| title | description | author | ms.author | ms.date | ms.service | ms.subservice | ms.topic | ms.custom | helpviewer_keywords | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Configure the Windows Firewall to allow SQL Server access |
Learn how to configure the Windows firewall to allow access to an instance of the SQL Server through the firewall. |
rwestMSFT |
randolphwest |
10/17/2022 |
sql |
install |
conceptual |
contperf-fy21q3 |
|
Configure the Windows Firewall to allow SQL Server access
[!INCLUDE SQL Server-Windows Only]
Firewall systems help prevent unauthorized access to computer resources. If a firewall is turned on but not correctly configured, attempts to connect to [!INCLUDEssNoVersion] might be blocked.
To access an instance of the [!INCLUDEssNoVersion] through a firewall, you must configure the firewall on the computer that is running [!INCLUDEssNoVersion]. The firewall is a component of [!INCLUDEmsCoName] Windows. You can also install a firewall from another vendor. This article discusses how to configure the Windows Firewall, but the basic principles apply to other firewall programs.
[!NOTE]
This article provides an overview of firewall configuration and summarizes information of interest to a [!INCLUDEssNoVersion] administrator. For more information about the firewall and for authoritative firewall information, see the firewall documentation, such as Windows Firewall security deployment guide.
Users familiar with managing the Windows Firewall, and know which firewall settings they want to configure can move directly to the more advanced articles:
- Configure a Windows Firewall for Database Engine Access
- Configure the Windows Firewall to Allow Analysis Services Access
- Configure a Firewall for Report Server Access
Basic firewall information
Firewalls work by inspecting incoming packets, and comparing them against the following set of rules:
- The packet meets the standards dictated by the rules, then the firewall passes the packet to the TCP/IP protocol for more processing.
- The packet doesn’t meet the standards specified by the rules.
- The firewall then discards the packet.- If logging is enabled, an entry is created in the firewall logging file.
The list of allowed traffic is populated in one of the following ways:
-
Automatically: When a computer with a firewall enabled starts communication, the firewall creates an entry in the list so that the response is allowed. The response is considered solicited traffic, and there’s nothing that needs to be configured.
-
Manually: An administrator configures exceptions to the firewall. It allows either access to specified programs or ports on your computer. In this case, the computer accepts unsolicited incoming traffic when acting as a server, a listener, or a peer. The configuration must be completed to connect to [!INCLUDEssNoVersion].
Choosing a firewall strategy is more complex than just deciding if a given port should be open or closed. When designing a firewall strategy for your enterprise, make sure you consider all the rules and configuration options available to you. This article doesn’t review all the possible firewall options. We recommend you review the following documents:
- Windows Firewall Deployment Guide
- Windows Firewall Design Guide
- Introduction to Server and Domain Isolation
Default firewall settings
The first step in planning your firewall configuration is to determine the current status of the firewall for your operating system. If the operating system was upgraded from a previous version, the earlier firewall settings may have been preserved. The Group Policy or Administrator can change the firewall settings in the domain.
[!NOTE]
Turning on the firewall will affect other programs that access this computer, such as file and print sharing, and remote desktop connections. Administrators should consider all applications that are running on the computer before adjusting the firewall settings.
Programs to configure the firewall
Configure the Windows Firewall settings with either Microsoft Management Console or netsh.
-
Microsoft Management Console (MMC)
The Windows Firewall with Advanced Security MMC snap-in lets you configure more advanced firewall settings. This snap-in presents most of the firewall options in an easy-to-use manner, and presents all firewall profiles. For more information, see Using the Windows Firewall with Advanced Security Snap-in later in this article.
-
netsh
The netsh.exe is an Administrator tool to configure and monitor Windows-based computers at a command prompt or using a batch file. By using the netsh tool, you can direct the context commands you enter to the appropriate helper, and the helper does the command. A helper is a Dynamic Link Library (.dll) file that extends the functionality. The helper provides: configuration, monitoring, and support for one or more services, utilities, or protocols for the netsh tool.
All operating systems that support [!INCLUDEssNoVersion] have a firewall helper. [!INCLUDEwinserver2008] also has an advanced firewall helper called advfirewall. Many of the configuration options described can be configured by using netsh. For example, run the following script at a command prompt to open TCP port 1433:
netsh firewall set portopening protocol = TCP port = 1433 name = SQLPort mode = ENABLE scope = SUBNET profile = CURRENTA similar example using the Windows Firewall for Advanced Security helper:
netsh advfirewall firewall add rule name = SQLPort dir = in protocol = tcp action = allow localport = 1433 remoteip = localsubnet profile = DOMAINFor more information about netsh, see the following links:
- Netsh Command Syntax, Contexts, and Formatting
- How to use the «netsh advfirewall firewall» context instead of the «netsh firewall» context to control Windows Firewall behavior in Windows Server 2008 and in Windows Vista
-
PowerShell
See the following example to open TCP port 1433 and UDP port 1434 for [!INCLUDEssNoVersion] default instance, and [!INCLUDEssNoVersion] Browser Service:
New-NetFirewallRule -DisplayName "SQLServer default instance" -Direction Inbound -LocalPort 1433 -Protocol TCP -Action Allow New-NetFirewallRule -DisplayName "SQLServer Browser service" -Direction Inbound -LocalPort 1434 -Protocol UDP -Action Allow
For more examples, see New-NetFirewallRule.
-
For Linux
On Linux, you also need to open the ports associated with the services you need access to. Different distributions of Linux and different firewalls have their own procedures. For two examples, see SQL Server on Red Hat, and SQL Server on SUSE.
Ports used by SQL Server
The following tables can help you identify the ports being used by [!INCLUDEssNoVersion].
Ports used by the Database Engine
By default, the typical ports used by [!INCLUDEssNoVersion] and associated database engine services are: TCP 1433, 4022, 135, 1434, UDP 1434. The table below explains these ports in greater detail. A named instance uses Dynamic ports.
The following table lists the ports that are frequently used by the [!INCLUDEssDE].
| Scenario | Port | Comments |
|---|---|---|
| Default instance running over TCP | TCP port 1433 | The most common port allowed through the firewall. It applies to routine connections to the default installation of the [!INCLUDEssDE], or a named instance that is the only instance running on the computer. (Named instances have special considerations. See Dynamic ports later in this article.) |
| Named instances with default port | The TCP port is a dynamic port determined at the time the [!INCLUDEssDE] starts. | See the discussion below in the section Dynamic ports. UDP port 1434 might be required for the [!INCLUDEssNoVersion] Browser Service when you’re using named instances. |
| Named instances with fixed port | The port number configured by the administrator. | See the discussion below in the section Dynamic ports. |
| Dedicated Admin Connection | TCP port 1434 for the default instance. Other ports are used for named instances. Check the error log for the port number. | By default, remote connections to the Dedicated Administrator Connection (DAC) aren’t enabled. To enable remote DAC, use the Surface Area Configuration facet. For more information, see Surface Area Configuration. |
| [!INCLUDEssNoVersion] Browser service | UDP port 1434 | The [!INCLUDEssNoVersion] browser service listens for incoming connections to a named instance.
The service provides the client the TCP port number that corresponds to that named instance. Normally the [!INCLUDEssNoVersion] Browser service is started whenever named instances of the [!INCLUDEssDE] are used. The [!INCLUDEssNoVersion] Browser service isn’t required if the client is configured to connect to the specific port of the named instance. |
| Instance with HTTP endpoint. | Can be specified when an HTTP endpoint is created. The default is TCP port 80 for CLEAR_PORT traffic and 443 for SSL_PORT traffic. | Used for an HTTP connection through a URL. |
| Default instance with HTTPS endpoint | TCP port 443 | Used for an HTTPS connection through a URL. HTTPS is an HTTP connection that uses Transport Layer Security (TLS), previously known as Secure Sockets Layer (SSL). |
| [!INCLUDEssSB] | TCP port 4022. To verify the port used, execute the following query:
|
There’s no default port for [!INCLUDEssNoVersion] [!INCLUDEssSB], Books Online examples use the conventional configuration. |
| Database Mirroring | Administrator chosen port. To determine the port, execute the following query:
|
There’s no default port for database mirroring however Books Online examples use TCP port 5022 or 7022. It’s important to avoid interrupting an in-use mirroring endpoint, especially in high-safety mode with automatic failover. Your firewall configuration must avoid breaking quorum. For more information, see Specify a Server Network Address (Database Mirroring). |
| Replication | Replication connections to [!INCLUDEssNoVersion] use the typical regular [!INCLUDEssDE] ports (TCP port 1433 is the default instance)
Web synchronization and FTP/UNC access for replication snapshot require more ports to be opened on the firewall. To transfer initial data and schema from one location to another, replication can use FTP (TCP port 21), or sync over HTTP (TCP port 80) or File Sharing. File sharing uses UDP port 137 and 138, and TCP port 139 if used along with NetBIOS. File Sharing uses TCP port 445. |
For sync over HTTP, replication uses the IIS endpoint (configurable; port 80 default), but the IIS process connects to the backend [!INCLUDEssNoVersion] through the standard ports (1433 for the default instance.
During Web synchronization using FTP, the FTP transfer is between IIS and the [!INCLUDEssNoVersion] publisher, not between subscriber and IIS. |
| [!INCLUDEtsql] debugger | TCP port 135
See Special Considerations for Port 135 The IPsec exception might also be required. |
If using [!INCLUDEvsprvs], on the [!INCLUDEvsprvs] host computer, you must also add Devenv.exe to the Exceptions list and open TCP port 135.
If using [!INCLUDEssManStudio], on the [!INCLUDEssManStudio] host computer, you must also add ssms.exe to the Exceptions list and open TCP port 135. For more information, see Configure firewall rules before running the TSQL Debugger. |
For step-by-step instructions to configure the Windows Firewall for the [!INCLUDEssDE], see Configure a Windows Firewall for Database Engine Access.
