| Filename extensions | .bat, .cmd, .btm |
|---|---|
| Internet media type |
|
| Type of format | Scripting |
| Container for | Scripts |
A batch file is a script file in DOS, OS/2 and Microsoft Windows. It consists of a series of commands to be executed by the command-line interpreter, stored in a plain text file. A batch file may contain any command the interpreter accepts interactively and use constructs that enable conditional branching and looping within the batch file, such as IF, FOR, and GOTO labels. The term «batch» is from batch processing, meaning «non-interactive execution», though a batch file might not process a batch of multiple data.
Similar to Job Control Language (JCL), DCL and other systems on mainframe and minicomputer systems, batch files were added to ease the work required for certain regular tasks by allowing the user to set up a script to automate them. When a batch file is run, the shell program (usually COMMAND.COM or cmd.exe) reads the file and executes its commands, normally line-by-line.[1] Unix-like operating systems, such as Linux, have a similar, but more flexible, type of file called a shell script.[2]
The filename extension .bat is used in DOS and Windows. Windows NT and OS/2 also added .cmd. Batch files for other environments may have different extensions, e.g., .btm in 4DOS, 4OS2 and 4NT related shells.
The detailed handling of batch files has changed significantly between versions. Some of the detail in this article applies to all batch files, while other details apply only to certain versions.
Variants[edit]
DOS[edit]
In MS-DOS, a batch file can be started from the command-line interface by typing its name, followed by any required parameters and pressing the ↵ Enter key. When DOS loads, the file AUTOEXEC.BAT, when present, is automatically executed, so any commands that need to be run to set up the DOS environment may be placed in this file. Computer users would have the AUTOEXEC.BAT file set up the system date and time, initialize the DOS environment, load any resident programs or device drivers, or initialize network connections and assignments.
A .bat file name extension identifies a file containing commands that are executed by the command interpreter COMMAND.COM line by line, as if it were a list of commands entered manually, with some extra batch-file-specific commands for basic programming functionality, including a GOTO command for changing flow of line execution.
Early Windows[edit]
Microsoft Windows was introduced in 1985 as a graphical user interface-based (GUI) overlay on text-based operating systems and was designed to run on DOS. In order to start it, the WIN command was used, which could be added to the end of the AUTOEXEC.BAT file to allow automatic loading of Windows. In the earlier versions, one could run a .bat type file from Windows in the MS-DOS Prompt. Windows 3.1x and earlier, as well as Windows 9x invoked COMMAND.COM to run batch files.
OS/2[edit]
The IBM OS/2 operating system supported DOS-style batch files. It also included a version of REXX, a more advanced batch-file scripting language. IBM and Microsoft started developing this system, but during the construction of it broke up after a dispute; as a result of this, IBM referred to their DOS-like console shell without mention of Microsoft, naming it just DOS, although this seemingly made no difference with regard to the way batch files worked from COMMAND.COM.
OS/2’s batch file interpreter also supports an EXTPROC command. This passes the batch file to the program named on the EXTPROC file as a data file. The named program can be a script file; this is similar to the #! mechanism used by Unix-like operating systems.
Windows NT[edit]
Unlike Windows 98 and earlier, the Windows NT family of operating systems does not depend on MS-DOS. Windows NT introduced an enhanced 32-bit command interpreter (cmd.exe) that could execute scripts with either the .CMD or .BAT extension. Cmd.exe added additional commands, and implemented existing ones in a slightly different way, so that the same batch file (with different extension) might work differently with cmd.exe and COMMAND.COM. In most cases, operation is identical if the few unsupported commands are not used. Cmd.exe’s extensions to COMMAND.COM can be disabled for compatibility.
Microsoft released a version of cmd.exe for Windows 9x and ME called WIN95CMD to allow users of older versions of Windows to use certain cmd.exe-style batch files.
As of Windows 8, cmd.exe is the normal command interpreter for batch files; the older COMMAND.COM can be run as well in 32-bit versions of Windows able to run 16-bit programs.[nb 1]
Filename extensions[edit]
- .bat
- The first filename extension used by Microsoft for batch files. This extension runs with DOS and all versions of Windows, under COMMAND.COM or cmd.exe, despite the different ways the two command interpreters execute batch files.
- .cmd
- Used for batch files in Windows NT family and sent to cmd.exe for interpretation. COMMAND.COM does not recognize this file name extension, so cmd.exe scripts are not executed in the wrong Windows environment by mistake. In addition,
append,dpath,ftype,set,path,assocandpromptcommands, when executed from a .bat file, alter the value of theerrorlevelvariable only upon an error, whereas from within a .cmd file, they would affect errorlevel even when returning without an error.[3] It is also used by IBM’s OS/2 for batch files. - .btm
- The extension used by 4DOS, 4OS2, 4NT and Take Command. These scripts are faster, especially with longer ones, as the script is loaded entirely ready for execution, rather than line-by-line.[4]
Batch file parameters[edit]
COMMAND.COM and cmd.exe support special variables (%0, %1 through %9) in order to refer to the path and name of the batch job and the first nine calling parameters from within the batch job, see also SHIFT. Non-existent parameters are replaced by a zero-length string. They can be used similar to environment variables, but are not stored in the environment. Microsoft and IBM refer to these variables as replacement parameters or replaceable parameters, whereas Digital Research, Novell and Caldera established the term replacement variables[5] for them. JP Software calls them batch file parameters.[6]
Examples[edit]
This example batch file displays Hello World!, prompts and waits for the user to press a key, and then terminates. (Note: It does not matter if commands are lowercase or uppercase unless working with variables)
@ECHO OFF ECHO Hello World! PAUSE
To execute the file, it must be saved with the filename extension suffix .bat (or .cmd for Windows NT-type operating systems) in plain text format, typically created by using a text editor such as Microsoft Notepad or a word processor working in plain text mode.
When executed, the following is displayed:
Hello World! Press any key to continue . . .
Explanation[edit]
The interpreter executes each line in turn, starting with the first. The @ symbol at the start of any line prevents the prompt from displaying that command as it is executed. The command ECHO OFF turns off the prompt permanently, or until it is turned on again. The combined @ECHO OFF is often as here the first line of a batch file, preventing any commands from displaying, itself included. Then the next line is executed and the ECHO Hello World! command outputs Hello World!. The next line is executed and the PAUSE command displays Press any key to continue . . . and pauses the script’s execution. After a key is pressed, the script terminates, as there are no more commands. In Windows, if the script is executed from an already running command prompt window, the window remains open at the prompt as in MS-DOS; otherwise, the window closes on termination.
Limitations and exceptions[edit]
Null values in variables[edit]
Variable expansions are substituted textually into the command, and thus variables which contain nothing simply disappear from the syntax, and variables which contain spaces turn into multiple tokens. This can lead to syntax errors or bugs.
For example, if %foo% is empty, this statement:
parses as the erroneous construct:
Similarly, if %foo% contains abc def, then a different syntax error results:
IF abc def==bar ECHO Equal
The usual way to prevent this problem is to surround variable expansions in quotes so that an empty variable expands into the valid expression IF ""=="bar" instead of the invalid IF ==bar. The text that is being compared to the variable must also be enclosed in quotes, because the quotes are not special delimiting syntax; these characters represent themselves.
IF "%foo%"=="bar" ECHO Equal
The delayed !VARIABLE! expansion available in Windows 2000 and later may be used to avoid these syntactical errors. In this case, null or multi-word variables do not fail syntactically because the value is expanded after the IF command is parsed:
Another difference in Windows 2000 or higher is that an empty variable (undefined) is not substituted. As described in previous examples, previous batch interpreter behaviour would have resulted in an empty string. Example:
C:>set MyVar= C:>echo %MyVar% %MyVar% C:>if "%MyVar%"=="" (echo MyVar is not defined) else (echo MyVar is %MyVar%) MyVar is %MyVar%
Batch interpreters prior to Windows 2000 would have displayed result MyVar is not defined.
Quotation marks and spaces in passed strings[edit]
Unlike Unix/POSIX processes, which receive their command-line arguments already split up by the shell into an array of strings, a Windows process receives the entire command-line as a single string, via the GetCommandLine API function. As a result, each Windows application can implement its own parser to split the entire command line into arguments. Many applications and command-line tools have evolved their own syntax for doing that, and so there is no single convention for quoting or escaping metacharacters on Windows command lines.
- For some commands, spaces are treated as delimiters that separate arguments, unless those spaces are enclosed by quotation marks. Various conventions exist of how quotation marks can be passed on to the application:
- A widely used convention is implemented by the command-line parser built into the Microsoft Visual C++ runtime library in the CommandLineToArgvW function. It uses the convention that 2n backslashes followed by a quotation mark («) produce n backslashes followed by a begin/end quote, whereas (2n)+1 backslashes followed by a quotation mark again produce n backslashes followed by a quotation mark literal. The same convention is part of the .NET Framework specification.[7]
- An undocumented aspect is that «» occurring in the middle of a quoted string produces a single quotation mark.[7] (A CRT change in 2008 [msvcr90] modified this undocumented handling of quotes.[8]) This is helpful for inserting a quotation mark in an argument without re-enabling interpretation of cmd metacharacters like |, & and >. (cmd does not recognize the usual « as escaping the quote. It re-enables these special meanings on seeing the quote, thinking the quotation has ended.)
- Another convention is that a single quotation mark («) is not included as part of the string. However, an escaped quotation mark («»») can be part of the string.[citation needed]
- Yet another common convention comes from the use of Cygwin-derived ported programs. It does not differentiate between backslashes occurring before or not before quotes. See glob (programming) § Windows and DOS for information on these alternative command-line parsers.[9]
- Some important Windows commands, like
cmd.exeandwscript.exe, use their own rules.[8]
- A widely used convention is implemented by the command-line parser built into the Microsoft Visual C++ runtime library in the CommandLineToArgvW function. It uses the convention that 2n backslashes followed by a quotation mark («) produce n backslashes followed by a begin/end quote, whereas (2n)+1 backslashes followed by a quotation mark again produce n backslashes followed by a quotation mark literal. The same convention is part of the .NET Framework specification.[7]
- For other commands, spaces are not treated as delimiters and therefore do not need quotation marks. If quotes are included they become part of the string. This applies to some built-in commands like echo.
Where a string contains quotation marks, and is to be inserted into another line of text that must also be enclosed in quotation marks, particular attention to the quoting mechanism is required:
C:>set foo="this string is enclosed in quotation marks" C:>echo "test 1 %foo%" "test 1 "this string is enclosed in quotation marks"" C:>eventcreate /T Warning /ID 1 /L System /SO "Source" /D "Example: %foo%" ERROR: Invalid Argument/Option - 'string'. Type "EVENTCREATE /?" for usage.
On Windows 2000 and later, the solution is to replace each occurrence of a quote character within a value by a series of three quote characters:
C:>set foo="this string is enclosed in quotes" C:>set foo=%foo:"="""% C:>echo "test 1 %foo%" "test 1 """this string is enclosed in quotes"""" C:>eventcreate /T Warning /ID 1 /L System /SO "Source" /D "Example: %foo%" SUCCESS: A 'Warning' type event is created in the 'Source' log/source.
