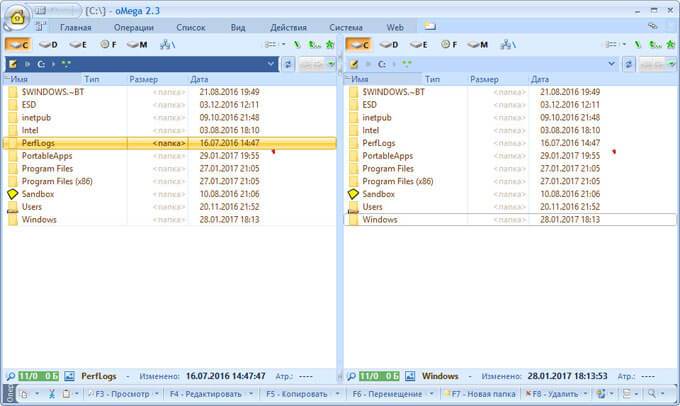
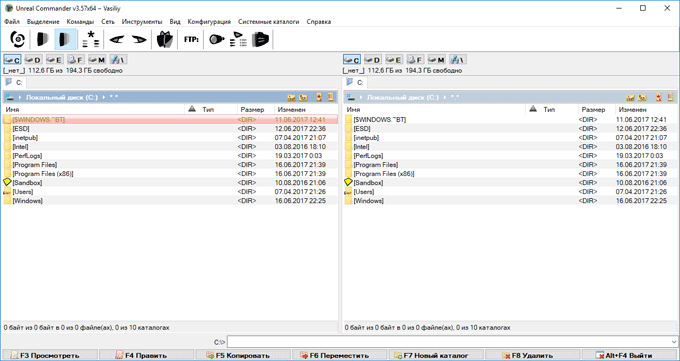
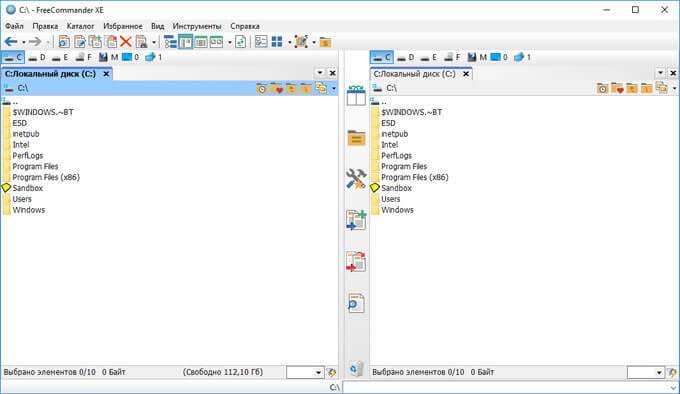
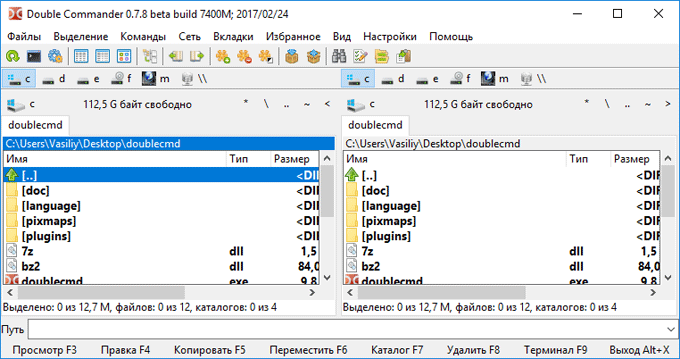
Тест по теме информационные технологии
1. В состав персонального компьютера входит?
А) Сканер, принтер, монитор
Б) Видеокарта, системная шина, устройство бесперебойного питания
В) Монитор, системный блок, клавиатура, мышь *
Г) Винчестер, мышь, монитор, клавиатура
2. Все файлы компьютера записываются на?
А) Винчестер *
Б) Модулятор
В) Флоппи-диск
Г) Генератор
3. Как включить на клавиатуре все заглавные буквы?
А) Alt + Ctrl
Б) Caps Lock *
В) Shift + Ctrl
Г) Shift + Ctrl + Alt
4. Как называется основное окно Windows, которое появляется на экране после полной загрузки операционной среды?
А) Окно загрузки
Б) Стол с ярлыками
В) Рабочий стол*
Г) Изображение монитора
5. Какую последовательность действий надо выполнить для запуска калькулятора в Windows?
А) Стандартные → Калькулятор
Б) Пуск → Программы → Стандартные → Калькулятор *
В) Пуск → Стандартные → Калькулятор
Г) Пуск → Калькулятор
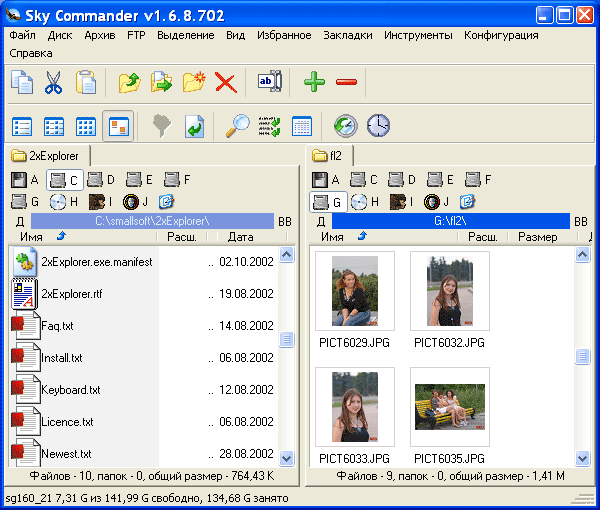
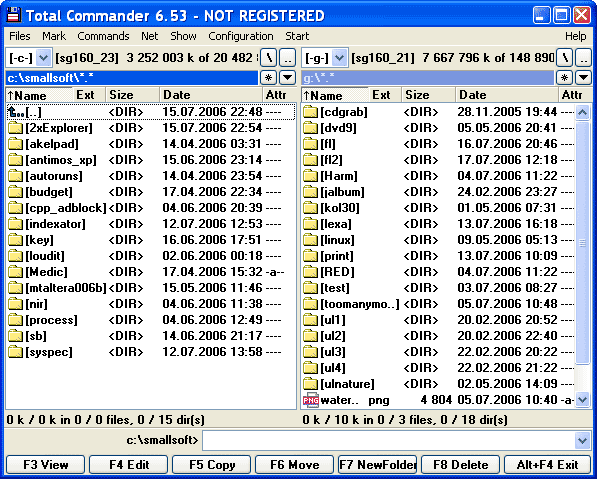
6. Как называется программа файловый менеджер, входящая в состав операционной среды Windows?
А) Проводник *
Б) Сопровождающий
В) Менеджер файлов
Г) Windows commander
7. Для создания новой папки в программе Windows commander надо нажать на клавиатуре кнопку?
А) F5
Б) F6
В) F7*
Г) F8
8. Для удаления файла в программе Windows commander следует нажать на клавиатуре кнопку?
А) F5
Б) F6
В) F7
Г) F8*
9. Для запуска любой программы надо на рабочем столе Windows нажать на?
А) Ссылку на программу
Б) Ярлык программы*
В) Кнопку запуска программы
Г) Рабочий стол
10. Чем отличается значок папки от ярлыка?
А) Признак ярлыка – узелок в левом нижнем углу значка, которым он «привязывается» к объекту
Б) Значок ярлыка крупнее всех остальных значков
В) На значке ярлыка написана буква «Я»
Г) Признак ярлыка – маленькая стрелка в левом нижнем углу значка *
11. Для того, чтобы найти файл в компьютере надо нажать?
А) Пуск → Найти → Файлы и папки*
Б) Пуск → Файлы и папки
В) Найти → Файл
Г) Пуск → Файл → Найти
12. Для настройки параметров работы мыши надо нажать?
А) Настройка → панель управления → мышь
Б) Пуск → панель управления → мышь
В) Пуск → настройка → мышь
Г) Пуск → настройка → панель управления → мышь*
13. Как установить время, через которое будет появляться заставка на рабочем столе Windows?
А) Свойства: экран → Заставка → Интервал *
Б) Заставка → Период времени
В) Свойства: экран → Заставка → Время
Г) Свойства: Интервал
14. Какие функции выполняет пункт Документы Главного меню Windows?
А) Пункт Документы Главного меню выводит список открытых в данный момент документов и позволяет переключаться между ними
Б) Пункт Документы Главного меню отображает список документов, с которыми работали последние 15 дней. Щелчок по названию или значку документа запускает приложение, с помощью которого он был создан и открывает документ
В) Пункт Документы Главного меню отображает список всех созданных документов и позволяет открыть любой из них
Г) Пункт Документы Главного меню выводит список последних открывавшихся документов. Щелчок по названию или значку документа запускает приложение, с помощью которого он был создан и открывает документ *
15. С какой целью производится выделение объектов?
А) С целью группировки и создания тематической группы
Б) С целью последующего изменения их внешнего вида (изменения размера, вида значка и др.
В) С целью их сортировки
Г) С тем, чтобы произвести с ними какие-либо действия (открыть, скопировать, переместить и др.) *
16. Как вызвать на экран контекстное меню?
А) Щелкнуть левой кнопкой мыши на объекте и в открывшемся списке выбрать команду «Контекстное меню»
Б) Открыть команду меню «СЕРВИС» и в ней выбрать команду «Контекстное меню»
В) Щелкнуть на объекте правой кнопкой мыши *
Г) Дважды щелкнуть левой кнопкой мыши на объекте
17. В какой программе можно создать текстовый документ (отчет по научной работе)?
А) Windows Word
Б) Microsoft Word *
В) Microsoft Excel
Г) Microsoft Power Point
18. Какое из изображений соответствует логотипу программы Microsoft Word?
А) *
Б)
В)
Г)
19. Сколько документов можно одновременно открыть в редакторе Word?
А) Только один
Б) Не более трех
В) Сколько необходимо
Г) Зависит от задач пользователя и ресурсов компьютера *
20. Открыть или создать новый документ в редакторе Microsoft Word можно используя панель?
А) Стандартная *
Б) Форматирование
В) Структура
Г) Элементы управления
21. Для включения или выключения панелей инструментов в Microsoft Word следует нажать?
А) Вид → панели инструментов
Б) Сервис → настройка → панели инструментов
В) Щелкнув правой копкой мыши по любой из панелей
Г) Подходят все пункты а, б и в *
22. Как создать новый документ «Стандартный отчет» из шаблонов Microsoft Word?
А) Файл → создать → общие шаблоны → отчеты → стандартный отчет*
Б) Общие шаблоны → отчеты → стандартный отчет
В) Файл → отчеты → стандартный отчет
Г) Файл → создать → стандартный отчет
23. Для настройки параметров страницы Word надо нажать последовательность?
А) Файл → параметры страницы *
Б) Файл → свойства → параметры страницы
В) Параметры страницы → свойства
Г) Правка → параметры страницы
24. Какая из представленных кнопок позволяет закрыть открытый документ Word?
А)
Б)
В) *
Г)
25. Какую кнопку надо нажать для вставки скопированного текста в Microsoft Word?
А)
Б)
В) *
Г)
26. Какую последовательность операций в Microsoft Word нужно выполнить для редактирования размера кегля шрифта в выделенном абзаце?
А) Вызвать быстрое меню → шрифт → размер
Б) Формат → шрифт → размер
В) На панели Форматирование изменить размер шрифта
Г) Подходят все пункты а, б и в *
27. Какую кнопку в Microsoft Word нужно нажать для создания нумерованного списка литературы?
А) *
Б)
В)
Г)
28. Как найти в тексте документа Microsoft Word необходимое слово?
А) Ctrl + F12
Б) Правка → найти *
В) Сервис → найти
Г) Подходят все пункты а, б и в
29. Что означает, если отдельные слова в документе Word подчеркнуты красной волнистой линией?
А) Это означает, что шрифтовое оформление этих слов отличается от принятых в документе
Б) Это означает, что эти слова занесены в буфер обмена и могут использоваться при наборе текста
В) Это означает, что в этих словах необходимо изменить регистр их написания
Г) Это означает, что по мнению Word в этих словах допущены ошибки *
Тесты по дисциплине по информационные технологии
30. Какую кнопку нужно нажать для автоматической вставки текущей даты в документ Microsoft Word?
А)
Б)
В) *
Г)
31. Как перенести фрагмент текста из начала в середину документа?
А) Стереть старый текст, и набрать его на новом месте
Б) Вырезать фрагмент текста, поместив его в буфер обмена. Затем установить курсор в средину документа, выполнить команду «Вставить» *
В) Выделить фрагмент текста, скопировать его в буфер обмена, установить курсор в средину документа, выполнить команду «Вставить»
Г) Данная операция в редакторе Word недоступна
32. Для создания диаграммы в программе Microsoft Word нужно нажать?
А)
Б) *
В)
Г)
33. Как сделать так, что компьютер самостоятельно создал оглавление (содержание) в документе Microsoft Word?
А) Правка → оглавление и указатели
Б) Вставка → ссылка → оглавление и указатели *
В) Правка → оглавление
Г) Формат → оглавление и указатели
34. Как установить автоматическую расстановку переносов в документе Microsoft Word?
А) Сервис → расстановка переносов
Б) Сервис → параметры → расстановка переносов
В) Сервис → язык → расстановка переносов → автоматическая расстановка *
Г) Вставка → автоматические переносы
35. Как установить язык проверки орфографии в документе Microsoft Word?
А) Сервис → параметры → язык
Б) Параметры → язык → установить
В) Сервис → настройка → язык
Г) Сервис → язык → выбрать язык *
36. Какую нужно нажать кнопку в Microsoft Word для создания таблицы?
А)
Б)
В) *
Г)
37. Какую кнопку в Microsoft Word нужно нажать для объединения выделенных ячеек?
А)
Б) *
В)
Г)
38. Какую кнопку нужно нажать для включения всех границ в таблице Microsoft Word?
А)
Б)
В)
Г) *
39. Какую нужно нажать кнопку для вставки в текст документа Microsoft Word объекта WordArt?
А)
Б)
В) *
Г)
40. Для создания многоколонного документа Word (например, газеты) нужно нажать кнопку?
А)
Б)
В)
Г) *
41. Как сохранить документ Microsoft Word с расширением типа *.rtf?
А) Файл → сохранить как → тип файла → текст в формате rtf *
Б) Файл → rtf
В) Параметры → текст → rtf
Г) Сервис → параметры → rtf
42. Какую кнопку нужно нажать для предварительного просмотра документа Microsoft Word перед печатью на принтере?
А)
Б) *
В)
Г)
43. Как просмотреть текст документа Word перед печатью?
А) Переключиться в режим «разметка страницы»
Б) Переключиться в режим «разметка страницы» и выбрать масштаб «страница целиком»
В) Установить масштаб просмотра документа «страница целиком»
Г) С помощью инструмента «предварительный просмотр» *
44. Как вставить в документе Microsoft Word разрыв со следующей страницы?
А) Вставка → разрыв со следующей страницы
Б) Вставка → параметры → со следующей страницы
В) Вставка → разрыв → со следующей страницы *
Г) Сервис → разрыв → со следующей страницы
45. Какое из изображений соответствует логотипу программы Microsoft Excel?
А)
Б) *
В)
Г)
46. Как называется панель кнопок, находящаяся под заголовком документа Microsoft Excel и включающая: Файл | Правка | Вид | Вставка и др.?
А) Панель форматирование
Б) Панель стандартная
В) Строка меню *
Г) Строка заголовков
47. Какие панели инструментов имеются в табличном редакторе Excel?
А) Стандартная, форматирование
Б) Внешние данные, формы
В) Сводные таблицы, элементы управления
Г) Подходят все пункты а, б и в *
48. С помощью какой кнопки можно создать новую рабочую книгу Microsoft Excel?
А) *
Б)
В)
Г)
49. Какой кнопкой можно закрыть рабочую книгу Microsoft Excel?
А)
Б)
В)
Г) *
50. Как в рабочей книге Microsoft Excel создать колонтитулы?
А) Вставка → колонтитулы
Б) Вид → колонтитулы *
В) Сервис → колонтитулы
Г) Параметры → колонтитулы
51. Как добавить лист в рабочую книгу Microsoft Excel?
А) Сервис → создать новый лист
Б) Вид → добавить новый лист
В) Вставка → лист *
Г) Подходят все пункты а, б и в
52. При помощи какой кнопки клавиатуры можно выделить не смежные ячейки листа Microsoft Excel?
А) Shift
Б) Ctrl *
В) Tab
Г) Alt
53. Для форматирования ячеек Microsoft Excel нужно нажать?
А) Сервис → формат ячеек
Б) Формат → содержимое → ячейки
В) Правка → ячейки
Г) Формат → ячейки *
54. Что такое табличный процессор Excel, его назначение?
А) Excel это приложение MS Windows, которое позволяет редактировать текст, рисовать различные картинки и выполнять расчеты
Б) Excel – предназначен для обработки данных (расчетов и построения диаграмм), представленных в табличном виде *
В) Excel – программное средство, предназначенное для редактирования данных наблюдений
Г) Процессор, устанавливаемый в компьютере и предназначенный для обработки данных, представленных в виде таблицы
55. Как переименовать лист рабочей книги Excel?
А) Выполнить команду Правка → Переименовать лист
Б) Щелкнуть на ярлычке листа правой кнопкой и в контекстном меню выбрать команду «Переименовать» *
В) Переименовать листы Excel нельзя. Они всегда имеют название «Лист1, Лист2 ……..»
Г) Щелкнуть правой кнопкой в середине рабочего листа и выбрать команду «Переименовать лист»
56. Что означает, если в ячейке Excel Вы видите группу символов ######?
А) Выбранная ширина ячейки, не позволяет разместить в ней результаты вычислений *
Б) В ячейку введена недопустимая информация
В) Произошла ошибка вычисления по формуле
Г) Выполненные действия привели к неправильной работе компьютера
57. Как сделать так, чтобы введенные в ячейку Excel числа воспринимались как текст?
А) Числа, введенные в ячейку, всегда воспринимаются Excel только как числа
Б) Выполнить команду Формат → Ячейки… и на вкладке «Формат ячеек – Число» выбрать «Текстовый» *
В) Сервис → параметры → текстовый
Г) Просто вводить число в ячейку. Компьютер сам определит число это или текст
58. Как изменить фон выделенной области ячеек Excel?
А) Выполнить команду «Вид → Фон» и выбрать необходимый цвет
Б) Щелкнуть правой кнопкой мыши по выделенному и в открывшемся окне выбрать команду «Заливка цветом»
В) Выполнить команду Правка → Фон и выбрать необходимый цвет
Г) Выполнить команду Формат → Ячейки… и в открывшемся диалоговом окне на вкладке «Вид» выбрать необходимый цвет *
59. Что позволяет в Excel делать черный квадратик, расположенный в правом нижнем углу активной ячейки?
А) Это говорит о том, что в эту ячейку можно вводить информацию (текст, число, формулу…)
Б) Позволяет выполнить копирование содержимого ячейки с помощью мыши *
В) Позволяет редактировать содержимое ячейки
Г) После щелчка левой кнопкой мыши на этом квадратике, содержимое ячейки будет помещено в буфер обмена
This article is about the Microsoft Windows file listing browser. For exploring file system listings, see file browser. For exploring inside files, see file viewer.

File Explorer on Windows 11 in Light App Mode showing special folders on Home, with the new command bar and tabs feature. |
|
| Developer(s) | Microsoft |
|---|---|
| Initial release | August 15, 1995; 27 years ago |
| Stable release |
22H2 (10.0.22621.1194) (January 26, 2023; 9 days ago[1]) [±] |
| Preview release |
;Release Preview Channel 22H2 (10.0.22621.1194) (January 26, 2023; 9 days ago[2][3]) [±]
22H2 (10.0.22623.1250) (February 2, 2023; 2 days ago[4]) [±]
10.0.25290.1000 (February 1, 2023; 3 days ago[5]) [±] |
| Included with | Windows 95 and later |
| Predecessor | Program Manager, File Manager |
| Type | Shell, file manager |
File Explorer, previously known as Windows Explorer, is a file manager application that is included with releases of the Microsoft Windows operating system from Windows 95 onwards. It provides a graphical user interface for accessing the file systems. It is also the component of the operating system that presents many user interface items on the screen such as the taskbar and desktop. Controlling the computer is possible without Windows Explorer running (for example, the File ▸ Run command in Task Manager on NT-derived versions of Windows will function without it, as will commands typed in a command prompt window).
