Currently I’m running Windows 7 x64 and usually I want all console tools to work with UTF-8 rather than with default code page 850.
Running chcp 65001 in the command prompt prior to use of any tools helps but is there any way to set is as default code page?
Update:
Changing HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINESYSTEMCurrentControlSetControlNlsCodePageOEMCP value to 65001 appear to make the system unable to boot in my case.
Proposed change of HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINESoftwareMicrosoftCommand ProcessorAutorun to @chcp 65001>nul served just well for my purpose. (thanks to Ole_Brun)
asked Apr 12, 2011 at 10:42
7
To change the codepage for the console only, do the following:
- Start -> Run -> regedit
- Go to
[HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINESoftwareMicrosoftCommand ProcessorAutorun] - Change the value to
@chcp 65001>nul
If Autorun is not present, you can add a New String
Nabi K.A.Z.
3801 gold badge5 silver badges10 bronze badges
answered Apr 12, 2011 at 12:22
Nils Magne LundeNils Magne Lunde
2,5421 gold badge16 silver badges14 bronze badges
11
Personally, I don’t like changing the registry. This can cause a lot of problems. I created a batch file:
@ECHO OFF
REM change CHCP to UTF-8
CHCP 65001
CLS
I saved at C:WindowsSystem32 as switch.bat and created a link for cmd.exe on the Desktop.
In the properties of the cmd shortcut, changed the destination to: C:WindowsSystem32cmd.exe /k switch
Voilà, when I need to type in UTF-8, I use this link.
answered Dec 7, 2013 at 15:36
jucajuca
6095 silver badges2 bronze badges
5
In the 1809 build of Windows 10 I’ve managed to permanently solve this by going to the system’s Language settings, selecting Administrative language settings, clicking Change system locale... and checking the Beta: Use Unicode UTF-8 for worldwide language support box and then restarting my pc.
This way it applies to all applications, even those ones that I don’t start from a command prompt!
(Which was necessary for me, since I was trying to edit Agda code from Atom.)
Bob Stein
1,3371 gold badge16 silver badges23 bronze badges
answered May 11, 2019 at 14:44
Isti115Isti115
89410 silver badges11 bronze badges
7
Edit the Registry:
Windows Registry Editor Version 5.00
[HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINESYSTEMCurrentControlSetControlNlsCodePage]
"OEMCP"="65001"
Then restart. With this fix, if you are using Consolas font, it seems to lock
PowerShell into a small font size. cmd.exe still works fine. As a workaround,
you can use Lucida Console, or I switched to Cascadia Mono:
https://github.com/microsoft/cascadia-code
answered Jun 13, 2015 at 20:39
1
This can be done by creating a PowerShell profile and adding the command «chcp 65001 >$null» to it:
PS> Set-ExecutionPolicy RemoteSigned
PS> New-Item -Path $Profile -ItemType file -Force
PS> notepad $Profile
This doesn’t require editing the registry and, unlike editing a shortcut, will work if PowerShell is started in a specific folder using the Windows Explorer context menu.
answered Sep 3, 2017 at 20:56
0
The command to change the codepage is chcp <codepage>. Example: chcp 1252. You should type it in a Powershell window.
To avoid the hassle of typing it everytime (if you always have to change the codepage), you may append it to the program’s command line. To do so, follow these steps:
- Right-click the Powershell icon on Start menu and choose «More» > «Open file Location».
- Right-click the Powershell shortcut and select «Properties».
- Add the following to the end of the «Target» command line:
-NoExit -Command "chcp 1252"
Be happy.
Don’t fuss with Windows Registry unless you have no other option.
answered Nov 2, 2016 at 21:11
JColaresJColares
591 silver badge1 bronze badge
1
Open in Powershell through Explorer still didn’t work for me even though I’ve tried enabling that Beta Unicode feature in the language settings.
However, I’ve just found this worked.
[HKEY_CURRENT_USERConsole%SystemRoot%_System32_WindowsPowerShell_v1.0_powershell.exe]
"CodePage"=dword:0000fde9
From: https://www.zhihu.com/question/54724102
answered Feb 15, 2021 at 11:09
If you’re using ConEmu then:
- Open up Settings from the upper right menu
- Go to Startup -> Environment
- Add
chcp 65001on a new line. - Click «Save Settings».
- Close ConEmu and re-open it
answered May 4, 2020 at 1:22
Instead of changing the registry, you can instead create %HOMEPATH%init.cmd.
Mine reads:
@ECHO OFF
CHCP 65001 > nul
answered Jan 21 at 9:39
Note:
-
This answer shows how to switch the character encoding in the Windows console to
(BOM-less) UTF-8 (code page65001), so that shells such ascmd.exeand PowerShell properly encode and decode characters (text) when communicating with external (console) programs with full Unicode support, and incmd.exealso for file I/O.[1] -
If, by contrast, your concern is about the separate aspect of the limitations of Unicode character rendering in console windows, see the middle and bottom sections of this answer, where alternative console (terminal) applications are discussed too.
Does Microsoft provide an improved / complete alternative to chcp 65001 that can be saved permanently without manual alteration of the Registry?
As of (at least) Windows 10, version 1903, you have the option to set the system locale (language for non-Unicode programs) to UTF-8, but the feature is still in beta as of this writing.
To activate it:
- Run
intl.cpl(which opens the regional settings in Control Panel) - Follow the instructions in the screen shot below.
-
This sets both the system’s active OEM and the ANSI code page to
65001, the UTF-8 code page, which therefore (a) makes all future console windows, which use the OEM code page, default to UTF-8 (as ifchcp 65001had been executed in acmd.exewindow) and (b) also makes legacy, non-Unicode GUI-subsystem applications, which (among others) use the ANSI code page, use UTF-8.-
Caveats:
-
If you’re using Windows PowerShell, this will also make
Get-ContentandSet-Contentand other contexts where Windows PowerShell default so the system’s active ANSI code page, notably reading source code from BOM-less files, default to UTF-8 (which PowerShell Core (v6+) always does). This means that, in the absence of an-Encodingargument, BOM-less files that are ANSI-encoded (which is historically common) will then be misread, and files created withSet-Contentwill be UTF-8 rather than ANSI-encoded. -
[Fixed in PowerShell 7.1] Up to at least PowerShell 7.0, a bug in the underlying .NET version (.NET Core 3.1) causes follow-on bugs in PowerShell: a UTF-8 BOM is unexpectedly prepended to data sent to external processes via stdin (irrespective of what you set
$OutputEncodingto), which notably breaksStart-Job— see this GitHub issue. -
Not all fonts speak Unicode, so pick a TT (TrueType) font, but even they usually support only a subset of all characters, so you may have to experiment with specific fonts to see if all characters you care about are represented — see this answer for details, which also discusses alternative console (terminal) applications that have better Unicode rendering support.
