From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
The Control Panel is a component of Microsoft Windows that provides the ability to view and change system settings. It consists of a set of applets that include adding or removing hardware and software, controlling user accounts, changing accessibility options, and accessing networking settings. Additional applets are provided by third parties, such as audio and video drivers, VPN tools, input devices, and networking tools.

Control Panel in Windows 11 |
|
| Developer(s) | Microsoft |
|---|---|
| Initial release | 1985; 38 years ago |
| Operating system | Microsoft Windows |
| Type | Control panel |
Overview[edit]
The Control Panel has been part of Microsoft Windows since Windows 1.0,[1] with each successive version introducing new applets. Beginning with Windows 95, the Control Panel is implemented as a special folder, i.e. the folder does not physically exist, but only contains shortcuts to various applets such as Add or Remove Programs and Internet Options. Physically, these applets are stored as .cpl files. For example, the Add or Remove Programs applet is stored under the name appwiz.cpl in the SYSTEM32 folder. ==
In Windows XP, the Control Panel home screen was changed to present a categorized navigation structure reminiscent of navigating a web page. Users can switch between this Category View and the grid-based Classic View through an option that appears on either the left side or top of the window. In Windows Vista and Windows 7, additional layers of navigation were introduced, and the Control Panel window itself became the main interface for editing settings, as opposed to launching separate dialogs.
Many of the individual Control Panel applets can be accessed in other ways. For instance, Display Properties can be accessed by right-clicking on an empty area of the desktop and choosing Properties. The Control Panel can be accessed from a command prompt by typing control; optional parameters are available to open specific control panels.[2]
On Windows 10, Control Panel is deprecated in favor of Settings app, which was originally introduced on Windows 8 as «PC settings» to provide a touchscreen-optimized settings area using its Metro-style app platform. Some functions, particularly the ability to add and remove user accounts, were moved exclusively to this app on Windows 8 and cannot be performed from Control Panel.[3][4]
As of the October 2020 update to Windows 10, opening up the System applet in Control Panel will now redirect users to the About section of the Windows 10 Settings application. The page for the applet in Control Panel still exists even in current versions of Windows 10, however Microsoft is actively trying to block shortcuts and third party applications that could have been used to get into the old System page, which could potentially lead to a permanent removal of said page from Control Panel in future versions of Windows.[citation needed]
List of Control Panel applets[edit]
The applets listed below are components of the Microsoft Windows control panel, which allows users to define a range of settings for their computer, monitor the status of devices such as printers and modems, and set up new hardware, programs and network connections. Each applet is stored individually as a separate file (usually a .cpl file), folder or DLL, the locations of which are stored in the registry under the following keys:
- HKLMSOFTWAREMicrosoftWindowsCurrentVersionControl PanelCpls
This contains the string format locations of all .cpl files on the hard drive used within the control panel. - HKLMSOFTWAREMicrosoftWindowsCurrentVersionExplorerControlPanelNamespace
This contains the location of the CLSID variables for all the panels not included as cpl files. These are commonly folders or shell applets, though Windows Vista allows physical programs themselves to be registered as well. The CLSID then allows items such as the icon, infobox and category to be set and gives the location of the file to be used.
The control panel then uses these lists to locate the applets and load them into the control panel program (control.exe) when started by the user. In addition to using the control panel, a user can also invoke the applets manually via the command processor. For instance, the syntax «Control.exe inetcpl.cpl» or «control.exe /name Microsoft.InternetOptions» will run the internet properties applet in Windows XP or Vista respectively. While both syntax examples are accepted on Windows Vista, only the former one is accepted on Windows XP.[5]
Standard applets[edit]
| Accessibility options (Access.cpl) (control /name microsoft.easeofaccesscenter) (Renamed «Ease of Access Center» in Windows Vista and later) |
|---|
Allows users to configure the accessibility of their PC. It comprises various settings primarily aimed at users with disabilities or hardware problems.
Note that in Windows Vista onwards, the Ease of Access control panel superseded the old access.cpl control panel applet found in previous versions. |
| Add New Hardware (hdwwiz.cpl) |
| Launches a wizard which allows users to add new hardware devices to the system. This can be done by selecting from a list of devices or by specifying the location of the driver installation files. |
| Add or Remove Programs (appwiz.cpl) (Renamed «Programs and Features» in Windows Vista and later) |
The Add/Remove Programs dialog allows the user to manipulate software installed on the system in a number of ways;
|
| Administrative Tools (control admintools) |
| Contains tools for system administration, including security, performance and service configuration. These are links to various configurations of the Microsoft Management Console such as the local services list and the Event Viewer. |
| Automatic Updates (wuaucpl.cpl) |
| This is used to specify how the Automatic Updates client (wuauclt.exe) should download updates from the Microsoft Update Website, by default this is set to download and install daily, however this can be changed to a more suitable frequency. This also allows the user to specify whether to ask permission before downloading and/or installing updates or to simply switch off Automatic Updates altogether.
Removed in Windows 10, and moved to the Settings App. |
| Date and Time (timedate.cpl) |
| Allows user to change the date and time stored in the machine’s BIOS, change the time zone and specify whether to synchronize the date and time with an Internet Time Server and which server to use. |
| Display (control desktop) (desk.cpl)
(Renamed «Personalization» in Windows Vista, 7 and 8.1) |
Allows the user to change the display characteristics of their computer;
Removed in Windows 10 and moved to the Settings App. |
| Folder Options (control folders) (rundll32.exe shell32.dll, Options_RunDLL 0) |
| This item allows for configuration of how folders and files are presented in Windows Explorer. More specifically it allows the user to specify general settings like whether folders open in a new window or the existing window and whether the common tasks pane is shown, as well as more advanced tasks such as whether windows should hide critical system files and whether to show file extensions. It is also used to modify file type associations in Windows; i.e., which program opens which type of file and other settings like actions for each file type and the file extension. |
| Fonts (control fonts) |
| Displays all fonts installed on the computer. Users can remove fonts, install new fonts or search for fonts using font characteristics. Note that «explorer WindowsFonts» has the same effect. This still exists on Windows 10, but there is a similar page in Settings starting from the Windows 10 April 2018 Update. |
| Internet Options (inetcpl.cpl) |
Allows the user to change the way the computer manages internet connections and browser settings for Internet Explorer, it has several tags specifying different attributes;
|
| Game controllers (joy.cpl) (control /name microsoft.gamecontrollers) |
| Allows one to add, display, troubleshoot, and use advanced settings on joysticks and game controllers and connect to other type of game controllers.
Moved to the Settings app on Windows 10 Anniversary Update. |
| Keyboard (control keyboard) (main.cpl) |
| Lets the user change and test keyboard settings, including cursor blink rate and key repeat rate. |
| Mail (mlcfg32.cpl) (mlcfg.cpl) |
| Mail allows for configuration of the mail client in Windows. Microsoft Outlook Express cannot be configured with this item; it is configured through its own interface. mlcfg.cpl is used for 64 bit office applications first available with the Office 2010 release. |
| Mouse (control mouse) (main.cpl) |
| Mouse allows the configuration of pointer options, such as the double click and scroll speed, and includes visibility options such as whether to use pointer trails and whether the pointer should disappear when typing. This also allows the user to specify the pointer appearance for each task, such as resize and busy. |
| Network Connections (control netconnections) (ncpa.cpl) |
| Displays and allows the user to edit or create network connections such as Local Area Networks (LAN) and internet connections. It also offers troubleshooting functions in case the computer has to be reconnected to the network. |
| Phone and Modem Options (telephon.cpl) |
| Manages telephone and modem connections. |
| Power Options (powercfg.cpl) |
Includes options to manage energy consumption such as;
|
| Printers and Faxes (control printers) (control /name microsoft.devicesandprinters) |
Displays all the printers and faxes currently installed on the computer, and has two main uses;
|
| Regional and Language Settings (intl.cpl) aka Regional and Language Options |
Various regional settings can be altered, for instance:
Removed in the Windows 10 April 2018 Update and moved to Settings App. |
| Security Center or Action Center (Windows 7 & 8.x) (wscui.cpl) Renamed «Security & Maintenance» in Windows 10 |
| First added in Windows XP with Service Pack 2, Security Center gives the user access to the inbuilt Windows security components, as well as providing information about any existing antivirus software such as McAfee or Zone Alarm. It includes access to Windows Update, where users can specify whether the computer should check for updates regularly (also available through the Windows Update panel), and options for managing internet security settings. It also includes links to internet articles about PC security and current virus threats and notifies the user when the PC’s security is compromised. |
| Sounds and Audio Devices (mmsys.cpl) |
This panel contains various audio-related functions;
|
| Speech (Sapi.cpl) |
This applet has two main functions, the first is specify settings for Speech synthesis, allowing the user to select the voice the computer should use to narrate text and how fast it should read. The second is to specify settings for Speech recognition, allowing the user to set up different profiles detailing how the computer should deal with an individual’s dialect, for instance;
This also allows the user to access the voice recognition training wizard, in which an individual ‘teaches’ the computer to recognize a person voice interactively using the microphone. |
| Stored User Names and Passwords (keymgr.dll) (control.exe /name microsoft.credentialmanager) (Renamed «Credential Manager» in Windows 7 and later) |
| This is used to view and edit logon credentials for servers, websites and programs. |
| System (Sysdm.cpl) |
This is used to view and change core system settings, a user can for instance:
Moved to the Settings App on Windows 10, but the shortcut still exists. Clicking on it goes to the Settings App. |
| Taskbar and Start Menu (rundll32.exe shell32.dll, Options_RunDLL 1) |
Allows the user to change the behavior and appearance of the task bar and Start Menu;
Moved to the Settings App on Windows 10, but the shortcut still exists. Clicking on it goes to the Settings App. |
| User Accounts (control userpasswords) (nusrmgr.cpl) |
| This allows the user to configure their account and other accounts used in the system, should they have sufficient privileges. They can change their username, password, their account picture (if enabled), and their .NET Passport (in versions of Windows prior to Vista). If the current user has an administrator account they can also add, delete, and modify other user accounts as well as make changes to core system settings. This panel also specifies whether or not the guest account should be active and (in Windows XP only) whether or not to use the Welcome screen when Windows loads.
This panel is not available in Windows Server 2003, where the syntax «control userpasswords» will instead run the Local Users and Groups utility. |
| Users and Passwords (control userpasswords2) (rundll32.exe netplwiz.dll, UsersRunDll) |
| This is the legacy user account utility that was first introduced in Windows 2000 Professional. This allows the user to configure their account and other accounts used in the system, change their .NET Passports (in versions of Windows prior to Vista), as well as configuring autologin settings. This panel also specifies whether or not to press Ctrl+Alt+Del before login.
This panel is not available in the Windows 2000 Server family, where it will instead run the Local Users and Groups utility. |
Peripheral devices[edit]
These are options in the control panel that show devices connected to the computer. They do not actually offer a direct interface to control these devices, but rather offer basic tasks such as removal procedures and links to wizards (Printers & Faxes is an exception). Such applets include Scanners and Cameras, Game Controllers, and Portable Media Devices.
