This article is about the original version used prior to Windows 8. For the successor version, see Media Player (Windows 11).

Windows Media Player 12 Legacy running on Windows 11 2022 Update |
|
| Developer(s) | Microsoft |
|---|---|
| Stable release | 12.0.22621.457 (September 20, 2022; 4 months ago) [±] |
| Preview release | 12.0.25120.1000 (May 18, 2022; 8 months ago) [±] |
| Operating system |
|
| Included with |
|
| Predecessor | ActiveMovie Control, CD Player, DVD Player (Win32 version) |
| Successor | Microsoft Movies & TV, Groove Music, Media Player (Windows 11) |
| Type | Media player |
| Website | support.microsoft.com/en-gb/windows/windows-media-player-d10303a5-896c-2ce2-53d4-5bd5b9fd888b |
Windows Media Player (WMP) is the first media player and media library application that was developed by Microsoft for playing audio, video and viewing images on personal computers running the Microsoft Windows operating system, as well as on Pocket PC and Windows Mobile-based devices. Editions of Windows Media Player were also released for classic Mac OS, Mac OS X, and Solaris but development of these has since been discontinued.
Windows Media Player was eventually replaced in Windows 8 with Groove Music. Groove Music persisted in Windows 8.1 and Windows 10, before being replaced in turn with the Media Player in Windows 11.
In addition to being a media player, the application has the ability to rip audio file from and copy to compact discs, burn recordable discs in Audio CD format or as data discs with playlists such as an MP3 CD, synchronize content with a digital audio player (MP3 player) or other mobile devices, and enable users to purchase or rent music from a number of online music stores.
Windows Media Player 11 was made available for Windows XP and included in Windows Vista and Windows Server 2008. The default file formats are Windows Media Video (WMV), Windows Media Audio (WMA), and Advanced Systems Format (ASF), and its own XML based playlist format called Windows Playlist (WPL). The player is also able to utilize a digital rights management service in the form of Windows Media DRM.
Windows Media Player 12 is the most recent version of Windows Media Player prior to Windows 11. It was released on October 22, 2009, along with Windows 7[b] and has not been made available for previous versions of Windows nor has it been updated since for Windows 8, Windows 8.1, Windows 10, and Windows 11.[2][3] Windows 8 and later instead use Groove Music (for audio) and Microsoft Movies & TV (for video) as the default playback applications for most media; As of October 2021, Windows Media Player is still included as a Windows component. Windows RT does not run Windows Media Player.
On November 16, 2021, Microsoft announced that it would replace Groove Music with the new Media Player application, though the legacy Windows Media Player will continue to be optionally available with Windows 11.[4]
History[edit]
Media Player 5 running in Windows 2000.
The first version of Windows Media Player appeared in 1991, when Windows 3.0 with Multimedia Extensions was released.[5] Originally called Media Player, this component was included with «Multimedia PC»-compatible machines but not available for retail sale. It was capable of playing .mmm animation files, and could be extended to support other formats.[6] It used MCI to handle media files. Being a component of Windows, Media Player shows the same version number as that of the version Windows with which it was included.
WMP running in Windows 8.
Microsoft continually produced new programs to play media files. In November of the following year, Video for Windows was introduced with the ability to play digital video files in an AVI container format,[7] with codec support for RLE and Video1, and support for playing uncompressed files. Indeo 3.2 was added in a later release. Video for Windows was first available as a free add-on to Windows 3.1, and later integrated into Windows 95 and Windows NT 4.0. In 1995, Microsoft released ActiveMovie with DirectX Media SDK. ActiveMovie incorporates a new way of dealing with media files, and adds support for streaming media (which the original Media Player could not handle). In 1996, ActiveMovie was renamed DirectShow.[8] However, Media Player continued to come with Windows until Windows XP, in which it was officially renamed Windows Media Player v5.1.[9] («v5.1» is the version number of Windows XP).
In 1999, Windows Media Player’s versioning broke away from that of Windows itself. Windows Media Player 6.4 came as an out-of-band update for Windows 95-98 and Windows NT 4.0 that co-existed with Media Player and became a built-in component of Windows 2000, Windows ME, and Windows XP with an mplayer2.exe stub allowing to use this built-in instead of newer versions.[10] Windows Media Player 7.0 and its successors also came in the same fashion, replacing each other but leaving Media Player and Windows Media Player 6.4 intact. Windows XP is the only operating system to have three different versions of Windows Media Player (v5.1, v6.4, and v8) side by side. All versions branded Windows Media Player (instead of simply Media Player) support DirectShow codecs. Windows Media Player version 7 was a large revamp, with a new user interface, visualizations and increased functionality. Windows Vista, however, dropped older versions of Windows Media Player in favor of v11, which included the removal of the Windows Media Source Filter (DirectShow codec).
In 2004, Microsoft launched digital music store MSN Music for new Windows Media Player 10 to compete with Apple iTunes.[11][12]
However, MSN Music was discontinued already in 2006 with the launch of Zune music players.[13]
Beginning with Windows Vista, Windows Media Player supports the Media Foundation framework besides DirectShow; as such it plays certain types of media using Media Foundation as well as some types of media using DirectShow.[14] Windows Media Player 12 was released with Windows 7. It included support for more media formats and added new features. With Windows 8, however, the player did not receive an upgrade.
On April 16, 2012, Microsoft announced that Windows Media Player would not be included in Windows RT, the line of Windows designed to run on ARM-based devices.[15]
Windows 11[edit]
A different app called Media Player is the successor to Groove Music for Windows 10 (previously Xbox Music) and Windows Media Player. Media Player started to be offered to all Windows 11 users on February 15, 2022.[16]
The new Media Player can also play video, as part of Groove’s rebranding from a music streaming service to a media player.[17] Other changes include the album cover view being in fullscreen, and a refresh to the mini player.[18] Accessibility has also been optimized, with some improved keyboard shortcuts and hotkey support for keyboard users and with other assistive technologies.[19]
Features[edit]
Core playback and library functions[edit]
Windows Media Player supports playback of audio, video and pictures, along with fast forward, reverse, file markers (if present) and variable playback speed (seek & time compression/dilation introduced in WMP 9 Series). It supports local playback, streaming playback with multicast streams and progressive downloads. Items in a playlist can be skipped over temporarily at playback time without removing them from the playlist. Full keyboard-based operation is possible in the player.
Windows Media Player supports full media management, via the integrated media library introduced first in version 7, which offers cataloguing and searching of media and viewing media metadata. Media can be arranged according to album, artist, genre, date et al. Windows Media Player 9 Series introduced Quick Access Panel to browse and navigate the entire library through a menu. The Quick Access Panel was also added to the mini mode in version 10 but was entirely removed in version 11. WMP 9 Series also introduced ratings and Auto Ratings. Windows Media Player 10 introduced support for aggregating pictures, Recorded TV shows, and other media into the library. A fully featured tag editor was featured in versions 9-11 of WMP, called the Advanced Tag Editor. However, the feature was removed in Windows Media Player 12. Since WMP 9 Series, the player features dynamically updated Auto Playlists based on criteria. Auto Playlists are updated every time users open them. WMP 9 Series and later also supports Auto Ratings which automatically assigns ratings based on the number of times a song is played. Pre-populated auto playlists are included in Windows Media Player 9 Series. Custom Auto Playlists can be created only on Windows XP and later.
In Windows Media Player 11, the Quick Access Panel was removed and replaced with an Explorer-style navigation pane on the left which can be customized for each library to show the user selected media or metadata categories, with contents appearing on the right, in a graphical manner with thumbnails featuring album art or other art depicting the item. Missing album art can be added directly to the placeholders in the Library itself (though the program re-renders all album art imported this way into 1×1 pixel ratio, 200×200 resolution JPEGs). There are separate Tiles, Icons, Details or Extended Tiles views for Music, Pictures, Video and Recorded TV which can be set individually from the navigation bar. Entries for Pictures and Video show their thumbnails. Version 11 also introduced the ability to search and display results on-the-fly as characters are being entered, without waiting for Enter key to be hit. Incremental search results are refined based on further characters that are typed. Stacking allows graphical representations of how many albums there are in a specific category or folder. The pile appears larger as the category contains more albums. The List pane includes an option to prompt the user to remove items skipped in a playlist upon save or skip them only during playback.
Visualizations[edit]
Windows Media Player 11 running in mini mode (in Windows XP MCE) showing the «Bars and Waves» visualization
While playing music, Windows Media Player can show visualizations. The current three visualizations are Alchemy, which was first introduced in version 9, Bars and Waves, which has been used since version 7, and Battery, introduced version 8. «Musical Colors» was removed starting with version 9, but is retained if Windows Media Player was upgraded from version 7 or 8. Version 11 and above refrains from having the former «Ambience,” «Particle,” «Plenoptic,” and «Spikes» visualizations. The «Battery» visualization was similarly removed in later editions of version 12. The reason for their removal was that the visualizations do not support full screen controls (either the visualization gets shifted to the left while there is a thick black bar to the right side of the screen, that there are no full screen controls, or that the visualization have DXE Problems). More visualizations such as «BlazingColors,” «ColorCubes,” «Softie the Snowman,» and «Yule Log» used to be downloadable however, the downloads from Microsoft’s website have mostly been taken down and it’s available on the WMP Goodies site.
Format support[edit]
The player includes intrinsic support for Windows Media codecs and also WAV and MP3 media formats. On Windows XP and above with WMP 9 Series and later, the Windows Media Audio Professional codec is included which supports multichannel audio at up to 24-bit 192 kHz resolution. Windows Media Player 11 includes the Windows Media Format 11 runtime which adds low bitrate support (below 128 kbit/s for WMA Pro), support for ripping music to WMA Pro 10 and updates the original WMA to version 9.2.[citation needed]
Support for any media codec and container format can be added using specific DirectShow filters or Media Foundation codecs (Media Foundation codecs only in Windows Vista and later). The player will not play MP3 files that contain compressed ID3 headers («tags»), trying to do so results in a «The input media file is invalid» error message. MP3 playback support was built-in beginning with version 6.1 and audio CD playback was natively supported with version 7.[citation needed]
DVD playback features minus the necessary decoders were integrated into Windows Media Player 8 for Windows XP. The player activates DVD and Blu-ray playback functionality with support for menus, titles and chapters, parental controls and audio track language selection if compatible decoders are installed. MPEG-2 and Dolby Digital (AC-3) decoders were included beginning with Windows Media Player 11 on Windows Vista (Home Premium and Ultimate editions only) and Windows 7 (Home Premium, Ultimate, or Enterprise editions) to allow DVD playback without additional software. However, the decoders were subsequently removed in Windows 8 and Windows 10 due to licensing costs.[20]
Windows Media Player 12 adds native support for H.264 and MPEG-4 Part 2 video formats, ALAC, AAC audio[21] and 3GP[clarification needed got no codec available for 3GP], MP4 and MOV container formats.[22] Windows Media Player 12 is also able to play AVCHD formats (.M2TS and .mts).[23]
As of Windows 10 version 1507, Windows Media Player 12 can play FLAC, HEVC, and SubRip subtitle, and Matroska container formats.[24] Although the WebM file type is not officially associated with Windows Media Player 12 (the default player is Microsoft Movies & TV), playback of VP9 video in WebM container is possible on Windows 10 version 1809 and later.[25]
Windows Media Player Mobile[edit]
Windows Media Player Mobile 10 on Windows Mobile 6.5 supports MP3, ASF, WMA, and WMV using WMV or MPEG-4 codecs.[26]
Disc burning, ripping, and playback[edit]
Windows Media Player features integrated Audio CD-burning support since version 7 as well as data CD burning support since Windows Media Player 9 Series on Windows XP and later. Data CDs can have any of the media formats supported by the player. While burning Data CDs, the media can, optionally, be transcoded into WMA format and playlists can be added to the CD as well. Starting with WMP 9 Series, audio CDs can be burnt with volume leveling.
Audio CDs can be ripped as WMA or WMA 10 Pro (WMA 10 Pro in WMP 11 and later) at 48, 64, 96, 128, 160, and 192 kbit/s, WMA lossless (470 to 940 kbit/s) (9 Series on XP and later), WMA variable bitrate (from 40 to 75 kbit/s up to 240-355 kbit/s), MP3 at 128, 192, 256, and 320 kbit/s, or uncompressed WAV (WAV ripping in WMP 11 and later). Since WMP 9 Series, 20 bit high-resolution CDs (HDCDs) are also supported, if capable audio hardware is present. Audio can be ripped using error correction and ripped audio can be protected with Windows Media DRM. Ripping to MP3 is supported only in Windows Media Player 8 for Windows XP and later if a compatible MP3 encoder is installed. Windows Media Player 10 included the Fraunhofer MP3 Professional encoder. Information on CDs such as album name, artist and track listings can optionally be automatically downloaded from the online Windows Media database when the CD is inserted. Version 11 added support for ripping audio CDs to WAV and WMA 10 Pro formats. With their 2015 implementation in Windows 10, Version 12 also added lossless FLAC and ALAC formats for ripping and playback. For burning, version 11 shows a graphical bar indicating how much space will be used on the disc and introduced Disc spanning which splits a burn list onto multiple discs in case the content does not fit on one disc.
Portable device sync[edit]
Windows Media Player allows the user to connect, share and sync data with portable handheld devices and game consoles since version 7. Media can be optionally transcoded to a format better suited for the target device, automatically, when synchronizing. When deleting playlists from devices, Windows Media Player can automatically remove their contents. Devices can be formatted using Windows Media Player 9 Series and later. Version 10 and later support the Media Transfer Protocol and Auto Sync. Auto Sync allows users to specify criteria such as recently added music or highest rated songs, by which media will be automatically synchronized with the portable device and other advanced features like setting the clock on the portable device automatically, communicating with the device to retrieve the user’s preferences. Windows Media Player 10 also introduced the UMDF-based Windows Portable Devices API.
Version 11 has improved synchronization features for loading content onto PlaysForSure-compatible portable players. WMP 11 supports reverse-synchronization, by which media present on the portable device can be replicated back to the PC. Shuffle Sync can be used to randomize content synced with the portable device, Multi PC Sync to synchronize portable device content across multiple PCs and Guest Sync to synchronize different content from multiple PCs with the portable device. Portable devices appear in the navigation pane of the library where their content can be browsed and searched.
Windows Media Player’s ‘Sync’ function has options that allow it to be set to automatically down-convert (transcode) high bit-rate song files to a lower bit-rate. This down-conversion function is switched on by default. This is useful for providing low bit-rate files to those portable devices that need them, and to save space on portable devices with smaller storage capacities. For high bit-rate capable devices with sufficient storage capabilities, the down conversion process can be omitted.
In versions 11 (2006) and 12 (2009), the Quality settings that the user has selected in the Windows Media Player settings for Sync, for that specific portable device, are used to control the quality (bit-rate) of files that are copied to the portable device. Leaving the Quality settings to Automatic will often result in 192kbs files being copied to the portable device. Manual settings can also be made. 192kbs is the highest quality down-conversion bit-rate that can be manually selected when the Sync function’s down-conversion function is turned on. Lower bit-rates can also be selected.
For portable devices that can handle high bit-rate files, the best quality files are obtained by leaving the down-conversion process switched off (unchecked) for that specific device. In Windows Media Player Version 11, switching off the down-conversion function is done in the Quality tab of the Advanced Options of the Sync settings for the device. In Windows Media Player Version 12, switching off the down-conversion function is done in the Quality tab of the Properties for the device in the Select Settings for the device in the Sync Options menu.
When set up in such a way, Windows Media Player’s ‘Sync’ function can be used to sync unchanged high bit-rate song files to suitable portable devices (i.e. those capable of using file formats such as WMA Lossless, mp3-360kbs, etc.). For example, some users have created large song libraries on their PCs containing .wma formatted song files using the high bit-rate WMA Lossless (WMA-LL) protocol, or using other high bit-rate song file formats. The WMA-LL protocol is selectable in Windows Media Player as an option when ripping songs from CDs. The resulting bit-rates seen on ripped WMA-LL files are often 3 to 6 times higher than 192kbs, and can typically fall anywhere in the range of 600kbs to 1200kbs, depending on the quality of the source file that was present on the CD in the first place. The sound quality is much improved over the default rate, although the file size is larger.
At the time that Versions 11 and 12 were released, the capabilities and capacities of portable devices typically required down-conversion of the bit-rates of the files placed on the portable devices. Thus, Sync down-conversion was turned on by default. This was to ensure playability of the files and to ensure that the file sizes were small enough to efficiently fit a reasonably large selection of songs on the portable device.
In recent years (circa 2012), portable devices became available that could natively play these Windows Media Player produced high bit-rate WMA-LL files (and others), and that have storage capacities suitable for large collections of high bit-rate song files. This made it much more practicable and desirable to use software programs such as Windows Media Player to synchronize previously PC-bound libraries of high bit-rate songs to these new portable devices.
