Group Policy Settings References for Windows and Windows Server.
Group Policy Settings Reference for Windows Server 2008 R2 and Windows 7: This spreadsheet lists the policy settings for computer and user configurations included in the Administrative template files (.admx/.adml) delivered with Windows Server 2008 R2 and Windows 7. The policy settings included in this spreadsheet cover Windows 7, Windows Server 2008 R2, Windows Server 2008, Windows Vista with SP1, Windows Server 2003 with SP2 and earlier service packs, Windows XP Professional with SP2 and earlier service packs, and Windows 2000 with SP5 and earlier service packs.
Group Policy Settings Reference for Windows Server 2008 and Windows Vista Service Pack 1: This spreadsheet lists the policy settings for computer and user configurations included in the Administrative template files (.admx/.adml) delivered with Windows Server 2008 and Windows Vista with Service Pack 1 (SP1). The policy settings included in this spreadsheet cover Windows Server 2008, Windows Vista with SP1, Windows Server 2003, Windows XP Professional with SP2 or earlier service packs, and Windows 2000 with SP5 or earlier service packs.
Group Policy Settings Reference for Windows Vista: This spreadsheet lists the policy settings for computer and user configurations included in the Administrative template files (.admx/.adml) delivered with Windows Vista with no service packs installed. The policy settings included in this spreadsheet cover Windows Vista, Microsoft Windows Server 2003, Windows XP Professional with SP2 or earlier service packs, and Windows 2000 with SP5 or earlier service packs.
Group Policy Settings Reference for Windows Server 2003 Service Pack 2: This spreadsheet lists the policy settings for computer and user configurations included in the Administrative template (.adm) files and Security Settings that shipped with Windows Server 2003 with SP2. The policy settings included in this spreadsheet cover Microsoft Windows Server 2003 with SP2 or earlier service packs, Windows XP Professional with SP3 or earlier service packs, and Microsoft Windows 2000 with SP5 or earlier service packs.
Group Policy Administrative Templates (ADM and ADMX): Downloads and Selected Content
Table of Contents
- Windows
- MS Edge browser
- MS Internet Explorer
- Blocker Toolkits for MS Internet Explorer
- MS Office
- MS OneDrive NGSC
- MS Applications
- MS Manageability
- Administrative Template guides, samples, references
- Important notes
You could have trouble finding ADM & ADMX Template downloads when you need them.
Maybe it’s the keywords/tags, maybe it’s the different product groups, thinking about them in different ways.
Anyway, here’s a selected collection of the ones you could go looking for.
 Important Important
|
|---|
| As of 2015/2016, recently released Security Updates or Cumulative Updates, for Windows and/or Internet Explorer, are shipping updated ADMX/ADML files e.g. inetres.admx/adml for IE.
So, if you can’t find the setting you’re looking for in the downloads section, you might need to grab the latest CU for Windows or IE to get the freshest ADMX/ADML. This concept also seems to apply to Win10 upgrades (e.g. 1507 -> 1511 -> 1607)… |
Windows
- Administrative Templates (.admx) for Windows 10 May 2019 Update (1903)
- Administrative Templates (.admx) for Windows 10 October 2018 Update (1809)
- Administrative Templates (.admx) for Windows 10 April 2018 Update (1803)
- Administrative Templates (.admx) for Windows 10 Fall Creators Update (1709)
- Administrative Templates (.admx) for Windows 10 Creators Update (1703)
- Administrative Templates (.admx) for Windows 10 1607 and Windows Server 2016
- Administrative Templates (.admx) for Windows 10 1507 and 1511
- Administrative Templates (.admx) for Windows 8.1 Update and Windows Server 2012 R2 Update
- Administrative Templates (.admx) for Windows 8.1 and Windows Server 2012 R2
- Administrative Templates (.admx) for Windows 8 and Windows Server 2012
- Administrative Templates (ADMX) for Windows Server 2008 R2 and Windows 7
- Administrative Templates (ADMX) for Windows Server 2008
- Administrative Templates (.admx) for Windows Vista
- Group Policy ADM Files: This page provides a complete set of current and previously shipped Administrative Template files (.adm files) included by default in Windows operating system
and service pack releases, beginning with Windows 2000 up to XP/2003 - Administrative Templates for Windows PowerShell: This page provides the Group Policy Administrative template file for Windows PowerShell.
- Windows Service Pack Blocker Tool Kit: A blocking tool is available for organizations that would like to temporarily prevent installation of Service Pack updates through Windows Update.
- Toolkit to Temporarily Block Delivery of Windows Server 2003 Service Pack 2: While recognizing the security benefits of Windows Server 2003 Service Pack 2 (SP2), some organizations
have requested the ability to temporarily disable the automatic delivery of this update through Automatic Updates (AU) and Windows Update (WU). - Microsoft DirectAccess Connectivity Assistant: The Microsoft DirectAccess Connectivity Assistant (DCA) helps organizations reduce the cost of supporting DirectAccess users and significantly
improve their connectivity experience. This Solution Accelerator is part of the Windows® Optimized Desktop Toolkit 2010 (WODT 2010). - Microsoft Azure Hybrid Connection Manager Administrative Templates: This download includes Group Policy Administrative Template files for Microsoft Azure Hybrid Connection Manager.
MS Edge browser
- Edge for business, select channel/version/build, then click GET POLICY FILES: Edge for business, select channel/version/build, then click GET POLICY FILES
MS Internet Explorer
- Administrative Templates for Internet Explorer 11: This page provides the Group Policy Administrative Template files for Internet Explorer 11.
- Administrative Templates for Windows Internet Explorer 10: This page provides the Group Policy Administrative Template files for Windows Internet Explorer 10.
** Warning: IE10 deprecates/removes the IEM methods.
Refer:
AskIEBlog - Administrative Templates for Windows Internet Explorer 9: This page provides the Group Policy Administrative Template files for Windows Internet Explorer 9
- Administrative Templates for Internet Explorer 7 for Windows: This page provides the Group Policy Administrative Template file for Internet Explorer 7 for Windows.
