Install Docker Desktop – the fastest way to containerize applications.
Docker Extensions
Transform and optimize workflows by connecting to an array of pre-built developer tools from our Docker Extensions Marketplace for things like debugging, testing, networking, and security. Explore near endless workflow possibilities by creating your own custom tools and share them with your team or the whole world.
Volume Management, Dev Environments and more
Takes the guesswork out of volume management. Pro, Team, and Business subscribers can quickly and easily explore their volumes, identify what’s taking up space and remove unneeded files and directories right from the Dashboard. Docker Desktop simplifies setting up common and consistent local developer environments across an organization.
Secure from the start
Docker Desktop helps you quickly and safely evaluate software so you can start secure and push with confidence. Docker Desktop now includes the ability to generate a Software Bill of Material (SBOM) pre-build, as well as vulnerability scanning powered by Snyk, which scans your containers and provides actionable insights and recommendations for remediation in your images. Learn more about end-to-end vulnerability scanning and how to shift security left in your app delivery pipeline.
Simplify Code to Cloud
Simplify code to cloud application development by closely integrating with Azure Container Instances (ACI). You get the same workflow in Docker Desktop and the Docker CLI with all the container compute you want. No infrastructure to manage. No clusters to provision.
Image Access Management
Stay more secure by managing which container images on Docker Hub developers can access, and gain more control by configuring organizations to only allow access to Docker Official Images and Docker Verified Publishers. Available with Docker Business.
Build Kubernetes-ready applications on your desktop
Docker Desktop is an application for MacOS, Linux, and Windows machines for the building and sharing of containerized applications and microservices.
Docker Desktop delivers the speed, choice and security you need for designing and delivering these containerized applications on your desktop. Docker Desktop includes Developer tools, Kubernetes and version synchronization to production Docker Engines. Docker Desktop allows you to leverage certified images and templates and your choice of languages and tools. Development workflows leverage Docker Hub to extend your development environment to a secure repository for rapid auto-building, continuous integration and secure collaboration.
Considering Alternatives?
Developers love using Docker Desktop for all the best reasons: it’s easy to use, it accelerates productivity, and it eliminates the toil of setting up complex environments for building modern applications.
And while Docker Engine is sometimes viewed as a drop-in DIY (do-it-yourself) alternative for Docker Desktop, it’s important to understand that there are vast differences between the two, and that going it alone might not be as simple – or economical – as it seems. Learn more.
Containerize and share any application
Across any combination of clouds, languages and frameworks
Exclusive content
Get scoops on new products and community management resources to help your group flourish. Join our special events and get sneak peaks of DockerCon.
Professional growth
Develop new skills and build your reputation as a key community leader. Expand your network, learn and connect with like-minded developers.
Community mentorship
Connect with fellow Community Leaders who can help you learn how to effectively build, manage and grow your community.
Choose a plan that is right for you
Benefit from more collaboration, increased security, without limits… all enabled with a Docker subscription.
Check out our pricing.
| description | keywords | title | redirect_from | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
How to install Docker Desktop for Windows |
windows, install, download, run, docker, local, Docker Desktop |
Install on Windows |
|
Docker Desktop terms
Commercial use of Docker Desktop in larger enterprises (more than 250
employees OR more than $10 million USD in annual revenue) requires a paid
subscription.
Welcome to Docker Desktop for Windows. This page contains information about Docker Desktop for Windows system requirements, download URL, instructions to install and update Docker Desktop for Windows.
Download Docker Desktop for Windows
Docker Desktop for Windows{: .button .primary-btn }
For checksums, see Release notes
System requirements
Your Windows machine must meet the following requirements to successfully install Docker Desktop.
- WSL 2 backend
- Hyper-V backend and Windows containers
WSL 2 backend
-
Windows 11 64-bit: Home or Pro version 21H2 or higher, or Enterprise or Education version 21H2 or higher.
-
Windows 10 64-bit: Home or Pro 21H1 (build 19043) or higher, or Enterprise or Education 20H2 (build 19042) or higher.
-
Enable the WSL 2 feature on Windows. For detailed instructions, refer to the
Microsoft documentation{: target=»blank» rel=»noopener» class=»«}. -
The following hardware prerequisites are required to successfully run
WSL 2 on Windows 10 or Windows 11:- 64-bit processor with Second Level Address Translation (SLAT){: target=»blank» rel=»noopener» class=»«}
- 4GB system RAM
- BIOS-level hardware virtualization support must be enabled in the
BIOS settings. For more information, see
Virtualization.
-
Download and install the Linux kernel update package{: target=»blank» rel=»noopener» class=»«}.
Hyper-V backend and Windows containers
-
Windows 11 64-bit: Pro version 21H2 or higher, or Enterprise or Education version 21H2 or higher.
-
Windows 10 64-bit: Pro 21H1 (build 19043) or higher, or Enterprise or Education 20H2 (build 19042) or higher.
For Windows 10 and Windows 11 Home, see the system requirements in the WSL 2 backend{: data-toggle=»tab» data-target=»#win-wsl2″ } tab.
-
Hyper-V and Containers Windows features must be enabled.
-
The following hardware prerequisites are required to successfully run Client
Hyper-V on Windows 10:- 64 bit processor with Second Level Address Translation (SLAT){: target=»blank» rel=»noopener» class=»«}
- 4GB system RAM
- BIOS-level hardware virtualization support must be enabled in the
BIOS settings. For more information, see
Virtualization.
Note
Docker only supports Docker Desktop on Windows for those versions of Windows 10 that are still within Microsoft’s servicing timeline{:target=»blank» rel=»noopener» class=»«}.
Containers and images created with Docker Desktop are shared between all
user accounts on machines where it is installed. This is because all Windows
accounts use the same VM to build and run containers. Note that it is not possible to share containers and images between user accounts when using the Docker Desktop WSL 2 backend.
Running Docker Desktop inside a VMware ESXi or Azure VM is supported for Docker Business customers.
It requires enabling nested virtualization on the hypervisor first.
For more information, see Running Docker Desktop in a VM or VDI environment.
About Windows containers
Looking for information on using Windows containers?
- Switch between Windows and Linux containers
describes how you can toggle between Linux and Windows containers in Docker Desktop and points you to the tutorial mentioned above.
- Getting Started with Windows Containers (Lab)
provides a tutorial on how to set up and run Windows containers on Windows 10, Windows Server 2016 and Windows Server 2019. It shows you how to use a MusicStore application
with Windows containers. - Docker Container Platform for Windows articles and blog
posts{:target=»blank» rel=»noopener» class=»«} on the Docker website.
Note
To run Windows containers, you need Windows 10 or Windows 11 Professional or Enterprise edition.
Windows Home or Education editions will only allow you to run Linux containers.
Install Docker Desktop on Windows
Install interactively
-
Double-click Docker Desktop Installer.exe to run the installer.
If you haven’t already downloaded the installer (
Docker Desktop Installer.exe), you can get it from
Docker Hub{:target=»blank» rel=»noopener» class=»«}.
It typically downloads to yourDownloadsfolder, or you can run it from
the recent downloads bar at the bottom of your web browser. -
When prompted, ensure the Use WSL 2 instead of Hyper-V option on the Configuration page is selected or not depending on your choice of backend.
If your system only supports one of the two options, you will not be able to select which backend to use.
-
Follow the instructions on the installation wizard to authorize the installer and proceed with the install.
