From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Original Windows logo from 1985
Current Windows logo (introduced in 2021)
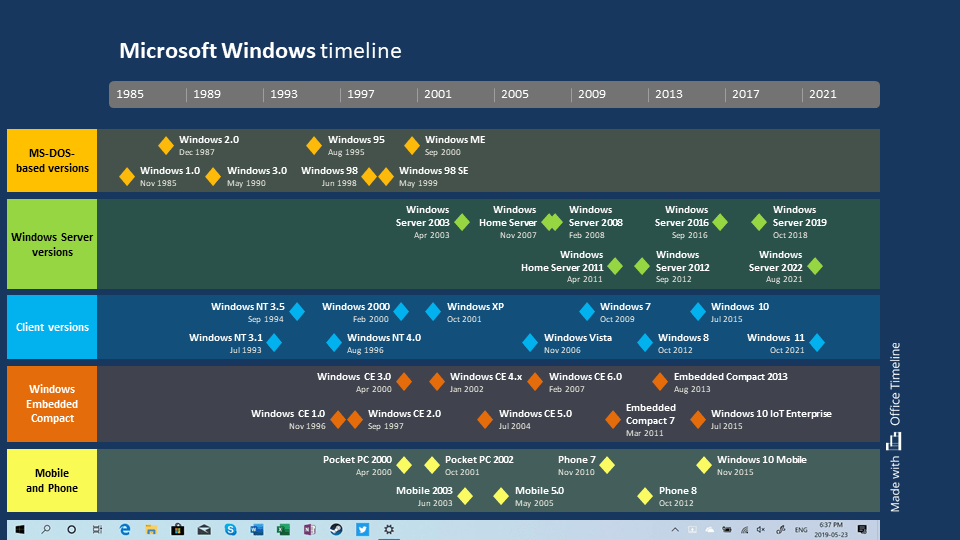
Timeline of Windows releases
Microsoft Windows is a computer operating system developed by Microsoft. It was first launched in 1985 as a graphical operating system built on MS-DOS. The initial version was followed by several subsequent releases, and by the early 1990s, the Windows line had split into two separate lines of releases: Windows 9x for consumers and Windows NT for businesses and enterprises. In the following years, several further variants of Windows would be released: Windows CE in 1996 for embedded systems; Pocket PC in 2000 (renamed to Windows Mobile in 2003 and Windows Phone in 2010) for personal digital assistants and, later, smartphones; Windows Holographic in 2016 for AR/VR headsets; and several other editions.
Personal computer versions[edit]
A «personal computer» version of Windows is considered to be a version that end-users or OEMs can install on personal computers, including desktop computers, laptops, and workstations.
The first five versions of Windows–Windows 1.0, Windows 2.0, Windows 2.1, Windows 3.0, and Windows 3.1–were all based on MS-DOS, and were aimed at both consumers and businesses. However, Windows 3.1 had two separate successors, splitting the Windows line in two: the consumer-focused «Windows 9x» line, consisting of Windows 95, Windows 98, and Windows Me; and the professional Windows NT line, comprising Windows NT 3.1, Windows NT 3.5, Windows NT 3.51, Windows NT 4.0, and Windows 2000. These two lines were reunited into a single line with the NT-based Windows XP; this Windows release succeeded both Windows Me and Windows 2000 and had separate editions for consumer and professional use. Since Windows XP, multiple further versions of Windows have been released, the most recent of which is Windows 11.
| Name | Codename | Release date | Version | Editions | Build number | Architecture | End of support |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Windows 1.01 | Interface Manager | 1985-11-20 | 1.01 | — | — | x86-16 | 2001-12-31 |
| Windows 1.02 | — | 1986-05-14 | 1.02 | — | — | ||
| Windows 1.03 | — | 1986-08-21 | 1.03 | — | — | ||
| Windows 1.04 | — | 1987-04-10 | 1.04 | — | — | ||
| Windows 2.01 | — | 1987-12-09 | 2.01 | — | — | x86-16, IA-32 | |
| Windows 2.03 | — | 1987-12-09 | 2.03 | — | — | ||
| Windows 2.1 | — | 1988-05-27 | 2.10 | — | — | ||
| Windows 2.11 | — | 1989-03-13 | 2.11 | — | — | ||
| Windows 3.0 | — | 1990-05-22 | 3.00 |
|
— | ||
| Windows 3.1 | — | 1992-04-06 | 3.10 |
|
103 | ||
| Sparta[a] | 1992-10 |
|
102 | IA-32 | |||
| Windows NT 3.1 | Razzle[1] | 1993-07-27 | NT 3.1 |
|
528 | IA-32, Alpha, MIPS | 2000-12-31 |
| Windows 3.11 | — | 1993-11-08 | 3.11 |
|
? | x86-16, IA-32 | 2001-12-31 |
| Snowball |
|
300 | IA-32 | ||||
| Windows 3.2 | — | 1993-11-22 | 3.2 |
|
153 | x86-16, IA-32 | |
| Windows NT 3.5 | Daytona | 1994-09-21 | NT 3.5 |
|
807 | IA-32, Alpha, MIPS, PowerPC | |
| Windows NT 3.51 | 1995-05-30 | NT 3.51 |
|
1057 | |||
| Windows 95 | Chicago | 1995-08-24 | 4.00 |
|
950 | IA-32 | |
| Windows NT 4.0 | Shell Update Release | 1996-08-24 | NT 4.0 |
|
1381 | IA-32, Alpha, MIPS, PowerPC | 2004-06-30 |
| Windows 98 | Memphis[b] | 1998-06-25 | 4.10 |
|
1998 | IA-32 | 2006-07-11 |
| Windows 98 Second Edition | — | 1999-05-05 |
|
2222A | |||
| Windows 2000 | Windows NT 5.0 | 2000-02-17 | NT 5.0 |
|
2195 | IA-32 | 2010-07-13 |
| Windows Me | Millennium | 2000-09-14 | 4.90 |
|
3000 | IA-32 | 2006-07-11 |
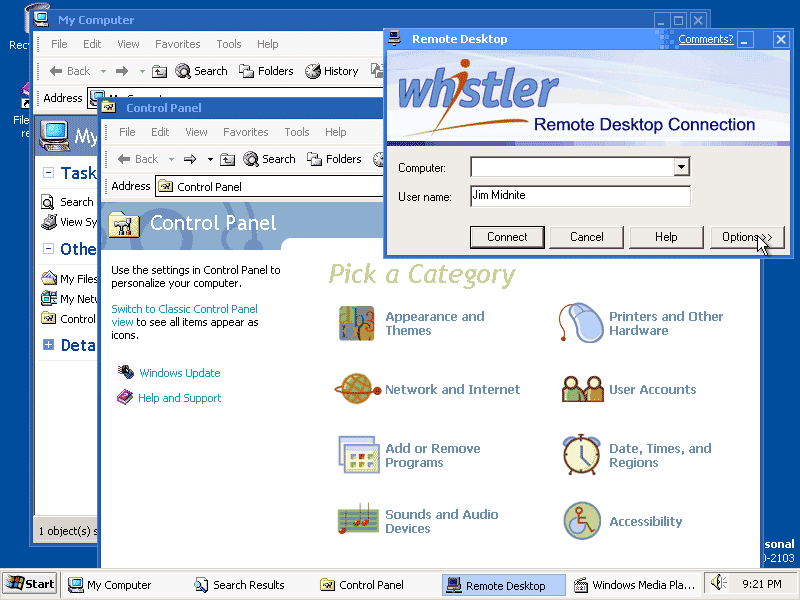
| Windows XP | Whistler | 2001-10-25 | NT 5.1 |
|
2600 | IA-32 | 2014-04-08 |
|
Itanium | ||||||
| Freestyle | 2002-10-29 |
|
IA-32 | ||||
| Harmony | 2003-09-30 |
|
|||||
| Symphony | 2004-10-12 |
|
2700 | ||||
| Emerald | 2005-10-14 |
|
2710 | ||||
| Anvil | 2005-04-25 | NT 5.2 |
|
3790 | x86-64 | ||
| Windows Vista | Longhorn[3] | 2007-01-30 | NT 6.0 |
|
6002[c] | IA-32, x86-64 | 2017-04-11 |
| Windows 7 | Windows 7[4] | 2009-10-22 | NT 6.1 |
|
7601[d] | IA-32, x86-64 | 2020-01-14 |
| Windows 8 | Windows 8 | 2012-10-26 | NT 6.2 |
|
9200 | IA-32, x86-64 | 2016-01-12 |
| Windows 8.1 | Blue | 2013-10-17 | NT 6.3 |
|
9600 | IA-32, x86-64 | 2023-01-10 |
| 2014-05-23[e] |
|
||||||
| Windows 10 version 1507 | Threshold[5][f] | 2015-07-29 | NT 10.0[g][h] |
|
10240 | IA-32, x86-64 | 2025-10-14[7][m] |
| Windows 10 version 1511 | Threshold 2 | 2015-11-10 | 1511 | 10586 | |||
| Windows 10 version 1607 | Redstone 1 | 2016-08-02 | 1607 | 14393 | |||
| Windows 10 version 1703 | Redstone 2[8] | 2017-04-05 | 1703 | 15063 | |||
| Windows 10 version 1709 | Redstone 3[9] | 2017-10-17 | 1709 | 16299 | IA-32, x86-64, ARM64 | ||
| Windows 10 version 1803 | Redstone 4 | 2018-04-30 | 1803 | 17134 | |||
| Windows 10 version 1809 | Redstone 5[10] | 2018-11-13 | 1809 | 17763 | |||
| Windows 10 version 1903 | 19H1[11] | 2019-05-21 | 1903 | 18362 | |||
| Windows 10 version 1909 | Vanadium[n][13] | 2019-11-12 | 1909 | 18363 | |||
| Windows 10 version 2004 | Vibranium[13][14][o] | 2020-05-27 | 2004 | 19041 | |||
| Windows 10 version 20H2 | 2020-10-20 | 20H2 | 19042 | ||||
| Windows 10 version 21H1 | 2021-05-18 | 21H1 | 19043 | ||||
| Windows 10 version 21H2 | 2021-11-16 | 21H2 | 19044 | ||||
| Windows 10 version 22H2 | 2022-10-18 | 22H2 | 19045 | ||||
| Windows 11 version 21H2 | Sun Valley[p] | 2021-10-05 | 21H2 |
|
22000 | x86-64, ARM64 | 2023-10-10[q] |
| Windows 11 version 22H2 | Sun Valley 2 | 2022-09-20 | 22H2 | 22621 | 2024-10-14[q] |
Mobile versions[edit]
Mobile versions refer to versions of Windows that can run on smartphones or personal digital assistants.
Pocket PC 2000 logo
Windows Phone 7 logo
Windows Phone 8 logo
Windows Phone 8.1 logo
Logo used for Windows 10 and Windows 10 Mobile
| Name | Codename | Architecture | Release date |
Version Number |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pocket PC 2000 | Rapier | ARMv4, MIPS, SH-3 | 2000-04-19 | CE 3.0 |
| Pocket PC 2002 | Merlin | ARMv4 | 2001-10-04 | |
| Windows Mobile 2003 | Ozone | ARMv5 | 2003-06-23 | CE 4.x |
| Windows Mobile 2003 SE | — | 2004-03-24 | ||
| Windows Mobile 5.0 | Magneto | 2005-05-09 | CE 5.0 | |
| Windows Mobile 6.0 | Crossbow | 2007-02-12 | ||
| Windows Mobile 6.1 | — | 2008-04-01 | CE 5.2 | |
| Windows Mobile 6.1.4 | 6 on 6 | 2008-11-11[16] | ||
| Windows Mobile 6.5 | Titanium | 2009-05-11 | CE 6.0 | |
| Windows Phone 7[r] | — | ARMv7 | 2010-10-29 | |
| Windows Phone 7.5 | Mango | 2011-09-27 | ||
| Windows Phone 7.8 | — | 2013-02-01 | ||
| Windows Phone 8 | Apollo | 2012-10-29 | NT 6.2 | |
| Windows Phone 8.1 | Blue | 2014-04-14 | NT 6.3 | |
| Windows 10 Mobile, version 1511 | Threshold 2 | 2015-11-12 | 1511 | |
| Windows 10 Mobile, version 1607 | Redstone 1 | 2016-08-16 | 1607 | |
| Windows 10 Mobile, version 1703 | Redstone 2 | 2017-04-24 | 1703 | |
| Windows 10 Mobile, version 1709 | feature2[17] | 2017-10-24 | 1709 |
Server versions[edit]
| Name | Release date | Version number | Editions | Build number | Architecture | End of support |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Windows NT 3.1 | 1993-07-27 | NT 3.1 |
|
528 | IA-32, Alpha, MIPS | 2000-12-31 |
| Windows NT 3.5 | 1994-09-20 | NT 3.5 |
|
807 | IA-32, Alpha, MIPS, PowerPC | 2001-12-31 |
| Windows NT 3.51 | 1995-05-29 | NT 3.51 |
|
1057 | 2001-12-31 | |
| Windows NT 4.0 | 1996-07-29 | NT 4.0 |
|
1381 | 2004-12-31 | |
| Windows 2000 | 2000-02-17 | NT 5.0 |
|
2195 | IA-32 | 2010-07-13 |
| Windows Server 2003 | 2003-04-24 | NT 5.2 |
|
3790 | IA-32, x86-64, Itanium | 2015-07-14 |
| Windows Server 2003 R2 | 2005-12-06 | 2015-07-14 | ||||
| Windows Server 2008 | 2008-02-27 | NT 6.0 |
|
6002[c] | IA-32, x86-64, Itanium | 2020-01-14 |
| Windows Server 2008 R2 | 2009-10-22 | NT 6.1 | 7601[d] | x86-64, Itanium | 2020-01-14 | |
| Windows Server 2012 | 2012-09-04 | NT 6.2 |
|
9200 | x86-64 | 2023-10-10 |
| Windows Server 2012 R2 | 2013-10-17 | NT 6.3 | 9600 | 2023-10-10 | ||
| Windows Server 2016 | 2016-10-12 | 1607[18] |
|
14393 | 2027-01-12 | |
| Windows Server, version 1709[19] | 2017-10-17 | 1709 | 16299 | 2019-04-09 | ||
| Windows Server, version 1803[20] | 2018-04-30 | 1803 | 17134 | 2019-11-12 | ||
| Windows Server, version 1809 | 2018-11-13[21] | 1809 | 17763 | 2020-11-10 | ||
| Windows Server 2019[18] | 2029-01-09[18] | |||||
| Windows Server, version 1903[18] | 2019-05-21 | 1903 | 18362 | 2020-12-08[18] | ||
| Windows Server, version 1909[18] | 2019-11-12 | 1909 | 18363 | 2021-05-11[18] | ||
| Windows Server, version 2004[22] | 2020-06-26 | 2004 | 19041 | 2021-12-14[18] | ||
| Windows Server, version 20H2[22] | 2020-10-20 | 20H2 | 19042 | 2022-08-09[18] | ||
| Windows Server 2022 | 2021-08-18 | 21H2[23] | 20348 | 2031-10-14[18] |
High-performance computing (HPC) servers[edit]
| Name | Codename | Release date | Based on |
|---|---|---|---|
| Windows Compute Cluster Server 2003 | — | 2006-06-09 | Windows Server 2003 R2 |
| Windows HPC Server 2008 | Socrates | 2008-09-22 | Windows Server 2008 |
| Windows HPC Server 2008 R2 | — | 2010-09-20 | Windows Server 2008 R2 |
Windows Essential Business Server[edit]
| Name | Codename | Release date | End-of-support date | Build number | Based on |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Windows Essential Business Server 2008 | Centro | 2008-09-15 | 2020-01-14 | 5700 | Windows Server 2008 |
Windows Home Server[edit]
| Name | Codename | Release date | End-of-support date | Based on |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Windows Home Server | Quattro | 2007-11-04 | 2013-01-08 | Windows Server 2003 R2 |
| Windows Home Server 2011 | Vail | 2011-04-06 | 2016-04-12 | Windows Server 2008 R2 |
Windows MultiPoint Server[edit]
Windows MultiPoint Server was an operating system based on Windows Server. It was succeeded by the MultiPoint Services role in Windows Server 2016 and Windows Server version 1709. It was no longer being developed in Windows Server version 1803 and later versions.
| Name | Codename | Release date | End-of-support date | Version number | Build number | Based on |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Windows MultiPoint Server 2010 | Solution Server | 2010-02-24 | 2020-07-14 | NT 6.1 | 537 | Windows Server 2008 R2 |
| Windows MultiPoint Server 2011 | WMS 2 | 2011-05-12 | 2021-07-13 | 1600 | Windows Server 2008 R2 Service Pack 1 | |
| Windows MultiPoint Server 2012 | WMS 3 | 2012-10-30 | 2023-10-10 | NT 6.2 | 2506 | Windows Server 2012 |
Windows Small Business Server[edit]
| Name | Codename | Release date | End-of-support date | Build number | Based on |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Small Business Server 2000 | — | 2001-02-21 | 2010-07-13 | 1343 | Windows 2000 Server |
| Windows Small Business Server 2003 | Bobcat | 2003-10-09 | 2015-07-14 | 2893 | Windows Server 2003 |
| Windows Small Business Server 2008 | Cougar | 2008-08-21 | 2020-01-14 | 5601 | Windows Server 2008 |
| Windows Small Business Server 2011 Standard | Windows Small Business Server 7 | 2010-12-13 | 2020-01-14 | 7900 | Windows Server 2008 R2 |
| Windows Small Business Server 2011 Essentials | Colorado | 2011-06-28 | 2013-01-05 | 8800 |
Device versions[edit]
ARM-based tablets[edit]
Windows RT logo
The Surface RT (shown with keyboard cover attached) was the flagship Windows RT device upon its release.
In 2012 and 2013, Microsoft released versions of Windows specially designed to run on ARM-based tablets; these versions of Windows were based on Windows 8 and Windows 8.1, respectively, although the standard versions could run on x86-based tablets without modification. Upon the release of Windows 10 in 2015, the ARM-specific version for large tablets was discontinued; large tablets (such as the Surface Pro 4) were only released with x86 processors and could run the full version of Windows 10. Windows 10 Mobile had the ability to be installed on smaller tablets (up to nine inches);[24] however, very few such tablets were released, and Windows 10 Mobile primarily ended up only running on smartphones until its discontinuation. In 2017, the full version of Windows 10 gained the ability to run on ARM, which rendered a specific version of Windows for ARM-based tablets unnecessary.
| Name | Release date | Version number | Build number | Based on |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Windows RT | 2012-10-26 | NT 6.2 | 9200 | Windows 8 |
| Windows RT 8.1 | 2013-10-18 | NT 6.3 | 9600 | Windows 8.1 |
Mixed reality and virtual reality headsets[edit]
| Name | Build number |
|---|---|
| Windows 10 Holographic, version 1607[25] | 14393 |
| Windows 10 Holographic, version 1803[25] | 17134 |
| Windows 10 Holographic, version 1809[25] | 17763 |
| Windows Holographic, version 1903[26] | 18362 |
| Windows Holographic, version 2004[26] | 19041 |
| Windows Holographic, version 20H2[26] | 19041 |
| Windows Holographic, version 21H1[26] | 20346 |
| Windows Holographic, version 21H2[26] | 20348 |
| Windows Holographic, version 22H1[26] | 20348 |
Surface Hub[edit]
Microsoft originally announced the Surface Hub, an interactive whiteboard, in January 2015. The Surface Hub family of devices runs a custom variant of Windows 10 known as Windows 10 Team.
| Name | Build number |
|---|---|
| Windows 10 Team, version 1511[27] | 10586 |
| Windows 10 Team, version 1607[27] | 14393 |
| Windows 10 Team, version 1703[27] | 15063 |
| Windows 10 Team, version 20H2[27] | 19042 |
Windows XP-based tablets[edit]
Tablet computer running a «Tablet PC Edition» of Windows XP
Two versions of Windows XP were released that were optimized for tablets. Beginning with Windows Vista, all tablet-specific components were included in the main version of the operating system.
| Name | Codename | Release date | Version number | Build number | Based on |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Windows XP Tablet PC Edition | — | 2002-11-07 | NT 5.1 | 2600 | Windows XP |
| Windows XP Tablet PC Edition 2005 | Lonestar | 2004-08 | NT 5.1 | 2600 | Windows XP |
Embedded versions[edit]
Windows Embedded Compact[edit]
| Name | Codename(s) | Release date |
|---|---|---|
| Windows CE 1.0 | Pegasus; Alder | 1996-11-16 |
| Windows CE 2.0 | Jupiter; Birch | 1997-09-29 |
| Windows CE 2.1 | — | 1998-07 |
| Windows CE 2.11 | — | 1998-10 |
| Windows CE 2.12 | — | 1999 |
| Windows CE 3.0 | Cedar; Galileo | 2000 |
| Windows CE 4.0 | Talisker | 2002-01-07 |
| Windows CE 4.1 | Jameson | 2002-07-30 |
| Windows CE 4.2 | McKendric | 2003-04-23 |
| Windows CE 5.0 | Macallan | 2004-07-09 |
| Windows Embedded CE 6.0 | Yamakazi | 2006-11-01 |
| Windows Embedded Compact 7 | Chelan | 2011-03-01 |
| Windows Embedded Compact 2013 | — | 2013-06-13 |
Windows Embedded Standard[edit]
| Name | Codename | Release date | Based on |
|---|---|---|---|
| Windows NT Embedded 4.0 | Impala | 1999-08-30 | Windows NT 4.0 Workstation |
| Windows XP Embedded | Mantis | 2001-11-28 | Windows XP Professional |
| Windows Embedded Standard 2009 | — | 2008-12-14 | Windows XP Service Pack 3 |
| Windows Embedded Standard 7 | Quebec | 2010 | Windows 7 |
| Windows Embedded 8 | — | 2013 | Windows 8 |
| Windows Embedded 8.1 | — | 2013 | Windows 8.1 |
Other embedded versions[edit]
- Windows Embedded Industry
- Windows Embedded Automotive
Cancelled versions[edit]
Cancelled personal computer versions[edit]
| Codename | Intended name | Discontinuation | Version | Latest known build number | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cairo | — | 1996 | NT 4.0 | 1175 | Originally announced in 1991 |
| Nashville[t] | Windows 96 | — | 4.1 | 999 | Planned to be released between Windows 95 and Windows 98 |
| Neptune | — | Early 2000 | NT 5.50 | 5111 | The first planned version of Microsoft Windows NT to have a consumer edition variant, based on the Windows 2000 codebase. A version was sent out to testers but was never released.[28] The teams working on Neptune and Odyssey combined to work on Windows XP. |
| Odyssey | — | Early 2000 | NT 6.0[29] | — | Planned to be the successor of Windows 2000. The teams working on Neptune and Odyssey combined to work on Windows XP. |
| Triton | — | — | — | — | Planned to be the successor of Windows Neptune and had been scheduled to be released in March 2001 |
| Blackcomb | — | 2006-01 | — | — | Blackcomb was originally planned to be a release of Windows following Windows XP. However, due to the large feature scope planned for Blackcomb, a smaller release codenamed «Longhorn» was planned first, and Blackcomb was delayed to 2003/2004. Both projects faced delays; Longhorn would go on to be released to consumers as «Windows Vista» in January 2007, while development on Blackcomb continued until the Blackcomb project was renamed «Vienna» in early 2006. |
| Vienna | — | 2007-07[u] | — | — | Vienna replaced Blackcomb and was intended as Windows Vista’s successor. Vienna was eventually cancelled in favor of a new project codenamed «Windows 7» (which went on to be released in 2009 with the same name). |
| Polaris | — | 2018 | — | 16299 | Cancelled in favor of Santorini |
| Santorini[v] | Windows 10X | 2021-05-18[w][31] | 21H1 | 20279 | Microsoft had been reported as working on a new «lite» version of Windows as early as December 2018.[32] Such a version was officially announced under the name «Windows 10X» at an event in October 2019; the operating system was intended to first launch on dual-screen devices. In May 2020, Microsoft announced that Windows 10X would instead be launching on single-screen PCs, such as laptops and 2-in-1 devices, first.[33] However, on May 18, 2021, Microsoft announced that Windows 10X would not be launching (at least not in 2021); many of its features were rolled into Windows 11 instead. |
Cancelled mobile versions[edit]
| Codename | Intended name | Discontinuation | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Photon | Windows Mobile 7 | September 2008[34] | Originally a successor of Windows Mobile, it had been scrapped for Windows Phone 7[35][36] |
| Phoenix | — | Early 2017 | Cancelled when Microsoft «wound down» its phone efforts.[37] |
| Andromeda | — | Mid-2018 | Much of the work that was put into Andromeda was migrated into Santorini. The Surface Duo, a dual-screen Android-powered smartphone launched by Microsoft in 2020, was loosely based on the prototype hardware that had been used to test Andromeda.[38] |
Cancelled server versions[edit]
| Codename | Intended name | Discontinuation | Latest known build number |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cascades | Windows Essential Business Server 2008 R2 | April 7, 2010[w] | 7224 |
See also[edit]
- List of Microsoft operating systems
- Microsoft Windows version history
- Windows 10 version history
- Windows 11 version history
- Comparison of Microsoft Windows versions
- List of Microsoft codenames
Notes[edit]
- ^ Originally codenamed Winball
- ^ Has also been called ChiCairo and London.[2]
- ^ a b Windows Vista and Windows Server 2008 originally had the build number 6000 when they were first released; the build number was increased by one with each of the two subsequent Service Packs.
