- Remove From My Forums
-
Question
-
I have been setting up a Windows Server 2012 R2 with DHCP/DNS/AD, I have finally got a client PC (connected directly through ethernet) to connect to the domain and successfully log in with a custom user account.
However when I shutdown/restart the client PC I get a BSOD with the error above, I can replicate this error every time I do this.
I have updated the NICs on the server if that was the problem but it didn’t help.
Here is the link to the Minidump
Any help would be greatly appreciated
Answers
-
Hi,
Please understand, to solidly troubleshoot the crash issue, we generally need to debug the crash dump files. Unfortunately, debugging is beyond what we can do in the forum. Therefore, we can only provide some general suggestions here.
If the issue still occurs, a support call to our product service team is needed for the debugging service. We’d like to recommend that you contact Microsoft Customer Support Service (CSS) for assistance so that this problem can be resolved efficiently. To
obtain the phone numbers for specific technology request please take a look at the web site listed below:https://support.microsoft.com/en-us/gp/customer-service-phone-numbers
________________________________________
Best Regards,
Cartman
Please remember to mark the replies as answers if they help and
unmark them if they provide no help. If you have feedback for TechNet Support, contact tnmff@microsoft.com.-
Proposed as answer by
Wednesday, August 3, 2016 8:48 AM
-
Marked as answer by
Cartman ShenMicrosoft contingent staff
Friday, August 5, 2016 2:41 AM
-
Proposed as answer by
| title | description | keywords | ms.date | topic_type | api_name | api_type | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Bug Check 0xD1 DRIVER_IRQL_NOT_LESS_OR_EQUAL |
The DRIVER_IRQL_NOT_LESS_OR_EQUAL bug check has a value of 0x000000D1. This indicates that a kernel-mode driver attempted to access pageable memory at a process IRQL that was too high. |
|
03/14/2022 |
apiref |
DRIVER_IRQL_NOT_LESS_OR_EQUAL |
NA |
Bug Check 0xD1: DRIVER_IRQL_NOT_LESS_OR_EQUAL
The DRIVER_IRQL_NOT_LESS_OR_EQUAL bug check has a value of 0x000000D1. This indicates that a kernel-mode driver attempted to access pageable memory while the process IRQL that was too high.
[!IMPORTANT]
This topic is for programmers. If you are a customer who has received a blue screen error code while using your computer, see Troubleshoot blue screen errors.
DRIVER_IRQL_NOT_LESS_OR_EQUAL parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
|
1 |
Memory referenced. |
|
2 |
IRQL at time of reference. |
|
3 |
|
|
4 |
Address that referenced memory. Use ln (list nearest symbols) on this address to see the name of the function. |
Cause
To determine the cause requires the Windows debugger, programming experience and access to the source code for the faulting module.
Typically, when this error occurs, a driver has tried to access an address that is pageable (or that is completely invalid) while the interrupt request level (IRQL) was too high. This can be caused by:
-
Dereferencing a bad pointer (such as a NULL or freed pointer) while executing at or above DISPATCH_LEVEL.
-
Accessing pageable data at or above DISPATCH_LEVEL.
-
Executing pageable code at or above DISPATCH_LEVEL.
If a driver that is responsible for the error can be identified, its name is printed on the blue screen and stored in memory at the location (PUNICODE_STRING) KiBugCheckDriver. You can use dx (display debugger object model expression), a debugger command, to display this: dx KiBugCheckDriver.
This bug check is usually caused by drivers that have used improper memory addresses.
Possible causes for the page fault include the following events:
-
The function was marked as pageable and was running at an elevated IRQL (which includes obtaining a lock).
-
The function call was made to a function in another driver, and that driver was unloaded.
-
The function was called by using a function pointer that was an invalid pointer.
For more information on Windows IRQLs, see Windows Internals 7th Edition Part 1 by Pavel Yosifovich, Mark E. Russinovich, David A. Solomon and Alex Ionescu.
Resolution
If the problem is caused by the driver that you are developing, make sure that the function that was executing at the time of the bug check is:
- Not marked as pageable
- Does not call any other inline functions that could be paged out.
The !analyze debugger extension displays information about the bug check and can be helpful in determining the root cause. The following example is output from !analyze.