Enhanced playback features[edit]
Windows Media Player features universal brightness, contrast, saturation and hue adjustments and pixel aspect ratio for supported video formats. It also includes a 10-band graphic equalizer with presets and SRS WOW audio post-processing system. Windows Media Player can also have attached audio and video DSP plug-ins which process the output audio or video data. Video Smoothing was introduced in WMP 9 Series (Windows XP and later only) which upscales frame-rate by interpolating added frames, in effect giving a smoother playback on low-framerate videos. The player supports subtitles and closed-captioning for local media, video on demand streaming or live streaming scenarios. Typically Windows Media captions support the SAMI file format but can also carry embedded closed caption data.
The player can use video overlays or VMR (Video Mixing Renderer) surfaces, if the video card supports them. In Windows XP, it uses VMR7 by default, but can also be made to use the more advanced YUV mixing mode by enabling the «Use high quality mode» option in Advanced Performance settings. This turns on deinterlacing, scaling and improved color accuracy.[27] WMP 9 Series introduced native playback for deinterlacing for TV output. Version 9 introduced DXVA accelerated playback. Version 11 introduced improved support for DirectX accelerated decoding of WMV video (DXVA decoding). Up to version 11, it supported static lyrics and «Synchronized Lyrics,” by which different lines of lyrics can be time-stamped, so that they display only at those times. Synchronized Lyrics also were accessible through the Advanced Tag Editor which was removed in version 12.
Since Windows Media Player 9 Series, the player supports crossfading, audio dynamic range (Quiet Mode) for WMA Pro and WMA Lossless, and auto volume leveling for certain media which includes volume level/gain information such as MP3 or Windows Media. The player also supports extensive configurable privacy and security settings.
Shell integration[edit]
The player has Windows Explorer shell integration to add files and playlist to the Now Playing pane and other playlists can be controlled from the Windows Explorer shell itself, via right-click menu. The My Music folder also includes a separate My Playlists folder where playlists are maintained. When the player is closed and reopened, simply clicking the play button restores the last playlist even if it was not saved. Starting with Windows Media Player 10, the playlist pane is also visible from the Library view. AutoPlay handlers in Windows expose various Windows Media Player tasks.
Windows Media Player 11 running in mini mode in Windows Vista and Windows XP respectively. Notice the difference in the logo.
Up to version 11, it featured a taskbar-mounted Mini mode in which the most common media control buttons are presented as a toolbar on the Windows taskbar. Flyout windows can display media information, the active visualization or the video being played back. Mini-mode was introduced as a shell player powertoy for Windows Media Player 8 in Windows XP and integrated later into WMP 9 Series. Mini-mode has been removed in Windows Media Player 12 in favor of controls in the taskbar’s interactive thumbnail preview which lacks volume control, a progress bar and information displayed whenever a new song is played.
The user interface has been redesigned in Windows Media Player 12 such that the Now Playing view plays media in a separate minimalist window with floating playback controls, and also gives access to the current playlist, visualizations, and enhancements.[21] Enhancements are housed in individual undocked windows. The library view includes the rest of the media management functions. It also can preview songs from the library when users hover over the media file and click the Preview button.[21] Windows Media Player 12 can play unprotected songs from the iTunes library. The taskbar-integrated Mini-player has been replaced with controls in the taskbar’s interactive thumbnail preview (called the Thumbnail Toolbar),[28] albeit minus the volume control function, track and album information shown whenever a new song is played and the progress bar. The taskbar icon also supports jump lists introduced in Windows 7.
The thumbnail viewer of Windows Media Player 12 in Windows 7 Home Premium
Extensibility[edit]
The player has had skinning support since Windows Media Player (WMP) 7 and includes a color chooser since the WMP 9 Series. Not all functions are usually exposed in skin mode. Windows Media Player 10 allows setting the video border color. Color chooser has been removed in WMP 12. It supports visualizations and Info Center View (Info Center View in WMP 9 Series and later) which displays media metadata fetched from the internet. Full screen visualizations are supported in WMP 9 Series and later. It supports Background plug-ins, window plug-ins and Now Playing plug-ins to control media playback besides DSP and renderer plug-ins. Plug-in support was introduced in WMP 9 Series.
Online features[edit]
The player integrates web-browsing support to browse online music stores, shop for music and tune to internet radio stations since version 7. It provides an embeddable ActiveX control for Internet Explorer so that developers can play Windows Media on web pages. Windows Media Player 10 and later feature integration with a large number of online music stores and selecting a music store switches the Info Center view, radio and other online features to use services from that store. Purchased music from a particular store appears in a separate library node under the respective category.
Media streaming[edit]
Previously, Microsoft had released Windows Media Connect for Windows XP to stream media content with its built-in UPnP media server. With version 11 of Windows Media Player, Media Sharing was integrated and allows content (Music, Pictures, Video) to be streamed to and from Universal Plug and Play (UPnP) AV enabled devices such as the PS3, Xbox 360, and Roku SoundBridge. This includes DRM protected PlaysForSure content. WMP 11 on Windows Vista can also act as a client to connect to remote media libraries using this feature; this is not available on the Windows XP version.
With version 12, media streaming was further improved. While previous versions streamed media to UPnP compliant devices (Digital Media Server role) and could play media by fetching it from a network share (Digital Media Player role),[29] Windows Media Player 12 can access media from the shared media libraries on the network or HomeGroup, stream media to DLNA 1.5 compliant devices and allows itself (once the remote control option is turned on) to be remotely controlled by Digital Media Controller devices which stream media (Digital Media Renderer role).[29] Similarly, the Play To feature once enabled for remote PCs, by turning on remote control of the player, allows compliant devices and computers to be discovered and controlled remotely from a computer running Windows Media Player 12 (Digital Media Controller role).[29] If the devices do not support the streamed format, Windows Media Player 12 transcodes the format on-the-fly. Media from a home network can also be streamed over the internet using an Online ID Provider service, which handles discovery of the computer’s IP address, authorization, security, connectivity and Quality of Service issues.[29]
Skin Mode[edit]
Windows Media Player also features skins. Currently, Windows Media Player has two default skins: «Corporate,” which was first introduced in version 8, and «Revert,” which first shipped with version 9. In versions 7 and 8, there were many unusual skins such as «Heart,” «Headspace,” «Canvas,” «Goo,” and «Atomic,” which were removed starting with version 9, but are retained if the player is upgraded, although some can still be downloaded from an archive of the Microsoft website.[30] In versions 7, 8, 9, and 10 there were many usual skins such as «9SeriesDefault,” «Atomic,” «Bluesky,” «Canvas,” «Classic,” «Compact,” «goo,” «Headspace,” «heart,” «iconic,” «Miniplayer,” «Optic,” «Pyrite,” «QuickSilver,” «Radio,” «Roundlet,” «Rusty,” «splat,” «Toothy,” «Windows Classic,” and «Windows XP,” which were removed starting with version 11. This Corporate skin is not deletable.
Security issues[edit]
Microsoft Windows Media Runtime in Windows 2000, Windows XP, Windows Vista and Windows Server contained a bug that permitted «remote code execution if a user opened a specially crafted media file». Such a file would allow the attacker to «then install programs; view, change, or delete data; or create new accounts with full user rights», if the account on which the file was played had administrator privileges.[31] The problem was addressed in a critical update issued on September 8, 2009.[32]
Other versions[edit]
Microsoft has also released versions of Windows Media Player for other platforms including Windows Mobile, classic Mac OS, Mac OS X, Palm-size PC, Handheld PC, and Solaris. Of these, only the Windows Mobile edition continues to be actively developed and supported by Microsoft. Version 1 of the Zune software was also based on Windows Media Player; later versions are not.
Windows Mobile[edit]
Windows Media Player 10.3 Mobile on a Windows Mobile Professional device
Windows Media Player for Pocket PC was first announced on January 6, 2000, and has been revised on a schedule roughly similar to that of the Windows version.[33] Currently known as «Media Player 10 Mobile,” this edition (released in October 2004) closely resembles the capabilities of the Windows version of WMP 10, including playlist capabilities, a media library, album art, WMA Lossless playback, support for DRM-protected media, video playback at 640×480 with stereo sound, and the same Energy Blue interface aesthetics also seen in Windows XP Media Center Edition 2005. It also supports synchronization with the desktop version of WMP 10, and additionally supports synchronizing and transcoding of recorded television shows from Media Center. Media Player 10 Mobile is not available as a download from Microsoft, distribution is done solely through OEM partners, and is typically included on devices based on Windows Mobile.
Windows Mobile 6 includes a copy of Windows Media Player 10 Mobile, but with a similar (but not quite identical) theme as Windows Media Player 11.
Mac OS X[edit]
Version 9 was the final version of Windows Media Player to be released for Mac OS X before development was canceled by Microsoft. It was developed by the Windows Media team at Microsoft instead of the Macintosh Business Unit and released in 2003. On release the application lacked many basic features that were found in other media players such as Apple’s iTunes and QuickTime.[citation needed] It also lacked support for many media formats that version 9 of the Windows counterpart supported on release 10 months earlier.
The Mac version supported only Windows Media encoded media (up to version 9) enclosed in the ASF format, lacking support for all other formats such as MP4, MPEG, and Microsoft’s own AVI format. On the user interface front, it did not prevent screensavers from running during playback, it did not support file drag-and-drop, nor did it support playlists. While Windows Media Player 9 had added support for some files that use the WMV9 codec (also known as the WMV3 codec by the FourCC), in other aspects it was seen as having degraded in features from previous versions.
On January 12, 2006, Microsoft announced it had ceased development of Windows Media Player for Mac. Microsoft now distributes a third-party plugin called WMV Player (produced and maintained by Flip4Mac) which allows some forms of Windows Media to be played within Apple’s QuickTime Player and other QuickTime-aware applications.[34]
European Commission case[edit]
In March 2004, the European Commission in the European Union Microsoft antitrust case fined Microsoft €497 million and ordered the company to provide a version of Windows without Windows Media Player, claiming Microsoft «broke European Union competition law by leveraging its near monopoly in the market for PC operating systems onto the markets for work group server operating systems and for media players.” The company has made available a compliant version of its flagship operating system under the negotiated name «Windows XP N,” though the product has not been very successful. Windows Vista, Windows 7 and Windows 8 are also available in «N» editions. However, it is possible to either install Windows Media Player (XP/Vista)[35] or the Media Restore Pack through Windows Update (Vista) to add the media player.
Release history[edit]
Prior to the release of Windows Media Player in Windows 98 Second Edition, separate programs, CD Player, Deluxe CD Player, DVD Player and Media Player, were included in old versions of Microsoft Windows for playback of media files.
| Version | Original release | Included with | Available for | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Microsoft Windows | ||||
| Media Player | February 15, 2022 | Windows 11 | — | |
| Windows Media Player 12 | July 22, 2009 | Windows 7 Windows 8 Windows 8.1 Windows 10 Windows 11 Windows Server 2008 R2 Windows Server 2012 Windows Server 2012 R2 Windows Server 2016 Windows Server 2019 Windows Server 2022 |
— | 
|
| Windows Media Player 11 | October 18, 2006 | Windows Vista Windows Server 2008 |
Windows XP (SP2+) Windows XP x64 Edition |
|
| Windows Media Player 10 | August 25, 2004 | Windows XP x64 Edition Windows XP Media Center Edition 2005 Windows Server 2003 (SP1+) |
Windows Server 2003 Windows XP[37] |
|
| Windows Media Player 9 Series | January 7, 2003[38] | Windows XP (SP2+) Windows Server 2003 (RTM) |
Windows XP Windows ME Windows 2000 Windows 98 SE[39] |
|
Windows Media Player for Windows XP (version  |
August 24, 2001 | Windows XP (RTM & SP1) | — | |
| Windows Media Player 7.1 | May 16, 2001 | Windows 2000 (SP2+) | Windows ME Windows 2000 Windows 98[39][40] |
|
| Windows Media Player 7.0 | June 19, 2000[41] | Windows ME | Windows 2000 Windows 98 Windows 95 |
|
| Windows Media Player 6.4[c] | September 15, 1999 | Windows 2000 Windows ME (hidden) Windows XP (hidden) Windows Server 2003 (hidden) Internet Explorer 5.01 Internet Explorer 5.5 Internet Explorer 6.0 |
Windows 98 Windows NT 4.0 Windows 95 |
|
| Windows Media Player 6.1 | March 1999 | Windows 98 SE Internet Explorer 5.0 |
Windows 98 Windows NT 4.0 Windows 95 |
|
| Microsoft Media Player 5.1 | 2001 | Windows XP (hidden) | — | |
| Media Player 5.0 | 1999 | Windows 2000 (hidden) | — | |
| Media Player 4.9 | 2000 | Windows ME (hidden) | — | |
| Media Player 4.1 | 1998 | Windows 98 Windows 98 SE (hidden) |
— | |
| Media Player 4.0 | 1995 | Windows 95 Windows NT 4.0 |
— | |
| Media Player 3.51 | 1995 | Windows NT 3.51 | — | |
| Media Player 3.5 | 1994 | Windows NT 3.5 | — | |
| Media Player 3.15 | 1992 | — | Windows 3.1 with Video for Windows | |
| Media Player 3.1 | 1992 | Windows 3.1 Windows NT 3.1 |
— | |
| Media Player 3.0 | 1991 | — | Windows 3.0 with Multimedia Extension | |
| Windows Mobile | ||||
| Windows Media Player 10.3 Mobile | February 12, 2007 (Windows Mobile 6) | Windows Mobile 6.1 Windows Mobile 6 |
Windows Mobile 5.0 | 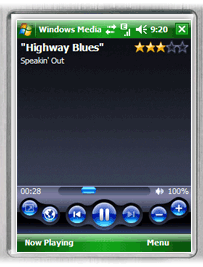
|
| Windows Media Player 10.2 Mobile | ? | Windows Mobile 5.0 | — | |
| Windows Media Player 10.1 Mobile | May 10, 2005 | Windows Mobile 5.0 | — | |
| Windows Media Player 10 Mobile | October 12, 2004 | Windows Mobile 2003 SE | — | |
| Windows Media Player 9.0.1 | March 24, 2004 | Windows Mobile 2003 SE | — | |
| Windows Media Player 9 Series | June 23, 2003 | Windows Mobile 2003 | — | |
| Windows Media Player 8.5 | October 11, 2002 | Pocket PC 2002 | — | |
| Windows Media Player 8.01 | July 2002 | Pocket PC 2002 | — | |
| Windows Media Player 8 | October 4, 2001 (Pocket PC) | Pocket PC 2002 Smartphone 2002 |
— | |
| Windows Media Player 7.1 | May 21, 2001 | Pocket PC 2000 | — | |
| Windows Media Player 7 | December 12, 2000 | Pocket PC 2000 | — | |
| Windows Media Player 1.2 | September 7, 2000 | Handheld PC 2000 | — | |
| Windows Media Player 1.1 | ? | Palm-size PC CE 2.11 | — | |
| Windows Media Player | April 19, 2000 | Pocket PC 2000 | — | |
| Mac | ||||
| Windows Media Player 9 Series | November 7, 2003 | — | Mac OS X | |
| Windows Media Player 7 | July 24, 2001 | Mac OS 9 | Mac OS 8.x | |
| Windows Media Player 6.3 | July 17, 2000 | Mac OS 8 | Mac OS 7.x | |
| Solaris | ||||
| Windows Media Player 6.3 | July 17, 2000 | — | Solaris |
See also[edit]
- Comparison of media players
- Comparison of video player software
- Groove Music
- Media Player Classic, a media player that mimics the appearance of Windows Media Player 6.4
- Media Transfer Protocol
- Windows Media Encoder
- Windows Media Services
Footnotes[edit]
- ^ Except for «N» and «KN» editions of Windows, as well as Windows RT
- ^ N and KN versions of Windows 7 do not include Windows Media Player by default.[1]
- ^ Windows Media Player 6.4 was shipped side-by-side with later versions of WMP in Windows ME and Windows XP
References[edit]
- ^ «Microsoft Documentation Page». Microsoft Docs. October 22, 2020. Archived from the original on February 9, 2021.
- ^ LeBlanc, Brandon (July 22, 2009). «Windows 7 Has Been Released to Manufacturing». Blogging Windows. Microsoft. Archived from the original on September 26, 2015. Retrieved December 21, 2020.
- ^ «Windows Media Player 12 — Windows 7 features». Windows. Microsoft. Archived from the original on September 22, 2009. Retrieved June 15, 2011.
- ^ Hachman, Mark (2021-11-16). «Windows Media Player is getting a long-overdue upgrade». PCWorld.
- ^ «Windows Version History». Support (4.0 ed.). Microsoft. September 23, 2011. Archived from the original on February 26, 2015. Retrieved May 2, 2009.
- ^ Lineback, Nathan. «Windows 3.0 with Multimedia Extensions». Toasty Tech. Archived from the original on April 15, 2009. Retrieved May 2, 2009.
- ^ «Video for Windows». PC Tech Guide. Archived from the original on April 10, 2009. Retrieved May 2, 2009.
- ^ Blome, Michael; Wasson, Mike (July 2002). «DirectShow: Core Media Technology in Windows XP Empowers You to Create Custom Audio/Video Processing Components». MSDN Magazine. Microsoft. Archived from the original on September 14, 2008. Retrieved May 1, 2009.
