Эта статья даст вам полное представление о Docker Desktop для пользователей Windows и MAC. Мы изучим установку Docker Desktop на компьютерах с Windows и Mac. После установки мы также попытаемся выполнить некоторые операции Docker.
Docker Desktop — это собственное настольное приложение, разработанное Docker для пользователей Windows и MAC. Это самый простой способ запуска, сборки, отладки и тестирования приложений Dockerized.
Docker Desktop предлагает важные и наиболее полезные функции, такие как быстрые циклы редактирования, уведомления об изменениях файлов, встроенная поддержка корпоративной сети и гибкость для работы с собственным выбором прокси и VPN.
Docker Desktop состоит из инструментов для разработчика, приложения Docker, Kubernetes и синхронизации версий. Он позволяет вам создавать сертифицированные образы и шаблоны языков и инструментов.
Скорость, безопасность и выбор — все, что вам нужно для разработки и доставки контейнерных приложений, доступных на вашем рабочем столе, будет представлено вам.
Прежде чем перейти к процессу установки, давайте разберемся с его версиями.
Версии Docker
Docker в основном поставляется в двух версиях, в Community и ENterprise.
Community версия поставляется с бесплатным набором продуктов Docker. ENterprise корпоративная версия представляет собой сертифицированную контейнерную платформу, которая предоставляет коммерческим пользователям дополнительные функции, такие как безопасность образов, управление образами, оркестровка и управление средой выполнения контейнеров, но по разумной цене.
Мы начнем наше обучение с Community Edition. Контейнеры Docker, работающие в конкретной операционной системе, совместно используют ядро ОС. Это означает, что мы не можем использовать ядро Windows (хост) для запуска контейнеров Linux или наоборот. Чтобы проделать это, у нас есть Docker Desktop для Windows и MAC.
Выпуски Docker Desktop
Docker Desktop выпускается в двух вариантах.
- Stable: как видно из названия, стабильный выпуск тщательно протестирован и может быть использован при разработке более надежных приложений. Его версии полностью синхронизированы с версиями Docker Engine.
- Edge: эти версии состоят из всех новых и экспериментальных функций Docker Engine. Есть больше шансов ошибок, сбоев и проблем, которые могут возникнуть. Тем не менее, пользователи получат возможность ознакомиться с предстоящими функциями.
Docker на Windows
Есть два варианта Docker на Windows.
1. Использование Docker Toolbox
Docker Toolbox предоставляет набор легких инструментов.
- Oracle virtual box
- Docker Engine
- Docker Machine
- Docker compose
- Kitematic GUI
Вышеуказанные инструменты устраняют необходимость развертывания отдельной виртуальной машины для запуска Docker. Просто установите исполняемый файл панели инструментов Docker непосредственно в Windows и начните разработку приложений. Требуется 64-битная ОС и Windows 7 или выше с включенным режимом виртуализации.
Но опять же, панель инструментов Docker — это оригинальная поддержка, предоставляемая в Windows для запуска Docker и его устаревшего решения для всех ОС Windows, которые не соответствуют требуемой конфигурации.
2. Использование Docker Desktop
Docker Desktop — это новейшая технология, используемая для Docker в Windows. Он заменяет виртуальную машину Oracle собственной технологией виртуализации, доступной в Windows, то есть Microsoft Hyper-V.
Он по-прежнему будет запускать Docker на Linux-машине, созданной под ним. Но на этот раз вместо виртуальной машины Oracle мы использовали нативный Microsoft Hyper-V.
Установка Docker на Windows
Вы можете скачать репозиторий Docker Desktop из Docker Hub.
истемные требования:
- Windows 10 или Windows Server 2016 Professional или Enterprise Edition
- Поддержка Hyper-V.
Чтобы запустить Hyper-V, оборудование должно соответствовать следующим требованиям:
- 64-битный процессор
- > = 4 ГБ ОЗУ
- Поддержка виртуализации оборудования на уровне BIOS
Следовательно, программная и аппаратная зависимость заключается в запуске Docker Desktop на Windows.