-
When the installation is successful, click Close to complete the installation process.
-
If your admin account is different to your user account, you must add the user to the docker-users group. Run Computer Management as an administrator and navigate to Local Users and Groups > Groups > docker-users. Right-click to add the user to the group.
Log out and log back in for the changes to take effect.
Install from the command line
After downloading Docker Desktop Installer.exe, run the following command in a terminal to install Docker Desktop:
$ "Docker Desktop Installer.exe" install
If you’re using PowerShell you should run it as:
Start-Process 'Docker Desktop Installer.exe' -Wait install
If using the Windows Command Prompt:
start /w "" "Docker Desktop Installer.exe" install
The install command accepts the following flags:
--quiet: suppresses information output when running the installer--accept-license: accepts the Docker Subscription Service Agreement{: target=»blank» rel=»noopener» class=»«} now, rather than requiring it to be accepted when the application is first run--no-windows-containers: disables Windows containers integration--allowed-org=<org name>: requires the user to sign in and be part of the specified Docker Hub organization when running the application--backend=<backend name>: selects the default backend to use for Docker Desktop,hyper-v,windowsorwsl-2(default)--installation-dir=<path>: changes the default installation location (C:Program FilesDockerDocker)--admin-settings: Automatically creates anadmin-settings.jsonfile which is used by admins to control certain Docker Desktop settings on client machines within their organization. For more information, see Settings Management.- It must be used together with the
--allowed-org=<org name>flag. - For example:
--allowed-org=<org name> --admin-settings='{"configurationFileVersion": 2, "enhancedContainerIsolation": {"value": true, "locked": false}}'
- It must be used together with the
If your admin account is different to your user account, you must add the user to the docker-users group:
$ net localgroup docker-users <user> /add
Start Docker Desktop
Docker Desktop does not start automatically after installation. To start Docker Desktop:
-
Search for Docker, and select Docker Desktop in the search results.
{:width=»300px»}
-
The Docker menu (
{: .inline}) displays the Docker Subscription Service Agreement window.
{% include desktop-license-update.md %}
-
Select Accept to continue. Docker Desktop starts after you accept the terms.
Important
If you do not agree to the terms, the Docker Desktop application will close and you can no longer run Docker Desktop on your machine. You can choose to accept the terms at a later date by opening Docker Desktop.
{: .important}For more information, see Docker Desktop Subscription Service Agreement{:target=»blank» rel=»noopener» class=»«}. We recommend that you also read the FAQs{: target=»_blank» rel=»noopener» class=»*» id=»dkr_docs_desktop_install_btl»}.
Where to go next
- Get started with Docker is a tutorial that teaches you how to deploy a multi-service stack.
- Troubleshooting describes common problems, workarounds, and
how to get support. - FAQs provide answers to frequently asked questions.
- Release notes lists component updates, new features, and improvements associated with Docker Desktop releases.
- Back up and restore data provides instructions on backing up and restoring data related to Docker.
Estimated reading time:
4 minutes
Docker Desktop for Windows is the Community version of Docker for Microsoft Windows.
You can download Docker Desktop for Windows from Docker Hub.
Download from Docker
Hub
What to know before you install
System Requirements
- Windows 10 64-bit: Pro, Enterprise, or Education (Build 15063 or later).
- Hyper-V and Containers Windows features must be enabled.
-
The following hardware prerequisites are required to successfully run Client
Hyper-V on Windows 10:- 64 bit processor with Second Level Address Translation (SLAT)
- 4GB system RAM
- BIOS-level hardware virtualization support must be enabled in the
BIOS settings. For more information, see
Virtualization.
Note: Docker supports Docker Desktop on Windows based on Microsoft’s support lifecycle for Windows 10 operating system. For more information, see the Windows lifecycle fact sheet.
README for Docker Toolbox and Docker Machine users: Microsoft Hyper-V is required to run Docker Desktop. The Docker Desktop Windows installer enables Hyper-V if required, and restarts your machine. When Hyper-V is enabled, VirtualBox no longer works. However, any existing VirtualBox VM images are retained.
VirtualBox VMs created with docker-machine (including the default one
typically created during Toolbox install) no longer start. These VMs cannot be
used side-by-side with Docker Desktop. However, you can still use
docker-machine to manage remote VMs.
What’s included in the installer
The Docker Desktop installation includes Docker Engine, Docker CLI client, Docker Compose, Docker Machine, and Kitematic.
Containers and images created with Docker Desktop are shared between all
user accounts on machines where it is installed. This is because all Windows
accounts use the same VM to build and run containers.
Nested virtualization scenarios, such as running Docker Desktop on a
VMWare or Parallels instance might work, but there are no guarantees. For
more information, see Running Docker Desktop in nested virtualization scenarios.
Note: Refer to the Docker compatibility matrix for complete Docker compatibility information with Windows Server.
About Windows containers
Looking for information on using Windows containers?
- Switch between Windows and Linux
containers
describes how you can toggle between Linux and Windows containers in Docker Desktop and points you to the tutorial mentioned above. - Getting Started with Windows Containers
(Lab)
provides a tutorial on how to set up and run Windows containers on Windows 10, Windows Server 2016 and Windows Server 2019. It shows you how to use a MusicStore application
with Windows containers. - Docker Container Platform for Windows articles and blog
posts on the Docker website.
Install Docker Desktop on Windows
-
Double-click Docker Desktop Installer.exe to run the installer.
If you haven’t already downloaded the installer (
Docker Desktop Installer.exe), you can get it from
Docker Hub.
It typically downloads to yourDownloadsfolder, or you can run it from
the recent downloads bar at the bottom of your web browser. -
Follow the instructions on the installation wizard to accept the license, authorize the installer, and proceed with the install.
When prompted, authorize the Docker Desktop Installer with your system password during the
install process. Privileged access is needed to install networking
components, links to the Docker apps, and manage the Hyper-V VMs. -
Click Finish on the setup complete dialog and launch the Docker Desktop application.
Start Docker Desktop
Docker Desktop does not start automatically after installation. To start Docker Desktop, search for Docker, and select Docker Desktop in the search results.
When the whale icon in the status bar stays steady, Docker Desktop is up-and-running, and is accessible from any terminal window.
If the whale icon is hidden in the Notifications area, click the up arrow on the
taskbar to show it. To learn more, see Docker Settings.
After installing the Docker Desktop app, you also get a pop-up success message with
suggested next steps, and a link to this documentation.
When initialization is complete, click the whale icon in the Notifications area and select About Docker Desktop to verify that you have the latest version.
Congratulations! You are successfully running Docker Desktop on Windows.
Uninstall Docker Desktop
To uninstall Docker Desktop from your Windows machine:
- From the Windows Start menu, select Settings > Apps > Apps & features.
- Select Docker Desktop from the Apps & features list and then select Uninstall.
- Click Uninstall to confirm your selection.
Note: Uninstalling Docker Desktop will destroy Docker containers and images local to the machine and remove the files generated by the application.
Where to go next
- Getting started introduces Docker Desktop for Windows.
- Get started with Docker is a tutorial that teaches you how to
deploy a multi-service stack. - Troubleshooting describes common problems, workarounds, and
how to get support. - FAQs provides answers to frequently asked questions.
- Stable Release Notes or Edge Release
Notes.
windows, beta, edge, alpha, install, download
