Each software is released under license type that can be found on program pages as well as on search or category pages. Here are the most common license types:
Freeware
Freeware programs can be downloaded used free of charge and without any time limitations. Freeware products can be used free of charge for both personal and professional (commercial use).
Open Source
Open Source software is software with source code that anyone can inspect, modify or enhance. Programs released under this license can be used at no cost for both personal and commercial purposes. There are many different open source licenses but they all must comply with the Open Source Definition — in brief: the software can be freely used, modified and shared.
Free to Play
This license is commonly used for video games and it allows users to download and play the game for free. Basically, a product is offered Free to Play (Freemium) and the user can decide if he wants to pay the money (Premium) for additional features, services, virtual or physical goods that expand the functionality of the game. In some cases, ads may be show to the users.
Demo
Demo programs have a limited functionality for free, but charge for an advanced set of features or for the removal of advertisements from the program’s interfaces. In some cases, all the functionality is disabled until the license is purchased. Demos are usually not time-limited (like Trial software) but the functionality is limited.
Trial
Trial software allows the user to evaluate the software for a limited amount of time. After that trial period (usually 15 to 90 days) the user can decide whether to buy the software or not. Even though, most trial software products are only time-limited some also have feature limitations.
Paid
Usually commercial software or games are produced for sale or to serve a commercial purpose.
Этап 1: Установка ПО
Перед тем как активировать вычислительные мощности ядер CUDA, необходимо установить специальное программное обеспечение от компании-производителя.
Перейти на ресурс NVIDIA
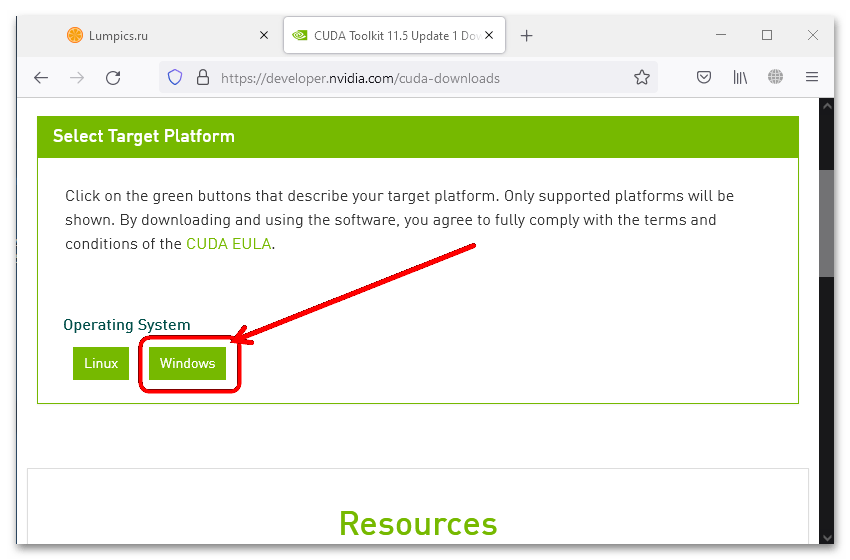
- Перейдя по предложенной выше ссылке, выберите операционную систему – «Windows» (наш пример) или «Linux».
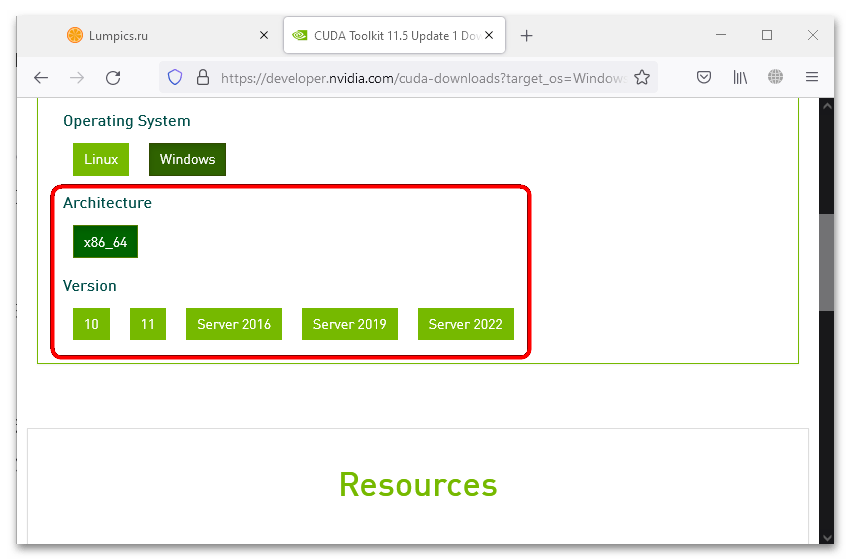
- Архитектура доступна только одна – «x86_64», она устанавливается автоматически. Дополнительно требуется указать конкретную версию Виндовс – поддерживаются как серверные, так и 10, и 11.