-
As eryksun points out, legacy console applications that do not «speak» UTF-8 will be limited to ASCII-only input and will produce incorrect output when trying to output characters outside the (7-bit) ASCII range. (In the obsolescent Windows 7 and below, programs may even crash).
If running legacy console applications is important to you, see eryksun’s recommendations in the comments.
-
-
-
However, for Windows PowerShell, that is not enough:
- You must additionally set the
$OutputEncodingpreference variable to UTF-8 as well:$OutputEncoding = [System.Text.UTF8Encoding]::new()[2]; it’s simplest to add that command to your$PROFILE(current user only) or$PROFILE.AllUsersCurrentHost(all users) file. - Fortunately, this is no longer necessary in PowerShell Core, which internally consistently defaults to BOM-less UTF-8.
- You must additionally set the
If setting the system locale to UTF-8 is not an option in your environment, use startup commands instead:
Note: The caveat re legacy console applications mentioned above equally applies here. If running legacy console applications is important to you, see eryksun’s recommendations in the comments.
-
For PowerShell (both editions), add the following line to your
$PROFILE(current user only) or$PROFILE.AllUsersCurrentHost(all users) file, which is the equivalent ofchcp 65001, supplemented with setting preference variable$OutputEncodingto instruct PowerShell to send data to external programs via the pipeline in UTF-8:- Note that running
chcp 65001from inside a PowerShell session is not effective, because .NET caches the console’s output encoding on startup and is unaware of later changes made withchcp; additionally, as stated, Windows PowerShell requires$OutputEncodingto be set — see this answer for details.
- Note that running
$OutputEncoding = [console]::InputEncoding = [console]::OutputEncoding = New-Object System.Text.UTF8Encoding
- For example, here’s a quick-and-dirty approach to add this line to
$PROFILEprogrammatically:
'$OutputEncoding = [console]::InputEncoding = [console]::OutputEncoding = New-Object System.Text.UTF8Encoding' + [Environment]::Newline + (Get-Content -Raw $PROFILE -ErrorAction SilentlyContinue) | Set-Content -Encoding utf8 $PROFILE
-
For
cmd.exe, define an auto-run command via the registry, in valueAutoRunof keyHKEY_CURRENT_USERSoftwareMicrosoftCommand Processor(current user only) orHKEY_LOCAL_MACHINESoftwareMicrosoftCommand Processor(all users):- For instance, you can use PowerShell to create this value for you:
# Auto-execute `chcp 65001` whenever the current user opens a `cmd.exe` console
# window (including when running a batch file):
Set-ItemProperty 'HKCU:SoftwareMicrosoftCommand Processor' AutoRun 'chcp 65001 >NUL'
Optional reading: Why the Windows PowerShell ISE is a poor choice:
While the ISE does have better Unicode rendering support than the console, it is generally a poor choice:
-
First and foremost, the ISE is obsolescent: it doesn’t support PowerShell (Core) 7+, where all future development will go, and it isn’t cross-platform, unlike the new premier IDE for both PowerShell editions, Visual Studio Code, which already speaks UTF-8 by default for PowerShell Core and can be configured to do so for Windows PowerShell.
-
The ISE is generally an environment for developing scripts, not for running them in production (if you’re writing scripts (also) for others, you should assume that they’ll be run in the console); notably, with respect to running code, the ISE’s behavior is not the same as that of a regular console:
-
Poor support for running external programs, not only due to lack of supporting interactive ones (see next point), but also with respect to:
-
character encoding: the ISE mistakenly assumes that external programs use the ANSI code page by default, when in reality it is the OEM code page. E.g., by default this simple command, which tries to simply pass a string echoed from
cmd.exethrough, malfunctions (see below for a fix):
cmd /c echo hü | Write-Output -
Inappropriate rendering of stderr output as PowerShell errors: see this answer.
-
-
The ISE dot-sources script-file invocations instead of running them in a child scope (the latter is what happens in a regular console window); that is, repeated invocations run in the very same scope. This can lead to subtle bugs, where definitions left behind by a previous run can affect subsequent ones.
-
-
As eryksun points out, the ISE doesn’t support running interactive external console programs, namely those that require user input:
The problem is that it hides the console and redirects the process output (but not input) to a pipe. Most console applications switch to full buffering when a file is a pipe. Also, interactive applications require reading from stdin, which isn’t possible from a hidden console window. (It can be unhidden via
ShowWindow, but a separate window for input is clunky.)
-
If you’re willing to live with that limitation, switching the active code page to
65001(UTF-8) for proper communication with external programs requires an awkward workaround:-
You must first force creation of the hidden console window by running any external program from the built-in console, e.g.,
chcp— you’ll see a console window flash briefly. -
Only then can you set
[console]::OutputEncoding(and$OutputEncoding) to UTF-8, as shown above (if the hidden console hasn’t been created yet, you’ll get ahandle is invalid error).
-
[1] In PowerShell, if you never call external programs, you needn’t worry about the system locale (active code pages): PowerShell-native commands and .NET calls always communicate via UTF-16 strings (native .NET strings) and on file I/O apply default encodings that are independent of the system locale. Similarly, because the Unicode versions of the Windows API functions are used to print to and read from the console, non-ASCII characters always print correctly (within the rendering limitations of the console).
In cmd.exe, by contrast, the system locale matters for file I/O (with < and > redirections, but notably including what encoding to assume for batch-file source code), not just for communicating with external programs in-memory (such as when reading program output in a for /f loop).
[2] In PowerShell v4-, where the static ::new() method isn’t available, use $OutputEncoding = (New-Object System.Text.UTF8Encoding).psobject.BaseObject. See GitHub issue #5763 for why the .psobject.BaseObject part is needed.
Одна из возможных проблем, с которыми можно столкнуться после установки Windows 10 — кракозябры вместо русских букв в интерфейсе программ, а также в документах. Чаще неправильное отображение кириллицы встречается в изначально англоязычных и не совсем лицензионных версиях системы, но бывают и исключения.
В этой инструкции — о том, как исправить «кракозябры» (или иероглифы), а точнее — отображение кириллицы в Windows 10 несколькими способами. Возможно, также будет полезным: Как установить и включить русский язык интерфейса в Windows 10 (для систем на английском и других языках).