Escaped characters in strings[edit]
Some characters, such as pipe (|) characters, have special meaning to the command line. They cannot be printed as text using the ECHO command unless escaped using the caret ^ symbol:
C:>Echo foo | bar 'bar' is not recognized as an internal or external command, operable program or batch file. C:>Echo foo ^| bar foo | bar
However, escaping does not work as expected when inserting the escaped character into an environment variable. The variable ends up containing a live pipe command when merely echoed. It is necessary to escape both the caret itself and the escaped character for the character display as text in the variable:
C:>set foo=bar | baz 'baz' is not recognized as an internal or external command, operable program or batch file. C:>set foo=bar ^| bar C:>echo %foo% 'baz' is not recognized as an internal or external command, operable program or batch file. C:>set foo=bar ^^^| baz C:>echo %foo% bar | baz
The delayed expansion available with or with in Windows 2000 and later may be used to show special characters stored in environment variables because the variable value is expanded after the command was parsed:
C:>cmd /V:ON Microsoft Windows [Version 6.1.7601] Copyright (c) 2009 Microsoft Corporation. All rights reserved. C:>set foo=bar ^| baz C:>echo !foo! bar | baz
Sleep or scripted delay[edit]
Until the TIMEOUT command was introduced with Windows Vista, there was no easy way to implement a timed pause, as the PAUSE command halts script activity indefinitely until any key is pressed.
Many workarounds were possible,[10] but generally only worked in some environments: The CHOICE command was not available in older DOS versions, PING was only available if TCP/IP was installed, and so on. No solution was available from Microsoft, but a number of small utility programs, could be installed from other sources. A commercial example would be the 1988 Norton Utilities Batch Enhancer (BE) command, where BE DELAY 18 would wait for 1 second, or the free 94-byte WAIT.COM[11] where WAIT 5 would wait for 5 seconds, then return control to the script. Most such programs are 16-bit .COM files, so are incompatible with 64-bit Windows.
Text output with stripped CR/LF[edit]
Normally, all printed text automatically has the control characters for carriage return (CR) and line feed (LF) appended to the end of each line.
- batchtest.bat
-
C:>batchtest.bat foo bar
-
It does not matter if the two echo commands share the same command line; the CR/LF codes are inserted to break the output onto separate lines:
C:>@echo Message 1&@echo Message 2 Message 1 Message 2
A trick discovered with Windows 2000 and later is to use the special prompt for input to output text without CR/LF trailing the text. In this example, the CR/LF does not follow Message 1, but does follow Line 2 and Line 3:
- batchtest2.bat
-
@echo off set /p ="Message 1"<nul echo Message 2 echo Message 3
-
C:>batchtest2.bat Message 1Message 2 Message 3
-
This can be used to output data to a text file without CR/LF appended to the end:
C:>set /p ="Message 1"<nul >data.txt C:>set /p ="Message 2"<nul >>data.txt C:>set /p ="Message 3"<nul >>data.txt C:>type data.txt Message 1Message 2Message 3
However, there is no way to inject this stripped CR/LF prompt output directly into an environment variable.
Setting a Uniform Naming Convention (UNC) working directory from a shortcut[edit]
It is not possible to have a command prompt that uses a UNC path as the current working directory; e.g. \serversharedirectory
The command prompt requires the use of drive letters to assign a working directory, which makes running complex batch files stored on a server UNC share more difficult. While a batch file can be run from a UNC file path, the working directory default is C:WindowsSystem32.
In Windows 2000 and later, a workaround is to use the PUSHD and POPD command with command extensions.[nb 2]
If not enabled by default, command extensions can be temporarily enabled using the /E:ON switch for the command interpreter.
So to run a batch file on a UNC share, assign a temporary drive letter to the UNC share, and use the UNC share as the working directory of the batch file, a Windows shortcut can be constructed that looks like this:
- Target:
The working directory attribute of this shortcut is ignored.
This also solves a problem related to User Account Control (UAC) on Windows Vista and newer. When an administrator is logged on and UAC is enabled, and they try to run a batch file as administrator from a network drive letter, using the right-click file context menu, the operation will unexpectedly fail. This is because the elevated UAC privileged account context does not have network drive letter assignments, and it is not possible to assign drive letters for the elevated context via the Explorer shell or logon scripts. However, by creating a shortcut to the batch file using the above PUSHD / POPD construct, and using the shortcut to run the batch file as administrator, the temporary drive letter will be created and removed in the elevated account context, and the batch file will function correctly.
The following syntax does correctly expand to the path of the current batch script.
%~dp0
UNC default paths are turned off by default as they used to crash older programs.[12]
The Dword registry value DisableUNCCheck at HKEY_CURRENT_USERSoftwareMicrosoftCommand Processor[12] allows the default directory to be UNC. CD command will refuse to change but placing a UNC path in Default Directory in a shortcut to Cmd or by using the Start command. (C$ share is for administrators).
Character set[edit]
Batch files use an OEM character set, as defined by the computer, e.g. Code page 437. The non-ASCII parts of these are incompatible with the Unicode or Windows character sets otherwise used in Windows so care needs to be taken.[13] Non-English file names work only if entered through a DOS character set compatible editor. File names with characters outside this set do not work in batch files.
To get a command prompt with Unicode instead of Code page 437 or similar, one can use the cmd /U command. In such a command prompt, a batch file with Unicode filenames will work. Also one can use cmd /U to directly execute commands with Unicode as character set. For example, cmd /U /C dir > files.txt creates a file containing a directory listing with correct Windows characters, in the UTF-16LE encoding.
Batch viruses and malware[edit]
As with any other programming language, batch files can be used maliciously. Simple trojans and fork bombs are easily created, and batch files can do a form of DNS poisoning by modifying the hosts file. Batch viruses are possible, and can also spread themselves via USB flash drives by using Windows’ Autorun capability.[14]
The following command in a batch file will delete all the data in the current directory (folder) — without first asking for confirmation:
These three commands are a simple fork bomb that will continually replicate itself to deplete available system resources, slowing down or crashing the system:
:TOP start "" %0 goto TOP
Other Windows scripting languages[edit]
The cmd.exe command processor that interprets .cmd files is supported in all 32- and 64-bit versions of Windows up to at least Windows 10. COMMAND.EXE, which interprets .BAT files, was supported in all 16- and 32-bit versions up to at least Windows 10.[nb 3]
There are other, later and more powerful, scripting languages available for Windows. However, these require the scripting language interpreter to be installed before they can be used:
- Extended Batch Language (EBL) (.bat) — developed by Frank Canova as an ‘own-time’ project while working at IBM in 1982. It was subsequently sold by Seaware Corp as an interpreter and compiler primarily for DOS, but later for Windows.
- KiXtart (.kix) — developed by a Microsoft employee in 1991, specifically to meet the need for commands useful in a network logon script while retaining the simple ‘feel’ of a .cmd file.
- Windows Script Host (.vbs , .js and .wsf) — released by Microsoft in 1998, and consisting of cscript.exe and wscript.exe, runs scripts written in VBScript or JScript. It can run them in windowed mode (with the wscript.exe host) or in console-based mode (with the cscript.exe host). They have been a part of Windows since Windows 98.
- PowerShell (.ps1) — released in 2006 by Microsoft and can operate with Windows XP (SP2/SP3) and later versions. PowerShell can operate both interactively (from a command-line interface) and also via saved scripts, and has a strong resemblance to Unix shells.[15]
- Unix-style shell scripting languages can be used if a Unix compatibility tool, such as Cygwin, is installed.
- Cross-platform scripting tools including Perl, Python, Ruby, Rexx, Node.js and PHP are available for Windows.
Script files run if the filename without extension is entered. There are rules of precedence governing interpretation of, say, DoThis if DoThis.com, DoThis.exe, DoThis.bat, DoThis.cmd, etc. exist; by default DoThis.com has highest priority. This default order may be modified in newer operating systems by the user-settable PATHEXT environment variable.
See also[edit]
- List of DOS commands
Notes[edit]
- ^ To verify that COMMAND.COM remains available (in the WINDOWSSYSTEM32 directory), type
COMMAND.COMat the 32-bit Windows 7 command prompt. - ^ «If Command Extensions are enabled the PUSHD command accepts network paths in addition to the normal drive letter and path. If a network path is specified, PUSHD creates a temporary drive letter that points to that specified network resource and then change the current drive and directory, using the newly defined drive letter. Temporary drive letters are allocated from Z: on down, using the first unused drive letter found.» —The help for PUSHD in Windows 7
- ^ Availability of CMD.EXE and COMMAND.COM can be confirmed by invoking them in any version of Windows (COMMAND.COM not in 64-bit versions; probably only available in Windows 8 32-bit versions if installed with option to support 16-bit programs).
References[edit]
- ^ «Using batch files: Scripting; Management Services». Technet.microsoft.com. 2005-01-21. Retrieved 2012-11-30.
- ^ Henry-Stocker, Sandra (2007-07-18). «Use your Unix scripting skills to write a batch file». itworld.com. IT World. Retrieved 2018-06-13.
- ^ «Difference between bat and cmd | WWoIT — Wayne’s World of IT». waynes-world-it.blogspot.fr. 2012-11-15. Retrieved 2012-11-30.
- ^ «btm file extension :: all about the .btm file type». Cryer.co.uk. Retrieved 2012-11-30.
- ^ Caldera DR-DOS 7.02 User Guide, Caldera, Inc., 1998 [1993, 1997], archived from the original on 2016-11-05, retrieved 2013-08-10
- ^ Brothers, Hardin; Rawson, Tom; Conn, Rex C.; Paul, Matthias R.; Dye, Charles E.; Georgiev, Luchezar I. (2002-02-27). 4DOS 8.00 online help.
- ^ a b «.NET Core Runtime: System.Diagnostics.Process.Unix». GitHub. Retrieved 2020-02-11.
Two consecutive double quotes inside an inQuotes region should result in a literal double quote (the parser is left in the inQuotes region). This behavior is not part of the spec of code:ParseArgumentsIntoList, but is compatible with CRT and .NET Framework.
- ^ a b Deley, David. «How Command Line Parameters Are Parsed».
- ^ «Child process documentation, section Windows Command Line, NodeJS PR #29576». GitHub. Retrieved 2020-02-11.
- ^ «How to do a delay», ericphelps.com
- ^ Utilities for DOS, linking to WAIT.ZIP (archive of WAIT.COM) and other programs
- ^ a b https://support.microsoft.com/en-us/kb/156276[dead link]
- ^ Chen, Raymond. «Keep your eye on the code page». Microsoft.
- ^ http://www.explorehacking.com/2011/01/batch-files-art-of-creating-viruses.html[bare URL]
- ^ «Windows PowerShell — Unix comes to Windows». Geekswithblogs.net. Retrieved 2012-11-30.
External links[edit]
- Microsoft Windows XP Batch file reference
- How Windows batch files work
- Windows 10 batch file commands
- FreeDOS’ FreeCOM : complete feature list
- Windows Command Line Interface script programming links
- scripting related information (also command line)
- dbenham. «How does the Windows Command Interpreter (CMD.EXE) parse scripts?». Stack Overflow.
| Filename extensions | .bat, .cmd, .btm |
|---|---|
| Internet media type |
|
| Type of format | Scripting |
| Container for | Scripts |
A batch file is a script file in DOS, OS/2 and Microsoft Windows. It consists of a series of commands to be executed by the command-line interpreter, stored in a plain text file. A batch file may contain any command the interpreter accepts interactively and use constructs that enable conditional branching and looping within the batch file, such as IF, FOR, and GOTO labels. The term «batch» is from batch processing, meaning «non-interactive execution», though a batch file might not process a batch of multiple data.
