Содержание
- Как установить Ubuntu вместе с Windows 10?
- Двойная загрузка Ubuntu Linux с Windows 10
- Проверки совместимости
- Предпосылки: что вам нужно?
- Шаг 1. Сделайте резервную копию вашей системы Windows [необязательно]
- Шаг 2. Загрузите Ubuntu (или любой другой дистрибутив Linux, который вы будете использовать)
- Шаг 3: Создайте live USB / диск Ubuntu
- Шаг 4. Освободите место на диске для установки Ubuntu
- Сколько места вам нужно для Linux при двойной загрузке?
- Что делать, если у вас есть диски D, E или F?
- Шаг 5: Загрузитесь с Live Ubuntu USB
- Нужно ли мне отключать безопасную загрузку для установки Linux?
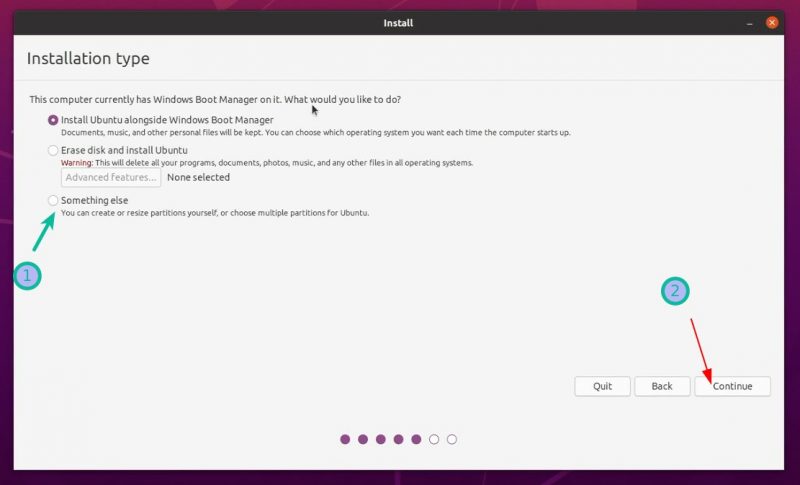
- Шаг 6: Установка Ubuntu вместе с Windows 10
- Подход 1. Вы видите «Установить Ubuntu вместе с Windows Boot Manager».
- Подход 2: Вы не видите параметр «Установить Ubuntu вместе с диспетчером загрузки Windows» или он неактивен
- Двойная загрузка не удалась? Вот несколько советов по устранению неполадок
- Попробуйте сменить порт USB
- Старайтесь не использовать интернет при установке Linux
- Отключите безопасную загрузку и / или быструю загрузку
- Двойная загрузка завершена, но вы не видите экран «grub» для загрузки в Ubuntu
Как установить Ubuntu вместе с Windows 10?
Двойная загрузка Linux с Windows — один из самых удобных способов использования двух операционных систем на одном компьютере.
Обе ОС установлены на диске, на реальном оборудовании, и при включении системы вы можете выбрать, какую операционную систему использовать.
В этом руководстве я покажу вам, как установить Ubuntu с уже установленной в системе Windows 10.
Прежде чем вы начнете следовать руководству, я советую сначала полностью его прочитать.
Посмотрите, что вам нужно и что вы должны делать в этом уроке.
Как только вы получите хорошее представление о процедуре и у вас все необходимое будет под рукой, приступайте к процессу.
Двойная загрузка — не сложный процесс. Просто нужно время и терпение.
Упомянутые здесь шаги применимы к другим версиям Ubuntu, таким как Lubuntu, Kubuntu, Xubuntu и дистрибутивам Linux на основе Ubuntu, таким как Linux Mint, elementary OS и т. д.
Двойная загрузка Ubuntu Linux с Windows 10
Это руководство подходит для систем с предустановленной Windows 10 с безопасной загрузкой UEFI и системой разбиения GPT.
Пожалуйста, проверьте, использует ли ваша система GPT или MBR?
Проверки совместимости
Убедитесь, что ваша система использует UEFI: это руководство применимо только для систем с загрузкой UEFI.
Если вы купили свою систему в последние 5-6 лет, скорее всего, у вас уже должна быть система UEFI в разделе GPT.
Однако нет ничего плохого в том, чтобы убедиться, что ваша система использует UEFI.
Если в вашей системе используется устаревшая версия BIOS с системой разбиения на разделы MBR, следуйте этому руководству по двойной загрузке.
Процесс шифрования Bitlocker отличается: в новых системах с Windows 10 Pro диск зашифрован с помощью Bitlocker.
Система с SSD и HDD: если у вас есть система с SSD и HDD, то есть с двумя дисками, процесс будет почти таким же.
Предпосылки: что вам нужно?
Для простой и безопасной установки Linux вместе с Windows вам понадобятся следующие вещи:
- Компьютер с предустановленной Windows 10;
- USB-ключ (флэш-накопитель или USB-накопитель) размером не менее 4 ГБ и без данных на нем;
- Подключение к интернету (для загрузки ISO-образа Ubuntu и инструмента для создания Live USB). Вы можете сделать это в любой системе, не обязательно в системе с двойной загрузкой.
- Необязательно: внешний USB-диск для резервного копирования существующих данных;
- Необязательно: восстановление Windows или загрузочный диск (если у вас возникнут серьезные проблемы с загрузкой, их можно будет исправить).
Давайте посмотрим, как установить Ubuntu вместе с Windows 10.
Шаг 1. Сделайте резервную копию вашей системы Windows [необязательно]
Всегда приятно иметь резервную копию ваших данных, на всякий случай, если вы испортите систему при работе с разделами диска.
Я советую скопировать все важные данные, которые вы не можете позволить себе потерять, на внешний USB-диск.
Вы можете использовать внешний жесткий диск (медленнее, но дешевле) или SSD (быстрее, но дороже) и копировать на него важные файлы и папки.
Шаг 2. Загрузите Ubuntu (или любой другой дистрибутив Linux, который вы будете использовать)
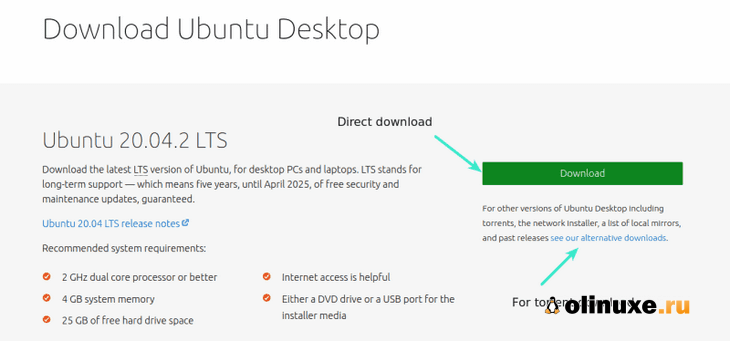
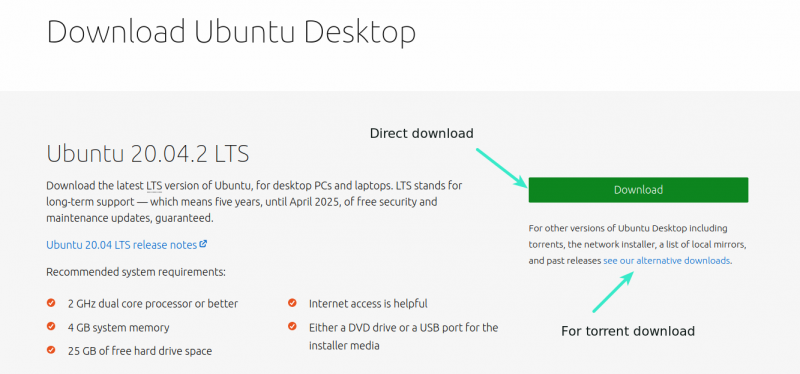
Перейдите на сайт Ubuntu и загрузите файл ISO.
Размер файла должен быть около 2,5 ГБ. Если вам нужно загрузить Ubuntu через торрент, вы можете нажать «Альтернативные загрузки».
Шаг 3: Создайте live USB / диск Ubuntu
Я предполагаю, что вы используете Windows для создания Live USB.
Есть несколько бесплатных приложений, которые позволяют создать Live Ubuntu USB.
Вы можете использовать любой из этих инструментов.
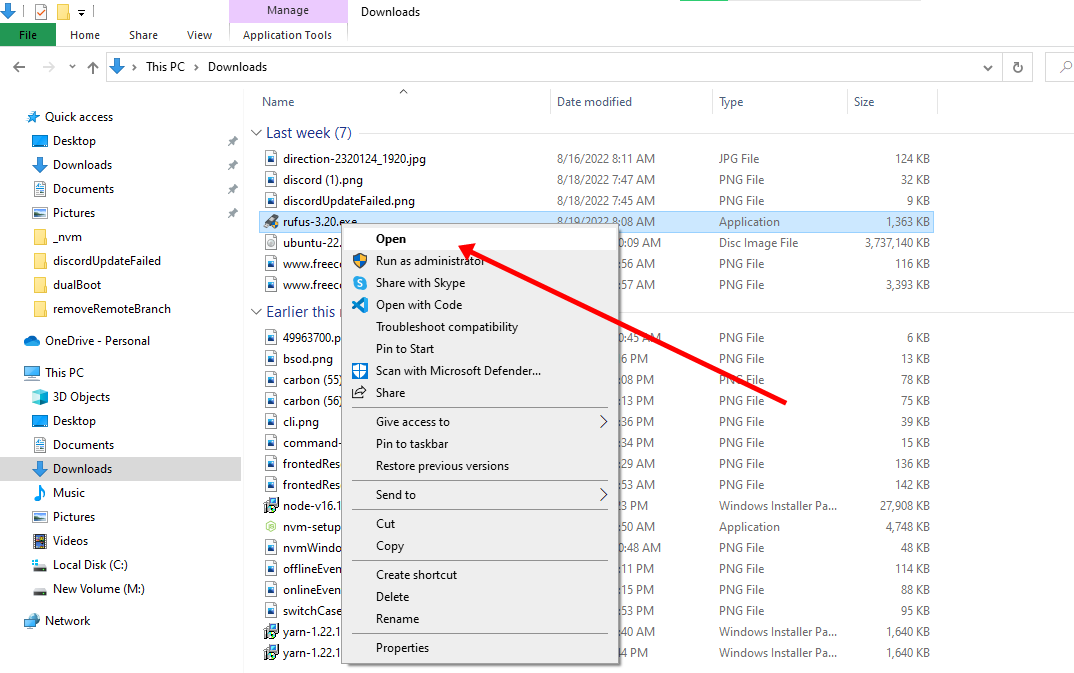
Поскольку я не могу показать их все, я буду все делать с Rufus.
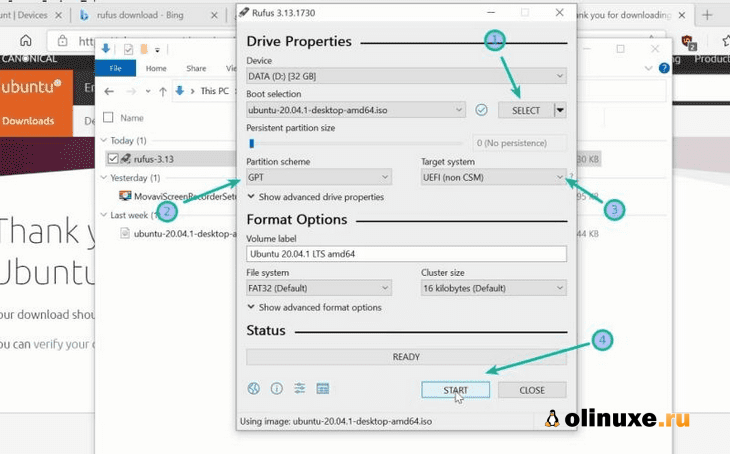
Загрузите Rufus бесплатно с его веб-сайта. Он загрузит файл с расширением .exe.
Это устройство будет отформатировано, поэтому убедитесь, что на нем нет важных данных.
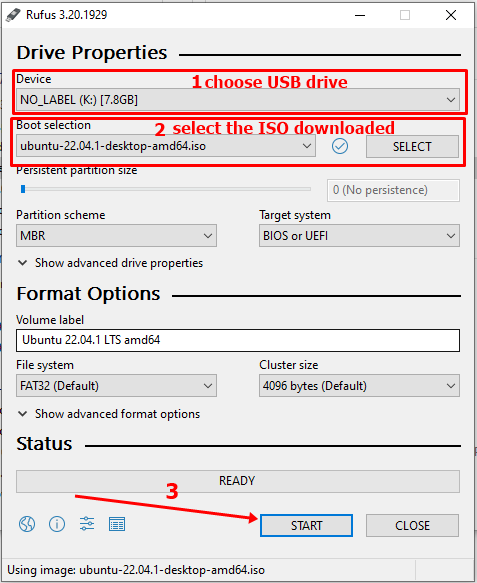
Запустите только что загруженный инструмент Rufus.
Он автоматически определяет подключенный USB-порт, но все равно дважды проверьте его.
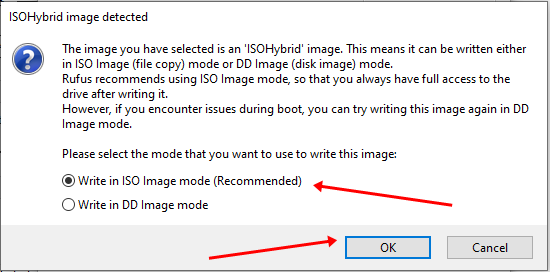
Теперь перейдите к местоположению загруженного образа ISO и убедитесь, что он использует схему разделения GPT и целевую систему UEFI.
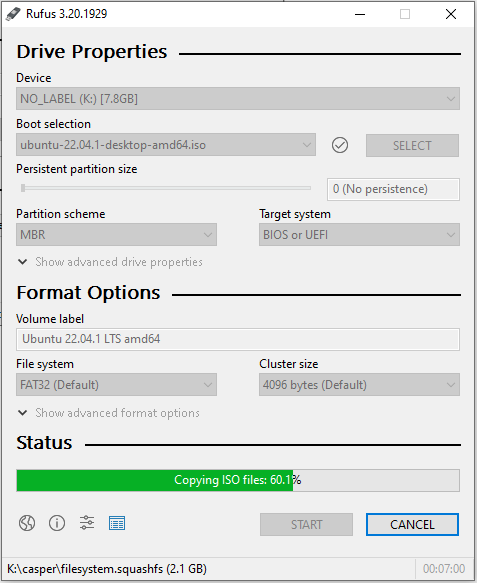
Нажмите кнопку «Пуск» и дождитесь завершения процесса. Ваш Live Linux USB готов.
Примечание. Установить Ubuntu и создать действующий USB-процесс Ubuntu можно на любом компьютере.
Но остальная часть процесса берет на себя система, в которой вы выполняете двойную загрузку.
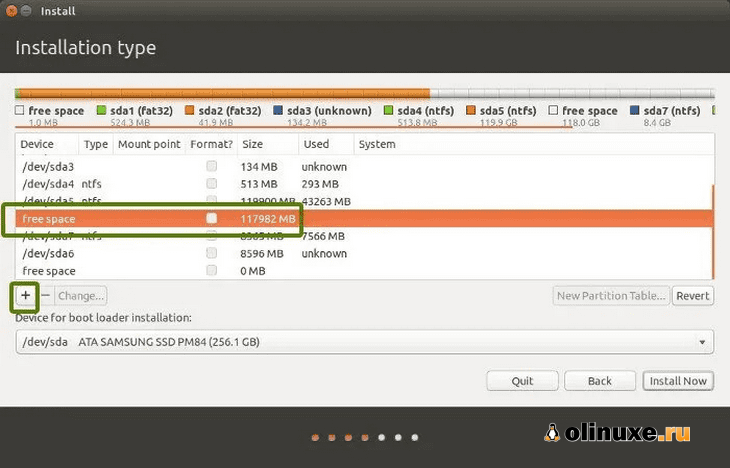
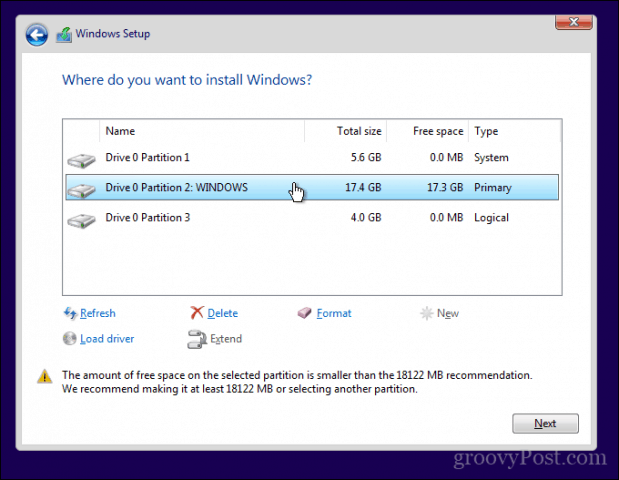
Шаг 4. Освободите место на диске для установки Ubuntu
Во многих системах при установке Ubuntu предоставляется возможность сделать раздел диска для Ubuntu.
Однако это не гарантия.
Поэтому перед установкой лучше освободить необходимое место на диске.
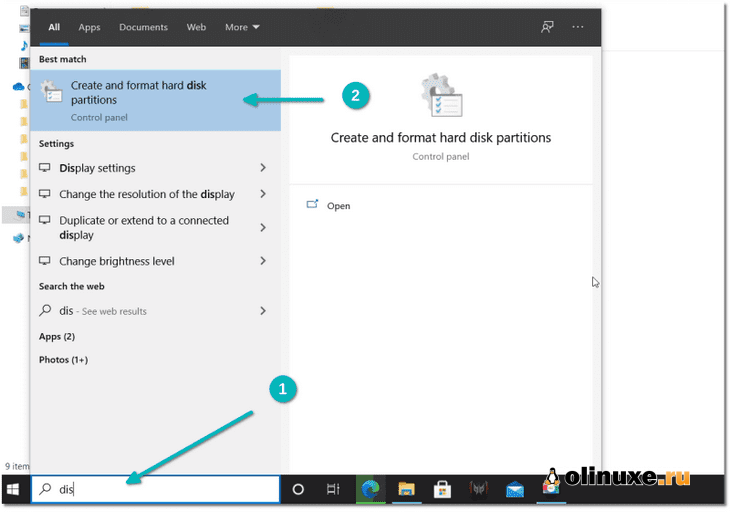
В меню Windows найдите «разделы диска» и выберите «Создать и отформатировать разделы жесткого диска».
В инструменте управления дисками щелкните правой кнопкой мыши диск, который вы хотите разделить, и выберите «Сжатый том».
Если у вас всего один такой раздел, вам нужно освободить на нем немного свободного места для Linux.
Если у вас есть несколько разделов значительного размера, используйте любой из них, кроме диска C, поскольку он может стереть данные.
На 256 ГБ в моей системе уже было несколько разделов от производителя, но в основном для резервного копирования и других целей.
Основным разделом был диск C объемом около 220 ГБ, на котором установлена Windows 10.
В моем случае я уменьшил диск C, чтобы освободить место для установки Linux.
Сколько места вам нужно для Linux при двойной загрузке?
Это зависит от того, сколько у вас общего дискового пространства.
Вы можете установить Ubuntu на 15 или 20 ГБ, но скоро у вас начнется нехватка места на диске.
В наши дни у вас должно быть не менее 120 ГБ на диске.
В этом случае выберите для Linux 30-40 ГБ диска.
Если у вас диск на 250 ГБ, выделите ему 60-80 ГБ или даже больше.
Если у вас больше места на диске, выделите ему еще больше свободного места, если хотите.
Что делать, если у вас есть диски D, E или F?
Это обычная путаница для многих людей, поскольку они думают, что Ubuntu можно установить только на диск C.
Понимаете, у меня был только один диск C, поэтому я его сжал.
Если у вас есть диск D, E или F, вы можете сжать один из этих дисков.
Вы также можете удалить диск D, E или F.
НИКОГДА НЕ УДАЛЯЙТЕ ДИСК С.
Шаг 5: Загрузитесь с Live Ubuntu USB
Вы создали действующий USB-накопитель Ubuntu на шаге 3.
Подключите его к системе.
Прежде чем вы загрузитесь с Live USB-накопителя, давайте вкратце расскажем о печально известной безопасной загрузке.
Нужно ли мне отключать безопасную загрузку для установки Linux?
6-8 лет назад безопасная загрузка UEFI не поддерживалась Linux, и поэтому вам пришлось отключить безопасную загрузку перед установкой Linux.
К счастью, в наши дни Ubuntu и многие другие дистрибутивы Linux очень хорошо поддерживают безопасную загрузку.
Обычно с этим ничего делать не нужно.
Однако, если ваша система не позволяет загружаться с Live USB или если вы видите какие-либо другие связанные проблемы, вы можете отключить безопасную загрузку в Windows.
Хорошо! Посмотрим, как загрузиться с USB.
Вы можете перейти к настройкам загрузки, нажав F2 / F10 или F12 во время запуска системы, и выбрать загрузку с USB.
Однако некоторым это трудно.
Более длинный, но простой шаг — получить доступ к настройкам загрузки UEFI из Windows.
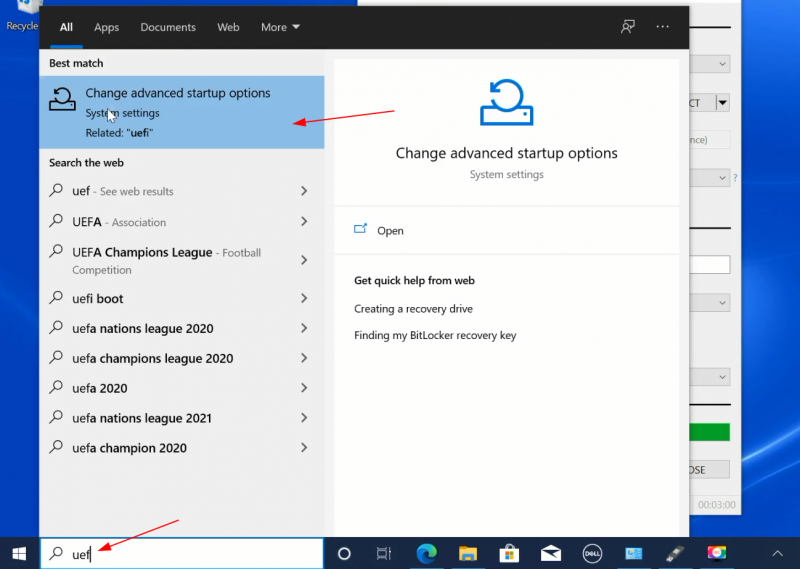
В меню Windows найдите UEFI и нажмите «Изменить дополнительные параметры запуска»:
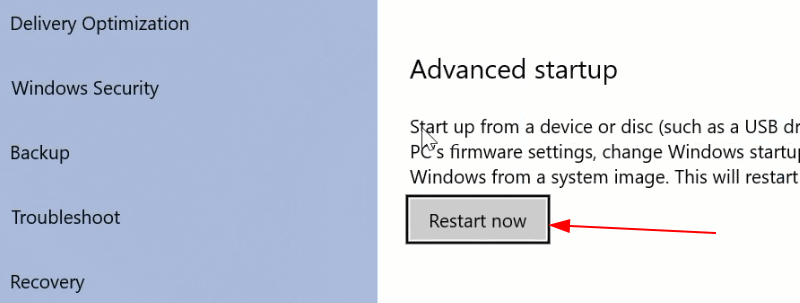
Перейдите к параметру «Расширенный запуск» и нажмите кнопку «Перезагрузить сейчас».