Docker is a platform for creating and deploying applications in self-sufficient containers. The installation of Docker is pretty easy in Linux, but this is usually not the case with Windows. In this post, I will show you how to install Docker in Windows 10 or Windows 11 in multiple ways. You’ll learn there is indeed a way that makes the Docker Desktop installation in Windows as simple as in Linux.
Contents
- Prerequisites
- Docker with WSL2 backend
- Docker with Hyper-V backend
- Install Docker using the GUI
- Install Docker using winget
- Install Docker using PowerShell
- Author
- Recent Posts
Surender Kumar has more than twelve years of experience in server and network administration. His fields of interest are Windows Servers, Active Directory, PowerShell, web servers, networking, Linux, virtualization, and penetration testing. He loves writing for his blog.
Latest posts by Surender Kumar (see all)
- Extending LVM space in Ubuntu — Thu, Feb 2 2023
- Backup in Proxmox VE — Thu, Jan 26 2023
- Snapshots in Proxmox VE — Wed, Jan 25 2023
Prerequisites
You might already be aware that Docker relies on virtualization technology. On Windows, Docker can use either the Windows Subsystem for Linux (WSL) 2 or Hyper-V as a backend.
Docker with WSL2 backend
The current version of Docker Desktop only works on the 64-bit edition of Windows, whether you’re running Windows 10 or Windows 11. To run Docker with the WSL2 backend, your system must meet the following prerequisites:
- Windows 10: Home/Pro 21H1 (build 19043) or higher, or Enterprise/Education 20H2 (build 19042) or higher
- Windows 11: Home/Pro version 21H2 or higher, or Enterprise/Education version 21H2 or higher
- WSL2 feature enabled
- Linux kernel update package for WSL2
- For WSL2, the following are the hardware requirements:
- 64-bit CPU with second-level address translation (SLAT)
- Hardware virtualization support, which must be enabled in BIOS/UEFI
- 4 GB RAM
Docker with Hyper-V backend
To be able to run Docker with a Hyper-V backend and Windows containers, your system must meet the following prerequisites:
- Windows 10: Pro 21H1 (build 19043) or higher, or Enterprise/Education 20H2 (build 19042) or higher
- Windows 11: Pro/Enterprise/Education version 21H2 or higher
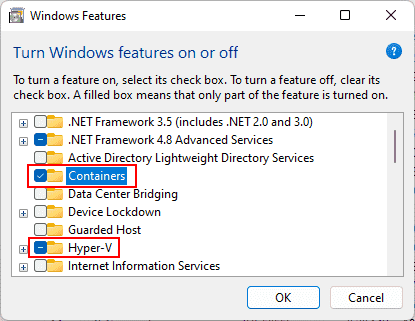
- Optional Windows features for Hyper-V and Containers must be enabled
Enable Hyper V and Containers windows features for Docker
For Hyper-V, following are the hardware requirements:
- 64-bit CPU with second-level address translation (SLAT)
- Hardware virtualization support, which must be enabled in BIOS/UEFI
- 4 GB RAM
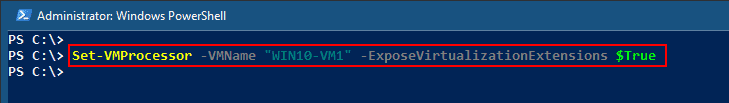
In addition to the aforementioned requirements, if you want to run Docker in a Hyper-V guest VM, you need to enable nested virtualization by running this PowerShell command on the Hyper-V host:
Set-VMProcessor -VMName <VMName> -ExposeVirtualizationExtensions $True
Enable nested virtualization for a VM on Hyper V host using PowerShell
Make sure your VM is powered off before running this command. Without nested virtualization support, Docker will not work in a VM, and you will receive the error message shown below.
Docker desktop cannot start An unexpected error occurred
Install Docker using the GUI
To install Docker Desktop in Windows using the GUI, follow these steps:
Download Docker Desktop. You will see a configuration screen, as shown in the screenshot:
Docker desktop configuration Use WSL 2 instead of Hyper V recommended
To use Docker with the WSL 2 backend, check the box that says Use WSL 2 instead of Hyper-V (recommended). If you want to use Hyper-V instead, uncheck this option and click OK.
When the installation is complete, click the Close and Restart button to restart your computer.
Close Docker installer and restart the computer to complete installation
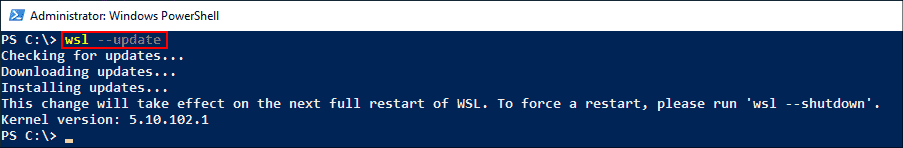
After restarting, you will be able to run Docker Desktop using either a shortcut or a command prompt. If you did not install WSL 2 before installing Docker, you will receive the WSL 2 installation is incomplete error when you try to start Docker.
Docker desktop error WSL 2 installation is incomplete
To fix this error, run the wsl —update command in an elevated PowerShell console, and restart your computer.
Installing WSL2 kernel updates to fix the WSL 2 installation is incomplete error
Install Docker using winget
Winget is a command-line package manager for modern versions of Windows, which works just like apt or DNF in Linux. If you have a little experience with package installation in Linux, you probably know that you usually just have to type a command and the package is ready for use. Well, winget does the exact same thing in Windows. All you need is Windows 10 1809 (build 17763) or Windows 11. To install Docker in Windows using winget, follow these steps:
Launch an elevated command prompt or PowerShell console, and type the following command:
winget install --exact --id Docker.DockerDesktop --accept-source-agreements --accept-package-agreements
Installing docker desktop in windows using winget
The —exact (or -e in short) parameter tells winget to find the package using an exact match. The installation can take a while, but it is pretty much automatic, so there is nothing you need to do but wait.
When the command is finished, open a new command prompt (or PowerShell console) and run the docker —version command.
If you try to run docker —version in the same command prompt, you will likely see The term ‘docker’ is not recognized as the name of a cmdlet, function, script file, or operable program error, as shown in the screenshot.
The term docker is not recognized as the name of a cmdlet function script file or operable program
This error occurs because your current command session (cmd or PowerShell) is still using the old environment variables. To be able to recognize the newly added Docker variable, you must reload the environment variables. Launching a new command session is the easiest way to load new variables.
Install Docker using PowerShell
To install Docker Desktop using PowerShell, follow these steps:
Download Docker Desktop.
Once the installer package is downloaded, open an elevated PowerShell console or Windows Terminal, and type the following command to start Docker installation:
Start-Process "D:Docker Desktop Installer.exe" -Wait -NoNewWindow "install --quiet --accept-license"
Installing Docker silently using PowerShell
Make sure you adjust the installer path. The -Wait parameter causes the Start-Process cmdlet to wait for the new process to finish, and the -NoNewWindow parameter prevents the new process from opening in a new window. The —quiet switch is offered by Docker’s install command and suppresses the installation information. To see the information, skip this switch. Since we are using PowerShell, notice how —quiet and other flags are enclosed in quotes along with the install command—this is very important to avoid errors. By default, Docker will use the WSL 2 backend, but you could include the —backend=hyper-v flag to use the Hyper-V backend instead.
Once the above command is finished, you will see a shortcut for Docker Desktop on your desktop. Double-click the shortcut to launch Docker.
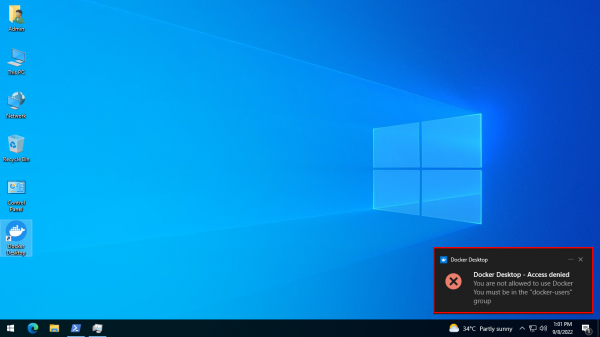
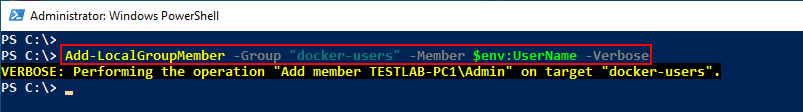
All of these installation methods are self-sufficient, so there is nothing additional you need to do. But you may still get an error message that says Docker Desktop – Access denied. You are not allowed to use Docker. You must be in the «docker-users» group.
Docker Desktop – Access denied. You are not allowed to use Docker. You must be in the docker users group
If you get this error, run the following command in an elevated PowerShell console:
Add-LocalGroupMember -Group "docker-users" -Member $env:UserName -Verbose
Adding the current user to the docker users group using PowerShell
Don’t forget to log off and log on again after running this command. If you want to delegate another user to run Docker Desktop, you can specify that username with the -Member parameter instead of $env:UserName.
Subscribe to 4sysops newsletter!
That was all for this guide. You just learned how to install Docker in Windows using the GUI, winget, and PowerShell. I am curious to know which method you prefer, and why.
Skip to content
Install Docker Desktop on Windows 10
In this tutorials, we are going to show how to install Docker Desktop on Windows 10 operating system.
Technology versions :
- Windows 10 64 Bit Operating System
- Docker Engine 18.09.1
Download Docker Desktop for Windows :
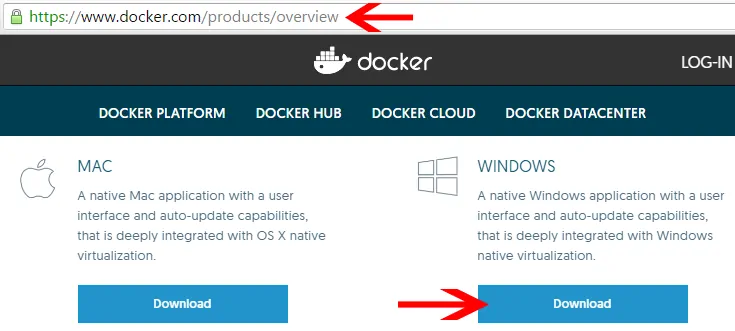
Step 1: Get Docker Desktop from the official docker hub.