Overview[edit]
Windows Explorer was first included with Windows 95 as a replacement for File Manager, which came with all versions of Windows 3.x operating systems. Explorer could be accessed by double-clicking the new My Computer desktop icon or launched from the new Start Menu that replaced the earlier Program Manager. There is also a shortcut key combination: Windows key+E. Successive versions of Windows (and in some cases, Internet Explorer) introduced new features and capabilities, removed other features, and generally progressed from being a simple file system navigation tool into a task-based file management system.
While «Windows Explorer» or «File Explorer» is a term most commonly used to describe the file management aspect of the operating system, the Explorer process also houses the operating system’s search functionality and File Type associations (based on filename extensions), and is responsible for displaying the desktop icons, the Start Menu, the Taskbar, and the Control Panel. Collectively, these features are known as the Windows shell.
After a user logs in, the explorer process is created by the userinit process. Userinit performs some initialization of the user environment (such as running the login script and applying group policies) and then looks in the registry at the Shell value and creates a process to run the system-defined shell – by default, Explorer.exe. Then Userinit exits. This is why Explorer.exe is shown by various process explorers with no parent – its parent has exited.
History[edit]
In 1995, Microsoft first released test versions of a shell refresh, named the Shell Technology Preview, and often referred to informally as «NewShell».[6] The update was designed to replace the Windows 3.x Program Manager/File Manager based shell with Windows Explorer. The release provided capabilities quite similar to that of the Windows «Chicago» (codename for Windows 95) shell during its late beta phases, however was intended to be nothing more than a test release.[7] There were two public releases of the Shell Technology Preview, made available to MSDN and CompuServe users: May 26, 1995 and August 8, 1995. Both held Windows Explorer builds of 3.51.1053.1. The Shell Technology Preview program never saw a final release under NT 3.51. The entire program was moved across to the Cairo development group who finally integrated the new shell design into the NT code with the release of NT 4.0 in July 1996.
Windows 98 and Windows Desktop Update[edit]
With the release of the Windows Desktop Update (packaged with Internet Explorer 4 as an optional component, and included in Windows 98), Windows Explorer became «integrated» with Internet Explorer, most notably with the addition of navigation arrows (back and forward) for moving between recently visited directories, as well as Internet Explorer’s Favorites menu.
An address bar was also added to Windows Explorer, which a user could type in directory paths directly, and be taken to that folder.
Another feature that was based on Internet Explorer technology was customized folders. Such folders contained a hidden web page that controlled the way the Windows Explorer displayed the contents of the folder.
Windows ME and Windows 2000[edit]
The integrated media player in Windows Explorer in Windows 2000, playing a MIDI sequence on Media folder
The «Web-style» folders view, with the left Explorer pane displaying details for the object currently selected, is turned on by default. For certain file types, such as pictures and media files, a preview is also displayed in the left pane.[8] The Windows 2000 Explorer featured an interactive media player as the previewer for sound and video files. However, such a previewer can be enabled in Windows ME through the use of folder customization templates.[9] Windows Explorer in Windows 2000 and Windows ME allows for custom thumbnail previewers and tooltip handlers. The default file tooltip displays file title, author, subject and comments;[10] this metadata may be read from a special NTFS stream, if the file is on an NTFS volume, or from a COM Structured Storage stream, if the file is a structured storage document. All Microsoft Office documents since Office 95[11] make use of structured storage, so their metadata is displayable in the Windows 2000 Explorer default tooltip. File shortcuts can also store comments which are displayed as a tooltip when the mouse hovers over the shortcut.
The right-hand pane, which usually just lists files and folders, can also be customized. For example, the contents of the system folders aren’t displayed by default, instead showing in the right pane a warning to the user that modifying the contents of the system folders could harm their computer. It’s possible to define additional Explorer panes by using DIV elements in folder template files.[12] This feature was abused by computer viruses that employed malicious scripts, Java applets, or ActiveX controls in folder template files as their infection vector. Two such viruses are VBS/Roor-C[13] and VBS.Redlof.a.[14]
Other Explorer UI elements that can be customized include columns in «Details» view, icon overlays, and search providers: the new DHTML-based search pane is integrated into Windows 2000 Explorer, unlike the separate search dialog found in all previous Explorer versions.[15]
Search capabilities were added, offering full-text searches of documents, with options to filter by date (including arbitrary ranges like «modified within the last week»), size, and file type. The Indexing Service has also been integrated into the operating system and the search pane built into Explorer allows searching files indexed by its database.[16] The ability to customize the standard buttons was also added.
Windows XP and Windows Server 2003[edit]
Windows Explorer in Windows XP, showing All Users folder contents
There were significant changes made to Windows Explorer in Windows XP, both visually and functionally. Microsoft focused especially on making Explorer more discoverable and task-based, as well as adding several new features to reflect the growing use of a computer as a digital hub.
Windows Explorer in Windows Server 2003 contains all the same features as Windows XP, but the task panes and search companion are disabled by default.
Task pane[edit]
The task pane is displayed on the left-hand side of the window instead of the traditional folder tree view. It presents the user with a list of common actions and destinations that are relevant to the current directory or file(s) selected. For instance, when in a directory containing mostly pictures, a set of «Picture tasks» is shown, offering the options to display these pictures as a slide show, to print them out, or to go online to order prints. Conversely, a folder containing music files would offer options to play those files in a media player or to go online to purchase music. Windows XP had a Media bar but it was removed with SP1. The Media Bar was only available with Windows XP RTM.
Every folder also has «File and Folder Tasks», offering options to create new folders, share a folder on the local network, publish files or folders to a website, and other common tasks like copying, renaming, moving, and deleting files or folders. File types that have identified themselves as being printable also have an option listed to print the file.
Underneath «Other Places» is a «Details» pane which gives additional information – typically file size and date, but depending on the file type, a thumbnail preview, author, image dimensions, or other details.
The «Folders» button on the Windows Explorer toolbar toggles between the traditional tree view of folders, and the task pane. Users can get rid of the task pane or restore it using the sequence: Tools – Folder Options – General – Show Common Tasks/Use Windows Classic Folders.
Search companion[edit]
Windows Explorer’s default Search Companion, Rover, in Windows XP
Microsoft introduced animated «Search Companions» in an attempt to make searching more engaging and friendly; the default character is a puppy named Rover (previously used in Microsoft Bob), with three other characters (Merlin the magician, Earl the surfer, and Courtney) also available. These search companions use the same technology as Microsoft Office’s Office Assistants, even incorporating «tricks» and sound effects, and they can be used as Office Assistants if their files are copied into the C:Windowsmsagentchars folder.[17]
The search capability itself is fairly similar to Windows ME and Windows 2000, with one major addition: Search can also be instructed to search only files that are categorical «Documents» or «Pictures, music and video»; this feature is noteworthy largely because of how Windows determines what types of files can be classified under these categories. In order to maintain a relevant list of file types, Windows Explorer connects to Microsoft and downloads a set of XML files that define what these file types are. The Search Companion can be disabled in favor of the classic search pane used in Windows 2000 by using the Tweak UI applet from Microsoft’s PowerToys for Windows XP, or by manually editing the registry.
Image handling[edit]
Windows XP improves image preview in Explorer by offering a Filmstrip view. «Back» and «Previous» buttons facilitate navigation through the pictures, and a pair of «Rotate» buttons offer 90-degree clockwise and counter-clockwise (lossy)[18] rotation of images. Aside from the Filmstrip view mode, there is a ‘Thumbnails’ mode, which displays thumbnail-sized images in the folder. A Folder containing images will also show thumbnails of four of the images from that folder overlaid on top of a large folder icon.
Web publishing[edit]
Web sites that offer image hosting services can be plugged into Windows Explorer, which the user can use to select images on their computer, and have them uploaded correctly without dealing with comparatively complex solutions involving FTP or web interfaces.[citation needed]
Other changes[edit]
- Explorer gained the ability to understand the metadata of a number of types of files. For example, with images from a digital camera, the Exif information can be viewed, both in the Properties pages for the photo itself, as well as via optional additional Details View columns.
- A Tile view mode was added, which displays the file’s icon in a larger size (48 × 48), and places the file name, descriptive type, and additional information (typically the file size for data files, and the publisher name for applications) to the right.
- The Details view also presented an additional option called «Show in Groups» which allows the Explorer to separate its contents by headings based on the field which is used to sort the items.
- The taskbar can be locked to prevent it from accidentally being moved.
- Windows Explorer also gained the ability to burn CDs and DVD-RAM discs in Windows XP.
- Ability to create and open ZIP files called «compressed folders».[19][20]
- Ability to open Cabined (.cab) files.[21]
- If a
.HTMor.HTMLfile is copied or moved, the accompanying_filessuffix folder is copied or moved among it automatically.[22]
Removed and changed features[edit]
|
This section needs expansion. You can help by adding to it. (December 2012) |
- The sort order has changed compared to the one in Windows 2000. For file names containing numbers Windows Explorer now tries to sort based on numerical value rather than just comparing each number digit by digit.[23]
Windows Vista and Windows Server 2008[edit]
Windows Explorer in Windows Vista, showing Public folder contents
Search, organizing and metadata[edit]
Windows Explorer includes significant changes from previous versions of Windows such as improved filtering, sorting, grouping and stacking. Combined with integrated desktop search, Windows Explorer allows users to find and organize their files in new ways, such as stacks.[24][25] The new Stacks viewing mode groups files according to the criterion specified by the user.[25] Stacks can be clicked to filter the files shown in Windows Explorer. There is also the ability to save searches as virtual folders or search folders.[26] A search folder is simply an XML file, which stores the query in a form that can be used by the Windows search subsystem.[27] When accessed, the search is executed and the results are aggregated and presented as a virtual folder.[26] Windows Vista includes six search folders by default: recent documents, recent e-mail, recent music, recent pictures and videos, recent changed, and «Shared by Me».[28] Additionally, search operators for properties were introduced, such as kind:music. [29] Since at least Windows 7, comparison operators «greater than» and «less than» are supported to search for any supported attribute such as date ranges and file sizes, like size:>100MB to search for all files that are greater than 100MB.[30] Attributes sortable and searchable in Windows Explorer include pictures’ dimensions, Exif data such as aperture and exposure, video duration and framerate and width.[31]
When sorting items, the sort order no longer remains consistently Ascending or Descending. Each property has a preferred sort direction. For example, sort by date defaults to descending order, as does size. But name and type default to ascending order.
Searching for files containing a given text string became problematic with Vista unless the files had been indexed. An alternative is to use the findstr command-line function.[32] After right-clicking on a folder one can open a command-line prompt in that folder.
Windows Explorer also contains modifications in the visualization of files on a computer. A new addition to Windows Explorer in Vista and Server 2008 is the details pane, which displays metadata and information relating to the currently selected file or folder. The details pane will also display a thumbnail of the file or an icon of the filetype if the file does not contain visual information. Furthermore, different imagery is overlaid on thumbnails to give more information about the file, such as a picture frame around the thumbnail of an image file, or a filmstrip on a video file.
The details pane also allows for the change of some textual metadata such as author and title in files that support them within Windows Explorer. A new type of metadata called tags allows users to add descriptive terms to documents for easier categorization and retrieval. Some files support open metadata, allowing users to define new types of metadata for their files. Out-of-the-box, Windows Vista and Windows Server 2008 supports Microsoft Office documents and most audio and video files. Support for other file types can however be added by writing specialized software to retrieve the metadata at the shell’s request. Metadata stored in a file’s alternate data stream only on NTFS volumes cannot be viewed and edited through the summary tab of the file’s properties anymore. Instead, all metadata is stored inside the file, so that it will always travel with the file and not be dependent on the file system.[33]
Layout and icons[edit]
Windows Explorer in Windows Vista and Windows Server 2008 also introduces a new layout. The task panes from Windows XP are replaced with a toolbar on top and a navigation pane on the left. The navigation pane contains commonly accessed folders and preconfigured search folders. Eight different views are available to view files and folders, including extra large, large, medium, small, list, details, tiles, and content. In addition, column headers now appear in all icon viewing modes,[25] unlike Windows XP where they only appear in the details icon viewing mode.[24] File and folder actions such as cut, copy, paste, undo, redo, delete, rename and properties are built into a dropdown menu which appears when the Organize button is clicked. It is also possible to change the layout of the Explorer window by using the Organize button. Users can select whether to display classic menus, a search pane, a preview pane, a reading pane, and the navigation pane. The preview pane enables users to preview files (e.g., documents or media files) without opening them. If an application, such as Office 2007, installs preview handlers for file types, then these files can also be edited within the preview pane itself.[34]
Windows Vista saw the introduction of the breadcrumb bar for easier navigation. As opposed to the prior address bar which displayed the current folder in a simple editable combobox, this new style structures the path into clickable levels of folder hierarchy (though falls back to the classic edit mode when a blank area is clicked), enabling the user to skip as many levels as desired in one click rather than repeatedly clicking «Up». It is also possible to navigate to any subfolder of the current folder using the arrow to the right of the last item. The menu bar is now hidden by default but reappears temporarily when the user presses Alt.
Check boxes in Windows Explorer allow the selection of multiple files.[35] Free and used space on all drives is shown in horizontal indicator bars. Icons of various sizes are supported: 16 x 16, 24 x 24, 32 x 32, 48 x 48, 64 x 64, 96 x 96, 128 x 128 and 256 x 256. Windows Explorer can zoom the icons in and out using a slider or by holding down the Ctrl key and using the mouse scrollwheel.[36] Live icons can display the content of folders and files themselves rather than generic icons.[37]
Other changes[edit]
With the release of Windows Vista and Server 2008 and Windows Internet Explorer 7 for Windows XP, Internet Explorer is no longer integrated with Windows Explorer. In Windows Vista and Server 2008 (and in Windows XP as well if IE7 or 8 is installed), Windows Explorer no longer displays web pages, and IE7 does not support use as a file manager, although one will separately launch the other as necessary.
When moving or copying files from one folder to another, if two files have the same name, an option is now available to rename the file; in previous versions of Windows, the user was prompted to choose either a replacement or cancel moving the file. Also, when renaming a file, Explorer only highlights the filename without selecting the extension. Renaming multiple files is quicker as pressing Tab automatically renames the existing file or folder and opens the file name text field for the next file for renaming. Shift+Tab allows renaming in the same manner upwards.
Support for burning data on DVDs (DVD±R, DVD±R DL, DVD±R RW) in addition to CDs and DVD-RAM using version 2.0 of the Image Mastering API, as well as Live File System support was added.[38]
If a file is in use by another application, Windows Explorer tells users to close the application and retry the file operation. Also, a new interface IFileIsInUse is introduced into the API which developers can use to let other applications switch to the main window of the application that has the file open or simply close the file from the «File in Use» dialog. If the running application exposes these operations by means of the IFileIsInUse interface, Windows Explorer, upon encountering a locked file, allows the user to close the file or switch to the application from the dialog box itself.[39]
Windows Vista introduced precluded support for the Media Transfer Protocol.[citation needed]
Removed and changed features[edit]
The ability to customize the layout and buttons on the toolbars has been removed in Windows Vista’s Explorer, as has the ability to add a password to a zip file (compressed folder). The Toolbar button in Explorer to go up one folder from the current folder has been removed (the function still exists however, one can move up a folder by pressing Alt + ↑). Although still fully available from the menus and keyboard shortcuts, toolbar buttons for Cut, Copy, Paste, Undo, Delete, Properties and some others are no longer available. The Menu Bar is also hidden by default but is still available by pressing the Alt key or changing its visibility in the layout options. Several other features are removed such as showing the size on the status bar without selecting items, storing metadata in NTFS alternate data streams,[40] the IColumnProvider interface which allowed addition of custom columns to Explorer[41] and folder background customization using desktop.ini.
The option «Managing pairs of Web pages and folders» is also removed, and the user has no way of telling Vista that a .html file and the folder with the same name that was created when saving a complete web page from IE should be treated separately, that is, they cannot delete the folder without deleting the html file as well.[42]
The ability to right-click a folder and hit «Search» was removed in Windows Vista Service Pack 1. Users must open the folder they wish to search in and enter their keywords in the search field located on the top right corner of the window. Alternatively, users can specify other search parameters through the «Advanced Search» UI, which can be accessed by clicking on the Organize Bar and selecting Search Pane under the Layout submenu. Pressing F3 also opens the «Advanced Search» interface.
Windows 7 and Windows Server 2008 R2[edit]
Windows Explorer in Windows 7, showing Libraries
Libraries[edit]
Windows Explorer in Windows 7 and Windows Server 2008 R2 supports libraries, virtual folders described in a .library-ms file that aggregates content from various locations – including shared folders on networked systems if the shared folder has been indexed by the host system – and present them in a unified view. Searching in a library automatically federates the query to the remote systems, in addition to searching on the local system, so that files on the remote systems are also searched. Unlike search folders, Libraries are backed by a physical location which allows files to be saved in the libraries. Such files are transparently saved in the backing physical folder. The default save location for a library may be configured by the user, as can the default view layout for each library. Libraries are generally stored in the libraries special folder, which allows them to be displayed on the navigation pane.
By default, a new user account in Windows 7 contains four libraries, for different file types: Documents, Music, Pictures, and Videos. They are configured to include the user’s profile folders for these respective file types, as well as the computer’s corresponding Public folders.
In addition to aggregating multiple storage locations, Libraries enable Arrangement Views and Search Filter Suggestions. Arrangement Views allow users to pivot their views of the library’s contents based on metadata. For example, selecting the «By Month» view in the Pictures library will display photos in stacks, where each stack represents a month of photos based on the date they were taken. In the Music library, the «By Artist» view will display stacks of albums from the artists in their collections, and browsing into an artist stack will then display the relevant albums.
Search Filter Suggestions are a new feature of the Windows 7 and Windows Server 2008 R2 Explorer’s search box. When the user clicks in the search box, a menu shows up below it showing recent searches as well as suggested Advanced Query Syntax filters that the user can type. When one is selected (or typed in manually), the menu will update to show the possible values to filter by for that property, and this list is based on the current location and other parts of the query already typed. For example, selecting the «tags» filter or typing «tags:» into the search box will display the list of possible tag values which will return search results.
The metadata written within the file, implemented in Vista, is also utilized in Windows 7. This can sometimes lead to long wait times displaying the contents of a folder. For example, if a folder contains many large video files totaling hundreds of gigabytes, and the Window Explorer pane is in Details view mode showing a property contained within the metadata (for example Date, Length, Frame Height), Windows Explorer might have to search the contents of the whole file for the meta data. Some damaged files can cause a prolonged delay as well. This is due to metadata information being able to be placed anywhere within the file, beginning, middle, or end, necessitating a search of the whole file. Lengthy delays also occur when displaying the contents of a folder with many different types of program icons. The icon is contained in the metadata. Some programs cause the activation of a virus scan when retrieving the icon information from the metadata, hence producing a lengthy delay.[33]
Arrangement Views and Search Filter Suggestions are database-backed features that require that all locations in the Library be indexed by the Windows Search service. Local disk locations must be indexed by the local indexer, and Windows Explorer will automatically add locations to the indexing scope when they are included in a library. Remote locations can be indexed by the indexer on another Windows 7 and Windows Server 2008 R2 machine, on a Windows machine running Windows Search 4 (such as Windows Vista or Windows Home Server), or on another device that implements the MS-WSP remote query protocol.[43]
Federated search[edit]
Windows Explorer also supports federating search to external data sources, such as custom databases or web services, that are exposed over the web and described via an OpenSearch definition. The federated location description (called a Search Connector) is provided as a .osdx file. Once installed, the data source becomes queryable directly from Windows Explorer. Windows Explorer features, such as previews and thumbnails, work with the results of a federated search as well.
Other changes[edit]
- Windows 7 and Windows Server 2008 R2 support showing icons in the context menu and creating cascaded context menus with static verbs in submenus using the Registry instead of a shell extension.[44]
- The search box in the Explorer window and the address bar can be resized.
