Содержание
- Установка QEMU
- Команды QEMU
- Основные
- Дополнительные
- Установка операционной системы в QEMU
- Запуск в QEMU образов LiveCD
- Qemu Manager
- Вопросы и ответы
Эмулятор QEMU является кроссплатформенным приложением, доступным в том числе для 32- и 64-битной версии Windows.
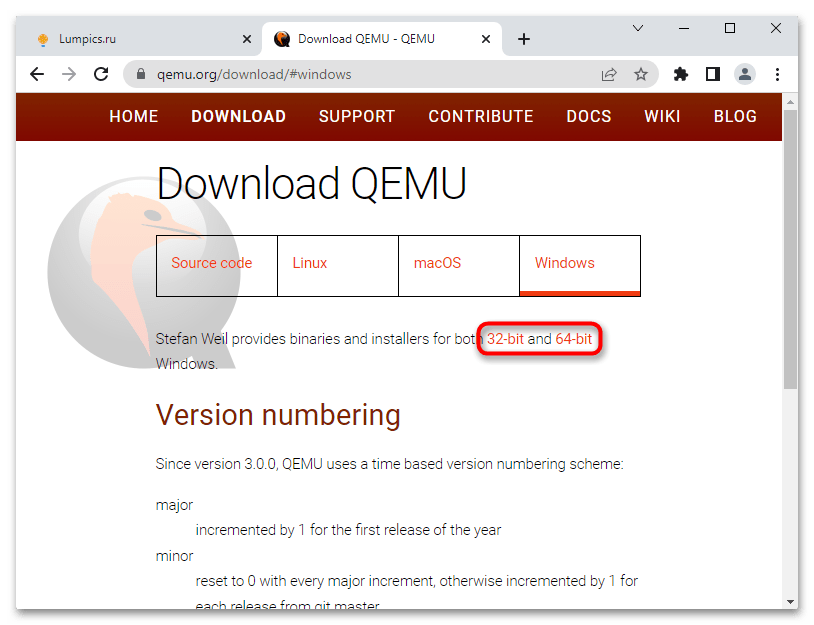
Скачать QEMU с официального сайта
- Откройте официальную страницу разработчика и выберите приложение нужной вам разрядности.
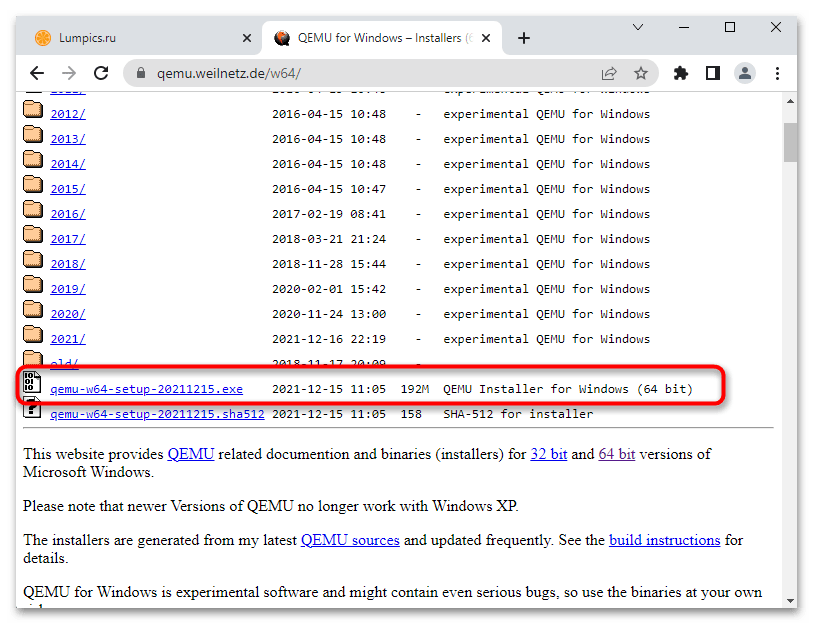
- Скачайте актуальную (последнюю) версию эмулятора.
- Запустите исполняемый файл программы и проследуйте указаниям мастера-установщика. В ходе установки вам будет предложено выбрать язык (русский отсутствует), принять условия лицензии, выбрать компоненты и путь установки. Все настройки оставьте по умолчанию, по завершении процедуры инсталляции нажмите кнопку «Finish».
Команды QEMU
QEMU является консольным приложением, то есть для работы с ним вам придется использовать «Командную строку» и вводимые вручную текстовые команды. Команд и параметров много, но для начала достаточно выучить самые главные.
Основные
qemu-system-архитектура— определяет архитектуру эмулируемого устройства. Одноименные исполняемые файлы располагаются в папке установки эмулятора.qemu-img create— команда создает файл в формате IMG, являющийся виртуальным диском, на который производится установка системы. В качестве аргумента передается произвольное имя IMG-контейнера.-hdaи-hdb— параметр подключает созданный виртуальный жесткий диск, название которого передается в качестве аргумента.-m— задает объем оперативной памяти, выделяемый эмулируемому устройству.-boot— задает ресурс, с которого выполняется загрузка операционной системы. Имя ресурса должно соответствовать названию виртуального жесткого диска (без указания расширения).cdrom— эмулирует дисковод, используется для установки операционных систем и запуска LiveCD, то есть портативных ОС. В качестве аргумента передается путь к образу ISO.
Дополнительные
-usb— активирует поддержку USB.-smp— эмулирует мультипроцессорную архитектуру.-full-screen— запускает виртуальную машину в полноэкранном режиме.cpu— задает тип процессора.-k— задает раскладку клавиатуры по умолчанию.-soundhw— подключает аудиокарту.usbdevice— подключает устройства USB.
Установка операционной системы в QEMU
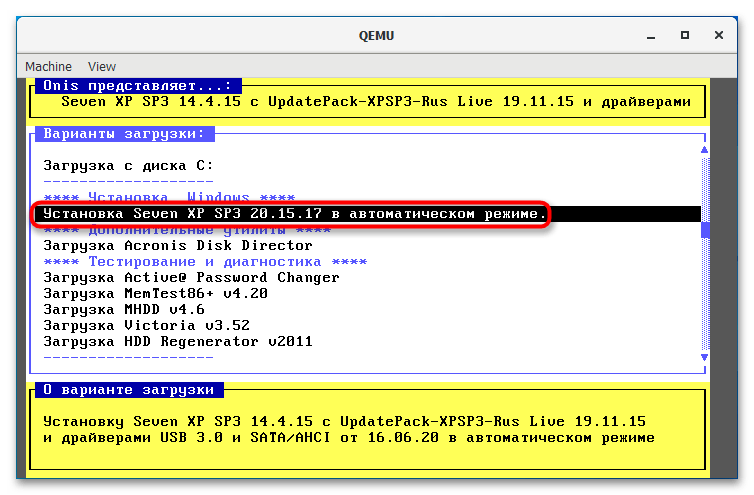
Предположим, вы хотите эмулировать компьютер с интеловским процессором и операционной системой Windows XP.
- Запустите классическую «Командную строку» и перейдите в расположение установки QEMU, для чего выполните команду
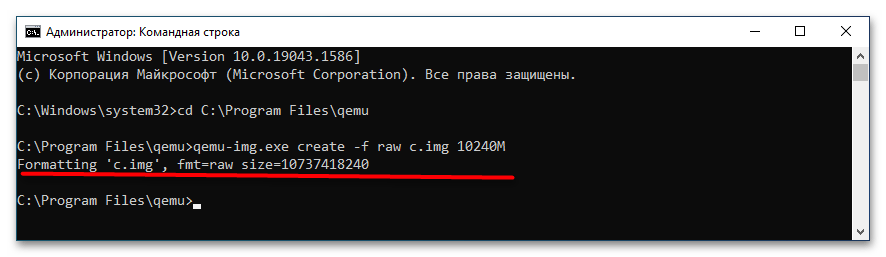
cd C:Program Filesqemu. Если эмулятор устанавливался в другую папку, после cd укажите путь к ней. - Создайте виртуальный жесткий диск, на который станет устанавливаться операционная система. Для этого выполните команду
qemu-img.exe create -f raw c.img 10240M, где c.img — название виртуального диска, а 10240 — его размер в мегабайтах. Размер диска-контейнера должен соответствовать требованиям запускаемой/устанавливаемой операционной системы. - Запустите установку дистрибутива операционной системы командой
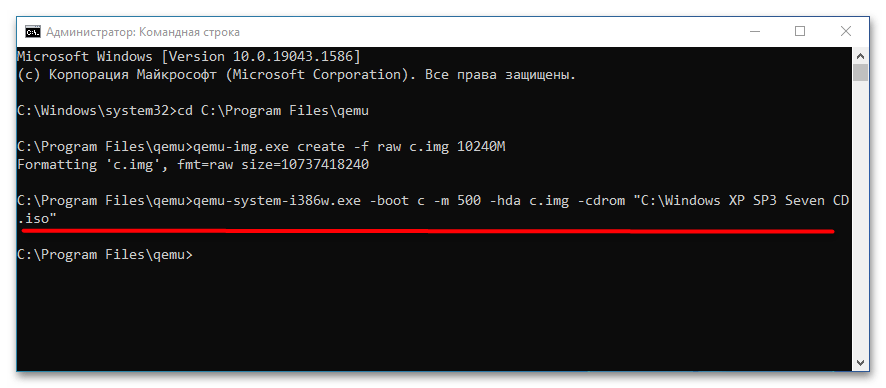
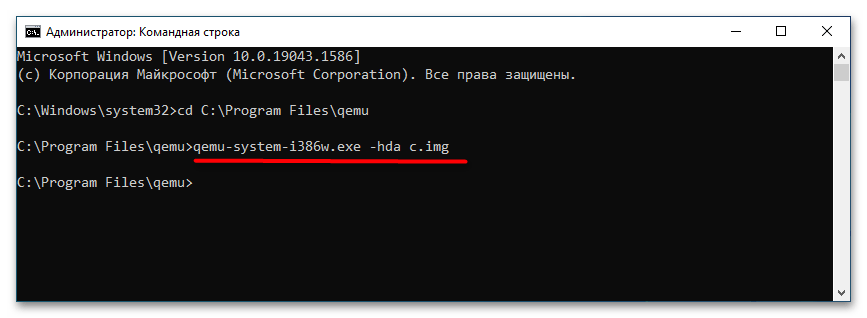
qemu-system-i386w.exe -boot c -m 512 -hda c.img -cdrom "C:Windows XP SP3 Seven CD.iso". -i386w в данном примере указывает, что виртуальная машина эмулирует архитектуру х86, -boot указывает загрузку с диска с названием «c», -m 512 выделяет виртуальной машине 512 МБ оперативной памяти, -hda c.img указывает, что система будет устанавливаться в файл-контейнер «c.img». Наконец, содержимое прямых кавычек после параметра –cdrom представляет собой путь к установочному образу. - В открывшемся окне QEMU выберите с помощью клавиш-стрелок вниз-вверх нужный пункт, в данном примере это установка операционной системы. Выполните традиционную процедуру установки системы на виртуальный жесткий диск.
- По завершении установки системы вы сможете запускать последнюю командой
qemu-system-i386w.exe -hda c.img.
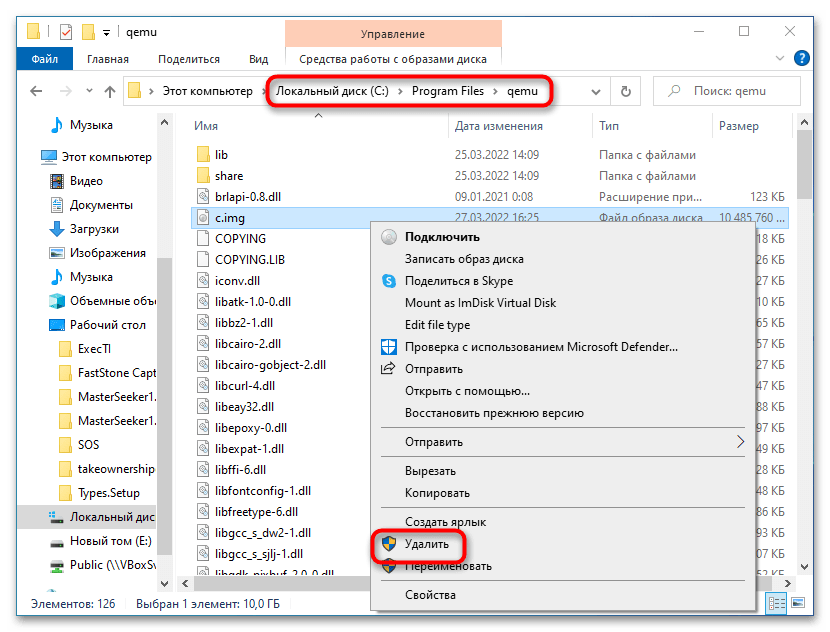
Если виртуальная система станет вам не нужна, удалите IMG-диск, на который она была установлена. По умолчанию файл диска IMG располагается в папке установки QEMU.
Запуск в QEMU образов LiveCD
Процедура запуска портативных операционных систем в QEMU намного проще, чтобы запустить в эмуляторе LiveCD, сформируйте и выполните команду следующего вида, заблаговременно перейдя в «Командной строке» в папку инсталляции эмулятора:
qemu-system-архитектура.exe -m 1024 -cdrom "путь к образу LiveCD"
Поскольку портативная ОС может загружаться в оперативную память, в предварительном создании виртуального диска нет необходимости.
Qemu Manager
Если вы не имеете навыков работы со штатной программой «Командная строка», можете попробовать воспользоваться приложением Qemu Manager — графическую оболочкой для эмулятора Qemu. Ниже прилагается краткая инструкция по использованию приложения.
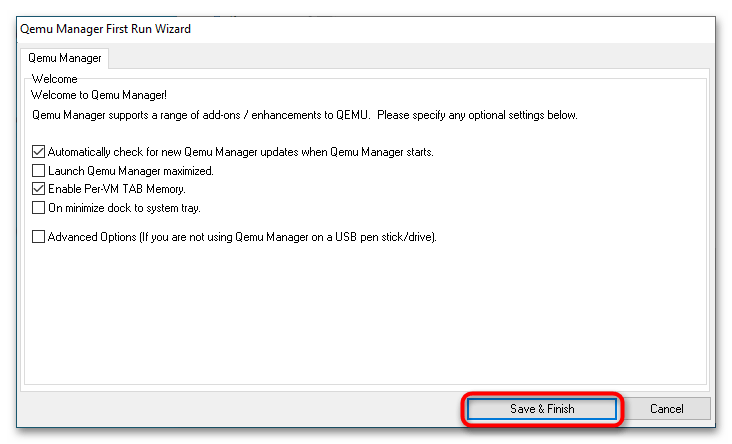
- Скачайте, установите и запустите Qemu Manager. В открывшемся окне настроек по умолчанию нажмите «Save & Finish».
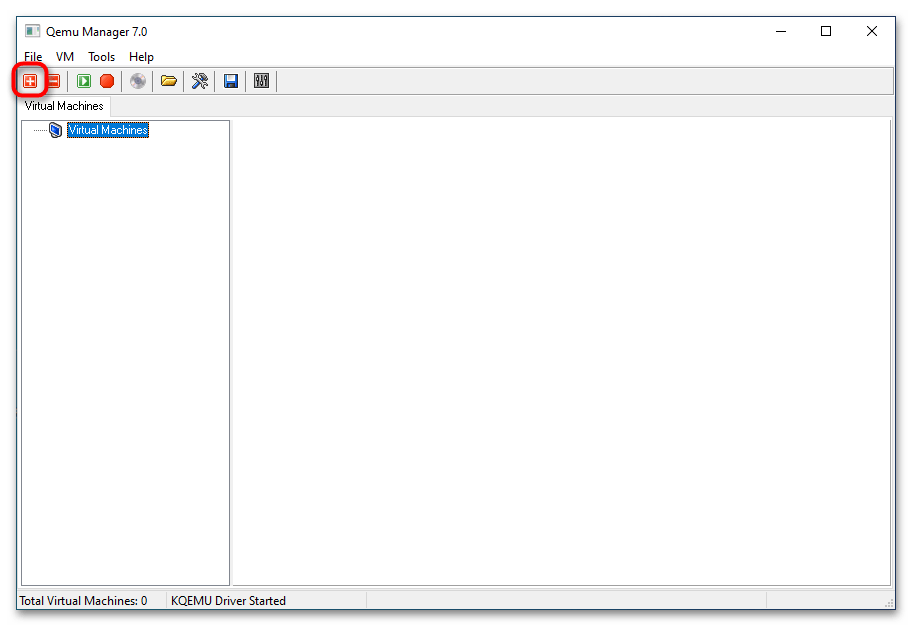
- В основном окне менеджера нажмите кнопку «+», чтобы приступить к созданию новой виртуальной машины (дальше VM).
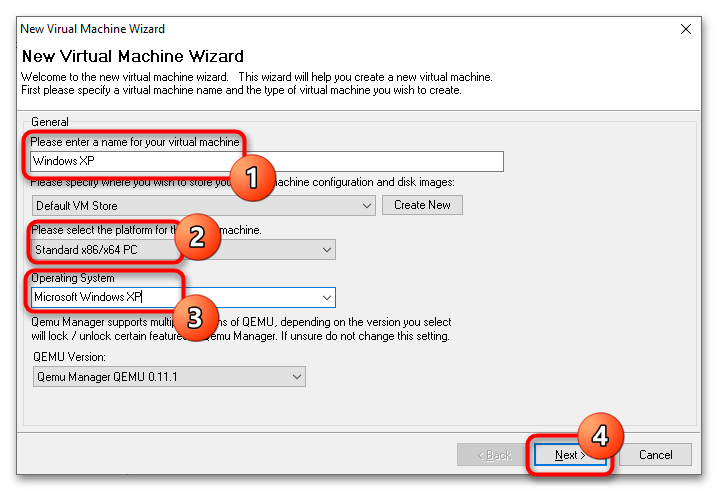
- В поле «Please enter a name for your virtual machine» введите произвольное название VM, в меню «Please select the platform for the virtual machine» укажите архитектуру VM, а из выпадающего списка «Operating System» выберите операционную систему.
