Visual Basic 6 (VB6) was one of the easiest programming languages to learn back in the day. It was released in 1998 and is now replaced by Visual Basic .NET (VB.NET). Even though it is outdated by several years, the programs created and compiled with VB6 can still work with the latest Windows operating systems which is why you can still find people attempting to install VB6 on Windows 10.
If you’re trying to install VB6 on newer operating systems starting from Windows 8 onward, especially with 64-bit architecture, you are sure to encounter installation problems. These range from not being able to continue the install without first installing discontinued versions of Java to the setup process hanging and crashing.
In this article, we’ll show you how to successfully install Visual Basic 6 (VB6) in Windows 10 64-bit.
Bypass Update Microsoft Virtual Machine for Java Requirement
A computer should always maintain the latest version of Java and it’s pointless having the discontinued Microsoft Virtual Machine for Java on the computer just to install Visual Basic 6. The problem is, the VB6 setup does not allow you to continue with the installation if you untick the “Update Microsoft Virtual Machine for Java” checkbox as it grays out the Next button.
The solution is to bypass the VB6 setup by either tricking it into thinking Microsoft Java is already installed or by telling it not to install Java in the first place. Then you can reach the next phase of the installation.
There are two ways in which you can do this which we’ll list below, you only need to use one of them.
Trick VB6 setup into thinking Microsoft Virtual Machine for Java is Installed
The VB6 installer checks if the file msjava.dll exists in the SysWOW64 folder for 64-bit systems or System32 for 32-bit systems. Placing the file into the right folder will let the VB6 install continue.
a) For the quickest and easiest way of doing this, you can download the msjava.dll file from the link below and copy it to the required directory.
Download MSJava.dll
If you’re unsure about the architecture of your Windows operating system, simply try to copy msjava.dll to the C:WindowsSysWOW64 folder. If it doesn’t exist, you have a 32-bit system and should copy the file to the C:WindowsSystem32 folder instead.
b) Alternatively, the same DLL file is also present on the installation disc. You can extract it if you have an archiver such as 7-Zip installed on your system. Go to the IE4 folder located on the install CD, right click on MSJAVX86.exe, go to 7-Zip and select “Open archive“.
In 7-Zip, double click on javabase.cab which will open it. Look for msjava.dll in the list, drag it onto the Desktop and then copy it to SysWOW64 or System32. Copying to the Desktop first will avoid any access denied error when trying to copy the file directly from 7-Zip.
After copying msjava.dll to either the System32 or SysWOW64 folder, you can launch the Visual Basic 6 setup.exe file to start the installation. It now doesn’t prompt you to update Microsoft Virtual Machine for Java.
Tell VB6 setup Not To Install Microsoft Virtual Machine for Java
If you have the VB6 setup files on your hard drive, it’s possible to edit the settings file for the installer and tell it not to ask for Microsoft Virtual Machine for Java. This will ignore the requirement and continue the install process.
a) The simplest option here is to download the SETUPWIZ.INI file from the link below. As the name implies, this is the setup wizard configuration file. Make sure to download the correct INI for your version of Visual Studio.
Download SETUPWIZ.INI (For Visual Studio 6 Enterprise)
Download SETUPWIZ.INI (For Visual Studio 6 Professional)
Place the INI file in the main installation files folder overwriting the current file. Then start the installation and it won’t ask to install Java.
b) If you want to edit the file manually, go to the main folder and open the SETUPWIZ.INI file with Notepad. Look for the line “VmPath=ie4msjavx86.exe”.
Simply delete the whole line or everything after the “=” sign and save the file. The install can be continued but you must also follow the next steps as well or the installation will not complete successfully.
Change VB6 Setup Options To Prevent The Install From Hanging Or Failing
While fixing the above issue gets round the first hurdle of installing Visual Basic 6 on Windows 10, there are some other things that will cause the install to fail.
First of all, you will likely experience the “Setup is updating your system…” progress getting stuck and doing nothing else. After a few seconds, the installer becomes unresponsive and then hangs. Looking in Task Manager will show high CPU usage for ACMSETUP.EXE and the setup window has to be closed manually.
If you fix that, another error that appears will be a “Setup was unable to create a DCOM user account in order to register…valec.exe” message box.
With the default install options, the VB6 installer will likely produce another error message which is “javasign.dll was unable to register itself in the system registry”.
These last two error messages will cause the install to halt with a message saying the setup could not be completed. Since the Visual Basic 6 installer is over 20 years old, there are unsurprisingly some components that will not install properly in Windows 10 which causes the failures. Excluding those components from the install process will allow VB6 to install without errors.
You can use either method below to turn off the options during setup that cause the install to fail.
Disable the Setup Components Automatically
This method is the easiest and requires no manual changes to the setup options during install. We found that the install process is handled by an STF file in the Setup folder on the disc. The optional components are pre-enabled in this file so we found the offenders and disabled them by default.
1. Download the correct file according to the version of Visual Studio you are using. Click on the link below then right click on the grey Download button and select “Save link as” in your browser. This stops the file opening in a browser tab as a text file.
Download VS98ENT.STF (For Visual Studio 6 Enterprise)
Download VS98PRO.STF (For Visual Studio 6 Professional)
2. Make sure that the VB6 install files are on your hard drive as you need to replace the original STF file. You can do that by simply copying all the files from the CD to a folder on your drive. This won’t work if you are trying to install from CD.
3. Go to the SETUP folder and copy the VS98***.STF you downloaded above replacing the file already there.
4. Run the installer and go through the setup steps as usual. When you reach the component selection window, nothing has to be changed because the edited STF already did it.
Any other options that you want to enable or disable can be changed although you must make sure “Microsoft Visual InterDev 6.0”, “ADO and RDS”, and “Visual Studio Analyzer” remain disabled.
Disable the VB6 Setup Components Manually
This method is useful if you are installing from CD or the automatic option above doesn’t work.
1. During the setup, make sure the Custom install option is selected.
2. Continue the install until you’re asked to choose the components from the list. Highlight Data Access and click the “Change Option…” button to the right, then click “Change Option..” for a second time.
3. Now you’ll get another list of components that belong to the ADO, RDS, and OLE DB Providers. Simply uncheck the first ADO and RDS option.
A warning will popup that this component is an essential part of the application and it will not run properly if not installed. Click OK to acknowledge the warning and then click OK two more times to get back to the main install options window.
This will stop the installer hanging and crashing at the updating your system window.
3. Highlight Enterprise Tools and click the “Change Option…” button. At the bottom, uncheck Visual Studio Analyzer and click OK. This option is not in Visual Studio Professional so those users can ignore it.
Disabling the Visual Studio Analyzer will stop the DCOM user account error.
4. Uncheck Microsoft Visual InterDev 6.0 box in the main install options window. This will stop the javasign.dll error from appearing during install.
You can, of course, enable or disable other options in this window depending on personal preference. But make sure the components mentioned here are not enabled or the install won’t finish properly. Continue with the install and you should be able to reach the end with no major errors after a reboot.
Run Visual Basic In Compatibility Mode
After the install is complete, Visual Basic 6 should start. If you get an error on the New Project screen, an optional step to help is running VB6 in compatibility mode. In Explorer, navigate to C:Program Files (x86)Microsoft Visual StudioVB98, right click on VB6.exe and select Properties.
In the Compatibility tab, check the “Run this program in compatibility mode for:” box and click OK. The default option of Windows XP (Service Pack 2) should be fine but you can experiment with Windows Vista or 98/Me if you wish.
|
0 / 0 / 0 Регистрация: 06.06.2017 Сообщений: 15 |
|
|
1 |
|
|
08.06.2017, 20:23. Показов 19024. Ответов 42
Ребята, помогите! Не запускается vb, ну ток заставка, а потом ошибка вылетает. Миниатюры
__________________
0 |
|
Модератор 6790 / 2811 / 527 Регистрация: 24.04.2011 Сообщений: 5,308 Записей в блоге: 10 |
|
|
09.06.2017, 06:08 |
2 |
|
Не запускается vb Не теряйте надежды, попробуйте ещё раз переустановить. От имени администратора.