- Certain folders in the navigation pane can be hidden to reduce clutter.
- Progress bars and overlay icons on an application’s button on the taskbar.
- Content view which shows thumbnails and metadata.
- Buttons to toggle the preview pane and create a new folder.
Removed or changed features[edit]
In Windows 7, several features have been removed from Windows Explorer, including the collapsible folder pane, overlay icon for shared items, remembering individual folder window sizes and positions, free disk space on the status bar, icons on the command bar, ability to disable Auto Arrange and Align to Grid, sortable column headings in other views except details view, ability to disable full row selection in details view, automatic horizontal scrolling and scrollbar in the navigation pane and maintaining selection when sorting from the Edit menu.
Windows 8 and Windows Server 2012[edit]
The new File Explorer with ribbon in Windows 8
The file manager on Windows 8 and Windows Server 2012 is renamed File Explorer and introduces new features such as a redesigned interface incorporating a ribbon toolbar, and a redesigned file operation dialog that displays more detailed progress and allows for file operations to be paused and resumed. The details pane from Windows Vista and 7 was removed and replaced with a narrower pane with no icons and fewer detail columns. But other details are displayed by hovering over the file’s name.[45][46]
Windows 10 and Windows Server 2016[edit]
The icons in File Explorer have been redesigned. They are flatter and simpler in design. The window border padding is thinner than previous versions. Windows 10 Creators Update and later versions come with a new Universal File Explorer (also known as the UWP File Explorer). Although hidden, it can be opened by creating a shortcut pointing to «explorer shell:AppsFolderc5e2524a-ea46-4f67-841f-6a9465d9d515_cw5n1h2txyewy!App» [47][48]
Windows 10, version 1809 and Windows Server 2019[edit]
A «dark mode» has been added to File Explorer in Windows 10, version 1809 and Windows Server 2019.[49] The Universal File Explorer also includes new features.[50][51]
Windows 10, version 1909[edit]
Windows Search and OneDrive have been integrated into File Explorer’s search feature in Windows 10, version 1909.[52]
Windows 11[edit]
In Windows 11, File Explorer had undergone significant UI changes with the Ribbon Interface simplified into a command bar. Translucency, shadows, and rounded geometry have also been added, following the Fluent Design System. In March 2022, Microsoft introduced adverts into the file explorer, but later stated that these were ‘not intended to be published externally’[53] after significant negative media coverage.
Windows 11 2022 Update[edit]
On April 5, 2022, Microsoft announced that it would be adding tabs, favorites, and a new homepage to File Explorer.[54] These features were eventually introduced via an update to the Windows 11 2022 Update on October 18, 2022.[55]
Extensibility[edit]
File Explorer can be extended to support non-default functionality by means of Windows shell extensions, which are COM objects that plug the extended functionality into Windows Explorer.[56] Shell extensions can be in the form of shell extension handlers, toolbars or even namespace extensions that allow certain folders (or even non-filesystem objects such as the images scanned by a scanner) to be presented as a special folder. File Explorer also allows metadata for files to be added as NTFS alternate data streams, separate from the data stream for the file.
Shell extension handlers are queried by the shell beforehand for modifying the action the shell takes. They can be associated on a per file type – where they will show up only when a particular action takes place on a particular file type – or on a global basis – which are always available. The shell supports the following extension handlers:
| Handler | Description | Can be implemented on | Required shell version |
|---|---|---|---|
| Context menu handler | Adds menu items to the context menu. It is called before the context menu is displayed. | Per file type | Windows 95 and later. Windows 7 introduced IExecuteCommand |
| Drag-and-drop handler | Controls the action upon right-click drag and drop and modifies the context menu that appears. | Global | Windows 95 and later |
| Drop target handler | Controls the action after a data object is dragged and dropped over a drop target such as a file. | Per file type | Windows 95 and later |
| Data object handler | Controls the action after a file is copied to the clipboard or dragged and dropped over a drop target. It can provide additional clipboard formats to the drop target. | Per file type | Windows 95 and later |
| Icon handler | Assigns a custom icon to an individual file amongst a class of file types. It is called before file icons are displayed. | Per file type | Windows 95 and later |
| Property sheet handler | Replaces or adds pages to the property sheet dialog box of an object. | Per file type | Windows 95 and later |
| Copy hook handler | Allows running, modifying or denying the action when a user or application tries to copy, move, delete, or rename an object. | Not associated with a file type | Windows 95 and later |
| Search handler | Allows shell integration of a custom search engine. | Not associated with a file type | Windows 95 through Windows XP |
| Infotip handler | Allows retrieving flags and infotip information for an item and displaying it inside a popup tooltip upon mouse hover. | Per file type | Windows Desktop Update and later |
| Thumbnail image handler | Provides for a thumbnail image to be generated and displayed along with its alpha type when a file is selected or the thumbnail view is activated. | Per file type | Windows Desktop Update and later. Windows Vista introduced a newer IThumbnailProvider interface that also shows thumbnails in the Details pane. The older IExtractImage is still supported but not in the Details pane.[57] |
| Disk Cleanup handler | Add a new entry to the Disk Cleanup application and allows specifying additional disk locations or files to clean up. | Per folder | Windows 98 and later |
| Column handler | Allows creating and displaying custom columns in Windows Explorer details view. It can be used to extend sorting and grouping. | Per folder | Windows 2000 and later |
| Icon overlay handler | Allows displaying an overlay icon over a shell object (a file or folder icon). | Per file type | Windows 2000 and later |
| Metadata handler | Allows viewing and modifying metadata stored in a file. It can be used to extend details view columns, infotips, property pages, sorting and grouping. | Per file type | Windows 2000 and later |
| Filter handler (IFilter) | Allows file properties and its contents to be indexed and searched by Indexing Service or Windows Search | Per file type | Windows 2000 and later |
| AutoPlay handler | Examines newly discovered removable media and devices and, based on content such as pictures, music or video files, launches an appropriate application to play or display the content. | Per file type category Windows XP only: per device and per file type category |
Windows XP and later |
| Property handler | Allows viewing and modifying system-defined and custom properties of a file. | Per file type | Windows Vista and later; on Windows XP if Windows Search is installed. |
| Preview handler | Renders enhanced previews of items without launching the default application when a file is selected. It can also provide file type-specific navigation such as browsing a document, or seeking inside a media file. | Per file type | Windows Vista and later |
Namespace extensions are used by Explorer and Common Dialogs to either display some data – which are not necessarily persisted as files – in a folder-like view or to present data in a way that is different from their organization on the file system. This feature can be exploited by a any hierarchical data source that can be represented as a file system like the Windows one, including Cloud-based implementation. Special folders, such as My Computer and Network Places in Windows Explorer are implemented this way, as are Explorer views that let items in a mobile phone or digital camera be explored. Source-control systems that use Explorer to browse source repositories also use Namespace extensions to allow Explorer to browse the revisions. To implement a namespace extension, the IPersistFolder, IShellView, IShellFolder, IShellBrowser and IOleWindow interfaces need to be implemented and registered. The implementation needs to provide the logic for navigating the data store as well as describing the presentation. Windows Explorer will instantiate the COM objects as required.[58]
While Windows Explorer natively exposes the extensibility points as COM interfaces, .NET Framework can also be used to write some types of extensions, using the COM Interop functionality of .NET Framework.[58] While Microsoft itself makes available extensions – such as the photo info tool[59] – which are authored using .NET Framework, they currently recommend against writing managed shell extensions, as only one instance of the CLR (prior to version 4.0) can be loaded per-process. This behavior will cause conflicts if multiple managed add-ins, targeting different versions of the CLR, are attempted to be run simultaneously.[60][61]
See also[edit]
- Comparison of file managers
- List of alternative shells for Windows
Notes and references[edit]
- ^ «January 26, 2023—KB5022360 (OS Build 22621.1194) Preview». Microsoft Support. Microsoft.
- ^ «Releasing Windows 11 Build 22621.1192 to the Release Preview Channel». Windows Insider Blog. January 17, 2023.
- ^ «January 26, 2023—KB5022360 (OS Build 22621.1194) Preview». Microsoft Support. Microsoft.
- ^ «Announcing Windows 11 Insider Preview Build 22621.1250 and 22623.1250». Windows Insider Blog. February 2, 2023.
- ^ «Announcing Windows 11 Insider Preview Build 25290». Windows Insider Blog. February 1, 2023.
- ^ Lineback, Nathan. «Misc Windows». toastytech.com. Archived from the original on July 3, 2018. Retrieved June 19, 2018.
- ^ John D. Ruley (September 1995). «NT Gets the Look But Not the Logo». How-To Columns. WinMag. Archived from the original on March 14, 2006. Retrieved September 4, 2009. Internet Archive
- ^ «Managing Files, Folders, and Search Methods: Microsoft TechNet». microsoft.com. Archived from the original on January 12, 2009. Retrieved June 19, 2018.
- ^ «Serenity Macros Home Page – Resources for MS Word». www.mvps.org. Archived from the original on June 27, 2018. Retrieved June 19, 2018.
- ^ Windows 2000 Registry: Latest Features and APIs Provide the Power to Customize and Extend Your Apps, MSDN Magazine, November 2000, archived from the original on April 15, 2003, retrieved August 26, 2007
- ^ «COM Objects and Structured Storage» Archived 2018-12-18 at the Wayback Machine, Windows Dev Center, May 31, 2018
- ^ Esposito, Dino (June 2000), More Windows 2000 UI Goodies: Extending Explorer Views by Customizing Hypertext Template Files, MSDN Magazine, archived from the original on August 24, 2007, retrieved August 26, 2007
- ^ Sophos, VBS/Roor-C threat analysis Archived 2007-11-30 at the Wayback Machine. Accessed August 26, 2007.
- ^ «Virus.VBS.Redlof.a», Virus Encyclopedia, Viruslist.com, January 15, 2004, archived from the original on October 28, 2007, retrieved August 26, 2007
- ^ Figure 1 Windows Shell Extensions, MSDN Magazine, June 2000, archived from the original on August 31, 2004, retrieved August 26, 2007
- ^ «What is Indexing Service?». msdn.microsoft.com. Archived from the original on January 1, 2011. Retrieved June 19, 2018.
- ^ «Is Microsoft Office 2003 still decent for general use on Windows 7, 8.1 and 10». answers.microsoft.com. Archived from the original on February 7, 2016. Retrieved June 19, 2018.
- ^ «What is Windows XP?». www.computerhope.com. Retrieved August 12, 2022.
- ^ «Windows XP – What’s new with files and folders». Windows. Microsoft. Archived from the original on May 23, 2007.
- ^ How to create and extract a Zip File in Windows ME/XP/2003
- ^ How To: Open a Cab file – Quote: «If you’re using Windows XP or Windows Vista, then your operating system has built-in support for opening Cab files.»
- ^ «Moving web pages saved by IE (HTM file & _FILES folder)». Directory Opus Resource Centre. May 4, 2009. Archived from the original on December 16, 2020. Retrieved December 16, 2020.
When Windows Explorer […] move a Web page both the HTML file and the directory are automatically moved together. […] Moreover, the user only has to drag EITHER part—the file or the directory and the other part will follow automatically. This way the page is kept intact irrespective of where Windows stores it.
- ^ The sort order for files and folders whose names contain numerals is different in Windows Vista, Windows XP, and Windows Server 2003 than it is in Windows 2000, support.microsoft.com, August 28, 2007, archived from the original on September 27, 2010, retrieved July 6, 2009
- ^ a b Shultz, Greg (August 10, 2006). «Examine the filtering, grouping, and stacking features in Windows Vista’s Windows Explorer». TechRepublic. CBS Interactive. Archived from the original on December 22, 2015. Retrieved December 19, 2015.
- ^ a b c Reid, Rory (January 30, 2007). «Seven days of Vista — day 4: Stacking and filtering». CNET. CBS Interactive. Archived from the original on December 22, 2015. Retrieved December 19, 2015.
- ^ a b Kaelin, Mark (July 17, 2007). «How do I… Save and refine desktop searches in Microsoft Windows Vista?». TechRepublic. CBS Interactive. Archived from the original on November 17, 2015. Retrieved November 11, 2015.
- ^ Microsoft. «Saved Search File Format». MSDN. Archived from the original on December 10, 2015. Retrieved December 21, 2015.
- ^ Bentz, Ben (October 31, 2006). «Query Composition: Building a search upon another search». Shell: Revealed Blog. Microsoft. Archived from the original on December 15, 2006. Retrieved December 21, 2015.
- ^ Using search operators to find pictures, music and videos in Windows Vista
- ^ Windows 7: Find/Search Files By Date And Size
- ^ Windows Explorer Columns — Are you Fully Using Them?
- ^ «How to Search for Contents in Any File Type Without Indexing Service Enabled in Windows Vista and Windows 7». Wikihow.com. January 27, 2014. Archived from the original on March 19, 2017. Retrieved January 31, 2014.
- ^ a b Microsoft. «Add tags or other properties to a file». Windows How-to. Archived from the original on December 22, 2015. Retrieved December 21, 2015.
- ^ White, Nick (July 13, 2007). «10 Things – Windows Explorer Has a New Preview Pane». Windows Vista Team Blog. Microsoft. Archived from the original on July 15, 2007. Retrieved December 14, 2015.
- ^ Microsoft. «Pen and Touch Input in Windows Vista». MSDN. Archived from the original on December 22, 2015. Retrieved December 21, 2015.
- ^ Oiaga, Marius (September 27, 2006). «Quick Zoom on the Windows Vista Desktop and in Explorer». Softpedia. Archived from the original on December 22, 2015. Retrieved December 21, 2015.
- ^ McFedries, Paul (2008). Microsoft Windows Vista Unleashed. Sams Publishing. p. 87. ISBN 978-0-672-33013-1. Retrieved December 21, 2015.
- ^ Mangefeste, Tony; Walp, David (2006). «Optical Platform: Windows Vista and Beyond». Microsoft. Archived from the original (PPT) on June 4, 2011. Retrieved December 21, 2015.
- ^ Davis, Christopher (March 29, 2007). «Your File Is In Use… Demystified». Shell: Revealed Blog. Microsoft. Archived from the original on April 29, 2007. Retrieved December 21, 2015.
- ^ «Properties». msdn2.microsoft.com. Archived from the original on October 9, 2007. Retrieved June 19, 2018.
- ^ «IColumnProvider interface (Windows)». msdn2.microsoft.com. Archived from the original on April 17, 2008. Retrieved June 19, 2018.
- ^ A solution to this is provided on http://windowsxp.mvps.org/webpairs.htm Archived 2010-12-24 at the Wayback Machine. After the webpairs.reg file has been merged into the registry, the «Managing pairs of Web pages and folders» option is available in the Folder Options View tab.
- ^ «MS-WSP: Windows Search Protocol», MSDN Library, Microsoft, December 18, 2006, archived from the original on May 16, 2010, retrieved June 10, 2009
- ^ «Creating Shortcut Menu Handlers (Windows)». msdn.microsoft.com. Archived from the original on November 22, 2010. Retrieved June 19, 2018.
- ^ «Improvements in Windows Explorer». Archived from the original on November 7, 2011. Retrieved October 30, 2011.
- ^ «Microsoft switches to File Explorer name in Windows 8, bids farewell to Windows Explorer». The Verge. June 29, 2012. Archived from the original on August 17, 2012. Retrieved August 3, 2012.
- ^ «How to open UWP File Explorer on Windows 10 – Step by step». Windows Latest. May 7, 2017. Archived from the original on August 24, 2018. Retrieved August 24, 2018.
- ^ «Windows 10 Tip: Unlock the UWP File Explorer – Thurrott.com». Thurrott.com. May 6, 2017. Archived from the original on August 24, 2018. Retrieved August 24, 2018.
- ^ «Inspired by Insiders – Dark Theme in File Explorer». August 8, 2018. Archived from the original on August 12, 2018. Retrieved August 23, 2018.
- ^ «Microsoft updates universal File Explorer with new features in Windows 10 version 1809». Windows Central. Archived from the original on August 25, 2018. Retrieved August 24, 2018.
- ^ «UWP File Explorer has got new features in Windows 10 version 1809». Winaero. August 23, 2018. Archived from the original on August 25, 2018. Retrieved August 24, 2018.
- ^ «Windows 10 version 1909: new and changed features — gHacks Tech News». www.ghacks.net. October 2019. Archived from the original on October 25, 2019. Retrieved October 25, 2019.
- ^ Warren, Tom (March 15, 2022). «Microsoft says Windows 11’s File Explorer ads were ‘not intended to be published externally’«. The Verge. Retrieved July 28, 2022.
- ^ Warren, Tom (April 5, 2022). «Windows 11’s refreshed File Explorer gets tabs, favorites, and a new homepage». The Verge. Retrieved August 12, 2022.
- ^ Warren, Tom (October 18, 2022). «Windows 11’s new tabbed File Explorer and taskbar improvements are available today». The Verge. Retrieved October 18, 2022.
- ^ ShellExView v1.19 – Shell Extensions Manager for Windows, archived from the original on October 24, 2010, retrieved March 31, 2008
- ^ «Thumbnail Handlers (Windows)». msdn.microsoft.com. Archived from the original on June 19, 2018. Retrieved June 19, 2018.
- ^ a b Rensin, Dave (January 2004). «Create Namespace Extensions for Windows Explorer with the .NET Framework». msdn.microsoft.com. Archived from the original on May 8, 2008. Retrieved March 31, 2008.
- ^ «Microsoft Download Center: Windows, Office, Xbox & More». www.microsoft.com. Archived from the original on May 13, 2008. Retrieved June 19, 2018.
- ^ «MSDN Magazine Issues». msdn.microsoft.com. Archived from the original on May 21, 2008. Retrieved June 19, 2018.
- ^ Zhang, Junfeng (November 18, 2005). «Don’t do Shell Extension Handlers in .NET». msdn.com. Archived from the original on January 5, 2010. Retrieved June 19, 2018.
External links[edit]
- Sullivan, Kent. «The Windows 95 User Interface: A Case Study in Usability Engineering» (1996) for Association for Computing Machinery. (Sullivan was a developer on the Windows 95 UI team)
- How To Customize the Windows Explorer Views in Windows XP
- MSDN: Creating Shell Extension Handlers, Windows Dev Center, May 31, 2018
- The Complete Idiot’s Guide to Writing Shell Extensions, by Michal Dunn, March 15, 2006
- Namespace extensions – the undocumented Windows Shell, by Henk Devos, November 30, 1999
This article is about the Microsoft Windows file listing browser. For exploring file system listings, see file browser. For exploring inside files, see file viewer.

File Explorer on Windows 11 in Light App Mode showing special folders on Home, with the new command bar and tabs feature. |
|
| Developer(s) | Microsoft |
|---|---|
| Initial release | August 15, 1995; 27 years ago |
| Stable release |
22H2 (10.0.22621.1194) (January 26, 2023; 9 days ago[1]) [±] |
| Preview release |
;Release Preview Channel 22H2 (10.0.22621.1194) (January 26, 2023; 9 days ago[2][3]) [±]
22H2 (10.0.22623.1250) (February 2, 2023; 2 days ago[4]) [±]
10.0.25290.1000 (February 1, 2023; 3 days ago[5]) [±] |
| Included with | Windows 95 and later |
| Predecessor | Program Manager, File Manager |
| Type | Shell, file manager |
File Explorer, previously known as Windows Explorer, is a file manager application that is included with releases of the Microsoft Windows operating system from Windows 95 onwards. It provides a graphical user interface for accessing the file systems. It is also the component of the operating system that presents many user interface items on the screen such as the taskbar and desktop. Controlling the computer is possible without Windows Explorer running (for example, the File ▸ Run command in Task Manager on NT-derived versions of Windows will function without it, as will commands typed in a command prompt window).
Overview[edit]
Windows Explorer was first included with Windows 95 as a replacement for File Manager, which came with all versions of Windows 3.x operating systems. Explorer could be accessed by double-clicking the new My Computer desktop icon or launched from the new Start Menu that replaced the earlier Program Manager. There is also a shortcut key combination: Windows key+E. Successive versions of Windows (and in some cases, Internet Explorer) introduced new features and capabilities, removed other features, and generally progressed from being a simple file system navigation tool into a task-based file management system.
