In this post we will see how to upgrade Windows Server 2008 R2 to Windows Server 2012. It’s been an year that Microsoft has released Windows Server 2012, when Windows Sever 2012 was released the IT professionals were eager to know what’s new in Windows Server 2012 and i was one of them. Microsoft releases all of its operating systems in multiple editions, which provides consumers with varying price points and feature sets. While choosing the edition make sure you choose the edition that suits your requirements. Before we go ahead and deploy Server 2012, let’s take a look at editions of Windows Server 2012.
1) Windows Server 2012 Datacenter Edition – The Datacenter edition is designed for large and powerful servers with up to 64 processors and fault-tolerance features such as hot add processor support. This edition is available only through the Microsoft volume licensing program and from original equipment manufacturers bundled with a server.
2) Windows Server 2012 Standard Edition – This is a fully functional edition of Windows Server 2012. Frankly speaking there is no much difference between Datacenter and Standard Edition of Windows Server 2012. What differentiates these 2 editions is the number of virtual machine instances that is permitted by the license. A Standard edition license will entitle you to run up to two VMs on up to two processors. A Datacenter edition license will entitle you to run an unlimited number of VMs on up to two processors.
3) Windows Server 2012 Essentials – The Essentials edition is suited for small organizations, this edition includes all the features of Standard and Datacenter edition except the Server Core, Hyper-v and ADFS (Active Directory Federation Services).
4) Windows Server 2012 Foundation – This edition is designed for small businesses that require only basic server features such as file and print services and application support. The edition includes no virtualization rights and is limited to 15 users.
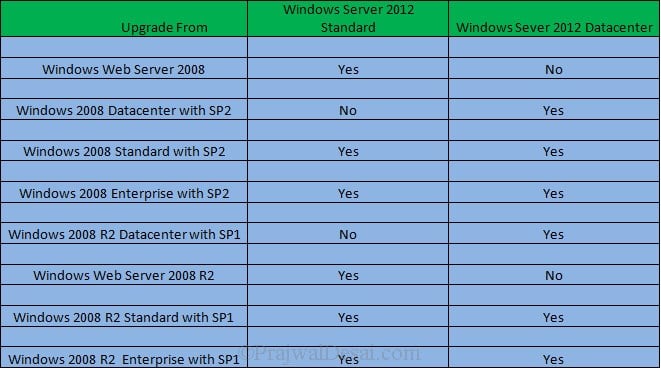
If i were to upgrade my existing windows server 2008 R2 Enterprise server to windows server 2012 i would first choose the edition and then i would check the upgrade paths. I have created a table which shows whether you can upgrade to windows server 2012 with you present operating system.
Lets take a look at hardware requirements for upgrading our server to windows server 2012. Windows Server 2012 requires minimum of 16 GB to 32 GB of disk space. When you install Windows Server 2012 it occupies 15.1 GB of space approximately but its good to allocate at least 32 GB of drive space for Windows Server 2012. You would require 1.4 GHz 64-bit processor, 512 MB of RAM, 32 GB of disk space, DVD Drive, Super VGA (800×600) or higher resolution monitor, keyboard and mouse.
The Windows Server 2012 evaluation software is available in Standard and Datacenter editions, you can download Windows Server 2012 from here :- http://technet.microsoft.com/en-in/evalcenter/hh670538.aspx.
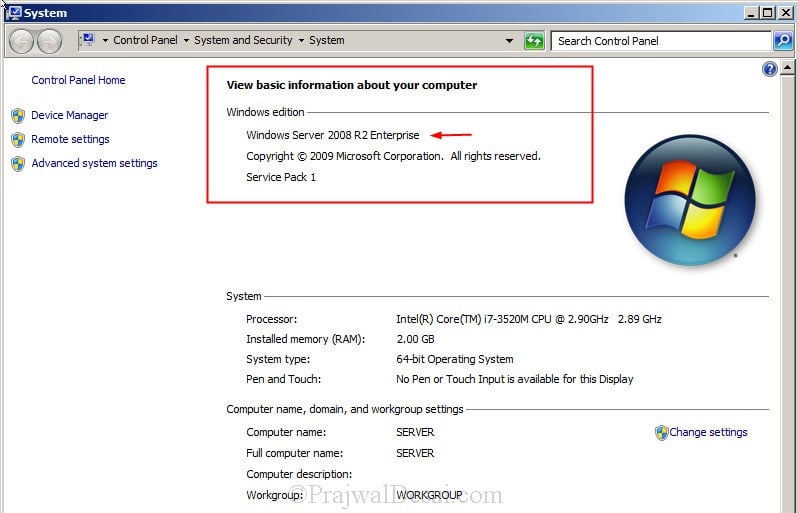
In this post i will be showing you how to upgrade a windows server 2008 R2 Enterprise SP1 to Windows Server 2012 Datacenter. Note that the existing server is in workgroup, do not consider this post to upgrade your domain controller to windows server 2012. I will be creating a separate post to show the upgrade of domain controller running on windows server 2008 r2 to windows server 2012.