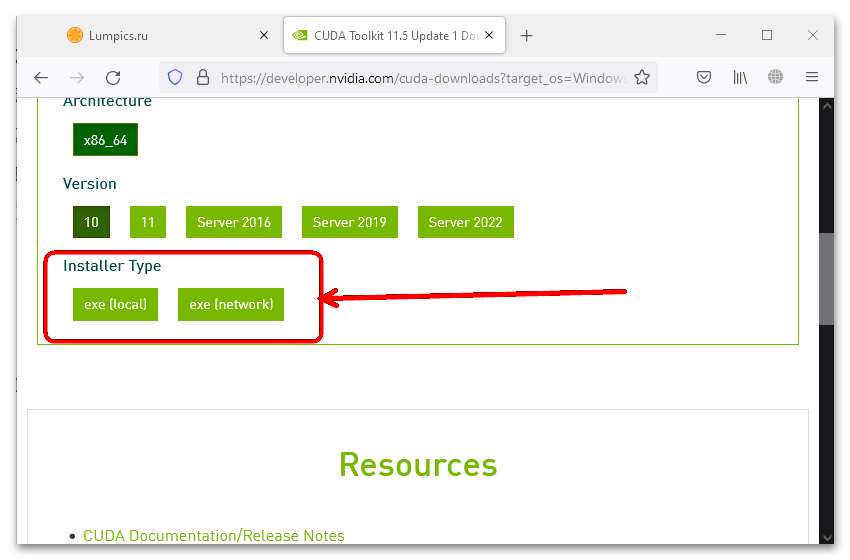
- Теперь укажите вариант инсталлятора. «exe(local)» подразумевает скачивание оффлайн-установщиа, который на момент написания настоящей статьи представляет собой файл размером 2,5 Гб. «exe(network)» является онлайновым, необходимые данные загружаются после запуска. Кликните по тому из них, который вам подойдёт.
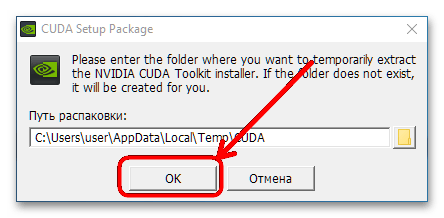
- Независимо от выбранного типа запустите файл после скачивания. Сначала выберите папку, куда будут распакованы временные файлы.
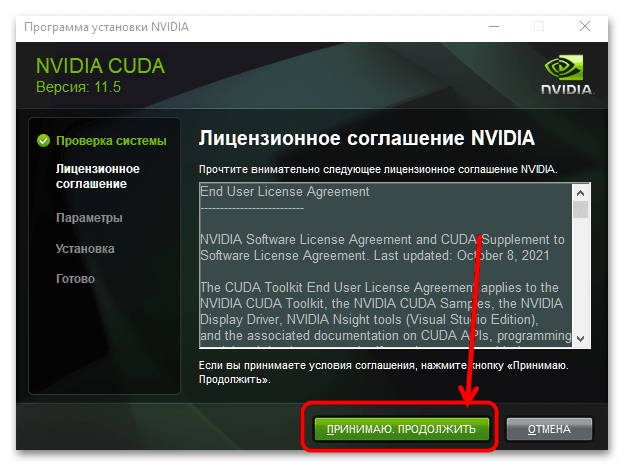
- Подождите, пока данные распакуются, а после появления непосредственно инсталлятора примите лицензионное соглашение.
