В этой статье мы поговорим об особенностях резервного копирования контроллеров домена Active Directory, рассмотрим, как настроить автоматическое резервное копирование AD с помощью PowerShell и встроенных средств Windows Server.
Содержание:
- Нужно ли бэкапить Active Directory?
- Как проверить дату последнего бэкапа контроллера домена Active Directory?
- Бэкап контроллера домена AD с помощью Windows Server Backup
- Резервное копирование Active Directory с помощью PowerShell
Нужно ли бэкапить Active Directory?
Не раз слышал от знакомых администраторов мысль, что если у тебя несколько (5, 10 и т.д.) территориально разнесенных контроллеров домена Active Directory, то бэкапать AD вообще не нужно, т.к. при нескольких DC вы уже обеспечили высокую отказоустойчивость домена. Ведь в такой схеме вероятность одновременного выхода из строя всех DC стремится к 0, а если один контроллер домена упал, то быстрее развернуть новый DC на площадке, а старый контроллер домена удалить согласно инструкции (или с помощью ntdsutil).
Однако в своей практике я встречался с различными сценариями, когда все контроллеры домена оказались повреждёнными: в одном случае все контроллеры домена (а их было более 20 штук в разных городах) оказались зашифрованными из-за перехвата пароля домена шифровальщиком через утилиту mimikatz (для предотвращения таких схем см. статьи “Защита Windows от mimikatz” и “Защита привилегированных групп администраторов”), в другом случае домен положила репликация поврежденного файла NTDS.DIT.
В общем, бэкапить AD можно и нужно. Как минимум вы должны регулярно создавать резервные копии ключевых контроллеров доменов, владельцев ролей FSMO (Flexible single-master operations). Вы можете получить список контролеров домена с ролями FSMO командой:
netdom query fsmo
Как проверить дату последнего бэкапа контроллера домена Active Directory?
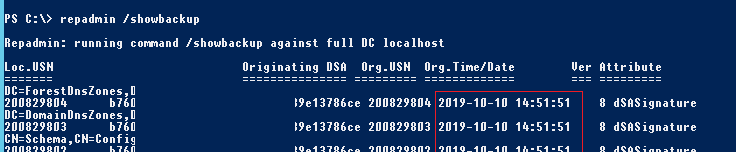
Вы можете проверить, когда создавалась резервная копия текущего контроллера домена Active Directory с помощью утилиты repadmin:
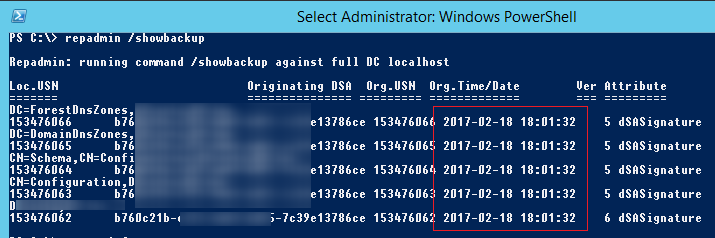
repadmin /showbackup
В данном примере видно, что последний раз бэкап DC и разделов AD выполнялся 2017-02-18 18:01:32 (скорее всего он не делался с момента развертывания контроллера домена).
Вы можете получить статус по резервному копированию всех DC в домене командой:
repadmin /showbackup *
Если ваши контроллеры домена запущены на виртуальных машинах, и вы создаете бэкап через снапшоты (см. пример с резервным копированием Hyper-V), то при бэкапе эти даты не обновляются по понятной причине. В большинстве современных средств резервного копирования есть опция, позволяющая указать что это DC и при бэкапе нужно обновлять данные в каталоге LDAP.
Бэкап контроллера домена AD с помощью Windows Server Backup
Если у вас нет специального ПО для резервного копирования, вы можете использовать для создания резервных копий встроенный Windows Server Backup (этот компонент пришел на замену NTBackup). Вы можете настроить автоматическое задание резервного копирования в графическом интерфейсе Windows Server Backup, но у него будут ряд ограничений. Основной недостаток – новая резервная копия сервера всегда будет перезаписывать старую.
При создании резервной копии контроллера домена через WSB, вы создаете резервную копию Состояния системы (System State). В System State попадает база Active Directory (NTDS.DIT), объекты групповых политик, содержимое каталога SYSVOL, реестр, метаданные IIS, база AD CS, и другие системные файлы и ресурсы. Резервная копия создается через службу теневого копирования VSS.
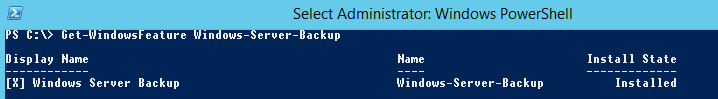
Вы можете проверить, установлен ли компонент Windows Server Backup с помощью PowerShell командлета Get-WindowsFeature:
Get-WindowsFeature Windows-Server-Backup
Если компонент WSB отсутствует, его можно установить с помощью PowerShell:
Add-Windowsfeature Windows-Server-Backup –Includeallsubfeature
Или установите его из Server Manager -> Features.
Я буду сохранять бэкап данного контроллера домена AD в сетевую папку на отдельном выделенном сервере для резевного копирования. Например, путь к каталогу будет таким \srvbak1backupdc01. Настроим NTFS разрешения на этой папке: предоставьте права чтения-записи в этот каталог только для Domain Admins и Domain Controllers.
Резервное копирование Active Directory с помощью PowerShell
Попробуем создать бэкап контроллера домена с помощью PowerShell. Для хранения нескольких уровней копий AD мы будем хранить каждый бэкап в отдельном каталоге с датой создания копии в качестве имени папки.
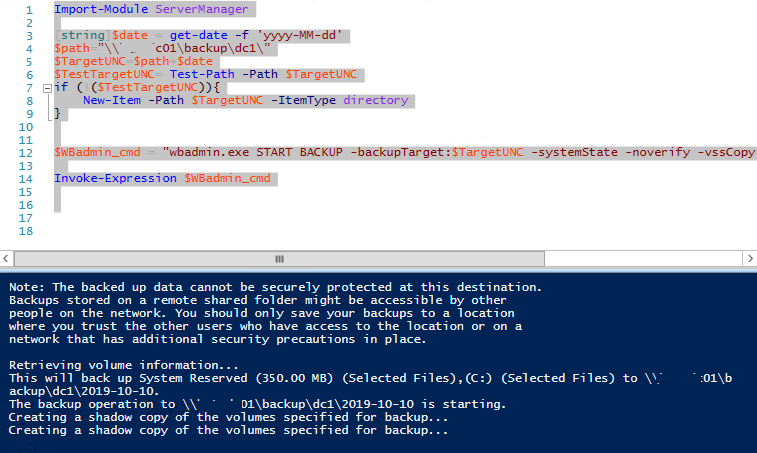
Import-Module ServerManager
[string]$date = get-date -f 'yyyy-MM-dd'
$path=”\srvbak1backupdc1”
$TargetUNC=$path+$date
$TestTargetUNC= Test-Path -Path $TargetUNC
if (!($TestTargetUNC)){
New-Item -Path $TargetUNC -ItemType directory
}
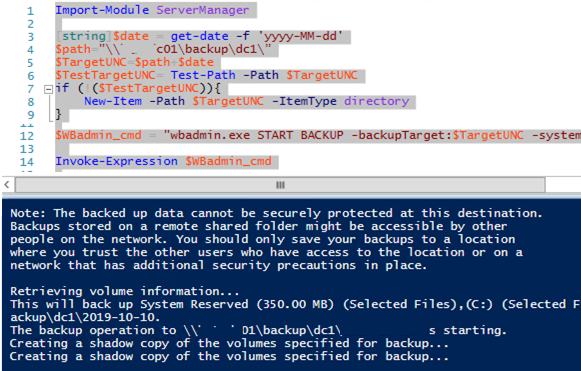
$WBadmin_cmd = "wbadmin.exe START BACKUP -backupTarget:$TargetUNC -systemState -noverify -vssCopy -quiet"
Invoke-Expression $WBadmin_cmd
Запустите данный скрипт. Должна появится консоль wbadmin с информацией о процессе создании резервной (теневой) копии диска:
The backup operation to \srvbak1backupdc12019-10-10 is starting. Creating a shadow copy of the volumes specified for backup...
У меня первая попытка создать бэкап DC завершилась с ошибкой (контролер домена — это виртуальная машина VMWare):
Detailed error: The filename, directory name, or volume label syntax is incorrect. The backup of the system state failed [10.10.2019 8:31].
Я открыл журнал ошибок WSB — C:WindowsLogsWindowsServerBackupBackup_Error-10-10-2019_08-30-24.log.
В файле содержится одна ошибка:
Error in backup of C:windows\systemroot during enumerate: Error [0x8007007b] The filename, directory name, or volume label syntax is incorrect.
Забегая вперед, скажу, что проблема оказалась в некорректном пути в одном из драйверов VMWware Tools.