Установка Docker на macOS
Вы можете скачать репозиторий Docker Desktop из Docker Hub.
Системные требования:
- MAC Hardware 2010 или новее с аппаратной поддержкой управления памятью и неограниченным режимом. Выполните команду kern.hv_support, чтобы проверить, поддерживает ли оборудование MAC инфраструктуру гипервизора.
- MAC OS версии 10.13 или новее.
- > = 4 ГБ ОЗУ
- Virtual-Box до версии 4.3.30
Работа с образами
После установки проверьте версию установленного Docker Engine.
docker --versionDocker работает с доставкой и запуском контейнерных приложений. Вам либо нужно создать свое собственное контейнерное приложение, либо Docker поддерживает контейнерные образы в Docker Hub, и его можно легко загрузить с помощью простой команды docker run.
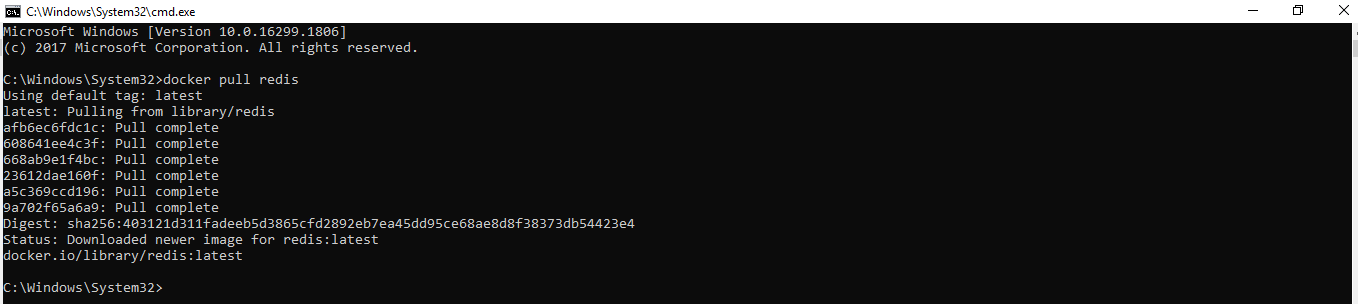
Здесь мы будем тянуть образ Redis.
docker pull redisС помощью простой команды run образы можно скачивать и загружать на GitHub или Docker Hub, и любой пользователь во всем мире может получить к нему доступ и начать работать с ним.
Docker Container запускает образ Docker. Следующим шагом является запуск контейнера.
docker run -p 6379 RedisБудет создан зашифрованный идентификатор контейнера. Вы можете быстро проверить состояние работающего экземпляра в Docker, нажав на Dashboard option.
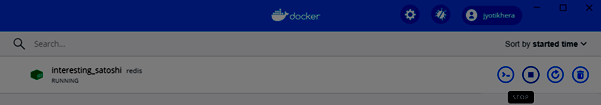
Обязательно остановите контейнер, прежде чем удалять его из Docker Engine.
Возможности Docker Desktop
Существует множество преимуществ:
- Поддерживает широкий спектр инструментов разработки.
- Обеспечьте быстрый и оптимизированный способ создания и публикации контейнерного образа на любой облачной платформе.
- Простота установки и настройки полной среды Docker
- Повышение производительности благодаря встроенной виртуализации Hyper-V для Windows и HyperKit для MAC.
- Возможность работать в Linux через WSL 2 на компьютерах с Windows.
- Легкий доступ к работающим контейнерам в локальной сети.
- Возможность поделиться любым приложением на облачной платформе, на разных языках и в разных средах.
- Для обеспечения безопасности и актуальности выполняются автоматические обновления.
- Включены последние версии Kubernetes.
- Возможность переключения между Linux и Windows сервером на Windows.
Docker Desktop — это нативное приложение, разработанное на Windows и MAC OS для запуска, сборки и доставки контейнерных приложений или сервисов.