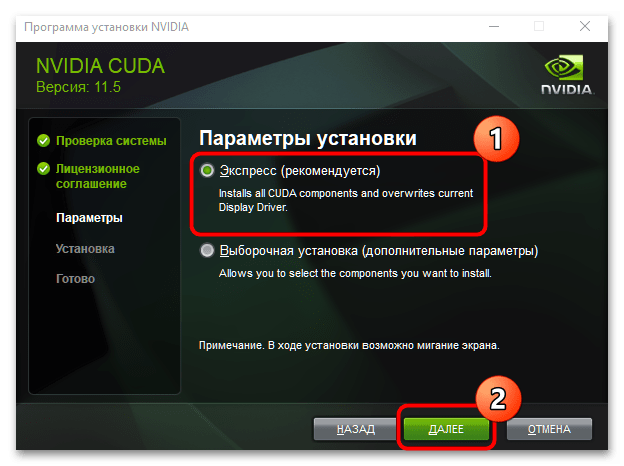
- Для малоопытных пользователей рекомендуется выбирать вариант установки «Экспресс».
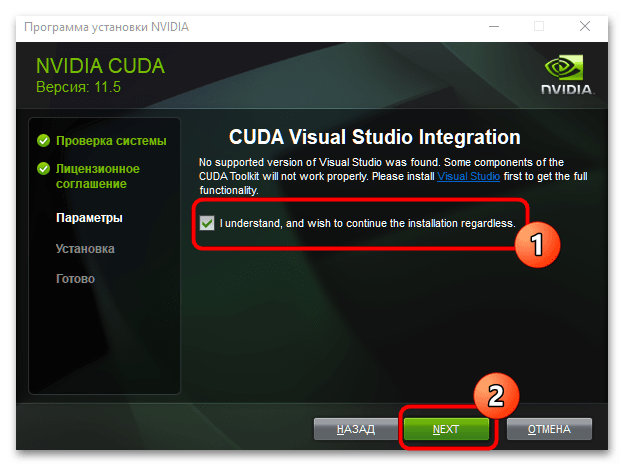
- На данном этапе система предлагает установить Visual Studio. Нам это не требуется, поэтому отметьте опцию, обозначенную на скриншоте, и нажмите «Next».
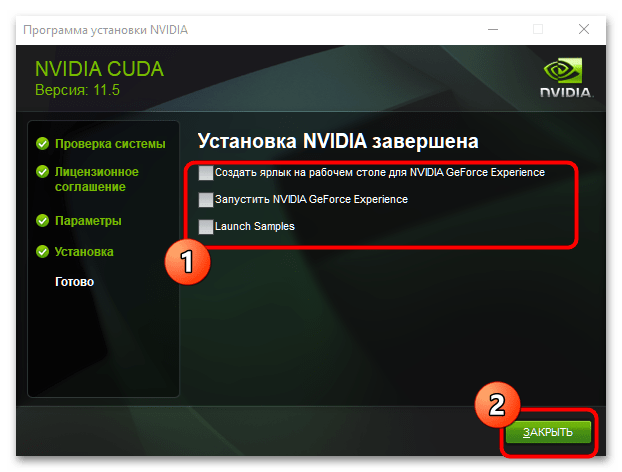
- Дождитесь установки компонента, снимите галочки, затем кликните «Закрыть».
На этом инсталляция средств работы с CUDA закончена.
Включить рассматриваемую технологию разом для всех программ не получится – необходимо её выбирать либо перед началом работы, либо в процессе, либо перед непосредственно вычислением. Использование данного средства покажем на примере программы Adobe After Effects последней версии.
