Самый простой способ вставить в командную строку путь к файлу или папке
Сталкиваясь с необходимостью выполнить какую-нибудь операцию в командной строке, начинающие пользователи очень скоро понимают, что возможности этого инструмента в отношении привычного copy-paste весьма ограничены. Командная строка не поддерживает работу с комбинациями Ctrl+C и Ctrl+V, копировать и вставлять текст в окошко консоли можно с помощью контекстного меню, вызываемого правой кликом правой клавишей мыши.
При работе с командной строкой Windows очень часто приходится переходить из одного каталога в другой, это понятно. Вот и получается так, что некоторые пользователи только ради того чтобы попасть в нужный каталог на жестком диске вручную прописывают в консоли длиннющие пути. Удовольствия при этом они явно не испытывают и это понятно почему. Во-первых, на это уходит драгоценное время, во-вторых, при ручном наборе адреса всегда имеется риск допустить ошибку.
Конечно, ручному набору есть альтернатива, например можно открыть целевой каталог в Проводнике, зайти в свойства папки или файла, скопировать оттуда полный путь, а затем уже вставить его в окно командной строки. Это уже быстрее и надежнее, но нет ли еще более удобного и быстрого способа? Оказывается есть! Способ этот прост, как и все гениальное. Просто так сложилось, что многие пользователи о нем не знают. А не знают потому, что мало об этом кто говорит.
Не нужно ничего копировать и вставлять, достаточно просто перетащить файл или папку в консоль и путь вставится сам, а если надо, то и кавычки подставятся, так что вам лишь останется нажать Enter.
Это правило действует для всех объектов файловой системы, начиная от логических разделов и заканчивая ярлыками и файлами без расширения. От необходимости использования команд перехода, таких как CD перетаскивание, конечно, не избавляет, но согласись, насколько же это удобнее ручного ввода!
Оцените Статью:

Загрузка…
На чтение 3 мин Просмотров 5.9к. Опубликовано 24.06.2019
Иногда пользователи Windows 10 оказываются в ситуации, требующей от них управления папкой через командную строку. С каждым обновлением компания Microsoft вносит различные изменения в операционную систему, в том числе, в этот процесс, поэтому не все методы, которые работали раньше, актуальны сейчас.
Итак, давайте разберемся, каким образом можно открывать папки в «десятке», используя командую строку.
Содержание
- Использование Проводника
- Как прописать путь к папке в командной строке
- Что делать, если командная строка отсутствует
- Заключение
Использование Проводника
Смотрите также: «Как изменить браузер по умолчанию в Windows 10»
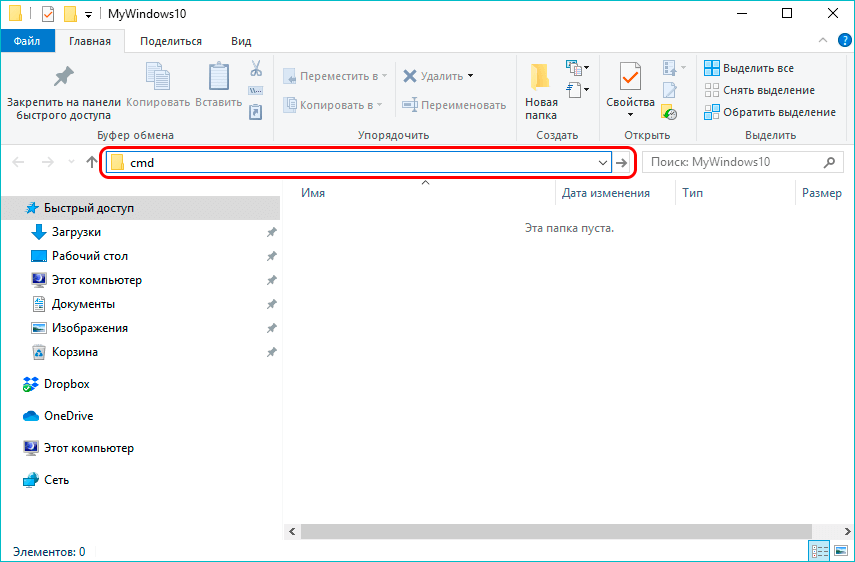
- Открываем желаемую папку в окне Проводника, который можно запустить нажатием клавиш Win+E. Вводим в адресной строке системную команду «cmd» и нажимаем клавишу Enter на клавиатуре.
- После этого откроется окно командной строки с расположением в той папке, которую мы открыли.
Как прописать путь к папке в командной строке
- Открываем командную строку. Сделать этом можно по-разному:
- Далее набираем команду «cd», ставим после нее пробел и пишем путь к желаемому каталогу.
Примечание: можно каждый раз писать «/d«. Разницы между командами «cd C:Music» и «cd /d C:Music» нет
Что делать, если командная строка отсутствует
Смотрите также: «Как узнать лицензионный ключ продукта Windows 10»
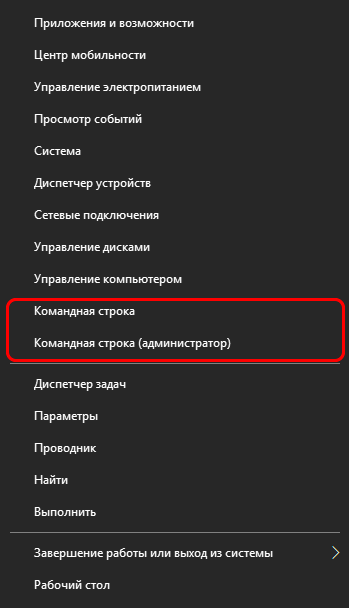
У некоторых пользователей при наличии определенных обновлений системы вместо привычной командной строки в контекстном меню Пуск отображается Windows PowerShell.
По сути, это некая новая оболочка командной строки, которая позволяет вводить те же команды и получать те же самые результаты. Например, команда «cd C:Music«, которую мы рассматривали выше.