Однако
Docker Desktop предназначен не для производственной среды, а для рабочего стола и среды разработки.
Также рекомендуем прочитать:
- Docker для начинающих — технология контейнеров
- В чем разница между Docker и Kubernetes?
- Введение в Docker Hub и все, что вы должны знать о нем
- Как установить Docker на Ubuntu, Windows, Debian и CentOS?
- Kubernetes — Введение для начинающих
- Docker посмотреть запущенные контейнеры, запустить или остановить контейнеры
| description | keywords | title | redirect_from | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
How to install Docker Desktop for Windows |
windows, install, download, run, docker, local, Docker Desktop |
Install on Windows |
|
Docker Desktop terms
Commercial use of Docker Desktop in larger enterprises (more than 250
employees OR more than $10 million USD in annual revenue) requires a paid
subscription.
Welcome to Docker Desktop for Windows. This page contains information about Docker Desktop for Windows system requirements, download URL, instructions to install and update Docker Desktop for Windows.
Download Docker Desktop for Windows
Docker Desktop for Windows{: .button .primary-btn }
For checksums, see Release notes
System requirements
Your Windows machine must meet the following requirements to successfully install Docker Desktop.
- WSL 2 backend
- Hyper-V backend and Windows containers
WSL 2 backend
-
Windows 11 64-bit: Home or Pro version 21H2 or higher, or Enterprise or Education version 21H2 or higher.
-
Windows 10 64-bit: Home or Pro 21H1 (build 19043) or higher, or Enterprise or Education 20H2 (build 19042) or higher.
-
Enable the WSL 2 feature on Windows. For detailed instructions, refer to the
Microsoft documentation{: target=»blank» rel=»noopener» class=»«}. -
The following hardware prerequisites are required to successfully run
WSL 2 on Windows 10 or Windows 11:- 64-bit processor with Second Level Address Translation (SLAT){: target=»blank» rel=»noopener» class=»«}
- 4GB system RAM
- BIOS-level hardware virtualization support must be enabled in the
BIOS settings. For more information, see
Virtualization.
-
Download and install the Linux kernel update package{: target=»blank» rel=»noopener» class=»«}.
Hyper-V backend and Windows containers
-
Windows 11 64-bit: Pro version 21H2 or higher, or Enterprise or Education version 21H2 or higher.
-
Windows 10 64-bit: Pro 21H1 (build 19043) or higher, or Enterprise or Education 20H2 (build 19042) or higher.
For Windows 10 and Windows 11 Home, see the system requirements in the WSL 2 backend{: data-toggle=»tab» data-target=»#win-wsl2″ } tab.
-
Hyper-V and Containers Windows features must be enabled.
-
The following hardware prerequisites are required to successfully run Client
Hyper-V on Windows 10:- 64 bit processor with Second Level Address Translation (SLAT){: target=»blank» rel=»noopener» class=»«}
- 4GB system RAM
- BIOS-level hardware virtualization support must be enabled in the
BIOS settings. For more information, see
Virtualization.
Note
Docker only supports Docker Desktop on Windows for those versions of Windows 10 that are still within Microsoft’s servicing timeline{:target=»blank» rel=»noopener» class=»«}.
Containers and images created with Docker Desktop are shared between all
user accounts on machines where it is installed. This is because all Windows
accounts use the same VM to build and run containers. Note that it is not possible to share containers and images between user accounts when using the Docker Desktop WSL 2 backend.
Running Docker Desktop inside a VMware ESXi or Azure VM is supported for Docker Business customers.
It requires enabling nested virtualization on the hypervisor first.
For more information, see Running Docker Desktop in a VM or VDI environment.
About Windows containers
Looking for information on using Windows containers?
- Switch between Windows and Linux containers
describes how you can toggle between Linux and Windows containers in Docker Desktop and points you to the tutorial mentioned above.
- Getting Started with Windows Containers (Lab)
provides a tutorial on how to set up and run Windows containers on Windows 10, Windows Server 2016 and Windows Server 2019. It shows you how to use a MusicStore application
with Windows containers. - Docker Container Platform for Windows articles and blog
posts{:target=»blank» rel=»noopener» class=»«} on the Docker website.
