Windows
- 09.06.2020
- 61 674
- 6
- 150
- 147
- 3
- Содержание статьи
- Исправляем проблему с кодировкой с помощью смены шрифта
- Исправляем проблему с кодировкой с помощью смены кодировки
- Комментарии к статье ( 6 шт )
- Добавить комментарий
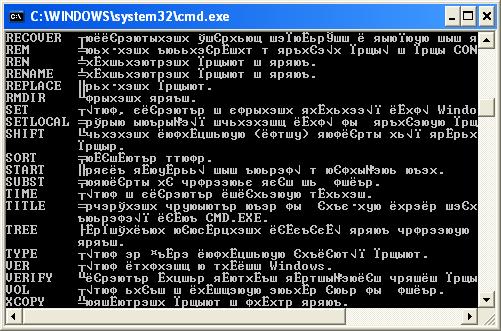
В некоторых случаях, когда используется неверная кодировка, могут возникать так называемые кракозябры или иероглифы, т.е. не читаемые символы, которые невозможно разобрать при работе с командной строкой. Эти проблемы могут также возникать и при запуске различных BAT-файлов. В данной статье мы расскажем о том, как можно сменить шрифт или кодировку, чтобы избавиться от этой проблемы. Пример таких не читаемых символов можно видеть на картинке ниже:
Исправляем проблему с кодировкой с помощью смены шрифта
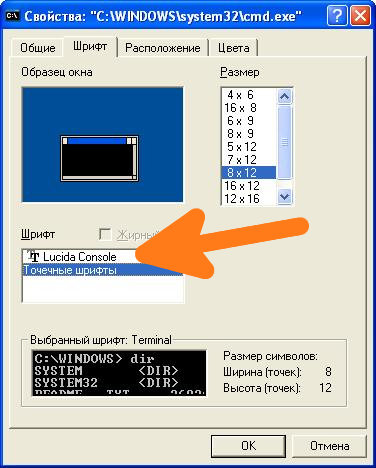
Первым делом нужно зайти в свойства окна: Правой кнопкой щелкнуть по верхней части окна -> Свойства -> в открывшемся окне в поле Шрифт выбрать Lucida Console и нажать кнопку ОК.
После этого не читаемые символы должны исчезнуть, а текст должен выводиться на русском языке.
Исправляем проблему с кодировкой с помощью смены кодировки
Вместо смены шрифта, можно сменить кодировку, которая используется при работе cmd.exe.
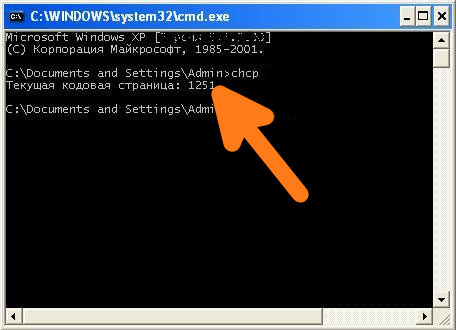
Узнать текущую кодировку можно введя в командной строке команду chcp, после ввода данной команды необходимо нажать Enter.
Как видно на скриншоте, текущая используемая кодировка Windows-1251
Для изменения кодировки нам необходимо воспользоваться командой chcp <код_новой_кодировки>, где <код_новой_кодировки> — это сам код кодировки, на которую мы хотим переключиться. Возможные значения:
- 1251 — Windows-кодировка (Кириллица);
- 866 — DOS-кодировка;
- 65001 — Кодировка UTF-8;
Т.е. для смены кодировки на DOS, команда примет следующий вид:
chcp 866Для смены кодировки на UTF-8, команда примет следующий вид:
chcp 65001Для смены кодировки на Windows-1251, команда примет следующий вид:
chcp 1251Currently I’m running Windows 7 x64 and usually I want all console tools to work with UTF-8 rather than with default code page 850.
Running chcp 65001 in the command prompt prior to use of any tools helps but is there any way to set is as default code page?
Update:
Changing HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINESYSTEMCurrentControlSetControlNlsCodePageOEMCP value to 65001 appear to make the system unable to boot in my case.