Similar to Job Control Language (JCL), DCL and other systems on mainframe and minicomputer systems, batch files were added to ease the work required for certain regular tasks by allowing the user to set up a script to automate them. When a batch file is run, the shell program (usually COMMAND.COM or cmd.exe) reads the file and executes its commands, normally line-by-line.[1] Unix-like operating systems, such as Linux, have a similar, but more flexible, type of file called a shell script.[2]
The filename extension .bat is used in DOS and Windows. Windows NT and OS/2 also added .cmd. Batch files for other environments may have different extensions, e.g., .btm in 4DOS, 4OS2 and 4NT related shells.
The detailed handling of batch files has changed significantly between versions. Some of the detail in this article applies to all batch files, while other details apply only to certain versions.
Variants[edit]
DOS[edit]
In MS-DOS, a batch file can be started from the command-line interface by typing its name, followed by any required parameters and pressing the ↵ Enter key. When DOS loads, the file AUTOEXEC.BAT, when present, is automatically executed, so any commands that need to be run to set up the DOS environment may be placed in this file. Computer users would have the AUTOEXEC.BAT file set up the system date and time, initialize the DOS environment, load any resident programs or device drivers, or initialize network connections and assignments.
A .bat file name extension identifies a file containing commands that are executed by the command interpreter COMMAND.COM line by line, as if it were a list of commands entered manually, with some extra batch-file-specific commands for basic programming functionality, including a GOTO command for changing flow of line execution.
Early Windows[edit]
Microsoft Windows was introduced in 1985 as a graphical user interface-based (GUI) overlay on text-based operating systems and was designed to run on DOS. In order to start it, the WIN command was used, which could be added to the end of the AUTOEXEC.BAT file to allow automatic loading of Windows. In the earlier versions, one could run a .bat type file from Windows in the MS-DOS Prompt. Windows 3.1x and earlier, as well as Windows 9x invoked COMMAND.COM to run batch files.
OS/2[edit]
The IBM OS/2 operating system supported DOS-style batch files. It also included a version of REXX, a more advanced batch-file scripting language. IBM and Microsoft started developing this system, but during the construction of it broke up after a dispute; as a result of this, IBM referred to their DOS-like console shell without mention of Microsoft, naming it just DOS, although this seemingly made no difference with regard to the way batch files worked from COMMAND.COM.
OS/2’s batch file interpreter also supports an EXTPROC command. This passes the batch file to the program named on the EXTPROC file as a data file. The named program can be a script file; this is similar to the #! mechanism used by Unix-like operating systems.
Windows NT[edit]
Unlike Windows 98 and earlier, the Windows NT family of operating systems does not depend on MS-DOS. Windows NT introduced an enhanced 32-bit command interpreter (cmd.exe) that could execute scripts with either the .CMD or .BAT extension. Cmd.exe added additional commands, and implemented existing ones in a slightly different way, so that the same batch file (with different extension) might work differently with cmd.exe and COMMAND.COM. In most cases, operation is identical if the few unsupported commands are not used. Cmd.exe’s extensions to COMMAND.COM can be disabled for compatibility.
Microsoft released a version of cmd.exe for Windows 9x and ME called WIN95CMD to allow users of older versions of Windows to use certain cmd.exe-style batch files.
As of Windows 8, cmd.exe is the normal command interpreter for batch files; the older COMMAND.COM can be run as well in 32-bit versions of Windows able to run 16-bit programs.[nb 1]
Filename extensions[edit]
- .bat
- The first filename extension used by Microsoft for batch files. This extension runs with DOS and all versions of Windows, under COMMAND.COM or cmd.exe, despite the different ways the two command interpreters execute batch files.
- .cmd
- Used for batch files in Windows NT family and sent to cmd.exe for interpretation. COMMAND.COM does not recognize this file name extension, so cmd.exe scripts are not executed in the wrong Windows environment by mistake. In addition,
append,dpath,ftype,set,path,assocandpromptcommands, when executed from a .bat file, alter the value of theerrorlevelvariable only upon an error, whereas from within a .cmd file, they would affect errorlevel even when returning without an error.[3] It is also used by IBM’s OS/2 for batch files. - .btm
- The extension used by 4DOS, 4OS2, 4NT and Take Command. These scripts are faster, especially with longer ones, as the script is loaded entirely ready for execution, rather than line-by-line.[4]
Batch file parameters[edit]
COMMAND.COM and cmd.exe support special variables (%0, %1 through %9) in order to refer to the path and name of the batch job and the first nine calling parameters from within the batch job, see also SHIFT. Non-existent parameters are replaced by a zero-length string. They can be used similar to environment variables, but are not stored in the environment. Microsoft and IBM refer to these variables as replacement parameters or replaceable parameters, whereas Digital Research, Novell and Caldera established the term replacement variables[5] for them. JP Software calls them batch file parameters.[6]
Examples[edit]
This example batch file displays Hello World!, prompts and waits for the user to press a key, and then terminates. (Note: It does not matter if commands are lowercase or uppercase unless working with variables)
@ECHO OFF ECHO Hello World! PAUSE
To execute the file, it must be saved with the filename extension suffix .bat (or .cmd for Windows NT-type operating systems) in plain text format, typically created by using a text editor such as Microsoft Notepad or a word processor working in plain text mode.
When executed, the following is displayed:
Hello World! Press any key to continue . . .
Explanation[edit]
The interpreter executes each line in turn, starting with the first. The @ symbol at the start of any line prevents the prompt from displaying that command as it is executed. The command ECHO OFF turns off the prompt permanently, or until it is turned on again. The combined @ECHO OFF is often as here the first line of a batch file, preventing any commands from displaying, itself included. Then the next line is executed and the ECHO Hello World! command outputs Hello World!. The next line is executed and the PAUSE command displays Press any key to continue . . . and pauses the script’s execution. After a key is pressed, the script terminates, as there are no more commands. In Windows, if the script is executed from an already running command prompt window, the window remains open at the prompt as in MS-DOS; otherwise, the window closes on termination.
Limitations and exceptions[edit]
Null values in variables[edit]
Variable expansions are substituted textually into the command, and thus variables which contain nothing simply disappear from the syntax, and variables which contain spaces turn into multiple tokens. This can lead to syntax errors or bugs.
For example, if %foo% is empty, this statement:
parses as the erroneous construct:
Similarly, if %foo% contains abc def, then a different syntax error results:
IF abc def==bar ECHO Equal
The usual way to prevent this problem is to surround variable expansions in quotes so that an empty variable expands into the valid expression IF ""=="bar" instead of the invalid IF ==bar. The text that is being compared to the variable must also be enclosed in quotes, because the quotes are not special delimiting syntax; these characters represent themselves.
IF "%foo%"=="bar" ECHO Equal
The delayed !VARIABLE! expansion available in Windows 2000 and later may be used to avoid these syntactical errors. In this case, null or multi-word variables do not fail syntactically because the value is expanded after the IF command is parsed:
Another difference in Windows 2000 or higher is that an empty variable (undefined) is not substituted. As described in previous examples, previous batch interpreter behaviour would have resulted in an empty string. Example:
C:>set MyVar= C:>echo %MyVar% %MyVar% C:>if "%MyVar%"=="" (echo MyVar is not defined) else (echo MyVar is %MyVar%) MyVar is %MyVar%
Batch interpreters prior to Windows 2000 would have displayed result MyVar is not defined.
Quotation marks and spaces in passed strings[edit]
Unlike Unix/POSIX processes, which receive their command-line arguments already split up by the shell into an array of strings, a Windows process receives the entire command-line as a single string, via the GetCommandLine API function. As a result, each Windows application can implement its own parser to split the entire command line into arguments. Many applications and command-line tools have evolved their own syntax for doing that, and so there is no single convention for quoting or escaping metacharacters on Windows command lines.
- For some commands, spaces are treated as delimiters that separate arguments, unless those spaces are enclosed by quotation marks. Various conventions exist of how quotation marks can be passed on to the application:
- A widely used convention is implemented by the command-line parser built into the Microsoft Visual C++ runtime library in the CommandLineToArgvW function. It uses the convention that 2n backslashes followed by a quotation mark («) produce n backslashes followed by a begin/end quote, whereas (2n)+1 backslashes followed by a quotation mark again produce n backslashes followed by a quotation mark literal. The same convention is part of the .NET Framework specification.[7]
- An undocumented aspect is that «» occurring in the middle of a quoted string produces a single quotation mark.[7] (A CRT change in 2008 [msvcr90] modified this undocumented handling of quotes.[8]) This is helpful for inserting a quotation mark in an argument without re-enabling interpretation of cmd metacharacters like |, & and >. (cmd does not recognize the usual « as escaping the quote. It re-enables these special meanings on seeing the quote, thinking the quotation has ended.)
- Another convention is that a single quotation mark («) is not included as part of the string. However, an escaped quotation mark («»») can be part of the string.[citation needed]
- Yet another common convention comes from the use of Cygwin-derived ported programs. It does not differentiate between backslashes occurring before or not before quotes. See glob (programming) § Windows and DOS for information on these alternative command-line parsers.[9]
- Some important Windows commands, like
cmd.exeandwscript.exe, use their own rules.[8]
- A widely used convention is implemented by the command-line parser built into the Microsoft Visual C++ runtime library in the CommandLineToArgvW function. It uses the convention that 2n backslashes followed by a quotation mark («) produce n backslashes followed by a begin/end quote, whereas (2n)+1 backslashes followed by a quotation mark again produce n backslashes followed by a quotation mark literal. The same convention is part of the .NET Framework specification.[7]
- For other commands, spaces are not treated as delimiters and therefore do not need quotation marks. If quotes are included they become part of the string. This applies to some built-in commands like echo.
Where a string contains quotation marks, and is to be inserted into another line of text that must also be enclosed in quotation marks, particular attention to the quoting mechanism is required:
C:>set foo="this string is enclosed in quotation marks" C:>echo "test 1 %foo%" "test 1 "this string is enclosed in quotation marks"" C:>eventcreate /T Warning /ID 1 /L System /SO "Source" /D "Example: %foo%" ERROR: Invalid Argument/Option - 'string'. Type "EVENTCREATE /?" for usage.
On Windows 2000 and later, the solution is to replace each occurrence of a quote character within a value by a series of three quote characters:
C:>set foo="this string is enclosed in quotes" C:>set foo=%foo:"="""% C:>echo "test 1 %foo%" "test 1 """this string is enclosed in quotes"""" C:>eventcreate /T Warning /ID 1 /L System /SO "Source" /D "Example: %foo%" SUCCESS: A 'Warning' type event is created in the 'Source' log/source.
Escaped characters in strings[edit]
Some characters, such as pipe (|) characters, have special meaning to the command line. They cannot be printed as text using the ECHO command unless escaped using the caret ^ symbol:
C:>Echo foo | bar 'bar' is not recognized as an internal or external command, operable program or batch file. C:>Echo foo ^| bar foo | bar
However, escaping does not work as expected when inserting the escaped character into an environment variable. The variable ends up containing a live pipe command when merely echoed. It is necessary to escape both the caret itself and the escaped character for the character display as text in the variable:
C:>set foo=bar | baz 'baz' is not recognized as an internal or external command, operable program or batch file. C:>set foo=bar ^| bar C:>echo %foo% 'baz' is not recognized as an internal or external command, operable program or batch file. C:>set foo=bar ^^^| baz C:>echo %foo% bar | baz
The delayed expansion available with or with in Windows 2000 and later may be used to show special characters stored in environment variables because the variable value is expanded after the command was parsed:
C:>cmd /V:ON Microsoft Windows [Version 6.1.7601] Copyright (c) 2009 Microsoft Corporation. All rights reserved. C:>set foo=bar ^| baz C:>echo !foo! bar | baz
Sleep or scripted delay[edit]
Until the TIMEOUT command was introduced with Windows Vista, there was no easy way to implement a timed pause, as the PAUSE command halts script activity indefinitely until any key is pressed.