Note
To run Windows containers, you need Windows 10 or Windows 11 Professional or Enterprise edition.
Windows Home or Education editions will only allow you to run Linux containers.
Install Docker Desktop on Windows
Install interactively
-
Double-click Docker Desktop Installer.exe to run the installer.
If you haven’t already downloaded the installer (
Docker Desktop Installer.exe), you can get it from
Docker Hub{:target=»blank» rel=»noopener» class=»«}.
It typically downloads to yourDownloadsfolder, or you can run it from
the recent downloads bar at the bottom of your web browser. -
When prompted, ensure the Use WSL 2 instead of Hyper-V option on the Configuration page is selected or not depending on your choice of backend.
If your system only supports one of the two options, you will not be able to select which backend to use.
-
Follow the instructions on the installation wizard to authorize the installer and proceed with the install.
-
When the installation is successful, click Close to complete the installation process.
-
If your admin account is different to your user account, you must add the user to the docker-users group. Run Computer Management as an administrator and navigate to Local Users and Groups > Groups > docker-users. Right-click to add the user to the group.
Log out and log back in for the changes to take effect.
Install from the command line
After downloading Docker Desktop Installer.exe, run the following command in a terminal to install Docker Desktop:
$ "Docker Desktop Installer.exe" install
If you’re using PowerShell you should run it as:
Start-Process 'Docker Desktop Installer.exe' -Wait install
If using the Windows Command Prompt:
start /w "" "Docker Desktop Installer.exe" install
The install command accepts the following flags:
--quiet: suppresses information output when running the installer--accept-license: accepts the Docker Subscription Service Agreement{: target=»blank» rel=»noopener» class=»«} now, rather than requiring it to be accepted when the application is first run--no-windows-containers: disables Windows containers integration--allowed-org=<org name>: requires the user to sign in and be part of the specified Docker Hub organization when running the application--backend=<backend name>: selects the default backend to use for Docker Desktop,hyper-v,windowsorwsl-2(default)--installation-dir=<path>: changes the default installation location (C:Program FilesDockerDocker)--admin-settings: Automatically creates anadmin-settings.jsonfile which is used by admins to control certain Docker Desktop settings on client machines within their organization. For more information, see Settings Management.- It must be used together with the
--allowed-org=<org name>flag. - For example:
--allowed-org=<org name> --admin-settings='{"configurationFileVersion": 2, "enhancedContainerIsolation": {"value": true, "locked": false}}'
- It must be used together with the
If your admin account is different to your user account, you must add the user to the docker-users group:
$ net localgroup docker-users <user> /add
Start Docker Desktop
Docker Desktop does not start automatically after installation. To start Docker Desktop:
-
Search for Docker, and select Docker Desktop in the search results.
{:width=»300px»}
-
The Docker menu (
{: .inline}) displays the Docker Subscription Service Agreement window.
{% include desktop-license-update.md %}
-
Select Accept to continue. Docker Desktop starts after you accept the terms.
Important
If you do not agree to the terms, the Docker Desktop application will close and you can no longer run Docker Desktop on your machine. You can choose to accept the terms at a later date by opening Docker Desktop.
{: .important}For more information, see Docker Desktop Subscription Service Agreement{:target=»blank» rel=»noopener» class=»«}. We recommend that you also read the FAQs{: target=»_blank» rel=»noopener» class=»*» id=»dkr_docs_desktop_install_btl»}.
Where to go next
- Get started with Docker is a tutorial that teaches you how to deploy a multi-service stack.
- Troubleshooting describes common problems, workarounds, and
how to get support. - FAQs provide answers to frequently asked questions.
- Release notes lists component updates, new features, and improvements associated with Docker Desktop releases.
- Back up and restore data provides instructions on backing up and restoring data related to Docker.
