В принципе все верно, однако Windows Update — слишком общее название, чтобы говорить о чем-то конкретном. Например есть прога с похожим названием — Windows Update MiniTool, она нужна для управления обновлениями, также умеет проверять наличие, скачивать их, устанавливать, удалять установленные, скрывать нежелательные, следить за историей.
Однако чаще всего под названием Windows Update имеют ввиду именно обновления Windows.
Важные моменты
- Обновления устраняют баги, глюки, а также критические уязвимости, которые могут использовать хакеры для атак. Простыми словами уязвимости, через которые может попасть на ПК вирус.
- В десятке обновления также могут приносить новые функции, то есть десятка как бы на ходу улучшается.
- Обновления, особенно в десятке — вещь требующая ресурсов. Да, может нагружаться процессор, использоваться много оперативы, особенно когда вы только установили чистую винду, то первые обновления — их много, и установка, скачивание, и еще какие-то служебные дела — будут кушать много оперы.. и грузить процессор.. нужно просто набраться терпения.
- Выходят не каждый день — примерно раз в неделю, раньше было каждый вторник. Точно не знаю, но в десятке вроде по умолчанию все настроено так, что скачиваться и устанавливаться будет автоматом, а вот перезагрузка только после вашего разрешения. Да, для установки часто требуется перезагрузка — это норма. Хотя читал что десятка может и принудительно как-то перезагрузить комп..
Внешний вид Windows Update
Windows Update — важная часть винды. Присутствует во всех версиях — в Windows 10, в Windows 8, семерке, и даже в XP. Скорее всего в старых он тоже был, так как обновления — очень важны. Представьте Microsoft выпускает винду, через месяц оказывается что в ней есть косяк.. как его исправить? Не переустанавливать же систему… тогда разработчики Microsoft создают обновление (заплатку) и оно через Windows Update попадает на ПК, устанавливается и исправляет косяк.
Картинка — окно Windows Update в десятке, не знаю какой билд, но думаю свежий:
Сразу лайф-хак. Чтобы запустить обновление в десятке — зажмите Win + I, далее в самом низу будет Обновление и безопасность. Нажимаете и у вас сразу появится Центр обновления Windows — нужно просто нажать Проверить наличие.
Windows Update — вообще-то Центр обновления Windows, именно так он назывался в семерке:
Если есть обновы, то будет указано сколько их, размер, в общем вся важная нужная инфа:
В семерке Центр обновления находится в панели управления. Там нужно найти значок. Кстати панель управления можно запустить так: Win + R, далее команда control или control panel (способ работает чуть ли не во всех версиях винды).
В Windows 8 все похоже:
Также находится в панели управления. И только в десятке теперь все находится в окне Параметры.
Как отключить Windows Update?
В семерке — идете в панель управления, находите значок Центр обновлений Windows, запускаете, там будет Настройка параметров:
Потом собственно отключаете:
После — нажимаете ОК.
В десятке запускаете окно Параметры (Win + I), далее в самом низу Обновление и безопасность:
Нажмите кнопку Дополнительные параметры:
Далее можете их отключить, но только временно. Используйте настройки:
- Приостановить до
- Выберите когда устанавливать
Можете выставить по максимум.. потом все равно придется обновиться.
На заметку. Я кстати использую утилиту DoNotSpy10, позволяющую отключить все лишнее/ненужное в винде. Пользуюсь давно, правда у меня еще версия Windows 10 LTSB.. где по умолчанию многое отключено. Короче возможно DoNotSpy10 может сделать так, что обновления вы будете получать только тогда когда нажмете на кнопку проверки их наличия. Попробуйте, винда быстрее даже станет работать после DoNotSpy10.
В принципе если на ПК установлен мощный антивирус, версия максимальная, например Касперский, лицензия, настроен на высокую безопасность.. то я думаю с таким антивирусом обновы можно временно отложить.
Заключение
Главное выяснили:
- Windows Update — системный компонент для обновления винды. Автоматически ищет, качает, устанавливает. Встроен в систему. Отключить можно, удалять нельзя (кажется есть даже служба).
- Присутствует во многих виндах, как в десятке, так и в старенькой Windows XP.
- При наличии мощного платного антивируса, обновления можно отложить. Особенно если за компом вы максимум играете или смотрите фильмы. При наличии важных/ценных данных на ПК — лучше не отключать.
Надеюсь информация оказалась полезной. Удачи, добра, до новых встреч господа!
На главную!
07.09.2019
Агент обновления Microsoft Windows (также называемый WUA) — это программа-агент. Он работает вместе со службами Windows Server Update Services для автоматической доставки исправлений. Он может сканировать ваш компьютер и определять, какая у вас версия Windows. … Агент обновления Windows был впервые представлен для Windows Vista.
Для получения дополнительных сведений о том, как проверить, какая версия агента обновления Windows установлена, выполните следующие действия:
- Откройте папку% systemroot% system32. % systemroot% — это папка, в которой установлена Windows. …
- Щелкните правой кнопкой мыши Wuaueng. …
- Выберите вкладку «Сведения» и найдите номер версии файла.
Как отключить агент Центра обновления Windows?
Тип «MSCONFIG»В поле« Выполнить »или« Поиск »в меню« Пуск ». Откроется окно, содержащее ваши файлы запуска. Щелкните вкладку «Запуск» и прокрутите вниз, чтобы найти «Центр обновления Windows». Снимите флажок рядом с «Обновить. »Нажмите« Применить », а затем выберите« Закрыть ».
Какая служба отвечает за Центр обновления Windows?
Microsoft Windows Update — это служба Microsoft для операционных систем семейств Windows 9x и Windows NT, которая автоматизирует загрузку и установку обновлений программного обеспечения Microsoft Windows через Интернет.
Что делает служба обновления Windows?
Обновляйте Windows с помощью службы обновления Windows
Центр обновления Windows — это бесплатная служба Microsoft, используется для предоставления обновлений, таких как пакеты обновления и исправления для операционной системы Windows и другого программного обеспечения Microsoft.. Центр обновления Windows также можно использовать для обновления драйверов для популярных аппаратных устройств.
Как найти агент обновления Windows?
Используйте следующие шаги, чтобы определить версия of Агент обновления Windows используйте следующую процедуру.
- В проводнике перейдите к C:WindowsSystem32 и найдите файл wuaueng. dll.
- Щелкните файл правой кнопкой мыши и выберите «Свойства».
- Щелкните вкладку Details, чтобы найти продукт. Версия.
Как называется процесс обновления Windows?
Это фоновый процесс, который проверяет наличие обновлений для операционной системы на веб-сайте Microsoft. Он отображается в списке процессов диспетчера задач, когда ожидает ответа, например, для подтверждения разрешения на загрузку обновления. Обратите внимание wuauclt.exe файл находится в папке C: WindowsSystem32.
Как использовать автономный установщик Центра обновления Windows?
Чтобы начать установку пакета обновления Windows, просто дважды щелкните файл MSU, который вы скачали. Если обновление применимо к этому компьютеру, откроется окно автономного установщика Центра обновления Windows, в котором вам будет предложено подтвердить установку обновления.
Как переустановить Центр обновления Windows?
Как переустановить обновление в Windows 10
- Открыть настройки.
- Щелкните Обновление и безопасность.
- Нажмите на Центр обновления Windows.
- Нажмите кнопку «Проверка обновлений», чтобы запустить проверку обновлений, которая автоматически загрузит и установит обновление.
- Нажмите кнопку «Перезагрузить сейчас», чтобы завершить задачу.
Как я могу бесплатно обновить Windows?
Посетите страницу загрузки Windows 10. Это официальная страница Microsoft, которая может позволить вам выполнить обновление бесплатно. Когда вы окажетесь там, откройте Windows 10 Media Creation Tool (нажмите «Загрузить инструмент сейчас») и выберите «Обновить этот компьютер сейчас».
Безопасно ли отключать службу Центра обновления Windows?
Мы не рекомендуем вам отключить автоматическое обновление Windows in Windows 10. Если на вашем компьютере все в порядке с загрузками в фоновом режиме и это не влияет на вашу работу, делать это не рекомендуется.
Что делать, если Windows зависает при обновлении?
Как исправить застрявшее обновление Windows
- Убедитесь, что обновления действительно застряли.
- Выключи и снова включи.
- Проверьте утилиту Центра обновления Windows.
- Запустите программу устранения неполадок Microsoft.
- Запустите Windows в безопасном режиме.
- Вернитесь в прошлое с помощью функции восстановления системы.
- Удалите кеш файлов Центра обновления Windows самостоятельно.
- Запустите тщательную проверку на вирусы.

Windows Update Agent – это официальная утилита от Microsoft, предназначенная для правильного обновления операционной системы Windows 7.
Описание программы
Приложение распространяется на полностью бесплатной основе и преследует единственную цель – обновление ОС до последней версии.
Важно понимать, что данное программное обеспечение работает с любыми разрядностьями Windows 7, включая x32 или 64 Bit.
Как установить
Переходим к делу. Давайте рассмотрим конкретный пример, который показывает, как устанавливается ПО:
- Обращаемся к концу этой странички и загружаем архив.
- Распаковываем содержимое, запускаем процесс инсталляции и устанавливаем флажок напротив пункта принятия лицензии.
- Переходим к следующему шагу и ждём несколько секунд, пока программа установится.
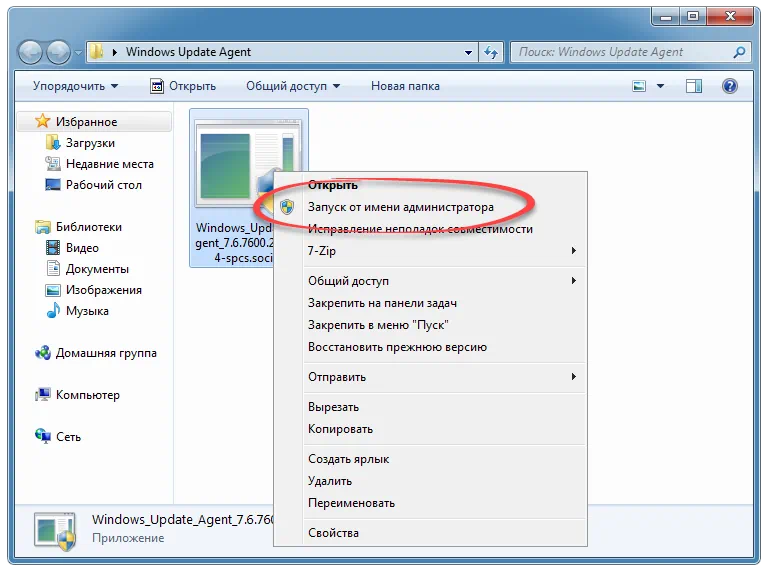
Как пользоваться
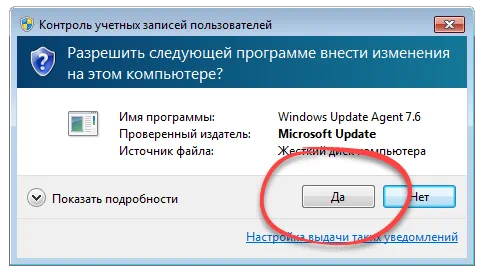
Основная особенность использования софта – это правильный запуск. Производим правый клик, из контекстного меню выбираем пункт работы с полномочиями администратора, затем в маленьком окошке нажимаем «Да». После этого появится пошаговый мастер, который позволит правильно обновить вашу операционную систему.
Достоинства и недостатки
Переходим к разбору сильных, а также слабых сторон утилиты для обновления Windows 7.