Dynamic ports
By default, named instances (including [!INCLUDEssExpress]) use dynamic ports. means each time [!INCLUDEssDE] starts, it identifies an available port and uses that port number. If the named instance is the only instance of the [!INCLUDEssDE] installed, it will probably use TCP port 1433. If other instances of the [!INCLUDEssDE] are installed, it will probably use a different TCP port. Because the port selected might change every time that the [!INCLUDEssDE] is started, it’s difficult to configure the firewall to enable access to the correct port number. If a firewall is used, we recommend reconfiguring the [!INCLUDEssDE] to use the same port number every time. A fixed port or a static port is recommended. For more information, see Configure a Server to Listen on a Specific TCP Port (SQL Server Configuration Manager).
An alternative to configuring a named instance to listen on a fixed port is to create an exception in the firewall for a [!INCLUDEssNoVersion] program such as sqlservr.exe (for the [!INCLUDEssDE]). The port number won’t appear in the Local Port column of the Inbound Rules page when you’re using the Windows Firewall with Advanced Security MMC snap-in. It can be difficult to audit which ports are open. Another consideration is that a service pack or cumulative update can change the path to the [!INCLUDEssNoVersion] executable file and invalidate the firewall rule.
To add an exception for SQL Server using Windows Firewall with Advanced Security, see Use the Windows Firewall with Advanced Security snap-in later in this article.
Ports used by Analysis Services
By default, the typical ports used by [!INCLUDEssNoVersion] Analysis Services and associated services are: TCP 2382, 2383, 80, 443. The table below explains these ports in greater detail.
The following table lists the ports that are frequently used by [!INCLUDEssASnoversion].
| Feature | Port | Comments |
|---|---|---|
| [!INCLUDEssASnoversion] | TCP port 2383 for the default instance | The standard port for the default instance of [!INCLUDEssASnoversion]. |
| [!INCLUDEssNoVersion] Browser service | TCP port 2382 only needed for an [!INCLUDEssASnoversion] named instance | Client connection requests for a named instance of [!INCLUDEssASnoversion] that don’t specify a port number are directed to port 2382, the port on which [!INCLUDEssNoVersion] Browser listens. [!INCLUDEssNoVersion] Browser then redirects the request to the port that the named instance uses. |
| [!INCLUDEssASnoversion] configured for use through IIS/HTTP
(The PivotTable® Service uses HTTP or HTTPS) |
TCP port 80 | Used for an HTTP connection through a URL. |
| [!INCLUDEssASnoversion] configured for use through IIS/HTTPS
(The PivotTable® Service uses HTTP or HTTPS) |
TCP port 443 | Used for an HTTPS connection through a URL. HTTPS is an HTTP connection that uses TLS. |
If users access [!INCLUDEssASnoversion] through IIS and the Internet, you must open the port on which IIS is listening. Next, specify port in the client connection string. In this case, no ports have to be open for direct access to [!INCLUDEssASnoversion]. The default port 2389, and port 2382, should be restricted together with all other ports that aren’t required.
For step-by-step instructions to configure the Windows Firewall for [!INCLUDEssASnoversion], see Configure the Windows Firewall to Allow Analysis Services Access.
Ports used By Reporting Services
By default, the typical ports used by [!INCLUDEssNoVersion] Reporting Services and associated services are: TCP 80, 443. The table below explains these ports in greater detail.
The following table lists the ports that are frequently used by [!INCLUDEssRSnoversion].
| Feature | Port | Comments |
|---|---|---|
| [!INCLUDEssRSnoversion] Web Services | TCP port 80 | Used for an HTTP connection to [!INCLUDEssRSnoversion] through a URL. We recommend that you don’t use the preconfigured rule World Wide Web Services (HTTP). For more information, see the Interaction with Other Firewall Rules section below. |
| [!INCLUDEssRSnoversion] configured for use through HTTPS | TCP port 443 | Used for an HTTPS connection through a URL. HTTPS is an HTTP connection that uses TLS. We recommend that you don’t use the preconfigured rule Secure World Wide Web Services (HTTPS). For more information, see the Interaction with Other Firewall Rules section below. |
When [!INCLUDEssRSnoversion] connects to an instance of the [!INCLUDEssDE] or [!INCLUDEssASnoversion], you must also open the appropriate ports for those services. For step-by-step instructions to configure the Windows Firewall for [!INCLUDEssRSnoversion], Configure a Firewall for Report Server Access.
Ports used by Integration Services
The following table lists the ports that are used by the [!INCLUDEssISnoversion] service.
| Feature | Port | Comments |
|---|---|---|
| [!INCLUDEmsCoName] remote procedure calls (MS RPC)
Used by the [!INCLUDEssISnoversion] runtime. |
TCP port 135
See Special Considerations for Port 135 |
The [!INCLUDEssISnoversion] service uses DCOM on port 135. The Service Control Manager uses port 135 to do tasks such as starting and stopping the [!INCLUDEssISnoversion] service and transmitting control requests to the running service. The port number can’t be changed.
This port is only required to be open if you’re connecting to a remote instance of the [!INCLUDEssISnoversion] service from [!INCLUDEssManStudio] or a custom application. |
For step-by-step instructions to configure the Windows Firewall for [!INCLUDEssISnoversion], see Integration Services Service (SSIS Service).
Other ports and services
The following table lists ports and services that [!INCLUDEssNoVersion] might depend on.
| Scenario | Port | Comments |
|---|---|---|
| Windows Management Instrumentation
For more information about Windows Management Instrumentation (WMI), see WMI Provider for Configuration Management Concepts |
WMI runs as part of a shared service host with ports assigned through DCOM. WMI might be using TCP port 135.
See Special Considerations for Port 135 |
[!INCLUDEssNoVersion] Configuration Manager uses WMI to list and manage services. We recommend that you use the preconfigured rule group Windows Management Instrumentation (WMI). For more information, see the Interaction with Other Firewall Rules section below. |
| [!INCLUDEmsCoName] Distributed Transaction Coordinator (MS DTC) | TCP port 135
See Special Considerations for Port 135 |
If your application uses distributed transactions, you might have to configure the firewall to allow [!INCLUDEmsCoName] Distributed Transaction Coordinator (MS DTC) traffic to flow between separate MS DTC instances, and between the MS DTC and resource managers such as [!INCLUDEssNoVersion]. We recommend that you use the preconfigured Distributed Transaction Coordinator rule group.
When a single shared MS DTC is configured for the entire cluster in a separate resource group, you should add sqlservr.exe as an exception to the firewall. |
| The browse button in [!INCLUDEssManStudio] uses UDP to connect to the [!INCLUDEssNoVersion] Browser Service. For more information, see SQL Server Browser Service (Database Engine and SSAS). | UDP port 1434 | UDP is a connectionless protocol.
The firewall has a setting (UnicastResponsesToMulticastBroadcastDisabled Property of the INetFwProfile Interface) which controls the behavior of the firewall and unicast responses to a broadcast (or multicast) UDP request. It has two behaviors: If the setting is TRUE, no unicast responses to a broadcast are permitted at all. Enumerating services will fail. If the setting is FALSE (default), unicast responses are permitted for 3 seconds. The length of time isn’t configurable. In a congested or high-latency network, or for heavily loaded servers, tries to enumerate instances of [!INCLUDEssNoVersion] might return a partial list, which might mislead users. |
| IPsec traffic | UDP port 500 and UDP port 4500 | If the domain policy requires network communications to be done through IPsec, you must also add UDP port 4500 and UDP port 500 to the exception list. IPsec is an option using the New Inbound Rule Wizard in the Windows Firewall snap-in. For more information, see Using the Windows Firewall with Advanced Security Snap-in below. |
| Using Windows Authentication with Trusted Domains | Firewalls must be configured to allow authentication requests. | For more information, see How to configure a firewall for domains and trusts. |
| [!INCLUDEssNoVersion] and Windows Clustering | Clustering requires extra ports that aren’t directly related to [!INCLUDEssNoVersion]. | For more information, see Enable a network for cluster use. |
| URL namespaces reserved in the HTTP Server API (HTTP.SYS) | Probably TCP port 80, but can be configured to other ports. For general information, see Configuring HTTP and HTTPS. | For [!INCLUDEssNoVersion] specific information about reserving an HTTP.SYS endpoint using HttpCfg.exe, see About URL Reservations and Registration (SSRS Configuration Manager). |
Special considerations for port 135
When you use RPC with TCP/IP or with UDP/IP as the transport, inbound ports are dynamically assigned to system services as required. TCP/IP and UDP/IP ports that are larger than port 1024 are used. The ports are referred to as «random RPC ports.» In these cases, RPC clients rely on the RPC endpoint mapper to tell them which dynamic ports were assigned to the server. For some RPC-based services, you can configure a specific port instead of letting RPC assign one dynamically. You can also restrict the range of ports that RPC dynamically assigns to a small range, independent of the service. Because port 135 is used for many services, it’s frequently attacked by malicious users. When opening port 135, consider restricting the scope of the firewall rule.
For more information about port 135, see the following references:
- Service overview and network port requirements for the Windows Server system
- Remote procedure call (RPC)
- How to configure RPC dynamic port allocation to work with firewalls
Interaction with other firewall rules
The Windows Firewall uses rules and rule groups to establish its configuration. Each rule or rule group is associated with a particular program or service, and that program or service might modify or delete that rule without your knowledge. For example, the rule groups World Wide Web Services (HTTP) and World Wide Web Services (HTTPS) are associated with IIS. Enabling those rules will open ports 80 and 443, and [!INCLUDEssNoVersion] features that depend on ports 80 and 443 will function if those rules are enabled. However, administrators configuring IIS might modify or disable those rules. If you’re using port 80 or port 443 for [!INCLUDEssNoVersion], you should create your own rule or rule group that maintains your preferred port configuration independently of the other IIS rules.
The Windows Firewall with Advanced Security MMC snap-in allows any traffic that matches any applicable allow rule. So if there are two rules that both apply to port 80 (with different parameters). Traffic that matches either rule will be permitted. So if one rule allows traffic over port 80 from local subnet and one rule allows traffic from any address, the net effect is that all traffic to port 80 is independent of the source. To effectively manage access to [!INCLUDEssNoVersion], administrators should periodically review all firewall rules enabled on the server.
Overview of firewall profiles
Firewall profiles are used by the operating systems to identify and remember each of the networks by: connectivity, connections, and category.
There are three network location types in Windows Firewall with Advanced Security:
- Domain: Windows can authenticate access to the domain controller for the domain to which the computer is joined.