Blocker Toolkits for MS Internet Explorer
- Toolkit to Disable Automatic Delivery of Internet Explorer 11: The Internet Explorer 11 Blocker Toolkit enables users to disable automatic delivery of Internet Explorer 11 as an important
class update via Automatic Updates (AU) feature of Windows Update (WU). - Toolkit to Disable Automatic Delivery of Internet Explorer 10
- Toolkit to Disable Automatic Delivery of Internet Explorer 9
- Toolkit to Disable Automatic Delivery of Internet Explorer 8
- Toolkit to Disable Automatic Delivery of Internet Explorer 7
MS Office
- Office 2016 Administrative Template files (ADMX/ADML) and Office Customization Tool: This download includes Group Policy Administrative Template (ADMX/ADML) and Office Customization
Tool (OPAX/OPAL) files for Microsoft Office 2016. - Office 2013 Administrative Template files (ADMX/ADML) and Office Customization Tool: This download includes Group Policy Administrative Template (ADMX/ADML) and Office Customization
Tool (OPAX/OPAL) files for Microsoft Office 2013. - Office 2013 Help Files: Office Fluent User Interface Control Identifiers: This download details the ControlIDs needed for OFF2013, if you want to disable specific UI controls, buttons,
menu items, via a registry policy. - Office 2010 Administrative Template files (ADM, ADMX/ADML) and Office Customization Tool: This download includes Group Policy Administrative Template (ADM, ADMX/ADML) and Office Customization
Tool (OPAX/OPAL) files for Microsoft Office 2010. - Office 2010 (Beta) Administrative Template files (ADM, ADMX/ADML) and Office Customization Tool: This download includes updated Group Policy Administrative Template and Office Customization
Tool OPA files; an updated Office Customization Tool; and ADMX and ADML versions of the Administrative Template files. - Office 2010 Help Files: Office Fluent User Interface Control Identifiers: This download details the ControlIDs needed for OFF2010, if you want to disable specific UI controls, buttons,
menu items, via a registry policy. - Microsoft Lync 2010 Client Group Policy Documentation: This download package contains the Microsoft Lync 2010 administrative template file (Communicator.adm) and a spreadsheet that
lists the Group Policy settings for the Lync 2010 client. - 2007 Office system (SP2) Administrative Template files (ADM, ADMX, ADML) and Office Customization Tool: This download includes updated Group Policy Administrative Template and Office
Customization Tool OPA files; an…Customization Tool; and ADMX and ADML versions of the Administrative Template files. This update assumes that you have updated… - 2007 Office system Administrative Template files (ADM, ADMX, ADML) and Office Customization Tool version 2.0: This download includes updated Group Policy Administrative Template and
Office Customization Tool OPA files; an updated Office Customization Tool; and ADMX and ADML versions of the Administrative Template files for Microsoft Windows Vista and Microsoft Windows Server 2008. - 2007 Microsoft Office System Open XML Format converters Administrative Template (ADM) version 2.0: This download contains an administrative template which can be used to modify the
default behavior of the Microsoft Office Word, Excel, and PowerPoint 2007 Open XML Format converters. - Microsoft Office Communications Server 2007 R2 Client Group Policy Documentation: This download package contains the Communicator.adm file and a Group Policies Spreadsheet that lists
the Group Policy settings for Office Communications Server 2007 R2 clients - Office Communicator 2007: Communicator 2007 Policies Documentation: This download package contains the Communicator.adm file and a Group Policies Spreadsheet that lists the Group
Policy settings for Office Communicator 2007. - Office 2003 Service Pack 3 Administrative Template (ADM), OPAs, and Explain Text Update: The download includes updated Group Policy Administrative Template files, OPA files, and an
updated Microsoft Excel workbook that lists the Administrative Template policy settings and OPA settings. - Microsoft Project 2002: System Policy Editor and Templates: The Microsoft Project 2002: System Policy Editor and Templates download includes the Microsoft Project 2002 system policy
template. You must install the System Policy Editor and the template on your computer before you can create a system policy file. - System Policy Editor and Office 97 Policy Templates
- Microsoft Office Configuration Analyzer Tool 1.1 ADM Template: The Office Configuration Analyzer Tool 1.1 (OffCAT ) provides a quick and easy method to analyze several Microsoft
Office programs for common configurations that may cause problems
MS OneDrive NGSC
- OneDrive NGSC Administrative settings — Deployment package
MS Applications
- Microsoft Desktop Optimization Pack Administrative Templates: ADMX templates for MDOP products — UE-V and App-V
These MDOP Group Policy Templates delivers .admx and .adml templates to manage policy across the enterprise for the following MDOP technologies:
- App-V 5.0
- App-V 5.0 SP1
- App-V 5.0 SP2
- MBAM 1.0
- MBAM 1.0 R1
- MBAM 2.0
- MBAM 2.0 SP1
- MBAM 2.5
- UE-V 1.0
- UE-V 1.0 SP1
- UE-V 2.0
- Help for Windows Administrative Templates (ADMX): This page provides the Group Policy Administrative Template files for Help for Windows (WinHlp32.exe).
- Microsoft Application Virtualization Administrative Template (ADM Template): The Microsoft Application Virtualization ADM template allows you to administer App-V client settings via
Preferences.The ADM Template for App-V 4.5/4.6 provides central client settings administration for App-V 4.5/4.6 deployment, including the following:
- Client permissions
- Client interface behavior
- Client communication settings
- Windows Live Toolbar Administrative Template (.adm) File: Windows Live Toolbar administrative template file for Group Policy Object Editor
- Windows Search 4.0 for Windows XP (KB940157): Windows Search 4.0 is an updated component of Windows that enables instant search on your computer.
- Windows Search 4.0 for Windows XP x64 Edition (KB940157)
- Windows Search 4.0 for Windows Server 2003 (KB940157)
- Windows Search 4.0 for Windows Server 2003 x64 Edition (KB940157)
- Windows Desktop Search 3.01 for Windows Server 2003 (KB917013)
- Windows Desktop Search 3.01 for Windows Server 2003 x64 Edition (KB917013)
- Windows Desktop Search 3.01 for Windows XP (KB917013)
- Windows Desktop Search 3.01 for Windows XP x64 Edition (KB917013)
- Silverlight: Technical Resources Reference, includes code for creating custom administrative template.
- Windows Defender: Description of the Windows Defender Group Policy administrative template settings
MS Manageability
- Microsoft System Center Mobile Device Manager 2008 SP1 Resource Kit Tools — Server Tools: System Center Mobile Device Manager (MDM) 2008 Service Pack 1 (SP1) Server Tools provides
tools to help administrators manage deployment and cleanup tasks in an MDM system - Microsoft System Center Mobile Device Manager 2008 Resource Kit — Server Tools: System Center Mobile Device Manager (MDM) 2008 Server Tools provides tools to help administrators manage
deployment and cleanup tasks in an MDM system. - Microsoft® Forefront™ Identity Manager 2010 Group Policy Templates: This download contains the Forefront Identity Manager 2010 Group Policy templates.
- SCOnline Group Policy Administrative Template: Group Policy administrative template for Asset Intelligence Service
Administrative Template guides, samples, references
- Group Policy Documentation Survival Guide: This document provides links to documentation and other technical information for Group Policy in Windows Server 2008.
- Group Policy Search tool: You can use the Group Policy Search tool to search and find Group Policy settings.
- Group Policy Settings Reference for Windows and Windows Server: These workbooks / spreadsheets list the policy settings for computer and user configurations included in the Administrative
template files delivered with the Windows operating systems specified. You can configure these policy settings when you edit Group Policy objects (GPOs).- WindowsServer2003SP2GroupPolicySettings.xls (includes Windows XP & IE6)
- WindowsServer2008andWindowsVistaSP1GroupPolicySettings.xlsx (includes IE7)
- WindowsServer2008R2andWindows7GroupPolicySettings.xlsx (includes IE8)
- WindowsServer2012andWindows8GroupPolicySettings.xlsx (includes IE10)
- WindowsServer2012R2andWindows8.1GroupPolicySettings.xlsx (includes IE11)
- WindowsVistaGroupPolicySettings.xls (includes IE7)
- Windows 10 ADMX spreadsheet.xlsx (includes IE11 and Edge)
- Group Policy Settings Reference for Windows Internet Explorer 8: This spreadsheet lists the policy settings for computer and user configurations included in the administrative template
files (admx/adml) delivered with Windows Internet Explorer 8. - Group Policy Settings Reference Windows Internet Explorer 9: This spreadsheet lists the policy settings for computer and user configurations included in the administrative template
files (admx/adml) delivered with Windows Internet Explorer 9. - Using Administrative Template Files with Registry-Based Group Policy: Explains the concepts, architecture, and implementation details for registry-based Group Policy, shows how to create
custom Administrative Template (.adm) files, and includes a complete reference for the .adm language. - Group Policy ADMX Syntax Reference Guide: This reference document describes the new Group Policy ADMX format. The intent of this document is to teach you how to create .admx and .adml
files for custom Group Policy administrative template settings. - Group Policy ADMX Schema files: This page provides the Group Policy Administrative Template ADMX schema files.
- Group Policy Sample ADMX Files: This page provides Group Policy Sample ADMX files.
- ADMX Migrator: ADMX Migrator is a snap-in for the Microsoft Management Console (MMC) that simplifies the process of converting your existing Group Policy ADM Templates to the new ADMX
format and provides a graphical user interface for creating and editing Administrative templates. - Starter Group Policy Objects (GPOs): Starter Group Policy objects (GPOs), introduced in Group Policy for Windows Server 2008, are collections of configured Administrative template (.admx)
policy settings that you can use to create a live GPO. Each of the two packages in this download contains four starter GPOs. - Security Compliance Toolkit: includes various tools, baselines and custom templates
Important notes
- New Group Policies in Internet Explorer 10
- Appendix B: Replacements for Internet Explorer Maintenance
- New group policy settings for Internet Explorer 11
- Missing Internet Explorer Maintenance settings for Internet Explorer 11
ADM, Administrative Templates, ADML, ADMX, Application Virtualization, App-V, en-US, GPO, Group Policy Objects, has comment, has links, Has Table, Has TOC, MDOP, policy

Comments
-
9 Mar 2012 12:27 AM
Nice Wiki. Helpful !
Microsoft has released a special spreadsheet which covers all Group Policy options for Windows 10 version 1803, known as «April 2018 Update». This document is useful for all Windows 10 users, especially for those who are is using Windows 10 Home. As you may already know, the Home edition doesn’t include the Local Group Policy Editor app (gpedit.msc), so having a list of Registry parameters you can apply is a must-have thing.
Group Policy is a way to configure computer and user settings for devices which are joined to Active Directory Domain Services (AD) as well as local user accounts. It controls a wide range of options and can be used to enforce settings and change the defaults for applicable users. Local Group Policy is a basic version of Group Policy for computers not included in a domain. The Local Group Policy settings are stored in the following folders:
C:WindowsSystem32GroupPolicy
C:WindowsSystem32GroupPolicyUsers.