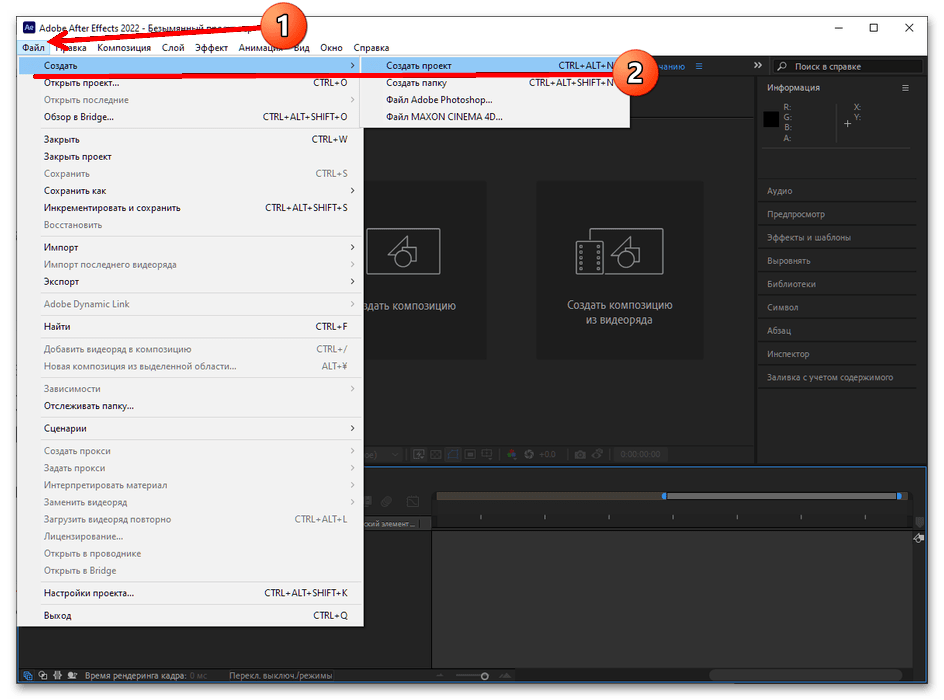
- Запустите Афтер Эффектс и выберите пункты «Файл» – «Создать» – «Создать проект».
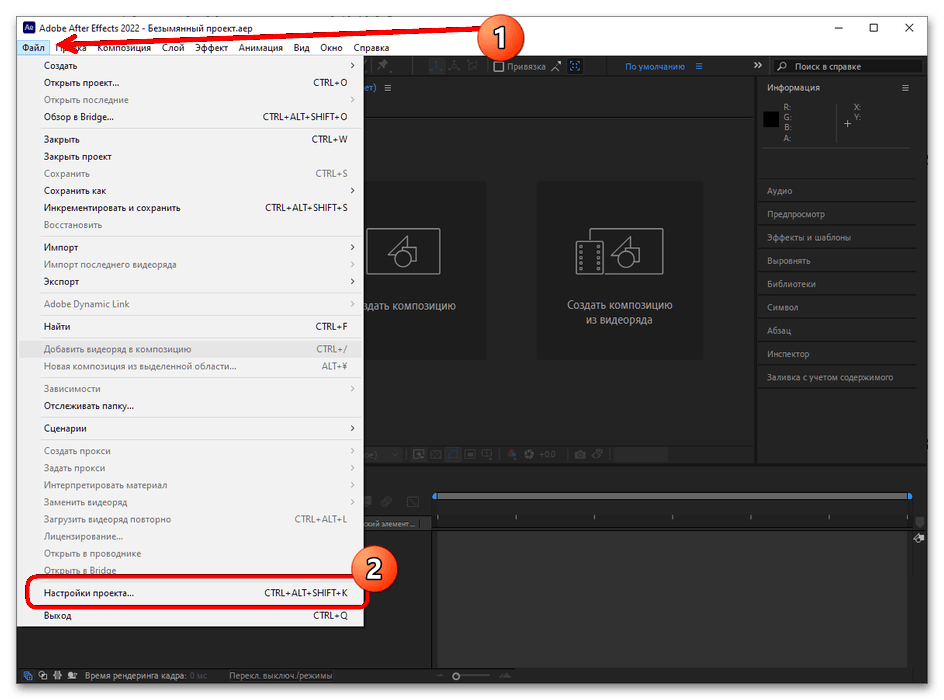
- После создания проекта снова воспользуйтесь элементом «Файл», только на этот раз укажите «Настройки проекта».