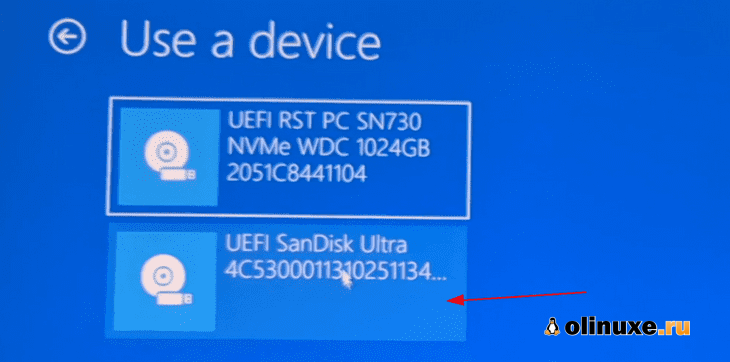
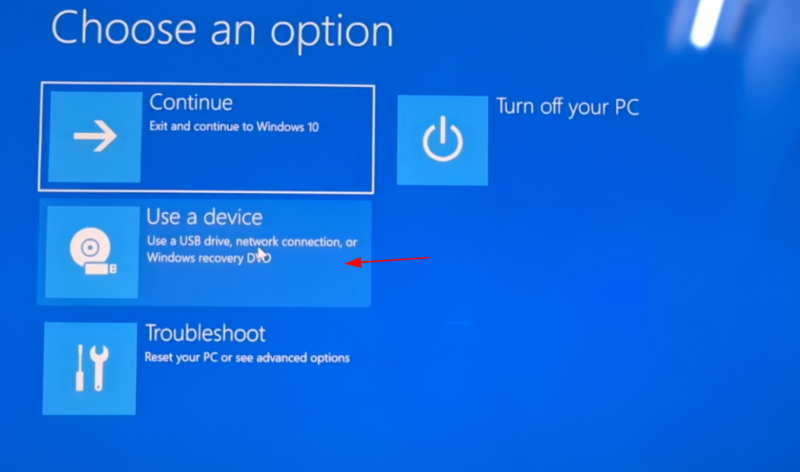
На следующем экране нажмите «Использовать устройство»:
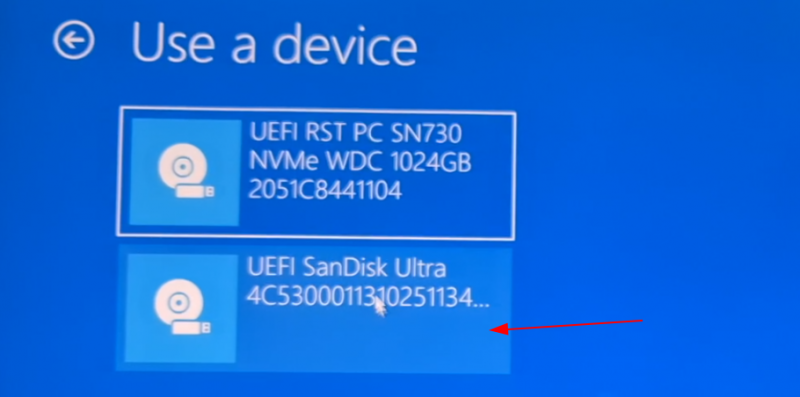
Распознайте USB-диск по его имени и размеру.
Он также может отображаться как USB-устройство EFI.
Теперь он выключит вашу систему и перезагрузится на выбранный вами диск, который должен быть активным USB-диском.
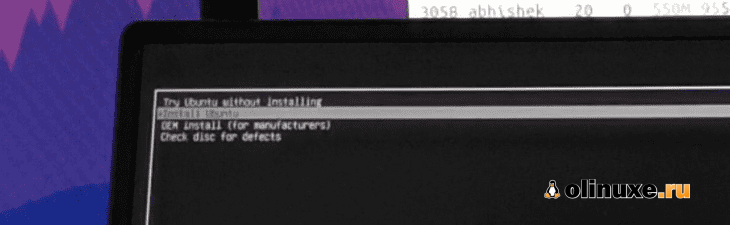
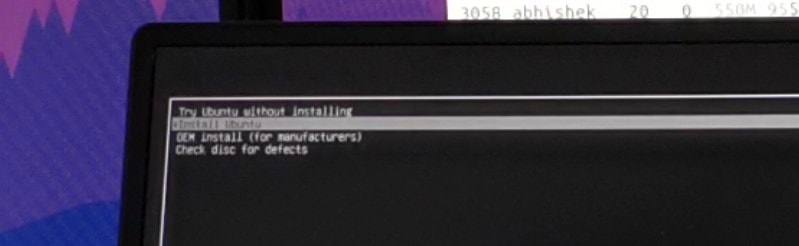
Через несколько секунд вы должны увидеть такой экран:
Опция «Попробовать Ubuntu без установки» позволяет вам испытать Ubuntu с Live диска.
Вариант установки Ubuntu можно найти на рабочем столе.
Опция «Установить Ubuntu» немедленно запустит установку Ubuntu.
Вы можете выбрать любой вариант в зависимости от ваших предпочтений.
Шаг 6: Установка Ubuntu вместе с Windows 10
Запустите процедуру установки.
Первые несколько шагов просты.
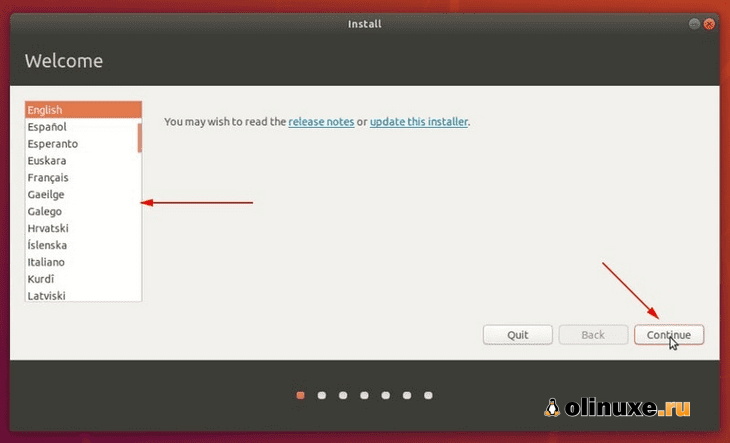
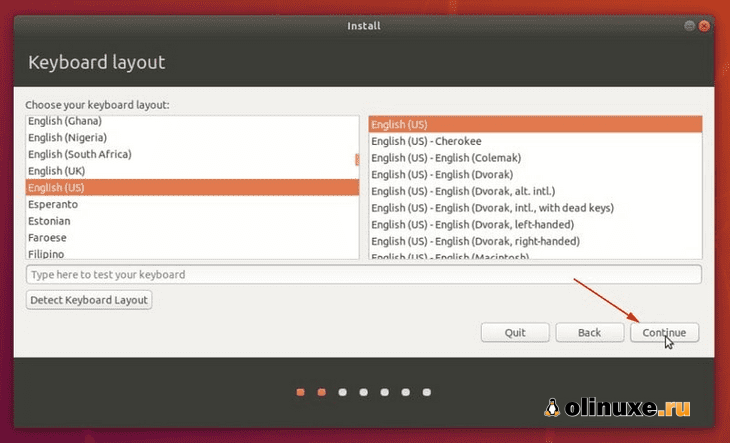
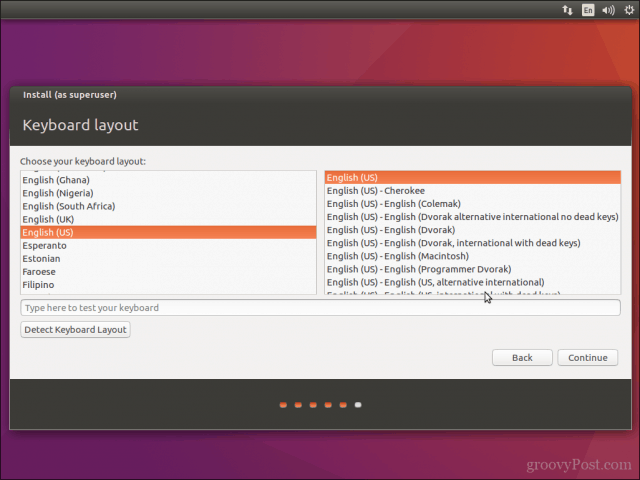
Вы выбираете язык и раскладку клавиатуры.
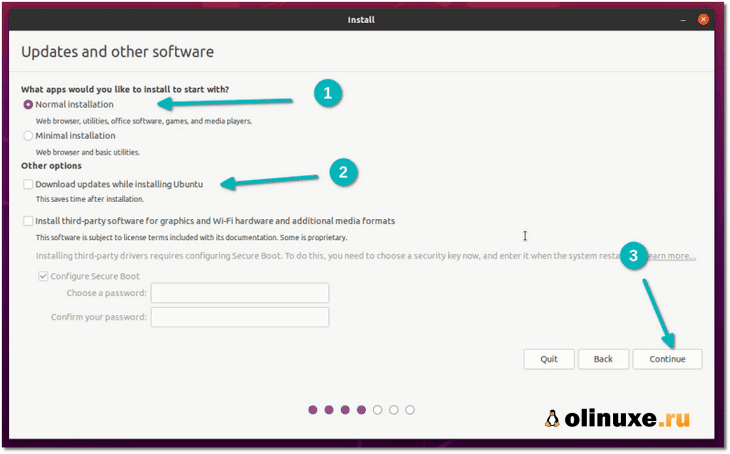
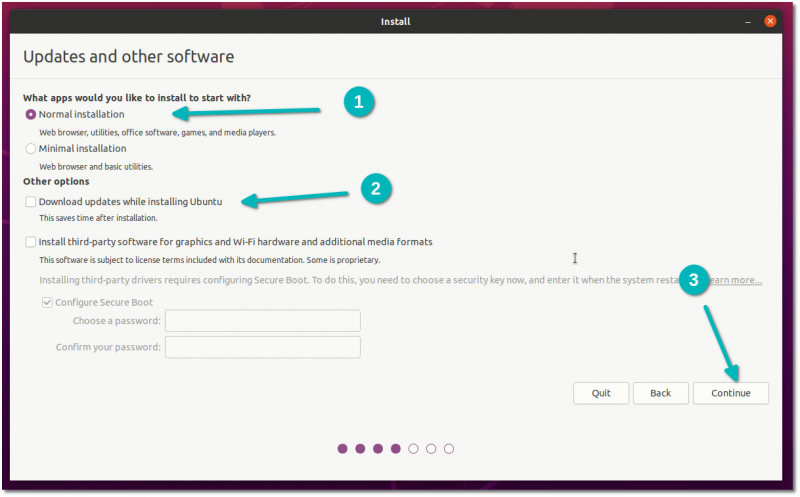
На следующем экране выберите «Обычная установка».
Пока не нужно загружать обновления или устанавливать стороннее программное обеспечение.
Вы можете сделать это после завершения установки.
Переход к следующему шагу может занять некоторое время.
Примечание. Некоторые люди пытаются загрузить обновления и установить медиа-кодеки во время установки.
По моему опыту, это иногда создает проблемы во время установки, а также может привести к сбою установки.
По этой причине я не советую их использовать.
Поскольку это подробное руководство, я рассмотрю оба аспекта.
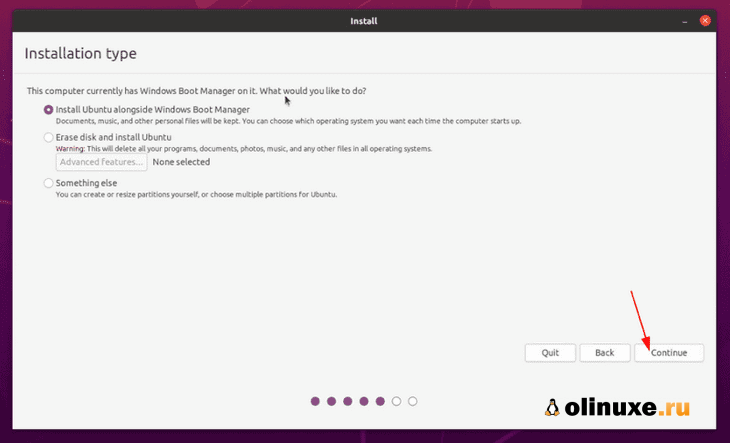
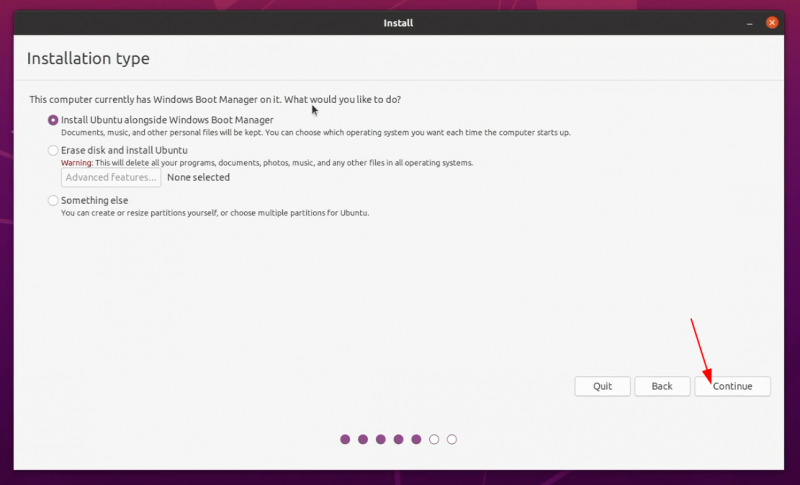
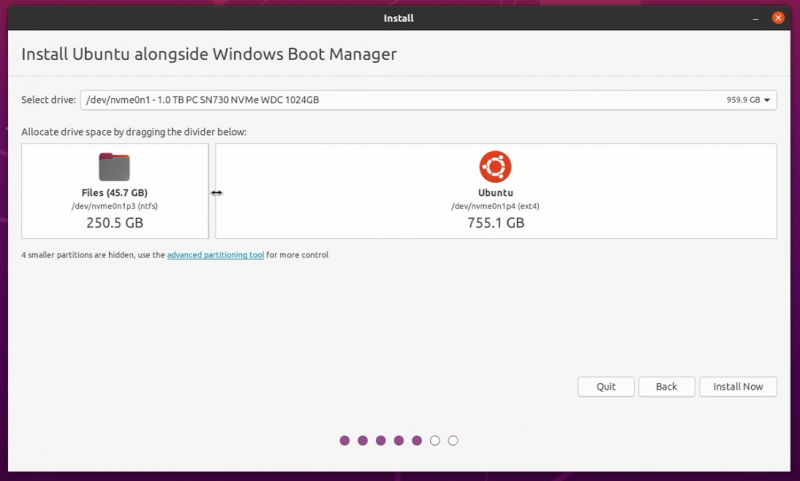
Подход 1. Вы видите «Установить Ubuntu вместе с Windows Boot Manager».
Если вы видите «Установить Ubuntu вместе с Windows Boot Manager» на экране установки, вам повезло.
Вы можете выбрать этот метод и нажать «Продолжить».
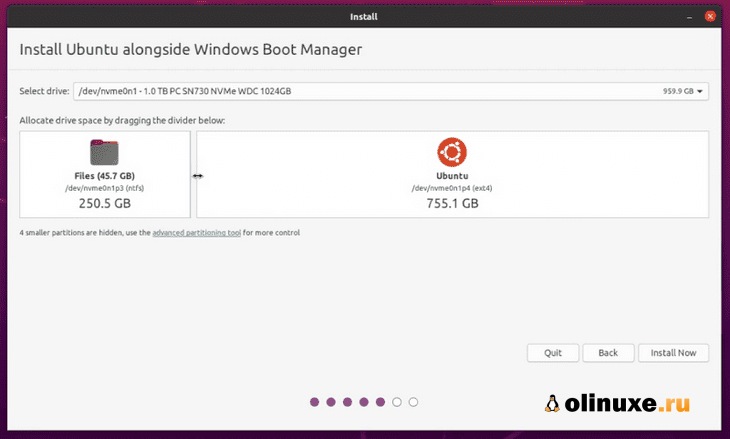
На следующем экране вы сможете создать раздел для Ubuntu, перетащив разделитель.
Вы можете выделить соответствующее дисковое пространство для Linux здесь.
Ubuntu создаст один раздел из выделенного дискового пространства, и у него будет root с home и swap (файл подкачки) размером 2 ГБ под root.
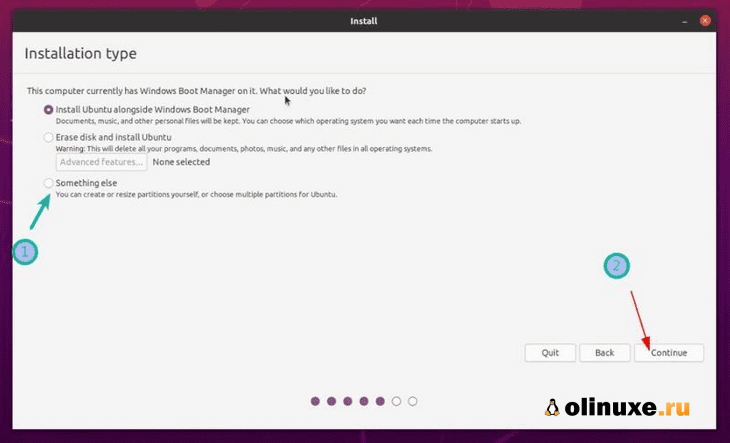
Подход 2: Вы не видите параметр «Установить Ubuntu вместе с диспетчером загрузки Windows» или он неактивен
Но если вы один из тех, кому не повезло, вам не о чем беспокоиться.
Для вас дела обстоят не так уж и плохо.
Вы все еще можете установить Ubuntu с Windows.
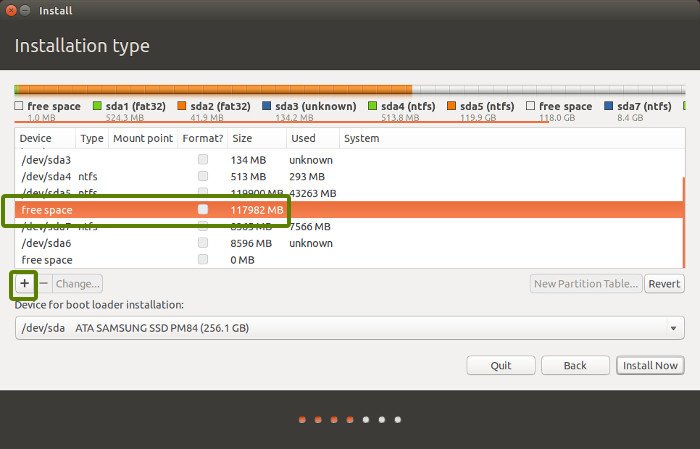
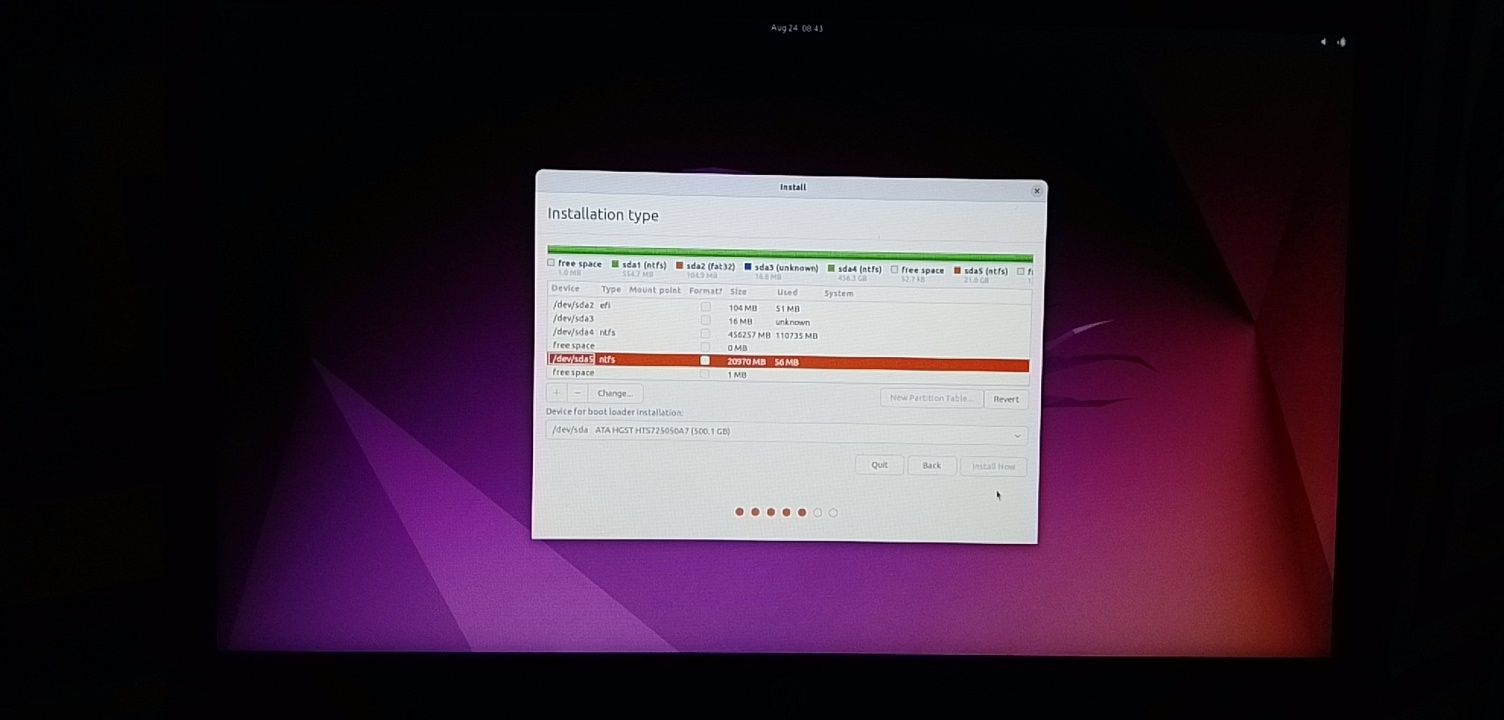
На экране «Тип установки» выберите «Что-нибудь еще».