While «Windows Explorer» or «File Explorer» is a term most commonly used to describe the file management aspect of the operating system, the Explorer process also houses the operating system’s search functionality and File Type associations (based on filename extensions), and is responsible for displaying the desktop icons, the Start Menu, the Taskbar, and the Control Panel. Collectively, these features are known as the Windows shell.
After a user logs in, the explorer process is created by the userinit process. Userinit performs some initialization of the user environment (such as running the login script and applying group policies) and then looks in the registry at the Shell value and creates a process to run the system-defined shell – by default, Explorer.exe. Then Userinit exits. This is why Explorer.exe is shown by various process explorers with no parent – its parent has exited.
History[edit]
In 1995, Microsoft first released test versions of a shell refresh, named the Shell Technology Preview, and often referred to informally as «NewShell».[6] The update was designed to replace the Windows 3.x Program Manager/File Manager based shell with Windows Explorer. The release provided capabilities quite similar to that of the Windows «Chicago» (codename for Windows 95) shell during its late beta phases, however was intended to be nothing more than a test release.[7] There were two public releases of the Shell Technology Preview, made available to MSDN and CompuServe users: May 26, 1995 and August 8, 1995. Both held Windows Explorer builds of 3.51.1053.1. The Shell Technology Preview program never saw a final release under NT 3.51. The entire program was moved across to the Cairo development group who finally integrated the new shell design into the NT code with the release of NT 4.0 in July 1996.
Windows 98 and Windows Desktop Update[edit]
With the release of the Windows Desktop Update (packaged with Internet Explorer 4 as an optional component, and included in Windows 98), Windows Explorer became «integrated» with Internet Explorer, most notably with the addition of navigation arrows (back and forward) for moving between recently visited directories, as well as Internet Explorer’s Favorites menu.
An address bar was also added to Windows Explorer, which a user could type in directory paths directly, and be taken to that folder.
Another feature that was based on Internet Explorer technology was customized folders. Such folders contained a hidden web page that controlled the way the Windows Explorer displayed the contents of the folder.
Windows ME and Windows 2000[edit]
The integrated media player in Windows Explorer in Windows 2000, playing a MIDI sequence on Media folder
The «Web-style» folders view, with the left Explorer pane displaying details for the object currently selected, is turned on by default. For certain file types, such as pictures and media files, a preview is also displayed in the left pane.[8] The Windows 2000 Explorer featured an interactive media player as the previewer for sound and video files. However, such a previewer can be enabled in Windows ME through the use of folder customization templates.[9] Windows Explorer in Windows 2000 and Windows ME allows for custom thumbnail previewers and tooltip handlers. The default file tooltip displays file title, author, subject and comments;[10] this metadata may be read from a special NTFS stream, if the file is on an NTFS volume, or from a COM Structured Storage stream, if the file is a structured storage document. All Microsoft Office documents since Office 95[11] make use of structured storage, so their metadata is displayable in the Windows 2000 Explorer default tooltip. File shortcuts can also store comments which are displayed as a tooltip when the mouse hovers over the shortcut.
The right-hand pane, which usually just lists files and folders, can also be customized. For example, the contents of the system folders aren’t displayed by default, instead showing in the right pane a warning to the user that modifying the contents of the system folders could harm their computer. It’s possible to define additional Explorer panes by using DIV elements in folder template files.[12] This feature was abused by computer viruses that employed malicious scripts, Java applets, or ActiveX controls in folder template files as their infection vector. Two such viruses are VBS/Roor-C[13] and VBS.Redlof.a.[14]
Other Explorer UI elements that can be customized include columns in «Details» view, icon overlays, and search providers: the new DHTML-based search pane is integrated into Windows 2000 Explorer, unlike the separate search dialog found in all previous Explorer versions.[15]
Search capabilities were added, offering full-text searches of documents, with options to filter by date (including arbitrary ranges like «modified within the last week»), size, and file type. The Indexing Service has also been integrated into the operating system and the search pane built into Explorer allows searching files indexed by its database.[16] The ability to customize the standard buttons was also added.
Windows XP and Windows Server 2003[edit]
Windows Explorer in Windows XP, showing All Users folder contents
There were significant changes made to Windows Explorer in Windows XP, both visually and functionally. Microsoft focused especially on making Explorer more discoverable and task-based, as well as adding several new features to reflect the growing use of a computer as a digital hub.
Windows Explorer in Windows Server 2003 contains all the same features as Windows XP, but the task panes and search companion are disabled by default.
Task pane[edit]
The task pane is displayed on the left-hand side of the window instead of the traditional folder tree view. It presents the user with a list of common actions and destinations that are relevant to the current directory or file(s) selected. For instance, when in a directory containing mostly pictures, a set of «Picture tasks» is shown, offering the options to display these pictures as a slide show, to print them out, or to go online to order prints. Conversely, a folder containing music files would offer options to play those files in a media player or to go online to purchase music. Windows XP had a Media bar but it was removed with SP1. The Media Bar was only available with Windows XP RTM.
Every folder also has «File and Folder Tasks», offering options to create new folders, share a folder on the local network, publish files or folders to a website, and other common tasks like copying, renaming, moving, and deleting files or folders. File types that have identified themselves as being printable also have an option listed to print the file.
Underneath «Other Places» is a «Details» pane which gives additional information – typically file size and date, but depending on the file type, a thumbnail preview, author, image dimensions, or other details.
The «Folders» button on the Windows Explorer toolbar toggles between the traditional tree view of folders, and the task pane. Users can get rid of the task pane or restore it using the sequence: Tools – Folder Options – General – Show Common Tasks/Use Windows Classic Folders.
Search companion[edit]
Windows Explorer’s default Search Companion, Rover, in Windows XP
Microsoft introduced animated «Search Companions» in an attempt to make searching more engaging and friendly; the default character is a puppy named Rover (previously used in Microsoft Bob), with three other characters (Merlin the magician, Earl the surfer, and Courtney) also available. These search companions use the same technology as Microsoft Office’s Office Assistants, even incorporating «tricks» and sound effects, and they can be used as Office Assistants if their files are copied into the C:Windowsmsagentchars folder.[17]
The search capability itself is fairly similar to Windows ME and Windows 2000, with one major addition: Search can also be instructed to search only files that are categorical «Documents» or «Pictures, music and video»; this feature is noteworthy largely because of how Windows determines what types of files can be classified under these categories. In order to maintain a relevant list of file types, Windows Explorer connects to Microsoft and downloads a set of XML files that define what these file types are. The Search Companion can be disabled in favor of the classic search pane used in Windows 2000 by using the Tweak UI applet from Microsoft’s PowerToys for Windows XP, or by manually editing the registry.
Image handling[edit]
Windows XP improves image preview in Explorer by offering a Filmstrip view. «Back» and «Previous» buttons facilitate navigation through the pictures, and a pair of «Rotate» buttons offer 90-degree clockwise and counter-clockwise (lossy)[18] rotation of images. Aside from the Filmstrip view mode, there is a ‘Thumbnails’ mode, which displays thumbnail-sized images in the folder. A Folder containing images will also show thumbnails of four of the images from that folder overlaid on top of a large folder icon.
Web publishing[edit]
Web sites that offer image hosting services can be plugged into Windows Explorer, which the user can use to select images on their computer, and have them uploaded correctly without dealing with comparatively complex solutions involving FTP or web interfaces.[citation needed]
Other changes[edit]
- Explorer gained the ability to understand the metadata of a number of types of files. For example, with images from a digital camera, the Exif information can be viewed, both in the Properties pages for the photo itself, as well as via optional additional Details View columns.
- A Tile view mode was added, which displays the file’s icon in a larger size (48 × 48), and places the file name, descriptive type, and additional information (typically the file size for data files, and the publisher name for applications) to the right.
- The Details view also presented an additional option called «Show in Groups» which allows the Explorer to separate its contents by headings based on the field which is used to sort the items.
- The taskbar can be locked to prevent it from accidentally being moved.
- Windows Explorer also gained the ability to burn CDs and DVD-RAM discs in Windows XP.
- Ability to create and open ZIP files called «compressed folders».[19][20]
- Ability to open Cabined (.cab) files.[21]
- If a
.HTMor.HTMLfile is copied or moved, the accompanying_filessuffix folder is copied or moved among it automatically.[22]
Removed and changed features[edit]
|
This section needs expansion. You can help by adding to it. (December 2012) |
- The sort order has changed compared to the one in Windows 2000. For file names containing numbers Windows Explorer now tries to sort based on numerical value rather than just comparing each number digit by digit.[23]
Windows Vista and Windows Server 2008[edit]
Windows Explorer in Windows Vista, showing Public folder contents
Search, organizing and metadata[edit]
Windows Explorer includes significant changes from previous versions of Windows such as improved filtering, sorting, grouping and stacking. Combined with integrated desktop search, Windows Explorer allows users to find and organize their files in new ways, such as stacks.[24][25] The new Stacks viewing mode groups files according to the criterion specified by the user.[25] Stacks can be clicked to filter the files shown in Windows Explorer. There is also the ability to save searches as virtual folders or search folders.[26] A search folder is simply an XML file, which stores the query in a form that can be used by the Windows search subsystem.[27] When accessed, the search is executed and the results are aggregated and presented as a virtual folder.[26] Windows Vista includes six search folders by default: recent documents, recent e-mail, recent music, recent pictures and videos, recent changed, and «Shared by Me».[28] Additionally, search operators for properties were introduced, such as kind:music. [29] Since at least Windows 7, comparison operators «greater than» and «less than» are supported to search for any supported attribute such as date ranges and file sizes, like size:>100MB to search for all files that are greater than 100MB.[30] Attributes sortable and searchable in Windows Explorer include pictures’ dimensions, Exif data such as aperture and exposure, video duration and framerate and width.[31]
When sorting items, the sort order no longer remains consistently Ascending or Descending. Each property has a preferred sort direction. For example, sort by date defaults to descending order, as does size. But name and type default to ascending order.
Searching for files containing a given text string became problematic with Vista unless the files had been indexed. An alternative is to use the findstr command-line function.[32] After right-clicking on a folder one can open a command-line prompt in that folder.
Windows Explorer also contains modifications in the visualization of files on a computer. A new addition to Windows Explorer in Vista and Server 2008 is the details pane, which displays metadata and information relating to the currently selected file or folder. The details pane will also display a thumbnail of the file or an icon of the filetype if the file does not contain visual information. Furthermore, different imagery is overlaid on thumbnails to give more information about the file, such as a picture frame around the thumbnail of an image file, or a filmstrip on a video file.
The details pane also allows for the change of some textual metadata such as author and title in files that support them within Windows Explorer. A new type of metadata called tags allows users to add descriptive terms to documents for easier categorization and retrieval. Some files support open metadata, allowing users to define new types of metadata for their files. Out-of-the-box, Windows Vista and Windows Server 2008 supports Microsoft Office documents and most audio and video files. Support for other file types can however be added by writing specialized software to retrieve the metadata at the shell’s request. Metadata stored in a file’s alternate data stream only on NTFS volumes cannot be viewed and edited through the summary tab of the file’s properties anymore. Instead, all metadata is stored inside the file, so that it will always travel with the file and not be dependent on the file system.[33]
Layout and icons[edit]
Windows Explorer in Windows Vista and Windows Server 2008 also introduces a new layout. The task panes from Windows XP are replaced with a toolbar on top and a navigation pane on the left. The navigation pane contains commonly accessed folders and preconfigured search folders. Eight different views are available to view files and folders, including extra large, large, medium, small, list, details, tiles, and content. In addition, column headers now appear in all icon viewing modes,[25] unlike Windows XP where they only appear in the details icon viewing mode.[24] File and folder actions such as cut, copy, paste, undo, redo, delete, rename and properties are built into a dropdown menu which appears when the Organize button is clicked. It is also possible to change the layout of the Explorer window by using the Organize button. Users can select whether to display classic menus, a search pane, a preview pane, a reading pane, and the navigation pane. The preview pane enables users to preview files (e.g., documents or media files) without opening them. If an application, such as Office 2007, installs preview handlers for file types, then these files can also be edited within the preview pane itself.[34]
Windows Vista saw the introduction of the breadcrumb bar for easier navigation. As opposed to the prior address bar which displayed the current folder in a simple editable combobox, this new style structures the path into clickable levels of folder hierarchy (though falls back to the classic edit mode when a blank area is clicked), enabling the user to skip as many levels as desired in one click rather than repeatedly clicking «Up». It is also possible to navigate to any subfolder of the current folder using the arrow to the right of the last item. The menu bar is now hidden by default but reappears temporarily when the user presses Alt.
Check boxes in Windows Explorer allow the selection of multiple files.[35] Free and used space on all drives is shown in horizontal indicator bars. Icons of various sizes are supported: 16 x 16, 24 x 24, 32 x 32, 48 x 48, 64 x 64, 96 x 96, 128 x 128 and 256 x 256. Windows Explorer can zoom the icons in and out using a slider or by holding down the Ctrl key and using the mouse scrollwheel.[36] Live icons can display the content of folders and files themselves rather than generic icons.[37]
Other changes[edit]
With the release of Windows Vista and Server 2008 and Windows Internet Explorer 7 for Windows XP, Internet Explorer is no longer integrated with Windows Explorer. In Windows Vista and Server 2008 (and in Windows XP as well if IE7 or 8 is installed), Windows Explorer no longer displays web pages, and IE7 does not support use as a file manager, although one will separately launch the other as necessary.
When moving or copying files from one folder to another, if two files have the same name, an option is now available to rename the file; in previous versions of Windows, the user was prompted to choose either a replacement or cancel moving the file. Also, when renaming a file, Explorer only highlights the filename without selecting the extension. Renaming multiple files is quicker as pressing Tab automatically renames the existing file or folder and opens the file name text field for the next file for renaming. Shift+Tab allows renaming in the same manner upwards.
Support for burning data on DVDs (DVD±R, DVD±R DL, DVD±R RW) in addition to CDs and DVD-RAM using version 2.0 of the Image Mastering API, as well as Live File System support was added.[38]
If a file is in use by another application, Windows Explorer tells users to close the application and retry the file operation. Also, a new interface IFileIsInUse is introduced into the API which developers can use to let other applications switch to the main window of the application that has the file open or simply close the file from the «File in Use» dialog. If the running application exposes these operations by means of the IFileIsInUse interface, Windows Explorer, upon encountering a locked file, allows the user to close the file or switch to the application from the dialog box itself.[39]
Windows Vista introduced precluded support for the Media Transfer Protocol.[citation needed]
Removed and changed features[edit]
The ability to customize the layout and buttons on the toolbars has been removed in Windows Vista’s Explorer, as has the ability to add a password to a zip file (compressed folder). The Toolbar button in Explorer to go up one folder from the current folder has been removed (the function still exists however, one can move up a folder by pressing Alt + ↑). Although still fully available from the menus and keyboard shortcuts, toolbar buttons for Cut, Copy, Paste, Undo, Delete, Properties and some others are no longer available. The Menu Bar is also hidden by default but is still available by pressing the Alt key or changing its visibility in the layout options. Several other features are removed such as showing the size on the status bar without selecting items, storing metadata in NTFS alternate data streams,[40] the IColumnProvider interface which allowed addition of custom columns to Explorer[41] and folder background customization using desktop.ini.
The option «Managing pairs of Web pages and folders» is also removed, and the user has no way of telling Vista that a .html file and the folder with the same name that was created when saving a complete web page from IE should be treated separately, that is, they cannot delete the folder without deleting the html file as well.[42]
The ability to right-click a folder and hit «Search» was removed in Windows Vista Service Pack 1. Users must open the folder they wish to search in and enter their keywords in the search field located on the top right corner of the window. Alternatively, users can specify other search parameters through the «Advanced Search» UI, which can be accessed by clicking on the Organize Bar and selecting Search Pane under the Layout submenu. Pressing F3 also opens the «Advanced Search» interface.
Windows 7 and Windows Server 2008 R2[edit]
Windows Explorer in Windows 7, showing Libraries
Libraries[edit]
Windows Explorer in Windows 7 and Windows Server 2008 R2 supports libraries, virtual folders described in a .library-ms file that aggregates content from various locations – including shared folders on networked systems if the shared folder has been indexed by the host system – and present them in a unified view. Searching in a library automatically federates the query to the remote systems, in addition to searching on the local system, so that files on the remote systems are also searched. Unlike search folders, Libraries are backed by a physical location which allows files to be saved in the libraries. Such files are transparently saved in the backing physical folder. The default save location for a library may be configured by the user, as can the default view layout for each library. Libraries are generally stored in the libraries special folder, which allows them to be displayed on the navigation pane.
By default, a new user account in Windows 7 contains four libraries, for different file types: Documents, Music, Pictures, and Videos. They are configured to include the user’s profile folders for these respective file types, as well as the computer’s corresponding Public folders.
In addition to aggregating multiple storage locations, Libraries enable Arrangement Views and Search Filter Suggestions. Arrangement Views allow users to pivot their views of the library’s contents based on metadata. For example, selecting the «By Month» view in the Pictures library will display photos in stacks, where each stack represents a month of photos based on the date they were taken. In the Music library, the «By Artist» view will display stacks of albums from the artists in their collections, and browsing into an artist stack will then display the relevant albums.
Search Filter Suggestions are a new feature of the Windows 7 and Windows Server 2008 R2 Explorer’s search box. When the user clicks in the search box, a menu shows up below it showing recent searches as well as suggested Advanced Query Syntax filters that the user can type. When one is selected (or typed in manually), the menu will update to show the possible values to filter by for that property, and this list is based on the current location and other parts of the query already typed. For example, selecting the «tags» filter or typing «tags:» into the search box will display the list of possible tag values which will return search results.
The metadata written within the file, implemented in Vista, is also utilized in Windows 7. This can sometimes lead to long wait times displaying the contents of a folder. For example, if a folder contains many large video files totaling hundreds of gigabytes, and the Window Explorer pane is in Details view mode showing a property contained within the metadata (for example Date, Length, Frame Height), Windows Explorer might have to search the contents of the whole file for the meta data. Some damaged files can cause a prolonged delay as well. This is due to metadata information being able to be placed anywhere within the file, beginning, middle, or end, necessitating a search of the whole file. Lengthy delays also occur when displaying the contents of a folder with many different types of program icons. The icon is contained in the metadata. Some programs cause the activation of a virus scan when retrieving the icon information from the metadata, hence producing a lengthy delay.[33]
Arrangement Views and Search Filter Suggestions are database-backed features that require that all locations in the Library be indexed by the Windows Search service. Local disk locations must be indexed by the local indexer, and Windows Explorer will automatically add locations to the indexing scope when they are included in a library. Remote locations can be indexed by the indexer on another Windows 7 and Windows Server 2008 R2 machine, on a Windows machine running Windows Search 4 (such as Windows Vista or Windows Home Server), or on another device that implements the MS-WSP remote query protocol.[43]
Federated search[edit]
Windows Explorer also supports federating search to external data sources, such as custom databases or web services, that are exposed over the web and described via an OpenSearch definition. The federated location description (called a Search Connector) is provided as a .osdx file. Once installed, the data source becomes queryable directly from Windows Explorer. Windows Explorer features, such as previews and thumbnails, work with the results of a federated search as well.
Other changes[edit]
- Windows 7 and Windows Server 2008 R2 support showing icons in the context menu and creating cascaded context menus with static verbs in submenus using the Registry instead of a shell extension.[44]
- The search box in the Explorer window and the address bar can be resized.
- Certain folders in the navigation pane can be hidden to reduce clutter.
- Progress bars and overlay icons on an application’s button on the taskbar.
- Content view which shows thumbnails and metadata.
- Buttons to toggle the preview pane and create a new folder.
Removed or changed features[edit]
In Windows 7, several features have been removed from Windows Explorer, including the collapsible folder pane, overlay icon for shared items, remembering individual folder window sizes and positions, free disk space on the status bar, icons on the command bar, ability to disable Auto Arrange and Align to Grid, sortable column headings in other views except details view, ability to disable full row selection in details view, automatic horizontal scrolling and scrollbar in the navigation pane and maintaining selection when sorting from the Edit menu.