- Public: Other than domain networks, all networks are initially categorized as public. Networks that represent direct connections to the Internet or are in public locations, such as airports and coffee shops should be left public.
- Private: A network identified by a user or application as private. Only trusted networks should be identified as private networks. Users will likely want to identify home or small business networks as private.
The administrator can create a profile for each network location type, with each profile containing different firewall policies. Only one profile is applied at any time. Profile order is applied as follows:
- The domain profile is applied if all interfaces are authenticated to the domain controller where the computer is a member.
- If all interfaces are either authenticated to the domain controller or are connected to networks that are classified as private network locations, the private profile is applied.
- Otherwise, the public profile is applied.
Use the Windows Firewall with Advanced Security MMC snap-in to view and configure all firewall profiles. The Windows Firewall item in Control Panel only configures the current profile.
Additional firewall settings using the Windows Firewall item in Control Panel
The added firewall can restrict the opening of the port to incoming connections from specific computers or local subnet. Limit the scope of the port opening to reduce how much your computer is exposed to malicious users.
[!NOTE]
Using the Windows Firewall item in Control Panel only configures the current firewall profile.
Change the scope of a firewall exception using the Windows Firewall item in Control Panel
-
In the Windows Firewall item in Control Panel, select a program or port on the Exceptions tab, and then select Properties or Edit.
-
In the Edit a Program or Edit a Port dialog box, select Change Scope.
-
Choose one of the following options:
-
Any computer (including computers on the Internet): Not recommended. Any computer that can address your computer to connect to the specified program or port. This setting might be necessary to allow information to be presented to anonymous users on the internet, but increases your exposure to malicious users. Enabling this setting an allow Network Address Translation (NAT) traversal, such as the Allow edge traversal option will increase exposure.
-
My network (subnet) only: A more secure setting than Any computer. Only computers on the local subnet of your network can connect to the program or port.
-
Custom list: Only computers that have the IP addresses listed can connect. A secure setting can be more secure than My network (subnet) only, however, client computers using DHCP can occasionally change their IP address; will disable the ability to connect. Another computer, which you had not intended to authorize, might accept the listed IP address and connect to it. The Custom list is appropriate for listing other servers that are configured to use a fixed IP address.
IP addresses can be spoofed by an intruder. Restricting firewall rules are only as strong as your network infrastructure.
-
Use the Windows Firewall with Advanced Security snap-in
Advanced firewall settings can be configured by using the Windows Firewall with Advanced Security MMC snap-in. The snap-in includes a rule wizard and settings that aren’t available in the Windows Firewall item in Control Panel. These settings include:
- Encryption settings
- Services restrictions
- Restricting connections for computers by name
- Restricting connections to specific users or profiles
- Edge traversal allowing traffic to bypass Network Address Translation (NAT) routers
- Configuring outbound rules
- Configuring security rules
- Requiring IPsec for incoming connections
Create a new firewall rule using the New Rule wizard
- On the Start menu, select Run, type
WF.msc, and then select OK. - In the Windows Firewall with Advanced Security, in the left pane, right-click Inbound Rules, and then select New Rule.
- Complete the New Inbound Rule Wizard using the settings that you want.
Add a program exception for the SQL Server executable
-
From the start menu, type wf.msc. Press Enter or select the search result wf.msc to open Windows Defender Firewall with Advanced Security.
-
In the left pane, select Inbound rules.
-
In the right pane, under Actions, select New rule…. New Inbound Rule Wizard opens.
-
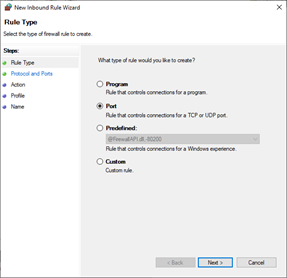
On Rule type, select Program. Select Next.
-
On Program, select This program path. Select Browse to locate your instance of [!INCLUDEssNoVersion]. The program is called
sqlservr.exe. It’s normally located at:C:Program FilesMicrosoft SQL ServerMSSQL<VersionNumber>.<InstanceName>MSSQLBinnsqlservr.exeSelect Next.
-
On Action, select Allow the connection. Select Next.
-
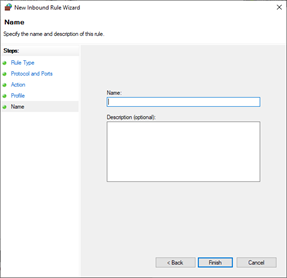
On Profile, include all three profiles. Select Next.
-
On Name, type a name for the rule. Select Finish.
For more information about endpoints, see:
- Configure the Database Engine to Listen on Multiple TCP Ports
- Endpoints Catalog Views (Transact-SQL)
Troubleshoot firewall settings
The following tools and techniques can be useful in troubleshooting firewall issues:
-
The effective port status is the union of all rules related to the port. It can be helpful to review all the rules that cite the port number, when trying to block access to a port. Review the rules with the Windows Firewall with Advanced Security MMC snap-in and sort the inbound and outbound rules by port number.
-
Review the ports that are active on the computer on which [!INCLUDEssNoVersion] is running. The review process includes verifying which TCP/IP ports are listening and also verifying the status of the ports.
-
The PortQry utility can be used to report the status of TCP/IP ports as listening, not listening, or filtered.
(The utility may not receive response from the port if it has a filtered status.)
The PortQry utility is available for download from the Microsoft Download Center.
List which TCP/IP ports are listening
To verify which ports are listening, display active TCP connections and IP statistics use the netstat command-line utility.
-
Open the Command Prompt window.
-
At the command prompt, type
netstat -n -a.The
-nswitch instructs netstat to numerically display the address and port number of active TCP connections. The-aswitch instructs netstat to display the TCP and UDP ports on which the computer is listening.
See also
- Service overview and network port requirements for the Windows Server system
- How to: Configure Firewall Settings (Azure SQL Database)
This document will show you how to open remote access to SQL Server by configuring Windows Firewall.
Applies To
- Windows 8.1
- Windows 10
- Windows Server 2016
- Windows Server 2019
- Microsoft SQL Server Express/Standard or higher editions 2012 or later.
- Microsoft SQL Server Compact Edition 4.0 or later.
Prerequisites
To follow the steps in this document you will need to have one of the versions of SQL Server running on one of the versions of Windows mentioned above.
This article only applies to Windows Defender Firewall. Other Firewalls may have similar settings that can be applied.
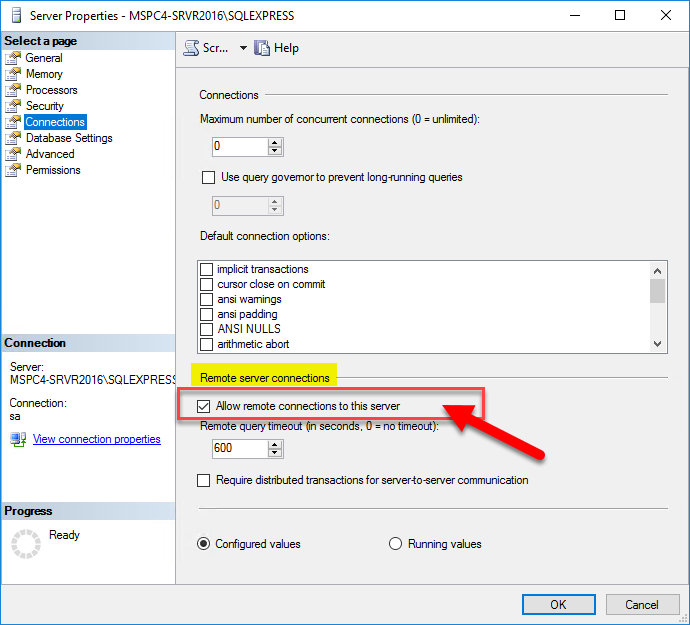
It is also assumed that you have configured SQL Server for remote access, either manually, or by following the steps in How To: Configure SQL Server for Remote Access.
You need to be a member of the Administrators group to perform the steps in this document.
Configure Windows Firewall
There are two methods for configuring Windows Firewall for SQL Server.
Choose one of the two methods below, that best suits your IT policy:
- Create Inbound Rules for the SQL Server Ports
- Allow the SQL Server applications in the Firewall
Create Inbound Rules for the SQL Server Ports
This method will target the specific ports SQL Server uses for communication.
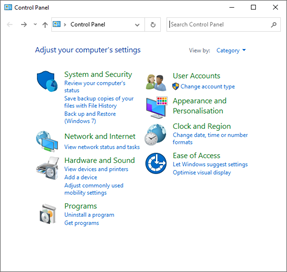
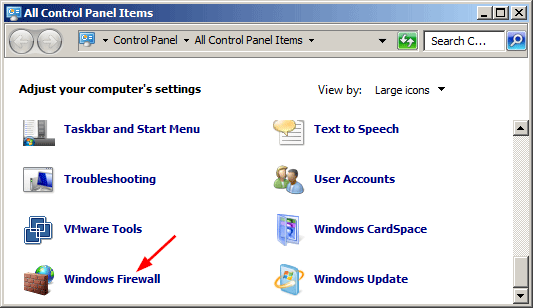
- Open Windows Control Panel and select System and Security.
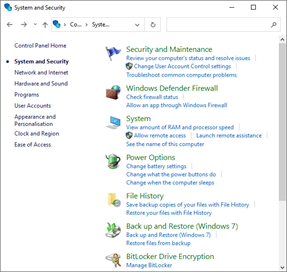
- From the System and Security window, click Windows Defender Firewall.
- From the Windows Defender Firewall window, click Advanced Settings.
- Add the port SQL uses for TCP.
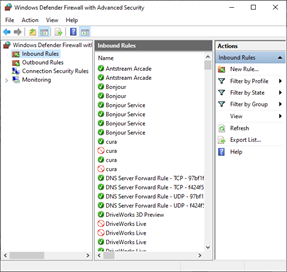
From the Windows Defender Firewall with Advanced Security window:
Select Inbound Rules from the left hand column.
Click New Rule… from the Actions column.
- From the New Inbound Rule Wizard, select Port.
Click Next.