Insert the windows server 2012 DVD into the DVD-ROM and click on Run Setup.exe.
On the Windows Setup screen, click on Install now.
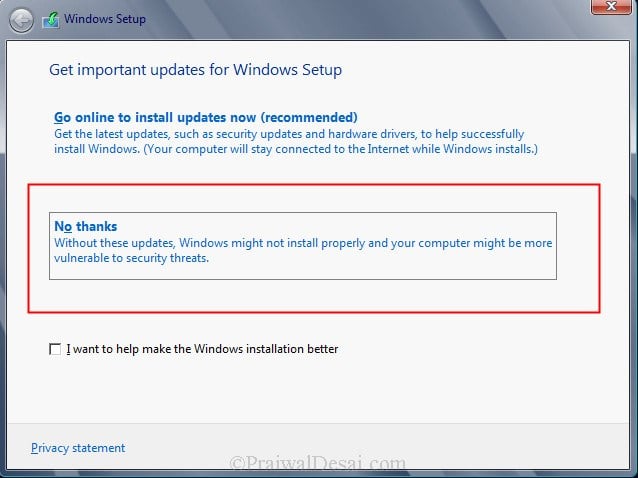
If you want to get security updates and latest drivers for your operating system select Go online to install updates now. We can also do a windows update once the upgrade is completed, so select No, Thanks.
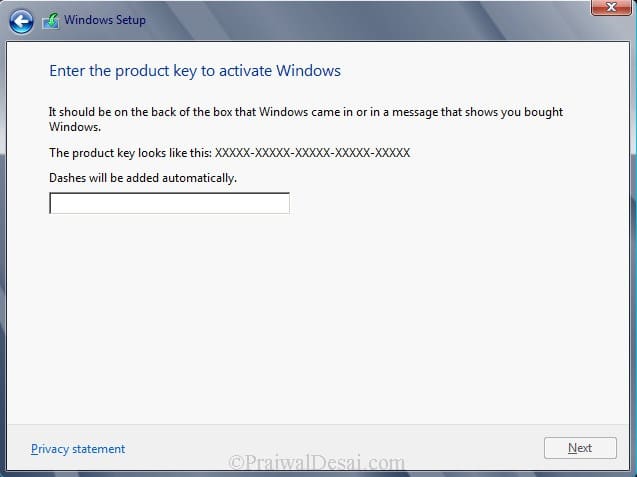
Enter your product key for windows server 2012 and click on Next. In this step i have entered server 2012 Datacenter edition key. Click on Next.
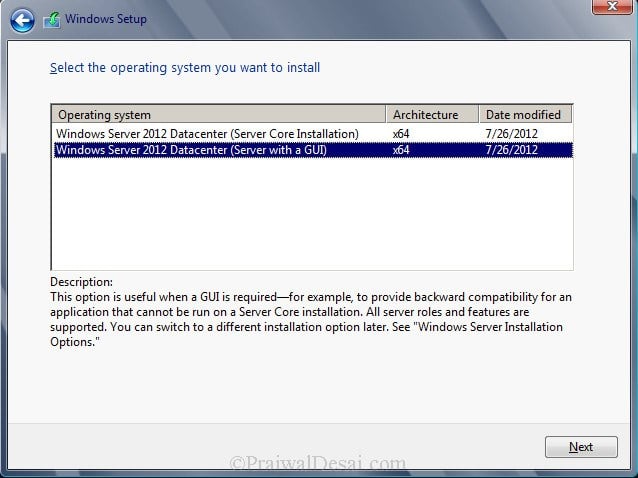
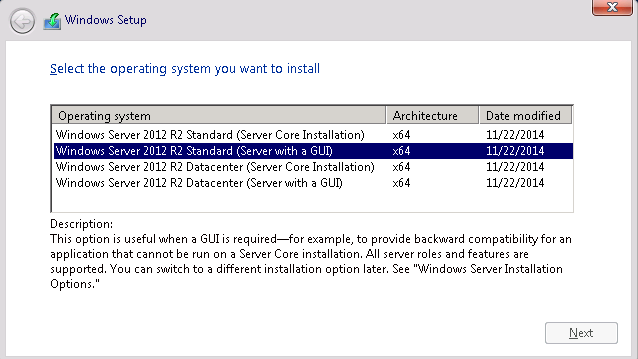
Server core installation has no Server Manager or any other MMCs to manage roles and features. The management must be done either remotely from a client machine or through the command prompt or Powershell at the console. There is no Start menu, no desktop Explorer shell, no Microsoft Management Console, and virtually no graphical applications. All you see when you start the computer is a single window with a command prompt. In this step i will select the second installation mode, Windows Server 2012 Datacenter (Server with a GUI). Click on Next.
