The following program will add the python executable path and the subdir Scripts (which is where e.g. pip and easy_install are installed) to your environment. It finds the path to the python executable from the registry key binding the .py extension. It will remove old python paths in your environment. Works with XP (and probably Vista) as well.
It only uses modules that come with the basic windows installer.
# coding: utf-8
import sys
import os
import time
import _winreg
import ctypes
def find_python():
"""
retrieves the commandline for .py extensions from the registry
"""
hKey = _winreg.OpenKey(_winreg.HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT,
r'Python.Fileshellopencommand')
# get the default value
value, typ = _winreg.QueryValueEx (hKey, None)
program = value.split('"')[1]
if not program.lower().endswith(r'python.exe'):
return None
return os.path.dirname(program)
def extend_path(pypath, remove=False, verbose=0, remove_old=True,
script=False):
"""
extend(pypath) adds pypath to the PATH env. variable as defined in the
registry, and then notifies applications (e.g. the desktop) of this change.
!!! Already opened DOS-Command prompts are not updated. !!!
Newly opened prompts will have the new path (inherited from the
updated windows explorer desktop)
options:
remove (default unset), remove from PATH instead of extend PATH
remove_old (default set), removes any (old) python paths first
script (default unset), try to add/remove the Scripts subdirectory
of pypath (pip, easy_install) as well
"""
_sd = 'Scripts' # scripts subdir
hKey = _winreg.OpenKey (_winreg.HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE,
r'SYSTEMCurrentControlSetControlSession ManagerEnvironment',
0, _winreg.KEY_READ | _winreg.KEY_SET_VALUE)
value, typ = _winreg.QueryValueEx (hKey, "PATH")
vals = value.split(';')
assert isinstance(vals, list)
if not remove and remove_old:
new_vals = []
for v in vals:
pyexe = os.path.join(v, 'python.exe')
if v != pypath and os.path.exists(pyexe):
if verbose > 0:
print 'removing from PATH:', v
continue
if script and v != os.path.join(pypath, _sd) and
os.path.exists(v.replace(_sd, pyexe)):
if verbose > 0:
print 'removing from PATH:', v
continue
new_vals.append(v)
vals = new_vals
if remove:
try:
vals.remove(pypath)
except ValueError:
if verbose > 0:
print 'path element', pypath, 'not found'
return
if script:
try:
vals.remove(os.path.join(pypath, _sd))
except ValueError:
pass
print 'removing from PATH:', pypath
else:
if pypath in vals:
if verbose > 0:
print 'path element', pypath, 'already in PATH'
return
vals.append(pypath)
if verbose > 1:
print 'adding to PATH:', pypath
if script:
if not pypath + '\Scripts' in vals:
vals.append(pypath + '\Scripts')
if verbose > 1:
print 'adding to PATH:', pypath + '\Scripts'
_winreg.SetValueEx(hKey, "PATH", 0, typ, ';'.join(vals) )
_winreg.SetValueEx(hKey, "OLDPATH", 0, typ, value )
_winreg.FlushKey(hKey)
# notify other programs
SendMessage = ctypes.windll.user32.SendMessageW
HWND_BROADCAST = 0xFFFF
WM_SETTINGCHANGE = 0x1A
SendMessage(HWND_BROADCAST, WM_SETTINGCHANGE, 0, u'Environment')
if verbose > 1:
print 'Do not forget to restart any command prompts'
if __name__ == '__main__':
remove = '--remove' in sys.argv
script = '--noscripts' not in sys.argv
extend_path(find_python(), verbose=2, remove=remove, script=script)
- 1. Настройка локальной среды
- 2. Получение Python
- 1. Платформа Windows
- 2. Платформа Linux
- 3. Mac OS
- 3. Настройка PATH
- 1. Настройка PATH в Unix / Linux
- 2. Настройка PATH в Windows
- 3. Переменные среды Python
- 4. Запуск Python
- 1. Интерактивный интерпретатор
- 2. Скрипт из командной строки
- 3. Интегрированная среда разработки
Python 3 доступен для Windows, Mac OS и большинства вариантов операционной системы Linux.
Настройка локальной среды
Откройте окно терминала и введите «python», чтобы узнать, установлен ли он и какая версия установлена.