Исправление отображения кириллицы с помощью настроек языка и региональных стандартов Windows 10
Самый простой и чаще всего работающий способ убрать кракозябры и вернуть русские буквы в Windows 10 — исправить некоторые неправильные настройки в параметрах системы.
Для этого потребуется выполнить следующие шаги (примечание: привожу также названия нужных пунктов на английском, так как иногда необходимость исправить кириллицу возникает в англоязычных версиях системы без нужды менять язык интерфейса).
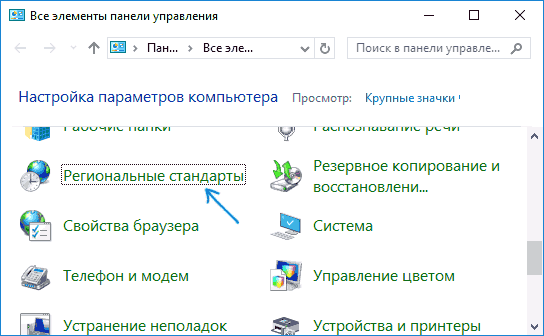
- Откройте панель управления (для этого можно начать набирать «Панель управления» или «Control Panel» в поиске на панели задач.
- Убедитесь, что в поле «Просмотр» (View by) установлено «Значки» (Icons) и выберите пункт «Региональные стандарты» (Region).
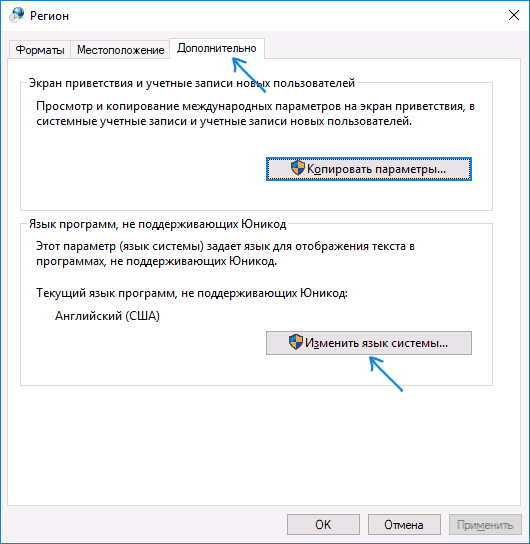
- На вкладке «Дополнительно» (Administrative) в разделе «Язык программ, не поддерживающих Юникод» (Language for non-Unicode programs) нажмите по кнопке «Изменить язык системы» (Change system locale).
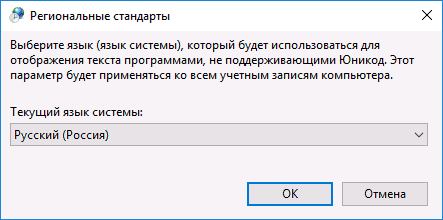
- Выберите русский язык, нажмите «Ок» и подтвердите перезагрузку компьютера.
После перезагрузки проверьте, была ли решена проблема с отображением русских букв в интерфейсе программ и (или) документах — обычно, кракозябры бывают исправлены после этих простых действий.
Как исправить иероглифы Windows 10 путем изменения кодовых страниц
Кодовые страницы представляют собой таблицы, в которых определенным байтам сопоставляются определенные символы, а отображение кириллицы в виде иероглифов в Windows 10 связано обычно с тем, что по умолчанию задана не та кодовая страница и это можно исправить несколькими способами, которые могут быть полезны, когда требуется не изменять язык системы в параметрах.
С помощью редактора реестра
Первый способ — использовать редактор реестра. На мой взгляд, это самый щадящий для системы метод, тем не менее, рекомендую создать точку восстановления прежде чем начинать. Совет про точки восстановления относится и ко всем последующим способам в этом руководстве.
- Нажмите клавиши Win+R на клавиатуре, введите regedit и нажмите Enter, откроется редактор реестра.
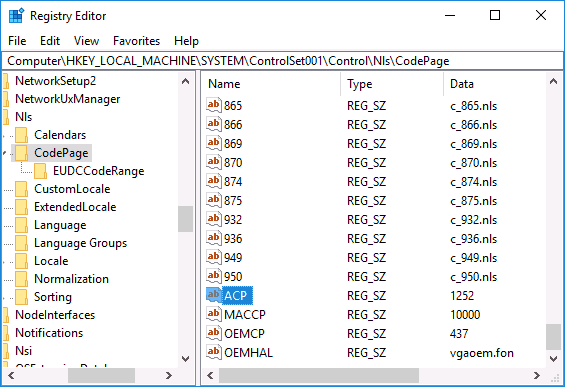
- Перейдите к разделу реестра
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINESYSTEMCurrentControlSetControlNlsCodePage
и в правой части пролистайте значения этого раздела до конца.
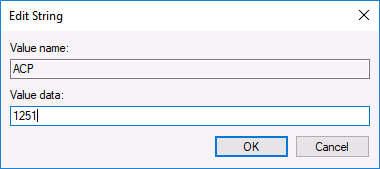
- Дважды нажмите по параметру ACP, установите значение 1251 (кодовая страница для кириллицы), нажмите Ок и закройте редактор реестра.
- Перезагрузите компьютер (именно перезагрузка, а не завершение работы и включение, в Windows 10 это может иметь значение).
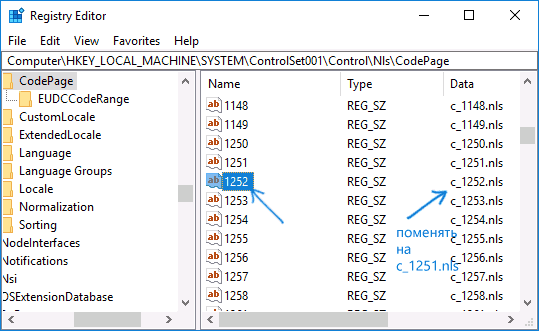
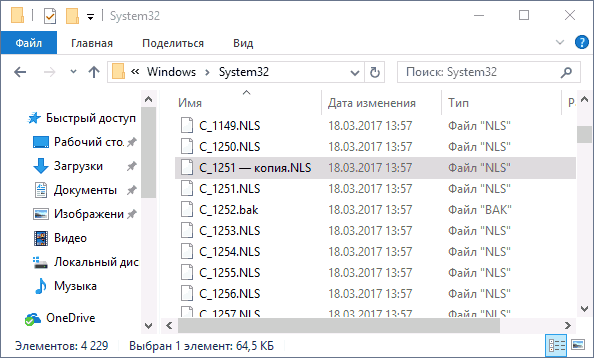
Обычно, это исправляет проблему с отображением русских букв. Вариация способа с помощью редактора реестра (но менее предпочтительная) — посмотреть на текущее значение параметра ACP (обычно — 1252 для изначально англоязычных систем), затем в том же разделе реестра найти параметр с именем 1252 и изменить его значение с c_1252.nls на c_1251.nls.