Click on Get Docker button, will download the Docker for Windows Installer.
Install Docker Desktop on Windows 10:
Step 2: After successfully downloaded, double click on the Docker For Windows Installer file then you can see the below window saying downloading packages.

Step 3: Soon after you can see the below window, asking for Add the desktop shortcut. You can leave it as is and click on Ok.

Step 4: Now you can see the installation process.

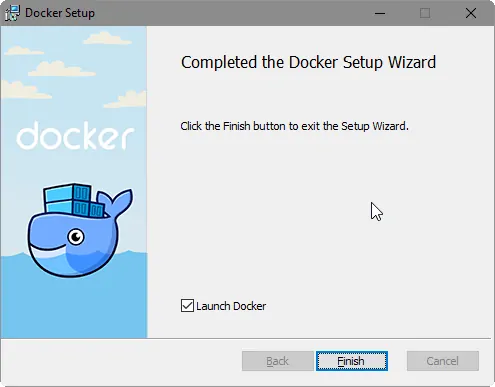
Step 5: If everything is done well, you can see the below success window saying Installation succeeded. Click on Close.

Step 6: Then go to windows command prompt and check for the installation confirmation. Check the installed docker version.

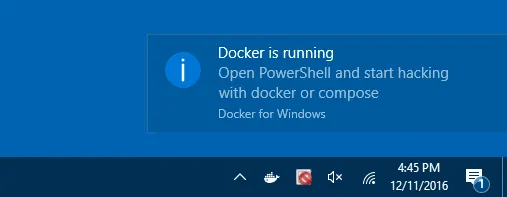
Step 7: Now let’s start docker by double-clicking on the desktop icon, it will take a while to start docker daemon. After a successful start, you can see the below window asking for docker hub credentials. If you have your docker hud credentials you can directly login from here.