Получение Python
Платформа Windows
Бинарники последней версии Python 3 (Python 3.6.4) доступны на этой странице
загрузки
Доступны следующие варианты установки.
- Windows x86-64 embeddable zip file
- Windows x86-64 executable installer
- Windows x86-64 web-based installer
- Windows x86 embeddable zip file
- Windows x86 executable installer
- Windows x86 web-based installer
Примечание. Для установки Python 3.6.4 минимальными требованиями к ОС являются Windows 7 с пакетом обновления 1 (SP1). Для версий от 3.0 до 3.4.x Windows XP является приемлемым.
Платформа Linux
Различные варианты использования Linux используют разные менеджеры пакетов для установки новых пакетов.
На Ubuntu Linux Python 3 устанавливается с помощью следующей команды из терминала.
sudo apt-get install python3-minimalУстановка из исходников
Загрузите исходный tar-файл Gzipped с URL-адреса загрузки Python
https://www.python.org/ftp/python/3.6.4/Python-3.6.4.tgz
Extract the tarball tar xvfz Python-3.5.1.tgz Configure and Install: cd Python-3.5.1 ./configure --prefix = /opt/python3.5.1 make sudo make installMac OS
Загрузите установщики Mac OS с этого URL-адреса
https://www.python.org/downloads/mac-osx/
Дважды щелкните этот файл пакета и следуйте инструкциям мастера для установки.
Самый современный и текущий исходный код, двоичные файлы, документация, новости и т.д. Доступны на официальном сайте Python —
Python Official Website
−https://www.python.org/
Вы можете загрузить документацию Python со следующего сайта. Документация доступна в форматах HTML, PDF и PostScript.
Python Documentation Website
−www.python.org/doc/
Настройка PATH
Программы и другие исполняемые файлы могут быть во многих каталогах. Следовательно, операционные системы предоставляют путь поиска, в котором перечислены каталоги, которые он ищет для исполняемых файлов.
Важными особенностями являются:
- Путь хранится в переменной среды, которая является именованной строкой, поддерживаемой операционной системой. Эта переменная содержит информацию, доступную для командной оболочки и других программ.
- Переменная пути называется PATH в Unix или Path в Windows (Unix чувствительна к регистру, Windows — нет).
- В Mac OS установщик обрабатывает детали пути. Чтобы вызвать интерпретатор Python из любого конкретного каталога, вы должны добавить каталог Python на свой путь.
Настройка PATH в Unix / Linux
Чтобы добавить каталог Python в путь для определенного сеанса в Unix —
В csh shell
— введите setenv PATH «$ PATH:/usr/local/bin/python3» и нажмите Enter.
В оболочке bash (Linux)
— введите PYTHONPATH=/usr/local/bin/python3.4 и нажмите Enter.
В оболочке sh или ksh
— введите PATH = «$PATH:/usr/local/bin/python3» и нажмите Enter.
Примечание.
/usr/local/bin/python3
— это путь к каталогу Python.
Настройка PATH в Windows
Чтобы добавить каталог Python в путь для определенного сеанса в Windows —
-
В командной строке введите путь
%path%;C:Python
и нажмите Enter.
Примечание.
C:Python
— это путь к каталогу Python.
Переменные среды Python
| S.No. | Переменная и описание |
|---|---|
| 1 | PYTHONPATH Он играет роль, подобную PATH. Эта переменная сообщает интерпретатору Python, где можно найти файлы модулей, импортированные в программу. Он должен включать каталог исходной библиотеки Python и каталоги, содержащие исходный код Python. PYTHONPATH иногда задается установщиком Python. |
| 2 | PYTHONSTARTUP Он содержит путь к файлу инициализации, содержащему исходный код Python. Он выполняется каждый раз, когда вы запускаете интерпретатор. Он называется как .pythonrc.py в Unix и содержит команды, которые загружают утилиты или изменяют PYTHONPATH. |
| 3 | PYTHONCASEOK Он используется в Windows, чтобы проинструктировать Python о поиске первого нечувствительного к регистру совпадения в инструкции импорта. Установите эту переменную на любое значение, чтобы ее активировать. |
| 4 | PYTHONHOME Это альтернативный путь поиска модуля. Он обычно встроен в каталоги PYTHONSTARTUP или PYTHONPATH, чтобы упростить библиотеку модулей коммутации. |
Запуск Python
Существует три разных способа запуска Python —
Интерактивный интерпретатор
Вы можете запустить Python из Unix, DOS или любой другой системы, которая предоставляет вам интерпретатор командной строки или окно оболочки.