- ^
C:Windowssystem32myplay32.exe. Windows XP. Microsoft Corporation. - ^ «MPLAYER2.EXE Is Linked to Missing Export MSDXM.OCX». Support. Microsoft. April 25, 2006. Archived from the original on March 14, 2007. Retrieved February 13, 2015.
- ^ «MSN Music to offer free songs». Archived from the original on 2020-09-21. Retrieved 2020-05-21.
- ^ «MSN Launches Preview Release of Music Download Service». September 2004. Archived from the original on 2020-08-06. Retrieved 2020-05-21.
- ^ «MSN Music Shutting Down for Zune». Archived from the original on 2020-08-13. Retrieved 2020-05-21.
- ^ «DSP Plug-in Packaging». MSDN. Microsoft. Archived from the original on 2010-11-05. Retrieved 2010-04-08.
- ^ LeBlanc, Brandon (April 16, 2012). «Windows Announcing the Windows 8 Editions». The Windows Blog. Archived from the original on April 18, 2012.
- ^ «Media Player is available for Windows 11». 16 November 2021.
- ^ «Microsoft is replacing Windows Media Player with Media Player for Windows 11». Engadget. Retrieved 2021-11-18.
- ^ «Full screen album art». 16 November 2021.
- ^ «Optimized accessibility». 16 November 2021.
- ^ «DVD playback options for Windows». Windows help & learning.
- ^ a b c Peter Bright (October 30, 2008). «Hands on: Windows Media Player 12’s surprising new features». ArsTechnica. Condé Nast Digital. Archived from the original on March 27, 2009. Retrieved March 25, 2009.
- ^ «Windows 7 RC to natively support .mov files». Chakkaradeep Chandran. Neowin.net. February 26, 2009. Archived from the original on July 3, 2012. Retrieved March 25, 2009.
- ^ «Windows 7 next generation camera support». Download Center. Microsoft. Archived from the original (PPTX) on December 27, 2008.
- ^ «Native MKV, FLAC And HEVC Support In Windows 10». Lifehacker Australia. 29 November 2014.
- ^ «Windows 10 1809 Built-In Apps: What to Keep». Vacuum Breather.
- ^ «Formats supported by Windows Media Player Mobile». MSDN. Microsoft. April 8, 2010. Archived from the original on November 18, 2012. Retrieved November 7, 2012.
- ^ «Windows Media Player manual». Download Center. Microsoft. September 1, 2004. Archived from the original (DOC) on June 7, 2005.
- ^ Kiriaty, Yochay; Goldshtein, Sasha (July 2009). «Introducing The Taskbar APIs». MSDN Magazine. Microsoft. Thumbnail Toolbars. Archived from the original on 2015-03-25. Retrieved 2015-04-23.
- ^ a b c d Sinofsky, Steven (May 12, 2009). «Media Streaming with Windows 7». Engineering Windows 7. Microsoft. Archived from the original on July 12, 2011. Retrieved April 23, 2015.
- ^ «Skins for Windows Media Player». Windows. Microsoft. Archived from the original on June 9, 2016.
- ^ «Microsoft Security Bulletin MS09-047: Critical Vulnerabilities in Windows Media Format Could Allow Remote Code Execution». Microsoft TechNet. Microsoft. September 8, 2009. Archived from the original on July 31, 2010. Retrieved June 5, 2010.
- ^ «MS09-047: Description of the security update for Windows Media Format Runtime, Windows Media Services, and Media Foundation: September 8, 2009». Support. Microsoft. September 10, 2009. Archived from the original on May 19, 2010. Retrieved June 5, 2010.
- ^ «Microsoft Unveils Windows Media Player for Palm-Size and Pocket PCs». News Center. Microsoft. January 6, 2000. Archived from the original on August 6, 2020. Retrieved January 31, 2017.
- ^ «Windows Media Components for QuickTime». Microsoft. Archived from the original on January 12, 2006. Retrieved March 30, 2007.
- ^ Microsoft. Download Center Archived 2017-07-25 at the Wayback Machine. «be used to restore Windows Media Player and related technologies to N and KN editions of Windows Vista.» Retrieved July 26, 2008
- ^ «Get Windows Media Player». Windows. Microsoft. Archived from the original on August 25, 2010. Retrieved November 5, 2011.
- ^ «MS09-037: Description of the security update for Windows Media Player: August 11, 2009». Support. Microsoft. May 8, 2012. Archived from the original on September 21, 2013. Retrieved August 12, 2013.
- ^ «Final Release of Windows Media 9 Series Starts Next Wave of Digital Media». News Center. Microsoft. January 7, 2003. Archived from the original on February 3, 2016. Retrieved September 29, 2015.
- ^ a b Petri, Daniel (2009-01-08). «Download Windows Media Player 9». Petri. Archived from the original on 2019-02-13. Retrieved 2019-02-12.
- ^ «Windows Media Player 7.1 for Windows 98, 2000, and Me 7.1 — BumperSoft». www.bumpersoft.com. Archived from the original on 2019-02-13. Retrieved 2019-02-12.
- ^ «Microsoft Windows Media Player 7 Brings Click and Play Digital Media To Millions Around the Globe». News Center. Microsoft. July 17, 2000. Archived from the original on May 27, 2015. Retrieved June 15, 2011.
Further reading[edit]
- Liron, Marc (2004). «A Little Windows Media Player History…» Windows XP Media Player — The Best There Is?. Archived from the original on January 18, 2008. Retrieved October 7, 2011.
- «The default codecs that are included with Windows Media Player 9 and with Windows Media Player 10 (Revision 1.1)». Microsoft Support Center. Microsoft Corporation. August 4, 2005. Archived from the original on November 20, 2011. Retrieved October 7, 2011.
External links[edit]
- Official website
- The Vintage Windows Media Player
- wmplugins.com — The place to find and share plug-ins, skins and visualizations.
This article is about the original version used prior to Windows 8. For the successor version, see Media Player (Windows 11).

Windows Media Player 12 Legacy running on Windows 11 2022 Update |
|
| Developer(s) | Microsoft |
|---|---|
| Stable release | 12.0.22621.457 (September 20, 2022; 4 months ago) [±] |
| Preview release | 12.0.25120.1000 (May 18, 2022; 8 months ago) [±] |
| Operating system |
|
| Included with |
|
| Predecessor | ActiveMovie Control, CD Player, DVD Player (Win32 version) |
| Successor | Microsoft Movies & TV, Groove Music, Media Player (Windows 11) |
| Type | Media player |
| Website | support.microsoft.com/en-gb/windows/windows-media-player-d10303a5-896c-2ce2-53d4-5bd5b9fd888b |
Windows Media Player (WMP) is the first media player and media library application that was developed by Microsoft for playing audio, video and viewing images on personal computers running the Microsoft Windows operating system, as well as on Pocket PC and Windows Mobile-based devices. Editions of Windows Media Player were also released for classic Mac OS, Mac OS X, and Solaris but development of these has since been discontinued.
Windows Media Player was eventually replaced in Windows 8 with Groove Music. Groove Music persisted in Windows 8.1 and Windows 10, before being replaced in turn with the Media Player in Windows 11.
In addition to being a media player, the application has the ability to rip audio file from and copy to compact discs, burn recordable discs in Audio CD format or as data discs with playlists such as an MP3 CD, synchronize content with a digital audio player (MP3 player) or other mobile devices, and enable users to purchase or rent music from a number of online music stores.
Windows Media Player 11 was made available for Windows XP and included in Windows Vista and Windows Server 2008. The default file formats are Windows Media Video (WMV), Windows Media Audio (WMA), and Advanced Systems Format (ASF), and its own XML based playlist format called Windows Playlist (WPL). The player is also able to utilize a digital rights management service in the form of Windows Media DRM.
Windows Media Player 12 is the most recent version of Windows Media Player prior to Windows 11. It was released on October 22, 2009, along with Windows 7[b] and has not been made available for previous versions of Windows nor has it been updated since for Windows 8, Windows 8.1, Windows 10, and Windows 11.[2][3] Windows 8 and later instead use Groove Music (for audio) and Microsoft Movies & TV (for video) as the default playback applications for most media; As of October 2021, Windows Media Player is still included as a Windows component. Windows RT does not run Windows Media Player.
On November 16, 2021, Microsoft announced that it would replace Groove Music with the new Media Player application, though the legacy Windows Media Player will continue to be optionally available with Windows 11.[4]
History[edit]
Media Player 5 running in Windows 2000.
The first version of Windows Media Player appeared in 1991, when Windows 3.0 with Multimedia Extensions was released.[5] Originally called Media Player, this component was included with «Multimedia PC»-compatible machines but not available for retail sale. It was capable of playing .mmm animation files, and could be extended to support other formats.[6] It used MCI to handle media files. Being a component of Windows, Media Player shows the same version number as that of the version Windows with which it was included.
WMP running in Windows 8.
Microsoft continually produced new programs to play media files. In November of the following year, Video for Windows was introduced with the ability to play digital video files in an AVI container format,[7] with codec support for RLE and Video1, and support for playing uncompressed files. Indeo 3.2 was added in a later release. Video for Windows was first available as a free add-on to Windows 3.1, and later integrated into Windows 95 and Windows NT 4.0. In 1995, Microsoft released ActiveMovie with DirectX Media SDK. ActiveMovie incorporates a new way of dealing with media files, and adds support for streaming media (which the original Media Player could not handle). In 1996, ActiveMovie was renamed DirectShow.[8] However, Media Player continued to come with Windows until Windows XP, in which it was officially renamed Windows Media Player v5.1.[9] («v5.1» is the version number of Windows XP).
In 1999, Windows Media Player’s versioning broke away from that of Windows itself. Windows Media Player 6.4 came as an out-of-band update for Windows 95-98 and Windows NT 4.0 that co-existed with Media Player and became a built-in component of Windows 2000, Windows ME, and Windows XP with an mplayer2.exe stub allowing to use this built-in instead of newer versions.[10] Windows Media Player 7.0 and its successors also came in the same fashion, replacing each other but leaving Media Player and Windows Media Player 6.4 intact. Windows XP is the only operating system to have three different versions of Windows Media Player (v5.1, v6.4, and v8) side by side. All versions branded Windows Media Player (instead of simply Media Player) support DirectShow codecs. Windows Media Player version 7 was a large revamp, with a new user interface, visualizations and increased functionality. Windows Vista, however, dropped older versions of Windows Media Player in favor of v11, which included the removal of the Windows Media Source Filter (DirectShow codec).
In 2004, Microsoft launched digital music store MSN Music for new Windows Media Player 10 to compete with Apple iTunes.[11][12]
However, MSN Music was discontinued already in 2006 with the launch of Zune music players.[13]
Beginning with Windows Vista, Windows Media Player supports the Media Foundation framework besides DirectShow; as such it plays certain types of media using Media Foundation as well as some types of media using DirectShow.[14] Windows Media Player 12 was released with Windows 7. It included support for more media formats and added new features. With Windows 8, however, the player did not receive an upgrade.
On April 16, 2012, Microsoft announced that Windows Media Player would not be included in Windows RT, the line of Windows designed to run on ARM-based devices.[15]
Windows 11[edit]
A different app called Media Player is the successor to Groove Music for Windows 10 (previously Xbox Music) and Windows Media Player. Media Player started to be offered to all Windows 11 users on February 15, 2022.[16]
The new Media Player can also play video, as part of Groove’s rebranding from a music streaming service to a media player.[17] Other changes include the album cover view being in fullscreen, and a refresh to the mini player.[18] Accessibility has also been optimized, with some improved keyboard shortcuts and hotkey support for keyboard users and with other assistive technologies.[19]
Features[edit]
Core playback and library functions[edit]
Windows Media Player supports playback of audio, video and pictures, along with fast forward, reverse, file markers (if present) and variable playback speed (seek & time compression/dilation introduced in WMP 9 Series). It supports local playback, streaming playback with multicast streams and progressive downloads. Items in a playlist can be skipped over temporarily at playback time without removing them from the playlist. Full keyboard-based operation is possible in the player.
Windows Media Player supports full media management, via the integrated media library introduced first in version 7, which offers cataloguing and searching of media and viewing media metadata. Media can be arranged according to album, artist, genre, date et al. Windows Media Player 9 Series introduced Quick Access Panel to browse and navigate the entire library through a menu. The Quick Access Panel was also added to the mini mode in version 10 but was entirely removed in version 11. WMP 9 Series also introduced ratings and Auto Ratings. Windows Media Player 10 introduced support for aggregating pictures, Recorded TV shows, and other media into the library. A fully featured tag editor was featured in versions 9-11 of WMP, called the Advanced Tag Editor. However, the feature was removed in Windows Media Player 12. Since WMP 9 Series, the player features dynamically updated Auto Playlists based on criteria. Auto Playlists are updated every time users open them. WMP 9 Series and later also supports Auto Ratings which automatically assigns ratings based on the number of times a song is played. Pre-populated auto playlists are included in Windows Media Player 9 Series. Custom Auto Playlists can be created only on Windows XP and later.
In Windows Media Player 11, the Quick Access Panel was removed and replaced with an Explorer-style navigation pane on the left which can be customized for each library to show the user selected media or metadata categories, with contents appearing on the right, in a graphical manner with thumbnails featuring album art or other art depicting the item. Missing album art can be added directly to the placeholders in the Library itself (though the program re-renders all album art imported this way into 1×1 pixel ratio, 200×200 resolution JPEGs). There are separate Tiles, Icons, Details or Extended Tiles views for Music, Pictures, Video and Recorded TV which can be set individually from the navigation bar. Entries for Pictures and Video show their thumbnails. Version 11 also introduced the ability to search and display results on-the-fly as characters are being entered, without waiting for Enter key to be hit. Incremental search results are refined based on further characters that are typed. Stacking allows graphical representations of how many albums there are in a specific category or folder. The pile appears larger as the category contains more albums. The List pane includes an option to prompt the user to remove items skipped in a playlist upon save or skip them only during playback.
Visualizations[edit]
Windows Media Player 11 running in mini mode (in Windows XP MCE) showing the «Bars and Waves» visualization
While playing music, Windows Media Player can show visualizations. The current three visualizations are Alchemy, which was first introduced in version 9, Bars and Waves, which has been used since version 7, and Battery, introduced version 8. «Musical Colors» was removed starting with version 9, but is retained if Windows Media Player was upgraded from version 7 or 8. Version 11 and above refrains from having the former «Ambience,” «Particle,” «Plenoptic,” and «Spikes» visualizations. The «Battery» visualization was similarly removed in later editions of version 12. The reason for their removal was that the visualizations do not support full screen controls (either the visualization gets shifted to the left while there is a thick black bar to the right side of the screen, that there are no full screen controls, or that the visualization have DXE Problems). More visualizations such as «BlazingColors,” «ColorCubes,” «Softie the Snowman,» and «Yule Log» used to be downloadable however, the downloads from Microsoft’s website have mostly been taken down and it’s available on the WMP Goodies site.
Format support[edit]
The player includes intrinsic support for Windows Media codecs and also WAV and MP3 media formats. On Windows XP and above with WMP 9 Series and later, the Windows Media Audio Professional codec is included which supports multichannel audio at up to 24-bit 192 kHz resolution. Windows Media Player 11 includes the Windows Media Format 11 runtime which adds low bitrate support (below 128 kbit/s for WMA Pro), support for ripping music to WMA Pro 10 and updates the original WMA to version 9.2.[citation needed]
Support for any media codec and container format can be added using specific DirectShow filters or Media Foundation codecs (Media Foundation codecs only in Windows Vista and later). The player will not play MP3 files that contain compressed ID3 headers («tags»), trying to do so results in a «The input media file is invalid» error message. MP3 playback support was built-in beginning with version 6.1 and audio CD playback was natively supported with version 7.[citation needed]
DVD playback features minus the necessary decoders were integrated into Windows Media Player 8 for Windows XP. The player activates DVD and Blu-ray playback functionality with support for menus, titles and chapters, parental controls and audio track language selection if compatible decoders are installed. MPEG-2 and Dolby Digital (AC-3) decoders were included beginning with Windows Media Player 11 on Windows Vista (Home Premium and Ultimate editions only) and Windows 7 (Home Premium, Ultimate, or Enterprise editions) to allow DVD playback without additional software. However, the decoders were subsequently removed in Windows 8 and Windows 10 due to licensing costs.[20]
Windows Media Player 12 adds native support for H.264 and MPEG-4 Part 2 video formats, ALAC, AAC audio[21] and 3GP[clarification needed got no codec available for 3GP], MP4 and MOV container formats.[22] Windows Media Player 12 is also able to play AVCHD formats (.M2TS and .mts).[23]
As of Windows 10 version 1507, Windows Media Player 12 can play FLAC, HEVC, and SubRip subtitle, and Matroska container formats.[24] Although the WebM file type is not officially associated with Windows Media Player 12 (the default player is Microsoft Movies & TV), playback of VP9 video in WebM container is possible on Windows 10 version 1809 and later.[25]
Windows Media Player Mobile[edit]
Windows Media Player Mobile 10 on Windows Mobile 6.5 supports MP3, ASF, WMA, and WMV using WMV or MPEG-4 codecs.[26]
Disc burning, ripping, and playback[edit]
Windows Media Player features integrated Audio CD-burning support since version 7 as well as data CD burning support since Windows Media Player 9 Series on Windows XP and later. Data CDs can have any of the media formats supported by the player. While burning Data CDs, the media can, optionally, be transcoded into WMA format and playlists can be added to the CD as well. Starting with WMP 9 Series, audio CDs can be burnt with volume leveling.