That’s it, now the docker desktop is successfully installed on Windows 10 operating system.
Docker Desktop Settings:
After all the above steps done successfully, you can see a small docker icon on your windows taskbar like below.
Right click on the docker icon there you can see the settings option, click on Settings you can see the below window having all the docker related setting tabs.
General Settings:
Here you can setup docker startup, updates and statistics settings.

Shared Drives:
If you want to make available your containers to a specific drive, you can do the drive settings here.

Advanced Settings:
Advanced settings are all about defining a number of cores, memory allocations. By default number of core defined based on your system settings and memory allocation would be 2 GB. You can freely alter this setting at any time.

Network Settings:
Configuring the way Docker containers interact with the network.

Proxy Settings:
It is used to configure the proxies used by the docker engine to pull the images.

Deamon Settings:
If you wanted to set the docker daemon settings, this is the right place to modify. Click on the configuration file hyperlink and do your modifications.

Kubernetes Settings:
There you can enable the kubernetes for docker. By enabling the kubernetes, by default it will start a single-node cluster for docker desktop.

Reset Settings:
If you want to reset all your settings, you can do here.

References:
- Docker Installation
Happy Learning 🙂
Share a word.
Related Posts
Page load link
Write for Us: Familiar with Smart Home Automation, Media Streaming, HTPC, and Home Server topics? Write for us and get paid. Writing experience not required. APPLY HERE.
In this guide, I will explain how to install Docker on Windows 10. Docker, if you do not know, self-contains apps, making them extremely easy to install and manage. Home Sever apps such as SickRage, Sonarr, CouchPotato, Plex, etc. can be installed in just seconds. Interesting? Read our guide on what is docker and how it is different from VirtualBox for more information on what it can do for you. We have already covered Docker setup on Ubuntu. In this Docker Windows tutorial, we will see how to setup Docker for Windows 10.
Must Read: Docker Media Server Ubuntu: Compose for 23 Awesome Apps
Table of Contents
- Install Docker on Windows 10
- 1. Download Docker for Windows 10
- 2. Setup Docker on Windows 10
- 3. Enable Hyper-V for Docker
- Docker is installed successfully. What to do next?
Docker is already builtin into Windows Server setups. On other Windows systems you will have to setup Docker yourself. There are two ways to install Docker on Windows depending on your Windows version.
- Docker Installer Method: Windows 10 64-bit Professional, Enterprise, and Education Versions include Hyper-V and therefore will support Docker natively. Follow this guide to install Docker for Windows 10.
- Docker ToolBox Method: Other editions of Windows 10 or older Windows versions (7 and
do not include a hypervisor such as Hyper-V. Therefore, Docker must be installed using Docker Toolbox. In this setup, Docker installs VirtualBox and use it as the Hypervisor.
If you have Windows 10 64-bit Pro, Ent, or Edu and use VirtualBox, then follow method 2. Following the first method will make your VirtualBox VMs inoperable.
Before you begin, enable Intel VT-x hardware virtualization in BIOS or UEFI firmware. This is required for Docker to run. Once this is done, installing Docker on Windows is as simple as downloading the installer and running it as you would for any software installation.
Recommended Guides on Docker:
- The Docker Book: Containerization is the new virtualization
- Docker Cookbook: Solutions and Examples
1. Download Docker for Windows 10
To install Docker on Windows 10, first visit Docker download page and download the latest installer as shown in the picture below.
Once downloaded, double click to run the Docker installer.
2. Setup Docker on Windows 10
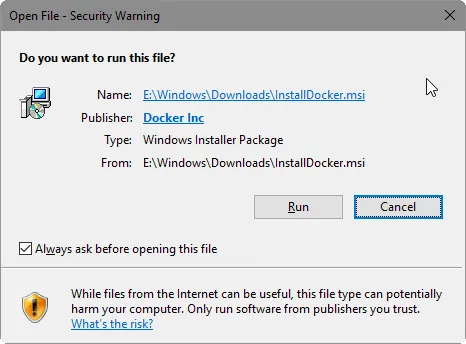
When Windows security warning appears, click «Run» to continue with Docker setup.
Once you agree to Docker Terms and Conditions, the Docker windows installation should begin.
When the installation completes, make sure that «Launch Docker» is checked and Click «OK».