DRIVER_IRQL_NOT_LESS_OR_EQUAL (d1)
An attempt was made to access a pageable (or completely invalid) address at an
interrupt request level (IRQL) that is too high. This is usually
caused by drivers using improper addresses.
If kernel debugger is available get stack backtrace.
Arguments:
Arg1: fffff808add27150, memory referenced
Arg2: 0000000000000002, IRQL
Arg3: 0000000000000000, value 0 = read operation, 1 = write operation
Arg4: fffff808adc386a6, address which referenced memory
If a driver that is responsible for the error can be identified, its name is printed on the blue screen and stored in memory at the location (PUNICODE_STRING) KiBugCheckDriver. You can use dx (display debugger object model expression), a debugger command, to display this: dx KiBugCheckDriver.
0: kd> dx KiBugCheckDriver
KiBugCheckDriver : 0xffffc6092de892c8 : "Wdf01000.sys" [Type: _UNICODE_STRING *]
If a trap frame is available in the dump file, use the .trap command to set your context to the provided address.
To start debugging this type of bug check, examine the stack trace by using the k, kb, kc, kd, kp, kP, kv (display stack backtrace) commands.
In the debugger, run the !irql command to display information about the IRQL of a processor on the target computer before the debugger break. For example:
0: kd> !irql
Debugger saved IRQL for processor 0x0 -- 2 (DISPATCH_LEVEL)
In the majority of cases of this type of bug check, the issue is not the IRQL level, but rather the memory that is being accessed.
Because this bug check is usually caused by drivers that have used improper memory addresses, use parameters 1, 3, and 4 to investigate further.
Use ln (list nearest symbols) with parameter 4 to see the name of the function that was called. Also examine the !analyze output to see if faulting code is identified.
Use !pool on the parameter 1 address to see whether it is paged pool. Use !address and the advanced !pte command to learn more about this area of memory.
Use the display memory commands to examine the memory referenced in command in parameter 1.
Use the u, ub, uu (unassemble) commands to look at the code in the address which referenced the memory in parameter 4.
Use the command lm t n to list modules that are loaded in the memory. Use !memusage and to examine the general state of the system memory.
Driver Verifier
Driver Verifier is a tool that runs in real time to examine the behavior of drivers. For example, Driver Verifier checks the use of memory resources, such as memory pools. If it identifies errors in the execution of driver code, it proactively creates an exception to allow that part of the driver code to be further scrutinized. Driver Verifier Manager is built into Windows and is available on all Windows PCs.
To start Driver Verifier Manager, type verifier at a command prompt. You can configure which drivers to verify. The code that verifies drivers adds overhead as it runs, so try to verify the smallest number of drivers possible. For more information, see Driver Verifier.
Remarks
If you are not equipped to use the Windows debugger to work on this problem, you can use some basic troubleshooting techniques.
-
Check the System Log in Event Viewer for additional error messages that might help identify the device or driver that is causing this bug check.
-
If a driver is identified in the bug check message, disable the driver or check with the manufacturer for driver updates.
-
Confirm that any new hardware that is installed is compatible with the installed version of Windows. For example, you can get information about required hardware at Windows 10 Specifications.
For additional general troubleshooting information, see Blue screen data.
I’ve a Windows Server 2012 R2 server which acts as Hyper-V host for multiplice Windows/Linux VMs. Since yesterday the server is offline from one second to another, and will reboot automatically. I found out that this is caused by a bluescreen:
Yesterday this happens three times:
20:57:26
20:15:29
19:57:17
I did a research and find out that this can maybe an issue with an driver, especially the network adapter, and the Large send offload setting. I had it activated, so I disabled it. After that the server runns stable up to now (near 24 hours). Just now the server crashed again.
So it seems like an software issue, but I can’t find out what’s causing the problem. I haven’t install new software or driver in this month, which may be responsible for those problems. Only Windows Updates a few days ago.
All crashes seems the same issue because the bug check string, code and first parameter are the same. Also the driver is equal.
What can I do to find and fix the issue?
DRIVER IRQL NOT LESS OR EQUAL — распространенная проблема в операционных системах Windows 7, 10, 11. Стандартно она возникает в двух проявлениях: просто вылетает активное окно с ошибкой (реже) и синий экран (чаще). В подавляющем большинстве случаев возникновение проблемы вызывает команду STOP и система перезагружается.
DRIVER_IRQL_NOT_LESS_OR_EQUAL – что это?