Proposed change of HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINESoftwareMicrosoftCommand ProcessorAutorun to @chcp 65001>nul served just well for my purpose. (thanks to Ole_Brun)
asked Apr 12, 2011 at 10:42
7
To change the codepage for the console only, do the following:
- Start -> Run -> regedit
- Go to
[HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINESoftwareMicrosoftCommand ProcessorAutorun] - Change the value to
@chcp 65001>nul
If Autorun is not present, you can add a New String
Nabi K.A.Z.
3801 gold badge5 silver badges10 bronze badges
answered Apr 12, 2011 at 12:22
Nils Magne LundeNils Magne Lunde
2,5421 gold badge16 silver badges14 bronze badges
11
Personally, I don’t like changing the registry. This can cause a lot of problems. I created a batch file:
@ECHO OFF
REM change CHCP to UTF-8
CHCP 65001
CLS
I saved at C:WindowsSystem32 as switch.bat and created a link for cmd.exe on the Desktop.
In the properties of the cmd shortcut, changed the destination to: C:WindowsSystem32cmd.exe /k switch
Voilà, when I need to type in UTF-8, I use this link.
answered Dec 7, 2013 at 15:36
jucajuca
6095 silver badges2 bronze badges
5
In the 1809 build of Windows 10 I’ve managed to permanently solve this by going to the system’s Language settings, selecting Administrative language settings, clicking Change system locale... and checking the Beta: Use Unicode UTF-8 for worldwide language support box and then restarting my pc.
This way it applies to all applications, even those ones that I don’t start from a command prompt!
(Which was necessary for me, since I was trying to edit Agda code from Atom.)
Bob Stein
1,3371 gold badge16 silver badges23 bronze badges
answered May 11, 2019 at 14:44
Isti115Isti115
89410 silver badges11 bronze badges
7
Edit the Registry:
Windows Registry Editor Version 5.00
[HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINESYSTEMCurrentControlSetControlNlsCodePage]
"OEMCP"="65001"
Then restart. With this fix, if you are using Consolas font, it seems to lock
PowerShell into a small font size. cmd.exe still works fine. As a workaround,
you can use Lucida Console, or I switched to Cascadia Mono:
https://github.com/microsoft/cascadia-code
answered Jun 13, 2015 at 20:39
1
This can be done by creating a PowerShell profile and adding the command «chcp 65001 >$null» to it:
PS> Set-ExecutionPolicy RemoteSigned
PS> New-Item -Path $Profile -ItemType file -Force
PS> notepad $Profile
This doesn’t require editing the registry and, unlike editing a shortcut, will work if PowerShell is started in a specific folder using the Windows Explorer context menu.
answered Sep 3, 2017 at 20:56
0
The command to change the codepage is chcp <codepage>. Example: chcp 1252. You should type it in a Powershell window.
To avoid the hassle of typing it everytime (if you always have to change the codepage), you may append it to the program’s command line. To do so, follow these steps:
- Right-click the Powershell icon on Start menu and choose «More» > «Open file Location».
- Right-click the Powershell shortcut and select «Properties».
- Add the following to the end of the «Target» command line:
-NoExit -Command "chcp 1252"
Be happy.
Don’t fuss with Windows Registry unless you have no other option.
answered Nov 2, 2016 at 21:11
JColaresJColares
591 silver badge1 bronze badge
1
Open in Powershell through Explorer still didn’t work for me even though I’ve tried enabling that Beta Unicode feature in the language settings.
However, I’ve just found this worked.
[HKEY_CURRENT_USERConsole%SystemRoot%_System32_WindowsPowerShell_v1.0_powershell.exe]
"CodePage"=dword:0000fde9
From: https://www.zhihu.com/question/54724102
answered Feb 15, 2021 at 11:09
If you’re using ConEmu then:
- Open up Settings from the upper right menu
- Go to Startup -> Environment
- Add
chcp 65001on a new line. - Click «Save Settings».
- Close ConEmu and re-open it
answered May 4, 2020 at 1:22
Instead of changing the registry, you can instead create %HOMEPATH%init.cmd.