Введите
python
в командной строке.
Начните кодирование сразу в интерактивном интерпретаторе.
$python # Unix/Linux or python% # Unix/Linux or C:>python # Windows/DOSВот список всех доступных параметров командной строки —
| S.No. | Вариант и описание |
|---|---|
| 1 | -d предоставлять отладочную информацию |
| 2 | -O генерировать оптимизированный байт-код (приводящий к .pyo-файлам) |
| 3 | -S не запускайте сайт импорта, чтобы искать пути Python при запуске |
| 4 | -v подробный вывод (подробная трассировка по операциям импорта) |
| 5 | -X отключить встроенные исключения на основе классов (просто используйте строки); устаревший, начиная с версии 1.6 |
| 6 | -c cmd запустить скрипт Python, отправленный в виде строки cmd |
| 7 | file запустить скрипт Python из заданного файла |
Скрипт из командной строки
Сценарий Python можно запустить в командной строке, вызвав интерпретатор в вашем приложении, как показано в следующем примере.
$python script.py # Unix/Linux or python% script.py # Unix/Linux or C:>python script.py # Windows/DOSПримечание. Убедитесь, что права файлов разрешают выполнение.
Интегрированная среда разработки
Вы можете запустить Python из среды графического интерфейса пользователя (GUI), если у вас есть приложение GUI в вашей системе, которое поддерживает Python.
Для разработки Python приложений рекомендую PyCharm от компании JetBrains, как наиболее развитую и удобную IDE.
Python is a great language! However, it doesn’t come pre-installed with Windows. Hence we download it to interpret the Python code which we write. But wait, windows don’t know where you have installed the Python so when trying to any Python code, you will get an error.
We will be using Windows10 and python3 for this article. (Most of the part is same for any other version of either windows or python)
Add Python to Windows Path
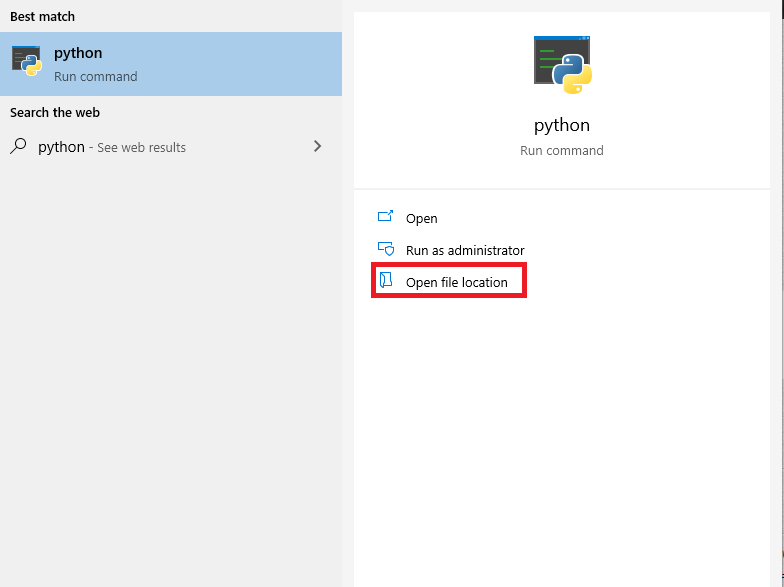
First, we need to locate where the python is being installed after downloading it. Press WINDOWS key and search for “Python”, you will get something like this:
If no results appear then Python is not installed on your machine, download it before proceeding further. Click on open file location and you will be in a location where Python is installed, Copy the location path from the top by clicking over it.