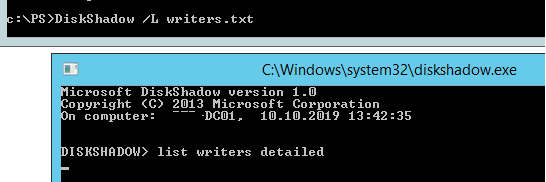
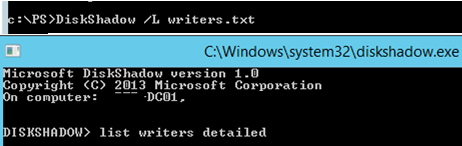
Чтобы исправить эту ошибку, откройте командную строку с правами администратора и выполните:
DiskShadow /L writers.txt
list writers detailed
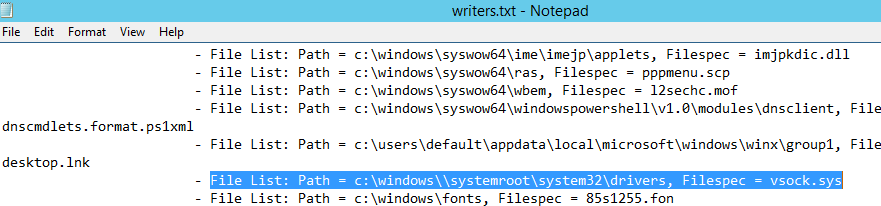
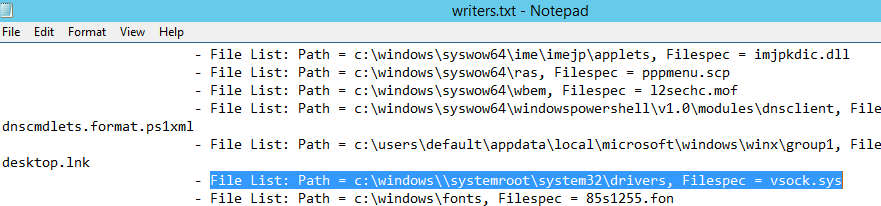
После формирование списка наберите quit и откройте файл «C:WindowsSystem32writers.txt». Найдите в нем строку, содержащую “windows\”.
В моем случае найденная строка выглядит так:
File List: Path = c:windows\systemrootsystem32drivers, Filespec = vsock.sys
Как вы видите, используется неверный путь к драйверу VSOCK.SYS.
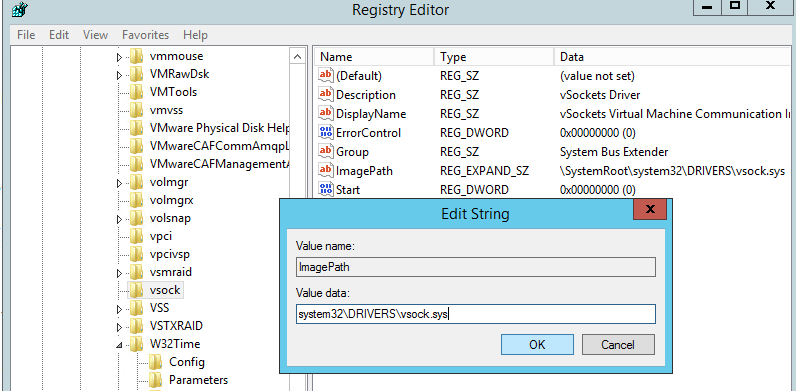
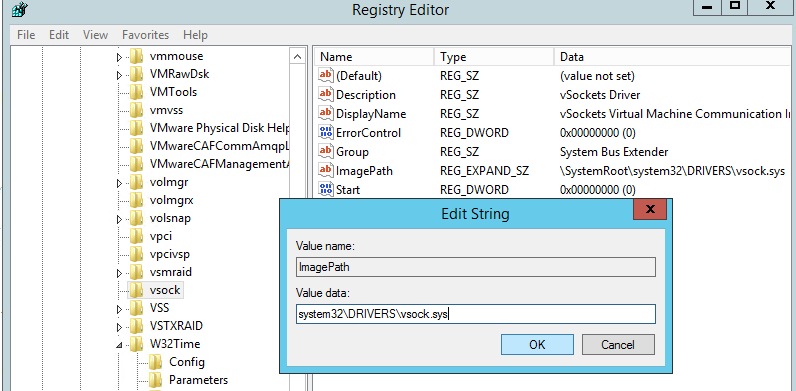
Чтобы исправить путь, откройте редактор реестра и перейдите в раздел HKLMSYSTEMCurrentControlSetServicesvsock.
Измените значение ImagePath с
systemrootsystem32DRIVERSvsock.sys
на
System32DRIVERSvsock.sys
Запустите скрипт бэкапа еще раз.
Если бэкап выполнен успешно, в логе появятся сообщения:
The backup operation successfully completed. The backup of volume (C:) completed successfully. The backup of the system state successfully completed [10.10.2019 9:52].
Проверим даты последнего бэкапа на DC:
repadmin /showbackup
Теперь тут указано, что последний раз бэкап контроллера домена выполнялся сегодня.
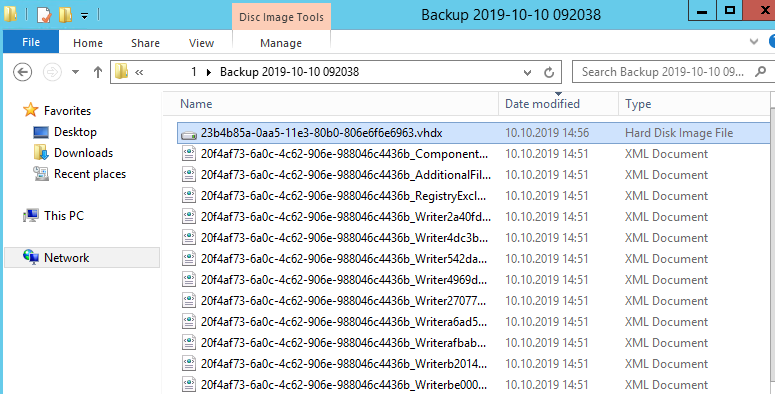
На сервере резевного копирования размер каталога с резервной копией контроллера домена занимает около 9 Гб. По сути на выходе вы получили vhdx файл, который можно использовать для восстановления ОС через WSB, или вы можете вручную смонтировать vhdx файл и скопировать из него нужные файлы или папки.
Если на площадке имеется несколько DC, то не обязательно бэкапить их все. Для экономии места достаточно периодически бэкапить базу данных AD — файл ntds.dit. Для этого используйте следующие команды:
$WBadmin_cmd = "wbadmin start backup -backuptarget:$path -include:C:WindowsNTDSntds.dit -quiet"
Invoke-Expression $WBadmin_cmd
Размер такого бэкапа будет составлять всего 50-500 Мб в зависимости от размера базы AD.
Для автоматического выполнения бэкапа, нужно на DC создать скрипт c:psbackup_ad.ps1. Этот скрипт нужно запускать по расписанию через Task Sheduler. Вы можете создать задание планировщика из графического интерфейса или из PowerShell. Главное требование — задание должно запускать от имени SYSTEM с включенной опцией Run with highest privileges. Для ежедневного бэкапа контролера домена AD создайте следующее задание:
$Trigger= New-ScheduledTaskTrigger -At 01:00am -Daily
$User= "NT AUTHORITYSYSTEM"
$Action= New-ScheduledTaskAction -Execute "PowerShell.exe" -Argument "c:psbackup_ad.ps1"
Register-ScheduledTask -TaskName "StartupScript_PS" -Trigger $Trigger -User $User -Action $Action -RunLevel Highest –Force
Итак, мы настроили резевное копирование состояния AD, а в следующей статье мы поговорим о способах восстановления AD из имеющейся резервной копии контроллера домена.
В этой статье мы посмотрим, как создать резервную копию контроллера домена Active Directory на базе Windows Server 2019. Такая резервная копия DC позволит вам восстановить как отдельные объекты AD, так и домен целиком при возникновении проблем.
Несмотря на то, что сервисы Active Directory разработаны с учетом избыточности, администратору AD нужно разработать и внедрить четкую политику резервного копирования Active Directory.
Как минимум, необходимо создавать резервную копию DC с ролями FSMO и по одному DC на каждой площадке (филиале). Конкретные рекомендации по стратегии резервного копирования сильно зависят от архитектуры вашего домена и структуры сети.
В Windows Server 2019 есть встроенный компонент Windows Server Backup, позволяющий создать резервную копию AD.
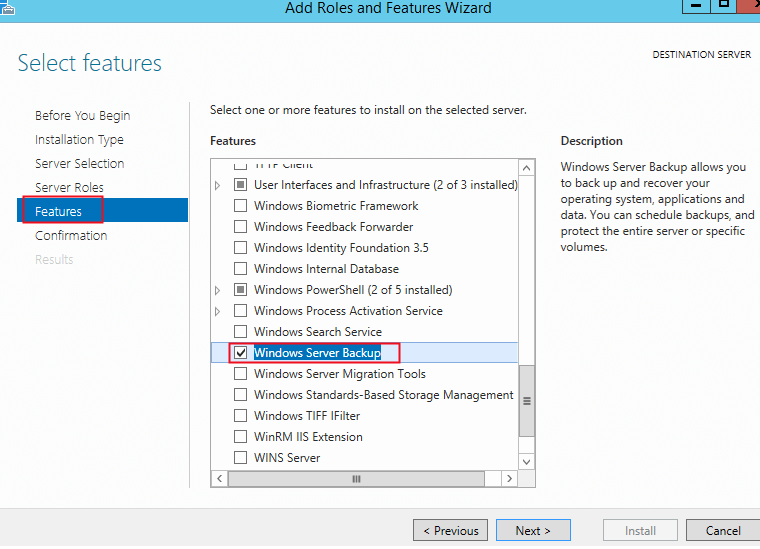
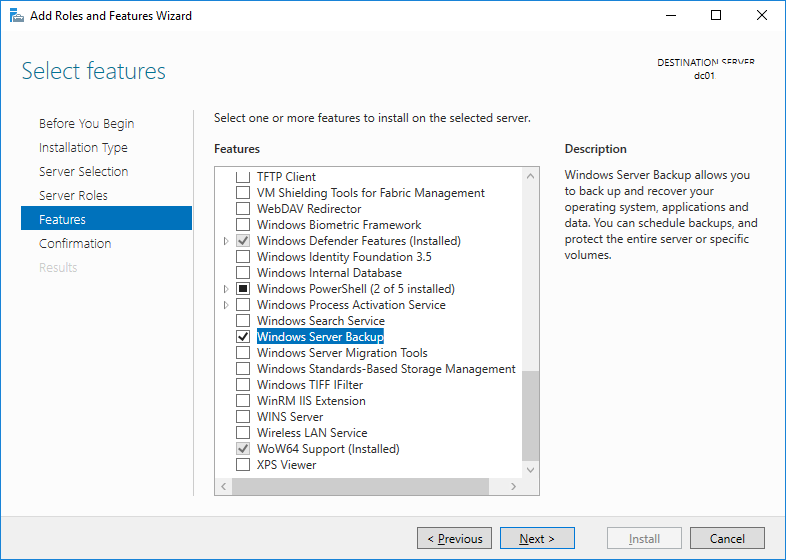
Запустите Server Manager на контроллере домена Windows Server и выберите Add Roles and Features. Затем нажмите Next несколько раз и выберите для установки компонент Windows Server Backup.