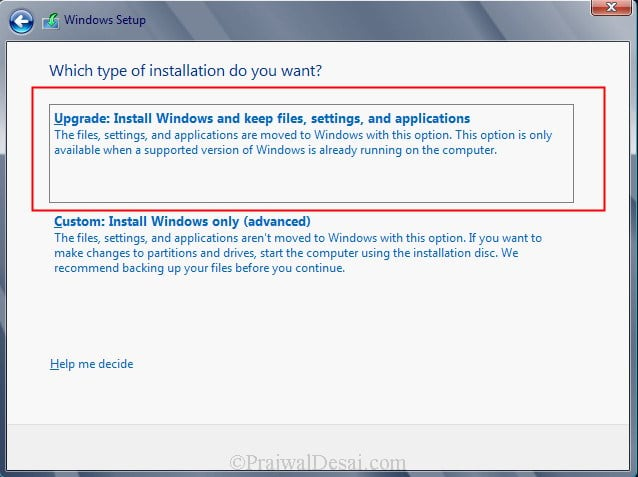
Select Upgrade: Install Windows and Keep files, settings and applications. This will keep existing files, settings and applications and upgrade our server to windows 2012.
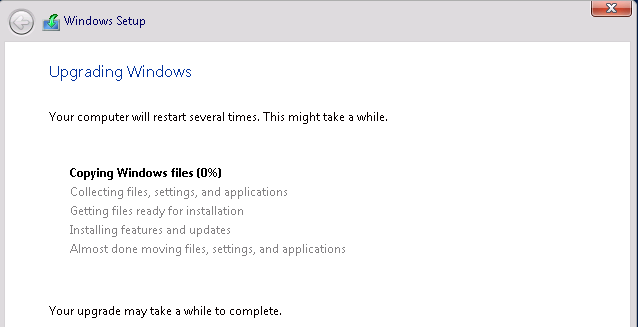
The upgrade will take close to 20 minutes. Sit back and relax until the upgrade is complete.
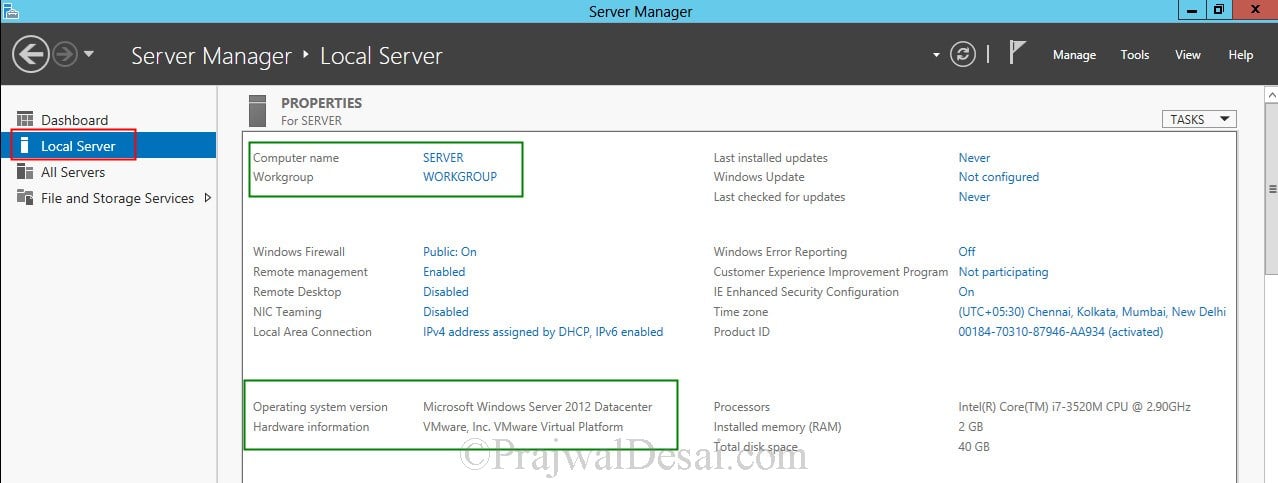
The upgrade from windows server 2008 R2 Enterprise to windows server 2012 Datacenter is complete. Let’s login to the server and check for the edition.
Click on Server Manager, Click on Local Server, check the properties of server. We see that the operating system version is Microsoft Windows Server 2012 Datacenter. The upgrade process has been completed successfully.

Prajwal Desai is a Microsoft MVP in Enterprise Mobility. He writes articles on SCCM, Intune, Configuration Manager, Microsoft Intune, Azure, Windows Server, Windows 11, WordPress and other topics, with the goal of providing people with useful information.