Плюсы:
- русский язык в пользовательском интерфейсе;
- полная бесплатность;
- отсутствие необходимости инсталляции.
Минусы:
- отсутствие каких-либо вспомогательных инструментов.
Скачать
Исполняемый файл программы может быть загружен немного ниже по прямой ссылке.
| Язык: | Русский |
| Активация: | Бесплатно |
| Разработчик: | Microsoft |
| Платформа: | Windows XP, 7, 8, 10, 11 |
Windows Update Agent 7.6.7600.256
The Microsoft Windows Update Agent (also referred to as WUA) is an agent program. It works together with the Windows Server Update Services to automatically deliver patches. It’s able to scan your computer and determine what version of Windows you’re running. This allows the update agent to push new updates onto your device, making the process easier.
Windows Update Agent was first introduced for Windows Vista. It replaced the Windows Update web application and the Automatic Updates client. Because it’s a much better solution for updates, Microsoft kept it in every future release.
The Windows Update Agent improves features of the Automatic Updates client. Browsing the Windows Update website was much of a hassle for many users. Not knowing what update you need can lead to loss of time and many errors.
Windows Update Agent can prevent this.
It can automatically select, download and install needed or recommended updates.
Have you ever had your computer unexpectedly crash?
When using the Windows Update Client, you can recover easier and faster. This is possible because the agent uses a feature introduced in Windows Vista. Windows handles its system files better, allowing for easier recovery.
How does Windows Update Agent Work?
The update agent searches and downloads updates from trusted Microsoft sources. This includes:
- Windows Server Update Services (WSUS) server
- Microsoft’s update websites
- Peer to peer distribution (Windows 10)
Once the update agent detects a new update that is missing from your computer, it begins working. You don’t have to spend any time looking for updates and trying to determine which one to install yourself.
You’re able to manage the Windows Update Agent in the following locations:
- Control Panel
- Settings app
- Group Policy
- Microsoft Intune
- Windows PowerShell
Windows Update Agent is compatible with these versions of Windows:
- Windows Vista
- Windows 7
- Windows 8
- Windows 10
How to check what version of Windows Update Agent is installed?
- Use APIs on WinHTTP (Windows HTTP Services) and download Wuredist.cab.
- With Cryptography Functions, check if the file has a digital signature from Microsoft. If a digital signature can’t be verified, do not continue with this file.
- Use File Decompression Interface APIs in order to extract the XML file in Wuredist.cab.
- Determine what architecture your computer is using. With the APIs of Microsoft XML Core Services (MSXML), locate the WURedist/StandaloneRedist/architecture node.
- Call IWindowsUpdateAgentInfo::GetInfo to determine the current version of Windows Update Agent.
This method is not able to tell you whether or not your Windows Update Agent version is the latest or not. However, identifying your version allows you to do some research and find out if you need to update it or not.
Parts of Windows Update Agent
Microsoft defines five important parts in the Windows Update Agent:
- Service Availability: This part is what detects, downloads and installs a Windows update. It also handles updates for some other programs.
- Server Connectivity: This is an API (Application Program Interface). It connects your computer to the locations Microsoft uses for delivering updates. You can see these above.
- Update Detection: Scans your computer for updates regularly. This allows you to automate the update process, as you don’t have to check for updates yourself.
- Update Downloads: Downloads available and mandatory updates from safe locations Microsoft uses. Once again, see the list above.
- Update Installation: Installs the available updates.
Changes to Windows Update Agent in Windows 10
The manual operation of the Windows Update Agent is no longer supported in Windows 10. This is a major change, as all updates get downloaded and installed automatically. What this means is you can no longer select installations and updates yourself.
Windows 10 users have access to peer-to-peer support when updating. Your systems’ bandwidth is used to distribute downloaded updates to other users. You can change this setting to only distribute within a local area network.
Cumulative updates are also included for Windows 10 users. What this means is that the Windows Update Agent is able to pack older updates together. For example, if updates came out in July, August and September, the October update contains all of them.
These cumulative updates end the need to download more than one update. It also spares you from having to restart your computer many times. But, it has a disadvantage. Downloading and installing updates that fix individual problems is no longer possible.
How to Update Windows Update Agent
Before you begin updating, check that your computer has automatic updates.
On Windows 10, search for Windows Update Settings in your search bar on the bottom left of your screen. Open the matching “System settings” result. Select Advanced Options and choose Automatic from the drop-down menu.
If you’re on an older version of Windows, find the classic Control Panel. Select the Windows Update icon and click the Change Settings link on the left. Under the Important Updates section, make sure that you enable automatic updates.
How to Update Windows Update Agent on Windows 10
- Type Run in your search bar and click on the application.
- Type services.msc and click OK. This is going to launch the Services Manager.
- Scroll down until you locate Windows Update from the list of services.
- Right-click on Windows Update and click on Stop.
- When you successfully stopped the service, right-click on Windows Update once again. This time click on Start.
- Close the Services Manager and run Windows Update.
How to Update Windows Update Agent on Windows 7
How to Reset or Fix Windows Update Agent on Windows PC
Are you still encountering problems and issues with the Windows Update Agent? There might be times when updating it to the latest version won’t help. Luckily, fixing it is an easy task.
Manuel F. Gil created a script available on Tech.net. It allows you to easily reset and fix the Windows Update Agent. In the past, this process often took hours as many files have to get deleted or renamed. The script is able to do this in bulk, quickly and efficiently.
They also published a software called the Reset Windows Update Tool. You can download it and run it similarly to the script. The website includes more information. You can check the features, requirements, documentation and in-depth licensing terms.
This method is tested to work on the following Windows platforms:
- Windows 10
- Windows 8
- Windows 7
- Windows Vista
- Windows XP
This method deletes and modifies system files. Please take the time to read these important notes before you begin this process:
- Only reset the Windows Update Agent if you’re having issues with Windows Updates. If your updates are fine, there’s no need to reset the agent.
- Make a backup of your files and system before attempting to reset the Windows Update Agent. As written in the Terms of Use, the creator of the script takes no responsibility for any damages that the script might cause.
- You’re required to have administrator rights on your user to run the script.
When you’re done taking the necessary steps to safely run the script, follow the guide below.
- Click on this link to open the Tech.net file. You can read about the script and how it works on this website to verify how trustworthy it is.
- Click on the ResetWUEng.zip button next to Download.
- Accept the license by clicking on I agree.
- Extract the folder in the downloaded .zip file somewhere on your computer
- Right-click on ResetWUEng.cmd then run as administrator
- Agree to the Terms and Conditions of Use by typing Y.
18 options will show up in the command window to choose from. These are all the tools to fix your system and run various check-ups. However, not all of them are directly needed to reset the Windows Update Agent.
You can run an option by typing in the number assigned to it and pressing the enter key on your keyboard. For example, if you want the script to restart your computer, type in 18 and press enter.
Some things we recommend running via the script to fix the Windows Update Agent:
- Reset the Windows Update Components (2)
- Delete temporary files in Windows (3)
- Run the System File Checker tool (6)
- Perform repair operations automatically (9)
- Delete incorrect registry values (11)
- Search Windows updates (13)
Warning: Once you press enter to run any of these options, there’s no confirmation or cancellation of the process. If you’re unsure whether you should run an option, type in a? symbol and press enter to access Help.
Learning about the Windows Update Agent is exciting, as it plays a vital part of your computer’s health. Always keep the agent up-to-date to assure you don’t run into any errors while updating.
If you’re looking for a software company you can trust for its integrity and honest business practices, look no further than SoftwareKeep. We are a Microsoft Certified Partner and a BBB Accredited Business that cares about bringing our customers a reliable, satisfying experience on the software products they need. We will be with you before, during, and after all the sales.
That’s our 360 Degree SoftwareKeep Guarantee. So, what are you waiting for? Call us Today on +1 877 315 1713 or email sales@softwarekeep.com. As well, you can reach us via Live Chat.
The Microsoft Windows Update Agent (also referred to as WUA) is an agent program. It works together with the Windows Server Update Services to automatically deliver patches. It’s able to scan your computer and determine what version of Windows you’re running. This allows the update agent to push new updates onto your device, making the process easier.
Windows Update Agent was first introduced for Windows Vista. It replaced the Windows Update web application and the Automatic Updates client. Because it’s a much better solution for updates, Microsoft kept it in every future release.
The Windows Update Agent improves features of the Automatic Updates client. Browsing the Windows Update website was much of a hassle for many users. Not knowing what update you need can lead to loss of time and many errors.
Windows Update Agent can prevent this.
It can automatically select, download and install needed or recommended updates.
Have you ever had your computer unexpectedly crash?
When using the Windows Update Client, you can recover easier and faster. This is possible because the agent uses a feature introduced in Windows Vista. Windows handles its system files better, allowing for easier recovery.
How does Windows Update Agent Work?
The update agent searches and downloads updates from trusted Microsoft sources. This includes:
- Windows Server Update Services (WSUS) server
- Microsoft’s update websites
- Peer to peer distribution (Windows 10)
Once the update agent detects a new update that is missing from your computer, it begins working. You don’t have to spend any time looking for updates and trying to determine which one to install yourself.
You’re able to manage the Windows Update Agent in the following locations:
- Control Panel
- Settings app
- Group Policy
- Microsoft Intune
- Windows PowerShell
Windows Update Agent is compatible with these versions of Windows:
- Windows Vista
- Windows 7
- Windows 8
- Windows 10
How to check what version of Windows Update Agent is installed?
- Use APIs on WinHTTP (Windows HTTP Services) and download Wuredist.cab.
- With Cryptography Functions, check if the file has a digital signature from Microsoft. If a digital signature can’t be verified, do not continue with this file.
- Use File Decompression Interface APIs in order to extract the XML file in Wuredist.cab.
- Determine what architecture your computer is using. With the APIs of Microsoft XML Core Services (MSXML), locate the WURedist/StandaloneRedist/architecture node.
- Call IWindowsUpdateAgentInfo::GetInfo to determine the current version of Windows Update Agent.
This method is not able to tell you whether or not your Windows Update Agent version is the latest or not. However, identifying your version allows you to do some research and find out if you need to update it or not.
Parts of Windows Update Agent
Microsoft defines five important parts in the Windows Update Agent:
- Service Availability: This part is what detects, downloads and installs a Windows update. It also handles updates for some other programs.
- Server Connectivity: This is an API (Application Program Interface). It connects your computer to the locations Microsoft uses for delivering updates. You can see these above.
- Update Detection: Scans your computer for updates regularly. This allows you to automate the update process, as you don’t have to check for updates yourself.
- Update Downloads: Downloads available and mandatory updates from safe locations Microsoft uses. Once again, see the list above.
- Update Installation: Installs the available updates.
Changes to Windows Update Agent in Windows 10
The manual operation of the Windows Update Agent is no longer supported in Windows 10. This is a major change, as all updates get downloaded and installed automatically. What this means is you can no longer select installations and updates yourself.
Windows 10 users have access to peer-to-peer support when updating. Your systems’ bandwidth is used to distribute downloaded updates to other users. You can change this setting to only distribute within a local area network.
Cumulative updates are also included for Windows 10 users. What this means is that the Windows Update Agent is able to pack older updates together. For example, if updates came out in July, August and September, the October update contains all of them.
These cumulative updates end the need to download more than one update. It also spares you from having to restart your computer many times. But, it has a disadvantage. Downloading and installing updates that fix individual problems is no longer possible.
How to Update Windows Update Agent
Before you begin updating, check that your computer has automatic updates.