Также вы можете установить компонент WSB в Windows Server с помощью команды PowerShell:
Install-WindowsFeature -Name Windows-Server-Backup -IncludeAllSubfeature –IncludeManagementTools
Дождитесь окончания установки Windows Server Backup и нажмите Close.
Теперь в Server Manager выберите Tools -> Windows Server Backup.
В левой панели выберите Local Backup, вызовите контекстное меню и выберите Backup Schedule.
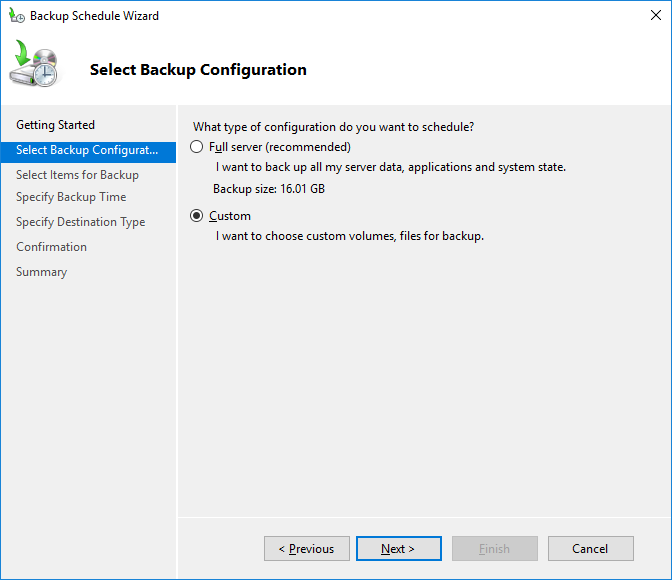
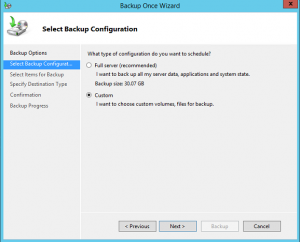
В настройках резервного копирования выберите Custom.
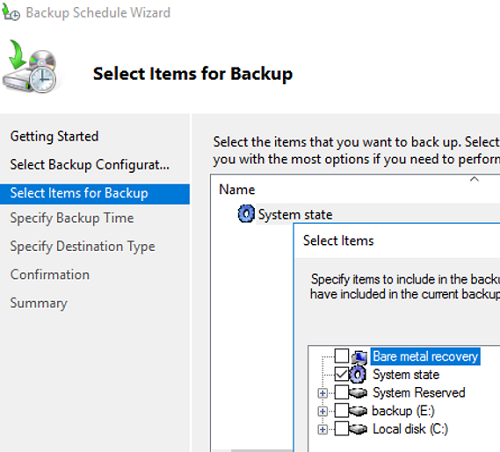
Для полного резевного копирования контоллера домена Active Directory нужно выбрать режим бэкапа System State. Такого образа вполне достаточно для восстановления контроллера домена Active Directory.
System State включает в себя:
- Базу Active Directory (ntds.dit)
- Каталог Sysvol (с объектами GPO)
- Встроенные DNS зоны со всеми записями
- Базу данных службы сертификации (Certificate Authority)
- Системные загрузочные файлы
- Реестр
- Базу данных службы компонентов (Component Services)
С помощью такого бэкапа вы сможете развернуть службы AD на том же самом сервере (не поддерживается восстановление ОС из system state backup на другом сервере). Если вы планируете восстанавливать контроллер домена на другом сервер, нужно выбрать опцию Bare metal recovery.
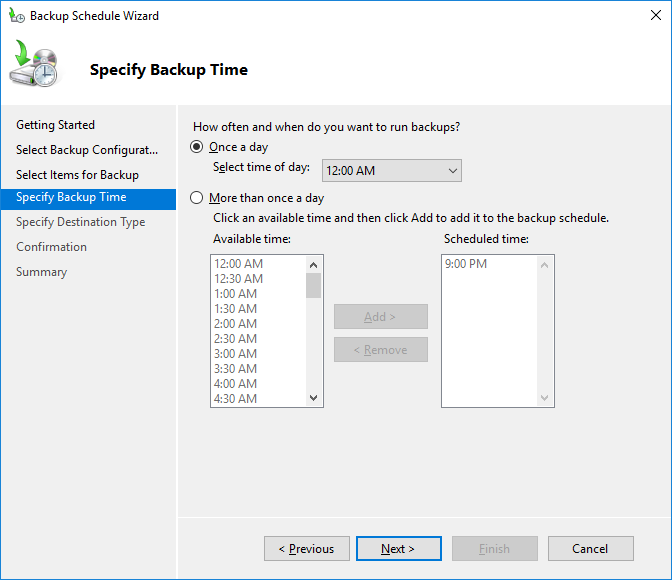
Задайте расписание резервного копирования. Например, я хочу создавать резервную копию AD ежедневно в 12:00.
Вы можете складывать резервные копии контроллера домена на отдельный физический диск или в сетевую папку на другом сервере или NAS устройстве. Я использую выделенный диск (выберите его в качества устройства для хранения резервных копий).
Нажмите Finish чтобы создать новое задание резервного копирования.
Вы можете найти созданное задание резервного копирования в Task Scheduler. Запустите taskschd.msc, перейдите в раздел Task Scheduler Library -> Microsoft -> Windows -> Backup и найдите задание Microsoft-Windows-WindowsBackup. Данное задание запускается от имени системы (аккаунта NT AuthoritySYSTEM). Если вы хотите создать резервную копию DC немедленно, в настройках задания на вкладке Settings включите опцию “Allow task to be run on demand”. Сохраните изменения, щелкните ПКМ по заданию и выберите Run (или дождитесь автоматического запуска задания по расписанию).
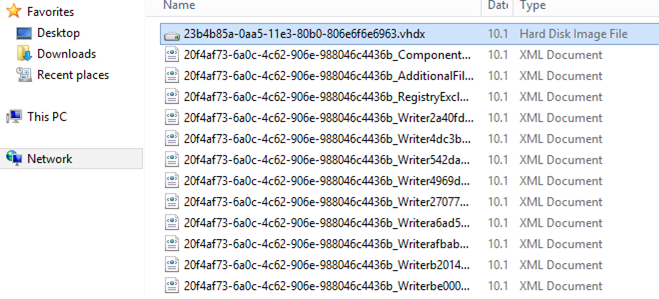
После окончания процесса резервного копирования на диске E: появится каталог с именем WindowsImageBackup. Обратите внимание на структуру каталога WindowsImageBackup. В нем содержится каталог с именем контроллера домена. В этой папке находится каталог с именем Backup и временем создания резервной копии (например, E:WindowsImageBackupdc01Backup 2021-10-17 120957). Внутри этого каталога находится файл vhdx. Это виртуальных диск с образом вашего контроллера домена. Вы можете вручную подключить его через Disk Manager и получить доступ к файлам.
Также вы можете выполнять резервное копирование DC с помощью консольной утилиты wbadmin. Например, чтобы создать резервную копию system state сервера и сохранить ее на отдельный диск, выполните команду:
wbadmin start systemstatebackup -backuptarget:e: -quiet
В этом примере содержимое каталога WindowsImageBackup на целевом диске перезаписывается.
Список доступных резервных копий на диске можно вывести так:
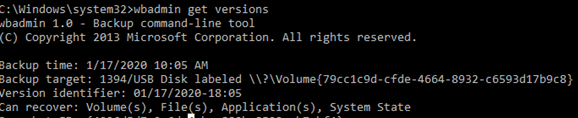
wbadmin get versions
Чтобы удалить все старые резервных копии, кроме последней, выполните команду:
wbadmin delete backup -keepVersions:1
Также вы можете использовать PowerShell модуль WindowsServerBackup для создания резервной копии Active Directory на DC. Следующий PowerShell скрипт создаст резервную копию System State на указанном диске:
$WBpolicy = New-WBPolicy
Add-WBSystemState -Policy $WBpolicy
$WBtarget = New-WBBackupTarget -VolumePath "E:"
Add-WBBackupTarget -Policy $policy -Target $WBtarget
Start-WBBackup -Policy $WBpolicy
Для восстановления AD в случае аварий вам понадобится SystemState Backup в корне локального диска DC. При восстановлении AD вам нужно загрузить сервер с ролью ADDS в режиме Directory Services Restore Mode (DSRM).
