Время прочтения
9 мин
Просмотры 22K
Введение
Консольные приложения до сих пор остаются наиболее востребованным видом приложений, большинство разработчиков оттачивают архитектуру и бизнес-логику именно в консоли. При этом они нередко сталкиваются с проблемой локализации — русский текст, который вполне адекватно отражается в исходном файле, при выводе на консоль приобретает вид т.н. «кракозябр».
В целом, локализация консоли Windows при наличии соответствующего языкового пакета не представляется сложной. Тем не менее, полное и однозначное решение этой проблемы, в сущности, до сих пор не найдено. Причина этого, главным образом, кроется в самой природе консоли, которая, являясь компонентом системы, реализованным статическим классом System.Console, предоставляет свои методы приложению через системные программы-оболочки, такие как командная строка или командный процессор (cmd.exe), PowerShell, Terminal и другие.
По сути, консоль находится под двойным управлением — приложения и оболочки, что является потенциально конфликтной ситуацией, в первую очередь в части использования кодировок.
Данный материал не предлагает строгий алгоритм действий, а направлен на описание узловых проблем, с которыми неизбежно сталкивается разработчик локализованного консольного приложения, а также некоторые возможные пути их разрешения. Предполагается, что это позволит разработчику сформировать стратегию работы с локализованной консолью и эффективно реализовать существующие технические возможности, большая часть которых хорошо описана и здесь опущена.
Виды консолей
В общем случае функции консоли таковы:
-
управление операционной системой и системным окружением приложений на основе применения стандартных системных устройств ввода-вывода (экран и клавиатура), использования команд операционной системы и/или собственно консоли;
-
запуск приложений и обеспечение их доступа к стандартным потокам ввода-вывода системы, также с помощью стандартных системных устройств ввода-вывода.
Основная консоль Windows — командная строка или иначе командный процессор (CMD). Большие возможности предоставляют оболочки PowerShell (PS), Windows PowerShell (WPS) и Terminal. По умолчанию Windows устанавливает Windows Power Shell мажорной версией до 5, однако предлагает перейти на новую версию — 7-ку, имеющую принципиальное отличие (вероятно, начинающееся с 6-ки) — кроссплатформенность. Terminal — также отдельно уставливаемое приложение, по сути интегратор всех ранее установленных оболочек PowerShell и командной строки.
Отдельным видом консоли можно считать консоль отладки Visual Studio (CMD-D).
Конфликт кодировок
Полностью локализованная консоль в идеале должна поддерживать все мыслимые и немыслимые кодировки приложений, включая свои собственные команды и команды Windows, меняя «на лету» кодовые страницы потоков ввода и вывода. Задача нетривиальная, а иногда и невозможная — кодовые страницы DOS (CP437, CP866) плохо совмещаются с кодовыми страницами Windows и Unicode.
История кодировок здесь: О кодировках и кодовых страницах / Хабр (habr.com)
Исторически кодовой страницей Windows является CP1251 (Windows-1251, ANSI, Windows-Cyr), уверенно вытесняемая 8-битной кодировкой Юникода CP65001 (UTF-8, Unicode Transformation Format), в которой выполняется большинство современных приложений, особенно кроссплатформенных. Между тем, в целях совместимости с устаревшими файловыми системами, именно в консоли Windows сохраняет базовые кодировки DOS — CP437 (DOSLatinUS, OEM) и русифицированную CP866 (AltDOS, OEM).
Совет 1. Выполнять разработку текстовых файлов (программных кодов, текстовых данных и др.) исключительно в кодировке UTF-8. Мир любит Юникод, а кроссплатформенность без него вообще невозможна.
Совет 2. Периодически проверять кодировку, например в текстовом редакторе Notepad++. Visual Studio может сбивать кодировку, особенно при редактировании за пределами VS.