If you’re new to containers and Docker and work primarily on Windows, you’re in for a treat. In this article, you’re going to learn how to set up Docker on Windows 10 using Docker Desktop for Windows or simply referred to as Docker Desktop in this article.
Not a reader? Watch this related video tutorial!
Not seeing the video? Make sure your ad blocker is disabled.
Docker Desktop is the Docker Engine and a management client packaged together for easy use in Windows 10. In this article, you will install Docker Desktop, deploy your first container, and share data between your host and your containers.
Prerequisites for Docker on Windows
This is a walkthrough article demonstrating various steps in Docker Desktop for Docker on Windows. To follow along, be sure you have a few specific requirements in place first.
- An Internet connection to download 800MB+ of data
- Windows 10 64-bit running Pro, Enterprise, or Education edition with release 1703 or newer. This is necessary to run Hyper-V on Windows 10.
- A CPU with SLAT (nested paging) compatibility. All AMD/Intel processors since approximately 2008 are SLAT compatible
- At least 4GB of RAM
- BIOS hardware virtualization sometimes labeled as Virtualization Technology or VTx. This must be enabled and show as Enabled in the performance tab of Task Manager as shown below.

Downloading and Installing Docker Desktop
Up first, you need to download and install Docker Desktop to get Docker on Windows going. Docker Desktop comes available in two releases; a stable release and a testing release.
The stable release is released quarterly and ensures a fully-tested application. In this article, you will be using the stable release.
Warning: Upon installation, Docker Desktop will prompt you to install the Hyper-V hypervisor if not already installed. By doing so, the Hyper-V hypervisor prevents any user-mode hypervisors such as VirtualBox, VMWare, etc. from running guest VMs. Hyper-V support for VirtualBox and VMWare is limited but coming.
You also have the option of a download source through manually downloading Docker Desktop directly from Docker.com or via the Windows package manager, Chocolatey. Let’s briefly cover each method.
From Docker.com
To download Docker Desktop directly from docker.com, you can go to the product page, register for an account and download it from there. This is preferred if you intend to use Docker in production by registering an account.
However, if you’re just testing Docker out for the first time, you can also download it directly which is much easier.
Once the EXE is downloaded, run the executable and click through the prompts accepting all of the defaults.
When asked whether you plan to Use Windows containers instead of Linux containers, as shown below, do not enable the checkbox. You will be using Linux containers in this article.

Once installation is complete, reboot your computer.
Selecting the option to use Windows containers or Linux containers tells Docker to attach images to a Windows kernel or Linux kernel. You can change this setting at any time after installation by right-clicking the Docker icon in the System Tray and selecting Switch to Windows containers as shown below.

Using Chocolatey
The other option to get Docker Desktop downloaded and installed is with Chocolatey. Chocolatey automates many of the download/install tasks for you. To do so, open up a command-line console (either cmd or PowerShell) as an administrator to download and install the program in one shot by running the command below.
choco install docker-desktopOnce complete, reboot Windows 10.
If you’d like to try out the testing release at some point, you can download and install this by running
choco install docker-desktop --pre.
Validating the Docker Desktop Installation
Once installed, Docker Desktop automatically runs as a service providing Docker on Windows. It’s shown in the system tray when you log in to Windows after you reboot. But how do you actually know it’s working?
To validate Docker Desktop is working correctly, open a command-line console and run the docker command. If the installation went well, you will see a Docker command reference.
Finally, have Docker download and run an example container image called hello-world by running the command docker run hello-world. If all is well, you will see output like below.

Running Commands in Docker Containers
Docker Desktop is installed and you’ve verified all is well? Now what? To get started with Docker on Windows, one common task to perform in a Docker container is running commands. Through the docker run command, you can send commands through the host (your Windows 10 PC) directly into a running container.
To run commands in a container with docker run, you’ll first specify an image name followed by the command. To get started, tell Docker to run the command hostname inside of a container called alpine as seen below.
> docker run alpine hostname
b74ff46601afSince you don’t have the alpine Docker image on your computer now, Docker on Windows will download the tiny image from the Docker Hub, bring up a container from that image, and send the command directly into the container and shut it down all in one swoop.