Путем подмена файла кодовой страницы на c_1251.nls
Второй, не рекомендуемый мной способ, но иногда выбираемый теми, кто считает, что правка реестра — это слишком сложно или опасно: подмена файла кодовой страницы в C: Windows System32 (предполагается, что у вас установлена западно-европейская кодовая страница — 1252, обычно это так. Посмотреть текущую кодовую страницу можно в параметре ACP в реестре, как было описано в предыдущем способе).
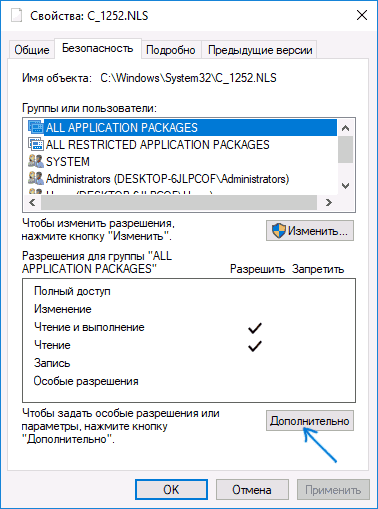
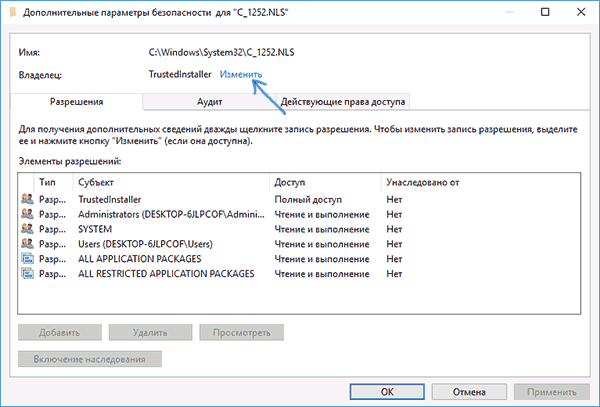
- Зайдите в папку C: Windows System32 и найдите файл c_1252.NLS, нажмите по нему правой кнопкой мыши, выберите пункт «Свойства» и откройте вкладку «Безопасность». На ней нажмите кнопку «Дополнительно».
- В поле «Владелец» нажмите «Изменить».
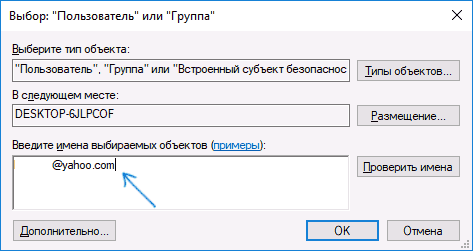
- В поле «Введите имена выбираемых объектов» укажите ваше имя пользователя (с правами администратора). Если в Windows 10 используется учетная запись Майкрософт, вместо имени пользователя укажите адрес электронной почты. Нажмите «Ок» в окне, где указывали пользователя и в следующем (Дополнительные параметры безопасности) окне.
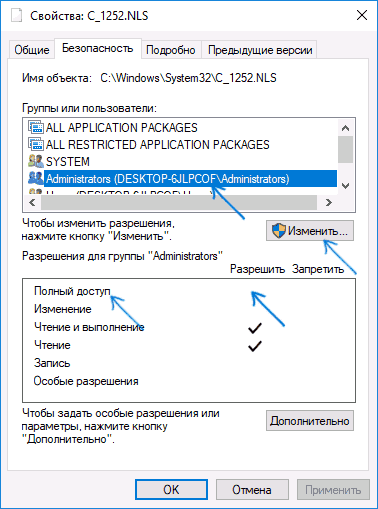
- Вы снова окажетесь на вкладке «Безопасность» в свойствах файла. Нажмите кнопку «Изменить».
- Выберите пункт «Администраторы» (Administrators) и включите полный доступ для них. Нажмите «Ок» и подтвердите изменение разрешений. Нажмите «Ок» в окне свойств файла.
- Переименуйте файл c_1252.NLS (например, измените расширение на .bak, чтобы не потерять этот файл).
- Удерживая клавишу Ctrl, перетащите находящийся там же в C:WindowsSystem32 файл c_1251.NLS (кодовая страница для кириллицы) в другое место этого же окна проводника, чтобы создать копию файла.
- Переименуйте копию файла c_1251.NLS в c_1252.NLS.
- Перезагрузите компьютер.
После перезагрузки Windows 10 кириллица должна будет отображаться не в виде иероглифов, а как обычные русские буквы.
Кодировка текста – это схема нумерации символов, в которой каждому символу, цифре или знаку присвоено соответствующее число. Кодировку используют для сохранения и обработки текста на компьютере. Каждый раз при сохранении текста в файл он сохраняется с использованием определенной схемы кодирования, и при открытии этого файла необходимо использовать такую же схему, иначе восстановить исходный текст не получится. Самыми популярными кодировками для кириллицы сейчас являются UTF-8, Windows-1251 (CP1251, ANSI).
Для того чтобы программа смогла правильно открыть текстовый файл, иногда приходится вручную менять кодировку, перекодируя текст из одной схемы в другую. Например, не редко возникают проблемы с открытием файлов CSV, XML, SQL, TXT, PHP.
В этой небольшой статье мы расскажем о том, как изменить кодировку текстового файла на UTF-8, Windows-1251 или любую другую.