Windows 8 and Windows Server 2012[edit]
The new File Explorer with ribbon in Windows 8
The file manager on Windows 8 and Windows Server 2012 is renamed File Explorer and introduces new features such as a redesigned interface incorporating a ribbon toolbar, and a redesigned file operation dialog that displays more detailed progress and allows for file operations to be paused and resumed. The details pane from Windows Vista and 7 was removed and replaced with a narrower pane with no icons and fewer detail columns. But other details are displayed by hovering over the file’s name.[45][46]
Windows 10 and Windows Server 2016[edit]
The icons in File Explorer have been redesigned. They are flatter and simpler in design. The window border padding is thinner than previous versions. Windows 10 Creators Update and later versions come with a new Universal File Explorer (also known as the UWP File Explorer). Although hidden, it can be opened by creating a shortcut pointing to «explorer shell:AppsFolderc5e2524a-ea46-4f67-841f-6a9465d9d515_cw5n1h2txyewy!App» [47][48]
Windows 10, version 1809 and Windows Server 2019[edit]
A «dark mode» has been added to File Explorer in Windows 10, version 1809 and Windows Server 2019.[49] The Universal File Explorer also includes new features.[50][51]
Windows 10, version 1909[edit]
Windows Search and OneDrive have been integrated into File Explorer’s search feature in Windows 10, version 1909.[52]
Windows 11[edit]
In Windows 11, File Explorer had undergone significant UI changes with the Ribbon Interface simplified into a command bar. Translucency, shadows, and rounded geometry have also been added, following the Fluent Design System. In March 2022, Microsoft introduced adverts into the file explorer, but later stated that these were ‘not intended to be published externally’[53] after significant negative media coverage.
Windows 11 2022 Update[edit]
On April 5, 2022, Microsoft announced that it would be adding tabs, favorites, and a new homepage to File Explorer.[54] These features were eventually introduced via an update to the Windows 11 2022 Update on October 18, 2022.[55]
Extensibility[edit]
File Explorer can be extended to support non-default functionality by means of Windows shell extensions, which are COM objects that plug the extended functionality into Windows Explorer.[56] Shell extensions can be in the form of shell extension handlers, toolbars or even namespace extensions that allow certain folders (or even non-filesystem objects such as the images scanned by a scanner) to be presented as a special folder. File Explorer also allows metadata for files to be added as NTFS alternate data streams, separate from the data stream for the file.
Shell extension handlers are queried by the shell beforehand for modifying the action the shell takes. They can be associated on a per file type – where they will show up only when a particular action takes place on a particular file type – or on a global basis – which are always available. The shell supports the following extension handlers:
| Handler | Description | Can be implemented on | Required shell version |
|---|---|---|---|
| Context menu handler | Adds menu items to the context menu. It is called before the context menu is displayed. | Per file type | Windows 95 and later. Windows 7 introduced IExecuteCommand |
| Drag-and-drop handler | Controls the action upon right-click drag and drop and modifies the context menu that appears. | Global | Windows 95 and later |
| Drop target handler | Controls the action after a data object is dragged and dropped over a drop target such as a file. | Per file type | Windows 95 and later |
| Data object handler | Controls the action after a file is copied to the clipboard or dragged and dropped over a drop target. It can provide additional clipboard formats to the drop target. | Per file type | Windows 95 and later |
| Icon handler | Assigns a custom icon to an individual file amongst a class of file types. It is called before file icons are displayed. | Per file type | Windows 95 and later |
| Property sheet handler | Replaces or adds pages to the property sheet dialog box of an object. | Per file type | Windows 95 and later |
| Copy hook handler | Allows running, modifying or denying the action when a user or application tries to copy, move, delete, or rename an object. | Not associated with a file type | Windows 95 and later |
| Search handler | Allows shell integration of a custom search engine. | Not associated with a file type | Windows 95 through Windows XP |
| Infotip handler | Allows retrieving flags and infotip information for an item and displaying it inside a popup tooltip upon mouse hover. | Per file type | Windows Desktop Update and later |
| Thumbnail image handler | Provides for a thumbnail image to be generated and displayed along with its alpha type when a file is selected or the thumbnail view is activated. | Per file type | Windows Desktop Update and later. Windows Vista introduced a newer IThumbnailProvider interface that also shows thumbnails in the Details pane. The older IExtractImage is still supported but not in the Details pane.[57] |
| Disk Cleanup handler | Add a new entry to the Disk Cleanup application and allows specifying additional disk locations or files to clean up. | Per folder | Windows 98 and later |
| Column handler | Allows creating and displaying custom columns in Windows Explorer details view. It can be used to extend sorting and grouping. | Per folder | Windows 2000 and later |
| Icon overlay handler | Allows displaying an overlay icon over a shell object (a file or folder icon). | Per file type | Windows 2000 and later |
| Metadata handler | Allows viewing and modifying metadata stored in a file. It can be used to extend details view columns, infotips, property pages, sorting and grouping. | Per file type | Windows 2000 and later |
| Filter handler (IFilter) | Allows file properties and its contents to be indexed and searched by Indexing Service or Windows Search | Per file type | Windows 2000 and later |
| AutoPlay handler | Examines newly discovered removable media and devices and, based on content such as pictures, music or video files, launches an appropriate application to play or display the content. | Per file type category Windows XP only: per device and per file type category |
Windows XP and later |
| Property handler | Allows viewing and modifying system-defined and custom properties of a file. | Per file type | Windows Vista and later; on Windows XP if Windows Search is installed. |
| Preview handler | Renders enhanced previews of items without launching the default application when a file is selected. It can also provide file type-specific navigation such as browsing a document, or seeking inside a media file. | Per file type | Windows Vista and later |
Namespace extensions are used by Explorer and Common Dialogs to either display some data – which are not necessarily persisted as files – in a folder-like view or to present data in a way that is different from their organization on the file system. This feature can be exploited by a any hierarchical data source that can be represented as a file system like the Windows one, including Cloud-based implementation. Special folders, such as My Computer and Network Places in Windows Explorer are implemented this way, as are Explorer views that let items in a mobile phone or digital camera be explored. Source-control systems that use Explorer to browse source repositories also use Namespace extensions to allow Explorer to browse the revisions. To implement a namespace extension, the IPersistFolder, IShellView, IShellFolder, IShellBrowser and IOleWindow interfaces need to be implemented and registered. The implementation needs to provide the logic for navigating the data store as well as describing the presentation. Windows Explorer will instantiate the COM objects as required.[58]
While Windows Explorer natively exposes the extensibility points as COM interfaces, .NET Framework can also be used to write some types of extensions, using the COM Interop functionality of .NET Framework.[58] While Microsoft itself makes available extensions – such as the photo info tool[59] – which are authored using .NET Framework, they currently recommend against writing managed shell extensions, as only one instance of the CLR (prior to version 4.0) can be loaded per-process. This behavior will cause conflicts if multiple managed add-ins, targeting different versions of the CLR, are attempted to be run simultaneously.[60][61]
See also[edit]
- Comparison of file managers
- List of alternative shells for Windows
Notes and references[edit]
- ^ «January 26, 2023—KB5022360 (OS Build 22621.1194) Preview». Microsoft Support. Microsoft.
- ^ «Releasing Windows 11 Build 22621.1192 to the Release Preview Channel». Windows Insider Blog. January 17, 2023.
- ^ «January 26, 2023—KB5022360 (OS Build 22621.1194) Preview». Microsoft Support. Microsoft.
- ^ «Announcing Windows 11 Insider Preview Build 22621.1250 and 22623.1250». Windows Insider Blog. February 2, 2023.
- ^ «Announcing Windows 11 Insider Preview Build 25290». Windows Insider Blog. February 1, 2023.
- ^ Lineback, Nathan. «Misc Windows». toastytech.com. Archived from the original on July 3, 2018. Retrieved June 19, 2018.
- ^ John D. Ruley (September 1995). «NT Gets the Look But Not the Logo». How-To Columns. WinMag. Archived from the original on March 14, 2006. Retrieved September 4, 2009. Internet Archive
- ^ «Managing Files, Folders, and Search Methods: Microsoft TechNet». microsoft.com. Archived from the original on January 12, 2009. Retrieved June 19, 2018.
- ^ «Serenity Macros Home Page – Resources for MS Word». www.mvps.org. Archived from the original on June 27, 2018. Retrieved June 19, 2018.
- ^ Windows 2000 Registry: Latest Features and APIs Provide the Power to Customize and Extend Your Apps, MSDN Magazine, November 2000, archived from the original on April 15, 2003, retrieved August 26, 2007
- ^ «COM Objects and Structured Storage» Archived 2018-12-18 at the Wayback Machine, Windows Dev Center, May 31, 2018
- ^ Esposito, Dino (June 2000), More Windows 2000 UI Goodies: Extending Explorer Views by Customizing Hypertext Template Files, MSDN Magazine, archived from the original on August 24, 2007, retrieved August 26, 2007
- ^ Sophos, VBS/Roor-C threat analysis Archived 2007-11-30 at the Wayback Machine. Accessed August 26, 2007.
- ^ «Virus.VBS.Redlof.a», Virus Encyclopedia, Viruslist.com, January 15, 2004, archived from the original on October 28, 2007, retrieved August 26, 2007
- ^ Figure 1 Windows Shell Extensions, MSDN Magazine, June 2000, archived from the original on August 31, 2004, retrieved August 26, 2007
- ^ «What is Indexing Service?». msdn.microsoft.com. Archived from the original on January 1, 2011. Retrieved June 19, 2018.
- ^ «Is Microsoft Office 2003 still decent for general use on Windows 7, 8.1 and 10». answers.microsoft.com. Archived from the original on February 7, 2016. Retrieved June 19, 2018.
- ^ «What is Windows XP?». www.computerhope.com. Retrieved August 12, 2022.
- ^ «Windows XP – What’s new with files and folders». Windows. Microsoft. Archived from the original on May 23, 2007.
- ^ How to create and extract a Zip File in Windows ME/XP/2003
- ^ How To: Open a Cab file – Quote: «If you’re using Windows XP or Windows Vista, then your operating system has built-in support for opening Cab files.»
- ^ «Moving web pages saved by IE (HTM file & _FILES folder)». Directory Opus Resource Centre. May 4, 2009. Archived from the original on December 16, 2020. Retrieved December 16, 2020.
When Windows Explorer […] move a Web page both the HTML file and the directory are automatically moved together. […] Moreover, the user only has to drag EITHER part—the file or the directory and the other part will follow automatically. This way the page is kept intact irrespective of where Windows stores it.
- ^ The sort order for files and folders whose names contain numerals is different in Windows Vista, Windows XP, and Windows Server 2003 than it is in Windows 2000, support.microsoft.com, August 28, 2007, archived from the original on September 27, 2010, retrieved July 6, 2009
- ^ a b Shultz, Greg (August 10, 2006). «Examine the filtering, grouping, and stacking features in Windows Vista’s Windows Explorer». TechRepublic. CBS Interactive. Archived from the original on December 22, 2015. Retrieved December 19, 2015.
- ^ a b c Reid, Rory (January 30, 2007). «Seven days of Vista — day 4: Stacking and filtering». CNET. CBS Interactive. Archived from the original on December 22, 2015. Retrieved December 19, 2015.
- ^ a b Kaelin, Mark (July 17, 2007). «How do I… Save and refine desktop searches in Microsoft Windows Vista?». TechRepublic. CBS Interactive. Archived from the original on November 17, 2015. Retrieved November 11, 2015.
- ^ Microsoft. «Saved Search File Format». MSDN. Archived from the original on December 10, 2015. Retrieved December 21, 2015.
- ^ Bentz, Ben (October 31, 2006). «Query Composition: Building a search upon another search». Shell: Revealed Blog. Microsoft. Archived from the original on December 15, 2006. Retrieved December 21, 2015.
- ^ Using search operators to find pictures, music and videos in Windows Vista
- ^ Windows 7: Find/Search Files By Date And Size
- ^ Windows Explorer Columns — Are you Fully Using Them?
- ^ «How to Search for Contents in Any File Type Without Indexing Service Enabled in Windows Vista and Windows 7». Wikihow.com. January 27, 2014. Archived from the original on March 19, 2017. Retrieved January 31, 2014.
- ^ a b Microsoft. «Add tags or other properties to a file». Windows How-to. Archived from the original on December 22, 2015. Retrieved December 21, 2015.
- ^ White, Nick (July 13, 2007). «10 Things – Windows Explorer Has a New Preview Pane». Windows Vista Team Blog. Microsoft. Archived from the original on July 15, 2007. Retrieved December 14, 2015.
- ^ Microsoft. «Pen and Touch Input in Windows Vista». MSDN. Archived from the original on December 22, 2015. Retrieved December 21, 2015.
- ^ Oiaga, Marius (September 27, 2006). «Quick Zoom on the Windows Vista Desktop and in Explorer». Softpedia. Archived from the original on December 22, 2015. Retrieved December 21, 2015.
- ^ McFedries, Paul (2008). Microsoft Windows Vista Unleashed. Sams Publishing. p. 87. ISBN 978-0-672-33013-1. Retrieved December 21, 2015.
- ^ Mangefeste, Tony; Walp, David (2006). «Optical Platform: Windows Vista and Beyond». Microsoft. Archived from the original (PPT) on June 4, 2011. Retrieved December 21, 2015.
- ^ Davis, Christopher (March 29, 2007). «Your File Is In Use… Demystified». Shell: Revealed Blog. Microsoft. Archived from the original on April 29, 2007. Retrieved December 21, 2015.
- ^ «Properties». msdn2.microsoft.com. Archived from the original on October 9, 2007. Retrieved June 19, 2018.
- ^ «IColumnProvider interface (Windows)». msdn2.microsoft.com. Archived from the original on April 17, 2008. Retrieved June 19, 2018.
- ^ A solution to this is provided on http://windowsxp.mvps.org/webpairs.htm Archived 2010-12-24 at the Wayback Machine. After the webpairs.reg file has been merged into the registry, the «Managing pairs of Web pages and folders» option is available in the Folder Options View tab.
- ^ «MS-WSP: Windows Search Protocol», MSDN Library, Microsoft, December 18, 2006, archived from the original on May 16, 2010, retrieved June 10, 2009
- ^ «Creating Shortcut Menu Handlers (Windows)». msdn.microsoft.com. Archived from the original on November 22, 2010. Retrieved June 19, 2018.
- ^ «Improvements in Windows Explorer». Archived from the original on November 7, 2011. Retrieved October 30, 2011.
- ^ «Microsoft switches to File Explorer name in Windows 8, bids farewell to Windows Explorer». The Verge. June 29, 2012. Archived from the original on August 17, 2012. Retrieved August 3, 2012.
- ^ «How to open UWP File Explorer on Windows 10 – Step by step». Windows Latest. May 7, 2017. Archived from the original on August 24, 2018. Retrieved August 24, 2018.
- ^ «Windows 10 Tip: Unlock the UWP File Explorer – Thurrott.com». Thurrott.com. May 6, 2017. Archived from the original on August 24, 2018. Retrieved August 24, 2018.
- ^ «Inspired by Insiders – Dark Theme in File Explorer». August 8, 2018. Archived from the original on August 12, 2018. Retrieved August 23, 2018.
- ^ «Microsoft updates universal File Explorer with new features in Windows 10 version 1809». Windows Central. Archived from the original on August 25, 2018. Retrieved August 24, 2018.
- ^ «UWP File Explorer has got new features in Windows 10 version 1809». Winaero. August 23, 2018. Archived from the original on August 25, 2018. Retrieved August 24, 2018.
- ^ «Windows 10 version 1909: new and changed features — gHacks Tech News». www.ghacks.net. October 2019. Archived from the original on October 25, 2019. Retrieved October 25, 2019.
- ^ Warren, Tom (March 15, 2022). «Microsoft says Windows 11’s File Explorer ads were ‘not intended to be published externally’«. The Verge. Retrieved July 28, 2022.
- ^ Warren, Tom (April 5, 2022). «Windows 11’s refreshed File Explorer gets tabs, favorites, and a new homepage». The Verge. Retrieved August 12, 2022.
- ^ Warren, Tom (October 18, 2022). «Windows 11’s new tabbed File Explorer and taskbar improvements are available today». The Verge. Retrieved October 18, 2022.
- ^ ShellExView v1.19 – Shell Extensions Manager for Windows, archived from the original on October 24, 2010, retrieved March 31, 2008
- ^ «Thumbnail Handlers (Windows)». msdn.microsoft.com. Archived from the original on June 19, 2018. Retrieved June 19, 2018.
- ^ a b Rensin, Dave (January 2004). «Create Namespace Extensions for Windows Explorer with the .NET Framework». msdn.microsoft.com. Archived from the original on May 8, 2008. Retrieved March 31, 2008.
- ^ «Microsoft Download Center: Windows, Office, Xbox & More». www.microsoft.com. Archived from the original on May 13, 2008. Retrieved June 19, 2018.
- ^ «MSDN Magazine Issues». msdn.microsoft.com. Archived from the original on May 21, 2008. Retrieved June 19, 2018.
- ^ Zhang, Junfeng (November 18, 2005). «Don’t do Shell Extension Handlers in .NET». msdn.com. Archived from the original on January 5, 2010. Retrieved June 19, 2018.
External links[edit]
- Sullivan, Kent. «The Windows 95 User Interface: A Case Study in Usability Engineering» (1996) for Association for Computing Machinery. (Sullivan was a developer on the Windows 95 UI team)
- How To Customize the Windows Explorer Views in Windows XP
- MSDN: Creating Shell Extension Handlers, Windows Dev Center, May 31, 2018
- The Complete Idiot’s Guide to Writing Shell Extensions, by Michal Dunn, March 15, 2006
- Namespace extensions – the undocumented Windows Shell, by Henk Devos, November 30, 1999
Тестовые
задания по дисциплине «Информатика»
для
специальности 31.02.01 Лечебное дело 1 курс
1. Основными понятиями и объектами Windows
не являются…
а) Рабочий стол.
б) Мой компьютер
в) Принтер
г) Панель задач.
2. Для того чтобы вынести контекстное меню объекта…
а) Щелкнуть правой кнопкой мыши.
б) Щелкнуть левой кнопки мыши.
в) Щелкнуть средней кнопки мыши.
г) Нет правильного ответа
3. Файл, содержащий ссылку на
представляемый объект:
а) документ
б) папка
в) ярлык
г) приложение
4. Меню, которое появляется при нажатии на
кнопку Пуск:
а) главное меню
б) контекстное меню
в) основное меню
г) системное меню
5. Меню для данного объекта
появляется при щелчке на правую кнопку:
а) главное меню
б) контекстное меню
в) основное меню
г) системное меню
6. Как включить на клавиатуре все заглавные
буквы?
а) Alt + Ctrl
б) Caps Lock
в) Shift + Ctrl
г) Shift + Ctrl + Alt
7. Какую последовательность действий надо
выполнить для запуска калькулятора в Windows?
а) Стандартные → Калькулятор
б) Пуск → Программы → Стандартные → Калькулятор
в) Пуск → Стандартные → Калькулятор
г) Пуск → Калькулятор
8. Что было первым вычислительным инструментом у человека?
а) лица
б) спицы
в) счеты
г) пяльцы
9. Как называется программа файловый менеджер, входящая в состав операционной среды
Windows?
а) Проводник
б) Сопровождающий
в) Менеджер файлов
г) Windows commander
10. Чем отличается значок папки от ярлыка?
а) Признак ярлыка – узелок в левом нижнем
углу значка, которым он «привязывается» к объекту
б) Значок ярлыка крупнее всех остальных
значков
в) На значке ярлыка написана буква
«Я»
г) Признак ярлыка –
маленькая стрелка в левом нижнем углу значка
11. Для того, чтобы найти файл в компьютере
надо нажать?
а) Пуск → Найти →
Файлы и папки
б) Пуск → Файлы и папки
в) Найти → Файл
г) Пуск → Файл → Найти
12. С какой целью производится выделение
объектов?
а) С целью группировки и создания
тематической группы
б) С целью последующего изменения их
внешнего вида (изменения размера, вида значка и др.
в) С целью их сортировки
г) С тем, чтобы произвести
с ними какие-либо действия (открыть, скопировать, переместить и др.)