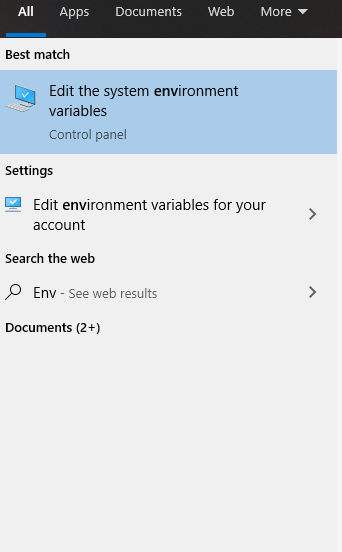
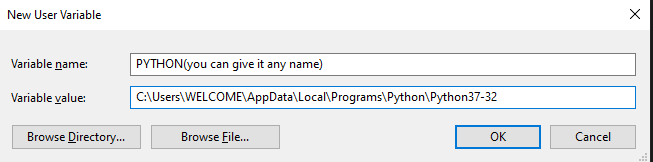
Now, we have to add the above-copied path as a variable so that windows can recognize. Search for “Environmental Variables”, you will see something like this:
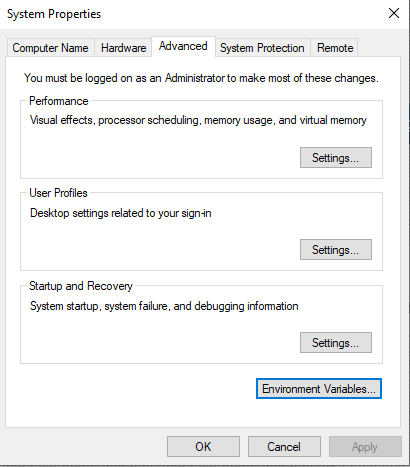
Click on that
Now click the “Environmental Variables” button
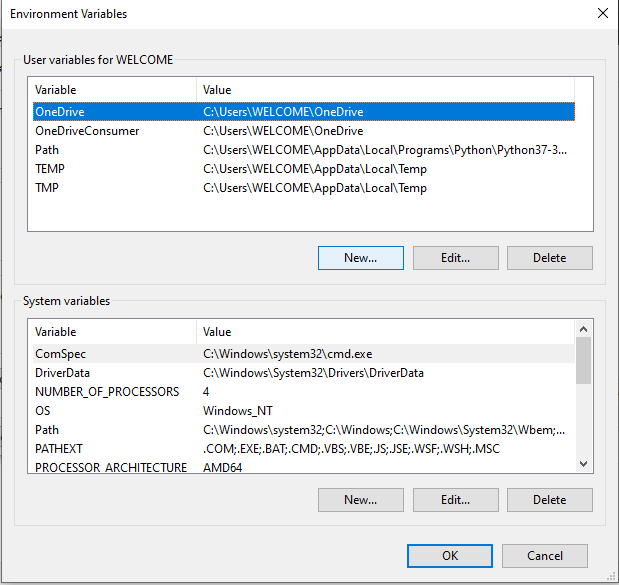
There will be two categories namely “User” and “System”, we have to add it in Users, click on New button in the User section. Now, add a Variable Name and Path which we copied previously and click OK. That’s it, DONE!
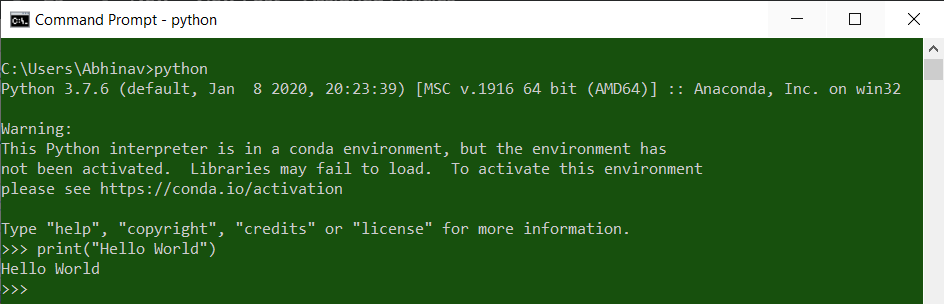
Check if the Environment variable is set or not
Now, after adding the Python to the Environment variable, let’s check if the Python is running anywhere in the windows or not. To do this open CMD and type Python. If the environment variable is set then the Python command will run otherwise not.