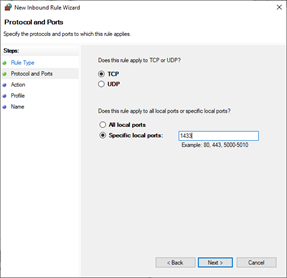
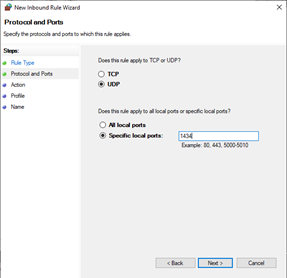
- Select TCP.
Select Specific local ports.
Enter 1433.
Click Next.
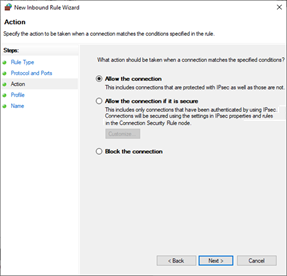
- Select Allow the connection.
Click Next.
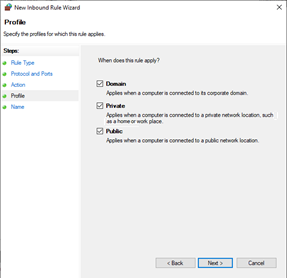
- Select Domain, Private and Public.
Click Next.
- Enter a name for the rule.
For example: SQL TCP.
- Add the port SQL uses for UDP.
From the Windows Defender Firewall with Advanced Security window:
Select Inbound Rules from the left hand column.
Click New Rule… from the Actions column.
- From the New Inbound Rule Wizard, select Port.
Click Next.
- Select UDP.
Select Specific local ports.
Enter 1434.
Click Next.
- Select Allow the connection.
Click Next.
- Select Domain, Private and Public.
Click Next.
- Enter a name for the rule.
For example: SQL TCP.
Click Finish.
Allow the SQL Server applications in the Firewall
This method will open all ports for access to SQL Server.
- Open Windows Control Panel and select System and Security.
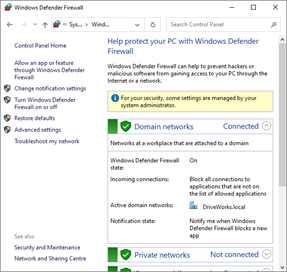
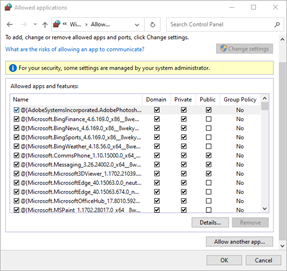
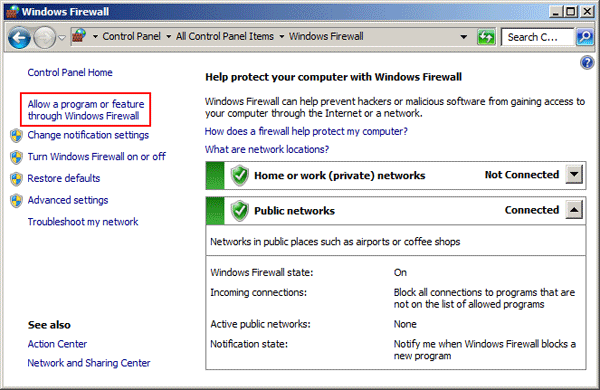
- From the System and Security window, click the link to Allow an app through Windows Firewall.
- Allow the SQL Server Browser:
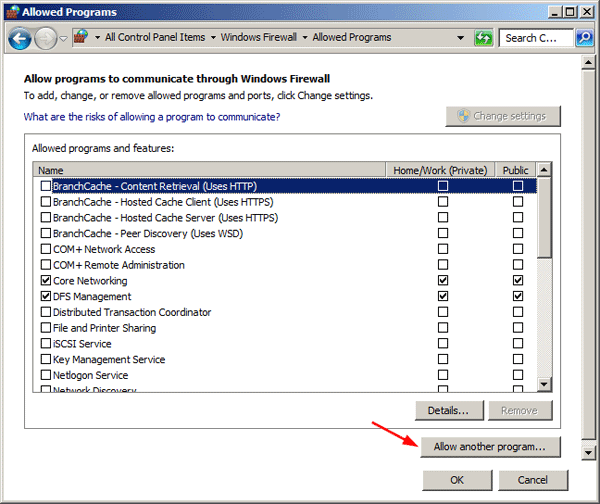
Click the Allow another app… button.
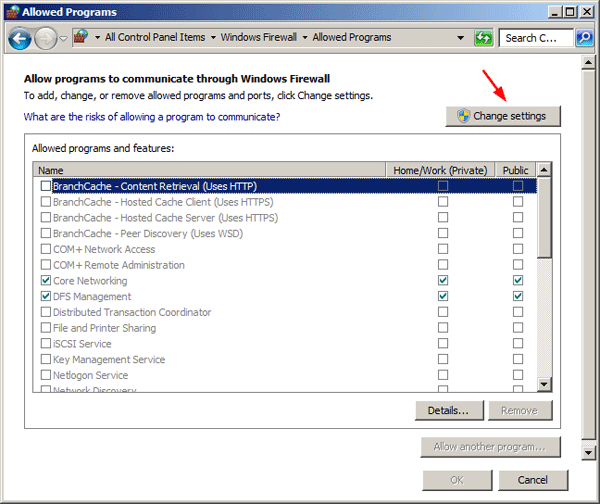
If your Windows Firewall settings are managed by your system administrator, you may need to click the Change Settings button.
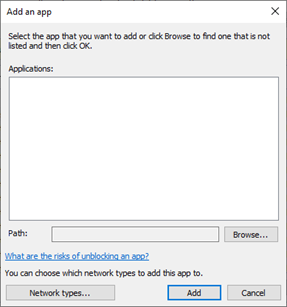
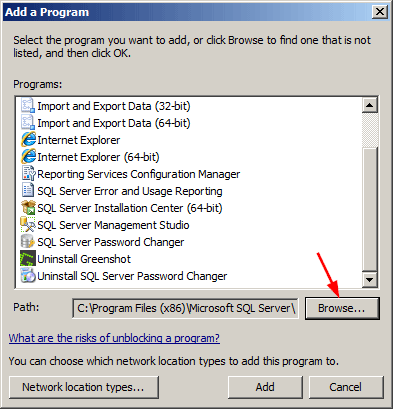
- Click the Browse button.
Browse to sqlbrowser.exe
This is located in the default installation folder:
C:Program Files (x86)Microsoft SQL Server90Shared
Click the Add button.
- Allow the SQL Server Application:
Click the Allow another app… button.
- Click the Browse button.
Browse to sqlserver.exe
This is located in the default installation folder:
C:Program FilesMicrosoft SQL Server<Version and Edition>MSSQLBinn
Version and Edition
The Version and Edition folder depends on the installed SQL Server.
For instance:
- SQL Server 2012 (Express) is located within the folder MSSQL11.SQLEXPRESS
- SQL Server 2017 (Express) is located within the folder MSSQL14.SQLEXPRESS
Other versions and editions will be similarly named and cannot be confused with the other folders in the Microsoft SQL Server folder.
Click the Add button.
- Click the OK button to save and apply the changes.
| Knowledge Base Article Ref: | KB13103002 |
|---|

0. Оглавление
- Что понадобится
- Определение / изменения порта для «экземпляра по умолчанию»
- Определение / изменения порта для именованного экземпляра SQL Server
- Добавление правила в Брандмауэр Windows
1. Что понадобится
- Статья будет актуальна для Microsoft SQL Server 2012 и для Microsoft SQL Server 2008 (R2).
- В качестве операционной системы сервера рассматриваются Microsoft Windows Server 2012 (R2) или Microsoft Windows Server 2008 (R2)
2. Определение / изменения порта для «экземпляра по умолчанию»
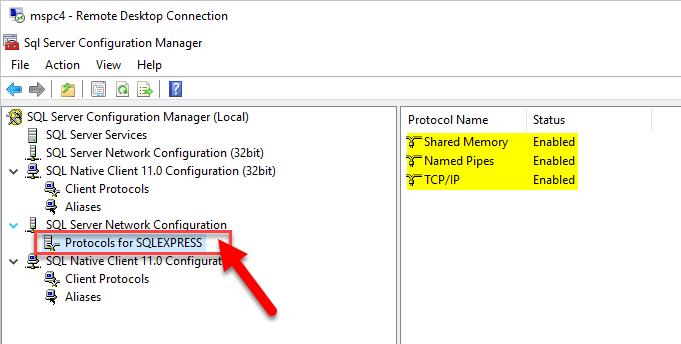
По умолчанию SQL Server использует для соединения порт 1433. Чтобы проверить это, запустим оснастку «Диспетчер конфигурации SQL Server» (SQL Server Configuration Manager). В Microsoft Windows Server 2012 (R2) ее можно найти в списке всех программ.
В Microsoft Windows Server 2008 (R2) в меню «Пуск» (Start) — «Microsoft SQL Server 2012» — «Средства настройки» (Configuration Tools) — «Диспетчер конфигурации SQL Server» (SQL Server Configuration Manager)
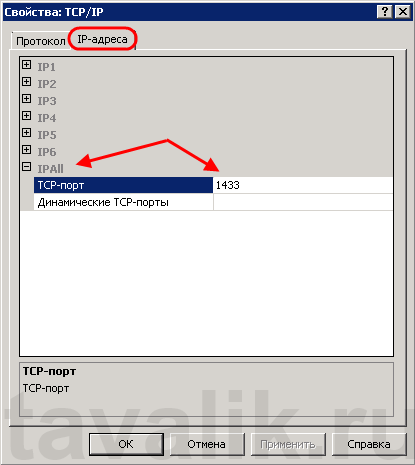
В запустившейся оснастке раскроем вкладку «Сетевая конфигурация SQL Server» (SQL Server Network Configuration), затем выделим вкладку «Протоколы для MSSQLSERVER» (Protocols for MSSQLSERVER). В окне слева в таблице найдем протокол TCP/IP, кликнем по нему правой кнопкой мыши и в контекстном меню выберем «Свойства» (Properties).