Many workarounds were possible,[10] but generally only worked in some environments: The CHOICE command was not available in older DOS versions, PING was only available if TCP/IP was installed, and so on. No solution was available from Microsoft, but a number of small utility programs, could be installed from other sources. A commercial example would be the 1988 Norton Utilities Batch Enhancer (BE) command, where BE DELAY 18 would wait for 1 second, or the free 94-byte WAIT.COM[11] where WAIT 5 would wait for 5 seconds, then return control to the script. Most such programs are 16-bit .COM files, so are incompatible with 64-bit Windows.
Text output with stripped CR/LF[edit]
Normally, all printed text automatically has the control characters for carriage return (CR) and line feed (LF) appended to the end of each line.
- batchtest.bat
-
C:>batchtest.bat foo bar
-
It does not matter if the two echo commands share the same command line; the CR/LF codes are inserted to break the output onto separate lines:
C:>@echo Message 1&@echo Message 2 Message 1 Message 2
A trick discovered with Windows 2000 and later is to use the special prompt for input to output text without CR/LF trailing the text. In this example, the CR/LF does not follow Message 1, but does follow Line 2 and Line 3:
- batchtest2.bat
-
@echo off set /p ="Message 1"<nul echo Message 2 echo Message 3
-
C:>batchtest2.bat Message 1Message 2 Message 3
-
This can be used to output data to a text file without CR/LF appended to the end:
C:>set /p ="Message 1"<nul >data.txt C:>set /p ="Message 2"<nul >>data.txt C:>set /p ="Message 3"<nul >>data.txt C:>type data.txt Message 1Message 2Message 3
However, there is no way to inject this stripped CR/LF prompt output directly into an environment variable.
Setting a Uniform Naming Convention (UNC) working directory from a shortcut[edit]
It is not possible to have a command prompt that uses a UNC path as the current working directory; e.g. \serversharedirectory
The command prompt requires the use of drive letters to assign a working directory, which makes running complex batch files stored on a server UNC share more difficult. While a batch file can be run from a UNC file path, the working directory default is C:WindowsSystem32.
In Windows 2000 and later, a workaround is to use the PUSHD and POPD command with command extensions.[nb 2]
If not enabled by default, command extensions can be temporarily enabled using the /E:ON switch for the command interpreter.
So to run a batch file on a UNC share, assign a temporary drive letter to the UNC share, and use the UNC share as the working directory of the batch file, a Windows shortcut can be constructed that looks like this:
- Target:
The working directory attribute of this shortcut is ignored.
This also solves a problem related to User Account Control (UAC) on Windows Vista and newer. When an administrator is logged on and UAC is enabled, and they try to run a batch file as administrator from a network drive letter, using the right-click file context menu, the operation will unexpectedly fail. This is because the elevated UAC privileged account context does not have network drive letter assignments, and it is not possible to assign drive letters for the elevated context via the Explorer shell or logon scripts. However, by creating a shortcut to the batch file using the above PUSHD / POPD construct, and using the shortcut to run the batch file as administrator, the temporary drive letter will be created and removed in the elevated account context, and the batch file will function correctly.
The following syntax does correctly expand to the path of the current batch script.
%~dp0
UNC default paths are turned off by default as they used to crash older programs.[12]
The Dword registry value DisableUNCCheck at HKEY_CURRENT_USERSoftwareMicrosoftCommand Processor[12] allows the default directory to be UNC. CD command will refuse to change but placing a UNC path in Default Directory in a shortcut to Cmd or by using the Start command. (C$ share is for administrators).
Character set[edit]
Batch files use an OEM character set, as defined by the computer, e.g. Code page 437. The non-ASCII parts of these are incompatible with the Unicode or Windows character sets otherwise used in Windows so care needs to be taken.[13] Non-English file names work only if entered through a DOS character set compatible editor. File names with characters outside this set do not work in batch files.
To get a command prompt with Unicode instead of Code page 437 or similar, one can use the cmd /U command. In such a command prompt, a batch file with Unicode filenames will work. Also one can use cmd /U to directly execute commands with Unicode as character set. For example, cmd /U /C dir > files.txt creates a file containing a directory listing with correct Windows characters, in the UTF-16LE encoding.
Batch viruses and malware[edit]
As with any other programming language, batch files can be used maliciously. Simple trojans and fork bombs are easily created, and batch files can do a form of DNS poisoning by modifying the hosts file. Batch viruses are possible, and can also spread themselves via USB flash drives by using Windows’ Autorun capability.[14]
The following command in a batch file will delete all the data in the current directory (folder) — without first asking for confirmation:
These three commands are a simple fork bomb that will continually replicate itself to deplete available system resources, slowing down or crashing the system:
:TOP start "" %0 goto TOP
Other Windows scripting languages[edit]
The cmd.exe command processor that interprets .cmd files is supported in all 32- and 64-bit versions of Windows up to at least Windows 10. COMMAND.EXE, which interprets .BAT files, was supported in all 16- and 32-bit versions up to at least Windows 10.[nb 3]
There are other, later and more powerful, scripting languages available for Windows. However, these require the scripting language interpreter to be installed before they can be used:
- Extended Batch Language (EBL) (.bat) — developed by Frank Canova as an ‘own-time’ project while working at IBM in 1982. It was subsequently sold by Seaware Corp as an interpreter and compiler primarily for DOS, but later for Windows.
- KiXtart (.kix) — developed by a Microsoft employee in 1991, specifically to meet the need for commands useful in a network logon script while retaining the simple ‘feel’ of a .cmd file.
- Windows Script Host (.vbs , .js and .wsf) — released by Microsoft in 1998, and consisting of cscript.exe and wscript.exe, runs scripts written in VBScript or JScript. It can run them in windowed mode (with the wscript.exe host) or in console-based mode (with the cscript.exe host). They have been a part of Windows since Windows 98.
- PowerShell (.ps1) — released in 2006 by Microsoft and can operate with Windows XP (SP2/SP3) and later versions. PowerShell can operate both interactively (from a command-line interface) and also via saved scripts, and has a strong resemblance to Unix shells.[15]
- Unix-style shell scripting languages can be used if a Unix compatibility tool, such as Cygwin, is installed.
- Cross-platform scripting tools including Perl, Python, Ruby, Rexx, Node.js and PHP are available for Windows.
Script files run if the filename without extension is entered. There are rules of precedence governing interpretation of, say, DoThis if DoThis.com, DoThis.exe, DoThis.bat, DoThis.cmd, etc. exist; by default DoThis.com has highest priority. This default order may be modified in newer operating systems by the user-settable PATHEXT environment variable.
See also[edit]
- List of DOS commands
Notes[edit]
- ^ To verify that COMMAND.COM remains available (in the WINDOWSSYSTEM32 directory), type
COMMAND.COMat the 32-bit Windows 7 command prompt. - ^ «If Command Extensions are enabled the PUSHD command accepts network paths in addition to the normal drive letter and path. If a network path is specified, PUSHD creates a temporary drive letter that points to that specified network resource and then change the current drive and directory, using the newly defined drive letter. Temporary drive letters are allocated from Z: on down, using the first unused drive letter found.» —The help for PUSHD in Windows 7
- ^ Availability of CMD.EXE and COMMAND.COM can be confirmed by invoking them in any version of Windows (COMMAND.COM not in 64-bit versions; probably only available in Windows 8 32-bit versions if installed with option to support 16-bit programs).
References[edit]
- ^ «Using batch files: Scripting; Management Services». Technet.microsoft.com. 2005-01-21. Retrieved 2012-11-30.
- ^ Henry-Stocker, Sandra (2007-07-18). «Use your Unix scripting skills to write a batch file». itworld.com. IT World. Retrieved 2018-06-13.
- ^ «Difference between bat and cmd | WWoIT — Wayne’s World of IT». waynes-world-it.blogspot.fr. 2012-11-15. Retrieved 2012-11-30.
- ^ «btm file extension :: all about the .btm file type». Cryer.co.uk. Retrieved 2012-11-30.
- ^ Caldera DR-DOS 7.02 User Guide, Caldera, Inc., 1998 [1993, 1997], archived from the original on 2016-11-05, retrieved 2013-08-10
- ^ Brothers, Hardin; Rawson, Tom; Conn, Rex C.; Paul, Matthias R.; Dye, Charles E.; Georgiev, Luchezar I. (2002-02-27). 4DOS 8.00 online help.
- ^ a b «.NET Core Runtime: System.Diagnostics.Process.Unix». GitHub. Retrieved 2020-02-11.
Two consecutive double quotes inside an inQuotes region should result in a literal double quote (the parser is left in the inQuotes region). This behavior is not part of the spec of code:ParseArgumentsIntoList, but is compatible with CRT and .NET Framework.
- ^ a b Deley, David. «How Command Line Parameters Are Parsed».
- ^ «Child process documentation, section Windows Command Line, NodeJS PR #29576». GitHub. Retrieved 2020-02-11.
- ^ «How to do a delay», ericphelps.com
- ^ Utilities for DOS, linking to WAIT.ZIP (archive of WAIT.COM) and other programs
- ^ a b https://support.microsoft.com/en-us/kb/156276[dead link]
- ^ Chen, Raymond. «Keep your eye on the code page». Microsoft.
- ^ http://www.explorehacking.com/2011/01/batch-files-art-of-creating-viruses.html[bare URL]
- ^ «Windows PowerShell — Unix comes to Windows». Geekswithblogs.net. Retrieved 2012-11-30.
External links[edit]
- Microsoft Windows XP Batch file reference
- How Windows batch files work
- Windows 10 batch file commands
- FreeDOS’ FreeCOM : complete feature list
- Windows Command Line Interface script programming links
- scripting related information (also command line)
- dbenham. «How does the Windows Command Interpreter (CMD.EXE) parse scripts?». Stack Overflow.
Рассмотрим мощный инструмент автоматизации рутинных задач в семействе операционных систем Windows.
BAT-файл — это последовательность команд для интерпретатора командной строки в виде текстового файла с расширением .bat или .cmd. Основное предназначение пакетных файлов — автоматизация рутинных действий пользователя компьютера.
Название BAT появилось от английского batch — пакетная обработка. В истории продуктов Microsoft пакетные файлы существовали с первой версии MS-DOS в 80-х годах и позже успешно интегрировались в Microsoft Windows. В MS-DOS командным интерпретатором выступает COMMAND.COM, а начиная с Windows NT и до сих пор используется CMD.EXE.
Интерпретатор COMMAND.COM принимает файлы с расширением .BAT. Расширение .CMD создано для интерпретатора CMD.EXE с целью различать файлы для «старого» и «нового» интерпретаторов. CMD.EXE корректно обрабатывает оба расширения.
Интерпретатор CMD.EXE является частью современных операционных систем семейства Microsoft Windows, несмотря на отсутствие развития с начала 2000-х.
Основы взаимодействия с bat-файлами
Пакетный файл bat — это текстовый документ со специальным расширением. Для создания своего первого bat-файла достаточно «Блокнота», который доступен в операционной системе. Для повышения удобства написания и поддержки bat-файлов рекомендуем использовать Notepad++ или любой другой текстовый редактор с подсветкой синтаксиса.
Создание bat-файлов
Для создания пакетных файлов необходимо открыть текстовый редактор и в меню Файл выбрать Сохранить как….
В появившемся окне выбрать Тип файла → Все файлы и задать имя с расширением .bat, как продемонстрировано на изображении выше. По умолчанию Windows скрывает расширения файлов, и пакетный файл можно отличить от текстового по пиктограмме окна с шестеренками.