If you’d like to keep the container running, you can also use the -it parameter. This parameter tells Docker to keep the container in “interactive mode” leaving it running in the foreground after executing the command. You’ll see that you are then presented with a terminal prompt ready to go.
> docker run -it alpine sh
/ #When you’re done in the terminal, type exit to return to Windows 10.
Accessing Files from the Docker Host in Containers
Another common task is accessing host files from containers. To access host files in containers, Docker on Windows allows you to link a folder path from your desktop to share that folder to your container. This process is called binding.
To create a binding, make a folder on a local drive. For this example, I’ll use E: and call it input. It’ll then create a new text document named file.txt in the folder. Feel free to use whatever path and file you wish.
Once you have the folder you’d like to share between the host and container, Docker needs to mount the folder using the --mount parameter. The --mount parameter requires three arguments; a mount type, a source host directory path and a target directory path. The target path will be a symbolic link within the container.
Below you will see an example of mounting the entire E: within the Windows 10 host to show up as the /home/TEST directory inside of the Linux container.
> docker run --mount type=bind,source="E:/",target=/home/TEST -it alpineWhen you attempt to mount a host folder, Docker Desktop will ask for your permission to share this drive with the Docker containers as seen below.

If you created the file.txt file in the Windows 10 folder as described earlier, run cat /home/TEST/input/file.txt. You will see that contents are displayed.
Now, delete the input folder that you just created and run the cat ... command again. Observe that the shell now reports that the file does not exist anymore.

Mapping Network Ports
Another important concept to know is how Docker on Windows handles networking. For a brief introduction, let’s see what it takes to access a web service running in a container from the local host.
First, spin up a demo image that will run an example webpage. Download and run the Docker image called dockersamples/static-site. You’ll use docker container run to do so.
The following command does four actions at once:
- Downloads a Docker image from Docker Hub called static-site in the docker-samples “directory”
- Starts a container instance up from the static-site image
- Immediately detaches the container from the terminal foreground (
—detach) - Makes the running container’s network ports accessible to the Windows 10 host (
—publish-all)
docker container run --detach --publish-all dockersamples/static-site
## Alternate/shorthand syntax that does the same thing:
## docker container run -d -P dockersamples/static-site
## docker run -d -P dockersamples/static-siteOnce run, Docker will return the container ID that was brought up as shown below.
Publishing Network Ports
Since using the --publish-all parameter, local host ports are now mapped to the container’s network stack. You can use the docker ps subcommand to list all running containers including what ports are assigned to all of the running containers. In the instance below, one container is running mapping host port 32777 to container port 80 and host port 32776 to container port 443.
Docker on Windows assigns containers random ports when using the --publish-all parameter unless explicitly define them.
Now open up a web browser and navigate to http://localhost:32777 or the port that Docker assigned to map to port 80 as output by docker ps. If all goes well, you should see the below webpage show up.

Changing the Published Ports
You now have a Docker container running in Docker on Windows serving up a simple web page. Congratulations! But now you need to specify a specific port binding not relying on the random port selection with --publish-all. No problem. Use the -p parameter.
First, stop the running container by specifying a unique string of it’s container ID. You can find this container ID by running docker ps. Once you know the container ID, stop the container and start a new one while designating Docker to assign a specific port to publish.
The syntax for specifying a port is <external port>:<container port>. For each port that you want to publish, use the --publish or -p switch with the external and container port numbers as shown below.
> docker stop f766
> docker run --detach -p 1337:80 dockersamples/static-siteWhen you are specifying a container ID, you only have to type enough of the ID to be unique. If you are only running a single container and its ID is
f766f4ac8d66bf7, you can identify the container using any number of characters including justf. The requirement is that whatever you type allows it to uniquely identify a single container.
Now go to your web browser and navigate to localhost:1337. Remember, you are not changing the image and it always listens on port 80; you are changing the port translation rule in the Docker configuration that lets you connect to the container.