Recommended HTPC / Home Server Builds:
- Best Home Theater PC Build 2017 to do it all (Plex, Kodi, NAS, Gaming)
- Best Emby Server builds 2018 – Pre-built and DIY options
- Medium Budget 4K HTPC Build 2017 for Kodi, Plex and Gaming
- Cheap 4K HTPC Build for Kodi, OpenELEC, and LibreELEC 2017
- Low Power Home Server Build 2017 for Network File and Media Storage
- Best HTPC for Kodi with 4K on a Medium Budget 2017 (~$400)
- Energy efficient budget HTPC-NAS combo build 2016
To run docker manually, open Docker from the apps menu. On Windows 10 64-bit Pro and Ent docker runs through Hyper-V on Windows Powershell. You can open Powershell through the apps menu as well.
3. Enable Hyper-V for Docker
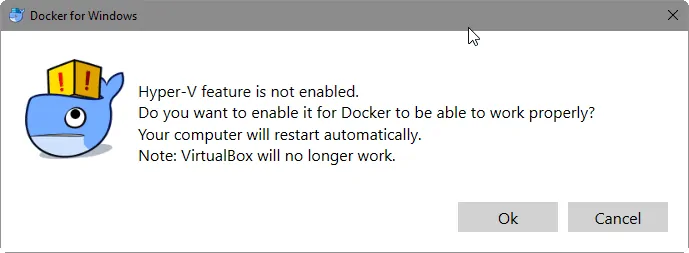
Windows 10 64-bit Pro, Ent, or Edu have Hyper-V, which is must be enabled for Docker to work on Windows. When you launch Docker after installation, you will receive the following warning.
If Hyper-V is not enabled, the Docker for Windows installer can enable it for you. Click «OK» to enable Hyper-V on Windows. Your computer will reboot to complete installation. Note that if you have VirtualBox installed at this point, your VMs will become inoperable.
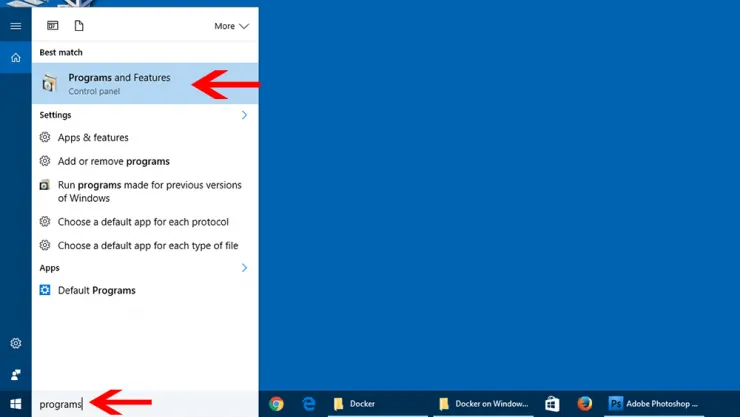
If for whatever reason, you want to manually enable Hyper-V, type «Programs» in the Windows Cortana search box as shown below.
Then, click on «Turn Windows Feature On or Off» (on the left side). From the list, find and check (enable) Hyper-V, click «OK», and apply changes. Your computer will reboot to enable Hyper-V on Windows.
Docker is installed successfully. What to do next?
If everything went well, you should have Docker for Windows installed, the service should be running and waiting to host containers with various apps. In the upcoming guides, we will show you how to install docker containers with apps (SickRage, Sonarr, CouchPotato, Plex, etc.) to build your home server on docker engine. This will enable you to install and manage home server software efficiently. Sounds exciting? Go ahead follow this Docker windows tutorial, install Docker on Windows and get ready for the ride.
Did this post help you?
SmartHomeBeginner brings in-depth tutorials easy enough to understand even for beginners. This takes a considerable amount of work. If this post helps you, please consider supporting us as a token of appreciation:
- Feeling generous? Become a Sponsor (discounted options) or a Patron. You will receive privileges on our Discord Server.
- Just want to thank us? Buy us a Coffee or a Ko-Fi.
- May be another day? Shop on Amazon using our links. Your prices won’t change but we get a small commission.
- Don’t feel like spending? You can still show your support by sharing this post, linking to it in forums, or even commenting below.
Anand is a self-learned computer enthusiast, hopeless tinkerer (if it ain’t broke, fix it), a part-time blogger, and a Scientist during the day. He has been blogging since 2010 on Linux, Ubuntu, Home/Media/File Servers, Smart Home Automation, and related HOW-TOs.
8 November, 2022
1,600 words, 8-minute read
Docker can be installed on Linux, mac OS, or Windows.
Requirements and installation instructions can be found on the Docker Docs help pages.
Install Docker on Linux #
Docker Desktop for Linux can be downloaded from Docker Hub. The installer includes the Docker server, CLI, Docker Compose, Docker Swarm, and Kubernetes.
Alternatively, the Docker command-line tool is available in official Linux repositories although these are often older editions. The latest edition is supported on recent 64-bit editions of popular Linux distros:
- Ubuntu (and derivatives such as Mint)
- CentOS
- Debian
- Fedora
Static binaries are available for other distros, although Googling “install Docker on [your OS]” may provide easier instructions, e.g. “install Docker on a Raspberry Pi”.
Follow the Docker documentation for your distro. For example, Docker for Ubuntu is installed with the following commands:
sudo apt-get remove docker docker-engine docker.io containerd runc
sudo apt-get update
sudo apt-get install ca-certificates curl gnupg lsb-release
sudo mkdir -p /etc/apt/keyrings
curl -fsSL https://download.docker.com/linux/ubuntu/gpg | sudo gpg --dearmor -o /etc/apt/keyrings/docker.gpg