Вы перейдете к экрану разбиения на разделы.
Помните, вы заранее создали свободное место?
Вы можете выделить все свободное пространство для root (файл подкачки и домашняя страница будут созданы автоматически под root) или вы можете разделить разделы root, swap и home.
Оба метода хороши.
Я показываю шаги для создания разделов root, swap и home по отдельности.
Но не стесняйтесь использовать один раздел для всех из них.
Выберите свободное место и нажмите на знак «+».
Он предоставит вам возможность создать раздел Linux.
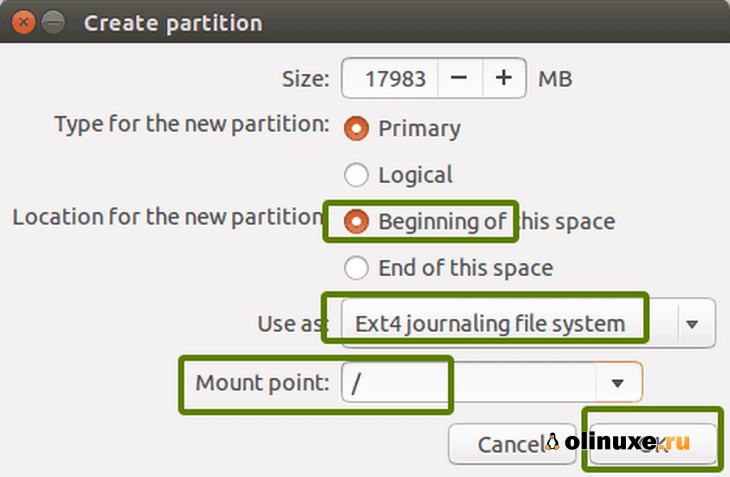
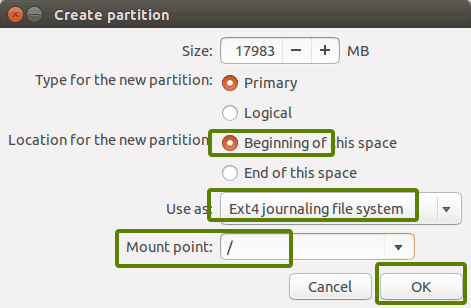
Вы создаете корневой (root) раздел.
Для этого более чем достаточно всего, что превышает 25 ГБ.
Выберите размер, выберите «Ext4» в качестве типа файла и / (означает root) в качестве точки монтирования.
Щелкнув «OK» на предыдущем шаге, вы перейдете к экрану раздела.
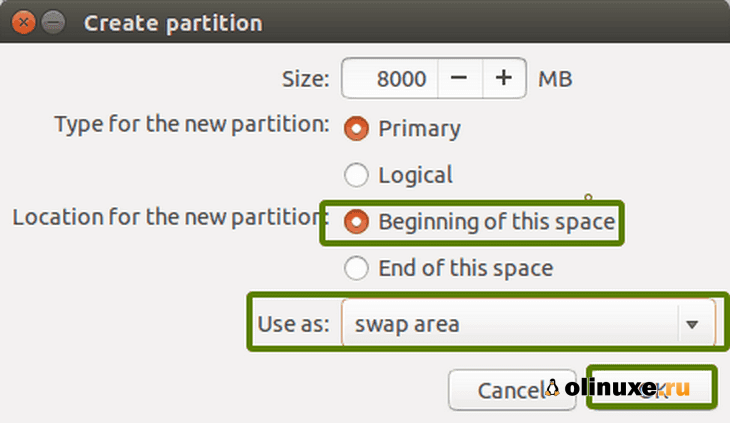
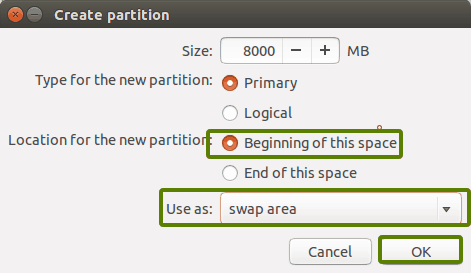
Затем создайте swap.
Как и раньше, снова нажмите на знак «+».
На этот раз используйте тип файла как область подкачки.
Вопрос об идеальном размере подкачки в Linux остается спорным.
Если у вас 2 ГБ или меньше ОЗУ, используйте подкачку, вдвое превышающую размер ОЗУ.
А если у вас 3-6 ГБ ОЗУ, используйте подкачку того же размера, что и ОЗУ.
Если у вас 8 ГБ или более ОЗУ, вы можете использовать подкачку, равную половине размера ОЗУ (если у вас не достаточно места на диске, и вы хотите использовать спящий режим, и в этом случае используйте подкачку не менее того же размера, что и ОЗУ).
Если вы чувствуете, что в вашей системе меньше swap, не волнуйтесь.
Вы можете легко создать файл подкачки и добавить больше места подкачки в свои системы.
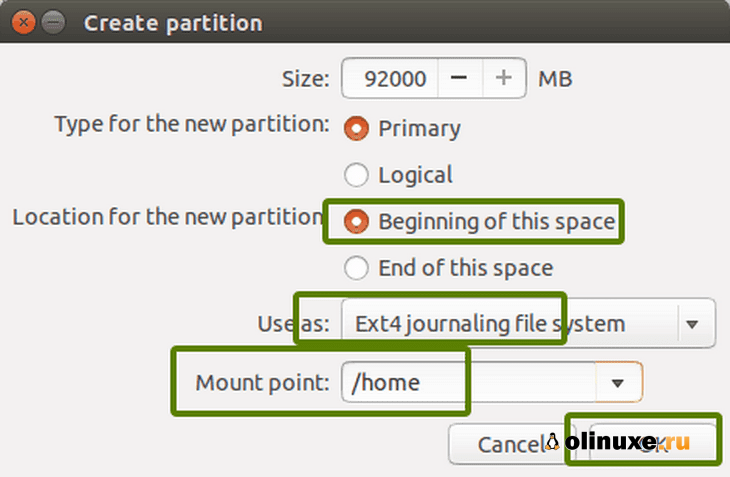
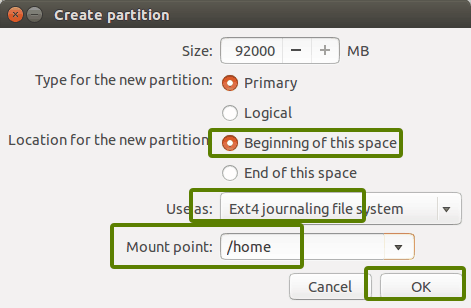
Таким же образом создайте домашний раздел.
Выделите ему максимальное пространство (фактически выделите ему остальное свободное пространство), потому что именно здесь вы будете сохранять музыку, изображения и загруженные файлы.
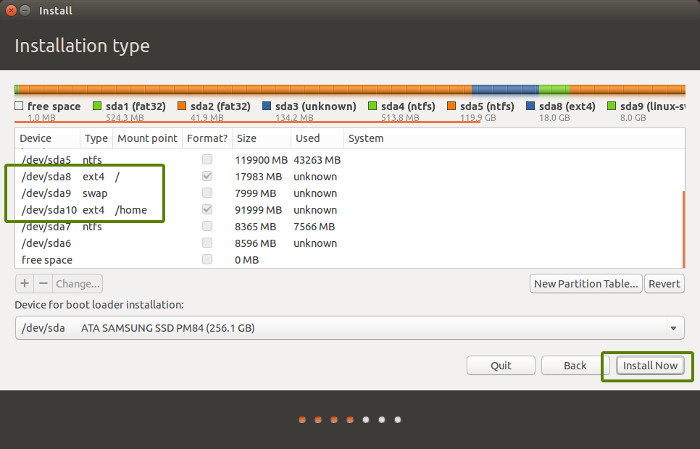
Когда вы будете готовы с root, swap и home, нажмите «Install Now»:
Что ж, вы почти выиграли битву.
Теперь вы чувствуете запах победы.
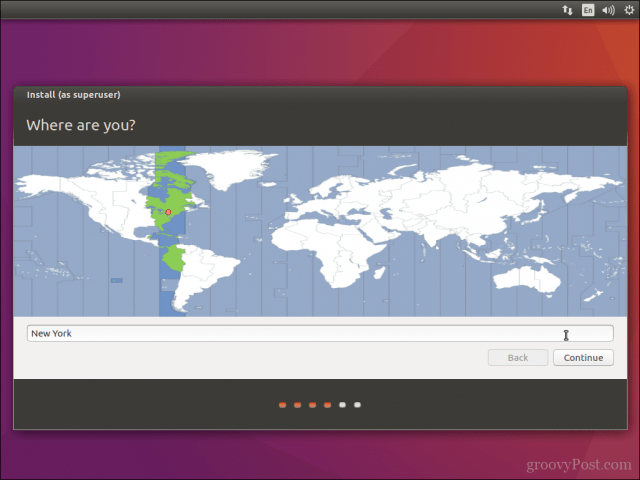
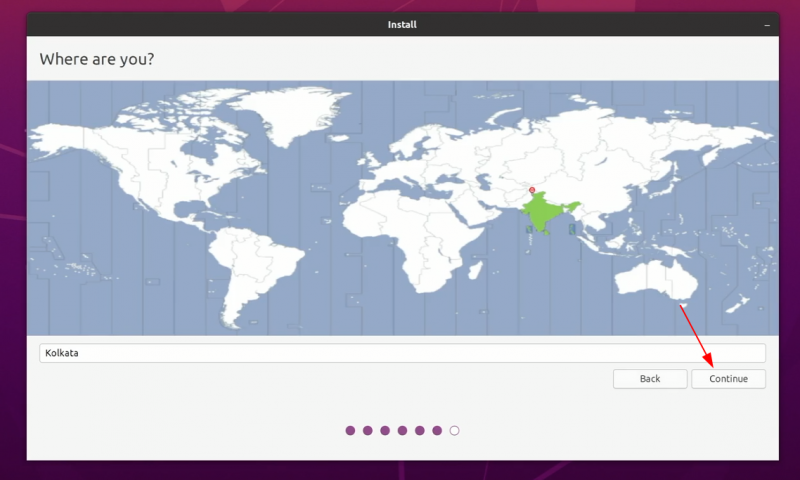
По запросу выберите часовой пояс.
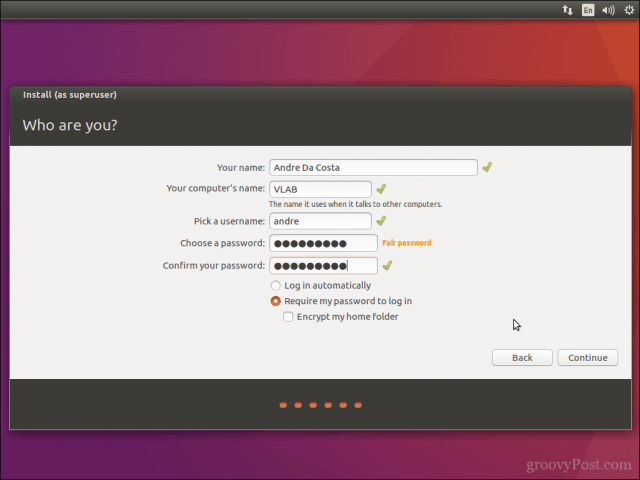
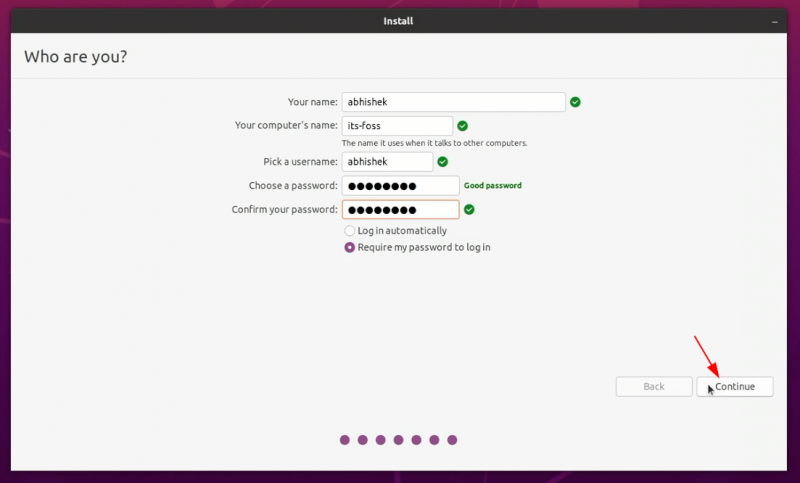
Затем вам будет предложено ввести имя пользователя, имя хоста (имя компьютера) и пароль.
Теперь осталось только подождать.
Для завершения установки потребуется 8-10 минут.
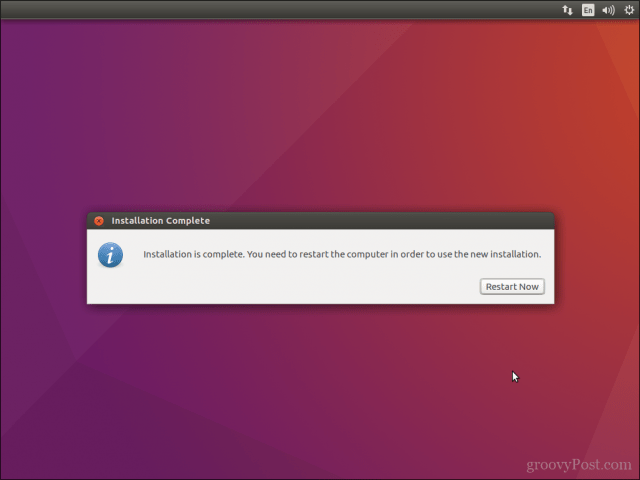
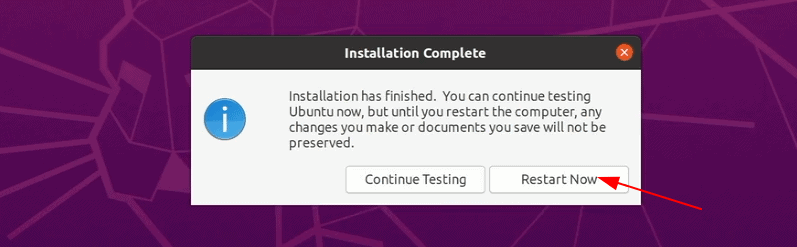
После завершения установки перезагрузите систему.
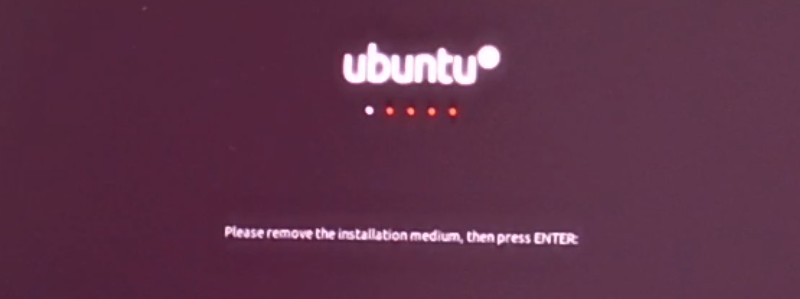
Вам будет предложено извлечь USB-диск.
На этом этапе вы можете удалить диск, не беспокоясь.
После этого система перезагрузится.
Для использования Linux вам больше не нужен Live USB-диск.
Вы установили Ubuntu на диск своего компьютера.
Удалите USB-накопитель и оставьте его на потом, если вы хотите использовать его для установки Linux в другой системе.
Вы также можете отформатировать его и использовать для обычного хранения или передачи данных.
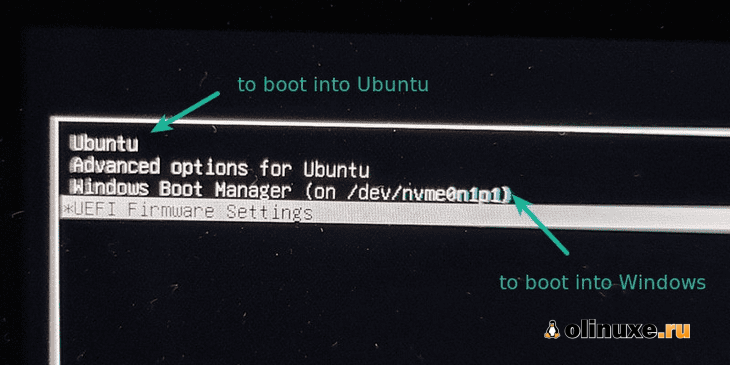
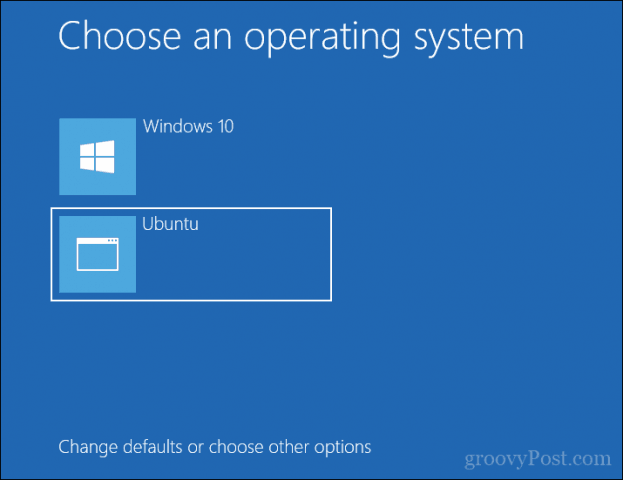
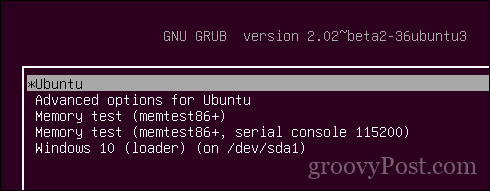
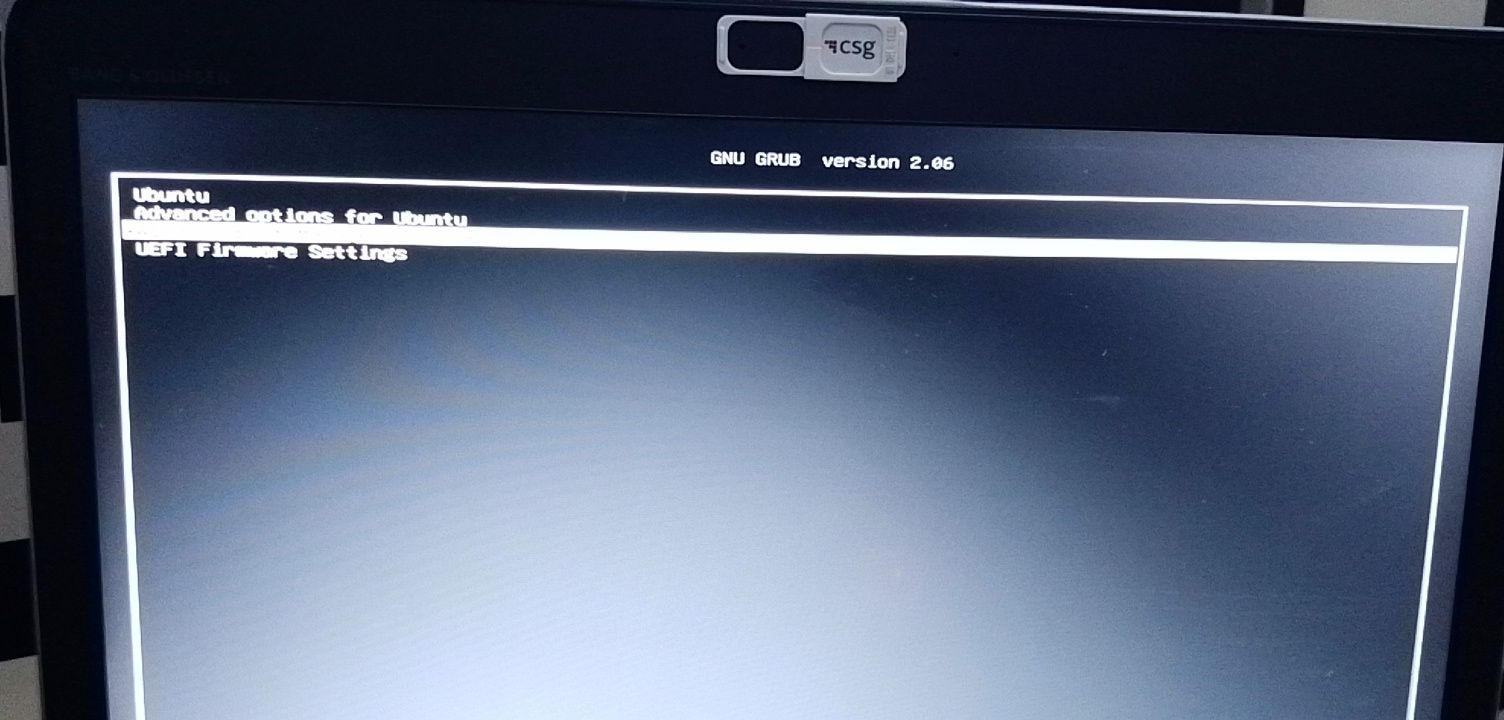
Если все прошло гладко, вы должны увидеть экран «grub» после включения системы.