On Windows 10, search for Windows Update Settings in your search bar on the bottom left of your screen. Open the matching “System settings” result. Select Advanced Options and choose Automatic from the drop-down menu.
If you’re on an older version of Windows, find the classic Control Panel. Select the Windows Update icon and click the Change Settings link on the left. Under the Important Updates section, make sure that you enable automatic updates.
How to Update Windows Update Agent on Windows 10
- Type Run in your search bar and click on the application.
- Type services.msc and click OK. This is going to launch the Services Manager.
- Scroll down until you locate Windows Update from the list of services.
- Right-click on Windows Update and click on Stop.
- When you successfully stopped the service, right-click on Windows Update once again. This time click on Start.
- Close the Services Manager and run Windows Update.
How to Update Windows Update Agent on Windows 7
How to Reset or Fix Windows Update Agent on Windows PC
Are you still encountering problems and issues with the Windows Update Agent? There might be times when updating it to the latest version won’t help. Luckily, fixing it is an easy task.
Manuel F. Gil created a script available on Tech.net. It allows you to easily reset and fix the Windows Update Agent. In the past, this process often took hours as many files have to get deleted or renamed. The script is able to do this in bulk, quickly and efficiently.
They also published a software called the Reset Windows Update Tool. You can download it and run it similarly to the script. The website includes more information. You can check the features, requirements, documentation and in-depth licensing terms.
This method is tested to work on the following Windows platforms:
- Windows 10
- Windows 8
- Windows 7
- Windows Vista
- Windows XP
This method deletes and modifies system files. Please take the time to read these important notes before you begin this process:
- Only reset the Windows Update Agent if you’re having issues with Windows Updates. If your updates are fine, there’s no need to reset the agent.
- Make a backup of your files and system before attempting to reset the Windows Update Agent. As written in the Terms of Use, the creator of the script takes no responsibility for any damages that the script might cause.
- You’re required to have administrator rights on your user to run the script.
When you’re done taking the necessary steps to safely run the script, follow the guide below.
- Click on this link to open the Tech.net file. You can read about the script and how it works on this website to verify how trustworthy it is.
- Click on the ResetWUEng.zip button next to Download.
- Accept the license by clicking on I agree.
- Extract the folder in the downloaded .zip file somewhere on your computer
- Right-click on ResetWUEng.cmd then run as administrator
- Agree to the Terms and Conditions of Use by typing Y.
18 options will show up in the command window to choose from. These are all the tools to fix your system and run various check-ups. However, not all of them are directly needed to reset the Windows Update Agent.
You can run an option by typing in the number assigned to it and pressing the enter key on your keyboard. For example, if you want the script to restart your computer, type in 18 and press enter.
Some things we recommend running via the script to fix the Windows Update Agent:
- Reset the Windows Update Components (2)
- Delete temporary files in Windows (3)
- Run the System File Checker tool (6)
- Perform repair operations automatically (9)
- Delete incorrect registry values (11)
- Search Windows updates (13)
Warning: Once you press enter to run any of these options, there’s no confirmation or cancellation of the process. If you’re unsure whether you should run an option, type in a? symbol and press enter to access Help.
Learning about the Windows Update Agent is exciting, as it plays a vital part of your computer’s health. Always keep the agent up-to-date to assure you don’t run into any errors while updating.
If you’re looking for a software company you can trust for its integrity and honest business practices, look no further than SoftwareKeep. We are a Microsoft Certified Partner and a BBB Accredited Business that cares about bringing our customers a reliable, satisfying experience on the software products they need. We will be with you before, during, and after all the sales.
That’s our 360 Degree SoftwareKeep Guarantee. So, what are you waiting for? Call us Today on +1 877 315 1713 or email sales@softwarekeep.com. As well, you can reach us via Live Chat.
Содержание
- Reset Windows Update Agent: новые возможности
- Обновление агента Windows обновления до последней версии
- Сводка
- Автоматическое скачивание Windows агента обновления
- Ручная загрузка Windows агента обновления из Центра загрузки Майкрософт
- Автономные пакеты для Windows 8 и Windows Server 2012
- Автономные пакеты для Windows 7 SP1 и Windows Server 2008 R2 SP1
- Дополнительная информация
- Улучшения в версии 7.6.7600.256 Windows агента обновления
- Улучшения версии 7.4.7600.226 Windows агента обновления
- Проблемы, исправленные в версии 7.2.6001.788 Windows агента обновления
- Улучшения версии 7.2.6001.784 Windows агента обновления
- Проблемы, исправленные версией 7.0.6000.381 Windows агента обновления
- обновление агента Центр обновления Windows
- Сведения для администраторов сети о получении последней версии агента обновления Windows
- Аннотация
- Дополнительная информация
- Сведения о файлах
- Усовершенствования, реализованные в версии 7.4.7600.226 агента обновления Windows
- Центр обновления Windows — дополнительные ресурсы
- Устранение неполадок WSUS
- Как сбросить компоненты Центра обновления Windows?
- Сброс компонентов Центра обновления Windows вручную
Reset Windows Update Agent: новые возможности
Впервые мы рассказали про бесплатное приложение Reset Windows Update Agent в 2015 году. Данный скрипт предоставляет пользователям и администраторам Windows удобный способ для выполнения необходимых задач администрирования на обслуживаемых системах.
За эти годы приложение активно развивалось, и список доступных команд увеличился с 9 в 2015 году до 18 в 2018 году. Все девять исходных команд по-прежнему доступны в Reset Windows Update Agent, а новые опции позволяют значительно расширить функциональность скрипта.
Скрипт доступен для загрузки на нашем сайте или в Центре сценариев Microsoft. Reset Windows Update Agent совместим с Windows XP, а также с новейшими версиями Windows 10 и Windows 10 Insider Preview.
Сначала нужно распаковать архив. Размер сжатого файла составляет всего 8 килобайт, а распакованная папка занимает 38 килобайт. Перед запуском скрипта можно ознакомиться с дополнительной информацией в файле README.txt. Обратите внимание, что для работы скрипта требуются права администратора.
Кликните правой кнопкой мыши по файлу ResetWUEng.cmd и выберите опцию Запуск от имени администратора. Перед тем, как выполнять какие-либо действия, рекомендуется создать резервную копию вашей системы.
При запуске отображается предупреждение об отказе от ответственности. Вам необходимо принять условия использования, чтобы отобразился список из 18 доступных команд:
Если предназначение некоторых команд вполне очевидно, например “Открыть настройки Защита системы», то подробности других операций остаются неизвестными, например “Удалить некорректные ключи реестра”.
Однако, вы всегда можете открыть скрипт в простом текстовом редакторе, чтобы проверить, какие действия он выполняет.
Например, при очистке временных файлов Windows используется две команды:
Некоторые опции запускают сразу большое количество команд. Так например, при выборе опции “Сбросить компоненты службы обновления Windows” будет выполняться последовательный набор команд, отвечающих за остановку служб, завершение их работы, удаление файлов, повторную регистрацию файлов и др.
Администраторы могут запускать команды скрипта вручную, если их знают. Тем не менее, данный скрипт позволяет ускорить выполнение задач администрирования, потому что вам достаточно выбрать номер опции и нажать Enter для запуска соответствующей команды.
Источник
Обновление агента Windows обновления до последней версии
В этой статье описывается, как обновить Windows агента обновления до последней версии.
Применяется к: Windows 7, Windows 8, Windows 2008 R2, Windows Server 2012
Исходный номер КБ: 949104
Сводка
Если включено автоматическое обновление, последняя версия агента обновления Windows автоматически загружается и устанавливается на компьютере. Или, вы можете вручную скачать и установить Windows агента обновления.
Автоматическое скачивание Windows агента обновления
Чтобы автоматически скачать Windows update Agent, выполните следующие действия:
Включаем автоматическое обновление. Следуйте этим шагам, чтобы Windows запущенной версии.
Windows 8.1 или Windows 8
Windows 7, Windows Vista или Windows XP
Чтобы автоматически включить автоматическое обновление, выберите кнопку Исправление или ссылку, а затем выберите Запустить в диалоговом окне Загрузка представления. Затем выполните действия мастера Fix it.
Перезапустите службу Windows обновления. Для этого выполните следующие действия:
Дождись Windows обновления, а затем убедитесь, что Windows агент обновления обновляется.
Ручная загрузка Windows агента обновления из Центра загрузки Майкрософт
Щелкните ссылку на скачивание для версии Windows, чтобы получить последний Windows агент обновления.
Автономные пакеты для Windows 8 и Windows Server 2012
Следующие файлы доступны для скачивания из Центра загрузки Майкрософт.
| Операционная система | Update |
|---|---|
| Все поддерживаемые x86-версии Windows 8 (KB2937636) | Скачайте пакет прямо сейчас. |
| Все поддерживаемые версии Windows 8 x64 (KB2937636) | Скачайте пакет прямо сейчас. |
| Все поддерживаемые версии Windows Server 2012 x64 (KB2937636) | Скачайте пакет прямо сейчас. |
Автономные пакеты для Windows 7 SP1 и Windows Server 2008 R2 SP1
Следующие файлы доступны для скачивания из Windows Update.
| Операционная система | Update |
|---|---|
| Все поддерживаемые x86-версии Windows 7 SP1 | Скачайте пакет прямо сейчас. |
| Все поддерживаемые x64-версии Windows 7 SP1 | Скачайте пакет прямо сейчас. |
| Все поддерживаемые x86-версии Windows Server 2008 R2 SP1 | Скачайте пакет прямо сейчас. |
| Все поддерживаемые x64-версии Windows Server 2008 R2 SP1 | Скачайте пакет прямо сейчас. |
| Все поддерживаемые итаниумные версии Windows Server 2008 R2 SP1 | Скачайте пакет прямо сейчас. |
Windows 8.1, Windows RT 8.1 и Windows Server 2012 R2 с обновлением 2919355 уже включают последнюю версию агента обновления Windows обновления.
Дополнительная информация
Если вы получаете ошибку Windows обновления, попробуйте решения для распространенных ошибок Windows обновления.
Дополнительные сведения о том, как проверить, какая Windows установлен агент обновления, выполните следующие действия:
Последняя версия агента обновления Windows для Windows 8.1 7.9600.16422. Последняя версия агента обновления Windows для Windows 8 7.8.9200.16693. Последняя версия Windows агента обновления для Windows 7, Windows Vista и Windows XP — 7.6.7600.256.
Улучшения в версии 7.6.7600.256 Windows агента обновления
Затвердеть инфраструктуру, чтобы клиент Windows обновления доверялся только тем файлам, которые подписаны новым сертификатом. Сертификат используется исключительно для защиты обновлений клиента Windows обновления.
Более безопасный канал связи для клиента Windows обновления
Улучшения версии 7.4.7600.226 Windows агента обновления
Проблемы, исправленные в версии 7.2.6001.788 Windows агента обновления
Версия 7.2.6001.788 агента обновления Windows устраняет следующую проблему. Эта проблема ранее не была задокументирована в статье Microsoft Knowledge Base:
Улучшения версии 7.2.6001.784 Windows агента обновления
Проблемы, исправленные версией 7.0.6000.381 Windows агента обновления
Версия 7.0.6000.381 агента обновления Windows устраняет следующие проблемы. Эти проблемы ранее не были задокументированы в статье Microsoft Knowledge Base:
Windows Обновление помогает поддерживать современный и безопасный компьютер, скачав и установив последние обновления и обновления от Microsoft. Windows Обновление определяет, какие обновления применяются к вашему компьютеру.