echo "deb [arch=$(dpkg --print-architecture) signed-by=/etc/apt/keyrings/docker.gpg] https://download.docker.com/linux/ubuntu $(lsb_release -cs) stable" | sudo tee /etc/apt/sources.list.d/docker.list > /dev/null
sudo apt-get update
sudo apt-get install docker-ce docker-ce-cli containerd.io docker-compose-pluginTo run Docker commands as a non-root user (without sudo), create and add yourself to a docker group:
sudo groupadd docker
sudo usermod -aG docker $USERThen reboot to apply all changes.
Install Docker on macOS #
Docker Desktop for macOS Sierra 10.13 and above can be downloaded from Docker Hub. The package includes the Docker server, CLI, Docker Compose, Docker Swarm, and Kubernetes.
Two editions are available: stable and edge with experimental features. The stable version is best for most developers.
Double-click Docker.dmg to open the installer, then drag the Docker icon to the Applications folder. Double-click Docker.app in that folder to launch Docker.
After completion, the whale icon in the status bar indicates Docker is running and commands can be entered in the terminal.
Install Docker on Windows #
Docker Desktop for Windows requires either WSL2 or Hyper-V.
Windows Subsystem for Linux (WSL) 2 #
WSL allows you to run full Linux environments directly on Windows 10 or Windows 11.
IMPORTANT!
You can not install the Linux edition of Docker within a WSL-powered Linux distro. You must install Docker Desktop for Windows which allows Docker commands to be run in all Windows and Linux terminals.
WSL2 is the recommended default option for Docker on Windows. It is faster than Hyper-V and available in all editions of Windows 11 and Windows 10 from the May 2020 update (version 2004, OS build 19041).
To install WSL2:
-
Enable hardware virtualization support in your BIOS.
This will be active on most devices, but check by rebooting and accessing your PC’s BIOS panels – typically by hitting DEL, F2, or F10 as your system starts. Look for Virtualization Technology, VTx or similar options. Ensure they are enabled, save, and reboot.
WARNING! Be careful when changing BIOS settings – one wrong move could trash your PC.
-
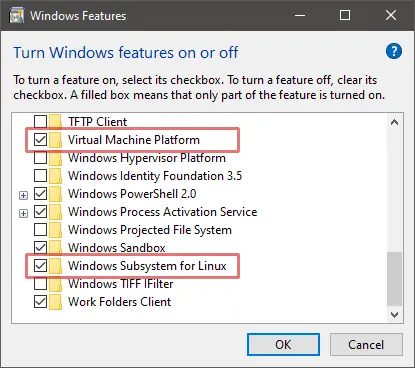
Enable the Virtual Machine Platform and Windows Subsystem for Linux options in the Turn Windows features on or off panel:
This can be accessed by hitting the Start button and typing the panel name or from Programs and Features in the classic Control Panel.
-
Reboot, then enter the following command in a Windows Powershell or
cmdprompt to set WSL2 as the default:wsl --set-default-version 2 -
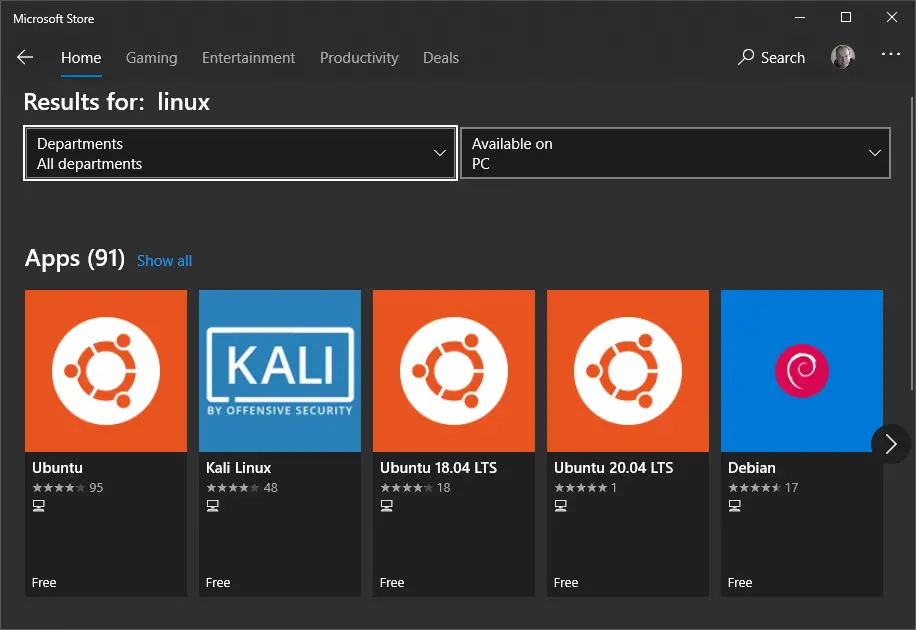
Download and install your preferred distro by searching for “Linux” in the Microsoft Store app. Ubuntu is a good choice.
-
To complete the installation, launch your distro by clicking its Store’s Launch button or choosing its icon from the Start menu.
You may be prompted to install a kernel update – follow the instructions and launch the distro again.
-
Enter a Linux username and password. These are separate from your Windows credentials although choosing the same ones can be practical.
-
Ensure your distro is up-to-date. For example, on an Ubuntu bash prompt enter:
sudo apt update && sudo apt upgrade
You can now install Docker Desktop (see below). For the best performance and stability, store development files in your Linux file system and run Docker from your Linux terminal.
More information about installing and using WSL2:
- Windows Subsystem for Linux 2: The Complete Guide, and
- optionally, Windows Terminal: The Complete Guide.
Hyper-V #
The Microsoft Hyper-V hypervisor is provided free with Windows 10 and 11 Professional and Enterprise. (Windows Home users must use WSL2.)
To install Hyper-V:
-
Enable hardware virtualization support in your BIOS.
This will be active on most devices, but check by rebooting and accessing your PC’s BIOS panels – typically by hitting DEL, F2, or F10 as your system starts. Look for Virtualization Technology, VTx or similar options. Ensure they are enabled, save, and reboot.
WARNING! Be careful when changing BIOS settings – one wrong move could trash your PC.
-
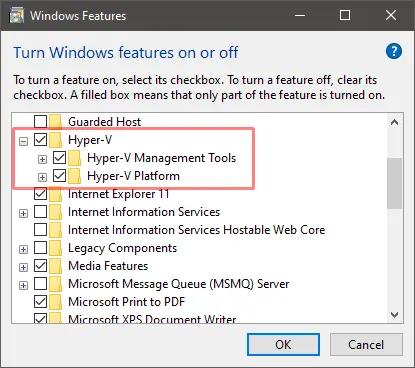
