбрать первый пункт.
Затем утилита начнет загрузку необходимых файлов. Эта процедура займет всего 1-2 минуты. После появится уведомление о том, что плагин установлен. Для применения изменений необходимо перезапустить браузер. Затем закройте инсталлятор кнопкой «Готово».
Если вам нужен дистрибутив плагина для другой операционной системы, то откройте данную ссылку. В левой части раскройте список и выберите операционную систему, а затем версию для определенного браузера. После чего точно так же снимите галочки возле согласия на установку дополнительного ПО и кликните на кнопку «Загрузить». Полученный инсталлятор можно скопировать на другой ПК и установить плагин Adobe Flash Player.
Мнение эксперта
Дарья Ступникова
Специалист по WEB-программированию и компьютерным системам. Редактор PHP/HTML/CSS сайта os-helper.ru.
Спросить у Дарьи
Данная инструкция подходит и для установки плагина с нуля, и для обновления уже инсталлированной версии программы.
Видеоинструкция
Для более подробного изучения темы Adobe Flash Player обязательно ознакомьтесь с представленной видеоинструкцией.
Заключение
Если при посещении сайтов вы часто сталкиваетесь с уведомлением о том, что для показа того или иного контента требуется Adobe Flash Player, то вам необходимо его установить. Мы расписали инструкцию по загрузке и инсталляции, поэтому наши читатели легко справятся с данной задачей.
А если какой-либо шаг вызовет у вас вопросы или трудности, то мы всегда готовы помочь с решением проблемы!
Содержание
- 1 Adobe Flash Player — что это такое?
- 2 Где можно безопасно скачать?
- 3 Как открыть настройки флеш плеера?
- 4 Как удалить флеш плеер?
- 5 Заключение
- 6 Где скачать Adobe Flash Player
- 7 Что такое Adobe Flash Player
- 8 Нужен ли вам Adobe Flash Player
- 9 Для каких браузеров есть Adobe Flash Player
- 10 Как обновить Flash Player в Windows 10 и связанные с этим проблемы
Приветствую друзья, сегодня мы поговорим о программе Adobe Flash Player — я постараюсь рассказать простыми словами что к чему. Так что поехали разбираться!
Скажу сразу — да, в интернете уже расписано что это такое.. что за прога.. но вот в итоге не все юзеры четко понимают. Я к тому что я тут сегодня постараюсь написать именно ПРОСТЫМИ СЛОВАМИ, чтобы было понятно с первого раза!))
Adobe Flash Player — что это такое?
Adobe Flash Player — плеер, который воспроизводит флеш элементы на сайтах. Это все, что можно сказать об этой программе, разве что можно добавить что она идет от Adobe.
Такс, а вот что пишет сам производитель о своей проге:
Ну а теперь давайте подробнее.
Самое главное — что вообще такое флеш? Это мини-программы, которые могут быть встроены в веб-страницу. То есть это именно программы, в них нет кода html. Если быть точнее, то именно программ — я не видел, так как чаще всего флеш используется для:
- Создания игр. Оч много игр, в которые можно поиграть в интернете, я имею ввиду онлайн, не какие-то там танки онлайн, а попроще, там шарики.. головоломки.. то часто они написано именно на флеше.
- Видео-плееры. Да, они тоже часто созданы именно по флеш-технологии. Но вообще флеш — не совсем новая технология. Можно сказать даже старая. Сейчас видео-плееры могут быть созданы и подругой технологии — HTML5. Здесь не нужен флеш, вот например Ютуб — там видео-плеер именно на HTML5, поэтому для чего работы не нужен флеш, и не нужна соответственно прога Adobe Flash Player.
- И еще один тип применения — рекламные баннеры. Красивая реклама, анимационная, где даже можно что-то нажать, либо та, которая реагирует на наведения мышки — тоже часто разработана на флеше.
Возможно я ошибаюсь, но вроде это три основных направления использования флеш-технологии.