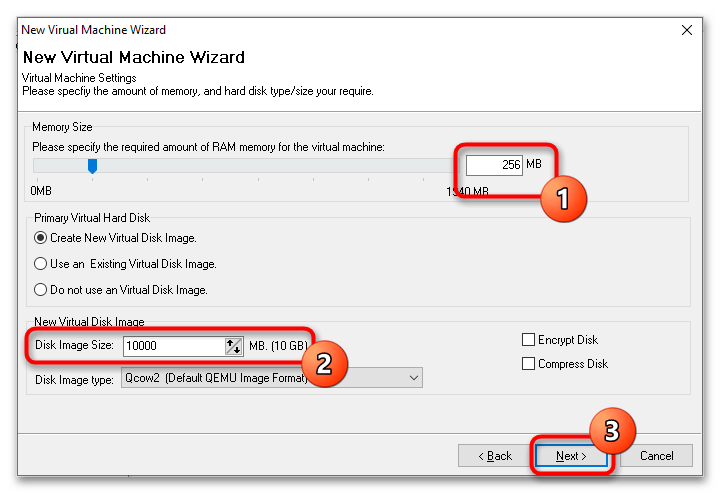
- Выделите с помощью ползунка «Memory Size» требуемый для VM объем оперативной памяти, а в меню «Disk Image Size» укажите размер виртуального диска. Если вы запускаете LiveCD, в настройках «Primary Virtual Hard Disk» следует выбрать опцию «Do not use an Virtual Disk Image».
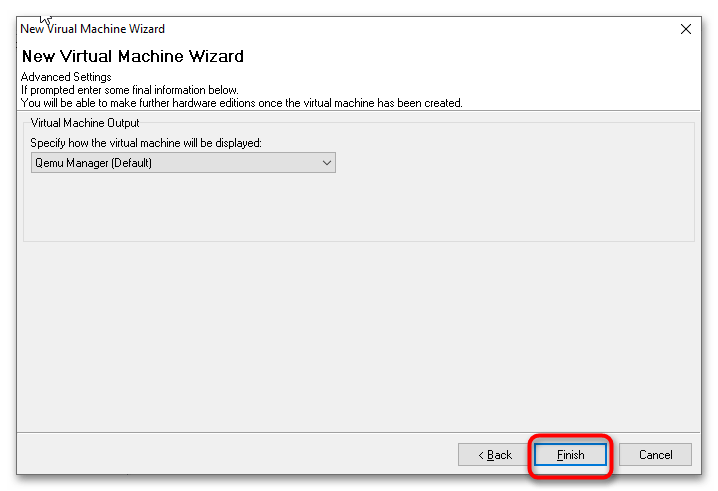
- В следующем окне нажмите кнопку «Finish».
- В результате в основном окне менеджера появится новая виртуальная машина с конфигурацией по умолчанию. При желании вы можете отредактировать параметры VM: например, изменить архитектуру процессора, выделяемый объем памяти, включить поддержку USB, создать и подключить новый виртуальный жесткий диск и так далее.
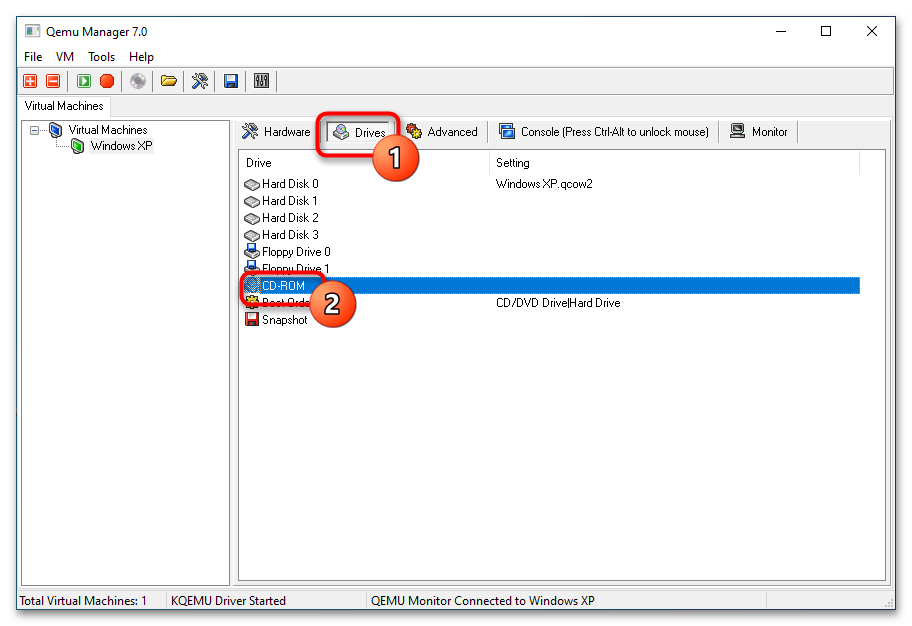
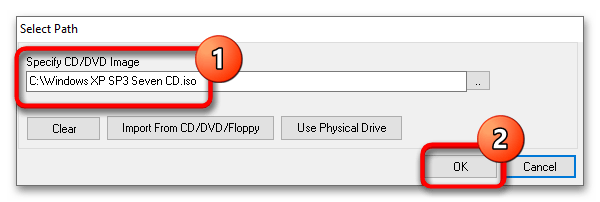
- Переключитесь на вкладку «Drives» и двойным кликом откройте настройку «CD-ROM».
- Укажите путь к установочному образу операционной системы или дистрибутиву LiveCD и сохраните настройки.
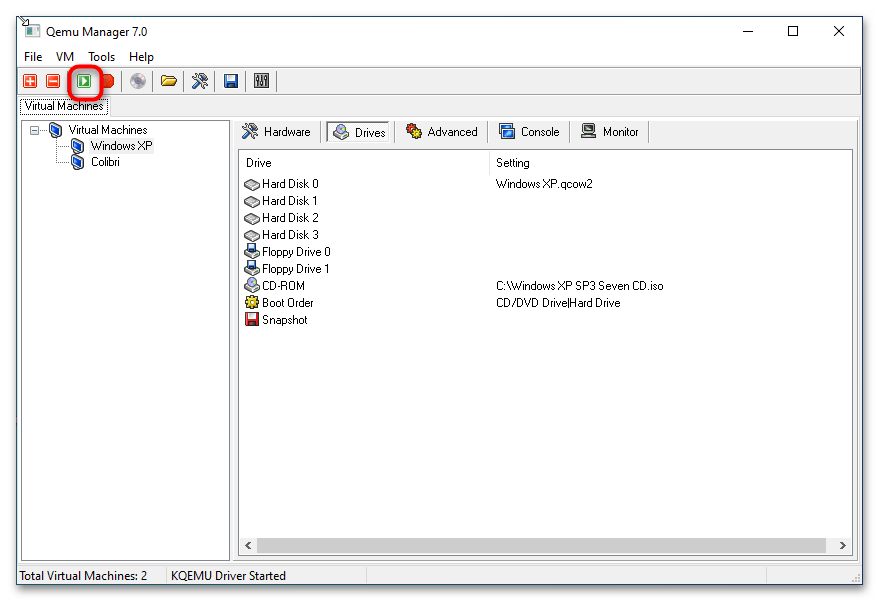
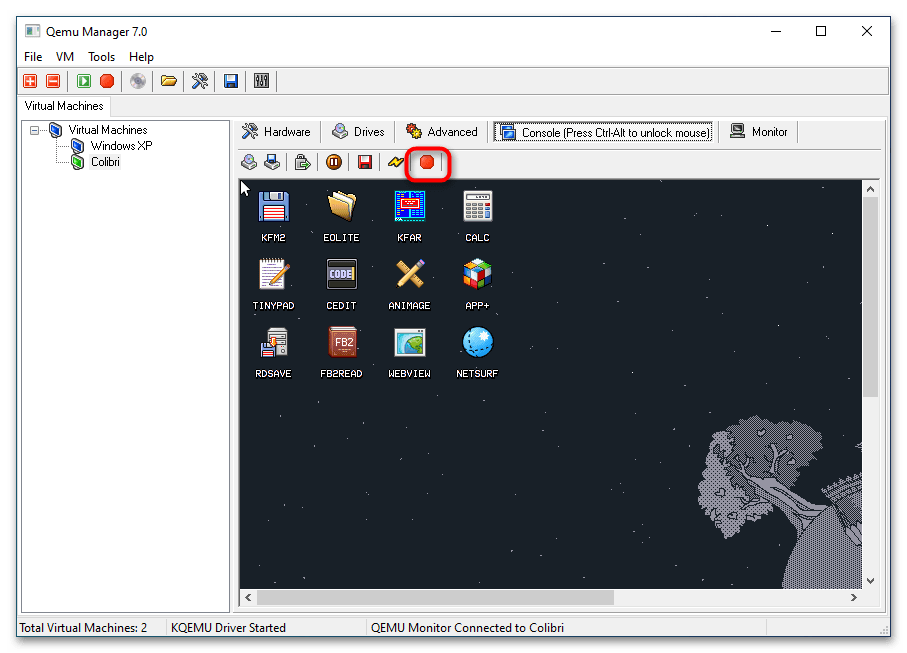
- Запустите виртуальную машину нажатием кнопки «Launch Selected VM». По умолчанию Qemu Manager захватывает мышку, так что она становится недоступной для хостовой операционной системы. Чтобы освободить курсор, нажмите комбинацию клавиш Ctrl + Alt.
- Чтобы завершить работу VM, нажмите кнопку «Quit Qemu».
Несмотря на отсутствие поддержки русского языка, Qemu Manager существенно упрощает работу с платформой Qemu. К сожалению, в настоящее время разработка данной программы прекращена, официальный сайт разработчика недоступен, но приложение по-прежнему доступно для скачивания из свободных источников.
Еще статьи по данной теме:
Помогла ли Вам статья?
Виртуализация — наиболее доступный способ запустить на одном ПК вторую операционную систему, не устанавливая ее непосредственно на жесткий диск. Вместо этого вторая ОС устанавливается на диск виртуальный, представленный специальным файлом-контейнером, созданным в гипервизоре — программе, позволяющей эмулировать работу гостевой системы в системе хостовой. Наибольшей популярностью среди домашних юзеров пользуются гипервизоры VirtualBox и VMware с мощным функционалом и наглядным GUI.
Но есть и другие, в чём-то даже более гибкие и продуктивные решения хотя и куда менее удобные в использовании. Например, QEMU — бесплатная программа с открытым исходным кодом, предназначенная для эмуляции программного обеспечения и операционных систем. Инструмент использует аппаратную виртуализацию, поддерживая два режима работы:
• Полная эмуляция — данный режим применяется для запуска операционных систем, в его рамках QEMU эмулирует физическое устройство со всеми его компонентами, встроенными и периферийными.
• Эмуляция пользовательского режима — дает возможность запускать программы, созданные для конкретной архитектуры на другой архитектуре, например, приложения ARM в x86. Режим доступен только в хостовой системе Linux.
QEMU поддерживается эмуляция архитектуры x86, ARM, MIPS, PowerPC, m68k, Alpha, SPARC, SH-4, CRISv2, MicroBlaze и это более солидный список, чем у того же Виртуалбокс.
Как установить QEMU в Windows
Скачать установочный файл эмулятора можно с официального сайта www.qemu.org/download/#windows,
есть редакции 32-битные и 64-битные, версию выбираем последнюю.
Устанавливается QEMU как обычная программа в папку Program Filesqemu, но можно выбрать и другое расположение.
Установку выполняем с параметрами по умолчанию, ничего менять не нужно, просто жмем в окне мастера «Next».
Виртуализация операционных систем в QEMU
В отличие от VirtualBox и подобных гипервизоров, QEMU не имеет графического интерфейса, работа с ней ведется через командную строку. Команд и параметров для создания и управления виртуальными машинами много, но для начала вам нужно знать хотя бы эти шесть.
• qemu-system — задает архитектуру виртуальной машины.
• qemu-img create — создает файл виртуального IMG-диска, на который будет устанавливаться операционная система.
• -m — выделяет виртуальной ОС указанный объем оперативной памяти.
• -hda — подключает созданный виртуальный диск.
• -boot IMG — указывает, что загрузка должна производиться с виртуального диска, вместо IMG следует указать имя IMG-файла.
• cdrom — содержит путь к установочному образу ISO, эмулирует дисковод.
Примечание: для запуска операционных систем, работающих в режиме LiveCD достаточно будет трех команд/параметров — первой, третьей и шестой.
Чтобы вам стало всё немного понятнее, установим и запустим с помощью QEMU какую-нибудь операционную систему. Для примера мы выбрали Windows XP, так как она легкая и занимает на диске мало места. QEMU у нас уже установлен, открываем командную строку, переходим в каталог установки и создаем виртуальный жесткий диск следующей командой:
qemu-img.exe create -f raw c.img 5000M
Файл qemu-img.exe в эмуляторе отвечает за создание IMG-образов, с — это название образа, 5000 — размер виртуального диска в мегабайтах. По умолчанию образ будет создан в папке QEMU.
Теперь сформируем следующую команду:
qemu-system-i386w.exe -boot c -m 350 -hda c.img -cdrom «E:WinXP_SP3.iso»
Исполняемый файл в начале команды отвечает за создание виртуальной машины с архитектурой х86, -boot с ключом -с сообщает, что грузиться она будет с диска, в значение параметра -hda подставляем созданный образ, а в качестве значения параметра –cdrom указываем путь к дистрибутиву Windows.
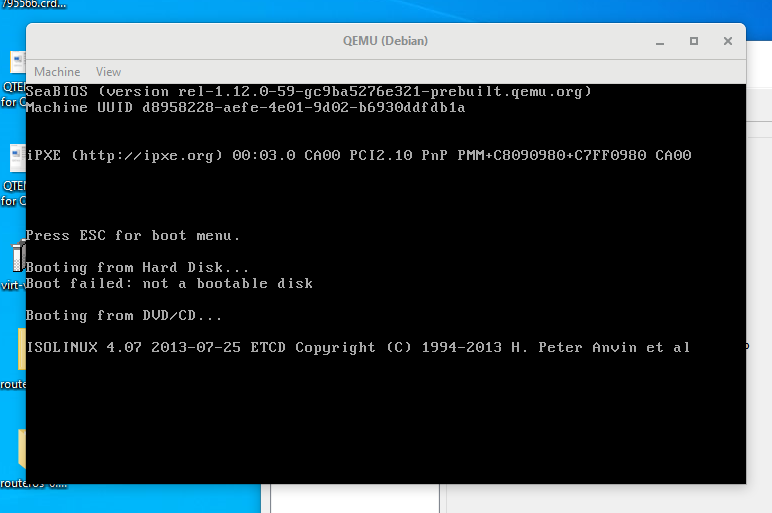
После выполнения команды появляется окошко QEMU с загрузочным меню, в котором мы выбираем установку на диск.
Далее проходим все этапы установки операционной системы вплоть до локальных настроек и загрузки рабочего стола.
Чтобы запустить закрытую виртуальную машину, выполните команду qemu-system-i386w.exe -hda name.img, где name — название вашего виртуального диска, чтобы удалить ставшую ненужной VM, просто удалите из каталога установки QEMU созданный IMG-образ.
Управлять QEMU можно с помощью клавиатуры и мыши, для переключения между эмулятором и хостовой машиной используйте комбинацию Ctrl+Alt+G. Запущенная с минимальными настройками ОС не будет иметь доступа к аудио- и сетевой карте, не будет также возможности обмена файлами между виртуальной и хостовой системами.
Нельзя сказать, что QEMU лучше или хуже VirtualBox либо VMware, это альтернативное средство виртуализации, имеющие как свои плюсы, так и минусы. QEMU менее удобен, требует знания документации и демонстрирует весьма небольшую производительность. Для ускорения работы в Windows требуется установка и настройка Диспетчера аппаратного ускорения HAXM, в Linux – подключение загружаемого модуля ядра KVM. С другой стороны, инструмент позволяет эмулировать работу устройств на базе разных архитектур, не поддерживаемые популярными гипервизорами.
Загрузка…
�������: ����� �������� <acid_jack@ukr.net>, ���� 2006
����������
- 1. ��������
- 1.1 �����������
- 2. ���������
- 2.1 Linux
- 2.2 Windows
- 2.3 Mac OS X
- 3. ������ QEMU � �������� ��������� ������� ���� PC
- 3.1 ��������
- 3.2 ������� ������
- 3.3 ������
- 3.4 �������
- 3.5 ������� QEMU
- 3.5.1 �������
- 3.5.2 ������������� ���������
- 3.6 ������ ������
- 3.6.1 ������� �������� ������ �����
- 3.6.2 ����� snapshot
- 3.6.3 ������
qemu-img
- 3.7 �������� ����
- 3.7.1 ������������� �������� ���������� tun/tap
- 3.7.2 ������������� �������� ����� � ������ ������������
- 3.8 ���������������� �������� Linux
- 3.9 ������������� GDB
- 3.10 �������������� ���������� �� ����������� ��
- 3.10.1 Linux
- 3.10.2 Windows
- 3.10.2.1 ��������� ����������� ������� SVGA
- 3.10.2.2 �������� �������� ����������
- 3.10.2.3 �������� � ������������� ����� � Windows 2000
- 3.10.2.4 ���������� ������ Windows 2000
- 3.10.2.5 ������������� ����� ��������� ��� Unix � Windows
- 3.10.2.6 �������� � ������������� � Windows XP
- 3.10.3 MS-DOS � FreeDOS
- 3.10.3.1 �������� �������� ����������
- 4. ������ QEMU � �������� ��������� ������� ���� PowerPC
- 5. ������ QEMU � �������� ��������� ������� ���� Sparc32
- 6. ������ QEMU � �������� ��������� ������� ���� Sparc64
- 7. ������ QEMU � �������� ��������� ������� ���� MIPS
- 8. ������ QEMU � �������� ��������� ����������������� ������������
- 8.1 ������� ������
- 8.2 ������ Wine
- 8.3 ����� ��������� ������
- 9. ���������� �� ��������� ����
- 9.1 Linux/Unix
- 9.1.1 ����������
- 9.1.2 ������ ����������� ������
- 9.2 Windows
- 9.3 �����-���������� � Linux ��� Windows
- 9.4 Mac OS X
- 9.1 Linux/Unix
| [Top] | [Contents] | [Index] | [ ? ] |
1. ��������
1.1 �����������
QEMU — ��� �������! �������� ����������, ������������ ������������ ���������� ��� ���������� ������� �������� ��������.