If you are running Windows 10 Pro, Enterprise, or Education edition, you can use the Local Group Policy Editor app to configure the options with a GUI.
- Open your favorite web browser.
- Navigate to the following page: Download Group Policy Settings Reference Spreadsheet Windows 1803
- Click on the download button.
- Open the downloaded Windows10andWindowsServer2016PolicySettings-1803.xlsx file with Microsoft Excel or LibreOffice Calc.
The spreadsheet lists the policy settings for computer and user configurations that are included in the Administrative template files delivered with the Windows operating systems specified. You can configure these policy settings when you edit Group Policy Objects.
You can use the filtering capabilities that are included in this spreadsheet to view a specific subset of data, based on one value or a combination of values that are available in one or more of the columns. In addition, you can click Custom in the drop-down list of any of the column headings to add additional filtering criteria within that column.
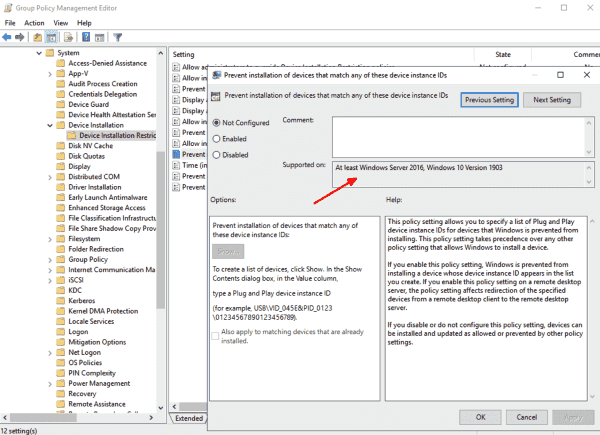
To view a specific subset of data, click the drop-down arrow in the column heading of cells that contain the value or combination of values on which you want to filter, and then click the desired value in the drop-down list. For example, to view policy settings that are available for Windows Server 2012 R2 or Windows 8.1, in the Administrative Template worksheet, click the drop-down arrow next to Supported On, and then click At least Microsoft Windows Server 2012 R2 or Windows 8.1.
Related articles.
- How To See Applied Group Policies in Windows 10
- See Applied Windows Update Group Policies in Windows 10
- Apply Group Policy to All Users Except Administrator in Windows 10
- Apply Group Policy to a Specific User in Windows 10
- Reset All Local Group Policy Settings at once in Windows 10
That’s it.
Support us
Winaero greatly relies on your support. You can help the site keep bringing you interesting and useful content and software by using these options:
If you like this article, please share it using the buttons below. It won’t take a lot from you, but it will help us grow. Thanks for your support!
With each new release of Windows 10, Microsoft used to document all the settings for the group policies in an Excel spreadsheet. This, however, has not been done since Version 1809. With a little help from PowerShell and by studying the ADMX file structure, I have now created one myself.
Contents
- ADMX data quality
- Multilingualism
- Availability
- Author
- Recent Posts
Wolfgang Sommergut has over 20 years of experience in IT journalism. He has also worked as a system administrator and as a tech consultant. Today he runs the German publication WindowsPro.de.
The regularly updated Excel spreadsheets were the official documentation for the GPO settings for Windows and Internet Explorer. Among other things, they showed where an option could be found in the GPO editor, from which version of the operating system it was available, and what purpose it served.
However, the quality of the document left much to be desired, and Microsoft apparently wanted to avoid the effort of creating the documentation from scratch. Currently, the Security Baseline also contains a list with all the settings for the group policies, but this list is even more confusing than the usual Excel sheet.
ADMX data quality
The root of the problem is the administrative templates, which have grown over the years and now comprise over 4,000 settings (if you count the entries for both computers and users separately). Over time, inconsistencies and errors have crept in that need to be corrected.
The data quality of the ADMX and ADML files not only affects tools for the automatic documentation, but also the GPO editor. The GPO editor obtains all the information from these XML files in order to build the navigation tree for the settings or to display the explanation for each setting.
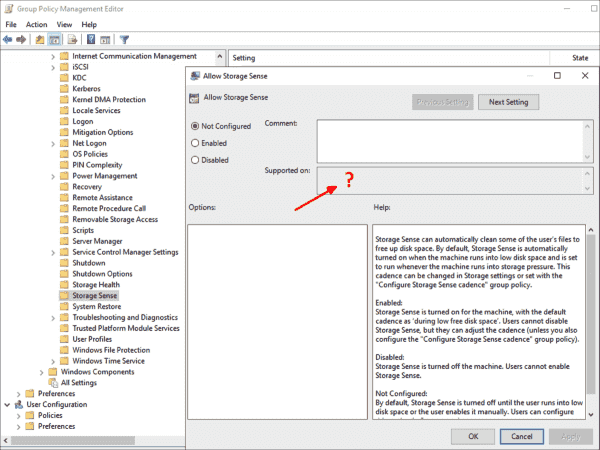
Accordingly, it cannot provide any information about the supported operating system, if, for example, the storagesense.admx introduced with Windows 10 1903 contains invalid references to the language files.
The storagesense.admx file contains invalid references to the ADML file; hence, the GPO editor cannot display the OS version
If the ADMX files declare the new settings for Windows 10 1909 as compatible with Server 2016 and Windows 10 1903, the editor will, of course, pass this wrong information to the user («garbage in, garbage out»).
The new settings for Windows 10 1909 are declared for the previous version
The security settings, which can be found in the GPO editor under the Windows settings, are not defined in the administrative templates. As nothing has changed there in recent versions of Windows 10, I have taken this list from Microsoft’s Excel spreadsheet for the sake of completeness.
Multilingualism
A fundamental advantage of separating the structure (ADMX) from the human-readable parts (ADML), e.g., explanations, is that the same tool can be used to generate the documentation for several languages.
Microsoft has translated the descriptions of the GPO settings into several languages
Unfortunately, Microsoft has so far ignored this option and only provided an English spreadsheet. My Excel document contains worksheets for seven languages.
In general, Excel is probably not the best tool for documenting GPO settings, mainly because the large amount of data affects its performance (at least when editing). But you can remove unwanted languages to trim the document. Reading the relatively long help text is easier if you double-click the corresponding cell.
Availability
Due to the large number of settings, I have only checked them randomly and have not found any major anomalies. Your feedback on any incorrect data is therefore welcome.
Subscribe to 4sysops newsletter!
The Excel spreadsheet with all GPO settings up to Windows 10 1909 can be downloaded here.
Содержание
- 1 Открыть редактор локальной групповой политики с помощью меню «Пуск».
- 2 Открыть редактор локальной групповой политики с помощью команды «Выполнить».
- 3 Открыть редактор локальной групповой политики с помощью Проводника Windows.
- 4 Открыть редактор локальной групповой политики из командной строки или PowerShell
- 5 Открыть редактор локальной групповой политики в качестве оснастки консоли управления.
- 6 Открыть редактор локальной групповой политики в Windows 10 Home.
- 7 Policy Plus
- 8 Установка редактора политик gpedit.msc в Windows 10 Домашняя
- 9 Старая версия редактора gpedit.msc от Windows 7
- 10 Утилита Policy Plus – универсальный редактор локальной политик для всех версий Windows
- 11 О редакторе
- 12 Как установить?
Групповая политика — это способ настройки параметров компьютера и пользователя для устройств, которые присоединены к доменным службам Active Directory (AD), а также к учетным записям локальных пользователей. Она контролирует широкий спектр параметров и может использоваться для принудительного применения и изменения настроек по умолчанию для соответствующих пользователей. Локальная групповая политика — это базовая версия групповой политики для компьютеров, не входящих в домен. Параметры локальной групповой политики хранятся в следующих папках:
- C:WindowsSystem32GroupPolicy
- C:WindowsSystem32GroupPolicyUsers.
Когда в Windows 10 вам необходимо открыть редактор локальной групповой политики, для этого вы можете использовать командную строку, команду выполнить, поиск на панели задач, меню Пуск или с помощью консоли управления (MMC).
Рассмотрим самые простые варианты:
- C помощью меню Пуск.
- C помощью команды Выполнить.
- C помощью Проводника Windows.
- С помощью командной строки или PowerShell
- Открыть редактор локальной групповой политики в качестве оснастки консоли управления.