Other Microsoft-distributed applets[edit]
| Biometric Devices (biocpl.dll) |
|---|
Available with Fingerprint enabled systems running 7 or later, this enables users to configure a Fingerprint reader, showing a list of all Biometric devices interacting with the system, in addition to the following items;
Moved to Settings on Windows 10. |
| Bluetooth Devices (bthprops.cpl) |
Available with Bluetooth enabled systems running XP SP2 or later, this enables users to configure a Bluetooth connection, showing a list of all Bluetooth devices interacting with the system, in addition to the following items;
Moved to Settings on Windows 10. |
| Color (color.cpl) |
| Enables a more advanced control of color settings within Windows than is available in ‘display’, suitable for developers and visual specialists it allows users to create and load International Color Consortium compliant color profiles, associate screen color with printers and cameras and view a 3D graphics plot of the color gamut. By default this applet is not installed, however it can be installed for free from the Microsoft Website. |
| Infrared (irprops.cpl) |
| Similar to the Bluetooth applet, this is used to configure how the computer manages any wireless infrared ports installed, including options such as connectivity and security. |
| Location and Other Sensors (SensorsCpl.dll) |
| Manages Location based data like addresses and other location based sensors. Available in Windows 7 & 8.x only. |
| CSNW (nwc.cpl) |
| The Client Service for NetWare applet is used to select a default tree and context in a Novell Directory Services (NDS) environment, or the NetWare server used most frequently in a non-NDS environment.
Requirement: Installing the Client Service for NetWare. |
| Software Explorers |
| Part of Windows Defender, allows users to view detailed information about software that is currently running on the computer that can affect the users’ privacy or the security of the computer.
Replaced by Windows Defender Security Center on Windows 10. |
Third-party applets[edit]
Third-party software vendors have released many applets. Although it is impossible to mention all of them, some of them are listed here:
| Icon | File name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| AC3 Filter | ac3filter.cpl | Configures speaker configuration and other parameters of the AC3 decoder filter. |
| Adobe Gamma | Adobe Gamma.cpl | For altering the screen display with Adobe Systems Imaging Software such as Photoshop. |
| Adobe Version Cue CS2 | VersionCueCS2.cpl | To configure Adobe Version Cue. |
| Application paths | apppaths.cpl | Sets application paths, start-up commands and system services, coded by Gregory Braun. |
| ATI DVD Player | QISWCINE.CPL | Changes setings for your DVD decoding. |
| AudioHQ | AudHQ.cpl | Creative Labs Soundblaster Audio HQ. |
| Autodesk Plotter Manager | plotman.cpl | Adds, remove and changes plotters properties for AutoCAD products. |
| AvantGo Connect | agcpl.cpl | Synchronizes mobile versions (called «channels») of websites to a smartphone or PDA, see AvantGo. |
| Avira AntiVir PersonalEdition | avconfig.cpl | Configures Avira Antivirus program. |
| BACKPACK Finder | bpcpl.cpl | To configure the Micro Solutions BackPack CD driver. |
| BDE Administrator | bdeadmin.cpl | To configure the Borland Database Engine. |
| Boot Camp Control Panel | Setting for Mac OS X based computers. | |
| Broadcom Advanced Control Suite | BACSCPL.cpl | Enables Broadcom network cards testing and diagnostics. |
| CD/DVD Drive Acoustic Silencer | TOSCDSPD.cpl | Configures the rotation speed of CD/DVD drive. (Toshiba ) |
| ClearCase | cc.cpl | To configure IBM Rational ClearCase. |
| Color Settings | 3dcc.cpl | Changes the look and feel of Windows. |
| Compaq Diagnostics | cpqdiag.cpl | To view information a computer’s hardware and software configuration, legacy application. |
| Control Panel | controlp.cpl | Control Panel Customization Toy, coded by Ali Lokhandwala. |
| Control Version System | cvsnt.cpl | Control Panel Customization Toy, by Brian Berliner. david d ‘zoo’ zuhn, Jeff Polk, Tony Hoyle |
| Creative Element Power Tools | To configure Creative Element Power Tools, a free-to-try program providing access to additional Windows tools. | |
| Corel Versions | verscpl.cpl | Configures Corel versions. |
| DANS | danetsvc.cpl | Configures the Shaffer Solutions DiskAccess Network Services, NFS client for Windows. |
| Diagnostics for Windows | cpqdiag.cpl | HP Diagnostics for Windows 4.15 replaces Compaq |
| Digidesign ElevenRack | DigidesignElevenRackControlPanelApplet.cpl | Launch Eleven Rack Control Panel |
| DiskAccess | dacfg.cpl | Configures how the Shaffer Solutions DiskAccess makes connections to remote NFS servers. |
| DS18x Applet | DS18xCPL.cpl | MR Soft DS18x Temperature Logging Service. |
| Flash Player | FlashPlayerCPLApp.cpl | For changing settings for the Flash Player. |
| Folder size | FolderSize.cpl | Folder Size for Windows shows the size of folders in Windows Explorer. |
| FirebirdSQL Service Manager | fmmgr.cpl | Configures Firebird (database server) service options. |
| HP Jetadmin | jetadmin.cpl | HP Jetadmin configures and monitors HP printers. |
| HP Lock | Hplock.cpl | A Windows 95 utility to lock the PC keyboard, mouse and on/off switch in one click on legacy HP Vectra. |
| IconPackager | ipcpl.cpl | To customize Windows icons and cursors, see IconPackager. |
| ImDisk Virtual Disk Driver | imdisk.cpl | Administration of ImDisk Virtual Disk Driver. |
| InstallShield Update Manager | isuspm.cpl | The InstallShield Update Manager allows users to receive program updates and messages from software makers who use the service. |
| Intel Extreme Graphics | igfxcpl.cpl | To change advanced settings on systems using Intel GPUs. |
| Intel Product Improvement Program | executable | Installed with Intel Driver Update Utility version 2.4 (on Vista and up) |
| IP Office Voicemail Pro | ims.cpl | To configure Avaya IP Office Voicemail Pro. |
| Java | jpicpl32.cpl | For changing settings with Java Runtime Console. |
| JInitiator 1.x.y.z | plugincpl1xyz.cpl | To configure Oracle’s JInitiator, note x.y.z are version numbers. |
| MLCFG32.cpl | Launches the Microsoft Outlook Profile Manager. | |
| MSConfig | MSConfig.cpl | Launches the Microsoft System Configuration Utility. |
| Multi-finger | ETDUI.cpl | Customize the Smart-Pad Multi-finger Setting. |
| MultiSite | ms.cpl | To configure IBM Rational ClearCase Multisite. |
| Nero BurnRights | NeroBurnRights.cpl | For specifying who is allowed to use the CD burner with Nero. |
| nVIDIA Control panel | nvidia.cpl | To change advanced settings on systems using nVIDIA GPUs. |
| Panda Media Booster | PMB.cpl | Panda Media Booster cache and network settings. |
| Parallel Port Joysticks | PPjoy.cpl | Configures Joysticks connected on the Parallel Port. |
| Pointer Devices | tbctlpnl.cpl | To configure the Touch-Base Universal Pointer Device Driver (UPDD). |
| QuickTime | quicktime.cpl | For specifying settings of the Apple QuickTime Player. |
| RealPlayer | prefscpl.cpl | To configure the RealPlayer preferences, older versions. |
| Realtek AC97 Audio Control Panel | alsndmgr.cpl | To configure the Realtek audio controller. |
| Realtek HD-Audio Manager | RTSnMg64.cpl | To launch the Realtek HD-Audio Manager |
| RESTrick Control Panel | rest2.cpl | Windows Tuning and system restrictions setup, by Rtsecurity. |
| Safarp | safarp.cpl | Safarp is a small and fast alternative to the Add or Remove Programs applet. |
| ScrewDrivers Client | sdclient.cpl | From Tricerat, remote desktop print management solution. |
| Send To Toys | sendtotoys.cpl | To configure the Send To right click system menu in Microsoft Windows. |
| Services and Devices | pserv.cpl | From p-nand-q to manage Windows services and devices and uninstall applications. |
| Softex OmniPass | scurecpl.cpl | Softex OmniPass provides password management capabilities to MS Windows. |
| SNTP Service | sntpserv.cpl | From Dillobits Software, to manage the SNTP client service. |
| Soundscape | scurecpl.cpl | Adds, removes or changes settings of Soundscape devices. |
| Startup | startup.cpl | Control programs that run at system start-up, coded by Mike Lin. |
| Startup Disk | Startup Disk.cpl | Boot Camp drivers, when Windows runs on a Mac OS virtual machine. |
| Symantec LiveUpdate | s32lucp2.cpl | Configures the Symantec LiveUpdate update service. |
| System Change Log | scl.cpl | From Greyware Automation Products, monitors disks for changes and records a detailed log. |
| System Information | Sancpl.cpl | Launches SiSoftware Sandra utility. |
| System Info for Windows | siw.cpl | Launches the SIW application. |
| Trust-No-Exe | trustnoexe.cpl | Configures the Beyond Logic Trust-No-Exe executable filter. |
| VMware Tools | VMControlPanel.cpl | To configure VMware Tools. |
| WIBU-KEY | wibuke32.cpl | To configure the WIBU-KEY Software Protection. |
| Winlogos | wnlgo.cpl | To change the Windows start-up and shutdown screens in Windows 98 or ME, coded by Ali Lokhandwala. |
| X-Setup Pro | xqdcXSPApplet.cpl | Launches X-Setup Pro, a Windows tweaker application. |
References[edit]
- ^ «A history of Windows». Windows. Microsoft. Archived from the original on November 17, 2010.
- ^ «Accessing the Control Panel via the Commandline». Microsoft. August 29, 2011.
- ^ Bradley, Tony (July 6, 2012). «Adding and Managing Users in Windows 8». PC World. IDG. Retrieved September 20, 2015.
- ^ Bright, Peter (March 25, 2013). «Windows Blue leaks: More Metro, more multitasking». Ars Technica. Condé Nast. Retrieved January 20, 2014.
- ^ «How to run Control Panel tools by typing a command». Support. Microsoft. Retrieved February 26, 2014.
External links[edit]
- How to run Control Panel tools by typing a command at Microsoft.com
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
The Control Panel is a component of Microsoft Windows that provides the ability to view and change system settings. It consists of a set of applets that include adding or removing hardware and software, controlling user accounts, changing accessibility options, and accessing networking settings. Additional applets are provided by third parties, such as audio and video drivers, VPN tools, input devices, and networking tools.

Control Panel in Windows 11 |
|
| Developer(s) | Microsoft |
|---|---|
| Initial release | 1985; 38 years ago |
| Operating system | Microsoft Windows |
| Type | Control panel |
Overview[edit]
The Control Panel has been part of Microsoft Windows since Windows 1.0,[1] with each successive version introducing new applets. Beginning with Windows 95, the Control Panel is implemented as a special folder, i.e. the folder does not physically exist, but only contains shortcuts to various applets such as Add or Remove Programs and Internet Options. Physically, these applets are stored as .cpl files. For example, the Add or Remove Programs applet is stored under the name appwiz.cpl in the SYSTEM32 folder. ==
In Windows XP, the Control Panel home screen was changed to present a categorized navigation structure reminiscent of navigating a web page. Users can switch between this Category View and the grid-based Classic View through an option that appears on either the left side or top of the window. In Windows Vista and Windows 7, additional layers of navigation were introduced, and the Control Panel window itself became the main interface for editing settings, as opposed to launching separate dialogs.