In this article we’ll talk about Active Directory domain controller backup and learn how to configure automatic AD backup using PowerShell and built-in Windows Server tools.
Contents:
- Do I Need to Back Up Active Directory?
- Get Last Active Directory Domain Controller Backup Date
- Backing Up AD Domain Controller Using Windows Server Backup
- Active Directory Backup with PowerShell
Do I Need to Back Up Active Directory?
Many times I have heard from my fellow administrators that if you have multiple (3, 8, etc.) domain controllers that are distributed across different geographic location, you don’t need to back up your AD at all. Since with multiple DCs you have provided domain fault tolerance. It is the schema when the simultaneous failure of all DCs tends to 0, and if one of the domain controllers fails, you can quickly deploy a new one on the same site and remove the old one using ntdsutil.
However, in my practice I have come across various scenarios when all domain controllers turned out to be damaged: in one case all domain controllers (although there were more than 20 of them in different cities) were encrypted due to a domain admin password capture by a ransomware using the mimikatz tool (to prevent these scenarios see “How to Protect Windows Against Mimikatz?” and“Securing Administrators Groups in Active Directory”), in another case a replication of a damaged NTDS.DIT file resulted in a domain failure.
So you can and should back up your AD. You must backup at least key domain controllers and FSMO (Flexible single-master operations) role owners regularly. You can get the list of domain controllers with FSMO roles using this command:
netdom query fsmo
Get Last Active Directory Domain Controller Backup Date
You can check when the current Active Directory domain controller was backed up last time using the repadmin tool:
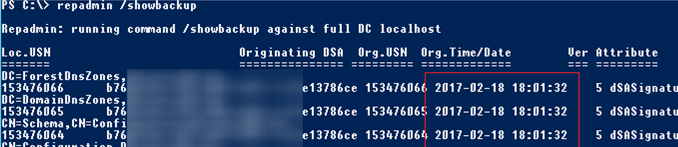
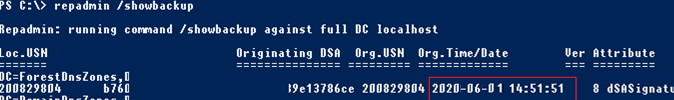
repadmin /showbackup
You can see that in this example the last time the DC and AD partitions had been backed up was 2017-02-18 (it is likely, the backup has not been done since the domain controller was deployed).
You can get the backup status for all DCs in the domain using this command:
repadmin /showbackup *
If your domain controllers are running on virtual machines and you back them up using snapshots (see the example with Hyper-V backup), the backup dates won’t be updated on an evident reason. Most modern backup tools have an option you can check to specify that it is a DC and data in LDAP directory must be updated during backup.
Backing Up AD Domain Controller Using Windows Server Backup
If you don’t have any special backup software, you can use the built-in Windows Server Backup (this component has replaced the NTBackup tool). You can configure an automatic backup task in the Windows Server Backup GUI, but it has some restrictions. The main disadvantage is that a new server backup will always overwrite a previous one.
When you back up a domain controller using WSB, you create a System State backup. The System State includes the Active Directory database (NTDS.DIT), Group Policy Objects, SYSVOL directory contents, the registry, the IIS metadata, the AD CS database and other system files and resources. The backup is created through the Volume Shadow Copy Service (VSS).
You can check if Windows Server Backup is installed using the Get-WindowsFeature PowerShell cmdlet:
Get-WindowsFeature Windows-Server-Backup
If WSB is not installed, you can add it with PowerShell:
Add-Windowsfeature Windows-Server-Backup –Includeallsubfeature
Or install Windows Server Backup via Server Manager -> Features.
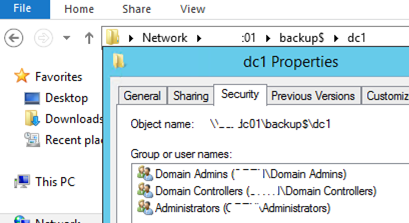
I will save the backup of this AD domain controller to a shared network folder on a dedicated backup server. For example, a path to the backup directory may look like this: \mun-back1backupdc01. Configure the NTFS permissions for this folder: grant Read and Write access permissions to Domain Admins and Domain Controllers groups only.
Active Directory Backup with PowerShell
Let’s try to back up a domain controller using PowerShell. To keep multiple levels of AD backup copies, we will store each backup copy in a separate directory with the date of backup creation as the folder name.
Import-Module ServerManager
[string]$date = get-date -f 'yyyy-MM-dd'
$path=”\mun-back1backupdc1”
$TargetUNC=$path+$date
$TestTargetUNC= Test-Path -Path $TargetUNC
if (!($TestTargetUNC)){
New-Item -Path $TargetUNC -ItemType directory
}
$WBadmin_cmd = "wbadmin.exe START BACKUP -backupTarget:$TargetUNC -systemState -noverify -vssCopy -quiet"
Invoke-Expression $WBadmin_cmd
Run the PowerShell script. The wbadmin console will appear. It contains information about the process of disk backup (shadow copy) creation:
The backup operation to \mun-back1backupdc12020-06-01 is starting. Creating a shadow copy of the volumes specified for backup...
My first attempt to back up a DC failed up with an error (the domain controller was a VMWare virtual machine):
Detailed error: The filename, directory name, or volume label syntax is incorrect. The backup of the system state failed [01.06.2020 8:31].
I opened the WSB error log — C:WindowsLogsWindowsServerBackupBackup_Error-01-06-2020_09-23-14.log.
There was the following error in the file:
Error in backup of C:windows\systemroot during enumerate: Error [0x8007007b] The filename, directory name, or volume label syntax is incorrect.
Looking ahead, I will tell that the problem was in the incorrect path of a VMWware Tools driver.
To fix the error, start the elevate command prompt and run this command:
DiskShadow /L writers.txt
list writers detailed
After getting the list, type quit and open C:WindowsSystem32writers.txt. Find the string containing “windows\” in it.
In my case the string I had found looked like this:
File List: Path = c:windows\systemrootsystem32drivers, Filespec = vsock.sys
As you can see, a wrong path to the VSOCK.SYS driver is used.
To correct the path, open the Registry Editor and go to reg key HKLMSYSTEMCurrentControlSetServicesvsock.
Change the ImagePath value from
systemrootsystem32DRIVERSvsock.sys
to
System32DRIVERSvsock.sys
Run the backup script again.
If the backup has been successful, you will see the following messages in the log:
The backup operation successfully completed. The backup of volume (C:) completed successfully. The backup of the system state successfully completed [01.06.2020 09:52].
Check the time of the last DC backup:
repadmin /showbackup
Now it says that the last domain controller backup was performed today.
The size of the directory with the domain controller backup on the server is about 9GB. In fact, we have got a VHDX file you can use to restore the OS from WSB, or you can manually mount the VHDX file and copy the files or folders you need from it.
If there are multiple DCs in Active Directory, you do not need to back up all of them. To save the space, it is enough to periodically backup the Active Directory database — ntds.dit file. To do it, use these commands:
$WBadmin_cmd = "wbadmin start backup -backuptarget:$path -include:C:WindowsNTDSntds.dit -quiet"
Invoke-Expression $WBadmin_cmd
The size of such a backup will be only 50-500MB depending on the AD database size.
For automatic AD backup, create the C:PSBackup_AD_DC.ps1 script on your DC. Run it according to the schedule using Task Scheduler. You can create a Scheduler task from the GUI or with PowerShell. The main requirement is that the task must be run under the NT AUTHORITYSYSTEMaccount with the Run with highest privileges option checked. For a daily AD domain controller backup, create the following scheduled task:
$Trigger= New-ScheduledTaskTrigger -At 02:00am -Daily
$User= "NT AUTHORITYSYSTEM"
$Action= New-ScheduledTaskAction -Execute "PowerShell.exe" -Argument "C:PSBackup_AD_DC.ps1"
Register-ScheduledTask -TaskName "BackupAD-DC-daily" -Trigger $Trigger -User $User -Action $Action -RunLevel Highest –Force
So, we have configured an AD backup, and we will talk ways to restore AD from a domain controller system state backup in our next article.
Active Directory is one of the most important components in any Windows network. Having no AD backup strategy could put your organization at risk. We provide a step-by-step guide on how to backup Active Directory running on Windows Server.
UPDATED: November 4, 2022
Active Directory (AD) is a Microsoft proprietary directory service developed for Windows domain networks. It was first introduced in Windows Server 2000 for centralized domain management.
It is now included in all subsequent Windows Server operating systems, enabling network administrators to create and manage domains, users, objects, privileges, and access within a network.
AD is great at managing traditional on-premises Microsoft infrastructure but not cloud environments. Microsoft cloud infrastructure uses Azure Active Directory, which serves the same purposes as its on-premises counterpart. Active Directory and Azure Active Directory are distinct but can work together to some degree if your organization has a hybrid deployment (on-premises and cloud).
The AD layout follows a tiered structure made up of domains, trees, and forests. A domain is a group of objects (such as users or devices) sharing the same AD database. A tree is a collection of domains, and a forest is a collection of trees. The main Active Directory service is Active Directory Domain Services (AD DS), which is part of the Windows Server operating system. The servers that run AD DS are called Domain Controllers (DCs). Some organizations have multiple DCs, and each one has a copy of the directory for the entire domain. To ensure that the DCs stay up to date, changes made to the directory on one DC such as change of password are also replicated to the other DCs.