Если вы ошиблись при сохранении и пакетный файл сохранился с расширением txt, то не обязательно совершать повторное сохранение. Можно включить отображение расширения имен файлов и переименовать файл.
Запуск bat-файлов
Запуск пакетных файлов производится двойным кликом по иконке. Дополнительно можно использовать команду Открыть из контекстного меню, которое доступно при нажатии правой клавиши мыши (ПКМ) по файлу. Если для выполнения команд требуются права администратора, то в том же контекстном меню есть пункт Запуск от имени администратора.
Исполняемые bat-файлы не могут запрашивать права администратора, если командам нужны расширенные права.
Запуск через контекстное меню откроет командный интерпретатор, в котором выполнятся команды bat-файла. По завершении команд окно закроется. Такое поведение неприемлемо, если от пакетного файла требуется какая-то обратная связь — например, сообщение об ошибке или результат вычислений. В таком случае интерпретатор следует запустить вручную и передать ему пакетный файл.
Для запуска интерпретатора командной строки необходимо открыть меню Выполнить сочетанием клавиш Win + R, вписать cmd и нажать ОК.
Для запуска пакетного файла его необходимо перенести мышкой в открывшееся окно и нажать Enter. Команды bat-файла будут выполнены, а его вывод вы увидите на экране.
Вне зависимости от способа запуска откроется окно, которое может привлекать внимание и раздражать. Для запуска в «скрытом» режиме необходимо использовать другой скриптовой язык Microsoft Windows — VBScript.
По аналогии создаем файл с расширением .vbs и заполняем его следующими командами:
Set WshShell = CreateObject("WScript.Shell")
WshShell.Run chr(34) & "С:путьдовашегоскрипта.bat" & Chr(34), 0
Set WshShell = NothingДля скрытого запуска следует запускать созданный файл, а не bat-файл. Скрытый запуск bat-файла актуален для автоматизации действий по расписанию, например, создание резервной копии.
Запуск по расписанию
За выполнение действий по расписанию отвечает Планировщик заданий. Открываем меню Выполнить и запускаем программу taskschd.msc.
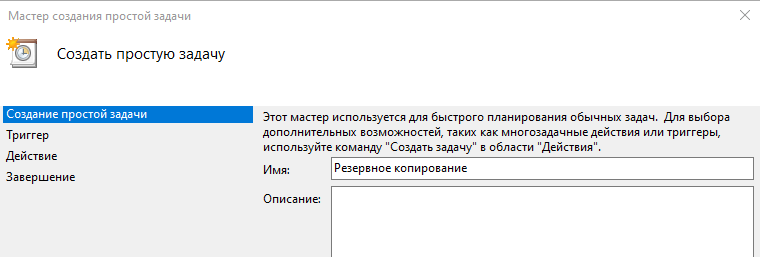
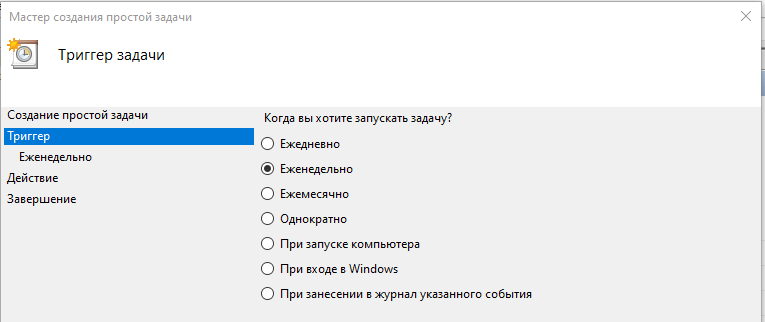
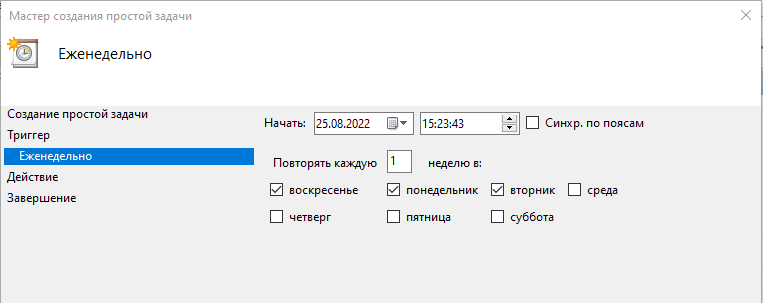
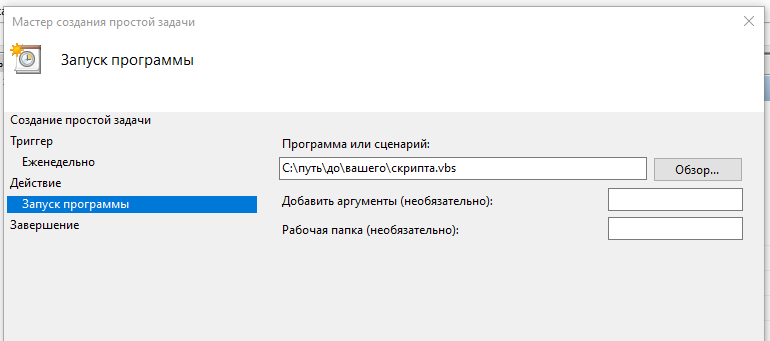
Выбираем пункт Создать простую задач и заполняем параметры задания:
- имя для простой идентификации,
- периодичность и время запуска,
- действие — Запустить программу,
- программа или сценарий — путь до вашего .bat-файла или .vbs-файла, который запускает .bat-файл скрытно.
Обратите внимание, что планировщик позволяет не только выполнять действие по времени, но и при наступлении события — например, при загрузке компьютера. Такой подход является альтернативой автозагрузке.
В случае разработки собственного bat-файла следует ознакомиться с основами командного интерпретатора.
Команды и синтаксис пакетных файлов
Командный интерпретатор выполняет команды из файла последовательно — строка за строкой. Исключение составляет только оператор GOTO, который «отправляет» к указанной строке. Командный интерпретатор выполняет два вида команд: встроенные команды и внешние исполняемые файлы.
Внешние исполняемые файлы — это любой исполняемый файл, то есть с расширением EXE, CMD или BAT, который доступен в операционной системе. Например, «Блокнот» — это исполняемый файл notepad.exe. Следующая команда приведет к запуску этого приложения с открытым файлом C:1.txt:
notepad.exe C:1.txtАргументом может быть не только путь, но и ключ — специальный аргумент, который начинается с символа слэш (/). У каждой программы свой «реестр» ключей и их значений.
Обратите внимание, что не все внешние команды «понимают» аргументы, переданные из интерпретатора командной строки. Например, исполняемый файл приложения калькулятор, calc.exe, игнорирует все аргументы командной строки. Внешним исполняемым файлом может быть в том числе другой bat-файл.
Встроенные команды — это команды, которые являются частью интерпретатора командной строки. Полный список команд доступен по команде HELP. Данные команды не имеют отдельного исполняемого файла.
Иногда в имени файла или каталога встречаются пробелы. Наиболее очевидный пример — каталог Program Files на диске C. В этом случае помогают кавычки. Их можно расставить различными способами. Например:
cd "C:Program Files123"
cd C:”Program Files”123Операционная система Windows запрещает использование множества специальных символов в именах файлов, в том числе кавычки, поэтому проблем с указанием файлов не возникнет.
Оставлять комментарии при разработке — хороший тон. Так можно объяснить выполняемые действия и потенциальные ошибки. В пакетных файлах можно оставлять комментарии несколькими способами.
Официальный способ — команда rem или два двоеточия.
rem Это первый комментарий
:: Это тоже комментарийПеречисленные команды позволяют оставлять однострочные комментарии. Если хочется оставить развернутый многострочный комментарий, то прибегают к хитрости с командной GOTO.
goto start
===
Здесь можно оставить большой комментарий,
лицензию или даже ASCII-арт
===
:startВ конце комментария задаем имя метки, а в начале комментария выполняем команду GOTO c именем метки. Этот способ требует внимания, так как для каждого комментария должна быть своя метка, иначе выполнение bat-файла может отличаться от ожидания разработчика.
Совместимость с MS-DOS
В старых ОС, таких как MS-DOS, было ограничение на отображение имени файлов. На экран выводилось восемь символов имени, точка и три символа расширения. Если имя файла превышало по длине восемь символов, то имя файла отображалось по следующей схеме:
<первые шесть символов имени>~<порядковый номер>Например, каталог Program Files выглядит следующим образом:
Progra~1В современных операционных системах такое отображение не применяется, но CMD.EXE до сих пор поддерживает такие запросы к файлам и каталогам.
Используйте bat-файлы в работе с выделенным сервером
Выберите подходящий из более 100 готовых конфигураций.
Подобрать сервер
Примеры bat-файлов
Рассмотрим несколько примеров bat-файлов. Начнем с базовых команд.
Обновление IP-адреса
Представим простой пример: необходимо обновить аренду IP-адресов на всех сетевых интерфейсах. В командной строке это делается одной командой:
ipconfig /renewДанная команда генерирует много текстового вывода, который может испугать неподготовленного пользователя. Сама команда также может быть непривлекательной. Поэтому отключим отображение команды и перенаправим вывод выполнения в «никуда». Вместо слова NUL может быть любое имя или путь. Тогда вывод будет перенаправлен в указанный файл.
rem Отключаем отображение команд. Символ @ отключает отображение текущей команды
@echo off
rem Переводим вывод выполнения в устройство NUL, вывод исчезнет
ipconfig /renew > NULПри запуске такого скрипта появляется черное окно, которое быстро исчезает. Можно оставить простые и понятные пользователю сообщения и не дать окну закрыться.
@echo off
echo Выполняется настройка, пожалуйста, подождите...
ipconfig /renew > NUL
echo Все хорошо.
rem Эта команда остановит выполнение до тех пор, пока пользователь не нажмет любую клавишу
pauseСкорее всего данный скрипт выведет набор непонятных символов вместо сообщения. Дело в том, что в русскоязычных ОС Windows по умолчанию в CMD.EXE используется кодировка CP866. Блокнот сохраняет в CP1251 (Windows-1251), а Notepad++ — в UTF-8. Для решения проблемы необходимо сменить кодировку интерпретатора командой chcp или сохранить bat-файл в кодировке интерпретатора.
rem Смена кодировки на Windows-1251
chcp 1251 > NUL
rem Смена кодировки на UTF-8
chcp 65001 > NULЯ сохранил файл в кодировке UTF-8 и итоговый скрипт получился таким:
@echo off
chcp 65001 > NUL
echo Выполняется настройка, пожалуйста, подождите...
ipconfig /renew > NUL
echo Все хорошо.
pauseСоздание резервной копии каталога
Перейдем к более жизненной ситуации — создание резервной копии (backup) каталога. Предположим, что каждый архив должен иметь в названии дату создания копии. Создадим каталог, имя которого — текущая дата. Текущая дата хранится в переменной DATE. Для обращения к переменным название переменной помещается между знаками процента.
mkdir %DATE%
cd %DATE%Копирование файлов в текущий каталог производится командой COPY.
rem файлы 1.txt и 2.txt будут скопированы в текущую папку
COPY C:1.txt C:2.txt .
rem файл 3.txt будет сохранен в текущую папку как example.txt
COPY C:1.txt .example.txtВозможно, в резервную копию необходимо дополнить служебную информацию — например, список файлов в корне копии и имя компьютера.
rem Имя компьютера записывается в файл computer.txt
hostname > computer.txt
rem Список файлов в текущем каталоге записывается в files.txt
dir . > files.txtОбычно резервные копии хранят в zip- или rar-архивах. Из командной строки отлично управляется архиватор 7z.
cd ..