То есть, если вы не установили себе флеш-плеер Adobe Flash Player, то у вас все вышеперечисленное работать не будет. Или частично, но скорее всего все таки не будет. Онлайн видео на некоторых сайтах все равно работать будет, так как может использоваться, как я уже писал видео-плеер не на флеше, а на HTML5.
Флеш плеер может немного грузить браузер. Но в онлайн игры многие без него не поиграть.
Где можно безопасно скачать?
Нужно скачивать только с офф сайта, а именно отсюда:
https://get.adobe.com/ru/flashplayer/otherversions/
Там же можно выбрать и версию операционки, а также браузер для которого нужен флеш — например Хром, Мозилла. Офф сайт выглядит так:
Как сказано на офф сайте — флеш-плеер установлен более чем на 1.3 миллиардов компов, является стандартом предоставления ресурсоемкого мультимедийного содержимого. Видите, даже у них написано — ресурсоемкого! То есть браузер может грузить этот флеш, и кстати HTML5 в этом плане куда легче. Но пока что HTML5 не везде есть к сожалению.. ((
И еще, флеш плеер может быть только от Adobe, от других компаний не бывает, ну по крайней мене я не встречал..
Совсем забыл — когда будете качать, то осторожно, там могут быть галочки по установке дополнительного софта, который вам возможно даром не нужен:
Как открыть настройки флеш плеера?
Если Adobe Flash Player установлен, то обычно есть его значок в панели управления:
А если его нет, то проверьте что у вас в панели именно значки отображаются:
И если все равно нет, значит он не установлен.. ну или установлен, но как-то криво. Так вот, этот значок если запустить, то будут настройки:
Лайфхак, как быстро открыть панель управления на любой виндовс: зажмите Win + R, далее напишите команду control или control panel, нажмите ОК. Вот и все))
Как удалить флеш плеер?
Здесь тоже все просто:
- Сперва закройте все браузеры!
- Зажмите Win + R, напишите команду appwiz.cpl, нажмите ОК. Либо просто откройте панель управления и найдите там значок Программы и компоненты.
- Откроется окно установленного софта. Найдите тут Adobe Flash Player, нажмите правой кнопкой, выберите Удалить.
- Потом появится мастер удаления, следуйте инструкциям.. там вроде бы нужно нажать Далее, Next, Uninstall.. в общем ничего сложного нет.
Вот я даже нашел картинку, будет вам подсказкой (это окно Программы и компоненты):
Да, у вас может быть несколько — начинайте с PPAPI, NPAPI, а потом уже удаляйте ActiveX. Ну а вот само окошко удаления флеш-плеера:
Заключение
Кажется главное мы все таки выяснили:
- Adobe Flash Player — плеер, который воспроизводит флеш-содержимое на сайтах.
- Если его не будет, то во многие онлайн-игры вы поиграть не сможете. И онлайн-видео на некоторых сайтах тоже работать не будет.
- Удалить можно без проблем, как собственно и потом повторно установить. Да, на всякий случай можно создать контрольную точку восстановления.
Надеюсь информация помогла. Удачи и добра, до новых встреч господа!
На главную!18.07.2019 «>Читать! —>
Что такое Adobe Flash Player, как работает, где используется, нужен ли обычному пользователю и как его установить.
</tr></tbody></table>
Об отходе от этой технологии говорит и тот факт, что мобильная операционная система Android начиная с 4-й версии уже не поддерживает Adobe Flash Player и прикрутить его туда довольно проблематично.
Тем не менее, Adobe Flash Player еще используется на многих сайтах, предоставляющих видео и игровой контент в формате Flash, что заставляет многих пользователей устанавливать Adobe Flash Player на ПК и мобильные устройства.
Где скачать Adobe Flash Player
Узнать больше об этой технологии, как она работает, как правильно установить и скачать Adobe Flash Player вы можете на сайте TheProgs.ru. Открывайте ссылку в браузере, в который хотите установить плагин, так как установщик автоматически выбирает версию для каждого браузера. Ну а дальше мы кратко расскажем о том что это такое и для чего нужно.