QEMU ����� ��� ������ ������:
- —
�������� ���� �������. � ���� ������ QEMU ��������� ����������� ������� (�������� ��), ������� ��������� � ��������� ������������ ������������. ��� ����� ������������ ��� ������� ��������� ������������ ������ ��� ������������� ������������ �� ��� ��� ������� ���� �������. - —
�������� ����������������� ������ (������ Linux-������). � ���� ������ QEMU ����� ��������� �������� Linux, ���������������� ��� ������ ����������, �� ������ ����������. ��� ����� ������������ ��� ������� Wine — ��������� API Windows (http://www.winehq.org), ��� ��� ����ݣ���� �����-���������� � �����-�������.
QEMU ����� �������� �� �������-������� ��� ��������, ����������� ��� ���� ������������������ ������������������.
��� �������� ����� ������� �������������� ��������� ������������:
- PC (��������� x86 ��� x86_64)
- PREP (��������� PowerPC)
- G3 BW PowerMac (��������� PowerPC)
- Mac99 PowerMac (��������� PowerPC, � �������� ����������)
- Sun4m (32-������ ��������� Sparc)
- Sun4u (64-������ ��������� Sparc processor, � �������� ����������)
- Malta board (32-������ ��������� MIPS, � �������� ����������)
��� �������� ������������ �������������� ���������� x86, PowerPC, ARM � Sparc32/64.
2. ���������
���� �� ������ �������������� �������������� QEMU, ���������� � compilation.
2.1 Linux
���� ��� ������ ������������ ���� ����� � ��� ������������������ ��������� ������� — ��� ����� ������ ���������� ��. � ��������� ������ ��. compilation.
2.2 Windows
����������������� �������� ����������� ����� ��������� � http://www.free.oszoo.org/download.php.
2.3 Mac OS X
����������������� �������� ����������� ����� ��������� �
http://www.freeoszoo.org/download.php.
3. ������ QEMU � �������� ��������� ������� ���� PC
3.1 ��������
��� �������� ������� QEMU ��������� ��������� ������������ ������������:
- —
i440FX host PCI bridge � PIIX3 PCI to ISA bridge - —
PCI VGA-����� Cirrus CLGD 5446 ��� ��������� VGA-����� � VESA-������������ Bochs (���������� �������, ������� ��� ������������� ������). - —
PS/2-���� � ���������� - —
2 PCI IDE-���������� � ���������� ֣����� � �������� CD-ROM - —
�������� - —
������� PCI-�������� NE2000 - —
���������������� ����� - —
�������� ����� Soundblaster 16
QEMU ���������� PC BIOS ������� Bochs � Plex86/Bochs LGPL VGA BIOS.
3.2 ������� ������
��������� � ���������� ����� linux (`linux.img’), � ����� ��������:
������ ����������� Linux, ����������� ��� ������ �����������.
3.3 ������
�������������: qemu [�����] [�����_�����] |
disk_image — ��� «�����» ����� ֣������ �����,
��������������� �������� ֣������ IDE-�����.
����� ���������:
- `-fda ����’
- `-fdb ����’
-
����� ���� — ����� ������� ��� ��������� 0/1 �������������� (See ������ ������.). �� ������ ������������ ������� �������-�������, ������ `/dev/fd0′ � �������� �����.
- `-hda ����’
- `-hdb ����’
- `-hdc ����’
- `-hdd ����’
-
����� ���� — ����� ֣������ ����� 0, 1, 2 ��� 3 �������������� (See ������ ������.).
- `-cdrom ����’
-
����� file — ����� CD-ROM (�� �� ������ ������������ ������������ `-hdc’ � `-cdrom’). �� ������ ������������ CD-ROM �������-�������, ������ `/dev/cdrom’ � �������� �����.
- `-boot [a|c|d]’
-
�������� � ������� (a), ֣������ ����� (c) ��� CD-ROM (d). �� ��������� ����������� �������� � ֣������ �����.
- `-snapshot’
-
������ �� ��������� ����, � �� � ���� ������ ֣������ �����. � ���� ������ ����� «������» ����� �������� ����������. ������ �� ������ ������������� �������� ������, ����� ������� C-a s (See ������ ������.).
- `-m megs’
-
������������� ��ߣ� ����������� ������ � megs ��������. �� ��������� �� ���������� 128 ��.
- `-nographic’
-
������ QEMU ���������� SDL ��� ������ VGA-������. ��������� ��� �����, �� ������ ������ ��������� ����������� �����, ������, ����� �������, QEMU ������� ���������� �����������. ����������� ���������������� ���� ���������������� � �������. ���� �� ��� �� ������ ������������ QEMU ��� ������� ���� Linux, ���� � ��ϣ� ������������ ���������������� �������.
- `-k ����’
-
������������� ��������� ���������� ��� ������� ����� (��������
ru��� ��������). ��� ����� ����� ������ � ��� �������, ����� ������ �������� «�����» ���� ������ (����., �� Mac’�� ��� � ��������� �������� X11). ��� �� ����� ������������ ţ �� ������� PC/Linux ��� PC/Windows.�������� ��������� ���������:
ar de-ch es fo fr-ca hu ja mk no pt-br sv da en-gb et fr fr-ch is lt nl pl ru th de en-us fi fr-be hr it lv nl-be pt sl tr
�� ��������� ������������ ���������
en-us. - `-enable-audio’
-
�� ��������� �������� SB16 ���������, ��������� ��� ����� ������� ��������� �������� � Windows. �� ������ �������� ţ ������� � ������� ���� �����.
- `-localtime’
-
����������� ���� ��������� ������� �������� ���������� ������� (�� ��������� � UTC). ��� ����� ����� ��� ����������� ����������� ������� � MS-DOS ��� Windows.
- `-full-screen’
-
������ � ������������� ������.
- `-pidfile ����’
-
��������� ������������� �������� QEMU � ����. �������, ���� �� ���������� QEMU �� �������.
- `-win2k-hack’
-
����������� ��� ����� ��� ��������� Windows 2000, ����� ������������� ������ ������������ �����. ����� ��������� Windows 2000, ��� ������ �� ����� ������������ ��� ����� (��� ��������� �������� ������ �� IDE).
������� �����:
- `-n ������’
-
������ ������ ������������� ���� TUN/TAP [default=/etc/qemu-ifup]. ���� ������ ����������� ��� ��������� �������� ���������� �������-������� (������ tun0), ���������������� ����������� ������� ����� NE2000.
- `-nics n’
-
�������� n-��� ����� ������� ���� (�� ��������� 1).
- `-macaddr �����’
-
������ mac-����� ������� ���������� (� hex-������� ���� aa:bb:cc:dd:ee:ff). Mac-����� ������������� ��� ������� ������ �������� ����������.
- `-tun-fd fd’
-
�������������, ��� fd �������� � ������� ����������� tap/tun �������-������� � ���������� ���. ������� ������������� ����� �������� �� ����� http://bellard.org/qemu/tetrinet.html.
- `-user-net’
-
������������� �������� ����� � ������ ������������. ������������ �� ���������, ���� �� ������ ������ ������������� ���� tun/tap.
- `-tftp �������’
-
��� ������������� �������� ����� � ������ ������������ ���������� ���������� ������ TFTP. ��� �����, ������������ � ��������, ����� ���� ��������� � �������-������� � �������� ������� � ������� ������� TFTP. ������ TFTP � �������� ������� ������ ���� �������� �� �������� ����� �������� ������ (����������� �������
bin��� TFTP-������� ��� Unix). IP-������� �������-������� ������ ��������� 10.0.2.2. - `-smb �������’
-
��� ������������� �������� ����� � ������ ������������ ���������� ���������� ������ SMB, ����� Windows-������� ����� ����� ���������� ������ � ������ �������-�������, ����������� � ��������� `��������’.
� �������� �� Windows ����� �������� ������:
� ���� `C:WINDOWSLMHOSTS’ (��� Windows 9x/Me) ��� `C:WINNTSYSTEM32DRIVERSETCLMHOSTS’ (Windows NT/2000).
����� ������ � `��������’ ����� �������� ����� `\smbserverqemu’.
������, ��� �� �������-������� ������ ���� ���������� ������ SAMBA ��� `/usr/sbin/smbd’. QEMU ��� ������� ������������� � smbd ������ 2.2.7a �� Red Hat 9 � ������ 3.0.10-1.fc3 �� Fedora Core 3.
- `-redir [tcp|udp]:����_�������:[�����_�������]:����_�����’
-
��� ������������� �������� ����� � ������ ������������ �������������� TCP- ��� UDP-�����������, �������� � ����_�������, �� �����_������� � ����_�����. ���� �����_������� �� ������, ������������ 10.0.2.15 (�����, ���������� �� ��������� ���������� �������� DHCP).
��������, ����� ������������� ����������� X11 ������� � ������ 1 �� ����� 0 �����, ����������� ��������� �������:
# �� ������� qemu -redir tcp:6001::6000 [...] # ������ xterm ������� ������ ��������� �� �������� ������� X11 xterm -display :1
����� ������������� telnet-����������� � ����� 5555 ������� �� telnet’������ ���� �����, ����������� ��������� �������:
# �� ������� qemu -redir tcp:5555::23 [...] telnet localhost 5555
�����, ���� �� ���������
telnet localhost 5555, �� ������������ � telnet-������� �����. - `-dummy-net’
-
������������� ���������� �������� �����: �������� ������� �� ����� �������� �� ������ ������.
�������� Linux. � ������� ���� ����� �� ������ ������������ �������� ���� Linux, �� ������������ ��� �� ����� �����. ��� ����� ���� �������� ��� ������� ������������ ��������� ����.
- `-kernel bzImage’
-
������������� bzImage � �������� ������ ����.
- `-append cmdline’
-
������������� cmdline � �������� ��������� ������ ����.
- `-initrd ����’
-
������������� ���� � �������� ��������� ram-�����.
����������/���������� �����:
- `-serial dev’
-
��������������� ������������ ����������������� ����� � ���������� dev �������-�������. ��������� ����������:
-
vc -
����������� �������
-
pty -
[������ ��� Linux] Pseudo TTY (����� PTY ���������� �������������)
-
null -
���������� void
-
stdio -
[������ ��� Unix] ����������� ����/�����
����������� ����������� � ����������� ������ ��������
vc, � � ������������� —stdio.��� ����� ����� ������������ ����������� ��� �������� �� ����ң� ���������������� ������.
-
- `-monitor dev’
-
��������������� �������� � ���������� dev �������-������� (�� �� ����� ����������, ��� � ��� ���������������� ������). ����������� ����������� � ����������� ������ ��������
vc, � � ������������� —stdio. - `-s’
-
�������� ����������� gdb � ����� 1234 (See ������������� GDB.).
- `-p ����’
-
��������� ����� ����������� gdb.
- `-S’
-
�� ��������� ��������� ��� ������� (�� ������ ������ ‘c’ � ��������).
- `-d’
-
�������� ������ ������� � /tmp/qemu.log.
- `-hdachs c,h,s,[,t]’
-
������������� ������������ ���������� ��������� ֣������ ����� 0 (1 <= c <= 16383, 1 <= h <= 16, 1 <= s <= 63) � ����������� ������������� �������������� ����� �������� ������ BIOS (t=none, lba ��� auto). ������ QEMU ����� ��� ���������� ��� ��� ���������. ��� ����� ������� ��� ������� ������ ������� MS-DOS.
- `-isa’
-
�������� ������� ������ � ISA (�� ��������� ����������� ������� � PCI).
- `-std-vga’
-
�������� ����������� VGA-����� � VBE-������������ Bochs (�� ��������� ����������� PCI VGA Cirrus Logic GD5446)
- `-loadvm ����’
-
������ �� ���������� ����� ��������� (
loadvm� ��������)
3.4 �������
�� ����� ����������� �������� �� ������ ������������ ��������� �������:
- Ctrl-Alt-f
-
������������ � ������������� �����.
- Ctrl-Alt-n
-
������������ � �����������. ������� ‘n’. ������������ ��������� ����� ����:
- 1
-
������� ������� ����������
- 2
-
�������
- 3
-
���������������� ����
- Ctrl-Alt
-
������������ ������� ���������� � ����.
� ����������� �������� �� ������ ������������ ��������� ������ Ctrl-Up,
Ctrl-Down, Ctrl-PageUp � Ctrl-PageDown ��� ����������� ��
������� ���������.
�� ����� ��������, ���� �� ����������� ����� `-nographic’, �������
����������� Ctrl-a h, ����� ����� ���� ������� � ��������� ���������
�������:
- Ctrl-a h
-
����� ���� �������.
- Ctrl-a x
-
����� �� ���������.
- Ctrl-a s
-
���������� ������ ����� � ���� (���� ������������ -snapshot).
- Ctrl-a b
-
�������� break (magic sysrq � Linux).
- Ctrl-a c
-
������������ ����� �������� � ���������.
- Ctrl-a Ctrl-a
-
�������� ���������� ������ Ctrl-a.
3.5 ������� QEMU
������� QEMU ������������ ��� ���������� ������� ������ � ��������� QEMU. ��
������ ������������ ��� ���:
- —
���������� ��� ������� ������� �ߣ���� ����������� (����� ��� CD-ROM ���
����������); - —
«������������»/»�������������» ����������� ������ (��) � ��������� ���
��������������� ţ ��������� �� ����� �� �����; - —
������� ��������� �� ��� ������������� ������������� �������� ���������.
3.5.1 �������
�������� ��������� �������:
- `help ��� ? [cmd]’
-
����� ������� �� ���� �������� ��� ������ �� ������� cmd.
- `commit’
-
������ ��������� � ����� ����� (���� ������������ -snapshot).
- `info ���-�������’
-
���������� ��������� ���������� � ��������� �������:
- `info network’
-
���������� ��������� ����
- `info block’
-
���������� ������� ����������
- `info registers’
-
���������� �������� ����������
- `info history’
-
���������� ������� ��������� ������
- `q ��� quit’
-
����� �� ���������.
- `eject [-f] ����������’
-
���������� �ߣ����� �������� (����������� ��� ��������������� ���������� -f).
- `change ���������� �����’
-
����� �ߣ����� ��������.
- `screendump �����’
-
���������� ����������� ������ � ���� PPM-����������� � ����.
- `log ������1[,…]’
-
��������� �������������� ��������� �������� � ���� `/tmp/qemu.log’.
- `savevm ����’
-
���������� ��������� ����������� ������ � ����.
- `loadvm ����’
-
�������������� ��������� ����������� ������ �� �����.
- `stop’
-
��������� ��������.
- `c ��� cont’
-
������������� ��������.
- `gdbserver [����]’
-
������ ������ gdbserver (�� ��������� ����=1234).
- `x/fmt �����’
-
���� ����������� ������, ������� � ���������� ������.
- `xp /fmt �����’
-
���� ���������� ������, ������� � ���������� ������.
fmt — ��� ������, ���������� �������, ��� ����� ������������� ������. ���
���������: `/{����������}{������}{������}’- ����������
-
��� ����� �������� ��� �����.
- ������
-
����� ���� x (�����������������), d (���������� �� ������), u (���������� ��� �����), o
(������������), c (����������) ��� i (���������� asm). - ������
-
����� ���� b (8 ���), h (16 ���), w (32 ���) ��� g (64 ���). �� ��������� x86
�������h���w����� ���� ������� � ��������i��� ������
������� ���������� ��� 16- ��� 32-������� ���� ��������������.
�������:
-
���� 10 ���������� ������������ �������� ���������:
(qemu) x/10i $eip 0x90107063: ret 0x90107064: sti 0x90107065: lea 0x0(%esi,1),%esi 0x90107069: lea 0x0(%edi,1),%edi 0x90107070: ret 0x90107071: jmp 0x90107080 0x90107073: nop 0x90107074: nop 0x90107075: nop 0x90107076: nop
-
���� 80-�� 16-������ �������� ������������ ������ �����������:
(qemu) xp/80hx 0xb8000 0x000b8000: 0x0b50 0x0b6c 0x0b65 0x0b78 0x0b38 0x0b36 0x0b2f 0x0b42 0x000b8010: 0x0b6f 0x0b63 0x0b68 0x0b73 0x0b20 0x0b56 0x0b47 0x0b41 0x000b8020: 0x0b42 0x0b69 0x0b6f 0x0b73 0x0b20 0x0b63 0x0b75 0x0b72 0x000b8030: 0x0b72 0x0b65 0x0b6e 0x0b74 0x0b2d 0x0b63 0x0b76 0x0b73 0x000b8040: 0x0b20 0x0b30 0x0b35 0x0b20 0x0b4e 0x0b6f 0x0b76 0x0b20 0x000b8050: 0x0b32 0x0b30 0x0b30 0x0b33 0x0720 0x0720 0x0720 0x0720 0x000b8060: 0x0720 0x0720 0x0720 0x0720 0x0720 0x0720 0x0720 0x0720 0x000b8070: 0x0720 0x0720 0x0720 0x0720 0x0720 0x0720 0x0720 0x0720 0x000b8080: 0x0720 0x0720 0x0720 0x0720 0x0720 0x0720 0x0720 0x0720 0x000b8090: 0x0720 0x0720 0x0720 0x0720 0x0720 0x0720 0x0720 0x0720
- `p ��� print/fmt ���������’
-
����� �������� ���������. ������������ ������ ����� format �� fmt.
- `sendkey �������’
-
���������� ������� � ��������. �����������
-��� ��������������
������� ���������� ������. ������:��� ������� ������� ��� �������� ������� ������, ������� ��� �����������
��������� ������������� �� ������ ������, ���������ctrl-alt-f1� X
Window. - `system_reset’
-
����� �������.
3.5.2 ������������� ���������
������� �������� ������������� ���������, ������� ����� ������������ ������
����� ������������� ����������. �� ������ ������������ �������� ��������� ���
��������� �������� ������̣���� ��������� ����������, �������� ����� ����
���� $.
3.6 ������ ������
QEMU, ������� � ������ 0.6.1, ������������ ��������� �������� ������� ������,
������� ������ ��������� ��ߣ�� (�� ������ ������������� �� ���� ������
�������� ��������), � ����� ������ � ������������� ������ ������.
3.6.1 ������� �������� ������ �����
�� ������ ������� ����� ����� � ������� �������:
qemu-img create �����.img ������ |
��� �����.img — ��� ��� ����� ������ �����, � ������ — ��� ������ �
����������. �� ������ �������� ��������� M, ����� ������� ������ �
����������, � G ��� ������� � ����������.
�������������� ���������� See ������ qemu-img.