The Active Directory database (directory) has a hierarchical tree-like structure and contains information about the AD objects in the domain. Common types of AD objects include users, computers, applications, printers, and shared folders. The Ntds.dit file is used to store the AD database. The database is divided into several sections that contain different types of information—a schema partition (which determines the AD database design), configuration partition (information about AD structure), and domain names context (users, groups, printer objects). Active Directory is tightly integrated with Windows protected system files, System Registry of a domain controller, Sysvol directory, COM+ Class Registration Database, and cluster service information. When planning for a backup strategy, it is important to consider such integration, especially because of the immediate impact it has on the AD.
Do you need to back up the active directory?
Active Directory is one of the most important components in any Windows network. Having no backup strategy whatsoever could put the entire organization at risk. Its best practice is to have multiple active directory domain controllers with fail-over functionalities so that when one fails, you would still be able to recover even without a backup. However, having multiple domain controllers is not enough justification to not do a backup. You should still be doing a backup of the active directory whether you have multiple domain controllers or not. Multiple domain controllers can fail at once, accidental or deliberate deletion of all the accounts or critical organizational units (OU) can occur, entire database corruption can occur, viruses, and ransomware or some other disaster could wipe out all domain controllers. In such a situation, you would need to restore it from a backup. This is why you need to backup.
You probably don’t need to back up every single domain controller, to get a good backup of the AD. You only really should have to back up one of the domain controllers. If your domain controller crashes, your network and by extension, business activities come to a halt. Although active directory services are designed with high redundancy (if you deployed several DCs in your network). It’s therefore important to develop and implement a clear active directory backup policy. If you have multiple DCs running, you need to back up at least one of them. The ideal DC to backup should be the one running the Flexible Single Master Operation (FSMO ) role. With a good backup and recovery strategy implementation, your organization can easily recover after your domain controllers crash.
If the Active Directory Domain Controller (AD DC) becomes unavailable for whatever reason, then users cannot log in and systems cannot function properly, which can cause disruption to business activities. That’s why backing up your Active Directory is important. In this article, we will show you how to backup an Active Directory domain controller running on Windows Server 2019. Before we begin we will take a look at a concept known as System State backup and how it affects Active Directory data.
System State backup
Microsoft Windows Server offers the possibility to perform a ‘Full’ backup or a ‘System State’ backup. A Full backup makes a copy of the system drives of a physical or a virtual machine, including applications, operating systems, and even the System State. This backup can be used for bare metal recovery—this allows you to easily reinstall the operating system and use the backup to recover.
System State backup on the other hand creates a backup file for critical system-related components. This backup file can be used to recover critical system components in case of a crash. Active Directory is backed up as part of the System State on a domain controller whenever you perform a backup using Windows Server Backup, Wbadmin.exe, or PowerShell. For the purpose of this guide, we will be using System State backup because it allows us to backup only the components needed to restore Active Directory. However note that Microsoft does not support restoring a System State backup from one server to another server of a different model, or hardware configuration. The System State backup is best suited for recovering Active Directory only on the same server.
As described later in this guide, Windows Server Backup must be installed through features in Server Manager before you can use it to back up or recover your server. The type of backup you select for your domain controllers will depend on the frequency of changes to Active Directory and the data or applications that might be installed on the domain controller. The bare minimum you need to back up to protect essential Active Directory data on a domain controller is the System State. The System State includes the following list plus some additional items depending on the roles that are installed:
- Domain controller: Active Directory DC database files (NTDS.DIT), boot files & system protected files, COM+ class registration database, registry, system volume (SYSVOL)
- Domain member: Boot files, COM+ class registration database, registry
- A machine running cluster services: Additionally backs up cluster server metadata
- A machine running certificate services: Additionally backs up certificate data
In addition, System State backups will back up Active Directory-integrated DNS zones but will not back up file-based DNS zones. File-based DNS zones must be backed up as part of a volume-level backup, such as a critical volume backup or full server backup. All the above backup types can be run manually on-demand, or they can be scheduled using Windows Server Backup. You can use either Windows Server backup or Wbadmin.exe to perform a System State backup of a domain controller to back up Active Directory. Microsoft recommends using either a dedicated internal disk or an external removable disk such as a USB hard disk to perform the backups.
Backup operators do not have the privileges required to schedule backups. You must have administrative rights to be able to schedule a System State backup or restore. A System State backup is particularly important for disaster recovery purposes as it eliminates the need to reconfigure Windows back to its original state before the system failure occurred. It is important that you always have a recent backup of your System State. They may require you to perform regular System State backups to increase your level of protection. We recommended that you perform System State backups before and after any major change is made to your server.
Before going ahead with the backup process, you need to take note of the following initial steps:
- It is important that you have the necessary amount of storage space to accommodate the backup you are about to perform.
- If you’re going to be backing up while the applications that produce the data are still running (which is usually the case), you need to configure the Volume Shadow Copy Service, also known as Volume Snapshot Service (VSS) on the drive for the backup to be successful. This service helps to create backup copies or snapshots of computer files or volumes, even when they are in use.
- You need to install the Windows Server Backup feature if you haven’t done this yet. Windows Server 2019 just like previous editions, comes with the Windows Server Backup feature that helps to perform Active Directory database backups and restores. Now we will go through the above steps in detail.
Configure the Volume Shadow Copy Service (VSS)
It is important to ensure that the AD database is backed up in a way that preserves database consistency. One way to preserve consistency is to back up the AD database when the server is in a powered-off state. However, backing up the Active Directory server in a powered-off state may not be a good idea if the server is operating in 24/7 mode.
For this reason, Microsoft recommends the use of Volume Shadow Copy Service (VSS) to back up a server running Active Directory. VSS is a technology included in Microsoft Windows that can create backup copies or snapshots of computer files or volumes, even when they are in use. VSS writers create a snapshot that freezes the System State until the backup is complete to prevent modifying active files used by Active Directory during a backup process. In this way, it is possible to back up a running server without affecting its performance. For this guide, we are going to show you how to change the Shadow Copy size limit configuration on the volume where we are going to store the AD database.
1. Press a combination of Win+X on your keyboard to open the Disk Manager. Select the partition where the server is installed, then right-click on it and click on Properties.
2. Go to the Shadow Copies tab and then click on Enable as shown on the image below.
3. In the next window, click Yes to confirm that you want to enable shadow copies as shown below.
4. After confirmation, you’ll see a restore point created in the selected partition. Click on Settings to continue.
5. In the Settings screen shown below, under Maximum size, select No limit. Once completed click the OK button, and that does it for this section—configure the Volume Shadow Copy Service (VSS).
Install the Windows Server backup feature
Windows Server Backup is a utility provided by Microsoft with Windows Server 2008 and later editions. It replaced the NTBackup utility which was built into the Windows Server 2003. Windows Server Backup is a feature that is installable in Windows Server 2019 just like in other previous editions. So if you haven’t used the backup feature yet, you will likely have to install it first. The way to install this feature is through the Server Manager.
1. Open the Server Manager console as shown in the image below.
2. Go to Local Server >> Manage tab >> and click on the Add Roles and Features as seen in the image below. This will open the Add Roles and Features Wizard.
3, In the Select installation type screen, select the Role-based or feature-based installation option and click Next.
4. In the next screen called Select destination server, you will be required to select the server on which you want to install roles and features. Windows will automatically display the server pool. In this case, we are going to select the local server, which is WD2K19-DC01-mylablocal.
5. In the Select server roles screen, you are required to select the roles to install on the server. Since we are installing a feature, you can ignore this section and continue to the next screen. Click Next to continue.
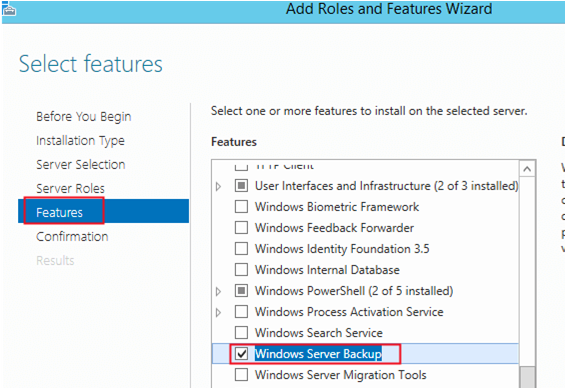
6. In the Select features screen below, scroll down to the Windows Server Backup feature, and select it as seen in the image below. Click Next to continue.
7. In the Confirm installation selections screen, make sure that the Windows Server Backup feature is on the screen and click on the Install button to begin the installation.
The Windows Server Backup feature will begin to install on your local server. Once the installation is completed, click the Close button to close the console.
Backup the Active Directory database
1. Now go to the Server Manager and click on Tools >> Windows Server Backup, in order to open it. You can also open this console by running the command wbadmin.msc on the Windows Run (Ctrl+R). Once it opens up, you’ll be able to see the scheduled and last backup status (unless this is the first time you’re doing this.)
2. Once the server backup opens, click on Backup Once to initiate a manual AD database backup. Although you can also create automatic scheduled backups by clicking Backup schedule, for this guide we are going to create a manual backup.
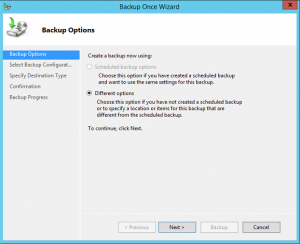
3. Under Backup Options select Different options and click on the Next button This option is used where there is no scheduled backup.