Many of the individual Control Panel applets can be accessed in other ways. For instance, Display Properties can be accessed by right-clicking on an empty area of the desktop and choosing Properties. The Control Panel can be accessed from a command prompt by typing control; optional parameters are available to open specific control panels.[2]
On Windows 10, Control Panel is deprecated in favor of Settings app, which was originally introduced on Windows 8 as «PC settings» to provide a touchscreen-optimized settings area using its Metro-style app platform. Some functions, particularly the ability to add and remove user accounts, were moved exclusively to this app on Windows 8 and cannot be performed from Control Panel.[3][4]
As of the October 2020 update to Windows 10, opening up the System applet in Control Panel will now redirect users to the About section of the Windows 10 Settings application. The page for the applet in Control Panel still exists even in current versions of Windows 10, however Microsoft is actively trying to block shortcuts and third party applications that could have been used to get into the old System page, which could potentially lead to a permanent removal of said page from Control Panel in future versions of Windows.[citation needed]
List of Control Panel applets[edit]
The applets listed below are components of the Microsoft Windows control panel, which allows users to define a range of settings for their computer, monitor the status of devices such as printers and modems, and set up new hardware, programs and network connections. Each applet is stored individually as a separate file (usually a .cpl file), folder or DLL, the locations of which are stored in the registry under the following keys:
- HKLMSOFTWAREMicrosoftWindowsCurrentVersionControl PanelCpls
This contains the string format locations of all .cpl files on the hard drive used within the control panel. - HKLMSOFTWAREMicrosoftWindowsCurrentVersionExplorerControlPanelNamespace
This contains the location of the CLSID variables for all the panels not included as cpl files. These are commonly folders or shell applets, though Windows Vista allows physical programs themselves to be registered as well. The CLSID then allows items such as the icon, infobox and category to be set and gives the location of the file to be used.
The control panel then uses these lists to locate the applets and load them into the control panel program (control.exe) when started by the user. In addition to using the control panel, a user can also invoke the applets manually via the command processor. For instance, the syntax «Control.exe inetcpl.cpl» or «control.exe /name Microsoft.InternetOptions» will run the internet properties applet in Windows XP or Vista respectively. While both syntax examples are accepted on Windows Vista, only the former one is accepted on Windows XP.[5]
Standard applets[edit]
| Accessibility options (Access.cpl) (control /name microsoft.easeofaccesscenter) (Renamed «Ease of Access Center» in Windows Vista and later) |
|---|
Allows users to configure the accessibility of their PC. It comprises various settings primarily aimed at users with disabilities or hardware problems.
Note that in Windows Vista onwards, the Ease of Access control panel superseded the old access.cpl control panel applet found in previous versions. |
| Add New Hardware (hdwwiz.cpl) |
| Launches a wizard which allows users to add new hardware devices to the system. This can be done by selecting from a list of devices or by specifying the location of the driver installation files. |
| Add or Remove Programs (appwiz.cpl) (Renamed «Programs and Features» in Windows Vista and later) |
The Add/Remove Programs dialog allows the user to manipulate software installed on the system in a number of ways;
|
| Administrative Tools (control admintools) |
| Contains tools for system administration, including security, performance and service configuration. These are links to various configurations of the Microsoft Management Console such as the local services list and the Event Viewer. |
| Automatic Updates (wuaucpl.cpl) |
| This is used to specify how the Automatic Updates client (wuauclt.exe) should download updates from the Microsoft Update Website, by default this is set to download and install daily, however this can be changed to a more suitable frequency. This also allows the user to specify whether to ask permission before downloading and/or installing updates or to simply switch off Automatic Updates altogether.
Removed in Windows 10, and moved to the Settings App. |
| Date and Time (timedate.cpl) |
| Allows user to change the date and time stored in the machine’s BIOS, change the time zone and specify whether to synchronize the date and time with an Internet Time Server and which server to use. |
| Display (control desktop) (desk.cpl)
(Renamed «Personalization» in Windows Vista, 7 and 8.1) |
Allows the user to change the display characteristics of their computer;
Removed in Windows 10 and moved to the Settings App. |
| Folder Options (control folders) (rundll32.exe shell32.dll, Options_RunDLL 0) |
| This item allows for configuration of how folders and files are presented in Windows Explorer. More specifically it allows the user to specify general settings like whether folders open in a new window or the existing window and whether the common tasks pane is shown, as well as more advanced tasks such as whether windows should hide critical system files and whether to show file extensions. It is also used to modify file type associations in Windows; i.e., which program opens which type of file and other settings like actions for each file type and the file extension. |
| Fonts (control fonts) |
| Displays all fonts installed on the computer. Users can remove fonts, install new fonts or search for fonts using font characteristics. Note that «explorer WindowsFonts» has the same effect. This still exists on Windows 10, but there is a similar page in Settings starting from the Windows 10 April 2018 Update. |
| Internet Options (inetcpl.cpl) |
Allows the user to change the way the computer manages internet connections and browser settings for Internet Explorer, it has several tags specifying different attributes;
|
| Game controllers (joy.cpl) (control /name microsoft.gamecontrollers) |
| Allows one to add, display, troubleshoot, and use advanced settings on joysticks and game controllers and connect to other type of game controllers.
Moved to the Settings app on Windows 10 Anniversary Update. |
| Keyboard (control keyboard) (main.cpl) |
| Lets the user change and test keyboard settings, including cursor blink rate and key repeat rate. |
| Mail (mlcfg32.cpl) (mlcfg.cpl) |
| Mail allows for configuration of the mail client in Windows. Microsoft Outlook Express cannot be configured with this item; it is configured through its own interface. mlcfg.cpl is used for 64 bit office applications first available with the Office 2010 release. |
| Mouse (control mouse) (main.cpl) |
| Mouse allows the configuration of pointer options, such as the double click and scroll speed, and includes visibility options such as whether to use pointer trails and whether the pointer should disappear when typing. This also allows the user to specify the pointer appearance for each task, such as resize and busy. |
| Network Connections (control netconnections) (ncpa.cpl) |
| Displays and allows the user to edit or create network connections such as Local Area Networks (LAN) and internet connections. It also offers troubleshooting functions in case the computer has to be reconnected to the network. |
| Phone and Modem Options (telephon.cpl) |
| Manages telephone and modem connections. |
| Power Options (powercfg.cpl) |
Includes options to manage energy consumption such as;
|
| Printers and Faxes (control printers) (control /name microsoft.devicesandprinters) |
Displays all the printers and faxes currently installed on the computer, and has two main uses;
|
| Regional and Language Settings (intl.cpl) aka Regional and Language Options |
Various regional settings can be altered, for instance:
Removed in the Windows 10 April 2018 Update and moved to Settings App. |
| Security Center or Action Center (Windows 7 & 8.x) (wscui.cpl) Renamed «Security & Maintenance» in Windows 10 |
| First added in Windows XP with Service Pack 2, Security Center gives the user access to the inbuilt Windows security components, as well as providing information about any existing antivirus software such as McAfee or Zone Alarm. It includes access to Windows Update, where users can specify whether the computer should check for updates regularly (also available through the Windows Update panel), and options for managing internet security settings. It also includes links to internet articles about PC security and current virus threats and notifies the user when the PC’s security is compromised. |
| Sounds and Audio Devices (mmsys.cpl) |
This panel contains various audio-related functions;
|
| Speech (Sapi.cpl) |
This applet has two main functions, the first is specify settings for Speech synthesis, allowing the user to select the voice the computer should use to narrate text and how fast it should read. The second is to specify settings for Speech recognition, allowing the user to set up different profiles detailing how the computer should deal with an individual’s dialect, for instance;
This also allows the user to access the voice recognition training wizard, in which an individual ‘teaches’ the computer to recognize a person voice interactively using the microphone. |
| Stored User Names and Passwords (keymgr.dll) (control.exe /name microsoft.credentialmanager) (Renamed «Credential Manager» in Windows 7 and later) |
| This is used to view and edit logon credentials for servers, websites and programs. |
| System (Sysdm.cpl) |
This is used to view and change core system settings, a user can for instance:
Moved to the Settings App on Windows 10, but the shortcut still exists. Clicking on it goes to the Settings App. |
| Taskbar and Start Menu (rundll32.exe shell32.dll, Options_RunDLL 1) |
Allows the user to change the behavior and appearance of the task bar and Start Menu;
Moved to the Settings App on Windows 10, but the shortcut still exists. Clicking on it goes to the Settings App. |
| User Accounts (control userpasswords) (nusrmgr.cpl) |
| This allows the user to configure their account and other accounts used in the system, should they have sufficient privileges. They can change their username, password, their account picture (if enabled), and their .NET Passport (in versions of Windows prior to Vista). If the current user has an administrator account they can also add, delete, and modify other user accounts as well as make changes to core system settings. This panel also specifies whether or not the guest account should be active and (in Windows XP only) whether or not to use the Welcome screen when Windows loads.
This panel is not available in Windows Server 2003, where the syntax «control userpasswords» will instead run the Local Users and Groups utility. |
| Users and Passwords (control userpasswords2) (rundll32.exe netplwiz.dll, UsersRunDll) |
| This is the legacy user account utility that was first introduced in Windows 2000 Professional. This allows the user to configure their account and other accounts used in the system, change their .NET Passports (in versions of Windows prior to Vista), as well as configuring autologin settings. This panel also specifies whether or not to press Ctrl+Alt+Del before login.
This panel is not available in the Windows 2000 Server family, where it will instead run the Local Users and Groups utility. |
Peripheral devices[edit]
These are options in the control panel that show devices connected to the computer. They do not actually offer a direct interface to control these devices, but rather offer basic tasks such as removal procedures and links to wizards (Printers & Faxes is an exception). Such applets include Scanners and Cameras, Game Controllers, and Portable Media Devices.
Other Microsoft-distributed applets[edit]
| Biometric Devices (biocpl.dll) |
|---|
Available with Fingerprint enabled systems running 7 or later, this enables users to configure a Fingerprint reader, showing a list of all Biometric devices interacting with the system, in addition to the following items;
Moved to Settings on Windows 10. |
| Bluetooth Devices (bthprops.cpl) |
Available with Bluetooth enabled systems running XP SP2 or later, this enables users to configure a Bluetooth connection, showing a list of all Bluetooth devices interacting with the system, in addition to the following items;
Moved to Settings on Windows 10. |
| Color (color.cpl) |
| Enables a more advanced control of color settings within Windows than is available in ‘display’, suitable for developers and visual specialists it allows users to create and load International Color Consortium compliant color profiles, associate screen color with printers and cameras and view a 3D graphics plot of the color gamut. By default this applet is not installed, however it can be installed for free from the Microsoft Website. |
| Infrared (irprops.cpl) |
| Similar to the Bluetooth applet, this is used to configure how the computer manages any wireless infrared ports installed, including options such as connectivity and security. |
| Location and Other Sensors (SensorsCpl.dll) |
| Manages Location based data like addresses and other location based sensors. Available in Windows 7 & 8.x only. |
| CSNW (nwc.cpl) |
| The Client Service for NetWare applet is used to select a default tree and context in a Novell Directory Services (NDS) environment, or the NetWare server used most frequently in a non-NDS environment.
Requirement: Installing the Client Service for NetWare. |
| Software Explorers |
| Part of Windows Defender, allows users to view detailed information about software that is currently running on the computer that can affect the users’ privacy or the security of the computer.