Корпорация Майкрософт периодически делает обновления программного обеспечения доступными для пользователей Windows и другого программного обеспечения Майкрософт. К ним относятся обновления, которые улучшают надежность и производительность, обновления, которые обеспечивают новые средства защиты от вредоносных программ и другого потенциально нежелательного программного обеспечения, а также обновления Windows функций. Чтобы повысить производительность или надежность компонентов оборудования на компьютере, Корпорация Майкрософт может также предоставлять обновления драйверам устройств, которые поставляются производителем компьютеров.
При включите Windows обновления компоненты программного обеспечения, непосредственно связанные с Windows обновления, будут периодически обновляться на компьютере. Эти обновления должны выполняться, прежде чем Windows обновление может проверить необходимые обновления или до установки других обновлений. Эти необходимые обновления устраняют ошибки, обеспечивают текущие улучшения и поддерживают совместимость с серверами Майкрософт, которые поддерживают Windows update. Если вы отключит Windows обновления, вы не получите эти обновления.
Windows Обновление настраивается для автоматической установки обновлений при выборе рекомендуемого параметра Windows установки out of Box Experience (OOBE). Вы также можете включить Windows обновления, выбрав один из следующих параметров в элементе Автоматические обновления в панели управления:
После включив Windows update, необходимые обновления для компонентов Windows update будут скачивать и устанавливаться автоматически без уведомления. Это поведение происходит независимо от того, какой параметр вы используете для Windows update. Если вы не хотите получать необходимые обновления, вы можете отключить автоматические обновления в панели управления.
Обновления для Windows обновления обычно делают следующее: адрес обратной связи от клиентов, улучшение совместимости, производительности и надежности службы, а также включить новые возможности службы. При обновлении Windows обновления обычно требуется соответствующее обновление клиента. Во время операции самообновки агента Windows файлы агента обновления могут быть добавлены, изменены или заменены. Например, Windows файлы агентов обновления, которые помогают отображать пользовательский интерфейс или определяют, применимы ли обновления к определенной системе. Такое поведение происходит, когда установлено, что система автоматически проверяет доступные обновления. Это не происходит при отключении автоматических обновлений. Например, такое поведение не происходит, если вы выбираете Never check for updates in Windows Vista и Windows 7 или если вы выберите отключить автоматические обновления в Windows XP.
Администраторы получат последнюю версию агента обновления Windows для развертывания через Windows Server Update Services (WSUS).
Источник
обновление агента Центр обновления Windows
Windows агент обновления (WUA) обновляется с помощью различных средств, в зависимости от версии Windows, выполняемой на устройстве. Старые версии WUA не могут подключаться к текущим службам обновления, могут быть несовместимы со всеми обновлениями и могут не поддерживать все документированные API. Вот как можно убедиться, что WUA полностью обновлен и совместим.
в версиях Windows начиная с Windows 7 и Windows Server 2008 R2
Windows обновления агента обновления (WUA) включены в регулярные периодические обновления для Windows, распределенных по Центр обновления Windows или Windows Server Update Services (WSUS). вам не нужно предпринимать никаких дополнительных действий по обновлению WUA на этих Windows версиях.
в версиях Windows до Windows 7 и Windows Server 2008 R2
WUA автоматически обновляется, когда автоматическое обновление подключается к службам Центр обновления Windows или WSUS.
если автоматическое обновление еще не удалось запустить, возможно, на устройстве, на котором работают эти Windowsные версии, установлена более старая версия WUA, которая не поддерживает все документированные api. если при использовании API-интерфейса WUA для выполнения проверки, загрузки или установки получен результат WU_E_SELFUPDATE_REQUIRED, эта ошибка говорит о том, что установленная версия WUA слишком старая для подключения к текущим службам Центр обновления Windows. Вы не можете использовать обычные API-интерфейсы WUA для обновления WUA в этих операционных системах.
пользователь может вручную обновить WUA до текущей версии, открыв панель управления Центр обновления Windows, выбрав пункт проверить обновления и приняв отображаемое самостоятельное обновление. Кроме того, агент WUA можно обновить программным способом.
для программного обновления агента WUA в версиях Windows до Windows 7 и Windows Server 2008 R2
Источник
Сведения для администраторов сети о получении последней версии агента обновления Windows
Автономного установщика у последней версии агента обновления Windows (7.6.7600.256) не существует. Далее приведены инструкции, позволяющие установить агент обновления Windows версии 7.4.7600.226.
Дополнительные сведения о последней версии агента обновления Windows (7.6.7600.256) см. здесь: http://support.microsoft.com/kb/949104/ru.
Если вы включили автоматическое обновление Windows, последняя версия агента обновления будет установлена на вашем компьютере автоматически.
Чтобы установить последнюю версию агента обновления, используйте Центр обновления Windows:
Аннотация
В этой статье приведены сведения о последней версии агента обновления Windows (7.4.7600.226) и ее содержимом.
Примечание. Раздел «Дополнительные сведения» данной статьи предназначен для ИТ-администраторов, использующих различные технологии обнаружения и развертывания обновлений корпорации Майкрософт в бизнес-среде, включая Центр обновления Windows, Центр обновления Майкрософт, WSUS, SMS, SCCM, SCE и MBSA.
Дополнительная информация
Для получения агента обновления Windows версии 7.4.7600.226 щелкните одну из следующих ссылок, соответствующую используемой операционной системе.
Версии Windows на основе платформы x86 
Версии Windows для платформы x64 
Версии Windows для платформы Itanium 
Дата выпуска: Четверг, 24 сентября 2009 г.
Дополнительные сведения о загрузке файлов поддержки Майкрософт см. в следующей статье базы знаний Майкрософт:
119591 Как загрузить файлы поддержки Microsoft из Интернета Корпорация Майкрософт проверила этот файл на наличие вирусов, используя последние на момент его публикации версии антивирусных программ. Файл хранится на защищенных серверах, что предотвращает его несанкционированное изменение.
Примечание. Если агент обновления Windows получен через службы WSUS, его версия может отличаться от описанной в этой статье. Версия, описываемая в этой статье, совместима со службами WSUS.
Администраторы могут получить дополнительные сведения о проверке версии агента обновления Windows в системе клиента на веб-узле корпорации Майкрософт по адресу:
http://technet.microsoft.com/ru-ru/library/bb680319.aspx (Эта ссылка может указывать на содержимое полностью или частично на английском языке.)
Сведения о файлах
Файлы английской версии обновления имеют атрибуты, приведенные в следующей таблице (или более поздние). Дата и время для файлов указаны в формате UTC. При просмотре сведений о файле происходит перевод соответствующих значений в местное время. Чтобы выяснить разницу между временем в формате UTC и местным временем, откройте вкладку Часовой пояс элемента Дата и время панели управления.
Усовершенствования, реализованные в версии 7.4.7600.226 агента обновления Windows
Сокращено время поиска обновлений в Центре обновления Windows.
Улучшен пользовательский интерфейс для компьютеров с системами Windows Vista и Windows Server 2008, использующих Центр обновления Windows.
Описания обновлений стали более подробными и удобными для чтения.
Улучшена процедура уведомления пользователей о пакетах обновления.
Источник
Центр обновления Windows — дополнительные ресурсы
Windows Server 2016 поддерживает политики, доступные в Windows 10 версии 1607. Windows Server 2019 поддерживает политики, доступные в Windows 10 версии 1809.
В следующих ресурсах содержатся дополнительные сведения об использовании Центра обновления Windows.
Устранение неполадок WSUS
Как сбросить компоненты Центра обновления Windows?
Если другие действия не помогают, попробуйте сбросить агент Центра обновления Windows, выполнив следующие команды из командной строки с повышенными привилегиями.
Сброс компонентов Центра обновления Windows вручную
Откройте командную строку Windows. Чтобы открыть командную строку, нажмите Пуск > Выполнить. Скопируйте и вставьте (или введите вручную) следующую команду в командную строку, затем нажмите клавишу ВВОД:
Остановите службу BITS, службу Центра обновления Windows и службу шифрования. Для этого введите следующие команды в командной строке. После ввода каждой команды нажимайте клавишу ВВОД.
Удалите файлы qmgr*.dat. Для этого введите следующую команду в командной строке и нажмите клавишу ВВОД:
Если вы впервые пытаетесь устранить неполадки Центра обновления Windows, выполнив действия, перечисленные в этой статье, перейдите к шагу 5, не выполняя действия шага 4. Действия, описанные на шаге 4, необходимо выполнять при устранении неполадок только в случае, если неполадки Центра обновления Windows не удается устранить, выполнив все шаги, кроме шага 4. Действия шага 4 также выполняются в «агрессивном» режиме указанного выше решения «Исправить».
Для этого введите следующие команды в командной строке. После ввода каждой команды нажимайте клавишу ВВОД.
Введите следующую команду в командной строке и нажмите клавишу ВВОД:
Зарегистрируйте файлы BITS и файлы Центра обновления Windows. Для этого введите следующие команды в командной строке. После ввода каждой команды нажимайте клавишу ВВОД.
Сбросьте WinSock. Для этого введите следующую команду в командной строке и нажмите клавишу ВВОД:
Если вы используете Windows XP или Windows Server 2003, необходимо настроить параметры прокси-сервера. Для этого введите следующую команду в командной строке и нажмите клавишу ВВОД:
Перезапустите службу BITS, службу Центра обновления Windows и службу шифрования. Для этого введите следующие команды в командной строке. После ввода каждой команды нажимайте клавишу ВВОД.
Если вы используете Windows Vista или Windows Server 2008, очистите очередь BITS. Для этого введите следующую команду в командной строке и нажмите клавишу ВВОД:
Источник

Windows Update on Windows 11 |
|
| Other names | Microsoft Update |
|---|---|
| Developer(s) | Microsoft |
| Operating system |
|
| Included with |
|
| Service name | Windows Update |
| Type | Network service |
| Website | support.microsoft.com/en-us/windows/windows-update-faq |
Windows Update is a Microsoft service for the Windows 9x and Windows NT families of operating system, which automates downloading and installing Microsoft Windows software updates over the Internet. The service delivers software updates for Windows, as well as the various Microsoft antivirus products, including Windows Defender and Microsoft Security Essentials. Since its inception, Microsoft has introduced two extensions of the service: Microsoft Update and Windows Update for Business. The former expands the core service to include other Microsoft products, such as Microsoft Office and Microsoft Expression Studio. The latter is available to business editions of Windows 10 and permits postponing updates or receiving updates only after they have undergone rigorous testing.
As the service has evolved over the years, so has its client software. For a decade, the primary client component of the service was the Windows Update web app that could only be run on Internet Explorer. Starting with Windows Vista, the primary client component became Windows Update Agent, an integral component of the operating system.
The service provides several kinds of updates. Security updates or critical updates mitigate vulnerabilities against security exploits against Microsoft Windows. Cumulative updates are updates that bundle multiple updates, both new and previously released updates. Cumulative updates were introduced with Windows 10 and have been backported to Windows 7 and Windows 8.1.
Microsoft routinely releases updates on the second Tuesday of each month (known as the Patch Tuesday), but can provide them whenever a new update is urgently required to prevent a newly discovered or prevalent exploit. System administrators can configure Windows Update to install critical updates for Microsoft Windows automatically, so long as the computer has an Internet connection.