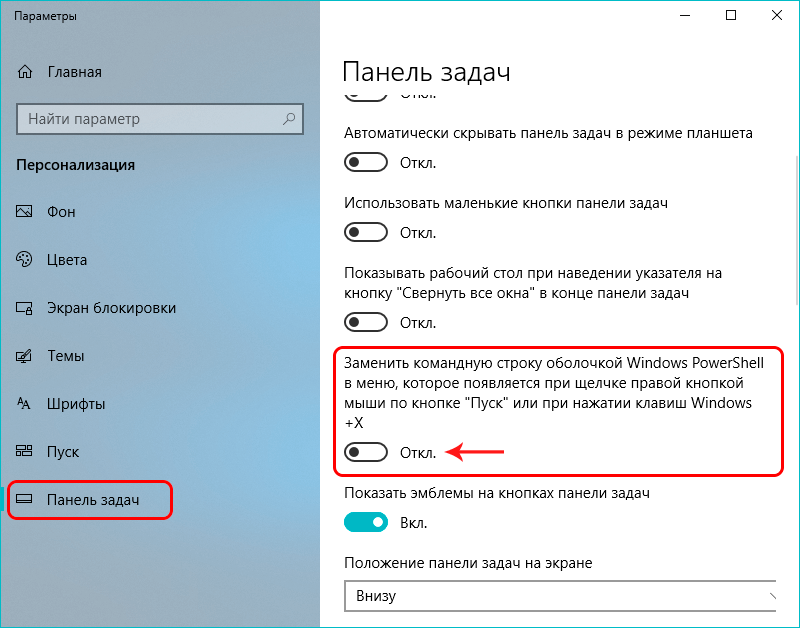
Но если, все же, хочется вернуть привычную нам командную строку, для этого делаем следующее:
- Открываем Параметры панели задач. Попасть в них можно разными способами:
- Пролистав правую часть окна с настройками, выключаем параметр «Заменить командную строку оболочкой Windows Power Shell…».
- Готово, с помощью этого несложного действия нам удалось вернуть командную строку в контекстное меню Пуск.
Заключение
Открытие папок через командную строку — крайне редкое действие, которым, вероятно, большинство пользователей Windows 10 никогда не пользовалось и не будет. Тем не менее, случаи бывают разные, и нелишним будет знать, как это можно сделать, когда вдруг потребуется.
Смотрите также: «Как перевернуть экран на компьютере в Windows 10»
I am trying to add C:xamppphp to my system PATH environment variable in Windows.
I have already added it using the Environment Variables dialog box.
But when I type into my console:
C:>path
it doesn’t show the new C:xamppphp directory:
PATH=D:Program FilesAutodeskMaya2008bin;C:Ruby192bin;C:WINDOWSsystem32;C:WINDOWS;
C:WINDOWSSystem32Wbem;C:PROGRA~1DISKEE~2DISKEE~1;c:Program FilesMicrosoft SQL
Server90Toolsbinn;C:Program FilesQuickTimeQTSystem;D:Program FilesTortoiseSVNbin
;D:Program FilesBazaar;C:Program FilesAndroidandroid-sdktools;D:Program Files
Microsoft Visual StudioCommonToolsWinNT;D:Program FilesMicrosoft Visual StudioCommon
MSDev98Bin;D:Program FilesMicrosoft Visual StudioCommonTools;D:Program Files
Microsoft Visual StudioVC98bin
I have two questions:
- Why did this happen? Is there something I did wrong?
- Also, how do I add directories to my
PATHvariable using the console (and programmatically, with a batch file)?
asked Mar 3, 2012 at 12:58
8
Option 1
After you change PATH with the GUI, close and reopen the console window.
This works because only programs started after the change will see the new PATH.
Option 2
This option only affects your current shell session, not the whole system. Execute this command in the command window you have open:
set PATH=%PATH%;C:yourpathhere
This command appends C:yourpathhere to the current PATH. If your path includes spaces, you do not need to include quote marks.
Breaking it down:
set– A command that changes cmd’s environment variables only for the current cmd session; other programs and the system are unaffected.PATH=– Signifies thatPATHis the environment variable to be temporarily changed.%PATH%;C:yourpathhere– The%PATH%part expands to the current value ofPATH, and;C:yourpathhereis then concatenated to it. This becomes the newPATH.
answered Mar 3, 2012 at 13:03
JimRJimR
15.1k2 gold badges20 silver badges26 bronze badges
12
WARNING: This solution may be destructive to your PATH, and the stability of your system. As a side effect, it will merge your user and system PATH, and truncate PATH to 1024 characters. The effect of this command is irreversible. Make a backup of PATH first. See the comments for more information.
Don’t blindly copy-and-paste this. Use with caution.
You can permanently add a path to PATH with the setx command:
setx /M path "%path%;C:yourpathhere"
Remove the /M flag if you want to set the user PATH instead of the system PATH.
Notes:
- The
setxcommand is only available in Windows 7 and later. -
You should run this command from an elevated command prompt.
-
If you only want to change it for the current session, use set.
StayOnTarget
11k10 gold badges49 silver badges75 bronze badges
answered Feb 28, 2015 at 5:12
NafscriptNafscript
4,9572 gold badges16 silver badges15 bronze badges
15
This only modifies the registry. An existing process won’t use these values. A new process will do so if it is started after this change and doesn’t inherit the old environment from its parent.
You didn’t specify how you started the console session. The best way to ensure this is to exit the command shell and run it again. It should then inherit the updated PATH environment variable.
answered Mar 3, 2012 at 13:23
Hans PassantHans Passant
913k145 gold badges1670 silver badges2507 bronze badges
6
You don’t need any set or setx command. Simply open the terminal and type:
PATH
This shows the current value of PATH variable. Now you want to add directory to it? Simply type:
PATH %PATH%;C:xamppphp
If for any reason you want to clear the PATH variable (no paths at all or delete all paths in it), type:
PATH ;
Update
Like Danial Wilson noted in comment below, it sets the path only in the current session. To set the path permanently, use setx but be aware, although that sets the path permanently, but not in the current session, so you have to start a new command line to see the changes. More information is here.
To check if an environmental variable exist or see its value, use the ECHO command:
echo %YOUR_ENV_VARIABLE%
answered Jul 1, 2015 at 15:11
zarzar
10.9k13 gold badges90 silver badges171 bronze badges
6
I would use PowerShell instead!