Replaced by Windows Defender Security Center on Windows 10. |
Third-party applets[edit]
Third-party software vendors have released many applets. Although it is impossible to mention all of them, some of them are listed here:
| Icon | File name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| AC3 Filter | ac3filter.cpl | Configures speaker configuration and other parameters of the AC3 decoder filter. |
| Adobe Gamma | Adobe Gamma.cpl | For altering the screen display with Adobe Systems Imaging Software such as Photoshop. |
| Adobe Version Cue CS2 | VersionCueCS2.cpl | To configure Adobe Version Cue. |
| Application paths | apppaths.cpl | Sets application paths, start-up commands and system services, coded by Gregory Braun. |
| ATI DVD Player | QISWCINE.CPL | Changes setings for your DVD decoding. |
| AudioHQ | AudHQ.cpl | Creative Labs Soundblaster Audio HQ. |
| Autodesk Plotter Manager | plotman.cpl | Adds, remove and changes plotters properties for AutoCAD products. |
| AvantGo Connect | agcpl.cpl | Synchronizes mobile versions (called «channels») of websites to a smartphone or PDA, see AvantGo. |
| Avira AntiVir PersonalEdition | avconfig.cpl | Configures Avira Antivirus program. |
| BACKPACK Finder | bpcpl.cpl | To configure the Micro Solutions BackPack CD driver. |
| BDE Administrator | bdeadmin.cpl | To configure the Borland Database Engine. |
| Boot Camp Control Panel | Setting for Mac OS X based computers. | |
| Broadcom Advanced Control Suite | BACSCPL.cpl | Enables Broadcom network cards testing and diagnostics. |
| CD/DVD Drive Acoustic Silencer | TOSCDSPD.cpl | Configures the rotation speed of CD/DVD drive. (Toshiba ) |
| ClearCase | cc.cpl | To configure IBM Rational ClearCase. |
| Color Settings | 3dcc.cpl | Changes the look and feel of Windows. |
| Compaq Diagnostics | cpqdiag.cpl | To view information a computer’s hardware and software configuration, legacy application. |
| Control Panel | controlp.cpl | Control Panel Customization Toy, coded by Ali Lokhandwala. |
| Control Version System | cvsnt.cpl | Control Panel Customization Toy, by Brian Berliner. david d ‘zoo’ zuhn, Jeff Polk, Tony Hoyle |
| Creative Element Power Tools | To configure Creative Element Power Tools, a free-to-try program providing access to additional Windows tools. | |
| Corel Versions | verscpl.cpl | Configures Corel versions. |
| DANS | danetsvc.cpl | Configures the Shaffer Solutions DiskAccess Network Services, NFS client for Windows. |
| Diagnostics for Windows | cpqdiag.cpl | HP Diagnostics for Windows 4.15 replaces Compaq |
| Digidesign ElevenRack | DigidesignElevenRackControlPanelApplet.cpl | Launch Eleven Rack Control Panel |
| DiskAccess | dacfg.cpl | Configures how the Shaffer Solutions DiskAccess makes connections to remote NFS servers. |
| DS18x Applet | DS18xCPL.cpl | MR Soft DS18x Temperature Logging Service. |
| Flash Player | FlashPlayerCPLApp.cpl | For changing settings for the Flash Player. |
| Folder size | FolderSize.cpl | Folder Size for Windows shows the size of folders in Windows Explorer. |
| FirebirdSQL Service Manager | fmmgr.cpl | Configures Firebird (database server) service options. |
| HP Jetadmin | jetadmin.cpl | HP Jetadmin configures and monitors HP printers. |
| HP Lock | Hplock.cpl | A Windows 95 utility to lock the PC keyboard, mouse and on/off switch in one click on legacy HP Vectra. |
| IconPackager | ipcpl.cpl | To customize Windows icons and cursors, see IconPackager. |
| ImDisk Virtual Disk Driver | imdisk.cpl | Administration of ImDisk Virtual Disk Driver. |
| InstallShield Update Manager | isuspm.cpl | The InstallShield Update Manager allows users to receive program updates and messages from software makers who use the service. |
| Intel Extreme Graphics | igfxcpl.cpl | To change advanced settings on systems using Intel GPUs. |
| Intel Product Improvement Program | executable | Installed with Intel Driver Update Utility version 2.4 (on Vista and up) |
| IP Office Voicemail Pro | ims.cpl | To configure Avaya IP Office Voicemail Pro. |
| Java | jpicpl32.cpl | For changing settings with Java Runtime Console. |
| JInitiator 1.x.y.z | plugincpl1xyz.cpl | To configure Oracle’s JInitiator, note x.y.z are version numbers. |
| MLCFG32.cpl | Launches the Microsoft Outlook Profile Manager. | |
| MSConfig | MSConfig.cpl | Launches the Microsoft System Configuration Utility. |
| Multi-finger | ETDUI.cpl | Customize the Smart-Pad Multi-finger Setting. |
| MultiSite | ms.cpl | To configure IBM Rational ClearCase Multisite. |
| Nero BurnRights | NeroBurnRights.cpl | For specifying who is allowed to use the CD burner with Nero. |
| nVIDIA Control panel | nvidia.cpl | To change advanced settings on systems using nVIDIA GPUs. |
| Panda Media Booster | PMB.cpl | Panda Media Booster cache and network settings. |
| Parallel Port Joysticks | PPjoy.cpl | Configures Joysticks connected on the Parallel Port. |
| Pointer Devices | tbctlpnl.cpl | To configure the Touch-Base Universal Pointer Device Driver (UPDD). |
| QuickTime | quicktime.cpl | For specifying settings of the Apple QuickTime Player. |
| RealPlayer | prefscpl.cpl | To configure the RealPlayer preferences, older versions. |
| Realtek AC97 Audio Control Panel | alsndmgr.cpl | To configure the Realtek audio controller. |
| Realtek HD-Audio Manager | RTSnMg64.cpl | To launch the Realtek HD-Audio Manager |
| RESTrick Control Panel | rest2.cpl | Windows Tuning and system restrictions setup, by Rtsecurity. |
| Safarp | safarp.cpl | Safarp is a small and fast alternative to the Add or Remove Programs applet. |
| ScrewDrivers Client | sdclient.cpl | From Tricerat, remote desktop print management solution. |
| Send To Toys | sendtotoys.cpl | To configure the Send To right click system menu in Microsoft Windows. |
| Services and Devices | pserv.cpl | From p-nand-q to manage Windows services and devices and uninstall applications. |
| Softex OmniPass | scurecpl.cpl | Softex OmniPass provides password management capabilities to MS Windows. |
| SNTP Service | sntpserv.cpl | From Dillobits Software, to manage the SNTP client service. |
| Soundscape | scurecpl.cpl | Adds, removes or changes settings of Soundscape devices. |
| Startup | startup.cpl | Control programs that run at system start-up, coded by Mike Lin. |
| Startup Disk | Startup Disk.cpl | Boot Camp drivers, when Windows runs on a Mac OS virtual machine. |
| Symantec LiveUpdate | s32lucp2.cpl | Configures the Symantec LiveUpdate update service. |
| System Change Log | scl.cpl | From Greyware Automation Products, monitors disks for changes and records a detailed log. |
| System Information | Sancpl.cpl | Launches SiSoftware Sandra utility. |
| System Info for Windows | siw.cpl | Launches the SIW application. |
| Trust-No-Exe | trustnoexe.cpl | Configures the Beyond Logic Trust-No-Exe executable filter. |
| VMware Tools | VMControlPanel.cpl | To configure VMware Tools. |
| WIBU-KEY | wibuke32.cpl | To configure the WIBU-KEY Software Protection. |
| Winlogos | wnlgo.cpl | To change the Windows start-up and shutdown screens in Windows 98 or ME, coded by Ali Lokhandwala. |
| X-Setup Pro | xqdcXSPApplet.cpl | Launches X-Setup Pro, a Windows tweaker application. |
References[edit]
- ^ «A history of Windows». Windows. Microsoft. Archived from the original on November 17, 2010.
- ^ «Accessing the Control Panel via the Commandline». Microsoft. August 29, 2011.
- ^ Bradley, Tony (July 6, 2012). «Adding and Managing Users in Windows 8». PC World. IDG. Retrieved September 20, 2015.
- ^ Bright, Peter (March 25, 2013). «Windows Blue leaks: More Metro, more multitasking». Ars Technica. Condé Nast. Retrieved January 20, 2014.
- ^ «How to run Control Panel tools by typing a command». Support. Microsoft. Retrieved February 26, 2014.
External links[edit]
- How to run Control Panel tools by typing a command at Microsoft.com

Хоть я и стараюсь публиковать на сайте статьи и видеоуроки для пользователей разных уровней компьютерной подготовки, но все же, действительно, есть вопросы, которые не освещаю ни я, ни мои коллеги по интернету, а именно эти вопросы возникают у начинающих и они по-прежнему остаются без ответа.
В этой заметке я хочу рассказать о Панели управления Windows. Далеко не все начинающие пользователи знают для чего она нужна и где ее найти.
Итак, давайте разбираться.
Зачем нужна Панель управления Windows
Операционная система Windows является программой, которая выступает в роли посредника между устройствами компьютера и нами – пользователями.
Также операционная система обеспечивает необходимые условия для установки и работы программ и приложений. Задачи операционной системы разнообразны и охватывают все области работы на компьютере. Можно сказать, что это самая главная и самая важная программа.
Но, если разобраться детально, то Windows – это не одна программа, а целый пакет программ, который позволяет нам работать с файлами, организовывать компьютерные сети и выходить в Интернет, управлять доступом пользователей к компьютеру, обеспечивать защиту компьютера от проникновения из сети и так далее… Задач операционная система выполняет действительно много.
За отдельные задачи, как правило, отвечают отдельные утилиты (маленькие программы), которые входят в состав операционной системы. Для того чтобы выполнить настройку каких-либо параметров с помощью такой утилиты, ее нужно запустить. Для удобства все основные настройки операционной системы и утилиты, отвечающие за различные аспекты работы на компьютере, собрали в одном месте. Думаю, что вы уже догадались — это место называют Панелью управления Windows.
Как запустить Панель управления Windows
Попасть в нее можно через меню Пуск, выбрав одноименный пункт.
На рисунке выше продемонстрировано меню Пуск Windows 7. В Windows XP ситуация будет аналогичная, а вот в Windows 8 нужно в меню Пуск, выбрать Приложения, а затем найти пункт Панель управления. Более подробно это можно увидеть в видеоролике Как создать пользователя в Windows 8
Откроется окно Панели управления.
Инструменты Панели управления Windows
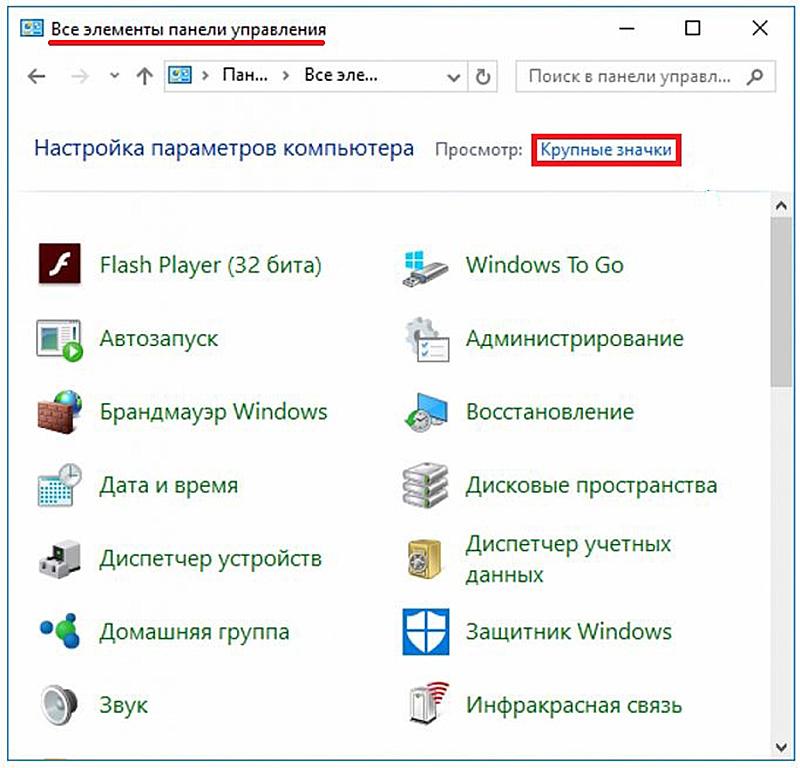
Инструменты Панели управления по умолчанию сгруппированы по категориям, но можно отобразить все инструменты, изменив режим отображения — установив режим «Мелкие значки» в настройке Просмотр.