In Windows 10 and Windows 11, the use of Windows Update is mandatory, however, the software agreement states that users may stop receiving updates on their device by disconnecting their device from the Internet.[1][2]
Clients[edit]
Windows Update web app[edit]
The Windows Update web app, version 4, in Windows Me
Windows Update was introduced as a web app with the launch of Windows 98 and offered additional desktop themes, games, device driver updates, and optional components such as NetMeeting.[3] Windows 95 and Windows NT 4.0 were retroactively given the ability to access the Windows Update website and download updates designed for those operating systems, starting with the release of Internet Explorer 4. The initial focus of Windows Update was free add-ons and new technologies for Windows. Security fixes for Outlook Express, Internet Explorer and other programs appeared later, as did access to beta versions of upcoming Microsoft software, e.g. Internet Explorer 5. Fixes to Windows 98 to resolve the Year 2000 problem were distributed using Windows Update in December 1998. Microsoft attributed the sales success of Windows 98 in part to Windows Update.[4]
The Windows Update web app requires either Internet Explorer or a third-party web browser that supports the ActiveX technology. The first version of the web app, version 3, does not send any personally-identifiable information to Microsoft. Instead, the app downloads a full list of every available update and chooses which one to download and install. But the list grew so large that the performance impact of processing became a concern. Arie Slob, writing for the Windows-help.net newsletter in March 2003, noted that the size of the update list had exceeded 400 KB, which caused delays of more than a minute for dial-up users.[5] Windows Update v4, released in 2001 in conjunction with Windows XP, changed this. This version of the app makes an inventory of the system’s hardware and Microsoft software and sends them to the service, thus offloading the processing burden to Microsoft servers.[5]
Critical Update Notification Utility[edit]
Critical Update Notification Utility (initially Critical Update Notification Tool) is a background process that checks the Windows Update web site on a regular schedule for new updates that have been marked as «Critical». It was released shortly after Windows 98.
By default, this check occurs every five minutes, plus when Internet Explorer starts; however, the user could configure the next check to occur only at certain times of the day or on certain days of the week. The tool queries the Microsoft server for a file called «cucif.cab«, which contained a list of all the critical updates released for the operating system. The tool then compares this list with the list of installed updates on its machine and displays an update availability notification. Once the check is executed, any custom schedule defined by the user is reverted to the default. Microsoft stated that this ensures that users received notification of critical updates in a timely manner.[6]
An analysis done by security researcher H. D. Moore in early 1999 was critical of this approach, describing it as «horribly inefficient» and susceptible to attacks. In a posting to BugTraq, he explained that, «every single Windows 98 computer that wishes to get an update has to rely on a single host for the security. If that one server got compromised one day, or an attacker cracks the [Microsoft] DNS server again, there could be millions of users installing trojans every hour. The scope of this attack is big enough to attract crackers who actually know what they are doing…»[7]
Microsoft continued to promote the tool through 1999 and the first half of 2000. Initial releases of Windows 2000 shipped with the tool. The tool did not support Windows 95 and Windows NT 4.0.
Automatic Updates[edit]
Automatic Updates is the successor of the Critical Update Notification Utility. It was released in 2000, along with Windows Me. It supports Windows 2000 SP3 as well.
Unlike its predecessor, Automatic Updates can download and install updates. Instead of the five-minute schedule used by its predecessor, Automatic Updates checks the Windows Update servers once a day. After Windows Me is installed, a notification balloon prompts the user to configure the Automatic Updates client. The user can choose from three notification schemes: Being notified before downloading the update, being notified before installing the update, or both. If new updates are ready to be installed, the user may install them before turning off the computer. A shield icon will be displayed on the Shutdown button during this time.
Windows XP and Windows 2000 SP3 include Background Intelligent Transfer Service, a Windows service for transferring files in the background without user interaction. As a system component, it is capable of monitoring the user’s Internet usage, and throttling its own bandwidth usage in order to prioritize user-initiated activities. The Automatic Updates client for these operating systems was updated to use this system service.
Automatic Updates in Windows XP gained notoriety for repeatedly interrupting the user while working on their computer. Every time an update requiring a reboot was installed, Automatic Updates would prompt the user with a dialog box that allowed the user to restart immediately or dismiss the dialog box, which would reappear in ten minutes; a behavior that Jeff Atwood described as «perhaps the naggiest dialog box ever.»[8]
In 2013, it was observed that shortly after the startup process, Automatic Updates (wuauclt.exe) and Service Host (svchost.exe) in Windows XP would claim 100% of a computer’s CPU capacity for extended periods of time (between ten minutes to two hours), making affected computers unusable. According to Woody Leonhart of InfoWorld, early reports of this issue could be seen in Microsoft TechNet forums in late May 2013, although Microsoft first received large number of complaints about this issue in September 2013. The cause was an exponential algorithm in the evaluation of superseded updates which had grown large over the decade following the release of Windows XP. Microsoft’s attempts to fix the issue in October, November and December proved futile, causing the issue to be escalated to the top priority.[9][10]
Windows Update Agent[edit]
Starting with Windows Vista and Windows Server 2008, Windows Update Agent replaces both the Windows Update web app and the Automatic Updates client.[11][12] It is in charge of downloading and installing software update from Windows Update, as well as the on-premises servers of Windows Server Updates Services or System Center Configuration Manager.[13][14]
Windows Update Agent can be managed through a Control Panel applet, as well as Group Policy, Microsoft Intune and Windows PowerShell. It can also be set to automatically download and install both important and recommended updates. In prior versions of Windows, such updates were only available through the Windows Update web site. Additionally, Windows Update in Windows Vista supports downloading Windows Ultimate Extras, optional software for Windows Vista Ultimate Edition.
Unlike Automatic Updates in Windows XP, Windows Update Agent in Windows Vista and Windows 7 allows the user to postpone the mandatory restart (required for the update process to complete) for up to four hours. The revised dialog box that prompts for the restart appears under other windows, instead of on top of them. However, standard user accounts only have 15 minutes to respond to this dialog box. This was changed with Windows 8: Users have 3 days (72 hours) before the computer reboots automatically after installing automatic updates that require a reboot. Windows 8 also consolidates the restart requests for non-critical updates into just one per month. Additionally, the login screen notifies them of the restart requirements.[15]
Windows Update Agent makes use of the Transactional NTFS feature introduced with Windows Vista to apply updates to Windows system files. This feature helps Windows recover cleanly in the event of an unexpected failure, as file changes are committed atomically.[16]
Windows 10 contains major changes to Windows Update Agent operations; it no longer allows the manual, selective installation of updates. All updates, regardless of type (this includes hardware drivers), are downloaded and installed automatically, and users are only given the option to choose whether their system would reboot automatically to install updates when the system is inactive, or be notified to schedule a reboot.[17][18] Microsoft offers a diagnostic tool that can be used to hide troublesome device drivers and prevent them from being reinstalled, but only after they had been already installed, then uninstalled without rebooting the system.[19][20]
Windows Update Agent on Windows 10 supports peer-to-peer distribution of updates; by default, systems’ bandwidth is used to distribute previously downloaded updates to other users, in combination with Microsoft servers. Users may optionally change Windows Update to only perform peer-to-peer updates within their local area network.[21]
Windows 10 also introduced cumulative updates. For example, if Microsoft released updates KB00001 in July, KB00002 in August, and KB00003 in September, Microsoft would release cumulative update KB00004 which packs KB00001, KB00002, and KB00003 together. Installing KB00004 will also install KB00001, KB00002 and KB00003, mitigating the need for multiple restarts and reducing the number of downloads needed. KB00004 may also include other fixes with their own KB-number that were not separately released.[22] A disadvantage of cumulative updates is that downloading and installing updates that fix individual problems is no longer possible. KB stands for knowledge base as in Microsoft Knowledge Base.
Windows Update for Business[edit]
Windows Update for Business is a term for a set of features in the Pro, Enterprise and Education editions of Windows 10, intended to ease the administration of Windows across organizations. It enables IT pros to:[23][24][25]
- Switch between the standard and the deferred release branches of Windows 10. This feature has since been removed as Microsoft retired the deferred branch.[26]
- Defer automatic installation of ordinary updates for 30 days. Starting with Windows 10 version 20H1, this feature is more difficult to access.[27]
- Defer automatic installation of Windows upgrades (a.k.a. «feature updates») for 365 days. Starting with Windows 10 version 20H1, these updates are no longer automatically offered.[27]
These features were added in Windows 10 version 1511.[28] They are intended for large organizations with many computers, so they can logically group their computers for gradual deployment. Microsoft recommends a small set of pilot computers to receive the updates almost immediately, while the set of most critical computers to receive them after every other group has done so, and has experienced their effects.[29]
Other Microsoft update management solutions, such as Windows Server Update Services or System Center Configuration Manager, do not override Windows Update for Business. Rather, they force Windows 10 into the «dual scan mode». This can cause confusion for administrators who do not comprehend the full ramifications of the dual scan mode.[30]
Complementary software and services[edit]
As organizations continued to use more computers, the per-machine Windows Update clients started to become unwieldy and insufficient. In response to the need of organizations for deploying updates to many machines, Microsoft introduced Software Update Services (SUS), which was later renamed Windows Server Update Services (WSUS). A component of the Windows Server family of operating systems, WSUS downloads updates for Microsoft products to a server computer on which it is running and redistributes them to the computers within the organization over a local area network (LAN). One of the benefits of this method is a reduction in the consumption of Internet bandwidth, equal to (N-1)×S, where N is the number of computers in the organization and S is the size made by the updates. Additionally, WSUS permits administrators to test updates on a small group of test computers before deploying them to all systems, in order to ensure that business continuity is not disrupted because of the changes of the updates. For very large organizations, multiple WSUS servers can be chained together hierarchically. Only one server in this hierarchy downloads from the Internet.
Update packages distributed via the Windows Update service can be individually downloaded from Microsoft Update Catalog. These updates can be installed on computers without internet access (e.g. via USB flash drive) or slipstreamed with a Windows installation. In case of the former, Windows Update Agent (wusa.exe) can install these files. In case of the latter, Microsoft deployment utilities such as DISM, WADK and MDT can consume these packages.
Microsoft offers System Center Configuration Manager for very complex deployment and servicing scenarios. The product integrates with all of the aforesaid tools (WSUS, DISM, WADK, MDT) to automate the process.
A number of tools have been created by independent software vendors which provide the ability for Windows Updates to be automatically downloaded for, or added to, an online or offline system. One common use for offline updates is to ensure a system is fully patched against security vulnerabilities before being connected to the Internet or another network. A second use is that downloads can be very large, but may be dependent on a slow or unreliable network connection, or the same updates may be needed for more than one machine. AutoPatcher, WSUS Offline Update, PortableUpdate, and Windows Updates Downloader are examples of such tools.[31]
Service[edit]
At the beginning of 2005, Windows Update was being accessed by about 150 million people,[32] with about 112 million of those using Automatic Updates.[33] As of 2008, Windows Update had about 500 million clients, processed about 350 million unique scans per day, and maintained an average of 1.5 million simultaneous connections to client machines. On Patch Tuesday, the day Microsoft typically releases new software updates, outbound traffic could exceed 500 gigabits per second.[34] Approximately 90% of all clients used automatic updates to initiate software updates, with the remaining 10% using the Windows Update web site. The web site is built using ASP.NET, and processes an average of 90,000 page requests per second.