- Открыть редактор локальной групповой политики в Windows 10 Home.
Открыть редактор локальной групповой политики с помощью меню «Пуск».
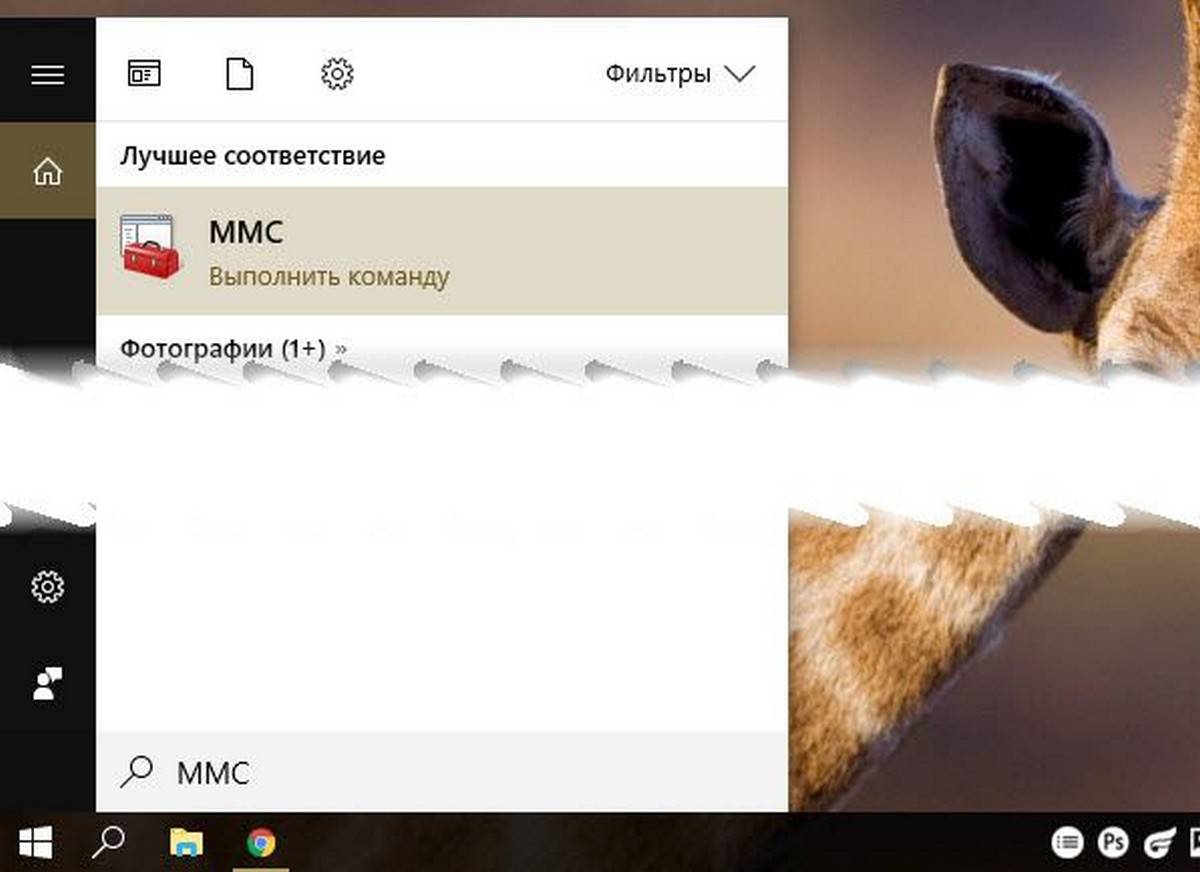
- Откройте меню «Пуск» и введите gpedit.msc в верхней части меню появится значок, при клике, на котором, откроется редактор политики.
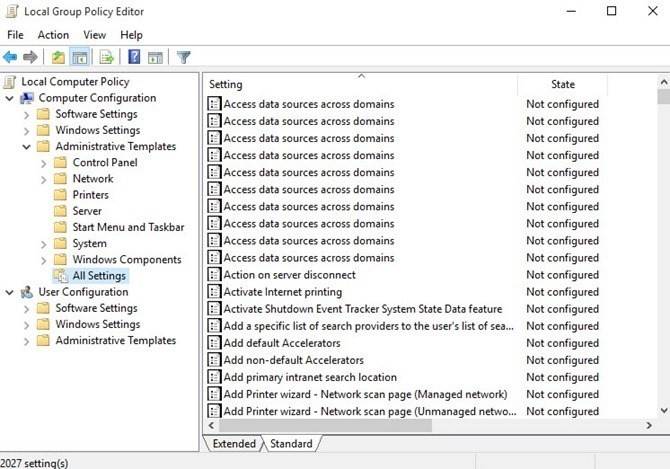
Чтобы просмотреть все применяемые политики в разделе «Конфигурация компьютера», перейдите в раздел «Конфигурация компьютера Административные шаблоны Все параметры»
Чтобы просмотреть все применяемые политики пользовательской настройки, перейдите в раздел «Конфигурация пользователя Административные шаблоны Все параметры».
Примечание: вы можете использовать поиск на панели задач.
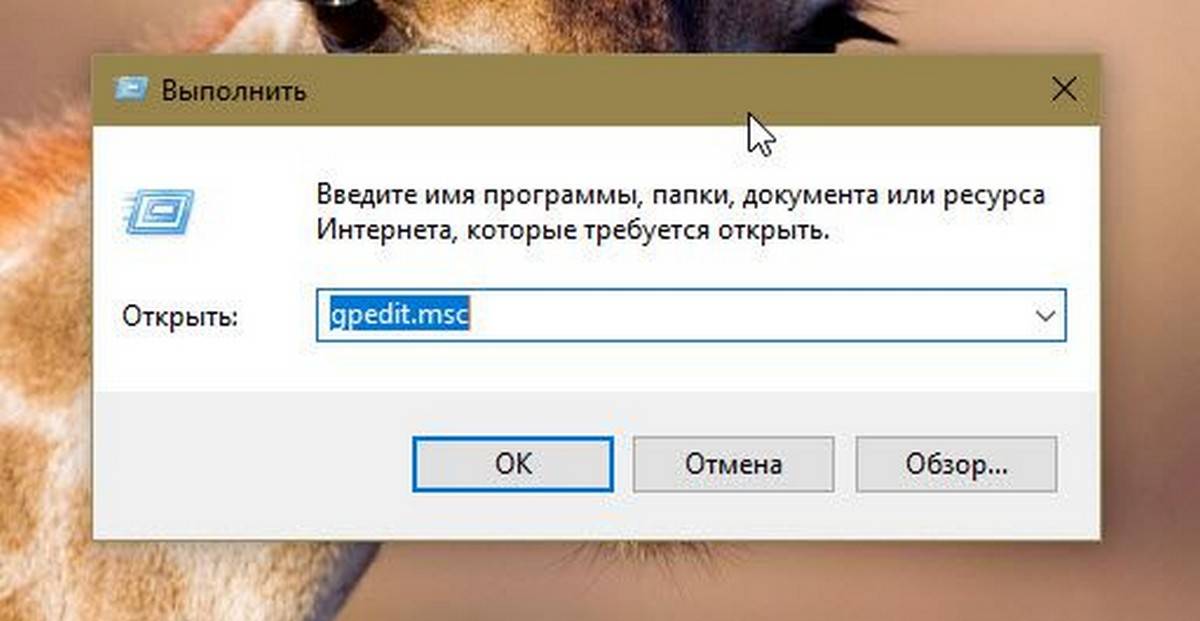
Открыть редактор локальной групповой политики с помощью команды «Выполнить».
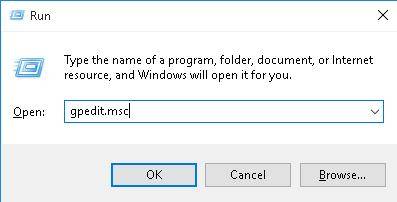
- Нажмите сочетание клавиш Win + X или кликните правой кнопкой мыши на меню «Пуск».
- В открывшемся меню выберите Выполнить.
- В строке «Открыть» введите — gpedit.msc и нажмите кнопку «ОК».