В Панели управления собраны все основные настройки Windows и именно выбрав соответствующий инструмент Панели управления, вы сможете, например, изменить языковые настройки операционной системы или поменять внешний вид окон и меню пуск. Также сможете создать нового пользователя на компьютере или поменять изображение на рабочем столе.
Кроме стандартных утилит в Панели управления могут быть инструменты, которые добавляются сюда некоторыми программами при их установке. Обычно эти программы являются дополнением к другим программам и позволяют расширить их функциональные возможности. Например, Flash Player добавляет свой значок в Панель управления и отсюда вы сможете произвести настройки этой программы в случае необходимости.
Большинство пунктов Панели управления практически никогда не используются, так как настройки, заложенные в них по умолчанию, удовлетворяют подавляющее большинство пользователей. К таким инструментам относятся, например, «Клавиатура», «Мышь», «Звук» или «Центр специальных возможностей».
Но все же есть пункты, которые довольно часто востребованы и применяются для настройки Windows, например, «Персонализация».
Правда, следует отметить, что большинство инструментов Панели управления можно вызвать не только из нее, но и альтернативным способом.
Например, в «Персонализацию» можно попасть из контекстного меню, вызвав его на пустой области рабочего стола, щелчком правой кнопкой мыши.
Ну и в заключение этой заметки хочу порекомендовать всем начинающим пройти мой бесплатный видеокурс «Компьютерная Азбука». Он состоит из 130 видео с текстовым вариантом уроков и в этом курсе изложены все базовые понятия операционной системы Windows 7.
Я убежден, что информации этого курса будет достаточно, чтобы начинающий пользователь стал чувствовать себя намного увереннее при работе на компьютере.
Для чего нужна панель управления
Начинающий пользователь персонального компьютера пользуется его возможностями, данными по умолчанию. По мере набора опыта и перехода в разряд продвинутого пользователя у него возникает потребность в более удобной и комфортной работе. Операционная система Windows предусмотрела возможность настройки ряда некритичных параметров компьютера под вкусы и предпочтения пользователя. Эти настройки сведены в компонент интерфейса, называемый панелью управления. Такое название очевидно и чётко определяет её назначение.
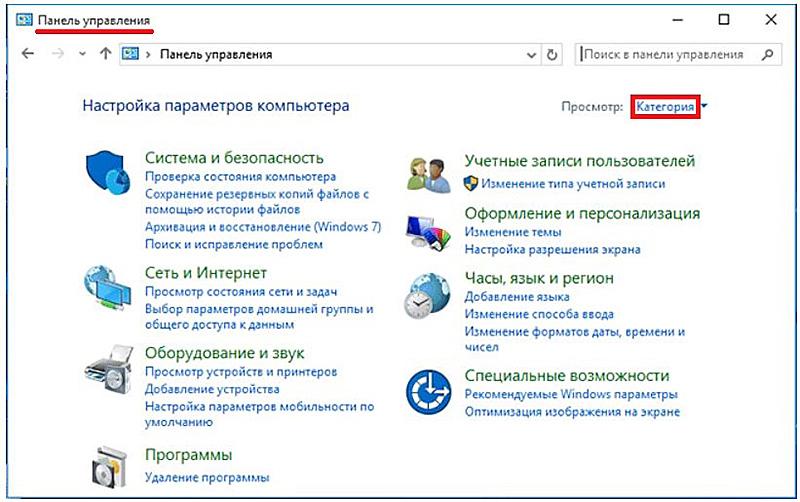
После вызова (способы которого будут рассмотрены ниже) окно панели управления по умолчанию имеет следующий вид.
Как видно, настраиваемые параметры компьютера разделены на восемь категорий и снабжены соответствующими значками. Рядом с ними и названием приведена краткая информация о возможностях данной настройки. Поясним эту информацию с тем, чтобы сделать её более понятной начинающему пользователю. Начнём с более простых категорий.
«Специальные возможности»
Абсолютное большинство пользователей может не обращать внимания на категорию «Специальные возможности». Она предназначена для людей, имеющих проблемы со зрением, слухом или двигательными функциями. Такие пользователи смогут внутри неё, например, сделать изображение более контрастным, сильно увеличить отображаемый на экране курсор мыши, заменить звуковые сигналы визуальными подсказками. Есть также возможность проще работать с сочетаниями клавиш: например, пользователь с дрожащей рукой сможет нажимать Ctrl+Alt+Del не одновременно, а по очереди.
«Часы, язык и регион»
Правильная настройка компьютера предполагает выбор форматов отображения на экране даты и времени, принятой для того региона, в котором эксплуатируется компьютер. Вряд ли можно считать удобным, если на работающем в России компьютере отображаются принятые в США форматы даты – 04/25/2017 (дата начинается с месяца) или 6:53 PM. Для их точного отображения нужно выбрать правильный часовой пояс. Можно также указать, происходит ли в данном регионе переход на летнее и зимнее время с тем, чтобы компьютер автоматически корректировал время.
В этой же категории пользователь выбирает, на каких языках ему придётся набирать текст в редакторе. К стандартным EN и RU можно добавить, например, DE для немецкого, что будет нужно переводчику на этот язык.
«Оформление и персонализация»
В этой категории настраивается оптимальное для используемого монитора разрешение экрана с тем, чтобы изображение на нём было комфортным для пользователя. Здесь же выбирается заставка экрана и размер текста и значков рабочего стола. Можно также добавлять значки и ярлыки в меню «Пуск» и на панель задач, примеры чего будут рассмотрены ниже.
«Учётные записи пользователей»
Единственному рядовому пользователю компьютера вряд ли пригодится эта категория. Но если компьютер находится в пользовании нескольких человек, то каждый из них сможет входить в систему под автономной учётной записью (т. е. аккаунтом), настроенным под его предпочтения и вкусы. Аккаунты могут иметь разные права в системе: в частности, опытным пользователям будут доступны расширенные возможности настройки.
Другие категории
Категории в левой части окна панели управления ориентированы на продвинутых пользователей.
Категория «Программы» предназначена для корректного удаления и добавления на компьютер внешних программ и компонентов Windows. В категории «Оборудование и звук» можно подключать к компьютеру внешние устройства, например, принтер или сканер. «Сеть и Интернет» позволяют, в частности, настраивать «домашнюю сеть», объединяющую, например, стационарный компьютер, ноутбук и смартфон с общим выходом в Интернет. С категорией «Система и безопасность» работают опытные пользователи. Ведь она позволяет устранять неполадки компьютера, например, возвратом к состоянию недельной давности или восстановлением повреждённых файлов из резервных (архивных).
Степень детализации возможностей панели управления может быть изменена, если в верхнем выпадающем списке «Просмотр» поменять «Категория» на «Крупные значки» или «Мелкие значки». В этом случае каждый инструмент отображается автономно (см. ниже).
Вызов панели управления
Пользователь Windows 7, привыкший вызывать панель управления через меню «Пуск», в Windows 10 не найдёт соответствующего пункта. Но перейти к ней нетрудно, и сделать это можно несколькими способами.
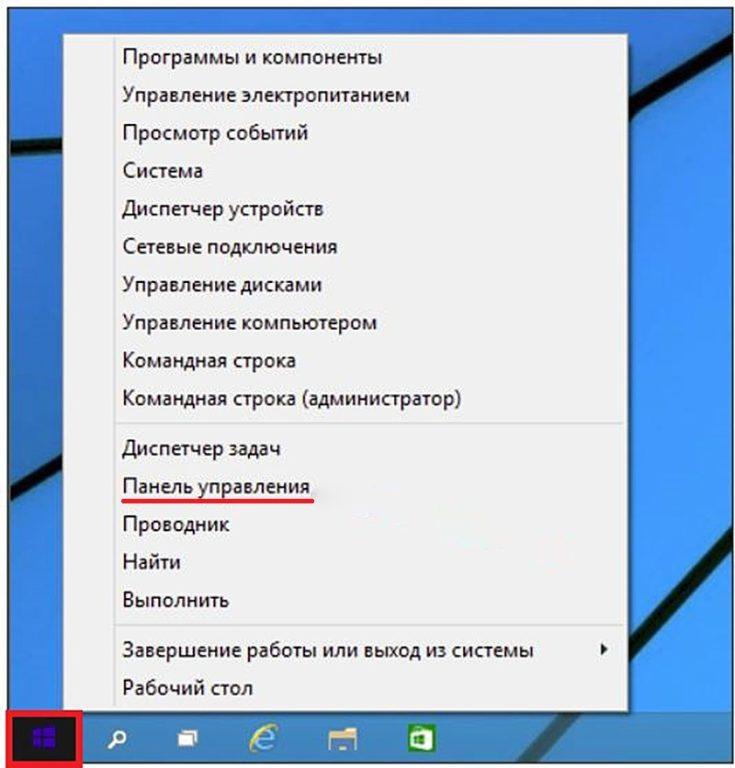
С помощью контекстного меню «Пуск»
Самый простой из них так же происходит через меню «Пуск», только не обычное, а контекстное (вызываемое нажатием правой клавиши на кнопке «Пуск»).
Представленное на скриншоте контекстное меню может быть открыто и другим способом – сочетанием клавиш Win+X.
Добавление в обычное меню «Пуск»
Пользователи Windows 7, предпочитающие открывать панель управления привычным способом – через обычное меню «Пуск», смогут делать это после выполнения следующей последовательности действий.