В открывшемся окне свойств перейдем на вкладку «IP-адреса» (IP Addresses), затем найдем и раскроем в дереве настроек ветку «IPAll». Здесь мы видим, что выбранный экземпляр SQL Server использует TCP-порт по умолчанию, а именно порт 1433. Если по каким то причинам требуется использовать другой номер порта, необходимо просто поменять текущее значение, нажать «Применить» (Apply) и перезапустить службу SQL Server.
3. Определение / изменения порта для именованного экземпляра SQL Server
В случае использования именованного экземпляра SQL Server ситуация аналогичная, за тем лишь исключением, что используются динамические TCP-порты. Это значит, что для каждого отдельного экземпляра будет назначен свой номер порта.
Для определения / изменения текущего порта, найдем в оснастке «Диспетчер конфигурации SQL Server» (SQL Server Configuration Manager) вкладку с сетевой конфигурацией необходимого нам экземпляра SQL Server и перейдем в свойства протокола TCP/IP для данного экземпляра. Здесь, как и в предыдущем случае, на вкладке «IP-адреса» (IP Addresses) в ветке «IPAll» можно узнать, а также изменить динамический TCP-порт для текущего экземпляра SQL Server.
4. Добавление правила в Брандмауэр Windows
Теперь, когда мы определились с номером порта, который будет использоваться для подключения к службе SQL Server, создадим разрешающее правило в Брандмауэре Windows на сервере, где запущена служба.
О том, как добавить разрешающее правило для определенного порта в Microsoft Windows Server 2008 (R2) я уже писал здесь. В Windows Server 2012 (R2) действия аналогичны.
Запускаем брандмауэр Windows (Windows Firewall). Сделать это можно кликнув правой кнопкой мыши по «Пуск» (Start), затем «Панель управления» (Control Panel) — «Система и безопасность» (System and Security) — «Брандмауэр Windows» (Windows Firewall). Или же выполнив команду firewall.cpl (для этого необходимо нажать комбинацию клавиш Win + R, в окне «Отрыть» (Open) ввести имя команды и нажать «ОК» ) .
Далее нажимаем на «Дополнительные параметры» (Advanced Settings) в меню слева.
В открывшемся окне, в дереве слева откроем вкладку «Правила для входящих подключений» (Inbound Rules), а затем в меню «Действия» (Actions) выберем пункт «Создать правило…» (New Rule…).
Запустится «Мастер создания правила для нового входящего подключения» (New Inbound Rule Wizard). На первой странице выберем тип правила (Rule Type) «Для порта» (Port) и нажмем «Далее» (Next).
Затем необходимо указать протокол (в нашем примере это TCP) и, непосредственно, номер порта (Specific local ports), который открываем. После чего жмем «Далее» (Next).
Теперь укажем действие связанное с добавляемым правилом. Выберем «Разрешить подключение» (Allow the connection) и нажмем «Далее» (Next).
На следующей странице нужно указать, для каких профилей брандмауэра будет действовать правило. Отмечаем нужные профили галочками и жмем «Далее» (Next).
Ну и наконец, вводим имя и описание для нового правила и нажимаем «Готово» (Finish) для завершения работы мастера.
А в оснастке «Брандмауэр Windows в режиме повышенной безопасности» (Windows Firewall with Advanced Security) в таблице «Правила для входящих подключений» (Inbound Rules) мы увидим только что созданное правило.
На этом настройка Брандмауэра завершена. Клиентские программы должны без препятствий подключиться к службе SQL Server.
5. Порт для администрирования MS SQL Server
Для того, чтобы к MS SQL Server можно было подключиться с помощью программы SQL Management Studio, необходимо также добавить правило для протокола UDP и порта 1434.
Подробнее о используемых SQL Server портах здесь.
Home » SQL » SQL Server Firewall Settings: A Complete Guide
SQL Server Firewall Settings: A Complete Guide
Stephen West ~
Published: January 12th, 2017 ~ SQL ~ 3 Minutes Reading
SQL server is a database management system developed by Microsoft and it is used to manage and store information on the SQL database. A database is a collection of data that is organised in such a way so that it can easily be managed, accessed, and updated. To prevent unauthorised access of a database, there is a need of firewall settings on the SQL server. SQL server firewall settings can be done by using SQL server configuration manager. Therefore, in this post, we are going to discussed how to configure firewall for SQL Server by using SQL Server configuration manager.
Ports Used By SQL Server
Static Port: At the time of SQL server configuration, default instance of SQL Server listens on port 1433. This is called static or fixed port. The port can be changed for security purpose or client application requirement.
Dynamic Port: The named instances (including SQL Server Express) are configured to listen on dynamic ports, by default. It means that, when the Database Engine starts, it finds an available port every time and uses that port number.
Configure Firewall For SQL Server Using Configuration Manager
Follow the below-mentioned procedures to configure firewall for SQL server using SQL server configuration manager:
For Static Port:
- Go to Start>Run and type WF.msc and then click on OK button
- Under the Windows Firewall with Advanced Security, right-click on Inbound Rules, and then click on New Rule
- In the Rule Type box, select the option Port, and then click on Next button
- In the dialog box of Port, select the option TCP. Then, select the option Specific local ports, after that type the port number 1433 for the static instance. After that click on Next button
- Select Allow the action under the Action dialog box and then click on Next button
- Now, Under the Profile dialog box, select any profiles which you want to connect to the SQL server, and then click on Next button
- Type a name and description of the rule, in the Name dialog box and then click on Finish button
For Dynamic Port:
- Go to Start>Run and type WF.msc and then click on OK button
- Under the Windows Firewall with Advanced Security, right-click on Inbound Rules, and then click on New Rule
- In the Rule Type box, select Program, and then click on Next button
- Now, under the Program dialog box, select the option This program path. After that, click on Browse, and go to the SQL Server instance that you want to access by using the firewall, and then click on Open. The location of SQL Server by default is C:ProgramFilesMicrosoftSQLServerMSSQL11.MSSQLSERVERMSSQLBinnSqlservr.exe. After that, click on Next
- Select Allow the action under the Action dialog box and then click on Next
- Now, Under the Profile dialog box, select any profiles which you want to connect to the SQL server, and then click on Next button
- Type a name and description of the rule, in the Name dialog box and then click on Finish button
Conclusion
In this post, we have discussed the procedures of SQL server firewall settings using SQL server configuration manager for static or dynamic port. By default, the value of static port is 1433. This port number can be changed for security purpose or client application requirement. If it is changed than, it becomes dynamic port. By following the above-mentioned steps, users can configure firewall for SQL server to prevent unauthorised access to a network.
SQL Server Setup
Firewall systems help prevent unauthorized access to computer resources. If a firewall is turned on but not correctly configured, attempts to connect to SQL Server might be blocked.
To access an instance of the SQL Server through a firewall, you must configure the firewall on the computer that is running SQL Server to allow access. The firewall is a component of Microsoft Windows. You can also install a firewall from another company. This topic discusses how to configure the Windows firewall, but the basic principles apply to other firewall programs.
Users familiar with the Windows Firewall item in Control Panel and with the Windows Firewall with Advanced Security Microsoft Management Console (MMC) snap-in and who know which firewall settings they want to configure can move directly to the topics in the following list:
-
How to: Configure a Windows Firewall for Database Engine Access
-
How to: Configure Windows Firewall for Analysis Services Access
-
How to: Configure a Firewall for Report Server Access
-
How to: Configure a Windows Firewall for Integration Services
 In this Topic
In this Topic
 Basic Firewall Information
Basic Firewall Information
Firewalls work by inspecting incoming packets, and comparing them against a set of rules. If the rules allow the packet, the firewall passes the packet to the TCP/IP protocol for additional processing. If the rules do not allow the packet, the firewall discards the packet and, if logging is enabled, creates an entry in the firewall logging file.
The list of allowed traffic is populated in one of the following ways:
- When the computer that has the firewall enabled initiates communication, the firewall creates an entry in the list so that the response is allowed. The incoming response is considered solicited traffic and you do not have to configure this.
- An administrator configures exceptions to the firewall. This allows either access to specified programs running on your computer, or access to specified connection ports on your computer. In this case, the computer accepts unsolicited incoming traffic when acting as a server, a listener, or a peer. This is the type of configuration that must be completed to connect to SQL Server.
Choosing a firewall strategy is more complex than just deciding if a given port should be open or closed. When designing a firewall strategy for your enterprise, make sure that you consider all the rules and configuration options available to you. This topic does not review all the possible firewall options. We recommend that you review the following documents:
Getting Started with Windows Firewall with Advanced Security in Windows Vista and Windows Server 2008
Windows Firewall with Advanced Security Design Guide
Introduction to Server and Domain
 Default Firewall Settings
Default Firewall Settings
The first step in planning your firewall configuration is to determine the current status of the firewall for your operating system. If the operating system was upgraded from a previous version, the earlier firewall settings may have been preserved. Also, the firewall settings could have been changed by another administrator or by a Group Policy in your domain. However, the default settings are as follows:
-
Windows Server 2008
The firewall is on and is blocking remote connections. -
Windows Server 2003
The firewall is off. Administrators should consider turning on the firewall. -
Windows Vista
The firewall is on and is blocking remote connections. -
Windows XP, Service Pack 2 or later
The firewall is on and is blocking remote connections. -
Window XP, Service Pack 1 or earlier
The firewall is off and should be turned on.
 Note: Note: |
|---|
| Turning on the firewall will affect other programs that access this computer, such as file and print sharing, and remote desktop connections. Administrators should consider all applications that are running on the computer before adjusting the firewall settings. |
 Programs to Configure the Firewall
Programs to Configure the Firewall
There are three ways to configure the Windows Firewall settings.
-
Windows Firewall item in Control Panel
The Windows Firewall item can be opened from Control Panel.The Windows Firewall item in Control Panel allows you to configure basic options. These include the following:
- Turning the Windows Firewall item in Control Panel on or off
- Enabling and disabling rules
- Granting exceptions for ports and programs
- Setting some scope restrictions
The Windows Firewall item in Control Panel is most appropriate for users who are not experienced in firewall configuration, and who are configuring basic firewall options for computers that are not mobile. You can also open the Windows Firewall item in Control Panel from the run command by using the following procedure:
To open the Windows Firewall item
-
On the Start menu, click Run, and then enter
firewall.cpl. -
Click OK.