Audio CDs can be ripped as WMA or WMA 10 Pro (WMA 10 Pro in WMP 11 and later) at 48, 64, 96, 128, 160, and 192 kbit/s, WMA lossless (470 to 940 kbit/s) (9 Series on XP and later), WMA variable bitrate (from 40 to 75 kbit/s up to 240-355 kbit/s), MP3 at 128, 192, 256, and 320 kbit/s, or uncompressed WAV (WAV ripping in WMP 11 and later). Since WMP 9 Series, 20 bit high-resolution CDs (HDCDs) are also supported, if capable audio hardware is present. Audio can be ripped using error correction and ripped audio can be protected with Windows Media DRM. Ripping to MP3 is supported only in Windows Media Player 8 for Windows XP and later if a compatible MP3 encoder is installed. Windows Media Player 10 included the Fraunhofer MP3 Professional encoder. Information on CDs such as album name, artist and track listings can optionally be automatically downloaded from the online Windows Media database when the CD is inserted. Version 11 added support for ripping audio CDs to WAV and WMA 10 Pro formats. With their 2015 implementation in Windows 10, Version 12 also added lossless FLAC and ALAC formats for ripping and playback. For burning, version 11 shows a graphical bar indicating how much space will be used on the disc and introduced Disc spanning which splits a burn list onto multiple discs in case the content does not fit on one disc.
Portable device sync[edit]
Windows Media Player allows the user to connect, share and sync data with portable handheld devices and game consoles since version 7. Media can be optionally transcoded to a format better suited for the target device, automatically, when synchronizing. When deleting playlists from devices, Windows Media Player can automatically remove their contents. Devices can be formatted using Windows Media Player 9 Series and later. Version 10 and later support the Media Transfer Protocol and Auto Sync. Auto Sync allows users to specify criteria such as recently added music or highest rated songs, by which media will be automatically synchronized with the portable device and other advanced features like setting the clock on the portable device automatically, communicating with the device to retrieve the user’s preferences. Windows Media Player 10 also introduced the UMDF-based Windows Portable Devices API.
Version 11 has improved synchronization features for loading content onto PlaysForSure-compatible portable players. WMP 11 supports reverse-synchronization, by which media present on the portable device can be replicated back to the PC. Shuffle Sync can be used to randomize content synced with the portable device, Multi PC Sync to synchronize portable device content across multiple PCs and Guest Sync to synchronize different content from multiple PCs with the portable device. Portable devices appear in the navigation pane of the library where their content can be browsed and searched.
Windows Media Player’s ‘Sync’ function has options that allow it to be set to automatically down-convert (transcode) high bit-rate song files to a lower bit-rate. This down-conversion function is switched on by default. This is useful for providing low bit-rate files to those portable devices that need them, and to save space on portable devices with smaller storage capacities. For high bit-rate capable devices with sufficient storage capabilities, the down conversion process can be omitted.
In versions 11 (2006) and 12 (2009), the Quality settings that the user has selected in the Windows Media Player settings for Sync, for that specific portable device, are used to control the quality (bit-rate) of files that are copied to the portable device. Leaving the Quality settings to Automatic will often result in 192kbs files being copied to the portable device. Manual settings can also be made. 192kbs is the highest quality down-conversion bit-rate that can be manually selected when the Sync function’s down-conversion function is turned on. Lower bit-rates can also be selected.
For portable devices that can handle high bit-rate files, the best quality files are obtained by leaving the down-conversion process switched off (unchecked) for that specific device. In Windows Media Player Version 11, switching off the down-conversion function is done in the Quality tab of the Advanced Options of the Sync settings for the device. In Windows Media Player Version 12, switching off the down-conversion function is done in the Quality tab of the Properties for the device in the Select Settings for the device in the Sync Options menu.
When set up in such a way, Windows Media Player’s ‘Sync’ function can be used to sync unchanged high bit-rate song files to suitable portable devices (i.e. those capable of using file formats such as WMA Lossless, mp3-360kbs, etc.). For example, some users have created large song libraries on their PCs containing .wma formatted song files using the high bit-rate WMA Lossless (WMA-LL) protocol, or using other high bit-rate song file formats. The WMA-LL protocol is selectable in Windows Media Player as an option when ripping songs from CDs. The resulting bit-rates seen on ripped WMA-LL files are often 3 to 6 times higher than 192kbs, and can typically fall anywhere in the range of 600kbs to 1200kbs, depending on the quality of the source file that was present on the CD in the first place. The sound quality is much improved over the default rate, although the file size is larger.
At the time that Versions 11 and 12 were released, the capabilities and capacities of portable devices typically required down-conversion of the bit-rates of the files placed on the portable devices. Thus, Sync down-conversion was turned on by default. This was to ensure playability of the files and to ensure that the file sizes were small enough to efficiently fit a reasonably large selection of songs on the portable device.
In recent years (circa 2012), portable devices became available that could natively play these Windows Media Player produced high bit-rate WMA-LL files (and others), and that have storage capacities suitable for large collections of high bit-rate song files. This made it much more practicable and desirable to use software programs such as Windows Media Player to synchronize previously PC-bound libraries of high bit-rate songs to these new portable devices.
Enhanced playback features[edit]
Windows Media Player features universal brightness, contrast, saturation and hue adjustments and pixel aspect ratio for supported video formats. It also includes a 10-band graphic equalizer with presets and SRS WOW audio post-processing system. Windows Media Player can also have attached audio and video DSP plug-ins which process the output audio or video data. Video Smoothing was introduced in WMP 9 Series (Windows XP and later only) which upscales frame-rate by interpolating added frames, in effect giving a smoother playback on low-framerate videos. The player supports subtitles and closed-captioning for local media, video on demand streaming or live streaming scenarios. Typically Windows Media captions support the SAMI file format but can also carry embedded closed caption data.
The player can use video overlays or VMR (Video Mixing Renderer) surfaces, if the video card supports them. In Windows XP, it uses VMR7 by default, but can also be made to use the more advanced YUV mixing mode by enabling the «Use high quality mode» option in Advanced Performance settings. This turns on deinterlacing, scaling and improved color accuracy.[27] WMP 9 Series introduced native playback for deinterlacing for TV output. Version 9 introduced DXVA accelerated playback. Version 11 introduced improved support for DirectX accelerated decoding of WMV video (DXVA decoding). Up to version 11, it supported static lyrics and «Synchronized Lyrics,” by which different lines of lyrics can be time-stamped, so that they display only at those times. Synchronized Lyrics also were accessible through the Advanced Tag Editor which was removed in version 12.
Since Windows Media Player 9 Series, the player supports crossfading, audio dynamic range (Quiet Mode) for WMA Pro and WMA Lossless, and auto volume leveling for certain media which includes volume level/gain information such as MP3 or Windows Media. The player also supports extensive configurable privacy and security settings.
Shell integration[edit]
The player has Windows Explorer shell integration to add files and playlist to the Now Playing pane and other playlists can be controlled from the Windows Explorer shell itself, via right-click menu. The My Music folder also includes a separate My Playlists folder where playlists are maintained. When the player is closed and reopened, simply clicking the play button restores the last playlist even if it was not saved. Starting with Windows Media Player 10, the playlist pane is also visible from the Library view. AutoPlay handlers in Windows expose various Windows Media Player tasks.
Windows Media Player 11 running in mini mode in Windows Vista and Windows XP respectively. Notice the difference in the logo.
Up to version 11, it featured a taskbar-mounted Mini mode in which the most common media control buttons are presented as a toolbar on the Windows taskbar. Flyout windows can display media information, the active visualization or the video being played back. Mini-mode was introduced as a shell player powertoy for Windows Media Player 8 in Windows XP and integrated later into WMP 9 Series. Mini-mode has been removed in Windows Media Player 12 in favor of controls in the taskbar’s interactive thumbnail preview which lacks volume control, a progress bar and information displayed whenever a new song is played.
The user interface has been redesigned in Windows Media Player 12 such that the Now Playing view plays media in a separate minimalist window with floating playback controls, and also gives access to the current playlist, visualizations, and enhancements.[21] Enhancements are housed in individual undocked windows. The library view includes the rest of the media management functions. It also can preview songs from the library when users hover over the media file and click the Preview button.[21] Windows Media Player 12 can play unprotected songs from the iTunes library. The taskbar-integrated Mini-player has been replaced with controls in the taskbar’s interactive thumbnail preview (called the Thumbnail Toolbar),[28] albeit minus the volume control function, track and album information shown whenever a new song is played and the progress bar. The taskbar icon also supports jump lists introduced in Windows 7.
The thumbnail viewer of Windows Media Player 12 in Windows 7 Home Premium
Extensibility[edit]
The player has had skinning support since Windows Media Player (WMP) 7 and includes a color chooser since the WMP 9 Series. Not all functions are usually exposed in skin mode. Windows Media Player 10 allows setting the video border color. Color chooser has been removed in WMP 12. It supports visualizations and Info Center View (Info Center View in WMP 9 Series and later) which displays media metadata fetched from the internet. Full screen visualizations are supported in WMP 9 Series and later. It supports Background plug-ins, window plug-ins and Now Playing plug-ins to control media playback besides DSP and renderer plug-ins. Plug-in support was introduced in WMP 9 Series.
Online features[edit]
The player integrates web-browsing support to browse online music stores, shop for music and tune to internet radio stations since version 7. It provides an embeddable ActiveX control for Internet Explorer so that developers can play Windows Media on web pages. Windows Media Player 10 and later feature integration with a large number of online music stores and selecting a music store switches the Info Center view, radio and other online features to use services from that store. Purchased music from a particular store appears in a separate library node under the respective category.
Media streaming[edit]
Previously, Microsoft had released Windows Media Connect for Windows XP to stream media content with its built-in UPnP media server. With version 11 of Windows Media Player, Media Sharing was integrated and allows content (Music, Pictures, Video) to be streamed to and from Universal Plug and Play (UPnP) AV enabled devices such as the PS3, Xbox 360, and Roku SoundBridge. This includes DRM protected PlaysForSure content. WMP 11 on Windows Vista can also act as a client to connect to remote media libraries using this feature; this is not available on the Windows XP version.
With version 12, media streaming was further improved. While previous versions streamed media to UPnP compliant devices (Digital Media Server role) and could play media by fetching it from a network share (Digital Media Player role),[29] Windows Media Player 12 can access media from the shared media libraries on the network or HomeGroup, stream media to DLNA 1.5 compliant devices and allows itself (once the remote control option is turned on) to be remotely controlled by Digital Media Controller devices which stream media (Digital Media Renderer role).[29] Similarly, the Play To feature once enabled for remote PCs, by turning on remote control of the player, allows compliant devices and computers to be discovered and controlled remotely from a computer running Windows Media Player 12 (Digital Media Controller role).[29] If the devices do not support the streamed format, Windows Media Player 12 transcodes the format on-the-fly. Media from a home network can also be streamed over the internet using an Online ID Provider service, which handles discovery of the computer’s IP address, authorization, security, connectivity and Quality of Service issues.[29]
Skin Mode[edit]
Windows Media Player also features skins. Currently, Windows Media Player has two default skins: «Corporate,” which was first introduced in version 8, and «Revert,” which first shipped with version 9. In versions 7 and 8, there were many unusual skins such as «Heart,” «Headspace,” «Canvas,” «Goo,” and «Atomic,” which were removed starting with version 9, but are retained if the player is upgraded, although some can still be downloaded from an archive of the Microsoft website.[30] In versions 7, 8, 9, and 10 there were many usual skins such as «9SeriesDefault,” «Atomic,” «Bluesky,” «Canvas,” «Classic,” «Compact,” «goo,” «Headspace,” «heart,” «iconic,” «Miniplayer,” «Optic,” «Pyrite,” «QuickSilver,” «Radio,” «Roundlet,” «Rusty,” «splat,” «Toothy,” «Windows Classic,” and «Windows XP,” which were removed starting with version 11. This Corporate skin is not deletable.
Security issues[edit]
Microsoft Windows Media Runtime in Windows 2000, Windows XP, Windows Vista and Windows Server contained a bug that permitted «remote code execution if a user opened a specially crafted media file». Such a file would allow the attacker to «then install programs; view, change, or delete data; or create new accounts with full user rights», if the account on which the file was played had administrator privileges.[31] The problem was addressed in a critical update issued on September 8, 2009.[32]
Other versions[edit]
Microsoft has also released versions of Windows Media Player for other platforms including Windows Mobile, classic Mac OS, Mac OS X, Palm-size PC, Handheld PC, and Solaris. Of these, only the Windows Mobile edition continues to be actively developed and supported by Microsoft. Version 1 of the Zune software was also based on Windows Media Player; later versions are not.
Windows Mobile[edit]
Windows Media Player 10.3 Mobile on a Windows Mobile Professional device
Windows Media Player for Pocket PC was first announced on January 6, 2000, and has been revised on a schedule roughly similar to that of the Windows version.[33] Currently known as «Media Player 10 Mobile,” this edition (released in October 2004) closely resembles the capabilities of the Windows version of WMP 10, including playlist capabilities, a media library, album art, WMA Lossless playback, support for DRM-protected media, video playback at 640×480 with stereo sound, and the same Energy Blue interface aesthetics also seen in Windows XP Media Center Edition 2005. It also supports synchronization with the desktop version of WMP 10, and additionally supports synchronizing and transcoding of recorded television shows from Media Center. Media Player 10 Mobile is not available as a download from Microsoft, distribution is done solely through OEM partners, and is typically included on devices based on Windows Mobile.
Windows Mobile 6 includes a copy of Windows Media Player 10 Mobile, but with a similar (but not quite identical) theme as Windows Media Player 11.
Mac OS X[edit]
Version 9 was the final version of Windows Media Player to be released for Mac OS X before development was canceled by Microsoft. It was developed by the Windows Media team at Microsoft instead of the Macintosh Business Unit and released in 2003. On release the application lacked many basic features that were found in other media players such as Apple’s iTunes and QuickTime.[citation needed] It also lacked support for many media formats that version 9 of the Windows counterpart supported on release 10 months earlier.
The Mac version supported only Windows Media encoded media (up to version 9) enclosed in the ASF format, lacking support for all other formats such as MP4, MPEG, and Microsoft’s own AVI format. On the user interface front, it did not prevent screensavers from running during playback, it did not support file drag-and-drop, nor did it support playlists. While Windows Media Player 9 had added support for some files that use the WMV9 codec (also known as the WMV3 codec by the FourCC), in other aspects it was seen as having degraded in features from previous versions.
On January 12, 2006, Microsoft announced it had ceased development of Windows Media Player for Mac. Microsoft now distributes a third-party plugin called WMV Player (produced and maintained by Flip4Mac) which allows some forms of Windows Media to be played within Apple’s QuickTime Player and other QuickTime-aware applications.[34]
European Commission case[edit]
In March 2004, the European Commission in the European Union Microsoft antitrust case fined Microsoft €497 million and ordered the company to provide a version of Windows without Windows Media Player, claiming Microsoft «broke European Union competition law by leveraging its near monopoly in the market for PC operating systems onto the markets for work group server operating systems and for media players.” The company has made available a compliant version of its flagship operating system under the negotiated name «Windows XP N,” though the product has not been very successful. Windows Vista, Windows 7 and Windows 8 are also available in «N» editions. However, it is possible to either install Windows Media Player (XP/Vista)[35] or the Media Restore Pack through Windows Update (Vista) to add the media player.