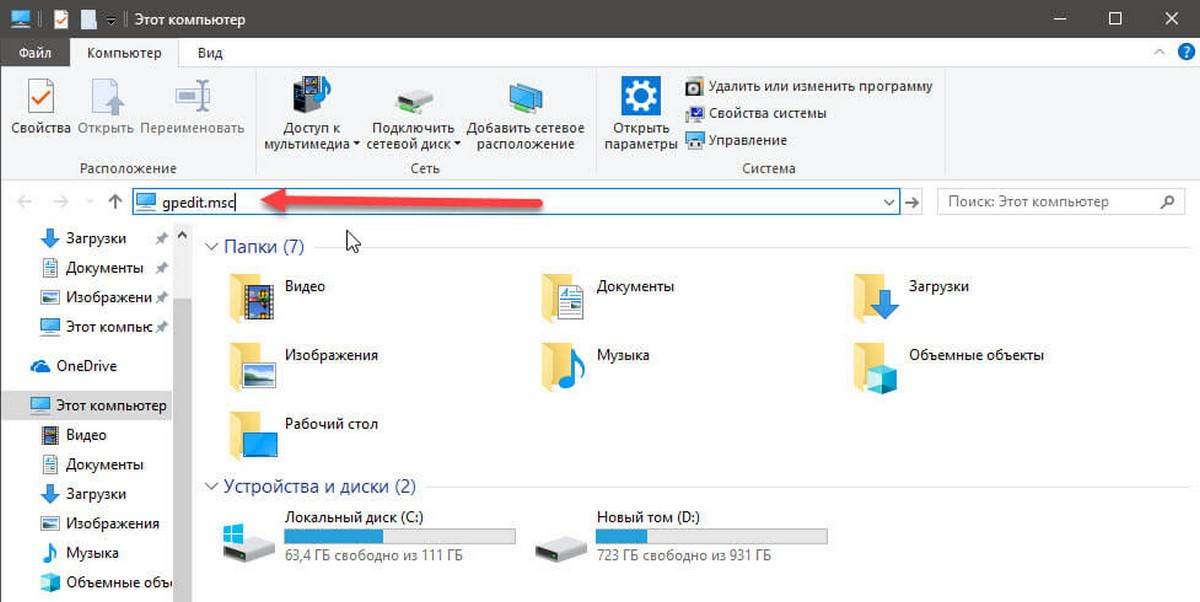
Открыть редактор локальной групповой политики с помощью Проводника Windows.
- Откройте Проводник с помощью ярлыка на панели задач или просто нажав сочетание клавиш Win + E
- В адресную строку проводника введите или скопируйте и вставьте:
gpedit.msc
- Нажмите Enter
Открыть редактор локальной групповой политики из командной строки или PowerShell
Откройте Командную строку или вы можете открыть новый экземпляр PowerShell.
Введите: gpedit.msc и нажмите клавишу Enter.
Открыть редактор локальной групповой политики в качестве оснастки консоли управления.
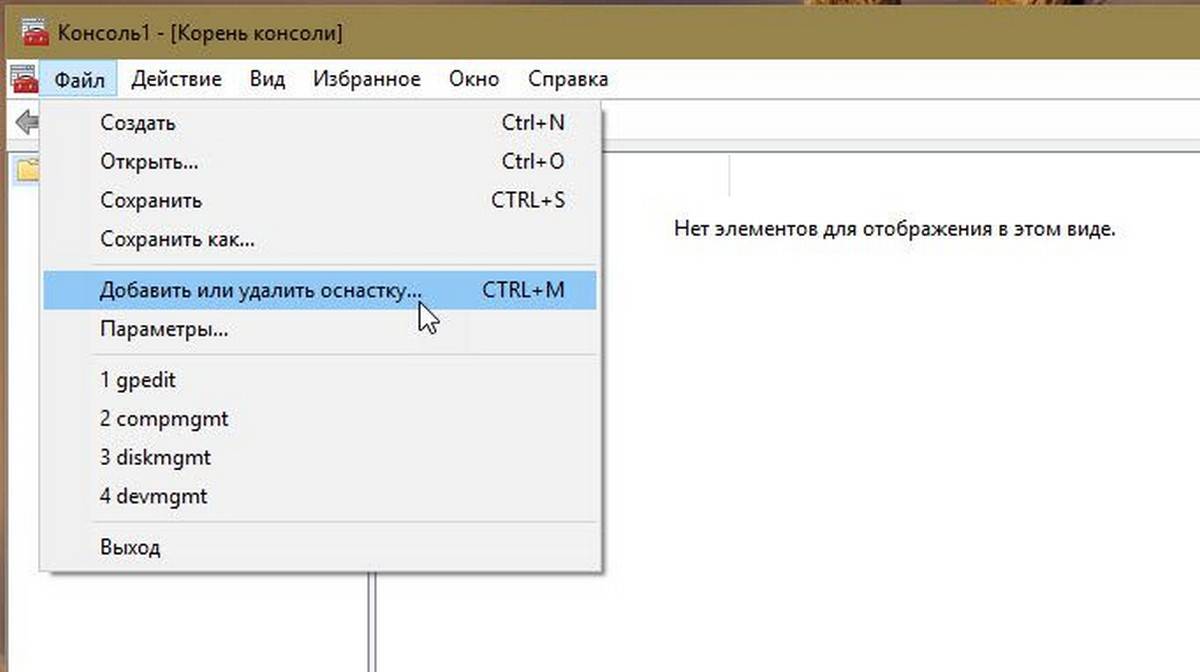
- Откройте консоль управления MMC. (Нажмите кнопку «Пуск», введите mmc и нажмите клавишу Enter).
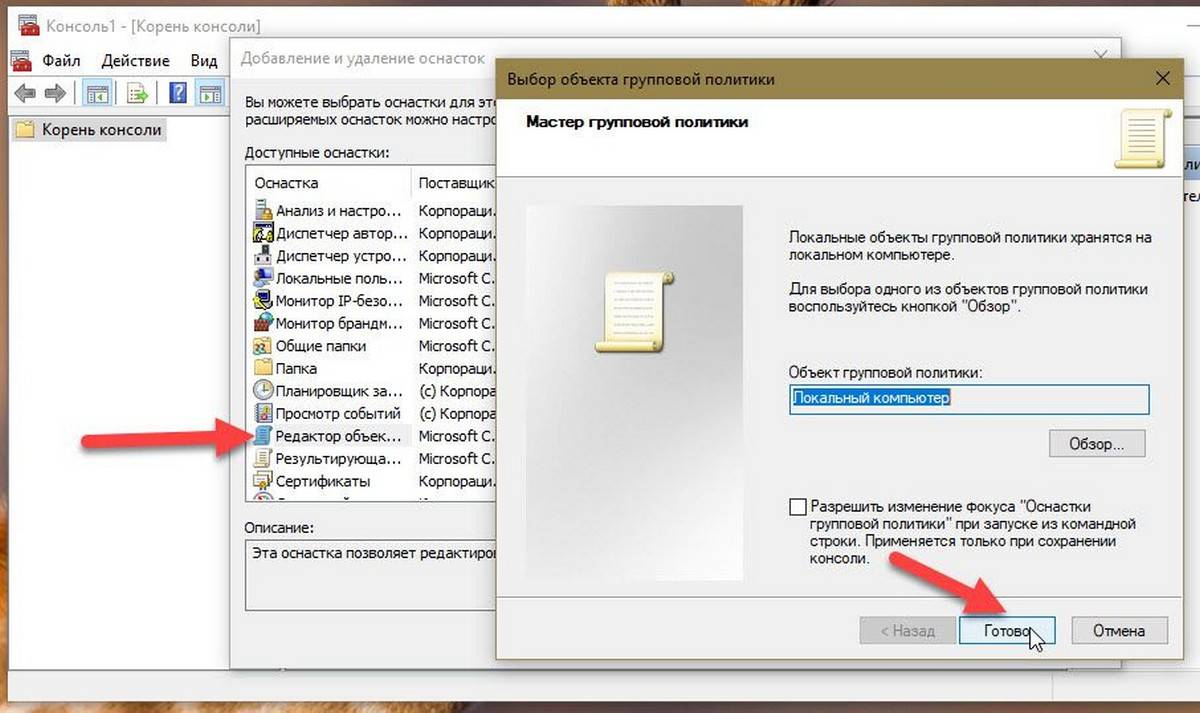
- В меню Файл выберите пункт Добавить или удалить оснастку.
- В открывшимся диалоговом окне, дважды кликните «Редактор объектов групповой политики» и нажмите кнопку «Готово» и «ОК».
Открыть редактор локальной групповой политики в Windows 10 Home.