В тексте сообщения DRIVER IRQL NOT LESS OR EQUAL скрыты некоторые сведения, которые понятны только системным администраторам. Чтобы понять, что это такое IRQL NOT LESS OR EQUAL, нам нужно расшифровать код. Условно мы можем поделить его на 3 части:
- DRIVER – проблема касается драйверов в системе. Это действительно так в большинстве случаев.
- IRQL – система прерывания запроса или алгоритм приоритизации. То есть сравнение приоритетов для драйверов.
- NOT_LESS_OR_EQUAL – «не меньше или равно». Это означает, что уровень приоритетов проблемного драйвера выше или равен другому процессу, который он пытается прервать. Здесь работает правило – чем ниже уровень, тем выше приоритет. То есть процесс 4 уровня более важен в сравнении с задачей 5 уровня.
Ищем причину ошибки DRIVER_IRQL_NOT_LESS_OR_EQUAL
Несмотря на то, что IRQL NOT LESS OR EQUAL указывает на проблемы драйверов, это далеко не всегда является первопричиной. Сбой драйверов может провоцировать и аппаратная платформа, а затем и саму ошибку.
Основные причины ошибки:
- eстаревший или битый драйвер, многие пользователи сталкиваются именно с этой неисправностью;
- конфликт драйверов после установки оборудования или некоторых программ;
- проблемы при разгоне частот оперативной памяти, видеокарты или процессора;
- поврежденные файлы системы;
- программная неполадка, связанная с некорректными утилитами;
- неисправные комплектующие: обычно HDD или ОЗУ.
Намного более точные результаты можем получить при условии, что проанализируем ошибку DRIVER_IRQL_NOT_LESS_OR_EQUAL с помощью журналов Windows. Если повезет, можем открыть «Просмотр журналов событий» в Windows 10 и посмотреть, на проблему в каком файле ссылается система. Затем останется узнать его причастность к программному обеспечению и исправить ошибку. Более надежный путь – анализ мини-дампов памяти, это делать непросто, но есть палочка-выручалочка – BlueScreenView. Она очень быстро покажет в каком именно файле (или цепочке файлов) проблема.
Способы исправления BSOD
К сожалению, как и большинство других «синих экранов смерти», DRIVER IRQL NOT LESS OR EQUAL в Windows 7, 10, 11 не имеет единственно верного решения. Причин много и способов исправления не меньше. Для компактности мы объединили некоторые исправления в логические блоки.
Работа с драйверами
Ошибка IRQL NOT LESS OR EQUAL может быть спровоцирована практически любым драйвером. Мы видели упоминания о проблемах с драйвером сетевой карты, жесткого диска, периферии, видеокарты. Очень поможет, если в результате исследования ошибки, по инструкции немного выше, будет сужен круг поиска. В остальных ситуациях придется перебирать методы в ручном порядке.
Что делать при ошибке DRIVER IRQL NOT LESS OR EQUAL в Windows 10:
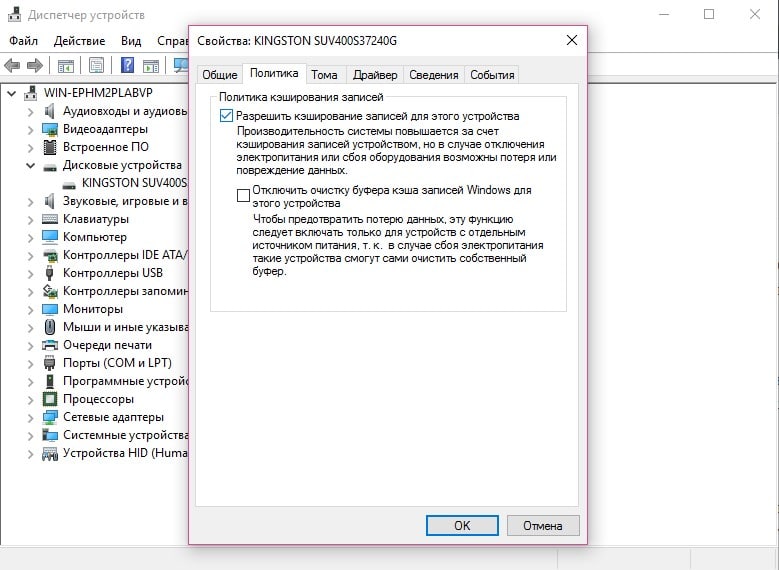
- Отключить кеширование накопителей. Следует открыть «Диспетчер устройств», развернуть список дисковых устройств и перейти в свойства диска. Затем на вкладке «Политика» стоит снять галочку с «Разрешить кэширование записей для этого устройства».