Hello fellow sys admins! In the following article, we will walk through an in-place upgrade from Windows Server 2008 R2 to 2012 R2. So let us dive right in.
The first step in any upgrade is to get the Installation Media. If you are using a Virtual Machine, then it’s as simple as adding the ISO to the Virtual CD-R Drive, either using the Hyper-V machine settings or the VMware console. If you are upgrading a physical server, then just unpack the ISO and copy it to either a secondary drive or flash drive, or you can just run it from a network share.
In our scenario, I am running the installation from a network share. In both cases, the upgrade process is the same; there is no difference between the VM OS or physical server OS as we all know so well.
Therefore, as I mentioned before. I have unpacked the ISO using WinRAR.
Afterwards, I just ran the setup.exe from inside the OS. A small tip is to make sure you don’t have any other users logged into the server in any way, RDP or console, since the prerequisite check will fail and you will have to go through the setup again.
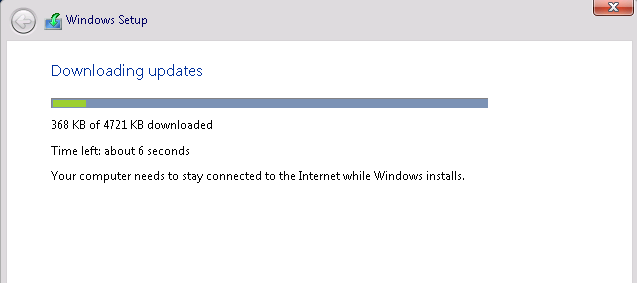
Once in the Setup Wizard, we will download the latest updates, which are required in order to bring the server to the latest compatible state for upgrading to Windows Server 2012 R2. This is a very important step, which most people choose to ignore, but it will save you a lot of hassle after you upgrade.
Next, we will choose the version of Windows Server 2012 R2. In our case, we are going from Windows Server 2008 R2 Standard Edition to Windows Server 2012 R2 Standard Edition.
Afterwards, we read the EULA from top to bottom, since it is very important. Hit Next and we then get to the eternal crossroad, where we have to choose whether to upgrade or to format. Since we want to upgrade, we will of course choose Upgrade!
Once Upgrade is selected, there is no going back. The train has left the station. The Upgrade process has commenced. Well, not really. First, it’s going to do the compatibility check, and if all goes well, you will be greeted with the following screen.
Then we hit Next, take a deep breath and watch and wait as the new version of Windows is being installed on top of our old one.
If everything goes well, we will be greeted with the Windows Server 2012 R2 loading screen and the Finalizing Settings window. This process will take a while, so even if at times it appears to be doing nothing, go take a break, come back later and then login to your new OS.
Thank you for taking this journey with me through the Upgrade of Windows Server 2008 R2 to Windows Server 2012 R2. Until next time! Enjoy!
- Remove From My Forums
-
Question
-
How do i upgrade windows server 2008 r2 32bit enterprise version to windows server 2012 r2?
Answers
-
Hi,
In my opinion, you can always add additional domain controller. I would highly recommend to switch to x64 version since there is no upgrade path to Windows 2008 R2 x32.
Installing new x64 Windows 2008 R2 machine, promote it to domain controller, then move all AD roles to this new DC, decommission the old x32 one and if you can afford it add another x64 DC for best practice. Never run AD on a single DC except if you are
testing. For production always use 2. If you are going to do as I suggest, please be patient. Add DC, wait for replication to take place, check DNS records and then move on. After each step check your logs.Some related article for your reference:
Upgrading an Active Directory Domain from Windows Server 2008 or Windows Server 2008 R2 to Windows Server 2012 or Windows Server 2012 R2
Best Regards,
Alvin Wang
Please remember to mark the replies as answers if they help and un-mark them if they provide no help. If you have feedback for TechNet Subscriber Support, contact tnmff@microsoft.com.
-
Marked as answer by
Tuesday, May 17, 2016 5:33 AM
-
Marked as answer by
- Remove From My Forums
-
Question
-
How do i upgrade windows server 2008 r2 32bit enterprise version to windows server 2012 r2?
Answers
-
Hi,
In my opinion, you can always add additional domain controller. I would highly recommend to switch to x64 version since there is no upgrade path to Windows 2008 R2 x32.
Installing new x64 Windows 2008 R2 machine, promote it to domain controller, then move all AD roles to this new DC, decommission the old x32 one and if you can afford it add another x64 DC for best practice. Never run AD on a single DC except if you are
testing. For production always use 2. If you are going to do as I suggest, please be patient. Add DC, wait for replication to take place, check DNS records and then move on. After each step check your logs.Some related article for your reference:
Upgrading an Active Directory Domain from Windows Server 2008 or Windows Server 2008 R2 to Windows Server 2012 or Windows Server 2012 R2
Best Regards,
Alvin Wang
Please remember to mark the replies as answers if they help and un-mark them if they provide no help. If you have feedback for TechNet Subscriber Support, contact tnmff@microsoft.com.