Release history[edit]
Prior to the release of Windows Media Player in Windows 98 Second Edition, separate programs, CD Player, Deluxe CD Player, DVD Player and Media Player, were included in old versions of Microsoft Windows for playback of media files.
| Version | Original release | Included with | Available for | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Microsoft Windows | ||||
| Media Player | February 15, 2022 | Windows 11 | — | |
| Windows Media Player 12 | July 22, 2009 | Windows 7 Windows 8 Windows 8.1 Windows 10 Windows 11 Windows Server 2008 R2 Windows Server 2012 Windows Server 2012 R2 Windows Server 2016 Windows Server 2019 Windows Server 2022 |
— | 
|
| Windows Media Player 11 | October 18, 2006 | Windows Vista Windows Server 2008 |
Windows XP (SP2+) Windows XP x64 Edition |
|
| Windows Media Player 10 | August 25, 2004 | Windows XP x64 Edition Windows XP Media Center Edition 2005 Windows Server 2003 (SP1+) |
Windows Server 2003 Windows XP[37] |
|
| Windows Media Player 9 Series | January 7, 2003[38] | Windows XP (SP2+) Windows Server 2003 (RTM) |
Windows XP Windows ME Windows 2000 Windows 98 SE[39] |
|
Windows Media Player for Windows XP (version  |
August 24, 2001 | Windows XP (RTM & SP1) | — | |
| Windows Media Player 7.1 | May 16, 2001 | Windows 2000 (SP2+) | Windows ME Windows 2000 Windows 98[39][40] |
|
| Windows Media Player 7.0 | June 19, 2000[41] | Windows ME | Windows 2000 Windows 98 Windows 95 |
|
| Windows Media Player 6.4[c] | September 15, 1999 | Windows 2000 Windows ME (hidden) Windows XP (hidden) Windows Server 2003 (hidden) Internet Explorer 5.01 Internet Explorer 5.5 Internet Explorer 6.0 |
Windows 98 Windows NT 4.0 Windows 95 |
|
| Windows Media Player 6.1 | March 1999 | Windows 98 SE Internet Explorer 5.0 |
Windows 98 Windows NT 4.0 Windows 95 |
|
| Microsoft Media Player 5.1 | 2001 | Windows XP (hidden) | — | |
| Media Player 5.0 | 1999 | Windows 2000 (hidden) | — | |
| Media Player 4.9 | 2000 | Windows ME (hidden) | — | |
| Media Player 4.1 | 1998 | Windows 98 Windows 98 SE (hidden) |
— | |
| Media Player 4.0 | 1995 | Windows 95 Windows NT 4.0 |
— | |
| Media Player 3.51 | 1995 | Windows NT 3.51 | — | |
| Media Player 3.5 | 1994 | Windows NT 3.5 | — | |
| Media Player 3.15 | 1992 | — | Windows 3.1 with Video for Windows | |
| Media Player 3.1 | 1992 | Windows 3.1 Windows NT 3.1 |
— | |
| Media Player 3.0 | 1991 | — | Windows 3.0 with Multimedia Extension | |
| Windows Mobile | ||||
| Windows Media Player 10.3 Mobile | February 12, 2007 (Windows Mobile 6) | Windows Mobile 6.1 Windows Mobile 6 |
Windows Mobile 5.0 | 
|
| Windows Media Player 10.2 Mobile | ? | Windows Mobile 5.0 | — | |
| Windows Media Player 10.1 Mobile | May 10, 2005 | Windows Mobile 5.0 | — | |
| Windows Media Player 10 Mobile | October 12, 2004 | Windows Mobile 2003 SE | — | |
| Windows Media Player 9.0.1 | March 24, 2004 | Windows Mobile 2003 SE | — | |
| Windows Media Player 9 Series | June 23, 2003 | Windows Mobile 2003 | — | |
| Windows Media Player 8.5 | October 11, 2002 | Pocket PC 2002 | — | |
| Windows Media Player 8.01 | July 2002 | Pocket PC 2002 | — | |
| Windows Media Player 8 | October 4, 2001 (Pocket PC) | Pocket PC 2002 Smartphone 2002 |
— | |
| Windows Media Player 7.1 | May 21, 2001 | Pocket PC 2000 | — | |
| Windows Media Player 7 | December 12, 2000 | Pocket PC 2000 | — | |
| Windows Media Player 1.2 | September 7, 2000 | Handheld PC 2000 | — | |
| Windows Media Player 1.1 | ? | Palm-size PC CE 2.11 | — | |
| Windows Media Player | April 19, 2000 | Pocket PC 2000 | — | |
| Mac | ||||
| Windows Media Player 9 Series | November 7, 2003 | — | Mac OS X | |
| Windows Media Player 7 | July 24, 2001 | Mac OS 9 | Mac OS 8.x | |
| Windows Media Player 6.3 | July 17, 2000 | Mac OS 8 | Mac OS 7.x | |
| Solaris | ||||
| Windows Media Player 6.3 | July 17, 2000 | — | Solaris |
See also[edit]
- Comparison of media players
- Comparison of video player software
- Groove Music
- Media Player Classic, a media player that mimics the appearance of Windows Media Player 6.4
- Media Transfer Protocol
- Windows Media Encoder
- Windows Media Services
Footnotes[edit]
- ^ Except for «N» and «KN» editions of Windows, as well as Windows RT
- ^ N and KN versions of Windows 7 do not include Windows Media Player by default.[1]
- ^ Windows Media Player 6.4 was shipped side-by-side with later versions of WMP in Windows ME and Windows XP
References[edit]
- ^ «Microsoft Documentation Page». Microsoft Docs. October 22, 2020. Archived from the original on February 9, 2021.
- ^ LeBlanc, Brandon (July 22, 2009). «Windows 7 Has Been Released to Manufacturing». Blogging Windows. Microsoft. Archived from the original on September 26, 2015. Retrieved December 21, 2020.
- ^ «Windows Media Player 12 — Windows 7 features». Windows. Microsoft. Archived from the original on September 22, 2009. Retrieved June 15, 2011.
- ^ Hachman, Mark (2021-11-16). «Windows Media Player is getting a long-overdue upgrade». PCWorld.
- ^ «Windows Version History». Support (4.0 ed.). Microsoft. September 23, 2011. Archived from the original on February 26, 2015. Retrieved May 2, 2009.
- ^ Lineback, Nathan. «Windows 3.0 with Multimedia Extensions». Toasty Tech. Archived from the original on April 15, 2009. Retrieved May 2, 2009.
- ^ «Video for Windows». PC Tech Guide. Archived from the original on April 10, 2009. Retrieved May 2, 2009.
- ^ Blome, Michael; Wasson, Mike (July 2002). «DirectShow: Core Media Technology in Windows XP Empowers You to Create Custom Audio/Video Processing Components». MSDN Magazine. Microsoft. Archived from the original on September 14, 2008. Retrieved May 1, 2009.
- ^
C:Windowssystem32myplay32.exe. Windows XP. Microsoft Corporation. - ^ «MPLAYER2.EXE Is Linked to Missing Export MSDXM.OCX». Support. Microsoft. April 25, 2006. Archived from the original on March 14, 2007. Retrieved February 13, 2015.
- ^ «MSN Music to offer free songs». Archived from the original on 2020-09-21. Retrieved 2020-05-21.
- ^ «MSN Launches Preview Release of Music Download Service». September 2004. Archived from the original on 2020-08-06. Retrieved 2020-05-21.
- ^ «MSN Music Shutting Down for Zune». Archived from the original on 2020-08-13. Retrieved 2020-05-21.
- ^ «DSP Plug-in Packaging». MSDN. Microsoft. Archived from the original on 2010-11-05. Retrieved 2010-04-08.
- ^ LeBlanc, Brandon (April 16, 2012). «Windows Announcing the Windows 8 Editions». The Windows Blog. Archived from the original on April 18, 2012.
- ^ «Media Player is available for Windows 11». 16 November 2021.
- ^ «Microsoft is replacing Windows Media Player with Media Player for Windows 11». Engadget. Retrieved 2021-11-18.
- ^ «Full screen album art». 16 November 2021.
- ^ «Optimized accessibility». 16 November 2021.
- ^ «DVD playback options for Windows». Windows help & learning.
- ^ a b c Peter Bright (October 30, 2008). «Hands on: Windows Media Player 12’s surprising new features». ArsTechnica. Condé Nast Digital. Archived from the original on March 27, 2009. Retrieved March 25, 2009.
- ^ «Windows 7 RC to natively support .mov files». Chakkaradeep Chandran. Neowin.net. February 26, 2009. Archived from the original on July 3, 2012. Retrieved March 25, 2009.
- ^ «Windows 7 next generation camera support». Download Center. Microsoft. Archived from the original (PPTX) on December 27, 2008.
- ^ «Native MKV, FLAC And HEVC Support In Windows 10». Lifehacker Australia. 29 November 2014.
- ^ «Windows 10 1809 Built-In Apps: What to Keep». Vacuum Breather.
- ^ «Formats supported by Windows Media Player Mobile». MSDN. Microsoft. April 8, 2010. Archived from the original on November 18, 2012. Retrieved November 7, 2012.
- ^ «Windows Media Player manual». Download Center. Microsoft. September 1, 2004. Archived from the original (DOC) on June 7, 2005.
- ^ Kiriaty, Yochay; Goldshtein, Sasha (July 2009). «Introducing The Taskbar APIs». MSDN Magazine. Microsoft. Thumbnail Toolbars. Archived from the original on 2015-03-25. Retrieved 2015-04-23.
- ^ a b c d Sinofsky, Steven (May 12, 2009). «Media Streaming with Windows 7». Engineering Windows 7. Microsoft. Archived from the original on July 12, 2011. Retrieved April 23, 2015.
- ^ «Skins for Windows Media Player». Windows. Microsoft. Archived from the original on June 9, 2016.
- ^ «Microsoft Security Bulletin MS09-047: Critical Vulnerabilities in Windows Media Format Could Allow Remote Code Execution». Microsoft TechNet. Microsoft. September 8, 2009. Archived from the original on July 31, 2010. Retrieved June 5, 2010.
- ^ «MS09-047: Description of the security update for Windows Media Format Runtime, Windows Media Services, and Media Foundation: September 8, 2009». Support. Microsoft. September 10, 2009. Archived from the original on May 19, 2010. Retrieved June 5, 2010.
- ^ «Microsoft Unveils Windows Media Player for Palm-Size and Pocket PCs». News Center. Microsoft. January 6, 2000. Archived from the original on August 6, 2020. Retrieved January 31, 2017.
- ^ «Windows Media Components for QuickTime». Microsoft. Archived from the original on January 12, 2006. Retrieved March 30, 2007.
- ^ Microsoft. Download Center Archived 2017-07-25 at the Wayback Machine. «be used to restore Windows Media Player and related technologies to N and KN editions of Windows Vista.» Retrieved July 26, 2008
- ^ «Get Windows Media Player». Windows. Microsoft. Archived from the original on August 25, 2010. Retrieved November 5, 2011.
- ^ «MS09-037: Description of the security update for Windows Media Player: August 11, 2009». Support. Microsoft. May 8, 2012. Archived from the original on September 21, 2013. Retrieved August 12, 2013.
- ^ «Final Release of Windows Media 9 Series Starts Next Wave of Digital Media». News Center. Microsoft. January 7, 2003. Archived from the original on February 3, 2016. Retrieved September 29, 2015.
- ^ a b Petri, Daniel (2009-01-08). «Download Windows Media Player 9». Petri. Archived from the original on 2019-02-13. Retrieved 2019-02-12.
- ^ «Windows Media Player 7.1 for Windows 98, 2000, and Me 7.1 — BumperSoft». www.bumpersoft.com. Archived from the original on 2019-02-13. Retrieved 2019-02-12.
- ^ «Microsoft Windows Media Player 7 Brings Click and Play Digital Media To Millions Around the Globe». News Center. Microsoft. July 17, 2000. Archived from the original on May 27, 2015. Retrieved June 15, 2011.
Further reading[edit]
- Liron, Marc (2004). «A Little Windows Media Player History…» Windows XP Media Player — The Best There Is?. Archived from the original on January 18, 2008. Retrieved October 7, 2011.
- «The default codecs that are included with Windows Media Player 9 and with Windows Media Player 10 (Revision 1.1)». Microsoft Support Center. Microsoft Corporation. August 4, 2005. Archived from the original on November 20, 2011. Retrieved October 7, 2011.
External links[edit]
- Official website
- The Vintage Windows Media Player
- wmplugins.com — The place to find and share plug-ins, skins and visualizations.
Windows Media Player
Программа-проигрыватель Windows Media Player установлена в ОС Windows по умолчанию. В русской версии эта программа называется Проигрыватель Windows Media. Она позволяет не только слушать музыку, но и смотреть видеофайлы.
Рассмотрим версию Windows Media Player 8 (рис. 12.11), которая входит в комплект поставки Windows XP.
Рис. 12.11. Основное окно программы Windows Media Player.
Обратите внимание, что в меню Воспроизведение находится пункт Диск DVD или компакт-диск. При выборе этого пункта открывается дополнительное меню, в котором перечислены все имеющиеся в системе устройства для воспроизведения лазерных дисков, а также сведения о том, какие диски в них сейчас находятся. Если приводы пусты, этот пункт недоступен.
Основные элементы управления стандартны. Прямо под областью воспроизведения видео расположена полоса поиска – перемещая по ней манипулятор, вы можете перейти в любое место загруженного фильма. Ниже находятся кнопки управления – такие же, как в рассмотренном выше проигрывателе Winamp. Справа расположен регулятор громкости, обозначенный значком динамика. При просмотре фильма можно увеличивать/уменьшать громкость клавишами ? и ?, а нажав сочетание Ctrl+M – временно убрать звук.
Внизу можно прочитать информацию об авторе загруженного файла, названии фильма, авторских правах и т. д., если создатели фильма указали ее.
В отличие от других программ, Windows Media Player рассчитан на работу с Интернетом, в частности, на воспроизведение передач сетевого радио. Поэтому не удивляйтесь, что в меню Файл кроме пункта Открыть есть пункт Открыть адрес URL, позволяющий просматривать файлы с удаленных компьютеров. При воспроизведении музыки и фильмов с дисков стандартных форматов ни тот, ни другой пункт не потребуются: достаточно использовать упомянутую ранее команду Диск DVD или компакт-диск в меню Воспроизведение.
Вы можете регулировать размер окна воспроизведения. По умолчанию фильм воспроизводится с оригинальным разрешением. Сочетанием Alt+Enter можно перевести воспроизведение в полноэкранный режим и обратно, клавишами Alt+1 размер окна можно уменьшить в два раза, а клавишами Alt+3 – в два раза увеличить. Нажатие Alt+2 восстанавливает исходный размер.
Чтобы окно проигрывателя всегда отображалось поверх других окон, нажмите Ctrl+T. Повторное нажатие Ctrl+T отменяет данный режим.
В ходе просмотра фильм можно приостановить и запустить снова с помощью клавиши Пробел. Того же эффекта можно добиться, щелкнув мышью на области воспроизведения.
Но есть еще и настройки, не вынесенные в основное окно. Чтобы открыть их, выберите в меню Сервис пункт Параметры. Откроется окно с десятью вкладками (рис. 12.12). Здесь можно указать, следует ли использовать аппаратное ускорение при воспроизведении видео, следует ли автоматически скачивать из Интернета обновление программы, указать реальное расположение динамиков для лучшего звука и т. д.
Рис. 12.12. Окно настроек, вкладка Проигрыватель.
Кроме того, указать, какие типы файлов следует открывать с помощью Windows Media Player, вы можете на вкладке File Types (Типы файлов) (рис. 12.13).
Рис. 12.13. Окно настроек, вкладка Типы файлов.
На вкладке Копировать музыку (рис. 12.14) можно настроить параметры имеющихся в программе кодеков (по умолчанию в программе есть только кодек потокового воспроизведения Windows Media).
Рис. 12.14. Окно настроек, вкладка Копировать музыку.
Чтобы настроить установленные в системе внешние кодеки, выберите в том же окне вкладку Подключаемые модули. Возможно, сначала кодеки придется подключить вручную с помощью кнопки Добавить.
Данный текст является ознакомительным фрагментом.
Читайте также
Проигрыватель Windows Media 11
Проигрыватель Windows Media 11
В данном разделе мы приступаем к рассмотрению популярнейшей программы – Проигрывателя Windows Media, с помощью которого вы сможете превратить свой компьютер в настоящий развлекательный центр. Проигрыватель Windows Media позволяет прослушивать звуковые
Добавляем Windows Media Center в меню автозапуска в Windows 7
Добавляем Windows Media Center в меню автозапуска в Windows 7
В Windows 7 меню автозапуска не предоставляет возможности воспроизведения мультимедиа в Windows Media Center. Вы не найдете такого пункта и в настройках параметров автозапуска в панели
Windows Meda Player
Windows Meda Player
Изменение заголовка в Windows Media Player
Для изменения заголовка в Windows Media Player откройте или создайте раздел HKEY_CURRENT_USERSoftwarePoliciesMicrosoftWindowsMediaPlayer с строковым параметром TitleBar, содержащим ваш текст
Изменение заголовка в Windows Media Player
Изменение заголовка в Windows Media Player
Для изменения заголовка в Windows Media Player откройте или создайте раздел HKEY_CURRENT_USERSoftwarePoliciesMicrosoftWindowsMediaPlayer с строковым параметром TitleBar, содержащим ваш текст
Windows Media Player
Windows Media Player
Изменение заголовка в Windows Media Player
Для изменения заголовка в Windows Media Player откройте или создайте раздел HKEY_CURRENT_USERSoftwarePoliciesMicrosoftWindowsMediaPlayer с строковым параметром TitleBar, содержащим ваш
Изменение заголовка в Windows Media Player
Изменение заголовка в Windows Media Player
Для изменения заголовка в Windows Media Player откройте или создайте раздел HKEY_CURRENT_USERSoftwarePoliciesMicrosoftWindowsMediaPlayer с строковым параметром TitleBar, содержащим ваш
Проигрыватель Windows Media
Проигрыватель Windows Media
Проигрыватель Windows Media объединяет в себе функции радиоприемника, аудио– и видеопроигрывателя, а также содержит информационную базу данных об исполнителях и сведения о самих файлах. Он применяется для воспроизведения и упорядочения файлов
VLC media player
VLC media player
Производитель: VideoLAN (http://www.videolan.org).Статус: бесплатная.Ссылка для скачивания: http://www.videolan.org/vlc/.Размер: 8,2 Мбайт.VLC media player отличается от большинства проигрывателей тем, что может воспроизводить передаваемое по сети видео, а также ретранслировать потоковые данные
Слушаем музыку и смотрим клипы Windows Media Player
Слушаем музыку и смотрим клипы Windows Media Player
Жили-были некогда в составе Windows два брата-проигрывателя – Универсальный проигрыватель (Media Player) и Проигрыватель компакт-дисков. Оба – как по внешности, так и по функциональности – звезд с неба не ловили, были туповаты и
4.3. Проигрыватель Windows Media
4.3. Проигрыватель Windows Media
В данном разделе мы рассмотрим, каким образом можно изменять стандартные настройки Проигрывателя Windows
Как настроить Media Player Classic?