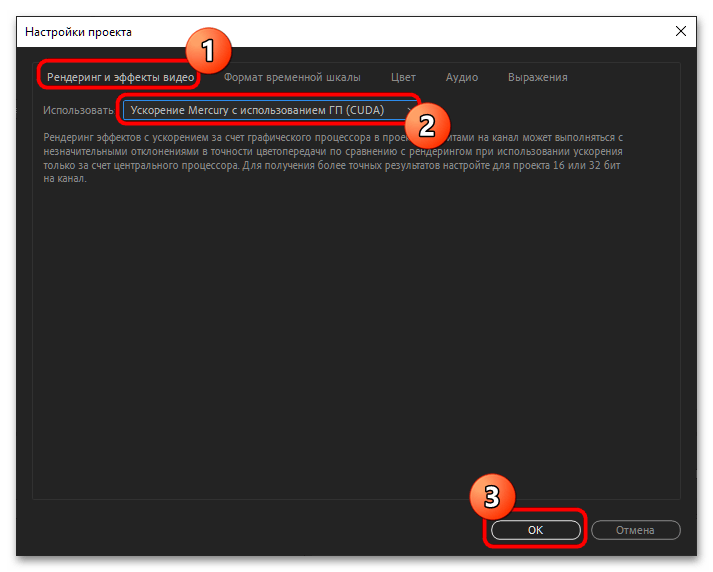
- На вкладке «Рендеринг и эффекты видео» в меню «Использовать» должен быть пункт «Ускорение Mercury с использованием ГП (CUDA)» – выберите его и нажмите «ОК».
В других приложениях данная технология активируется подобным образом.
Еще статьи по данной теме:
Помогла ли Вам статья?
Overview
Certified 
What’s New
Features:
- C/C++ compiler
- Visual Profiler
- GPU-accelerated BLAS library
- GPU-accelerated FFT library
- GPU-accelerated Sparse Matrix library
- GPU-accelerated RNG library
- Additional tools and documentation
Highlights:
- Easier Application Porting
- Share GPUs across multiple threads
- Use all GPUs in the system concurrently from a single host thread
- No-copy pinning of system memory, a faster alternative to cudaMallocHost()
- C++ new/delete and support for virtual functions
- Support for inline PTX assembly
- Thrust library of templated performance primitives such as sort, reduce, etc.
- Nvidia Performance Primitives (NPP) library for image/video processing
- Layered Textures for working with same size/format textures at larger sizes and higher performance
- Faster Multi-GPU Programming
- Unified Virtual Addressing
- GPUDirect v2.0 support for Peer-to-Peer Communication
- New & Improved Developer Tools
- Automated Performance Analysis in Visual Profiler
- C++ debugging in CUDA-GDB for Linux and MacOS
- GPU binary disassembler for Fermi architecture (cuobjdump)
- Parallel Nsight 2.0 now available for Windows developers with new debugging and profiling features.
What’s New:
- Added a new API, cudaGraphNodeSetEnabled(), to allow disabling nodes in an instantiated graph. Support is limited to kernel nodes in this release. A corresponding API, cudaGraphNodeGetEnabled(), allows querying the enabled state of a node.
- Full release of 128-bit integer (__int128) data type including compiler and developer tools support. The host-side compiler must support the __int128 type to use this feature.
- Added ability to disable NULL kernel graph node launches.
- Added new NVML public APIs for querying functionality under Wayland.
- Added L2 cache control descriptors for atomics.
- Large CPU page support for UVM managed memory.
1.3. CUDA Compilers
11.6
- VS2022 Support: CUDA 11.6 officially supports the latest VS2022 as host compiler. A separate Nsight Visual Studio installer 2022.1.1 must be downloaded from here. A future CUDA release will have the Nsight Visual Studio installer with VS2022 support integrated into it.
- New instructions in public PTX: New instructions for bit mask creation — BMSK and sign extension — SZEXT are added to the public PTX ISA. You can find documentation for these instructions in the PTX ISA guide: BMSK and SZEXT.
- Unused Kernel Optimization: In CUDA 11.5, unused kernel pruning was introduced with the potential benefits of reducing binary size and improving performance through more efficient optimizations. This was an opt-in feature but in 11.6, this feature is enabled by default. As mentioned in the 11.5 blog here, there is an opt-out flag that can be used in case it becomes necessary for debug purposes or for other special situations.
- $ nvcc -rdc=true user.cu testlib.a -o user -Xnvlink -ignore-host-info
- In addition to the -arch=all and -arch=all-major options added in CUDA 11.5, NVCC introduced -arch= native in CUDA 11.5 update1. This -arch=native option is a convenient way for users to let NVCC determine the right target architecture to compile the CUDA device code to based on the GPU installed on the system. This can be particularly helpful for testing when applications are run on the same system they are compiled in.