To add a directory to PATH using PowerShell, do the following:
$PATH = [Environment]::GetEnvironmentVariable("PATH")
$xampp_path = "C:xamppphp"
[Environment]::SetEnvironmentVariable("PATH", "$PATH;$xampp_path")
To set the variable for all users, machine-wide, the last line should be like:
[Environment]::SetEnvironmentVariable("PATH", "$PATH;$xampp_path", "Machine")
In a PowerShell script, you might want to check for the presence of your C:xamppphp before adding to PATH (in case it has been previously added). You can wrap it in an if conditional.
So putting it all together:
$PATH = [Environment]::GetEnvironmentVariable("PATH", "Machine")
$xampp_path = "C:xamppphp"
if( $PATH -notlike "*"+$xampp_path+"*" ){
[Environment]::SetEnvironmentVariable("PATH", "$PATH;$xampp_path", "Machine")
}
Better still, one could create a generic function. Just supply the directory you wish to add:
function AddTo-Path{
param(
[string]$Dir
)
if( !(Test-Path $Dir) ){
Write-warning "Supplied directory was not found!"
return
}
$PATH = [Environment]::GetEnvironmentVariable("PATH", "Machine")
if( $PATH -notlike "*"+$Dir+"*" ){
[Environment]::SetEnvironmentVariable("PATH", "$PATH;$Dir", "Machine")
}
}
You could make things better by doing some polishing. For example, using Test-Path to confirm that your directory actually exists.
answered Mar 17, 2015 at 20:24
Ifedi OkonkwoIfedi Okonkwo
3,3064 gold badges31 silver badges45 bronze badges
4
Safer SETX
Nod to all the comments on the @Nafscript’s initial SETX answer.
SETXby default will update your user path.SETX ... /Mwill update your system path.%PATH%contains the system path with the user path appended
Warnings
- Backup your
PATH—SETXwill truncate your junk longer than 1024 characters - Don’t call
SETX %PATH%;xxx— adds the system path into the user path - Don’t call
SETX %PATH%;xxx /M— adds the user path into the system path - Excessive batch file use can cause blindness1
The ss64 SETX page has some very good examples. Importantly it points to where the registry keys are for SETX vs SETX /M
User Variables:
HKCUEnvironmentSystem Variables:
HKLMSYSTEMCurrentControlSetControlSession ManagerEnvironment
Usage instructions
Append to User PATH
append_user_path.cmd
@ECHO OFF
REM usage: append_user_path "path"
SET Key="HKCUEnvironment"
FOR /F "usebackq tokens=2*" %%A IN (`REG QUERY %Key% /v PATH`) DO Set CurrPath=%%B
ECHO %CurrPath% > user_path_bak.txt
SETX PATH "%CurrPath%";%1
Append to System PATH
append_system_path.cmd. Must be run as administrator.
(It’s basically the same except with a different Key and the SETX /M modifier.)
@ECHO OFF
REM usage: append_system_path "path"
SET Key="HKLMSYSTEMCurrentControlSetControlSession ManagerEnvironment"
FOR /F "usebackq tokens=2*" %%A IN (`REG QUERY %Key% /v PATH`) DO Set CurrPath=%%B
ECHO %CurrPath% > system_path_bak.txt
SETX PATH "%CurrPath%";%1 /M
Alternatives
Finally there’s potentially an improved version called SETENV recommended by the ss64 SETX page that splits out setting the user or system environment variables.
Example
Here’s a full example that works on Windows 7 to set the PATH environment variable system wide. The example detects if the software has already been added to the PATH before attempting to change the value. There are a number of minor technical differences from the examples given above:
@echo off
set OWNPATH=%~dp0
set PLATFORM=mswin
if defined ProgramFiles(x86) set PLATFORM=win64
if "%PROCESSOR_ARCHITECTURE%"=="AMD64" set PLATFORM=win64
if exist "%OWNPATH%textexmf-mswinbincontext.exe" set PLATFORM=mswin
if exist "%OWNPATH%textexmf-win64bincontext.exe" set PLATFORM=win64
rem Check if the PATH was updated previously
echo %PATH% | findstr "texmf-%PLATFORM%" > nul
rem Only update the PATH if not previously updated
if ERRORLEVEL 1 (
set Key="HKLMSYSTEMCurrentControlSetControlSession ManagerEnvironment"
for /F "USEBACKQ tokens=2*" %%A in (`reg query %%Key%% /v PATH`) do (
if not "%%~B" == "" (
rem Preserve the existing PATH
echo %%B > currpath.txt
rem Update the current session
set PATH=%PATH%;%OWNPATH%textexmf-%PLATFORM%bin
rem Persist the PATH environment variable
setx PATH "%%B;%OWNPATH%textexmf-%PLATFORM%bin" /M
)
)
)
1. Not strictly true
Dave Jarvis
29.9k39 gold badges177 silver badges310 bronze badges
answered Dec 29, 2016 at 12:04
icc97icc97
10.7k8 gold badges69 silver badges88 bronze badges
0
Handy if you are already in the directory you want to add to PATH:
set PATH=%PATH%;%CD%
It works with the standard Windows cmd, but not in PowerShell.
For PowerShell, the %CD% equivalent is [System.Environment]::CurrentDirectory.
answered Mar 18, 2016 at 16:09
nclordnclord
1,2271 gold badge16 silver badges17 bronze badges
2
Aside from all the answers, if you want a nice GUI tool to edit your Windows environment variables you can use Rapid Environment Editor.
Try it! It’s safe to use and is awesome!
answered Feb 17, 2016 at 4:10
NetoricaNetorica
18.1k17 gold badges72 silver badges108 bronze badges
1
- Command line changes will not be permanent and will be lost when the console closes.
- The path works like first comes first served.
- You may want to override other already included executables. For instance, if you already have another version on your path and you want to add different version without making a permanent change on path, you should put the directory at the beginning of the command.
To override already included executables;
set PATH=C:xamppphp;%PATH%;
answered Sep 6, 2016 at 14:37
hevihevi
2,3501 gold badge32 silver badges51 bronze badges
Use pathed from gtools.