-
Marked as answer by
Tuesday, May 17, 2016 5:33 AM
-
Marked as answer by
- Remove From My Forums
-
Вопрос
-
Имеется Windows Server 2008R2 SP1. Установлены роли: DC, DNS, DHCP, CA, IIS для CA; этот сервер — root CA.
Как правильно обновить этот сервер с его ролями до 2012? особенно переживаю за CA…
Ответы
-
Понимаете, любой процесс апгрейда — непредсказуем. Как двух одинаковых людей, так и двух одинаковых систем не бывает. Даже если Вы откатаете upgrade-in-place на тестовой машине, всё равно остаётся вероятность, что на рабочей что-то пойдёт не так. Если случаются
проблемы даже при установке рекомендованных патчей, то что уж говорить про обновление всей системы, да ещё с такими важными ролями?Да, Microsoft считает возможным такой апгрейд. Но он не гарантирует его успешность. Сколько рабочего времени Ваша компания готова потерять? Сколько времени она проживёт без этого AD, DHCP и root CA? Сколько времени у Вас уйдёт на восстановление убитой системы
из дампа? Если Вы готовы дать на все эти вопросы ответы, то заданный в начале темы вопрос получит ответ.Ну, а кратко так: сделайте надёжный бэкап. Подготовьтесь к восстановлению системы в случае неудачи. И — вперёд…
Сергей Панченко
-
Предложено в качестве ответа
5 мая 2013 г. 14:04
-
Помечено в качестве ответа
Petko KrushevMicrosoft contingent staff, Moderator
6 мая 2013 г. 10:30
-
Предложено в качестве ответа
Прочитано:
1 652
Итак появилось свободное время в которое никто не отвлекает, все налажено и все работает, а потому пора заняться самообразование ведь никто кроме меня не заинтересован чтобы я был квалификационным сотрудником. Но это все лирика, а т. к. мой блог в последнее время что-то замер в наполнении практический заметок, то пора это дело исправлять. Может конечно всему виной хорошая погода, а не загруженность, но это не важно. Когда в твою команду приходит новый сотрудник и рассказывает что он успешно переводил всю инфраструктуру на новый уровень в частности серверной операционной системы становится как-то жалко себя, — а почему же я сам этого не сделал и сижу на отлаженном старом. Без думно переходить на что-то не опробовав самостоятельно я не делаю — только тест тест тест и потом практика. И вот сейчас я покажу все шаги через которые я прошел дабы произвести миграцию с домена уровня Server 2008 R2 до уровня Server 2012 R2.
Ну что ж пора:
1) Домен (polygon.local) на системе Server 2008 R2 Ent (srv-dc) развернутый по шагам заметки. Текущие действующие роли: AD + DHCP + DNS, IP Address = 10.9.9.1
2) Развернут Server 2012 R2 Standard (srv-ad), IP Address = 10.9.9.20 получен от DHCP сервера.
3) Поставлены все обновления на Server 2012 R2, предварительно у Вас должен быть развернут сервис обновления Windows систем именуемый, как WSUS, IP Address = 10.9.9.3
4) Ввести в текущий домен систему Server 2012 R2
Win + X — Control Panel — Category (Small icons) — System — Advanced system settings — вкладка Computer Name — Change
Computer name: srv-ad
Member of (Domain:) polygon.local
и нажимаю кнопку OK, затем указываю идентификационные данные учетной записи у которой есть права ввода станций в домен, в моем случае:
Login: ekzorchik
Pass: 712mbddr@
и нажимаю кнопку OK, успехом считается появление сообщения: Welcome to the polygon.local domain
и нажимаю кнопку Ok, OK (соглашаемся о том чтобы изменения применились текущую систему следует перезагрузить), Close (окна System Properties), Restart Now (окна Microsoft Windows).
5) Опираясь на инструкцию (не которые моменты будут отличаться) установки AD сделать данную систему как домен контроллер, а до этого авторизуюсь под учетной записью ekzorchik&712mbddr@, данная учетная запись является Администратором домена и обладает всеми группами которые нужны для полного администрирования AD (Domain Admins, Enterprise Admins, Schema Admins) и обязательно не забудьте сделать статический IP адрес у данного сервера.
6) Текущее положение FSMO ролей
srv-ad.polygon.local: Win + X — Command Prompt (Admin) —
C:Windowssystem32>netdom query fsmo
Schema master srv-dc.polygon.local
Domain naming master srv-dc.polygon.local
PDC srv-dc.polygon.local
RID pool manager srv-dc.polygon.local
Infrastructure master srv-dc.polygon.local
The command completed successfully.