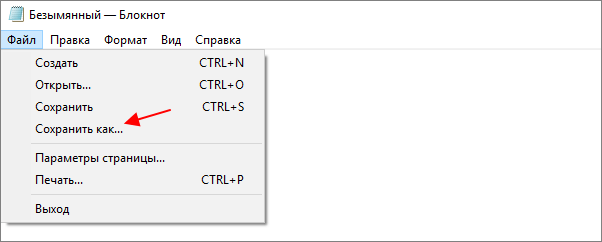
Блокнот Windows
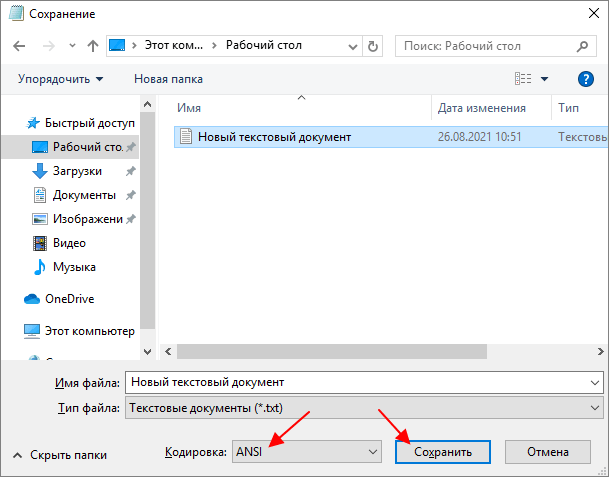
Если вы используете операционную систему Windows 10 или Windows 11, то вы можете изменить кодировку текста с помощью стандартной программы Блокнот. Для этого нужно открыть текстовый файл с помощью Блокнота и воспользоваться меню «Файл – Сохранить как».
В открывшемся окне нужно указать новое название для файла, выбрать подходящую кодировку и нажать на кнопку «Сохранить».
К сожалению, для подобных задач программа Блокнот часто не подходит. С ее помощью нельзя открывать документы большого размера, и она не поддерживает многие кодировки. Например, с помощью Блокнота нельзя открыть текстовые файлы в DOS 866.
Notepad++
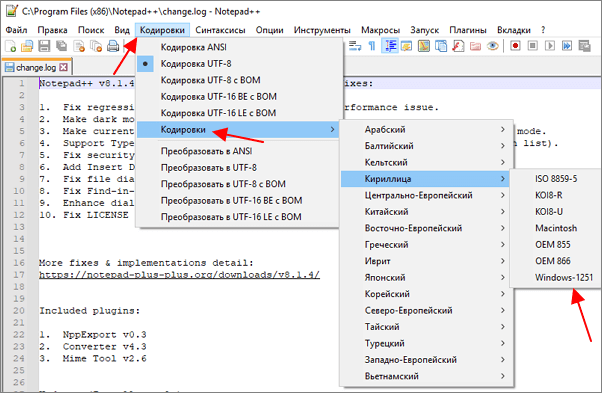
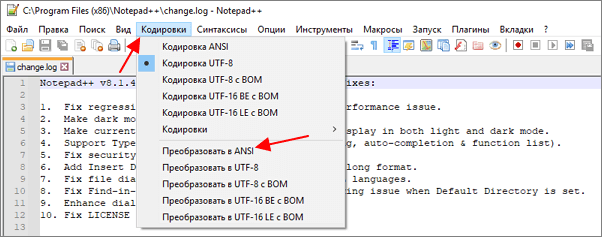
Notepad++ (скачать) является одним из наиболее продвинутых текстовых редакторов. Он обладает подсветкой синтаксиса языков программирования, позволяет выполнять поиск и замену по регулярным выражениям, отслеживать изменения в файлах, записывать и воспроизводить макросы, считать хеш-сумы и многое другое. Одной из основных функций Notepad++ является поддержка большого количества кодировок текста и возможность изменения кодировки текстового файла в UTF-8 или Windows 1251.
Для того чтобы изменить кодировку текста с помощью Notepad++ файл нужно открыть в данной программе. Если программа не смогла правильно определить схему кодирования текста, то это можно сделать вручную. Для этого нужно открыть меню «Кодировки – Кириллица» и выбрать нужный вариант.
После открытия текста можно изменить его кодировку. Для этого нужно открыть меню «Кодировки» и выбрать один из вариантов преобразования. Notepad++ позволяет изменить текущую кодировку текста на ANSI (Windows-1251), UTF-8, UTF-8 BOM, UTF-8 BE BOM, UTF-8 LE BOM.
После преобразования файл нужно сохранить с помощью меню «Файл – Сохранить» или комбинации клавиш Ctrl-S.
Akelpad
Akelpad (скачать) – достаточно старая программа для работы с текстовыми файлами, которая все еще актуальна и может быть полезной. Фактически Akelpad является более продвинутой версией стандартной программы Блокнот из Windows. С его помощью можно открывать текстовые файлы большого размера, которые не открываются в Блокноте, выполнять поиск и замену с использованием регулярных выражений и менять кодировку текста.
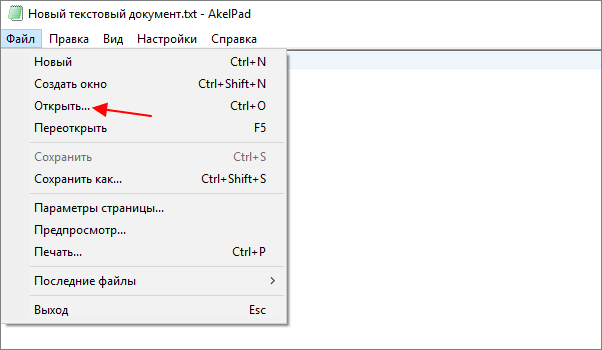
Для того чтобы изменить кодировку текста с помощью Akelpad файл нужно открыть в данной программе. Если после открытия файла текст не читается, то нужно воспользоваться меню «Файл – Открыть».
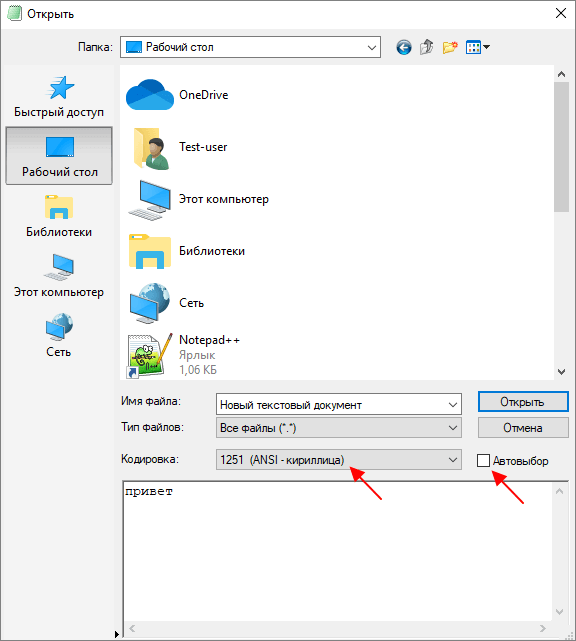
В открывшемся окне нужно выделить текстовый файл, снять отметку «Автовыбор» и выбрать подходящую кодировку из списка. При этом в нижней части окна можно видеть, как будет отображаться текст.