3.6.2 ����� snapshot
���� �� ����������� ����� `-snapshot’, ��� ������ ������ ������������
������ ��� ������. ��� ������ �������� ��� ������������ �� ��������� ����,
��������� � `/tmp’. ������ �� ������ �������� �������������� ������ �
«�����» ����� ����� � ������� ������� commit � �������� (���
������ C-a s � ���������������� �������).
3.6.3 ������ qemu-img
usage: qemu-img ������� [����� �������] |
�������������� ��������� �������:
- `create [-e] [-b �������_�����] [-f ������] ���� [������]’
- `commit [-f ������] ����‘
- `convert [-c] [-e] [-f ������] ���� [-O ��������_������] �������_����‘
- `info [-f ������] ����‘
��������� ������:
- ����
-
��� ����� � ������� �����
- �������_�����
-
����� �����, ��������� ������ ��� ������, ������� ������������ � �������� ���� ��� ������ �.�. copy-on-write; � ���� ������ ����������� ������ �������� ������.
- ������
-
��� ������ ������ �����. � ����������� ������� �� ������������ �������������. �������������� ��������� �������:
-
raw -
«�����» ������ (�� ���������). ������������� ����� ������� �������� ��, ��� �� ����� � ����� �������������� � ������ ���������. ���� ���� �������� ������� ������������ ���� (holes) (��������, � ext2 ��� ext3 � Linux), ����� ����� �� ����� ����� �������� ������ ���������� �������. �����������
qemu-img info, ����� ������ �������� ������, ���������� �������, ���ls -ls� Unix/Linux (���du -h— ����. �����������). -
qcow -
������ QEMU — �������� ������������� ������. �� ��������� �������� ������ �������� ������� (������� � ��� ������, ���� �� ���� �������� ������� �� ������������ «����», ��������, � Windows), ������������ ���������� AES � ������ zlib.
-
cow -
������ User Mode Linux Copy On Write. ������������ � QEMU ��� ������� � ��������������� ��ߣ���. �������������� ������ ��� ������������� � ����������� ��������. �� �������� � win32.
-
vmdk -
������, ����������� � VMware 3 � 4.
-
cloop -
������ Linux Compressed Loop. ������� ������ ��� ���������� ������������� ������ ������� CD-ROM, ��������������, ��������, �� LiveCD � Knoppix.
-
- ������
-
������ ������ ����� � ����������. �������� ������������� �������������� ���������:
M(��������) �G(��������). - ��������_����
-
��� ����� ������������ ������ �����.
- ��������_������
-
������ ������������ �����.
- -c
-
��������, ��� ����������� ����� ������ ���� ���� (������ ��� ������� qcow).
- -e
-
��������, ��� ����������� ����� ������ ���� ���������� (������ ��� ������� qcow).
�������� �������:
- `create [-e] [-b �������_�����] [-f ������] ���� [������]’
-
������� ����� ������ ����� � ���� ���������� ����� ���������� ������� � �������.
���� ������ �������_�����, ����� � ����� ����� ������������ ������ ���������, ������������ ��������_������. �������_����� �� ����� ����������, ������ ���� �� �� �������������� � �������� ��������
commit. - `commit [-f ������] ����‘
-
������ � ������� ����� ���������, ���������� � ����.
- `convert [-c] [-e] [-f ������] ���� [-O ��������_������] ��������_����‘
-
��������������� ����� ����� ���� � ����� ��������_���� � �������������� ���������� �������. ����������� �� ����� ���� ���������� (�����
-e) ��� ���� (�����-c).���������� � ������ �������������� ������ � �������
qcow. ������ �������� � ������ «������ ��� ������», �.�. ���� ���������������� ������ ������, �� ������ � ���� ������� � �������� ����.��� ���������� ������������ �������� ���������� �������� AES (�� 128-������� �������). ��� ����������� ������������ ������ ����������� ������� ������ (������� 16 ��������).
�������������� ������� ����� ������� ��� ���������� �� �������� ��� ������������� ������� ���������������� �������, ������ ���
qcow���cow: ��� ���� ���������� ������ ������� � � ���������� ������ ��� ���������. - `info [-f ������] ����‘
-
������� ���������� �� ������ ����� filename. ����������� ţ ��� ����������� ������������, ������������������ �� ֣����� ����� ��� ���� �����, ��������� ��� ����� ���������� �� ������������� �������.
3.7 �������� ����
QEMU ����� ����������� �� 6-� ������� ���� (NE2000-����). ������ �� ���� ����� ���� ���������� � ������̣����� �������� ���������� �������-�������.
3.7.1 ������������� �������� ���������� tun/tap
��� ����������� ������ �������� ����. QEMU ��������� � �������-������� ����������� ������� ���������� (��� ��������� tun0), � ����� �� ������ ��������� ��� ���, ��� ���� �� ��� ���� ��������� ethernet-�����.
� �������� ������� �� ������ ��������� ����� `linux-test-xxx.tar.gz’, ����������� ������ `qemu-ifup’ � `/etc’ � ��������� ��������������� ������� sudo, ����� ������� ifconfig, ����������� � `qemu-ifup’, ����� ���� ��������� � ������� root’�. ������� �� ������ ��������� � ���, ��� ���� �������-������� ������������ ������� ���������� TUN/TAP: ������ ������������ ���������� `/dev/net/tun’.
� direct_linux_boot ���� ������ ������������� ����� ���� � ������������ Linux.
3.7.2 ������������� �������� ����� � ������ ������������
��� ������������� ����� `-user-net’, ��� ���� � ��� ��� ������� ������������� tun/tap, QEMU ���������� ��������� ���������������� ������� ���� (��� �� ����� ����� root’� ��� ������������� ����������� ����). ������������ ����������� ���� ������������ ����� ���������:
����������� ������ QEMU <------> ��������/DHCP-������ <-----> ��������
(10.0.2.x) | (10.0.2.2)
|
----> DNS-������ (10.0.2.3)
|
----> SMB-������ (10.0.2.4)
|
�� QEMU ��ģ� ���� ���, ��� ���� �� ��� ���������� �� ����������, ����������� ��� �������� �����������. �� ������ ������������ ������ DHCP ��� �������������� ��������� ���� � �� QEMU.
����� ��������� ������ ���� � ������ ������������, ����������� ����� 10.0.2.2 � ���������, �������� �� �� ����� �� ��������� 10.0.2.x �� ������������ DHCP-������� QEMU.
�������� ��������, ��� ping �� �������� �� ��������� � ��������-�������, ��������� ��� ����� ��������� ���������� root’�. ��� ��������, ��� �� ������ ������������ ������ ��������� ������������� (10.0.2.2).
��� ������������� ����������� ������� TFTP, ������������� ����� ��������� � ���� TFTP-�������.
��� ������������� ����� `-redir’, TCP- ��� UDP-����������� � �������-������� ����� ���� �������������� � �������� �������. ��������, ��� ��������� �������������� X11-, telnet- ��� SSH-�����������.
3.8 ���������������� �������� Linux
� ���� ������� ���������� � ���, ��� ��������� ���� Linux ������ QEMU ��� ������������� �������� ������ ������������ �����. ��� ����� ������� ��� �������� ������������ ���� Linux. ����� ���������� ��������� ���� � QEMU.
- ��������� ����� `linux-test-xxx.tar.gz’, ���������� ���� Linux � ����� �����.
- �������������: ���� ��� ����� ��������� ���� (�������� ��� ������� X11-����������), �� ������ ����������� ������ `qemu-ifup’ � `/etc’ � ��������� ��������������� �������
sudo, ����� �������ifconfig, ����������� � `qemu-ifup’, ����� ���� ��������� � ������� root’�. ������� �� ������ ��������� � ���, ��� ���� �������-������� ������������ ������� ���������� TUN/TAP: ������ ������������ ���������� `/dev/net/tun’.���� ���� ��������, ����� ����� �������-������� � ����������� ����� ��������������� ����������� ������� ����������. �� ���� ������� ����������� ���� �������� �� IP-������ 172.20.0.2, � ���� ������� �������� � ����������� �� IP-������ 172.20.0.1.
- ���������
qemu.sh. �� ������ ������ ������� ���������:
> ./qemu.sh Connected to host network interface: tun0 Linux version 2.4.21 (bellard@voyager.localdomain) (gcc version 3.2.2 20030222 (Red Hat Linux 3.2.2-5)) #5 Tue Nov 11 18:18:53 CET 2003 BIOS-provided physical RAM map: BIOS-e801: 0000000000000000 - 000000000009f000 (usable) BIOS-e801: 0000000000100000 - 0000000002000000 (usable) 32MB LOWMEM available. On node 0 totalpages: 8192 zone(0): 4096 pages. zone(1): 4096 pages. zone(2): 0 pages. Kernel command line: root=/dev/hda sb=0x220,5,1,5 ide2=noprobe ide3=noprobe ide4=noprobe ide5=noprobe console=ttyS0 ide_setup: ide2=noprobe ide_setup: ide3=noprobe ide_setup: ide4=noprobe ide_setup: ide5=noprobe Initializing CPU#0 Detected 2399.621 MHz processor. Console: colour EGA 80x25 Calibrating delay loop... 4744.80 BogoMIPS Memory: 28872k/32768k available (1210k kernel code, 3508k reserved, 266k data, 64k init, 0k highmem) Dentry cache hash table entries: 4096 (order: 3, 32768 bytes) Inode cache hash table entries: 2048 (order: 2, 16384 bytes) Mount cache hash table entries: 512 (order: 0, 4096 bytes) Buffer-cache hash table entries: 1024 (order: 0, 4096 bytes) Page-cache hash table entries: 8192 (order: 3, 32768 bytes) CPU: Intel Pentium Pro stepping 03 Checking 'hlt' instruction... OK. POSIX conformance testing by UNIFIX Linux NET4.0 for Linux 2.4 Based upon Swansea University Computer Society NET3.039 Initializing RT netlink socket apm: BIOS not found. Starting kswapd Journalled Block Device driver loaded Detected PS/2 Mouse Port. pty: 256 Unix98 ptys configured Serial driver version 5.05c (2001-07-08) with no serial options enabled ttyS00 at 0x03f8 (irq = 4) is a 16450 ne.c:v1.10 9/23/94 Donald Becker (becker@scyld.com) Last modified Nov 1, 2000 by Paul Gortmaker NE*000 ethercard probe at 0x300: 52 54 00 12 34 56 eth0: NE2000 found at 0x300, using IRQ 9. RAMDISK driver initialized: 16 RAM disks of 4096K size 1024 blocksize Uniform Multi-Platform E-IDE driver Revision: 7.00beta4-2.4 ide: Assuming 50MHz system bus speed for PIO modes; override with idebus=xx hda: QEMU HARDDISK, ATA DISK drive ide0 at 0x1f0-0x1f7,0x3f6 on irq 14 hda: attached ide-disk driver. hda: 20480 sectors (10 MB) w/256KiB Cache, CHS=20/16/63 Partition check: hda: Soundblaster audio driver Copyright (C) by Hannu Savolainen 1993-1996 NET4: Linux TCP/IP 1.0 for NET4.0 IP Protocols: ICMP, UDP, TCP, IGMP IP: routing cache hash table of 512 buckets, 4Kbytes TCP: Hash tables configured (established 2048 bind 4096) NET4: Unix domain sockets 1.0/SMP for Linux NET4.0. EXT2-fs warning: mounting unchecked fs, running e2fsck is recommended VFS: Mounted root (ext2 filesystem). Freeing unused kernel memory: 64k freed Linux version 2.4.21 (bellard@voyager.localdomain) (gcc version 3.2.2 20030222 (Red Hat Linux 3.2.2-5)) #5 Tue Nov 11 18:18:53 CET 2003 QEMU Linux test distribution (based on Redhat 9) Type 'exit' to halt the system sh-2.05b#
-
����� �� ������ ���������� � �����, ��������� ����������� ���������������� �������. ��������, �� ������ ��������� �������
ls. ������� Ctrl-a h, ����� �������� ������� � ��������, ������� �� ������ ������������ � ����������� ���������������� �������. � ��������� ����������� Ctrl-a x ��� ������ �� QEMU � Ctrl-a b � �������� «����������» ������� ���������� ������ (Magic SysRq). -
���� ���� ��������, ��������� � ��������� ������ `/etc/linuxrc’ (�� �������� ����� � ������):
����� ��������� X11-����������� � ������ �� �� ������������ Linux’�:
������ �� ������ ��������� `xterm’ ��� `xlogo’, ����� �������� � ���, ��� ����� ���� ������������� ����������� ������� Linux!
���������:
- � ������ ������ ����� ������ ���� ������ 2.5.74. ����� ����������� ���, ������ �������� �� bzImage � qemu.sh.
- ����� ��������� ��������� ������ � qemu, �� ������ ��������� � � ������� shutdown. qemu ������������� ��������� �� ���������� ������ Linux.
-
�� ������ ������� ��������� �������� ��������, �������� ����� ������������� ����������� IDE. ��� ����� �������� ��������� ��������� � ��������� ������ ����:
ide1=noprobe ide2=noprobe ide3=noprobe ide4=noprobe ide5=noprobe
- ���� ����� ����� �������� �������� ������� ������, ���������� ������� �������� (Kevin Lawton) ��� ������� plex86 (www.plex86.org).
3.9 ������������� GDB
QEMU ������������ ����ݣ���� ������ � gdb. ����� ������� �� ������ ������ ‘Ctrl-C’ �� ����� ������ ����������� ������ � ����������� ţ ���������.
����� ����� ���� ������������ gdb, ��������� qemu � ������ ‘-s’. ��� ���� �� ����� ������� ����������� gdb:
> qemu -s -kernel arch/i386/boot/bzImage -hda root-2.4.20.img -append "root=/dev/hda" Connected to host network interface: tun0 Waiting gdb connection on port 1234 |
����� ��������� gdb, ������� ��� � �������� ��������� ����������� ���� ‘vmlinux’:
� gdb ������������ � QEMU:
(gdb) target remote localhost:1234 |
����� �� ������ ������������ gdb ������� �������. ��������, ������� ‘c’, ����� ��������� ����:
��� ��������� �������� ��������� �� ������������� gdb ��� ������ � ��������� �����:
-
�����������
info reg��� ������ ���� ��������� ����������. -
�����������
x/10i $eip��� ������ ���� � ������� PC. -
�����������
set architecture i8086����� 16-������� ����. ����� ��������������x/10i $cs*16+*eip��� ��������� ����� ���� � ������� PC.
3.10 �������������� ���������� �� ����������� ��
3.10.1 Linux
����� ����� ������ � ����������� ������� SVGA � X11, ����������� ������� vesa ��� cirrus. ��� ��������� ����������� ������������������ ����������� 16-������ ������� ����� � � �������� �������, � � �������-�������.
��� ������������� � �������� ������� ���� Linux ������ 2.6 ��� ������� �������� �������� clock=pit � ��������� ������ ����, ������ ��� ���� Linux ����� 2.6 �� ��������� ��������� ����� ������������ �������� ����� ��������� �������, ������� QEMU �� ����� � �������� ������������.
��� �� ��� ������������� � �������� ������� ���� Linux ������ 2.6 ���������, ��� �� ������������ ���� 4G/4G, ������ ��� � ���� ������ QEMU �������� ���������. ������ ��������� QEMU (QEMU Accelerator Module) � ���� ������ ����� �������� ������� ���������. ���� ���� ������������� �� ��������� � ������ ������� ���� Linux � Fedora Core 3 (< 2.6.9-1.724_FC3). � ����� ����� ������� ��� ���.
3.10.2 Windows
���� ���� ������� �������� ���������, ����� ����������� Windows 95, ��������� ��� �������� ������� ����. ����� �������� ��������� ����� Windows 2000.
3.10.2.1 ��������� ����������� ������� SVGA
QEMU ��������� ���������� Cirrus Logic GD5446. ��� ������ Windows, ������� � Windows 95, ������ ��������� ������������ � �������� � ���� �����������. ��� ��������� ����������� ������������������ ����������� 16-������ ������� ����� � � �������� �������, � � �������-�������.
3.10.2.2 �������� �������� ����������
Windows 9x ����������� ���������� ���������� CPU HLT. � ���������� ��������� �������-������� ���������� �������������� ���� ��� �������. ��� ���������� ���� �������� �� ������ ���������� ����������� ������� http://www.user.cityline.ru/~maxamn/amnhltm.zip. �������� ��������, ��� ��� NT, 2000 � XP ����� ������� �� �����.
3.10.2.3 �������� � ������������� ����� � Windows 2000
� Windows 2000 ���� ������, ���������� � �������� ������������ ����� �� ����� ���������. ������� ��� ţ ��������� ����������� � QEMU ����� `-win2k-hack’, ����� ��������� ��� ��������. ����� ��������� Windows 2000 ��� ������ �� ����� ������������ ��� ����� (��� ��������� �������� ������ �� IDE).
3.10.2.4 ���������� ������ Windows 2000
Windows 2000 �� ����� ������������� ��������� ���� ������ � QEMU � ������� �� Windows 98. ��� ������� � ���, ��� Windows 2000 �� ��������� �� ���������� ������� ��������������� ���������� �������� (APM), ���������������� BIOS’��.
����� ��������� ���, ��������� ��������� (������� ������� �������� (Struan
Bartlett)): �������� Control Panel => Add/Remove Hardware & Next => Add/Troubleshoot a device => Add a new device & Next => No, select the hardware from a list & Next => NT Apm/Legacy Support & Next => Next (�����) ��������� ���. ������ ������� ���������� � Windows 2000 ����� ��������� �������� QEMU � ���������� ����� ������ � ������ ������.
3.10.2.5 ������������� ����� ��������� ��� Unix � Windows
�������� sec_invocation �� ������������� ����� `-smb’.
3.10.2.6 �������� � ������������� � Windows XP
��������� ������ Windows XP ��������� ���������������, ������ �� ����� �������� ������ ��������� �� ������ ������������:
A problem is preventing Windows from accurately checking the license for this computer. Error code: 0x800703e6. |
������������ �������� ������ ��� �������� �������� �������� � ���������� ������ � ����������� ���������� ����.
� ��������� ������� QEMU ��� �������� ������ ����� ����� ���������.
3.10.3 MS-DOS � FreeDOS
3.10.3.1 �������� �������� ����������
DOS ����������� ���������� ���������� CPU HLT. � ���������� ��������� �������-������� ���������� �������������� ���� ��� �������. ��� ���������� ���� �������� �� ������ ���������� ����������� ������� http://www.vmware.com/software/dosidle210.zip.