7z -tzip a backup.zip %DATE% Переименование файлов
Переименование файлов в Windows производится командой RENAME. Однако эта команда имеет свои особенности.
Во-первых, переименование возможно только в рамках одного диска и одного каталога. Между каталогами одного диска допустимо перемещение, а между разными дисками — только копирование.
rename abc.txt cba.txtВо-вторых, возможно переименование по маске. Допустим, есть список фотографий photo000.jpeg, photo001.jpeg и так далее. Нужно сменить префикс с photo на mobile.
rename photo* mobile*Если в текущем каталоге есть другие файлы с префиксом photo, а переименовать надо только изображения с расширением jpeg, то команда модифицируется:
rename photo*.jpeg mobile*.jpegУдаление файлов
Программы и пользователи оставляют следы работы в виде файлов, которые не удаляются автоматически. К счастью, процесс очистки поддается автоматизации.
Предположим, что в процессе работы пользователя генерируется большое количество файлов с расширением jpeg, которые нужно удалять. На помощь приходит оператор цикла FOR.
rem Ищем все файлы с расширением jpeg в каталоге work
rem Ключ /r включает в поиск все подкаталоги в каталоге work
for /r work %%file in (*.jpeg) do (
rem Выводим имя файла
echo %%file
delete %%i
)Заключение
Командный интерпретатор CMD.EXE существует долгое время, но, даже несмотря на отсутствия развития, остается востребованным инструментом для автоматизации рутинных действий в операционной системе Microsoft Windows.

И в итоге получается файл с набором команд. Благодаря этому упрощается работа самой операционной системы. Есть определенный список команд, которые запускаются только из пакетного документа.
Содержание
- Пакетные (BAT) файлы — что такое
- Файлы стали называть bat из-за указанного выше расширения
- Как создать самостоятельно пакетный файл
- Комментарий в файлах Bat
- Импорт и экспорт переменных реестра из пакетного файла
Пакетные (BAT) файлы — что такое
Файлы стали называть bat из-за указанного выше расширения
Пакетные документы запускаются также, как приложения .exe и .com. Но есть и отличие от этих программ. Документы с расширением Bat не имеют внутри кода. В них содержится только текстовая информация, которую считывает командный процессор dos.
Есть следующие варианты:
- Команды для вывода некоторой информации на экран
- Происходит вызов пакетных документов
- Работа с другими программами
- Команды для создания циклов, и ветвей.
Особенность пакетных файлов заключается также в том, что они могут выполнять сложные и многоуровневые последовательности. Также пакетные документы имеют свойство автоматизации работы по заданиям.
Работа происходит без посторонних вмешательств от пользователя системы. Запускать файлы с расширением Bat можно на всех этапах установки операционной системы Windows.
В пакетные документы можно размещать все известные команды. Можно усложнять задачу, ставить новые условия. Могут помочь команды goto, if, for.
Как создать самостоятельно пакетный файл
Чтобы создать пакетный файл нужно открыть новый текстовый документ и ввести туда требуемый текст. Дальше документ нужно сохранить, и дать ему любое название. Также важно задать документу расширения cmd или bat. И произвести запуск. Работа документа будет выражаться в том, что откроется блокнот и будет выполнен запрос на нажатие любой клавиши. При выполнении этого окно закроется. Пакетные файлы часто используют, и пользователям это упрощает жизнь и работу для выполнения ежедневных задач, это касается программистов. Наиболее часто файлы Bat используют для отмены резервного копирования данных, переименования файлов, удаления документов и другие задачи.
Большую часть действий в операционной системе можно делать только тогда, если у пользователя права администратора.
Комментарий в файлах Bat
Чтобы понимать, что делает созданный Bat документ, используются комментарии. Использование комментариев нужно для работы с большим объёмом тестовой информации. И если вы будите работать с файлом спустя время, то вы разберётесь с его работой.
Писать комментарии можно несколькими способами. Если вы работаете с большим количеством текста, то можно использовать:
— goto start. Это пакетный файл, он нужен для автоматизации обычных операций, которые выполняются ночью для синхронизации информации.
— :start. Здесь можно запустить пакетный файл, и выполнить переход контроля команде, которая находится после Start. Иногда можно использовать и другой подход, например команду rem или два двоеточия. Они больше подойдут для небольших комментариев, которые в длину не более одной строки.
Чтобы удобно разбирать свои записи в дальнейшем желательно использовать комментирование. Речь не идёт о том, чтобы описывать каждый шаг, но по основным блокам стоит оставить комментарии. Для программистов комментарии это хороший тон.
Импорт и экспорт переменных реестра из пакетного файла
Если требуется выполнить импорт в реестр некоторых переменных, то для решения этой задачи нужно использовать команду regedit.Exe -s C:environment.reg
После этого начнётся импорт в реестр сведений из документа. Здесь используется специальный ключ, иначе не будет вывода сообщений для подтверждения действия.
Если стоит задача по экспорту данных, то нужно использовать другой подход:
regedit.exe
-ea Cenvironment.reg «HKEY_CURRENT_USEREnvironment»
Ветка будет сохранено, и при запросе на восстановление значений нужно выполнить pапуск этого файла. Пример использования этой команды это осуществление возврата настроек программного обеспечения или операционной системы. Это информация хранится в реестре и выгружается оттуда при необходимости.
Министерство
образования Российской Федерации
Саратовский
государственный технический университет
Методические
указания к лабораторной работе
по
курсу «Операционные системы»
для
студентов специальности 220200
дневной
формы обучения
Одобрено
редакционно-издательским
советом
Саратовского
государственного
технического
университета
Саратов 2010
РАБОТА
С ПАКЕТНЫМИ ФАЙЛАМИ
В
СРЕДЕ WINDOWS
Методические
указания к лабораторной работе
по
курсу «Операционные ситемы»
-
Составили:
ПЕТРОВ
Дмитрий ЮрьевичМАКСИМОВА
Наталия НиколаевнаБАРЫШНИКОВА
Елена Сергеевна
Рецензент
А.Ф. Резчиков
Редактор
О.А. Панина
Лицензия
ИД № 06268 от 14.11.01
Подписано
в печать 27.10.10
Формат 60х84 1/16
-
Бум.
тип.Усл.
печ. л. 0,93 (1,0)Уч.-
изд. л. 0,9Тираж
100 экз.Заказ
Бесплатно
Саратовский
государственный технический университет
410054
г. Саратов, ул. Политехническая, 77
Введение
В
методических указаниях рассматриваются
структура пакетных файлов, методика
создания этих файлов, методы автоматизации
выполнения нескольких операций.
Методические
указания содержат описание интерпретатора
команд, структуры пакетных файлов,
описание функций, используемых в
командных файлах, примеры решений
учебной задачи, задание для выполнения
лабораторной работы, требования к
оформлению отчета по лабораторной
работе, а также список литературы,
необходимой для выполнения данной
лабораторной работы.
Методические
указания предназначены для студентов
специальности 220200, а также могут быть
использованы студентами других
специальностей, связанных с разработкой
системных программ.
Цель
работы:
создание пакетных файлов, автоматизирование
выполнение нескольких заданий при
установке и загрузке Windows, оптимизация
и повышение надежности функционирования
системы.
Интерпретатор команд и пакетные файлы
Пакетный
файл (англ. batch
file) —
текстовый
файл
в MS-DOS,
OS/2
или Windows,
содержащий последовательность команд,
предназначенных для исполнения командным
интерпретатором. После запуска пакетного
файла, программа — интерпретатор
(как правило COMMAND.COM
или CMD.EXE)
читает его строка за строкой и
последовательно исполняет команды..
В
Windows используется два интерпретатора
команд commad.com и cmd.exe, которые можно
запустить через меню «Пуск» (Пуск->
Выполнить-> cmd -> ОК или Пуск->
Выполнить-> commad -> ОК). На рис. 1 показана
возможность использования справки по
командам DOS/Windows. Справка становится
доступной при наборе команды help в
командной строке.
Р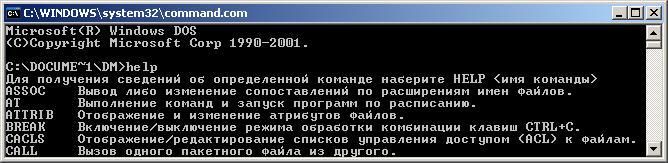
Интерпретатор команд commad.com
На
рис. 2 показана возможность создания
нового файла с использованием команды
copy con имя_файла.расширение.
Р
Интерпретатор команд cmd.exe
Использование
пакетных файлов (*.cmd или *.bat) помогает
автоматизировать выполнение нескольких
заданий при установке и загрузке Windows.
При этом никакого вмешательства
пользователя не требуется. Эти файлы
могут быть выполнены из cmdlines.txt,
svcpack.inf,
RunOnceEx раздела в реестре, или из секции
[GuiRunOnce] в файле winnt.sif.
Пакетные
файлы поддерживают все команды, которые
могут быть выполнены из командной
строки. Чтобы увидеть командую строку
достаточно проделать следующее:
Пуск->Выполнить->cmd->ОК
Рассмотрим
простейший пакетный файл. Для этого
необходимо открыть Блокнот и набрать
в нем следующий текст:
TITLE
Batch File Testing
ECHO
Hello World
ECHO.
ECHO
Starting Notepad
START
notepad
ECHO.
ECHO
Starting Wordpad
START
Wordpad
ECHO.
PAUSE
EXIT
Затем
нужно сохранить файл с любым именем и
в любом месте, но с расширением *.cmd (а не
.txt, которое Блокнот присвоит по умолчанию).
При запуске этого файла он назначит
окну имя «Batch File Testing», запустит
Блокнот и WordPad, попросит нажать любую
клавишу для продолжения работы и закроет
окно.
Таблица
1
Значения
команд, использованных в пакетном файле
|
@echo |
Скрывает |
|
echo. |
Создает |
|
echo |
Отображает |
|
Title |
Название |
|
Start |
Запускает |
|
Pause |
Отображает |
|
Exit |
Закрывает |
При
добавлении приложения для автоматической
установки с инсталляционного диска XP,
команды будут выглядить следующим
образом:
start
/wait %systemdrive%installsome_applicationsetup.exe /ключ
/еще
ключ,
start
запустит установку приложения, а /wait
дождется ее окончания перед тем, как
выполнить установку следующего
приложения. Использование /wait
очень важно,
т.к. в противном случае одновременно
запустится установка сразу нескольких
приложений и конфликты неизбежны.
Пакетные
файлы могут быть запущены из cmdlines.txt
или svcpack.inf,
которые будут исполнены на Т-13/Т-12 этапе
установки Windows (Т-13 означает 13 минут до
окончания установки).cmdlines.txt
удобен для таких задач как Добавление
Пользователей, или для импортирования
заранее подготовленных ключей реестра
HKEY_CURRENT_USER в профиль по умолчанию (Default
Profile).
Метод
svcpack.inf, как правило, используется для
установки обновлений (хотфиксов). Однако
ничто не мешает рассматривать пакетный
файл как еще один хотфикс.
Пример
содержимого пакетного файла:
@echo
off
TITLE
Windows XP SP2 — Unattended Installation
ECHO.
ECHO
Over the next few minutes you will see automated installations
ECHO
of various sofware applications, and registry tweaks being
ECHO
implemented.
ECHO.