Stopping all Containers
Using docker stop, you can stop a container but how do you stop multiple containers at once? One way to do so is by providing multiple, space-delimited container IDs. You can see below an example of how to stop three containers with IDs of fd50b0a446e7, 36ee57c3b7da, and 7c45664906ff.
> docker stop fd50 36ee 7c45If you’re managing Docker containers in PowerShell, you can also use a shortcut to stop all containers. Feed a list of container IDs via
docker ps -qto the stop parameter through PowerShell’s command expansiondocker stop (docker ps -q).
Confirm all containers are stopped by seeing no containers listed when you type docker ps.
Cleaning Up
You’ve downloaded a few container images and run some containers that are now stopped. Even though they’re stopped, their allocated storage isn’t gone off of the local host disk. You must delete the containers free up that space and avoid cluttering up your workspace.
To delete a single container, use the container remove rm parameter like below.
> docker container rm <container ID>Or, to delete all stopped containers, use the prune parameter as below.
Рассмотрим установку Docker Desktop for Windows — это Community-версия Docker для систем Microsoft Windows.
Системные требования
- Windows 10 64-bit: Pro, Enterprise, Education (Build 16299 или выше).
Для успешного запуска Client Hyper-V в Windows 10 требуются следующие предварительные требования к оборудованию:
- 64 bit процессор c поддержкой Second Level Address Translation (SLAT).
- 4GB системной памяти.
- Поддержка аппаратной виртуализации на уровне BIOS должна быть включена в настройках BIOS.
Подготовка
Включаем функции Hyper-V Containers Window. Для этого переходим в панель управления — установка и удаление программ — включение или отключение компонентов Windows. Активируем пункт Hyper-V, который включает Hyper-V Managment Tools, Hyper-V Platform.
Также это можно выполнить через powershell или dism (все команды необходимо выполнять с правами администратора).
Powershell:
Enable-WindowsOptionalFeature -Online -FeatureName Microsoft-Hyper-V -All
DISM:
DISM /Online /Enable-Feature /All /FeatureName:Microsoft-Hyper-V
Установка
Скачиваем установщик Docker (Docker Desktop Installer) с Docker Hub.
Установка Docker Desktop включает Docker Engine, Docker CLI client, Docker Compose, Notary, Kubernetes и Credential Helper. Контейнеры и образы, созданные с помощью Docker Desktop, используются всеми учетными записями пользователей на компьютерах, на которых он установлен. Это связано с тем, что все учетные записи Windows используют одну и ту же виртуальную машину для создания и запуска контейнеров. При использовании Docker Desktop WSL 2 невозможно обмениваться контейнерами и образами между учетными записями пользователей.
Запускаем установщик Docker Desktop Installer.exe и ожидаем пока он скачает все необходимые компоненты.
После установки система потребует перезагрузки. Перезагружаемся и входим в систему.
После входа может возникнут запрос на установку дополнительного компонента WSL2. Переходим по ссылке и скачиваем необходимый пакет с официального сайта Microsoft.
После скачивания выполняем установку WSL2, после которой снова потребуется перезагрузка.
Настройка и запуск приложения
Входим в систему и ждем запуска всех служб Docker. Когда все службы будут запущены, мы увидим в трее классический значок Docker — это значит что служба установлена и запущена. Далее можно запустить приложение Docker desktop. Далее можно изменить настройки Docker при необходимости:

Рисунок 1 — Изменение параметров Docker desktop
Далее управление Docker выполняется через Powershell. Проверяем версию и выполняем тестовый запуск контейнера:

Рисунок 2 — Проверка версии Docker
После выполнения всех этих действий, Docker готов к использованию.
Нужна помощь? Настройки docker/docker swarm/docker compose мы осуществляем в рамках услуги DevOps-аутсорсинг.


 {:width=»300px»}
{:width=»300px»} {: .inline}) displays the Docker Subscription Service Agreement window.
{: .inline}) displays the Docker Subscription Service Agreement window.