- Переустановить драйвера для сетевого адаптера. Следует попробовать удалить и установить повторно драйвер для Ethernet-карты, а также для Wi-Fi-модуля. Обычно его можем найти на сайте производителя ноутбука или самого оборудования.
- Установить новый драйвер для «Дисковых устройств». Известны случаи, когда BSOD появляется только при работе с SSD, а с HDD работает стабильно. Нужно понаблюдать за поведением системы и установить соответствующий драйвер.
- Отключить всю периферию и воспроизвести условия, в которых появляется синий экран. Если ничего в этот раз не будет, подключаем оборудование по одному, таким образом вычисляя виновника.
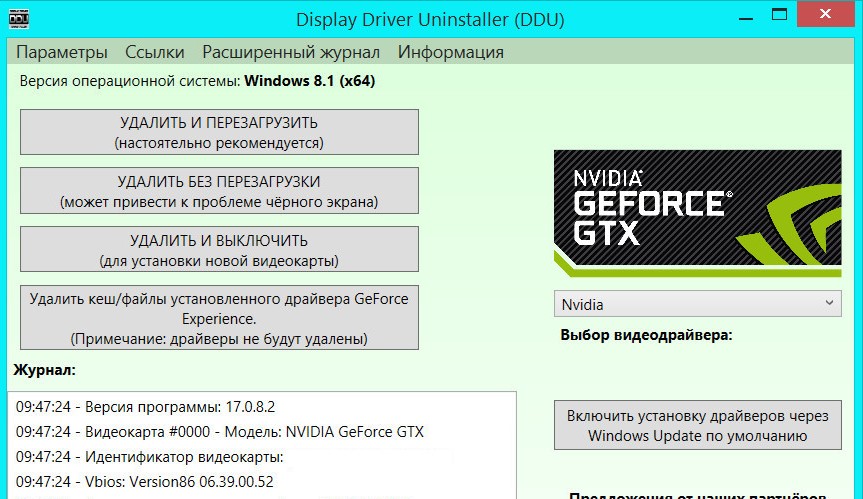
- Полностью удалить и установить новый драйвер Nvidia. Для этого рекомендуем использовать утилиту DDU, она подчищает все следы старого ПО. Загрузить новый драйвер можем с официального сайта.
Читайте также: Как обновить драйвера видеокарты?
Использовать диагностику памяти
Очень часто IRQL NOT LESS OR EQUAL становится следствием проблем с оперативной памятью. Сперва рекомендуем провести процедуру первичной диагностики самостоятельно: проверить качество фиксации планок (есть случаи, когда ошибка появлялась из-за того, что планка не застегнута до конца) и попробовать запустить ПК только с одним модулем памяти. Таким образом следует проверить каждую планку ОЗУ.
Следующий этап – просканировать оперативную память с помощью MemTest86. Программа умеет находить ошибки ОЗУ и исправлять некоторые из них.
Неполадка при разгоне
К сожалению, разгон тактовых частот оборудования – потенциально опасная технология, которая нарушает стабильность работы системы. Он может приводить и к BSOD DRIVER_IRQL_NOT_LESS_OR_EQUAL в Windows 10.