Как вы уже знаете, приложение Редактора локальной групповой политики доступно в Windows 10 Pro, Enterprise или Education. Пользователи Windows 10 Home не имеют доступа к gpedit.msc из-за ограничений ОС. Вот простое и элегантное решение, которое позволяет разблокировать его без установки сторонних приложений.
Существует простой способ включить Редактор локальных групповых политик в Windows 10 Home запустив всего лишь один пакетный файл.
Чтобы включить Gpedit.msc (групповая политика) в Windows 10 Home
- Загрузите следующий ZIP-архив: Скачать ZIP-архив.
- Распакуйте его содержимое в любую папку. Он содержит только один файл, gpedit_home.cmd
- Кликните правой кнопкой мыши по файлу.
- Выберите в контекстном меню «Запуск от имени администратора».
Все!
Пакетный файл вызовет DISM для активации редактора локальной групповой политики. Подождите, пока командный файл не завершит свою работу.
Помните, что некоторые политики не будут работать в Windows Home. Некоторые политики жестко заданы для версий Windows Pro. Кроме того, если вы активируете gpedit.msc с помощью предоставленного пакетного файла, изменение политик для отдельных пользователей не вступит в силу. Они по-прежнему требуют настройки реестра.
Вы можете самостоятельно создать пакетный файл. Прежде чем начать, рекомендуем создать точку восстановления системы, и вы могли в любой момент отменить произведенные изменения в системе.
- Откройте текстовый редактор, например «Блокнот».
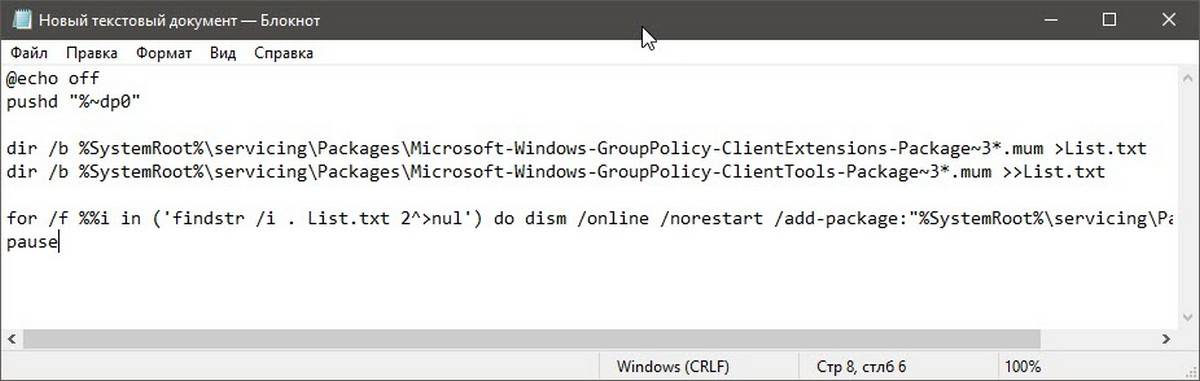
- Скопируйте и вставьте следующие строки:
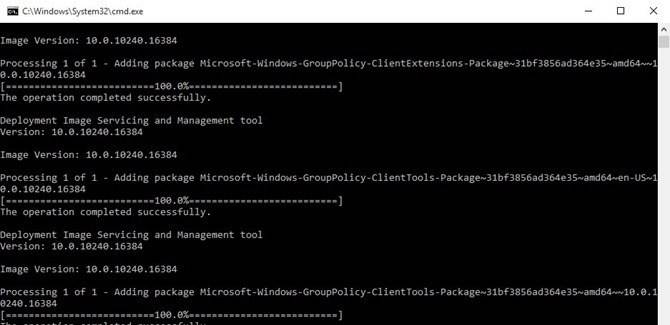
@echo off pushd "%~dp0" dir /b %SystemRoot%servicingPackagesMicrosoft-Windows-GroupPolicy-ClientExtensions-Package~3*.mum >List.txt dir /b %SystemRoot%servicingPackagesMicrosoft-Windows-GroupPolicy-ClientTools-Package~3*.mum >>List.txt for /f %%i in ('findstr /i . List.txt 2^>nul') do dism /online /norestart /add-package:"%SystemRoot%servicingPackages%%i" pause
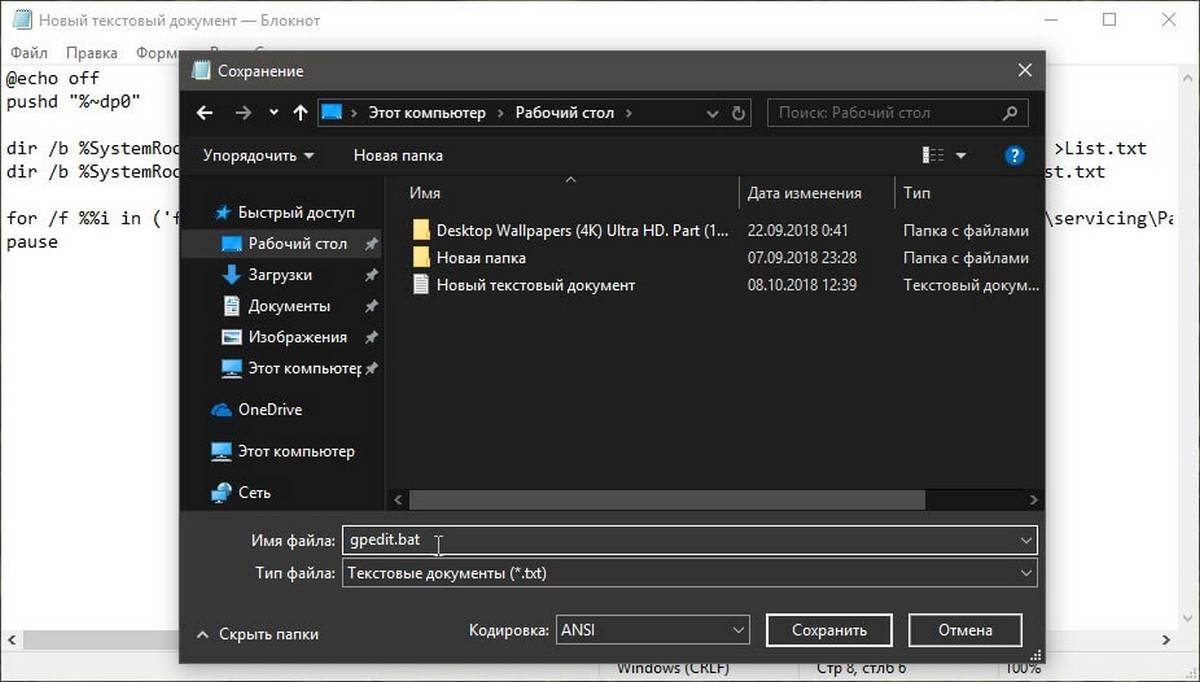
- В меню «Файл» текстового редактора выберите «Сохранить как» в диалоговом окне в строке «Имя файла» введите — gpedit.bat и нажмите кнопку «Сохранить».
- Запустите от имени Администратора полученный пакетный файл gpedit.bat
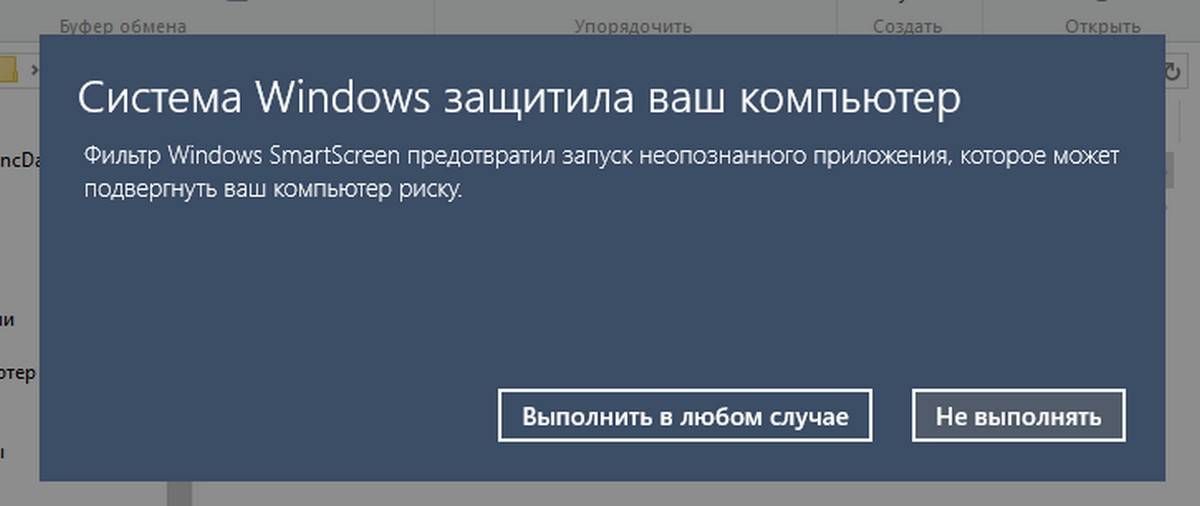
- При запросе фильтра Windows SmartScreen, нажмите «Подробнее», затем нажмите кнопку «Выполнить в любом случае».