Mine reads:
@ECHO OFF
CHCP 65001 > nul
answered Jan 21 at 9:39
Note:
-
This answer shows how to switch the character encoding in the Windows console to
(BOM-less) UTF-8 (code page65001), so that shells such ascmd.exeand PowerShell properly encode and decode characters (text) when communicating with external (console) programs with full Unicode support, and incmd.exealso for file I/O.[1] -
If, by contrast, your concern is about the separate aspect of the limitations of Unicode character rendering in console windows, see the middle and bottom sections of this answer, where alternative console (terminal) applications are discussed too.
Does Microsoft provide an improved / complete alternative to chcp 65001 that can be saved permanently without manual alteration of the Registry?
As of (at least) Windows 10, version 1903, you have the option to set the system locale (language for non-Unicode programs) to UTF-8, but the feature is still in beta as of this writing.
To activate it:
- Run
intl.cpl(which opens the regional settings in Control Panel) - Follow the instructions in the screen shot below.
-
This sets both the system’s active OEM and the ANSI code page to
65001, the UTF-8 code page, which therefore (a) makes all future console windows, which use the OEM code page, default to UTF-8 (as ifchcp 65001had been executed in acmd.exewindow) and (b) also makes legacy, non-Unicode GUI-subsystem applications, which (among others) use the ANSI code page, use UTF-8.-
Caveats:
-
If you’re using Windows PowerShell, this will also make
Get-ContentandSet-Contentand other contexts where Windows PowerShell default so the system’s active ANSI code page, notably reading source code from BOM-less files, default to UTF-8 (which PowerShell Core (v6+) always does). This means that, in the absence of an-Encodingargument, BOM-less files that are ANSI-encoded (which is historically common) will then be misread, and files created withSet-Contentwill be UTF-8 rather than ANSI-encoded. -
[Fixed in PowerShell 7.1] Up to at least PowerShell 7.0, a bug in the underlying .NET version (.NET Core 3.1) causes follow-on bugs in PowerShell: a UTF-8 BOM is unexpectedly prepended to data sent to external processes via stdin (irrespective of what you set
$OutputEncodingto), which notably breaksStart-Job— see this GitHub issue. -
Not all fonts speak Unicode, so pick a TT (TrueType) font, but even they usually support only a subset of all characters, so you may have to experiment with specific fonts to see if all characters you care about are represented — see this answer for details, which also discusses alternative console (terminal) applications that have better Unicode rendering support.
-
As eryksun points out, legacy console applications that do not «speak» UTF-8 will be limited to ASCII-only input and will produce incorrect output when trying to output characters outside the (7-bit) ASCII range. (In the obsolescent Windows 7 and below, programs may even crash).
If running legacy console applications is important to you, see eryksun’s recommendations in the comments.
-
-
-
However, for Windows PowerShell, that is not enough:
- You must additionally set the
$OutputEncodingpreference variable to UTF-8 as well:$OutputEncoding = [System.Text.UTF8Encoding]::new()[2]; it’s simplest to add that command to your$PROFILE(current user only) or$PROFILE.AllUsersCurrentHost(all users) file. - Fortunately, this is no longer necessary in PowerShell Core, which internally consistently defaults to BOM-less UTF-8.
- You must additionally set the
If setting the system locale to UTF-8 is not an option in your environment, use startup commands instead:
Note: The caveat re legacy console applications mentioned above equally applies here. If running legacy console applications is important to you, see eryksun’s recommendations in the comments.
-
For PowerShell (both editions), add the following line to your
$PROFILE(current user only) or$PROFILE.AllUsersCurrentHost(all users) file, which is the equivalent ofchcp 65001, supplemented with setting preference variable$OutputEncodingto instruct PowerShell to send data to external programs via the pipeline in UTF-8:- Note that running
chcp 65001from inside a PowerShell session is not effective, because .NET caches the console’s output encoding on startup and is unaware of later changes made withchcp; additionally, as stated, Windows PowerShell requires$OutputEncodingto be set — see this answer for details.