4. ������ QEMU � �������� ��������� ������� ���� PowerPC
����������� ����������� ���� `qemu-system-ppc’, ����� ����������� ����� ������� ���� PREP ��� PowerMac PowerPC.
QEMU ��������� ��������� ������������ ������������ PowerMac:
- —
UniNorth PCI Bridge - —
PCI VGA-����������� ����� � VESA-������������ Bochs - —
2 PCI IDE-���������� � ���������� ֣����� � �������� CD-ROM - —
������� PCI-�������� NE2000 - —
����������������� ����������� ������ - —
VIA-CUDA � ����������� � ����� ADB.
QEMU ��������� ��������� ������������ ������������ PREP:
- —
PCI Bridge - —
PCI VGA-����������� ����� � VESA-������������ Bochs - —
2 PCI IDE-���������� � ���������� ֣����� � �������� CD-ROM - —
�������� - —
������� PCI-�������� NE2000 - —
���������������� ����� - —
����������������� ����������� ������ PREP - —
PC-����������� ���������� � ����
� QEMU ������������ Open Hack’Ware Open Firmware Compatible BIOS, ��������� �� ����� http://site.voila.fr/jmayer/OpenHackWare/index.htm.
�� ������ ��������� ����� �� �������� ������� ���� PC, ����� �������� ������� ������������� �� ������������� QEMU.
��������� ����� �������� ������ �������� PowerPC:
- `-prep’
-
�������� ������� PREP (�� ��������� ��� PowerMAC)
- `-g �x�[x�������]’
-
�������� ����������� ����� VGA. �� ��������� ������������ 800x600x15.
�������������� ���������� �������� �� ������ http://jocelyn.mayer.free.fr/qemu-ppc/.
5. ������ QEMU � �������� ��������� ������� ���� Sparc32
����������� ����������� ���� `qemu-system-sparc’, ����� ����������� JavaStation (����������� sun4m). ���������� ����� ������ ��������.
QEMU ��������� ��������� ������������ ������������ sun4m:
- —
IOMMU - —
���������� TCX - —
������� ����� Lance (Am7990) - —
����������������� ����������� ������ M48T08 - —
Slave I/O: �������, ����������� ����������, ���������������� ����� Zilog, ���������� � ���������� power/reset - —
ESP SCSI-���������� � ���������� ֣����� � �������� CD-ROM - —
��������
� ���� ����������� ���������� ������������ �������� �������������.
� QEMU ������������ Proll — ������ PROM, ��������� �� ����� http://people.redhat.com/zaitcev/linux/. ����������� ����� ��� QEMU �������� � ����� � ��������� ��������.
������� ���� Linux ����� 2.6 � ����� ram-����� �������� �� ���-����� QEMU. �������� ��������, ��� � ��������� ������ �� �������� ���� Linux ����� 2.4, NetBSD � OpenBSD.
��������� ����� �������� ������ �������� Sparc:
- `-g �x�’
-
�������� ����������� ����� TCX. �� ��������� ������������ 1024×768.
6. ������ QEMU � �������� ��������� ������� ���� Sparc64
����������� ����������� ���� `qemu-system-sparc64′, ����� ����������� vfibye Sun4u. ���� ��� �������� �� ��� ���� ������� �� ��������.
QEMU ��������� ��������� ������������ ������������ sun4u:
- —
UltraSparc IIi APB PCI Bridge - —
PCI VGA-����������� ����� � VESA-������������ Bochs - —
����������������� ����������� ������ M48T59 - —
PC-����������� ���������������� �����
7. ������ QEMU � �������� ��������� ������� ���� MIPS
����������� ����������� ���� `qemu-system-mips’, ����� ����������� ������ MIPS. �������� �������� ��������� ���� Linux.
8. ������ QEMU � �������� ��������� ����������������� ������������
8.1 ������� ������
����� ��������� ������� Linux, QEMU ����� ��� ����������� ���� �������� � ��� ������������ �� ������������ ���������� (x86).
- ��� ����������� x86 �� ������ ������ ����������� ��������� ����� �������, ��������� ������ ����������:
�����
-L /��������, ��� ������������ ����������� x86 ���������� ������ � ��������� `/’. - ��������� QEMU ����� �������� ��������� linux, �� ����� ��������� qemu � ������� qemu (���������: �� ������� ������� ��� ������ � ��� ������, ���� �� ���� �������������� QEMU �� �������� �����):
qemu-i386 -L / qemu-i386 -L / /bin/ls
- �� �� x86 ����������� ��� ����� ������� ��������� ��� ������� glibc ��� x86 (`qemu-runtime-i386-XXX-.tar.gz’ �� ���-����� QEMU). ���������, ��� �� ����������� ���������� ���������
LD_LIBRARY_PATH:����� �� ������ ��������� ����������� ���� `ls’, ���������������� ��� x86:
�� ������ ��������� �� `qemu-binfmt-conf.sh’, ����� ������, ��� QEMU ������������� ����������� ����� Linux, ����� �� ��������� ��������� ����������� ����� x86. ��� ����� � ���� Linux ������ ���� �������� ������
binfmt_misc. - ������ QEMU ��� x86 ����� ������������. �� ������ ����������� ��������� ����:
qemu-i386 /usr/local/qemu-i386/bin/qemu-i386 /usr/local/qemu-i386/bin/ls-i386
8.2 ������ Wine
- ���������, ��� � ��� ���� ���������� QEMU � ����������� glibc ��� x86 (��. ���������� ������). ����� ��������� ���, ��������� ���������:
qemu-i386 /usr/local/qemu-i386/bin/ls-i386
- ��������� �������� ����������� Wine ��� x86
(`qemu-XXX-i386-wine.tar.gz’ �� ���-����� QEMU). - ��������� ���� �ޣ���� ������. ��� ����� ��������� �� ������ `/usr/local/qemu-i386/bin/wine-conf.sh’. ��� ������ �������
${HOME}/.wine����� �����Σ� �${HOME}/.wine.org. - ������ ���������� ���������, ��������, `putty.exe’:
qemu-i386 /usr/local/qemu-i386/wine/bin/wine /usr/local/qemu-i386/wine/c/Program Files/putty.exe
8.3 ����� ��������� ������
�������������: qemu-i386 [-h] [-d] [-L ����] [-s ������] ��������� [���������...] |
- `-h’
-
����� �������.
- `-L path’
-
������� �������������� x86 elf (�� ��������� ������������ /usr/local/qemu-i386)
- `-s ������’
-
������ ����� x86 � ������ (�� ��������� 524288)
����� �������:
- `-d’
-
�������� �������������� (logfile=/tmp/qemu.log)
- `-p ������_��������’
-
�������� ���, ��� ���� �� ������ �������� �������-������� ��������� ��������� ��������.
9. ���������� �� ��������� ����
9.1 Linux/Unix
9.1.1 ����������
������� ���������� ����� � ��������� ��������:
cd /tmp tar zxvf qemu-x.y.z.tar.gz cd qemu-x.y.z |
����� ��������� QEMU � �������� ��� (������ ������� ����� �� �����):
����� ��������� ��� root’��:
����� ���������� QEMU � `/usr/local’.
9.1.2 ������ ����������� ������
����� ������� �������������� QEMU, ����� �����, ����� � ��� ���� ���������� ������ ������. ����� ������ �������� gcc. � �� ���� ������������� ������ QEMU, ���� �� �� ����������� ����������� ������ gcc. ��������� �� ���������� ������ ‘configure’ � ‘Makefile’, ���� �� ������ ��������� �������� ������ ������ gcc.
���� gcc binutils glibc linux �����������
----------------------------------------------------------------------
x86 3.2 2.13.2 2.1.3 2.4.18
2.96 2.11.93.0.2 2.2.5 2.4.18 Red Hat 7.3
3.2.2 2.13.90.0.18 2.3.2 2.4.20 Red Hat 9
PowerPC 3.3 [4] 2.13.90.0.18 2.3.1 2.4.20briq
3.2
Alpha 3.3 [1] 2.14.90.0.4 2.2.5 2.2.20 [2] Debian 3.0
Sparc32 2.95.4 2.12.90.0.1 2.2.5 2.4.18 Debian 3.0
ARM 2.95.4 2.12.90.0.1 2.2.5 2.4.9 [3] Debian 3.0
[1] �� Alpha ��� QEMU ����� ������� '���������' gcc, ��������� ������
��� gcc ������ >= 3.3.
[2] ����� Linux >= 2.4.20 ��� ��������� ���������� ��������
(�� ���������).
[3] 2.4.9-ac10-rmk2-np1-cerf2
[4] gcc 2.95.x ������� �������� ��� ��� ������������� ������� �������� �����
���������� ���������. �� PowerPC ��� ���������� ������������ gcc 3.x.
|
9.2 Windows
- ���������� ��������� ������ MSYS � MinGW � ����� http://www.mingw.org/. �� ������ ����� ��������� ���������� �� ��������� � ������� �������� � � FAQ’�.
- ��������� devel-���������� MinGW ��� SDL 1.2.x (`SDL-devel-1.2.x-mingw32.tar.gz’) � ����� http://www.libsdl.org. ���������� ţ �� ��������� ������� � ���������� ����� `i386-mingw32msvc.tar.gz’ � ������� MinGW. �������������� ������ `sdl-config’, ����� ��� ������� � Σ� ������������� ���������� ������� SDL.
- ���������� ����� � ��������� ������� QEMU.
- ��������� ��������� ��������� MSYS (���� `msys.bat’).
- ��������� � ������� QEMU. ��������� `./configure’ � `make’. ���� � ��� �������� �������� � SDL, ���������, ����� �� ��������� `sdl-config’ �� ��������� ������ MSYS.
- �� ������ ���������� QEMU � `Program Files/Qemu’, �������� ������� `make install’. �� �������� ����������� `SDL.dll’ � `Program Files/Qemu’.
9.3 �����-���������� � Linux ��� Windows
- ���������� ������� �����-���������� MinGW, ��������� �� ����� http://www.mingw.org/.
- ���������� ������ SDL ��� Win32 (http://www.libsdl.org), ���������� `i386-mingw32msvc.tar.gz’. ��������� ���������� ��������� PATH, ����� `i386-mingw32msvc-sdl-config’ ��� ���� ������� �������� ��������� QEMU.
-
��������� QEMU ��� �����-���������� ��� Windows:
./configure --enable-mingw32
���� ����������, �� ������ �������� �����-������� �������� ��������, ���������� ��� ������ MinGW, � ������� ����� -cross-prefix. �� ����� ������ ������������ -prefix ��� �������� ���� ��������� Win32.
- �� ������ ���������� QEMU � ������� ���������, �������� `make install’. �� �������� ����������� `SDL.dll’ � ������� ���������.
���������: � ��������� ������ ������, ��� Wine �� ����� ��������� QEMU ��� Win32.
9.4 Mac OS X
����� Mac OS X �� ��������� ������������� � QEMU, ������� ��� ����������� ���������� ������� ������ � ������ �������� �������� QEMU.
| [Top] | [Contents] | [Index] | [ ? ] |
About This Document
This document was generated by Acid Jack on March, 19 2006 using texi2html 1.76.
The buttons in the navigation panels have the following meaning:
| Button | Name | Go to | From 1.2.3 go to |
|---|---|---|---|
| [ < ] | Back | previous section in reading order | 1.2.2 |
| [ > ] | Forward | next section in reading order | 1.2.4 |
| [ << ] | FastBack | beginning of this chapter or previous chapter | 1 |
| [ Up ] | Up | up section | 1.2 |
| [ >> ] | FastForward | next chapter | 2 |
| [Top] | Top | cover (top) of document | |
| [Contents] | Contents | table of contents | |
| [Index] | Index | index | |
| [ ? ] | About | about (help) |
where the Example assumes that the current position is at Subsubsection One-Two-Three of a document of the following structure:
- 1. Section One
- 1.1 Subsection One-One
- …
- 1.2 Subsection One-Two
- 1.2.1 Subsubsection One-Two-One
- 1.2.2 Subsubsection One-Two-Two
- 1.2.3 Subsubsection One-Two-Three
<== Current Position - 1.2.4 Subsubsection One-Two-Four
- 1.3 Subsection One-Three
- …
- 1.4 Subsection One-Four
- 1.1 Subsection One-One
This document was generated by Acid Jack on March, 19 2006 using texi2html 1.76.
���� ��������� ������ �������� HTML-���� �� ������������� ��������� 
Do you want to use QEMU for Windows? This post from MiniTool shows you how to download and install the QEMU software on Windows. It also shows you how to use QEMU on Windows to create an Ubuntu VM.
What Is QEMU
QEMU, short for Quick Emulator, is a free open-source hosted virtual machine manager that can execute hardware virtualization. With the help of KVM (Kernel-based Virtual Machine), QEMU can offer fast running speed. Therefore, it develops fast and is going to replace VirtualBox and VMware on Linux.
Tip: On Linux, with the help of quickgui, QEMU can create some macOS, Windows, and Linux virtual machines without downloading the ISO files manually. Please refer to this post: How to Install macOS and Windows 11 Virtual Machines on Ubuntu.
However, on Windows, the advantages of QEMU are not significant, because the KVM technology is not applicable on the Windows host machine. In addition, the quickgui is also not available to Windows. But QEMU develops fast and many people still want to use this VM software on Windows.
QEMU for Windows Download and Install
1. Download QEMU for Windows
To use QEMU for Windows, you should download and install it first. Please refer to the following QEMU download guide:
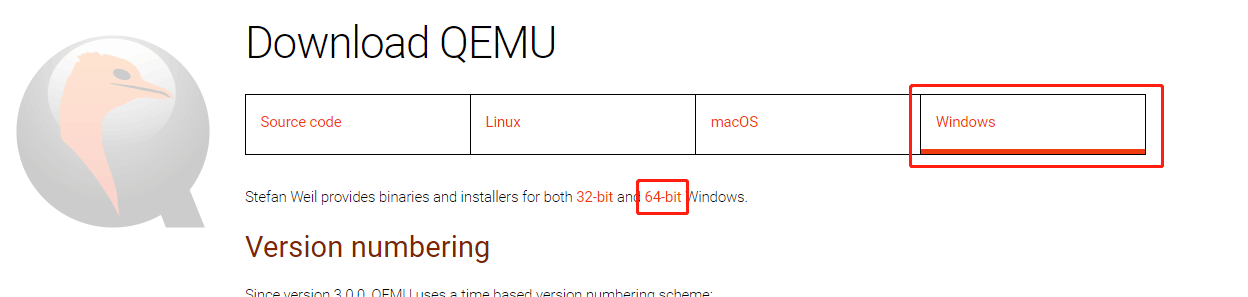
Step 1: Go to the official QEMU website (https://www.qemu.org). Click the Download button at the top section. You will go to the QEMU download page.
Step 2: Click the Windows tab to get the QEMU Windows version. Click 32-bit or 64-bit according to what OS you are running (for me, I click the 64-bit because my OS is 64-bit).
Step 3: On the new page, click the .exe file to download it. This file is the installer file.
2. Install QEMU for Windows
After the installer file is downloaded, you can double-click it to run directly. Before doing that, I recommend you to create a partition separately for it. For any virtual machine software, I will recommend you create a separate partition to store the software and the VM files so that you can manage them better.
To create a separate partition, you can use the shrink feature in the Windows Disk Management tool. But this tool can’t help you move the location of partitions, so I recommend you to use MiniTool Partition Wizard.
If the free space of one partition is not enough, you can move/resize another partition to get more unallocated space and then gather the unallocated space together to create one partition. Here is the guide:
Free Download
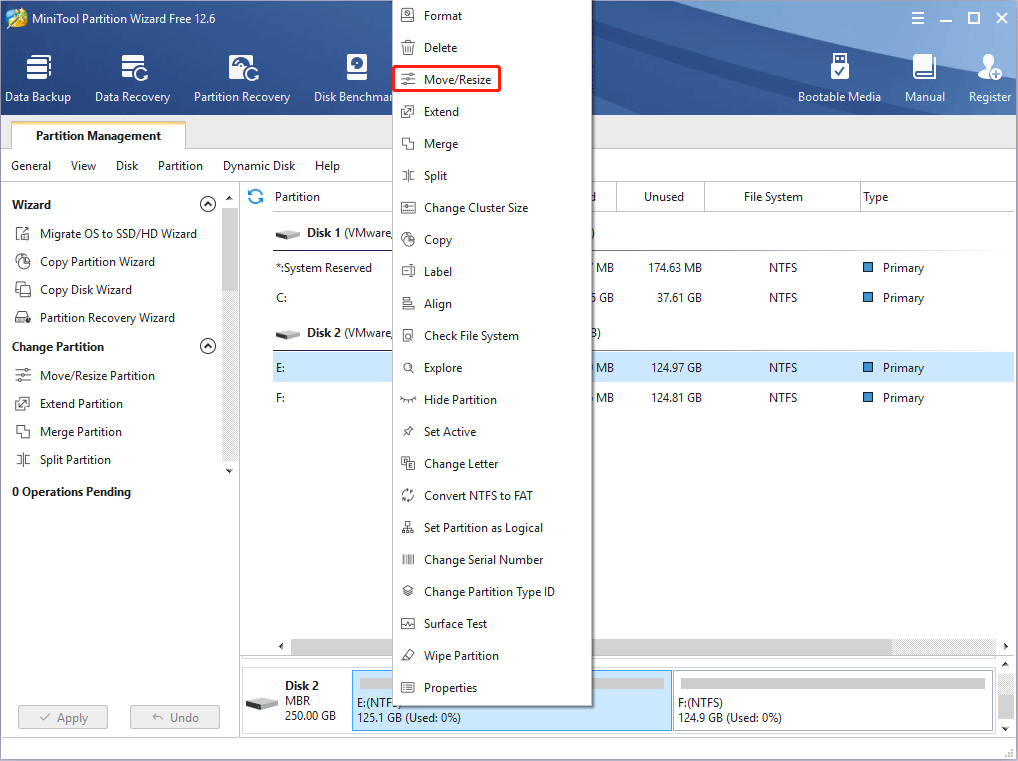
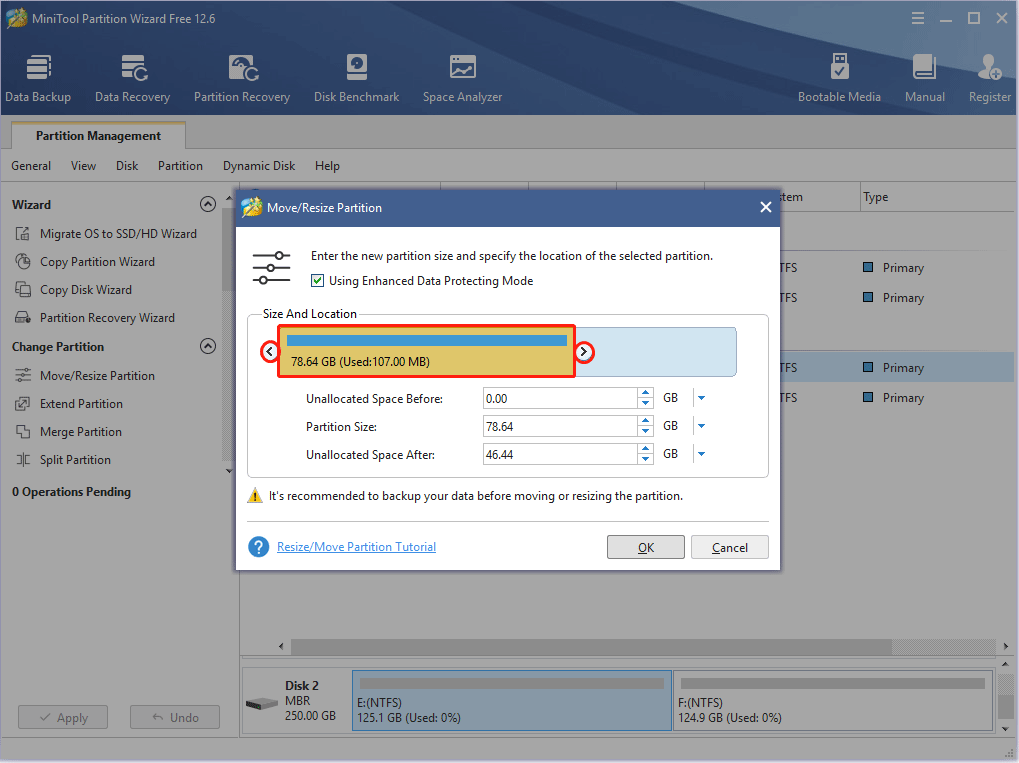
Step 1: Launch MiniTool Partition Wizard and go to its main interface. Right-click a partition and choose Move/Resize.