Как настроить Media Player Classic?
Если в процессе установки вы назначили Media Player Classic проигрывателем по умолчанию, то при двойном щелчке на значке любого видеофайла начнется его воспроизведение именно в этой программе (1).Чтобы выбрать, какой программой проиграть фильм, щелкните
Windows Media Player
Windows Media Player
Программа-проигрыватель Windows Media Player установлена в ОС Windows по умолчанию. В русской версии эта программа называется Проигрыватель Windows Media. Она позволяет не только слушать музыку, но и смотреть видеофайлы.Рассмотрим версию Windows Media Player 8 (рис. 12.11), которая входит в
Проигрыватель Windows Media Компонент Microsoft Windows |
|
 |
|
|
Проигрыватель Windows Media 12 для Windows 7 |
|
| Детали | |
|---|---|
| Другие названия |
Windows Media Player |
| Тип |
медиаплеер |
| Поставляется с |
Windows Me |
| Также доступен для |
Mac OS, Solaris |
| Заменяет |
Media Player |
| Связанные компоненты | |
|
Windows Media Center |
Проигрыватель Windows Media (Windows Media Player, сокращённо WMP) — проигрыватель звуковых и видео файлов для операционных систем семейства Windows. Версии Windows Media Player были также выпущены для Mac OS, Mac OS X и Solaris, но развитие этих версий с тех пор было прекращено. В дополнение к проигрывателю, Windows Media Player включает в себя возможность копировать музыку с компакт-дисков, записывать диски в Audio CD формате или в виде дисков с данными с плейлистами, такие как MP3 CD, синхронизировать файлы мультимедиа с цифровых плееров или других мобильных устройств, и позволяет пользователям покупать музыку из онлайновых музыкальных магазинов.
О продукте
WMP производится корпорацией Microsoft и прилагается бесплатно к операционным системам семейств Windows. Microsoft производила также бесплатные версии этого плеера для других операционных систем, таких как Mac OS и Solaris, но они уступают версии для Windows по ряду параметров: меньшая функциональность, реже появляются новые версии, поддерживаются меньшее количество типов медиафайлов.
Windows Media Player впервые появился в Windows 98 SE. Его предшественником (в составе Windows 98 и Windows 95) был «Media Player». В Media Player отсутствовали некоторые возможности WMP, такие как копирование музыки с компакт-диска на компьютер, запись музыки с компьютера на компакт-диск и возможность покупать музыку в интернет-магазинах.
Windows XP поставлялся с Windows Media Player 8, но начиная с SP2, в нём предустановлена версия Windows Media Player 9. Версии 9, 10, 11 имеют режим воспроизведения музыки с панели задач. В 12 версии этот режим отсутствует. Текущая версия Windows Media Player — 12, она выпущена в июле 2009 года и её можно было загрузить с сайта компании[3]. Она планировалась к включению в дистрибутив Windows 7, который поступил в продажу 22 октября 2009 года. Эта версия проигрывателя поддерживает H.264, Xvid и видео DivX, AAC и .mov.
В марте 2004 года Европейская комиссия оштрафовала Microsoft на 497 млн евро, а также обязала компанию создать для продажи в Европе версию Windows NT без Windows Media Player (Windows XP N).[4] Microsoft подала на апелляцию, а пока выпускает урезанную версию Windows — Windows XP Reduced Media Edition. В ней также можно установить WMP, предварительно загрузив его через Интернет.
Хронология версий
| дата | версия | платформа |
|---|---|---|
| 25 июня 1998 | WMP 6.1 | Windows 98 SE |
| 22 ноября 1999 | WMP 6.4 | Windows 95, Windows 98, Windows NT 4.0 |
| 17 июля 2000 | WMP 6.3 | Mac OS |
| 17 июля 2000 | WMP 6.3 | Solaris |
| 17 июля 2000 | WMP 7 | Windows 98, Windows 2000. |
| 14 сентября 2000 | WMP 7.1 | Windows ME |
| 12 декабря 2000 | WMP 7 | Pocket PC |
| 24 июля 2001 | WMP 7.0.1 | Mac OS |
| 25 октября 2001 | WMP 8 | Windows XP |
| 8 января 2002 | WMP 7.1 | Mac OS |
| 27 января 2003 | WMP 9 | Windows 98 SE, Windows ME, Windows 2000, Windows XP. |
| 23 июня 2003 | WMP 9 | Pocket PC |
| 7 ноября 2003 | WMP 9 | Mac OS X |
| 6 августа 2004 | WMP 9 | Windows XP SP2 |
| 2 сентября 2004 | WMP 10 | Windows XP, Windows XP Media Center Edition |
| октябрь 2004 | WMP 10 Mobile | Pocket PC, смартфоны |
| июль 2006 | WMP 10.3 Mobile | Pocket PC, смартфоны |
| ноябрь 2006 | WMP 11.0.5721.5268 | Windows XP |
| ноябрь 2010 | WMP 11.0.5721.5280 | Windows XP |
| январь 2007 | WMP 11.0.6000.6344 | Windows Vista |
| март 2008 | WMP 11.0.6001.7000 | Windows Vista SP1 |
| апрель 2009 | WMP 11.0.6002.18005 | Windows Vista SP2 |
| 22 октября 2009 | WMP 12.0.7600.16415 | Windows 7 |
| 22 февраля 2011 | WMP 12.0.7601.17514 | Windows 7 SP1 |
| 1 августа 2012 | WMP 12.0.9200.16384 | Windows 8 |
Плагины к проигрывателю
- AC3filter — фильтр, предназначенный для декодирования и обработки звука в реальном времени. Фильтр декодирует форматы аудио AC3/DTS, поддерживает многоканальный и/или цифровой (S/PDIF) выходы.
Примечания
- ↑ 1 2 Кроме Windows XP и Windows Vista версий N, K и KN.
- ↑ Кроме Windows 7 версии N.
- ↑ В настоящий момент[когда?] Windows Media Player 12 не доступен для загрузки с официального сайта Microsoft. Ранее для его загрузки требовалась проверка подлинности Windows)
- ↑ Description of Windows XP Home Edition N and Windows XP Professional N
Ссылки
- Официальный сайт
- Центр загрузки Windows Media Player 11
| |
|
|---|---|
| Основные |
Aero • ClearType • Диспетчер рабочего стола • DirectX • Панель задач (Пуск • Область уведомлений) • Проводник (Пространство имён • Специальные папки • Ассоциации файлов) • Windows Search (Smart folders • iFilters) • GDI • WIM • SMB • .NET Framework • XPS • Active Scripting (WSH • VBScript • JScript) • COM (OLE • DCOM • ActiveX • Структурированное хранилище • Сервер транзакций) • Теневая копия • WDDM • UAA • Консоль Win32 |
| Службы управления |
Архивация и восстановление • COMMAND.COM • cmd.exe • Средство переноса данных • Просмотр событий • Установщик • netsh.exe • PowerShell • Отчёты о проблемах • rundll32.exe • Программа подготовки системы (Sysprep) • Настройка системы (MSConfig) • Проверка системных файлов • Индекс производительности • Центр обновления • Восстановление системы • Дефрагментация диска • Диспетчер задач • Диспетчер устройств • Консоль управления • Очистка диска • Панель управления (элементы) |
| Приложения |
Контакты • DVD Maker • Факсы и сканирование • Internet Explorer • Журнал • Экранная лупа • Media Center • Проигрыватель Windows Media • Программа совместной работы • Центр устройств Windows Mobile • Центр мобильности • Экранный диктор • Paint • Редактор личных символов • Удалённый помощник • Распознавание речи • WordPad • Блокнот • Боковая панель • Звукозапись • Календарь • Калькулятор • Ножницы • Почта • Таблица символов • Исторические: Movie Maker • NetMeeting • Outlook Express • Диспетчер программ • Диспетчер файлов • Фотоальбом |
| Игры |
Chess Titans • Mahjong Titans • Purble Place • Пасьянсы (Косынка • Паук • Солитер) • Сапёр • Пинбол • Червы |
| Ядро ОС |
Ntoskrnl.exe • Слой аппаратных абстракций (hal.dll) • Бездействие системы • svchost.exe • Реестр • Службы • Диспетчер управления сервисами • DLL (формат модулей) • PE • NTLDR • Диспетчер загрузки • Программа входа в систему (winlogon.exe) • Консоль восстановления • Windows RE • Windows PE • Защита ядра от изменений |
| Службы |
Autorun.inf • Фоновая интеллектуальная служба передачи • Файловая система стандартного журналирования • Отчёты об ошибках • Планировщик классов мультимедиа • Теневая копия • Планировщик задач • Беспроводная настройка |
| Файловые системы |
Protogon • NTFS (Жёсткая ссылка • Точка соединения • Точка монтирования • Точка повторной обработки • Символьная ссылка • TxF • EFS) • WinFS • FAT • exFAT • CDFS • UDF • DFS • IFS |
| Сервер |
Active Directory • Службы развёртывания • Служба репликации файлов • DNS • Домены • Перенаправление папок • Hyper-V • IIS • Media Services • MSMQ • Защита доступа к сети (NAP) • Службы печати для UNIX • Удалённое разностное сжатие • Службы удаленной установки • Служба управления правами • Перемещаемые профили пользователей • SharePoint • Диспетчер системных ресурсов • Удаленный рабочий стол • WSUS • Групповая политика • Координатор распределённых транзакций |
| Архитектура |
NT • Диспетчер объектов • Пакеты запроса ввода/вывода • Диспетчер транзакций ядра • Диспетчер логических дисков • Диспетчер учетных записей безопасности • Защита ресурсов • lsass.exe • csrss.exe • smss.exe • spoolsv.exe • Запуск |
| Безопасность |
BitLocker • Защитник • Предотвращение выполнения данных • Обязательный контроль целостности • Защищенный канал данных • UAC • UIPI • Брандмауэр • Центр обеспечения безопасности • Защита файлов |
| Совместимость |
Подсистема UNIX (Interix) • Виртуальная машина DOS • Windows on Windows • WOW64 |
| |
|
|---|---|
| Freeware |
1by1 • AIMP • Apollo • Bearshare • Evil Player • foobar2000 • GOM Player • iTunes • Light Alloy • MusicBee • OrangeCD Player • QuickTime • Quintessential Media Player • Sony SonicStage • Spider Player • The KMPlayer • Media Player Classic • Windows Media Player |
| Shareware |
Audio Studio • jetAudio • BS.Player • @MAX Tray Player • MediaMonkey • Winamp |
| Open Source |
aTunes • Kantaris • Media Player Classic • MPlayer • SMPlayer • UMPlayer • Songbird • VLC • xine • Zinf |
| |
|
|---|---|
| Windows |
1by1 • AIMP • ALLPlayer • Apollo • Arcsoft TotalMedia Theatre • aTunes • BS.Player • Clementine • Crystal Player • Daum PotPlayer • DivX Player • Evil Player • Adobe Flash Player • foobar2000 • GOM Player • iTunes • jetAudio • Kantaris • Light Alloy • @MAX Tray Player • MPlayer • Media Player Classic • MediaMonkey • Miro • MusicBee • OrangeCD Player • PocketOgg • PowerDVD • QuickTime • Quintessential Media Player • RealPlayer • RealJukebox • Shockwave • Songbird • Spider Player • The Core Media Player • The KMPlayer • VLC • WinDVD • Winamp • Windows Media Center • Windows Media Player • XBMC • Zinf • Zoom Player |
| Mac OS X |
Apple DVD Player • Adobe Flash Player • Clementine • Front Row • iTunes • MPlayer • Miro • QuickTime • RealPlayer • Adobe Shockwave • Songbird • VLC • Windows Media Player • XBMC |
| Linux |
Amarok • Audacious Media Player • BMPx • Banshee • Beep Media Player • Clementine • Cmus • DeaDBeeF • Exaile • Adobe Flash Player • JuK • Kaffeine • LinDVD • LinuxMCE • Mp3blaster • MPlayer • Miro • Mpg123 • Mpg321 • Music Player Daemon • Music On Console • Noatun • Parole • QMMP • Quod Libet • RealPlayer • Rhythmbox • Songbird • Totem • VLC • XBMC • XMMS • XMMS2 • Xine • Xawtv • Zinf |
| Технологии |
Плей-лист • Интернет-радио • Интернет-телевидение • Подкастинг • Кодек • Медиаконтейнер |
| Прочее |
Сетевой медиаплеер • Портативный мультимедийный проигрыватель |
Архитектура Windows Media
Создание и редактирование
Распространение
Воспроизведение
Windows Media Tools
Синхронизация
Windows Media Services
Коммерческие решения
и режим Pay-Per-View
Защита содержимого
и управление правами
Поддержка электронной
коммерции
Windows Media Player 7
Системные требования
Эволюция Windows
Media
В данном обзоре мы ознакомимся с технологией Windows Media
— технологией, обеспечивающей платформу Windows NT 4.0 или Windows 2000 богатыми
мультимедийными возможностями. Мы рассмотрим архитектуру Windows Media и основные
компоненты, а также более подробно расскажем о новой версии проигрывателя мультимедийных
файлов — Windows Media Player 7.0. Начнем с краткого описания архитектуры.
Архитектура Windows Media
Архитектура Windows Media построена по простой формуле: «Создавайте. Храните.
Воспроизводите». Для достижения цели предоставляется платформа, практически
не требующая сопровождения, обладающая минимальным временем отклика и поддерживающая
различные скорости передачи информации. Архитектура Windows
Media показана на рис. 1. Платформа Windows Media, обеспечивающая все необходимые
средства для создания, распространения и воспроизведения мультимедийной информации,
состоит из ряда компонентов, которые перечислены ниже.
|
|
Создание и редактирование
Указанная платформа содержит большое число компонентов для создания и редактирования
мультимедийной информации, а именно:
- Windows Media Encoder. Служит для преобразования существующих AVI-,
WAV- и MP3-файлов, а также «живой» аудио- и видеоинформации в формат Windows
Media. Данный компонент может преобразовывать содержимое файлов в потоковую
информацию для немедленной передачи в режимах unicast или multicast либо сохранять
их в файлах Windows Media для последующей передачи средствами Windows Media
Services. - Windows Media On-Demand Producer. Преобразует AVI- и WAV-файлы в
формат Windows Media, обеспечивая более высокое качество аудио- и видеоинформации
без каких-либо дополнительных затрат. С помощью редакторов можно изменять
такие характеристики, как яркость и контрастность, вставлять маркеры, скриптовые
команды и добавлять различные визуальные эффекты. - Windows Media Plug-In for Adobe Premiere. Позволяет авторам, использующим
Adobe Premiere, воспроизводить созданные в Adobe Premiere видеофильмы средствами
Windows Media. - PowerPoint 2000 Presentation Broadcaster. Позволяет интегрировать
созданные в PowerPoint 2000 слайды в любые мультимедийные данные. - Windows Media Presenter and Windows Media Publish to ASF. Позволяет
создавать мультимедийные презентации средствами Microsoft PowerPoint 97. Используется
для сохранения слайдов и сопутствующих аудиоклипов в виде единого ASF-файла. - Windows Media Author. Редактор, позволяющий объединять аудиоинформацию
с графическими изображениями, созданный на основе редактора T.A.G Editor фирмы
Digital Renaissance. Этот редактор может использоваться для вставки графики,
маркеров и переходов в потоковую информацию в формате Windows Media. - Windows Media ASF Indexer. Используется для изменения содержимого
существующих ASF-файлов. Позволяет редактировать маркеры, скриптовые команды,
свойства файлов и ряд других свойств.
|
|
Распространение
Распространение мультимедийной информации осуществляется путем использования
следующих компонентов Windows Media:
- Windows Media Services 4.1 for Windows NT 4.0 and Windows 2000. Эти
сервисы используются для посылки аудио- и видеоинформации клиентам. Посылка
может осуществляться как в режиме unicast, так и в режиме multicast. Windows
Media Services позволяют серверу на базе Windows NT 4.0 или Windows 2000 осуществлять
потоковую рассылку аудио и видео по сети и используют компоненты, перечисленные
ниже. - Windows Media Rights Manager. Данный компонент даст авторам возможность
защищать интеллектуальную собственность и получать прибыль от использования
предоставляемой ими информации. - Windows Media Event Guide. Позволяет создавать и поддерживать информационное
наполнение Web-сервера. Используется для управления системой на базе SQL Server
для публикации информации и обеспечения поиска и создания событийно-ориентированной
модели. - Windows Media Digital Broadcast Manager. Позволяет компаниям продавать
информацию по принципу Pay-Рer-View или Pay-Per-Download. С помощью Windows
Media Digital Broadcast Manager любой Web-узел может быть легко превращен
в коммерческий узел с защищенным содержимым.
|
|
Воспроизведение
Для воспроизведения мультимедийной информации фирма Microsoft предлагает такие
компоненты, как Windows Media Player 7.0, Windows Media Player 6.4 и Windows
Media Player for Palm-Sized and Pocket PCs.