0 |
|
oh my god 1454 / 793 / 161 Регистрация: 05.01.2016 Сообщений: 2,307 Записей в блоге: 8 |
|
|
09.06.2017, 06:22 |
3 |
|
Я мог-бы скинуть портабельную версию VB-6, если разрешат админы, разрешат ? Добавлено через 4 минуты
1 |
|
oh my god 1454 / 793 / 161 Регистрация: 05.01.2016 Сообщений: 2,307 Записей в блоге: 8 |
|
|
09.06.2017, 06:29 |
4 |
|
ну раз никто не против заливаю
2 |
|
oh my god 1454 / 793 / 161 Регистрация: 05.01.2016 Сообщений: 2,307 Записей в блоге: 8 |
|
|
09.06.2017, 06:36 |
5 |
|
вот еще…
2 |
|
oh my god 1454 / 793 / 161 Регистрация: 05.01.2016 Сообщений: 2,307 Записей в блоге: 8 |
|
|
09.06.2017, 06:41 |
6 |
|
и еще …
2 |
|
oh my god 1454 / 793 / 161 Регистрация: 05.01.2016 Сообщений: 2,307 Записей в блоге: 8 |
|
|
09.06.2017, 06:43 |
7 |
|
Последняя часть. Миниатюры
4 |
|
193 / 113 / 30 Регистрация: 05.08.2013 Сообщений: 491 |
|
|
09.06.2017, 13:02 |
8 |
|
fever brain, Не пошла на 10-ке. Сначала ругалась на отсутствие dao350.dll, скачал. Потом ругается на: «Missing or not registeredVB6TMPL.TLB Режимы совместимости не помогли.
1 |
|
oh my god 1454 / 793 / 161 Регистрация: 05.01.2016 Сообщений: 2,307 Записей в блоге: 8 |
|
|
09.06.2017, 13:39 |
9 |
|
Спасибо за конструктивные сведения, поддержка vb6 прекратилась уже давно, соответственно
0 |
|
dr_Morro |
|
09.06.2017, 13:46
|
|
Не по теме:
сам я 10-кой не пользуюсь и нет никакого желания переходить Да та же фигня. Это я на работе экспериментировал… Дома то семерка. Вполне устраивает.
0 |
|
0 / 0 / 0 Регистрация: 06.06.2017 Сообщений: 15 |
|
|
09.06.2017, 20:40 [ТС] |
12 |
|
это и так была портативная версия
0 |
|
Модератор 6790 / 2811 / 527 Регистрация: 24.04.2011 Сообщений: 5,308 Записей в блоге: 10 |
|
|
09.06.2017, 21:30 |
13 |
|
это и так была портативная версия Значит тот, кто её создавал не рассчитывал на win10.
1 |
|
oh my god 1454 / 793 / 161 Регистрация: 05.01.2016 Сообщений: 2,307 Записей в блоге: 8 |
|
|
10.06.2017, 01:16 |
14 |
|
Установите себе бесплатную виртуальную машину, например VirtualBox, на неё систему winXP Если интересно, в Windows 10 предусмотрен такой компонент — виртуальная машина Hyper-V По умолчанию, компоненты Hyper-V в Windows 10 отключены. Для установки, зайдите в Панель управления — Программы и компоненты — Включение или отключение компонентов Windows, отметьте пункт Hyper-V и нажмите «Ок». Установка произойдет автоматически, возможно потребуется перезагрузить компьютер. http://remontka.pro/hyper-v-windows-10/
0 |
|
Модератор 6790 / 2811 / 527 Регистрация: 24.04.2011 Сообщений: 5,308 Записей в блоге: 10 |
|
|
10.06.2017, 06:14 |
15 |
|
в Windows 10 предусмотрен такой компонент — виртуальная машина Hyper-V Не думаю, что у кого то дома установлена Windows 10 Pro или Enterprise. Вроде в комплекте с покупным ноутом или компом её не ставят, а отдельно покупать за 15 штук вряд ли кто будет в здравом уме. Если только пиратка?
0 |
|
oh my god 1454 / 793 / 161 Регистрация: 05.01.2016 Сообщений: 2,307 Записей в блоге: 8 |
|
|
11.06.2017, 08:02 |
16 |
|
Подведем итоги: Делаете виртуалку, в ней савьте windows На ней же устанавливаете софт
0 |
|
28 / 28 / 4 Регистрация: 07.06.2017 Сообщений: 166 |
|
|
13.06.2017, 10:07 |
17 |
|
Подведем итоги: Делаете виртуалку, в ней савьте windows На ней же устанавливаете софт Если важен вопрос лицензионной чистоты, то на ОС в виртуальной среде тоже нужна лицензия.
0 |
|
185 / 183 / 31 Регистрация: 11.10.2016 Сообщений: 599 |
|
|
13.06.2017, 11:37 |
18 |
|
если VB нужен только лишь для решения студенческих задач, то проще поставить Офис и там уже писать под VBA
0 |
|
Модератор 6790 / 2811 / 527 Регистрация: 24.04.2011 Сообщений: 5,308 Записей в блоге: 10 |
|
|
13.06.2017, 17:00 |
19 |
|
Если важен вопрос лицензионной чистоты Тогда вообще нет смысла рассматривать VB6. Невозможно сейчас купить его легально. Добавлено через 15 секунд
Если важен вопрос лицензионной чистоты Тогда вообще нет смысла рассматривать VB6. Невозможно сейчас купить его легально.
0 |
|
28 / 28 / 4 Регистрация: 07.06.2017 Сообщений: 166 |
|
|
13.06.2017, 17:06 |
20 |
|
Невозможно сейчас купить его легально. В беседе с представителями MS была фраза — «лицензии на старые продукты мы то же можем продать».
0 |
I made this script a while ago because I was having trouble with the installers and fixes I found around the internet. It incorporates all the tricks and tips that I found around the internet into one powershell script.
To run the script you will need to following:
- VB6 Installer
- Service Pack 6
- Mouse Wheel Fix (Optional, set
-SkipMouseWheelswitch to skip.)
Each of the above should be placed in its own folder. If you save (and then dot-source) the script in a folder that contains these three folders it’ll auto-detect everything for you. You can also set your current location in powershell to this folder and copy the script directly to you session and it’ll detect everything as well.
Once the script is dot-sourced or pasted in an elevated powershell instance you can run it by calling Install-VB6.
It also has the following parameters if you want to override any default behaviour:
| Parameter | Type | Usage |
|---|---|---|
Vb6InstallerPath |
String | Path of main VB6 Installer folder |
SP6InstallerPath |
String | Path of Service Pack 6 Installer folder |
SkipMouseWheel |
Switch | Skip installing the Mouse Wheel Fixer folder |
MouseWheelPath |
String | Path of Mouse Wheel fixer. Ignored if -SkipMouseWheel is specified |
Regsvr32Path |
String | Path to regsvr32.exe. Uses ‘%SYSTEMROOT%SysWoW64regsvr32.exe’ if not specified |
RegEditPath |
String | Path to regedit.exe. ‘%SYSTEMROOT%regedit.exe’ if not specified |
OrganizationName |
String | Sets the organization name in the VB6 installer |
Notes:
- The VB6 and SP6 installer don’t like being run from a network drive, so the script will stop if it detects one of the install folders is not on a local drive.
- I’ve only tested this with VB6 Pro, not VB6 Enterprise.
- It doesn’t install MSDN.
Install-VB6.ps1
#Requires -RunAsAdministrator
#Requires -Version 3
<#
.SYNOPSIS
Installs VB6 to the computer.
.DESCRIPTION
Installs VB6 ide with Service Pack 6 and (optional) Mouse Wheel Fix to the local computer.
.PARAMETER Vb6InstallerPath
The path to the VB6 installer folder.
.PARAMETER SP6InstallerPath
The path the the Service Pack 6 installer folder.
.PARAMETER SkipMouseWheel
Skip installing the Mouse Wheel fix.
.PARAMETER MouseWheelPath
The path the Mouse wheel fix folder.