- ^ a b Windows 7 and Windows Server 2008 R2 originally had the build number 7600 when they were first released; the build number was increased to 7601 with the release of Service Pack 1.
- ^ Announcement date
- ^ Retroactively referred to as Threshold 1
- ^ Early preview builds of Windows 10 had the version number NT 6.4.[6]
- ^ Retroactively referred to as version 1507
- ^ Windows 10 Pro for Workstations became a Windows 10 edition starting with version 1709. Prior versions of Windows 10 do not include this as an edition.
- ^ Windows 10 versions 1507 and 1511 do not include a «Windows 10 Pro Education» edition; that edition was only added with version 1607.
- ^ Windows 10 S is only available in version 1703 and 1709.
- ^ Windows 10 Enterprise LTSC is only available for versions 1507, 1607, 1809, and 21H2. It had originally been named Windows 10 Enterprise LTSB in version 1507.
- ^ October 14, 2025 is the general end-of-support date for Windows 10. Specific versions and editions of Windows 10 have different end of support dates; see Windows 10 version history for a breakdown of dates by version and edition.
- ^ Originally codenamed 19H2[12]
- ^ Vibranium was the codename for Windows 10 version 2004. During the 20H2, 21H1, and 21H2 development cycles, builds were compiled under the codenames Manganese, Iron, and Cobalt, respectively. However, the versions of 20H2 and 21H1 that were released were built on top of version 2004 instead of these new builds. Windows 10 version 21H2 was similarly built on top of the Vibranium/2004 codebase instead of the Cobalt codebase; Cobalt builds were instead used as the base for the first version of Windows 11 (which had a core based on Cobalt in addition to a UI codenamed Sun Valley, and which also carries the version 21H2).
- ^ The core of Windows 11 version 21H2 is codenamed Cobalt;[15] the «Sun Valley» codename refers to the UI layer of Windows 11 version 21H2 and is commonly used to address Windows 11 version 21H2 as a whole.
- ^ a b The end-of-support date listed in the table refers to Home and Pro editions. The date for other editions, such as Education and Enterprise, may differ.
- ^ Originally named «Windows Phone 7 Series»
- ^ Between versions 1709 and 20H2 of Windows Server, the «Windows Server Essentials» edition of Windows Server was only included in Windows Server 2019.
- ^ Nashville was originally codenamed Cleveland.
- ^ July 2007 is when it was reported that the Vista’s successor was codenamed «7,» rather than «Vienna,» indicating that Vienna’s discontinuation had occurred by then. However, Vienna may have been cancelled prior to then.
- ^ While Santorini was the general codename for Windows 10X, Centaurus was the specific codename for Windows 10X on foldable PCs and Pegasus was the codename for Windows 10X on «traditional» PCs (such as laptops or 2-in-1 computers).[30]
- ^ a b Date refers to when the cancellation of the operating system was announced. The decision for the operating system to be cancelled may have occurred prior to then.
References[edit]
- ^ «Random internal Windows terminology:IDW, Razzle, and their forgotten partners IDS and Dazzle». The Old New Thing. 2018-12-24. Retrieved 2020-04-09.
- ^ «Systems Release Strategy — Draft:10/10/93» (PDF). Slated Antitrust. November 10, 1993.
- ^ Martens, China (July 22, 2005). «Update:Microsoft’s Longhorn becomes Windows Vista». IDG Communications, Inc. Retrieved 13 June 2021.
Microsoft Corp. has announced the official name for its upcoming operating system, previously known under the code name Longhorn. The operating system, now due out in 2006, will be called Windows Vista
- ^ «What was the code name for Windows 7?». The Old New Thing. 2019-07-22. Retrieved 2021-05-09.
- ^ Foley, Mary Jo. «Microsoft to share Windows Threshold plans at Build 2014 show: Report». ZDNet. ZDNET. Retrieved 7 April 2022.
- ^ Warren, Tom. «Windows 10 won’t be Windows 6.4». The Verge. Vox Media, LLC. Retrieved 3 January 2022.
Windows 10 Technical Preview builds are currently identified as Windows NT 6.4, but future builds will include the change
- ^ Warren, Tom. «Microsoft to end Windows 10 support on October 14th, 2025». The Verge. Vox Media, LLC. Retrieved 5 January 2022.
- ^ Bowden, Zac (August 4, 2016). «Microsoft confirms two major updates planned for Windows 10 in 2017». Windows Central. Future US, Inc. Retrieved 13 June 2021.
Windows Central understands that the first major update for 2017 (codenamed Redstone 2) will release in the early part of 2017.
- ^ Bowden, Zac (August 4, 2016). «Microsoft confirms two major updates planned for Windows 10 in 2017». Windows Central. Future US, Inc. Retrieved 13 June 2021.
The second major update scheduled for 2017 is codenamed «Redstone 3»
- ^ Woods, Rich. «Windows 10 Redstone 5 is officially version 1809». Neowin. Neowin LLC. Retrieved 13 June 2021.
Redstone 5 is now officially Windows 10 version 1809.
- ^ Hassan, Mehedi (October 31, 2018). «Windows 10’s Next Major Updates Will Be Codenamed Vanadium, Vibranium». Thurrott. BWW Media Group. Retrieved 13 June 2021.
Windows 10’s next major update is codenamed 19H1.
- ^ Hassan, Mehedi (October 31, 2018). «Windows 10’s Next Major Updates Will Be Codenamed Vanadium, Vibranium». Thurrott. BWW Media Group. Retrieved 13 June 2021.
This means the next Windows 10 update, previously codenamed 19H2, will be called Vanadium (comes after Titanium/19H1).
- ^ a b Brown, Matt (October 31, 2018). «Next Windows 10 updates reportedly codenamed ‘Vanadium’ and ‘Vibranium’«. Windows Central. Future US, Inc. Retrieved 13 June 2021.
- ^ Hassan, Mehedi (October 31, 2018). «Windows 10’s Next Major Updates Will Be Codenamed Vanadium, Vibranium». Thurrott. BWW Media Group. Retrieved 13 June 2021.
- ^ Parmar, Mayank (3 September 2021). «Windows 11 Build 22449 is now available with new loading animation». Windows Latest. Retrieved 4 September 2021.
Windows 11 version 21H2 (shipping on October 5)=Cobalt (Co).
- ^ Foley, Mary Jo. «Microsoft starts rolling out IE 6 for Windows Mobile». ZDNET. ZDNET. Retrieved 23 September 2022.
The new IE 6 bits were released on November 11 as part of the Windows Mobile 6.1.4 release from Microsoft’s Download Center Web site.
- ^ Woods, Rich. «It’s finally dead: Windows 10 Mobile is no longer supported after today». Neowin. Neowin LLC. Retrieved 23 December 2021.
Windows 10 feature2 ended up being version 1709, and it was the final feature update for Windows 10 Mobile.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j Gerend, Jason. «Windows Server release information». docs.microsoft.com. Retrieved 2020-09-09.
- ^ «What’s New in Windows Server version 1709». Microsoft Docs. Microsoft. Retrieved 2 January 2022.
- ^ «Windows Server, version 1803 end of servicing on November 12, 2019». Microsoft Docs. Microsoft. Retrieved 2 January 2022.
- ^ Woods, Rich. «Microsoft re-releases Windows Server 2019 and Windows Server, version 1809». Neowin. Neowin LLC. Retrieved 2 January 2022.
- ^ a b Gerend, Jason. «Windows Server servicing channels». docs.microsoft.com. Retrieved 2020-09-09.
- ^ Sharma, Mayank. «Microsoft has snuck out its Windows Server 2022 release». TechRadar. Future US, Inc. Retrieved 3 January 2022.
Windows Server 2022 identifies itself as version 21H2
- ^ Foley, Mary Jo. «Microsoft ups allowable Windows 10 Mobile screen size to nearly nine inches». ZDNET. ZDNET. Retrieved 11 September 2022.
- ^ a b c «HoloLens 1st (gen) release notes». Retrieved 18 July 2021.
- ^ a b c d e f «HoloLens 2 release notes». Retrieved 18 July 2021.
- ^ a b c d «Surface Hub update history». Retrieved 18 July 2021.
- ^ «Microsoft combines Neptune, Odyssey into Whistler». CNN. January 27, 2000. Archived from the original on September 1, 2008. Retrieved January 6, 2010.
- ^ «Windows Odyssey». Retrieved 16 July 2021.
Knowing that Neptune is 5.50, it’s only logical to conclude Odyssey was to be 6.0
- ^ Bowden, Zac (October 30, 2019). «Windows Core OS:The complete guide». Windows Central. Future US, Inc. Retrieved 14 June 2021.
- ^ Warren, Tom (May 18, 2021). «Microsoft confirms Windows 10X is dead». The Verge. Vox Media, LLC. Retrieved 14 June 2021.
- ^ Sams, Brad (December 3, 2018). «What is Windows Lite? It’s Microsoft’s Chrome OS Killer». Petri. BWW Media Group. Retrieved 16 July 2021.
- ^ Bowden, Zac (May 4, 2020). «Windows 10X will now launch first on single-screen PCs». Windows Central. Future US, Inc. Retrieved 16 July 2021.
- ^ Litvinenko, Yuri. «Microsoft’s Project Photon:A Stunted Effort to Rebuild Windows Mobile». Retrieved 16 July 2021.
Checking reports against each other provides the grounds to assume Microsoft kept working on Photon till September 2008.
- ^ «Windows Mobile 7 vs Windows Phone 7». Popular Pages at brighthub.com. May 20, 2011. Retrieved December 15, 2016.
- ^ «Revealed:Original Windows Mobile 7 UI». neowin.net. February 20, 2010. Retrieved December 15, 2016.
- ^ Bowden, Zac (September 18, 2020). «Project Andromeda:The secret history of Windows on Surface Duo». Windows Central. Future US, Inc. Retrieved 16 July 2021.
Microsoft had originally planned to ship CShell on Windows 10 Mobile under the codename Pheonix [sic], but that plan very quickly went away once the company decided to wind down its existing phone efforts in early 2017.
- ^ Bowden, Zac (September 18, 2020). «Project Andromeda:The secret history of Windows on Surface Duo». Windows Central. Future US, Inc. Retrieved 16 July 2021.
The Windows operating system (Windows OS) refers to a family of operating systems developed by Microsoft Corporation. We look at the history of Windows OS from 1985 to present day.
The Windows operating system (Windows OS) for desktop PCs is more formally called Microsoft Windows and is actually a family of operating systems for personal computers. Windows has traditionally dominated the personal computer world, running, by some estimates, more than 75 percent of all personal computers. Beginning in the early 2000s, Windows dominance has lessened with the growth of the Linux and Mac operating systems.
Windows provides a graphical user interface (GUI), virtual memory management, multitasking, and support for many peripheral devices. In addition to Windows operating systems for personal computers, Microsoft also offers operating systems for servers and mobile devices.
Windows is also the foundation for the Microsoft Office productivity suite. Introduced in 1990 as a Windows-only family of applications for desktop computers, Office has grown to become the world’s most widely used productivity suite, with windowscentral.com reporting an estimated 1.2 billion + user worldwide as of 2016.
Microsoft Windows Operating Systems for PCs
The following details the history of MS-DOS and Windows operating systems designed for personal computers (PCs).
MS-DOS – Microsoft Disk Operating System
Release date: August 1981
Cost: $40 USD
Originally developed by Microsoft for IBM, MS-DOS was the standard operating system for IBM-compatible personal computers. The initial versions of DOS were very simple and resembled another operating system called CP/M. Subsequent versions have become increasingly sophisticated as they incorporated features of minicomputer operating systems.
Windows 1.0
Source: GUIdebook Gallery
Initial release date: November 20, 1985
Cost: $99 USD
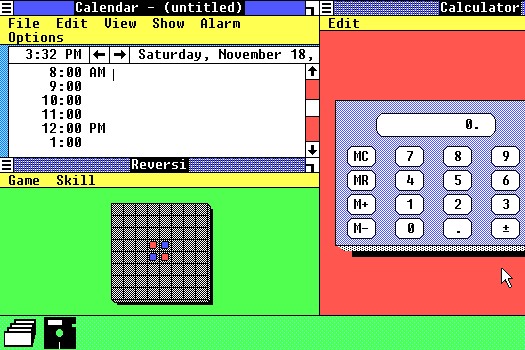
Introduced in 1985, Microsoft Windows 1.0 was named due to the computing boxes, or “windows” that represented a fundamental aspect of the operating system. Instead of typing MS-DOS commands, Windows 1.0 allowed users to point and click to access the windows.
Windows 2.0
Source: GUIdebook Gallery
Initial release date: December 9, 1987
Cost: $100 USD
In 1987 Microsoft released Windows 2.0, which was designed for the designed for the Intel 286 processor. This version added desktop icons, keyboard shortcuts and improved graphics support.
Windows 3.0
Source: GUIdebook Gallery
Initial release date: May 22, 1990
Cost: $149.95 USD new; $79.95 USD upgrade
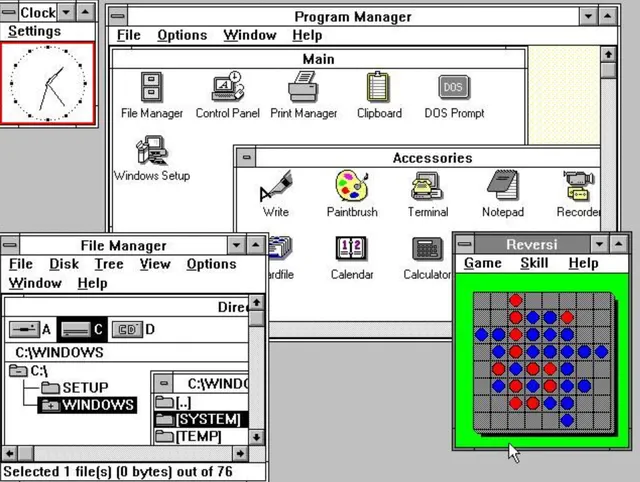
Windows 3.0 was released in May, 1900 offering better icons, performance and advanced graphics with 16 colors designed for Intel 386 processors. This version was the first release that provided the standard “look and feel” of Microsoft Windows for many years to come. Windows 3.0 included Program Manager, File Manager, Print Manager and games like Hearts, Minesweeper, and Solitaire. Microsoft released Windows 3.1 in 1992.
Windows NT 3.1 – 4.0
Source: GUIdebook Gallery
Initial release date: July 27, 1993
Cost: $495 USD new; $295 USD upgrade
Windows NT (New Technology) was a 32-bit operating system that supported preemptive multitasking. There are actually two versions of Windows NT: Windows NT Server, designed to act as a server in networks, and Windows NT Workstation for stand-alone or client workstations.
Windows 95
Source: GUIdebook Gallery
Initial release date: August 24, 1995
Cost: $209.95 USD new; $109.95 USD upgrade
Windows 95 was a major upgrade to the Windows operating system. This OS was a significant advancement over its precursor, Windows 3.1. In addition to sporting a new user interface, Windows 95 also included a number of important internal improvements. Perhaps most important, it supported 32-bit applications, which meant that applications written specifically for this operating system would run much faster.
Although Windows 95 was able to run older Windows and DOS applications, it essentially removed DOS as the underlying platform. This resulted in the removal of many of the old DOS limitations, such as 640K of main memory and 8-character filenames. Other important features in this operating system were the ability to automatically detect and configure installed hardware (Plug-and-Play).
Windows 98
Source: GUIdebook Gallery
Initial release date: June 25, 1998
Cost: $209.95 USD new; $109.95 USD upgrade
Windows 98 supported a number of new technologies, including FAT32, AGP, MMX, USB, DVD, and ACPI. Its most visible feature, though, was the Active Desktop, which integrated the Web browser (Internet Explorer) with the operating system. From the user’s point of view, there was no difference between accessing a document residing locally on the user’s hard disk or on a Web server halfway around the world.
Windows 2000
Source: GUIdebook Gallery
Initial release date: February 17, 2000
Cost: $319 USD new; $149 USD upgrade
Often abbreviated as “W2K,” Windows 2000 was an operating system for business desktop and laptop systems to run software applications, connect to Internet and intranet sites, and access files, printers, and network resources. Microsoft released four versions of Windows 2000: Professional (for business desktop and laptop systems); Server (both a Web server and an office server); Advanced Server (for line-of-business applications); and Datacenter Server (for high-traffic computer networks).
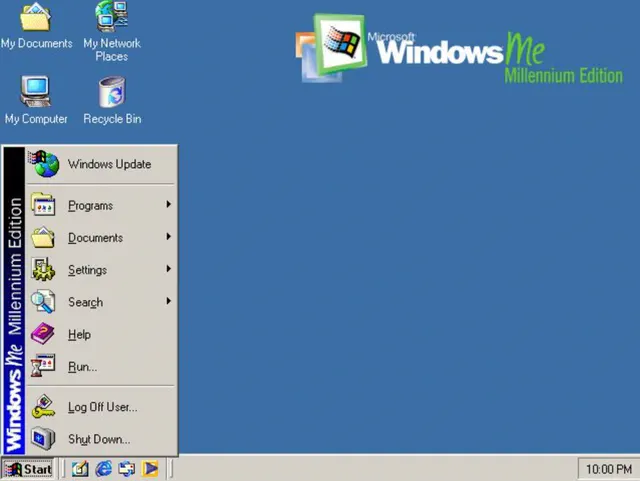
Windows Millennium Edition (ME)
Source: GUIdebook Gallery
Initial release date: June 19, 2000
Cost: $209 USD new; $109 USD upgrade
The Windows Millennium Edition, called “Windows Me” was an update to the Windows 98 core and included some features that would be part of the Windows 2000 operating system. This version also removed the “Boot in DOS” option.
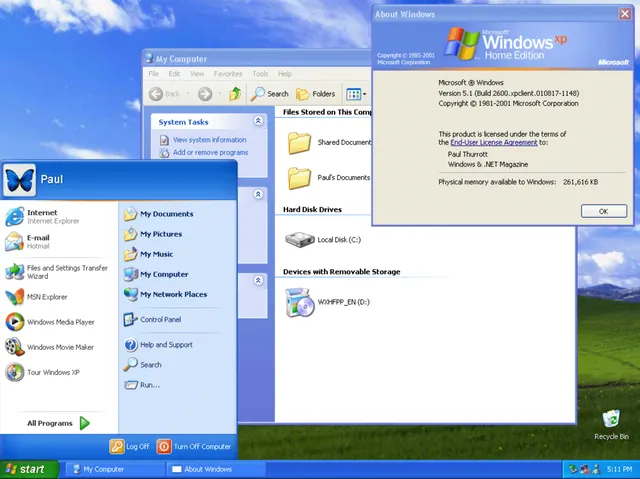
Windows XP
Source: GUIdebook Gallery
Initial release date: October 25, 2001
Cost:
- Home: $199 USD new; $99 USD upgrade
- Professional: $299 USD new; $199 upgrade
Windows XP was released in 2001. Along with a redesigned look and feel to the user interface, the new operating system was built on the Windows 2000 kernel, giving the user a more stable and reliable environment than previous versions of Windows. Windows XP came in two versions, Home and Professional. Microsoft focused on mobility for both editions and including plug-and-play features for connecting to wireless networks. The operating system also utilized the 802.11x wireless security standard. Windows XP went on to become one of Microsoft’s best-selling products.