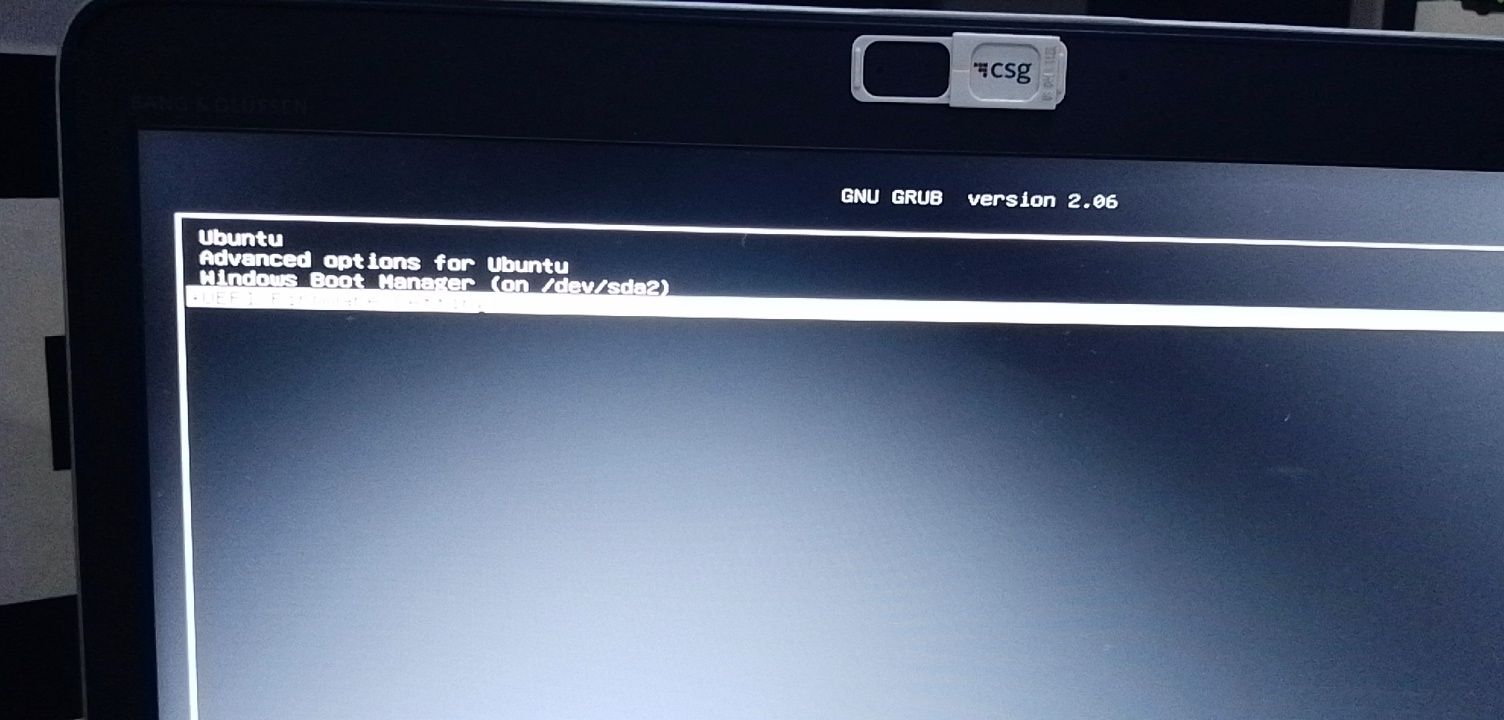
Здесь вы можете выбрать Ubuntu для загрузки в Ubuntu и диспетчер загрузки Windows для загрузки в Windows.
Довольно круто, правда?
Двойная загрузка не удалась? Вот несколько советов по устранению неполадок
Для некоторых двойная загрузка может пока не работать.
Однако вместо того, чтобы сдаваться, вы можете следовать нескольким советам и повторить процедуру установки.
Попробуйте сменить порт USB
Это может показаться смешным, но иногда некоторые порты USB вызывают проблемы с загрузкой USB или установкой Linux.
Изменение USB-порта может быть хитростью.
Старайтесь не использовать интернет при установке Linux
Я испытал, что иногда установка Linux выдает ошибку, если он подключен к интернету.
Если вы столкнулись с ошибкой «’grub-efi-amd64-signed’ package failed to install into /target», попробуйте установить Ubuntu без интернета.
Отключите безопасную загрузку и / или быструю загрузку
В некоторых редких случаях безопасная загрузка не позволит вам загрузиться с Live USB или установить Linux.
Отключите безопасную загрузку.
В некоторых случаях вы также можете отключить быструю загрузку.
Двойная загрузка завершена, но вы не видите экран «grub» для загрузки в Ubuntu
Пожалуйста, проверьте порядок загрузки в настройках UEFI.
Вы видите Ubuntu / UEFI под диспетчером загрузки Windows?
Если да, переместите его вверх по порядку.
Надеюсь, это руководство помогло вам выполнить двойную загрузку Ubuntu с Windows 10 UEFI.
Я здесь слишком подробно остановился на деталях, но я хотел ответить на все распространенные заблуждения и показать все необходимые шаги.
Если у вас все еще есть сомнения или возникла странная ошибка, оставьте комментарий, и я постараюсь вам помочь.
Источник
Running Windows 10 and Linux on the same computer is easier than ever. Here’s how to do it.
A computer that boots both Windows 10 and Linux can easily be the best of both worlds. Having easy access to either of the operating systems lets you enjoy the benefits of both. You can hone your Linux skills and enjoy the free software only available for Linux platforms. Or, you can switch back to Windows 10 to use apps like Photoshop, AutoCAD or Microsoft Office. The beauty of dual booting is that it lets each operating system take full advantage of the hardware resources of your computer. While virtual machines and the Windows Subsystem for Linux can give you a taste of the Linux experience, dual booting lets you tap its full potential.
The good news is that Windows 10 and Linux live in harmony better than ever these days. Dual booting Windows 10 and Linux used to be a precarious process that could wreck your Windows installation, your Linux installation or both. While the process isn’t quite a smooth as dual booting macOS and Windows with Boot Camp, it comes close. In this article, we’ll show you how to safely install Windows 10 and Linux on the same hard drive. It doesn’t matter if you’re starting with Linux or starting with Windows—dual booting is easy to set up either way.
Dual Boot Linux with Windows 10 – Linux Installed First
Let’s start with the (slightly) harder way first; you already have a copy Linux installed and you want to install Windows on a partition. The first step is to create the partition where Windows 10 will be installed. We have covered how to create partitions in Linux, so, start by reviewing our article on how to do that.
Once you have your partition set up, you will need to purchase Windows 10, download the ISO file then create a bootable copy. Creating a bootable copy of Windows 10 on Linux can be done using the free Unetbootin (USB thumb drive) or Brasero software if you are installing from a DVD.
Create Bootable Windows 10 Install Media Using Unetbootin
Unetbootin can be downloaded from the Software Center in Ubuntu. Once you have it up and running, launch it. Make sure you are using a thumb drive with at least 8 GBs of free space.
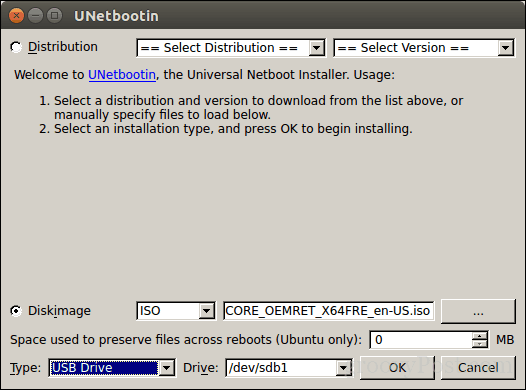
Select the Disk Image radio box, click the browse button (represented by an ellipsis …), browse to the ISO file then click Open. Chose the medium from the Type list box—in this case, your USB drive. Click on the drive list box then select your USB thumb drive.
Note: If you are not offered the option to select your thumb drive, you need to format it using the FAT32 file system. Open the file manager, right-click the thumb drive then click Format.
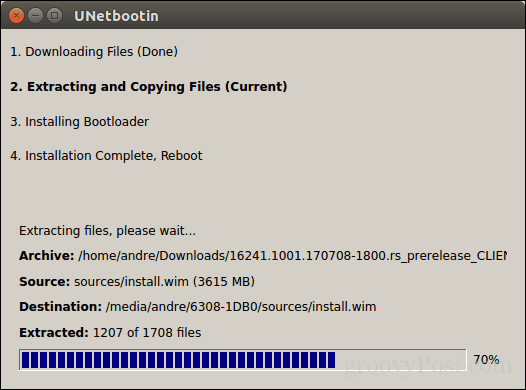
Click OK, then wait while the bootable copy is created.
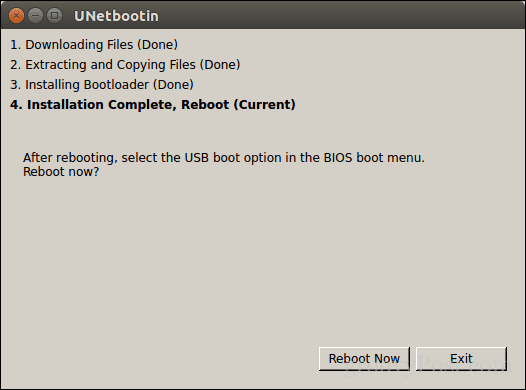
When complete, click Exit.
Create Bootable Windows 10 Install Media Using Brasero
If you already made a bootable USB with Unetbootin, you can skip this part. If you are still using an old school system with a DVD drive, you can use the Brasero DVD Burning software, which you can download from the Software Center also. Please keep in mind, Windows 10 ISO files are getting larger beyond the standard 4.7 GB DVDs. So, in some cases, it’s best you use 8.5 GB dual-layer DVDs if supported by your drive. If you can’t, then it’s best you use a USB thumb drive.
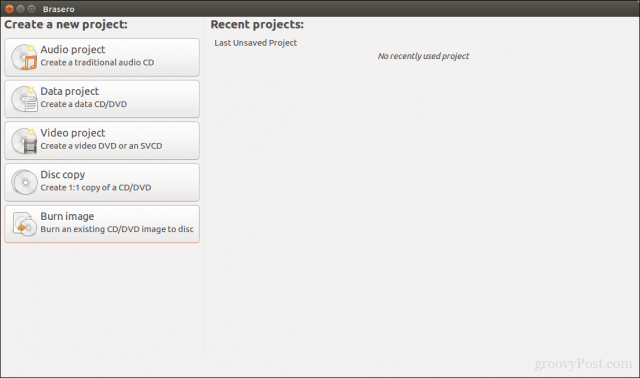
In Brasero, click Burn Image.
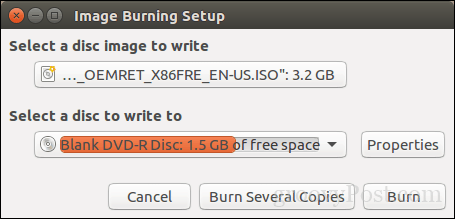
Select your disc image, make sure a blank DVD disc is inserted then click Burn.
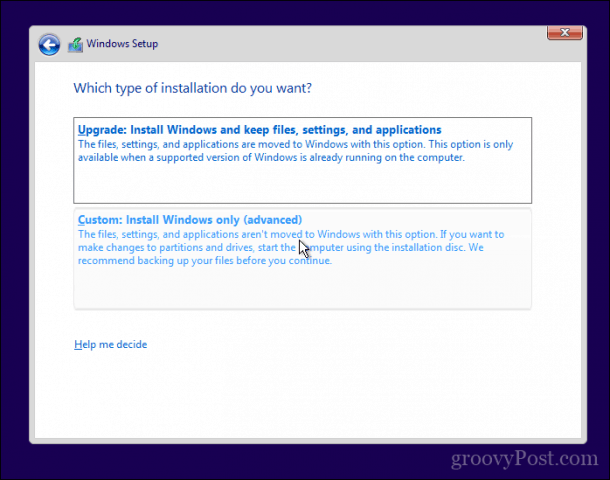
After preparing your install media, insert it or connect it. Reboot your computer, then configure your BIOS to boot from the drive. Windows 10 will boot into setup as it normally does. After you arrive at the setup screen, click Custom: Install Windows only (advanced).
Make sure you select the right partition; don’t wipe out your Linux installation. Click Next then wait while Windows 10 Setup copies files to the drive. Your computer will be rebooted several times.
When setup is complete, follow the instructions to complete the out of box experience.
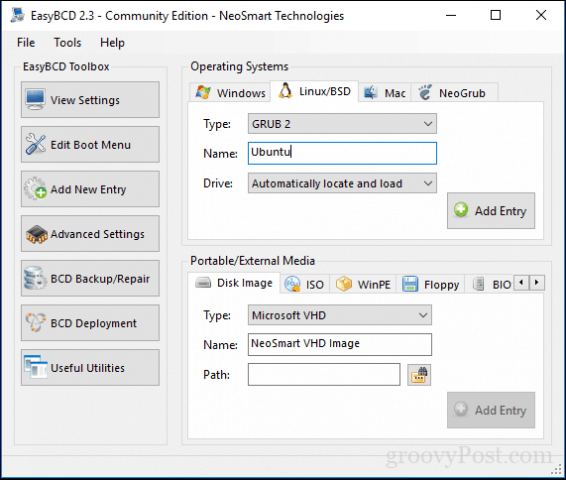
After that’s complete, you might notice the obvious—there is no way to boot into Linux anymore. Here is how you fix that. Download a free utility called EasyBCD from Neosmart Technologies. Proceed to install EasyBCD then launch it. Select the Linux/BSD tab. Click in the type list box, select Ubuntu; enter the name of the Linux distribution, choose automatically locate and load then click Add Entry. Reboot your computer.
You will now see a boot entry for Linux on the Windows graphical boot manager.
Dual Boot Linux with Windows 10 – Windows Installed First
For many users, Windows 10 installed first will be the likely configuration. In fact, this is the ideal way to dual boot Windows and Linux. Again, I will be using the Ubuntu Linux distribution. You can download the Ubuntu Linux ISO image from Canonical’s web page then create a bootable copy using Unetbootin for Windows or burn to a blank DVD using disc image in Windows 10.
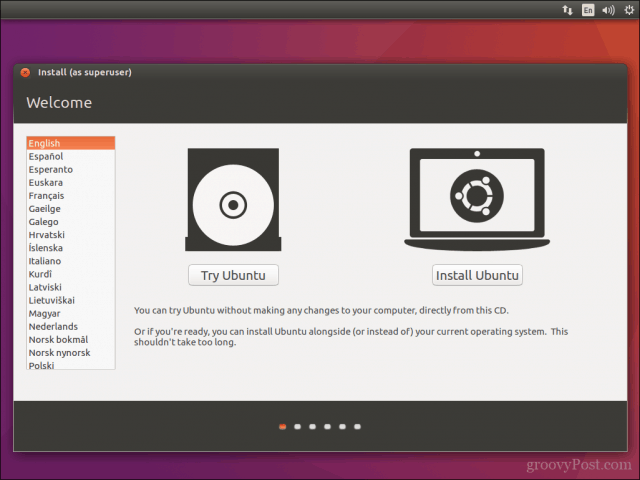
After creating your install media, configure your BIOS to boot from it. Ubuntu’s installation wizard intelligently detects existing Windows installations. It will ask you if you would like to install Ubuntu alongside Windows.
At the Ubuntu install screen, click Install Ubuntu.
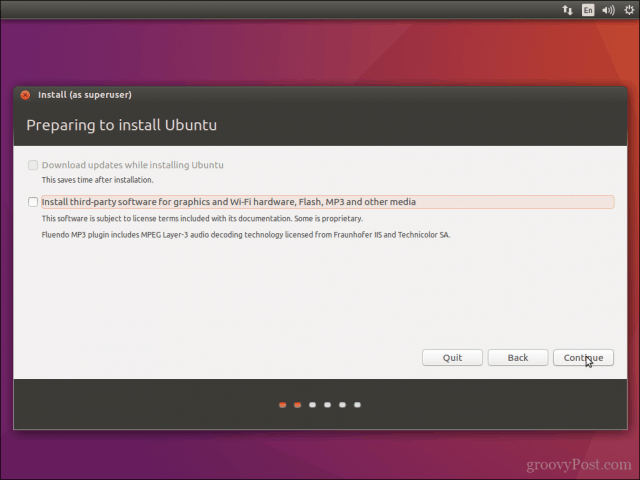
Choose whether you want to download and install updates and third-party drivers and codecs then click Continue.
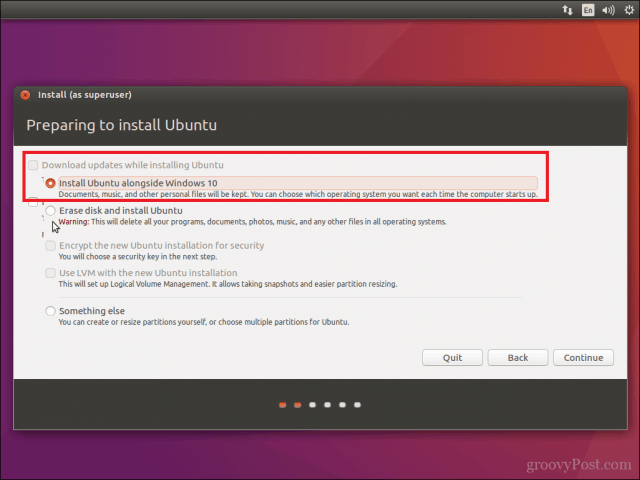
Select the option Install Ubuntu alongside Windows 10 then click Continue.
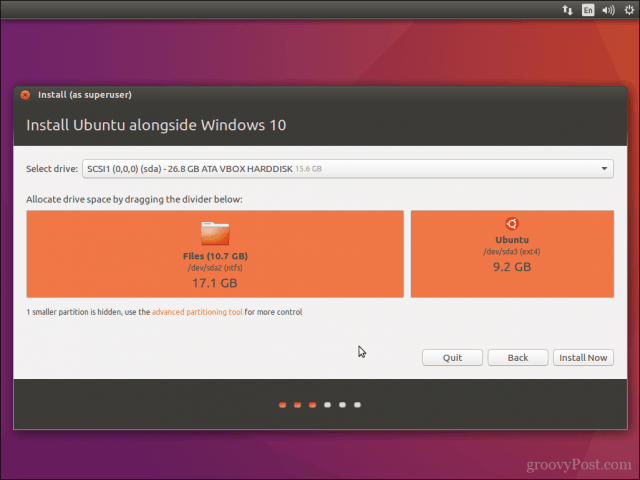
Ubuntu’s installer will set a default allocation of space for the installation. If you have enough space, you can resize the partition by placing your mouse between the divider then drag it left or right to make adjustments. Once you are satisfied with the allocated amount for your Ubuntu installation, click Install Now.
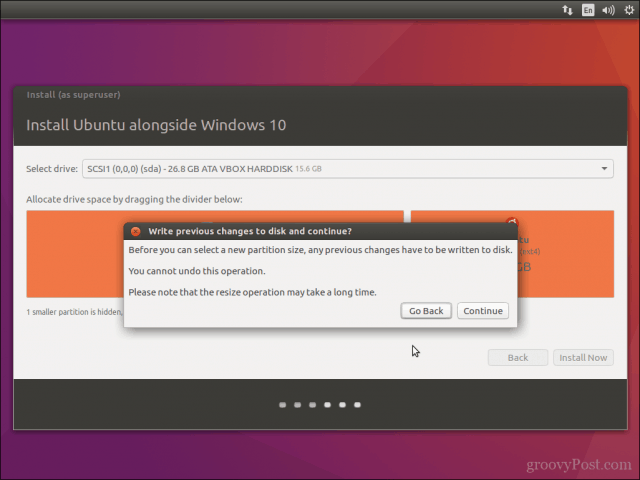
Click Continue to confirm changes.
Click Continue again.
Enter your time zone then click Continue.
Select your keyboard layout, click Continue.
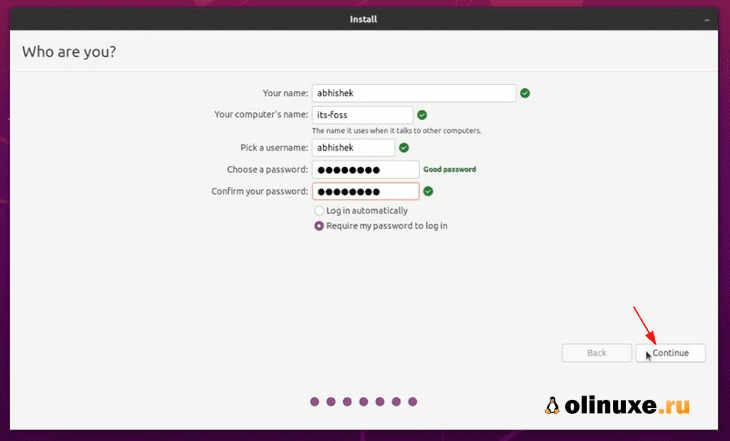
Create your user account by providing your full name, computer name, login name, and password. Choose whether you want to log in automatically or be prompted for a password. You can also encrypt your home folder for extra security. Click Continue.
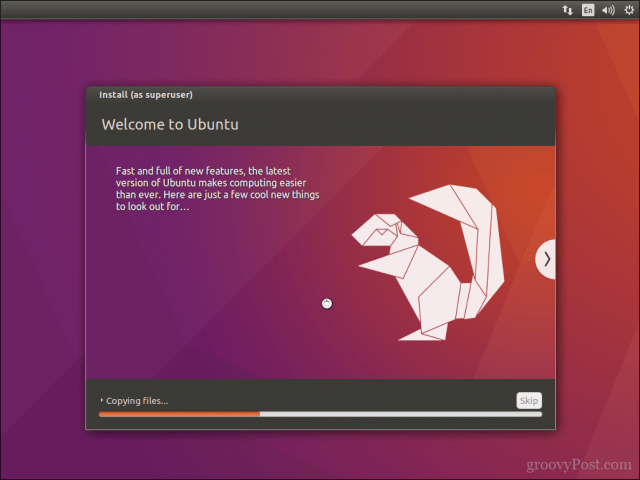
Wait while Ubuntu copies files.
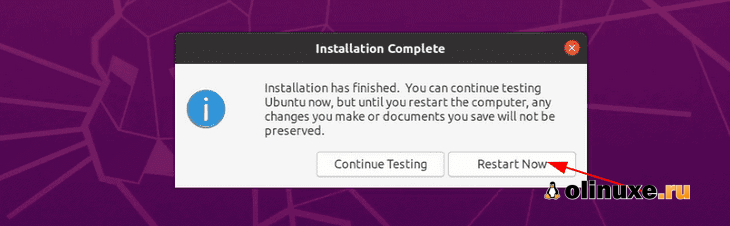
When complete, click Restart Now.
Ubuntu will add a boot entry for Windows 10 to the GRUB boot manager, which you can select using the up or down arrow then hitting Enter.
That’s it, Windows 10 and Ubuntu is now set up on your computer.
Let us know what you think. If you have done this before, share some of your tips with us. By the way, what’s your favorite distro?
Dual booting Linux with Windows is one of the most convenient ways of enjoying the two operating systems on the same computer.
You have both OS installed on the disk, on real hardware and when you power on your system, you can choose which operating system to use.
In an earlier tutorial, I showed the steps to dual boot Ubuntu with Windows 7 which comes with an MBR partition. The steps are almost the same for the newer systems that come preinstalled with Windows 10.
In this tutorial, I’ll show you how to install Ubuntu with Windows 10 already installed on the system.
💡
Before you start following the tutorial, I advise reading it entirely first. See what you need and what you should do in this tutorial. Once you have a good idea about the procedure and have all the necessary things on hand, start the process. Dual-boot is not a complicated process. It just takes some time and patience.
The steps mentioned here apply to other Ubuntu versions such as Lubuntu, Kubuntu, Xubuntu and Ubuntu-based Linux distributions such as Linux Mint, elementary OS, etc.