It does things in an intuitive way. For example:
pathed /REMOVE "c:myfolder"
pathed /APPEND "c:myfolder"
It shows results without the need to spawn a new cmd!
answered Mar 19, 2019 at 9:37
womdwomd
2,97325 silver badges19 bronze badges
1
Regarding point 2, I’m using a simple batch file that is populating PATH or other environment variables for me. Therefore, there isn’t any pollution of environment variables by default. This batch file is accessible from everywhere so I can type:
mybatchfile
Output:
-- Here all environment variables are available
And:
php file.php
answered Oct 30, 2015 at 14:22
3
Checking the above suggestions on Windows 10 LTSB, and with a glimpse on the «help» outlines (that can be viewed when typing ‘command /?’ on the cmd), brought me to the conclusion that the PATH command changes the system environment variable Path values only for the current session, but after reboot all the values reset to their default- just as they were prior to using the PATH command.
On the other hand using the SETX command with administrative privileges is way more powerful. It changes those values for good (or at least until the next time this command is used or until next time those values are manually GUI manipulated… ).
The best SETX syntax usage that worked for me:
SETX PATH "%PATH%;C:pathtowherethecommandresides"
where any equal sign ‘=’ should be avoided, and don’t you worry about spaces! There isn’t any need to insert any more quotation marks for a path that contains spaces inside it — the split sign ‘;’ does the job.
The PATH keyword that follows the SETX defines which set of values should be changed among the System Environment Variables possible values, and the %PATH% (the word PATH surrounded by the percent sign) inside the quotation marks, tells the OS to leave the existing PATH values as they are and add the following path (the one that follows the split sign ‘;’) to the existing values.
answered Nov 22, 2016 at 20:34
1
Use these commands in the Bash shell on Windows to append a new location to the PATH variable
PATH=$PATH:/path/to/mydir
Or prepend this location
PATH=/path/to/mydir:$PATH
In your case, for instance, do
PATH=$PATH:C:xamppphp
You can echo $PATH to see the PATH variable in the shell.
answered Sep 1, 2021 at 6:48
kiriloffkiriloff
25.2k36 gold badges143 silver badges222 bronze badges
1
If you run the command cmd, it will update all system variables for that command window.
answered Oct 17, 2018 at 2:06
1
In a command prompt you tell Cmd to use Windows Explorer’s command line by prefacing it with start.
So start Yourbatchname.
Note you have to register as if its name is batchfile.exe.
Programs and documents can be added to the registry so typing their name without their path in the Start — Run dialog box or shortcut enables Windows to find them.
This is a generic reg file. Copy the lines below to a new Text Document and save it as anyname.reg. Edit it with your programs or documents.
In paths, use \ to separate folder names in key paths as regedit uses a single to separate its key names. All reg files start with REGEDIT4. A semicolon turns a line into a comment. The @ symbol means to assign the value to the key rather than a named value.
The file doesn’t have to exist. This can be used to set Word.exe to open Winword.exe.
Typing start batchfile will start iexplore.exe.
REGEDIT4
;The bolded name below is the name of the document or program, <filename>.<file extension>
[HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINESoftwareMicrosoftWindowsCurrentVersionApp PathsBatchfile.exe]
; The @ means the path to the file is assigned to the default value for the key.
; The whole path in enclosed in a quotation mark ".
@=""C:\Program Files\Internet Explorer\iexplore.exe""
; Optional Parameters. The semicolon means don't process the line. Remove it if you want to put it in the registry
; Informs the shell that the program accepts URLs.
;"useURL"="1"
; Sets the path that a program will use as its' default directory. This is commented out.
;"Path"="C:\Program Files\Microsoft Office\Office\"
You’ve already been told about path in another answer. Also see doskey /? for cmd macros (they only work when typing).
You can run startup commands for CMD. From Windows Resource Kit Technical Reference
AutoRun
HKCUSoftwareMicrosoftCommand Processor
Data type Range Default value
REG_SZ list of commands There is no default value for this entry.
Description
Contains commands which are executed each time you start Cmd.exe.
answered Dec 21, 2016 at 1:08
A better alternative to Control Panel is to use this freeware program from SourceForge called Pathenator.
However, it only works for a system that has .NET 4.0 or greater such as Windows 7, Windows 8, or Windows 10.
answered Aug 28, 2017 at 1:24
BimoBimo
5,5972 gold badges35 silver badges57 bronze badges
0
As trivial as it may be, I had to restart Windows when faced with this problem.
I am running Windows 7 x64. I did a manual update to the system PATH variable. This worked okay if I ran cmd.exe from the stat menu. But if I type «cmd» in the Windows Explorer address bar, it seems to load the PATH from elsewhere, which doesn’t have my manual changes.
(To avoid doubt — yes, I did close and rerun cmd a couple of times before I restarted and it didn’t help.)
answered Oct 20, 2019 at 18:03
svinecsvinec
6298 silver badges9 bronze badges
3
The below solution worked perfectly.
Try the below command in your Windows terminal.
setx PATH "C:myfolder;%PATH%"
SUCCESS: Specified value was saved.
You can refer to more on here.
answered Jun 5, 2021 at 13:42
-
I have installed PHP that time. I extracted php-7***.zip into C:php</i>
-
Back up my current PATH environment variable: run
cmd, and execute command:path >C:path-backup.txt -
Get my current path value into C:path.txt file (the same way)
-
Modify path.txt (sure, my path length is more than 1024 characters, and Windows is running few years)
- I have removed duplicates paths in there, like ‘C:Windows; or C:WindowsSystem32; or C:WindowsSystem32Wbem; — I’ve got twice.
- Remove uninstalled programs paths as well. Example: C:Program FilesNonExistSoftware;
- This way, my path string length < 1024 :)))
- at the end of the path string, add
;C:php - Copy path value only into buffer with framed double quotes! Example: «C:Windows;****;C:php» No PATH= should be there!!!
-
Open Windows PowerShell as Administrator (e.g., Win + X).
-
Run command:
setx path "Here you should insert string from buffer (new path value)" -
Rerun your terminal (I use «Far Manager») and check:
php -v
answered Oct 24, 2018 at 20:50
SerbSerb
214 bronze badges
How to open the Environment Variables window from cmd.exe/Run… dialog
SystemPropertiesAdvancedand click «Environment Variables», no UACrundll32 sysdm.cpl,EditEnvironmentVariablesdirect, might trigger UAC
Via Can the environment variables tool in Windows be launched directly? on Server Fault.