ECHO
Removing Wallpapers and Screensavers…
DEL
«%systemroot%*.bmp»
DEL
«%systemroot%WebWallpaper*.jpg»
DEL
«%systemroot%system32dllcache*.scr»
DEL
«%systemroot%system32*.scr»
ECHO.
ECHO
Removing useless shortcuts…
DEL
«%systemdrive%Documents and SettingsAll UsersStart
MenuWindows
Update.lnk»
DEL
«%systemdrive%Documents and SettingsAll UsersStart MenuSet
Program
Access and Defaults.lnk»
DEL
«%systemdrive%Documents and SettingsAll UsersStart
MenuWindows
Catalog.lnk»
ECHO.
ECHO
Installing TweakUI 2.10 Powertoy
ECHO
Please wait…
start
/wait %systemdrive%InstallTweakUI.msi /qn
ECHO.
ECHO
Applying Registry Tweaks…
REGEDIT
/S %systemdrive%InstallRegTweaks.reg
ECHO.
ECHO
Deleting ASP.NET User Account created by .NET Framework 1.1…
net
user aspnet /delete
ECHO.
EXIT
Данный
пакетный файл производит удаление обоев
и скринсэйверов, устанавливаемых по
умолчанию системой, а также некоторых
ярлыков. Затем устанавливает TweakUI,
импортирует ключи реестра и удаляет
учетную запись ASP.NET, созданную при
установке .NET Framework.
Вызов
внешних командных файлов:
1.
После выполнения вызванного файла
управление не передается в вызывающий
файл.
@ECHO
OFF
CLS
REM
Вывод списка log-файлов
DIR
C:*.log
REM
Передача выполнения файлу f.bat
f.bat
COPY
A:*.* C:
PAUSE
2.
После выполнения вызванного файла
управление передается в вызывающий
файл:
@ECHO
OFF
CLS
REM
Вывод списка log-файлов
DIR
C:*.log
REM
Передача выполнения файлу f.bat
CALL
f.bat
COPY
A:*.* C:
PAUSE
Файл
cmdlines.txt
нужно положить в директорию $OEM$, и Windows
автоматически найдет его во время
установки. Все пакетные файлы, запускаемые
из cmdlines.txt,
должны находиться в той же директории,
что и cmdlines.txt.
Файл
svcpack.inf
сохраняется в директории I386 на
инсталляционном диске (необходимо
удалить оттуда
svcpack.in_). Все
пакетные файлы, запускаемые из svcpack.inf,
должны находиться в директории
I386svcpack, если только это не прописано
иначе в самом файле.
В
пакетных файлах широко используются
команды передачи управления IF,
FOR,
SHIFT,
а также параметры, передаваемые из
командной строки и операторы перенаправления
ввода-вывода >, >>, <, |. Полезными
оказываются операторы: «+» ‑ слияния
файлов, «?» ‑ замены одного символа
в имени файла или расширении, «*» ‑
замены нескольких символов в имени
файла или расширении.
Системными
именами являются: CON,
NULL,
AUX,
COM1,
COM2,
PRN,
LPT1,
LPT2.
Ими нельзя называть файлы.
Не
смотря на то, что теперь пользователи
компьютеров могут легко обойтись без
знания DOS,
тем более, что в новых ОС DOS
похоже будет отсутствовать вообще, их
знание может, пригодятся в нештатных
ситуациях, когда Windows по каким-то причинам
запускаться не желает и доступна только
командная строка. Справку по командам
можно, получить, выполнив команду help.
Соседние файлы в папке Лабораторные работы
- #
- #
- #
При использовании ПК с Windows вы, вероятно, использовали, сталкивались или слышали о пакетном файле. Однако не многие люди могут четко сказать, что такое командный файл, как он используется или как он запускается в Windows. Эта статья поможет вам понять командные файлы, почему они используются и как их использовать.
Связанный: Что такое драйверы в Windows 10 и как устранить неполадки с драйверами?
Что такое пакетный файл?
Проще говоря, командный файл — это особый тип обычного текстового файла, содержащий несколько команд или список команд для запуска интерпретатора командной строки (cmd). Пакетные файлы имеют расширение .bat и используются только в ОС Windows. В некоторых случаях командные файлы называются файлами сценариев. Командная строка Windows может понимать и выполнять команды пакетного файла в последовательности для выполнения данной задачи.
Зачем использовать пакетные файлы?
В Windows 10 вы можете использовать командный файл для выполнения различных действий, включая загрузку программ, автоматизацию повторяющихся задач и, среди прочего, изменение системных настроек. Хотя вы можете выполнять эти действия или вводить команды каждый раз, когда вам нужно их запускать, пакетный файл экономит ваше время и энергию, автоматизируя процесс. Кроме того, с помощью командного файла вы можете выполнять множество процессов без вмешательства пользователя. Пользователи могут запускать командные файлы, чтобы:
- Запускать программы или запускать процессы при запуске.
- Планируйте такие задачи, как резервное копирование файлов.
- Настроить устройства.
- Автоматизируйте рутины.
- Запускайте приложения или веб-сайты.
Внимание: Хотя командные файлы очень полезны, их можно использовать для выполнения вредоносных действий. Злоумышленники могут использовать командные файлы для выполнения команд, которые могут нанести вред вашему компьютеру. Поэтому перед запуском командного файла убедитесь, что знаете источник и доверяете ему.
Создание пакетного файла
Чтобы создать командный файл в Windows, вам понадобится только текстовый редактор и команды cmd.
- Откройте «Блокнот» или любой другой текстовый редактор, например Notepad ++, и введите свои команды.
- Вы можете вводить команды для выполнения нескольких задач в одном файле.
- Щелкните меню «Файл», затем сохраните и введите имя командного файла, добавив .bat в конце имени.
- Нажмите кнопку «Сохранить». Вы можете идентифицировать файл .bat по миниатюре с двумя значками шестеренки.
Вы можете использовать различные методы в Windows 10 для запуска командного файла в зависимости от того, как и когда вы хотите выполнять задачи.
Метод 1: запуск командного файла по запросу
Вы можете запустить файл из файлового проводника или командной строки Windows для выполнения задач только тогда, когда вам нужно.
Из проводника
- В проводнике откройте папку, содержащую командный файл.
- Дважды щелкните файл или щелкните правой кнопкой мыши, чтобы запустить файл от имени администратора, если для выполнения задачи требуются права администратора.
Из командной строки Windows
- Запустите командную строку с опцией «Запуск от имени администратора».
- Измените каталог на папку, содержащую ваш командный файл «C: [user][file location path]»
- Затем введите в команде имя файла с расширением .bat или без него и нажмите Enter.
Метод 2: как запустить командный файл во время запуска?
Если вы хотите запускать командный файл при каждом входе в Windows, вы можете сделать это, выполнив следующие действия.
- Нажмите сочетание клавиш «Win + R», чтобы открыть служебную программу «Выполнить». Введите «shell: startup» и нажмите Enter на клавиатуре.
- Это откроет папку «Автозагрузка».
- Скопируйте и вставьте командный файл или его ярлык в эту папку, а затем закройте.
- Вы можете выйти из своей учетной записи и войти снова, чтобы убедиться, что она работает.
Метод 3: запуск командного файла с помощью планировщика задач
Если вы хотите выполнить задачу позже, вы можете использовать планировщик задач Windows 10 для запуска командного файла.
- Перейдите в меню «Пуск», найдите «Планировщик заданий» и выберите соответствующий вариант в результате.
- Под библиотекой планировщика на левой панели создайте папку для своей задачи и нажмите «Создать базовую задачу…» в разделе «Действия» на правой панели.
- Введите имя и описание (необязательно) вашей задачи в открывшемся мастере и нажмите «Далее».
- Установите триггер задачи в зависимости от того, когда вам нужно запустить задачу, и нажмите кнопку «Далее».
- В разделе «Действие» выберите вариант «Запустить программу» и перейдите на следующую страницу.
- В поле «Сценарий» нажмите «Обзор», перейдите в папку, в которой вы сохранили командный файл, и выберите файл.
- Проверьте сведения о задаче и нажмите «Готово», чтобы завершить процесс.
- Windows автоматически запустит командный файл в указанное вами время.
Вывод
В пакетных файлах хранятся инструкции по выполнению определенной задачи в Windows. Вы можете использовать командный файл для автоматизации процедур, настройки параметров системы и многих других основных задач. Вы можете создать и сохранить пакетный файл и использовать любой из вышеперечисленных методов для выполнения файла в Windows 10. Единственное серьезное ограничение — пакетные файлы являются эксклюзивными для ПК с Windows.
В DOS, OS / 2, а также в Microsoft Windows командный файл представляет собой файл сценария или текстовый файл, содержащий серию команд, которые должны быть выполнены интерпретатором команд, например командная строка в Windows .
Пакетные файлы: как они работают, для чего они хороши и как мы их используем
- Как работают пакетные файлы
- Как использовать командный файл
- Для чего они хороши
Как работают пакетные файлы
Пакетный файл может содержать любую команду, которую интерпретатор принимает в интерактивном режиме в командной строке. Пакетный файл с расширением .bat также может иметь конструкции, которые обеспечивают условное разветвление и циклизацию внутри пакетного файла.
Windows распознает расширение .bat как исполняемый файл , хотя они состоят из текстовых команд. Таким образом, вы можете открыть командный файл даже с помощью Блокнота, и он покажет вам код, который составляет файл.
Как использовать командный файл
Прежде всего, чтобы использовать командный файл, вам необходимо открыть его. Для этого в блокноте щелкните правой кнопкой мыши файл и выберите «Изменить». Существуют текстовые редакторы, которые более полезны для пакетных файлов, потому что они выделяют определенные части текста.

- Читайте также: 6 из лучших альтернатив Блокнот для использования

Кроме того, .bat-файлы — это исполняемые файлы, которые могут выполнять определенные задачи, такие как удаление определенных файлов. В этом смысле функция похожа на командную строку, только для доступа к файлам .bat, а не для записи команд в диалоговом окне CMD.
Для чего они хороши
Пакетные файлы имеют много ролей. Это универсальные инструменты, которые сделают вашу жизнь проще (если вы знаете, как их использовать). Например, вы можете открыть несколько папок, используя пакетные файлы. Вот полное руководство, которое покажет вам, как это сделать.
Кроме того, вы можете конвертировать или создавать пакетные файлы, чтобы служить вам в ваших целях. Преобразование измененного пакетного файла в .exe или .txt целесообразно, поскольку отредактированные пакетные файлы могут серьезно повлиять на ваш компьютер.
Кроме того, пакетные файлы могут помочь вам решить определенные проблемы с вашим компьютером, такие как папка автозагрузки, не работающая в Windows 10 .
Что такое пакетный файл? В двух словах, пакетный файл — это особый тип обычного текстового файла, который содержит различные команды или список команд для запуска интерпретатора командной строки (cmd). Пакетные файлы имеют расширение .bat и используются только в Windows. В некоторых случаях пакетные файлы называются файлами сценариев. Командная строка Windows может понимать и запускать команды пакетного файла последовательно для выполнения заданной задачи.
Зачем использовать пакетные файлы?
В Windows 10 вы можете использовать пакетный файл для выполнения различных действий, включая загрузку программ, автоматизацию повторяющихся задач и изменение настроек системы, среди прочего. Хотя вы можете выполнять эти действия или вводить команды каждый раз, когда вам нужно их запустить, пакетный файл экономит ваше время и энергию за счет автоматизации процесса. Кроме того, с помощью пакетного файла вы можете запускать многие процессы без вмешательства пользователя. Пользователи могут запускать пакетные файлы для:
- Запускать программы или запускать процессы при запуске.