Dual boot Ubuntu Linux with Windows 10
Compatibility checks
This tutorial is suitable for systems that come with Windows 10 pre-installed with UEFI secure boot and GPT partitioning system. Please check whether your system uses GPT or MBR.
Make sure your system uses UEFI: This tutorial is only applicable for systems with UEFI boot. If you have bought your system in the last 5-6 years, chances are that you should already have a UEFI system on GPT partition. However, there is no harm in verifying that your system uses UEFI. If your system uses legacy BIOS with MBR partitioning system, please follow this dual boot tutorial.
Bitlocker encryption process is different: Newer systems with Windows 10 Pro have their disk encrypted with Bitlocker. If you have such a system, please follow this tutorial to dual boot with Bitclocker encryption.
Dual Booting Ubuntu With Windows 10 Pro With BitLocker Encryption
I have written about dual booting Windows and Ubuntu in the past. The process has improved so much in the last few years. Ubuntu and other Linux play very well with secure boot and UEFI now. So, why I am I writing about installing Ubuntu with Windows 10 once again?

System with both SSD and HDD: If you have a system with both SSD and HDD, i.e. dual disk system, the process is pretty much the same. However, you’ll be a lot better following this dedicated tutorial on dual booting dual disk system.
Dual Booting Ubuntu and Windows With a SSD and a HDD
Dual booting Ubuntu and Windows is not that complicated and I have covered it in detailed tutorial in the past. Recently, I also wrote about dual booting on a Bitlocker encrypted Windows system. And yet here I am talking about it again. Why? Because the scenario is slightly different and

Prerequisites: What do you need?
You’ll need the following things to easily and safely install Linux alongside Windows:
- A computer that comes preinstalled with Windows 10.
- A USB key (pen drive or USB drive) of at least 4 GB in size and no data on it.
- Internet connection (for downloading Ubuntu ISO image and live USB creating tool). You can do this on any system, not necessarily on the system you are dual booting.
- Optional: External USB disk for making back up of your existing data.
- Optional: Windows recovery or bootable disk (if you encounter any major boot issues, it could be fixed).
Let’s see the steps of installing Ubuntu alongside Windows 10. I have made a video of the entire process. You may watch that as well.
Step 1: Make a backup of your Windows system [optional]
It is always nice to have a backup of your data, just in case you mess up with the system while dealing with disk partitions.
I advise copying all the essential data you cannot afford to lose on an external USB disk. You can use an external HDD (slower but cheaper) or SSD (faster but expensive) and copy the important files and folders.
Step 2: Download Ubuntu (or whichever Linux distribution you are using)
Head over to Ubuntu’s website and download the ISO file. The file should be around 2.5 GB in size. If you need to download Ubuntu via torrents, you can click the ‘alternative downloads.’
Step 3: Create a live USB/disk of Ubuntu
I presume that you are using Windows to create the live USB. Several free applications allow you to create a live Ubuntu USB. You can use any of these tools. Since I cannot show all of them, I’ll go with Rufus.
Download Rufus for free from its website. It will download a .exe file.
Plug in your USB. This device will be formatted so make sure you don’t have any important data on this USB disk.
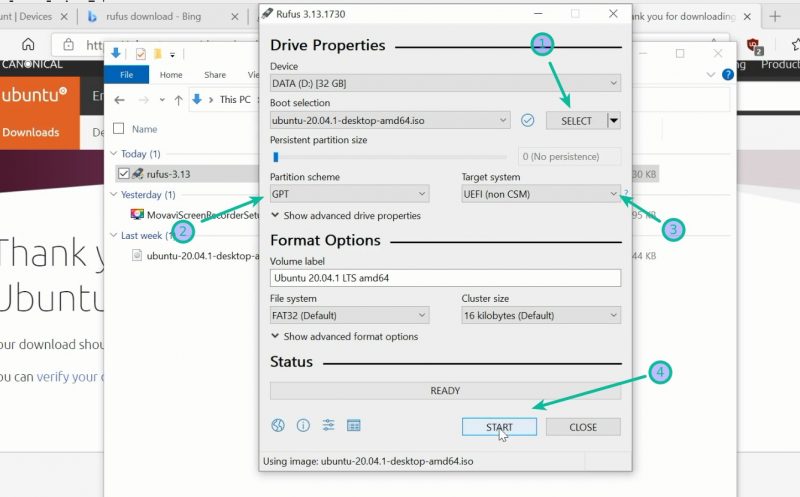
Run the Rufus tool you just downloaded. It automatically identifies the plugged-in USB but double-check it anyway. Now, browse to the location of the downloaded ISO image and ensure that it uses GPT partitioning scheme and UEFI target system.
Hit the start button and wait for the process to complete. Your live Linux USB is ready.
📋
Installing Ubuntu and creating the live Ubuntu USB process can be done on any computer. But the rest of the process takes on the system on which you are dual booting.
Step 4: Make some free space on your disk for Ubuntu installation
In many systems, while installing Ubuntu, it gives the option to make a disk partition for Ubuntu. However, that is not a surety. This is why making the required free space on the disk would be better before starting the installation procedure.
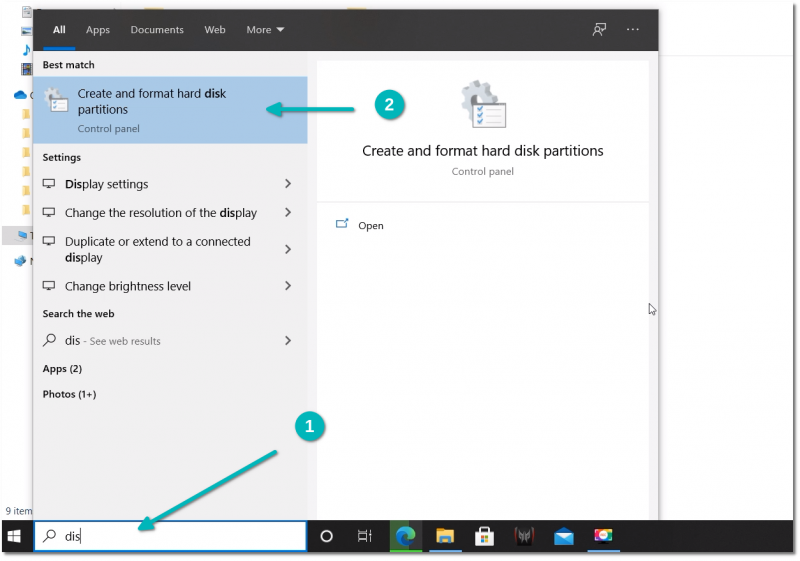
In the Windows menu, search for ‘disk partitions’ and go to ‘Create and format hard disk partitions.’
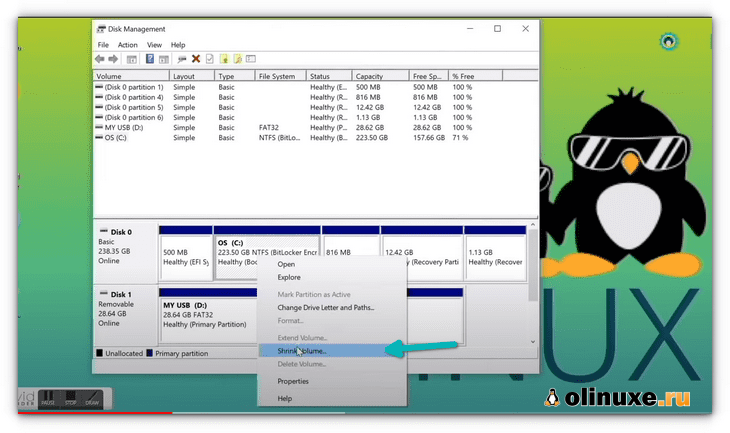
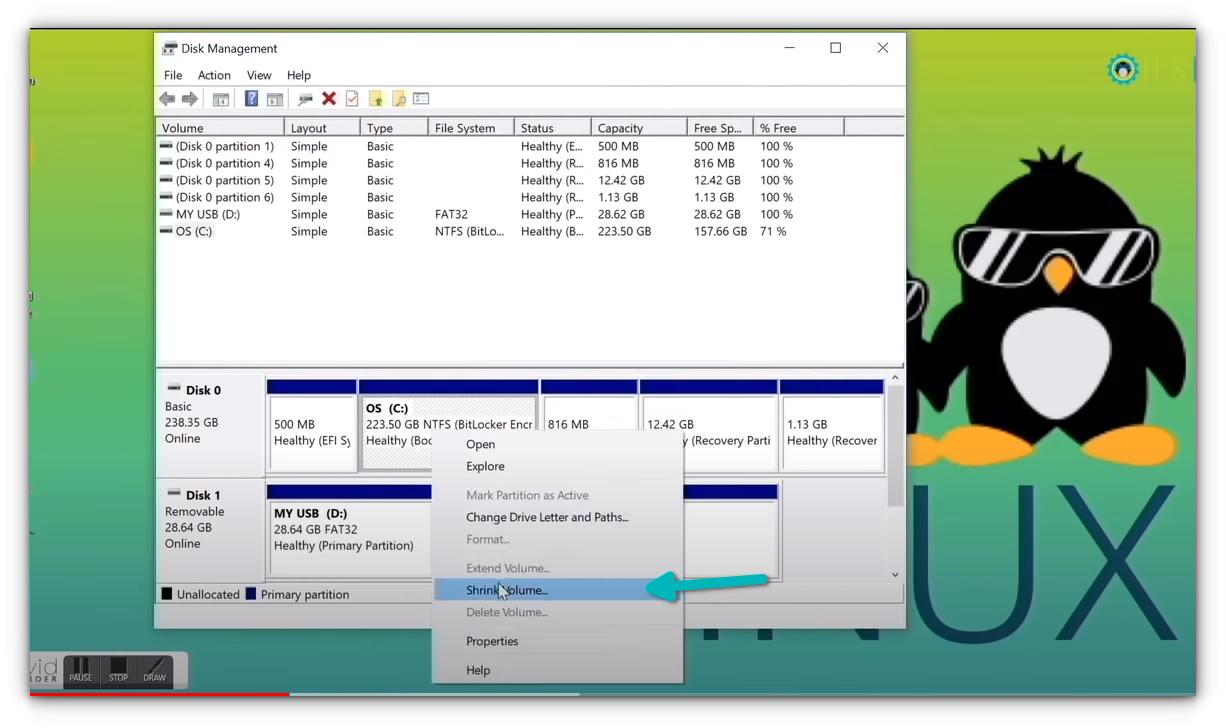
In the Disk Management tool, right-click on the drive which you want to partition and select shrink volume.
If you have just one partition like this, you need to make some free space out of it for Linux. Use any of them except C drive if you have several partitions of considerable size because it may erase the data.
The 256 GB in my system already had several partitions from the manufacturer but mainly for backup and other purposes. The primary partition was the C drive, around 220 GB, where Windows 10 is installed. In my case, I shrank the C drive to make some free space for Linux installation.
How much space do you need for Linux in dual boot?
This depends on how much total disk space you have. You may install Ubuntu on 15 or 20 GB but you’ll soon start running out of disk space. These days, you should have at least 120 GB of disk. In that case, go for 30-40 GB of disk for Linux. If you have 250 GB disk, allocate 60-80 GB or even more. If you have more disk space, allocate even more free space, if you want.
What if you have D, E or F drives?
This is a common confusion for many people as they think Ubuntu can only be installed on the C drive. That’s not true. I had only one C drive, so I shrank it. If you have D, E or F drive, you may shrink one of those drives. You may also choose to delete the D, E or F drive. NEVER DELETE C DRIVE.
Step 5: Boot from live Ubuntu USB
You created a live Ubuntu USB in step 3. Plug it into the system. Before you go and boot from the live USB, let’s have a quick word about the infamous secure boot.
Do I need to disable the secure boot for installing Linux?
6-8 years back, the UEFI secure boot was not well-supported by Linux; hence, you had to disable secure boot before installing Linux. Thankfully, Ubuntu and many other Linux distributions currently support secure boot very well. Usually, you should not need to do anything about it. However, if your system doesn’t allow booting from live USB or if you see any other related issue, you may disable the secure boot on Windows.
Alright! Let’s see how to boot from the USB. You can go to the boot settings by pressing F2/F10 or F12 at the system start time and selecting to boot from the USB. However, some people find it difficult.
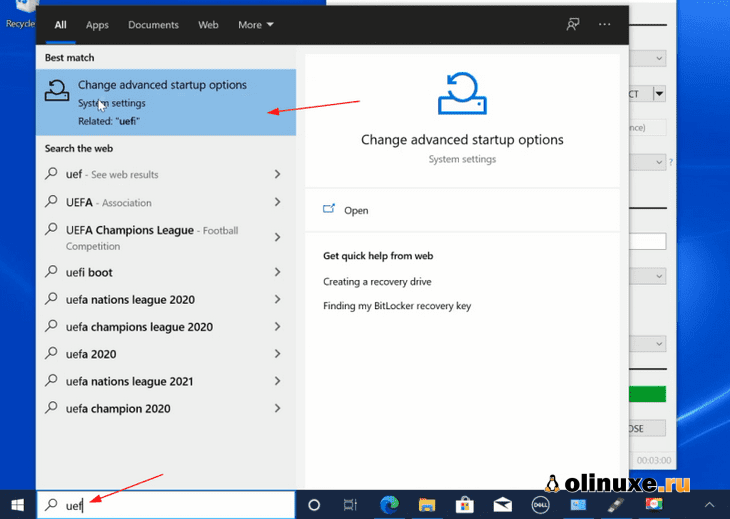
The longer but an easier step is to access the UEFI boot settings from within Windows. In the Windows menu, search for UEFI and then click on ‘Change advanced startup options’:
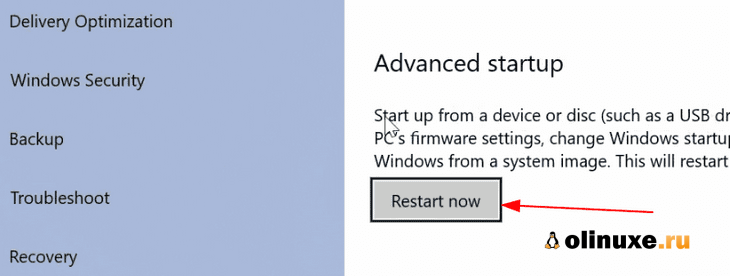
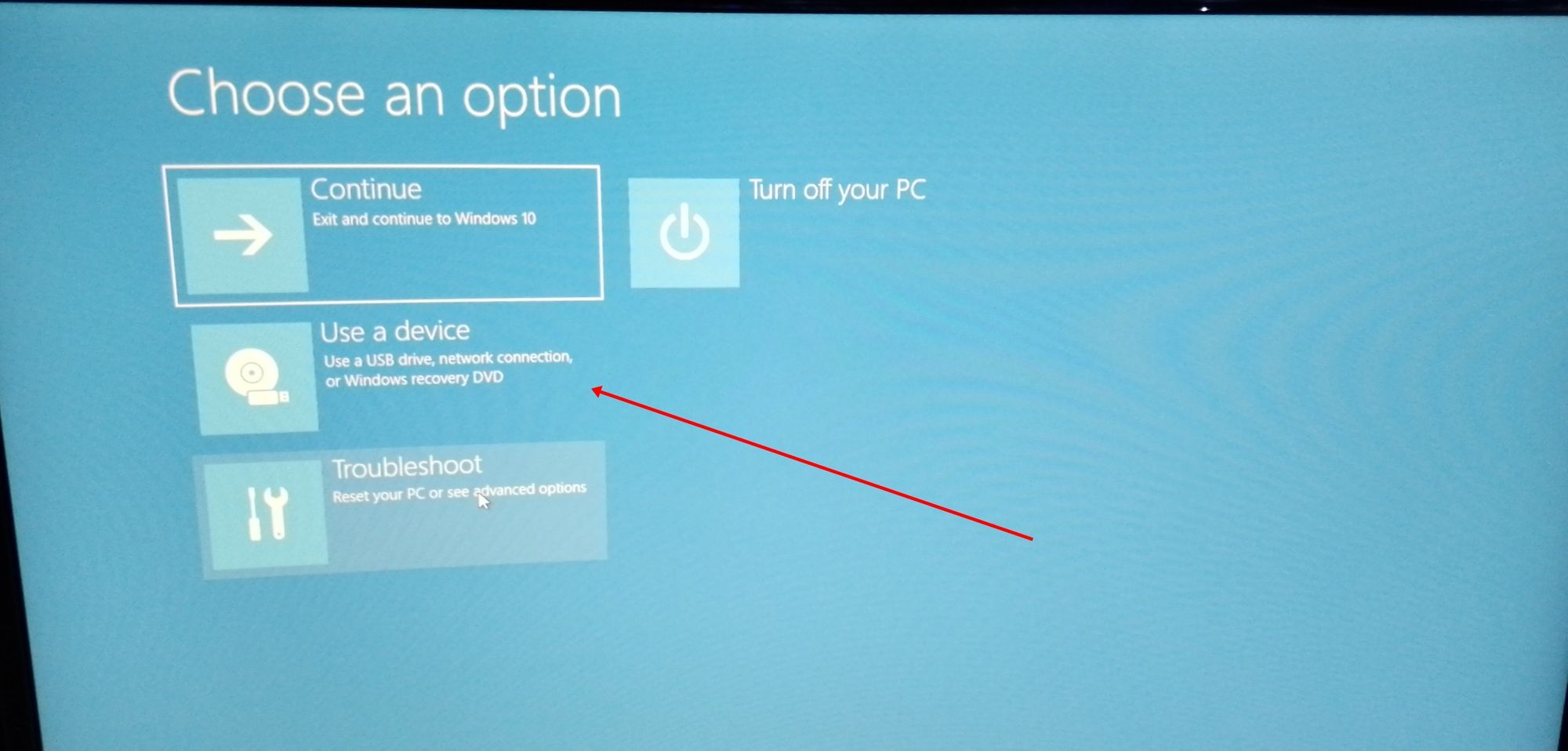
Go to the Advanced startup option and click on Restart now button.
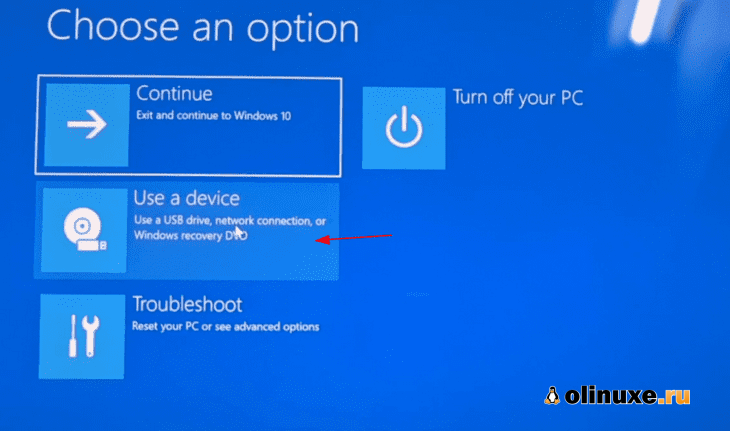
On the next screen, click on ‘Use a device’:
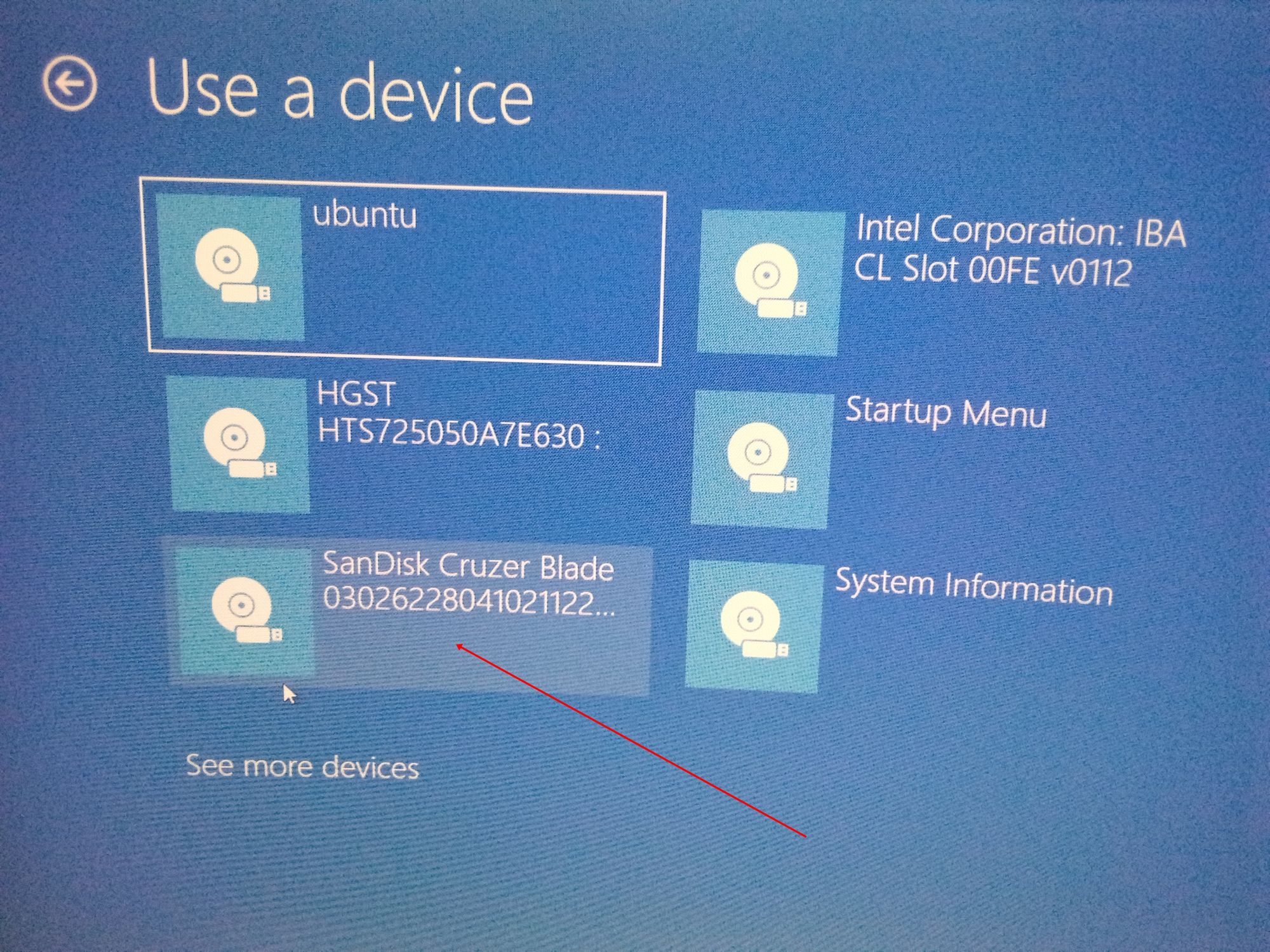
Recognize the USB disk with its name and size. It may also be displayed as EFI USB Device.