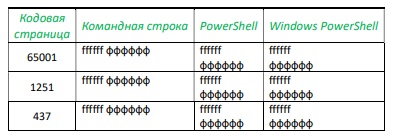
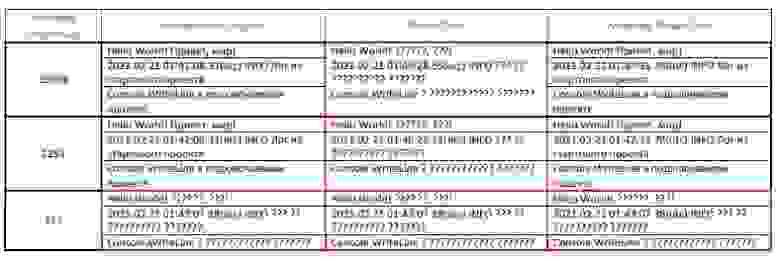
Поскольку в консоли постоянно происходит передача управления от приложений к собственно командному процессору и обратно, регулярно возникает «конфликт кодировок», наглядно иллюстрируемый таблица 1 и 2, сформированных следующим образом:
Были запущены три консоли — CMD, PS и WPS. В каждой консоли менялась кодовая страница с помощью команды CHCP, выполнялась команда Echo c двуязычной строкой в качестве параметра (табл. 1), а затем в консоли запускалось тестовое приложение, исходные файлы которого были созданы в кодировке UTF-8 (CP65001): первая строка формируется и направляется в поток главным модулем, вторая вызывается им же, формируется в подключаемой библиотеке классов и направляется в поток опять главным модулем, третья строка полностью формируется и направляется в поток подключаемой библиотекой.
Команды и код приложения под катом
команды консоли:
-
> Echo ffffff фффффф // в командной строке
-
PS> Echo ffffff фффффф // в PowerShell
-
PS> Echo ffffff ?????? // так выглядит та же команда в Windows PowerShell
код тестового приложения:
using System;
using ova.common.logging.LogConsole;
using Microsoft.Extensions.Logging;
using ova.common.logging.LogConsole.Colors;
namespace LoggingConsole.Test
{
partial class Program
{
static void Main2(string[] args)
{
ColorLevels.ColorsDictionaryCreate();
Console.WriteLine("Hello World! Привет, мир!"); //вывод строки приветствия на двух языках
LogConsole.Write("Лог из стартового проекта", LogLevel.Information);
Console.WriteLine($"8. Active codepage: input {Console.InputEncoding.CodePage}, output {Console.OutputEncoding.CodePage}");
Console.ReadKey();
}
}
}Командную часть задания все консоли локализовали практически без сбоев во всех кодировках, за исключением: в WPS неверно отображена русскоязычная часть команды во всех кодировках.
Вывод тестового приложения локализован лишь в 50% испытаний, как показано в табл.2.
Сoвет 3. Про PowerShell забываем раз и навсегда. Ну может не навсегда, а до следующей мажорной версии…
По умолчанию Windows устанавливает для консоли кодовые страницы DOS. Чаще всего CP437, иногда CP866. Актуальные версии командной строки cmd.exe способны локализовать приложения на основе русифицированной кодовой страницы 866, но не 437, отсюда и изначальный конфликт кодировок консоли и приложения. Поэтому
Совет 4. Перед запуском приложения необходимо проверить кодовую страницу консоли командой CHCP и ей же изменить кодировку на совместимую — 866, 1251, 65001.
Совет 5. Можно установить кодовую страницу консоли по умолчанию. Кратко: в разделе реестра HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINESOFTWAREMicrosoftCommand Processor добавить или изменить значение параметра Autorun на: chcp <номер кодовой страницы>. Очень подробно здесь: Изменить кодовую страницу консоли Windows по умолчанию на UTF-8 (qastack.ru), оригинал на английском здесь: Change default code page of Windows console to UTF-8.
Проблемы консолей Visual Studio
В Visual Studio имеется возможность подключения консолей, по умолчанию подключены командная строка для разработчика и Windows PowerShell для разработчика. К достоинствам можно отнести возможности определения собственных параметров консоли, отдельных от общесистемных, а также запуск консоли непосредственно в директории разработки. В остальном — это обычные стандартные консоли Windows, включая, как показано ранее, установленную кодовую страницу по умолчанию.