.PARAMETER Regsvr32Path
The path to RegSvr32.exe
.PARAMETER OrganizationName
The organization name
.PARAMETER RegEditPath
The path to regedit.exe
#>
Function Install-VB6{
[CmdletBinding()]
param (
[Parameter(Mandatory=$false)]
[string]$Vb6InstallerPath,
[Parameter(Mandatory=$false)]
[string]$SP6InstallerPath,
[Parameter(Mandatory=$false)]
[switch]$SkipMouseWheel,
[Parameter(Mandatory=$false)]
[string]$MouseWheelPath,
[Parameter(Mandatory=$false)]
[string]$Regsvr32Path,
[Parameter(Mandatory=$false)]
[string]$OrganizationName,
[Parameter(Mandatory=$false)]
[string]$RegEditPath
)
# Tests if the path is a local path. The installer doesn't like network paths.
function Test-LocalDrive{
[CmdletBinding()]
[OutputType([bool])]
param(
[Parameter(Mandatory=$true,
Position=0)]
[string]$Path
)
begin{
$localDrives = Get-WmiObject -Class Win32_logicaldisk -Filter "DriveType<>4" -Property "DeviceID" | Foreach-Object {$_.DeviceID.Replace(":", "")}
}
process{
if(!([bool](Test-Path -Path $Path))){
return $false
}
$item = Get-Item -Path $Path
$drive = $item.PSDrive
if($null -eq $drive){
return $false
}
return ($localDrives -contains $drive.Name)
}
}
function Search-ForFile{
[CmdletBinding()]
[OutputType([System.IO.FileInfo])]
param(
[Parameter(Mandatory=$true,
Position=0)]
[string]$File,
[Parameter(Mandatory=$true,
Position=1)]
[string]$CurrentLocation,
[switch]$IncludeSubDirectory
)
process{
$newPath = $currentLocation
if($IncludeSubDirectory.IsPresent){
$newPath = Join-Path -Path $newPath -ChildPath "*"
}
$newPath = Join-Path -Path $newPath -ChildPath $file
$item = @(Get-Item -Path $newPath)
if($null -eq $item -or $item.Count -eq 0 -or $null -eq $item[0]){
throw ("Could Not find the {0} file." -f $file)
}
return $item[0]
}
}
#region Setting Up File Paths
$currentLocation = $PSScriptRoot
if([System.String]::IsNullOrWhiteSpace($currentLocation)){
$currentLocation = (Get-Location)
}
if([System.String]::IsNullOrWhiteSpace($currentLocation)){
throw "Unable to determine current location"
}
if(!$PSBoundParameters.ContainsKey("Vb6InstallerPath") -or [System.String]::IsNullOrWhiteSpace($Vb6InstallerPath)){
if(!(Test-LocalDrive -Path ($currentLocation))){
Write-Error "The script cannot be ran from a network share."
Write-Host -NoNewLine 'Press any key to continue...';
$null = $Host.UI.RawUI.ReadKey('NoEcho,IncludeKeyDown');
return
}
$installerInfo = Search-ForFile -File "SETUP.EXE" -CurrentLocation $currentLocation -IncludeSubDirectory
$installFolder = $installerInfo.DirectoryName
}
else {
if(!(Test-LocalDrive -Path ($Vb6InstallerPath))){
Write-Error "The VB6 Installer Path cannot be a share."
Write-Host -NoNewLine 'Press any key to continue...';
$null = $Host.UI.RawUI.ReadKey('NoEcho,IncludeKeyDown');
return
}
$installFolder = $Vb6InstallerPath
$installerInfo = Search-ForFile -File "SETUP.EXE" -CurrentLocation $installFolder
}
$installer2Info = Search-ForFile -File "ACMSETUP.EXE" -CurrentLocation $installFolder -IncludeSubDirectory
$installLocation = $installerInfo.FullName
$install2Location = $installer2Info.FullName
if(!$PSBoundParameters.ContainsKey("SP6InstallerPath") -or [System.String]::IsNullOrWhiteSpace($SP6InstallerPath)){
if(!(Test-LocalDrive -Path ($currentLocation))){
Write-Error "The script cannot be ran from a network share."
Write-Host -NoNewLine 'Press any key to continue...';
$null = $Host.UI.RawUI.ReadKey('NoEcho,IncludeKeyDown');
return
}
$SP6Info = Search-ForFile -File "setupsp6.exe" -CurrentLocation $currentLocation -IncludeSubDirectory
$SP6Folder = $SP6Info.DirectoryName
}
else {
if(!(Test-LocalDrive -Path ($SP6InstallerPath))){
Write-Error "The SP6 Installer Path cannot be a network share."
Write-Host -NoNewLine 'Press any key to continue...';
$null = $Host.UI.RawUI.ReadKey('NoEcho,IncludeKeyDown');
return
}
$SP6Folder = $SP6InstallerPath
$SP6Info = Search-ForFile -File "setupsp6.exe" -CurrentLocation $SP6Folder
}
$SP6Location = $SP6Info.FullName
if(!$SkipMouseWheel.IsPresent){
if(!$PSBoundParameters.ContainsKey("MouseWheelPath") -or [System.String]::IsNullOrWhiteSpace($MouseWheelPath)){
if(!(Test-LocalDrive -Path ($currentLocation))){
Write-Error "The script cannot be ran from a network share."
Write-Host -NoNewLine 'Press any key to continue...';
$null = $Host.UI.RawUI.ReadKey('NoEcho,IncludeKeyDown');
return
}
$MouseWheelDllInfo = Search-ForFile -File "VB6IDEMouseWheelAddin.dll" -CurrentLocation $currentLocation -IncludeSubDirectory
$MouseWheelRegistryInfo = Search-ForFile -File "VBA Mouse Wheel Fix.reg" -CurrentLocation $currentLocation -IncludeSubDirectory
}
else {
if(!(Test-LocalDrive -Path ($SP6InstallerPath))){
Write-Error "The Mouse Wheel Path cannot be a network share."
Write-Host -NoNewLine 'Press any key to continue...';
$null = $Host.UI.RawUI.ReadKey('NoEcho,IncludeKeyDown');
return
}
$MouseWheelDllInfo = Search-ForFile -File "VB6IDEMouseWheelAddin.dll" -CurrentLocation $MouseWheelPath
$MouseWheelRegistryInfo = Search-ForFile -File "VBA Mouse Wheel Fix.reg" -CurrentLocation $MouseWheelPath
}
$MouseWheelDll = $MouseWheelDllInfo.FullName
$MouseWheelRegistry = $MouseWheelRegistryInfo.FullName
}
if(!$PSBoundParameters.ContainsKey("Regsvr32Path") -or [System.String]::IsNullOrWhiteSpace($Regsvr32Path)){
$regSvrPath = "$($env:systemroot)SysWoW64regsvr32.exe"
}
else{
$regSvrPath = $Regsvr32Path
}
if(!$PSBoundParameters.ContainsKey("RegEditPath") -or [System.String]::IsNullOrWhiteSpace($RegEditPath)){
$RegEditPath = "$($env:systemroot)regedit.exe"
}
#endregion Setting Up File Paths
#region Test Required Installer Paths Exist
if(!([bool](Test-Path -Path $regSvrPath))){
Write-Error ("Unable to find '{0}'.`r`nThe exe must exist." -f $regSvrPath)
Write-Host -NoNewLine 'Press any key to continue...';
$null = $Host.UI.RawUI.ReadKey('NoEcho,IncludeKeyDown');
return
}
if(!([bool](Test-Path -Path $RegEditPath))){
Write-Error ("Unable to find '{0}'.`r`nThe exe must exist." -f $RegEditPath)
Write-Host -NoNewLine 'Press any key to continue...';
$null = $Host.UI.RawUI.ReadKey('NoEcho,IncludeKeyDown');
return
}
if(!$SkipMouseWheel.IsPresent){
if(!([bool](Test-Path -Path $MouseWheelDll))){
Write-Error ("Unable to find '{0}'.`r`nThe 'MouseWheel' Folder must be in the same directory as the install script and the file must exist." -f $MouseWheelDll)
Write-Host -NoNewLine 'Press any key to continue...';
$null = $Host.UI.RawUI.ReadKey('NoEcho,IncludeKeyDown');
return
}
if(!([bool](Test-Path -Path $MouseWheelRegistry))){
Write-Error ("Unable to find '{0}'.`r`nThe 'MouseWheel' Folder must be in the same directory as the install script and the file must exist." -f $MouseWheelRegistry)
Write-Host -NoNewLine 'Press any key to continue...';
$null = $Host.UI.RawUI.ReadKey('NoEcho,IncludeKeyDown');
return
}
}
if(!([bool](Test-Path -Path $installFolder))){
Write-Error ("Unable to find '{0}'.`r`nThe 'Installer' Folder must be in the same directory as the install script." -f $installFolder)
Write-Host -NoNewLine 'Press any key to continue...';
$null = $Host.UI.RawUI.ReadKey('NoEcho,IncludeKeyDown');
return
}
if(!([bool](Test-Path -Path $installLocation))){
Write-Error ("Unable to find '{0}'.`r`nThe 'Installer' Folder must be in the same directory as the install script and the file must exist." -f $installLocation)
Write-Host -NoNewLine 'Press any key to continue...';
$null = $Host.UI.RawUI.ReadKey('NoEcho,IncludeKeyDown');
return
}
if(!([bool](Test-Path -Path $install2Location))){
Write-Error ("Unable to find '{0}'.`r`nThe 'Installer' Folder must be in the same directory as the install script and the file must exist." -f $install2Location)
Write-Host -NoNewLine 'Press any key to continue...';
$null = $Host.UI.RawUI.ReadKey('NoEcho,IncludeKeyDown');
return
}
if(!([bool](Test-Path -Path $SP6Location))){
Write-Error ("Unable to find '{0}'.`r`nThe 'SP6' Folder must be in the same directory as the install script and the file must exist." -f $SP6Location)
Write-Host -NoNewLine 'Press any key to continue...';
$null = $Host.UI.RawUI.ReadKey('NoEcho,IncludeKeyDown');
return
}
#endregion Test Required Installer Paths Exist
#region Installer Compatibility
# The installer doesn't auto-elevate to run as an administrator.
# We are setting the required keys in the registry to force the installers to run as administrator
# Same as running the 'troubleshoot compatibilty' wizard and selecting the exe's to run as admins.
Write-Host "Setting compatibility mode on setup files."