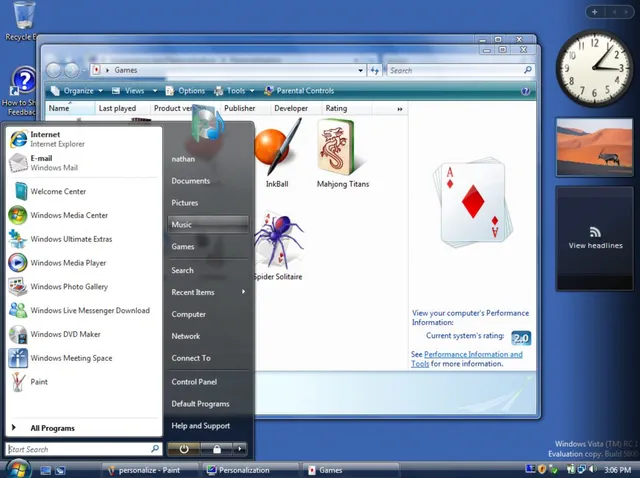
Windows Vista
Source: GUIdebook Gallery
Initial release date: November 30, 2006 (corporate); January 30, 2007 (public)
Cost:
- Home Basic: $199 USD new; $99.95 USD upgrade
- Home Premium: $239 USD new; $159 USD upgrade
- Business: $299 USD new; $199 upgrade
- Ultimate: $399 USD new; $259 USD upgrade
Windows Vista offered an advancement in reliability, security, ease of deployment, performance and manageability over Windows XP. New in this version were capabilities to detect hardware problems before they occurred, security features to protect against the latest generation of threats, a faster start-up time, and low power consumption when placed in the new sleep state. In many cases, Windows Vista was noticeably more responsive than Windows XP on identical hardware. Windows Vista simplified and centralized desktop configuration management, which reduced the cost of keeping systems updated.
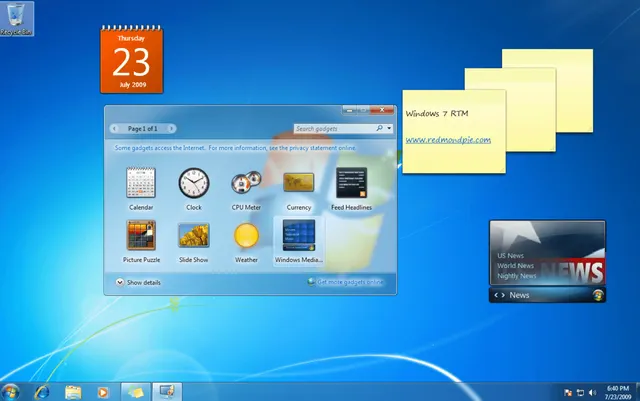
Windows 7
Source: Lifewire
Initial release date: October 22, 2009
Cost:
- Home Premium: $199.99 USD new; $119.99 USD upgrade
- Business: $299.99 USD new; $199.99 upgrade
- Ultimate: $319.99 USD new; $219.99 USD upgrade
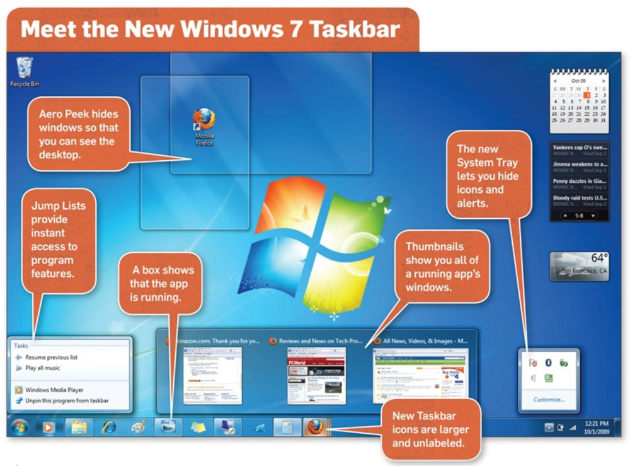
Windows 7 was released in conjunction with Windows Server 2008 R2, Windows 7’s server counterpart. Enhancements and new features in Windows 7 included multi-touch support, Internet Explorer 8, improved performance, faster start-up time, Aero Snap, Aero Shake, support for virtual hard disks, a new and improved Windows Media Center, and improved security.
Windows 8
Source: Ars Technica
Initial release date: October 26, 2012
Cost:
- Windows 8: $119.99 USD
- Windows 8 Pro: $199.99 USD
Windows 8 was a completely redesigned operating system that’s been developed from the ground up with touchscreen use in mind as well as near-instant-on capabilities that enable a Windows 8 PC to load and start up in a matter of seconds rather than in minutes.
Windows 8 replaced the more traditional Microsoft Windows OS look and feel with a new “Metro” design system interface that first debuted in the Windows Phone 7 mobile operating system. The Metro user interface primarily consisted of a “Start screen” made up of “Live Tiles,” which linked to applications and features that were dynamic and updated in real time. Windows 8 supported both x86 PCs and ARM processors.
Windows 10
Source: Microsoft
Initial release date: July 29, 2015
Cost:
- Windows 10 Home: $139 USD
- Windows 10 Pro: $199.99 USD
- Windows 10 Pro for Workstations: $309 USD
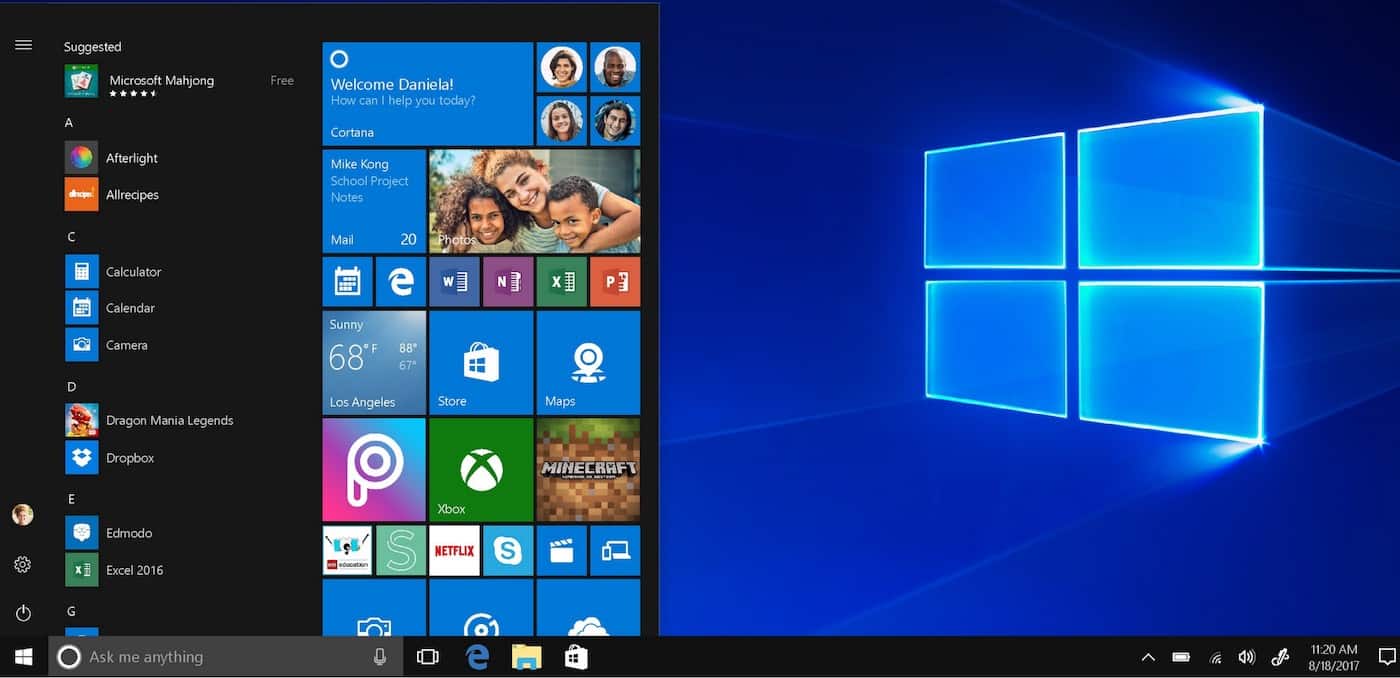
Windows 10 was the successor to Windows 8. Windows 10 debuted on July 29, 2015, following a “technical preview” beta release of the new operating system (Fall 2014) and a “consumer preview” beta (Early 2015). Windows 10 featured fast start-up and resume, built-in security, and the return of the Start Menu in an expanded form. This version of Windows also featured Microsoft Edge, Microsoft’s new browser. Any qualified device (such as tablets, PCs, smartphones and Xbox consoles) was able to upgrade to Windows 10, including those with pirated copies of Windows.
Windows 11
Source: PCMag
Initial release date: October 5, 2021
Cost: Free (for Windows 10 users)
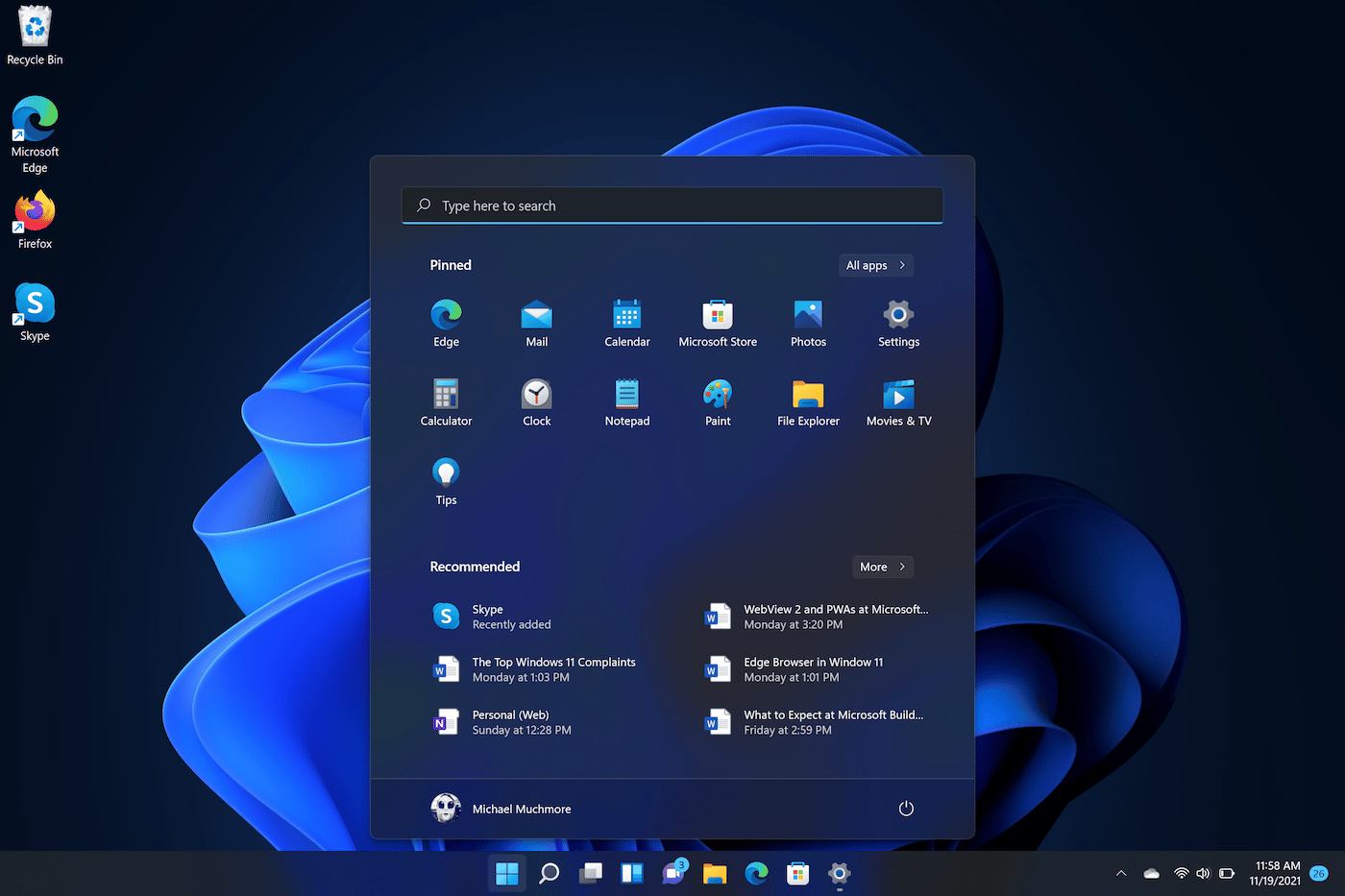
Though Microsoft claimed Windows 10 would be the last version of Windows ever, Windows 11 came with a new visual design, updated apps, touchscreen optimizations, and multitasking features. Microsoft also claims Windows 11 is the most secure release yet. Existing Windows 10 users will be able to upgrade to Windows 11 for free as long as their PC meets the system requirements.
Microsoft Operating Systems for Servers and Mobile Devices
Aside from operating systems designed for use on personal computers (PCs) and laptops, Microsoft has also developed operating systems for servers, handheld devices, and mobile phones.
Windows Server
Initial release date: May 28, 2003
Windows Server is a series of Microsoft server operating systems. Windows servers are more powerful versions of their desktop operating system counterparts and are designed to more efficiently handle corporate networking, internet/intranet hosting, databases, enterprise-scale messaging and similar functions. The Windows Server name made its debut with the release of Windows Server 2003 and continues with the current release, Windows Server 2022.
Windows CE (November 2006)
Initial release date: November 1, 2006
A version of the Windows operating system was designed for small devices such as personal digital assistants (PDAs) or Handheld PCs in the Microsoft vernacular). The Windows CE graphical user interface (GUI) was very similar to Windows 95 so devices running Windows CE were meant to be familiar to Windows 95 users.
Windows Home Server
Initial release date: November 4, 2007
Announced in January 2007, Windows Home Server (WHS) was a “consumer server” designed to use with multiple computers connected in the home. Home Server allowed users to share files such as digital photos and media files, and also automatically backed up home networked computers. Through Windows Media Connect, Windows Home Server shared any media located on your WHS with compatible devices.
Windows Mobile
Initial release date: April 19, 2000
The mobile operating system for smartphones and mobile devices from Microsoft was based on the Windows CE kernel and designed to look and operate similar to desktop versions of Microsoft Windows. Windows Mobile was largely been supplanted by Windows Phone 7, although Microsoft did release, in 2011, Windows Embedded Handheld 6.5, a mobile OS compatible with Windows Mobile 6.5 that was designed for enterprise mobile and handheld computing devices.
Windows Phone
Initial release date: October 21, 2010
Windows’ mobile operating system for smartphones and mobile devices served as the successor to Microsoft’s initial mobile OS platform system, Windows Mobile. Unlike Windows Mobile, Windows Phone 7 was targeted more to the consumer market than the enterprise market. “WinPhone7” replaced the more traditional Microsoft Windows OS look and feel with new “Metro” design system introduced in Windows 8.
Windows Phone 7 featured a multi-tab Internet Explorer Mobile Web browser that used a rendering engine based on Internet Explorer 9. It also included Microsoft Office Mobile, a version of Microsoft Office tailored for mobile devices. Its successors included Windows Phone 8 and Windows 10 Mobile. Microsoft announced the end of life for Windows Phone on January 14, 2020.
This article was last updated February 22, 2021 by Kaiti Norton.
Vangie Beal
Vangie Beal is a freelance business and technology writer covering Internet technologies and online business since the late ’90s.
Microsoft Windows is a group of operating systems. We take a gander at the historical backdrop of Microsoft’s Windows operating systems (Windows OS) and Windows versions from 1985 to present day. Windows Evolution started way back in 1981.

As Microsoft Windows Evolution, here we discussed different versions of Windows operating systems with the launch year.
History of Microsoft Windows Evolution
The Microsoft Windows operating systems (Windows OS) are more popular and are a group of operating systems for personal computers.
Microsoft’s complete term is “Microcomputer software,” which was founded by Bill Gates and Paul Allen on April 4th, 1975. the CEO of Microsoft corporation is Satya nadella
What is the brief Windows version history? Microsoft Windows is the best operating system for personal computers and mobile phones.
It commands the lion’s share of the OS market worldwide. Microsoft Windows is being replaced by Linux and Mac operating systems.
Windows provides a graphical user interface (GUI), virtual memory management, multitasking, and support for some peripheral devices.
Microsoft also provides operating systems for servers and mobile phones.
The evolution of Windows computers has been taking place for some decades. Along with disk defragmenter and other system tools, system restore was a useful feature that was kept in later versions of Windows.
Subsequent versions have become increasingly sophisticated as they incorporate features of minicomputer operating systems.
history of windows operating system
The following Windows Evolution details, along with the details of the history of MS DOS and Windows operating systems, are intended for personal computers (PCs).
You will find a detailed chronology of Windows’ evolution (the evolution of Windows operating system) here.
History of windows operating system
Let us see the history of microsoft windows below.
The first version of Microsoft Windows, released in 1985, was a primitive operating system with a graphical user interface (GUI) that was inspired by the Apple Macintosh.
Despite its limitations, Windows quickly became popular, due in part to its competitive pricing. Microsoft released several subsequent versions of Windows over the next two decades, each with increasingly more advanced features.
The release of Windows NT in 1993 marked a major milestone, as it was the first version of Windows designed to be a true multi-user operating system. Windows NT was also the first version of Windows to be based on a protected, 32-bit microkernel.
Windows 2000, released in 2000, was a significant upgrade from previous versions, with improved security features, Active Directory support, and better performance. Windows XP, released in 2001, built on these improvements and became the most widely used version of Windows ever.
In 2009, Microsoft released Windows 7, which made further improvements to performance, security, and stability. Windows 8, released in 2012, introduced a new user interface and was designed to be used on touchscreen devices.
Windows 10, released in 2015, is the most recent version of Windows and includes a number of significant improvements, such as the new Edge web browser and the Cortana digital assistant.
What was Before Windows 95?
1. MS DOS – Microsoft Disk Operating System (1981)
When did Microsoft release its first version of Windows? MS DOS was the standard operating system for IBM-compatible personal computers when it was first made by Microsoft for IBM. This is the first Windows operating system.
The underlying forms of DOS were exceptionally straightforward and looked like another operating framework called CP/M. The resultant structures have turned out to be progressively more advanced as they consolidated the highlights of minicomputer operating systems.
2. Windows 1.0 (1985)
In which year was the first edition of Windows launched? What year was the first version of Windows introduced? Presented in 1985, Microsoft Windows 1.0 was named because of the processing boxes, or “windows,” that spoke to a major part of the operating framework. This is the first Windows version.
Rather than composing MS-DOS charges, Windows 1.0 enabled clients to point and snap to get to the windows.
Microsoft released the first graphical user interface in Windows 1.0, but it was not released until November 1985, nearly two years after Apple introduced the Mac OS.
3. Windows 2.0 (1987)
In 1987, Microsoft launched Windows 2.0, which was intended for the Intel 286 processor. This adaptation included work area symbols, console alternate ways, and enhanced design bolsters.
Windows 2.0 was released in November 1987. It offered a cogent advance over Windows 1.0. It has several appearances, like the overlapping of Windows, new keyboard shortcuts, and a bigger GUI. It also featured a plethora of new applications.
After some time windows, 2.1 was released, which could multi-task several applications and had bigger anamnesis administration schemes. Visually, it was identical to Windows 2.0.
4. Windows 3 (1990)

Windows 3.0 was launched in May 1990, offering better symbols, execution, and propelled illustrations with 16 hues intended for Intel 386 processors.
This adaptation is the first launch that gives the standard “look and feel” of Microsoft Windows for a long time to come. MS Windows 3.0 included a Program Manager, File Manager, and Print Manager, and diversions (Hearts, Minesweeper, and Solitaire).
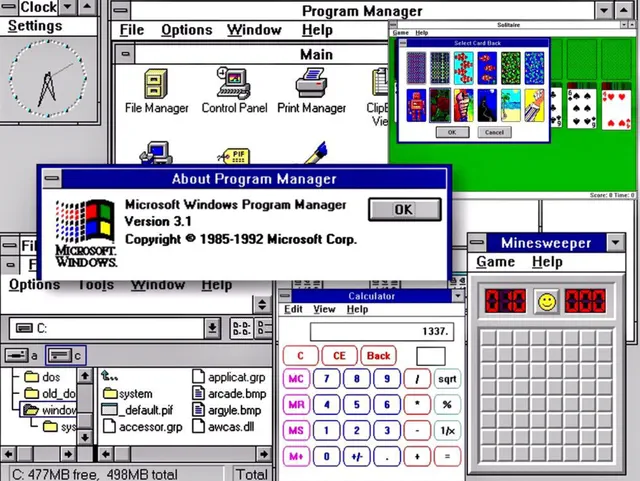
Microsoft released Windows 3.1 in 1992. Windows NT 3.1 came out in 1993. It was the first version of the new Windows NT operating system.
The first version of the Windows media player was introduced in 1991 with Windows 3 by including a Multimedia extension.
Windows 3.0 and 3.1 brought an advance in the computer industry. They were broadly adopted by several pc manufacturers. Apple’s Mac OS was accustomed to being installed on Apple computers.
Windows 3.0 brought an abundance of new features into the Windows realm. It actually improved multitasking and gave users access to more anamnesis modules than previous versions.
Because the majority of the coding was done in accumulation language, this Windows was faster and more reliable. Windows 3.1 was the first released 16-bit operating system.
5. Microsoft Bob

Microsoft Bob was a GUI experiment by Microsoft that was innovative, but it failed. It presented a cartoon view of an office, where users could easily access their programs. Microsoft Bob is usually mentioned as one of the worst products from Microsoft.
6. Windows 95 (August 1995)
Windows 95 came out in 1995, and it was a big step forward for the Windows operating system. This OS was a critical progression over its forerunner, Windows 3.1.
In addition to a new user interface, Windows 95 includes several important interior improvements.
Maybe most significantly, it supports 32-bit applications, which implies that applications composed particularly for this operating framework should run substantially faster.
Even though Windows 95 can run both old Windows and DOS programs, it has mostly replaced DOS as the main platform.
This has implied the expulsion of a significant number of the old DOS impediments, for example, 640K of the first memory and 8-character filenames.
It was released on August 24th, 1995, and sold more than one million copies within four days.
Other vital highlights of this operating framework are the capacity to consequently recognize and design equipment (attachment and play).
7 Windows NT 3.1 – 4.0 (1993-1996)

Microsoft Windows NT (New Technology) is a 32-bit operating framework that backs preemptive multitasking.
Windows NT comes in two versions: Windows NT Server, intended to go about as a server in systems, and Windows NT Workstation, for remaining solitary or customer workstations.