Что нужно сделать:
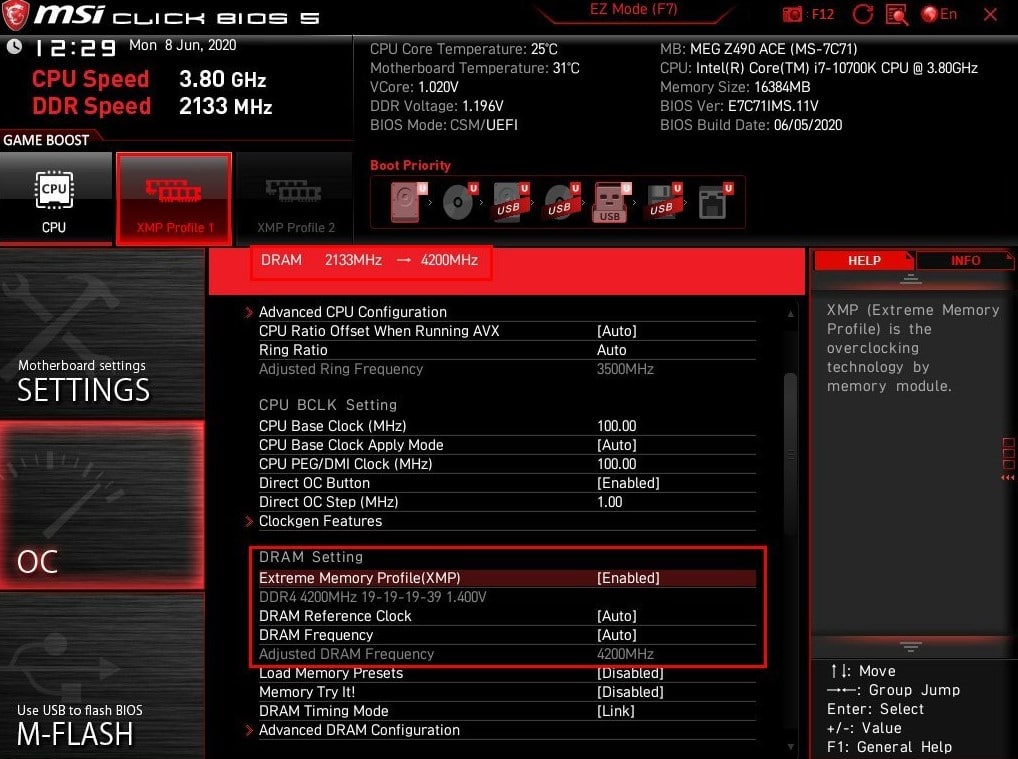
- Отключить XMP (Nvidia) или DOCP-профили (AMD) памяти. На форумах советуют отключить эту технологию, так как она может вызывать синий экран. По крайней мере для теста, это сделать следует. Нужно перейти в BIOS и в одном из разделов, может называть DRAM Settings или несколько иначе, найти Extreme Memory Profile (X.M.P). Остается только перевести его в положение Disable.
- Улучшить охлаждение. Таким образом мы исключим вероятность перегрева.
- Удалить ASUS AI Suite. Утилита нужна для контроля параметров работы системы и считывания значений с датчиков. Известны случаи, когда программа вызывает BSOD.
- Вернуть частоты компьютера к заводским настройкам. Никто не гарантирует, что оборудование будет работать стабильно на повышенных частотах. Да и разные комплектующие имеют свой предел. Если система некорректно функционирует, разумно вернуть ее к штатным параметрам.
Дополнительные решения
Также нам известна серия не совсем стандартных способов исправления ошибки DRIVER IRQL NOT LESS OR EQUAL, которые на не позволяет совесть утаить от вас, хотя они и выбиваются из общего ряда.
Как еще можно исправить ошибку DRIVER IRQL NOT LESS OR EQUAL:
- Удалить SoftEther VPN, Zone Alarm, HWiNFO. По неизвестным причинам, эти программы склонны вызывать данную ошибку. Следует их убрать с компьютера и проверить результат. Если проблема в них, можно найти аналог, например, вот список лучших бесплатных VPN для Windows 10.
- Восстановить системные файлы. В Windows существует специальная утилита для проверки целостности и работает в автоматическом режиме. Она не только поможет найти проблему, но и устранит её, если такая возможность есть. Просто нужно нажать Win + R, ввести cmd и кликнуть по кнопке Ок. Затем следует вставить sfc /scannow и дождаться окончания процедуры. После процедуры вы увидите отчет о том, найдены ли проблемы и удалось ли их устранить.
- Восстановить систему. В поиск нужно ввести «Восстановление системы», после выбрать нужную точку. Действие автоматическое, но от вас могут потребоваться некоторый выбор, просто следуйте инструкции.
Если у Вас остались вопросы по теме «Как исправить ошибку DRIVER IRQL NOT LESS OR EQUAL?», то можете задать их в комментариях

Андрей
Системный администратор
Задать вопрос
Отображается ошибка DRIVER IRQL NOT LESS OR EQUAL Windows 10, что делать?