$layersPath = "REGISTRY::HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINESOFTWAREMicrosoftWindows NTCurrentVersionAppCompatFlagsLayers"
if(){
New-Item -Path $layersPath -Force | Out-Null
}
$registryPath = Get-Item -LiteralPath $layersPath
if($null -eq $registryPath.GetValue($installLocation, $null)){
New-ItemProperty -Path $layersPath -Name $installLocation -Value "^ WINXPSP3" -PropertyType "String" -Force | Out-Null
}
if($null -eq $registryPath.GetValue($SP6Location, $null)){
New-ItemProperty -Path $layersPath -Name $SP6Location -Value "^ WINXPSP3" -PropertyType "String" -Force | Out-Null
}
#endregion Installer Compatibility
#region Previous Install Cleanup
# Locations and keys where old vb6 installs can live.
Write-Host "Cleaning up previous install."
$itemsToDelete = @(
"C:Program Files*Microsoft Visual StudioCommon",
"C:Program Files*Microsoft Visual StudioMSDN",
"C:Program Files*Microsoft Visual StudioMSDN98",
"C:Program Files*Microsoft Visual StudioVB98",
"C:Program Files*Microsoft Visual StudioVC98",
"C:Program Files*Microsoft Visual Studio*.HTM",
"C:Program Files*Microsoft Visual Studio*.TXT",
"C:Program Files*Common FilesMicrosoft SharedMSDesigners98",
"C:Program Files*Common FilesMicrosoft SharedMSDN",
"C:Program Files*Common FilesMicrosoft SharedVS98",
"C:Program Files*Common FilesMicrosoft SharedWizards98",
"REGISTRY::HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINESoftwareMicrosoftDevStudio",
"REGISTRY::HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINESoftwareMicrosoftHTML Help Collections",
"REGISTRY::HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINESoftwareMicrosoftMSVSDG",
"REGISTRY::HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINESoftwareMicrosoftVisual Basic6.0",
"REGISTRY::HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINESoftwareMicrosoftVisual Component Manager",
"REGISTRY::HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINESoftwareMicrosoftVisual Modeler",
"REGISTRY::HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINESoftwareMicrosoftVisualStudio6.0",
"REGISTRY::HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINESoftwareWow6432NodeMicrosoftDevStudio",
"REGISTRY::HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINESoftwareWow6432NodeMicrosoftHTML Help Collections",
"REGISTRY::HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINESoftwareWow6432NodeMicrosoftMSVSDG",
"REGISTRY::HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINESoftwareWow6432NodeMicrosoftVisual Basic6.0",
"REGISTRY::HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINESoftwareWow6432NodeMicrosoftVisual Component Manager",
"REGISTRY::HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINESoftwareWow6432NodeMicrosoftVisual Modeler",
"REGISTRY::HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINESoftwareWow6432NodeMicrosoftVisualStudio6.0",
"REGISTRY::HKEY_CURRENT_USERSoftwareMicrosoftDevStudio",
"REGISTRY::HKEY_CURRENT_USERSoftwareMicrosoftMSVSDG",
"REGISTRY::HKEY_CURRENT_USERSoftwareMicrosoftVisual Basic6.0",
"REGISTRY::HKEY_CURRENT_USERSoftwareMicrosoftVisual Modeler",
"REGISTRY::HKEY_CURRENT_USERSoftwareMicrosoftVisualFoxPro",
"REGISTRY::HKEY_CURRENT_USERSoftwareMicrosoftVisualStudio6.0"
)
$itemsToDelete | Where-Object { Test-Path -Path $_ } | Remove-Item -Force -Recurse | Out-Null
#endregion Previous Install Cleanup
#region Installer Registry Permissions
# The installer needs to be able to write to 'HKEY_CLASSES_ROOTRDSServer.DataFactoryClsid'
# but since the installer isn't built for windows and we have to force it to run as an administrator
# we have to give explicit permissions for your computers Administrators group to write to this key (and all its children)
Write-Host "Setting required permissions for installing user on registry."
$registryPermissionPath = "REGISTRY::HKEY_CLASSES_ROOTRDSServer.DataFactoryClsid"
Write-Host "`tSetting Up required information."
$acl = Get-ACL -Path $registryPermissionPath
$oldOwner = [System.Security.Principal.NTAccount]::new($acl.Owner)
$administratorIdentity = [System.Security.Principal.NTAccount]::new("Administrators")
Write-Host "`tGiving the script required permissions."
$import = '[DllImport("ntdll.dll")] public static extern int RtlAdjustPrivilege(ulong a, bool b, bool c, ref bool d);'
$ntdll = Add-Type -Member $import -Name NtDll -PassThru
$privileges = @{ SeTakeOwnership = 9; SeBackup = 17; SeRestore = 18 }
foreach ($i in $privileges.Values) {
$null = $ntdll::RtlAdjustPrivilege($i, 1, 0, [ref]0)
}
Write-Host "`tGettting The registry key."
$regKey = [Microsoft.Win32.Registry]::ClassesRoot.OpenSubKey("RDSServer.DataFactoryClsid", 'ReadWriteSubTree', 'TakeOwnership')
# We force the Administrators group to be the owner on the key so we can then add required the permissions.
Write-Host "`tSetting Owner."
$acl.SetOwner($administratorIdentity)
$regKey.SetAccessControl($acl)
Write-Host "`tSetting Permission."
$permission = [System.Security.AccessControl.RegistryAccessRule]::new($administratorIdentity, "FullControl", "ContainerInherit", "InheritOnly", "Allow")
$acl.AddAccessRule($permission)
$permission2 = [System.Security.AccessControl.RegistryAccessRule]::new($administratorIdentity, "FullControl", "Allow")
$acl.AddAccessRule($permission2)
$regKey.SetAccessControl($acl)
# Reset the owner to clean-up
Write-Host "`tResetting Owner."
$acl.SetOwner($oldOwner)
$regKey.SetAccessControl($acl)
#endregion Installer Registry Permissions
#region Install
Write-Host "`tStarting Install."