The desktop interface is also present for running Windows-based applications, but it will not run any desktop applications not included in the system.
the 1995 consumer release windows 95 fully integrated windows and dos and offered built-in internet support including the world wide web browser internet explorer
What was after 1995?
8. Windows 98 (June 1998)

Windows 98 offers bolster for various new advancements, including FAT32, AGP, MMX, USB, DVD, and ACPI.
The most noticeable element, however, is the Active Desktop, which coordinates the Web program (Internet Explorer) with the operating framework.
Windows 98 was the last great DOS-based window. From the client’s perspective, there is no distinction between getting to an archive living locally on the client’s hard drive or on a Web server most of the way around the globe.
It is a hybrid 16–bit and 32–bit monolithic product with the boot stage based on MS-DOS.
The Windows 98 start menu introduced an attractive button. In 1999, Microsoft released Windows 98 Second Edition. The user control panel is an added feature to see the installed programs.
Windows 98 introduced the address bar and front-back navigation buttons in Windows Explorer, along with useful options for easy browsing.
9. Windows 2000 (February 2000)

Windows 2000 is an operating framework for business work areas and PC systems to run programming applications, interface with Internet and intranet destinations, and access records, printers, and system assets.
Microsoft launched four versions of Windows 2000: Professional (for business work areas and workstation systems), Server (both a Web server and an office server), Advanced Server (for line-of-business applications), and Data-centre Server (for high-activity PC systems). Microsoft Windows 2000 was released on February 17, 2000.
10. Windows ME – Millennium Edition (September 2000)
The Windows Millennium Edition, called “Windows Me” was a refresh to the Microsoft Windows 98 center and incorporated a few highlights of the Windows 2000 operating framework. This adaptation likewise evacuated the “boot in DOS” choice. It was released on 14 September 2000.
11. Windows XP (October 2001)

Windows XP was released on August 24th, 2001. Alongside an overhauled look and feel to the user interface, the new operating framework is based on the Windows 2000 portion, giving the client a more steady and solid condition than past forms of Windows.
Windows XP comes in two adaptations, Windows XP Home and Professional. Microsoft concentrated on portability for the two releases, including attachment and playback highlights for interfacing with remote systems. The operating framework likewise uses the 802.11x remote security standard. Windows XP is one of Microsoft’s top-of-the-line items.
The users gave Microsoft XP Service Pack 2 great popularity. Microsoft Windows XP media center edition 2005 was released on October 12, 2004
Microsoft introduced a series of Windows XP products between 2001 and 2006
| Versions | Released Dates |
|---|---|
| MS Windows XP 64 Bit Edition V92202) | October 2001 |
| Windows XP Media Centre Edition | October 2002 |
| MS Windows XP 64 Bit Edition V(2003) | March 2003 |
| Windows Server 2003 | April 2003 |
| MS Windows XP Media Centre Edition 2004 | September 2003 |
| Windows XP Media Centre Edition 2005 | October 2004 |
| MS Windows XP Professional X64 Edition | April 2005 |
| Windows Server 2003 R2 | December 2005 |
| MS Windows Fundamentals for Legacy PCs | July 2006 |
12. Windows Vista (November 2006)

In 2005, Microsoft announced its next operating system code-named “Longhorn”. After a few days, it was named “Windows Vista” and released on July 23, 2005.
Windows Vista was an improvement over Windows XP in terms of quality, security, ease of sending, performance, and sense. It was released in November 2006.
This version added the ability to detect equipment issues before they occur, security features to protect against the most recent dangers, a faster start-up time, and low power utilization of the new rest state.
Most of the time, Windows Vista works better than Windows XP on the same hardware. Microsoft Windows Vista simplifies and unifies how work areas are designed and managed, which lowers the cost of keeping systems up to date.
13. MS Windows 7 (October 2009)
Microsoft Corporation launched Windows 7 on July 22, 2009, as the most recent in the 25-year-old line of Windows operating systems and as the successor to Windows Vista (which itself had taken after Windows XP). This product came out at the same time as Windows Server 2008 R2, which is a server that works with Windows 7.
Multi-touch support; Internet Explorer 8, improved execution and startup time; Aero Snap, Aero Shake, support for virtual hard drives, a better-than-ever Windows Media Center, and enhanced security are among the upgrades and new features in Microsoft Windows 7.
Microsoft introduced Windows Home Server on April 7th, 2008, and Windows Server 2008 on February 27th, 2008. The desktop was still included, which resembled Windows 7.
Microsoft Windows Movie Maker and Windows DVD Maker were introduced in this version. It is not available with the Windows 10 version.
14. MS Windows 8

Microsoft Corporation launched MS Windows 8, released on October 17, 2013. This is an upgraded operating framework. Microsoft produced this product from the beginning on account of touchscreen use. This product is also a close moment in the capabilities that empower MS Windows 8 PCs to load and start up in a matter of seconds as opposed to minutes.
Microsoft Windows 8 will replace the traditional look and feel of the Microsoft Windows OS with the “Metro” design system interface that was first used in the Windows Phone 7 mobile operating system.
The main part of the Metro UI is the “Begin screen,” which is made up of “Live Tiles,” which are links to apps and features that change and update as you use them. Windows 8 underpins both x86 PCs and ARM processors.
After the introduction of Microsoft Windows 8, Microsoft introduced Windows Server 2008 R2 in 2009, MS Windows Home Server 2001 in 2011, Windows Thin PC in 2011, and MS Windows Server 2012 in September 2012. The desktop was still included, which resembled Windows 7 after the last update. Windows 8 features a newly designed user interface.
It was designed to make it easier for touchscreen users to use windows. The new interface came with a new full-screen application platform and a new version of the start menu called the “start screen.”
The Microsoft Windows store was introduced in this version. Most of the applications or software are available in the Windows store.
15. Windows 10

What is the latest version of Microsoft Windows called? Windows 10 is Microsoft’s Windows successor to Windows 8. Windows 10 is the last version of Windows released traditionally.
After a “specialized see” beta of the new operating framework in the fall of 2014 and a “shopper see” beta in the middle of 2015, Windows 10 came out on July 29, 2015.
Microsoft says that Windows 10 will start up and run quickly, improve security, and bring back the Start button Menu in a longer form. This adaptation of Windows will likewise highlight Microsoft Edge, Microsoft’s new program.
Any device that can run Windows 10, like tablets, PCs, cell phones, and Xboxes, can upgrade to Windows 10. This includes pirated copies of Windows. This is a powerful version of personal computing.
Cortana is a special feature in this version. It is a specially designed virtual assistant. Tablet mode is another added feature with improved performance.
Windows 10 is the latest development in Windows Evolution history. Memory management, maximum hardware support, and Internet Explorer for Microsoft Edge, a new browser built on the Google Chrome platform, are all important features that come with this version.
Windows provides a graphical user interface (GUI), virtual memory management, multitasking, and support for many peripheral devices
16. Window 11
Windows 11 is not another operating system. There is not an upcoming version from Microsoft. This is confirmed by the Microsoft community. So beware of the pirated versions before buying the original version. A few of the sites are promoting this version. Here is the confirmation of the Windows 11 version. In 2020, Microsoft is planning to release two important Windows updates for the Windows 10 version.
Windows 11 is the next operating system after Windows 10. It is likely to be released in 2018. But the features of Windows 11 haven’t been revealed yet. However, it is expected to have some great features. It is likely to come up with quantum paper and a new browser. Windows 11 will be more secure than Windows 10.
Microsoft Operating Systems for Servers and Mobile Devices
Microsoft has made operating systems for government agencies, handheld devices, and cell phones, as well as operating systems for personal computers (PCs).
- Released Windows Server (March 2003)
- MS Windows CE (November 2006)
- Windows Mobile (April 2000)
- MS Windows Phone (November 2010)
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
-
What is the order of Windows operating systems?
The first Windows operating system is released in 1985 officially. Till now 15 versions from DoS mode to Windows 10.
-
Will there be a Windows 11?
Microsoft team officially announced their latest windows version as “Windows 10 is the last version of Windows, we are still working on Windows 10”. this is the message from Jerry Nixion (Microsoft Employee)
-
Is Windows 10 the last OS?
Yes, Windows 10 is the last version of Windows and was officially announced by the Microsoft team.
-
How long will Windows 10 be supported?
We will receive a minimum of 10 years of updating support from the Windows team. The mainstream support is scheduled to end on October 13, 2020, and extended support will end on October 14, 2025.
-
What is the latest Windows version 2021?
Windows 11 latest updated version, which is released on September 24, 2021. Maybe the new update released within six months.
Conclusion
The above Microsoft Windows Evolution is one of the top trending programming technologies in the world. Every time Microsoft releases a new feature as part of a security update,
Bill Gates announced that the new version of Windows CE will be called Pocket PC.
Over the last thirty years, the advancement of technology has progressed at a rapid pace and given a chance for a better life to human beings.
- Top 9 Best Mobile Phone Operating Systems overview in 2022
Before releasing the complete version, Microsoft is releasing a technical preview (consumer version) that includes support. After testing those versions with users and developers, they are finally released into the enterprise market at attractive prices.
Windows 10 is the current release of the Microsoft Windows operating system.
This technology may even be more advanced in the coming decades.
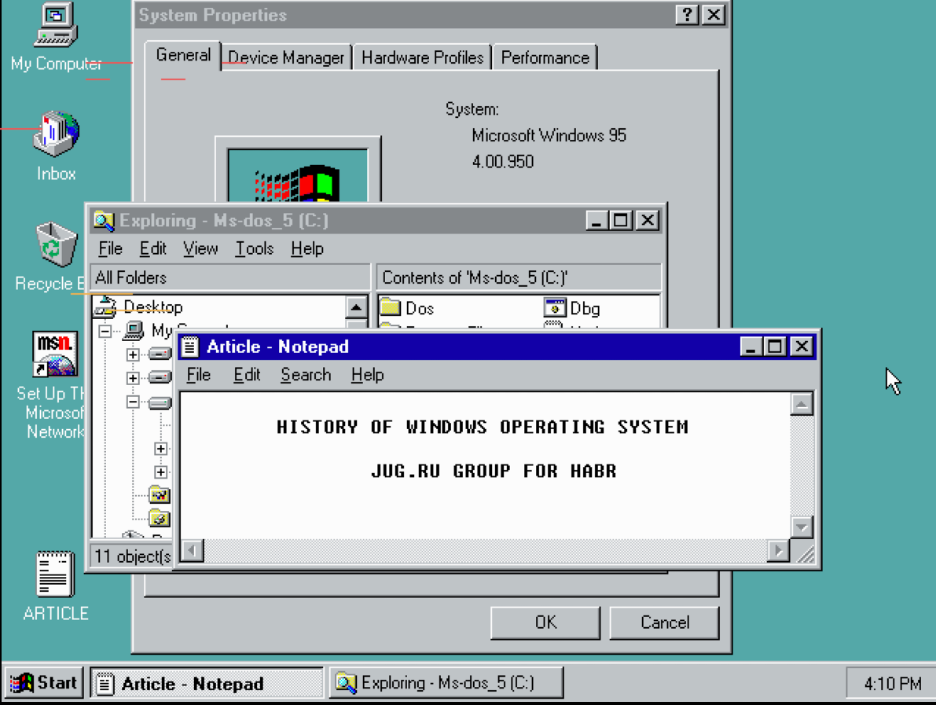
Выход Windows 11 — хороший повод вспомнить всю историю MS Windows длиной почти в 36 лет. Журналист PCMag Джон Дворак как-то пошутил, что когда Microsoft анонсировала Windows, у Стива Балмера еще были волосы (во что сложно поверить).
Так что теперь, когда на Хабре уже обсудили новую версию, давайте вспомним предыдущие. Чтобы пост не вышел слишком длинным, пришлось описывать их кратко. Но если у вас есть что добавить, смело делайте это в комментариях.
А если текст вызовет прилив ностальгии, запустить первые версии Windows можно в эмуляторе на сайте PCjs Machines. Из-за пребывания на нём был немного сорван дедлайн сдачи этой статьи.
Предыстория: MS-DOS (1981)
В 70-х оказалось, что компьютеры могут быть не только громоздкими устройствами для крупных организаций. Рынок «микрокомпьютеров» вроде Apple II, подходящих для домашнего использования, рос бурными темпами. В IBM решили не упускать его и принялись за работу над моделью 5150, которая вошла в историю как «IBM PC». Компании нужно было разобраться не только с самим компьютером, но и с софтом: тогда бытовало понятие «дисковые операционные системы» (disk operating system, DOS), и компьютеру с новым 16-битным процессором Intel 8088 требовалась такая.
Для гиганта IBM это было не вполне профильной деятельностью: компания была известна «громоздкими устройствами», ориентирована на корпоративных клиентов, даже её название означает «International Business Machines». А вот по названию Microsoft можно было понять, что тут разрабатывают ПО как раз для микрокомпьютеров. В IBM уже сотрудничали с этой молодой компанией из-за её флагманского продукта Microsoft Basic, и в итоге ОС поручили тоже ей.
Вообще говоря, MS-DOS не целиком сделана в Microsoft: там купили и доработали чужую систему 86-DOS. А вот в IBM не купили целиком MS-DOS, просто лицензировали её и поставляли под названием PC DOS. Дальновидный Билл Гейтс сохранил права на систему, и в контракте с IBM было прописано, что Microsoft может лицензировать её другим производителям компьютеров. Это и стало своеобразным трамплином, позволившим Microsoft стать ведущей технологической компанией.
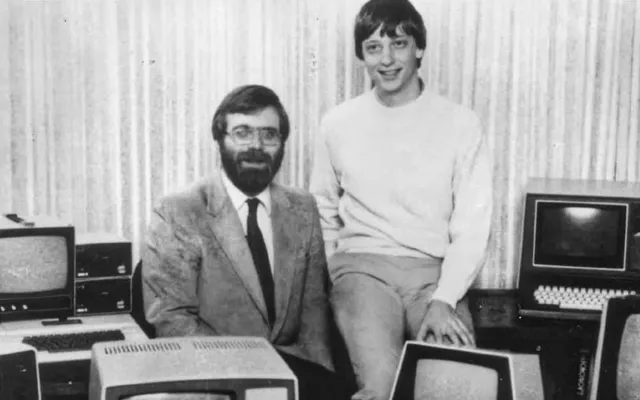
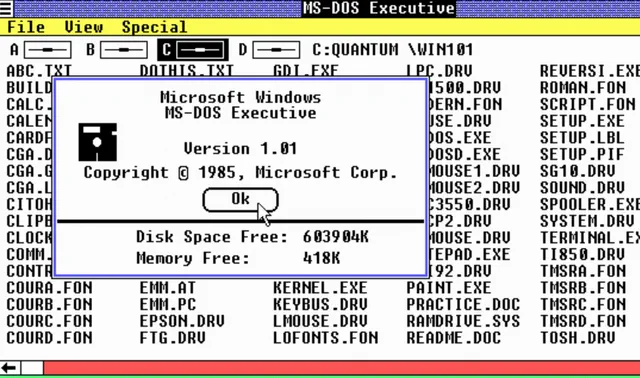
Windows 1.0 (1985)
А ведь у нас мог бы быть «манагер» вместо «винды». Изначально проект Microsoft, возникший в 1981 году, назывался Interface Manager.
Однако самым заметным в этом проекте была концепция «окон». Несколько задач на одном экране, раскрывающиеся меню, полосы прокрутки — в новом GUI было многое, что мы сейчас знаем и любим. Так что неудивительно, что в ноябре 1983-го проект был анонсирован уже под названием Windows.
А вышла Windows 1.0 лишь спустя два года после анонса, 20 ноября 1985 года. Сейчас эта дата может звучать как день, когда мир перевернулся: вот оно, пришествие ОС, которая покорила человечество и перевела его от командной строки к современному GUI.
Но тогда мир особо не заметил, что он перевернулся.
Во-первых, технически Windows 1.0 даже не была полноценной ОС — это «надстройка» над DOS. И её зачастую воспринимали лишь как программу с графическим интерфейсом, работающую в MS-DOS: можно использовать по необходимости, но не сидеть же там всё время!
Во-вторых, чтобы оценить преимущества графического интерфейса, требовалась мышь. Сейчас людям проще кликать, чем учить и вводить бесконечные команды, но тогда пользователям было непривычно — многие по-прежнему хотели стучать по клавиатуре в пику коварному Биллу Гейтсу, желающему всех чипировать приучить к мыши.
А если вспомнить компьютерные мощности того времени, неудивительно, что все эти новомодные GUI-штуки плохо работали на слабом железе.
В итоге продажи были скромными, отзывы — критическими, и всё это совершенно не ощущалось революцией.
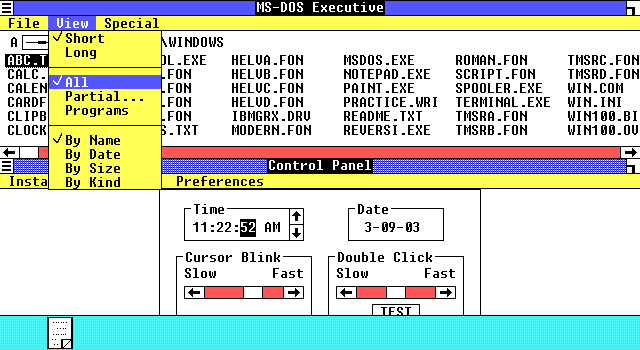
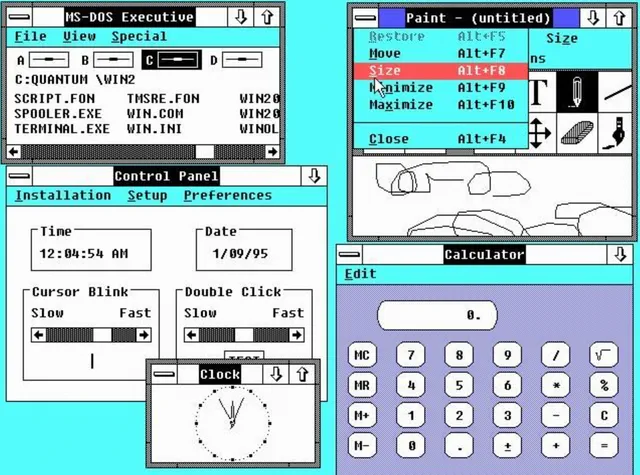
А как именно Windows тогда выглядела? В поставку входили блокнот, календарь, калькулятор, приложение для рисования, часы, игра «Реверси» и т. д. Увидеть систему можно в ролике Windows 1.0 Features Demo (заметьте, на открывающем экране она названа не «operating system», а «operating environment»):
В 1986 году Стив Балмер в роли безумного коммивояжера снялся в странном видео про Windows 1.0. До сих пор ходят споры, настоящее это видео или стеб для корпоратива MS. А вот такой пресс-кит был разослан к анонсу Windows 1.0:
Windows 2.0 (1987)
Вторая версия была выпущена 9 декабря 1987 года. Её самое заметное отличие — теперь окна могли перекрывать друг друга (в Windows 1.0 было возможно только тайловое расположение «бок о бок»). Были также некоторые другие доработки GUI.
И из-за этого компания получила судебный иск от Apple. Чтобы понять произошедшее, стоит начать с предыстории, насколько её сейчас можно восстановить по имеющимся источникам.
Распространена следующая версия. В 1970-х в исследовательском центре Xerox PARC опередили время в разработке компьютерного GUI, но руководство Xerox не понимало, что эти идеи представляют большую ценность. Зато Стив Джобс, оказавшись там, понял, что видит будущее — и принялся реализовывать аналогичные идеи в Apple Lisa (1983) и Apple Macintosh (1984).
В тот период у Microsoft и Apple были партнёрские отношения, так что у Microsoft была инсайдерская информация о разработках Apple. И из-за этого анонс Windows в ноябре 1983-го (всего за пару месяцев до выхода Macintosh) взбесил Джобса. По воспоминаниям участника команды Macintosh Энди Хертфельца, Джобс срочно вызвал Гейтса и наорал на него: «Я доверился тебе, а ты крадёшь у нас!» В ответ на что Гейтс заметил, что вообще-то Джобс сам позаимствовал идеи у Xerox, так что не ему обвинять в краже.
Тогда, в 1983-м, конфликт дальше не зашёл. Но вот спустя четыре года визуальные изменения Windows 2.0 вывели его на новый виток. В Apple подали судебный иск, утверждая, что теперь общий стиль («look and feel») новой Windows слишком похож на GUI компьютеров Lisa и Macintosh, так что это уже нарушает авторские права. Судебные тяжбы, тянувшиеся шесть лет, завершились победой Microsoft.
Windows 3.x (1990–1994)
В третьей версии Windows по-настоящему расцвела. Система, выпущенная в 1990 году, стала хитом, разошедшимся тиражом более 10 миллионов копий.
Сделаем уточнение — версия 3.0 была уже хороша, но реальную популярность снискали более поздние версии 3.1/3.11.
Они были и красивее 2.x (доработанный GUI, поддержка TrueType, больше цветов), и функциональнее (появление реестра Windows, поддержка TCP/IP, новый файловый менеджер). А с точки зрения скучающих офисных сотрудников, наверное, главным нововведением стал убийца времени «Солитер». Его целью было не только развлекать, но и дальше приучать пользователей к мыши — например, тренироваться в перетаскивании.
Технически всё это по-прежнему оставалось надстройкой над MS-DOS, но вот теперь эту надстройку восприняли всерьёз. Отчасти способствовала цена: в 1990 году недорогой ПК с Windows 3.0 можно было купить менее чем за 1000 долларов, а самый дешевый цветной Macintosh за 2400.
В итоге маховик раскручивался: пользователей становилось всё больше, что стимулировало разработчиков писать программы под Windows, что в свою очередь стимулировало пользователей ещё активнее переходить на неё.
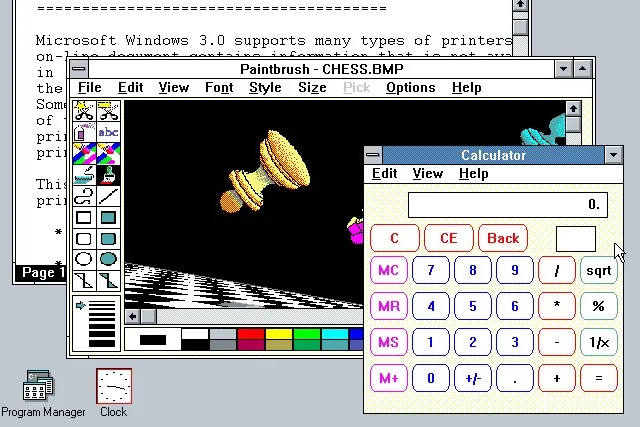
Тем временем начиналась новая эра: компьютеры теперь были не только для текстов и таблиц, но и для мультимедиа; разрешение у пользователей подросло аж до 640×480. В Microsoft реагировали на это: в системе появились приложения Media Player и Sound Recorder, а в поставку «тройки» включили потрясающие обои CHESS.BMP.