Что такое Adobe Flash Player
Adobe Flash Player это специальный проигрыватель мультимедийного контента в формате Flash с расширенной функциональностью, позволяющей реализовать даже множество разнообразных игр.
Технология Flash выходит далеко за рамки простого проигрывания видео, на ней реализуется различные мультимедийные функции с интерактивным управлением с помощью клавиатуры и мыши.
Adobe Flash Player устанавливается как дополнение (расширение или плагин) к браузеру и существует версия для всех современных браузеров.
Нужен ли вам Adobe Flash Player
Технология массово используется в браузерных играх, от таких издателей как Mail.ru и других. Если вы играете в такие игры, то без Adobe Flash Player вам никак не обойтись, придется устанавливать его в ваш браузер.
Даже если вы не играете в игры в браузере, то Adobe Flash Player скорее всего вам все равно понадобится, так как на нем реализовывается дополнительный функционал на некоторых популярных сайтах, в том числе в соцсетях.
Без этого плагина вы просто не сможете использовать все возможности популярных ресурсов. Поэтому обычно Adobe Flash Player входит в обязательный пакет системных компонентов, которые устанавливаются в первую очередь после установки Windows.
Для каких браузеров есть Adobe Flash Player
Браузер Google Chrome содержит в своем составе базовую версию Adobe Flash Player. Для большинства остальных популярных браузеров Adobe Flash Player нужно устанавливать отдельно.
Для каждого браузера есть своя версия Adobe Flash Player и его нужно устанавливать в каждый браузер, которым вы пользуетесь. Но происходит это довольно просто, всего в несколько кликов.
Transcend StoreJet 25A3 TS1TSJ25A3KTranscend JetFlash 790 8GBA-Data Ultimate SU650 120GB
2017-10-23
Adobe Flash когда-то был вездесущим в Интернете, но сейчас он выглядит странно. Эксперты и разработчики утверждали, что пришло время отойти от этого плагина. В сравнении с HTML5 и другими веб-стандартами, флеш является ресурсоемким и небезопасным. Фактически, Adobe планирует прекратить развитие своей же технологии к 2020 году.

Тем не менее процесс поэтапного отказа от флеша работает медленно. При разработке заметок для вебсайтов и утилит на другой основе затрачиваются время, усилия и деньги, и многие крупные адреса в Интернете все еще полагаются на флеш, даже если его поддержка начинает ослабевать.
Когда мы имеем дело с современными операционными системами, как Windows 10, в комплекте с которыми идет обновленный браузер (Microsoft Edge), то их сочетание со старыми технологиями приводит к некоторой непредсказуемости. У вас возникают очевидные вопросы: Flash Player безопасен? Он работает? Включен ли в Windows 10? Совместим ли с Microsoft Edge?
В зависимости от опыта, вы можете прийти к разным выводам насчет этих вопросов. Некоторые сайты работают нормально, а другие нет. Возможно, вы даже пытались установить Adobe Flash в Windows 10, чтобы проверить его работоспособность.

К счастью, мы объясним, как обновить Flash Player в Windows 10 и разобраться со всеми сопутствующими этой задаче проблемами.
Мы также рассмотрим процесс обновления флеша в двух популярных браузерах и решим распространенные проблемы, которые могут возникнуть при выполнении предписанных условий.
Как обновить Flash Player в Windows 10 и связанные с этим проблемы
Даже когда основные вебсайты и онлайн-платформы отказываются от тяжелых плагинов, многие из них по-прежнему требуют установки плеера. Например, популярные ресурсы, как Главная лига бейсбола MLB.tv и инструменты, такие как Pixlr, до сих пор поддерживают флеш-технологию. К счастью, Microsoft начала связывать Adobe Flash Player в своем браузере после выпуска Windows 8 и продолжает это делать в последней десятой версии.