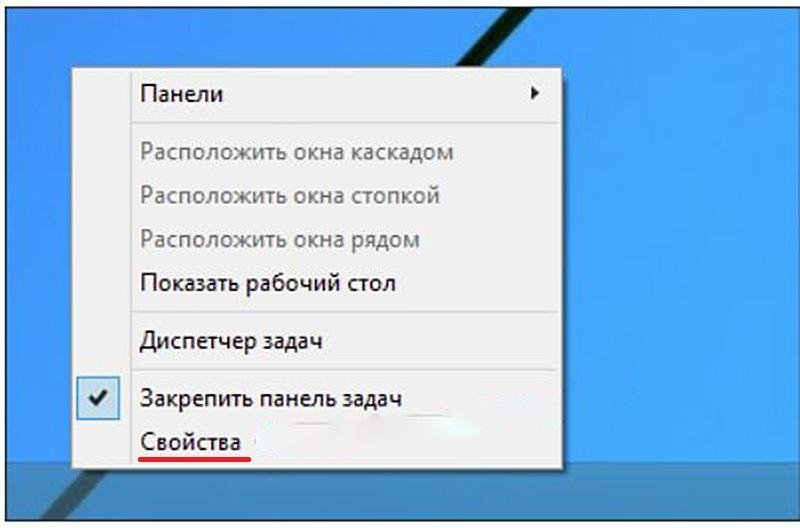
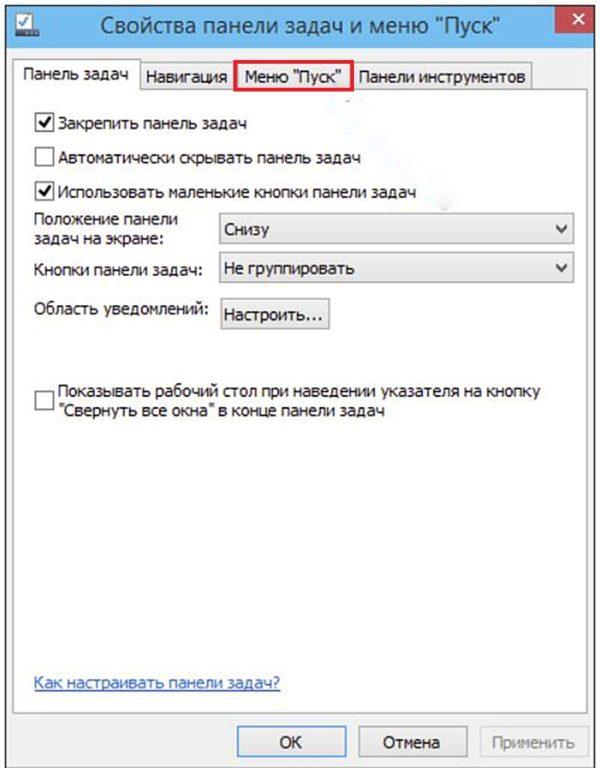
- На панели задач (нижней строке с кнопкой «Пуск») щёлкаемна свободном месте правой клавишей мыши. В появившемся окне выбираем пункт «Свойства».
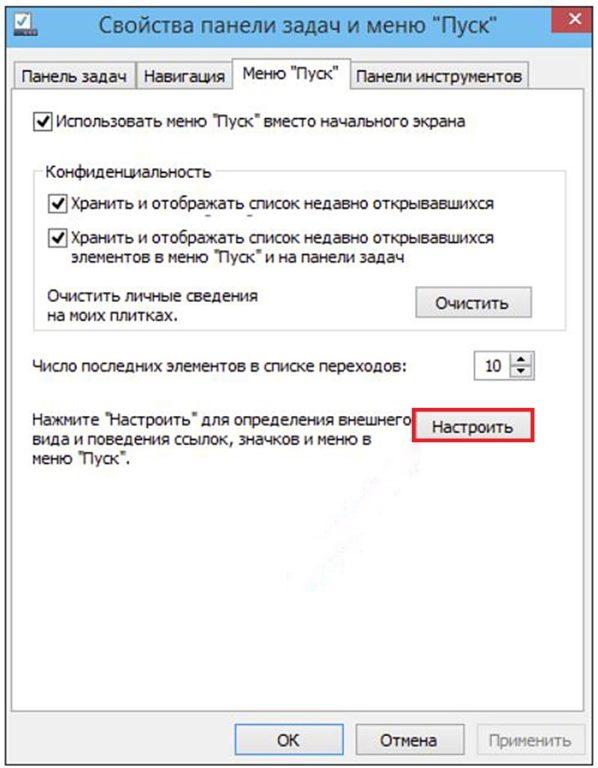
- В окне «Свойства панели задач и меню «Пуск» переходим на вкладку Меню «Пуск».
- На этой вкладке нажимаем кнопку «Настроить».
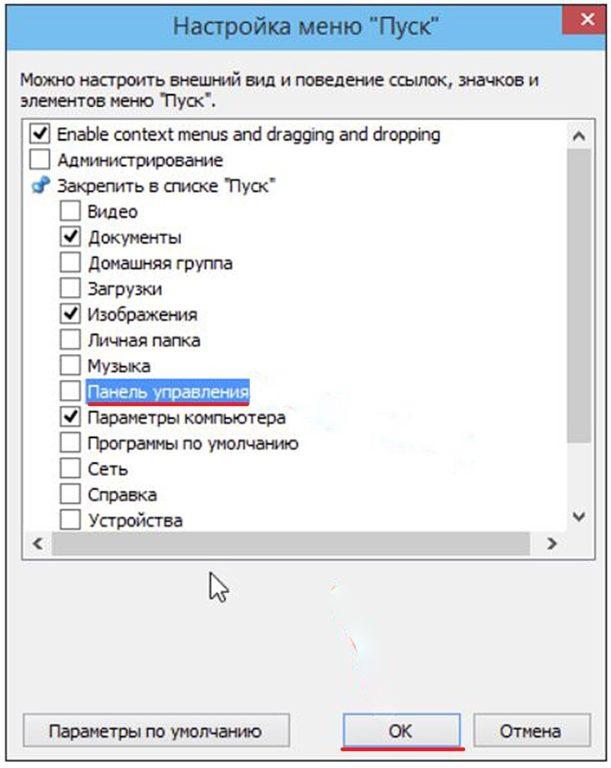
- В окне «Настройка» меню «Пуск» ставим галочку рядом со словосочетанием «Панель управления» и жмем OK.
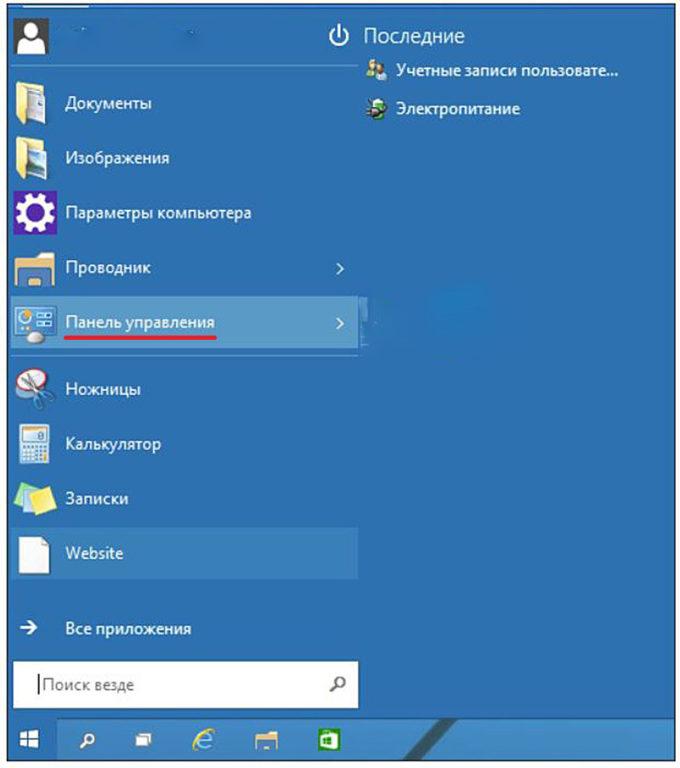
- После этого в стандартном меню «Пуск» появится новая, но привычная строка «Панель управления».
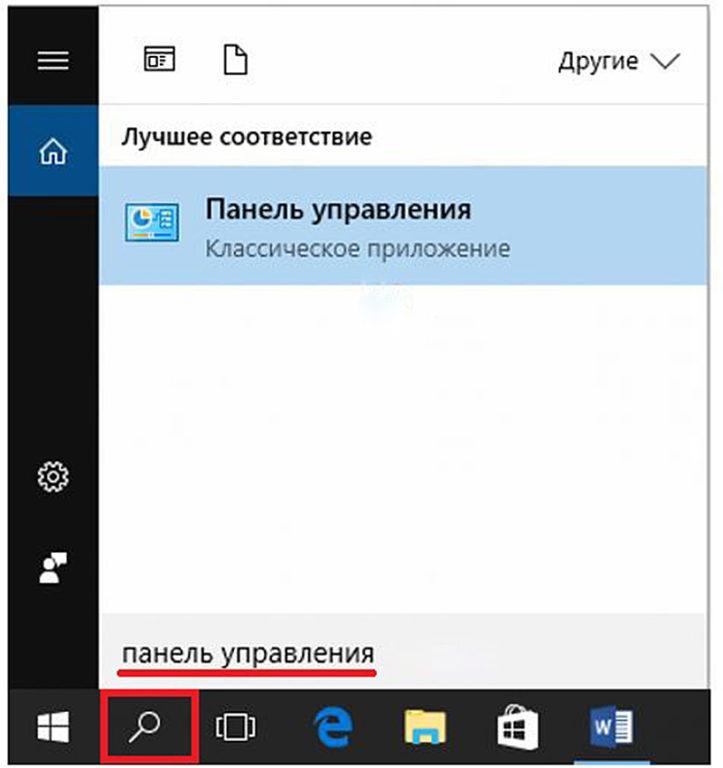
Встроенной функцией поиска
Панель управления может быть вызвана посредством поисковой системы, обозначаемой значком лупы в левой части панели задач. После нажатия на этом значке в появившейся строке следует ввести «панель управления». Как правило, искомый результат появляется ещё до полного ввода этого словосочетания.
Поисковая строка может быть вызвана не только через значок лупы, но сочетанием клавиш Win+S. Более того, указанное словосочетание можно набирать и без предварительного вызова поисковой строки. По мере набора система «соображает», что хочет пользователь, и автоматически предоставляет ему поисковую строку.
Поиск посредством функции поиска, разумеется, применим при поиске не только панели управления, но и произвольного приложения, место расположения которого неизвестно пользователю.
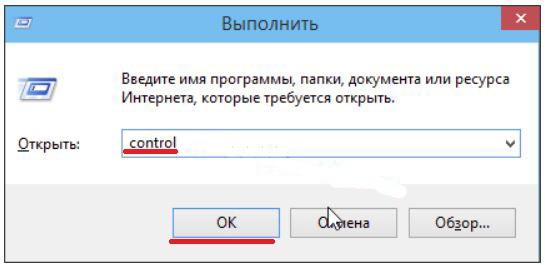
С помощью команды в строке «Выполнить»
К панели управления можно перейти и с помощью строки «Выполнить». Она возникает при нажатии сочетания клавиш Win+R. В появившейся строке «Открыть» нужно набрать команду control.
Добавление значка на рабочем столе
После инсталляции Windows 10 на рабочем столе системы по умолчанию появляются значки «Этот компьютер» и «Корзина». Пользователь, однако, имеет возможность добавить на него и некоторые другие значки, включая «Панель управления». Для этого следует выполнить приводимую последовательность действий:
- В свободном месте рабочего стола кликаем правой клавишей мыши.
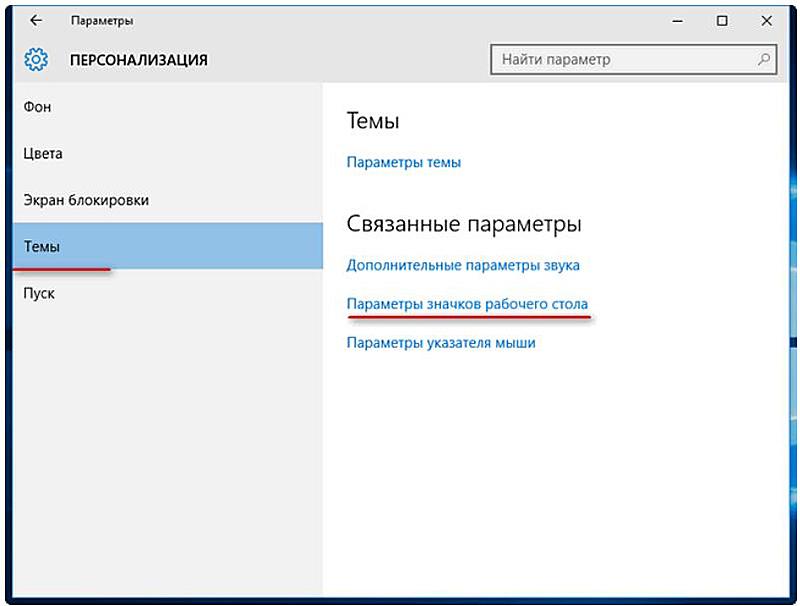
- В появившемся контекстном меню щёлкаем пункт «Персонализация».