$tempPath = [System.IO.Path]::GetTempPath()
$tempFolder = Join-Path -Path $tempPath -ChildPath ([System.Guid]::NewGuid().ToString("n"))
New-Item -Path $tempFolder -ItemType Directory -Force | Out-Null
$KeyFile = Join-Path -Path $tempFolder -ChildPath ("{0}.dat" -f [System.Guid]::NewGuid().ToString("n"))
$keyFileText = @"
REGEDIT4
[HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINESOFTWAREMicrosoftVisualStudio6.0SetupMicrosoft Visual BasicSetupWizard]
"aspo"=dword:00000000
[HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINESOFTWAREWow6432NodeMicrosoftVisualStudio6.0SetupMicrosoft Visual BasicSetupWizard]
"aspo"=dword:00000000
"@
$keyFileText | Set-Content -Path $keyFile -Force
& $RegEditPath /S $KeyFile
[string[]]$installerArguments = ("/T", "VB98PRO.stf", "/S", $installFolder, "/n", ($env:USERNAME), "/k", "0000000000", "/b", "1", "/qn1")
if($PSBoundParameters.ContainsKey("OrganizationName") -and ![System.String]::IsNullOrWhiteSpace($OrganizationName)){
$installerArguments += "/o"
$installerArguments += $OrganizationName
}
Start-Process -FilePath $install2Location -wait -NoNewWindow -ArgumentList $installerArguments
Start-Process -FilePath $SP6Location -wait -NoNewWindow -ArgumentList ("/qn1")
Write-Host "Setting Vb6 Compatibility"
$vb6ExeLocations = @(Get-Item -Path "C:Program Files*Microsoft Visual StudioVB98VB6.EXE" | Select-Object -ExpandProperty FullName)
$registryPath = Get-Item -LiteralPath $layersPath
foreach($vb6ExeLocation in $vb6ExeLocations){
if($null -eq $registryPath.GetValue($vb6ExeLocation, $null)){
New-ItemProperty -Path $layersPath -Name $vb6ExeLocation -Value "^ WINXPSP3" -PropertyType "String" -Force | Out-Null
}
}
if(!$SkipMouseWheel.IsPresent){
Write-Host "Installing Mouse Wheel"
& $regSvrPath /s $MouseWheelDll
& $RegEditPath /S $MouseWheelRegistry
$registryHeaderText = @"
Windows Registry Editor Version 5.00
"@
$registryItemFormat = @"
[{0}SOFTWAREMicrosoftVisual Basic6.0AddinsVB6IDEMouseWheelAddin.Connect]
"FriendlyName"="MouseWheel Fix"
"LoadBehavior"=dword:00000003
"CommandLineSafe"=dword:00000000
"@
$users = Get-ChildItem -Path "REGISTRY::HKEY_USERS" | Where-Object {$_.Name -notlike "*_Classes"} | Select-Object -ExpandProperty Name
$content = $registryHeaderText
# Install for every user.
foreach($user in $users){
$content += ($registryItemFormat -f $user)
}
$MouseWheelApplyRegistry = Join-Path -Path $tempFolder -ChildPath ("{0}.reg" -f [System.Guid]::NewGuid().ToString("n"))
$content | Set-Content -Path $MouseWheelApplyRegistry -Force
Start-Process $RegEditPath -wait -NoNewWindow -ArgumentList ("/S", $MouseWheelApplyRegistry)
Write-Host "You will still need to enable Mouse Wheel fix in the VB6 IDE." -BackgroundColor Black -ForegroundColor Red
Write-Host "Open a Visual Basic project and go to 'Add-Ins' -> 'Add-In Manager...' " -BackgroundColor Black -ForegroundColor Red
Write-Host "Select 'MouseWheel Fix' and click 'Loaded/Unloaded' and 'Load on Startup'" -BackgroundColor Black -ForegroundColor Red
}
Remove-Item -Path $tempFolder -Force -Recurse | Out-Null
#endregion Install
Write-Host "Install Complete"
Write-Host -NoNewLine 'Press any key to continue...';
$null = $Host.UI.RawUI.ReadKey('NoEcho,IncludeKeyDown');
}
Back to the past
Publicado en CodingMarkers el 28 de marzo del 2018
I was recently requested to debug a pre-.NET application Visual Basic, so I had to set up the environment for Windows 98 development… but nowdays all that software is deprecated and has no support. This is what I learned from my experience to get it up and running, but in case you can make a choice, I’d recommend you to rewrite the code in .NET, as this kind of DLL code relies platform, and things have changed a lot in 20 years.
1.- Delete all the files from the previously failed VB6 installation attempts
Be careful to avoid deleting the recent Visual Studio versions, as they may have similar paths.
The Visual Studio 6.0 files are by default under ‘C:Program Files (x86)’ in 64 bits systems.
C:Program Files (x86)Microsoft Visual StudioCommon C:Program Files (x86)Microsoft Visual StudioMSDN C:Program Files (x86)Microsoft Visual StudioMSDN98 C:Program Files (x86)Microsoft Visual StudioVB98 C:Program Files (x86)Microsoft Visual StudioVC98 C:Program Files (x86)Microsoft Visual Studio*.HTM C:Program Files (x86)Microsoft Visual Studio*.TXT C:Program Files (x86)Common FilesMicrosoft SharedMSDesigners98 C:Program Files (x86)Common FilesMicrosoft SharedMSDN C:Program Files (x86)Common FilesMicrosoft SharedVS98 C:Program Files (x86)Common FilesMicrosoft SharedWizards98
Clean up the Windows registry entrys: run ‘regedit.exe’ and delete the following keys if they exist.
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINESoftwareMicrosoftDevStudio HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINESoftwareMicrosoftHTML Help Collections HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINESoftwareMicrosoftMSVSDG HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINESoftwareMicrosoftVisual Basic6.0 HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINESoftwareMicrosoftVisual Component Manager HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINESoftwareMicrosoftVisual Modeler HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINESoftwareMicrosoftVisualStudio6.0 HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINESoftwareWow6432NodeMicrosoftDevStudio HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINESoftwareWow6432NodeMicrosoftHTML Help Collections HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINESoftwareWow6432NodeMicrosoftMSVSDG HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINESoftwareWow6432NodeMicrosoftVisual Basic6.0 HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINESoftwareWow6432NodeMicrosoftVisual Component Manager HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINESoftwareWow6432NodeMicrosoftVisual Modeler HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINESoftwareWow6432NodeMicrosoftVisualStudio6.0 HKEY_CURRENT_USERSoftwareMicrosoftDevStudio HKEY_CURRENT_USERSoftwareMicrosoftMSVSDG HKEY_CURRENT_USERSoftwareMicrosoftVisual Basic6.0 HKEY_CURRENT_USERSoftwareMicrosoftVisual Modeler HKEY_CURRENT_USERSoftwareMicrosoftVisualFoxPro HKEY_CURRENT_USERSoftwareMicrosoftVisualStudio6.0
2.- Modify the installation files to adapt them to current tech
First of all you will need a copy of the Visual Studio installer in your hard drive. I copied the content of an old college licensed CD into a folder, and proceeded to edit.
- Open ‘SETUPWIZ.INI’ with a text editor (e.g. Notepad++), and replace ‘VmPath=ie4msjavx86.exe’, which tries to install a really old Java implementation and makes the installation process fail, with an empty va. So the first part of the file should look like this:
[setup wizard] eula = eula.txt NTSP = NTsp3nt4sp3_i.exe NTSpMinVer = 3 IE4 = ie4ie4setup.exe CommonFilesMin = 50 IEIni=ie4check.ini WFCClean = setupwfcclean.exe readme = readmevs.htm pid = setup.ini MSDN = setup.exe Acme = acmboot.exe AcmeId = vs98ecd1.inf STF = setupvs98ent.stf DCOM98 = dcom98dcom98.exe MSDNID = msdn3?1.inf NtSpUrl = ftp://ftp.microsoft.com/bussys/winnt/winnt-public/fixes/ IeUrl = http://www.microsoft.com/ie/ie40/download/ UsrUrl = http://msdn.microsoft.com/vstudio/register/default.htm RegUrl = http://www.microsoft.com/isapi/redir.dll?Prd=vstudio&Pver=98&Ar=register VmPath=
- You must also edit the ‘SETUP.EXE’ properties. Go to the context menu of the file (right click as default), select properties, and got to the ‘compatibility’ tab. Check that you have selected:
- Compatibility mode: execute as ‘Windows XP (Service Pack 3)’.
- Configuration: ‘execute this program as administrator’.
3.- Execute the wizard installer
- Open the context menu of ‘SETUP.EXE’ and choose ‘run as administrator’.
- Don’t install ‘Source Safe’, as it fails.
- When we get to ‘choose the installation mode’ select ‘Custom’. Then follow these steps:
- Do not install (as they fail):
- Microsoft Visual FoxPro 6.0
- Microsoft Visual InterDev 6.0
- Microsoft Visual SourceDafe 6.0
- ActiveX (obsolete version, generates conflict with the current version)
- Install the unicode libraries: from the custom main menu, select the text ‘Microsoft Visual C++ 6.0’, and the button ‘Change option’ on the right side will be set as active. Click on it and follow a similar process for ‘VC++ MFC and Template Libraries’ and ‘MS Foundation Class Libraries’. Finally select all these options:
- Static libraries
- Shared libraries
- Static libraries for Unicode
- Shared libraries for Unicode
- Browser database
- Source code
- Install the database: from the main ‘Custom’ menu, click on the ‘Data Access’ text , and the button ‘Change option’ on the right side will be set as active. Click on it and make sure that ‘ADO, RDS and OLE DB Providers’ is not selected. You will get a warning message saying that this component is esential for the application, but you should ignore it, as it will crash on Windows 10. Do select only the following options:
- Microsoft ODBC Drivers
- Remote Data Objects and Controls
- Data environment
- Install the tools: from the main ‘Custom’ menu, click on the ‘Enterprise Tools’ text, and the button ‘Change option’ on the right side will be set as active. Check that ‘Visual Studio Analyzer’ is not selected. Therefore, select only:
- Aplication Performance Explorer
- Repository
- Visual Component Manager
- Visual Basic Enterprise Components
- VC++ Enterprise Tools
- Microsoft Visual Modeler
- As the last step, before pressing on ‘Finish’, do not let the program configure the environment vars.