Отдельной опцией Visual Studio является встроенная односеансная консоль отладки, которая перехватывает команду Visual Studio на запуск приложения, запускается сама, ожидает компиляцию приложения, запускает его и отдает ему управление. Таким образом, отладочная консоль в течение всего рабочего сеанса находится под управлением приложения и возможность использования команд Windows или самой консоли, включая команду CHCP, не предусмотрена. Более того, отладочная консоль не воспринимает кодовую страницу по умолчанию, определенную в реестре, и всегда запускается в кодировке 437 или 866.
Совет 6. Тестирование приложения целесообразно выполнять во внешних консолях, более дружелюбных к локализации.
Анализ проблем консолей был бы не полон без ответа на вопрос — можно ли запустить консольное приложение без консоли? Можно — любой файл «.exe» запустится двойным кликом, и даже откроется окно приложения. Однако консольное приложение, по крайней мере однопоточное, по двойному клику запустится, но консольный режим не поддержит — все консольные вводы-выводы будут проигнорированы, и приложение завершится
Локализация отладочной консоли Visual Studio
Отладочная консоль — наиболее востребованная консоль разработчика, гораздо более удобная, чем внешняя консоль, поэтому резонно приложить максимум усилий для ее локализации.
На самом деле, правильнее говорить о локализации приложения в консоли — это важное уточнение. Microsoft по этому поводу высказывается недвусмысленно: «Programs that you start after you assign a new code page use the new code page. However, programs (except Cmd.exe) that you started before assigning the new code page will continue to use the original code page». Иными словами, консоль можно локализовать когда угодно и как угодно, но приложение будет локализовано в момент стабилизации взаимодействия с консолью в соответствии с текущей локализацией консоли, и эта локализация сохранится до завершения работы приложения. В связи с этим возникает вопрос — в какой момент окончательно устанавливается связь консоли и приложения?
Важно! Приложение окончательно стабилизирует взаимодействие с консолью в момент начала ввода-вывода в консоль, благодаря чему и появляется возможность программного управления локализацией приложения в консоли — до первого оператора ввода-вывода.
Ниже приведен пример вывода тестового приложения в консоль, иллюстрирующий изложенное. Метод Write получает номера текущих страниц, устанавливает новые кодовые страницы вводного и выводного потоков, выполняет чтение с консоли и записывает выводную строку, содержащий русский текст, в том числе считанный с консоли, обратно в консоль. Операция повторяется несколько раз для всех основных кодовых страниц, упомянутых ранее.
F:LoggingConsole.TestbinReleasenet5.0>chcp
Active code page: 1251
F:LoggingConsole.TestbinReleasenet5.0>loggingconsole.test
Codepages: current 1251:1251, setted 437:437, ΓΓεΣΦ∞ 5 ±Φ∞ΓεδεΓ ∩ε-≡≤±±ΩΦ: Θ÷≤Ωσ=Θ÷≤Ωσ
Codepages: current 437:437, setted 65001:65001, 5 -: =
Codepages: current 65001:65001, setted 1252:1252, ââîäèì 5 ñèìâîëîâ ïî-ðóññêè: éöóêå=éöóêå
Codepages: current 1252:1252, setted 1251:1251, вводим 5 символов по-русски: йцуке=йцуке
Codepages: current 1251:1251, setted 866:866, ттюфшь 5 ёшьтюыют яю-Ёєёёъш: щЎєъх=щЎєъх
Codepages: current 866:866, setted 1251:1251, вводим 5 символов по-русски: йцуке=йцуке
Codepages: current 1251:1251, setted 1252:1252, ââîäèì 5 ñèìâîëîâ ïî-ðóññêè: éöóêå=éöóêå
F:LoggingConsole.TestbinReleasenet5.0>chcp
Active code page: 1252-
приложение запущено в консоли с кодовыми страницами 1251 (строка 2);
-
приложение меняет кодовые страницы консоли (current, setted);
-
приложение остановлено в консоли с кодовыми страницами 1252 (строка 11, setted);
-
по окончании работы приложения изменения консоли сохраняются (строка 14 — Active codepage 1252);
-
Приложение адекватно локализовано только в случае совпадения текущих кодовых страниц консоли (setted 1251:1251) с начальными кодовыми страницами (строки 8 и 10).