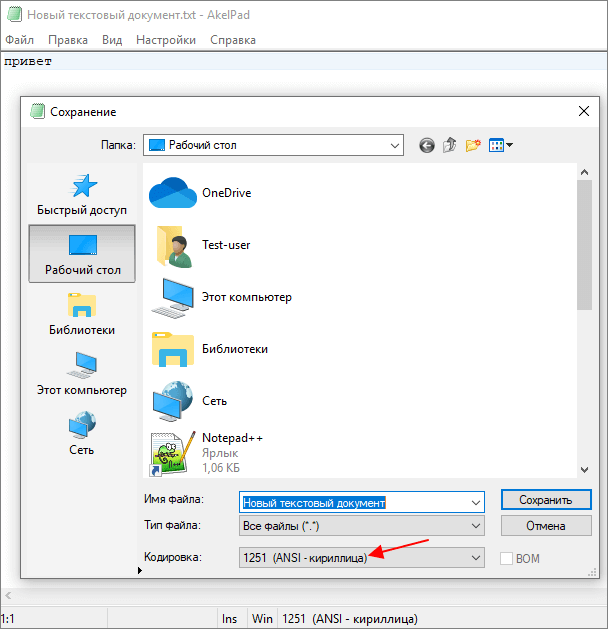
Для того чтобы изменить текущую кодировку текста нужно воспользоваться меню «Файл – Сохранить как» и сохранить документ с указанием новой схемы кодирования.
В отличие от Notepad++, текстовый редактор Akelpad позволяет сохранить файл в практически любой кодировке. В частности, доступны Windows 1251, DOS 886, UTF-8 и многие другие.
Посмотрите также:
- Чем открыть PDF файл в Windows 7 или Windows 10
- Как перевернуть страницу в Word
- Как копировать текст с помощью клавиатуры
- Как сделать рамку в Word
- Как сделать буклет в Word
Автор
Александр Степушин
Создатель сайта comp-security.net, автор более 2000 статей о ремонте компьютеров, работе с программами, настройке операционных систем.
Остались вопросы?
Задайте вопрос в комментариях под статьей или на странице
«Задать вопрос»
и вы обязательно получите ответ.
-
Natalia Novoselova
- Гуру
- Сообщения: 3017
- Зарегистрирован: 15 янв 2013, 20:14
- Репутация: 69
- Ваше звание: Лиса
- Откуда: **
- Контактная информация:
Как поставить кодировку UTF-8 в Windows-8
Есть скрипт для R, где комментарии написаны на русском языке в кодировке UTF-8. При открытии скрипта у меня крякозябы, несмотря на то, что в систем на компе язык «для приложений не использующих Unicode» стоит русский. То есть — надо поставить еще кодировку UTF-8. Как это сделать для всей ОС (Windows-8)? Нигде не могу найти таких настроек. В самом R тоже.
-
Игорь Белов
- Гуру
- Сообщения: 2186
- Зарегистрирован: 04 янв 2011, 22:00
- Статьи: 12
- Проекты: 1
- Репутация: 1481
- Откуда: Казань
Re: Как поставить кодировку UTF-8 в Windows-8
Сообщение
Игорь Белов » 27 окт 2018, 21:24
Проще всего перекодировать файл в CP1251. Это можно сделать в большинстве текстовых редакторов. Или погуглите онлайн-конвертеры.
The purpose of computing is insight, not numbers
-
rhot
- Гуру
- Сообщения: 1727
- Зарегистрирован: 25 янв 2011, 17:50
- Статьи: 1
- Репутация: 194
- Ваше звание: доктор
- Откуда: Архангельск
Re: Как поставить кодировку UTF-8 в Windows-8
Сообщение
rhot » 27 окт 2018, 21:26
В RStudio кодировка выбирается через File —> Reopen with encoding
___________(¯`·.¸(¯`·.¸ Scientia potentia est _/ {SILVA}:::{FOSS}:::{GIS} _ Знание сила ¸.·´¯)¸.·´¯)___________
-
Natalia Novoselova
- Гуру
- Сообщения: 3017
- Зарегистрирован: 15 янв 2013, 20:14
- Репутация: 69
- Ваше звание: Лиса
- Откуда: **
- Контактная информация:
Re: Как поставить кодировку UTF-8 в Windows-8
Сообщение
Natalia Novoselova » 30 окт 2018, 22:09
Игорь Белов писал(а): ↑
27 окт 2018, 21:24
Проще всего перекодировать файл в CP1251. Это можно сделать в большинстве текстовых редакторов. Или погуглите онлайн-конвертеры.
Почему-то на моем компе такая перезапись скрипта тоже дала крякозябы.
В RStudio кодировка выбирается через File —> Reopen with encoding
Я пользуюсь обычной R консолью, там такого нет. Попробую перейти в RStudio.
-
rhot
- Гуру
- Сообщения: 1727
- Зарегистрирован: 25 янв 2011, 17:50
- Статьи: 1
- Репутация: 194
- Ваше звание: доктор
- Откуда: Архангельск
Re: Как поставить кодировку UTF-8 в Windows-8
Сообщение
rhot » 31 окт 2018, 10:25
Natalia Novoselova писал(а): ↑
30 окт 2018, 22:09
Я пользуюсь обычной R консолью, там такого нет. Попробую перейти в RStudio.
Тогда не знаю как. Могу предложить последовать примеру редактирования реестра. Правда это для семёрки…
___________(¯`·.¸(¯`·.¸ Scientia potentia est _/ {SILVA}:::{FOSS}:::{GIS} _ Знание сила ¸.·´¯)¸.·´¯)___________
-
gamm
- Гуру
- Сообщения: 3825
- Зарегистрирован: 15 окт 2010, 08:33
- Репутация: 997
- Ваше звание: программист
- Откуда: Казань
Re: Как поставить кодировку UTF-8 в Windows-8
Сообщение
gamm » 31 окт 2018, 14:05
Поставьте FAR (он бесплатный), откройте файл во встроенном редакторе, выберите исходную кодировку (если не распознает), выделите все (Ctrl/a), уберите в буфер (ctrl/x), выберите новую кодировку, и вставьте (ctrl/v).
Выбор кодировки типа ctrl/F8 или alt/F8 или около. Если нужной кодировки нет, установите, в папке, где far стоит, есть скрипты.