- If you have waited more than 5 minutes and the program is still ‘configuring the system’, you can assume something has gone wrong and the install has been frozen somewhere. Cancel it, clean up (see the first section on top of this post) and start all over again, reading carefully the steps.
- If there is an error message about the Java machine you can ignore it. At that point you should be able by then to run ‘Visual Basic’ without the MSDN help package, so you get the bare bones yet fully functional experience.
4.- Execute the application
Run it always in administrator mode (right click on Visual Basic 6.0, and select ‘run as administrator’). Then, here it is, ready to run and debug ancient DLLs.
❗️ If you want it the program to run using a Microsoft Office 2010 instance, you will need to load some dependencies. Go to ‘Project/References’ and select:
- Visual Basic for Applications
- Visual Basic runtime objects and procedures
- Visual Basic objects and procedures
- OLE Automation
- Microsoft Excel 15.0 Object Library
- Microsoft Word 15.0 Object Library
5.- References
My sources should get the credit they deserve for their help:
- Installing Visual Basic/Studio 6 on Windows 10 | danbrust.net: the blog
- Install Visual Studio 6.0 on Windows 10 — CodeProject
As I’ve worked my way through the various oddities of Windows 10, I’ve found that most applications work great. For the most part, anything that worked on Windows 7 works on Windows 10. Visual Basic 6 (VB6) has been one of the few exceptions, so far.
Why install Visual Basic 6? It’s a long-dead program, after all. Well, like many companies out there, mine has a few proprietary programs that were written, long ago, in VB6. The apps work great, so it just hasn’t made sense to spend the time and/or money it would take to upgrade them to VB.Net. Yet, we still need to be able to make minor changes to the programs now and then.
We could keep an old XP machine around just for VB6, or set up a virtual instance of XP, or go for either of those options with Windows 7 (VB6 installed on Win7, though not perfectly). Instead of going those routes, though, I decided to look into getting VB6 properly installed on Windows 10. These notes should work for the Pro and Enterprise editions of both Visual Basic 6 and Visual Studio 6.
Note that this tutorial is really geared toward getting Visual Basic 6 up and running. I do not know whether any of the other Visual Studio applications will work after the steps below have been followed.
Also note that this process will not allow you to install the Data Access components. They just don’t work with Windows 10.
Remove Any Remnants of VB6/VS6
If you’re like me, you probably tried to install Visual Basic 6 on your computer the old fashioned way. When the install failed, you were then left with bits and pieces of VB laying around, and no uninstaller. Luckily, Microsoft wrote up an article about removing Visual Studio manually (How To Manually Uninstall Visual Studio with MSDN Library). I do not believe searching your hard drive for some of the files, as they mention, is necessary. Here are the most important steps to follow:
- Delete the installation folders for any Visual Studio products. Note that the following are the default locations; the actual locations may be different on your system if you did a custom installation or if you are on a 64-Bit computer:
- Program FilesMicrosoft Visual Studio
- Program FilesCommon FilesMicrosoft SharedMSDesigners98
- Program FilesCommon FilesMicrosoft SharedMSDN
- Program FilesCommon FilesMicrosoft SharedVS98
- Program FilesCommon FilesMicrosoft SharedWizards98
- Delete the installation folders for any MSDN Libraries (the previous step may have deleted these if they were installed to the default location). The default folders are as follows:
- Program FilesMicrosoft Visual StudioMSDN98 (for the MSDN Library for Visual Studio 6.0)
- Program FilesMicrosoft Visual StudioMSDN (for the MSDN Quarterly Library releases)
- Use Regedit.exe to delete the following Registry keys if they exist:
- HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINESoftwareMicrosoftDevStudio
- HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINESoftwareMicrosoftMSVSDG
- HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINESoftwareMicrosoftHTML Help Collections
- HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINESoftwareMicrosoftVisual Basic6.0
- HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINESoftwareMicrosoftVisual Component Manager
- HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINESoftwareMicrosoftVisual Modeler
- HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINESoftwareMicrosoftVisualStudio6.0
- HKEY_CURRENT_USERSoftwareMicrosoftDevStudio
- HKEY_CURRENT_USERSoftwareMicrosoftMSVSDG
- HKEY_CURRENT_USERSoftwareMicrosoftVisual Basic6.0
- HKEY_CURRENT_USERSoftwareMicrosoftVisual Modeler
- HKEY_CURRENT_USERSoftwareMicrosoftVisualFoxPro
- HKEY_CURRENT_USERSoftwareMicrosoftVisualStudio6.0
- If you’re on a 64-Bit system, check here, as well:
- HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINESoftwareWow6432NodeMicrosoftDevStudio
- HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINESoftwareWow6432NodeMicrosoftMSVSDG
- HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINESoftwareWow6432NodeMicrosoftHTML Help Collections
- HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINESoftwareWow6432NodeMicrosoftVisual Basic6.0
- HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINESoftwareWow6432NodeMicrosoftVisual Component Manager
- HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINESoftwareWow6432NodeMicrosoftVisual Modeler
- HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINESoftwareWow6432NodeMicrosoftVisualStudio6.0
- Use Regedit.exe to delete any instance of the key for Visual Studio or MSDN Library under the following keys. Since you don’t have an uninstaller, you probably won’t find anything here. It’s worth looking through the keys, anyway, to see if you find any mentions of Visual Studio or MSDN. WARNING: Do not delete the “Uninstall” key; only delete MSDN or Visual Studio keys listed within it.
- HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINESOFTWAREMicrosoftWindowsCurrentVersionUninstall
- 64-Bit systems only: HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINESOFTWAREWow6432NodeMicrosoftWindowsCurrentVersionUninstall
Prepare Your Files
Now, we need to get all of our files in place. The tool we’re going to use for the installation can actually read off the CDs, but I find it much quicker to have already copied the necessary files to my hard drive. In my case, I setup everything in C:Visual Studio 6.
- First, copy the contents of all Visual Basic/Studio 6 and MSDN CDs to the folder you’ve chosen.
- Next, download and extract the Visual Studio SP6 patch (https://www.microsoft.com/en-us/download/details.aspx?id=9183). Place the extracted contents in a folder named VS6SP6.
- You should end up with a set of directories that look like those shown below. The names aren’t important, as long as you know what’s what.
We’re going to use a handy tool put together by Giorgio Brausi to complete our installation. It takes care of some of the trickier parts of getting Visual Basic/Studio 6 installed on a Windows 10 computer.
- Download Giorgio’s installation program from his website, nuke.vbcorner.net (http://nuke.vbcorner.net/Articles/VB60/VisualStudio6Installer/tabid/93/language/en-US/Default.aspx).
- The program does not need to be installed. Simply extract the contents of the zip file and run vs6installer.exe.
- The first thing we need to do is setup the program’s working folder. This is where the installer program will copy it’s working fileset to. I suggest using a folder you know the program will have permission to access. Something in your Documents folder should work.
- Click the “Set Root folder” button.
- Browse to where you want to create the root folder, then click Make New Folder. Using the tool to make the folder will ensure that it has the necessary permissions. Click “Yes” to confirm that it is the correct location.
- If you want to install the various graphic files included with VS6, then make sure that option is checked.
- Make sure the “Disable Data Access” option is chosen. It should already be selected, by default, on Windows 10 systems.
- Select the edition you will be installing. In my case, I chose Visual Studio 6 Professional Edition. You should choose whatever matches the CDs you are using for the installation. Your options should look similar to this:
- Click the “Step 1” button. The program will now have you select the source location for Visual Basic/Studio’s files. The files can be on CDs, or on your hard drive (as I previously recommended). Select the set of files referenced at the top of the selection window, confirm that the copy procedure is correct, then wait as the necessary files are copied to the new root location.