Traditionally, the service provided each patch in its own proprietary archive file. Occasionally, Microsoft released service packs which bundled all updates released over the course of years for a certain product. Starting with Windows 10, however, all patches are delivered in cumulative packages.[35] On 15 August 2016, Microsoft announced that effective October 2016, all future patches to Windows 7 and 8.1 would become cumulative as with Windows 10. The ability to download and install individual updates would be removed as existing updates are transitioned to this model.[36] This has resulted in increasing download sizes of each monthly update. An analysis done by Computerworld determined that the download size for Windows 7 x64 has increased from 119.4MB in October 2016 to 203MB in October 2017.[37] Initially, Microsoft was very vague about specific changes within each cumulative update package.[35] However, since early 2016, Microsoft has begun releasing more detailed information on the specific changes.[38]
In 2011, the update service was decommissioned for Windows 98, 98 SE, ME and NT4 and the old updates for those systems were removed from its servers.[39][40]
On August 3, 2020, the update service was decommissioned for Windows 2000, XP, Server 2003 and Vista due to Microsoft discontinuing SHA-1 updates. The old updates are still available on the Microsoft Update Catalog.[41]
Microsoft Update[edit]
At the February 2005 RSA Conference, Microsoft announced the first beta of Microsoft Update, an optional replacement for Windows Update that provides security patches, service packs and other updates for both Windows and other Microsoft software.[42] The initial release in June 2005 provided support for Microsoft Office 2003, Exchange 2003, and SQL Server 2000, running on Windows 2000, XP, and Server 2003. Over time, the list has expanded to include other Microsoft products, such as Windows Live, Windows Defender, Visual Studio, runtimes and redistributables, Zune Software, Virtual PC and Virtual Server, CAPICOM, Microsoft Lync, Microsoft Expression Studio, and other server products. It also offers Silverlight and Windows Media Player as optional downloads if applicable to the operating system.
Office Update[edit]
Office Update is a free online service that allows users to detect and install updates for certain Microsoft Office products.
The original update service supported Office 2000, Office XP, Office 2003 and Office 2007. On 1 August 2009 Microsoft decommissioned the Office Update service, merging it with Microsoft Update.[43] Microsoft Update does not support Office 2000.
With the introduction of the Office 365 licensing program, however, Microsoft once again activated a separate Office update service.[44][45]
References[edit]
- ^ «Microsoft License Terms». www.microsoft.com. Section 13b. Retrieved 30 March 2020.
- ^ «MICROSOFT SOFTWARE LICENSE TERMS». www.microsoft.com. Retrieved 20 July 2022.
Canada. You may stop receiving updates on your device by turning off Internet access. If and when you re-connect to the Internet, the software will resume checking for and installing updates.
- ^ Gartner, John (24 August 1995). «Taking Windows 98 For A Test-Drive». TechWeb. CMP Net. Archived from the original on 3 December 1998.
- ^ «Strong Holiday Sales Make Windows 98 Best-Selling Software of 1998». PressPass (Press release). Microsoft. 9 February 1999. Archived from the original on 6 March 2012. Retrieved 29 July 2008.
- ^ a b Slob, Arie (22 March 2003). «Windows Update is Spying on You!». Windows-Help.NET. InfiniSource. Archived from the original on 14 January 2018. Retrieved 12 September 2019.
- ^ «Description of the Windows Critical Update Notification utility». Support. Microsoft. 5 December 2007. Archived from the original on 26 July 2020. Retrieved 22 November 2018.
- ^ Moore, H. D. (29 January 1999). «How the MS Critical Update Notification works…» BugTraq mailing list archive. Archived from the original on 21 June 2009. Retrieved 30 July 2008 – via seclists.org.
- ^ Atwood, Jeff (13 May 2005). «XP Automatic Update Nagging». Coding Horror: Programming and Human Factors. Archived from the original on 9 November 2021. Retrieved 12 September 2019.
- ^ Bright, Peter (16 December 2013). «Exponential algorithm making Windows XP miserable could be fixed». Ars Technica. Condé Nast. Archived from the original on 6 May 2021. Retrieved 12 September 2019.
- ^ Leonhard, Woody (16 December 2013). «Microsoft promises to fix Windows XP SVCHOST redlining ‘as soon as possible’«. InfoWorld. IDG. Archived from the original on 30 March 2019. Retrieved 12 September 2019.
- ^ «How to update the Windows Update Agent to the latest version». Support. Microsoft. 6 June 2017. Archived from the original on 4 September 2020. Retrieved 22 November 2018.
- ^ «Windows Update Agent». TechNet. Microsoft. 13 December 2007. Archived from the original on 14 January 2018. Retrieved 22 November 2018.
- ^ «How to Install the Windows Update Agent on Client Computers». TechNet. Microsoft. 2007. Archived from the original on 11 October 2018. Retrieved 22 November 2018.
- ^ Rouse, Margaret (May 2014). «Microsoft Windows Update Agent». TechTarget. Archived from the original on 27 January 2021. Retrieved 22 November 2018.
- ^ Savov, Vlad (15 November 2011). «Windows 8 auto-update will consolidate restarts into one per month, give you three days to do it». The Verge. Vox Media. Archived from the original on 29 August 2021. Retrieved 22 November 2018.
- ^ «NTFS Beta Chat Transcript (July 12, 2006)». Storage at Microsoft. Microsoft. 12 July 2006. Archived from the original on 20 April 2019. Retrieved 22 November 2018.
- ^ «Windows 10 lets you schedule Windows Update restarts». CNET. Archived from the original on 19 February 2015. Retrieved 4 August 2015.
- ^ «Did Microsoft Just Backtrack On Forced Updates For Windows 10?». CRN.com. 27 July 2015. Archived from the original on 28 July 2015. Retrieved 4 August 2015.
- ^ «On the road to Windows 10: Nvidia driver tests KB 3073930 patch blocker». InfoWorld. 27 July 2015. Archived from the original on 20 June 2017. Retrieved 31 July 2015.
- ^ «On the road to Windows 10: Problems with forced updates and KB 3073930». InfoWorld. 22 July 2015. Archived from the original on 20 June 2017. Retrieved 31 July 2015.
- ^ «How to stop Windows 10 from using your PC’s bandwidth to update strangers’ systems». PC World. IDG. Archived from the original on 5 August 2015. Retrieved 4 August 2015.
- ^ «User can’t log on to a POP/IMAP account by using NTLM authentication in Exchange Server 2013». Archived from the original on 10 February 2021. Retrieved 24 March 2020.
To resolve this issue, install Cumulative Update 21
- ^ Hammoudi, Samir (15 November 2015). «Windows Update for Business explained». beanexpert. Microsoft. Archived from the original on 19 April 2019. Retrieved 14 January 2018.
- ^ Azzarello, Pat (10 May 2017). «What is Windows Update for Business?». Windows for IT Pros. Microsoft. Archived from the original on 11 June 2018. Retrieved 14 January 2018.
Windows Update for Business is intended for machines running Windows 10 or later, and Windows 10 Education, Professional, or Enterprise editions managed in organizations.
- ^ Halfin, Danni; Brower, Nick; Lich, Brian; Poggemeyer, Liza (13 October 2017). «Deploy updates using Windows Update for Business». Microsoft Docs. Microsoft. Archived from the original on 22 October 2021. Retrieved 22 November 2018.
- ^ «Microsoft changes Windows Update for Business options — gHacks Tech News». www.ghacks.net. 15 February 2019. Archived from the original on 6 October 2021. Retrieved 3 November 2020.
- ^ a b «Microsoft removes Setting to defer feature updates from Windows 10 version 2004 — gHacks Tech News». www.ghacks.net. 25 June 2020. Archived from the original on 27 August 2021. Retrieved 3 November 2020.
- ^ Bott, Ed (17 January 2018). «How to take control of Windows 10 updates and upgrades (even if you don’t own a business)». ZDNet. CBS Interactive. Archived from the original on 12 November 2021. Retrieved 22 November 2018.
- ^ Halfin, Danni; Lich, Brian (27 July 2017). «Build deployment rings for Windows 10 updates». Microsoft Docs. Microsoft. Archived from the original on 24 May 2021. Retrieved 22 November 2018.
- ^ Rasheed, Shadab (9 January 2017). «Why WSUS and SCCM managed clients are reaching out to Microsoft Online». Windows Server Blog. Microsoft. Archived from the original on 14 January 2018. Retrieved 22 November 2018.
- ^ «4 Tools to Update Windows Offline and install Hotfixes from a Local Source». raymond.cc. 14 November 2005. Archived from the original on 20 October 2021. Retrieved 22 November 2018.
- ^ «RSA Conference 2005: «Security: Raising the Bar» (speech transcript)». PressPass. Microsoft. 15 February 2005. Archived from the original on 8 March 2009. Retrieved 30 July 2008.
- ^ «Microsoft Announces Availability of New Solutions to Help Protect Customers Against Spyware and Viruses». PressPass. Microsoft. 6 January 2005. Archived from the original on 2 April 2012. Retrieved 30 July 2008.
- ^ «Introducing the Microsoft.com Engineering Operations Team». Microsoft TechNet. Microsoft. 2008. Archived from the original on 26 August 2017. Retrieved 31 May 2012.
- ^ a b «Windows 10 users beg Microsoft for more info on updates». Computerworld. IDG. 14 September 2015. Archived from the original on 14 September 2015. Retrieved 30 September 2015.
- ^ «Windows 7, 8.1 moving to Windows 10’s cumulative update model». Ars Technica. Conde Nast Digital. 15 August 2016. Archived from the original on 14 February 2017. Retrieved 16 August 2016.
- ^ Gregg Keizer (14 December 2017). «Why Windows 7 updates are getting bigger». Computerworld. Archived from the original on 22 November 2018. Retrieved 22 November 2018.
- ^ «Windows 10 update details». Windows 10 update history. Microsoft. Archived from the original on 5 March 2016. Retrieved 4 March 2016.
- ^ «I can’t access Windows Update v4 — Windows 9x/ME — MSFN». msfn.org. Archived from the original on 9 November 2021. Retrieved 25 April 2021.
- ^ «Where is Windows Update for Win98? — BetaArchive». www.betaarchive.com. Archived from the original on 8 November 2021. Retrieved 25 April 2021.
- ^ «Windows Update SHA-1 based endpoints discontinued for older Windows devices». Archived from the original on 18 December 2020. Retrieved 5 August 2020.
- ^ «Microsoft Update Site Launched». helpwithwindows.com. 10 June 2005. Archived from the original on 22 November 2018. Retrieved 30 July 2008.
- ^ «About Office Update». office.microsoft.com. Microsoft. Archived from the original on 28 May 2010.
- ^ «Install Office updates». support.office.com. Microsoft. Archived from the original on 23 May 2020. Retrieved 4 December 2017.
- ^ «Check for Office for Mac updates automatically». support.office.com. Microsoft. Archived from the original on 9 August 2018. Retrieved 4 December 2017.
External links[edit]
- Microsoft Update website
- Microsoft Technical Security Notifications

Windows Update on Windows 11 |
|
| Other names | Microsoft Update |
|---|---|
| Developer(s) | Microsoft |
| Operating system |
|
| Included with |
|
| Service name | Windows Update |
| Type | Network service |
| Website | support.microsoft.com/en-us/windows/windows-update-faq |
Windows Update is a Microsoft service for the Windows 9x and Windows NT families of operating system, which automates downloading and installing Microsoft Windows software updates over the Internet. The service delivers software updates for Windows, as well as the various Microsoft antivirus products, including Windows Defender and Microsoft Security Essentials. Since its inception, Microsoft has introduced two extensions of the service: Microsoft Update and Windows Update for Business. The former expands the core service to include other Microsoft products, such as Microsoft Office and Microsoft Expression Studio. The latter is available to business editions of Windows 10 and permits postponing updates or receiving updates only after they have undergone rigorous testing.