-
nplatonov
- Интересующийся
- Сообщения: 25
- Зарегистрирован: 07 фев 2012, 12:00
- Репутация: 20
Re: Как поставить кодировку UTF-8 в Windows-8
Сообщение
nplatonov » 04 ноя 2018, 20:42
Можно попробовать задавать кодировку следующим образом:
path_to_R_binRterm —encoding UTF-8 —file=test.R —args pi 3.1415
-
nkljdubin
- Новоприбывший
- Сообщения: 0
- Зарегистрирован: 13 мар 2021, 05:44
- Репутация: 0
- Откуда: Санкт-Петербу́рг
- Контактная информация:
Re: Как поставить кодировку UTF-8 в Windows-8
Сообщение
nkljdubin » 13 мар 2021, 05:49
Тоже интересовался данным вопросом, спасибо за советы.
-
AlexTim
- Интересующийся
- Сообщения: 19
- Зарегистрирован: 25 ноя 2021, 14:11
- Репутация: 7
- Откуда: Оренбург
Re: Как поставить кодировку UTF-8 в Windows-8
Сообщение
AlexTim » 22 дек 2021, 13:36
Попробуйте
«Панель управления» —> «Региональные стандарты» —> «Дополнительно» —> [«Изменить язык системы»] —>
(v) «Использовать Юникод (UTF-8) для поддержки языка во всем Мире».
Перезагрузка.
Download PC Repair Tool to quickly find & fix Windows errors automatically
If you want to change the default character encoding in Notepad in Windows 11/10, this tutorial will guide you through the process. It is possible to change the default encoding from UTF-8 to ANSI or other using the Registry Editor. Notepad started using UTF-8 as the default character encoding – it used ANSI as the default encoding.
Let’s assume that you have a text file showing some unusual characters such as “ð???”. If you want to extract the original human-readable text out of these strange characters, you may need to switch between character encodings.
We have already shown the process to change the character encoding in the Outlook app, now let us see how to do it for Notepad. While Notepad allows you to change the encoding while saving the file, it is better to change it while creating or editing a file. The following character encodings are available:
- ANSI
- UTF-16 LE
- UTF-16 BE
- UTF-8
- UTF-8 with BOM
Precaution: As you will use Registry Editor, it is recommended to backup all Registry files and create a System Restore point.
To change default encoding in Notepad, follow these steps-
- Press Win+R to open the Run prompt.
- Type regedit and hit the Enter button.
- Click on the Yes button.
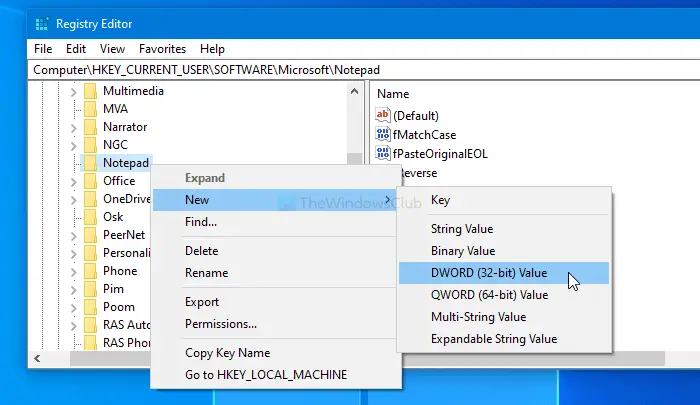
- Navigate to Notepad in HKCU.
- Right-click on Notepad > New > DWORD (32-bit) Value.
- Name it as iDefaultEncoding.
- Double-click on it to set the Value data.
- Click the OK button.
You will have to open the Registry Editor on your computer. For that, press Win+R, type regedit, and hit the Enter button. If the UAC prompt appears, click on the Yes button. After opening the Registry Editor, navigate to the following path-
HKEY_CURRENT_USERSOFTWAREMicrosoftNotepad
Right-click on Notepad and select New > DWORD (32-bit) Value.
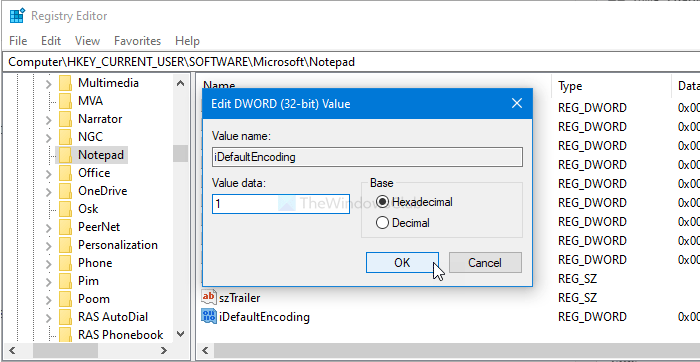
Once it is created, name it as iDefaultEncoding. Now, double-click on iDefaultEncoding and set the Value data as following-
- ANSI: 1
- UTF-16 LE: 2
- UTF-16 BE: 3
- UTF-8 BOM: 4
- UTF-8: 5
After setting the Value data, click on the OK button to save the change.
Once done, restart the Notepad app to find the difference. You can see the selected character encoding in the Status Bar.
In case you want to get back to the original, navigate to the same path in the Registry Editor and right-click on iDefaultEncoding. Then, select the Delete button and confirm the removal.
Hope all goes well.
Anand Khanse is the Admin of TheWindowsClub.com, a 10-year Microsoft MVP (2006-16) & a Windows Insider MVP (2016-2022). Please read the entire post & the comments first, create a System Restore Point before making any changes to your system & be careful about any 3rd-party offers while installing freeware.
Download PC Repair Tool to quickly find & fix Windows errors automatically
If you want to change the default character encoding in Notepad in Windows 11/10, this tutorial will guide you through the process. It is possible to change the default encoding from UTF-8 to ANSI or other using the Registry Editor. Notepad started using UTF-8 as the default character encoding – it used ANSI as the default encoding.
Let’s assume that you have a text file showing some unusual characters such as “ð???”. If you want to extract the original human-readable text out of these strange characters, you may need to switch between character encodings.
We have already shown the process to change the character encoding in the Outlook app, now let us see how to do it for Notepad. While Notepad allows you to change the encoding while saving the file, it is better to change it while creating or editing a file. The following character encodings are available:
- ANSI
- UTF-16 LE
- UTF-16 BE
- UTF-8
- UTF-8 with BOM
Precaution: As you will use Registry Editor, it is recommended to backup all Registry files and create a System Restore point.
To change default encoding in Notepad, follow these steps-
- Press Win+R to open the Run prompt.
- Type regedit and hit the Enter button.