-
Microsoft Management Console (MMC)
The Windows Firewall with Advanced Security MMC snap-in lets you configure more advanced firewall settings. This snap-in is only available for Microsoft Vista and Windows Server 2008; however, it presents most of the firewall options in an easy-to-use manner, and presents all firewall profiles. For more information, see Using the Windows Firewall with Advanced Security Snap-in later in this topic. -
netsh
The netsh.exe tool can be used by an administrator to configure and monitor Windows-based computers at a command prompt. By using the netsh tool, you can direct the context commands you enter to the appropriate helper, and the helper then performs the command. A helper is a Dynamic Link Library (.dll) file that extends the functionality of the netsh tool by providing configuration, monitoring, and support for one or more services, utilities, or protocols. All operating systems that support SQL Server have a firewall helper. Microsoft Windows Vista and Windows Server 2008 also have an advanced firewall helper called advfirewall. How to use netsh is not discussed in this topic. However, many of the configuration options described can be configured by using netsh. For scripts to configure SQL Server using netsh, see How to use a script to programmatically open ports for SQL Server to use on systems that are running Windows XP Service Pack. For more information about netsh, see the following links:-
How to Use the Netsh.exe Tool and Command-Line Switches
-
How to use the “netsh advfirewall firewall” context instead of the “netsh firewall” context to control Windows Firewall behavior in Windows Server 2008 and in Windows Vista
-
The «netsh firewall» command together with the «profile=all» parameter does not configure the public profile on a Windows Vista-based computer
-
Troubleshooting Windows Firewall settings in Windows XP Service Pack 2 for advanced users
-
How to Use the Netsh.exe Tool and Command-Line Switches
 Ports Used By SQL Server
Ports Used By SQL Server
The following tables can help you identify the ports being used by SQL Server.
Ports Used By the Database Engine
The following table lists the ports that are frequently used by the Database Engine.
| Scenario | Port | Comments |
|---|---|---|
|
SQL Server default instance running over TCP |
TCP port 1433 |
This is the most common port allowed through the firewall. It applies to routine connections to the default installation of the Database Engine, or a named instance that is the only instance running on the computer. (Named instances have special considerations. See Dynamic Ports later in this topic.) |
|
SQL Server named instances in the default configuration |
The TCP port is a dynamic port determined at the time the Database Engine starts. |
See the discussion below in the section Dynamic Ports. UDP port 1434 might be required for the SQL Server Browser Service when you are using named instances. |
|
SQL Server named instances when they are configured to use a fixed port |
The port number configured by the administrator. |
See the discussion below in the section Dynamic Ports. |
|
Dedicated Admin Connection |
TCP port 1434 |
By default, remote connections to the Dedicated Administrator Connection (DAC) are not enabled. To enable remote DAC, use the Surface Area Configuration facet. For more information, see Understanding Surface Area Configuration. |
|
SQL Server Browser service |
UDP port 1434 |
The SQL Server Browser service listens for incoming connections to a named instance and provides the client the TCP port number that corresponds to that named instance. Normally the SQL Server Browser service is started whenever named instances of the Database Engine are used. The SQL Server Browser service does not have to be started if the client is configured to connect to the specific port of the named instance. |
|
SQL Server default instance running over an HTTP endpoint. |
TCP port 80 |
Used for an HTTP connection through a URL. |
|
SQL Server default instance running over an HTTPS endpoint. |
TCP port 443 |
Used for an HTTPS connection through a URL. HTTPS is an HTTP connection that uses secure sockets layer (SSL). |
|
Service Broker |
TCP port 4022 |
There is no default port for SQL Server Service Broker, but this is the conventional configuration. |
|
Database Mirroring |
Administrator chosen port. To determine the port, execute the following query:
|
There is no default port for Database mirroring, but this is the conventional configuration. It is very important to avoid interrupting an in-use mirroring endpoint, especially in high-safety mode with automatic failover. Your firewall configuration must avoid breaking quorum. For more information, see Specifying a Server Network Address (Database Mirroring). |
|
Replication |
Replication connections to SQL Server use the typical regular Database Engine ports (TCP port 1433, etc.) Web synchronization and FTP/UNC access for replication snapshot require additional ports to be opened on the firewall. To transfer initial data and schema from one location to another, replication can use FTP (TCP port 21), or sync over HTTP (TCP port 80) or File and Print Sharing (TCP port 137,138, or 139). |
For sync over HTTP, replication uses the IIS endpoint (ports for which are configurable but is port 80 by default), but the IIS process connects to the backend SQL Server through the standard ports (1433 for the default instance. During Web synchronization using FTP, the FTP transfer is between IIS and the SQL Server publisher, not between subscriber and IIS. For more information, see Configuring Microsoft Internet Security and Acceleration Server for Microsoft SQL Server 2000 Replication over the Internet. |
|
Transact-SQL debugger |
TCP port 135 See Special Considerations for Port 135 The IPsec exception might also be required. |
If using Visual Studio, on the Visual Studio host computer, you must also add Devenv.exe to the Exceptions list and open TCP port 135. If using Management Studio, on the Management Studio host computer, you must also add ssms.exe to the Exceptions list and open TCP port 135. For more information, see Configuring and Starting the Transact-SQL Debugger. |
For step by step instructions to configure the Windows Firewall for the Database Engine, see How to: Configure a Windows Firewall for Database Engine Access.
Dynamic Ports
Named instances (including SQL Server Express) use dynamic ports. That means that every time that the Database Engine starts, it identifies an available port and uses that port number. If the named instance is the only instance of the Database Engine installed, it will probably use TCP port 1433. If other instances of the Database Engine are installed, it will probably use a different TCP port. Because the port selected might change every time that the Database Engine is started, it is difficult to configure the firewall to enable access to the correct port number. Therefore, if a firewall is started, we recommend reconfiguring the Database Engine to use the same port number every time. This is called a fixed port or a static port. For more information, see Configuring a Fixed Port.
An alternative to configuring a named instance to listen on a fixed port is to create an exception in the firewall for a SQL Server program such as sqlservr.exe (for the Database Engine). This can be convenient, but the port number will not appear in the Local Port column of the Inbound Rules page when you are using the Windows Firewall with Advanced Security MMC snap-in. This can make it more difficult to audit which ports are open. Another consideration is that a service pack or cumulative update can change the path to the SQL Server executable which will invalidate the firewall rule.
 Note: Note: |
|---|
| The following procedure uses the Windows Firewall item in Control Panel. The Windows Firewall with Advanced Security MMC snap-in can configure a more complex rule. This includes configuring a service exception which can be useful for providing defense in depth. See Using the Windows Firewall with Advanced Security Snap-in below. |
To add a program exception to the firewall using the Windows Firewall item in Control Panel.
-
On the Exceptions tab of the Windows Firewall item in Control Panel, click Add a program.
-
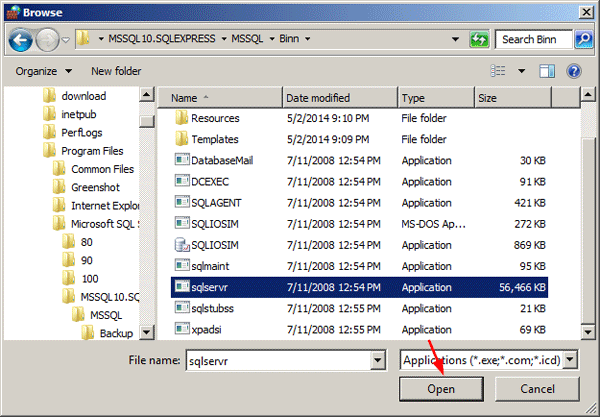
Browse to the location of the instance of SQL Server that you want to allow through the firewall, for example C:Program FilesMicrosoft SQL ServerMSSQL10.<instance_name>MSSQLBinn, select sqlservr.exe, and then click Open.
-
Click OK.
For more information about endpoints, see Network Protocols and TDS Endpoints and Endpoints Catalog Views (Transact-SQL).
Ports Used By Analysis Services
The following table lists the ports that are frequently used by Analysis Services.
| Feature | Port | Comments |
|---|---|---|
|
Analysis Services |
TCP port 2383 for the default instance |
The standard port for the default instance of Analysis Services. |
|
SQL Server Browser service |
TCP port 2382 only needed for an Analysis Services named instance |
Client connection requests for a named instance of Analysis Services that do not specify a port number are directed to port 2382, the port on which SQL Server Browser listens. SQL Server Browser then redirects the request to the port that the named instance uses. |
|
Analysis Services configured for use through IIS/HTTP (The PivotTable® Service uses HTTP or HTTPS) |
TCP port 80 |
Used for an HTTP connection through a URL. |
|
Analysis Services configured for use through IIS/HTTPS (The PivotTable® Service uses HTTP or HTTPS) |
TCP port 443 |
Used for an HTTPS connection through a URL. HTTPS is an HTTP connection that uses secure sockets layer (SSL). |
If users access Analysis Services through IIS and the Internet, you must open the port on which IIS is listening and specify that port in the client connection string. In this case, no ports have to be open for direct access to Analysis Services. The default port 2389, and port 2382, should be restricted together with all other ports that are not required.
For step by step instructions to configure the Windows Firewall for Analysis Services, see How to: Configure Windows Firewall for Analysis Services Access.
Ports Used By Reporting Services
The following table lists the ports that are frequently used by Reporting Services.
| Feature | Port | Comments |
|---|---|---|
|
Reporting Services Web Services |
TCP port 80 |
Used for an HTTP connection to Reporting Services through a URL. We recommend that you do not use the preconfigured rule World Wide Web Services (HTTP). For more information, see the Interaction with Other Firewall Rules section below. |
|
Reporting Services configured for use through HTTPS |
TCP port 443 |
Used for an HTTPS connection through a URL. HTTPS is an HTTP connection that uses secure sockets layer (SSL). We recommend that you do not use the preconfigured rule Secure World Wide Web Services (HTTPS). For more information, see the Interaction with Other Firewall Rules section below. |
When Reporting Services connects to an instance of the Database Engine or Analysis Services, you must also open the appropriate ports for those services. For step-by-step instructions to configure the Windows Firewall for Reporting Services, How to: Configure a Firewall for Report Server Access.