Now it will power off your system and reboot into the disk you chose which should be the live USB disk. You should see a screen like this after a few seconds:
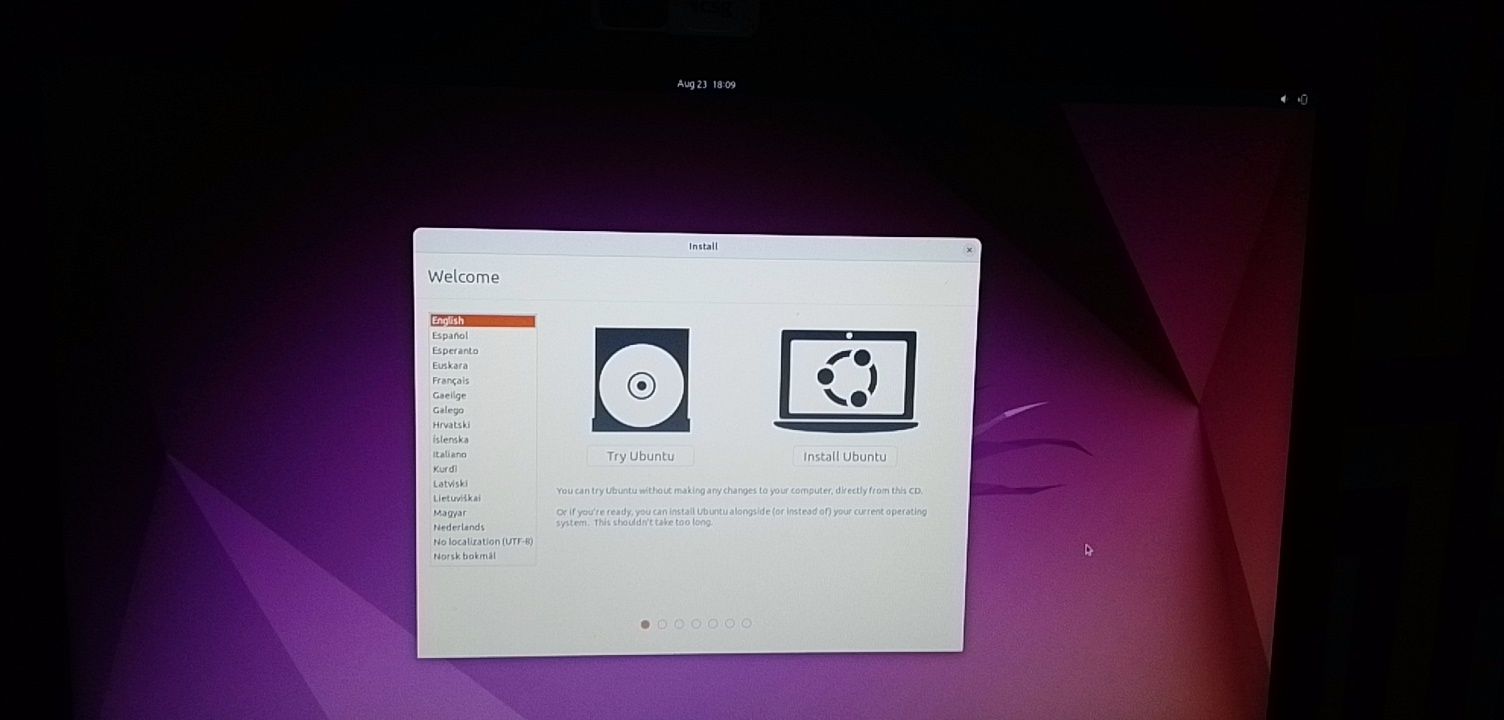
The ‘Try Ubuntu without installing’ option allows you to experience Ubuntu from the live disk. The option to install Ubuntu can be found on the desktop.
The “Install Ubuntu” option will start the Ubuntu installation immediately.
You can opt for either option based on your preference.
Step 6: Installing Ubuntu along with Windows 10
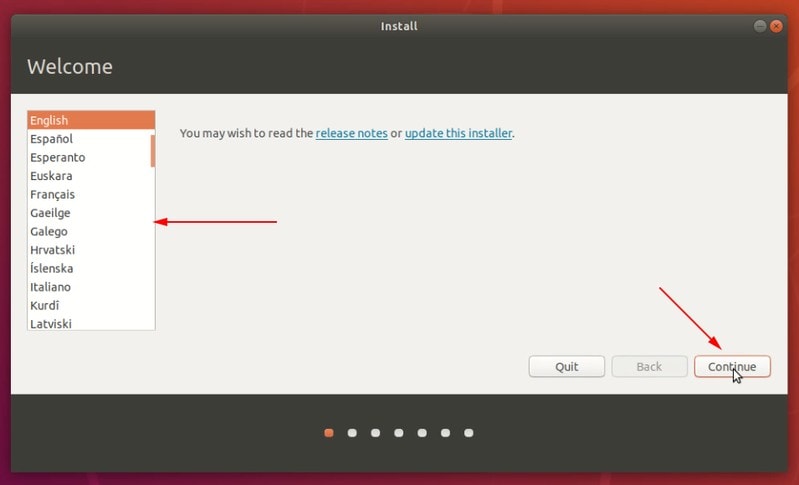
Start the installation procedure. The first few steps are simple. You choose the language and keyboard layout.
On the next screen, choose Normal installation. No need to download updates or install third-party software just yet. You may do it after the installation completes.
Hit continue. It may take some time to go to the next step.
Note: Some people try to download updates and install media codes while installing. In my experience, it sometimes creates issues during installation and may also cause the installation to fail. For this reason, I advise against them.
Important: Installation takes two approaches based on what you see on the next screen
Since this is a detailed tutorial, I’ll cover both aspects.
Approach 1: You see the “Install Ubuntu alongside Windows Boot Manager”
If you see the “Install Ubuntu alongside Windows Boot Manager” on the Installation type screen, you are in luck. You can select this method and hit continue.
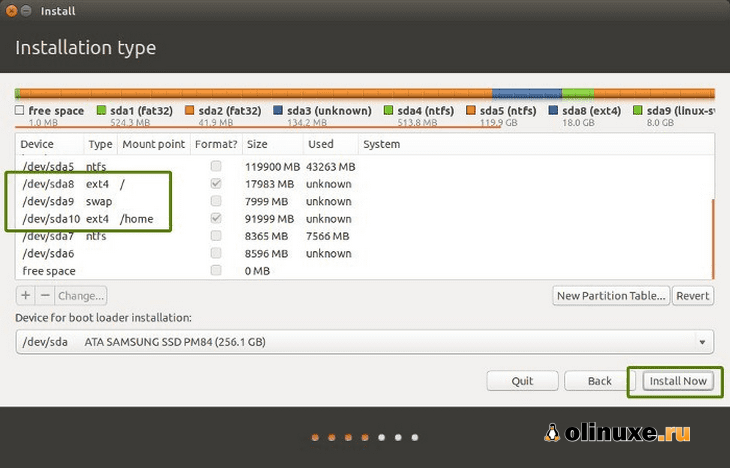
The next screen will give you the option to create a partition for Ubuntu by dragging the divider. You can allocate appropriate disk space to Linux here. Ubuntu will create one partition of the allocated disk space and it will have root with home and a swapfile of 2 GB in size under root itself.
Approach 2: You don’t see ‘Install Ubuntu alongside Windows Boot Manager’ option or it is greyed out
But if you are one of the unlucky ones who don’t see this option, no need to worry. Things are not that bad for you. You can still install Ubuntu with Windows.
On the Installation type screen, go with Something Else.
It will take you to the partitioning screen. Remember you had created some free space beforehand?
You may allocate the entire free space to root (swapfile and home will be created automatically under root) or separate root, swap and home partitioning. Both methods are acceptable.
I show the steps for creating root, swap and home partitions separately. But feel free to use a single partition for all of them.
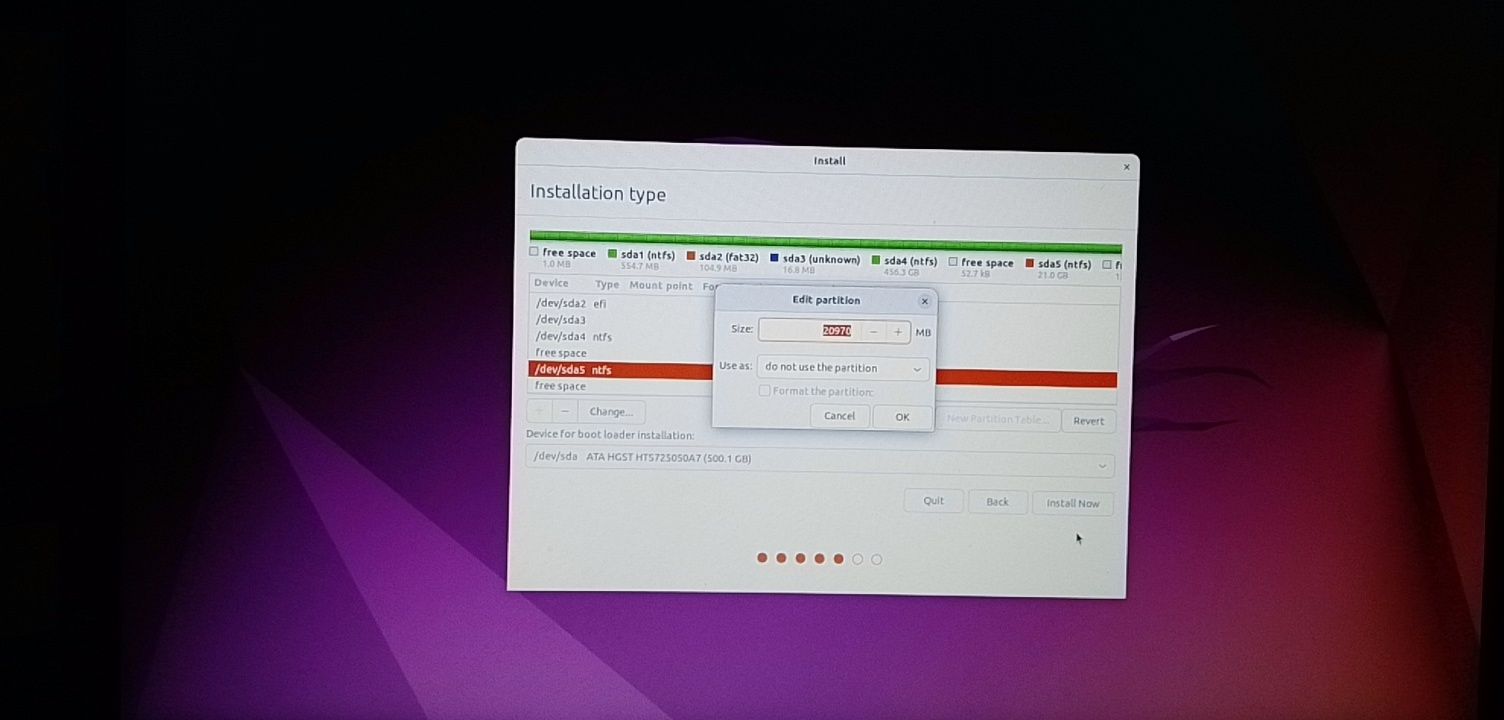
Select the free space and click on the + sign.
It will provide you with the option to create a Linux partition. You are creating the Root partition. Anything above 25 GB is more than sufficient for it. Choose the size, select Ext 4 as the file type and / (means root) as the mount point.
Clicking on OK in the previous step will bring you to the partition screen. Next, create a swap. Like previously, click on the + sign again. This time, use the file type as the Swap area.
Ideal swap size in Linux is debatable. If you have 2 GB or less RAM, use swap double the size of RAM. If you have 3-6 GB of RAM, use a swap of the same size as RAM. If you have 8 GB or more RAM, you may use swap half the size of RAM (unless you have plenty of disk space, and you want to use hibernation and in that case, use a swap of at least the same size as RAM).
If you feel like you have less swap on your system, don’t worry. You can easily create swapfile and add more swap space to your systems.
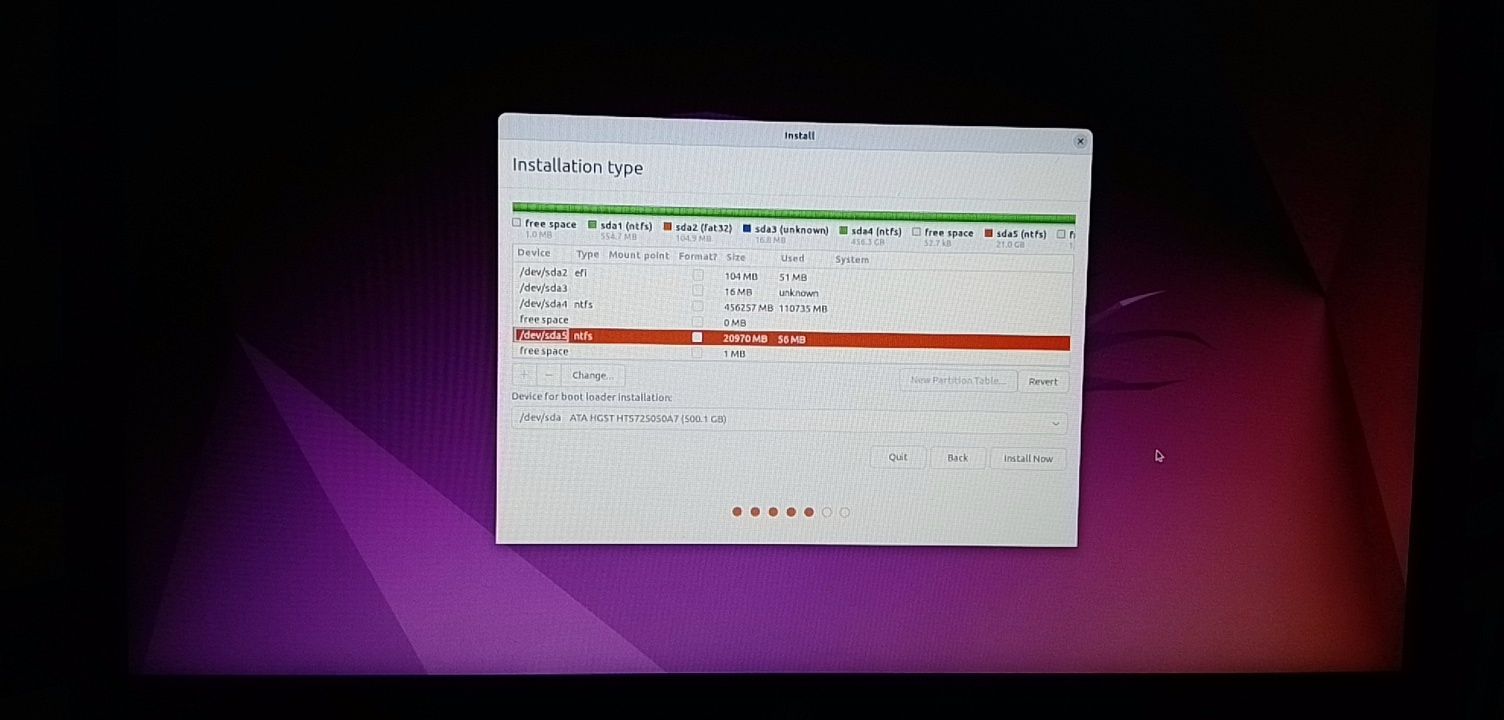
Similarly, create a Home partition. Allocate it maximum space (in fact allocate it the rest of the free space) because this is where you’ll save music, pictures and downloaded files.
Once you are ready with Root, Swap and Home, click on Install Now:
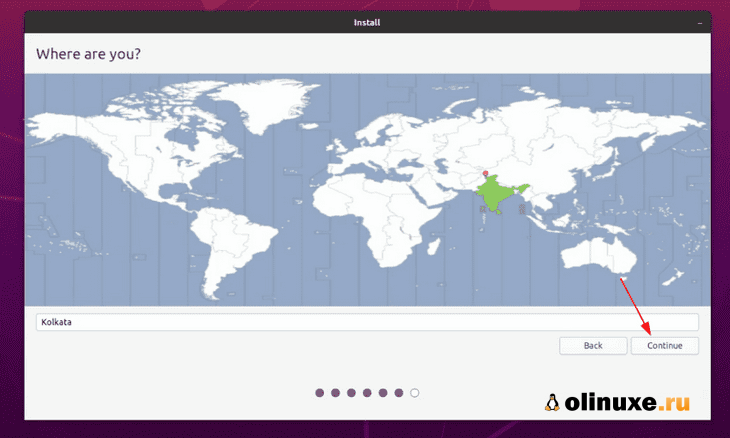
Well, you have almost won the battle. You can smell victory now. Select a timezone when asked.
Next, you’ll be asked to enter a username, hostname (computer’s name) and password.
Now it’s just a matter of waiting. It should take 8-10 minutes to complete the installation.
Once the installation finishes, restart the system.
You’ll be asked to remove the USB disk. You can remove the disk at this stage without worrying. The system reboots after this.
💡
You do not need the live USB disk to use Linux anymore. You have installed Ubuntu on your computer’s disk. Remove the USB and keep it for later if you want to use it for installing Linux on some other system. You may also format and use it for regular data storage or transfer.
If everything goes smoothly, you should see the grub screen once the system powers on. Here, you can choose Ubuntu to boot into Ubuntu and Windows boot manager to boot into Windows. Pretty cool, right?
Dual boot did not succeed? Here are some troubleshooting tips
Life is not even for everyone. For some, the dual boot might not succeed just yet. However, instead of giving up, you may follow a couple of tips and retry the installation procedure.
Try changing the USB port
This may sound ridiculous but sometimes some USB ports cause issue with booting the USB or installing Linux. Changing the USB port could be a trick.
Try not using internet while installing Linux
I have experienced that sometimes Linux installation throws error if it is connected to the internet. If you encountered a “‘grub-efi-amd64-signed’ package failed to install into /target” error, please try installing Ubuntu without internet.
Disable secure boot and/or fast boot
In some rare cases, secure boot would not allow you to boot from live USB or install Linux. Disable secure boot. You may also disable fast boot in some cases.
Dual boot finished but you don’t see the grub screen to boot into Ubuntu
Please check your boot order in the UEFI settings. Do you see Ubuntu/UEFI below Windows Boot Manager? If yes, move it up the order. If you don’t see grub at all, you may carefully try this or this tutorial.
Grub rescue error or no bootable device found after dual booting
Use this tutorial for no bootable device found error. And this one is for grub rescue error.
Additional Tips: You’ll notice that there is a time difference between Windows and Ubuntu You can fix the time gap issue in dual boot easily. Also, in the grub screen, Ubuntu is up the priority. You can also change the boot order to make Windows default if you are going to use Windows more often than Linux. If you want to reverse the process, follow this guide to remove Ubuntu from dual boot with Windows.
I hope this guide helped you to dual boot Ubuntu with Windows 10 UEFI. I went into too much detail here, but I wanted to answer all the typical confusion and show all the required steps.
If you still have doubts or face strange errors, please comment, and I’ll try to help you out.
Приветствую, друзья!
Двойная загрузка Linux с Windows — один из самых удобных способов использования двух операционных систем на одном компьютере.
Обе ОС установлены на диске, на реальном оборудовании, и при включении системы вы можете выбрать, какую операционную систему использовать.
В режиме двойной загрузки вы можете выбрать операционную систему для загрузки
В этом руководстве я покажу вам, как установить Ubuntu с уже установленной в системе Windows 10.
Прежде чем вы начнете следовать руководству, я советую сначала полностью его прочитать.
Посмотрите, что вам нужно и что вы должны делать в этом уроке.
Как только вы получите хорошее представление о процедуре и у вас все необходимое будет под рукой, приступайте к процессу.
Двойная загрузка — не сложный процесс. Просто нужно время и терпение.
Упомянутые здесь шаги применимы к другим версиям Ubuntu, таким как Lubuntu, Kubuntu, Xubuntu и дистрибутивам Linux на основе Ubuntu, таким как Linux Mint, elementary OS и т. д.
Двойная загрузка Ubuntu Linux с Windows 10
Это руководство подходит для систем с предустановленной Windows 10 с безопасной загрузкой UEFI и системой разбиения GPT.
Пожалуйста, проверьте, использует ли ваша система GPT или MBR?
Проверки совместимости
Убедитесь, что ваша система использует UEFI: это руководство применимо только для систем с загрузкой UEFI.
Если вы купили свою систему в последние 5-6 лет, скорее всего, у вас уже должна быть система UEFI в разделе GPT.
Однако нет ничего плохого в том, чтобы убедиться, что ваша система использует UEFI.
Если в вашей системе используется устаревшая версия BIOS с системой разбиения на разделы MBR, следуйте этому руководству по двойной загрузке.
Процесс шифрования Bitlocker отличается: в новых системах с Windows 10 Pro диск зашифрован с помощью Bitlocker.
Система с SSD и HDD: если у вас есть система с SSD и HDD, то есть с двумя дисками, процесс будет почти таким же.
Предпосылки: что вам нужно?
Для простой и безопасной установки Linux вместе с Windows вам понадобятся следующие вещи:
- Компьютер с предустановленной Windows 10;
- USB-ключ (флэш-накопитель или USB-накопитель) размером не менее 4 ГБ и без данных на нем;
- Подключение к интернету (для загрузки ISO-образа Ubuntu и инструмента для создания Live USB). Вы можете сделать это в любой системе, не обязательно в системе с двойной загрузкой.
- Необязательно: внешний USB-диск для резервного копирования существующих данных;
- Необязательно: восстановление Windows или загрузочный диск (если у вас возникнут серьезные проблемы с загрузкой, их можно будет исправить).
Давайте посмотрим, как установить Ubuntu вместе с Windows 10.
Шаг 1. Сделайте резервную копию вашей системы Windows [необязательно]
Всегда приятно иметь резервную копию ваших данных, на всякий случай, если вы испортите систему при работе с разделами диска.
Я советую скопировать все важные данные, которые вы не можете позволить себе потерять, на внешний USB-диск.
Вы можете использовать внешний жесткий диск (медленнее, но дешевле) или SSD (быстрее, но дороже) и копировать на него важные файлы и папки.
Шаг 2. Загрузите Ubuntu (или любой другой дистрибутив Linux, который вы будете использовать)
Перейдите на сайт Ubuntu и загрузите файл ISO.
Размер файла должен быть около 2,5 ГБ. Если вам нужно загрузить Ubuntu через торрент, вы можете нажать «Альтернативные загрузки».
Шаг 3: Создайте live USB / диск Ubuntu
Я предполагаю, что вы используете Windows для создания Live USB.