How to open the Environment Variables window from Explorer
- right-click on «This PC»
- Click on «Properties»
- On the left panel of the window that pops up, click on «Advanced System Settings»
- Click on the «Advanced» tab
- Click on «Environment Variables» button at the bottom of the window
You can also search for Variables in the Start menu search.
Reference images how the Environment Variables window looks like:
Windows 10

via
Windows 7

via
Windows XP

via
On Windows 10, I was able to search for set path environment variable and got these instructions:
- From the desktop, right-click the very bottom-left corner of the screen to get the Power User Task Menu.
- From the Power User Task Menu, click System.
- In the Settings window, scroll down to the Related settings section and click the System info link.
- In the System window, click the Advanced system settings link in the left navigation panel.
- In the System Properties window, click the Advanced tab, then click the Environment Variables button near the bottom of that tab.
- In the Environment Variables window (pictured below), highlight the Path variable in the System variables section and click the Edit button. Add or modify the path lines with the paths you want the computer to access. Each different directory is separated with a semicolon, as shown below:
C:Program Files;C:Winnt;C:WinntSystem32
The first time I searched for it, it immediately popped up the System Properties Window. After that, I found the above instructions.
answered Nov 12, 2020 at 1:38
JaninJanin
2721 gold badge2 silver badges7 bronze badges
I am trying to add C:xamppphp to my system PATH environment variable in Windows.
I have already added it using the Environment Variables dialog box.
But when I type into my console:
C:>path
it doesn’t show the new C:xamppphp directory:
PATH=D:Program FilesAutodeskMaya2008bin;C:Ruby192bin;C:WINDOWSsystem32;C:WINDOWS;
C:WINDOWSSystem32Wbem;C:PROGRA~1DISKEE~2DISKEE~1;c:Program FilesMicrosoft SQL
Server90Toolsbinn;C:Program FilesQuickTimeQTSystem;D:Program FilesTortoiseSVNbin
;D:Program FilesBazaar;C:Program FilesAndroidandroid-sdktools;D:Program Files
Microsoft Visual StudioCommonToolsWinNT;D:Program FilesMicrosoft Visual StudioCommon
MSDev98Bin;D:Program FilesMicrosoft Visual StudioCommonTools;D:Program Files
Microsoft Visual StudioVC98bin
I have two questions:
- Why did this happen? Is there something I did wrong?
- Also, how do I add directories to my
PATHvariable using the console (and programmatically, with a batch file)?
asked Mar 3, 2012 at 12:58
8
Option 1
After you change PATH with the GUI, close and reopen the console window.
This works because only programs started after the change will see the new PATH.
Option 2
This option only affects your current shell session, not the whole system. Execute this command in the command window you have open:
set PATH=%PATH%;C:yourpathhere
This command appends C:yourpathhere to the current PATH. If your path includes spaces, you do not need to include quote marks.
Breaking it down:
set– A command that changes cmd’s environment variables only for the current cmd session; other programs and the system are unaffected.PATH=– Signifies thatPATHis the environment variable to be temporarily changed.%PATH%;C:yourpathhere– The%PATH%part expands to the current value ofPATH, and;C:yourpathhereis then concatenated to it. This becomes the newPATH.
answered Mar 3, 2012 at 13:03
JimRJimR
15.1k2 gold badges20 silver badges26 bronze badges
12
WARNING: This solution may be destructive to your PATH, and the stability of your system. As a side effect, it will merge your user and system PATH, and truncate PATH to 1024 characters. The effect of this command is irreversible. Make a backup of PATH first. See the comments for more information.
Don’t blindly copy-and-paste this. Use with caution.
You can permanently add a path to PATH with the setx command:
setx /M path "%path%;C:yourpathhere"
Remove the /M flag if you want to set the user PATH instead of the system PATH.
Notes:
- The
setxcommand is only available in Windows 7 and later. -
You should run this command from an elevated command prompt.
-
If you only want to change it for the current session, use set.
StayOnTarget
11k10 gold badges49 silver badges75 bronze badges
answered Feb 28, 2015 at 5:12
NafscriptNafscript
4,9572 gold badges16 silver badges15 bronze badges
15
This only modifies the registry. An existing process won’t use these values. A new process will do so if it is started after this change and doesn’t inherit the old environment from its parent.
You didn’t specify how you started the console session. The best way to ensure this is to exit the command shell and run it again. It should then inherit the updated PATH environment variable.
answered Mar 3, 2012 at 13:23
Hans PassantHans Passant
913k145 gold badges1670 silver badges2507 bronze badges
6
You don’t need any set or setx command. Simply open the terminal and type:
PATH
This shows the current value of PATH variable. Now you want to add directory to it? Simply type:
PATH %PATH%;C:xamppphp
If for any reason you want to clear the PATH variable (no paths at all or delete all paths in it), type:
PATH ;
Update
Like Danial Wilson noted in comment below, it sets the path only in the current session. To set the path permanently, use setx but be aware, although that sets the path permanently, but not in the current session, so you have to start a new command line to see the changes. More information is here.
To check if an environmental variable exist or see its value, use the ECHO command:
echo %YOUR_ENV_VARIABLE%
answered Jul 1, 2015 at 15:11
zarzar
10.9k13 gold badges90 silver badges171 bronze badges
6
I would use PowerShell instead!
To add a directory to PATH using PowerShell, do the following:
$PATH = [Environment]::GetEnvironmentVariable("PATH")
$xampp_path = "C:xamppphp"
[Environment]::SetEnvironmentVariable("PATH", "$PATH;$xampp_path")
To set the variable for all users, machine-wide, the last line should be like:
[Environment]::SetEnvironmentVariable("PATH", "$PATH;$xampp_path", "Machine")
In a PowerShell script, you might want to check for the presence of your C:xamppphp before adding to PATH (in case it has been previously added). You can wrap it in an if conditional.