Для сравнения, Windows Media Player поддерживает следующие форматы: ASF, WAV,
AVI, MOV, MPEG, MIDI, VOD, AU, MP3 и ID3, тогда как проигрыватель RealSystem
G2 — только форматы RM, WAV, AVI, VIVO и MP3.
Разработчикам предлагается специальный набор компонентов — Windows Media Software
Development Kit (SDK), а также средство для тестирования сервисов — Windows
Media Load Simulator.
После того как мы получили общее представление о Windows Media, ее архитектуре
и компонентах, давайте рассмотрим некоторые из них более подробно. Начнем со
средств, позволяющих создавать мультимедийное информационное наполнение, — Windows
Media Tools.
|
|
Windows Media Tools
Windows Media Tools — компоненты Windows Media для создания и редактирования
мультимедийного содержимого. Обеспечивают поддержку основных возможностей технологии
Windows Media, включая работу с новыми кодеками и Intelligent Streaming. Windows
Media Encoder (рис. 2) включает полную поддержку кодека
Windows Media Audio, обеспечивающего наиболее достоверную передачу аудиоинформации.
Windows Media Encoder также поддерживает Intelligent Streaming — протокол, позволяющий
авторам легко создавать единый ASF-файл или поток, динамически переключающийся
между шестью скоростями передачи видеоинформации.
Среди основных возможностей Windows Media Encoder следует также упомянуть способность
преобразовывать «живое» видео и аудио CD-качества в сжатый ASF-поток, который
могут воспроизводить даже пользователи, подключенные к Internet со скоростью
28,8 Кбит/с. Упомянутая выше поддержка Intelligent Streaming обеспечивает поддержку
шести скоростей воспроизведения видеоинформации: данные могут поставляться в
диапазоне от 16 Кбит/с до 1 Мбит/с. При этом вся информация хранится в едином
ASF-файле, а Windows Media Player автоматически выбирает оптимальные скорость
и качество в зависимости от выбранного пользователем типа сетевого соединения.
Для создания различных мультимедийных бизнес-приложений и презентаций можно
использовать средства, расширяющие функции Microsoft PowerPoint. Используя PowerPoint
2000 Presentation Broadcast, можно превращать существующие слайд-шоу в поток
мультимедийной информации и интегрировать их с другими видами медиа. При работе
с PowerPoint 97 можно воспользоваться двумя дополнениями — Publish to ASF
и Windows Media Presenter. Publish to ASF превращает существующие презентации,
созданные средствами PowerPoint 97, в ASF-файлы. Используя средство Narration,
авторы могут добавлять аудиокомментарии к слайд-шоу, а затем сохранять их вместе
со слайдами в едином ASF-файле. Вся синхронизация между аудио- и визуальной
информацией поддерживается Publish to ASF.
Windows Media Presenter преобразует слайды, созданные в PowerPoint, в JPG-изображения
и динамически размещает их в потоке, автоматически синхронизируя аудиоинформацией.
С помощью Windows Media Presenter компьютер, на котором установлен PowerPoint,
может быть подключен к Windows Media Presenter для облегчения синхронизации.
В этом случае клиенты используют обычный Web-браузер для просмотра аудио- и
видеоинформации.
Windows Media Author (рис. 3) — это редактор, позволяющий
объединять аудиоинформацию с графическими изображениями, маркерами, URL-элементами
в рамках единого ASF-потока. Данный редактор может использоваться для изменения
таких характеристик графических изображений, как число цветов или качество,
для синхронизации аудиоинформации, графики, задания субтитров и скриптовых команд.
Созданный таким образом ASF-поток можно либо просматривать как файл, либо включать
в состав HTML-документов.
Кроме того, Windows Media Author можно использовать для изменения формата и
размера аудио- и графических файлов, для установки предельной скорости передачи
потока и т.п. Если размер результирующего файла оказывается слишком большим
для выбранной скорости передачи, то Windows Media Author использует средства
компрессии для уменьшения его размера без потери качества содержимого.
Помимо рассмотренных выше средств для создания и редактирования мультимедийной
информации, в Windows Media Tools входит ряд утилит, среди которых:
- VidToASF и WavToASF — для преобразования AVI-, MOV- и WAV-файлов
в ASF-формат; - ASFChop — для редактирования ASF-файлов; может использоваться для
добавления маркеров, скриптовых программ и изменения свойств, а также для
удаления маркеров из ASF-файлов; - ASFCheck — для проверки содержимого файлов в ASF-формате; может обнаруживать
существующие проблемы и при возможности исправлять их; - ASX3Test — для проверки синтаксиса ASF-файлов, созданных вручную.
В состав Windows Media также входит ряд кодеков, среди которых следует в первую
очередь отметить кодеки Microsoft MPEG-4 V3 Video Codec и Windows Media Audio
Codec. Microsoft MPEG-4 V3 Video Codec представляет собой новейшую версию
кодека MPEG-4 Video Codec, оптимизированного для Pentium III, но прекрасно
работающего и на системах с процессором Pentium II. На процессорах Pentium II
и Pentium III кодек MPEG-4 V3 обеспечивает наивысшую производительность,
частоту кадров, скорость передачи данных и разрешение для кодирования «вживую».
Windows Media Audio Codec является новейшей версией аудиокодека, оптимизированного
для воспроизведения голосовой информации и музыки. Он обеспечивает оптимальный
размер файлов без потери качества, быстрое раскодирование и высокое качество
воспроизведения по сравнению с предыдущими версиями кодеков (Sipro и Voxware).
Загрузка файлов занимает вдвое меньше времени по сравнению с загрузкой MP3-файлов;
WMA-файлы занимают практически вдвое меньше места. WMA поддерживает множество
моно- и стереостандартов для различных скоростей передачи данных по сети.
Для создания содержимого в формате Windows Media можно также использовать средства,
предоставляемые фирмами Sound Forge, Digital Renaissance, Ulead, Veon и Terran.
|
|
Синхронизация
Не последнее место в Windows Media занимает поддержка синхронизации мультимедийных
потоков. Здесь поддерживается синхронизация с использованием временных отметок
и скриптовых языков. Любой элемент Web-страницы, отображаемый в браузерах Microsoft
Internet Explorer или Netscape Navigator, может быть синхронизирован. К таким
элементам относятся: HTML, DHTML, Java-аплеты, компоненты ActiveX, VRML, элементы
для управления Chat, анимация, текст, графические изображения и даже данные
Telnet.
Сравнивая возможности синхронизации, предоставляемые Windows Media, с аналогичными
возможностями, например, RealSystems G2, следует отметить, что G2 работает как
обособленный проигрыватель, который не может быть встроен в Web-браузер. Это
ограничивает возможности синхронизации — она распространяется лишь на те типы
данных, которые поддерживает проигрыватель G2.
Дополнительно G2 использует стандарт SMIL для синхронизации мультимедийных
элементов. Этот формат обеспечивает базовую функциональность, но поддерживает
только ограниченное число типов данных. В Windows Media, напротив, используется
стандарт HTML+TIME, позволяющий синхронизировать любые элементы Web-страницы,
используя скриптовые языки типа JavaScript или VBScript. В настоящее время стандарт
HTML+TIME поддерживается в Internet Explorer 5, но ожидается, что вскоре он
будет принят всеми производителями.
Продолжая сравнивать Windows Media Player и G2, отметим, что Windows Media
Player имеет более богатый программный интерфейс, который позволяет управлять
этим проигрывателем из скриптовых языков. Например, PowerPoint 2000 Online Broadcasts
создаются на основе XML-синхронизированных слайдов за счет интеграции Windows
Media Encoder в PowerPoint. Анимационные эффекты реализованы с использованием
Dynamic HTML: клиенты получают полноценные визуальные эффекты, а не просто набор
статических слайдов. Дополнение для PowerPoint в G2 не обеспечивает этой функциональности.
|
|
Windows Media Services
Сервисы Windows Media, работающие на базе операционной системы Microsoft Windows
NT Server, позволяют посылать аудио- и видеоинформацию клиентам, использующим
операционные системы Microsoft Windows, Apple Macintosh или UNIX (проигрыватели
для систем Macintosh и UNIX в настоящее время находятся в стадии бета-тестирования).
Информация доступна одновременно многочисленным клиентам (multicast) или только
одному клиенту (unicast). В Windows Media Services используется система для
администрирования приложений и просмотра протокола их работы в реальном времени,
для управления содержимым и конфигурации, являющаяся Web-клиентом.
Для достижения максимальной масштабируемости сервисы Windows Media используют
поддержку многопоточности, реализованную в Windows NT Server. Например, компьютер
на базе Pentium II/233 может обслуживать до 2 тыс. клиентов, подключенных со
скоростью 28,8 Кбит/с.
Windows NT Server Event Manager и Performance Monitor обеспечивают средства
для слежения за состоянием и активностью Windows Media Services. Используя интегрированные
в операционную систему средства, Windows Media Services позволяют легко управлять
всей системой и ее отдельными компонентами. В противоположность этому, в RealSystem
G2 отсутствуют интегрированные средства администрирования и слежения, которые
сложны в использовании для тех, кто не знаком с UNIX.
К тому же Windows Media Services более просты в настройке, поддерживают D
DCOM и модель защиты, реализованную в Windows NT.
В состав Windows Media Services входит утилита Load Simulator, с помощью
которой можно сгенерировать несколько сотен запросов на предоставление потоковой
информации и таким образом проверить производительность сервера и сетевой архитектуры.
Это позволяет администратору убедиться в том, что все компоненты мультимедийной
системы — от жестких дисков до сети — выдерживают пиковые нагрузки.
Windows Media Services поддерживают файлы протоколов в стандартном формате
W3C, который распознается множеством программных продуктов, включая Microsoft
Site Server Usage Analyst. Помимо стандартного протокола предоставляется различная
дополнительная статистическая информация, в частности:
- число созданных потоков;
- максимальное число одновременных соединений;
- общее число уникальных идентификаторов проигрывателей;
- версия клиента, язык и данные об операционной системе;
- число потоков для каждого элемента информации;
- статистические данные об ошибках.
|
|
Коммерческие решения и режим Pay-Per-View
Используя компоненты Windows Media, можно организовывать онлайновую продажу
ASF-информации. Для этого следует обратиться к Windows Media Pay-Per-View Wizard
— специальному мастеру, который реализует защитный «барьер» между клиентом и
ASF-потоком. Доступ к информации может быть предоставлен после оплаты или соответствующей
авторизации. Реализация режима Pay-Per-View в Windows Media
Services происходит с помощью специальных компонентов, обеспечивающих интерфейс
между базой данных пользователей или другим механизмом авторизации и сервером
Windows Media (рис. 4).
Режим Pay-Per-View впервые появился в Windows Media Technologies 3.0. Для
создания коммерческих узлов требовалось написание собственных модулей авторизации.
В версии 4.0 все намного проще — используются механизмы авторизации Windows
NT.
|
|
Защита содержимого и управление правами
Digital Rights Management (DRM) — средство для защиты содержимого и управления
доступом к нему. Windows Media Rights Manager является специальным DRM-приложением,
препятствующим нелегальному распространению содержимого Windows Media. С помощью
специальных средств осуществляется кодирование содержимого и лицензирование
пользователей. Авторы могут сами выбирать способы распространения лицензионных
ключей. Это может быть, например, бесплатная регистрация либо онлайновая транзакция
с использованием кредитной карточки. В любом случае, после того как пользователь
загрузил файл, он не сможет распространять его. Используя DRM, можно обеспечивать
цифровую подпись для любого содержимого или проверять легальность использования
информации.
|
|
Поддержка электронной коммерции
Windows Media содержит встроенные интерфейсы к Site Server As Server, Site
Server Commerce Server и Site Server Membership Server. Эта функциональность
лежит в основе режима Pay-Per-View и динамического размещения рекламных объявлений
в потоковом мультимедийном наполнении Internet. В дополнение к этому в Windows
Media 4.0 добавлены HTML-шаблоны для быстрого и простого создания корпоративных
приложений.
Нам осталось рассмотреть только один компонент Microsoft Windows Media — проигрыватель
Windows Media Player. Весной этого года фирма Microsoft выпустила предварительную
версию своего мультимедийного проигрывателя — Windows Media Player 7. Именно
о ней мы и расскажем в следующем разделе.
|
|
Windows Media Player 7
Уверен, что большинство наших читателей знакомо с той или иной версий проигрывателя
Windows Media Player. Поэтому начнем с рассмотрения того, что нового появилось
в Windows Media Player 7.
Windows Media Player 7 продолжает серию проигрывателей и содержит следующие
расширения и улучшения:
- Внешний вид и дизайн. В новой версии проигрывателя кнопки стали более
наглядными; многие часто выполняемые действия и часто используемые функции
теперь доступны после нажатия всего одной кнопки. - Запись CD to PC. Поддерживаются функция записи содержимого CD на
жесткий диск всего за несколько минут и даже возможность прослушивания при
записи. За счет сохранения информации в формате Windows Media Audio, необходимый
для хранения объем в два раза меньше, чем при хранении в формате MP3. - Поддержка переносных устройств. Проигрыватель позволяет копировать
музыку на современные переносные устройства и носители, такие как Creative
Nomad II, RCA Lyra, CompactFlash, SmartMedia и устройства на базе Windows
CE. - Media Guide и радиотюнер. Руководство по интерактивной информации
в Internet — WindowsMedia.com и радиотюнер теперь являются интегрированными
компонентами проигрывателя. Щелкните всего одной кнопкой — и вам станет
доступно многое: лучшая музыка, радиостанции, фильмы, Internet-вещание и т.д. - Расширенная библиотека. Вся мультимедийная информация, как локальная,
так и удаленная, хранится в одном месте — в Media Library, где вы можете настраивать,
редактировать и организовывать ее по своему усмотрению. - Улучшенное управление. Проигрыватель содержит интегрированный 10-полосный
аудиоэквалайзер более чем с 20 настройками, позволяющими вам слушать звук
таким, каким он вам нравится. Для видеоклипов предоставляется средство для
изменения яркости, контрастности и насыщенности. - Интерактивные «накладки». «Накладки» (skins) позволяют изменять внешний
вид проигрывателя. В отличие от проигрывателей других фирм, Windows Media
Player поддерживает расширенную функциональность, анимацию и дополнительные
расширения. - Поддержка визуализации. Проигрыватель поставляется более чем с 20
профессиональными, настраиваемыми двух- и трехмерными анимациями, которые
могут сопровождать воспроизводимую проигрывателем музыку. - Расширенная информация. Можно получить подробную информацию о вашем
любимом артисте (биография, дискография, обзоры и т.п.), не покидая проигрывателя,
прямо из лучшего источника — All Music Guide. - Управление правами. Встроенная поддержка DRM 2.0 обеспечивает сохранение
авторских прав и возможность приобретения любой информации и ее воспроизведения
без использования каких-либо дополнительных программных средств. - Локализация. Клиентская часть проигрывателя и содержимое Media
Guide переведены более чем на 20 языков.
После того как мы ознакомились с основными новинками в Windows Media Player
7, остановимся на некоторых нововведениях более подробно. Начнем с простоты
использования, а также с нового внешнего вида и дизайна.
Как показали исследования, проведенные фирмой Microsoft, большинству пользователей
абсолютно неинтересны такие технические характеристики, как скорость передачи,
кодеки, различия в цифровой и аналоговой записи. Все, что им нужно, — это быстрый
и удобный доступ к информации. Исходя из этого Microsoft разработала новый интуитивный
интерфейс, существенно облегчающий основные операции: поиск информации, копирование
музыки на переносные устройства и т.п. Так, в новой версии проигрывателя появились
более наглядные кнопки, доступ к списку проигрывателя и увеличенные в размере
кнопки Play, Pause и Stop.
Как видно из рис. 5, интерфейс Windows Media Player 7
стал более простым. В частности, появились кнопки, обеспечивающие доступ к наиболее
часто используемым функциям, улучшен поиск радиостанций (Radio Guide) —
теперь есть функции поиска более чем 1500 радиостанций по местоположению, жанрам,
языкам, частоте и даже позывным. Встроенные функции обновления позволяют пользователям
всегда иметь самую последнюю версию проигрывателя — все необходимые компоненты
устанавливаются автоматически.