- В окне Контроля учетных записей, нажмите кнопку «Да».
- Дождитесь пока утилита DISM внесет изменения и закройте окно.
Все! Редактор локальных групповых политик (gpedit.msc) включен и теперь Вы можете его запустить любым из описанных выше способов.
Policy Plus
Существует хорошая альтернатива встроенному приложению gpedit.msc, которое называется Policy Plus. Это стороннее приложение с открытым исходным кодом: PolicyPlus
Policy Plus предназначен для того, чтобы сделать параметры групповой политики доступными для всех.
- Редактор работает на всех выпусках Windows, не только на Pro и Enterprise
- Полностью соблюдает условия лицензирования
- Просмотр и редактирование политик на основе реестра в локальных объектах групповой политики, объектах групповой политики для отдельных пользователей, отдельных файлах POL, автономных кустах пользователей реестра и действующем реестре
- Переход к политикам по идентификатору, тексту или отдельным записям реестра.
- Просмотр дополнительной технической информации об объектах (политики, категории, продукты)
- Удобные способы изменить и импортировать настройки политики
Рекомендуем: Как Windows 10 вернуть настройки локальной групповой политики по умолчанию.
Рейтинг: /5 — голосов —>
—>
Очень часто для тонкой настройки параметров Windows используется консоль редактора групповых политик (gpedit.msc). Однако в домашних редакциях Windows 10 Home консоль редактор политик отсутствует(в отличии от Windows 10 Pro и Enterprise). Вероятно, что по логике Microsoft домашнему пользователя не нужно править локальные настройки через графический интерфейс gpedit.msc. Соответственно, пользователям домашней редакции Windows 10 приходится вносить изменения через редактор реестра, что не так наглядно и более рискованно с точки зрения возможности ошибиться и что-нибудь сломать в системе.
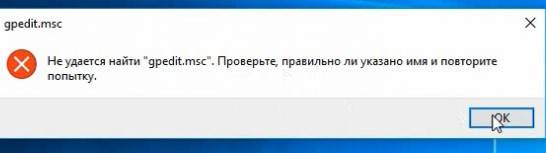
При попытке выполнить команду запуска Group Policy Editor в Windows 10 Домашняя и Домашняя для одного языка: Win+R -> gpedit.msc
Появляется ошибка: Не удается найти «gpedit.msc». Проверьте, правильно ли указано имя и повторите попытку.
В этой статье мы разберемся как установить и запустить редактор локальной групповой политики в редакции Windows 10 Home.
Содержание:
Редактор групповой политики это отдельная MMC оснастка, которая по сути представляет собой графическую надстройку для удобного управления параметрами Windows в реестре. При изменении настроек какой-то политики, редактор сразу вносит изменения в связанный параметр реестра. Вместо того, чтобы искать необходимый ключ и вручную править параметр реестра, гораздо проще найти и отредактировать настройку в редакторе gpedit.msc. В редакторе GPO содержится более двух тысяч настроек Windows, которые расположены в стройной иерархии, имеют подробное описание и предлагают для выбора предопределенные опции настройки.
Совет. Соответствие между политиками и ключами реестра можно найти в XLSX документе Microsoft Group Policy Settings Reference Spreadsheet Windows. Версию документа Windows10andWindowsServer2016PolicySettings-1803.xlsx для Windows Server 2016 и Windows 10 1803 можно скачать по ссылке: https://www.microsoft.com/en-us/download/details.aspx?id=56946. В этом таблице вы можете найти какой ключ реестра правиться той или иной настройкой конкретной политики.
Все примененные настройки локальных политик хранятся в registry.pol файлах в каталогах (вы можете преобразовать данные pol файлы в удобный текстовый формат с помощью утилиты lgpo.exe):
- %SystemRoot%System32GroupPolicy;
- %SystemRoot%System32GroupPolicyUsers.
Если вы удалите файлы из этих папок, вы сбросите все настройки локальных политик (это бывает полезно, когда после изменения каких-то настроек Windows в политиках компьютер перестал пускать пользователя или не загружается).
Какое-то время назад я нашел сторонний установщик редактора gpedit.msc для Windows 7. Его можно использовать и в Windows 10 (описано в отдельном разделе этой статьи), однако в Windows 10 Home появилась возможность скрытая возможность установки редактора gpedit.msc прямо из установочных файлов образа.
Установка редактора политик gpedit.msc в Windows 10 Домашняя
Для установки редактора локальных групповых политик в Windows 10 в редакции Домашняя, откройте командную строку с правами администратора и последовательно выполните команды:FOR %F IN ("%SystemRoot%servicingPackagesMicrosoft-Windows-GroupPolicy-ClientTools-Package~*.mum") DO (DISM /Online /NoRestart /Add-Package:"%F")
FOR %F IN ("%SystemRoot%servicingPackagesMicrosoft-Windows-GroupPolicy-ClientExtensions-Package~*.mum") DO (DISM /Online /NoRestart /Add-Package:"%F")
Для удобства данный код можно сохранить в текстовый файл gpedit-install.bat и запустить с правами администратора. Подождите какое-то время, пока DISM производит установку пакетов из внутреннего хранилища компонентов Windows 10.
В моем случае в английской редакции Windows 10 Home были установлены пакеты ClientTools и ClientExtensions:Microsoft-Windows-GroupPolicy-ClientTools-Package~…~amd64~~….mumMicrosoft-Windows-GroupPolicy-ClientTools-Package~…~amd64~en-US~….mumMicrosoft-Windows-GroupPolicy-ClientExtensions-Package~…~amd64~~….mumMicrosoft-Windows-GroupPolicy-ClientExtensions-Package~…~amd64~en-US~….mum
Теперь попробуйте запустить консоль gpedit.msc – должен открыться интерфейс редактор локальной групповой политики (перезагрузка не требуется). Редактор GPO полностью работоспособен даже в домашней версии Windows 10 и содержит все необходимые разделы политик, которые доступны в старших редакциях Windows.
Старая версия редактора gpedit.msc от Windows 7
Чтобы запустить редактор групповых политик в Windows 10 Home, можно воспользоваться неофициальным патчем от энтузиастов, который включает в себя все необходимые библиотеки и файлы для работы редактора локальных групповых политик.
- Скачать архив с установочным файлом можно здесь: add_gpedit_msc.zip;
- Распакуйте архив и запустите с правами администратора мастер установки setup.exe;
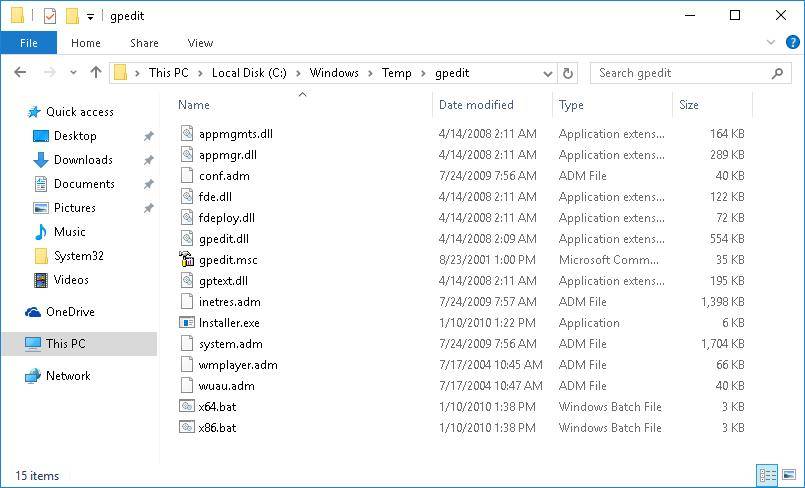
- Если у вас 64-битная версия Windows 10, то не закрывая окно установщика (не нажимая кнопку Finish), перейдите в каталог %WinDir%Temp и скопируйте файлы gpedit.dll,fde.dll, gptext.dll, appmgr.dll, fdeploy.dll и gpedit.msc в папку %WinDir%System32;
- Затем скопируйте папки GroupPolicy, GroupPolicyUsers, GPBAK и файл gpedit.msc из каталога %WinDir%SysWOW64 в папку %WinDir%System32;
- Перезагрузите компьютер и попробуйте запустить консоль редактора, выполнив команду gpedit.msc .