Windows NT (1993 и далее)
С версиями 3.x к Windows пришла массовая популярность на ПК. Но вот серверам и рабочим станциям нужны не красивые обои и залипательные пасьянсы, там рынок диктовал свои потребности: например, поддержку разных архитектур процессора. И для этого рынка в Microsoft представили семейство Windows NT.
Нумерацию версий NT начали не с 1.0, а сразу с 3.1, чтобы соответствовало тогдашней версии «основной» Windows. И из-за этого NT может показаться лишь небольшой доработкой «обычной» Windows. Но это была не доработка, а совершенно отдельное явление, уходящее корнями в систему OS/2.
Пока стандартная Windows оставалась «надстройкой» над MS-DOS, NT была полноценной ОС со своим ядром. Также она сразу делалась с расчётом на то, чтобы при помощи HAL поддерживать самые разные процессоры. И ещё NT 3.1 была первой по-настоящему 32-битной версией Windows. И полной совместимости между двумя семействами Windows не было. В общем, тут был не просто «специализированный вариант», а параллельная разработка двух разных (но при этом взаимосвязанных) ОС.
Тут напрашивается вопрос. Разрабатывать параллельно сразу две больших ОС, которые ещё и должны быть максимально совместимы — это сложно и дорого. Предположим, ограничения «обычной» Windows мешали использованию её на серверах. Но почему тогда было не дать обычным пользователям NT? Неужели в Microsoft не хотели упростить себе жизнь, ограничившись одной системой?
Вообще говоря, хотели. Но в 1993-м были причины, мешавшие этому: например, системные требования NT для серверов и рабочих станций подходили, а вот для массового рынка тогда были слишком высокими.
Поэтому весь XX век две системы продолжали развиваться параллельно, в NT-семействе появились Windows NT 4.0 (1996) и Windows 2000. Ради экономии места не станем расписывать их подробно, а продолжим идти по «пользовательским».
Windows 95 (1995)
В августе 1995 года мир бесповоротно изменился — в новом релизе Windows появилась кнопка «Пуск» (Start). И её маркетинговая поддержка обошлась Microsoft в 8 миллионов долларов — именно столько было заплачено The Rolling Stones за право использовать их песню «Start Me Up» в рекламе.
Вообще, маркетинг Win95 был впечатляющим. Башня Си-Эн в Торонто была украшена баннерами Windows 95, а Эмпайр-стейт-билдинг в Нью-Йорке был подсвечен цветами Microsoft. Тогда компьютерная революция была настолько на хайпе, что ОС могли рекламировать звёзды суперпопулярного сериала «Друзья»: Мэтью Пэрри и Дженнифер Энистон снялись в «первом в мире киберситкоме», где рассказывают об основных 25 функциях новой ОС.
Сейчас сложно представить себе подобную интеграцию с сериалом для Windows 11. А еще на CD-дистрибутиве Win95 бонусом был записан клип группы Weezer Buddy Holly, что привело к резкому росту её популярности.
Но вернёмся к старту: сначала пользователем кнопка «Пуск» казалось нелепой и нелогичной, но со временем она стала такой неотъемлемой частью системы, что удаление ее в восьмой версии вызвало шквал негодования. Вместе с её появлением произошли многие другие изменения интерфейса — например, появился таскбар. Некоторые новые возможности повторяли то, что давно было доступно в Mac OS, и это спровоцировало издевательскую «рекламу» со стороны Apple:
Другими важными фичами была система Plug-and-Play, упрощение выхода в интернет, появление учетных записей, DirectX в более поздних версиях.
К 1995-му уже не было проблемы из 1985-го «люди предпочитают по старинке сидеть в DOS». Наоборот, теперь было бы сложно объяснить обычному пользователю, зачем ему командная строка, когда есть GUI и мышка. Продвинутые пользователи могли скучать по эпохе DOS (см. песню российских фидошников), но было очевидно, что эта эпоха уходит. И при использовании Windows 95 пользователь практически не сталкивался с MS-DOS — вот только полностью удалить его из системы было бы затруднительно. То, что когда-то привело компанию к успеху, превратилось в кусок легаси, от которого в перспективе хотелось избавиться.
Windows CE (1996 и далее)
Статья посвящена десктопным ОС, так что не станем разбирать каждую из версий Windows CE отдельно. Но мобильные устройства — такая масштабная для MS история, что пару слов сказать надо. Закончилась она провалом (проект поглотил гигантское количество ресурсов и закрылся), а как начиналась?
Отсчёт можно вести с 1996 года. Тогда была представлена Windows CE — система, оптимизированная для устройств с минимально возможными техническими характеристиками. Сами устройства оказывались разными, от плееров Zune до автомобилей. Но уже при запуске системы в 1996-м в качестве важной категории видели PDA (personal digital assistant, в России — «карманные персональные компьютеры», КПК).
Внутри у новой системы было собственное ядро, требующее для работы всего мегабайт памяти, что заметно отличало её от десктопных версий. А вот внешне она напоминала привычную Windows, утрамбованную ногами в маленький экран: тут были и меню «Пуск», и рабочий стол с иконками, и прочие привычные вещи. В 2000-м из Windows CE вырастет Pocket PC — система уже для КПК. Пару лет спустя станут появляться КПК с возможностью звонить, и в 2003-м систему переименуют в Windows Mobile с вариантом «Phone Edition». В нулевых она хорошо показывала себя, успешно конкурируя с Symbian и Blackberry. И такой успех ослепил Microsoft — они не смогли вовремя увидеть угрозу в iOS/Android. Но об этом позже.
Windows 98 (1998)
Новый релиз состоялся в июне 1998 года. Возможно, самая известная история про эту ОС — синий экран смерти, появившийся на презентации.
Больших потрясений для пользователей тут не было: компания и сама презентовала систему не как сенсацию, а как доработанную Windows 95, на которой «лучше работать и лучше играть». Например, идя в ногу со временем, тут поработали над поддержкой DVD, USB, FAT32, AGP.
А ещё новые времена были неразрывно связаны с интернетом. И это тоже нашло отражение: в состав новой системы входили Internet Explorer, Outlook Express и FrontPage Express.
Ну и появился ряд вещей, менее бросавшихся в глаза рядовому пользователю, от новой системы драйверов Windows Driver Model до приложения Disk Cleanup.
Windows ME (2000)
Сейчас Millennium Edition вспоминают как какое-то недоразумение и расшифровывают аббревиатуру как «Mistake Edition». Гигантского шага вперёд по сравнению с Windows 98 не было, а вот проблемы со стабильностью были, при этом система вышла в один год с успешной Windows 2000 (из NT-семейства) и за год до суперуспешной XP — в общем, последний вздох линейки 9x.
Конечно, какие-то новые вещи там были. Например, появился Windows Movie Maker: медиареволюция продолжала менять мир, и монтаж видео теперь тоже попал в список того, что должно быть доступно из коробки обычному пользователю.
Но в итоге версия осталась в истории благодаря не этому событию, а разве что шутками по её поводу:
Windows XP (2001)
Windows XP (она же eXPerience, она же Whistler, она же Windows NT 5.1, она же «Хрюша» у российских пользователей) стала, пожалуй, одной из самых успешных версий Windows. Рекламная кампания тоже была помпезной, хотя и не такой, как планировалась изначально, из-за терактов 11 сентября. Но Microsoft все же устроила вечеринку, где выступали Стинг и Мадонна.
XP знаменовала собой событие, крайне важное для Microsoft, хотя и не слишком очевидное рядовым пользователям: впервые в «пользовательской» ОС использовалось ядро Windows NT. Два больших мира наконец сошлись в одном. И больше не расходились: все дальнейшие крупные релизы были только на ядре NT. Если открыть в Википедии страницу только что вышедшей Windows 11, можно увидеть, что она классифицируется как версия Windows NT.
Переход к XP не был безболезненным. Системные требования по сравнению с Windows 98 резко выросли. Поначалу возникали вопросы совместимости приложений. Систему критиковали с точки безопасности. А кроме того, ещё и изменившийся внешний вид нравился не всем: часть пользователей называла его «игрушечным». Так что в первый год существования XP отношение к ней было настороженным.
Но со временем ситуация улучшилась — компьютеры становились всё мощнее, а проблемы совместимости всё менее заметны. И в итоге система оказалась такой популярной, что это даже стало проблемой: когда компания решила прекратить её поддержку спустя 12 лет (срок заметно больше среднего), многие по-прежнему не хотели пересаживаться с XP на что-то новее. Даже в этом году, когда системе исполнилось 20 лет, некоторые продолжают ей пользоваться.
У меня до сих пор лежит потрепанная книга «Хитрости Windows XP», зачитанная до дыр. Автор рассказывал, как добиться максимальной гибкости от этой системы, правильно работая с реестром.
Windows Vista (2006)
Многие считают «Висту» самой отвратительной версией. Основной заявленной целью было устранение проблем безопасности, которыми грешила XP. Но реализация оказалась неудачной: например, контроль учетных записей пользователей (UAC) так часто рвался помочь пользователю, что в итоге всех раздражал. Есть даже издевательский ролик от Apple, где это высмеивается (заметим в скобках, что позже в macOS Catalina сама Apple наступила на те же грабли):
Также интерфейс сделали «покрасивше», но новый визуальный стиль Aero тоже не всем нравился. Опубликованные до релиза скриншоты вызвали в рунете мем «уже сейчас понятно, что всё это будет глючить и тормозить».
И даже Стив Балмер признал потом, что Vista «просто не была реализована должным образом».
В итоге, хотя результаты продаж в первый месяц были бодрыми (20 миллионов копий, больше XP за тот же период), долгосрочно Vista проиграла. Когда спустя три года вышла следующая Windows, Vista занимала лишь 19% рынка против 63% у XP. Большинство людей с XP сразу перепрыгнули дальше, пропустив эту версию. Не пропустить её можно было разве что геймерам из-за DirectX 10, который давал еще больше удовольствия от графики, чем когда-либо прежде: он не был доступен на предыдущих версиях Windows.
Впрочем, пока пользователи негодовали, внутри происходила незаметная им работа. При серверном использовании Windows был спрос на версию без «ненужных частей» вроде браузера, чтобы сократить поверхность атаки. Но Windows, в отличие от Linux, поначалу не могла это дать из-за хаотичной кучи внутренних зависимостей: выкинешь браузер — сломаешь полсистемы. И в Vista была проведена громадная работа по «распутыванию», после которой любой компонент мог зависеть только от того, что «ниже него», и «высокоуровневые» компоненты можно было легко убирать из поставки.
Windows 7 (2009)
Система, вышедшая 22 октября 2009 года, стала примерно тем, чего изначально ожидали от «Висты». Переделывать всё масштабно тут не стали и тот же стиль Aero остался, зато доработали таскбар и дали новые возможности управления окнами. А критику учли, и UAC стал не таким маниакальным.
Также улучшили поддержку сенсорных экранов (хоть их тогда и было немного), ускорили загрузку, обновили Internet Explorer до восьмой версии… В итоге вроде бы никаких подвигов компания не совершила, но перешла от провала к успеху. «Семёрка» понравилась и журналистам IT-изданий, и пользователям, так что за первый год было продано более 240 миллионов копий.
Windows 8 (2012) и Windows 8.1 (2013)
А дальше была великая и ужасная Windows 8 — третья ненавидимая система в линейке Windows. По выражению одного блогера, интерфейс этой системы спроектировали для людей, которые сами не понимают, что делают. Пользователи недоумевали: зачем всё поменяли, когда людям нравилась «семёрка»? Где моя кнопка «Пуск»?
Тут нужно понимать контекст. Вспомним, на чём мы оставили линейку Windows CE: основанная на ней Windows Mobile в нулевые показывала хорошие результаты среди ранних смартфонов.
Вот только затем появление iOS/Android всё поменяло. Внезапно оказалось, что люди хотят не тыкать стилусом в малюсенькое меню «Пуск», а нажимать пальцами на крупные иконки. А ещё вслед за смартфонами появились планшеты, и тогда могло казаться, что они вот-вот заменят компьютеры.
В Microsoft решили срочно и радикально исправлять ситуацию. На смену Windows Mobile пришла система Windows Phone (и с восьмой версии в ней сменили ядро с Windows CE на Windows NT). У десктопной Windows появилось отдельное ответвление Windows RT для планшетов с ARM-процессорами. И у всего этого — Windows Phone, Windows RT, Windows 8 — был новый стиль интерфейса Metro с «живыми плитками» (Live Tiles).
Microsoft хотел создать в Windows 8 гибридную систему для разных устройств (планшетов и компьютеров), но получилось раздвоение личности: традиционный рабочий стол, скопипащенный из Windows 7 (без меню «Пуск»), все ещё оставался. Было ясно, что Microsoft хочет настроить людей на использование новых современных приложений. Но только люди не особо настроились.
В итоге Windows RT просуществовала всего пару лет. Windows Phone была официально признана мёртвой в 2017-м. А для основной десктопной версии в конце 2013-го Microsoft выпустила крупное бесплатное обновление Windows 8.1. Оно устраняло множество проблем, касающихся плиток рабочего стола, и возвращало кнопку «Пуск» — по сути, признавало, что погорячились. Но осадочек у пользователей остался.
Windows 9 (?)
— Почему в линейке Microsoft не было Windows 9?
— Потому что Windows 7 съела 9 (It’s because Windows 7 8 9).
Но вероятно всего, это маркетинговый ход — Microsoft пыталась установить дистанцию между провальной Windows 8 и ее преемницей. Таким образом, Windows 10 — это большой шаг вперед.
Windows 10 (2015)
В смутный 2015 год появилась Windows 10. Она стала бесплатным обновлением для всех пользователей Windows 7, 8 и 8.1. В новую ОС вернулось меню «Пуск», и по изначальной задумке Windows 10 якобы должна стать последней версией Windows — дальше должны были появляться лишь обновления, а не отдельные новые версии. Но теперь мы знаем, что это не так.
Систему оценили в целом положительно — хвалили за интерфейс, кроссплатформенность, DirectX 12, улучшенную производительность и системные требования, которые в целом остались такими же, как и для Windows 7. Ну и в целом «спасибо, что признали провал с мобильными устройствами и вернули нам нормальный десктоп».
Вместе с мобильными начинаниями закопали и Internet Explorer: его сменили новым браузером Edge.
Если релиз Windows 95 или XP сопровождался разухабистыми рекламными кампаниями со звездами и вечеринками, то кампания в поддержку Windows 10 имела другую направленность — благотворительную. В 2015 году Microsoft запустила инициативу Upgrade Your World в рамках глобального релиза Windows 10, пожертвовав более 10 миллионов долларов некоммерческим организациям по всему миру.
Microsoft изначально поставил амбициозный срок по достижению миллиарда пользователей — и хотя его соблюсти не вполне удалось, сейчас на Windows 10 работает уже более 1,3 миллиарда компьютеров. Компания будет поддерживать ее до 14 октября 2025 года.
Windows 11 (2021)
Ну и теперь состоялся официальный релиз Windows 11, о ней на Хабре уже подробно писали. На официальном сайте система описана красивыми словами вроде «каждая деталь тщательно продумана». Вот только на практике можно услышать голоса против: на Хабре ещё летом писали «Windows 11 движется не в ту сторону», в The Verge громили новый таскбар.
А ещё есть забавное наблюдение «удачные и неудачные версии Windows чередуются». На протяжении последних 22 лет постоянно менялось то, как пользователи принимают очередную систему: «Windows 98 — хорошо, Windows ME — плохо» и так далее. Windows 10 восприняли хорошо.
Значит ли это, что Windows 11 предначертано остаться в истории «неудачной»? Мы воздержимся от комментариев (ещё не успели её как следует рассмотреть-то). Зато вы не воздерживайтесь: смело пишите, что думаете и о новой версии, и о старых!
Если экосистема Microsoft интересна вам, потому что вы .NET-разработчик — обратите внимание, скоро мы проведём онлайн-конференцию DotNext (например, там будет много спикеров из Microsoft вроде Стивена Тауба).
А если вы не дотнетчик — у нас сейчас вообще большой конференционный сезон, от Java-конференции до DevOops. Полный список из 8 мероприятий можно посмотреть на сайте.
When you think about the history of Windows, what comes to mind? Iconic logos? Changing Start menus? The introduction of Live Tiles? The history of Microsoft’s flagship operating system (OS) includes all of that and so much more. Over the past 35 years, the Windows operating system has been through many reinventions. There have been many versions of Windows over the years — in this guide, we’ll be taking a closer look at 14 different versions, as they all represent major milestones in Windows’ development.
Before we jump into the history of Windows, let’s take a look at what the state of computing was like before Windows.
MS-DOS and what came before
Windows might seem like it’s been around forever, but it hasn’t. Windows was not Microsoft’s first OS. In fact, before Windows ever came along, PCs were run by another OS known as MS-DOS. Unlike even the first version of Windows, navigating your PC with MS-DOS was time-consuming, required the manual input of text commands to get anything done, and didn’t allow for multitasking (the ability to run multiple programs at once).
Windows, at least in 1985, wasn’t so much a brand new OS as it was a solution to the complications that an OS like MS-DOS presented. Windows 1.0 was created to be a graphical user interface (GUI) to be placed on top of MS-DOS, which made PCs that ran MS-DOS easier to navigate — it’s easier to look at a screen and click an icon to open a program than it is to type several commands just to complete the same task.
Windows wasn’t the first GUI created to solve issues like having to navigate via text commands, though. Two other companies got there first: Apple and Xerox. According to Wired, Apple released “the first commercial computer with a graphical user interface” in 1983. It was known as the Lisa. While the Lisa was the first commercial computer with a GUI, it still wasn’t the first computer ever with a GUI. The first one ever was introduced by Xerox in 1981, and it was known as the Star.
While Microsoft was late to the GUI party by about three or four years, it was able to sell its first version of Windows at a much more affordable price than its competitors, giving it a significant advantage.
The evolution of Windows
Windows 1.0
This is the version that started it all. Windows 1.0 debuted in 1985 and was designed to be a GUI to be used in conjunction with MS-DOS. The use of Windows 1.0 as a GUI meant that MS-DOS users didn’t have to manually enter text commands just to complete basic tasks. Now, they could carry out tasks and browse their own files by just pointing and clicking on icons and menus. At the time of its release, Windows 1.0 cost $99 and introduced many computer users to drop-down menus, icons, and dialogue boxes. According to Microsoft, it also featured the ability to multitask applications and “transfer data between programs,” a first for a Microsoft OS.
Don’t let the bare-bones aesthetic of Windows 1.0 fool you — as The Verge notes, Windows 1.0 also came with a number of programs, including Windows Write, Windows Paint, a clock, a calendar, a notepad, a file manager, a cardfile, a terminal application, and even a game called Reversi.
Windows 2.0
It wasn’t long before Microsoft released a successor to its first GUI-enhanced OS. Just two years later, in 1987, the technology company released Windows 2.0. This version of Windows included such notable features as overlapping windows, resizable windows, keyboard shortcuts, and support for VGA graphics. The first Windows versions of Word and Excel also made their debut with Windows 2.0.
Windows 3.0
Microsoft’s next major milestone came with its release of Windows 3.0. This version of Windows is widely considered to be the start of Windows’ worldwide popularity as a desktop OS. Windows 3.0 came out in 1990 and offered 256 color support. More importantly, as PCMag notes, it featured “multitasking DOS programs,” which may have contributed to Windows’ surge in popularity. Another notable feature of Windows 3.0 is that it’s the version that saw the first appearance of the classic desktop game Solitaire.
Windows 3.1
A mere two years later, another OS update appeared, upgrading Windows to one of its most iconic versions, 3.1. The decimal in its name may make it sound like it was just a minor update to 3.0, but it wasn’t. Instead, in 1992, Windows 3.1 delivered quite a few new and essential features, such as support for TrueType fonts, the ability to drag and drop icons, and support for OLE compound documents (documents that combine elements from different programs). Also, according to The Guardian, it’s also the first version of Windows to have been distributed via CD-ROM.
Windows 95
When you think of the most iconic version of Windows, you’re probably thinking of Windows 95. That’s because it was such a huge departure from previous versions of Windows and aesthetically-speaking, and it set the tone for what we’ve come to expect from the Windows OS. As its name suggests, Windows 95 came out in 1995. It was the first 32-bit version of Windows (previous versions had been 16-bit), and it brought quite a few new features that ended up becoming historic additions. These include the taskbar, the Start menu, long file names, and plug-and-play capabilities (in which peripheral devices only needed to be connected to a PC in order to work properly). Windows 95 also saw the introduction of Microsoft’s web browser, Internet Explorer.
Another significant feature? Though Windows 95 still worked in conjunction with MS-DOS, as PCMag notes, unlike its predecessor, Windows 95 didn’t have to have to wait for the PC to boot into DOS first. This version marked the first time Windows was allowed to boot directly.
Windows 98
This is yet another version of Windows with a name that indicates the year it was released. If Windows 95 (eventually) brought us Internet Explorer, then Windows 98 strengthened the web browser’s grip on Microsoft’s OS. Indeed, this version of Windows not only brought us Internet Explorer 4.01, but it also delivered a slew of other internet-based programs and tools, such as Outlook Express, Microsoft Chat, and the Web Publishing Wizard.
Windows 98 also came with increased support for USB devices and Macromedia players (Shockwave and Flash).
Windows 2000
Windows 2000 had a real focus on accessibility and introduced a laundry list of features to the OS, including StickyKeys, a high-contrast theme, Microsoft Magnifier, an on-screen keyboard, and a screen reader known as Microsoft Narrator.
Windows 2000 also delivered the Multilingual User Interface, which allowed users to choose the language in which their display would be viewed. Windows 2000 users could choose from a variety of languages, including Arabic, Japanese, and Greek.
Windows ME
The “ME” in Windows ME stands for “Millennium Edition.” It was also known by another, less flattering moniker: The Mistake Edition. According to PC World, Windows ME earned that nickname when it launched in 2000 because “users reported problems installing it, getting it to run, getting it to work with other hardware or software, and getting it to stop running.”