- В новом окне «Параметры» следует щёлкнуть пункт «Темы», а затем – «Параметры значков рабочего стола»;
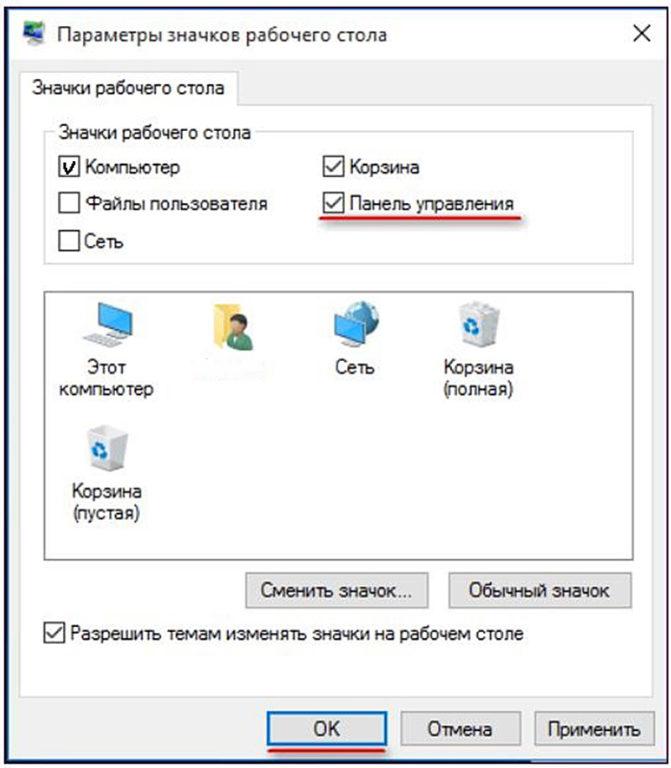
- В появившемся одноимённом окне необходимо поставить галочку рядом со словосочетанием «Панель управления» и подтвердить намерение, щёлкнув OK.
В результате панель управления будет постоянно отображаться на рабочем столе.
В скобках отметим, что для внимательного читателя будет очевидно, что при открытой панели управления окно «Персонализация» может вызвано через категорию «Оформление и персонализация» (см. первый скриншот).
Добавление ярлыка на рабочем столе
Элементы управления, обычно находящиеся на рабочем столе, подразделяются на значки и ярлыки. Последние легко отличить по стрелке рядом со значком (указывающей, что само приложение находится в другом месте). Для добавления ярлыка на рабочий стол должна быть выполнена следующая последовательность действий.
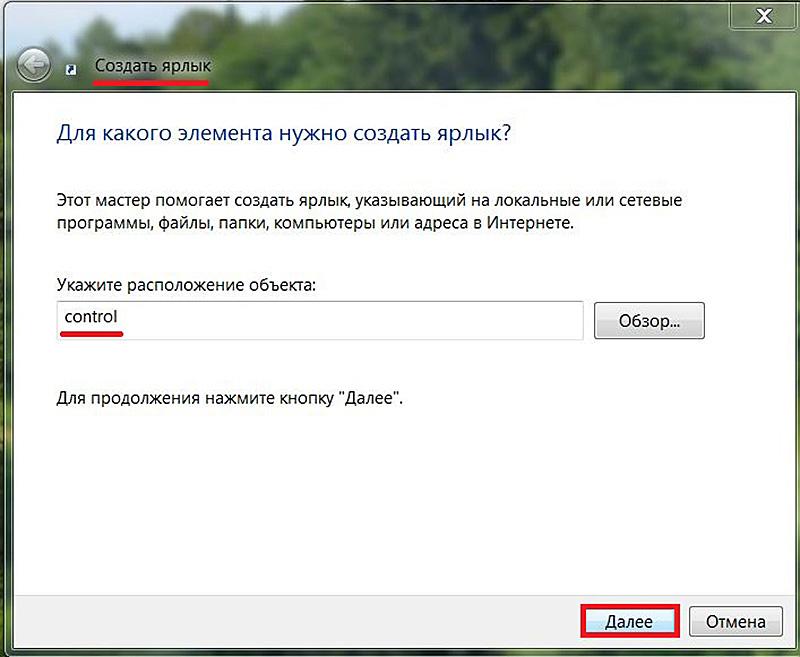
- В контекстном меню рабочего стола в выпадающем списке «Создать» выбираем пункт «Ярлык».
- В появившемся окне в поле «Укажите расположение объекта» вводим control и жмем кнопку «Далее».
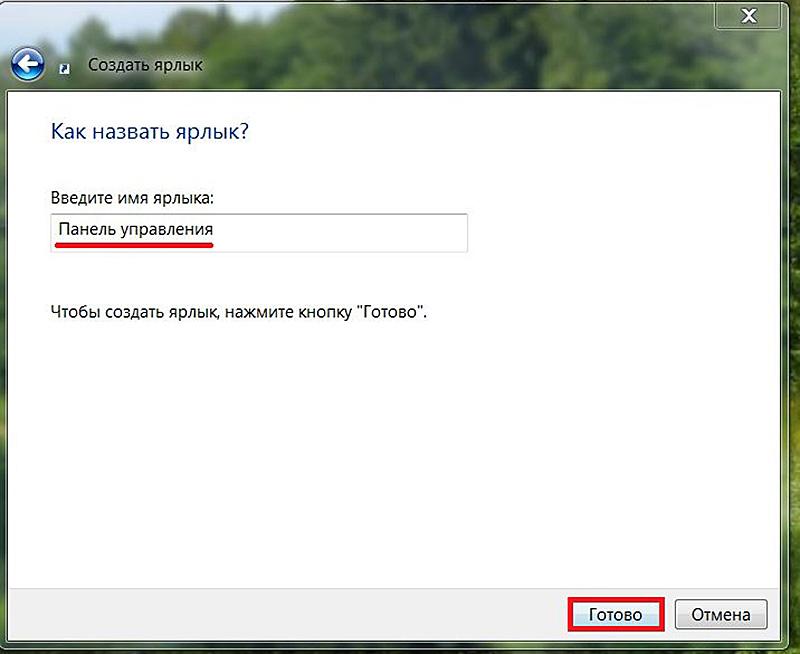
- В новом окне вводим желаемое имя и жмем «Готово».
Вызов панели управления с помощью «горячих клавиш»
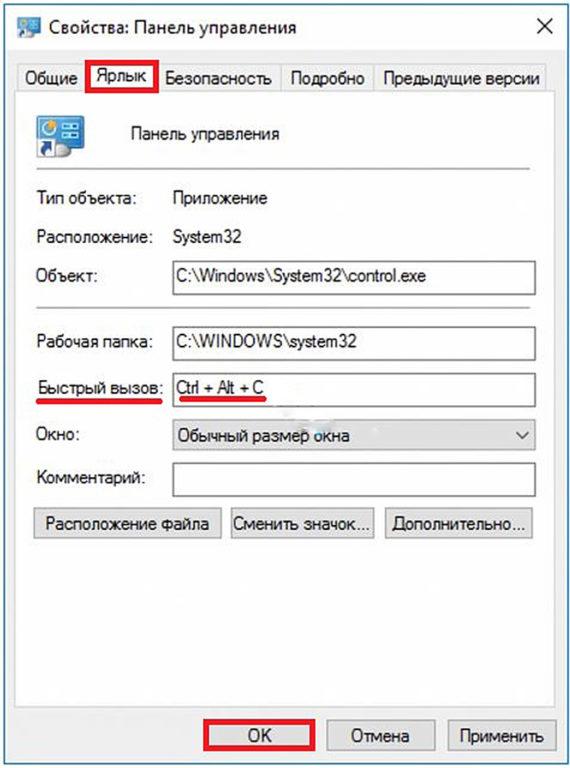
После создания ярлыка на рабочем столе его можно связать с комбинацией «горячих клавиш». Для этого следует вызвать контекстное меню ярлыка «Панель управления», щёлкнуть пункт «Свойства», и в поле «Быстрый вызов» набрать комбинацию клавиш, разделяя их знаком +. Первые две клавиши – Ctrl+Alt, а третья – на усмотрение пользователя.
Post Views: 3 519
Панель управления — святая святых любого девайса от смартфона до космического корабля. С его помощью можно настраивать и управлять устройством, изменять параметры и характеристики. Каждая операционная система Windows также имеет свою среду управления, хотя в Windows 10 разработчики хотят постепенно отказаться от «Панели управления».
Что такое «Панель управления» и для чего она нужна
«Панель управления» — особая среда для управления операционной системой. Её основная функция — изменять настройки ОС. Все утилиты «Панели управления» делятся на восемь категорий:
- «Система и безопасность»;
- «Сеть и Интернет»;
- «Оборудование и звук»;
- «Программы»;
- «Учётные записи пользователей»;
- «Оформление и персонализация»;
- «Часы и регион»;
- «Специальные возможности».
В зависимости от сборки количество категорий может отличаться.
По названию категории легко определить, за какой раздел работы компьютера она отвечает. Также можно изменить отображение категорий на значки, чтобы найти настройку или утилиту без переходов по группам. Для этого нажмите на «Просмотр» и измените фильтр с «Категория» на «Мелкие значки».
После этого в «Панели управления» появится больше категорий, упорядоченных по столбцам.
Лично для меня «Панель управления» — очень важный инструмент в работе с компьютером. Сразу после переустановки системы около получаса копаюсь в настройках электропитания, персонализации и других параметрах Windows, чтобы сделать ОС наиболее комфортной. Если заводские настройки не устраивают, меняю их в «Панели управления».
Возможностей достаточно: исполняющие утилиты, поиск, ярлыки и даже горячие клавиши.
Через поиск
Поиск Windows ассоциативно найдёт на компьютере любой файл или приложение.
Чтобы открыть окно поиска, нажмите на значок лупы в левом нижнем углу рядом с кнопкой «Пуск». В поле ввода введите «Панель управления» и кликните на программу.
Через команду «Выполнить» или терминал командной строки
Команда control в исполняющей программе или консоли командной строки также откроет «Панель управления».
Нажмите клавиши Win+R, в диалоговом окне введите control и запустите.
Через терминал «Командная строка» можно запустить любое приложение и процесс, включая «Панель управления». Вот как это сделать:
- В окне поиска Windows введите запрос «Командная строка» и выберите программу.
Выберите терминал «Командная строка» со значком окна программы - В консоли введите команду control и запустите клавишей Enter.
После нажатия клавиши Enter откроется «Панель управления»
Через меню Windows
Меню Windows — элемент для запуска наиболее часто используемых апплетов системы.
Вызвать меню можно двумя способами:
- клавишами Win+X;
- щёлчком правой кнопкой мыши по значку Windows (иначе — кнопки «Пуск»).