Если при запуске gpedit.msc появляется ошибка “MMC could not create the snap-in”, вручную запустите из папки %WinDir%Tempgpedit файл x86.bat или x64.bat (в зависимости от разрядности системы). Также может помочь ручное копирование файлов архива в папку %SystemRoot%System32.
Совет. В установленной версии редактора будет отсутствовать ряд политик, появившихся в Windows 8 и Windows 10, т.к. данная версия редактора GPO разрабатывалась еще под Windows 7. Т.е. могут отсутствовать новые параметры политик, которые появились после Windows 7, например политика, связанная с недавней проблемой с credssp. Кроме того, имеется только английская версия редактора GPO.
Утилита Policy Plus – универсальный редактор локальной политик для всех версий Windows
Недавно я наткнулся на полезную бесплатную утилиту PolicyPlus, которая представляет собой альтернативу встроенному редактору групповых политик Windows – gpedit.msc для всех версий Windows: Windows 10, Windows 8.1, Windows 7, (в том числе в Windows 10 Home). Скачать утилиту можно по ссылке из репозитория на GitHub: https://github.com/Fleex255/PolicyPlus
Скачайте и запустите Policy Plus с правами администратора (программа портабельная, установки не требует).
Как вы видите, консоль Policy Plus очень похожа на редактор gpedit.msc: дерево с разделами в левом окне и политики в правом.
Функционал Policy Plus существенно превосходит возможности редактора политик gpedit.msc. Утилита позволяет подключать файлы административных шаблонов (admx), а при необходимости сама может скачать последние версии шаблонов с сайта Microsoft (Help -> Acquire AMDX Files). Это обязательно нужно сделать пользователям домашних редакций Windows 10, т.к. в системе отсутствует большинство файлов административных шаблонов.
В Policy Plus имеется удобный встроенного поиска политик. Можно искать по тексту, описанию политики, связанным веткам реестра.
Можно редактировать реестр офлайн образа Windows, загружать POL файлы политик и экспортировать настройки групповых политик в файл для переноса на другие компьютеры (Импорт / Экспорт reg и pol файлов).
Довольно удобно, что с помощью встроенного инспектора (Element Inspector) можно посмотреть какие ключи реестра включает та или иная политика и возможные значения параметра.
Обратите внимание, что после изменения локальных политик, для применения настроек системы пользователям редакций Windows 10 Home необходимо перезагрузить компьютер или выполнить логоф/логон. В редакция Pro и Enterprise большинство изменений вступает в силу немедленно, либо после выполнения команды gpupdate /force.
Кроме того, в Home редакциях Windows не поддерживаются множественные локальные политики (MLGPO).
Пользователи Windows 10, у которых установлена «Начальная» или «Домашняя» версии, сталкиваются с проблемой при выполнении команды gpedit.msc. На экране появляется надпись: «Не удается найти «gpedit.msc». Проверьте, правильно ли указано имя и повторите попытку». Почему редактор локальной групповой политики (который вызывается командой gpedit.msc) не найден в Windows 10, читайте в рамках данной статьи.
О редакторе
Редактор локальной групповой политики по своей сути является редактором реестра с графическим интерфейсом. Он предназначен для проведения тонких настроек Windows. В данный момент, разработчики вырезали редактор в версиях Домашняя (Home) и Начальная (Starter), оставив его в Windows 10 Профессиональная (Pro) и Корпоративная (Enterprise). Официально, воспользоваться редактором в версиях где он вырезан не получится, поэтому пользователи могут проделать необходимые настройки в редакторе реестра. Но можно вернуть кастомный «редактор с графическим интерфейсом».
Совет! Узнать соответствие политик редактора со значением реестра помогут специальные таблицы от Microsoft: Group Policy Settings Reference for Windows and Windows Server.
Как установить?
Есть 2 решения:
- перенос файлов редактора из версии Pro, установка компонентов из дистрибутива и установка неофициального приложения, скомпилированного в установщик пользователем для Windows 7 (но оно подходит для версий 8.1 и 10);
- установка приложения с последующим переносом системных файлов и библиотек.
Важно! Так как вы будете работать с системными файлами, всегда есть вероятность повреждения системы. Рекомендую создать точку восстановления.
Способ 1
Чтобы перенести файлы нужны права администратора.
Полезно знать! В Windows 10 разработчики отключили функцию входа в безопасный режим по нажатию кнопки F8 перед загрузкой системы. Они это сделали для более быстрой загрузки ОС. Читать подробнее.
Отключение UAC
Также рекомендуем отключить UAC прежде чем приступать к переносу. Для этого:
- Нажмите правой кнопкой мыши по «Пуск» и выберите «Панель управления».
- Перейдите в раздел «Учетные записи пользователей».
- В новом окне нажмите «Изменить параметры контроля учетных записей».
- Поставьте ползунок в крайнее нижнее состояние «Никогда не уведомлять» и нажмите «ОК».
Процедура переноса
Для установки «Редактора локальной групповой политики», необходим дистрибутив Windows 10. Скачать его можно на сайте Microsoft с помощью MediaCreationTool. Также утилита позволит установить образ на флешку или DVD-диск или же создаст ISO-образ диска. Еще, необходим сам файл gpedit.msc, который нужно скопировать с компьютера под управлением Windows 10 Pro. Если такового нет в наличии, вы можете установить Windows 10 Pro на флешку.
Для переноса:
- Подключите диск или флешку с дистрибутивом системы или монтируйте ISO-образ на виртуальный привод.
- Загрузите и установите утилиту Far Manager 3, которая поможет корректно перенести системные файлы.
- Скопируйте файл gpedit.msc из системы Windows 10 Pro и перенесите ее в свою версию в директорию:
C:WindowsSystem32
- Теперь установите системные файлы из пакета .Net Framework 3.5. Их нужно установить локально из ранее созданного дистрибутива Windows. Зайдите в командную строку (Администратор) и выполните команду:
Dism /online /enable-feature /featurename:NetFx3 /All /Source:D:sourcessxs /LimitAccess
где, D:sourcessxs — путь к установочным файлам .Net Framework 3.5, что расположены на носителе Windows 10.
- Запустится установка .Net Framework 3.5. Требуется некоторое время для завершения процедуры.
- Скачайте и запустите установщик [download id=»13714″].
- Следуйте подсказкам иннсталятора и завершите установку. Затем зайдите в
C:WindowsSystem32
и запустите ранее скопированный файл gpedit.msc
Важно! Редактор создавался до выхода Windows 8 и 10, в нем нет политик, добавленных в эти версии систем.
Способ 2
Для этого способа не требуется дополнительный дистрибутив или файлы версии Windows Pro, но придется некоторые системные файлы переносить вручную. Чтобы запустить редактор:
- Скачайте [download id=»13714″] и установите на свой компьютер.
- Если ваша версия системы x64, не нажимая кнопку «Finish», нажмите Win+R и выполните команду
%WinDir%Temp
- Из папки gpedit скопируйте файлы gpedit.dll, fde.dll, gptext.dll, appmgr.dll, fdeploy.dll, gpedit.msc в директорию C:WindowsSystem32
- Затем скопируйте папки GroupPolicy, GroupPolicyUsers, GPBAK и файл gpedit.msc из директории C:WindowsSysWOW64 в C:WindowsSystem32.
- Перезагрузите ПК и запустите редактор.
Если после запуска появляется ошибка — зайдите в C:WindowsTempgpedit и запустите файл x86.bat или x64.bat в зависимости от разрядности вашей Windows 10.
Возникли вопросы после написания статьи? Поделитесь ими в комментариях или используйте форму обратной связи с администрацией.
Используемые источники:
- https://g-ek.com/kak-otkryit-redaktor-gpedit-windows10
- https://winitpro.ru/index.php/2015/10/02/redaktor-gruppovyx-politik-dlya-windows-10-home-edition/
- https://geekon.media/kak-zapustit-redaktor-lokalnoj-gruppovoj-politiki/