Есть несколько бесплатных приложений, которые позволяют создать Live Ubuntu USB.
Вы можете использовать любой из этих инструментов.
Поскольку я не могу показать их все, я буду все делать с Rufus.
Загрузите Rufus бесплатно с его веб-сайта. Он загрузит файл с расширением .exe.
Подключите USB.
Это устройство будет отформатировано, поэтому убедитесь, что на нем нет важных данных.
Запустите только что загруженный инструмент Rufus.
Он автоматически определяет подключенный USB-порт, но все равно дважды проверьте его.
Теперь перейдите к местоположению загруженного образа ISO и убедитесь, что он использует схему разделения GPT и целевую систему UEFI.
Нажмите кнопку «Пуск» и дождитесь завершения процесса. Ваш Live Linux USB готов.
Примечание. Установить Ubuntu и создать действующий USB-процесс Ubuntu можно на любом компьютере.
Но остальная часть процесса берет на себя система, в которой вы выполняете двойную загрузку.
Шаг 4. Освободите место на диске для установки Ubuntu
Во многих системах при установке Ubuntu предоставляется возможность сделать раздел диска для Ubuntu.
Однако это не гарантия.
Поэтому перед установкой лучше освободить необходимое место на диске.
В меню Windows найдите «разделы диска» и выберите «Создать и отформатировать разделы жесткого диска».
В инструменте управления дисками щелкните правой кнопкой мыши диск, который вы хотите разделить, и выберите «Сжатый том».
Если у вас всего один такой раздел, вам нужно освободить на нем немного свободного места для Linux.
Если у вас есть несколько разделов значительного размера, используйте любой из них, кроме диска C, поскольку он может стереть данные.
На 256 ГБ в моей системе уже было несколько разделов от производителя, но в основном для резервного копирования и других целей.
Основным разделом был диск C объемом около 220 ГБ, на котором установлена Windows 10.
В моем случае я уменьшил диск C, чтобы освободить место для установки Linux.
Сколько места вам нужно для Linux при двойной загрузке?
Это зависит от того, сколько у вас общего дискового пространства.
Вы можете установить Ubuntu на 15 или 20 ГБ, но скоро у вас начнется нехватка места на диске.
В наши дни у вас должно быть не менее 120 ГБ на диске.
В этом случае выберите для Linux 30-40 ГБ диска.
Если у вас диск на 250 ГБ, выделите ему 60-80 ГБ или даже больше.
Если у вас больше места на диске, выделите ему еще больше свободного места, если хотите.
Что делать, если у вас есть диски D, E или F?
Это обычная путаница для многих людей, поскольку они думают, что Ubuntu можно установить только на диск C.
Это не правда.
Понимаете, у меня был только один диск C, поэтому я его сжал.
Если у вас есть диск D, E или F, вы можете сжать один из этих дисков.
Вы также можете удалить диск D, E или F.
НИКОГДА НЕ УДАЛЯЙТЕ ДИСК С.
Шаг 5: Загрузитесь с Live Ubuntu USB
Вы создали действующий USB-накопитель Ubuntu на шаге 3.
Подключите его к системе.
Прежде чем вы загрузитесь с Live USB-накопителя, давайте вкратце расскажем о печально известной безопасной загрузке.
Нужно ли мне отключать безопасную загрузку для установки Linux?
6-8 лет назад безопасная загрузка UEFI не поддерживалась Linux, и поэтому вам пришлось отключить безопасную загрузку перед установкой Linux.
К счастью, в наши дни Ubuntu и многие другие дистрибутивы Linux очень хорошо поддерживают безопасную загрузку.
Обычно с этим ничего делать не нужно.
Однако, если ваша система не позволяет загружаться с Live USB или если вы видите какие-либо другие связанные проблемы, вы можете отключить безопасную загрузку в Windows.
Хорошо! Посмотрим, как загрузиться с USB.
Вы можете перейти к настройкам загрузки, нажав F2 / F10 или F12 во время запуска системы, и выбрать загрузку с USB.
Однако некоторым это трудно.
Более длинный, но простой шаг — получить доступ к настройкам загрузки UEFI из Windows.
В меню Windows найдите UEFI и нажмите «Изменить дополнительные параметры запуска»:
Перейдите к параметру «Расширенный запуск» и нажмите кнопку «Перезагрузить сейчас».
На следующем экране нажмите «Использовать устройство»:
Распознайте USB-диск по его имени и размеру.
Он также может отображаться как USB-устройство EFI.
Теперь он выключит вашу систему и перезагрузится на выбранный вами диск, который должен быть активным USB-диском.
Через несколько секунд вы должны увидеть такой экран:
Опция «Попробовать Ubuntu без установки» позволяет вам испытать Ubuntu с Live диска.
Вариант установки Ubuntu можно найти на рабочем столе.
Опция «Установить Ubuntu» немедленно запустит установку Ubuntu.
Вы можете выбрать любой вариант в зависимости от ваших предпочтений.
Шаг 6: Установка Ubuntu вместе с Windows 10
Запустите процедуру установки.
Первые несколько шагов просты.
Вы выбираете язык и раскладку клавиатуры.
На следующем экране выберите «Обычная установка».
Пока не нужно загружать обновления или устанавливать стороннее программное обеспечение.
Вы можете сделать это после завершения установки.
Нажмите «Продолжить».
Переход к следующему шагу может занять некоторое время.
Примечание. Некоторые люди пытаются загрузить обновления и установить медиа-кодеки во время установки.
По моему опыту, это иногда создает проблемы во время установки, а также может привести к сбою установки.
По этой причине я не советую их использовать.
Важно: установка требует двух подходов в зависимости от того, что вы видите на следующем экране.
Поскольку это подробное руководство, я рассмотрю оба аспекта.
Подход 1. Вы видите «Установить Ubuntu вместе с Windows Boot Manager».
Если вы видите «Установить Ubuntu вместе с Windows Boot Manager» на экране установки, вам повезло.
Вы можете выбрать этот метод и нажать «Продолжить».
Если вы видите «Установить Ubuntu вместе с диспетчером загрузки Windows», выберите его
На следующем экране вы сможете создать раздел для Ubuntu, перетащив разделитель.
Вы можете выделить соответствующее дисковое пространство для Linux здесь.
Ubuntu создаст один раздел из выделенного дискового пространства, и у него будет root с home и swap (файл подкачки) размером 2 ГБ под root.
Подход 2: Вы не видите параметр «Установить Ubuntu вместе с диспетчером загрузки Windows» или он неактивен
Но если вы один из тех, кому не повезло, вам не о чем беспокоиться.
Для вас дела обстоят не так уж и плохо.
Вы все еще можете установить Ubuntu с Windows.
На экране «Тип установки» выберите «Что-нибудь еще».
Вы перейдете к экрану разбиения на разделы.
Помните, вы заранее создали свободное место?
Вы можете выделить все свободное пространство для root (файл подкачки и домашняя страница будут созданы автоматически под root) или вы можете разделить разделы root, swap и home.
Оба метода хороши.
Я показываю шаги для создания разделов root, swap и home по отдельности.
Но не стесняйтесь использовать один раздел для всех из них.
Выберите свободное место и нажмите на знак «+».
Он предоставит вам возможность создать раздел Linux.
Вы создаете корневой (root) раздел.
Для этого более чем достаточно всего, что превышает 25 ГБ.
Выберите размер, выберите «Ext4» в качестве типа файла и / (означает root) в качестве точки монтирования.
Щелкнув «OK» на предыдущем шаге, вы перейдете к экрану раздела.
Затем создайте swap.
Как и раньше, снова нажмите на знак «+».
На этот раз используйте тип файла как область подкачки.
Вопрос об идеальном размере подкачки в Linux остается спорным.
Если у вас 2 ГБ или меньше ОЗУ, используйте подкачку, вдвое превышающую размер ОЗУ.
А если у вас 3-6 ГБ ОЗУ, используйте подкачку того же размера, что и ОЗУ.
Если у вас 8 ГБ или более ОЗУ, вы можете использовать подкачку, равную половине размера ОЗУ (если у вас не достаточно места на диске, и вы хотите использовать спящий режим, и в этом случае используйте подкачку не менее того же размера, что и ОЗУ).
Если вы чувствуете, что в вашей системе меньше swap, не волнуйтесь.
Вы можете легко создать файл подкачки и добавить больше места подкачки в свои системы.
Таким же образом создайте домашний раздел.
Выделите ему максимальное пространство (фактически выделите ему остальное свободное пространство), потому что именно здесь вы будете сохранять музыку, изображения и загруженные файлы.
Когда вы будете готовы с root, swap и home, нажмите «Install Now»:
Что ж, вы почти выиграли битву.
Теперь вы чувствуете запах победы.
По запросу выберите часовой пояс.
Затем вам будет предложено ввести имя пользователя, имя хоста (имя компьютера) и пароль.
Теперь осталось только подождать.
Для завершения установки потребуется 8-10 минут.
После завершения установки перезагрузите систему.
Перезагрузите компьютер после завершения установки
Вам будет предложено извлечь USB-диск.
На этом этапе вы можете удалить диск, не беспокоясь.
После этого система перезагрузится.
Удалите USB и нажмите ENTER
Для использования Linux вам больше не нужен Live USB-диск.
Вы установили Ubuntu на диск своего компьютера.
Удалите USB-накопитель и оставьте его на потом, если вы хотите использовать его для установки Linux в другой системе.
Вы также можете отформатировать его и использовать для обычного хранения или передачи данных.
Если все прошло гладко, вы должны увидеть экран «grub» после включения системы.
Здесь вы можете выбрать Ubuntu для загрузки в Ubuntu и диспетчер загрузки Windows для загрузки в Windows.
Довольно круто, правда?
Вы можете выбрать операционную систему на экране «grub»
Двойная загрузка не удалась? Вот несколько советов по устранению неполадок
Для некоторых двойная загрузка может пока не работать.
Однако вместо того, чтобы сдаваться, вы можете следовать нескольким советам и повторить процедуру установки.
Попробуйте сменить порт USB
Это может показаться смешным, но иногда некоторые порты USB вызывают проблемы с загрузкой USB или установкой Linux.
Изменение USB-порта может быть хитростью.
Старайтесь не использовать интернет при установке Linux
Я испытал, что иногда установка Linux выдает ошибку, если он подключен к интернету.
Если вы столкнулись с ошибкой «’grub-efi-amd64-signed’ package failed to install into /target», попробуйте установить Ubuntu без интернета.
Отключите безопасную загрузку и / или быструю загрузку
В некоторых редких случаях безопасная загрузка не позволит вам загрузиться с Live USB или установить Linux.
Отключите безопасную загрузку.
В некоторых случаях вы также можете отключить быструю загрузку.
Двойная загрузка завершена, но вы не видите экран «grub» для загрузки в Ubuntu
Пожалуйста, проверьте порядок загрузки в настройках UEFI.
Вы видите Ubuntu / UEFI под диспетчером загрузки Windows?
Если да, переместите его вверх по порядку.
Надеюсь, это руководство помогло вам выполнить двойную загрузку Ubuntu с Windows 10 UEFI.
Я здесь слишком подробно остановился на деталях, но я хотел ответить на все распространенные заблуждения и показать все необходимые шаги.
Если у вас все еще есть сомнения или возникла странная ошибка, оставьте комментарий, и я постараюсь вам помочь.
До скорых встреч!
До скорых встреч! Заходите!
Подписаться на обновления блога!
Contents
- Introduction
- Back Up Your Data
-
Have a Windows recovery CD/DVD available
- Getting Recovery Media
-
Install Ubuntu after Windows
-
Install Ubuntu
- Automatic partition resizing (not recommended)
- Manual partitioning
-
Install Ubuntu
- Master Boot Record and Boot Manager
-
Installing Windows After Ubuntu
- Recovering GRUB after reinstalling Windows
- Master Boot Record backup and replacement
- Also see
Introduction
This page describes how to set up your computer in order to dual boot Ubuntu and Windows. While there are some benefits to dual-booting (e.g. better performance for a native install), it is not recommended. Instead, it is best to do a native install of Ubuntu, and then virtualize the other operating system.
Back Up Your Data
Although this may seem obvious, it is important to back up your files to an external backup medium before attempting a dual-boot installation (or any other hard drive manipulation), in case your hard drive becomes corrupted during the process. External hard drives, USB flash drives, and multiple DVDs or CDs are all useful for this purpose.
Have a Windows recovery CD/DVD available
Some computer manufacturers that pre-install Windows provide a Windows recovery/re-installation CD or DVD with the computer. However, many companies no longer ship a physical disc but instead create a hidden partition on the hard drive in which the recovery-disk information is stored. A utility is then usually provided which allows the user to burn a recovery/re-installation CD or DVD from it. If you are buying a new computer and intend on dual-booting, make sure you have (or can make) a physical Windows recovery/re-installation CD or DVD. If neither a CD/DVD nor a recovery partition/burning utility is provided by your computer manufacturer, you may need to contact your vendor and ask for a CD or DVD (to which you are normally entitled under the Windows EULA).
You may need to request a physical recovery/re-installation CD or DVD directly from your computer manufacturer. See WindowsRecoveryCd.
Once you have created a physical backup disc from a restore-image partition on the hard-drive, the restore-image partition can either be removed or left in place. Ubuntu can be installed with it intact without problems.
Install Ubuntu after Windows
A Windows OS should be installed first, because its bootloader is very particular and the installer tends to overwrite the entire hard drive, wiping out any data stored on it. If Windows isn’t already installed, install it first. If you are able to partition the drive prior to installing Windows, leave space for Ubuntu during the initial partitioning process. Then you won’t have to resize your NTFS partition to make room for Ubuntu later, saving a bit of time.
When a Windows installation already occupies the entire hard drive, its partition needs to be shrunk, creating free space for the Ubuntu partition. You can do this during the Ubuntu installation procedure, or you can see How to Resize Windows Partitions for other options.
If you have resized a Windows 7 or Vista partition and cannot boot up Windows, you can use the instructions from WindowsRecovery to fix it.
Install Ubuntu
-
Download an Ubuntu LiveCD image (.iso) from Ubuntu Downloads and burn it to a disc (see BurningIsoHowto).
- Insert the LiveCD into your CD-ROM drive and reboot your PC.
- If the computer does not boot from the CD (e.g. Windows starts again instead), reboot and check your BIOS settings by pressing F2, F12, Delete, or ESC. Select «boot from CD».
- Proceed with installation until you are asked this question: «How do you want to partition the disk?».
- If you have already partitioned the disk and left space for Ubuntu, install it to that and then follow the rest of the steps.
- Otherwise, choose one of the next two steps.
Automatic partition resizing (not recommended)
- Choose the first option, which should say «Install them side by side, choosing between them each startup».
- Specify the size of the new partition by dragging the slider at the bottom of the window.
- Click on «Forward».
-
Continue on to Finishing Ubuntu Installation
Manual partitioning
- Choose «Manually edit partition table».
- Listed will be your current partitions.
- Select the partition you want to resize and press Enter.
- Select «Size:», press Enter.
- Select Yes, press Enter.
- Type in a new size in gigabytes for your partition, it’s recommended you free up at least 10 GB of free space for your Ubuntu install. Press Enter when happy with your changes. It may take some time to apply the changes.
-
Create a swap partition of at least your amount of RAM (if you don’t know, 8000 MB is a good value).
- Create a partition for your Ubuntu installation.
-
Create other partitions if necessary: see DiskSpace
- Select «Finish partitioning and write changes to disk».
Master Boot Record and Boot Manager
GRUB2 is the boot manager installed in Ubuntu by default. GRUB2 is an open source boot manager that install the main parts of the boot loaders inside Ubuntu. This means Ubuntu is independent and avoids any need for writing to other operating systems. To accomplish this, the only thing in your computer outside of Ubuntu that needs to be changed is a small code in the MBR (Master Boot Record) of the first hard disk, or the EFI partition. The boot code is changed to point to the boot loader in Ubuntu. You will be presented with a list of operating systems and you can choose one to boot. If you do nothing the first option will boot after a ten second countdown. If you select Windows then GRUB or LILO will chain-load Windows for you at the Windows boot sector, which is the first sector of the Windows partition.
Windows Vista no longer utilizes boot.ini, ntdetect.com, and ntldr when booting. Instead, Vista stores all data for its new boot manager in a boot folder. Windows Vista ships with an command line utility called bcdedit.exe, which requires administrator credentials to use. You may want to read http://go.microsoft.com/fwlink/?LinkId=112156 about it.
Using a command line utility always has its learning curve, so a more productive and better job can be done with a free utility called EasyBCD, developed and mastered during the times of Vista Beta. EasyBCD is very user friendly and many Vista users highly recommend it.
Installing Windows After Ubuntu
There are two different approaches:
Recovering GRUB after reinstalling Windows
Please refer to the Reinstalling GRUB2 guide.
Master Boot Record backup and replacement
This method does not work for computers with UEFI boot. In consequence, it won’t work for pre-installed Windows 8 and some pre-installed with Windows 7.
Back-up the existing MBR, install Windows, replace your backup overwriting the Windows boot code:
- Create an NTFS partition for Windows (using fdisk, GParted or whatever tool you are familiar with)
-
Backup the MBR e.g. dd if=/dev/sda of=/mbr.bin bs=446 count=1
- Install Windows
-
Boot into a LiveCD
- Mount your root partition in the LiveCD
-
Restore the MBR e.g. dd if=/media/sda/mbr.bin of=/dev/sda bs=446 count=1
- Restart and Ubuntu will boot
- Setup GRUB to boot Windows
Also see
-
MultiOSBoot — How to boot more than two operating systems from a single hard drive.
-
Virtualization Category
You don’t have to have two different computers to use Linux and Windows 10. It’s possible to have a Linux distro installed on a computer with Windows 10 preinstalled.
In this article, I will show you how to dual boot Windows 10 and the popular Ubuntu Linux distro. But before that, you have to install Ubuntu on your Windows 10 PC.
Before you go through this process, you must backup your files. That’s because installing an OS is a risky process. Sometimes it can overwrite the existing OS and delete all your files.
N.B.: Most of the processes in this article take time to get done, so you need to be patient.
What We’ll Cover – A step-by-step Guide to Dual-Booting Windows 10 and Linux
- Prerequisites
- How to Partition your Hard Drive for Ubuntu
- How to Optimize your Hard Drive for More Partition Space (Optional)
- How to Download Ubuntu in ISO Image Format
- How to Make an Ubuntu (Linux) Bootable USB Drive
- How to Install Ubuntu Linux Distro along with Windows 10
- Now You Can Dual Boot Ubuntu and Windows 10
- Conclusion
Prerequisites
Most importantly, there are some things you must have in place if you want to use (and dual boot) Ubuntu and Windows 10 on the same PC:
- A computer preinstalled with Windows 10
- A partitioned hard drive
- A BIOS in UEFI mode (Unified Extensible Firmware Interface)
- An empty USB drive of at least 4Gig for creating a bootable disk
- An internet connection to download Ubuntu ISO image (the Linux distro) and Rufus (a bootable drive creation tool)
How to Check If Your PC BIOS is in UEFI Mode
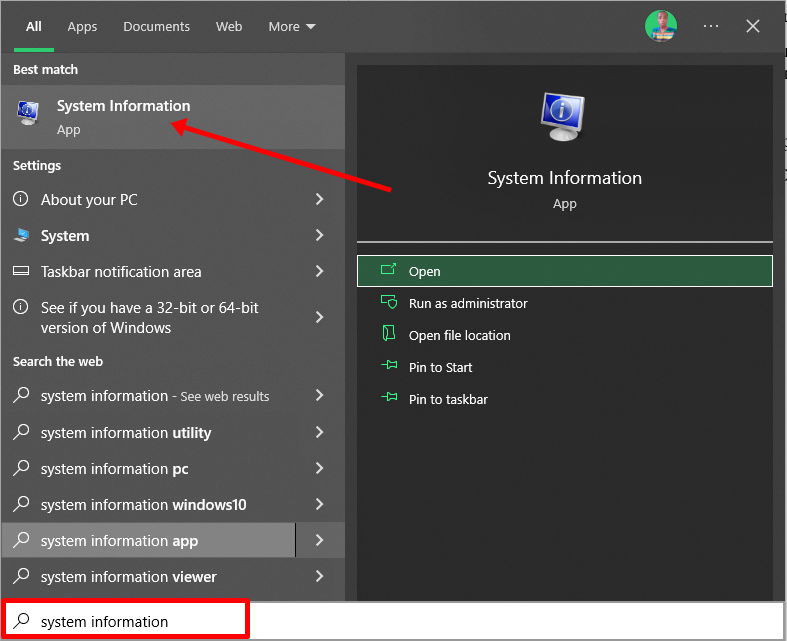
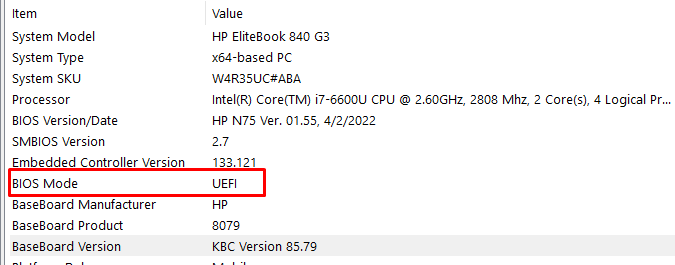
To check if your PC BIOS comes in UEFI mode, search for “system information” and hit ENTER.
Look under BIOS mode to confirm that your PC BIOS mode comes as UEFI.
If your PC BIOS is not in UEFI mode, the two operating systems won’t see each other. You can learn more about the difference between these two modes here.
How to Partition your Hard Drive for Ubuntu
You have to partition your hard drive because you must set aside at least 20Gig for Ubuntu to live in and boot from.
To partition your hard drive, follow the steps below:
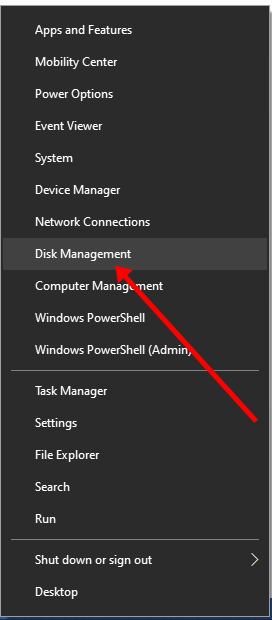
Step 1: Right-click on Start and select “Disk Management”.