Step 2: Drag the two arrows on the two sides of the partition to shrink the partition, and then drag the block to move the location of the partition. Then, click the OK button. In this way, you can get unallocated space.
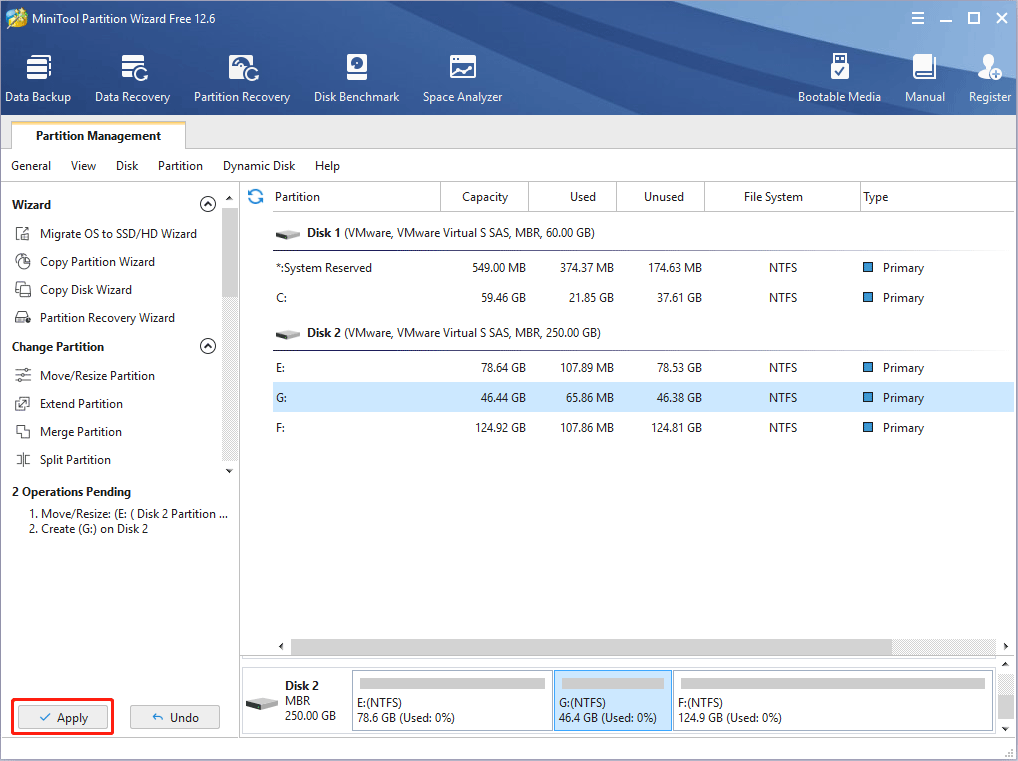
Step 3: Right-click the unallocated space and choose the Create button.
Step 4: Set parameters for the new partition. You can keep all of them to the default value if you don’t have specific demands. Then, click the OK button.
Step 5: Click the Apply button to execute pending operations.
How to Merge Unallocated Space in Windows 10 for a Large Drive
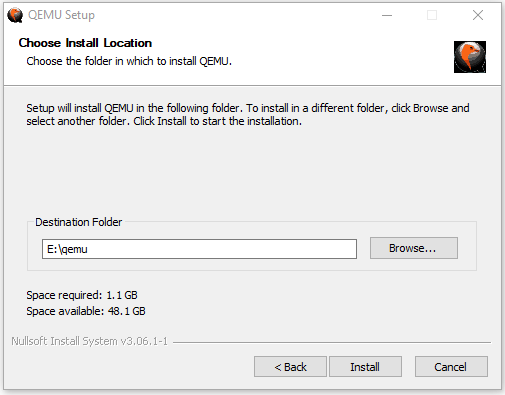
After the new partition is created, you can then double-click the QEMU installer file to install this VM software. You just need to follow the on-screen instructions to complete the installation.
Tip: When you are asked to choose the install location, please choose the newly-created partition (taking E drive as an example).
How to Use QEMU on Windows
After installing the QEMU Windows version, you may want to know how to use QEMU to create a virtual machine. Here are 2 ways and the 2nd way is better.
Way 1. Create a Virtual Machine Using Commands
QEMU doesn’t come with a GUI. If you don’t install a GUI manually, you need to use commands to run QEMU. Here is the guide on how to use QEMU on Windows to create a VM via commands (taking Ubuntu as an example).
Step 1: Download the Ubuntu ISO file from the official website.
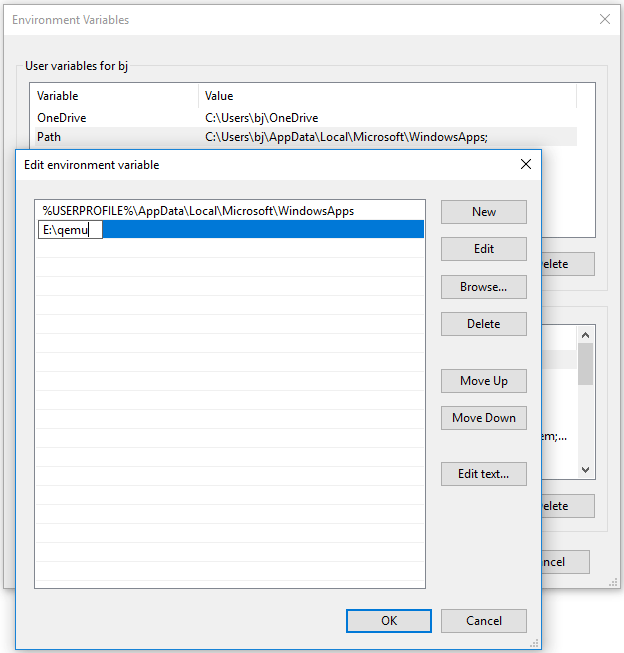
Step 2: Add QEMU path into Environment Variables.
- Open File Explorer, go to the QEMU installation location, and then copy the path (E:qemu).
- Right-click This PC / Computer, choose Properties, and then click Advanced system settings.
- Under the Advanced tab, click Environment Variables.
- In the User variables box, double-click the Path variable, click New, and then paste the QEMU path.
- Click the OK button to save changes, and then click the OK button again to save and exit the Environment Variables
Tip:
1. If you use Windows 7, the adding process may be a little different.
2. If there is no Path variable under the User box, you can create one, or you can add the QEMU path into the System variables.
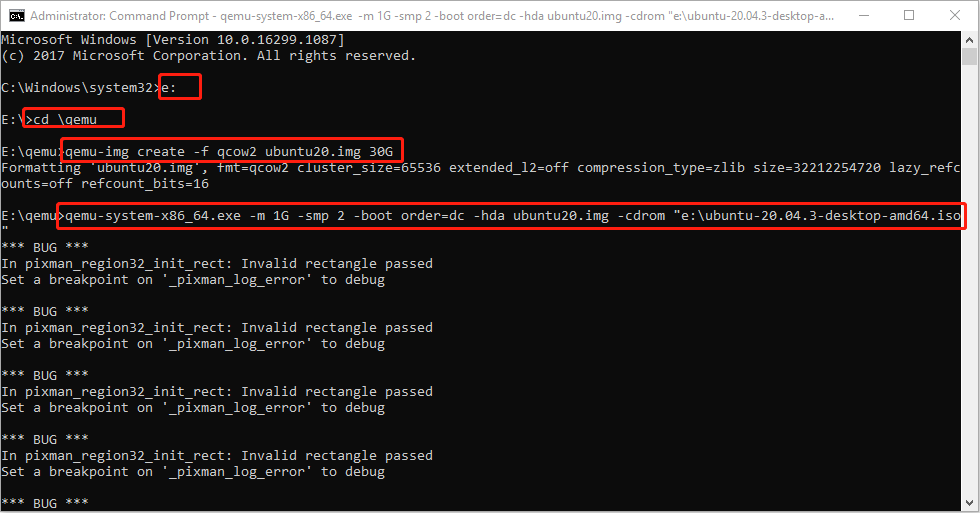
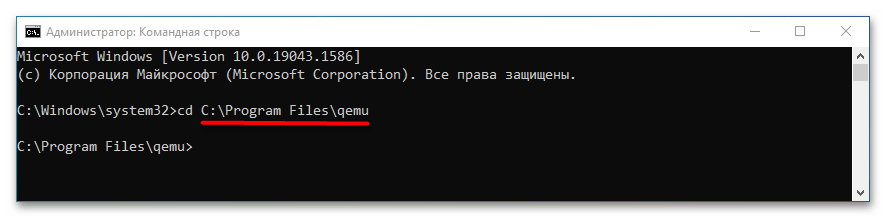
Step 3: Run Command Prompt as administrator and then execute the following commands.
- E: (this will open the e drive where QEMU is installed).
- cd qemu (this will open the qemu folder).
- qemu-img create -f qcow2 ubuntu20.img 30G (this will create a virtual hard drive of 30GB).
- qemu-system-x86_64.exe -m 1G -smp 2 -boot order=dc -hda ubuntu20.img -cdrom “e:ubuntu-20.04.3-desktop-amd64.iso” (this will run Ubuntu using CD/ROM).
Tip:
1. If you want to install other VMs (macOS, ARMs, etc.), the qemu-system may vary greatly.
2. The above commands are not perfect. If you have better commands, you can run them.
3. The QEMU installation path and the location of the Ubuntu ISO file in the above commands should be changed accordingly.
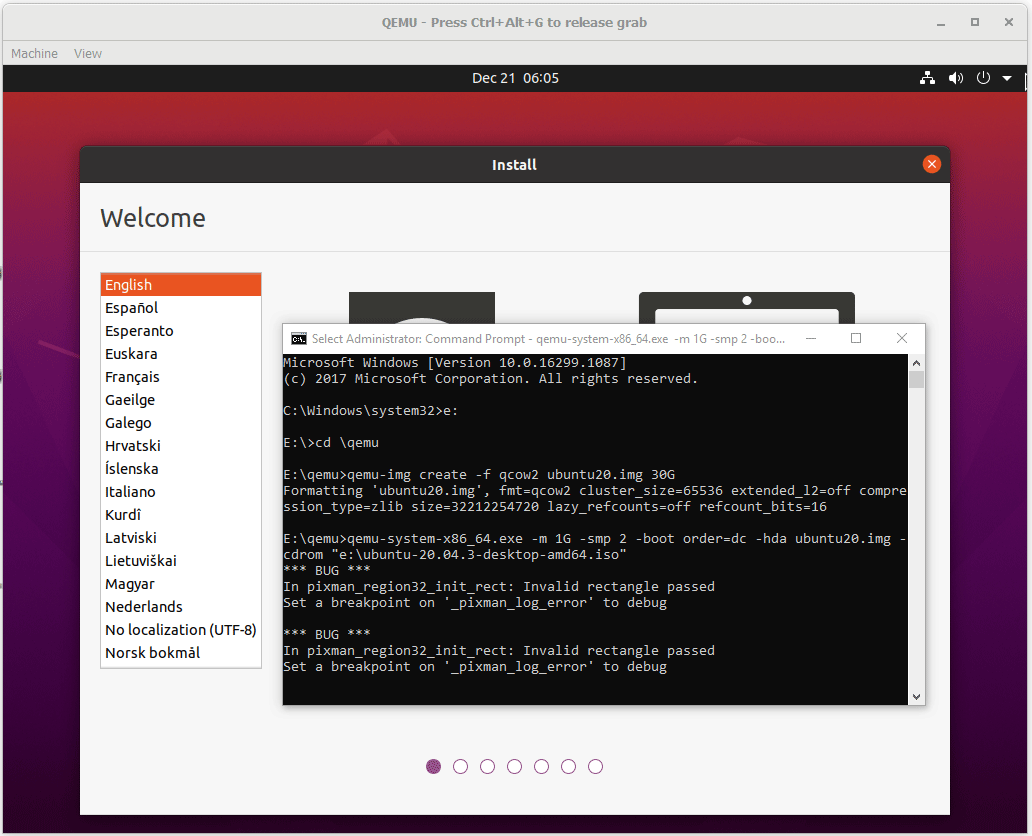
Step 4: Go through the Ubuntu installation process. Although there may be many bugs, I launch Ubuntu 20 successfully and then just need to complete the installation process.
How to Install Linux (Ubuntu) on Windows 10 [Ultimate Guide 2022]
Way 2. Create a Virtual Machine Using QtEmu
As you can see, creating a VM using QEMU via commands is a tough job. You need to search for various tutorials online. In addition, once errors occur, you may have no idea how to solve them. Therefore, I recommend you to use QtEmu, an open-source GUI for QEMU Windows.
How to use QEMU on Windows via QtEmu? Here is the guide:
Step 1: Download the Ubuntu ISO file and QtEmu. The QtEmu official website is https://qtemu.org and the QtEmu source is placed on https://gitlab.com/qtemu/gui. Go to the GitLab source page, scroll down to find the Downloads section, and click the first link to download the QtEmu installer.
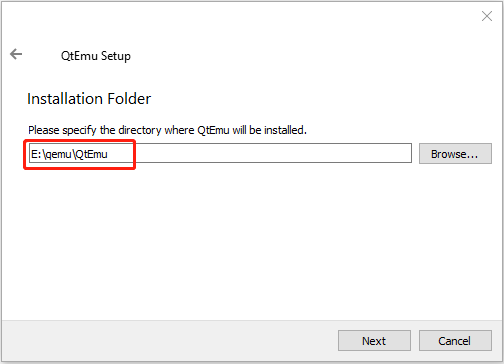
Step 2: Double-click the QtEmu installer file and go through the installation process. When you are asked to specify the installation location (where to create the QtEmu folder), please install the QtEmu under the QEMU folder. For me, I type: E:qemuQtEmu.
Step 3: After QtEmu is installed, go to E:qemuQtEmu. Right-click the qtemu.exe file and choose Send to > Desktop (create shortcut). Then, create a folder named VMs under the E drive to store all VM files to be created.
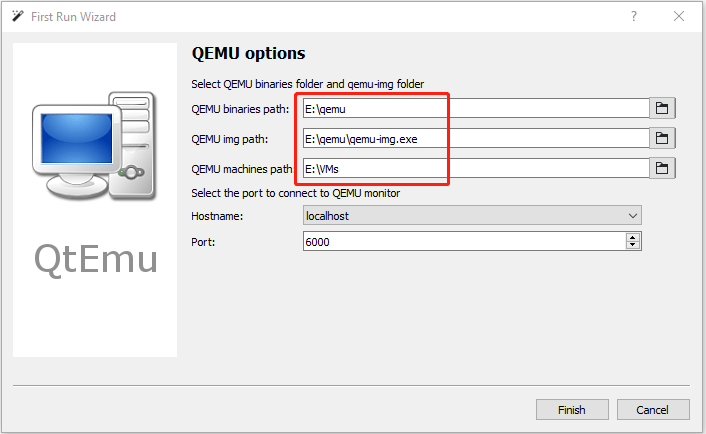
Step 4: Double-click the QtEmu shortcut to launch this software. In the QEMU options window, please set QEMU binaries path to E:qemu, set QEMU img path to E:qemu, and set QEMU machines path to E:VMs. Then, click the Finish button.