- Запланируйте задачи, такие как резервное копирование файлов.
- Настройте устройства.
- Автоматизируйте рутину.
- Запуск приложений или веб-сайтов.
Предупреждение. Хотя пакетные файлы очень полезны, их можно использовать для выполнения вредоносных действий. Злоумышленники могут использовать пакетные файлы для запуска команд, которые могут нанести вред вашему компьютеру. Поэтому перед запуском пакетного файла убедитесь, что вы знаете источник и доверяете ему.
Создание пакетного файла
Чтобы создать пакетный файл в Windows, все, что вам нужно, это текстовый редактор и команды cmd.
- Откройте Блокнот или любой другой текстовый редактор, например Notepad++, и введите свои команды.
- Вы можете вводить команды для выполнения нескольких задач в одном файле.
Пример пакетного файла
- Щелкните меню «Файл», затем сохраните пакетный файл и назовите его, добавив .bat в конце имени.
- Нажмите кнопку «Сохранить». Вы можете идентифицировать файл .bat по его миниатюре с двумя значками шестеренки.
Пример пакетного файла
Вы можете использовать различные методы в Windows 10 для запуска пакетного файла в зависимости от того, как и когда вы хотите выполнять задачи.
Метод 1: запуск командного файла по запросу
Вы можете запустить файл из проводника или командной строки Windows, чтобы выполнять задачи только тогда, когда они вам нужны.
Из проводника
- В проводнике откройте папку, содержащую пакетный файл.
- Дважды щелкните файл или щелкните правой кнопкой мыши, чтобы запустить файл от имени администратора, если задача требует прав администратора.
Запустить пакетный файл вручную
Из командной строки Windows
- Запустите командную строку с параметром «Запуск от имени администратора».
- Измените каталог на папку, содержащую ваш пакетный файл «C: [пользователь] [путь к файлу]»
- Затем введите в команде имя файла с расширением .bat или без него и нажмите Enter.
Запустить файл
Метод 2: как запустить командный файл во время запуска?
Если вы хотите запускать пакетный файл каждый раз при входе в Windows, вы можете сделать это, выполнив следующие действия.
- Нажмите сочетание клавиш Win + R, чтобы открыть утилиту «Выполнить». Введите «shell:startup» и нажмите Enter на клавиатуре.

- Откроется домашняя папка».
- Скопируйте и вставьте пакетный файл или его ярлык в эту папку, а затем закройте.

- Вы можете выйти из своей учетной записи и войти снова, чтобы убедиться, что она работает.
Метод 3: запуск командного файла с помощью планировщика задач
Если вы хотите запустить задачу позже, вы можете использовать планировщик задач Windows 10 для запуска пакетного файла.
- Перейдите в меню «Пуск», найдите «Планировщик заданий» и выберите соответствующий вариант из результата.
- В разделе «Библиотека разработчика» на левой панели создайте папку для своей задачи и нажмите «Создать базовую задачу…» в разделе «Действия» на правой панели.
- Введите имя и описание (необязательно) для своей задачи в открывшемся мастере и нажмите «Далее».

- Установите триггер задачи в зависимости от того, когда вам нужно запустить задачу, и нажмите «Далее».

- В разделе «Действие» выберите опцию «Запустить программу» и перейдите на следующую страницу.
- В поле «Сценарий» нажмите «Обзор», перейдите в папку, в которой вы сохранили пакетный файл, и выберите файл.

- Просмотрите сведения о задаче и нажмите «Готово», чтобы завершить процесс.

- Windows автоматически запустит пакетный файл в указанное вами время.
Вывод
Пакетные файлы хранят инструкции для выполнения определенной задачи в Windows. Пакетный файл можно использовать для автоматизации процедур, настройки системных параметров и многих других основных задач. Вы можете создать и сохранить пакетный файл и использовать любой из вышеперечисленных методов для запуска файла в Windows 10. Единственным серьезным ограничением является то, что пакетные файлы предназначены исключительно для ПК с Windows.
Пакетные файлы в Windows являются файлами сценариев. Пакетный файл – это неформатированный текстовый файл. Этот файл состоит из серии команд и имеет расширение имени файла .bat или .cmd . Термин «пакетная обработка» адаптирован для пакетной обработки, что означает неинтерактивное выполнение. С помощью пакетных файлов в Windows пользователи могут упростить повторяющиеся или рутинные задачи. Когда пользователи вводят имя файла в командной строке, cmd.exe запускает команды последовательно, как они появляются в файле. Некоторые типичные команды, используемые в пакетных файлах в Windows, – Call, Echo, Endlocal, For, Goto, If, Pause, Rem, Setlocal и Shift.
Как создать .bat или пакетные файлы в Windows
Как упоминалось ранее, командный файл содержит серию команд DOS и используется для автоматизации часто выполняемых задач. Таким образом, вам не нужно многократно писать одни и те же команды.
Пакетный файл создается с помощью Блокнота . Текстовый файл состоит из команд, которые вы хотите выполнить. Чтобы создать пакетный файл , необходимо написать команду в виде текста в Блокноте и сохранить файл в виде файла .bat. Чтобы выполнить команду , вам просто нужно дважды щелкнуть командный файл. Следовательно, хорошо написанный пакетный файл в Windows может сэкономить много времени.
Некоторые основные команды в пакетных файлах:
- ЭХО: для отображения текста на экране
- @ECHO OFF: скрыть текст
- START: запустить файл с приложением по умолчанию
- REM: ввести строку комментария в программу
- MKDIR: для создания каталогов
- RMDIR: удалить каталоги
- DEL: чтобы удалить файлы
- COPY: для копирования файла или файлов
- XCOPY: для копирования файлов с дополнительными параметрами
- FOR/IN/DO: указать файлы
- НАЗВАНИЕ: Редактировать заголовок окна
Крутые и забавные трюки с пакетными файлами
1. Матрица

Помните фильм «Матрица»? Вы можете сделать свой фон похожим на зеленый экран Матрицы с помощью этого командного файла. Это определенно для классного взгляда и ничего больше. Чтобы создать пакетные файлы такого типа в Windows, выполните следующие действия:
Шаг 1. Откройте текстовый документ и переименуйте его в «matrix.bat». Как только расширение текстового файла изменяется на .bat, его значок меняется на шестерёнку.

Шаг 2. . Теперь вы можете отредактировать файл, чтобы написать свою программу. Для этого щелкните файл правой кнопкой мыши и выберите «Изменить». Он должен открыться в блокноте. Вот командные строки, которые нужно вставить в блокнот.
@echo off цвет 2 :Начните эхо% случайный%% случайный%% случайный%% случайный%% случайный%% случайный%% случайный%% случайный%% случайный%% случайный%% случайный%% случайный%% случайный%% случайный% перейти к началу
Нажмите «Сохранить» и дважды щелкните по нему. Это даст эффект Матрицы в окне. Разверните окна CMD и нажмите F11, чтобы получить лучший полноэкранный эффект.
2. Создатель паролей
Вы даже можете создать защищенный паролем файл, который создается и доступен с помощью пакетного (.bat) файла. Это один из слегка полезных пакетных файлов в Windows, который прекрасно работает для сокрытия вещей от людей, у которых мало или совсем нет знаний о компьютере или пакетных файлах.
Выполните следующие действия, чтобы создать пакетные файлы Password Creator в Windows:
Шаг 1. Откройте Блокнот
Шаг 2. . Скопируйте и вставьте следующий код:
ЦБС
@ECHO OFF
название Система оружия кибер-атаки
если EXIST "Панель управления. {21EC2020-3AEA-1069-A2DD-08002B30309D}" перейти к РАЗБЛОКИРОВАНУ
если НЕ СУЩЕСТВУЕТ Скрытый Перейти к MDHidden
: ПОДТВЕРДИТЬ
эхо Вы уверены, что заблокировать эту папку? (Y/N)
set/p "cho =>"
если% cho% == Y перейти к LOCK
если% cho% == y Перейти к LOCK
если% cho% == n перейти END
если% cho% == N перейти END
Эхо Неверный выбор.
Перейти к ПОДТВЕРДИТЬ
:ЗАМОК
ren Hidden "Панель управления. {21EC2020-3AEA-1069-A2DD-08002B30309D}"
attrib + h + s "Панель управления. {21EC2020-3AEA-1069-A2DD-08002B30309D}"
эхо папка заблокирована
Goto End
: ОТКРЫТЬ
echo Введите пароль, чтобы разблокировать вашу защищенную папку
set/p "pass =>"
если НЕТ% pass% == 1234 goto FAIL
Перейти к UNLOCK2
: UNLOCK2
ЦБС
echo Введите пароль, чтобы разблокировать вашу защищенную папку
set/p "pass =>"
если НЕТ% pass% == 1234 goto FAIL
attrib -h -s "Панель управления. {21EC2020-3AEA-1069-A2DD-08002B30309D}"
Рен "Панель управления.{21EC2020-3AEA-1069-A2DD-08002B30309D} "Скрытый
Папка эха успешно разблокирована
Goto End
:Потерпеть поражение
@ эхо выключено
цвет 02
echo Warning-Virus Инициируется полное повреждение жесткого диска
таймаут/t 5/nobreak> нуль
установить количество = 0
:трюки
если% count% == 200 Перейти к выключению
echo% random %% random %% random %% random %% random %% random %% random %% random%
set/a count =% count% + 1
трюки
:неисправность
ЦБС
:неисправность
shutdown -s -t 45/c "Вы пытались получить доступ к файлу, который не принадлежит вам. До свидания."
echo Введите пароль Начать последовательность отмены
set/p "pass =>"
если НЕ% pass% == 1234 goto shutdown
эхо отменено
Перейти к Abort
: Прервать
C: Windows System32 shutdown.exe -a
Прервать Успешно
тайм-аут/т 3/nobreak> нуль
ЦБС
перейти к разблокировке
конец
: MDHidden
MD Hidden
echo Hidden создан успешно
Шаг 3. Установите пароль
Пароли по умолчанию установлены на 1234. Их также можно изменить. Чтобы изменить пароль, найдите в коде, где написано:
если НЕ% pass% == 1234 Перейти
И замените 1234 на ваш пароль. Сохраните файл с расширением .bat.
Когда вы открываете файл в первый раз, он будет мигать, и появится другой файл с именем «Скрытый». Чтобы скрыть этот файл, просто щелкните оригинальный файл еще раз, и он спросит вас, хотите ли вы скрыть файл. Если вы вводите Y, то оно скрывается, но если вы набираете N, ничего не происходит. После того, как вы скроете его, а затем захотите получить к нему доступ, вам нужно снова щелкнуть оригинальный файл, и он запросит у вас пароль.
Тем не менее, вы должны помнить, что этот метод не является надежным. Любой, у кого мало знаний или опыта в компьютерных системах и пакетных файлах, скорее всего, сможет обойти его довольно быстро.
3. Color Tester

Если вы хотите попробовать цветовое тестирование, используя пакетные файлы в Windows, то вот код для этого. Это просто, и это может быть довольно полезно.
Откройте блокнот и скопируйте следующий код.
@echo off :тестовое задание помочь цвет эхо ------------------------------------------------- --------- эхо. echo Введите цветовой код для проверки цветов. эхо Чтобы выйти, просто нажмите X. set/p color = цвет% цвет% Перейти к тесту
Сохраните файлы с расширением .bat.
Если вы хотите узнать больше о таких хитростях пакетных файлов в Windows, вы можете посетить Instructable.com.