, как видно всеми ролями владеет сервер под управлением Windows Server 2008 R2 (Ent), ну что же буду мигрировать на текущий:
Текущий список всех контроллеров домена:
C:Windowssystem32>dsquery server -forest
«CN=SRV-DC,CN=Servers,CN=Default-First-Site-Name,CN=Sites,CN=Configuration,DC=polygon,DC=local»
«CN=SRV-AD,CN=Servers,CN=Default-First-Site-Name,CN=Sites,CN=Configuration,DC=polygon,DC=local»
Дальнейшие действия опираются на следующую заметку.
Важно добиться чтобы вывод команды netdom query fsmo показал что все роли у srv-ad.polygon.local. У меня уже первая ошибка (или не знаю как по другому выразится), при попытке смены владельца Schema появляется всплывающее сообщение вида:
Active Directory Schema snap-in is not connected to the schema operations master. You will not be able to perform any changes Schema modifications can only be made on the schema FSMO holder.
Изменив шаги на:
Win + X — Command Prompts (Admin)
C:Windowssystem32>ntdsutil
ntdsutil: roles
fsmo maintenance: connections
server connections: connect to server srv-ad.polygon.local
Binding to srv-ad.polygon.local …
Connected to srv-ad.polygon.local using credentials of locally logged on user.
server connections: quit
fsmo maintenance: seize RID Master
fsmo maintenance: seize PDC
fsmo maintenance: seize infrastructure master
fsmo maintenance: seize naming master
fsmo maintenance: seize schema master
C:Windowssystem32>netdom query fsmo
Schema master srv-ad.polygon.local
Domain naming master srv-ad.polygon.local
PDC srv-ad.polygon.local
RID pool manager srv-ad.polygon.local
Infrastructure master srv-ad.polygon.local
The command completed successfully.
Отлично все роли на новом сервере под управлением Windows Server 2012 R2 (Std), теперь удаляю контроллер домена под управлением Windows Server 2008 R2 из глобального каталога (Global Catalog):
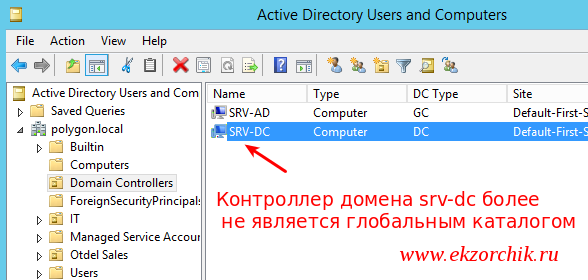
Win + X — Control Panel — Administrative Tools — Active Directory Sites and Services —
Sites — Default-First-Site-Name — Server — разворачиваю и нахожу SRV-DC — затем открываю свойства (Properties) на NTDS Settings и внутри вкладки General снимаю галочку Global Catalog после чего нажимаю Apply , OK. Когда откроем оснастку Active Directory Users and Computer в организационном юните Domain Controllers будет видно, что сервер srv-dc больше не является глобальным каталогом:
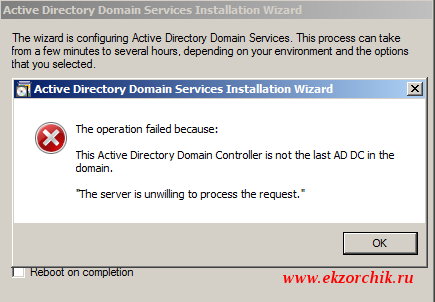
Отлично, теперь ранее имевший место быть контроллер домена со всеми ролями по обслуживанию инфраструктуры можно деинсталлировать с помощью команды запущенной с правами администратора — dcpromo:
Start — All Programs — Accessories — Command Prompts (Run as Administrator) —
dcpromo, Next — отмечаю галочкой: Delete the domain because this server is the last domain controller in the domain, Next — Yes — указываю пароль на административный аккаунт указываемый при разворачивании домена:
Password: 712mbddr@
Confirm password: 712mbddr@
И нажимаю кнопку Next , Next но вот почему-то не все так просто как должно быть:
раз установщик не хочет по хорошему буду по плохому — удалю принудительно:
С:Windowssystem32dcpromo /forceremoval, Yes — Next — Next — указываю пароль на административный аккаунт указываемый при разворачивании домена:
Password: 712mbddr@
Confirm password: 712mbddr@
И нажимаю кнопку Next, — Next — отмечаю галочкой Reboot on competion и вот только после принудительно удаления контроллер домена удаляется без каких либо проблем:
По окончании процедуры удаления нажимаем Finish — Restart Now.