4. In the Select Backup Configuration screen, you have two options:
-
- Full Server backs up all server data, applications, and System State
- Custom lets you choose what you want to back up.
Since we just want to back up the active directory, we choose the second option. So select Custom and click Next.
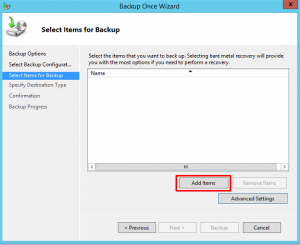
5. In the Select Items for Backup screen, specify the items that you want to include in the backup. In this backup, we are going to choose the System State Backup item. To do this, click on the Add items button >> select System State option >> and click on the Ok button to complete the process.
6. Now we are going to enable the Volume Shadow Copy Service for this backup item. Doing this prevents AD data from being modified while the backup is in progress. To enable VSS, click on Advanced Settings >> VSS Settings >> Select VSS Full Backup, and click Ok. The VSS Full Backup is the recommended option if it is your first backup, and you are not using any third-party backup tool. This option allows you to create a backup of all the files. It is also the preferred method for incremental backups, as it does not affect the sequence of backup.
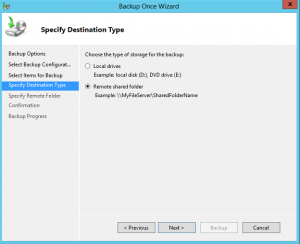
7. In the next screen, you would need to specify the backup destination type — Local drives or Remote shared folder. For the purpose of this demonstration, we are using a local hard drive to store the backup. So choose Local drives and click Next.
8. In the Select Backup Destination screen you can choose the actual partition where you want to store the backup. Once you are done, click Next to proceed to the next screen.
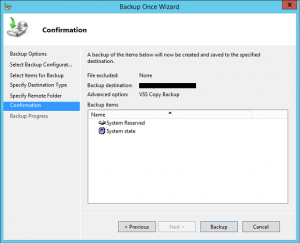
9. The Confirmation screen lets you double-check that all backup parameters are correctly configured. Once you are good to go, click the Backup button. The backup should take some time depending on the size of the domain controller server. Once the backup is successfully completed, you can close the Backup Wizard.
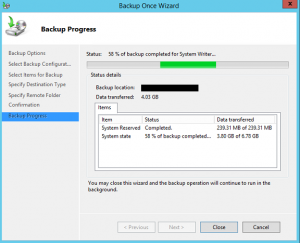
If you closed the Backup Wizard without waiting for the last message status, the backup will continue to run in the background. You can also confirm the status and completion results of the backup from the webadmin console (or Windows Server Backup Feature). The console will display a message with information from this backup (and others).
Active Directory backup automation
There are a number of tools available to manage backup and restore functions for applications or entire disks and these can help you save time with backing up Active Directory. Such systems can also be used to replicate and migrate the objects in a domain controller.
ManageEngine AD360 (FREE TRIAL)
An example of an Active Directory backup system can be found in ManageEngine AD360.
The Standard edition of this bundle includes a tool called RecoveryManager Plus. The advantage of this tool is that it is integrated into a package of tools to manage Active Directory, so you get all of your AD management systems in one console.
AD360 is able to manage both cloud and on-premises implementations of Active Directory. This is a software bundle and you install it on Windows Server. It is also available from the marketplace of AWS and Azure – these are not SaaS platforms but software packages that you run in your cloud account space.
Why do we recommend it?
ManageEngine AD360 is a collection of many Active Directory-related tools offered by ManageEngine – there are seven in total. Among this list is ADAudit Plus package, which provides controls that prevent unauthorized changes to AD objects. Another unit, ADManager Plus lets you assess, improve, and monitor the efficiency and security of user accounts. Recovery Manager Plus is another component and this manages the backup of Active Directory instances.
Who is it recommended for?
ManageEngine AD360 is a comprehensive package of everything you will need to manage and control Active Directory. The package is very large and you might not need all of the components. If you are only interested in the backup and recovery services of AD360, you might prefer to just buy RecoveryManager Plus.
Pros:
- Dramatically improves the usability of Active Directory, making routine tasks easier to perform and automate
- Can monitor changes across both local and cloud-based AD environments
- Supports SSO and MFA, great for securing your access management with multiple layers of authentication
- Extensive 60-day trial period
Cons:
- Can take time to fully explore the entire platform
The best way to understand the Active Directory backup capabilities of AD360 is to access it on a 30-day free trial.
ManageEngine 360
Start 30-day FREE Trial
Active Directory backup FAQs
Is it necessary to backup Active Directory?
It is very important to backup Active Directory. The system won’t back itself up without your intervention. However, there is a native backup system built into Windows Server, which makes the process of saving a copy of Active Directory easy.
What are the different types of backup in Active Directory?
You can run a full backup to take a copy of the entire Active Directory database and then repeat this process periodically on a schedule to create rollback points. This is the system that is available in the native backup service in Windows Server, which is called Volume Shadow Copy Service (VSS). It is more efficient to take periodical full backups and then perform incremental or differential backups more frequently. These just extract the objects that have changed since the last backup and so are much quicker and take up less space. However, you need a third-party tool to implement these strategies because they are not available in Windows Server VSS.
How does Windows Server backup work?
Windows Server Backup uses a method called Volume Shadow Copy Service (VSS). this gives you the option to backup the operating system and all of the contents of the disk This is called a Bare Metal Backup and it will copy everything on the computer, not just Active Directory. The other option is called System State Backup. This copies important system files as well as the items you select. This is the option to choose in order to back up Active Directory.
Conclusion
We have explained in detail how to back up the Active Directory using the Windows Server backup. We used the manual “Backup Once” approach, but of course, you can also configure a “Backup Schedule,” to run periodic AD backup tasks.
As already mentioned, the Windows Server Backup feature is an easy to use free tool that is bundled in most Windows Server OS, and it can work with VSS to perform Full or System State backups. However, there are also lots of third party Active Directory backup tools out there that you can use. In fact, almost every enterprise-level backup service should be capable of backing up Active Directory with little to no difficulty. The difference between all those tools lies mostly in the way some of them provide more capabilities, especially when it comes to backing up and restoring the Active Directory.
In this article, we will take a look on how to backup an Active Directory domain controller running on Windows Server 2016. This backup will allow you to restore both individual AD objects and the entire AD domain in case of problems.
Although Active Directory services are designed with high redundancy (if you deployed several DCs in your company), an AD administrator needs to develop and implement a clear Active Directory backup policy. At least, you need to back up a DCs with FSMO roles and one DC per site. The specific recommendations for the backup strategy are highly dependent on your domain architecture and network structure.
Windows Server 2016 has a built-in Windows Server Backup component that allows you to backup Active Directory.
Open the Server Manager on your DC running Windows Server 2016 and select Add Roles and Features. Then click Next several times and set the Windows Server Backup checkbox on the Select features step.
Also, you can install the WSB feature on Windows Server using the PowerShell command:
Install-WindowsFeature -Name Windows-Server-Backup -IncludeAllSubfeature –IncludeManagementTools
Wait for the installation of Windows Server Backup to complete and click Close.
Now in the Server Manager select Tools > Windows Server Backup.
Right click Local Backup item in the left pane and select Backup Schedule.
On the Select Backup Configuration step select Custom.
On the Select Items for Backup stage press Add Item and select the System State. This is enough to restore an Active Directory domain controller in failure cases.
The System State includes:
- Active Directory database;
- The Sysvol folder (with GPO objects);
- Integrated DNS zones and records;
- Certificate Authority service database;
- System boot files;
- System registry;
- Component Services database.
As a result, you can restore ADDS services on the same server (OS recovery from system state backup on another server is not supported). If you plan to restore the domain controller on another server, you need to select the Bare metal recovery option.
Set a backup schedule. For example, we want to back up AD daily at 12:00 AM.
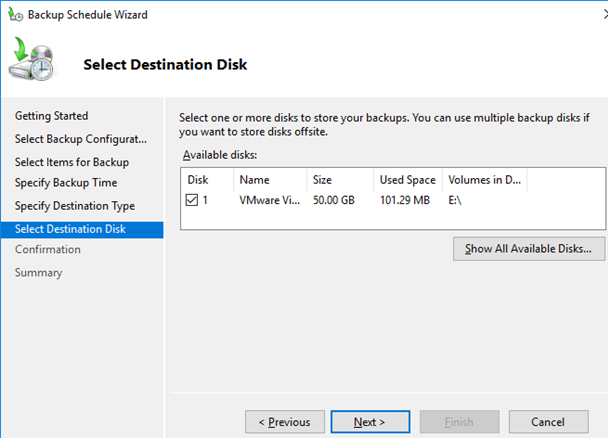
You can backup your DC to a dedicated backup volume, or a shared network folder. I am using a dedicated volume, select it as a backup Destination Target.
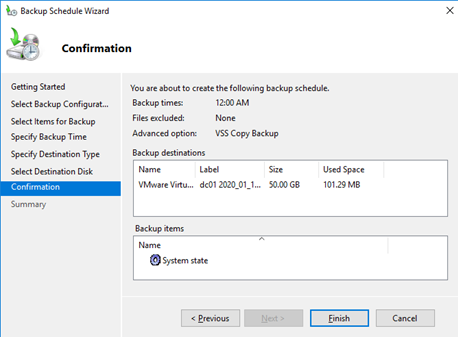
Press Finish to create a backup task.