Despite its rocky start, it still managed to give us a useful tool: System Restore, a recovery feature that, in the event your computer starts having problems due to a poorly executed installation of a program or update, could remove those updates and restore your computer back to how it was before the offending update messed with your computer. In true Mistake Edition fashion, though, System Restore had its own issues to grapple with before it became truly great. For example, it sometimes bungled the restoration process by restoring things like malware that had already been removed.
Windows XP
Windows XP was released in 2001 and is widely considered to be among the great versions of Windows that Microsoft had to offer. There were two main versions of the OS: Home and Professional. Home was for personal use, and Professional was geared toward being used in work settings. As TechRadar notes, part of XP’s success can be attributed to the fact that XP launched right around the same time that there was a sudden increase in PC sales, and so for many new users, “Windows XP was just what came on their first computer.”
Some of XP’s popularity can be traced to the OS itself. After all, something had to be pleasing about its design if it ran for 13 years until Microsoft finally ended support for it in 2014. Some of its commercial success is because it is truly designed to be consumer-friendly. Its warm and inviting aesthetic is well-known: Bright colors, a happy green Start button, and customizable themes finally came standard with this version of Windows. It also came with new features, like native CD burning software, desktop search, remote desktop, and (eventually) improved security.
Windows Vista
Vista was, unfortunately, another widely panned version of Windows. Vista was released in 2007, and one of the biggest sticking points was that its newly designed interface (known as Aero Glass) didn’t necessarily mesh well with older hardware or certain graphics drivers in newer PCs. Other criticisms of Vista included slow performance, overpriced, system resource consumption was too high, and, while the User Account Control feature kept you secure, the constant dialog boxes it generated were annoying.
Vista tried to accomplish too much too fast and got burned for it. It did introduce some helpful features, though, like Windows Defender, DirectX 10 (for PC gaming), speech recognition, and Windows DVD Maker.
Windows 7
Two years later, Microsoft came back with a new version of Windows, known as Windows 7. Microsoft had to make up for Vista’s failures and was able to do just that with Windows 7. Compared to Vista, Windows 7 is a bit more streamlined, and it actually removed many features from previous versions of Windows, including Vista. In fact, there were at least four Vista programs — Windows Photo Gallery, Windows Calendar, Windows Movie Maker, and Windows Mail — that Microsoft did not include in Windows 7.
Windows 7 did, however, come with things like handwriting recognition, faster overall performance, interactive thumbnail previews for minimized app windows, a desktop slideshow feature, Internet Explorer 9, and Windows Media Player 12.
Windows 8
Visually-speaking, Windows 8 was radically different from its predecessors. It’s time to talk about that tile-filled Start screen. The Start screen featured tiles known as Live Tiles that acted as animated app shortcuts, which allowed you to open your apps and also displayed mini-updates about your apps (such as the number of unread messages). The Start screen was supposed to take over the role of the Start menu. In this setup, the traditional Windows desktop still exists in Windows 8, and it’s still where apps are run.
While not everyone was thrilled by the tablet-focused overhaul of Windows 8, it did offer a few other features, such as the ability to log in with a Microsoft account, support for USB 3.0, an actual lock screen (visually similar to a smartphone lock screen), and Xbox Live integration.
Windows 8.1
That jarring Windows 8 Start screen and removal of the Start menu wasn’t particularly well-received by consumers. In response, Windows 8.1 was released as a free upgrade to help address the concerns customers had about its predecessor.
Some of the corrections Microsoft made in Windows 8.1 included having an actual Start button on the taskbar again and letting users see the desktop first after logging in (instead of being greeted by the dreaded Start screen). It didn’t take long for Microsoft to issue this corrective version of Windows: Windows 8 was released in 2012, and Windows 8.1 was released in 2013.
Windows 10
Windows 10 came out in 2015 and is Microsoft’s current iteration of its Windows OS. When it debuted, it was apparent that Microsoft wanted to refine its use of Live Tiles rather than get rid of them altogether. In Windows 10, it compromised: It got rid of the unloved Start screen from Windows 8 and replaced it with a larger Start menu that features the use of Live Tiles, among other kinds of app icons. It worked.
Other features that came with the 2015 version of Windows 10 included the introduction of Cortana, a native digital personal assistant; the ability to switch between tablet and desktop mode; and a new web browser (Microsoft Edge), as per the Verge.
Windows 10 has also received fairly frequent updates since its launch in 2015. They’re called Feature updates, and they happen every six months. They’re always free and available within Windows Update. In fact, the next feature isn’t that far away: Windows 10 20H1 is slated to be released some time in spring 2020, possibly May 2020. This update is expected to include changes such as an overhauled Cortana experience and a new ability to reinstall Windows “by choosing the option to Cloud download Windows, without having to create installation media.”
The future of Windows
We won’t say that Windows 11 will never happen, but it has been five years since Windows 10 first debuted, and Microsoft seems content with just rolling out new feature updates every six months for the latest version of its OS. Plus, it’s not like those feature updates leave Windows users starved for new features and design tweaks to Windows 10. They happen twice a year and often come with a laundry list of bug fixes, new tools, and cosmetic changes to its aesthetic — even if they do have the odd problem of their own.
Just because Windows 11 may not happen, though, that doesn’t mean Windows’ long tradition of reinvention and innovation has to come to an end. Windows, especially in recent years, has become more than just a desktop OS. Take, for instance, Windows Core OS. The future of the Windows OS brand may lie with Core OS, which is expected to be an OS in its own right (not just an upgrade to Windows 10). Core OS is likely to become the flagship OS for more lightweight devices like phones, tablets, and Chromebook-like laptops, with different versions of Core OS for each type of device. It’s possible that the future of Windows may just mean developing different (but still connected) operating systems to accommodate the needs of a more mobile world.

Today’s tech news, curated and condensed for your inbox
Check your inbox!
Please provide a valid email address to continue.
This email address is currently on file. If you are not receiving newsletters, please check your spam folder.
Sorry, an error occurred during subscription. Please try again later.
Editors’ Recommendations
-
Best Gaming PC Deals: Save on RTX 3070, 3080, 3090 PCs
-
Best HP laptop deals: HP Envy, HP Spectre x360, and more
-
Best 17-inch Laptop Deals: Get a large laptop for $330
-
Best Alienware Deals: Save on gaming laptops, PCs and monitors
-
Best gaming laptop deals: Save on Alienware, Asus and more
Updated on July 28, 2022
Since its first release in 1985, the Microsoft Windows operating system has seen numerous adjustments and quite a few major transformations. Now, almost four decades later, the OS looks very different, but still familiar, with staple features that have survived throughout the years.
Let’s take a brief look into the history of the world’s most ubiquitous operating system, from its birth to the latest arrivals on the market. The Microsoft Windows timeline illustrates some of the most important releases in the history of the OS, from version 1.0, Windows 95 and the first mobile versions, to Windows 11 and Server 2022.
As an interesting fact, Windows 1.0, Microsoft’s first graphical user interface, was received poorly by critics because they considered it too mouse-focused (the mouse was relatively new at the time). It was Windows 95, released a decade later, that truly managed to cement the company’s dominance in the computer industry.
History of Microsoft Windows: a timeline
- 1985, November: Windows 1.0
- 1987, December: Windows 2.0
- 1990, May: Windows 3.0
- 1993, July: Windows NT 3.1
- 1994, September: Windows NT 3.5
- 1995, August: Windows 95
- 1996, August: Windows NT 4.0
- 1996, November: Windows CE 1.0
- 1997, September: Windows CE 2.0
- 1998, June: Windows 98
- 1999, May: Windows 98 SE
- 2000, February: Windows 2000
- 2000, April: Windows CE 3.0
- 2000, April: Pocket PC 2000
- 2000, September: Windows ME
- 2001, October: Windows XP
- 2001, October: Pocket PC 2002
- 2002, January: Windows CE 4.x
- 2003, April: Windows Server 2003
- 2003, June: Mobile 2003
- 2004, July: Windows CE 5.0
- 2005, May: Mobile 5.0
- 2006, November: Windows Vista
- 2007, February: Windows CE 6.0
- 2007, November: Windows Home Server
- 2008, February: Windows Server 2008
- 2009, October: Windows 7
- 2010, November: Windows Phone 7
- 2011, March: Embedded Compact 7
- 2011, April: Windows Home Server 2011
- 2012, September: Windows Server 2012
- 2012, October: Windows Phone 8
- 2012, October: Windows 8
- 2015, July: Windows 10
- 2015, November: Windows 10 Mobile
- 2016, September: Windows Server 2016
- 2018, October: Windows Server 2019
- 2021, August: Windows Server 2022
- 2021, October: Windows 11
Frequently asked questions about the history of Microsoft Windows
What is the history of Microsoft Windows?
The first version of the Windows OS was released in 1985, and it was a Graphical User Interface (GUI) offered as an extension of Microsoft’s existing disk operating system (MS-DOS). It was partially based on licensed concepts that Apple Inc. had used for its Macintosh System Software and included drop-down menus, scroll bars and other features.
Since its release, there have been several major versions of the Windows OS. Currently, Windows dominates the desktop PC market, with more than a billion active devices that run on the most recent Windows 11 and 10 systems.
Who invented Windows operating system?
Bill Gates, the co-founder of Microsoft, ran the development of Windows 1.0, the first version of this operating system.
In 1985, Microsoft introduced an operating environment named Windows. Although, in theory, Windows was designed to replace MS-DOS, it was in fact a graphical user interface running on top of MS-DOS.
How many versions of Microsoft Windows are there?
There has been a multitude of versions of the Microsoft Windows OS since its first release in 1985.
We’ve put together a list of 14 of the major Windows versions that marked key OS updates:
- Windows 1.0 (1985)
- Windows 2.0 (1987)
- Windows 3.1 (1992)
- Windows NT (1993)
- Windows 95 (1995)
- Windows 98 (1998)
- Windows ME and 2000 (2000)
- Windows XP (2001)
- Windows Vista (2007)
- Windows 7 (2009)
- Windows 8 (2012)
- Windows 8.1 (2013)
- Windows 10 (2015)
- Windows 11 (2021)
Microsoft released a lot of intermediary Windows versions, developed for several main use categories:
- Personal computer versions (totaling around 40, plus several cancelled)
- Mobile versions (totaling around 17, plus several cancelled)
- Server versions (totaling around 24)
- Device versions (totaling around 16)
- Embedded versions (totaling around 20)
What are the different versions of Microsoft Windows operating system for mobile devices?
This is a short history of Microsoft’s operating systems for mobile devices:
Windows Mobile operating systems developed by Microsoft for smartphones (currently discontinued) include the following versions:
- Windows CE
- Pocket PC 2000
- Pocket PC 2002
- Windows Mobile 2003
- Windows Mobile 2003 SE
- Windows Mobile 5
- Windows Mobile 6
- Windows Mobile 6.1
- Windows Mobile 6.5
Windows Phone (WP) mobile operating systems developed by Microsoft for smartphones as the replacement successor to Windows Mobile and Zune (currently discontinued) include the following versions:
- Windows Phone 7
- Windows Phone 8
- Windows Phone 8.1
- Windows 10 Mobile
The latest Microsoft OS for mobile devices is Windows 10 Mobile OS and is currently discontinued. Microsoft ended support for Windows 10 Mobile in 2020.
When was Microsoft Windows invented?
In 1985, Microsoft released the operating environment named Windows, which was a graphical user interface for MS-DOS. Bill Gates, the co-founder of Microsoft, is the person credited for its development.
What are the Windows versions in order?
Here is a list of the major Microsoft Windows versions ordered by release year:
- Windows 1.0 (1985)
- Windows 2.0 (1987)
- Windows 3.1 (1992)
- Windows NT (1993)
- Windows 95 (1995)
- Windows 98 (1998)
- Windows ME and 2000 (2000)
- Windows XP (2001)
- Windows Vista (2007)
- Windows 7 (2009)
- Windows 8 (2012)
- Windows 8.1 (2013)
- Windows 10 (2015)
- Windows 11 (2021)
What is the latest Windows version?
Windows 11 is the most recent version of Windows for PCs, tablets and embedded devices. It was released in October 2021.
The most recent version for server computers is Windows Server 2022. It was released in August 2021.
Is there a mobile version of Windows?
Not anymore. The latest mobile version of the Windows OS is Windows 10 Mobile, released on February 12, 2015. It is a mobile operating system for smartphones and tablets with screens smaller than 8 inches. The last OS/security update was in 2020 and the OS is now in a declining phase.
Is Windows Mobile OS still available?
Not for long. Windows 10 Mobile is a discontinued mobile operating system developed by Microsoft. First released in 2015, it is a successor to Windows Phone 8.1, but was marketed by Microsoft as being an edition of its PC operating system Windows 10.
About the Microsoft Windows timeline
The Microsoft Windows timeline was created using Office Timeline, a PowerPoint add-in that helps you build impressive timelines, schedules and charts fast and easily.
The illustration can be downloaded free of charge as a PowerPoint slide, and it is fully customizable. To edit or update the graphic, you can install the free trial of Office Timeline and add any milestones we might have missed. Or create your own timelines and roadmaps from scratch, all in a matter of minutes.
Turn project data into professional timelines
Get the advanced features of Office Timeline Pro+ free for 14 days.
Get free trial
Windows 11 – это ещё один шаг вперёд в развитии операционных систем. Но премьера последнего продукта Microsoft – это также повод оглянуться назад и вспомнить, как выглядели предыдущие версии Windows. История операционной системы от Microsoft насчитывает более 40 лет, за это время появилось несколько более или менее успешных редакций.
Познакомьтесь с историей Windows, которая непременно верн`т воспоминания из прошлого (более или менее далекого).
История самой популярной в настоящее время компьютерной системы в мире началась в семидесятых годах двадцатого века. Тогда Билл Гейтс и Пол Аллен, буквально работая в гараже, занимались разработкой программного обеспечения для аналитиков. Их продукт Xenix, предназначенный для бизнес-клиентов, показал себя неплохо. Это была разновидность популярной тогда системы Unix.
Компания называлась Micro-Soft, и тогда никто не ожидал, что через несколько лет Гейтс и Аллен станут одними из самых узнаваемых людей в мире.
MS-DOS и Microsoft Interface Manager
Дуэт разработчиков начал набирать популярность в начале 1980-х, когда хорошо продавалась система MS-DOS. Это была текстовая среда, которая была далека от внешнего вида и возможностей более поздней Windows. Благодаря сотрудничеству с IBM, с каждым годом всё больше и больше компаний использовали эту систему.
Выставка COMDEX стала настоящим прорывом. Именно на ней Гейтс увидел концепцию графического интерфейса Visi On и сказал, что пора начать разрабатывать MS-DOS в том направлении, которое мы знаем сегодня – оконная система.
Графический интерфейс для MS-DOS должен был называться Microsoft Interface Manager. Роланд Хэнсон, глава отдела маркетинга Microsoft, предложил другое название – Windows. По его словам, оно должно был быть более удобным для пользователя, и поэтому Хэнсону удалось убедить команду пойти на изменение.
В первой половине 1980-х истории Microsoft и Apple пересекаются. Можно сказать, что тогда компании одновременно сотрудничали и конкурировали друг с другом. Премьера Macintosh ускорила работу над первой Windows, а планы Билла Гейтса побудили Стива Джобса действовать. Однако, первые системы Microsoft, работающие на компьютерах Apple, имели определенные ограничения по внешнему виду, связанные с лицензией. Компания под знаком надкушенного яблока запретила, в том числе, перекрытие окон и использование корзины файлов, потому что эти решения уже были реализованы в Apple OS. Так что гигант из Купертино хотел оставить некоторые решения только себе.
В конце концов, 80-е годы были тесным сотрудничеством между Microsoft и Apple. Компании уже были в авангарде развития компьютеризации, а Гейтса и Джобса называли провидцами.
Windows 1 – первая и не очень удачная
Так мы добрались до 1985 года, потому что именно тогда на рынок вышла Windows 1.0. Именно MS-DOS предложила новые графические решения, а не только текст, как раньше. Таким образом, первая Windows содержала недостатки своей базовой системы, но вместе с ней дебютировали приложения, известные по сей день – Калькулятор, Календарь, Часы, Буфер обмена, Панель управления, Блокнот, Paint, Write (предшественник Word) и игра Reversi.
Хотя Windows 1 на тот момент можно было назвать прорывом, она не пользовалась особой популярностью среди пользователей. Система требовала управления мышью, и тогда это было что-то совершенно новое, что не нравилось пользователям Windows 1.
Однако, дебют новой системы стал большим кирпичом в фундаменте дальнейшего успеха Microsoft. Через год после выпуска Windows 1 компания Билла Гейтса публично дебютировала и перенесла свою штаб-квартиру из Белвью в Редмонд.
Windows 2 – определенно лучше своей предшественницы
Любые нелестные отзывы о первой Windows не помешали Microsoft разработать свою флагманскую систему. В 1987 году дебютировала Windows 2. Улучшения в управлении памятью, благодаря которым она лучше справлялась с многозадачностью. Сам интерфейс претерпел некоторые изменения – использовались перекрывающиеся окна. Apple даже подала в суд на Microsoft за это изменение, но компания из Редмонда выиграла спор.
Windows 2 представила новые сочетания клавиш и, кроме того, базовое офисное программное обеспечение – Word и Excel, которые по-прежнему отлично работают. Aldus PageMaker DTP позволил подготавливать контент для печати и был очень хорошо принят пользователями. Это также была первая программа, созданная сторонней компанией.
Windows 2 стала для Microsoft очень большим шагом вперед. Его успех убедительно свидетельствовал о том, что развитие системы идет в правильном направлении.
Windows 3 и Windows 3.1 – начало настоящего расширения
Появление Windows 3 на рынке в 1990 году открыло совершенно новую главу в истории Microsoft. Успех был огромным – 2 миллиона копий было продано за первые шесть месяцев и 10 миллионов за два года после выпуска.
Что в первую очередь повлияло на успех? Улучшение интерфейса и новые возможности системы. И здесь Apple снова обратилась в суд – Microsoft было предъявлено 189 обвинений, связанных с «внешним видом и работой» системы. Суд отклонил 179 из них и признал 10 идеями, не защищенными авторским правом.
Виртуальная память была введена в Windows 3, что позволило системе работать с несколькими программами одновременно. Таким образом, она была подготовлена к многозадачности. Вышеупомянутый графический интерфейс был улучшен благодаря расширенной цветовой палитре, а также возможностям, предлагаемым видеокартами VGA того времени.
Пользователи также нашли Windows 3 очень интуитивно понятной: не нужно было учиться использовать систему, как раньше. Microsoft использовала цветные значки для каждой программы, можно было перетаскивать файлы, а двойной щелчок на рабочем столе открывал список задач. Всем известный пасьянс также дебютировал в этой версии системы.
Вся система стала более быстрой и надёжной, чем предыдущие, и позволила более эффективно работать. Конечно, необходимо уточнить, что когда мы говорим «система», мы всё ещё говорим об MS-DOS.
Windows 3.1 – первая с 32-битной архитектурой
До того, как Windows 3.1 стала доступной для пользователей, ранее (в 1991 году) Microsoft выпустила Windows 3.0 с мультимедийными расширениями. Она устанавливалась в компьютеры со звуковыми картами и приводами CD-ROM. Появились новые приложения: Media Player, Music Box и Sound Recorder. С помощью расширений можно было установить заставку или изменить системные звуки.
Все эти функции были включены в Windows 3.1, выпущенную в 1992 году. Изначально она создавалась в сотрудничестве с IBM. Однако, в конечном итоге, компании не пришли к соглашению, и Microsoft пошла своим путем, выпустив Windows 3.1.
Использование 32-битной архитектуры стало значительным шагом вперёд. В результате на рынке стало появляться все больше и больше программ, написанных для Windows. Minesweeper появился в системных играх, а Doom начал раскручивать настоящие компьютерные игры.
Кроме того, Microsoft выпустила надстройку «Windows для рабочих групп». В ней были специальные сетевые драйверы, а также большее количество офисных программ. А в свободное от работы время пользователи могли поиграть в «Червы» – сетевую игру.
Windows NT 3.1 – для бизнес-клиентов
В 1993 году Microsoft представила новую линейку систем. NT или New Technology не нуждалась в MS-DOS для работы, она использовала файловую систему NTFS и была нацелена на бизнес-клиентов. Название было унаследовано от Windows 3.1, потому что у неё был тот же интерфейс. Однако, система предъявляла высокие требования к оборудованию и плохо работала с 16-битными программами.
Windows 3.1 NT отлично работала в локальных сетях. Благодаря расширенным сетевым возможностям она стала основной операционной системой, используемой на компьютерах в компаниях. Вскоре появились версии 3.5 и 3.51, улучшившие работу системы.
Windows 95 – классика в чистом смысле этого слова
Windows 95 стала системой, которая подверглась значительному обновлению, если сравнивать её со своим предшественником. Microsoft продала 7 миллионов копий за месяц, и можно с уверенностью сказать, что глобальное доминирование Windows среди компьютерных операционных систем стало фактом.
Microsoft полностью перестроила интерфейс – вы могли размещать папки и ярлыки на рабочем столе, панель задач впервые появилась внизу экрана, а в левом нижнем углу появилась кнопка «Пуск» с выпадающим меню. На уровне меню у пользователя был лёгкий доступ ко всем программам, документам, настройкам, поисковой системе и командной строке. Там же была кнопка для выключения компьютера, а в верхней части меню «Пуск» можно было закрепить собственные ярлыки.
Диспетчер файлов, использовавшийся в предыдущих версиях, заменил известный по сей день проводник Windows. На рабочем столе появилась чрезвычайно важная папка – «Мой компьютер». Здесь находился список дисков, дисководов для гибких дисков, приводов компакт-дисков, принтеров и сетевых подключений. Рабочий стол также был дополнен корзиной, куда отправлялись все удаленные файлы. Таким образом Microsoft «дала Apple по носу», продемонстрировав бесполезность судебных исков.
В правом верхнем углу каждого окна были кнопки: свернуть, развернуть и закрыть окно. Щелкнув правой кнопкой мыши, можно было запустить меню.
Если смотреть на Windows 95 с технической стороны, MS-DOS была просто элементом процедуры запуска компьютера. Но, приложения MS-DOS всё ещё можно было открывать, потому что Win95 была с ними совместима. Значительным улучшением стала функция Plug and Play, благодаря которой система автоматически обнаруживала новые устройства и устанавливала драйверы.
Обновления Windows 95
Сама Windows 95 была успешной системой. Обновления добавили к ней новые функции, в том числе: Internet Explorer, поддержку файловой системы FAT32 и USB-портов, инструмент сжатия диска (DriveSpace 3) или визуальные темы.