Теперь нужно с мигрировать роль DHCP сервера с сервера srv-dc:
На srv-dc экспортирую настройки DHCP в файл:
Start — Control panels — Administrative Tools — DHCP — DHCP — srv-dc.polygon.local и через правый клик выбираю Backup… и указываю путь сохранения: c:1 — внутри сохраняется файл: DhcpCfg
копирую данный файл (каталог net и файл DhcpCfg) на srv-ad:
c:>xcopy c:1* \10.9.9.20c$1
но сперва поднять роль DHCP на srv-ad делать это лучше через мастер добавления ролей:
Win + X — Control Panel — Administrative Tools — Server Manager — и добавляю роль DHCP (и устанавливаю в довесок компоненты DHCP Server Tools. Почему в Microsoft ни как не могут сделать чтобы при добавлении/удалении ролей системы не нужно было перезагружать не понимаю. Перезагружаю, после запускаю оснастку DHCP:
Win + X — Control Panel — Administrative Tools — DHCP — DHCP — srv-ad.polygon.local и через правый клик мышью импортирую настройки DHCP взятые с ранее имевшего место быть сервера srv-dc.polygon.local — Restore — C:DhcpCfg
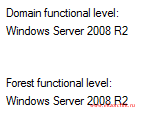
Следующим шагом проверяю какой функциональный уровень домена и леса через оснастку Active Directory Users and Computer — polygon.local — Properties и вижу не порядок (разве все это затевалось чтобы остаться как и было):
или же посмотреть текущий уровень домена можно через консоль командной строки PowerShell:
Win + X — Command Prompts (Admin) —
C:Windowssystem32>cd c:WindowsSystem32WindowsPowerShellv1.0
c:WindowsSystem32WindowsPowerShellv1.0>powershell.exe
Windows PowerShell
Copyright (C) 2013 Microsoft Corporation. All rights reserved.
c:WindowsSystem32WindowsPowerShellv1.0> import-module -name activedirectory
PS C:WindowsSystem32WindowsPowerShellv1.0> get-adforest | format-table name,
ForestMode
name ForestMode
—- ———-
polygon.local Windows2008R2Forest
PS C:WindowsSystem32WindowsPowerShellv1.0> exit
C:Windows>cd %systemroot%system32
Буду изменять:
через оснастку Active Directory Users and Computer — polygon.local — Raise domain functional level и опачки, мастер говорит что я не могу изменить функциональность домена потому что это домен включен в Active Directory Domain Controllers
Ладно значит нужно удалить из текущего домена (За основу беру заметку по удалению неисправного контроллера домена:) все упоминания об ранее имевшем место быть srv-dc:
C:Windowssystem32>ntdsutil
ntdsutil: metadata cleanup
metadata cleanup: connections
server connections: connect to server srv-ad
Binding to srv-ad …
Connected to srv-ad using credentials of locally logged on user.
server connections: quit
metadata cleanup: select operation target
select operation target: list sites
Found 1 site(s)
0 — CN=Default-First-Site-Name,CN=Sites,CN=Configuration,DC=polygon,DC=local
select operation target: select site 0
Site — CN=Default-First-Site-Name,CN=Sites,CN=Configuration,DC=polygon,DC=local
No current domain
No current server
No current Naming Context
select operation target: list servers in site
Found 2 server(s)
0 — CN=SRV-DC,CN=Servers,CN=Default-First-Site-Name,CN=Sites,CN=Configuration,DC
=polygon,DC=local
1 — CN=SRV-AD,CN=Servers,CN=Default-First-Site-Name,CN=Sites,CN=Configuration,DC
=polygon,DC=local
select operation target: select server 0
Site — CN=Default-First-Site-Name,CN=Sites,CN=Configuration,DC=polygon,DC=local
No current domain
Server — CN=SRV-DC,CN=Servers,CN=Default-First-Site-Name,CN=Sites,CN=Configurati
on,DC=polygon,DC=local
DSA object — CN=NTDS Settings,CN=SRV-DC,CN=Servers,CN=Default-First-Site
-Name,CN=Sites,CN=Configuration,DC=polygon,DC=local
DNS host name — srv-dc.polygon.local
Computer object — CN=SRV-DC,OU=Domain Controllers,DC=polygon,DC=local
No current Naming Context
select operation target: list domains
Found 1 domain(s)
0 — DC=polygon,DC=local
select operation target: select domain 0
Site — CN=Default-First-Site-Name,CN=Sites,CN=Configuration,DC=polygon,DC=local
Domain — DC=polygon,DC=local
Server — CN=SRV-DC,CN=Servers,CN=Default-First-Site-Name,CN=Sites,CN=Configurati
on,DC=polygon,DC=local
DSA object — CN=NTDS Settings,CN=SRV-DC,CN=Servers,CN=Default-First-Site
-Name,CN=Sites,CN=Configuration,DC=polygon,DC=local
DNS host name — srv-dc.polygon.local
Computer object — CN=SRV-DC,OU=Domain Controllers,DC=polygon,DC=local
No current Naming Context
select operation target: quit
metadata cleanup: remove selected server
Transferring / Seizing FSMO roles off the selected server.