- Click “Step 2” and select the MSDN files. Technically, you don’t need to install MSDN, but it doesn’t hurt. You will need to select both CDs for this step. After CD1 has finished copying, you will be prompted to select CD2.
- On to “Step 3”. This will prepare the Service Pack 6 files. Browse to and select the files you previously extracted to the VS6SP6 directory.
- You may run into an issue here if you are installing the Professional Edition of VB6/VS6. The Service Pack 6 files that are still available on the Net are actually for the Enterprise Edition. I have, so far, been unable to source a Pro version of SP6. If you get an error about missing files (see below), then simply move on with the installation. We’ll manually install SP6, later.
Install Visual Basic/Studio
Now that our files are in place, it’s time to begin installing the program.
- Click the first Install button.
- Click “Yes” to confirm you wish to continue with the installation.
- The standard installer will now launch. Make your way through it, entering your Serial Number as necessary.
- Make sure to choose the standard Install option, NOT the Server Applications option.
- Keep clicking Next, Continue, OK, etc., until you get to this screen. Click the Custom button.
- The installer tool will have already made the appropriate selections based upon what you chose before launching the installer, so there should be no need to make any changes here. I believe you can install the options besides Visual Basic 6, but they were unnecessary for me. Some of the items under “Data Access” are incompatible with Windows 10. They should already be disabled if you left the “Disable Data Access” option checked in the installer tool.
- If your version of Visual Studio/Basic has a SourceSafe option, then it is probably wise to uncheck that option.
- Here’s how my installation options looked:
- Click Continue and the program will install.
- Click OK when you get the Success message.
- You may need to Restart your system at this point. If so, wait for the restart to finish, then pick up where you left off.
- The MSDN installer will now launch. Make sure to UNCHECK the “Install MSDN” option, then click Next.
- Click “Yes” to the message warning you about not installing MSDN, click Next to skip any additional installers, then UNCHECK “Register Now” and click Finish.
- If you were to check Programs and Features now, you would see that you now have a proper Visual Basic/Studio 6 uninstaller.
Install the MSDN Library
Time to install the MSDN Library. This step is optional, but I recommend it as Visual Basic 6 Help files are only going to get harder to find on the Net as time goes by.
Install Service Pack 6
There are two ways to install Service Pack 6. If you have the proper service pack files for your installation, then you will be able to use the installer tool to launch the installation. If not, then you’ll need to launch the installer manually.
Note that Service Pack 6 only contains updates for Visual Studio, Visual C++, and Visual Basic, and Visual SourceSafe. If you installed any other programs (FoxPro or InterDev), then you should first install Service Pack 5. I find it hard to justify installing those programs, so won’t go over that scenario here.
- If you were able to find the right version of SP6 for your installation, then you can click the third Install button.
- Click “Yes” to confirm you want to install SP6.
- If you were unable to find the correct version of SP6, then find the folder you previously extracted the SP6 files to (during this step), right click on the setupsp6.exe file, and choose “Run as administrator”.
- From here on, the installation of SP6 will be the same for both scenarios.
- Click “Continue”, then click “I Agree”.
- If you get an option to click a “Complete” button, then do so.
- Click “OK” once installation has finished.
A Few More Steps
Just a few more steps until we’re done. These steps will take care of a few errors/annoyances you may encounter.
- Go to the Options tab in the Visual Studio 6 Installer program and click “Create Desktop shortcut”.
- Run the newly created shortcut from your Desktop.
- If you get an “Automation error”, then close VB6, return to the installer tool, and click the “Run As Administrator” option.
- Relaunch VB6, and the error should be gone.
- You can now return to the installer tool and click the “Run As Administrator” option again to turn off that setting. It is not needed after the necessary registrations have been completed.
- We have just one more setting to change. VB6, when run on Windows 10, will experience a delay whenever you draw, move, or resize objects on a Form in the VB IDE. To correct this issue, click the “Set Vista SP2 compatible” button.
- If the “Set Vista SP2 compatible” button does not work, then you may need to set that option manually. To do so, navigate to where VB6 is installed (most likely C:Program Files (x86)Microsoft Visual StudioVB98).
- Right click on VB6.exe and choose “Properties”.
- Go to the Compatibility tab, check the “Run this program in compatibility mode for” option, and choose “Windows Vista (Service Pack 2)”.
- Click OK, then try running the program again. You should now find that controls can be manipulated without issue.
And you’re done! Visual Basic 6 should now run just as well as it ever did. Now then, time to get back to work on converting those VB6 apps to VB.Net 😉
4 Years Ago
rproffitt
1 Tallied Votes
3K
Views
Yes, you’ve been told it’s dead, gone and to move off this old beast of a system from 1998 but here you are, tasked with fixing an old legacy app so let me share that I’ve been there and how I got around some of the issues. These are:
- Install issues on Windows 10.
- A workaround to code that seemed fine but failed.
- What may never work again.
Installing VB6
Installing Visual Studio 6.0 from 1998 is a challenge. Be sure to have your media ready and if need be, print out the instructions so you can follow them step by step.
I used this search for how to isntall -> https://www.google.com/search?q=Install+Visual+Studio+6.0+on+Windows+10
This seems to work but badly and you have to deal with the install appearing to fail but I was able to pick up the pieces by copying the missing dao35.dll from my Visual Studio 6.0 CD (or VB6 Media) to the folder where the VB6.EXE is. This might be C:Program Files (x86)Microsoft Visual StudioVB98 on a stock install.
Before you try to run VB6, be sure to install Service Patch 6.
When you run VB6 for the first time it may cough up errors and complaints but plow ahead and when it’s done, quit and try again. Here it stoped complaining on the second run.
Be sure to experiment with the Compatibility Tab on the VB6.EXE file. For me the usual sluggish behavior in dragging items around vanished when I set compatibility to Vista Service Pack 2.
An odd workaround
Our old app uses images for some buttons and VB6 would complain the images couldn’t be found. The images were there but the fix was simple but unintuitive. The current directory appeared to be somewhere else and I have yet to find out why CurrDIR() returns what we expected yet the following code was required. Let’s hope this helps a few out there.
Debug.Print CurDir() ' Show in IDE
Debug.Print App.Path ' Show in IDE
ChDir (App.Path) ' Set the CurDir()What may never work again
So that’s the basics to get VB6 up and running again and the odd issue I bumped into and now to what we had to forget about. What I can’t seem to find a fix for is the old SQL interface system. That’s in DAO but that doesn’t seem to have a patch or fix so if you rely on any SQL you need to inform your management that it’s dead.
ddanbe
2,724
Professional Procrastinator
Featured Poster
4 Years Ago
Yes, conservative, afraid to change anything managments.
That is why COBOL is also still around, I guess.
rproffitt
2,382
«Nothing to see here.»
Moderator
4 Years Ago
Microsoft issued the following at https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/previous-versions/visualstudio/visual-basic-6/visual-basic-6-support-policy
Executive summary
The Visual Basic team is committed to «It Just Works» compatibility for Visual Basic 6.0 applications on the following supported Windows operating systems:
Windows 10
Windows 8.1
Windows 7
Windows Server 2016
Windows Server 2012 including R2
Windows Server 2008 including R2«The Visual Basic team’s goal is that Visual Basic 6.0 applications continue to run on supported Windows versions. As detailed in this document, the core Visual Basic 6.0 runtime will be supported for the full lifetime of supported Windows versions, which is five years of mainstream support followed by five years of extended support.»
While the support for the development system is gone and there are issues, the runtime and if you know what you are doing, you can keep your app running for a very long time.
What is gone and I can’t find a fast workaround is SQL support. Also known as DAO.
Hope this helps if someone tells you it’s dead. While I think it’s unacceptable for a new project, just like Cobol, it lives.
4 Years Ago
I already installed vb6 on windows 10 and no problems occur
Reply to this topic
Be a part of the DaniWeb community
We’re a friendly, industry-focused community of developers, IT pros, digital marketers,
and technology enthusiasts meeting, networking, learning, and sharing knowledge.
Reply to this Topic
This topic is old!
No one has contributed to this discussion in over 4 years.
Are you sure you have something valuable to add to revive the existing conversation?
Consider starting a new topic instead.
Otherwise, please be thoughtful, detailed and courteous, and adhere to our posting rules.