13. Windows – это:
а) Графическая программа
б) Операционная
система
в) Текстовый редактор
г) Окно
14. Экран монитора называют:
а) Окно Windows
б) Рабочий стол
в) Панель Windows
г) Обои Windows
15. Корзина служит для:
а) Хранения и сортировки файлов
б) Хранения
удаленных файлов
в) Хранения созданных документов
г) Хранения фотографий
16. Для запуска программы
необходимо:
а) Щелкнуть левой кнопкой мыши по значку на
рабочем столе
б) Двойной щелчок
левой кнопкой мыши по значку на рабочем столе
в) Двойной щелчок правой кнопкой мыши по
значку на рабочем столе
г) Щелкнуть правой кнопкой мыши по значку на
рабочем столе
17. Для переключения в другую программу необходимо:
а) Пуск → Программы → (Нужная программа)
б) Alt+Tab
в) Щелчок по программе в панели задач
г) Ctrl+ Esc
18. Свернуть окно:
а) Щелкнуть по кнопке
б) Щелкнуть по кнопке
в) Сократить окно до значка в панели задач
г) Щелкнуть по кнопке
19. Развернуть окно:
а) Щелкнуть по кнопке
б) Щелкнуть по кнопке
в) Щелкнуть по кнопке
г) Щелкнуть по кнопке
20. Восстановить окно:
а) Щелкнуть по кнопке
б) Щелкнуть по кнопке
в) Щелкнуть по кнопке
г) Щелкнуть по кнопке
21. Закрыть окно:
а) Щелкнуть по кнопке
б) Щелкнуть по кнопке
в) Нажать Ctrl+F6
г) Нажать Alt+F4
22. Клавиатура – это:
а) Устройство вывода информации
б) Устройство ввода
алфавитно-цифровой информации
в) Устройство управления
г) Один из блоков Персонального компьютера
23. Клавиша Enter:
а) Клавиша Отмены
б) Клавиша ввода
в) Перенос курсора на
следующий абзац
г) Перенос курсора на следующую строку
24. К
стандартным программам Windows относятся:
а) Write
б) Word
в) Excel
г) Калькулятор
25.
Каково назначение клавиатурной клавиши PrintScreen?
a) Распечатать активное окно
б) Копировать
изображение экрана в буфер
в) Печать содержимого экрана на принтер
г) Обновить содержимое экрана
26.
Устройствами вывода данных являются
а)
плоттер б) процессор в) блок питания г) монитор д) сканер
a) а, г
б) б, г, д
в) в, г
г) в, г, д
27.
Несмежные файлы можно выделить с помощью нажатия………
a) клавиши Ctrl и правой клавиши мыши
б) клавиши Alt и левой клавиши мыши
в) клавиши Ctrl и
левой клавиши мыши
г) клавиши Shift и правой клавиши мыши
28. Из чего
состоит имя файла?
a)
Только из набора символов латинского алфавита
б)
Из имени и расширения
в)
Из набора символов русского или латинского алфавита
г)
Из понятного процессору набора двоичных кодов
29. В
минимальный состав компьютера входят:
а) винчестер, «мышь», процессор;
б) монитор, системный
блок, клавиатура;
в) принтер, клавиатура, CD—ROM;
г) системный блок, сканер, монитор
30. Какие функции выполняет операционная система?
a) организация
диалога с пользователем, управления аппаратурой и ресурсами компьютера
б) все перечисленные варианты
в) подключение устройств ввода/вывода
г) организация обмена данными между компьютером и
различными периферийными устройствами
31.
Какие виды оформления шрифта не присутствуют в текстовом редакторе
a) тонкий
б) подчеркнутый
в) курсивный
г) полужирный
32.
Какой вид оформления абзацев не присутствует в текстовом редакторе
a) Выравнивание по левому краю
б) По правому краю
в) по середине
г) по центру
33.
В текстовом редакторе стиль документа это:
a) формат абзаца и формат символов
б) только формат абзаца
в) Набор используемых шрифтов в тексте
г) внешний вид
документа, начиная с заголовка
34.
В текстовом редакторе невозможно применить форматирование к…
a) рисунку
б) номеру страницы
в) имени файла
г) колонтитулу
29.
Колонтитул — это
a) первая буква абзаца
б) первая строка абзаца
в) заголовочные
данные, помещаемые сверху или снизу страницы в области нижнего или верхнего
поля
г) пояснение к тексту, библиографическая справка, перевод,
толкование, помещаемые в нижние части полосы страницы
30.
Какой список называется «маркированным»:
a) каждая строка помечена красной строкой и буквой
б) каждая строка
начинается с определенного символа
в) каждая строка помечена красной строкой и цифрой
г) такого списка нет
31.
Что такое Times New Roman
a) имя стиля
б) гарнитура шрифта
в) формат абзаца
г) кегель шрифта
32.
Клавишу Enter при наборе документа в MS Word нажимают
a) для проверки правописания
б) в конце каждой строки
в) в конце абзаца
г) в конце предложения
33. С помощью какого значка на рабочем столе
запускается программа Word?
а) б)
в)
г)
34. Как называется эта строка?
а) строка состояния
б) строка меню
в) строка заголовка
г) панель
инструментов
35. Какая вкладка является первой в окне
программы Microsoft Word 2010?
а) главная
б) файл
в) разметка страницы
г) вставка
36. Чтобы создать новый документ в программе Microsoft
Word 2010 надо открыть вкладку:
а) Файл
б) Главная
в)
Вставка
г) Разметка
страницы
37. Какая вкладка отвечает за настройку
параметров страницы?
а) Главная
б) Вставка
в) Разметка страницы
г) Макет
38. Какой ориентации листа нет?
а) Книжная
б) Журнальная
в) Альбомная
39. С помощью какой вкладки можно вставить
Таблицу?
а) Главная
б) Вставка
в) Разметка
страницы
г) Файл
40. Если
вы хотите сохранить измененный документ вторично под тем же названием
необходимо выбрать команду:
а) Сохранить
б) Открыть
в) Сохранить как
г) Открыть
1.1 Назначение и особенности использования файловых менеджеров
Файловый
менеджер (англ. file
manager)
– компьютерная программа,
предоставляющая интерфейс
пользователя для
работы с файловой
системой и файлами.
Файловый менеджер позволяет выполнять
наиболее частые операции над файлами
– создание, открытие/проигрывание/просмотр,
редактирование, перемещение, переименование,
копирование, удаление, изменение
атрибутов и свойств, поиск файлов и
назначение прав. Помимо основных функций,
многие файловые менеджеры включают ряд
дополнительных возможностей, например,
таких как работа с сетью (через FTP, NFSи
т. п.), резервное копирование,
управление принтерами и
пр.
Файловые
менеджеры обеспечивают более удобный
и наглядный способ общения с ПК по
сравнению с операционной системой (ОС).
Одна из самых известных первых программных
оболочек называлась Norton Commander. Ее
разработал американский программист
Питер Нортон. Файловый менеджер наглядно
показывал на экране всю файловую
структуру компьютера: диски, каталоги
и файлы. С такой программой не надо было
набирать сложные команды MS-DOS в командной
строке. Файлы можно было копировать,
перемещать, разыскивать, удалять,
сортировать, изменять, запускать,
пользуясь всего лишь несколькими
клавишами.
В
настоящее время в операционной системе
Windows имеются средства визуальной работы
с файловой системы: программа Проводник,
отображение объектов непосредственно
в папках и т.п. Однако, несмотря на это,
файловые менеджеры продолжают пользоваться
большой популярностью. Практика
показывает, что это действительно
удобное средство для большого круга
пользователей.
Выделяют
различные типы файловых менеджеров:
1)
навигационные и пространственные –
иногда поддерживается переключение
между этими режимами;
2)
двупанельные – в общем случае имеют
две равноценных панели для списка
файлов, дерева каталогов и т. п.
Таким
образом, файловые менеджеры – специальные
программы, предназначенные для облегчения
общения пользователя с командами
операционной системы. Это программы,
запускаемые под управлением ОС, занимающие
промежуточное положение между ОС и
прикладными программами и служащие для
интеграции прикладных пакетов. Наиболее
распространенные
файловые
менеджеры:
Norton Commander, Volkov Commander, FAR Manager, Widnows3.1, Windows
(Total) Commander и
др.
1.2 Особенности использования свободно-распространяемых программных средств
Свободное
программное обеспечение – широкий
спектр программных
решений,
в которых права пользователя («свободы»)
на неограниченные установку, запуск, а
также свободное использование, изучение,
распространение и изменение
(совершенствование) программ защищены
юридически авторскими
правами при
помощи свободных
лицензий.
В
соответствии с современным законодательством
большинства стран, программный продукт
и его исходный
кодохраняется авторским
правом,
которое даёт авторам и правообладателю
(чаще всего правообладателем является
организация-наниматель автора служебных
произведений),
власть над изменением, распространением,
способом использования и поведением
программы, включая случаи, когда исходный
код опубликован. Сила власти авторских
прав в
современном обществе настолько велика,
что даже изучение или попытки исправления
ошибок программ путёмдизассемблирования могут
преследоваться уголовным
правом.
Чтобы
избавить пользователей программ от
проблем, вызванных перекосом
законодательства об охране результатов
интеллектуальной деятельности в сторону
правообладателя, авторы и правообладатели
могут передать пользователям права на
четыре вышеперечисленные свободы
действий. Это достигается путём выпуска
исходного кода программного обеспечения
на условиях одной из особого рода лицензий,
называемых свободными
лицензиями.
Несмотря на то, что по условиям свободных
лицензий выданные пользователям
разрешения правообладатель отозвать
не может, свои права, гарантированные
законодательством, авторы сохраняют.
Свободное
ПО легко коммерциализируется –
существует множество бизнес-моделей,
где исключена необходимость оплаты
копий программы. Например, высокую
популярность имеет бизнес-модель, когда
предприниматель может заработать за
счёт предоставления услуг технической
поддержки. Правообладателю свободного
кода может быть интересен другой вариант
– реализация программных продуктов на
условиях коммерческой лицензии, в
случае, если клиенту необходимо
интегрировать свободный код
в собственническое
ПО,
но он не желает раскрытия своих разработок.
Для
того, чтобы сохранить модель научного
сотрудничества между разработчиками,
необходимо было обеспечить, чтобы
исходные тексты программ, написанных
разработчиками, оставались доступными
для чтения и критики всему научному
сообществу с сохранением авторства
произведений. Для этого Ричард Столлман,
фотография которого представлена на
рисунке 1, сформулировал понятие свободное
программное обеспечение, в котором
отразились принципы открытой разработки
программ в научном сообществе, сложившемся
в американских университетах в 1970-е
годы.
Столлман
явно сформулировал принципы, они же –
критерии свободного программного
обеспечения. Эти критерии оговаривают
те права, которые авторы свободных
программ передаёт любому пользователю:
1)
программу можно свободно использовать
с любой целью («нулевая свобода»);
2)
можно изучать, как программа работает,
и адаптировать её для своих целей
(«первая свобода»). Условием этого
является доступность исходного текста
программы;
3)
можно свободно распространять копии
программы – в помощь товарищу («вторая
свобода»);
4)
программу можно свободно улучшать
и публиковать свою улучшенную версию
– с тем, чтобы принести пользу всему
сообществу («третья свобода»). Условием
этой третьей свободы является доступность
исходного текста программы и возможность
внесения в них модификаций и исправлений.
Возможность
исправления ошибок и улучшения программ
– самая важная особенность свободного
и открытого программного обеспечения,
что просто невозможно для пользователей
закрытых частных программ даже при
обнаружении в них ошибок и дефектов,
количество которых, как правило,
неизвестно никому.
Только
удовлетворяющая всем четырём перечисленным
принципам программа может считаться
свободной программой, то есть гарантированно
открытой и доступной для модернизации
и исправления ошибок и дефектов, и не
имеющая ограничений на использование
и распространение. Нужно подчеркнуть,
что эти принципы оговаривают только
доступность исходного текста программ
для всеобщего использования, критики
и улучшения, и права пользователя,
получившего двоичный или исходный код
программы, но никак не оговаривают
связанные с распространением программ
денежные отношения, в том числе не
предполагают и бесплатности. В англоязычных
текстах здесь часто возникает путаница,
поскольку слово «free» по-английски
означает не только «свободное», но и
«бесплатное» и нередко употребляется
по отношению к бесплатному программному
обеспечению, которое распространяется
без взимания платы за использование,
но которое недоступно для изменения
сообществом, потому что его исходные
тексты не опубликованы. Такое бесплатное
ПО вовсе не является свободным. Наоборот,
свободное ПО вполне можно распространять
(и распространяют), взимая при этом
плату, однако, соблюдая при этом критерии
свободы: каждому пользователю
предоставляется право получить исходные
тексты программ без дополнительной
платы (за исключением цены носителя),
изменять их и распространять далее.
Всякое программное обеспечение,
пользователям которого не предоставляется
такого права, является несвободным –
независимо от любых других условий.
Соседние файлы в предмете [НЕСОРТИРОВАННОЕ]
- #
- #
- #
- #
- #
24.12.2018420.86 Кб1Инфа ответы, .doc
- #
- #
- #
- #
- #
- #
Представляю ТОП 10 лучших файловых менеджеров для операционной системы Windows. При составлении списка, в расчет принимались только файловые менеджеры с графическим интерфейсом, с которыми удобно работать большинству пользователей. Поэтому здесь отсутствую файловые менеджеры c текстовым интерфейсом, например FAR Manager или Midnight Commander.
Вне списка лучших файловых менеджеров оказались программы, которые давно не обновлялись, например, EF Commander, ViewFD, или менее известные приложения: FileVoyager, Tablacus Explorer, muCommander, One Commander и т. д.
Программа файловый менеджер («файловый командир») предназначена для работы с файлами, дисками и папками на компьютере. В основном, в подобных программах выполняются рутинные операции по копированию, переносу или удалению файлов, открытие папок и файлов, запуск приложений.
В операционной системе Windows установлен файловый менеджер по умолчанию — Проводник. Многих пользователей не удовлетворяют функциональные возможности стандартного файлового менеджера, поэтому для работы на компьютере они используют другие альтернативные файловые менеджеры.
Большинство из представленных программ работает только на платформе Windows, но среди них есть и мультиплатформенные приложения.
Total Commander
Total Commander — один из лучших, самый популярный альтернативный двухпанельный файловый менеджер для Windows (еще поддерживается Android). Total Commander ранее назывался Windows Commander.
В Total Commander можно выполнить различные операции с файлами, в приложении настраиваемое меню и внешний вид, встроен FTP клиент с поддержкой защищенного соединения, работа с архивами собственными средствами, пакетный режим работы, расширенный поиск с возможностью использования регулярных выражений и множество других функций.
Возможности программы Total Commander значительно расширяются с помощью скриптов и многочисленных плагинов.
Total Commander работает на русском языке, программу создал разработчик из Швейцарии — Кристиан Гислер. Программа платная, но может работать бесплатно.
SpeedCommander
SpeedCommander — двухпанельный файловый менеджер с огромным набором возможностей для работы с файлами. Окно SpeedCommander можно разделить на две части в горизонтальном или вертикальном положении.
В SpeedCommander встроена полная поддержка Юникода, реализована поддержка мультивкладочности, виртуальных папок, пакетных операций и макросов. В файловый менеджер встроен просмотрщик для более 80 типов файлов, клиент для подключения по FTP, FTP-SSL, SFTP, встроен текстовый редактор с поддержкой синтаксиса, поддерживаются плагины, расширяющие возможности программы.
Программа работает с 13 типами архивов (распаковка, запаковка), в приложение встроена мощная система шифрования и защита файлов паролем. SpeedCommander может синхронизировать данные в папках, сравнивать данные в папках и файлах, в файловом менеджере есть инструменты для группировки и фильтрации и т. д.
SpeedCommander — платная программа, разработана в Германии (SpeedProject). Для поддержки русского языка необходимо установить русификатор.
oMega Commander
oMega Commander — мощный файловый менеджер с большим количеством полезных функций. Возможности приложения расширяются с помощью плагинов. Программа oMega Commander имеет дружелюбный, полностью настраиваемый интерфейс.
Основные возможности oMega Commander: ленточный интерфейс, перенос, переименование, форматирование лент, открытие файлов в разных программах, цветовая группировка вкладок, закрепление и сохранение вкладок, флажки файлов, подсветка файлов по типу, многооконный интерфейс, список избранных окон, умное копирование, работа с архивами, как с обычными папками, безопасное удаление данных без возможности восстановления, разрезание и склейка файлов, мультифункциональный поиск, встроенный редактор, контроль свободного места и многое другое.
oMega Commander — платная программа с поддержкой русского языка (разработчик — Pylonos.com LLC).
Unreal Commander
Unreal Commander — бесплатный двухпанельный файловый менеджер с широкими функциональными возможностями. Программа в работе и по внешнему виду похожа на Total Commander. В программе Unreal Commander поддерживаются плагины, созданные для Total Commander (кроме плагинов файловой системы).
Unreal Commander умеет синхронизировать папки, поддерживается пакетное переименование файлов, поддерживаются основные типы архивов, встроен FTP клиент, панель расширенного поиска, медиапроигрыватель, реализован предпросмотр файлов в форме эскизов, быстрый просмотр встроенными средствами, проверка контрольных сумм файлов, в приложение встроены утилиты для скачивания и резервного копирования и многое другое.
Разработчик Unreal Commander — Max Diesel. Программа поддерживает русский язык. Для включения полнофункционального режима необходимо получить бесплатный лицензионный ключ.
FreeCommander
FreeCommander — бесплатный мощный двухпанельный (горизонтальная или вертикальная панель) файловый менеджер. Программа поддерживает множество вкладок, но также может работать в однопанельном режиме.
Программа FreeCommander может работать с архивами, проверять контрольные суммы файлов, выполнять сравнение и синхронизацию каталогов, быстрый поиск, в приложение встроена командная консоль DOS, поддерживается групповое переименование файлов, безвозвратное удаление файлов, создание скриншотов и многое другое.
Программу FreeCommander создал разработчик из Польши — Marek Jasinski, приложение работает на русском языке.
Double Commander
Double Commander — бесплатный файловый менеджер с двухоконным интерфейсом. Программа работает на разных платформах (Windows, Linux, macOS, FreeBSD).
В программу Double Commander встроены инструменты для группового переименования файлов и синхронизации, все операции выполняются в фоновом режиме, реализована поддержка вкладок, встроен просмотрщик файлов, просмотр эскизов, работа с архивами, расширенный поиск файлов, в том числе с регулярными выражениями, функция приостановки файловых операций, имеется поддержка некоторых плагинов для Total Commander и т. д.
Программа Double Commander создана коллективом разработчиков из России, которые стремятся создать файловый менеджер, аналогичный по функциональности Total Commander.
Multi Commander
Multi Commander — мощный многооконный двухпанельный файловый менеджер. Кроме выполнения стандартных операций, программа обладает дополнительными функциональными возможностями.
В бесплатной программе Multi Commander реализована поддержка плагинов, работа с архивами, встроены утилиты для работы с изображениями, инструменты для работы с аудиофайлами, есть возможность настройки внешнего вида программы под свои потребности, операции выполняются в фоновом режиме, встроен редактор реестра, клиент FTP, реализована поддержка сценариев и т. д.
Программа Multi Commander работает на русском языке (разработчик — Mathias Svensson).
XYplorer
XYplorer — функциональный файловый менеджер, разработанный в качестве замены Проводнику. Программа имеет две версии: полная версия XYplorer Pro (платная) и версия с ограниченным функционалом XYplorer Free (бесплатная).
В XYplorer поддерживается работа в неограниченном количестве мультивкладок, в приложении настраиваемый интерфейс в однопанельном или двухпанельном режиме, в программу встроено много дополнительных инструментов и функций, есть откат изменений, просмотр мультимедиа файлов, сравнение и переименование файлов, поддержка скриптов и пакетных операций, расчет и отображение размера папок, расширенный поиск, синхронизация между каталогами, просмотр свойств и редактирование тегов файлов, есть возможность присваивать теги и цветовые метки файлам и т. д.
Разработчик XYplorer — Donald Lessau, программа поддерживает русский язык.