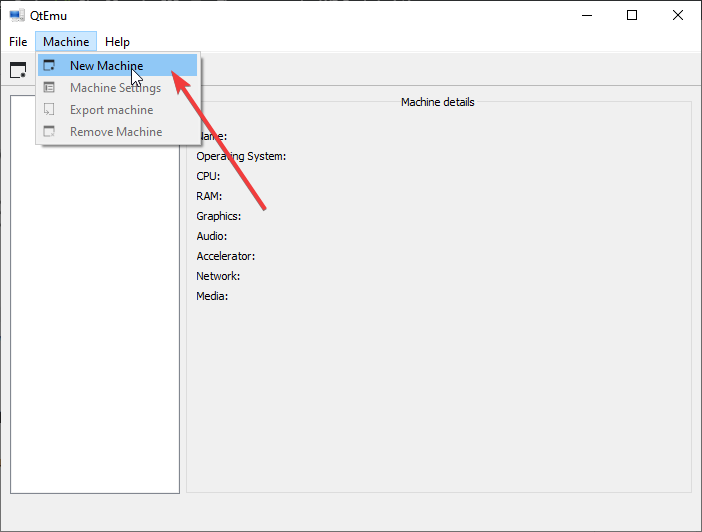
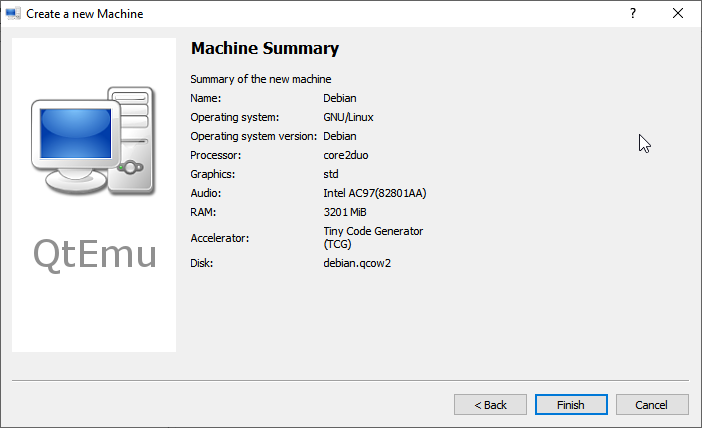
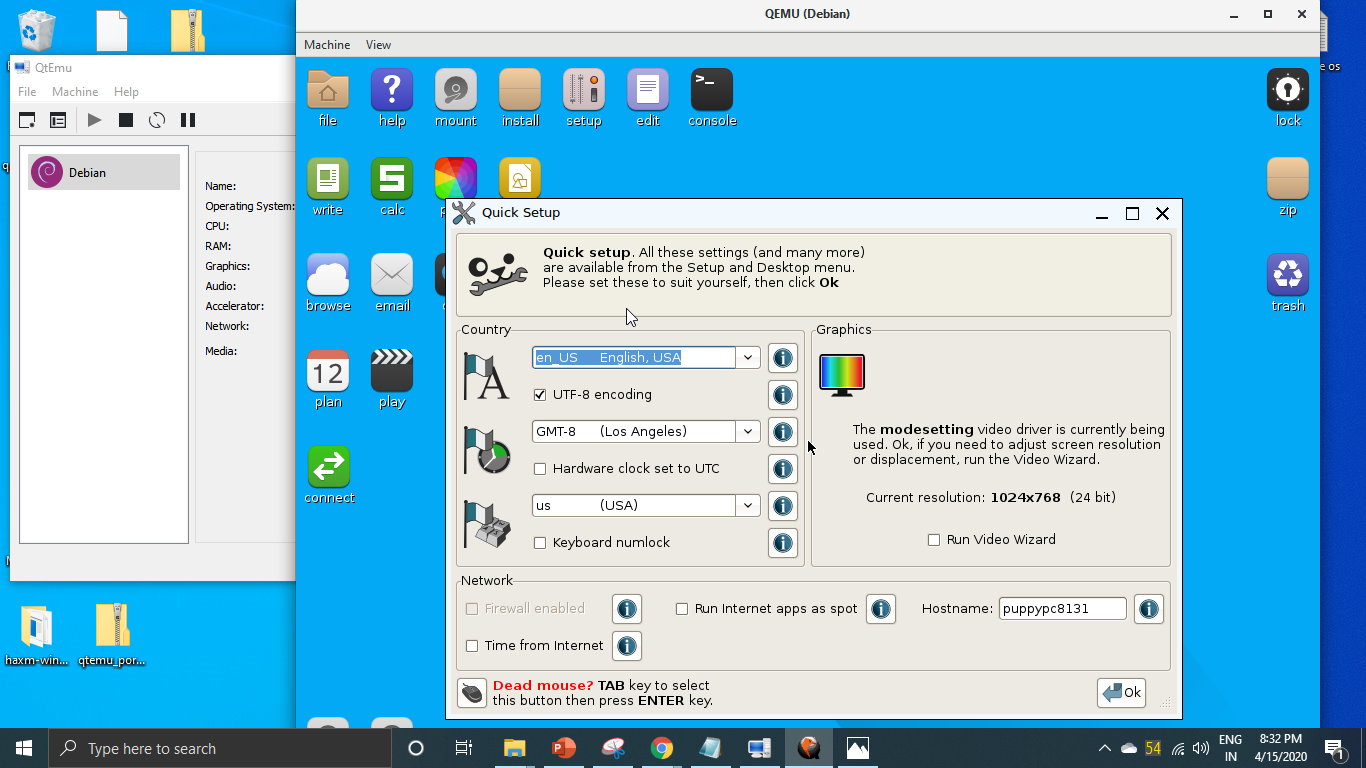
Step 5: Click Machine > New Machine. Then, give a name to the new machine (Ubuntu20), choose OS type (GNU/Linux), choose OS version (Ubuntu), and then click Next.
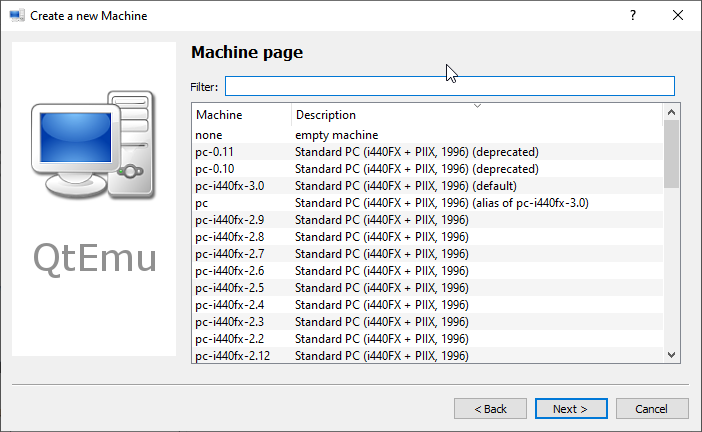
Step 6: On the Filter page, if you don’t need to specify certain motherboard chipsets, you can click the Next button directly to skip this step.
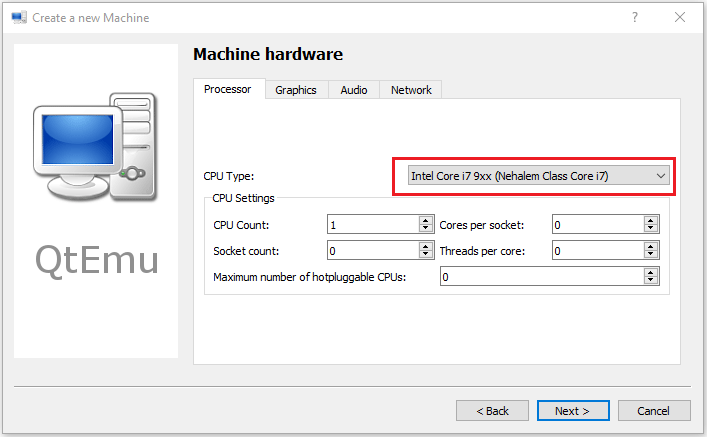
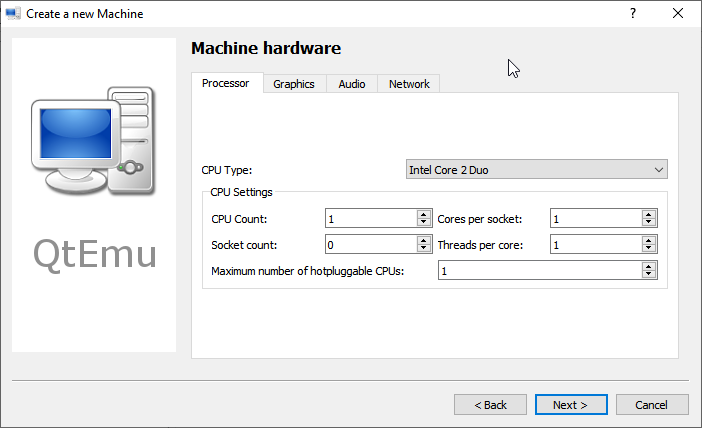
Step 7: Select a correct CPU Type, and set CPU, Graphics, Audio, and Network parameters. If all is OK, click the Next button.
Tip: The Ubuntu 20 version requires a 64-bit CPU. If you choose a 32-bit CPU, the VM may not boot.
What Is the Difference Between 32 Bit and 64 Bit (x86 vs x64)
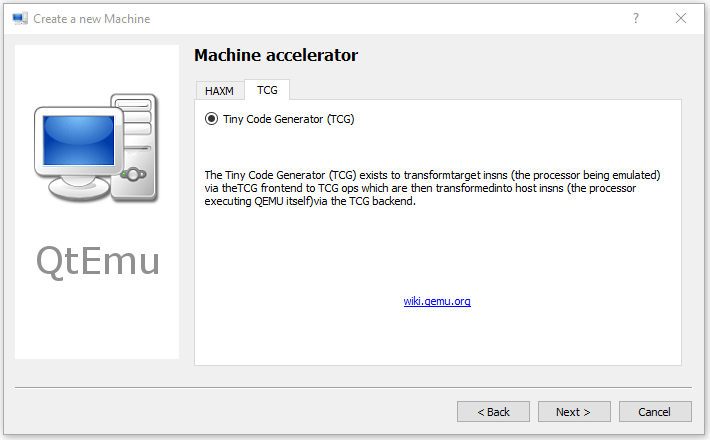
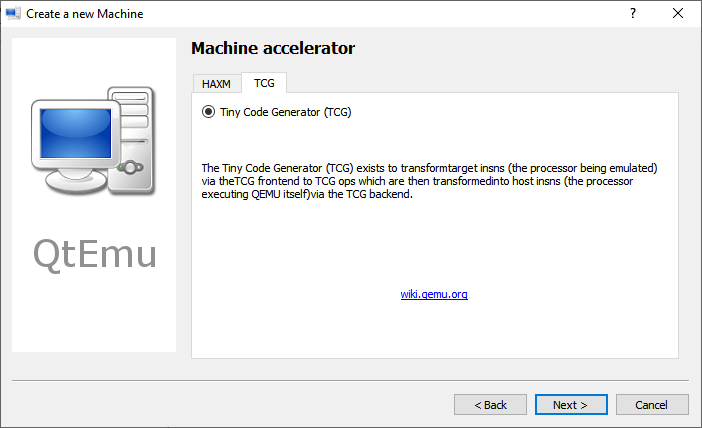
Step 8: Select the machine accelerator. HAXM is chosen by default. However, some computers may not support this technology. Therefore, I recommend you uncheck HAXM and then choose TCG instead. Then, click Next.
Tip: Some people report that nothing happens when they play the VM. The culprit is likely to be the HAXM. To ensure the VM can work on most PCs, TCG is recommended.
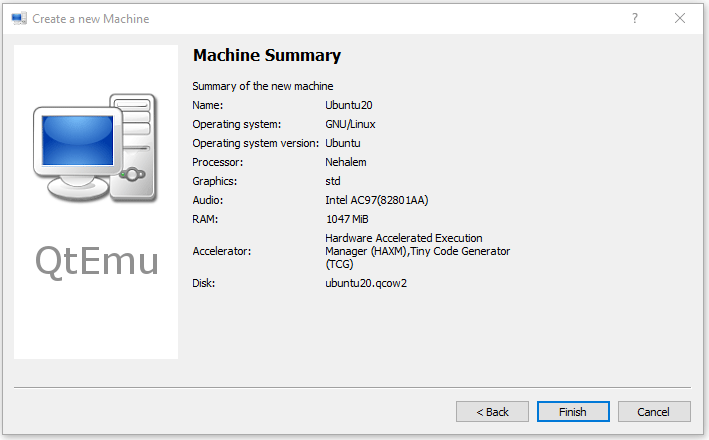
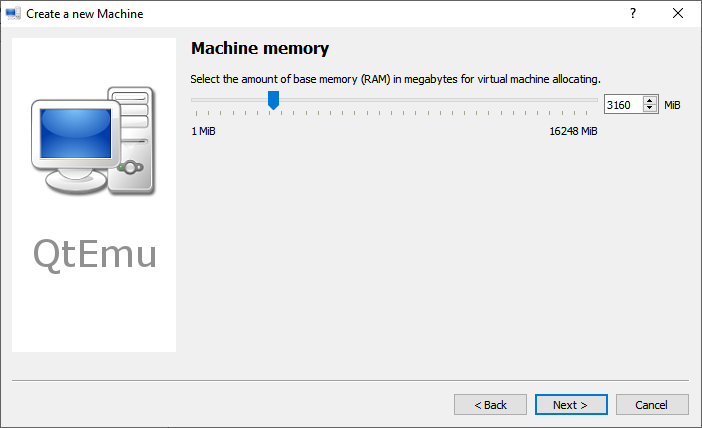
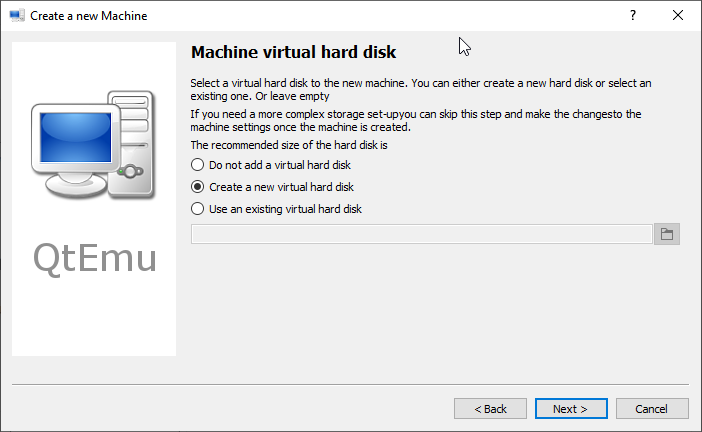
Step 9: Follow the on-screen wizard to set memory size, create a new virtual hard disk, set disk size and type, and then check the VM summary.
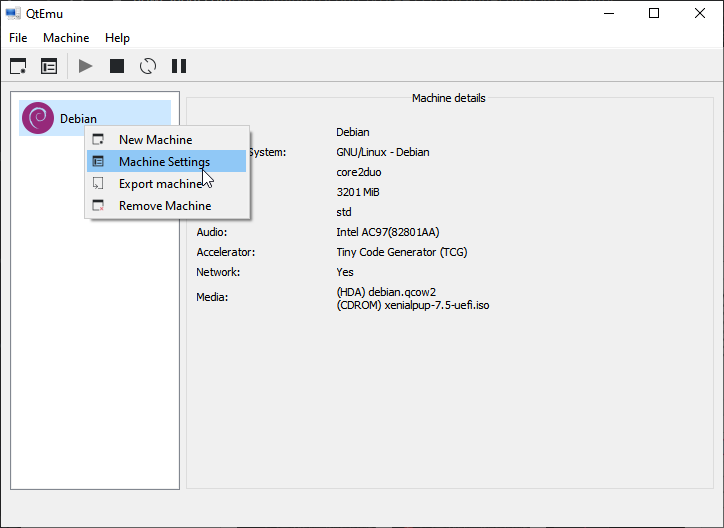
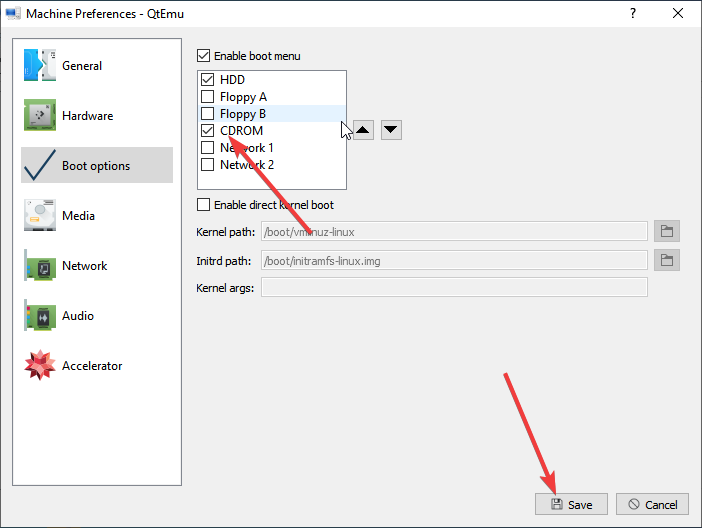
Step 10: Right-click on the newly-created VM and choose Machine Settings. Go to the Boot options tab, and tick CDROM.
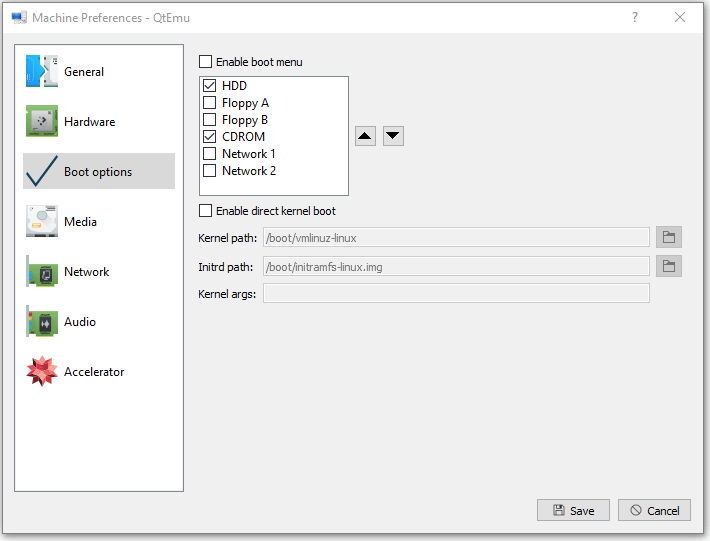
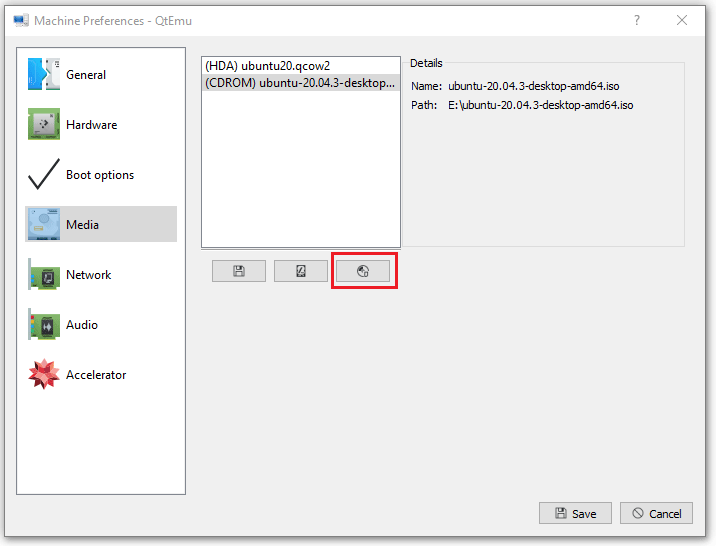
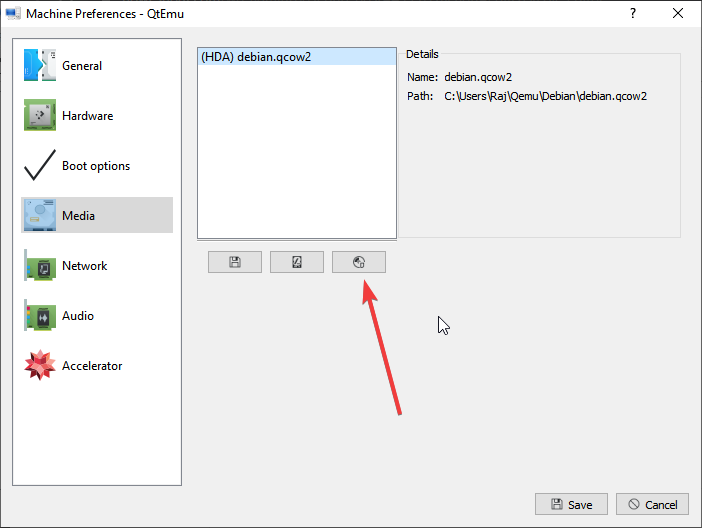
Step 11: Go to the Media tab, click the disc icon, and select the Ubuntu ISO file. Then, click Save.