Ports Used By Integration Services
The following table lists the ports that are used by the Integration Services service.
| Feature | Port | Comments |
|---|---|---|
|
Microsoft remote procedure calls (MS RPC) Used by the Integration Services runtime. |
TCP port 135 See Special Considerations for Port 135 |
The Integration Services service uses DCOM on port 135. The Service Control Manager uses port 135 to perform tasks such as starting and stopping the Integration Services service and transmitting control requests to the running service. The port number cannot be changed. This port is only required to be open if you are connecting to a remote instance of the Integration Services service from Management Studio or a custom application. |
For step-by-step instructions to configure the Windows Firewall for Integration Services, see Configuring a Windows Firewall for Integration Services Access and How to: Configure a Windows Firewall for Integration Services.
Additional Ports and Services
The following table lists ports and services that SQL Server might depend on.
| Scenario | Port | Comments |
|---|---|---|
|
Windows Management Instrumentation For more information about WMI, see WMI Provider for Configuration Management Concepts |
WMI runs as part of a shared service host with ports assigned through DCOM. WMI might be using TCP port 135. See Special Considerations for Port 135 |
SQL Server Configuration Manager uses WMI to list and manage services. We recommend that you use the preconfigured rule group Windows Management Instrumentation (WMI). For more information, see the Interaction with Other Firewall Rules section below. |
|
Microsoft Distributed Transaction Coordinator (MS DTC) |
TCP port 135 See Special Considerations for Port 135 |
If your application uses distributed transactions, you might have to configure the firewall to allow Microsoft Distributed Transaction Coordinator (MS DTC) traffic to flow between separate MS DTC instances, and between the MS DTC and resource managers such as SQL Server. We recommend that you use the preconfigured Distributed Transaction Coordinator rule group. |
|
The browse button in Management Studio uses UDP to connect to the SQL Server Browser Service. For more information, see SQL Server Browser Service. |
UDP port 1434 |
UDP is a connectionless protocol. The firewall has a setting, which is named UnicastResponsesToMulticastBroadcastDisabled Property of the INetFwProfile Interface which controls the behavior of the firewall with respect to unicast responses to a broadcast (or multicast) UDP request. It has two behaviors:
|
|
IPsec traffic |
UDP port 500 and UDP port 4500 |
If the domain policy requires network communications to be done through IPsec, you must also add UDP port 4500 and UDP port 500 to the exception list. IPsec is an option using the New Inbound Rule Wizard in the Windows Firewall snap-in. For more information, see Using the Windows Firewall with Advanced Security Snap-in below. |
|
Using Windows Authentication with Trusted Domains |
Firewalls must be configured to allow authentication requests. |
For more information, see How to configure a firewall for domains and trusts. |
|
SQL Server and Windows Clustering |
Clustering requires additional ports that are not directly related to SQL Server. |
For more information, see Enable a network for cluster use. |
|
URL namespaces reserved in the HTTP Server API (HTTP.SYS) |
Probably TCP port 80, but can be configured to other ports. For general information, see Configuring HTTP and HTTPS. |
For SQL Server specific information about reserving an HTTP.SYS endpoint using HttpCfg.exe, see Reserving URL Namespaces by Using Http.sys. |
 Special Considerations for Port 135
Special Considerations for Port 135
 Interaction with Other Firewall Rules
Interaction with Other Firewall Rules
The Windows Firewall uses rules and rule groups to establish its configuration. Each rule or rule group is generally associated with a particular program or service, and that program or service might modify or delete that rule without your knowledge. For example, the rule groups World Wide Web Services (HTTP) and World Wide Web Services (HTTPS) are associated with IIS. Enabling those rules will open ports 80 and 443, and SQL Server features that depend on ports 80 and 443 will function if those rules are enabled. However, administrators configuring IIS might modify or disable those rules. Therefore, if you are using port 80 or port 443 for SQL Server, you should create your own rule or rule group that maintains your desired port configuration independently of the other IIS rules.
The Windows Firewall with Advanced Security MMC snap-in allows any traffic that matches any applicable allow rule. So if there are two rules that both apply to port 80 (with different parameters), traffic that matches either rule will be permitted. So if one rule allows traffic over port 80 from local subnet and one rule allows traffic from any address, the net effect is that all traffic to port 80 is permitted regardless of the source. To effectively manage access to SQL Server, administrators should periodically review all firewall rules enabled on the server.
 Overview of Firewall Profiles
Overview of Firewall Profiles
Firewall profiles are discussed in Getting Started with Windows Firewall with Advanced Security in Windows Vista and Windows Server 2008 in the section Network location-aware host firewall. To summarize, Windows Vista and Windows Server 2008 identify and remember each of the networks to which they connect with regard to connectivity, connections, and category.
There are three network location types in Windows Firewall with Advanced Security:
- Domain. Windows can authenticate access to the domain controller for the domain to which the computer is joined.
- Public. Other than domain networks, all networks are initially categorized as public. Networks that represent direct connections to the Internet or are in public locations, such as airports and coffee shops should be left public.
- Private. A network identified by a user or application as private. Only trusted networks should be identified as private networks. Users will likely want to identify home or small business networks as private.
The administrator can create a profile for each network location type, with each profile containing different firewall policies. Only one profile is applied at any time. Profile order is applied as follows:
- If all interfaces are authenticated to the domain controller for the domain of which the computer is a member, the domain profile is applied.
- If all interfaces are either authenticated to the domain controller or are connected to networks that are classified as private network locations, the private profile is applied.
- Otherwise, the public profile is applied.
Use the Windows Firewall with Advanced Security MMC snap-in to view and configure all firewall profiles. The Windows Firewall item in Control Panel only configures the current profile.
 Additional Firewall Settings Using the Windows Firewall item in Control Panel
Additional Firewall Settings Using the Windows Firewall item in Control Panel
Exceptions that you add to the firewall can restrict the opening of the port to incoming connections from specific computers or the local subnet. This restriction of the scope of the port opening can reduce how much your computer is exposed to malicious users, and is recommended.
 Note: Note: |
|---|
| Using the Windows Firewall item in Control Panel only configures the current firewall profile. |
To change the scope of a firewall exception using the Windows Firewall item in Control Panel
-
In the Windows Firewall item in Control Panel, select a program or port on the Exceptions tab, and then click Properties or Edit.
-
In the Edit a Program or Edit a Port dialog box, click Change Scope.
-
Choose one of the following options:
-
Any computer (including those on the Internet)
Not recommended. This will allow any computer that can address your computer to connect to the specified program or port. This setting might be necessary to allow information to be presented to anonymous users on the internet, but increases your exposure to malicious users. Your exposure can be further increased if you enable this setting and also allow Network Address Translation (NAT) traversal, such as the Allow edge traversal option. -
My network (subnet) only
This is a more secure setting than Any computer. Only computers on the local subnet of your network can connect to the program or port. -
Custom list:
Only computers that have the IP addresses you list can connect. This can be a more secure setting than My network (subnet) only, however, client computers using DHCP can occasionally change their IP address. Then the intended computer will not be able to connect. Another computer, which you had not intended to authorize, might accept the listed IP address and then be able to connect. The Custom list option might be appropriate for listing other servers which are configured to use a fixed IP address; however, IP addresses might be spoofed by an intruder. Restricting firewall rules are only as strong as your network infrastructure.
-
Any computer (including those on the Internet)
 Using the Windows Firewall with Advanced Security Snap-in
Using the Windows Firewall with Advanced Security Snap-in
On computers that are running Vista or Windows Server 2008, additional advanced firewall settings can be configured by using the Windows Firewall with Advanced Security MMC snap-in. The snap-in includes a rule wizard and exposes additional settings that are not available in the Windows Firewall item in Control Panel. These settings include the following:
- Encryption settings
- Services restrictions
- Restricting connections for computers by name
- Restricting connections to specific users or profiles
- Edge traversal allowing traffic to bypass Network Address Translation (NAT) routers
- Configuring outbound rules
- Configuring security rules
- Requiring IPsec for incoming connections
To create a new firewall rule using the New Rule wizard
-
On the Start menu, click Run, type WF.msc, and then click OK.
-
In the Windows Firewall with Advanced Security, in the left pane, right-click Inbound Rules, and then click New Rule.
-
Complete the New Inbound Rule Wizard using the settings that you want.
 Troubleshooting Firewall Settings
Troubleshooting Firewall Settings
The following tools and techniques can be useful in troubleshooting firewall issues:
- The effective port status is the union of all rules related to the port. When trying to block access through a port, it can be helpful to review all the rules which cite the port number. To do this, use the Windows Firewall with Advanced Security MMC snap-in and sort the inbound and outbound rules by port number.
-
Review the ports that are active on the computer on which SQL Server is running. This review process includes verifying which TCP/IP ports are listening and also verifying the status of the ports.
To verify which ports are listening, use the netstat command-line utility. In addition to displaying active TCP connections, the netstat utility also displays a variety of IP statistics and information.To list which TCP/IP ports are listening
-
Open the Command Prompt window.
-
At the command prompt, type netstat -n -a.
The -n switch instructs netstat to numerically display the address and port number of active TCP connections. The -a switch instructs netstat to display the TCP and UPD ports on which the computer is listening.
-
- The PortQry utility can be used to report the status of TCP/IP ports as listening, not listening, or filtered. (With a filtered status, the port might or might not be listening; this status indicates that the utility did not receive a response from the port.) The PortQry utility is available for download from the Microsoft Download Center.
For additional troubleshooting topics, see:
-
Troubleshooting Windows Firewall with Advanced Security in Windows Vista and Windows Server 2008 — Diagnostics and Tools
-
Troubleshooting (Database Engine)
-
Troubleshooting (Analysis Services — Data Mining)
-
Troubleshooting (Reporting Services)
-
Troubleshooting (Integration Services)
 See Also
See Also
May 2, 2016 updated by
Leave a reply »
By default, Windows Firewall doesn’t allow inbound / outbound requests for SQL Server. If you try to connect to a SQL Server instance from network, you might get the error saying “The server was not found or was not accessible”. In this tutorial we’ll show you 2 ways to configure Windows Firewall to allow SQL Server access.