Windows NT 4.0
При выпуске Windows NT 4.0 в 1996 году Microsoft планировала использовать линейку NT для нужд рабочих станций. Система переняла интерфейс после Windows 95, и в дополнение к надстройкам, которые были включены в обновления Win95, она поддерживала DirectX 2, получила Internet Explorer 2.0 и новый диспетчер задач.
Всего было выпущено пять версий: Workstation для использования на рабочих станциях, три варианта для серверов и Embedded для использования в банкоматах.
Windows 98 – одна из самых успешных систем Microsoft
История систем Windows уходит в те времена, когда компьютеры были оборудованием не только будущего, но и настоящего. В июне 1998 года Microsoft запустила в продажу Windows 98. На первый взгляд она показалась улучшенной «девять-пять». Однако, первую версию часто критиковали за медлительность и ненадёжность.
Только год спустя была выпущена Windows 98 SE, которая была улучшена, и можно смело сказать, что мы имели дело с лучшей системой для того времени. Он была быстрее, стабильнее и безопаснее своего предшественника. Windows 98 определенно покорила компьютерный мир в конце двадцатого века и оказалась огромным успехом для Microsoft.
Windows 98, помимо всех полезных решений и инструментов, содержащихся в Win95, принесла некоторые обновления. Сразу после запуска была заметна строка заголовка, фон которого состоял из двух пересекающихся друг с другом цветов. В проводнике Windows появились кнопки Назад и Вперёд, на рабочем столе место для папки «Мои документы», а специальная функция Active Desktop позволила установить веб-сайт в качестве фона рабочего стола. Кроме того, вышеупомянутая версия Windows 98 SE добавила пользователям Windows Media Player.
Если посмотреть на техническую страницу, Windows 98 поддерживает файловую систему FAT32. Это позволяло создавать разделы диска емкостью не менее 2 ГБ. Была улучшена совместимость с модемами и устройствами, подключенными через USB, а известный по сей день Центр обновления Windows отвечал за обновления системы.
Не обошлось и без разногласий. Интеграция Internet Explorer с пользовательским интерфейсом и файловым менеджером закончилась судебным разбирательством. Правительство США обвинило Microsoft в использовании своего доминирующего положения на рынке для продвижения собственных продуктов. Спор закончился необходимостью выпустить больше систем без популярного браузера.
Windows 2000 – продолжение линейки NT
Microsoft продолжала работать над линейкой NT, которая предназначалась для серверов и рабочих станций. Windows 2000, первоначально разработанная как Windows NT 5.0, была выпущена в феврале 2000 года. Хотя и появилась её версия для домашних компьютеров, особого признания она не нашла, в основном из-за отсутствия драйверов для внешних устройств.
Наиболее важными особенностями Windows 2000 являются поддержка файловой системы NTFS 3.0, возможность шифрования файлов, служба Active Directory, улучшенные драйверы DirectX, функция служб терминалов (уже доступная во всех версиях системы) и появление шрифтов OpenType. Кроме того, Microsoft опубликовала выпуски Advanced Server, DataCenter Server, Advanded Server LE и DataCenter LE.
Windows 2000 не достигла большого коммерческого успеха, но не из-за её недостатков, а из-за её предназначения. Сама по себе это была довольно хорошая система, и она неплохо зарекомендовала себя в компаниях.
Windows Millenium Edition, а точнее Mistake Edition
Вы знаете кого-нибудь, кто положительно отзывался о Windows Millennium? Знакомьтесь… это я. Потому что я был единственным среди моих друзей, у кого не было серьёзных проблем с Windows Me. Почему так было? Я не знаю и, наверное, никогда не узнаю.
Windows Millenium Edition была выпущена в 2000 году как преемница Win98. Она расширила возможности мультимедиа и Интернета с введением Windows Movie Marker, нового медиаплеера, DVD-плеера и функций универсального Plug and Play, которые сделали подключение устройств ещё проще, чем раньше.
Windows ME больше не позволяла запускать приложения MS-DOS (хотя она была основана на ней) и должна была стать первой системой серии NT, которая также была нацелена на домашних пользователей. Microsoft планировала объединить потребительское и бизнес-направления. Однако, в конечном итоге, планы изменились, и можно сказать, что система писалась «на коленях». Нестабильность и количество ошибок, появившихся при использовании Windows ME, сделали её известной как Windows Mistake Edition, и она стала известной во всем мире как худшая система Microsoft за всю историю.
Windows XP – лучшая Windows на свете
Windows XP уже стала легендой среди операционных систем. Она появилась в октябре 2001 года и стал ответом на ранее неудачную версию Millennium Edition. В то время компьютер стал входить «в стандартную комплектацию каждого дома», и благодаря этому миллионы людей только в России выросли на XP (не говоря уже о мировом успехе). По оценкам, XP всё ещё работает на 10% компьютеров по всему миру, и многие пользователи считают её лучшей в истории.
Система была основана на коде, используемом в NT. Microsoft решила представить две основные версии: Home Edition – для домашнего использования, которая является прямым преемником ME, и Professional – предназначенная для компаний и заменяющая Windows 2000. Таким образом, Windows XP объединила потребительские и бизнес-направления.
Системные значки претерпели значительные изменения, а двухколоночное меню «Пуск» упростило доступ к любимым программам, играм или файлам. Если на панели задач было слишком много значков, система группировала их вместе, чтобы освободить место. Хорошим решением было также введение автоматически открывающегося окна, которое предлагало определенное действие после обнаружения нового носителя данных.
Введение учетных записей пользователей было большим новшеством. Это позволило легко переключаться между ними, не закрывая все свои программы. Пользователи ноутбуков могли следить за состоянием заряда аккумулятора, и если он был низким, система переходила в спящий режим. Браузером по умолчанию для Windows XP был Internet Explorer 6. Отображение шрифтов на ЖК-экранах также улучшилось благодаря технологии ClearType.
Windows XP была первой системой, которая требовала активации через Интернет или по телефону. Это должно было защитить продукт от пиратства, но как это было на самом деле, мы все хорошо помним.
Windows XP в других выпусках
Помимо основных версий –А Home и Professional, со временем на рынке стали появляться и другие редакции новейшей системы. Media Center Edition – это не только немного измененный внешний вид, но больше всего мультимедийные функции и возможность дистанционного управления. Tablet PC Edition – это, как следует из названия, система для планшетов, которая отличалась возможностью подключения стилуса. Обе системы были выпущены в 2004 и 2005 годах.
Windows XP также была первой системой, поддерживающей 64-битную архитектуру. Это стало возможным благодаря специальным выпускам: XP 64-bit Edition и Professional x64 Edition. Полная противоположность этому – Windows XP Starter Edition, нацеленная на пользователей в странах, где компьютеры были в новинку. Она даже включал учебные пособия по использованию оборудования и системы, но была лишена многих функций. Windows Fundamental for Legacy PC имела аналогичную цель, потому что имела низкие требования к оборудованию и была нацелена на устройства с низкой производительностью.
Пакеты обновлений – исправления и новые функции
Патчи Service Pack были очень популярны во времена, когда Windows XP была королем. SP1, выпущенный в 2002 году, добавил поддержку жёстких дисков USB 2.0 и 128 ГБ.
Пакет обновления 2 (SP2), который появился на компьютерах в 2004 году, внёс дополнительные изменения. Благодаря этой поправке пользователи могли использовать расширенный центр безопасности, система получила совершенно новый межсетевой экран, а технология NoExecute помогала бороться с вирусами. Internet Explorer получил чрезвычайно полезный блокировщик всплывающих окон.
Последним исправлением был Service Pack 3. Он дебютировал в 2008 году, после премьеры Windows Vista, о которой мы поговорим позже. SP3 повысил производительность системы и включил новые драйверы. Microsoft попыталась бороться с чрезвычайно процветающим пиратством с помощью нового метода активации.
Поддержка SP3, как и всей Windows XP, закончилась в 2014 году. Таким образом, это была самая долго разрабатываемая система Microsoft в истории.
Windows Server 2003
Microsoft также не отказалась от серверных решений. Через два года после выхода Windows XP на её основе появилась Windows Server 2003.
WS2003 представил функцию «Управление сервером», которая упростила ввод настроек сервера. Internet Explorer был модифицирован под нужды системы – в первую очередь, в нём появилась надстройка Enhanced Security Configuration, отвечающая за защиту от заражённых сайтов. На практике оказалось, что он относился ко всему Интернету как к опасному.
Кроме того, Microsoft улучшила сетевые функции, чтобы сделать их более стабильными. Windows 2003 включала .NET Framework 1.1 и поддержку файловых систем FAT, FAT32 и NTFS.
Существовали также версии системы для других приложений – всего Microsoft выпустила их пять. В 2005 и 2007 годах тоже были исправления – SP1 и SP2. Они представили, среди прочего, мастер безопасности системы или брандмауэр Windows, а также дополнительно улучшили производительность. Кроме того, Microsoft выпустила вторую редакцию под названием Windows Server 2003 R2. Она предоставила пользователям новые инструменты администрирования и функции совместного использования ресурсов.
Windows Longhorn – проект, превратившийся в Vista
Прежде чем мы пойдём дальше, рекомендуется на мгновение остановиться на системе Windows Longhorn (или, скорее, на её прототипе). Изначально она должна была стать преемником Windows XP, и Microsoft начала работать над ней в 2002 году. В продажу планировалось поступить через два года. Однако, несколько раз отложенная премьера привела к приостановке проекта. Лонгхорн «умерла», и родилась Vista.
Windows Vista – красивая, но бездушная
2007 год принёс новую систему – Windows Vista. Главной новинкой стал полностью новый пользовательский интерфейс под названием Aero, который отличался частично прозрачными окнами. К счастью, для более слабых компьютеров были доступны и другие, более лёгкие стили с классическим видом, известным по Windows 2000.
Кнопка «Пуск» изменилась, превратившись в круглый логотип Windows. Диалоги и значки получили новый вид. В правой части экрана была полоска, к которой можно было прикрепить гаджеты – часы, календарь или погоду. В системе установлены новые версии программ – Internet Explorer 7 и Windows Media Player 11. Появилась возможность записывать популярные в то время DVD. При перемещении курсора по приложению на панели задач открывалось небольшое окно с предварительным просмотром его текущего состояния.
Microsoft посвятила много работы повышению безопасности. Был расширен системный брандмауэр, введен контроль учетных записей пользователей (любое изменение в системе должно было подтверждаться вручную), а также множество инструментов было передано родительскому контролю. Vista была первой системой, предлагающей BitLocker, то есть шифрование целых дисков или разделов. Большинство обновлений происходило в фоновом режиме, и перезагружать компьютер не требовалось.
Windows Vista, хотя казалась большим шагом вперед, оказалась неудачной. Бесчисленные ошибки и высокие требования к оборудованию заставили многих пользователей вернуться к «честной XP».
Microsoft выпустила шесть версий системы, которые также не встретили одобрения. Vista Starter выходила на рынках развивающихся стран, Vista Home Basic – это домашняя версия, но без многих мультимедийных функций. Vista Home Premium можно сравнить с Windows XP Media Center Edition. Также были версии для компаний – Vista Business и Vista Enterprise. Самым обширным вариантом была Vista Ultimate, которая включала в себя все функции, известные из других вариантов.
Для Vista Microsoft выпустила два исправления. Первый пакет обновления улучшил стабильность и производительность системы. Исправлено множество ошибок и решено множество проблем. Так что это был настоящий фикс, в котором сложно было уместить новизну. Тот же подход был использован для SP2, который также был типичным Repair Pack. Vista поддерживалась до 2017 года.
Windows Server 2008 и Windows Home Server
Windows Server 2008 принесла много нового. Одним из наиболее интересных был режим установки Core, то есть система без графического интерфейса, управляемая через командную строку, Power Shell или удаленно с помощью MMC. Пользователи также получили новые и более обширные инструменты управления сервером.
Windows Home Server была разработана для небольших домашних сетей. Её основная идея заключалась в том, чтобы облегчить подключение компьютеров, консолей и других устройств к серверу. Благодаря этому было легко делиться мультимедиа в домашней сети.
Windows 7 – стабильная версия Vista
Премьера Windows 7 в 2009 году подтвердила, что история прошла полный круг – Microsoft выпускает лучшую, а иногда и худшую систему. После не очень удачного предшественника «семёрка» пришлась по душе пользователям. Об этом свидетельствует тот факт, что через год после премьеры Windows 7 превзошла Vista по количеству установок.
Начнём с интерфейса, который выглядел в слегка обновленным стилем Aero. В нём есть несколько полезных опций – настройка области уведомлений в соответствии с вашими потребностями, разделение экрана путём перетаскивания окон к левому или правому краю или приложение Sticky Notes, которое позволяет закреплять заметки в любом месте. Боковая панель с гаджетами исчезла, теперь их можно было разместить где угодно на рабочем столе. Microsoft также перенесла поле поиска файлов – в Win7 оно попало в верхний угол файлового проводника.
Windows 7 была доступна в 64-битной и 32-битной версиях. Microsoft посвятила много работы обеспечению стабильности и оптимизации системы. И это окупилось – новейшая Windows загружалась быстрее, хорошо работала с приложениями и играми, это также позволило улучшить управление энергопотреблением в ноутбуках (тогда они начали медленно завоевывать рынок). Windows 7 также поддерживала Multi-Touch или мультисенсорные экраны, которые в то время были новинкой.
Как и в случае с Vista, Microsoft выпустила шесть версий «семерки». Появился традиционно сильно урезанный Starter для развивающихся рынков, а также две версии Home для нужд домашних компьютеров. Опытные пользователи могли использовать версию Professional, которая уже поддерживала диски с максимальной емкостью 192 ГБ, двухъядерные процессоры или режим Windows XP (разрешено запускать приложения, несовместимые с Win7). Версии Enterprise и Ultimate предназначались для компаний и включали BitLocker, DirectAccess и Virtual Hard Disk.
Фактически был выпущен один пакет обновлений, который содержал обновления и исправления. Windows 7 поддерживалась до 2020 года, и, как оказалось, её по-прежнему использует около 15% пользователей по всему миру.
Windows Server 2008 R2
Серверным эквивалентом Win7 была Windows Server 2008 R2. Она включала новые функции Active Directory, улучшения DHCP-сервера и расширенные возможности виртуализации. Она поддерживает до 64 физических процессоров или 256 логических ядер.
Всего существует семь версий: Foundation, Web, Standard, HPC Server, Enterprise, Datacenter, Itanium. Windows Home Server 2011 была предназначена для малых предприятий и домашних компьютеров.
Windows 8 – больше плиток, чем окон
Windows 8 – это попытка устроить революцию среди систем Microsoft. Прежде всего, она была адаптирована под сенсорные экраны. Она стартовала в 2012 году, и именно тогда устройства с сенсорным управлением начали набирать популярность.
Windows 8 принесла полностью переработанный интерфейс – Modern UI. Если бы описать это одним словом – минималистично. Меню «Пуск» было заменено стартовым экраном, на котором мы могли найти значки в виде плиток. Впервые в системе появились приложения, доступные в Магазине Windows. Кнопка «Пуск» исчезла с панели задач и перешла в скользящее меню в правой части экрана, которое также содержало, среди прочего, поисковую систему, ярлык для системных настроек или кнопку для выключения компьютера.
Новая система уже поддерживала USB 3.0, NFC, поддерживала UEFI и была подготовлена для облачных вычислений.
Microsoft выпустила четыре версии:
- Windows 8 – для домашних компьютеров.
- Windows 8 Pro – разрешала использовать, например, BitLocker и Windows Remote Desktop.
- Windows 8 Enterprise – редакция, предназначенная для компаний; он включала прямой доступ, блокировку приложений и функцию Windows To Go, что позволяло установить систему на USB-накопитель и запустить её на другом компьютере.
- Windows RT – предназначена для устройств ARM, включая планшеты.
Однако, Windows 8 вызвала серьёзную критику. Наибольший удар пришёлся по интерфейсу Modern UI, который считался неинтуитивным и совершенно неудобным при традиционном использовании мыши и клавиатуры. Говорили, что Microsoft настолько переработала интерфейс под сенсорные устройства, что забыла о самых обычных компьютерах. Но были и более теплые слова о Win8 – пользователи оценили лучшую производительность системы и хорошую безопасность.
Стоит отметить, что в 2012 году на рынке также появилась Windows Phone 8, предназначенная для смартфонов. Однако, это принесло убытки Microsoft и она определенно проиграла борьбу Android.
Windows 8.1
В ответ на критику Win8 Microsoft обновила систему до Windows 8.1. Кнопка «Пуск» снова появилась на панели задач. На стартовом экране появилось больше возможностей персонализации, на нём также есть кнопка включения, так что вам не приходилось искать её где-то в не очень интуитивно понятном боковом меню. В обновлении появился новый браузер Internet Explorer 11, который позволял запускать любое количество вкладок. Кроме того, была внедрена интеграция с OneDrive, благодаря которой локальные файлы можно было автоматически синхронизировать с облаком.
В какой-то степени Windows 8.1 заставила критиков замолчать, в основном из-за улучшенного современного пользовательского интерфейса. Однако, по-прежнему преобладали мнения о том, что «восьмерка» – несостоятельная система. Во всяком случае, по популярности она так и не превзошла своего предшественника.
Windows Server 2012
Windows Server 2012 основана на Win 8. Основными нововведениями стали: возможность создавать виртуальные машины с UEFI, поддержка Office 365, Automated Tiering или Windows Power Shell 4 (в нём около 2300 команд, у предшественника только 200).
Существует четыре версии системы – Foundation, Essentials, Standard и Datacenter.
Windows 10 – снова успех
Microsoft довольно быстро приступила к работе над новой системой. Было решено пропустить число девять в названии, и была создана Windows 10.
Она должна символизировать платформу, которая будет универсальной и сможет управлять различными типами устройств – компьютерами, планшетами, ноутбуками или смартфонами. Одно из основных предположений заключалось в том, чтобы объединить решения, известные из Windows 7 и Windows 8, таким образом, создав целостную систему. Кстати, использование 10 в названии предназначалось для предотвращения возможных аналогий с уже историческими системами Win95 и Win98.
Ещё до выпуска «десятки» Microsoft сделала доступной программу Windows Insider, участники которой могли протестировать систему и прокомментировать её. Гигант из Редмонда хотел использовать отзывы пользователей для создания Windows 10. Программа также использовалась для тестирования Windows 11.
Windows 10 появилась на рынке в 2015 году. Устройства с установленной Windows 7 или Windows 8 можно бесплатно обновить до Win10.
В связи с универсальностью системы выпущено несколько редакций:
- домашние версии – S, Home и Pro
- выпуски для компаний, организаций или учреждений – Enterprise, Education, Pro Education, Remote Server, Professional Workstation
- версии для различных типов устройств – Xbox One, Mobile, Mobile Enterprise, IoT Core, IoT Enterprise, IoT Mobile Enterprise
Что нового в Windows 10
Наиболее важные изменения были внесены в интерфейс, который, как было заявлено, объединил внешний вид и функциональность двух предыдущих систем. Мы получили меню «Пуск» с плитками, приложения из Microsoft Store, открываемые классически в окнах, а поисковая система на панели задач совместима с голосовым помощником – Cortana.
Вы можете использовать представление задач, в котором представлены все включенные приложения, а также создавать дополнительные рабочие столы. В правом нижнем углу находится Центр уведомлений, который используется для отображения уведомлений и позволяет перейти к настройкам.
Кроме того, новинкой стало введение входа в систему с помощью распознавания лиц. С запуском Windows 10 старый Internet Explorer был закрыт. На его месте появился модернизированный Microsoft Edge.
В 2021 году Windows 10 установлена на 60% компьютеров по всему миру, оставив конкурентов далеко позади. Она использовалась шесть лет, и в этом отношении лучше была только Windows XP, которая хорошо себя чувствовала около 10 лет (отчасти из-за слабых преемников).
Windows Server 2016 и Windows Server 2019
Нельзя не упомянуть серверные системы. Первой, основанной на «десятке», была Windows Server 2016. В ней появились Защитник Windows и PowerShell 5.1, были оптимизированы сервисы облачного хранилища, а в Hyper-V внесено множество улучшений для виртуализации.
Преемником является Windows Server 2019, которая (на дату публикации) постепенно уступает место версии 2022 года на базе Windows 11. Версия 2019 года интегрирована со средой Linux, поддерживает Kubernets и имеет такие функции, как: Служба миграции хранилища, System Insights или реплика хранилища.
Windows 11 – конец и начало истории
Невозможно даже сравнивать возможности упомянутых в начале статьи систем и оборудования с известными на данный момент решениями. В мире технологий время имеет совершенно другое значение, и то, что было 40 лет назад, можно рассматривать как предысторию. Но когда-нибудь и Windows 11 станет архаичной, смею сказать, намного быстрее, чем через 40 лет. Однако, сейчас она открывает совершенно новую главу в истории операционных систем.


Данная статья представляет краткий обзор всех версий операционной системы Windows.