Step 12: Select the VM and then click the Play icon. Then, you may need to go through the Ubuntu installation process. After the installation process is completed, you can enjoy the VM.
Best Virtual Machine for Windows, Linux, and Mac Systems
Here is a post talking about how to download, install, and use QEMU on Windows. If you are interested in this software, this post may help you.Click to Tweet
Bottom Line
Is this post helpful to you? Do you have other ideas about how to run QEMU on Windows? Please leave a comment in the following zone for sharing. In addition, if you have difficulty in moving or resizing partitions, please feel free to contact us via [email protected]. We will get back to you as soon as possible.
Synopsis¶
qemu-system-x86_64 [options] [disk_image]
Description¶
The QEMU PC System emulator simulates the following peripherals:
-
i440FX host PCI bridge and PIIX3 PCI to ISA bridge
-
Cirrus CLGD 5446 PCI VGA card or dummy VGA card with Bochs VESA
extensions (hardware level, including all non standard modes). -
PS/2 mouse and keyboard
-
2 PCI IDE interfaces with hard disk and CD-ROM support
-
Floppy disk
-
PCI and ISA network adapters
-
Serial ports
-
IPMI BMC, either and internal or external one
-
Creative SoundBlaster 16 sound card
-
ENSONIQ AudioPCI ES1370 sound card
-
Intel 82801AA AC97 Audio compatible sound card
-
Intel HD Audio Controller and HDA codec
-
Adlib (OPL2) — Yamaha YM3812 compatible chip
-
Gravis Ultrasound GF1 sound card
-
CS4231A compatible sound card
-
PC speaker
-
PCI UHCI, OHCI, EHCI or XHCI USB controller and a virtual USB-1.1
hub.
SMP is supported with up to 255 CPUs.
QEMU uses the PC BIOS from the Seabios project and the Plex86/Bochs LGPL
VGA BIOS.
QEMU uses YM3812 emulation by Tatsuyuki Satoh.
QEMU uses GUS emulation (GUSEMU32 http://www.deinmeister.de/gusemu/) by
Tibor «TS» Schütz.
Note that, by default, GUS shares IRQ(7) with parallel ports and so QEMU
must be told to not have parallel ports to have working GUS.
qemu-system-x86_64 dos.img -device gus -parallel none
Alternatively:
qemu-system-x86_64 dos.img -device gus,irq=5
Or some other unclaimed IRQ.
CS4231A is the chip used in Windows Sound System and GUSMAX products
The PC speaker audio device can be configured using the pcspk-audiodev
machine property, i.e.
qemu-system-x86_64 some.img -audiodev <backend>,id=<name> -machine pcspk-audiodev=<name>
Options¶
disk_image is a raw hard disk image for IDE hard disk 0. Some targets do
not need a disk image.
During the graphical emulation, you can use special key combinations to
change modes. The default key mappings are shown below, but if you use
-alt-grab then the modifier is Ctrl-Alt-Shift (instead of Ctrl-Alt)
and if you use -ctrl-grab then the modifier is the right Ctrl key
(instead of Ctrl-Alt):
- Ctrl-Alt-f
-
Toggle full screen
- Ctrl-Alt-+
-
Enlarge the screen
- Ctrl-Alt—
-
Shrink the screen
- Ctrl-Alt-u
-
Restore the screen’s un-scaled dimensions
- Ctrl-Alt-n
-
Switch to virtual console ‘n’. Standard console mappings are:
- 1
-
Target system display
- 2
-
Monitor
- 3
-
Serial port
- Ctrl-Alt
-
Toggle mouse and keyboard grab.
In the virtual consoles, you can use Ctrl-Up, Ctrl-Down, Ctrl-PageUp and
Ctrl-PageDown to move in the back log.
During emulation, if you are using a character backend multiplexer
(which is the default if you are using -nographic) then several
commands are available via an escape sequence. These key sequences all
start with an escape character, which is Ctrl-a by default, but can be
changed with -echr. The list below assumes you’re using the default.
- Ctrl-a h
-
Print this help
- Ctrl-a x
-
Exit emulator
- Ctrl-a s
-
Save disk data back to file (if -snapshot)
- Ctrl-a t
-
Toggle console timestamps
- Ctrl-a b
-
Send break (magic sysrq in Linux)
- Ctrl-a c
-
Rotate between the frontends connected to the multiplexer (usually
this switches between the monitor and the console) - Ctrl-a Ctrl-a
-
Send the escape character to the frontend
Notes¶
In addition to using normal file images for the emulated storage
devices, QEMU can also use networked resources such as iSCSI devices.
These are specified using a special URL syntax.
iSCSI-
iSCSI support allows QEMU to access iSCSI resources directly and use
as images for the guest storage. Both disk and cdrom images are
supported.Syntax for specifying iSCSI LUNs is
“iscsi://<target-ip>[:<port>]/<target-iqn>/<lun>”By default qemu will use the iSCSI initiator-name
‘iqn.2008-11.org.linux-kvm[:<name>]’ but this can also be set from
the command line or a configuration file.Since version QEMU 2.4 it is possible to specify a iSCSI request
timeout to detect stalled requests and force a reestablishment of the
session. The timeout is specified in seconds. The default is 0 which
means no timeout. Libiscsi 1.15.0 or greater is required for this
feature.Example (without authentication):
qemu-system-x86_64 -iscsi initiator-name=iqn.2001-04.com.example:my-initiator -cdrom iscsi://192.0.2.1/iqn.2001-04.com.example/2 -drive file=iscsi://192.0.2.1/iqn.2001-04.com.example/1Example (CHAP username/password via URL):
qemu-system-x86_64 -drive file=iscsi://user%password@192.0.2.1/iqn.2001-04.com.example/1
Example (CHAP username/password via environment variables):
LIBISCSI_CHAP_USERNAME="user" LIBISCSI_CHAP_PASSWORD="password" qemu-system-x86_64 -drive file=iscsi://192.0.2.1/iqn.2001-04.com.example/1
NBD-
QEMU supports NBD (Network Block Devices) both using TCP protocol as
well as Unix Domain Sockets. With TCP, the default port is 10809.Syntax for specifying a NBD device using TCP, in preferred URI form:
“nbd://<server-ip>[:<port>]/[<export>]”Syntax for specifying a NBD device using Unix Domain Sockets;
remember that ‘?’ is a shell glob character and may need quoting:
“nbd+unix:///[<export>]?socket=<domain-socket>”Older syntax that is also recognized:
“nbd:<server-ip>:<port>[:exportname=<export>]”Syntax for specifying a NBD device using Unix Domain Sockets
“nbd:unix:<domain-socket>[:exportname=<export>]”Example for TCP
qemu-system-x86_64 --drive file=nbd:192.0.2.1:30000
Example for Unix Domain Sockets
qemu-system-x86_64 --drive file=nbd:unix:/tmp/nbd-socket
SSH-
QEMU supports SSH (Secure Shell) access to remote disks.
Examples:
qemu-system-x86_64 -drive file=ssh://user@host/path/to/disk.img qemu-system-x86_64 -drive file.driver=ssh,file.user=user,file.host=host,file.port=22,file.path=/path/to/disk.img
Currently authentication must be done using ssh-agent. Other
authentication methods may be supported in future. GlusterFS-
GlusterFS is a user space distributed file system. QEMU supports the
use of GlusterFS volumes for hosting VM disk images using TCP, Unix
Domain Sockets and RDMA transport protocols.Syntax for specifying a VM disk image on GlusterFS volume is
URI: gluster[+type]://[host[:port]]/volume/path[?socket=...][,debug=N][,logfile=...] JSON: 'json:{"driver":"qcow2","file":{"driver":"gluster","volume":"testvol","path":"a.img","debug":N,"logfile":"...", "server":[{"type":"tcp","host":"...","port":"..."}, {"type":"unix","socket":"..."}]}}'Example
URI: qemu-system-x86_64 --drive file=gluster://192.0.2.1/testvol/a.img, file.debug=9,file.logfile=/var/log/qemu-gluster.log JSON: qemu-system-x86_64 'json:{"driver":"qcow2", "file":{"driver":"gluster", "volume":"testvol","path":"a.img", "debug":9,"logfile":"/var/log/qemu-gluster.log", "server":[{"type":"tcp","host":"1.2.3.4","port":24007}, {"type":"unix","socket":"/var/run/glusterd.socket"}]}}' qemu-system-x86_64 -drive driver=qcow2,file.driver=gluster,file.volume=testvol,file.path=/path/a.img, file.debug=9,file.logfile=/var/log/qemu-gluster.log, file.server.0.type=tcp,file.server.0.host=1.2.3.4,file.server.0.port=24007, file.server.1.type=unix,file.server.1.socket=/var/run/glusterd.socketSee also http://www.gluster.org.
HTTP/HTTPS/FTP/FTPS-
QEMU supports read-only access to files accessed over http(s) and
ftp(s).Syntax using a single filename:
<protocol>://[<username>[:<password>]@]<host>/<path>
where:
protocol-
‘http’, ‘https’, ‘ftp’, or ‘ftps’.
username-
Optional username for authentication to the remote server.
password-
Optional password for authentication to the remote server.
host-
Address of the remote server.
path-
Path on the remote server, including any query string.
The following options are also supported:
url-
The full URL when passing options to the driver explicitly.
readahead-
The amount of data to read ahead with each range request to the
remote server. This value may optionally have the suffix ‘T’, ‘G’,
‘M’, ‘K’, ‘k’ or ‘b’. If it does not have a suffix, it will be
assumed to be in bytes. The value must be a multiple of 512 bytes.
It defaults to 256k. sslverify-
Whether to verify the remote server’s certificate when connecting
over SSL. It can have the value ‘on’ or ‘off’. It defaults to
‘on’. cookie-
Send this cookie (it can also be a list of cookies separated by
‘;’) with each outgoing request. Only supported when using
protocols such as HTTP which support cookies, otherwise ignored. timeout-
Set the timeout in seconds of the CURL connection. This timeout is
the time that CURL waits for a response from the remote server to
get the size of the image to be downloaded. If not set, the
default timeout of 5 seconds is used.
Note that when passing options to qemu explicitly,
driveris the
value of <protocol>.Example: boot from a remote Fedora 20 live ISO image
qemu-system-x86_64 --drive media=cdrom,file=https://archives.fedoraproject.org/pub/archive/fedora/linux/releases/20/Live/x86_64/Fedora-Live-Desktop-x86_64-20-1.iso,readonly qemu-system-x86_64 --drive media=cdrom,file.driver=http,file.url=http://archives.fedoraproject.org/pub/fedora/linux/releases/20/Live/x86_64/Fedora-Live-Desktop-x86_64-20-1.iso,readonly
Example: boot from a remote Fedora 20 cloud image using a local
overlay for writes, copy-on-read, and a readahead of 64kqemu-img create -f qcow2 -o backing_file='json:{"file.driver":"http",, "file.url":"http://archives.fedoraproject.org/pub/archive/fedora/linux/releases/20/Images/x86_64/Fedora-x86_64-20-20131211.1-sda.qcow2",, "file.readahead":"64k"}' /tmp/Fedora-x86_64-20-20131211.1-sda.qcow2 qemu-system-x86_64 -drive file=/tmp/Fedora-x86_64-20-20131211.1-sda.qcow2,copy-on-read=onExample: boot from an image stored on a VMware vSphere server with a
self-signed certificate using a local overlay for writes, a readahead
of 64k and a timeout of 10 seconds.qemu-img create -f qcow2 -o backing_file='json:{"file.driver":"https",, "file.url":"https://user:password@vsphere.example.com/folder/test/test-flat.vmdk?dcPath=Datacenter&dsName=datastore1",, "file.sslverify":"off",, "file.readahead":"64k",, "file.timeout":10}' /tmp/test.qcow2 qemu-system-x86_64 -drive file=/tmp/test.qcow2
See also¶
The HTML documentation of QEMU for more precise information and Linux
user mode emulator invocation.
Qemu is open-source software for virtualization on Windows 10/8/7, Linux, and macOS but with a command-line interface, lightweight, and low hardware requirements.
QEMU stands for “Quick Emulator” and is the standard tool for virtualization and CPU emulation under Linux, Windows, and macOS. On Linux systems, QEMU uses the functions of the Linux kernel for virtualization (KVM- Kernel Virtual Machine), which are not available under Windows.
Thus, the binaries of Qemu’s ported version for Windows by Stefan Weil couldn’t provide the performance as it gives on Linux OS with KVM. Thus VirtualBox or Vmware player will be the best alternative options; still, if you want to try then here in this Qemu tutorial, we will let know the way to download, install and use Qemu on Windows 10 or 7 using its GUI VM manager Qtemu, an open-source software.
Qemu installation on Windows 10 with Qtemu GUI
Step 1: Download Qemu for Windows
From the official website of the Qemu, we can download it easily even the source code. Visit it and click on the Windows tab, it will take you to another page https://qemu.weilnetz.de to download 32 bit or 64 bit of this virtualization platform. Here we are getting the 64 bit.
Step 2: Install Qemu
Now, like any other Windows 10/7 software, just double click on the downloaded setup of Qemu and follow the installation wizard.
- Accept the suggested language setting, by default it will be English. Select the “OK” button.
- Press the NEXT button.
- Confirm the usual license terms (GNU General Public License) with “Accept“.
- All modules required for QEMU have already been selected in the “Select components” dialogue. Confirm with “Next”.
- Check the suggested destination folder and go to “Install“.
- Click on “Finish” to complete the setup of QEMU.
Step 3: Install GUI for QEMU on Windows 10
As we know the QEMU uses the command line to create virtual machines by default. But it would be not feasible for standard computer users using CLI to manage virtual machines, thus we install another open-source application to provide a Graphical user interface (GUI) to QEMU. This program is known as Qtemu which is a fork of a dead project available at https://qtemu.org.
Here are the links to download an active Qtemu project for Windows 10/8/7 available on Gitlab.
Windows x86_64 installer
If you don’t want to install it, go for the portable version.
Windows x86_64 portable
Gitlab Page Link of the project.
Step 4: Setup QEMU manager Qtemu GUI
After the installation of Qtemu run it from the Windows Start menu.
- In the first column “QEMU binaries path” copy-paste this: C:Program Filesqemu Or enter the path where you have installed the QEMU.
- For the second column enter the path of the Qemu-img file that is: C:Program Filesqemuqemu-img.exe
- Now create a folder anywhere on your computer where you want to save the virtual machines created by QEMU. And click on the folder icon given in the front of the third column to select that particular folder.
Note: You can change this configuration any time from the Qtemu Settings.
After that click on the Finish button.
Step 5: Create a Virtual machine
Now, from Qemu GUI manager Qtemu, simply click on Machine and select New Machine.
Leave the Machine which is meant to select some particular motherboard chipset.
Configure the Virtual Machine hardware, select the CPU type such as Core 2 Duo, Base, or any CPU that Qemu would be able to emulate on your system whereas setting the CPU count, cores, Thread as shown below screenshot.
By Default, the HAXM- Hardware Accelerated Execution will be selected in the Qtemu but in case the HAXM is not supported by your system or not available, thus uncheck it and check TCG- Tiny Code Generator.
Set the amount of RAM you want to assign to your VM.
Step 6: Set bootable medium CD/DVD
Now, everything is ready, we have created a Virtual machine, its time to set a bootable medium to CD; so that our ISO file could be used while booting the QEMU VM.
For that right-click on the created VM on the QTEMU interface and select Machine Settings.
There select the Boot options from the right-side panel and after that check the “Enable boot menu” and then the CD ROM option following the Save button.
Step 7: Insert ISO file in QEMU via Qtemu GUI
Under the Machine settings, go to the Media menu and click on the CD icon. This will open the Windows file explorer, navigate to the ISO file of the OS with which you want to boot in QEMU, and click on the Save button.
Step 8: Boot Qemu Virtual Machine via GUI
Now, on the main interface of the Qtemu GUI, select the created VM and click on the start button. This will open the boot screen.
Wait for a few minutes depending upon the OS distribution you are using, it will show the LIVE screen of the same. However, I tried to boot and install Windows 10 on Qemu using the GUI but it was quite sluggish and slow.
Verdict:
Although the CLI can be used to create and manage a Virtual machine on Windows 10 using the QEMU, with the Qtemu GUI tool it becomes quite easy, however, in my case it worked well with Lightweight Linux Distros but for Windows guest VMs quite slow and low performance. I recommend using VirtualBox instead. Yet, if someone wants to experience Qemu on Windows 10 this is the easiest possible way. Still, be cautious with Qtemu hardware configuration because slight here and there will not let you boot the VM.