Поскольку Microsoft связала Adobe Flash с Windows, вы получите его свежую версию через «Центр обновления». Итак, попробуйте обновится вручную.
- Кликните по меню «Пуск» и нажмите по шестеренке.
Открываем «Пуск» и нажимаем по шестеренке
- Откройте раздел «Обновление и безопасность», как на скриншоте ниже.
Переходим в раздел «Обновление и безопасность»
- Затем для проверки наличия обновлений, щелкните на соответствующую кнопку в «Центре обновления Windows».
В «Центре обновления Windows» нажимаем «Проверка наличия обновлений»
-
Нажмите кнопку «Установить сейчас», еслипоследняя версия флеш-плеера доступна. Вы также можете попробовать другие способы обновления.
Если доступна версия обновления флеш плеера, нажимаем «Установить сейчас» или «Restart now»
Как установить новую версию Adobe Flash Player для Windows 10
Ручной процесс очень прост и состоит всего лишь из нескольких шагов:
- Загрузите Adobe Flash Player Uninstaller по ссылке https://helpx.adobe.com/flash-player/kb/uninstall-flash-player-windows.html. Adobe Flash Player Uninstaller помогает при переустановке любых версий плеера. Его также можно использовать для его обновления. Инструмент удалит все флеш-плееры, кроме ActiveX на Windows 8/10.
Нажимаем «Скачать Uninstaller для flash-плеера»
- Запустите установочный файл из папки «Загрузки», разрешите внести изменения на ваш компьютер.
В папке «Загрузки» открываем установочный файл двойным щелчком левой кнопкой мыши
- Нажмите «Удаление», таким образом Adobe Flash Player Uninstaller ликвидирует на компьютере старую версию флеш-плеера.
Нажимаем «Удаление»
Флеш плеер удален, нажимаем «Готово»
-
Всебраузеры должны быть закрыты. Загрузитеираспакуйтепоследниеавтономныезагрузчикидлякаждогоизних, открыв ссылку https://get.adobe.com/ru (установитетолькоте, которыевамнужны).
На сайте разработчика выбираем параметры для своего компьютера и браузера, нажимаем «Загрузить»
Отмечаем пункт, который рекомендует разрабочтик «Разрешить Adobe устанавливать обновления»
Двойным кликом левой кнопки мыши запускаем установочный файл
При установке следуем инструкции установщика
Важно! Существует 3 типа плагинов для флеш-плееров, и все они должны быть установлены отдельно. Вам придется переустанавливать каждый тип для конкретного браузера. Важно отметить, что вы можете иметь разные версии, потому что не все браузеры и приложения используют один и тот же плагин. Помните об этом.
- NPAPI — предназначен для Firefox (Safari для Windows);
- ActiveX — Internet Explorer/EDGE (Windows 10);
- PPAPI — браузер Opera.
Для каждого браузера нужно поочередно установить каждый плагин, в зависимости от количества используемых браузеров
Google Chrome
В Chrome уже установлена свежая версия плеера, так что обновление обрабатывается на 100%. Вам не нужно ничего скачивать и устанавливать, поскольку все происходит в автоматическом режиме.
Единственный способ устранения неполадок, кроме повторной установки Adobe Flash, — удаление следующего файла, поскольку он вызывает ошибки при воспроизведении контента: «c:users→username→AppData→Local→Google→Chrome→User Data→PepperFlash».
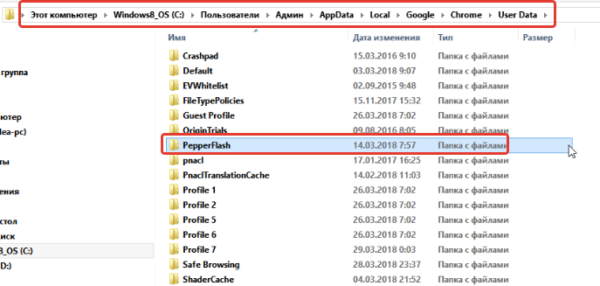
Mozilla Firefox
Сначала проверьте, включен ли Flash в Firefox.