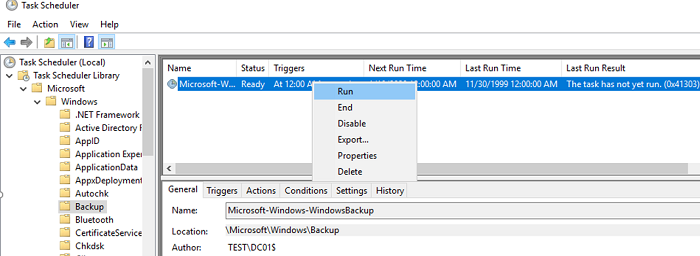
You can find the created backup task in the Task Scheduler. Browse to the Task Sheduler Library > Microsoft > Windows > Backup and find a task named Microsoft-Windows-WindowsBackup. This task is run NT AuthoritySYSTEM account. If you want to create a DC backup immediately, open the task properties, go to the tab Setting and check the box “Allow task to be run on demand”. Save the changes by pressing OK. Then right click on task and select Run (or wait for the scheduled task to start).
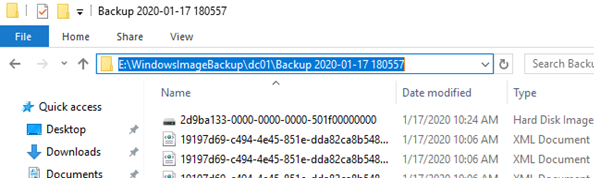
After the backup process is completed, a directory with the name WindowsImageBackup appears on drive E:. Pay attention to the structure of the WindowsImageBackup directory. It contains a directory with the name of the domain controller, which contains the folder named by the backup copy creation time (for example, E:WindowsImageBackupdc01Backup 2020-01-17 180557).
You can find a vhdx file inside this directory. This is a virtual hard disk image file with the backup Windows image of your domain controller. You can manually connect it through Disk Manager and access backup files.
How to Backup AD using Wbadmin and PowerShell?
You can also backup DCs using the wbadmin console utility. For example, to backup the system state of the running Windows Server and save it to a separate disk, run the command:
wbadmin start systemstatebackup -backuptarget:e: -quiet
This example overwrites the contents of the WindowsImageBackup directory on the target drive.
The list of available backup copies on the disk can be displayed as follows:
wbadmin get versions
To delete all old backup copies except the last, run the command:
wbadmin delete backup -keepVersions:1
You can also use the WindowsServerBackup module to backup Active Directory on a domain controller with PowerShell. The following PowerShell script will backup server’s System State to the specified drive:
$WBpolicy = New-WBPolicy Add-WBSystemState -Policy $WBpolicy $WBtarget = New-WBBackupTarget -VolumePath "E:" Add-WBBackupTarget -Policy $policy -Target $WBtarget Start-WBBackup -Policy $WBpolicy
To restore AD in the event of a disaster, you will need SystemState Backup in the root of the local DC drive. When restoring AD, you need to boot the server with the ADDS role in the Directory Services Restore Mode (DSRM).
- About
- Latest Posts
I enjoy technology and developing websites. Since 2012 I’m running a few of my own websites, and share useful content on gadgets, PC administration and website promotion.
Here’s a step-by-step procedure to back up the System State on a Windows Server 2012 R2 using the Windows Server Backup tool. Backing up the System State also backs up Active Directory Domain Services.
What Does System State Include?
On a Domain Controller, the System State generally includes the following but the data that is included really depends on the server roles that are installed on the server. For example, if you don’t have Active Directory Certificate Services (AD CS) installed then it won’t include that data.
- Registry
- COM+ Class Registration database
- Boot files
- Active Directory Certificate Services (AD CS) database
- Active Directory database (Ntds.dit) file and log files
- SYSVOL directory
- Cluster service information
- Microsoft Internet Information Services (IIS) metadirectory
- System files that are under Windows Resource Protection
NOTE: You can also use the command line options to back up the System State as described here.
Step-By-Step Procedure
- To use the Windows Server Backup console go to Server Manager and on the Tools menu select Windows Server Backup, or type wbadmin.msc at the command prompt.NOTE: If you don’t see the Windows Server Backup option under Tools then you need to install the Windows Server Backup role. By default, this role is not installed.
- Click Backup once in the Actions menu on the right hand side.
- Click Different option and then click Next.
- Click Custom and then click Next.
- Click Add Items.
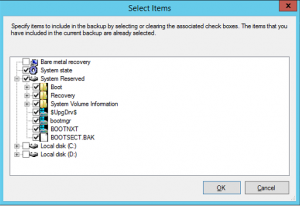
- In the Select Items window select System state and System Reserved. Click OK to close the window.
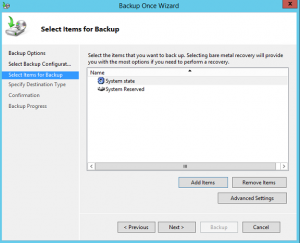
- In the Select Items for Backup window click Next.
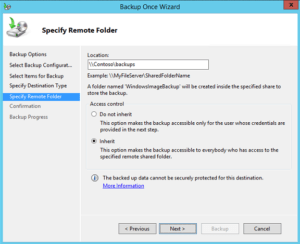
- You can backup the System State to either a local disk or a network share. I prefer to back it to a network share.
- Enter the server and share name and then click Next.
- On the Confirmation screen click Backup to start the backup.
- On the Backup Progress screen you can close the wizard and let the backup operation run in the background, or you can click Close after the backup is complete.
As a best practice, verify your backups occasionally by doing trial restores to make sure your backups are working. Since this is your first backup, it is a good idea to test this backup as well.
One thing to keep in mind is that Win32 service files are not reported by the System Writer as part of the System Component for Windows Server 2012. They are, however, reported as part of the System Component for Windows 8. To include or exclude the Win32 service files in the system state you can set the value of the registry key HKLMSystemCurrentControlSetControlSystemWriterReportWin32ServicesNonSystemState to either 0 or 1. Zero will include the Win32 service files, while 1 will exclude them. Be careful, on a server if you delete this registry key it will exclude the Win32 service files but if you delete the registry key on a client, it will include them.
To learn more about Windows Server Backup role click here.
Copyright ©2013 Zubair Alexander. All rights reserved.
This div height required for enabling the sticky sidebar
We use cookies on our website to give you the most relevant experience by remembering your preferences and repeat visits. By clicking “Accept”, you consent to the use of ALL the cookies.
Table of Contents
- Introduction
- Before we proceed
- Backup Policy
- Backup Approach
- Backup Tool
- Backup Frequency
- Which Domain Controllers to Backup
- Backup Method
- Backup Location
- Backup Versioning
- Disk Space Management
- Service Account
- Review Backup Policy
- Configure System State Backup
- Step 1: Provision a dedicated volume to store the backup
- Step 2: Remove Shadow Copy Limit on Backup Volume
- Step 3: Install Windows Server Backup Feature
- Step 4: Configure System State Backup
- Step 5: Configure the Schedule Task
- Step 6: Run the first backup.
- Step 7: Run Subsequent Backups
- Common issues and mitigation
- Summary
- Next Step
- References
Introduction
Active Directory (AD) is one of the most critical component of any IT infrastructure. In a Windows-based environment, almost all the applications and tools are integrated with Active Directory for authentication, directory browsing,
and single sign-on.
Due to this heavy dependency, it is necessary to have a well-defined process for AD Backup.
In this article, we will discuss some of the key points related to Active Directory Backup. We will also see how to automate the AD Backup without using any third party backup solution.
Before we proceed
Before we proceed, it is important to keep below points in mind:
- Restoring Active Directory Backup should be the LAST option for any Disaster Recovery.
- For a single Domain Controller failure, the recommended option is to demote the Domain Controller, wait for few hours to replicate the demotion, and then promote it back again.
- There is no need to restore Active Directory Backup to recover a single Domain Controller. Active Directory backup restoration is required only when the AD Database needs to be recovered/restored for some reason.
- Do not restore Active Directory backup to recover deleted objects. We strongly recommend to enable AD Recycle Bin and use that feature for object level recovery, rather than restoring AD Backup.
- Perform restoration drill periodically, in a test environment, which is completely isolated from your production AD environment. A successful restoration drill will ensure that your backup methodology
is accurate, also you can document the restoration procedure and lesson learned. This will be handy during actual restoration.
- If you do not have prior experience in AD backup restoration, please take professional help in a production or business critical environment.
Backup Policy
Our first goal is to create an effective Active Directory Backup Policy. The backup policy would define the backup approach, tool, frequency, backup location and many other important points.
Backup Approach
The most common and recommended approach for AD Backup is the System State Backup of Domain Controller.
A System State Backup of Domain Controller includes following:
- Sysvol
- Active Directory Database and related files.
- DNS Zones and records (Only for AD Integrated DNS)
- System Registry.
- Call Registration database of Component Service.
- System Start up files.
Backup Tool
There are many third party tools available in the market for backing up and restoring Active Directory. However, the
Windows Server Backup (WBADMIN) tool that comes bundled with all versions of Windows Servers is just fine for this purpose.
In this article, we will discuss the WBADMIN tool that comes bundled with Windows Server 2012 R2. In this edition, the WBADMIN tool is equipped with some great features which we will discuss in the upcoming sections.
Backup Frequency
We strongly recommend the daily backup. In an enterprise environment where data changes in every second, restoring an old backup does not make sense.
Moreover, Microsoft recommends that: “Any backup older than the tombstone lifetime set in Active Directory is not a good backup.“.