- Note that running
$OutputEncoding = [console]::InputEncoding = [console]::OutputEncoding = New-Object System.Text.UTF8Encoding
- For example, here’s a quick-and-dirty approach to add this line to
$PROFILEprogrammatically:
'$OutputEncoding = [console]::InputEncoding = [console]::OutputEncoding = New-Object System.Text.UTF8Encoding' + [Environment]::Newline + (Get-Content -Raw $PROFILE -ErrorAction SilentlyContinue) | Set-Content -Encoding utf8 $PROFILE
-
For
cmd.exe, define an auto-run command via the registry, in valueAutoRunof keyHKEY_CURRENT_USERSoftwareMicrosoftCommand Processor(current user only) orHKEY_LOCAL_MACHINESoftwareMicrosoftCommand Processor(all users):- For instance, you can use PowerShell to create this value for you:
# Auto-execute `chcp 65001` whenever the current user opens a `cmd.exe` console
# window (including when running a batch file):
Set-ItemProperty 'HKCU:SoftwareMicrosoftCommand Processor' AutoRun 'chcp 65001 >NUL'
Optional reading: Why the Windows PowerShell ISE is a poor choice:
While the ISE does have better Unicode rendering support than the console, it is generally a poor choice:
-
First and foremost, the ISE is obsolescent: it doesn’t support PowerShell (Core) 7+, where all future development will go, and it isn’t cross-platform, unlike the new premier IDE for both PowerShell editions, Visual Studio Code, which already speaks UTF-8 by default for PowerShell Core and can be configured to do so for Windows PowerShell.
-
The ISE is generally an environment for developing scripts, not for running them in production (if you’re writing scripts (also) for others, you should assume that they’ll be run in the console); notably, with respect to running code, the ISE’s behavior is not the same as that of a regular console:
-
Poor support for running external programs, not only due to lack of supporting interactive ones (see next point), but also with respect to:
-
character encoding: the ISE mistakenly assumes that external programs use the ANSI code page by default, when in reality it is the OEM code page. E.g., by default this simple command, which tries to simply pass a string echoed from
cmd.exethrough, malfunctions (see below for a fix):
cmd /c echo hü | Write-Output -
Inappropriate rendering of stderr output as PowerShell errors: see this answer.
-
-
The ISE dot-sources script-file invocations instead of running them in a child scope (the latter is what happens in a regular console window); that is, repeated invocations run in the very same scope. This can lead to subtle bugs, where definitions left behind by a previous run can affect subsequent ones.
-
-
As eryksun points out, the ISE doesn’t support running interactive external console programs, namely those that require user input:
The problem is that it hides the console and redirects the process output (but not input) to a pipe. Most console applications switch to full buffering when a file is a pipe. Also, interactive applications require reading from stdin, which isn’t possible from a hidden console window. (It can be unhidden via
ShowWindow, but a separate window for input is clunky.)
-
If you’re willing to live with that limitation, switching the active code page to
65001(UTF-8) for proper communication with external programs requires an awkward workaround:-
You must first force creation of the hidden console window by running any external program from the built-in console, e.g.,
chcp— you’ll see a console window flash briefly. -
Only then can you set
[console]::OutputEncoding(and$OutputEncoding) to UTF-8, as shown above (if the hidden console hasn’t been created yet, you’ll get ahandle is invalid error).
-
[1] In PowerShell, if you never call external programs, you needn’t worry about the system locale (active code pages): PowerShell-native commands and .NET calls always communicate via UTF-16 strings (native .NET strings) and on file I/O apply default encodings that are independent of the system locale. Similarly, because the Unicode versions of the Windows API functions are used to print to and read from the console, non-ASCII characters always print correctly (within the rendering limitations of the console).
In cmd.exe, by contrast, the system locale matters for file I/O (with < and > redirections, but notably including what encoding to assume for batch-file source code), not just for communicating with external programs in-memory (such as when reading program output in a for /f loop).
[2] In PowerShell v4-, where the static ::new() method isn’t available, use $OutputEncoding = (New-Object System.Text.UTF8Encoding).psobject.BaseObject. See GitHub issue #5763 for why the .psobject.BaseObject part is needed.