Версия Вашей системы: Windows 7
Версии для настольных компьютеров
| Логотип | Версия | Год | Статус |
|---|---|---|---|
 |
Windows 1 | 1985 | Не поддерживается Не используется |
 |
Windows 2 | 1987 | |
 |
Windows 3 | 1990 | |
 |
Windows NT 3.1 | 1993 | |
 |
Windows NT 3.5 Workstation | 1994 | |
 |
Windows NT 3.51 | 1995 | |
 |
Windows 95 | 1995 | |
 |
Windows NT 4.0 | 1996 | |
 |
Windows 98 | 1998 | |
 |
Windows Millenium | 2000 | |
 |
Windows 2000 (NT 5.0) | 2000 | |
 |
Windows XP (NT 5.1) | 2001 | Не поддерживается Встречается редко |
 |
Windows Vista (NT 6.0) | 2006 | Не поддерживается Почти, не используется |
 |
Windows 7 (NT 6.1) | 2009 | Не поддерживается Пока используется |
 |
Windows 8 (NT 6.2) | 2012 | Не поддерживается Почти, не используется |
 |
Windows 8.1 (NT 6.3) | 2013 | Поддерживается Почти, не используется |
 |
Windows 10 (NT 10) | 2015 | Поддерживается Активно используется |
 |
Windows 11 (NT 10) | 2021 | Поддерживается Начинает применяться |
Серверные Windows
| Логотип | Версия | Год | Статус |
|---|---|---|---|
 |
Windows NT 3.1 Advanced Server | 1993 | Не поддерживается Как правило, не используется |
 |
Windows NT 3.5 Server | 1994 | |
 |
Windows NT 3.51 Server | 1995 | |
 |
Windows NT 4.0 Server | 1996 | |
 |
Windows 2000 Server | 2000 | |
 |
Windows Server 2003 | 2003 | |
 |
Windows Server 2003 R2 | 2005 | |
 |
Windows Server 2008 | 2008 | |
 |
Windows Server 2008 R2 | 2009 | Не поддерживается Пока еще используется |
 |
Windows Server 2012 | 2012 | Поддерживается Активно используется |
 |
Windows Server 2012 R2 | 2013 | |
 |
Windows Server 2016 | 2016 | |
 |
Windows Server 2019 | 2018 | |
 |
Windows Server 2022 | 2021 | Начало использования |
Все версии Windows по линейкам + хронология
| Линейка | Годы | Перечисление версий |
|---|---|---|
| 16 бит | 1985 — 1995 | Windows 1 / 2 / 3 |
| 32 бита (9x) |
1995 — 2001 | Windows 95 / 98 / ME |
| NT (32 и 64 бита) |
с 1993 | Windows NT 3.1 / NT 3.5 / NT 3.51 / NT 4.0 Workstation / 2000 / XP / Vista / 7 / 8 / 8.1 / 10 |
| NT Servers (32 и 64 бита) |
с 1993 | Windows NT 3.1 / NT 3.5 / NT 3.51 / NT 4.0 Server / 2000 Server / 2003 / 2003 R2 / 2008 / 2008 R2 / 2012 / 2012 R2 / 2016 / 2019 / 2022 |
История успеха
Данная история успеха отражает частоту использования системы; количество глюков, с которыми столкнулись пользователи; отзывы.
 |
Windows 1 | Неудача |
 |
Windows 2 | Нейтрально |
 |
Windows 3 | Успех |
 |
Windows 95 | Неудача |
 |
Windows 98 | Успех |
 |
Windows Millenium | Провал |
 |
Windows 2000 | Нейтрально |
 |
Windows XP | Большой успех |
 |
Windows Vista | Провал |
 |
Windows 7 | Успех |
 |
Windows 8 | Провал |
 |
Windows 8.1 | Неудача |
 |
Windows 10 | Успех |
 |
Windows 11 | Нейтрально |
* несмотря на провал некоторых версий операционной системы, они несли новые функции, которые перешли в уже успешные версии. Например, в миллениум появились красивые иконки и окна, которые перешли в Windows 2000. Поэтому провал не стоит оценивать, как неудачную работу.
 Windows 1
Windows 1
Годы поддержки: 1985 — 2001. Ветка: 16 бит.
Издания: —
Что нового
До Windows 1 был MS-DOS, поэтому самое главное новшество — графический интерфейс и возможность управления при помощи мыши.
Системные требования
| Процессор | 8088 |
|---|---|
| Оперативная память | 256 Кбайт |
| Объем жесткого диска | 3 Мб |
 Windows 2
Windows 2
Годы поддержки: 1989 — 2001. Ветка: 16 бит.
Издания: —
Что нового
- Возможность использования сочетания клавиш.
- Появились перекрывающиеся окна.
- Возможность увеличить и уменьшить окно.
Системные требования
| Процессор | 8088 |
|---|---|
| Оперативная память | 256 Кбайт |
| Объем жесткого диска | 3 Мб |
 Windows 3
Windows 3
Годы поддержки: 1990 — 2008. Ветка: 16 бит.
Издания: —
Что нового
- Первый (от Microsoft) удобный для пользователя интерфейс.
- Появление диспетчера программ.
- Появление мультимедийных возможностей.
- Поддержка сети (с 3.1).
Системные требования
| Минимальные | Рекомендуемые | |
|---|---|---|
| Процессор | 8086/8088 | 80486DX 33 МГц |
| Оперативная память | 640 Кбайт | 4 Мб |
| Объем жесткого диска | 6,5 Мб | 60 Мб |
 Windows NT 3.1
Windows NT 3.1
Годы поддержки: 1993 — 2001. Ветка: NT. Разрядность: 16, 32 и 64 бита.
Издания: —
Что нового
- Первая система на базе ядра NT.
- Поддержка файловой системы NTFS.
Системные требования
| Процессор | Intel 80386 |
|---|---|
| Оперативная память | 2 Мб |
| Объем жесткого диска | 8 Мб |
 Windows NT 3.5 Workstation
Windows NT 3.5 Workstation
Годы поддержки: 1994 — 2001. Ветка: NT. Разрядность: 16, 32 и 64 бита.
Издания: —
Что нового
- Встроенная поддержка Winsock и TCP/IP.
- Появление сервера и клиента DHCP и WINS.
- Предоставление общего доступа к файлам и принтерам.
- Поддержка VFAT.
Системные требования
| Процессор | 33 МГц |
|---|---|
| Оперативная память | 12 Мб |
| Объем жесткого диска | 70 Мб |
 Windows NT 3.51 Workstation
Windows NT 3.51 Workstation
Годы поддержки: 1995 — 2001. Ветка: NT. Разрядность: 16, 32 и 64 бита.
Издания: —
Системные требования
| Процессор | 33 МГц |
|---|---|
| Оперативная память | 12 Мб |
| Объем жесткого диска | 70 Мб |
 Windows 95
Windows 95
Годы поддержки: 1995 — 2001. Ветка: 9x (32 бита).
Системные требования
| Минимальные | Рекомендуемые | |
|---|---|---|
| Процессор | 80386 DX | Pentium |
| Оперативная память | 4 Мб | 8 Мб |
| Объем жесткого диска | 50 Мб | 100 Мб |
 Windows NT 4.0 Workstation
Windows NT 4.0 Workstation
Годы поддержки: 1996 — 2004. Ветка: NT. Разрядность: 32 и 64 бита.
Издания: —
Системные требования
| Минимальные | Рекомендуемые | |
|---|---|---|
| Процессор | 486/25 | 486DX2/50 |
| Оперативная память | 12 Мб | 24 Мб |
| Объем жесткого диска | 128 Мб | 1 Гб |
 Windows 98
Windows 98
Годы поддержки: 1998 — 2006. Ветка: 9x (32 бита).
Системные требования
| Минимальные | Рекомендуемые | |
|---|---|---|
| Процессор | 486DX 66 МГц | Pentium |
| Оперативная память | 16 Мб | 24 Мб |
| Объем жесткого диска | 200 Мб | 500 Мб |
 Windows Millenium
Windows Millenium
Годы поддержки: 2000 — 2006. Ветка: 9x (32 бита).
Системные требования
| Минимальные | Рекомендуемые | |
|---|---|---|
| Процессор | 150 МГц | 300 МГц |
| Оперативная память | 32 Мб | 128 Мб |
| Объем жесткого диска | 200 Мб | 500 Мб |
 Windows 2000
Windows 2000
Годы поддержки: 2000 — 2010. Ветка: NT.
Системные требования
| Минимальные | Рекомендуемые | |
|---|---|---|
| Процессор | 133 МГц | 1 ГГц |
| Оперативная память | 32 Мб | 128 Мб |
| Объем жесткого диска | 2 Гб | 20 Гб |
 Windows XP
Windows XP
Годы поддержки: 2000 — 2010. Ветка: NT. Разрядность: 32 и 64 бита.
Редакции: XP, XP Professional
Системные требования
| Минимальные | Рекомендуемые | |
|---|---|---|
| Процессор | 233 МГц | 300 МГц |
| Оперативная память | 64 Мб | 128 Мб |
| Объем жесткого диска | 1,5 Гб | от 1,5 Гб |
 Windows Vista
Windows Vista
Годы поддержки: 2006 — 2017. Ветка: NT. Разрядность: 32 и 64 бита.
Издания: Начальная (Starter), Домашняя базовая (Basic), Домашняя расширенная (Premium), Бизнес (Business), Корпоративная (Enterprise), Максимальная (Ultimate)
Системные требования
| Минимальные | Рекомендуемые | |
|---|---|---|
| Процессор | 800 МГц | 1 ГГц |
| Оперативная память | 512 Мб | 1 Гб |
| Объем жесткого диска | 20 Гб | 40 Гб |
 Windows 7
Windows 7
Годы поддержки: 2009 — 2020. Ветка: NT. Разрядность: 32 и 64 бита.
Издания: Начальная (Starter), Домашняя базовая (Home Basic), Домашняя расширенная (Home Premium), Профессиональная (Professional), Корпоративная (Enterprise), Максимальная (Ultimate)
Системные требования
| Минимальные | Рекомендуемые | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Архитектура | 32-бит | 64-бит | 32-бит | 64-бит |
| Процессор | 1 ГГц | |||
| Оперативная память | 1 Гб | 2 Гб | 4 Гб | |
| Объем жесткого диска | 16 Гб | 20 Гб | 16 Гб | 20 Гб |
 Windows 8
Windows 8
Годы поддержки: 2012 — 2016. Ветка: NT. Разрядность: 32 и 64 бита.
Издания: 8, 8 Профессиональная (Pro), 8 Корпоративная (Enterprise)
Системные требования
| Минимальные | Рекомендуемые | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Архитектура | 32-бит | 64-бит | 32-бит | 64-бит |
| Процессор | 1 ГГц | |||
| Оперативная память | 1 Гб | 2 Гб | 4 Гб | |
| Объем жесткого диска | 16 Гб | 20 Гб | 16 Гб | 20 Гб |
 Windows 8.1
Windows 8.1
Годы поддержки: 2013 — 2023. Ветка: NT. Разрядность: 32 и 64 бита.
Издания: 8, 8 Профессиональная (Pro), 8 Корпоративная (Enterprise)
Системные требования
| Минимальные | Рекомендуемые | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Архитектура | 32-бит | 64-бит | 32-бит | 64-бит |
| Процессор | 1 ГГц | |||
| Оперативная память | 1 Гб | 2 Гб | 4 Гб | |
| Объем жесткого диска | 16 Гб | 20 Гб | 16 Гб | 20 Гб |
 Windows 10
Windows 10
Годы поддержки: 2015 — 2025. Ветка: NT. Разрядность: 32 и 64 бита.
Издания
- Домашняя (Home). Для большинства домашних компьютеров. Нет возможности настроить удаленный рабочий стол для того, чтобы к систему можно было подключиться удаленно; нет возможности использования групповых политик и присоединения к домену.
- Профессиональная (Pro). Содержит все функции домашней версии + возможность присоединения к домену, использования групповых политик, возможность подключения к компьютеру с использованием удаленного рабочего стола.
- Корпоративная (Enterprise). Урезаны некоторые функции домашней версии. Есть все дополнительные функции версии Pro + DirectAccess, AppLocker.
- S. Является урезанной версией; предустановлена на некоторые устройства. Не поддерживает стандартную установку приложений — возможна установка только из магазина Windows.
Что нового
Windows 10 претерпевает сильные изменения с выходом новых билдов. Поэтому нововведения будем рассматривать исходя из этого.
Билд 1507 (ноябрь 2015):
- Улучшенная производительность.
- Новый встроенный браузер Microsoft Edge.
- Автоматическое сжимание соседнего окна, при прижимании активного окна в одной из сторон рабочего стола.
- «Все приложения» в «Пуск» поддерживают отображение в 2048 элементов (раньше только 512).
- Принудительная установка обновлений.
- Использование виртуального голосового помощника Кортана.
- Обновленный меню пуск — представляет из себя гибрид предыдущих версий и Windows 8 (вернулся старый вариант раскрытия, а в правой части появились плитки).
- Возможность создания нескольких рабочих столов.
- Отказ от плиточной системы Windows 8.
1607 (август 2016):
- Возможность рукописного ввода (Windows Ink).
- Идентификация с помощью веб-камеры.
- Синхронизация с мобильного устройства уведомлений.
- Изменение меню параметров системы.
1703 (апрель 2017):
- Встроенная поддержка шлемов виртуальной реальности.
- Игровой режим
- По умолчанию предлагается командная строка в Powershell.
- Доступ к классической панели управления скрыт из контекстного меню. Теперь его можно вызвать командой control.
- Улучшение работы встроенного антивируса.
- Идентификация с помощью веб-камеры для Active Directory.
- Возможность создавать скриншот с выделением области с помощью сочетания клавиш Win + Shaft + S.
- Поддержка шрифта Брайля.
- Увеличенное время работы от батареи.
1709 (октябрь 2017):
- Возможность работы Cortana на одном устройстве и окончание работы на другом.
- Отключение протокола SMBv1. Включить можно вручную.
- Появление панели «Люди».
- Информация о GPU в диспетчере задач.
- Полноэкранный режим Microsoft Edge
- Увеличенное время работы от батареи (функция Power Throttling).
- Появление панели эмодзи.
- Выборочная синхронизация OneDrive.
- Исправление проблемы торможения в играх.
1803 (апрель 2018):
- Возможность восстановить пароль с помощью контрольных вопросов.
1809 (октябрь 2018):
- Темная тема для проводника.
- Возможность получения доступа к сообщениям с телефона (функция «Ваш телефон»).
1903 (май 2019):
- Изолированный рабочий стол для безопасного запуска приложений.
1909 (ноябрь 2019):
- Универсальный поиск в Проводнике.
- Улучшение производительности.
2004 (май 2020):
- Функция «Загрузка из облака» для переустановки Windows 10.
- Регулирование пропускной способности для обновлений Windows.
- Отображение температуры видеоядра в Диспетчере задач.
- Возможность удаления Блокнот, Paint, WordPad.
- Возможность использование Windows без пароля.
* данный список содержит часть нововведений. Полный список на странице в Википедии.
Системные требования
| Минимальные | Рекомендуемые | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Архитектура | 32-бит | 64-бит | 32-бит | 64-бит |
| Процессор | 1 ГГц | |||
| Оперативная память | 1 Гб | 2 Гб | 4 Гб | |
| Объем жесткого диска | 16 Гб | 20 Гб | 16 Гб | 20 Гб |
 Windows 11 (последняя для настольных компьютеров)
Windows 11 (последняя для настольных компьютеров)
Годы поддержки: 2021 — 2031. Ветка: NT. Разрядность: только 64 бита.
Основные издания: Домашняя (Home), Профессиональная (Pro), 8 Корпоративная (Enterprise).
Дополнительные издания: для обучения (Education), для облаков (Cloud).
Системные требования
| Процессор | 2 ядра, 1 ГГц |
|---|---|
| Оперативная память | 4 Гб |
| Объем жесткого диска | 64 Гб |
| БИОС (прошивка) | UEFI |
| Видеоадаптер | Совместимый с DirectX 12 / WDDM 2.x |
| Интернет | Для Home необходим вход под учетной записью Microsoft. |
 Windows NT 3.1 Advanced Server
Windows NT 3.1 Advanced Server
Годы поддержки: 1993 — 2001. Ветка: NT. Разрядность: 16, 32 и 64 бита.
Издания: —
Системные требования
| Процессор | Intel 80386 |
|---|---|
| Оперативная память | 2 Мб |
| Объем жесткого диска | 8 Мб |
 Windows NT 3.5 Server
Windows NT 3.5 Server
Годы поддержки: 1994 — 2001. Ветка: NT. Разрядность: 16, 32 и 64 бита.
Издания: —
Что нового
- Встроенная поддержка Winsock и TCP/IP.
- Появление сервера DHCP и WINS.
- Предоставление общего доступа к файлам и принтерам.
- Поддержка VFAT.
Системные требования
| Процессор | 33 МГц |
|---|---|
| Оперативная память | 16 Мб |
| Объем жесткого диска | 70 Мб |
 Windows NT 3.51 Server
Windows NT 3.51 Server
Годы поддержки: 1995 — 2001. Ветка: NT. Разрядность: 16, 32 и 64 бита.
Издания: —
Системные требования
| Процессор | 33 МГц |
|---|---|
| Оперативная память | 16 Мб |
| Объем жесткого диска | 70 Мб |
 Windows NT 4.0 Server
Windows NT 4.0 Server
Годы поддержки: 1996 — 2004. Ветка: NT. Разрядность: 32 и 64 бита.
Издания: Server, Enterprise Edition, Terminal Server
Системные требования
| Минимальные | Рекомендуемые | |
|---|---|---|
| Процессор | 486/25 | 486DX2/50 |
| Оперативная память | 16 Мб | 24 Мб |
| Объем жесткого диска | 128 Мб | 1 Гб |
 Windows 2000 Server
Windows 2000 Server
Годы поддержки: 2000 — 2010. Ветка: NT. Разрядность: 32 и 64 бита.
Издания: Server, Advanced Server и Datacenter Server
Системные требования
| Минимальные | Рекомендуемые | |
|---|---|---|
| Процессор | 133 МГц | 1 ГГц |
| Оперативная память | 32 Мб | 128 Мб |
| Объем жесткого диска | 2 Гб | 20 Гб |
 Windows Server 2003
Windows Server 2003
Годы поддержки: 2003 — 2015. Ветка: NT. Разрядность: 32 и 64 бита.
Издания: Web, Standard, Enterprise, Datacenter
Системные требования
Web, Standard, Enterprise:
| Минимальные | Рекомендуемые | |
|---|---|---|
| Процессор | 133 МГц | 550 МГц |
| Оперативная память | 128 Мб | 256 Мб |
| Объем жесткого диска | 1,5 Гб | 2 Гб |
Datacenter Edition:
| Минимальные | Рекомендуемые | |
|---|---|---|
| Процессор | 400 МГц | 733 МГц |
| Оперативная память | 512 Мб | 1 Гб |
| Объем жесткого диска | 1,5 Гб | 2 Гб |
 Windows Server 2003 R2
Windows Server 2003 R2
Годы поддержки: 2005 — 2015. Ветка: NT. Разрядность: 32 и 64 бита.
Издания: Standard, Enterprise, Datacenter
Системные требования
Standard, Enterprise:
| Минимальные | Рекомендуемые | |
|---|---|---|
| Процессор | 133 МГц | 550 МГц |
| Оперативная память | 128 Мб | 256 Мб |
| Объем жесткого диска | 1,2 Гб | 2 Гб |
Datacenter Edition:
| Минимальные | Рекомендуемые | |
|---|---|---|
| Процессор | 400 МГц | 733 МГц |
| Оперативная память | 512 Мб | 1 Гб |
| Объем жесткого диска | 1,2 Гб | 2 Гб |
 Windows Server 2008
Windows Server 2008
Годы поддержки: 2008 — 2020. Ветка: NT. Разрядность: 32 и 64 бита.
Издания: Web, Standard, Enterprise, Datacenter, HPC, Storage, Itanium
Системные требования
| Минимальные | Рекомендуемые | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Архитектура | 32-бит | 64-бит | 32-бит | 64-бит |
| Процессор | 1 ГГц | 1.4 ГГц | 2 ГГц | |
| Оперативная память | 512 Мб | 2 Гб | ||
| Объем жесткого диска | 10 Гб | 40 Гб |
 Windows Server 2008 R2
Windows Server 2008 R2
Годы поддержки: 2009 — 2020. Ветка: NT. Разрядность: 64 бита.
Издания: Foundation, Small Business, Web, Standard, Enterprise, Datacenter, HPC, Itanium
Системные требования
| Минимальные | Рекомендуемые | |
|---|---|---|
| Процессор | 1.4 ГГц | 2 ГГц |
| Оперативная память | 512 Мб | 2 Гб |
| Объем жесткого диска | 10 Гб | 40 Гб |
 Windows Server 2012
Windows Server 2012
Годы поддержки: 2012 — 2023. Ветка: NT. Разрядность: 64 бита.
Издания: Foundation, Essentials, Standard, Datacenter
Системные требования
| Минимальные | Рекомендуемые | |
|---|---|---|
| Процессор | 1.4 ГГц | 2 ГГц |
| Оперативная память | 2 Гб | 4 Гб |
| Объем жесткого диска | 32 Гб | 60 Гб |
 Windows Server 2012 R2
Windows Server 2012 R2
Годы поддержки: 2013 — 2023. Ветка: NT. Разрядность: 64 бита.
Издания: Foundation, Essentials, Standard, Datacenter
Системные требования
| Минимальные | Рекомендуемые | |
|---|---|---|
| Процессор | 1.4 ГГц | 2 ГГц |
| Оперативная память | 2 Гб | 4 Гб |
| Объем жесткого диска | 32 Гб | 60 Гб |
 Windows Server 2016
Windows Server 2016
Годы поддержки: 2016 — 2026. Ветка: NT. Разрядность: 64 бита.
Издания: Essentials, Standard, Datacenter
Что нового
- Лицензирование на физические ядра процессора (минимум 16).
- Новый режим установки — Nano.
- Появление контейнерной виртуализации.
- OpenGL и OpenCL для RDP.
- Шифрование виртуальных машин и внутреннего сетевого трафика.
- Блочная репликация файловых хранилищ.
Системные требования
| Минимальные | Рекомендуемые | |
|---|---|---|
| Процессор | 1.4 ГГц | 3.1 ГГц |
| Оперативная память | 2 Гб | 4 Гб |
| Объем жесткого диска | 32 Гб | 60 Гб |
Более подробно в обзоре Windows Server 2016.
 Windows Server 2019
Windows Server 2019
Годы поддержки: 2018 — 2029. Ветка: NT. Разрядность: 64 бита.
Издания: Standard, Datacenter
Что нового
- Улучшенная безопасность — встроенные технологии Defender ATP и Defender Exploit Guard.
- Windows Subsystem Linux (WSL) — контейнеры для поддержки приложений Linux.
- Для построения кластера с четным количеством узлов в качестве диска-свидетеля может выступать USB-диск.
Системные требования
| Минимальные | Рекомендуемые | |
|---|---|---|
| Процессор | 1.4 ГГц | 3.1 ГГц |
| Оперативная память | 512 Мб (Nano) 2 Гб (GUI) |
4 Гб |
| Объем жесткого диска | 32 Гб | 60 Гб |
 Windows Server 2022 (последняя для серверов)
Windows Server 2022 (последняя для серверов)
Годы поддержки: 2021 — 2031. Ветка: NT. Разрядность: 64 бита.
Издания: Standard, Datacenter
Что нового
- Улучшенная безопасность.
- Больше возможностей для работы с облаками, особенно, Microsoft Azure.
Системные требования
| Минимальные | Рекомендуемые | |
|---|---|---|
| Процессор | 1.4 ГГц | 3.1 ГГц |
| Оперативная память | 512 Мб (Nano) 2 Гб (GUI) Поддержка ECC |
4 Гб
Поддержка ECC |
| Объем жесткого диска | 32 Гб | 60 Гб |
| Сетевой адаптер | 1 гигабит в секунду |