For a large enterprise, we strongly recommend to take System State Backup twice a day. Windows Server backup tools take incremental backup, so disk space is not a big concern here.
Which Domain Controllers to Backup
Please note that in a multi domain forest, every Domain needs to be backed up separately.
This is because there are few partitions which are different for every Domain, like Domain Partition and DomainDnsZone partition.
Microsoft recommends to take backup of at least two Domain Controllers for each Domain, and one of those two Domain Controllers should be the Operation Master role holder. However, Microsoft does not recommend
restoring a Domain Controller which is holding the RID Master role. This is to avoid any future RID block conflict.
Based on the Microsoft recommendation, we have decided to configure backup in two Domain Controllers in each Domain, which are in different geographical locations and far from each other. This will offer better redundancy and
we will schedule the backup in such a way that both Domain Controllers will be backed up in different point of time.
Backup Method
Once the System State Backup is scheduled through the WBADMIN tool, the first backup will be Full Backup, followed by 14 subsequent incremental backups , and then again another full backup.
So it will follow the below pattern and this cannot be modified :
First Full Backup > 14 Incremental Backups > 1 Full backup > 14 Incremental Backups > 1 Full backup > 14 Incremental Backups…and so on.
↑ Back to top
Backup Location
Do not store the backup in a network share. Backup versioning and automatic space management (which we will cover in next section) will not work through a network share.
This is because WBADMIN takes block level backup using VSS, which does not work through SMB.
Always store the backup in a local, non-system volume which is dedicated for storing backup. The local disk can be mounted from SAN or (in case of VM) can come from a datastore, but it has to be mounted in such a way that it is
displayed as a locally mounted disk in the Disk Management tool.
As mentioned before, we will not store anything else on that volume. Also, we cannot use System Drive (typically C drive) to store the backup as WBADMIN will not allow storing the backup in system drive.
The disk where the system state backup is stored should be backed up on a regular basis. This will be “Backup of Backup” which ensures availability of backup in case the drive is not available or corrupted.
Backup Versioning
Windows Server Backup stores backup versions in volume shadow copies. Once the data write is complete, WBADMIN creates a shadow copy of the volume where the backup is stored using Volume Shadow Copy Service (VSS).
This shadow copy retains the Point in time state of the Storage volume where the backup is stored, and each Point in Time State is called a Backup Version.
Backup versioning is one of the most exiting feature of WBADMIN tool. There will be no separate folder for each backup, instead, there will be versioning for each instance of backup.
Every time the backup job is triggered (manually or through scheduled task), a new version is created along with a unique snapshot ID and timestamp.
The command «WBADMIN get versions» will show all the point in time snapshots which are present on that server.
Disk Space Management
WBADMIN in Windows Server 2012 R2 offers another great feature, which is automatic disk space management.
When we schedule the backup using WBADMIN tool, we do not need to worry about disk space management, and we do not need to delete any backup to accommodate newer backups. This is entirely managed and taken care by the tool, which
deletes the oldest backup versions as and when required to manage disk space.
Automatic Disk Management feature does not work when backups are stored in a network share.
Service Account
The last thing that we have to plan is the Service Account, which will be used to run the scheduled task.
We recommend using built in “NT AUTHORITYSYSTEM” account. The advantage is we do not need to worry about password management and password expiry. However, this decision depends on organization policy.
If we use any other AD account to run the task, we have to ensure that “Password Never Expires” is enabled, otherwise backup will stop once password will expire.
Review Backup Policy
Now that we have considered all the points, let’s summarize our backup policy. For an organization, it is important to document this backup policy and get a sign off from all key stakeholders.
| Backup Approach | System State Backup |
| Backup Tool | Windows Server Backup (WBADMIN.EXE) |
| Operating System | Windows Server 2012 R2 |
| Backup Frequency | Daily |
| Domain Controllers to Backup | At least Two DCs per Domain, one of those should be FSMO role holder |
| Backup Method | Through Scheduled Task (1 Full > 14 Incremental > 1 Full > 14 Incremental ) |
| Where to Store the Backup | In a non-system disk, mounted as a local disk. Not in network share. |
| Backup Versioning | Versioning will be managed automatically by the backup tool |
| Disk Space Management | Will be managed automatically by the backup tool |
| Service Account | NT AUTHORITYSYSTEM |
Configure System State Backup
We have created our backup policy and reviewed it. Now it’s time to implement the backup solution.
We are going to configure it on a Domain Controller DC1.subhro.org. The operating System of the Domain Controller is Windows Server 2012 R2.
Step 1: Provision a dedicated volume to store the backup
We have provisioned a new volume (E:) which is formatted with NTFS. Since this is a test environment, the Disk size is 20 GB. However, for the production environment, we recommend at least 200 GB or higher. Higher disk size would
allow number of versions (snapshots) to be stored in the disk.
↑ Back to top
Step 2: Remove Shadow Copy Limit on Backup Volume
- Go to My Computer > Backup Drive (E: Drive in this case) > Right Click > Properties.
- Go to Shadow Copies and select E drive > Properties.
- Set the Maximum Size to “No Limit” and save the settings.
Step 3: Install Windows Server Backup Feature
- Go to Server manager > Add Roles and Features > Features > Windows Server backup.
- Install the tool.
- Once done, go to Run > Type “wbadmin.msc”
- We should now see the WBADMIN console.
As we can see, there is no backup configured, or no manual backup run on this Domain Controller.
At this stage, if we run the command «WBADMIN get versions», we will see below output that there is no backup version available.
↑ Back to top
Step 4: Configure System State Backup
We have the tool and the volume ready, so now let’s configure the scheduled task.
- On the right-hand side of the console, click “Backup Schedule”.
- Click “Custom” on Backup Configuration.
- In the next screen, click on Advanced Settings > VSS Settings.
- As we are not using any other third party tool to take AD Backup, select ‘VSS Full backup”.
- Select «System State» from the Backup Items list.
- Configure Backup schedule.
- Select «Backup to a hard disk«, which is the recommended option. The hard disk will be formatted.
- In case you cannot dedicate an entire hard disk for backup, choose «Backup to a volume» in the destination type.
- As discussed earlier, some key features will not work if the destination is a network folder and this option is not recommended.
- Select destination volume.
- Review the configuration.
- A confirmation message will appear if the configuration is successful.
↑ Back to top
Step 5: Configure the Schedule Task
- Go to Computer Management (Compmgmt.msc) and open the Task Scheduler.
- Go to the Task Scheduler Library > Microsoft > Windows > backup
- We should see the scheduled task already created by the WBADMIN wizard, which we ran in the previous section.
Open the Scheduled Task and changed the value of “Configured For” to “Windows Server 2012 R2 , as shown in the below diagram.
We also have to ensure that the task is running under «NT AUTHORITYSYSTEM» account.
↑ Back to top
Step 6: Run the first backup.
We will run the first backup manually to verify things are working as expected.
To run the scheduled task, we have to enable “Run the Task on Demand” option in the task settings. Once the first backup is complete, we should disable this option so that no one runs it manually.
So we have enabled that option and run the scheduled task. Since this is the first backup and a full backup, it will take some time to complete the backup.
Step 7: Run Subsequent Backups
The next backup would be incremental, whether we run it manually or through scheduled task.
Once the next backup is complete, we can check the versions again, and now we should see two versions available created in two different timestamp.
Please note that backups will be stored in Hyper-V Disk (VHDX) format.
Below screenshot captures the version details after 3 runs.
↑ Back to top
Common issues and mitigation
We have faced the following error in multiple Domain Controllers, and backup failed with this error :
The filename, directory name, or volume label syntax is incorrect.
When we get this error, we should check below two registry keys and ensure they contain the correct key value:
-
Key Path: HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINESYSTEMControlSet001ServicesLSI_SAS
- Key value: system32driverslsi_sas.sys
-
2) Key Path: HKLMSYSTEMCurrentControlSetServicesvsock
- Key value: system32DRIVERSvsock.sys
If the value is anything other than this, please correct the value and reboot the Domain Controller. Please take downtime and proper approval before changing the registry values, and please backup the registry before making any
change.
Also, sometimes the automatic space management does not work correctly and backup fails due to disk space issue. Generally, a reboot of the Domain Controller solves this problem.
Summary
In this article, we have discussed the Active Directory Backup Policy. We have also discussed how to deploy and automate daily System State Backup using Windows native backup tool. As mentioned earlier, restoring AD Backup should
be the LAST option in any production environment.
Next Step
Configuring and automating AD Backup is one part. Another part, which is equally important, is to monitor and ensure that the backup jobs are running as per the schedule, and more importantly, the backup is successful. Unlike the
backup configuration, this is not a one-time task but daily or weekly; depending on your backup frequency.
Can we automate this backup monitoring without using any third party tool? Can we receive an email notification after every backup job, indicating the success/failure status of the backup?
The answer is yes, we can automate this without using any additional tool, and using windows native solution.
The solution which I am going to propose here is tested, and we are running this in the production environment for last 1 year. Since then, we have got every single backup success and failure report without any slippage. It saved
us a lot of time and effort, and I believe it would save a lot of your effort too, once you implement it.
Read my next article:
Automate Backup Success-Failure Notification
↑ Back to top
References
- https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/previous-versions/windows/it-pro/windows-server-2000/bb727048(v=technet.10)
- https://blogs.technet.microsoft.com/filecab/2009/06/22/backup-version-and-space-management-in-windows-server-backup/
- https://lennox-it.uk/a-complete-guide-to-wbadmin-windows-backups