Поддержка протокола рlug-and-рlay для связи с переносными устройствами и компьютерами
на базе Windows CE позволяет переносить музыкальные файлы и
списки проигрывателя нажатием всего одной клавиши (рис. 6).
В табл. 1 показаны переносные устройства, поддерживающие
Windows Media.
Как видно из табл. 1, помимо переносных проигрывателей,
Windows Media поддерживает различные устройства хранения мультимедийной информации.
Для этого используется специальный менеджер устройств — Windows Media Device
Manager (WMDM), представляющий собой универсальный драйвер, схожий с используемым
в Windows универсальным драйвером принтера или привода CD-ROM. С таким универсальным
драйвером проигрыватель не зависит от конкретного устройства — эти функции возлагаются
на специальный модуль, предоставляемый производителем устройства.
Не менее важной функцией является поддержка управления авторскими правами — Digital Rights Management. В отличие от других проигрывателей, Windows Media
Player 7 полностью поддерживает управление правами, включая управление копиями,
загруженными из онлайновых магазинов.
В табл. 2 и 3 приводится сравнение
проигрывателя Windows Media Player 7 с проигрывателями фирмы RealNetworks.
Среди множества функций, поддерживаемых Windows Media Player 7, следует выделить
возможность сохранения аудиотреков музыкальных CD-ROM в виде файлов (в формате
Windows Media). С помощью этой функции можно создавать коллекции для последующего
прослушивания. В зависимости от выбранного качества целый музыкальный CD-ROM
может занимать от 28 Мбайт (Radio Quality) до 69 Мбайт (CD Quality).
Следующая функция, которую нужно отметить, — это улучшенные возможности для
воспроизведения видеоинформации. Как известно, монитор, установленный у каждого
пользователя, отличается настройками, и даже обычный свет может влиять на качество
воспроизводимого видеоклипа.
В Windows Media Player 7 реализован ряд функций для оптимизации настроек при
воспроизведении видеоклипов. Улучшенные органы настройки позволяют изменять
такие характеристики, как яркость, насыщенность, контрастность, и создавать
собственные наборы настроек (рис. 7). Более того, Windows Media Player 7
дает возможность просматривать видео непосредственно из Internet, автоматически
подбирая наиболее подходящее качество для данной скорости соединения. Встроенный
в проигрыватель кодек MPEG реализован по той же технологии, что и кодек, используемый
в DVD (в проигрывателях и спутниковом телевидении), и оптимизирован для использования
с новейшими моделями процессоров фирм Intel и AMD.
Встроенный 10-полосный эквалайзер позволяет либо использовать
предопределенные настройки (pop, rock и т.п.), либо создавать собственные и
сохранять их для дальнейшего использования.
Выше мы уже сказали о возможности сохранения аудиотреков музыкальных CD-ROM
в виде файлов. При этом Windows Media обеспечивает CD-качество, занимая вдвое
меньше места, чем хранение в формате MP3. Исследования, проведенные ZD Labs,
показали, что более 90% слушателей не смогли обнаружить каких-либо различий
между WMF-файлами и MP3-файлами, созданными RealJukebox. При этом WMF-файлы
занимали вдвое меньше места. Заметим, что в настоящее время все ведущие производители
аудиопродукции поставляют аудио в формате WMF. Этот формат поддерживается и
всеми производителями переносных музыкальных устройств.
Говоря о воспроизведении видео, отметим, что данный проигрыватель использует
стандартные кодеки и воспроизводит видео с более высоким качеством.
Перечисляя основные новинки проигрывателя Windows Media Player 7, мы упомянули
об интерактивных накладках (skins). С их помощью пользователи могут легко
изменять внешний вид проигрывателя, руководствуясь своими вкусами или какими-либо
иными критериями. Более того, некоторые фирмы производят специализированные
тематические накладки. Например, можно приобрести накладку, стилизованную под
гитару, что прекрасно подходит для прослушивания альбомов Эрика Клэптона, или
же абстрактную накладку для альбомов Pink Floyd.
В Windows Media Player имеется набор предопределенных накладок. Дополнительные
накладки можно купить либо создать самостоятельно, с помощью средств, входящих
в состав Windows Media Software Development Kit (SDK). Разработчики для создания
собственных накладок могут использовать стандартную графику, XML и JavaScript.
Завершая данный обзор, подчеркнем, что Windows Media Player 7 представляет
собой лучший на сегодня проигрыватель мультимедийной информации, тесно интегрированный
с технологией Windows Media. Он обеспечивает, помимо стандартных, множество
дополнительных функций и позволяет использовать его как для простого воспроизведения
аудио- и видеоинформации, так и в составе мультимедийных разработок.
На нашем CD-ROM вы найдете проигрыватель Windows Media Player 7, Windows Media
Player 7 SDK, Windows Media Format SDK (для получения компоновочной библиотеки
вы должны зарегистрироваться на Web-сайте фирмы Microsoft) и рассмотренные в
данном обзоре средства для создания Windows Media-файлов.
КомпьютерПресс 6’2000
Windows 10 Windows 8.1 Windows 7 Windows Media Player Еще…Меньше
Предназначены для любителей мультимедиа любителей. Проигрыватель Windows Media 12, который входит в состав Windows 7, Windows 8.1 и Windows 10*, воспроизводит больше музыки и видео, чем когда-либо раньше, в том числе записи с видеокамер Flip Video и незащищенные песни из библиотеки iTunes. Упорядочивайте свою цифровую медиаколлекцию, синхронизируйте медиафайлы с портативным устройством, покупайте цифровой мультимедийный контент в Интернете и выполняйте другие операции с помощью проигрывателя Windows Media Player 12.
Более удобные режимы воспроизведения
Режим текущего списка воспроизведения — это воплощение минимализма: в нем отображаются только необходимые элементы управления, поэтому ничто не мешает вам воспринимать музыку или видео. Новый эскиз панели задач (с элементами управления воспроизведением) делает предварительный просмотр более простым и увлекательным.
Больше мультимедиа на всех ваших устройствах
Проигрыватель Windows Media 12 поддерживает многие распространенные аудио- и видеоформаты. Синхронизируйте музыку, видео и фотографии или передавайте медиафайлы на другие устройства, чтобы наслаждаться своей библиотекой и дома, и в дороге.
Сведения о последней версии вашей системы см. в разделе Скачать проигрыватель Windows Media.
Чтобы вручную устранить неполадки или обновить установку проигрывателя, выполните следующие действия.
-
Нажмите кнопку Пуск , введите компоненты и выберите Включение или отключение компонентов Windows.
-
Разверните Компоненты для работы с мультимедиа и проверьте, установлен ли флажок Проигрыватель Windows Media. Если это так, снимите флажок.
-
Нажмите кнопку ОК и перезагрузите компьютер. Это приведет к удалению текущей версии проигрывателя Windows Media.
-
После перезапуска компьютера повторите шаг 1.
-
Разверните Компоненты для работы с мультимедиа и установите флажок Проигрыватель Windows Media.
-
Нажмите кнопку ОК и перезагрузите компьютер. Это приведет к переустановке последней версии проигрывателя Windows Media в вашей системе (чаще всего это проигрыватель Windows Media 12 с некоторыми исключениями).
Примечание: Проигрыватель Windows Media недоступен для Windows RT 8.1.
* Проигрыватель Windows Media 12 входит в чистые установки Windows 10, а также обновления до Windows 10 с Windows 8,1 или Windows 7. Воспроизведение DVD-дисков в Windows 10 или Windows 8.1 не поддерживается. Перейдите на страницу Параметры воспроизведения DVD для Windows, чтобы узнать, как добавить функцию воспроизведения DVD.
Нужна дополнительная помощь?
Содержание
- Windows Player — простота и функционал
- Скачиваем и устанавливаем Windows Player
- Управление просмотром видео
- Подробнее о функции HQ — улучшение видео
- Заключение
Привет друзья! Сегодня решил подготовить статью, которая будет полезная всем без исключения. На моем блоге можно встретить не много статей, в которых я делаю обзоры и рекомендую какие-то программы для определенных задач. Меня часто спрашивают и не только в интернете, а какую программу лучше использовать для прослушивания музыки, для серфинга в интернете, просмотра видео и т. д. И как правило, я рекомендую то, чем пользуюсь сам и те программы, которые действительно заслуживают внимания.
Сегодня постараемся решить, какая же программа лучше всего подходит для просмотра видео. Видеоплеер, ну наверное очень нужная программа, которую многие устанавливают сразу же после установки операционной системы. Смотрите фильмы на компьютере? Думаю что да, я лично смотрю. Сейчас уже модно смотреть все онлайн, но я как-то по старинке сначала скачиваю на компьютер и тогда уже смотрю, да и не всегда подключен к скоростному интернету, а на выходные через 3G много не посмотришь, тем более с их ценами :).
Windows Player — простота и функционал
Так вот, значит сейчас поговорим о видеоплеерах, точнее об одном — Windows Player. Сразу скажу, не путать со стандартным плеером Windows Media Player, который по умолчанию установлен в операционной системе Windows, а в Windows 8 он вообще с урезанным функционалом. Но это наверное не страшно, стандартным Windows Media Player и так никто не пользуется, или единицы, которые не хотят тратить несколько минут на установку нормального плеера.
Я уже некоторое время пользуюсь видеоплеером Windows Player, реально классная программа для просмотра видео. Сейчас напишу несколько слов о преимуществах и функционале, а затем расскажу откуда можно скачать, как установить и пользоваться. Хотя много писать не придется, действительно простая программа.
Главное преимущество Windows Player перед другими аналогичными программами и тем более стандартным проигрывателем, это простота и функциональность. Да, эти два пункта удалось совместить создателям Windows Player. Сейчас что модно и актуально? Минимализм и функционал. Много кнопок, меню на пол экрана и несколько часов на настройку программы — это все в прошлом. Ну и конечно же качество воспроизведение видео. У Windows Player с этим проблем нет, проверено.
Основные преимущества:
- Вы знаете что такое «кодек»? Наверное не раз искали и устанавливали их. Так вот Windows Player воспроизводит видео без кодеков. Аудио кстати тоже 🙂
- Очень красивый интерфейс и простое управление
- Качество воспроизведение видео высокой четкости
- Функция улучшения звука (пригодится, когда смотрите фильм на ноутбуке, а звук в фильме очень тихий)
- Функция HQ для улучшения качества изображения. Работает действительно классно, напишу о ней подробнее.
Подробнее о плеере можете почить на официальном сайте http://windowsplayer.ru
Я в последнее время делаю очень длинные вступления. Нет? Мне кажется, что до основной части немногие дочитывают :).
Скачиваем и устанавливаем Windows Player
Забыл сказать, что этот плеер абсолютно бесплатный. Для загрузки заходим на страницу http://windowsplayer.ru/download и нажимаем на ссылку загрузки установочного файла в формате .exe, но можно скачать и в архиве.
Я советую выбрать «Запуск», так установка начнется автоматически. Если Вы сохраните установочный файл, то для установки плеера нужно будет его запустить.
Установка очень простая. В основном это нажатие на кнопку «Далее». Я не буду показывать весь процесс установки, это только множество ненужных скриншотов. Покажу только первый и несколько последних. В начале установки нажимаем кнопку «Далее».
Продолжаем установку. Когда увидите окно, как на скриншоте ниже, то советую установить галочку возле «Открывать все видеофайлы в Windows Player». Это значит, что при двойном нажатии на фильм, он будет открываться через Windows Player. Так же можете установить открытие музыки через Windows Player.
Продолжаем установку, пока не увидите вот такое окно:
Все, установка завершена. Windows Player должен запустится сам.
Управление просмотром видео
Уже можно приступить к просмотру Ваших любимых фильмов, ничего настраивать не нужно. Но я хочу написать еще о некоторых функция, а особенно о HQ, которая улучшает изображение и судя по скриншоте на официальном сайте, улучшает неплохо.
Сделаю описание некоторых кнопок на главной панели:
- Открыть файл. Вы можете в проводнике выбрать файл для воспроизведения
- Активация функции HQ — улучшение видео
- Улучшение звука
- Выводит изображение на ТВ
- Параметры видео. Можно отрегулировать яркость, контраст и т. д.
- Эквалайзер
Остальные элементы, это управление воспроизведением и звуком.
Что бы открыть дополнительные настройки, нажмите на иконку в верхнем левом углу.
Подробнее о функции HQ — улучшение видео
На сайте проигрывателя предоставлены очень красивые скриншоты по работе функции HQ. Вот один из них:
Действительно хороший эффект. Правда? Но я решил сам протестировать эту функцию и предоставить Вам свои скриншоты. Вот что у меня получилось.
Функция HQ отключена:
Функция HQ включена:
Как видите, эффект от включения HQ есть и хороший, (правда качество самых скриншотов не очень).
Заключение
Современный, простой и функциональный плеер, который отлично справляется со своей основной задачей. Так же у команды которая создала Windows Player большие планы на будущие. На официальном сайте есть список функций, которые в ближайшее время будут добавлены в проигрыватель. Среди которых: конвертирование видео, воспроизведение потокового видео и ТВ и т. д.
Больше ничего писать не буду. Скачивайте, устанавливайте, пользуйтесь и не забивайте обновлять, что бы не пропустить новые фишки от Windows Player.
Как и всегда, жду Ваши мнения в комментариях ниже. Всего хорошего!
«Виндовс Медиаплеер» является неотъемлемым компонентом любой операционной системы Windows. Даже после первоначальной инсталляции системы на компьютер или ноутбук он устанавливается проигрывателем файлов мультимедиа (аудио и видео) по умолчанию. Однако многие пользователи Windows-систем его, мягко говоря, недолюбливают из-за ограниченных возможностей и сбоев в работе. По всей видимости, такие юзеры просто не до конца разобрались со всем тем, на что способен этот плеер.
«Виндовс Медиаплеер»: основные характеристики
Давайте начнем с того, что сам проигрыватель совмещает в себе достаточного много возможностей. Он умеет не только воспроизводить мультимедиа-контент.
Среди основных инструментов стоит отметить четкую систему организации плейлистов, быстрое извлечение треков или запись музыки на оптические или USB-носители, сортировку коллекций, поиск нужного материала в Интернете, редактирование информационных ID3-тэгов, подключение дополнительных модулей в виде плагинов для обработки звука, создание и использование инструментов визуализации и многое другое.
Все это хорошо, но есть и свои минусы. Например, «Медиаплеер» для «Виндовс 7» совершенно неадекватно относится к открытию некоторых файлов вроде роликов, имеющих расширение DAT. Да, действительно, такие файлы могут относиться и к базам данных, а открывать в проигрывателе их приходится вручную. Но самое основное состоит в том, что «Виндовс Медиаплеер» ориентирован изначально на «родные» форматы Windows (WMA, WMV), а для остальных просто заявлена поддержка.
Проблемы проигрывателя
Кроме всего прочего, данный проигрыватель не всегда ведет себя адекватно при воспроизведении. Например, если на DVD присутствуют титры, плеер может их не воспроизводить или выдавать какой-то несуразный набор нечитаемых символов. Связано это с тем, что в нем изначально нет поддержки необходимых кодеков и декодеров.
Впрочем, проблема совершенно элементарно решается за счет установки пакетов K-Lite (лучше всего для инсталляции выбрать Mega Pack), в которых сразу же нужно задать применение ассоциаций. После этого, правда, оригинальный проигрыватель может быть деактивирован, а система выдаст сообщение о том, что стандартное приложение сброшено. Почему так происходит? Да только потому, что при установке пакета в систему (если, конечно, пользователь отметил этот пункт) дополнительно устанавливается плеер в виде версии Classic.
«Виндовс Медиаплеер Классик»: скрытые возможности
Раньше отдельно инсталлировать классическую версию проигрывателя было не нужно. Она и так присутствовала в системе, хотя и была скрыта от глаз пользователя. Почему так произошло, доподлинно неизвестно. Но, по всей видимости, корпорация Microsoft просто пыталась актуализировать свою основную разработку, которая, к сожалению, оказалась намного хуже классической.
Основное преимущество классического проигрывателя состоит в том, что он не только распознает абсолютно все доступные форматы (хотя открывать их и приходится вручную), но и в сравнении с оригинальным плеером ресурсов потребляет как минимум вдвое меньше. Почему так? Всему виной, как оказывается, графическая оболочка (в Windows XP при использовании оригинального «Виндовс Медиаплеера» наблюдается такое торможение, что загрузка системных ресурсов достигает пиковых значений, а воспроизведение идет с постоянным прерыванием звука или появлением квадратиков на изображении).
Что использовать для воспроизведения мультимедиа?
Как уже понятно, если не говорить о сторонних программах, лучше отдать предпочтение все-таки классической версии проигрывателя, которую можно установить в процессе инсталляции набора кодеков и декодеров. Таким образом можно и снизить нагрузку на использование системных ресурсов, и добиться возможности воспроизведения любого контента мультимедиа, известного на сегодняшний день.