- Откройте меню, затем «Дополнения» и перейдите в «Плагины».
Заходим в меню браузера, открываем «Дополнения»
- Выберите «Shockwave Flash», а затем опцию «Всегда включать».
Открываем раздел «Плагины», выбираем «Shockwave Flash», а затем опцию «Всегда включать»
-
Для обновления Flashв Mozilla FirefoxпользователидолжныпосетитьстраницузагрузкиAdobe.
В браузере Mozilla заходим на официальный сайт разработчика и устанавливаем обновление
Важно! С недавних пор последняя версия Mozilla Firefox не поддерживает флеш-плеер и некоторые другие плагины, поэтому его может не быть в списке.
Flash повсеместно рассматривается как небезопасное решение, а новые веб-стандарты типа HTML5 продолжают лидировать. Программы на основе этой устаревшей технологии все еще не вымерли, поэтому вы будете встречать их в Интернете довольно долгое время.
Видео — Как скачать и установить Adobe Flash Player в Windows 10
Используемые источники:
- http://virtmachine.ru/adobe-flash-player-chto-eto-za-programma-i-nuzhna-li-ona.html
- http://ironfriends.ru/nuzhen-li-vam-adobe-flash-player/
- https://pc-consultant.ru/soft/kak-obnovit-flesh-pleer-na-vindovs-10/







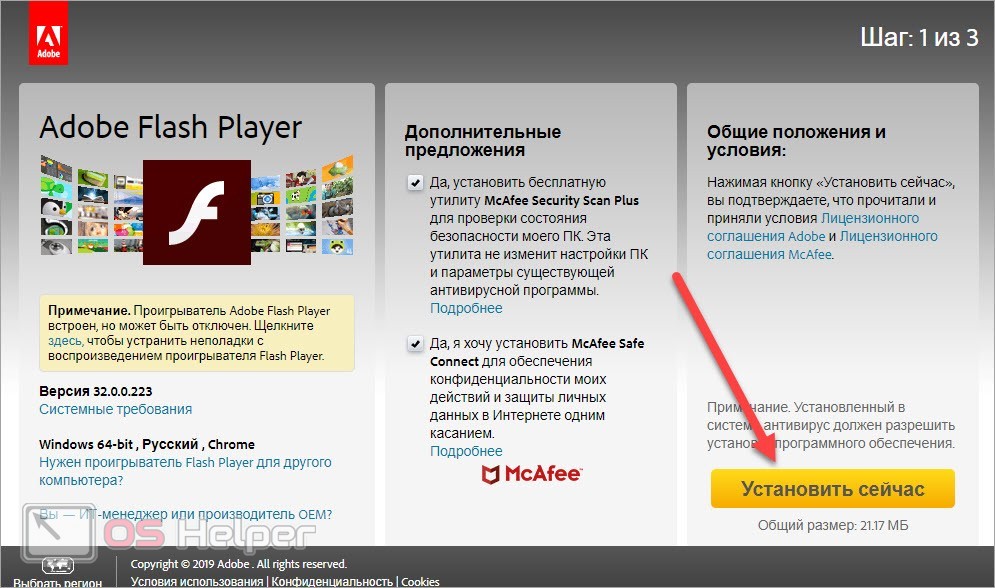