Код тестового приложения под катом
using System;
using System.Runtime.InteropServices;
namespace LoggingConsole.Test
{
partial class Program
{
[DllImport("kernel32.dll")] static extern uint GetConsoleCP();
[DllImport("kernel32.dll")] static extern bool SetConsoleCP(uint pagenum);
[DllImport("kernel32.dll")] static extern uint GetConsoleOutputCP();
[DllImport("kernel32.dll")] static extern bool SetConsoleOutputCP(uint pagenum);
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Write(437);
Write(65001);
Write(1252);
Write(1251);
Write(866);
Write(1251);
Write(1252);
}
static internal void Write(uint WantedIn, uint WantedOut)
{
uint CurrentIn = GetConsoleCP();
uint CurrentOut = GetConsoleOutputCP();
Console.Write($"current {CurrentIn}:{CurrentOut} - текущая кодировка, "); /*wanted {WantedIn}:{WantedOut},*/
SetConsoleCP(WantedIn);
SetConsoleOutputCP(WantedOut);
Console.Write($"setted {GetConsoleCP()}:{GetConsoleOutputCP()} - новая кодировка, ");
Console.Write($"вводим 3 символа по-русски: ");
string str = "" + Console.ReadKey().KeyChar.ToString();
str += Console.ReadKey().KeyChar.ToString();
str += Console.ReadKey().KeyChar.ToString();
Console.WriteLine($"={str}");
}
static internal void Write(uint ChangeTo)
{
Write(ChangeTo, ChangeTo);
}
}
}
Программное управление кодировками консоли — это единственный способ гарантированной адекватной локализацией приложения в консоли. Языки .Net такой возможности не предоставляют, однако предоставляют функции WinAPI: SetConsoleCP(uint numcp) и SetConsoleOutputCP(uint numcp), где numcp — номер кодовой страницы потоков ввода и вывода соответственно. Подробнее здесь: Console Functions — Windows Console | Microsoft Docs. Пример применения консольных функций WInAPI можно посмотреть в тестовом приложении под катом выше.
Совет 7. Обязательный и повторный! Функции SetConsoleCP должны размещаться в коде до первого оператора ввода-вывода в консоль.
Стратегия локализации приложения в консоли
-
Удалить приложение PowerShell (если установлено), сохранив Windows PowerShell;
-
Установить в качестве кодовую страницу консоли по умолчанию CP65001 (utf-8 Unicode) или CP1251 (Windows-1251-Cyr), см. совет 5;
-
Разработку приложений выполнять в кодировке utf-8 Unicode;
-
Контролировать кодировку файлов исходных кодов, текстовых файлов данных, например с помощью Notepad++;
-
Реализовать программное управление локализацией приложения в консоли, пример ниже под катом:
Пример программной установки кодовой страницы и локализации приложения в консоли
using System;
using System.Runtime.InteropServices;
namespace LoggingConsole.Test
{
partial class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
[DllImport("kernel32.dll")] static extern bool SetConsoleCP(uint pagenum);
[DllImport("kernel32.dll")] static extern bool SetConsoleOutputCP(uint pagenum);
SetConsoleCP(65001); //установка кодовой страницы utf-8 (Unicode) для вводного потока