- Click on the Yes button.
- Navigate to Notepad in HKCU.
- Right-click on Notepad > New > DWORD (32-bit) Value.
- Name it as iDefaultEncoding.
- Double-click on it to set the Value data.
- Click the OK button.
You will have to open the Registry Editor on your computer. For that, press Win+R, type regedit, and hit the Enter button. If the UAC prompt appears, click on the Yes button. After opening the Registry Editor, navigate to the following path-
HKEY_CURRENT_USERSOFTWAREMicrosoftNotepad
Right-click on Notepad and select New > DWORD (32-bit) Value.
Once it is created, name it as iDefaultEncoding. Now, double-click on iDefaultEncoding and set the Value data as following-
- ANSI: 1
- UTF-16 LE: 2
- UTF-16 BE: 3
- UTF-8 BOM: 4
- UTF-8: 5
After setting the Value data, click on the OK button to save the change.
Once done, restart the Notepad app to find the difference. You can see the selected character encoding in the Status Bar.
In case you want to get back to the original, navigate to the same path in the Registry Editor and right-click on iDefaultEncoding. Then, select the Delete button and confirm the removal.
Hope all goes well.
Anand Khanse is the Admin of TheWindowsClub.com, a 10-year Microsoft MVP (2006-16) & a Windows Insider MVP (2016-2022). Please read the entire post & the comments first, create a System Restore Point before making any changes to your system & be careful about any 3rd-party offers while installing freeware.
Просмотр настроек языкового стандарта системы для Windows
- Щелкните Пуск, затем Панель управления.
- Щелкните Часы, язык и регион.
- Windows 10, Windows 8: щелкните Регион. …
- Щелкните вкладку «Администрирование». …
- В разделе «Язык для программ, не поддерживающих Юникод» щелкните «Изменить языковой стандарт системы» и выберите нужный язык.
- Нажмите кнопку ОК.
Как изменить кодировку по умолчанию?
2 ответы
- Для Eclipse кодировку по умолчанию для новых файлов можно установить в Windows> Preferences> General> Content Types (см. Сообщение в Eclipse Community Forms)
- Для Notepad ++ перейдите в «Настройки»> «Настройки»> «Новый документ / по умолчанию / каталог» и установите для параметра «Кодирование» значение UTF-8.
Какая кодировка используется по умолчанию в Windows 10?
В Windows предполагается, что кодировка символов по умолчанию — UTF-8. Так что, если Локаль операционной системы по умолчанию — «English_USA. 1252 ”- языковой стандарт по умолчанию для Boost.
Как изменить кодировку Windows по умолчанию на UTF-8?
Откройте Панель управления Windows -> Регион. Перейдите на вкладку «Администрирование» и нажмите «Изменить язык системы…» Снимите флажок рядом с бета-версией: использовать UTF-8 для поддержки языков по всему миру. Щелкните ОК и перезагрузите компьютер.
Использует ли Windows 10 UTF8?
Начиная с Windows 10, сборка 17134 (обновление за апрель 2018 г.), универсальная среда выполнения C поддерживает использование кодовой страницы UTF-8. Это означает, что строки символов, передаваемые функциям времени выполнения C, будут ожидать строки в кодировке UTF-8. … Для операционных систем Windows 10 до 17134 поддерживается только статическое связывание.
Как изменить кодировку файла в Windows?
Выберите стандарт кодировки при открытии файла
- Перейдите на вкладку «Файл».
- Нажмите Опции.
- Нажмите Дополнительно.
- Прокрутите до раздела «Общие» и установите флажок «Подтверждать преобразование формата файла при открытии». …
- Закройте и снова откройте файл.
- В диалоговом окне «Преобразовать файл» выберите «Закодированный текст».
Какая кодировка по умолчанию для блокнота?
Блокнот обычно использует кодировку ANSI, поэтому, если он читает файл как UTF-8, он должен угадать кодировку на основе данных в файле. Если вы сохраните файл как UTF-8, Блокнот поместит BOM (отметку порядка байтов) EF BB BF в начало файла.
Как изменить кодировку по умолчанию на UTF-8 в Excel?
Щелкните Инструменты, затем выберите Параметры Интернета. Перейдите на вкладку Кодировка. В раскрывающемся списке Сохранить этот документ как: выберите Юникод (UTF-8). Щелкните ОК.
Почему мы используем кодировку UTF-8?
Зачем использовать UTF-8? HTML-страница может быть только в одной кодировке. Вы не можете кодировать разные части документа в разных кодировках. Кодировка на основе Unicode, такая как UTF-8, может поддерживать множество языков и может размещать страницы и формы на любом сочетании этих языков.
В чем разница между UTF-8 и utf16?
Разница
Utf-8 и utf-16 обрабатывают одни и те же символы Unicode. Это обе кодировки переменной длины, требующие до 32 бит на символ. Разница в том, что Utf-8 кодирует общие символы, включая английский язык и числа, с использованием 8-бит. Utf-16 использует не менее 16 бит для каждого символа.
Какая кодировка используется по умолчанию для Excel?
По памяти Excel использует машинно-зависимую кодировку ANSI. Таким образом, это будет Windows-1252 для установки EN-US, 1251 для русского языка и т. Д.
Как изменить кодировку по умолчанию в Notepad ++?
перейдите в настройки меню блокнота ++> настройки> разное. и отключите автоматическое определение кодировки символов, как показано на скриншоте ниже. затем перейдите в настройки> настройки> новый документ и установите желаемую кодировку.
Как изменить ANSI на UTF-8?
Попробуйте «Настройки» -> «Настройки» -> «Новый документ» -> «Кодировка» -> выберите UTF-8 без спецификации и установите флажок «Применить к открытым файлам ANSI». Таким образом, все открытые файлы ANSI будут обрабатываться как UTF-8 без спецификации.
Как изменить локаль Windows?
Системный язык
- Выберите Пуск> Панель управления> Часы, язык и регион> Регион и язык.
- Откройте вкладку «Администрирование».
- В разделе «Язык для программ, не поддерживающих Юникод» щелкните «Изменить языковой стандарт системы…».
- Выберите целевой языковой стандарт из раскрывающегося списка Текущий языковой стандарт системы.
- Перезагрузите систему.
Какую кодировку символов использует Windows?
Набор символов, наиболее часто используемый сегодня в компьютерах, — это Unicode, глобальный стандарт кодировки символов. На внутреннем уровне приложения Windows используют реализацию Unicode в кодировке UTF-16. В UTF-16 большинство символов идентифицируются двухбайтовыми кодами.