So putting it all together:
$PATH = [Environment]::GetEnvironmentVariable("PATH", "Machine")
$xampp_path = "C:xamppphp"
if( $PATH -notlike "*"+$xampp_path+"*" ){
[Environment]::SetEnvironmentVariable("PATH", "$PATH;$xampp_path", "Machine")
}
Better still, one could create a generic function. Just supply the directory you wish to add:
function AddTo-Path{
param(
[string]$Dir
)
if( !(Test-Path $Dir) ){
Write-warning "Supplied directory was not found!"
return
}
$PATH = [Environment]::GetEnvironmentVariable("PATH", "Machine")
if( $PATH -notlike "*"+$Dir+"*" ){
[Environment]::SetEnvironmentVariable("PATH", "$PATH;$Dir", "Machine")
}
}
You could make things better by doing some polishing. For example, using Test-Path to confirm that your directory actually exists.
answered Mar 17, 2015 at 20:24
Ifedi OkonkwoIfedi Okonkwo
3,3064 gold badges31 silver badges45 bronze badges
4
Safer SETX
Nod to all the comments on the @Nafscript’s initial SETX answer.
SETXby default will update your user path.SETX ... /Mwill update your system path.%PATH%contains the system path with the user path appended
Warnings
- Backup your
PATH—SETXwill truncate your junk longer than 1024 characters - Don’t call
SETX %PATH%;xxx— adds the system path into the user path - Don’t call
SETX %PATH%;xxx /M— adds the user path into the system path - Excessive batch file use can cause blindness1
The ss64 SETX page has some very good examples. Importantly it points to where the registry keys are for SETX vs SETX /M
User Variables:
HKCUEnvironmentSystem Variables:
HKLMSYSTEMCurrentControlSetControlSession ManagerEnvironment
Usage instructions
Append to User PATH
append_user_path.cmd
@ECHO OFF
REM usage: append_user_path "path"
SET Key="HKCUEnvironment"
FOR /F "usebackq tokens=2*" %%A IN (`REG QUERY %Key% /v PATH`) DO Set CurrPath=%%B
ECHO %CurrPath% > user_path_bak.txt
SETX PATH "%CurrPath%";%1
Append to System PATH
append_system_path.cmd. Must be run as administrator.
(It’s basically the same except with a different Key and the SETX /M modifier.)
@ECHO OFF
REM usage: append_system_path "path"
SET Key="HKLMSYSTEMCurrentControlSetControlSession ManagerEnvironment"
FOR /F "usebackq tokens=2*" %%A IN (`REG QUERY %Key% /v PATH`) DO Set CurrPath=%%B
ECHO %CurrPath% > system_path_bak.txt
SETX PATH "%CurrPath%";%1 /M
Alternatives
Finally there’s potentially an improved version called SETENV recommended by the ss64 SETX page that splits out setting the user or system environment variables.
Example
Here’s a full example that works on Windows 7 to set the PATH environment variable system wide. The example detects if the software has already been added to the PATH before attempting to change the value. There are a number of minor technical differences from the examples given above:
@echo off
set OWNPATH=%~dp0
set PLATFORM=mswin
if defined ProgramFiles(x86) set PLATFORM=win64
if "%PROCESSOR_ARCHITECTURE%"=="AMD64" set PLATFORM=win64
if exist "%OWNPATH%textexmf-mswinbincontext.exe" set PLATFORM=mswin
if exist "%OWNPATH%textexmf-win64bincontext.exe" set PLATFORM=win64
rem Check if the PATH was updated previously
echo %PATH% | findstr "texmf-%PLATFORM%" > nul
rem Only update the PATH if not previously updated
if ERRORLEVEL 1 (
set Key="HKLMSYSTEMCurrentControlSetControlSession ManagerEnvironment"
for /F "USEBACKQ tokens=2*" %%A in (`reg query %%Key%% /v PATH`) do (
if not "%%~B" == "" (
rem Preserve the existing PATH
echo %%B > currpath.txt
rem Update the current session
set PATH=%PATH%;%OWNPATH%textexmf-%PLATFORM%bin
rem Persist the PATH environment variable
setx PATH "%%B;%OWNPATH%textexmf-%PLATFORM%bin" /M
)
)
)
1. Not strictly true
Dave Jarvis
29.9k39 gold badges177 silver badges310 bronze badges
answered Dec 29, 2016 at 12:04
icc97icc97
10.7k8 gold badges69 silver badges88 bronze badges
0
Handy if you are already in the directory you want to add to PATH:
set PATH=%PATH%;%CD%
It works with the standard Windows cmd, but not in PowerShell.
For PowerShell, the %CD% equivalent is [System.Environment]::CurrentDirectory.
answered Mar 18, 2016 at 16:09
nclordnclord
1,2271 gold badge16 silver badges17 bronze badges
2
Aside from all the answers, if you want a nice GUI tool to edit your Windows environment variables you can use Rapid Environment Editor.
Try it! It’s safe to use and is awesome!
answered Feb 17, 2016 at 4:10
NetoricaNetorica
18.1k17 gold badges72 silver badges108 bronze badges
1
- Command line changes will not be permanent and will be lost when the console closes.
- The path works like first comes first served.
- You may want to override other already included executables. For instance, if you already have another version on your path and you want to add different version without making a permanent change on path, you should put the directory at the beginning of the command.
To override already included executables;
set PATH=C:xamppphp;%PATH%;
answered Sep 6, 2016 at 14:37
hevihevi
2,3501 gold badge32 silver badges51 bronze badges
Use pathed from gtools.
It does things in an intuitive way. For example:
pathed /REMOVE "c:myfolder"
pathed /APPEND "c:myfolder"
It shows results without the need to spawn a new cmd!
answered Mar 19, 2019 at 9:37
womdwomd
2,97325 silver badges19 bronze badges
1
Regarding point 2, I’m using a simple batch file that is populating PATH or other environment variables for me. Therefore, there isn’t any pollution of environment variables by default. This batch file is accessible from everywhere so I can type:
mybatchfile
Output:
-- Here all environment variables are available
And:
php file.php
answered Oct 30, 2015 at 14:22
3
Checking the above suggestions on Windows 10 LTSB, and with a glimpse on the «help» outlines (that can be viewed when typing ‘command /?’ on the cmd), brought me to the conclusion that the PATH command changes the system environment variable Path values only for the current session, but after reboot all the values reset to their default- just as they were prior to using the PATH command.
On the other hand using the SETX command with administrative privileges is way more powerful. It changes those values for good (or at least until the next time this command is used or until next time those values are manually GUI manipulated… ).