SetConsoleOutputCP(65001); //установка кодовой страницы utf-8 (Unicode) для выводного потока
Console.WriteLine($"Hello, World!");
}
}
}
Windows
- 09.06.2020
- 61 679
- 6
- 150
- 147
- 3
- Содержание статьи
- Исправляем проблему с кодировкой с помощью смены шрифта
- Исправляем проблему с кодировкой с помощью смены кодировки
- Комментарии к статье ( 6 шт )
- Добавить комментарий
В некоторых случаях, когда используется неверная кодировка, могут возникать так называемые кракозябры или иероглифы, т.е. не читаемые символы, которые невозможно разобрать при работе с командной строкой. Эти проблемы могут также возникать и при запуске различных BAT-файлов. В данной статье мы расскажем о том, как можно сменить шрифт или кодировку, чтобы избавиться от этой проблемы. Пример таких не читаемых символов можно видеть на картинке ниже:
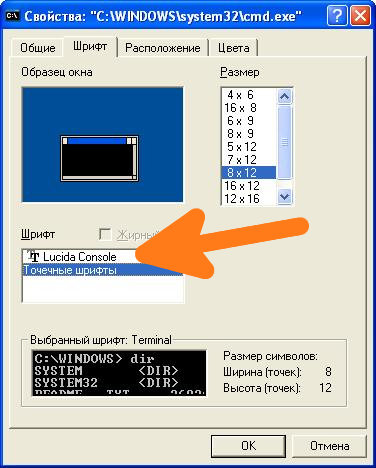
Исправляем проблему с кодировкой с помощью смены шрифта
Первым делом нужно зайти в свойства окна: Правой кнопкой щелкнуть по верхней части окна -> Свойства -> в открывшемся окне в поле Шрифт выбрать Lucida Console и нажать кнопку ОК.
После этого не читаемые символы должны исчезнуть, а текст должен выводиться на русском языке.
Исправляем проблему с кодировкой с помощью смены кодировки
Вместо смены шрифта, можно сменить кодировку, которая используется при работе cmd.exe.
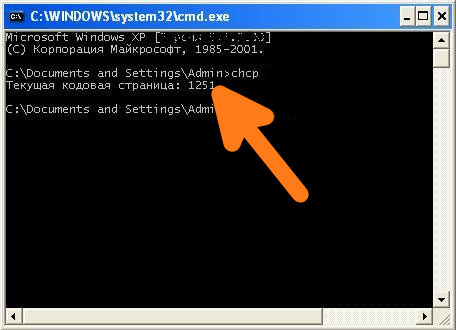
Узнать текущую кодировку можно введя в командной строке команду chcp, после ввода данной команды необходимо нажать Enter.
Как видно на скриншоте, текущая используемая кодировка Windows-1251
Для изменения кодировки нам необходимо воспользоваться командой chcp <код_новой_кодировки>, где <код_новой_кодировки> — это сам код кодировки, на которую мы хотим переключиться. Возможные значения:
- 1251 — Windows-кодировка (Кириллица);
- 866 — DOS-кодировка;
- 65001 — Кодировка UTF-8;
Т.е. для смены кодировки на DOS, команда примет следующий вид:
chcp 866Для смены кодировки на UTF-8, команда примет следующий вид:
chcp 65001Для смены кодировки на Windows-1251, команда примет следующий вид:
chcp 1251Время чтение: 4 минуты
2014-01-19
Как корректно отобразить Русский текст в CMD. Проблемы с кодировкой могут возникнуть, например, при выполнении Bat файла, когда нужно вывести в консоль русский текст и при других обстоятельствах, о которых речь пойдёт далее.
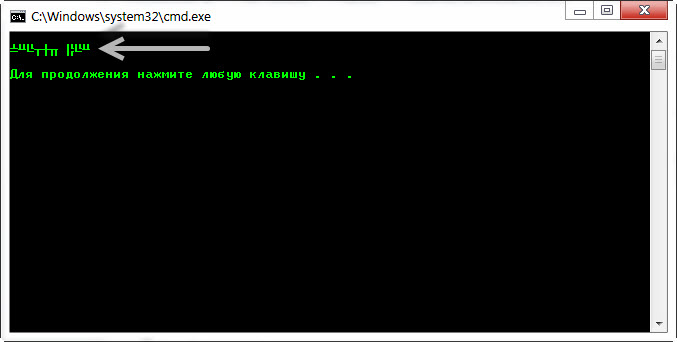
Рассмотрим пример: когда нужно вывести в консоль Русский текст, скажем «Примет мир». Для этого создадим Bat файл с именем «1.bat». Используйте для этого обычный Блокнот Windows (Notepad.exe) Запишем в него следующие строки!
|
@Echo off echo. echo ПРИВЕТ МИР echo. Pause |
Для тех, кто не понял или не в курсе, строчки «echo.» я добавил специально, что бы были отступы, от строки «Примет мир»
Теперь запускаем файл 1.bat и результат будет такого вида.