As the service has evolved over the years, so has its client software. For a decade, the primary client component of the service was the Windows Update web app that could only be run on Internet Explorer. Starting with Windows Vista, the primary client component became Windows Update Agent, an integral component of the operating system.
The service provides several kinds of updates. Security updates or critical updates mitigate vulnerabilities against security exploits against Microsoft Windows. Cumulative updates are updates that bundle multiple updates, both new and previously released updates. Cumulative updates were introduced with Windows 10 and have been backported to Windows 7 and Windows 8.1.
Microsoft routinely releases updates on the second Tuesday of each month (known as the Patch Tuesday), but can provide them whenever a new update is urgently required to prevent a newly discovered or prevalent exploit. System administrators can configure Windows Update to install critical updates for Microsoft Windows automatically, so long as the computer has an Internet connection.
In Windows 10 and Windows 11, the use of Windows Update is mandatory, however, the software agreement states that users may stop receiving updates on their device by disconnecting their device from the Internet.[1][2]
Clients[edit]
Windows Update web app[edit]
The Windows Update web app, version 4, in Windows Me
Windows Update was introduced as a web app with the launch of Windows 98 and offered additional desktop themes, games, device driver updates, and optional components such as NetMeeting.[3] Windows 95 and Windows NT 4.0 were retroactively given the ability to access the Windows Update website and download updates designed for those operating systems, starting with the release of Internet Explorer 4. The initial focus of Windows Update was free add-ons and new technologies for Windows. Security fixes for Outlook Express, Internet Explorer and other programs appeared later, as did access to beta versions of upcoming Microsoft software, e.g. Internet Explorer 5. Fixes to Windows 98 to resolve the Year 2000 problem were distributed using Windows Update in December 1998. Microsoft attributed the sales success of Windows 98 in part to Windows Update.[4]
The Windows Update web app requires either Internet Explorer or a third-party web browser that supports the ActiveX technology. The first version of the web app, version 3, does not send any personally-identifiable information to Microsoft. Instead, the app downloads a full list of every available update and chooses which one to download and install. But the list grew so large that the performance impact of processing became a concern. Arie Slob, writing for the Windows-help.net newsletter in March 2003, noted that the size of the update list had exceeded 400 KB, which caused delays of more than a minute for dial-up users.[5] Windows Update v4, released in 2001 in conjunction with Windows XP, changed this. This version of the app makes an inventory of the system’s hardware and Microsoft software and sends them to the service, thus offloading the processing burden to Microsoft servers.[5]
Critical Update Notification Utility[edit]
Critical Update Notification Utility (initially Critical Update Notification Tool) is a background process that checks the Windows Update web site on a regular schedule for new updates that have been marked as «Critical». It was released shortly after Windows 98.
By default, this check occurs every five minutes, plus when Internet Explorer starts; however, the user could configure the next check to occur only at certain times of the day or on certain days of the week. The tool queries the Microsoft server for a file called «cucif.cab«, which contained a list of all the critical updates released for the operating system. The tool then compares this list with the list of installed updates on its machine and displays an update availability notification. Once the check is executed, any custom schedule defined by the user is reverted to the default. Microsoft stated that this ensures that users received notification of critical updates in a timely manner.[6]
An analysis done by security researcher H. D. Moore in early 1999 was critical of this approach, describing it as «horribly inefficient» and susceptible to attacks. In a posting to BugTraq, he explained that, «every single Windows 98 computer that wishes to get an update has to rely on a single host for the security. If that one server got compromised one day, or an attacker cracks the [Microsoft] DNS server again, there could be millions of users installing trojans every hour. The scope of this attack is big enough to attract crackers who actually know what they are doing…»[7]
Microsoft continued to promote the tool through 1999 and the first half of 2000. Initial releases of Windows 2000 shipped with the tool. The tool did not support Windows 95 and Windows NT 4.0.
Automatic Updates[edit]
Automatic Updates is the successor of the Critical Update Notification Utility. It was released in 2000, along with Windows Me. It supports Windows 2000 SP3 as well.
Unlike its predecessor, Automatic Updates can download and install updates. Instead of the five-minute schedule used by its predecessor, Automatic Updates checks the Windows Update servers once a day. After Windows Me is installed, a notification balloon prompts the user to configure the Automatic Updates client. The user can choose from three notification schemes: Being notified before downloading the update, being notified before installing the update, or both. If new updates are ready to be installed, the user may install them before turning off the computer. A shield icon will be displayed on the Shutdown button during this time.
Windows XP and Windows 2000 SP3 include Background Intelligent Transfer Service, a Windows service for transferring files in the background without user interaction. As a system component, it is capable of monitoring the user’s Internet usage, and throttling its own bandwidth usage in order to prioritize user-initiated activities. The Automatic Updates client for these operating systems was updated to use this system service.
Automatic Updates in Windows XP gained notoriety for repeatedly interrupting the user while working on their computer. Every time an update requiring a reboot was installed, Automatic Updates would prompt the user with a dialog box that allowed the user to restart immediately or dismiss the dialog box, which would reappear in ten minutes; a behavior that Jeff Atwood described as «perhaps the naggiest dialog box ever.»[8]
In 2013, it was observed that shortly after the startup process, Automatic Updates (wuauclt.exe) and Service Host (svchost.exe) in Windows XP would claim 100% of a computer’s CPU capacity for extended periods of time (between ten minutes to two hours), making affected computers unusable. According to Woody Leonhart of InfoWorld, early reports of this issue could be seen in Microsoft TechNet forums in late May 2013, although Microsoft first received large number of complaints about this issue in September 2013. The cause was an exponential algorithm in the evaluation of superseded updates which had grown large over the decade following the release of Windows XP. Microsoft’s attempts to fix the issue in October, November and December proved futile, causing the issue to be escalated to the top priority.[9][10]
Windows Update Agent[edit]
Starting with Windows Vista and Windows Server 2008, Windows Update Agent replaces both the Windows Update web app and the Automatic Updates client.[11][12] It is in charge of downloading and installing software update from Windows Update, as well as the on-premises servers of Windows Server Updates Services or System Center Configuration Manager.[13][14]
Windows Update Agent can be managed through a Control Panel applet, as well as Group Policy, Microsoft Intune and Windows PowerShell. It can also be set to automatically download and install both important and recommended updates. In prior versions of Windows, such updates were only available through the Windows Update web site. Additionally, Windows Update in Windows Vista supports downloading Windows Ultimate Extras, optional software for Windows Vista Ultimate Edition.
Unlike Automatic Updates in Windows XP, Windows Update Agent in Windows Vista and Windows 7 allows the user to postpone the mandatory restart (required for the update process to complete) for up to four hours. The revised dialog box that prompts for the restart appears under other windows, instead of on top of them. However, standard user accounts only have 15 minutes to respond to this dialog box. This was changed with Windows 8: Users have 3 days (72 hours) before the computer reboots automatically after installing automatic updates that require a reboot. Windows 8 also consolidates the restart requests for non-critical updates into just one per month. Additionally, the login screen notifies them of the restart requirements.[15]
Windows Update Agent makes use of the Transactional NTFS feature introduced with Windows Vista to apply updates to Windows system files. This feature helps Windows recover cleanly in the event of an unexpected failure, as file changes are committed atomically.[16]
Windows 10 contains major changes to Windows Update Agent operations; it no longer allows the manual, selective installation of updates. All updates, regardless of type (this includes hardware drivers), are downloaded and installed automatically, and users are only given the option to choose whether their system would reboot automatically to install updates when the system is inactive, or be notified to schedule a reboot.[17][18] Microsoft offers a diagnostic tool that can be used to hide troublesome device drivers and prevent them from being reinstalled, but only after they had been already installed, then uninstalled without rebooting the system.[19][20]
Windows Update Agent on Windows 10 supports peer-to-peer distribution of updates; by default, systems’ bandwidth is used to distribute previously downloaded updates to other users, in combination with Microsoft servers. Users may optionally change Windows Update to only perform peer-to-peer updates within their local area network.[21]
Windows 10 also introduced cumulative updates. For example, if Microsoft released updates KB00001 in July, KB00002 in August, and KB00003 in September, Microsoft would release cumulative update KB00004 which packs KB00001, KB00002, and KB00003 together. Installing KB00004 will also install KB00001, KB00002 and KB00003, mitigating the need for multiple restarts and reducing the number of downloads needed. KB00004 may also include other fixes with their own KB-number that were not separately released.[22] A disadvantage of cumulative updates is that downloading and installing updates that fix individual problems is no longer possible. KB stands for knowledge base as in Microsoft Knowledge Base.
Windows Update for Business[edit]
Windows Update for Business is a term for a set of features in the Pro, Enterprise and Education editions of Windows 10, intended to ease the administration of Windows across organizations. It enables IT pros to:[23][24][25]
- Switch between the standard and the deferred release branches of Windows 10. This feature has since been removed as Microsoft retired the deferred branch.[26]
- Defer automatic installation of ordinary updates for 30 days. Starting with Windows 10 version 20H1, this feature is more difficult to access.[27]
- Defer automatic installation of Windows upgrades (a.k.a. «feature updates») for 365 days. Starting with Windows 10 version 20H1, these updates are no longer automatically offered.[27]
These features were added in Windows 10 version 1511.[28] They are intended for large organizations with many computers, so they can logically group their computers for gradual deployment. Microsoft recommends a small set of pilot computers to receive the updates almost immediately, while the set of most critical computers to receive them after every other group has done so, and has experienced their effects.[29]
Other Microsoft update management solutions, such as Windows Server Update Services or System Center Configuration Manager, do not override Windows Update for Business. Rather, they force Windows 10 into the «dual scan mode». This can cause confusion for administrators who do not comprehend the full ramifications of the dual scan mode.[30]
Complementary software and services[edit]
As organizations continued to use more computers, the per-machine Windows Update clients started to become unwieldy and insufficient. In response to the need of organizations for deploying updates to many machines, Microsoft introduced Software Update Services (SUS), which was later renamed Windows Server Update Services (WSUS). A component of the Windows Server family of operating systems, WSUS downloads updates for Microsoft products to a server computer on which it is running and redistributes them to the computers within the organization over a local area network (LAN). One of the benefits of this method is a reduction in the consumption of Internet bandwidth, equal to (N-1)×S, where N is the number of computers in the organization and S is the size made by the updates. Additionally, WSUS permits administrators to test updates on a small group of test computers before deploying them to all systems, in order to ensure that business continuity is not disrupted because of the changes of the updates. For very large organizations, multiple WSUS servers can be chained together hierarchically. Only one server in this hierarchy downloads from the Internet.
Update packages distributed via the Windows Update service can be individually downloaded from Microsoft Update Catalog. These updates can be installed on computers without internet access (e.g. via USB flash drive) or slipstreamed with a Windows installation. In case of the former, Windows Update Agent (wusa.exe) can install these files. In case of the latter, Microsoft deployment utilities such as DISM, WADK and MDT can consume these packages.
Microsoft offers System Center Configuration Manager for very complex deployment and servicing scenarios. The product integrates with all of the aforesaid tools (WSUS, DISM, WADK, MDT) to automate the process.
A number of tools have been created by independent software vendors which provide the ability for Windows Updates to be automatically downloaded for, or added to, an online or offline system. One common use for offline updates is to ensure a system is fully patched against security vulnerabilities before being connected to the Internet or another network. A second use is that downloads can be very large, but may be dependent on a slow or unreliable network connection, or the same updates may be needed for more than one machine. AutoPatcher, WSUS Offline Update, PortableUpdate, and Windows Updates Downloader are examples of such tools.[31]
Service[edit]
At the beginning of 2005, Windows Update was being accessed by about 150 million people,[32] with about 112 million of those using Automatic Updates.[33] As of 2008, Windows Update had about 500 million clients, processed about 350 million unique scans per day, and maintained an average of 1.5 million simultaneous connections to client machines. On Patch Tuesday, the day Microsoft typically releases new software updates, outbound traffic could exceed 500 gigabits per second.[34] Approximately 90% of all clients used automatic updates to initiate software updates, with the remaining 10% using the Windows Update web site. The web site is built using ASP.NET, and processes an average of 90,000 page requests per second.