The best SETX syntax usage that worked for me:
SETX PATH "%PATH%;C:pathtowherethecommandresides"
where any equal sign ‘=’ should be avoided, and don’t you worry about spaces! There isn’t any need to insert any more quotation marks for a path that contains spaces inside it — the split sign ‘;’ does the job.
The PATH keyword that follows the SETX defines which set of values should be changed among the System Environment Variables possible values, and the %PATH% (the word PATH surrounded by the percent sign) inside the quotation marks, tells the OS to leave the existing PATH values as they are and add the following path (the one that follows the split sign ‘;’) to the existing values.
answered Nov 22, 2016 at 20:34
1
Use these commands in the Bash shell on Windows to append a new location to the PATH variable
PATH=$PATH:/path/to/mydir
Or prepend this location
PATH=/path/to/mydir:$PATH
In your case, for instance, do
PATH=$PATH:C:xamppphp
You can echo $PATH to see the PATH variable in the shell.
answered Sep 1, 2021 at 6:48
kiriloffkiriloff
25.2k36 gold badges143 silver badges222 bronze badges
1
If you run the command cmd, it will update all system variables for that command window.
answered Oct 17, 2018 at 2:06
1
In a command prompt you tell Cmd to use Windows Explorer’s command line by prefacing it with start.
So start Yourbatchname.
Note you have to register as if its name is batchfile.exe.
Programs and documents can be added to the registry so typing their name without their path in the Start — Run dialog box or shortcut enables Windows to find them.
This is a generic reg file. Copy the lines below to a new Text Document and save it as anyname.reg. Edit it with your programs or documents.
In paths, use \ to separate folder names in key paths as regedit uses a single to separate its key names. All reg files start with REGEDIT4. A semicolon turns a line into a comment. The @ symbol means to assign the value to the key rather than a named value.
The file doesn’t have to exist. This can be used to set Word.exe to open Winword.exe.
Typing start batchfile will start iexplore.exe.
REGEDIT4
;The bolded name below is the name of the document or program, <filename>.<file extension>
[HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINESoftwareMicrosoftWindowsCurrentVersionApp PathsBatchfile.exe]
; The @ means the path to the file is assigned to the default value for the key.
; The whole path in enclosed in a quotation mark ".
@=""C:\Program Files\Internet Explorer\iexplore.exe""
; Optional Parameters. The semicolon means don't process the line. Remove it if you want to put it in the registry
; Informs the shell that the program accepts URLs.
;"useURL"="1"
; Sets the path that a program will use as its' default directory. This is commented out.
;"Path"="C:\Program Files\Microsoft Office\Office\"
You’ve already been told about path in another answer. Also see doskey /? for cmd macros (they only work when typing).
You can run startup commands for CMD. From Windows Resource Kit Technical Reference
AutoRun
HKCUSoftwareMicrosoftCommand Processor
Data type Range Default value
REG_SZ list of commands There is no default value for this entry.
Description
Contains commands which are executed each time you start Cmd.exe.
answered Dec 21, 2016 at 1:08
A better alternative to Control Panel is to use this freeware program from SourceForge called Pathenator.
However, it only works for a system that has .NET 4.0 or greater such as Windows 7, Windows 8, or Windows 10.
answered Aug 28, 2017 at 1:24
BimoBimo
5,5972 gold badges35 silver badges57 bronze badges
0
As trivial as it may be, I had to restart Windows when faced with this problem.
I am running Windows 7 x64. I did a manual update to the system PATH variable. This worked okay if I ran cmd.exe from the stat menu. But if I type «cmd» in the Windows Explorer address bar, it seems to load the PATH from elsewhere, which doesn’t have my manual changes.
(To avoid doubt — yes, I did close and rerun cmd a couple of times before I restarted and it didn’t help.)
answered Oct 20, 2019 at 18:03
svinecsvinec
6298 silver badges9 bronze badges
3
The below solution worked perfectly.
Try the below command in your Windows terminal.
setx PATH "C:myfolder;%PATH%"
SUCCESS: Specified value was saved.
You can refer to more on here.
answered Jun 5, 2021 at 13:42
-
I have installed PHP that time. I extracted php-7***.zip into C:php</i>
-
Back up my current PATH environment variable: run
cmd, and execute command:path >C:path-backup.txt -
Get my current path value into C:path.txt file (the same way)
-
Modify path.txt (sure, my path length is more than 1024 characters, and Windows is running few years)
- I have removed duplicates paths in there, like ‘C:Windows; or C:WindowsSystem32; or C:WindowsSystem32Wbem; — I’ve got twice.
- Remove uninstalled programs paths as well. Example: C:Program FilesNonExistSoftware;
- This way, my path string length < 1024 :)))
- at the end of the path string, add
;C:php - Copy path value only into buffer with framed double quotes! Example: «C:Windows;****;C:php» No PATH= should be there!!!
-
Open Windows PowerShell as Administrator (e.g., Win + X).
-
Run command:
setx path "Here you should insert string from buffer (new path value)" -
Rerun your terminal (I use «Far Manager») and check:
php -v
answered Oct 24, 2018 at 20:50
SerbSerb
214 bronze badges
How to open the Environment Variables window from cmd.exe/Run… dialog
SystemPropertiesAdvancedand click «Environment Variables», no UACrundll32 sysdm.cpl,EditEnvironmentVariablesdirect, might trigger UAC
Via Can the environment variables tool in Windows be launched directly? on Server Fault.
How to open the Environment Variables window from Explorer
- right-click on «This PC»
- Click on «Properties»
- On the left panel of the window that pops up, click on «Advanced System Settings»
- Click on the «Advanced» tab
- Click on «Environment Variables» button at the bottom of the window
You can also search for Variables in the Start menu search.
Reference images how the Environment Variables window looks like:
Windows 10

via
Windows 7

via
Windows XP

via
On Windows 10, I was able to search for set path environment variable and got these instructions:
- From the desktop, right-click the very bottom-left corner of the screen to get the Power User Task Menu.
- From the Power User Task Menu, click System.
- In the Settings window, scroll down to the Related settings section and click the System info link.
- In the System window, click the Advanced system settings link in the left navigation panel.