- Generate PTX from nvlink: Using the following command line, device linker, nvlink will produce PTX as an output in addition to CUBIN:
- nvcc -dlto -dlink -ptx
- Device linking by nvlink is the final stage in the CUDA compilation process. Applications that have multiple source translation units have to be compiled in separate compilation mode. LTO (introduced in CUDA 11.4) allowed nvlink to perform optimizations at device link time instead of at compile time so that separately compiled applications with several translation units can be optimized to the same level as whole program compilations with a single translation unit. However, without the option to output PTX, applications that cared about forward compatibility of device code could not benefit from Link Time Optimization or had to constrain the device code to a single source file.
- With the option for nvlink that performs LTO to generate the output in PTX, customer applications that require forward compatibility across GPU architectures can span across multiple files and can also take advantage of Link Time Optimization.
- Bullseye support: NVCC compiled source code will work with code coverage tool Bullseye. The code coverage is only for the CPU or the host functions. Code coverage for device function is not supported through bullseye.
- INT128 developer tool support: In 11.5, CUDA C++ support for 128-bit was added. In this release, developer tools supports the datatype as well. With the latest version of libcu++, int 128 data type is supported by math functions.
cuSOLVER
New Features:
- New singular value decomposition (GESVDR) is added. GESVDR computes partial spectrum with random sampling, an order of magnitude faster than GESVD.
- libcusolver.so no longer links libcublas_static.a; instead, it depends on libcublas.so. This reduces the binary size of libcusolver.so. However, it breaks backward compatibility. The user has to link libcusolver.so with the correct version of libcublas.so.
cuSPARSE
New Features:
- New Tensor Core-accelerated Block Sparse Matrix — Matrix Multiplication (cusparseSpMM) and introduction of the Blocked-Ellpack storage format.
- New algorithms for CSR/COO Sparse Matrix — Vector Multiplication (cusparseSpMV) with better performance.
- Extended functionalities for cusparseSpMV:
- Support for the CSC format.
- Support for regular/complex bfloat16 data types for both uniform and mixed-precision computation.
- Support for mixed regular-complex data type computation.
- Support for deterministic and non-deterministic computation.
- New algorithm (CUSPARSE_SPMM_CSR_ALG3) for Sparse Matrix — Matrix Multiplication (cusparseSpMM) with better performance especially for small matrices.
- New routine for Sampled Dense Matrix — Dense Matrix Multiplication (cusparseSDDMM) which deprecated cusparseConstrainedGeMM and provides better performance.
- Better accuracy of cusparseAxpby, cusparseRot, cusparseSpVV for bfloat16 and half regular/complex data types.
- All routines support NVTX annotation for enhancing the profiler time line on complex applications.
Deprecations:
- cusparseConstrainedGeMM has been deprecated in favor of cusparseSDDMM.
- cusparseCsrmvEx has been deprecated in favor of cusparseSpMV.
- COO Array of Structure (CooAoS) format has been deprecated including cusparseCreateCooAoS, cusparseCooAoSGet, and its support for cusparseSpMV.
Known Issues:
- cusparseDestroySpVec, cusparseDestroyDnVec, cusparseDestroySpMat, cusparseDestroyDnMat, cusparseDestroy with NULL argument could cause segmentation fault on Windows.
Resolved Issues:
- cusparseAxpby, cusparseGather, cusparseScatter, cusparseRot, cusparseSpVV, cusparseSpMV now support zero-size matrices.
- cusparseCsr2cscEx2 now correctly handles empty matrices (nnz = 0).
- cusparseXcsr2csr_compress now uses 2-norm for the comparison of complex values instead of only the real part.
- NPPNew features:New APIs added to compute Distance Transform using Parallel Banding Algorithm (PBA):
- nppiDistanceTransformPBA_xxxxx_C1R_Ctx() — where xxxxx specifies the input and output combination: 8u16u, 8s16u, 16u16u, 16s16u, 8u32f, 8s32f, 16u32f, 16s32f
- nppiSignedDistanceTransformPBA_32f_C1R_Ctx()
Resolved issues:
- Fixed the issue in which Label Markers adds zero pixel as object region.
- NVJPEG
New Features:
- nvJPEG decoder added a new API to support region of interest (ROI) based decoding for batched hardware decoder:
- nvjpegDecodeBatchedEx()
- nvjpegDecodeBatchedSupportedEx()
cuFFTKnown Issues:
- cuFFT planning and plan estimation functions may not restore correct context affecting CUDA driver API applications.