Traditionally, the service provided each patch in its own proprietary archive file. Occasionally, Microsoft released service packs which bundled all updates released over the course of years for a certain product. Starting with Windows 10, however, all patches are delivered in cumulative packages.[35] On 15 August 2016, Microsoft announced that effective October 2016, all future patches to Windows 7 and 8.1 would become cumulative as with Windows 10. The ability to download and install individual updates would be removed as existing updates are transitioned to this model.[36] This has resulted in increasing download sizes of each monthly update. An analysis done by Computerworld determined that the download size for Windows 7 x64 has increased from 119.4MB in October 2016 to 203MB in October 2017.[37] Initially, Microsoft was very vague about specific changes within each cumulative update package.[35] However, since early 2016, Microsoft has begun releasing more detailed information on the specific changes.[38]
In 2011, the update service was decommissioned for Windows 98, 98 SE, ME and NT4 and the old updates for those systems were removed from its servers.[39][40]
On August 3, 2020, the update service was decommissioned for Windows 2000, XP, Server 2003 and Vista due to Microsoft discontinuing SHA-1 updates. The old updates are still available on the Microsoft Update Catalog.[41]
Microsoft Update[edit]
At the February 2005 RSA Conference, Microsoft announced the first beta of Microsoft Update, an optional replacement for Windows Update that provides security patches, service packs and other updates for both Windows and other Microsoft software.[42] The initial release in June 2005 provided support for Microsoft Office 2003, Exchange 2003, and SQL Server 2000, running on Windows 2000, XP, and Server 2003. Over time, the list has expanded to include other Microsoft products, such as Windows Live, Windows Defender, Visual Studio, runtimes and redistributables, Zune Software, Virtual PC and Virtual Server, CAPICOM, Microsoft Lync, Microsoft Expression Studio, and other server products. It also offers Silverlight and Windows Media Player as optional downloads if applicable to the operating system.
Office Update[edit]
Office Update is a free online service that allows users to detect and install updates for certain Microsoft Office products.
The original update service supported Office 2000, Office XP, Office 2003 and Office 2007. On 1 August 2009 Microsoft decommissioned the Office Update service, merging it with Microsoft Update.[43] Microsoft Update does not support Office 2000.
With the introduction of the Office 365 licensing program, however, Microsoft once again activated a separate Office update service.[44][45]
References[edit]
- ^ «Microsoft License Terms». www.microsoft.com. Section 13b. Retrieved 30 March 2020.
- ^ «MICROSOFT SOFTWARE LICENSE TERMS». www.microsoft.com. Retrieved 20 July 2022.
Canada. You may stop receiving updates on your device by turning off Internet access. If and when you re-connect to the Internet, the software will resume checking for and installing updates.
- ^ Gartner, John (24 August 1995). «Taking Windows 98 For A Test-Drive». TechWeb. CMP Net. Archived from the original on 3 December 1998.
- ^ «Strong Holiday Sales Make Windows 98 Best-Selling Software of 1998». PressPass (Press release). Microsoft. 9 February 1999. Archived from the original on 6 March 2012. Retrieved 29 July 2008.
- ^ a b Slob, Arie (22 March 2003). «Windows Update is Spying on You!». Windows-Help.NET. InfiniSource. Archived from the original on 14 January 2018. Retrieved 12 September 2019.
- ^ «Description of the Windows Critical Update Notification utility». Support. Microsoft. 5 December 2007. Archived from the original on 26 July 2020. Retrieved 22 November 2018.
- ^ Moore, H. D. (29 January 1999). «How the MS Critical Update Notification works…» BugTraq mailing list archive. Archived from the original on 21 June 2009. Retrieved 30 July 2008 – via seclists.org.
- ^ Atwood, Jeff (13 May 2005). «XP Automatic Update Nagging». Coding Horror: Programming and Human Factors. Archived from the original on 9 November 2021. Retrieved 12 September 2019.
- ^ Bright, Peter (16 December 2013). «Exponential algorithm making Windows XP miserable could be fixed». Ars Technica. Condé Nast. Archived from the original on 6 May 2021. Retrieved 12 September 2019.
- ^ Leonhard, Woody (16 December 2013). «Microsoft promises to fix Windows XP SVCHOST redlining ‘as soon as possible’«. InfoWorld. IDG. Archived from the original on 30 March 2019. Retrieved 12 September 2019.
- ^ «How to update the Windows Update Agent to the latest version». Support. Microsoft. 6 June 2017. Archived from the original on 4 September 2020. Retrieved 22 November 2018.
- ^ «Windows Update Agent». TechNet. Microsoft. 13 December 2007. Archived from the original on 14 January 2018. Retrieved 22 November 2018.
- ^ «How to Install the Windows Update Agent on Client Computers». TechNet. Microsoft. 2007. Archived from the original on 11 October 2018. Retrieved 22 November 2018.
- ^ Rouse, Margaret (May 2014). «Microsoft Windows Update Agent». TechTarget. Archived from the original on 27 January 2021. Retrieved 22 November 2018.
- ^ Savov, Vlad (15 November 2011). «Windows 8 auto-update will consolidate restarts into one per month, give you three days to do it». The Verge. Vox Media. Archived from the original on 29 August 2021. Retrieved 22 November 2018.
- ^ «NTFS Beta Chat Transcript (July 12, 2006)». Storage at Microsoft. Microsoft. 12 July 2006. Archived from the original on 20 April 2019. Retrieved 22 November 2018.
- ^ «Windows 10 lets you schedule Windows Update restarts». CNET. Archived from the original on 19 February 2015. Retrieved 4 August 2015.
- ^ «Did Microsoft Just Backtrack On Forced Updates For Windows 10?». CRN.com. 27 July 2015. Archived from the original on 28 July 2015. Retrieved 4 August 2015.
- ^ «On the road to Windows 10: Nvidia driver tests KB 3073930 patch blocker». InfoWorld. 27 July 2015. Archived from the original on 20 June 2017. Retrieved 31 July 2015.
- ^ «On the road to Windows 10: Problems with forced updates and KB 3073930». InfoWorld. 22 July 2015. Archived from the original on 20 June 2017. Retrieved 31 July 2015.
- ^ «How to stop Windows 10 from using your PC’s bandwidth to update strangers’ systems». PC World. IDG. Archived from the original on 5 August 2015. Retrieved 4 August 2015.
- ^ «User can’t log on to a POP/IMAP account by using NTLM authentication in Exchange Server 2013». Archived from the original on 10 February 2021. Retrieved 24 March 2020.
To resolve this issue, install Cumulative Update 21
- ^ Hammoudi, Samir (15 November 2015). «Windows Update for Business explained». beanexpert. Microsoft. Archived from the original on 19 April 2019. Retrieved 14 January 2018.
- ^ Azzarello, Pat (10 May 2017). «What is Windows Update for Business?». Windows for IT Pros. Microsoft. Archived from the original on 11 June 2018. Retrieved 14 January 2018.
Windows Update for Business is intended for machines running Windows 10 or later, and Windows 10 Education, Professional, or Enterprise editions managed in organizations.
- ^ Halfin, Danni; Brower, Nick; Lich, Brian; Poggemeyer, Liza (13 October 2017). «Deploy updates using Windows Update for Business». Microsoft Docs. Microsoft. Archived from the original on 22 October 2021. Retrieved 22 November 2018.
- ^ «Microsoft changes Windows Update for Business options — gHacks Tech News». www.ghacks.net. 15 February 2019. Archived from the original on 6 October 2021. Retrieved 3 November 2020.
- ^ a b «Microsoft removes Setting to defer feature updates from Windows 10 version 2004 — gHacks Tech News». www.ghacks.net. 25 June 2020. Archived from the original on 27 August 2021. Retrieved 3 November 2020.
- ^ Bott, Ed (17 January 2018). «How to take control of Windows 10 updates and upgrades (even if you don’t own a business)». ZDNet. CBS Interactive. Archived from the original on 12 November 2021. Retrieved 22 November 2018.
- ^ Halfin, Danni; Lich, Brian (27 July 2017). «Build deployment rings for Windows 10 updates». Microsoft Docs. Microsoft. Archived from the original on 24 May 2021. Retrieved 22 November 2018.
- ^ Rasheed, Shadab (9 January 2017). «Why WSUS and SCCM managed clients are reaching out to Microsoft Online». Windows Server Blog. Microsoft. Archived from the original on 14 January 2018. Retrieved 22 November 2018.
- ^ «4 Tools to Update Windows Offline and install Hotfixes from a Local Source». raymond.cc. 14 November 2005. Archived from the original on 20 October 2021. Retrieved 22 November 2018.
- ^ «RSA Conference 2005: «Security: Raising the Bar» (speech transcript)». PressPass. Microsoft. 15 February 2005. Archived from the original on 8 March 2009. Retrieved 30 July 2008.
- ^ «Microsoft Announces Availability of New Solutions to Help Protect Customers Against Spyware and Viruses». PressPass. Microsoft. 6 January 2005. Archived from the original on 2 April 2012. Retrieved 30 July 2008.
- ^ «Introducing the Microsoft.com Engineering Operations Team». Microsoft TechNet. Microsoft. 2008. Archived from the original on 26 August 2017. Retrieved 31 May 2012.
- ^ a b «Windows 10 users beg Microsoft for more info on updates». Computerworld. IDG. 14 September 2015. Archived from the original on 14 September 2015. Retrieved 30 September 2015.
- ^ «Windows 7, 8.1 moving to Windows 10’s cumulative update model». Ars Technica. Conde Nast Digital. 15 August 2016. Archived from the original on 14 February 2017. Retrieved 16 August 2016.
- ^ Gregg Keizer (14 December 2017). «Why Windows 7 updates are getting bigger». Computerworld. Archived from the original on 22 November 2018. Retrieved 22 November 2018.
- ^ «Windows 10 update details». Windows 10 update history. Microsoft. Archived from the original on 5 March 2016. Retrieved 4 March 2016.
- ^ «I can’t access Windows Update v4 — Windows 9x/ME — MSFN». msfn.org. Archived from the original on 9 November 2021. Retrieved 25 April 2021.
- ^ «Where is Windows Update for Win98? — BetaArchive». www.betaarchive.com. Archived from the original on 8 November 2021. Retrieved 25 April 2021.
- ^ «Windows Update SHA-1 based endpoints discontinued for older Windows devices». Archived from the original on 18 December 2020. Retrieved 5 August 2020.
- ^ «Microsoft Update Site Launched». helpwithwindows.com. 10 June 2005. Archived from the original on 22 November 2018. Retrieved 30 July 2008.
- ^ «About Office Update». office.microsoft.com. Microsoft. Archived from the original on 28 May 2010.
- ^ «Install Office updates». support.office.com. Microsoft. Archived from the original on 23 May 2020. Retrieved 4 December 2017.
- ^ «Check for Office for Mac updates automatically». support.office.com. Microsoft. Archived from the original on 9 August 2018. Retrieved 4 December 2017.
External links[edit]
- Microsoft Update website
- Microsoft Technical Security Notifications