Removing FRS metadata for the selected server.
Searching for FRS members under «CN=SRV-DC,OU=Domain Controllers,DC=polygon,DC=local».
Deleting subtree under «CN=SRV-DC,OU=Domain Controllers,DC=polygon,DC=local».
The attempt to remove the FRS settings on CN=SRV-DC,CN=Servers,CN=Default-First-
Site-Name,CN=Sites,CN=Configuration,DC=polygon,DC=local failed because «Element not found.»;
metadata cleanup is continuing.
«CN=SRV-DC,CN=Servers,CN=Default-First-Site-Name,CN=Sites,CN=Configuration,DC=po
lygon,DC=local» removed from server «srv-ad»
metadata cleanup: quit
ntdsutil: quit
Удаляю хост srv-dc из оснастки Active Directory Sites and Services
Удаляю все записи в DNS относящиеся к хосту srv-dc
и вот только после этого появляется возможность изменить функциональный уровень текущего домен контроллера с Server 2008 R2 на более высокий:
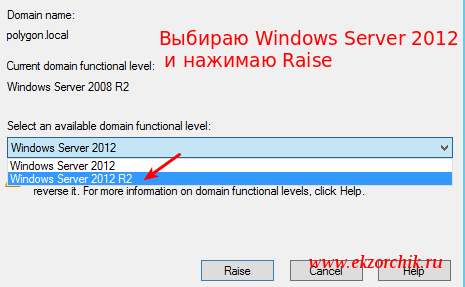
Active Directory Users and Computer — polygon.local — Raise domain functional level… — теперь доступны следующие уровни: Windows Server 2012 & Windows Server 2012 R2 — выбираю R2 и нажимаю Raise, OK, OK
И по такому же принципу изменяем функциональный уровень и для всего леса:
Active Directory Domains and Trusts — Active Directory Domains and Trusts [srv-ad.polygon.local] —
Raise Forest Functional Level… — Select an available forest functional level: сейчас установлено Windows Server 2012 изменяю на Windows Server 2012 R2 и нажимаю Raise, OK, OK. Изменения применяют сейчас, но все же это же Windows по возможности осуществите перезагрузку всего сервера: Win + X — Shut down or sign out — Restart — Continue — после перезагрузки проверяю какой функциональный уровень и вуаля и там и там значится Windows Server 2012 R2, а это новые возможности. Вот теперь я готов чтобы перевести все имеющее место быть собственно развернутое на самое последнее и стабильное. На этом я прощаюсь, с уважением автор блога — ekzorchik.
-
-
February 17 2015, 16:41
- IT
- Cancel
Так-то я уже несколько раз in-place обновлял разные системы, серверы с CA, WSUS`ом или Veeam Backup`ом, но недавно решил замахнуться на святое — DC. На удивление, всё прошло неплохо. Не то, чтобы на ура, но скорее хорошо.
Итак, DC, он же Print Server, он же Remote Desktop Licensing, он же NPS (RADIUS). Всё стандартно — adprep, setup.exe, «Update current installation» (или как там). RD Licensing потребовал переактивации потом, BIOS->UEFI, ну и всё, пожалуй. А, ещё — убедившись, что всё поднялось и заработало, удалил каталог Windows.old (что не очень то просто, см. ниже).
На всякий случай, памятка.
Сам каталог так просто не убивается, средство для его удаления («Disk cleanup utility») есть только в «Desktop Experience», который мне на DC нахрен не нужен. Поэтому призовём на помощь великий гугль и сделаем так — скачаем junction.exe и поместим её куда-нибудь в %PATH%, после чего запустим маленький PowerShell:
$ErrorActionPreference = "Inquire"
junction.exe -accepteula -s -q C:windows.old | out-file $env:tempjuncts.txt -force
foreach ($line in [System.IO.File]::ReadLines("$env:tempjuncts.txt"))
{
if ($line -match "^\\")
{
$file = $line -replace "(: JUNCTION)|(: SYMBOLIC LINK)",""
& junction.exe -d "$file"
}
}
takeown /F C:windows.old /R /D Y
echo y | cacls C:windows.old /T /G Everyone:F
rm C:windows.old -recurse -force
rm "$env:tempjuncts.txt" -force
Лопатить будет довольно долго, но чего уж, хрен с ним, в конце концов всё удалит.
Неделю погляжу как оно живёт, если ок — следующий DC (fileserver) поедет аналогично. Главное, чтобы XP-клиенты не отвалились