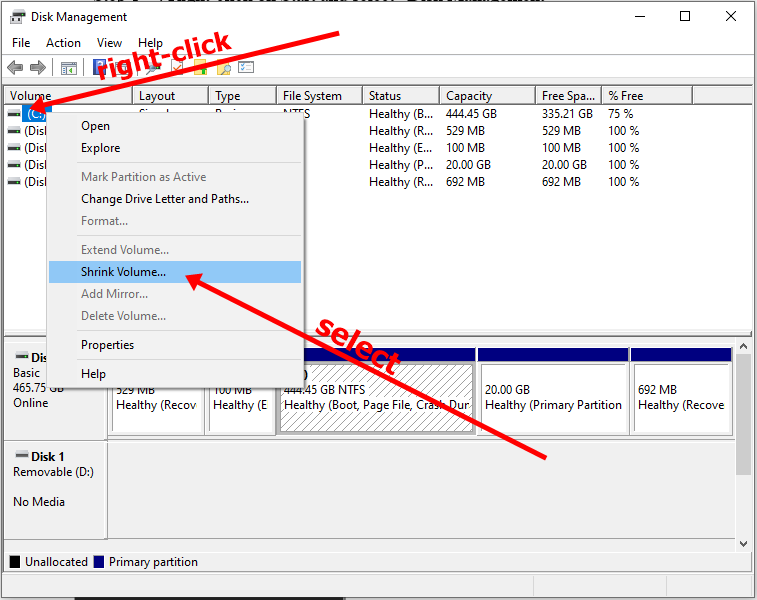
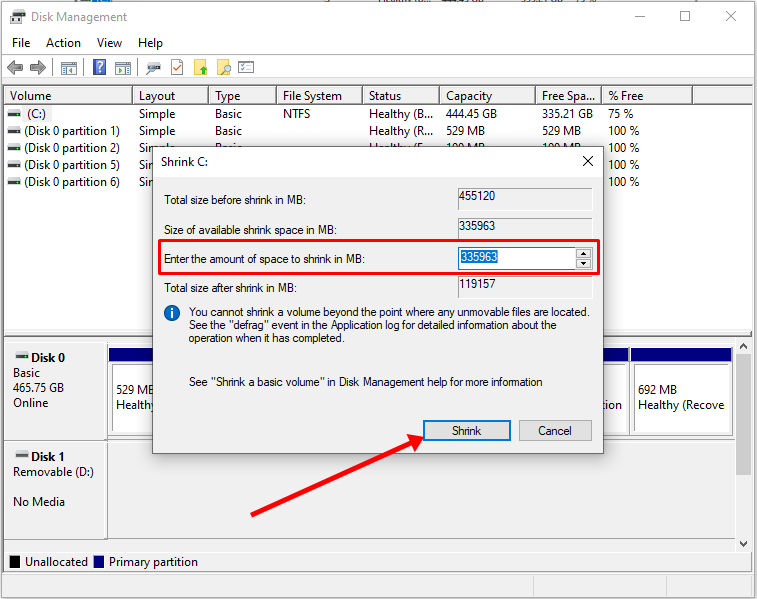
Step 2: Right-click on your C drive and select shrink volume.
Step 3: Select at least (20000) 20Gig for Ubuntu and click “Shrink”. IT can take some time to complete, so be patient.
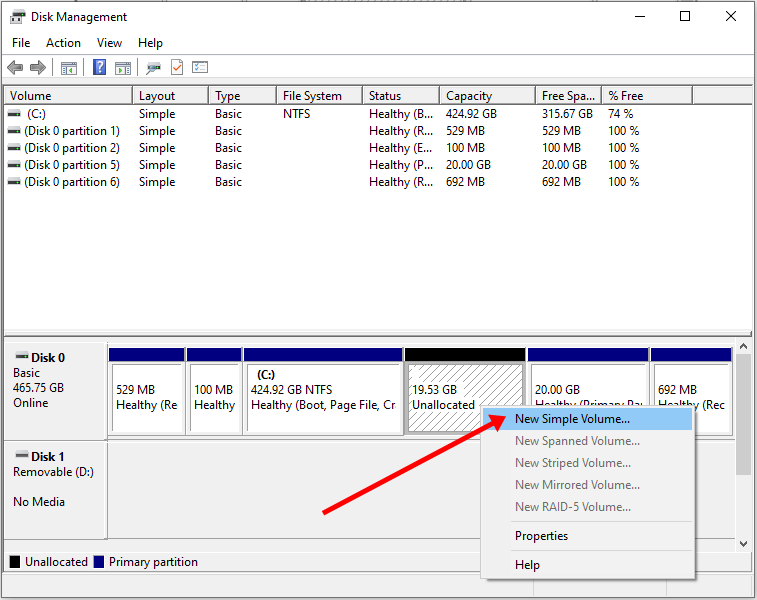
Step 4 (optional): You can go ahead and assign a letter to the new volume. Right-click on the unallocated space and select “New Simple Volume”.
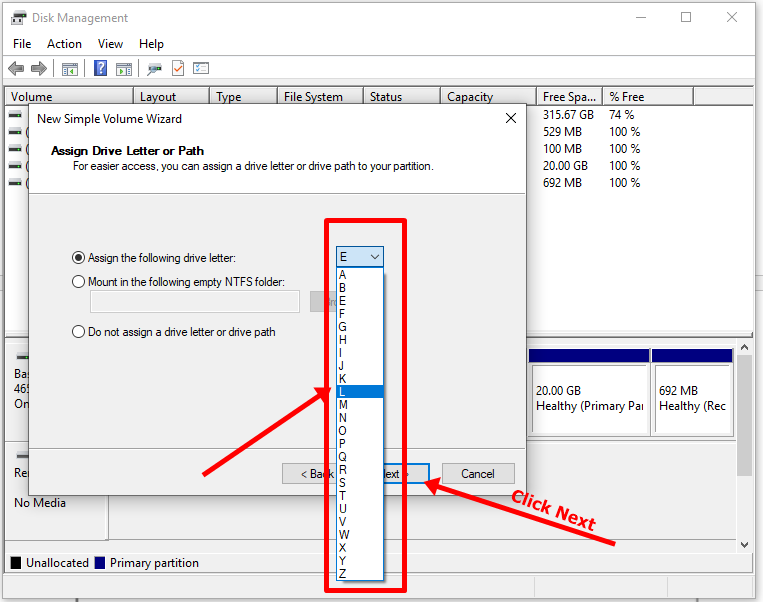
Step 5: Follow the wizard and assign a letter to the drive, then follow the rest of it.
After completing the wizard, the drive should be listed on your computer.
Congrats! You’ve successfully partitioned your hard drive.
N.B.: If you have a lot of free space in your hard drive but your PC still didn’t give you up to 20Gig partition space, then you need to optimize your PC’s hard drive. Proceed to the next section of this article to do that.
How to Optimize your Hard Drive for More Partition Space (Optional)
The common purpose of hard disk optimization is to speed up your computer during boot time and make it run smoother.
At the same time, the process will defragment the hard disk and make free space more available for partitioning.
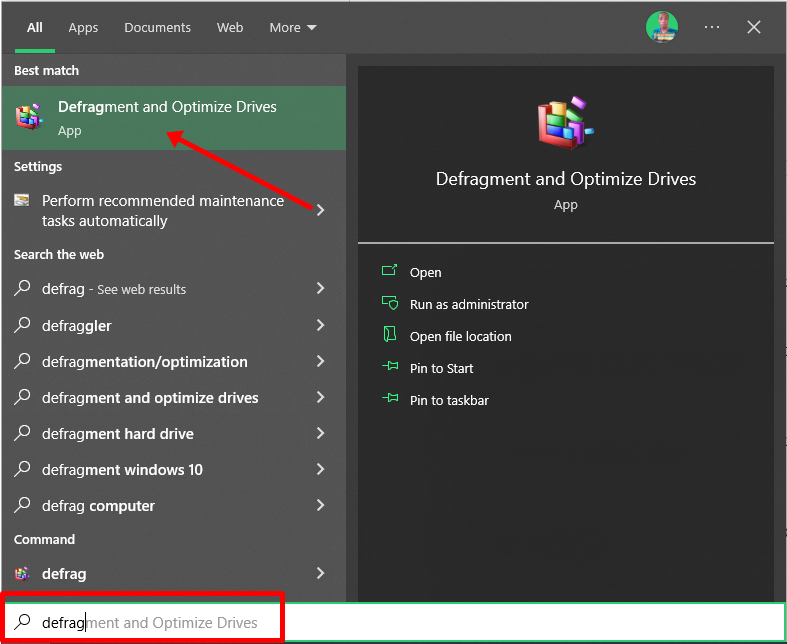
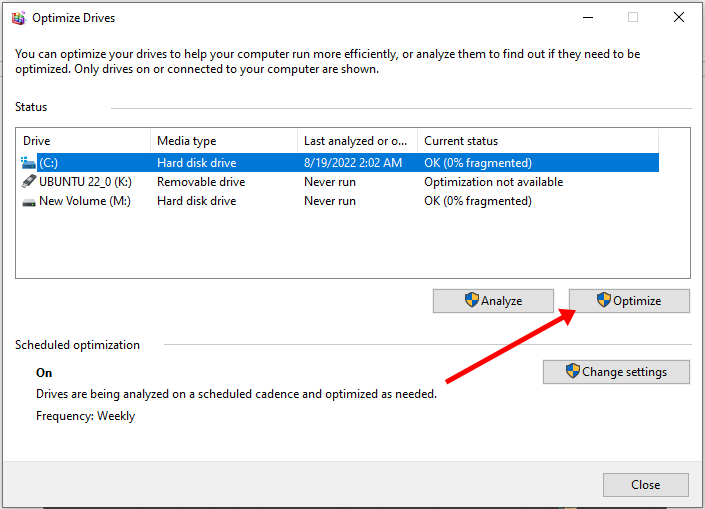
To optimize your hard drive, click Start (Windows logo key), search for “defrag” and select “Defragment and Optimize Drives”.
Make sure your C drive is highlighted, then click “Optimize”.
After you’ve been able to set aside at least 20Gig for Ubuntu by partitioning your hard drive, then it’s time to download Ubuntu and make a bootable USB.
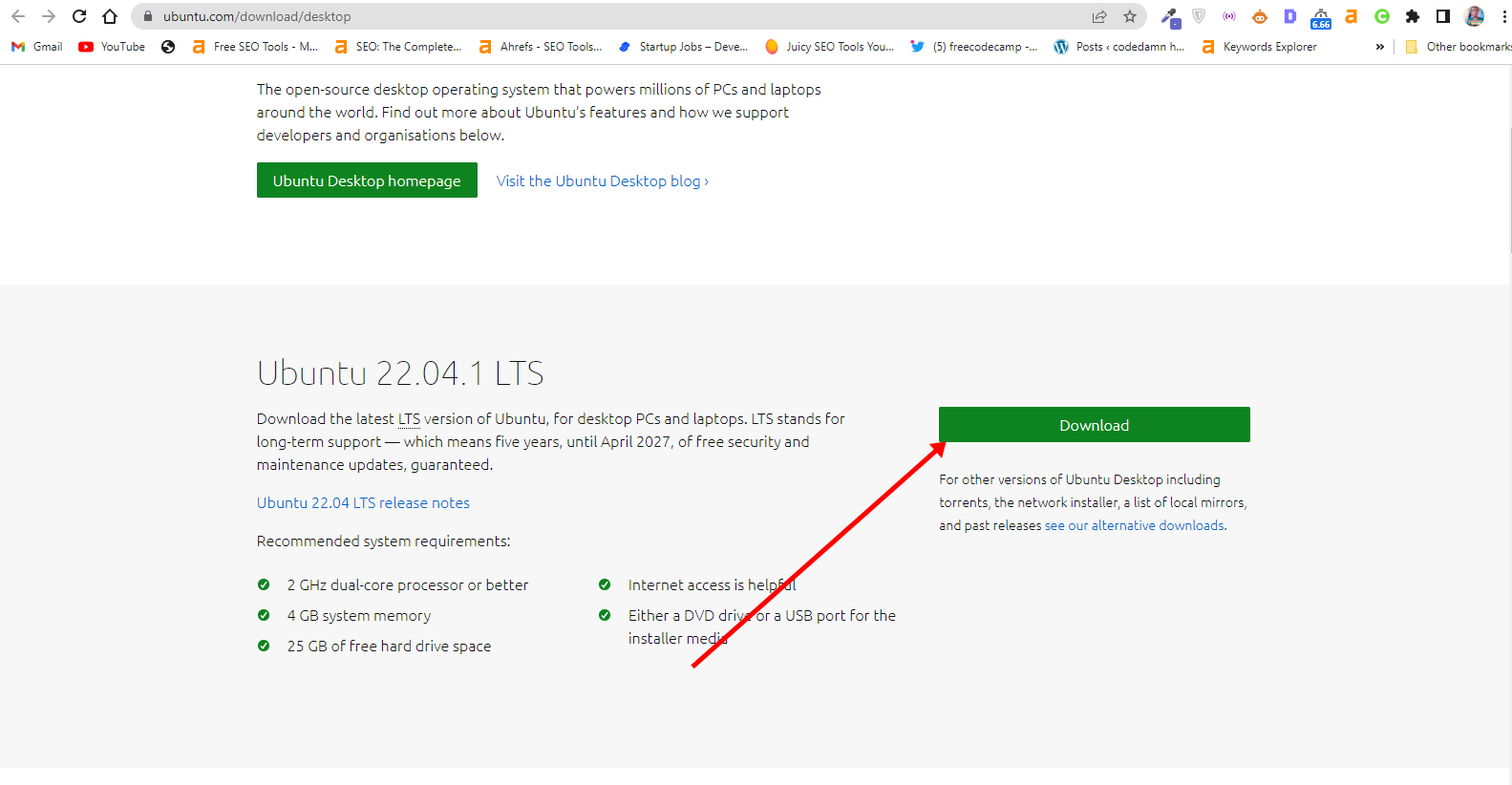
How to Download Ubuntu in ISO Image Format
The next thing is to download Ubuntu in ISO image format so you can install Ubuntu. You can download it from the Ubuntu distro website.
After downloading Ubuntu, don’t do anything with it yet. You need to make a bootable USB and put it in there. That’s how you’ll be able to use it.
The reason you can’t install Ubuntu just like that is that it doesn’t come as an executable. It comes in form of ISO (optical disk image). That means you have to find a disk to put it in before it can work.
The next part of this guide shows how you can put the downloaded Ubuntu ISO on a USB stick.
How to Make an Ubuntu (Linux) Bootable USB Drive
You won’t be able to make a bootable USB drive for Ubuntu by just placing the downloaded ISO image in it. Follow these steps to get it done:
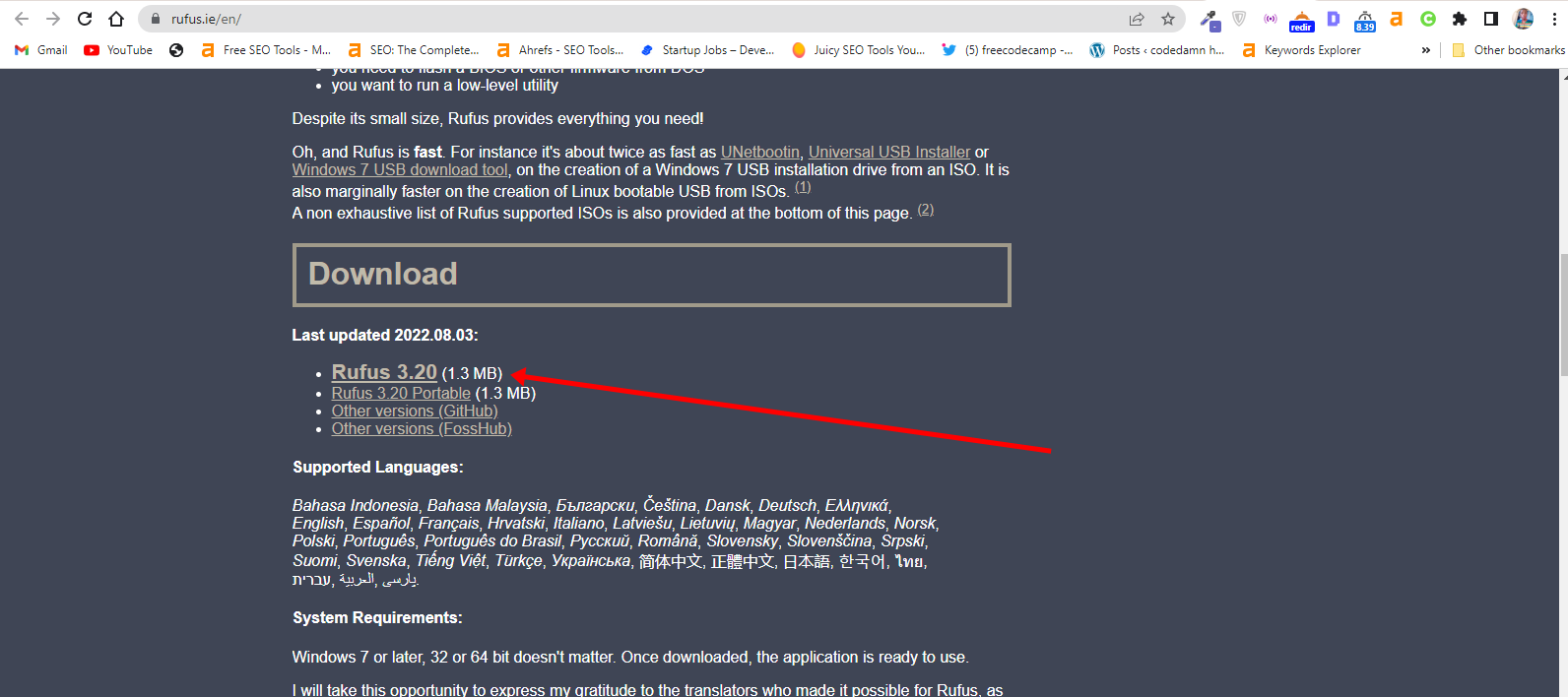
Step 1: You need to download a bootable USB drive creation tool like Rufus. You can download Rufus from their website.
Step 2: Insert the empty USB drive into your Windows 10 PC. Right-click on Rufus and select “Open”.
Step 3: Under “Device”, select your USB drive. And under “Boot selection”, click the “Select” button and select the Ubuntu ISO file you downloaded
Step 4: Leave every other thing as default and click the “START” button to start burning the Ubuntu distro to the drive.
Step 5: Click OK to start the process.
Once the process is done, you should see “READY” on a green background. Click the Close button. Its time to install Ubuntu.
Congrats! Now you have a bootable drive with which you can install Linux.
The next step is to install the Ubuntu distro on your Windows 10 PC. To do this, you have to boot your PC from the bootable USB drive you created.
How to Install Ubuntu Linux Distro along with Windows 10
Step 1: Ensure the bootable drive is inserted into your Windows 10 PC
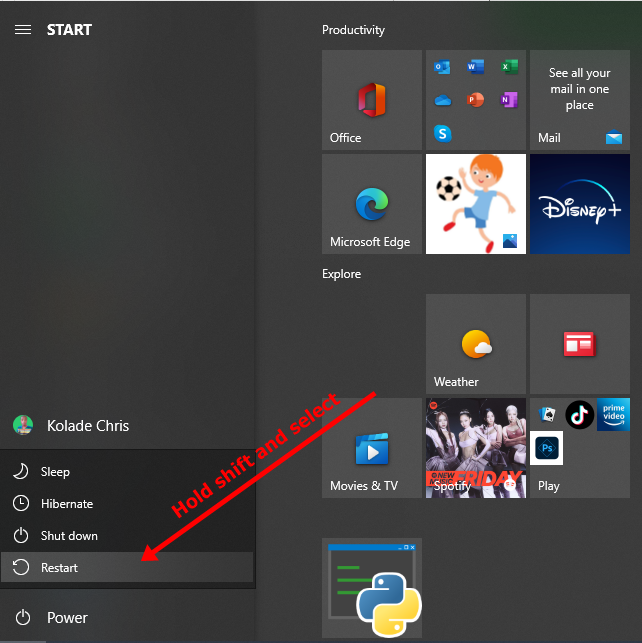
Step 2: Right-click on Start, hold SHIFT, and select Restart.
Step 2: Select “Use a Device”.
Step 3: On the next screen, you should see several devices you can boot from.
You may see the bootable drive as the name of the USB brand.
It’s possible to see it as “Ubuntu” too. Some other times, you might not see it, so you need to click on “See more devices».
If you still cannot see your bootable drive, head over to your boot menu by getting into BIOS. You will see it there.
N.B.: You should be very careful while making changes in BIOS. Whatever you do there has a lasting effect on your computer. If you are not sure of what you’re doing there, you should contact an IT professional.
Step 4: Choose «Install Ubuntu». You can also try it before installing it.
Follow other prompts of the installation wizard and make sure you don’t replace your Windows 10 OS installation with Ubuntu. This is why I suggested you back up all your files.
When you get to the point to select the partition you made, scroll to the partition you made earlier and press ENTER.
Click OK to select all the space in the partition.
This time around, the “Install now” button will not be greyed out anymore.
Follow other prompts until Ubuntu starts installing.
After the installation is done, Ubuntu will prompt you to remove the bootable drive and press ENTER to reboot your Computer.
Now You Can Dual Boot Ubuntu and Windows 10
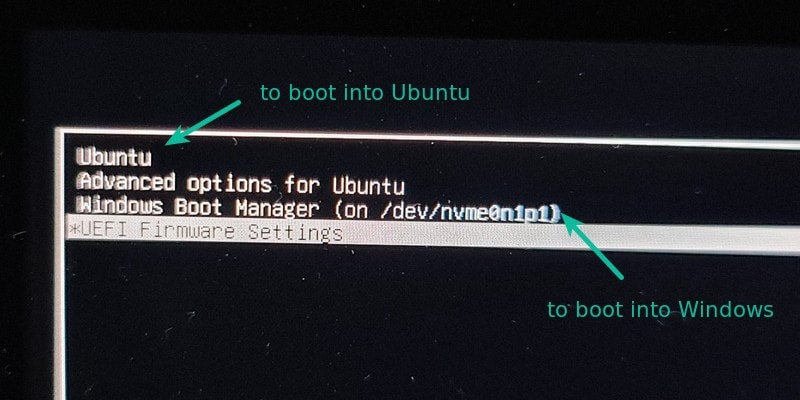
Immediately after you reboot the computer, you should see a screen that looks as shown below:
Now, you can select which one to boot into between Ubuntu and Windows 10.
To boot into Ubuntu, select Ubuntu. And to boot into Windows 10, select Windows boot manager.
You can also get into your BIOS from the same place by choosing UEFI Firmware Settings.
Conclusion
I hope this article helps you dual boot Ubuntu and Windows 10 on your computer.
The ultimate aim of this article was to show you how to dual boot Ubuntu and Windows 10.
But the article went beyond that to show you how to:
- check if your PC’s BIOS is in UEFI mode
- partition your hard drive
- optimize your hard drive
- make a bootable USB drive
- install Ubuntu Linux Distro along with Windows on your Windows 10 PC.
If you find this article helpful, kindly share it with your friends and family.
Learn to code for free. freeCodeCamp’s open source curriculum has helped more than 40,000 people get jobs as developers. Get started