С версии Windows 10 1703 «Панель управления» в меню ОС заменили на среду «Параметры», и теперь этот способ невозможен на новых версиях.
Через системные параметры
Во встроенной среде «Параметры» есть свой системный поиск, который можно использовать для открытия «Панели управления».
- Нажмите клавиши Win+I, вызывая «Параметры».
- На главной странице в строке поиска введите «Панель управления» и выберите выпавший результат.
Поле поиска находится сверху, над остальными категориями
Через «Проводник»
«Проводник» является универсальным файловым менеджером Windows, с его помощью очень просто открыть «Панель управления».
- Откройте любую папку компьютера. Запустится «Проводник».
- В адресной строке рядом со значком монитора нажмите на стрелочку, в выпавшем меню выберите «Панель управления».
Адресная строка проводника находится в самом верху
Через меню «Пуск» (начальный экран)
Самый простой способ открыть «Панель управления» — через меню «Пуск».
Нажмите на кнопку Windows, прокрутите список программ до папки «Служебные», в ней щёлкните по «Панели управления».
Как создать ярлык для входа в «Панель управления» на Windows 10
Чтобы не искать сервис раз за разом, можно добавить ярлык инструмента на рабочий стол.
- Щёлкните правой кнопкой мыши по пустому месту рабочего стола, выберите пункт «Создать» — «Ярлык».
Выберите в контекстном меню пункт «Создать» — «Ярлык» - В окне мастера создания ярлыка пропишите control, нажмите «Далее».
Control — уже знакомая команда вызова «Панели управления» - Далее присвойте ярлыку имя: можно выбрать любое, но правильнее назвать «Панель управления». Затем нажмите «Готово». Теперь на рабочем столе есть быстрый доступ к «Панели управления».
Заполните поле «Введите имя ярлыка» и нажимаем «Готово»
Как задать горячие клавиши для вызова панели управления на Windows 10
В Windows можно задать горячие (глобальные) клавиши для вызова ярлыка. С их помощью ярлык запускается в любом приложении без использования мышки. Вот как их создать:
- Щёлкните правой кнопкой мыши по ярлыку и выберите пункт «Свойства».
Пункт «Свойства» находится в контекстном меню - Перейдите во вкладку «Ярлык», щелкните на поле «Быстрый вызов» и нажмите клавиши Ctrl+Alt+G. Первые две кнопки обязательны и задают быстрый вызов. Третью кнопку выберите самостоятельно.
В поле «Быстрый вызов» выберите нужные клавиши - Сохраните изменения, нажав на кнопку OK.
После этого нажатие горячих клавиш будет сопровождаться открытием «Панели управления».
Видео: как открыть «Панель управления»
Открыть командную строку очень просто. Пользуйтесь любым способом по душе: горячими клавишами, ярлыком или вызовом через командную строку.
- Распечатать
Здравствуйте! Меня зовут Алексей. Мне 27 лет. По образованию — менеджер и филолог.
Оцените статью:
- 5
- 4
- 3
- 2
- 1
(2 голоса, среднее: 5 из 5)
Поделитесь с друзьями!
С помощью панели управления можно менять параметры в Windows. Используя эти параметры, можно управлять внешним видом и работой Windows, а также настраивать Windows в соответствии со своими потребностями.
Открытие панели управления
|
В Windows 10 |
Чтобы получить доступ к дополнительным параметрам, введите панель управления в поле поиска на панели задач, а затем в списке результатов выберите Панель управления. |
|
В Windows 8.1 и Windows RT 8.1 |
Проведите пальцем от правого края экрана и нажмите Поиск (если используется мышь, переместите указатель в правый верхний угол экрана, затем вниз и выберите Поиск), в поле поиска введите панель управления, а затем в списке результатов выберите Панель управления. |
|
В Windows 7 |
Нажмите кнопку «Пуск» и выберите пункт Панель управления. |
Поиск элементов панели управления
Работа на панели управления:
-
Использование поиска. Чтобы найти необходимую настройку или задачу, введите слово или фразу в поле поиска. Например, введите «звук», чтобы найти настройки для звуковой карты, системных сигналов, а также значок громкости на панели задач.
-
Обзор. На панели управления можно выбирать различные категории (например, «Система и безопасность», «Программы» или «Специальные возможности») и просматривать часто используемые задачи для каждой категории. В разделе Просмотр можно выбрать категорию Крупные значки или Мелкие значки для просмотра списка всех элементов панели управления.
Советы:
-
Если вы просматриваете панель управления в виде значков, можно быстро найти элемент из списка, введя первую букву названия этого элемента. Например, чтобы найти элемент «Клавиатура», введите К, и первым в списке элементов на панели управления, название которого начинается с буквы «К», будет «Клавиатура».
-
Кроме того, для прокрутки списка значков панели управления можно использовать клавиши со стрелками (СТРЕЛКА ВВЕРХ, ВНИЗ, ВЛЕВО и ВПРАВО).
-
Если вы не можете найти параметр на панели управления, нажмите кнопку Пуск , > Параметры . Многие возможности панели управления теперь доступны в настройках .
Нужна дополнительная помощь?
Перейти к содержанию
На чтение 3 мин Просмотров 3 Опубликовано 01.02.2023
Сколь бы удобна ни была Windows 10, ее оформление способно ввести в ступор пользователя, привыкшего к лаконичному стилю 7 версии. Все важные элементы управления создатели спрятали от пользователя, и даже самые простые задачи вызывают немало проблем с поиском.
Содержание
- Зачем нужна Панель Управления Windows
- Где искать
- Как закрепить значок
Зачем нужна Панель Управления Windows
Панель управления – важный элемент управления системой. С ее помощью можно менять параметры и настройки Windows . Это дает пользователю возможность влиять на оформление и производительность ПО, настраивать систему под свои нужды.
Где искать
Обычно в «десятке» панель управления открывается через Пуск > Служебные программы > Панель управления.
Что содержит
Именно здесь собраны основные элементы управления и настройки Windows. В зависимости от конфигурации набор параметров может разниться, но обычно он включает такие элементы:
- автозапуск;
- восстановление;
- часы и регион;
- диспетчер устройств;
- звук;
- оформление и персонализация;
- сеть и интернет;
- устройства и принтеры;
- программы;
- учетные записи пользователей;
- специальные возможности.
Как зайти
Что делать, если пропала панель управления? Большинство пользователей, недавно перешедших на новую для себя систему, не могут решить этот вопрос.
Открыть панель управления можно несколькими способами:
Как закрепить значок
Если вы часто обращаетесь к этому разделу, то будет совсем нелишним обеспечить к нему быстрый доступ. Для этого откройте контекстное меню, можно через поиск или через «выполнить». Кликните по строке правой кнопкой мыши и выберите из списка вариант:
- закрепить на начальном экране;
- закрепить на панели задач.
Вячеслав Вяткин
Приветствую тебя мой друг! Давай знакомиться?! Я администратор и автор данного сайта. Специалист с 10 летним опытом работы в сфере ИТ-технологий. Проконсультирую вас по настройке: компьютеров, ноутбуков, периферийного оборудования. Помогу решить проблемы в работе операционной системы Windows или компонентов компьютера. Подскажу как настроить ваши гаджеты.
Оцените автора
( 1 оценка, среднее 5 из 5 )
Операционная система включает
разнообразные возможности настройки
интерфейса и параметров и предоставляет
различные способы ее выполнения. Это
позволяет адаптировать систему к
требованиям пользователя.
В ОС Windows
настраиваются: Рабочий стол, текущие
дата и время, клавиатура, мышь, опции в
меню [Пуск] (Главное меню) и многое другое.
Настройки называются пользовательской
конфигурацией и
сохраняются для каждого зарегистрированного
пользователя. При последующей загрузке
ОС запрашивает имя (учетную запись) и
пароль пользователя. В случае совпадения
восстанавливается сделанная им ранее
конфигурация настроек.
Средствами
настройки являются: компоненты системной
папки Панель
управления,
контекстное меню объектов Windows,
элементы управления диалоговых окон
операционной системы и ее приложений.
В системной папке
Панель
управления
собраны
административные утилиты,
которые предоставляют один из наиболее
удобных и не приводящих к катастрофическим
последствиям способов настройки системы,
программного и аппаратного обеспечения.
Диалоговое окно этой панели активизируется
командой Пуск►Настройка►Панель
управления.
Для получения
подробной информации о назначении
приложений панели управления следует
раскрыть окно Панель
управления и
выполнить команду Вид►Таблица.
Рассмотрим
наиболее часто используемые возможности
настройки.
Все задачи,
связанные с настройкой аппаратных
средств выполняются с использованием
мастера аппаратных средств Мастера
оборудования,
который
вызывается запуском
утилиты Установка
оборудования.
С его помощью можно устанавливать новые
аппаратные устройства, осуществлять
диагностику аппаратных конфликтов,
задавать свойства устройств, отключать
устройства.
В Windows
реализована возможность автоматизации
процесса установки нового оборудования
за счет поддержки механизма plug-and-play
(установи и используй), который предполагает
автоматическое распознавание системой
нового устройства и подбор необходимого
драйвера (ОС включает множество встроенных
драйверов для наиболее распространенных
устройств различных производителей).
Установку и
удаление программных продуктов и
компонентов операционной системы,
офисного пакета Microsoft
Office,
а также других установленных на компьютере
пакетов осуществляет утилита Установка
и удаление
программ.
С ее помощью можно также создать
загрузочный диск, позволяющий запустить
систему в критических ситуациях (при
разрушении операционной системы на
компьютере).
Утилита Язык
и стандарты
позволяет
устанавливать региональные стандарты
(отображение чисел, даты, времени,
денежных единиц) и выбирать языки ввода.
Утилита Свойства
обозревателя
позволяет выполнять индивидуальную
настройку вывода на экран и параметров
подключения к Internet.
С помощью утилиты
Дата и
Время пользователь
может
установить часовой пояс, текущие дату
и время, а также автоматический переход
на летнее время.
Утилита Клавиатура
служит для настройки языковой раскладки
клавиатуры (обычно устанавливаются
языки английский и русский, но можно
добавлять и новые, например, немецкий,
белорусский и другие), отображения ее
индикатора на Панели задач, а также
скорости повторного ввода символа.
С помощью утилиты
Мышь
можно изменить вид указателей мыши,
обеспечить удобство работы левшей.
Утилита Экран
служит для настройки фона Рабочего
стола, цветового и шрифтового оформления
элементов оконного интерфейса, параметров
монитора, заставки, появляющейся на
экране в период временного прекращения
работы пользователя.
С помощью команды
Свойства
контекстного меню объекта Windows
есть возможность настраивать некоторые
его параметры, например, можно открыть
папку для общего доступа; ограничить
доступ к ней, задав список пользователей,
имеющих разрешение на работу с ее
содержимым; разрешить только чтение
файлов из папки и др. Набор свойств,
доступных для изменения, определяется
типом объекта.
Основные возможности
настройки с использованием элементов
управления диалоговых окон операционной
системы заложены в меню Вид
и
Сервис,
например, с помощью команды Вид►Упорядочить
значки►По
имени диска в
окне Мой компьютер устанавливается
вывод списка дисков в алфавитном порядке,
а по команде Сервис►Подключить
сетевой
диск
выбранный
диск любого компьютера сети воспринимается
системой данного компьютера как один
из его «родных» дисков. В конце работы
с сетевым диском его необходимо отключить
по команде Сервис►Отключить
сетевой
диск.