Инструкция по Windows 7 остается актуальной и для «десятки». Если по шагам, что делать при ошибке DRIVER IRQL NOT LESS OR EQUAL Windows 10: обновляем драйвера для графической карты, чистим реестр любой удобной утилитой, к примеру, CCleaner и сканируем систему утилитой sfc /scannow. В случае безрезультатного выполнения процедур можем отключить антивирус, отключить всю второстепенную периферию и запустить диагностику оперативной памяти через BIOS. Если в безопасном режиме все работает, может помочь откат системы.
driver irql not less or equal Windows 8, как убрать?
Ошибка DRIVER IRQL NOT LESS OR EQUAL в Windows 8 обычно вызвана проблемами с драйверами. Рекомендуем проверить не только исправность графического драйвера, но и остальных. Чтобы быстро обновить все доступное ПО, лучше использовать утилиты вроде Driver Pack Solution. Если не помогает, стоит почистить реестр с помощью CCleaner и запустить сканирование системных файлов командой sfc /scannow. Ее можно вставить в консоль.
A Guide to the “IRQL Not Less Or Equal” Blue Screen of Death Error

This error means you’re having a driver or service issue.
This article is part of a continuing series on Blue Screen of Death errors. A Blue Screen of Death (BSoD) is the error screen you see when Windows has a major issue. It halts the PC and displays some very important information.
Depending on the error message you get, the steps you need to take are different.
Error Name:
IRQL_NOT_LESS_OR_EQUAL
IRQL_NOT_LESS_OR_EQUAL means one of two things: driver issues, or a bad Windows Service caused by a backup utility or antivirus scanner. This is a similar, but different error to the previous one we discussed, KMODE_EXCEPTION_NOT_HANDLED, so much of this guide will be familiar.
Driver Issues
Sometimes the additional information on your Blue Screen will list the specific driver causing the problem, but this isn’t always the case.
If it does list the driver, you’re going to want to disable it. If it doesn’t list it, read below.
Disabling a specific driver is tricky, but here’s how you do it.
Disable the Problem Driver
To track down the specific problem driver, you’ll need to run Driver Verifier, an application included with Windows.
- Click Start
- Type verifier in the box and press Enter
- Select Create Standard Settings, then click Next, then select Automatically Select all Drivers Installed on this Computer
- Click Next, then Finish
- Reboot your computer, and you will see the list of drivers to be verified during startup. If there is a faulty driver you will get a BSOD with its respective error message
- When you have determined the faulty driver, log back into Windows and you can uninstall the driver via the Device Manager (see below)
- Click Start and type verifier /reset
You can then identify the driver listed and uninstall it when you log back into Windows
Next, you will want to disable the Driver Verification so it doesn’t always check on startup.
To disable a driver once you’ve identified it:
- Restart your PC in Safe Mode in order to avoid any further Blue Screens of Death while you’re trying to take care of the problem
- Click Start
- Click Control Panel
- Click Device Manager
- Click the arrow next to individual devices, right click on the device, and click Properties
- click Details to see the driver name. If you see any devices with a yellow exclamation mark, you’re on the right track, but this will not necessarily be the case
- Additionally, try doing a CTRL + F on the Windows desktop for the driver name to see what folder it’s in; this will provide a clue as to what device the driver belongs to
- Once you find the offending driver, click Uninstall from that same Properties screen
- Windows will attempt to reinstall the driver itself from information it provides from the Internet. This is called Plug and Play. Allow it to do so
- Run Driver Reviver to update the new driver to the most recent version
Run Driver Reviver
Alternatively, run Driver Reviver first, and see if updating your drivers to the latest version takes care of the problem.
Faulty Windows Service
Sometimes, this error will occur when a backup utility or antivirus scanner makes changes to Windows that it doesn’t like. If you’ve installed and run such an app lately, you’re going to want to reboot in Safe Mode and uninstall it. If that doesn’t work, restore to a Restore Point that’s just before you installed said app, and use a different app instead. We’ve got recommendations for reputable backup utilities as well as antivirus scanners.

Running Windows Restore will remove all traces of the application.
More Information from Microsoft
Here’s a page on Microsoft’s website about this specific BSoD error. It’s pretty technical, but worth checking out if the above solutions don’t work.
Good luck!
Steve Horton