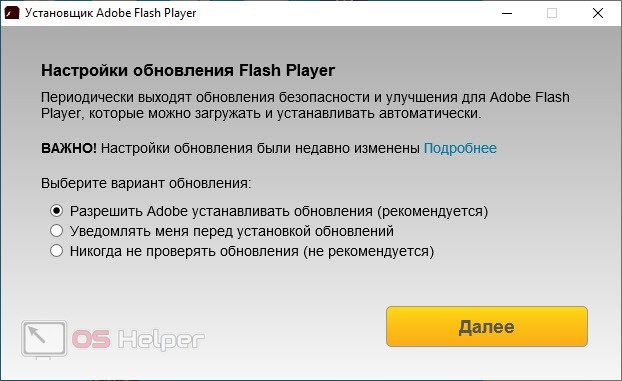
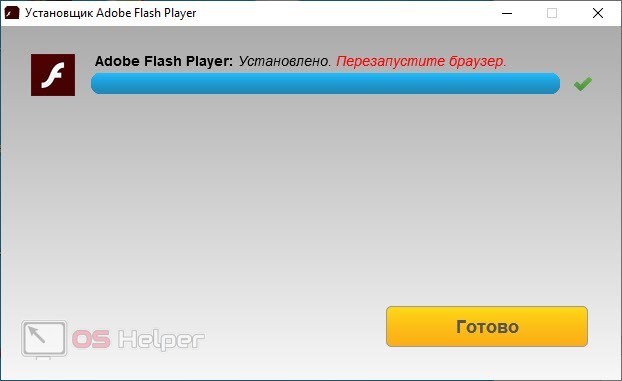
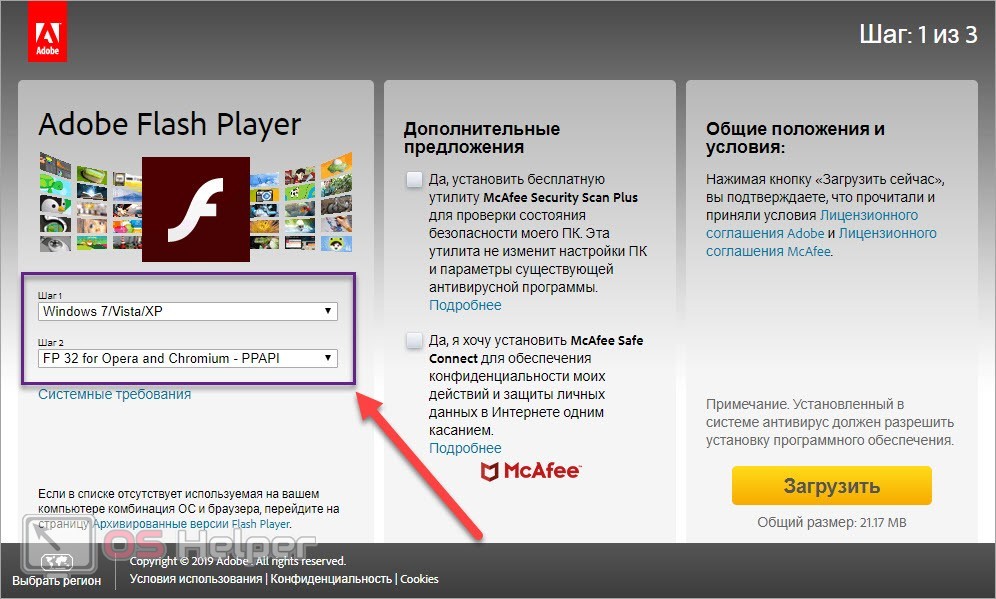


 Открываем «Пуск» и нажимаем по шестеренке
Открываем «Пуск» и нажимаем по шестеренке Переходим в раздел «Обновление и безопасность»
Переходим в раздел «Обновление и безопасность» В «Центре обновления Windows» нажимаем «Проверка наличия обновлений»
В «Центре обновления Windows» нажимаем «Проверка наличия обновлений» Если доступна версия обновления флеш плеера, нажимаем «Установить сейчас» или «Restart now»
Если доступна версия обновления флеш плеера, нажимаем «Установить сейчас» или «Restart now» Нажимаем «Скачать Uninstaller для flash-плеера»
Нажимаем «Скачать Uninstaller для flash-плеера»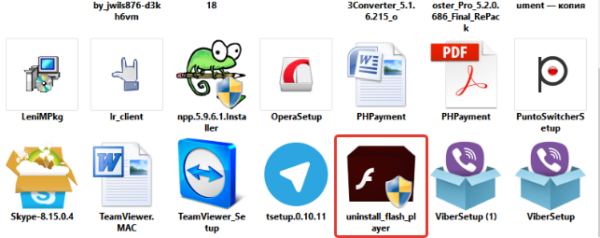 В папке «Загрузки» открываем установочный файл двойным щелчком левой кнопкой мыши
В папке «Загрузки» открываем установочный файл двойным щелчком левой кнопкой мыши Нажимаем «Удаление»
Нажимаем «Удаление» Флеш плеер удален, нажимаем «Готово»
Флеш плеер удален, нажимаем «Готово» На сайте разработчика выбираем параметры для своего компьютера и браузера, нажимаем «Загрузить»