Directory Opus
Directory Opus — файловый менеджер, созданный для компьютеров Commodore AMIGA, на которых были установлены свои операционные системы. В дальнейшем, программа стала применяться в качестве альтернативы для Проводника Windows.
Программа Directory Opus имеет настраиваемые панели инструментов, двухпанельный интерфейс с древом папок, реализована возможность замены Проводника, есть возможность изменения цветов интерфейса, присутствует расширенная функция поиска, поиск дубликатов файлов, работает технология виртуальных папок, в приложении можно настроить синхронизацию файлов и папок, работает FTP, реализован просмотр графических файлов, поддерживаются плагины, возможен запуск слайд-шоу и т. п.
Directory Opus — платная программа, разработана в Австралии (GPSoftware), поддерживает русский язык.
Q-Dir
Q-Dir — бесплатный файловый менеджер с необычным четырехпанельным интерфейсом. Пользователь может изменить интерфейс программы, оставив только одно, два или три окна в горизонтальном или вертикальном расположении.
Q-Dir интегрируется с Проводником в контекстное меню, в программу встроена экранная лупа, возможен быстрый переход к избранным папкам, работает цветовое выделение разного типа файлов, программа имеет крошечный размер (менее 2 Мб), и т. д.
Программа Q-Dir работает на русском языке (разработчик из Германии — Nenad Hrg).
Заключение
10 лучших файловых менеджеров: Total Commander, SpeedCommander, oMega Commander, Unreal Commander, FreeCommander, Double Commander, Multi Commander, XYplorer, Directory Opus, Q-Dir могут с успехом заменить Проводник — стандартный файловый менеджер Windows.
Источник
Содержание
- 10 лучших файловых менеджеров для Windows
- Total Commander
- SpeedCommander
- oMega Commander
- Unreal Commander
- FreeCommander
- Double Commander
- Multi Commander
- XYplorer
- Directory Opus
- Выводы статьи
- Файловый менеджер, инструмент для управления файлами в Windows 3.0
- Скачать классический файловый менеджер Windows
- Как использовать диспетчер файлов в Windows 10
- Классический интерфейс полностью на английском языке
- Используйте вкладки вверху для выполнения действий
- Добавление и удаление элементов с панели инструментов
- Как удалить диспетчер файлов Windows
10 лучших файловых менеджеров для Windows
Представляю ТОП 10 лучших файловых менеджеров для операционной системы Windows. При составлении списка, в расчет принимались только файловые менеджеры с графическим интерфейсом, с которыми удобно работать большинству пользователей. Поэтому здесь отсутствую файловые менеджеры c текстовым интерфейсом, например FAR Manager или Midnight Commander.
Вне списка лучших файловых менеджеров оказались программы, которые давно не обновлялись, например, EF Commander, ViewFD, или менее известные приложения: FileVoyager, Tablacus Explorer, muCommander, One Commander и т. д.
Программа файловый менеджер («файловый командир») предназначена для работы с файлами, дисками и папками на компьютере. В основном, в подобных программах выполняются рутинные операции по копированию, переносу или удалению файлов, открытие папок и файлов, запуск приложений.
В операционной системе Windows установлен файловый менеджер по умолчанию — Проводник. Многих пользователей не удовлетворяют функциональные возможности стандартного файлового менеджера, поэтому для работы на компьютере они используют другие альтернативные файловые менеджеры.
Большинство из представленных программ работает только на платформе Windows, но среди них есть и мультиплатформенные приложения.
Total Commander
Total Commander — один из лучших, самый популярный альтернативный двухпанельный файловый менеджер для Windows (еще поддерживается Android). Total Commander ранее назывался Windows Commander.
В Total Commander можно выполнить различные операции с файлами, в приложении настраиваемое меню и внешний вид, встроен FTP клиент с поддержкой защищенного соединения, работа с архивами собственными средствами, пакетный режим работы, расширенный поиск с возможностью использования регулярных выражений и множество других функций.
Возможности программы Total Commander значительно расширяются с помощью скриптов и многочисленных плагинов.
Total Commander работает на русском языке, программу создал разработчик из Швейцарии — Кристиан Гислер. Программа платная, но может работать бесплатно.
SpeedCommander
SpeedCommander — двухпанельный файловый менеджер с огромным набором возможностей для работы с файлами. Окно SpeedCommander можно разделить на две части в горизонтальном или вертикальном положении.
В SpeedCommander встроена полная поддержка Юникода, реализована поддержка мультивкладочности, виртуальных папок, пакетных операций и макросов. В файловый менеджер встроен просмотрщик для более 80 типов файлов, клиент для подключения по FTP, FTP-SSL, SFTP, встроен текстовый редактор с поддержкой синтаксиса, поддерживаются плагины, расширяющие возможности программы.
Программа работает с 13 типами архивов (распаковка, запаковка), в приложение встроена мощная система шифрования и защита файлов паролем. SpeedCommander может синхронизировать данные в папках, сравнивать данные в папках и файлах, в файловом менеджере есть инструменты для группировки и фильтрации и т. д.
SpeedCommander — платная программа, разработана в Германии (SpeedProject). Для поддержки русского языка необходимо установить русификатор.
oMega Commander
oMega Commander — мощный файловый менеджер с большим количеством полезных функций. Возможности приложения расширяются с помощью плагинов. Программа oMega Commander имеет дружелюбный, полностью настраиваемый интерфейс.
Основные возможности oMega Commander: ленточный интерфейс, перенос, переименование, форматирование лент, открытие файлов в разных программах, цветовая группировка вкладок, закрепление и сохранение вкладок, флажки файлов, подсветка файлов по типу, многооконный интерфейс, список избранных окон, умное копирование, работа с архивами, как с обычными папками, безопасное удаление данных без возможности восстановления, разрезание и склейка файлов, мультифункциональный поиск, встроенный редактор, контроль свободного места и многое другое.
oMega Commander — платная программа с поддержкой русского языка (разработчик — Pylonos.com LLC).
Unreal Commander
Unreal Commander — бесплатный двухпанельный файловый менеджер с широкими функциональными возможностями. Программа в работе и по внешнему виду похожа на Total Commander. В программе Unreal Commander поддерживаются плагины, созданные для Total Commander (кроме плагинов файловой системы).
Unreal Commander умеет синхронизировать папки, поддерживается пакетное переименование файлов, поддерживаются основные типы архивов, встроен FTP клиент, панель расширенного поиска, медиапроигрыватель, реализован предпросмотр файлов в форме эскизов, быстрый просмотр встроенными средствами, проверка контрольных сумм файлов, в приложение встроены утилиты для скачивания и резервного копирования и многое другое.
Разработчик Unreal Commander — Max Diesel. Программа поддерживает русский язык. Для включения полнофункционального режима необходимо получить бесплатный лицензионный ключ.
FreeCommander
FreeCommander — бесплатный мощный двухпанельный (горизонтальная или вертикальная панель) файловый менеджер. Программа поддерживает множество вкладок, но также может работать в однопанельном режиме.
Программа FreeCommander может работать с архивами, проверять контрольные суммы файлов, выполнять сравнение и синхронизацию каталогов, быстрый поиск, в приложение встроена командная консоль DOS, поддерживается групповое переименование файлов, безвозвратное удаление файлов, создание скриншотов и многое другое.
Программу FreeCommander создал разработчик из Польши — Marek Jasinski, приложение работает на русском языке.
Double Commander
Double Commander — бесплатный файловый менеджер с двухоконным интерфейсом. Программа работает на разных платформах (Windows, Linux, macOS, FreeBSD).
В программу Double Commander встроены инструменты для группового переименования файлов и синхронизации, все операции выполняются в фоновом режиме, реализована поддержка вкладок, встроен просмотрщик файлов, просмотр эскизов, работа с архивами, расширенный поиск файлов, в том числе с регулярными выражениями, функция приостановки файловых операций, имеется поддержка некоторых плагинов для Total Commander и т. д.
Программа Double Commander создана коллективом разработчиков из России, которые стремятся создать файловый менеджер, аналогичный по функциональности Total Commander.
Multi Commander
Multi Commander — мощный многооконный двухпанельный файловый менеджер. Кроме выполнения стандартных операций, программа обладает дополнительными функциональными возможностями.
В бесплатной программе Multi Commander реализована поддержка плагинов, работа с архивами, встроены утилиты для работы с изображениями, инструменты для работы с аудиофайлами, есть возможность настройки внешнего вида программы под свои потребности, операции выполняются в фоновом режиме, встроен редактор реестра, клиент FTP, реализована поддержка сценариев и т. д.
Программа Multi Commander работает на русском языке (разработчик — Mathias Svensson).
XYplorer
XYplorer — функциональный файловый менеджер, разработанный в качестве замены Проводнику. Программа имеет две версии: полная версия XYplorer Pro (платная) и версия с ограниченным функционалом XYplorer Free (бесплатная).
В XYplorer поддерживается работа в неограниченном количестве мультивкладок, в приложении настраиваемый интерфейс в однопанельном или двухпанельном режиме, в программу встроено много дополнительных инструментов и функций, есть откат изменений, просмотр мультимедиа файлов, сравнение и переименование файлов, поддержка скриптов и пакетных операций, расчет и отображение размера папок, расширенный поиск, синхронизация между каталогами, просмотр свойств и редактирование тегов файлов, есть возможность присваивать теги и цветовые метки файлам и т. д.
Разработчик XYplorer — Donald Lessau, программа поддерживает русский язык.
Directory Opus
Directory Opus — файловый менеджер, созданный для компьютеров Commodore AMIGA, на которых были установлены свои операционные системы. В дальнейшем, программа стала применяться в качестве альтернативы для Проводника Windows.
Программа Directory Opus имеет настраиваемые панели инструментов, двухпанельный интерфейс с древом папок, реализована возможность замены Проводника, есть возможность изменения цветов интерфейса, присутствует расширенная функция поиска, поиск дубликатов файлов, работает технология виртуальных папок, в приложении можно настроить синхронизацию файлов и папок, работает FTP, реализован просмотр графических файлов, поддерживаются плагины, возможен запуск слайд-шоу и т. п.
Directory Opus — платная программа, разработана в Австралии (GPSoftware), поддерживает русский язык.
Q-Dir — бесплатный файловый менеджер с необычным четырехпанельным интерфейсом. Пользователь может изменить интерфейс программы, оставив только одно, два или три окна в горизонтальном или вертикальном расположении.
Q-Dir интегрируется с Проводником в контекстное меню, в программу встроена экранная лупа, возможен быстрый переход к избранным папкам, работает цветовое выделение разного типа файлов, программа имеет крошечный размер (менее 2 МБ), и т. д.
Программа Q-Dir работает на русском языке (разработчик из Германии — Nenad Hrg).
Выводы статьи
10 лучших файловых менеджеров: Total Commander, SpeedCommander, oMega Commander, Unreal Commander, FreeCommander, Double Commander, Multi Commander, XYplorer, Directory Opus, Q-Dir могут с успехом заменить Проводник — стандартный файловый менеджер Windows.
Источник
Еще в золотой век 90-х годов старейшие из них помнили такое приложение, как File Manager, которое Windows файловый менеджер в то время. С тех пор многое произошло, но немало пользователей упускают этот эффективный инструмент. и это то, что File Explorer что Microsoft позже включенный в его операционную систему, не имеет слишком много последователей. Если вы пережили те времена, теперь вы можете использовать диспетчер файлов Windows 3.0 на своем компьютере с Windows 10.
Файловый менеджер, инструмент для управления файлами в Windows 3.0
Этот классический файловый менеджер имеет дизайн, который может напоминать нам о том, что впоследствии стало нынешним проводником Windows. В нем есть два столбца, в которых мы можем видеть в виде дерева все папки и файлы, размещенные на нашем компьютере. В верхней части мы могли получить доступ и изменить устройство, изменить вид файлов или выполнить различные операции с файлами.
Скачать классический файловый менеджер Windows
Мы можем бесплатно скачать его из Microsoft Store, перейдя по ссылке ниже. Будет необходимо только получить доступ с помощью нашей учетной записи Microsoft, чтобы она загружалась и устанавливалась автоматически.
Как использовать диспетчер файлов в Windows 10
После того, как Windows позаботится о загрузке и установке приложения, все, что вам нужно сделать, это нажать кнопку «Пуск», чтобы запустить его. Интерфейс нового файлового менеджера появится сразу же, и он в основном тот же, что мы видели в начале девяностых годов под управлением Windows 3.0. Мы сможем выполнять все задачи прошлых лет, такие как упорядочивание файлов с помощью кнопок на панели инструментов, управление дисками и каталогами в различных подокнах, а также форматирование диска. Все это при совместимости с более современными утилитами, такими как 64-битные окна совместимость, сочетания клавиш и длинные имена файлов.
Классический интерфейс полностью на английском языке
Весь интерфейс приложения полностью на английском языке, без возможности выбрать испанский в качестве языка, хотя все функции более или менее понятны. Вверху мы находим панель инструментов в виде вкладок с параметрами «Файл», «Диск», «Дерево», «Просмотр», «Параметры», «Окно» и «Справка». Чуть ниже у нас есть возможность выбирать между различными жесткими дисками, которые у нас есть.
В окне слева он показывает нам древовидный список папок, составляющих жесткий диск, которые мы можем развернуть, чтобы выбрать различные подпапки. Все содержимое папки можно просмотреть в правом столбце. Как могло быть иначе, каждая папка представлена значком желтого цвета, а каждый файл представляет собой белый документ.
Используйте вкладки вверху для выполнения действий
На вкладке «Диск» мы можем выполнять некоторые операции, связанные с нашим жестким диском, такие как копирование диска, маркировка диска, форматирование, подключение и отключение от сетевого диска и выбор диска. Если мы перейдем на вкладку «Просмотр», это позволит нам изменить вид каталогов, имея возможность выбирать между деревом и видом каталогов, только деревом или только каталогом. Мы также можем отсортировать контент по имени, типу, размеру, дате и дате пересылки.
Добавление и удаление элементов с панели инструментов
Если мы перейдем в раздел Опции, мы найдем возможность настройка панели задач с помощью нажав на «Настроить панель инструментов». Если мы щелкнем по нему, появится новое окно (любопытно, что это, если оно отображается на испанском языке). В нем мы можем видеть кнопки, доступные с левой стороны, и кнопки панели инструментов с правой стороны. Таким образом, если мы выберем кнопку слева и нажмем кнопку «Добавить», они будут автоматически добавлены на панель инструментов. Точно так же мы можем удалить любую кнопку, которая нас не интересует, выбрав ее в правом столбце и нажав кнопку «Удалить». Если в любой момент мы захотим оставить конфигурацию, которая отображается по умолчанию, необходимо только нажать кнопку «Сброс».
Как удалить диспетчер файлов Windows
В случае, если диспетчер файлов Windows является для нас чем-то более анекдотическим, чем полезным, у нас всегда есть возможность удалить приложение. Для этого мы должны получить доступ к меню «Конфигурация». Мы можем получить доступ к меню настроек, используя сочетание клавиш «Windows + I». Когда появится окно «Настройки», щелкните вкладку «Приложения».
В меню «Приложения» щелкните в правом столбце вкладку «Приложения и функции». Теперь в правой части экрана мы должны прокрутить вниз. Здесь мы должны найти приложение «Диспетчер файлов Windows» и щелкнуть по нему. Наконец, мы нажимаем кнопку «Удалить», чтобы полностью удалить его с жесткого диска.
Источник
Содержание
- 2xExplorer 1.4.1.12
- AccelMan 3.0.0.3250
- Directory Opus 8.2.2.2
- EF Commander 5.50
- FAR 1.7
- File Ant 20050830
- Frigate 3.33
- Sky Commander 1.6.8.702
- Speed Commander 11.1
- Total Commander 6.53
- Сводная таблица
2xExplorer 1.4.1.12
Официальный сайт: http://netez.com/2xExplorer
2xExplorer 1.4.1.12
Как назывался ваш первый файловый менеджер? Если в прошлом десятилетии можно было смело ожидать ответ «Norton Commander», то сегодня знакомство с файловой структурой чаще всего начинается с Проводника Windows. 2xExplorer во многом повторяет концепцию стандартного инструмента Windows, при этом имея массу дополнительных полезных функций.
Сразу стоит отметить небольшой размер дистрибутива и бесплатный статус программы. Оба эти фактора делают 2xExplorer максимально доступным.
Файловый менеджер, имея поддержку множества горячих клавиш, позволяет осуществлять управление только с клавиатуры. Для часто используемых папок можно назначать собственные клавиатурные сочетания. Разработчики уделили пристальное внимание просмотру и изменению файлов, включив в дистрибутив неплохой редактор. 2xExplorer позволяет создавать миниатюры для BMP и HTML-файлов с целью более удобного просмотра.
Основная часть функций вынесена на панель инструментов, располагающуюся в нижней части рабочего окна приложения.
Использование программы омрачает лишь один факт. Разработка 2xExplorer прекращена несколько лет назад, перспектив улучшения продукта нет.
К содержаниюAccelMan 3.0.0.3250
Официальный сайт: http://www.flexigensoft.com
AccelMan 3.0.0.3250
AccelMan объединяет в себе функции файлового менеджера и программы для просмотра множества различных типов документов. Файловый менеджер содержит полноценный медиа-проигрыватель, текстовый редактор с возможностью подсветки синтаксиса, а также с поддержкой документов, использующих сложное форматирование (RTF, DOC). Рабочее окно AccelMan предоставляет множество полезной информации. В верхней части каждой панели располагается контекстно-зависимое меню. Во время стандартного просмотра папок вы видите список логических дисков. Если переходите в другой режим, то вместе с этим поменяются и элементы меню. Например, если на панели отображается содержимое файла, то вы можете видеть инструменты управления редактированием.
Во время установки AccelMan вы можете импортировать множество пользовательских данных из Total Commander, что заметно облегчает переход с популярнейшего файлового менеджера.
AccelMan понимает несколько типов архивов, в число которых входит TAR, GZIP, ARJ и RAR, а также имеет встроенный ZIP-архиватор. В файловый менеджер встроен инструмент конвертирования графических документов с поддержкой форматов JPEG, TIFF, GIF, PNG и BMP.
При разработке программы учитывается множество факторов. Конечный продукт должен обладать достаточным количеством возможностей, чтобы заинтересовать пользователя, но при этом иметь простой, доступный интерфейс и приемлемую скорость. AccelMan, безусловно, заслуживает самых лестных слов в плане функциональности. Но при этом разработчики забывают о том, что файловый менеджер — это один из самых первых инструментов, устанавливаемых на рабочей станции. Соответственно, программа должна работать максимально быстро и не забивать голову пользователя необходимостью изучения десятков кнопок и пунктов меню. AccelMan — далеко не самая быстрая и интуитивно понятная программа. Ее нужно детально изучать, чтобы получить максимальную выгоду от использования. Впрочем, лицензия позволяет потратить на изучение целый месяц, чтобы самостоятельно сделать окончательный вывод.
К содержаниюDirectory Opus 8.2.2.2
Официальный сайт: http://www.gpsoft.com.au
Directory Opus 8.2.2.2
Файловые менеджеры делятся на две группы — двухпанельные и имеющие вид Проводника Windows. Directory Opus объединяет в себе оба способа представления информации, являясь примером завидной универсальности. Несмотря на огромное количество возможностей, рабочее окно программы не перегружено сложными элементами, Directory Opus легко осваивается даже при наличии только базовых знаний о файловой структуре.
Вы можете выбирать несколько режимов просмотра с помощью вкладок, расположенных в верхней части панелей. В нижней части также имеется подобный элемент, который служит для традиционного переключения между группами панелей.
С помощью Directory Opus вы можете просматривать огромное количество типов документов. Файловый менеджер позволяет подключать плагины, цель которых сводится именно к обеспечению подобного просмотра внутри рабочего окна приложения. В программу встроен небольшой браузер, инструмент просмотра документов MS Office, проигрыватель аудио и видео информации. С помощью Directory Opus можно просматривать большое количество типов графических файлов, включая формат RAW. Стоит заметить, что Directory Opus не имеет встроенных редакторов, все внимание сосредоточено именно на просмотре информации. В целом, все подобные инструменты работают хорошо, однако видеопроигрыватель работает очень медленно, даже обычные фильмы в формате DivX воспроизводятся с сильными рывками. Впрочем, это нельзя считать большим недостатком, ведь мы говорим о файловом менеджере.