Method 1: Allow SQL Server Access Through Control Panel
- Open Control Panel in Large icons or Small icons view, click on Windows Firewall.
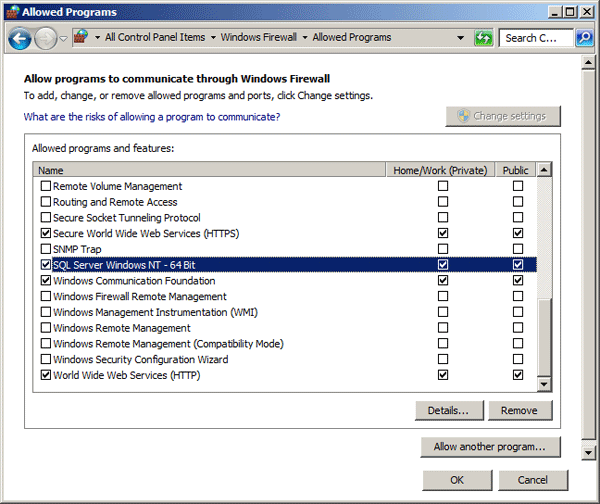
- Click the link “Allow a program or feature through Windows Firewall” on the left of window.
- You will now see a list with all the apps which are allowed to communicate through the Windows Firewall. To change the rules, you need to click the Change Settings button. The list of rules will no longer be gray and you will be able to edit it.
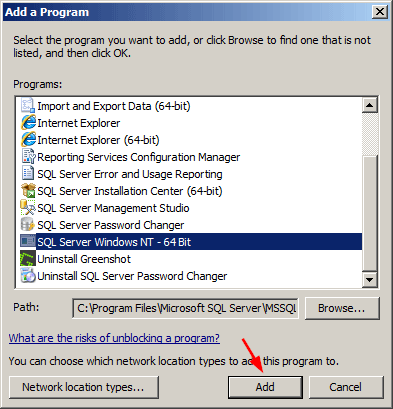
- Click the “Allow another program…” button.
- From the “Add a Program” window, click the Browse button.
- Navigate to the installation path for your SQL Server instance and select sqlservr.exe, and click Open. In my example, the location is
C:Program FilesMicrosoft SQL ServerMSSQL10.SQLEXPRESSMSSQLBinnsqlservr.exe. - You’ll back to the “Add a Program” window and see SQL Server is added to the list. Click the Add button.
- SQL Server now appears in the list of Allowed programs and features. You can check any of the location types: private or public. When done, press OK.
Method 2: Allow SQL Server Access Through Command Prompt
- Open an elevated Command Prompt.
-
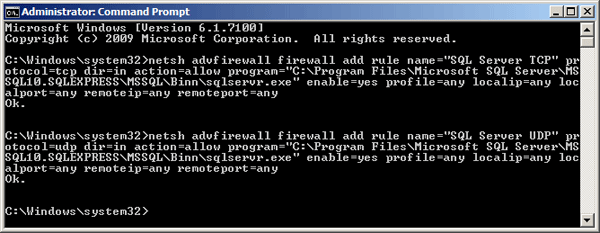
You can run the Netsh advfirewall command to open all ports for SQL Server connections. Assuming the path of your SQL Server service is C:Program FilesMicrosoft SQL ServerMSSQL10.SQLEXPRESSMSSQLBinnsqlservr.exe, copy / and paste the following commands in the Command Prompt, press Enter after each.
netsh advfirewall firewall add rule name="SQL Server TCP" protocol=tcp dir=in action=allow program="C:Program FilesMicrosoft SQL ServerMSSQL10.SQLEXPRESSMSSQLBinnsqlservr.exe" enable=yes profile=any localip=any localport=any remoteip=any remoteport=anynetsh advfirewall firewall add rule name="SQL Server UDP" protocol=udp dir=in action=allow program="C:Program FilesMicrosoft SQL ServerMSSQL10.SQLEXPRESSMSSQLBinnsqlservr.exe" enable=yes profile=any localip=any localport=any remoteip=any remoteport=any - When it’s done, you’ve successfully opened up all ports to allow SQL Server access through Windows Firewall.
- Previous Post: How to Reset Start Menu Layout to Default in Windows 10
- Next Post: How to Block An Application from Running in Windows 10
(Updated 2016-10-24)
Intro
If you want to allow remote computers on your network to access an instance of Sql Server running on one machine, you’ll have to add some new Incoming rules to the Windows Firewall, or no connections can come through. So, let’s show you what has to be considered and how to achieve this.
Sql Server Instance Types
Before you can configure the Windows Firewall to allow remote access to your Sql Server instance, it’s important to understand the “instance type” of the Sql Server that you are running. For Sql Server, its “instance type” can either be the default instance, an unnamed instance, or a named instance. Which one you have determines which port you have to open in Windows Firewall.
- When SQL Server is installed as the default instance, it does not require a client to specify the name of the instance to make a connection. The client only has to know the server name. This typically uses Port 1433 in the TCP protocol.
- A named instance is identified by the network name of the computer plus the instance name that you specify during installation (i.e. \ComputerNameSqlExpress or something similar). The client must specify both the server name and the instance name when connecting. This typically uses the Sql Server Browser service to find the Sql Server instance, and that requires access to Port 1434 UDP protocol.
Windows Firewall Setup to Allow Remote Access
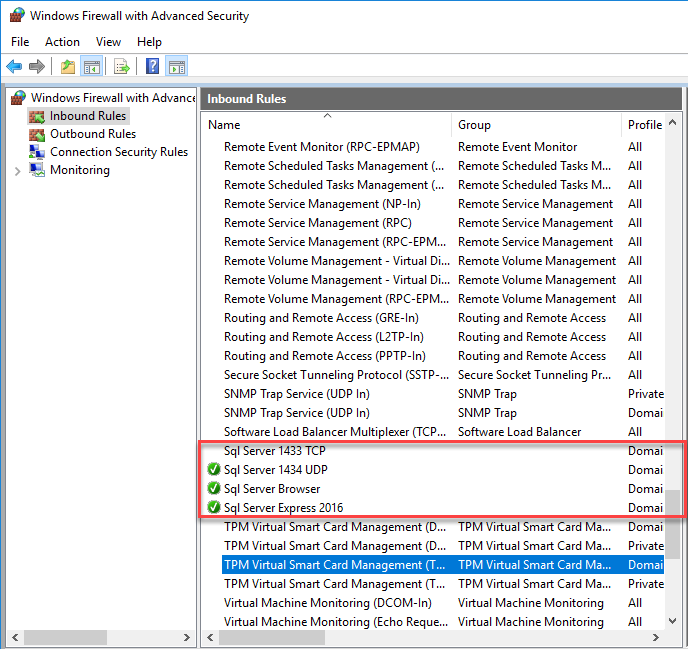
So, in order to allow remote access to the Sql Server instance, you will need to add these Incoming rules to the Windows Firewall:
- Add an Incoming rule to all access the application SqlServr.exe (C:Program FilesMicrosoft SQL ServerMSSQL13.SQLEXPRESSMSSQLBinnsqlservr.exe)
- If you want to access the Sql Server Instance from other computers by using the computer name (i.e. {ComputerName}SQLEXPRESS, you will need to add an Incoming rule to allow access to the application SqlBrowser.exe (C:Program Files (x86)Microsoft SQL Server90Sharedsqlbrowser.exe). Note: If you are only going to use the IP address {xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx}SQLEXPRESS, then you will not need this rule for SqlBrowser.exe.
- Add an Incoming rule for the correct port (1433 TCP or 1434 UDP depending on Sql Server instance type (from above)).
You can use these handy Poweshell scripts to add the above Firewall rules:
|
# http://mattslay.com/opening-up-windows-firewall-to-allow-sql-server-to-allow-remote-connections/ # https://blog.brankovucinec.com/2015/12/04/scripts-to-open-windows-firewall-ports-for-sql-server/ Write-host Enabling SQLServer Default instance port 1433 TCP Inbound New-NetFirewallRule -DisplayName «SQL Server TCP Port 1433» –Direction inbound -Protocol TCP –LocalPort 1433 -Action Allow Write-host Enabling SQLServer Named Instance port 143 UDP Inbound New-NetFirewallRule -DisplayName “SQL Server UDP Port 1434” -Direction Inbound –Protocol UDP –LocalPort 1434 -Action allow Write-host Enabling SQLServer EXE Application rule New-NetFirewallRule -DisplayName “SQL Server EXE” -Direction Inbound -Program «C:Program FilesMicrosoft SQL ServerMSSQL13.SQLEXPRESSMSSQLBinnsqlservr.exe» -Action allow Write-host Enabling SQLServer Browser Application rule New-NetFirewallRule -DisplayName “SQL Server Browser” -Direction Inbound -Program «C:Program Files (x86)Microsoft SQL Server90Sharedsqlbrowser.exe» -Action allow |
You should see the new rules here:
Sql Server Full version
For the full version of Sql Server (not Express), by default it installs as the default instance unless you specify an instance name. So, the next step to allow remote connections to the default instance is to add a Port Rule to open Port 1433 for the TCP protocol.
Sql Server Express
SQL Server Express always installs by default as a named instance unless you force a default instance during setup. So, if you are running a named instance of Sql Server (or Sql Server Express), and you want to allow remote connections to it, add an Incoming port rule for Port 1434 for the UDP protocol.
Since I was running a named instance, I found that I did not need the 1433 TCP port rule at all, I only needed the 1434 UDP port rule (along with the two application rules) to get it working on my network.
Other steps to check
This post only covers the Windows Firewall. There are other steps required in configuring Sql Server itself:
- Enabling the correct protocols, and make sure Sql Server has the option “Allow remote connections to this server” checked on the Connections tab of the Server properties. You can access this setting in Sql Server Management Studio tool.
- Enable the correct protocols in the Sql Server Configuration Management Tool, under the Sql Server Network Configuration node. Honest, I wasn’t sure exactly which I needed, so I enabled all 3. I’m pretty sure TCP/IP was disable by default.
Some details pulled from these links:
https://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/ms165614%28v=sql.90%29.aspx
and a comment by user J_m on this Technet article: https://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/ms175043%28v=sql.110%29.aspx