Enable the Hyper-V option in the Turn Windows features on or off panel then reboot.
This can be accessed by hitting the Start button and typing the panel name or from Programs and Features in the classic Control Panel.
You can now install Docker Desktop.
Install Docker Desktop for Windows #
Docker Desktop for Windows 10 and 11 can be downloaded from Docker Hub. The installer includes the Docker server, CLI, Docker Compose, Docker Swarm, and Kubernetes.
Two editions are available: stable and edge with experimental features. The stable version is best for most developers.
Double-click Docker Desktop Installer.exe to start the installation process. After completion and launch, the whale icon in the notification area of the task bar indicates Docker is running and ready to accept commands in the Windows Powershell/cmd terminal (and Linux if using WSL2).
Docker Engine Settings #
Docker uses WSL2 as the default engine when available. You will be prompted to confirm this choice during installation and after WSL2 is installed.
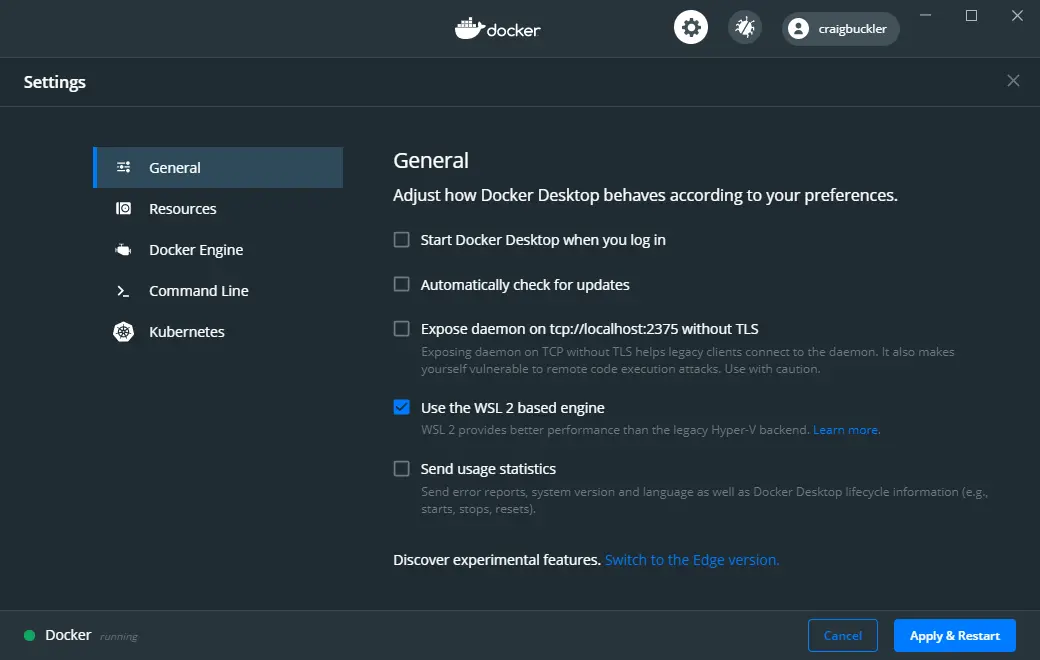
Alternatively, WSL2 can be enabled by checking Use the WSL 2 based engine in the General tab of Settings accessed from the Docker task bar icon. Unchecking the option reverts to Hyper-V.
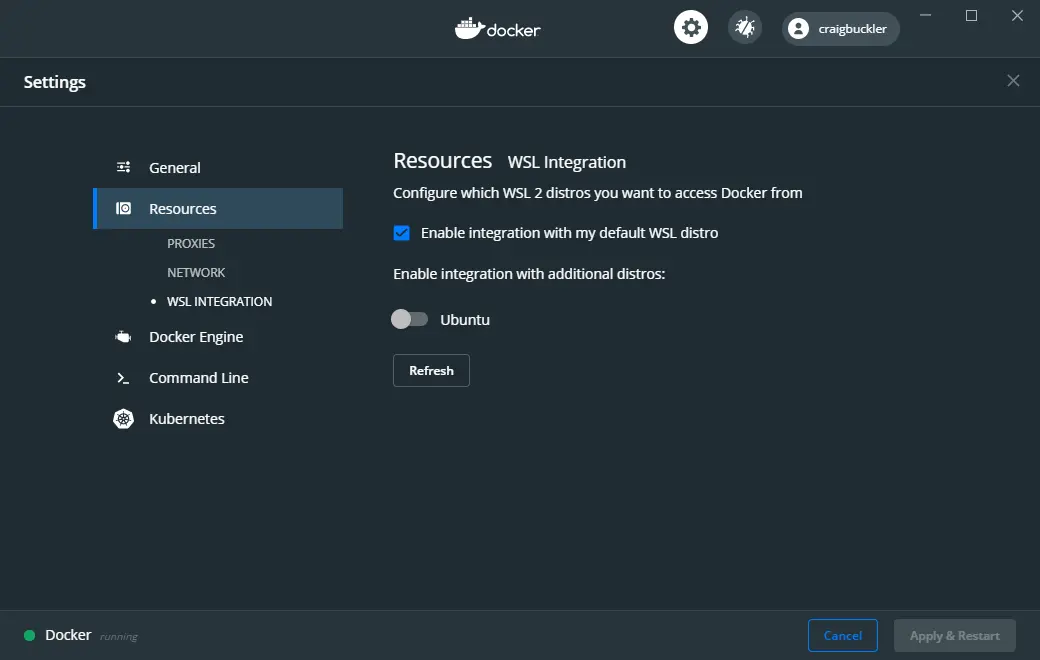
When using WSL2, at least one Linux distro must be enabled – the default is chosen. You can also permit Docker commands in other distros by accessing the WSL integration panel in the Resources section of the Docker Settings:
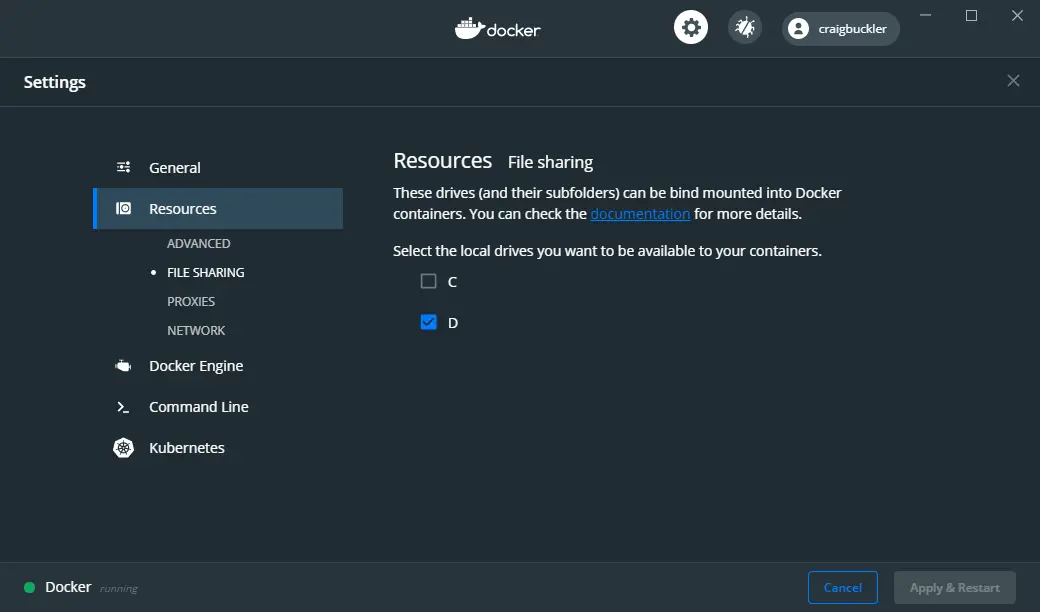
When using Hyper-V, Docker must be granted access to the Windows file system. Select the drives it is permitted to use by accessing the File Sharing panel in the Resources section of the Docker Settings:
(This option was named Shared Drives in previous editions of Docker Desktop.)
Test your Docker installation #
Check Docker has successfully installed by entering the following command in your terminal:
docker versionA response similar to the following is displayed:
Client: Docker Engine - Community
Version: 19.03.12
API version: 1.40
Go version: go1.13.10
Git commit: abcdef0
Built: Mon Jun 22 15:45:36 2020
OS/Arch: linux/amd64
Experimental: false
Server: Docker Engine - Community
Engine:
Version: 19.03.12
API version: 1.40 (minimum version 1.12)
...etc...Ensure Docker Compose is working by entering:
docker-compose versionTo receive something like:
docker-compose version 1.27.2, build 8d51620a
docker-py version: 4.3.1
CPython version: 3.7.7
OpenSSL version: OpenSSL 1.1.1c 10 Sep 2019Optionally, try entering:
docker run hello-worldto verify Docker can pull an image from Docker Hub and start containers as expected…
Unable to find image 'hello-world:latest' locally
latest: Pulling from library/hello-world
1b930d010525: Pull complete
Digest: sha256:f9dfddf63636d84ef479d645ab5885156ae030f611a56f3a7ac
Status: Downloaded newer image for hello-world:latest
Hello from Docker!
This message shows your installation appears to be working correctly.Key points #
What you’ve learned in this chapter:
- How to install and configure Docker on your Linux, macOS, or Windows system.
- How to install Docker Compose.
- How to test the Docker installation.
The following chapters demonstrate how to use Docker during development…
…but to continue reading, you need to buy the book.
Do you want an easy-to-follow course which demonstrates how to use Docker and create practical web development environments on your Windows, macOS, or Linux PC?
Buy the «Docker for Web Developers» book & video course…
-
full course
$99 $50 £43 / €49
buy all
-
ebooks only
$30 $15 £13 / €15
buy books
-
videos only
$80 $40 £34 / €40
buy videos
plus your country’s sales tax where applicable

 {:width=»300px»}
{:width=»300px»} {: .inline}) displays the Docker Subscription Service Agreement window.
{: .inline}) displays the Docker Subscription Service Agreement window.








 do not include a hypervisor such as Hyper-V. Therefore, Docker must be installed using Docker Toolbox. In this setup, Docker installs VirtualBox and use it as the Hypervisor.
do not include a hypervisor such as Hyper-V. Therefore, Docker must be installed using Docker Toolbox. In this setup, Docker installs VirtualBox and use it as the Hypervisor.