- Plans with strides, primes larger than 127 in FFT size decomposition and total size of transform including strides bigger than 32GB produce incorrect results.
Resolved Issues:
- Previously, reduced performance of power-of-2 single precision FFTs was observed on GPUs with sm_86 architecture. This issue has been resolved.
- Large prime factors in size decomposition and real to complex or complex to real FFT type no longer cause cuFFT plan functions to fail.
- CUPTIDeprecations early notice:The following functions are scheduled to be deprecated in 11.3 and will be removed in a future release:
- NVPW_MetricsContext_RunScript and NVPW_MetricsContext_ExecScript_Begin from the header nvperf_host.h.
- cuptiDeviceGetTimestamp from the header cupti_events.h
Complete release notes can be found here.
Fast servers and clean downloads. Tested on TechSpot Labs. Here’s why you can trust us.

Last updated:
March 11, 2022
User rating:
23 votes
Popular apps
in For Developers
Thanks to this software, users are able to create fast and flexible computer programs. It also includes detailed documentation and a library of samples.
Windows version:
Windows 10, Windows 11
CUDA is a powerful program package that enables you to develop, test, optimize and deploy new applications, as well as increase your computing power and performance.
Components
During installation, you can choose from four components. CUDA is the main module which provides the development environment, Nsight Systems, Visual Studio integration and more. Other options include, NVIDIA GeForce Experience, the driver components and the PhysX engine.
Main functions
Using this utility, you get access to a set of instruments for implementing parallel algorithms using various programming languages. You can improve the computing power and overall performance of your computer by managing your CPU and GPU.
Moreover, you are able to use the extensive libraries to create applications for different types of purposes such as advanced calculations, signal and image processing, as well as motion tracking. But before trying the actual tools, it is good to know that the software comes with detailed documentation and a large collection of samples and resources.
Nsight capabilities
It is worth mentioning that the Nsight component contained in the CUDA package will add some extra functions to your environment such as an interactive kernel profiler, a graphics utility for debugging and profiling, as well as a performance analysis tool.
Features
- free to download and use;
- compatible with modern Windows versions;
- gives you the ability to develop and test apps;
- it is possible to increase the computing power;
- includes detailed documentation.
BBSAK
Windows XP, Windows Vista, Windows 7, Windows 8, Windows 10, Windows 11 Free
The software solution is intended to assist you in configuring your BlackBerry mobile device. Moreover, you can install and manage multiple operating systems.
ver 1.9.2
XULRunner
Windows XP, Windows Vista, Windows 7, Windows 8, Windows 10, Windows 11 Free
Using this comprehensive utility, you are able to develop and deploy Mozilla-based applications. It requires advanced programming knowledge to use efficiently.
ver 41.0.2
Samsung Tool Pro
Windows 7, Windows 8, Windows 10, Windows 11 Free
The application enables users to perform various operations with Samsung smartphones. It is possible to update firmware, read device information and more.
ver 34.11
Node js
Windows XP, Windows Vista, Windows 7, Windows 8, Windows 10, Windows 11 Free
With the help of this powerful utility, users are able to develop network apps using JavaScript. Moreover, it is possible to extend its functionality via plugins.
ver 18.13.0
PowerDesigner
Windows XP, Windows Vista, Windows 7, Windows 8, Windows 10 Free
The application was designed to help users design and schedule important business transformations. It is also possible to connect to a wide range of databases.
ver 16.7.5.0
Libero SoC
Windows 7, Windows 8, Windows 8.1, Windows 10, Windows 11 Free
With the help of this specialized utility users can design complex field-programmable gate array processors. There are tools for optimizing hardware performance.
ver 2022.3
Western Digital Data Lifeguard Tools
Windows XP, Windows Vista, Windows 7, Windows 8, Windows 10, Windows 11 Free
The software solution gives users the possibility to set up and configure HDDs manufactured by Western Digital. It is also possible to create bootable diskettes.
ver 11.2
BlueVoda Website Builder
Windows XP, Windows Vista, Windows 7, Windows 8, Windows 10, Windows 11 Free
The software distribution was developed to help users build websites. Additionally, it is possible to import and modify a wide array of multimedia objects.
ver 12.2.0.0