-
Edit -
Preview
Insert Code Block
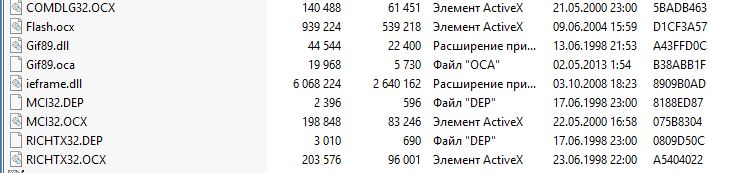
В общем, как и сказал в статье про запуск моей программы Viewer, копируем все библиотеки которые использует программа и на которые жалуется при попытке запуска, у меня это данные библиотеки :
в системную папку — для 32-разрядных систем это C:WindowsSystem32 и для 64-разрядных систем это C:WindowsSysWOW64. Далее регистрируем их в системе, для этого через правую кнопку мышки/Запуск от имени администратора, запускаем файл cmd.exe (Командная строка) в той же системной папке. В ней пишем команду для 64-битной системы C:windowssyswow64Regsvr32 имя библиотеки
(и C:WINDOWSsystem32Regsvr32 имя библиотеки
для 32-битной системы, если таковые еще остались).
Эту команду нужно прописать для каждой библиотеки из списка , то есть:
C:windowssyswow64Regsvr32 COMDLG32.OCX
C:windowssyswow64Regsvr32 gif89.dll
C:windowssyswow64Regsvr32 richtx32.ocx
C:windowssyswow64Regsvr32 MCI32.OCX
C:windowssyswow64Regsvr32 gif89.oca
C:windowssyswow64Regsvr32 flash.ocx
C:windowssyswow64Regsvr32 ieframe.dll
После каждой команды должно появляться окошко об успешной регистрации библиотеки. Если появляется ошибка, что-то сделано не так, ошибка в команде или в названии библиотеки или что-то еще.
Ну и всё, собственно, на этом, старые программы с Visual Basic 6 (ну моя во всяком случае) должны заработать. Для других программ могут понадобиться другие подобные библиотеки, регистрировать в системе их нужно точно также.
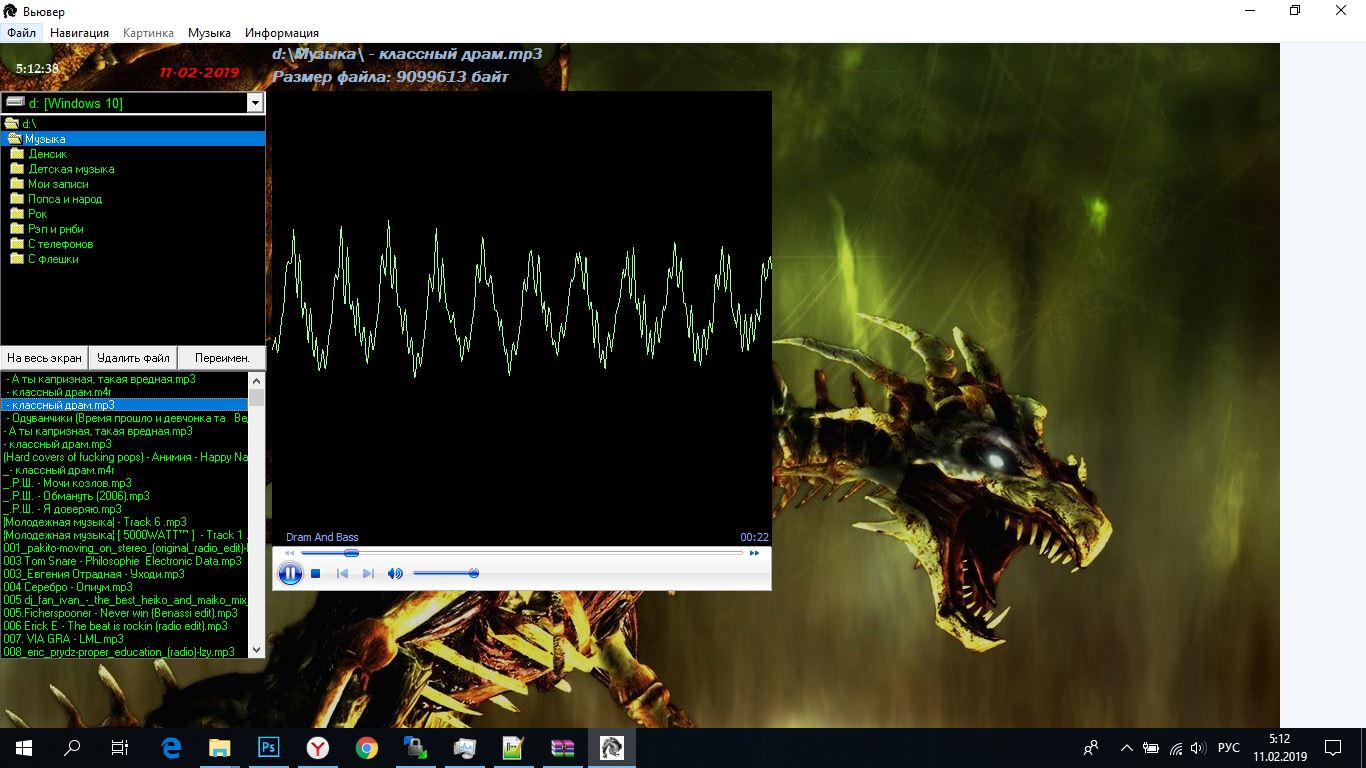
Вот так выглядит моя программа Viewer на Windows 10 в 2019 году
(справа белый незаполненный пробел и по высоте неверно немного заполнило экран, а так все вполне работоспособно) :
Всем спасибо, всем удачи 
P.S. Скачать её по-прежнему можно здесь https://disc-c.ru/programs/viewer.zip
Forum Rules |
|
Skip to content
VB6 installs just fine on Windows 7, Windows 8 and even Windows 10 with a few caveats.
Just follow instructions bellow to make VisualBasic 6 IDE (VisualStudio) works on your system.
Here is how to install VB6 on Windows 7/8/10
- Before proceeding with the installation process below, create a zero-byte file in
C:WindowscalledMSJAVA.DLL. The setup process will look for this file, and if it doesn’t find it, will force an installation of old, old Java, and require a reboot. By creating the zero-byte file, the installation of moldy Java is bypassed, and no reboot will be required. - Turn off UAC.
- Insert Visual Studio 6 CD.
- Exit from the Autorun setup.
- Browse to the root folder of the VS6 CD.
- Right-click
SETUP.EXE, selectRun As Administrator. - On this and other Program Compatibility Assistant warnings, click Run Program.
- Click Next.
- Click “I accept agreement”, then Next.
- Enter name and company information, click Next.
- Select Custom Setup, click Next.
- Click Continue, then Ok.
- Setup will “think to itself” for about 2 minutes. Processing can be verified by starting Task Manager, and checking the CPU usage of ACMSETUP.EXE.
- On the options list, select the following:
- Microsoft Visual Basic 6.0
- ActiveX
- Data Access
- Graphics
- All other options should be unchecked.
- Click Continue, setup will continue.
- Finally, a successful completion dialog will appear, at which click Ok. At this point, Visual Basic 6 is installed.
- If you do not have the MSDN CD, clear the checkbox on the next dialog, and click next. You’ll be warned of the lack of MSDN, but just click Yes to accept.
- Click Next to skip the installation of Installshield. This is a really old version you don’t want anyway.
- Click Next again to skip the installation of BackOffice, VSS, and SNA Server. Not needed!
- On the next dialog, clear the checkbox for “Register Now”, and click Finish.
- The wizard will exit, and you’re done. You can find VB6 under Start, All Programs, Microsoft Visual Studio 6. Enjoy!
- Turn On UAC again
What to do after VB6 installation on Windows 7/8/10
You might notice after successfully installing VB6 on Windows 7 that working in the IDE is a bit, well, sluggish. For example, resizing objects on a form is a real pain.
- After installing VB6, you’ll want to change the compatibility settings for the IDE executable.
- Using Windows Explorer, browse the location where you installed VB6. By default, the path is
C:Program FilesMicrosoft Visual StudioVB98 - Right click the VB6.exe program file, and select properties from the context menu.
- Click on the Compatibility tab.
- Place a check in each of these checkboxes:
- Run this program in compatibility mode for Windows XP (Service Pack 3)
- Disable Visual Themes
- Disable Desktop Composition
- Disable display scaling on high DPI settings
- If you have UAC turned on, it is probably advisable to check the ‘Run this program as an Administrator’ box
After changing these settings, fire up the IDE, and things should be back to normal, and the IDE is no longer sluggish.