- In the System Properties window, click the Advanced tab, then click the Environment Variables button near the bottom of that tab.
- In the Environment Variables window (pictured below), highlight the Path variable in the System variables section and click the Edit button. Add or modify the path lines with the paths you want the computer to access. Each different directory is separated with a semicolon, as shown below:
C:Program Files;C:Winnt;C:WinntSystem32
The first time I searched for it, it immediately popped up the System Properties Window. After that, I found the above instructions.
answered Nov 12, 2020 at 1:38
JaninJanin
2721 gold badge2 silver badges7 bronze badges
Как прописать путь к файлу в командной строке
Задает путь к команде в переменной среды PATH, указывающий набор каталогов, используемых для поиска исполняемых файлов (.exe). При использовании без параметров эта команда отображает текущий путь к команде.
Синтаксис
Параметры
| Параметр | Описание |
|---|---|
| [<drive>:]<path> | Указывает диск и каталог, который нужно задать в пути к команде. Текущий каталог всегда ищется перед каталогами, указанными в пути к команде. |
| ; | Разделяет каталоги в пути команды. При использовании без параметров ; очищает существующие пути к командам из переменной среды PATH и направляет Cmd.exe для поиска только в текущем каталоге. |
| %PATH% | Добавляет путь команды к существующему набору каталогов, перечисленных в переменной среды PATH. Если включить этот параметр, Cmd.exe заменит его значениями пути к командам, найденными в переменной среды PATH, что устраняет необходимость вручную вводить эти значения в командной строке. |
| /? | Отображение справки в командной строке. |
Комментарии
Windows операционная система выполняет поиск по умолчанию расширений имен файлов в следующем порядке приоритета: .exe, com, .bat и. cmd. Это означает, что если вы ищете пакетный файл с именем, acct.bat, но у вас есть приложение с именем acct.exe в том же каталоге, необходимо включить расширение .bat в командной строке.
Если два или более файлов в пути команды имеют одинаковое имя файла и расширение, эта команда сначала выполняет поиск указанного имени файла в текущем каталоге. Затем он ищет каталоги в пути команды в том порядке, в котором они указаны в переменной среды PATH.
если поместить команду path в файл Autoexec. nt, операционная система Windows автоматически добавит указанный путь поиска подсистемы MS-DOS при каждом входе в систему. Cmd.exe не использует файл AUTOEXEC. NT. При запуске из ярлыка Cmd.exe наследует переменные среды, заданные в Мой компьютер/свойствах/дополнительном/окружении.
Примеры
Для поиска по путям к:усертаксес, б:усеринвести б:бин для внешних команд введите:
Открытие папки в командной строке в Windows 10
Иногда пользователи Windows 10 оказываются в ситуации, требующей от них управления папкой через командную строку. С каждым обновлением компания Microsoft вносит различные изменения в операционную систему, в том числе, в этот процесс, поэтому не все методы, которые работали раньше, актуальны сейчас.
Итак, давайте разберемся, каким образом можно открывать папки в “десятке”, используя командую строку.
Использование Проводника
- Открываем желаемую папку в окне Проводника, который можно запустить нажатием клавиш Win+E. Вводим в адресной строке системную команду “cmd” и нажимаем клавишу Enter на клавиатуре.
- После этого откроется окно командной строки с расположением в той папке, которую мы открыли.
Как прописать путь к папке в командной строке
- Открываем командную строку. Сделать этом можно по-разному:
- нажимаем сочетание клавиш Win+R, чтобы вызвать окно “Выполнить”, набираем команду “cmd” и нажимаем Enter.
Примечание: можно каждый раз писать “/d“. Разницы между командами “cd C:Music” и “cd /d C:Music” нет
Что делать, если командная строка отсутствует
У некоторых пользователей при наличии определенных обновлений системы вместо привычной командной строки в контекстном меню Пуск отображается Windows PowerShell.
По сути, это некая новая оболочка командной строки, которая позволяет вводить те же команды и получать те же самые результаты. Например, команда “cd C:Music“, которую мы рассматривали выше.
Но если, все же, хочется вернуть привычную нам командную строку, для этого делаем следующее:
- Открываем Параметры панели задач. Попасть в них можно разными способами:
Заключение
Открытие папок через командную строку – крайне редкое действие, которым, вероятно, большинство пользователей Windows 10 никогда не пользовалось и не будет. Тем не менее, случаи бывают разные, и нелишним будет знать, как это можно сделать, когда вдруг потребуется.
Самый простой способ вставить в командную строку путь к файлу или папке
С талкиваясь с необходимостью выполнить какую-нибудь операцию в командной строке, начинающие пользователи очень скоро понимают, что возможности этого инструмента в отношении привычного copy-paste весьма ограничены. Командная строка не поддерживает работу с комбинациями Ctrl + C и Ctrl + V , копировать и вставлять текст в окошко консоли можно с помощью контекстного меню, вызываемого правой кликом правой клавишей мыши.
При работе с командной строкой Windows очень часто приходится переходить из одного каталога в другой, это понятно. Вот и получается так, что некоторые пользователи только ради того чтобы попасть в нужный каталог на жестком диске вручную прописывают в консоли длиннющие пути. Удовольствия при этом они явно не испытывают и это понятно почему. Во-первых, на это уходит драгоценное время, во-вторых, при ручном наборе адреса всегда имеется риск допустить ошибку.
Конечно, ручному набору есть альтернатива, например можно открыть целевой каталог в Проводнике, зайти в свойства папки или файла, скопировать оттуда полный путь, а затем уже вставить его в окно командной строки. Это уже быстрее и надежнее, но нет ли еще более удобного и быстрого способа? Оказывается есть! Способ этот прост, как и все гениальное. Просто так сложилось, что многие пользователи о нем не знают. А не знают потому, что мало об этом кто говорит.
Не нужно ничего копировать и вставлять, достаточно просто перетащить файл или папку в консоль и путь вставится сам, а если надо, то и кавычки подставятся, так что вам лишь останется нажать Enter .
Это правило действует для всех объектов файловой системы, начиная от логических разделов и заканчивая ярлыками и файлами без расширения. От необходимости использования команд перехода, таких как CD перетаскивание, конечно, не избавляет, но согласись, насколько же это удобнее ручного ввода!