Directory Opus позволяет очень гибко настраивать свои панели инструментов, горячие клавиши. В дистрибутив включено большое количество панелей, включающее в себя как управление работой непосредственно файлового менеджера, так и осуществление взаимодействия с внешними инструментами. На каждую кнопку, пункт меню может быть назначено произвольное клавиатурное сочетание.
Вы можете преобразовывать форматы графических файлов, а также управлять яркостью во время просмотра.
При ознакомлении с программой стоит обратить внимание на то, что большинство кнопок на панелях инструментов могут выполнять три функции, в зависимости от того, какой кнопкой мыши их активировать — левой, средней или правой.
К содержаниюEF Commander 5.50
Официальный сайт: http://www.efsoftware.com/cw/e.htm
EF Commander 5.50
EF Commander — один из старейших файловых менеджеров на сегодняшнем рынке. Изначально он был написан в 1994 году для OS/2 и лишь два года спустя портирован в среду Win32.
За долгие годы своего развития программный продукт не превратился в тяжелого монстра, так и оставшись компактной и быстрой программой. Рабочее окно приложения очень напоминает Total Commander, что многим облегчит знакомство, ведь не секрет, что продукт Кристиана Гислера пользуется огромной популярностью среди русскоязычных пользователей.
Между тем, EF Commander обладает мощными средствами просмотра документов, вплоть до HEX-редактора. С помощью плагинов можно осуществлять поддержку дополнительных типов документов. Файловый менеджер понимает более 20 типов архивов.
Вы можете стирать перезаписываемые оптические диски, а также записывать данные на большинство типов болванок. Для корректной работы данных механизмов, необходимо иметь установленный пакет Nero Burning ROM в системе.
EF Commander в свое время был первым файловым менеджером, в котором появился инструмент сопряжения с карманными ПК, на которых установлен Windows CE.
Разработчики дают 30 дней на ознакомление с программой. Знакомство проходит под градом постоянно выскакивающих окон с предложением в десятый, сотый раз согласиться с лицензией и приобрести программу online. Разумеется, необходимо соглашаться, иначе программа закрывается. Согласие дает передышку на несколько минут, после чего снова следует предложение о покупке…
К содержаниюFAR 1.7
Официальный сайт: http://www.rarlab.com/far_manager.htm
FAR 1.7
Легендарные синие текстовые панели впервые появились в Norton Commander. Само слово «нортон» в начале 90-х годов воспринималось как обозначение любого файлового менеджера. Впрочем, немного позже среди русскоязычных пользователей заслуженную популярность завоевал Dos Navigator, обладающий массой новых, по тем временам уникальных возможностей. С приходом Windows 95 и массовым переводом всего программного обеспечения в 32-битную среду старые легенды стали потихоньку забываться.
Александр Рошал, автор архиватора RAR, хотел в то время написать его консольную 32-битную версию. Видимо, дело пошло даже лучше, чем ожидалось, и вместо простой оболочки в стиле RAR для DOS, мы увидели настоящий файловый менеджер, несущий старые, проверенные временем традиции управления файлами.
FAR позволяет работать не только с локальными ресурсами, но и с сетевыми дисками, а также имеет FTP-клиент. В дистрибутив FAR включено несколько дополнительных модулей, позволяющих организовывать временную панель, список системных процессов, редактор реестра, а также инструмент, позволяющий изменять регистры букв в названиях групп файлов.
Отсутствие GUI сильно сковывает возможности файлового менеджера, но, вместе с тем, позволяет ему считаться самым быстрым продуктом данного класса ПО. Однако разработчики и не ставят перед собой задачу наполнения своего продукта массой функций. Вместо этого, FAR позволяет подключать внешние модули, с помощью которых можно выполнять самые неожиданные операции. На странице загрузки плагинов вы можете загрузить базу данных всех доступных модулей, насчитывающих более 600 штук.
FAR бесплатен для пользователей, проживающих на территории xUSSR. Для регистрации запустите файловый менеджер с ключом «-r», введите имя пользователя «xUSSR регистрация», а вместо кода регистрации наберите строчными русскими буквами текущий день недели.
К содержаниюFile Ant 20050830
Официальный сайт: http://www.fileant.com
File Ant 20050830
FileAnt — весьма необычный файловый менеджер для Windows. Во-первых, управление программой с клавиатуры резко отличается от принятых стандартов (F5 — копировать, F7 — создать папку и т.д.). Во-вторых, программа сочетает в себе как дерево каталогов (как Проводник), так и две традиционные панели (Norton Commander).
По умолчанию, программа загружается в системный лоток, откуда ее можно быстро вызывать в любое время. Поддержка архивов по умолчанию осуществляется с помощью установленного в системе 7-zip, который, в свою очередь, понимает множество типов сжатия.
Просмотр документов осуществляется внутри специальной панели, расположенной над списком файлов и каталогов. Если вы просматриваете изображения, то программа может автоматически масштабировать их в пределах панели. При включении режима миниатюр все графические файлы индексируются, и вы можете видеть небольшие копии изображений так же, как в Проводнике.
Файловый менеджер содержит множество мелких необычных функций, например, выделение файлов, имеющих определенный процент от общего объема каталога, сравнение файлов с учетом CRC32, поддержку собственных хранителей экрана и другое.
Во время тестирования FileAnt работал очень нестабильно. Кстати, это единственная программа во всем путеводителе, у которой наблюдались подобные проблемы. Во время попытки посмотреть видео, файловый менеджер зависал через раз. Один раз программа вылетела на ровном месте. И еще одна проблема связана с отображением заголовок вкладок — кириллица не поддерживается.
К содержаниюFrigate 3.33
Официальный сайт: http://www.frigate3.com/rus
Frigate 3.33
Разработчики, отбросив всякую скромность, называют свой продукт «самым функциональным и самым мощным средством работы с файлами». Но не это главное. Важнейшим достоинством Frigate является сохранение простоты освоения при всем богатстве возможностей.
Файловый менеджер позволяет просматривать огромное количество типов документов. Помимо традиционных архивов, текстовых документов, аудио и видео информации, вы можете открывать базы данных (DBF) и электронные таблицы (XLS).
Frigate имеет несколько оригинальных утилит в своем составе, не имеющих аналогов у конкурентов. С помощью калькулятора можно выполнять простейшие арифметические вычисления, блокнот помогает вести заметки, а часы с поддержкой тем оформления помогут не пропустить конец рабочего дня. Кроме того, в файловый менеджер встроена утилита контроля за автоматически запускающимися программами Windows, неплохой браузер, использующий движок Trident (возможно, даже не хуже, чем Internet Explorer), а также собственная консоль.
Поклонникам Total Commander будет приятно узнать, что Frigate поддерживает большинство плагинов легендарного файлового менеджера. Но и среди собственных дополнений можно найти весьма интересные примеры. Например, можно подключить проверку орфографии на русском языке. Работая в текстовом редакторе, вы можете использовать подсветку для множества типов документов (исходные тексты, HTML и другие). Если вы работаете над документом типа HTML, то можете сразу просматривать результат во встроенном браузере. Редактор поддерживает различные кодовые страницы. Frigate позволяет редактировать не только plain-text, но и RTF-документы.
Многие пользователи Total Commander облюбовали возможность запуска приложений прямо из панели инструментов. Frigate выполняет данную задачу несколько иначе. В правой части главного меню располагается панель быстрого запуска. При желании ее можно перенести в любое место. Панель выглядит очень компактно и позволяет сохранить драгоценное место для традиционных инструментов файлового менеджера.
Frigate распространяется в трех вариантах. Облегченный вариант (Lite) можно установить бесплатно и пользоваться без ограничений по времени. Остальные варианты имеют ознакомительный период 30 дней.
К содержаниюSky Commander 1.6.8.702
Официальный сайт: http://www.nmzlabs.com
Sky Commander 1.6.8.702
Sky Commander — молодой и весьма амбициозный проект. За основу файлового менеджера взята концепция Проводника Windows. По умолчанию вы видите довольно крупные значки файлов и папок. Для графических файлов сразу создаются миниатюры.
Файловый менеджер обладает стандартным для программ подобного класса интерфейсом. Панели инструментов настраиваются не очень гибко — вам разрешается лишь выбирать кнопки из строго заданного списка. Очень красиво реализованы подсказки. Вы наводите мышь на произвольную кнопку, и если вызов функции дублируется с помощью сочетания клавиш, то выскакивает окошко, в котором нарисованы кнопки с надписями, аналогичными их маркировке на клавиатуре. При помощи клавиши F11 можно перевести файловый менеджер в полноэкранный режим, в котором не будут отображаться заголовки окна.
При наведении мышью на файл внутри панелей появляется подсказка, кратко раскрывающая его содержание. Для графических файлов отображаются довольно крупные миниатюры, в MP3-файлах показываются теги, а содержание текстовых документов раскрывается с помощью первых двух строк.
Вы можете безопасно удалять свои файлы так, что потом ни одна программа восстановления данных не позволит получить информацию обратно.
Одна из особенностей Sky Commander заключается в наличии пакетного режима работы с архивами. C помощью специального инструмента вы можете указать произвольное количество архивов, а затем выполнить распаковку с помощью одной команды. Кроме того, файловый менеджер позволяет восстанавливать поврежденные ZIP-архивы.
Как было сказано ранее, проект еще очень молодой. Sky Commander еще не успел обрасти огромным количеством функций и в некоторых вопросах уступает конкурентам. С другой стороны, возможности продукта намного выше, чем у Проводника. А ведь многим пользователям достаточно стандартных средств Windows управления файлами. Может быть, и не нужно Sky Commander становиться вторым Фрегатом?
К содержаниюSpeed Commander 11.1
Официальный сайт: http://www.speedproject.de/enu/speedcommander
Speed Commander 11.1
Название программы обещает высокую скорость, однако нельзя сказать, что Speed Commander является чем-то выдающимся в данном аспекте. Расход оперативной памяти весьма значителен, если сравнивать с конкурентами, да и интерфейс, наполненный множеством графических элементов, нельзя однозначно назвать быстрым. Между тем, если проанализировать отзывы пользователей Speed Commander на форумах, то нетрудно обнаружить доминирование положительной риторики.
Первое, на что следует обратить внимание во время ознакомления — это удивительная гибкость настроек всех панелей, горячих клавиш. Вы можете свободного перемещать любые панели, а с помощью правой кнопки мыши вызывать инструмент конфигурирования. Speed Commander позволяет создать кнопку и привязать к ней любую поддерживаемую программой операцию. Вы можете указать свой графический файл для кнопки. Любая операция может дублироваться с помощью сочетания клавиш. Программа поддерживает смену тем оформления, которые, впрочем, не меняют дизайн кнопок, но могут управлять цветовыми и дизайнерскими решениями, затрагивающими панели в целом. Вы можете указывать размер кнопок на панелях.
Speed Commander поддерживает множество типов архивов, причем архивирование может происходить вместе с шифрованием. Вы можете создать архив, зашифровать данные и имена файлов и поставить на него пароль. В Speed Commander имеется встроенная поддержка просмотра около 80 (!) графических и текстовых форматов. Текстовый редактор допускает возможность подсветки синтаксиса.
Метафора быстрого запуска приложений реализована не совсем обычно. На панели инструментов есть кнопка, нажав на которую, вы попадаете в аналог стартового меню Windows. Кроме того, можно назначить кнопки на открытие рабочего стола, элемента «Мой компьютер», системных папок, а также Избранного Internet Explorer.
К счастью, погоня за необычными функциями не привела Speed Commander в разряд сложных, тяжело осваиваемых программ. По крайней мере, пользователю Total Commander, скорее всего, будет казаться, что все элементы расположены логично. Speed Commander во многом похож на программу Кристиана Гислера, о которой и пойдет речь далее.
К содержаниюTotal Commander 6.53
Официальный сайт: http://www.ghisler.com/
Total Commander 6.53
«Пришел, увидел, победил» — сообщал о победе над Понтийским царем Юлий Цезарь. Кристиан Гислер, будучи студентом Университета Берна, в 1993 году написал файловый менеджер. Ему не нравились другие программы. Написал и победил.
Много ли вы помните файловых менеджеров с графическим интерфейсом, написанных во времена царствования Windows 3.x? Вопрос практически риторический. В начале 90-х годов большинство программ подобного класса были рассчитаны на работу в MS DOS. Windows Commander (старое название продукта) фактически стал первой ласточкой, первой программой, использовавшей все преимущества GUI.
Total Commander нельзя назвать самой функциональной, самой красивой или самой быстрой программой данного класса. Причина популярности файлового менеджера кроется в сбалансированности всех составляющих.
Несмотря на то, что в последнее время все больше программ рассчитано на управление с помощью мыши, работа с Total Commander может осуществляться исключительно с помощью клавиатуры, что значительно увеличивает скорость выполнения повторяющихся задач. Файловый менеджер обладает массой мелких возможностей, ставших для многих предметами первой необходимости. «Чем архивировал?» — задается вопрос, «Total Commander» — дается ответ, подразумевающий использование алгоритма ZIP. Навигация по FTP-серверам постепенно стала привычной операцией, без которой работа с файловым менеджером кажется неполноценной. Возможность добавления собственных кнопок на панель инструментов, пакетное переименование файлов, история каталогов и список любимых папок, разбиение и объединение файлов — все это лишь малая часть большого списка возможностей Total Commander. А многое из того, что находится за пределами данного списка, реализовано в виде плагинов.
Как уже было сказано ранее, Total Commander не идеален в плане абсолютных качеств. Frigate обладает более широкими возможностями, Far менее требователен к ресурсам, Speed Commander позволяет более гибко настраивать внешний вид. Может быть, в данном случае работает пословица «лучшее — враг хорошего?»
Стоит обратить внимание на условия распространения программы. Если очень сильно упростить условия всех современных лицензий, то программы бывают либо платными, имея некоторый срок для ознакомления, либо бесплатными. Лицензия Total Commander позволяет вам бесплатно использовать продукт неограниченное количество времени. В этом случае при старте программы отображается окно с предложением купить программу. Вы закрываете его и после этого пользуете полнофункциональной версией файлового менеджера. Заплатив за программу, вы сможете работать с Total Commander без назойливого стартового окна.
К содержаниюСводная таблица
| Размер дистрибутива, МБ | 0.39 | 5.31 | 7.95 | 3.75 | 1.18 | 1.94 | 9.02 | 1.79 | 5.08 | 1.64 |
| Цена | — | 39.95$ | 65.87$ | 25$ | — | 30$ | 300р | 300р | 35$ | 34$ |
| Объем занимаемой оперативной памяти, МБ | 10 | 21 | 23 | 11 | 4 | 8 | 30 | 10 | 18 | 11 |
| GUI | + | + | + | + | — | + | + | + | + | + |
| Вкладки | — | + | + | + | — | + | + | + | + | + |
| FTP | — | — | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| Текстовый редактор | + | + | + | + | + | — | + | + | + | — |
| Просмотр изображений | — | + | + | + | — | + | + | + | + | — |
| Просмотр видео | — | + | + | + | — | + | + | — | + | + |
| Просмотр HTML | — | + | + | + | — | + | + | + | + | + |
| Просмотр RTF | + | + | + | + | — | + | + | + | + | + |
| Просмотр DOC | — | + | + | — | — | — | + | + | + | — |
| HEX-редактор | — | + | — | + | — | — | + | + | — | — |
| Подсветка типов файлов | — | + | + | — | + | — | + | — | — | + |
| Быстрые папки | + | + | + | — | + | — | + | + | + | + |
| История папок | — | + | + | — | + | — | + | + | — | + |
| Панель быстрого запуска | — | — | — | — | — | + | + | — | + | + |
| Плагины | — | — | + | + | + | — | + | — | — | + |
| Многозадачность | — | + | + | + | — | + | + | + | + | + |
| 2xExplorer | |
| AccelMan | |
| Directory Opus | |
| EF Commander | |
| FAR | |
| File Ant | |
| Frigate | |
| Sky Commander | |
| Speed Commander | |
| Total Commander |
Ответ: Проводник Windows известен как файловый менеджер в MS Windows. Объяснение: Проводник ранее назывался проводником Windows, который представляет собой приложение для управления файлами, которое входит в выпуски ОС Microsoft Windows (Операционная система) из Windows 95.
Проводник, ранее известный как Проводник Windows, представляет собой приложение для управления файлами, которое входит в версии операционной системы Microsoft Windows, начиная с Windows 95. Он предоставляет графический пользовательский интерфейс для доступа к файловым системам.
Где находится файловый менеджер Windows?
Чтобы открыть проводник, щелкните значок проводника, расположенный на панели задач. Кроме того, вы можете открыть проводник, нажав кнопку «Пуск», а затем — «Проводник».
Какой файловый менеджер приведите в пример?
Файловый менеджер — это программа, которая помогает пользователю управлять всеми файлами на своем компьютере. Например, все файловые менеджеры позволяют пользователю просматривать, редактировать, копировать и удалять файлы на запоминающих устройствах своего компьютера.
Что такое система управления файлами Windows?
Управление файлами Windows предназначено для обучения управлению файлами и эффективному изменению настроек в операционной системе Windows. Учащийся сможет использовать проводник Windows для создания иерархической структуры папок, а также для перемещения, копирования, переименования и удаления файлов.
Как называется приложение для управления файлами?
Традиционные приложения для управления файлами, такие как File Explorer — де-факто файловый менеджер в Windows — достаточно мощны только для личного использования. Проще говоря, это базовые инструменты, предназначенные для помощи пользователям в управлении файлами и папками на локальных компьютерах.
Каковы свойства файла?
В окне свойств файла отображается такая информация, как тип файла, размер файла и время последнего изменения. Если вам часто нужна эта информация, вы можете отобразить ее в столбцах списка или в заголовках значков.
Каковы 4 категории файлового проводника?
Навигация в проводнике
В верхней части строки меню проводника есть четыре категории: «Файл», «Домашняя страница», «Общий доступ» и «Просмотр».
Как открыть Диспетчер файлов на моем компьютере?
Давайте начнем :
- Нажмите Win + E на клавиатуре. …
- Используйте ярлык проводника на панели задач. …
- Воспользуйтесь поиском Кортаны. …
- Используйте ярлык проводника из меню WinX. …
- Используйте ярлык проводника из меню «Пуск». …
- Запустите explorer.exe. …
- Создайте ярлык и закрепите его на рабочем столе. …
- Используйте командную строку или Powershell.
22 февраля. 2017 г.
В чем смысл файлового менеджера?
Файловый менеджер или файловый браузер — это компьютерная программа, которая предоставляет пользовательский интерфейс для управления файлами и папками. … Папки и файлы могут отображаться в иерархическом дереве на основе их структуры каталогов.
Почему важно управление файлами?
Управление файлами — это процесс администрирования системы, которая правильно обрабатывает цифровые данные. Таким образом, эффективная система управления файлами улучшает общую функцию рабочего процесса. Он также систематизирует важные данные и предоставляет базу данных с возможностью поиска для быстрого поиска.
Какая польза от файлового менеджера файлов?
Кратко объясните использование файлового менеджера Files и его компонентов. Ответ: Файловый менеджер файлов используется для просмотра файлов и папок. Он используется для доступа и организации файлов и папок, хранящихся на компьютере. На левой панели браузера файлов с заголовком «Места» отображаются наиболее часто используемые папки.
Какие бывают типы управления файлами?
6 Лучшая система управления файлами
- PDFelement для бизнеса. PDFelement для бизнеса — это один из его видов по функциям, управляемости и простоте использования. …
- Agiloft. Agiloft отлично подходит для управления большими корпоративными документами. …
- Альфреско Один. …
- Кабинет. …
- Контентверс. …
- Цифровой ящик.
Что такое файловая система и ее типы?
Существует несколько типов файловых систем с разными логическими структурами и свойствами, такими как скорость и размер. Тип файловой системы может различаться в зависимости от ОС и потребностей этой ОС. Три наиболее распространенных операционных системы для ПК — это Microsoft Windows, Mac OS X и Linux.