На сайте разработчика выбираем параметры для своего компьютера и браузера, нажимаем «Загрузить»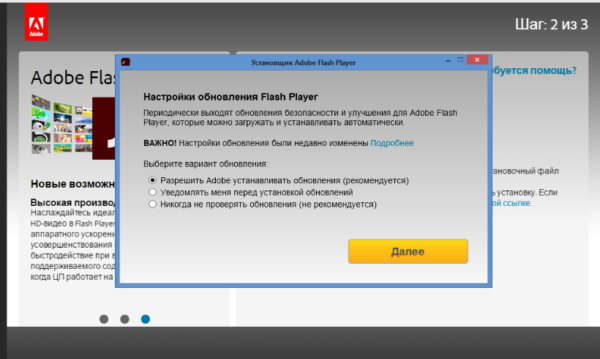 Отмечаем пункт, который рекомендует разрабочтик «Разрешить Adobe устанавливать обновления»
Отмечаем пункт, который рекомендует разрабочтик «Разрешить Adobe устанавливать обновления» Двойным кликом левой кнопки мыши запускаем установочный файл
Двойным кликом левой кнопки мыши запускаем установочный файл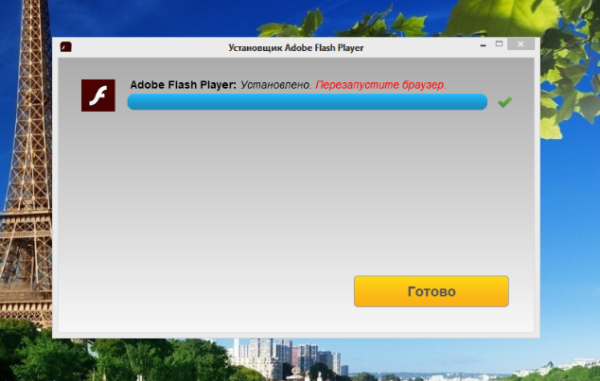 При установке следуем инструкции установщика
При установке следуем инструкции установщика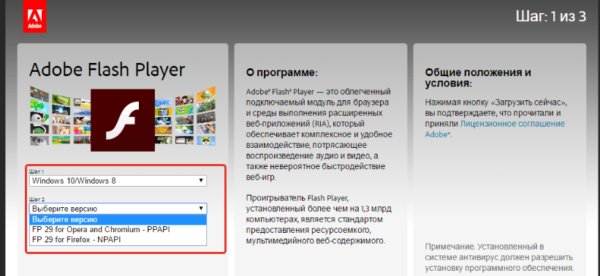 Для каждого браузера нужно поочередно установить каждый плагин, в зависимости от количества используемых браузеров
Для каждого браузера нужно поочередно установить каждый плагин, в зависимости от количества используемых браузеров Заходим в меню браузера, открываем «Дополнения»
Заходим в меню браузера, открываем «Дополнения» Открываем раздел «Плагины», выбираем «Shockwave Flash», а затем опцию «Всегда включать»
Открываем раздел «Плагины», выбираем «Shockwave Flash», а затем опцию «Всегда включать» В браузере Mozilla заходим на официальный сайт разработчика и устанавливаем обновление
В браузере Mozilla заходим на официальный сайт разработчика и устанавливаем обновление