Как видим проблема с кодировкой в cmd на лицо. И произошло это по следующей причине.
Стандартный блокнот Windows сохранил Bat файл в кодировке «1251» а консоль вывела его в кодировки «866». Вот от сюда все проблемы!
Решения проблемы с кодировкой в CMD. 1 Способ.
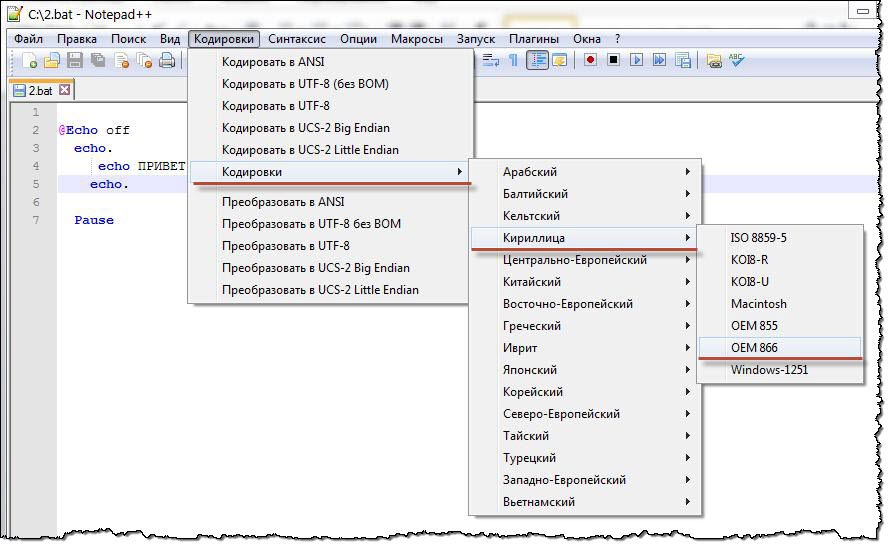
Для решения проблемы нужно просто использовать текстовой редактор, с помощью которого можно сохранить текст в кодировке «866». Для этих целей прекрасно подходит «Notepad++» (Ссылку для загрузки Вы можете найти в моём Twitter-e).
Скачиваем и устанавливаем на свой компьютер «Notepad++».
После запуска «Notepad++» запишете в документ те же строки, которые мы уже ранние записывали в стандартный блокнот.
|
@Echo off echo. echo ПРИВЕТ МИР echo. Pause |
Теперь осталось сохранить документ с именем «2.bat» в правильной кодировке. Для этого идём в меню «Кодировки > Кодировки > Кириллица > OEM-866»
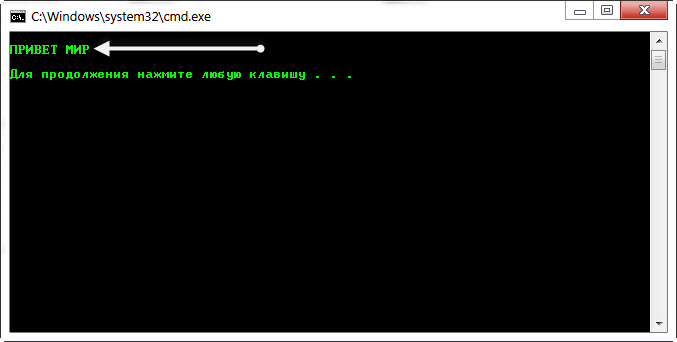
и теперь сохраняем файл с именем «2.bat» и запускаем его! Поле запуска результат на лицо.
Как видим, текст на Русском в CMD отобразился, как положено.
Решения проблемы с кодировкой в CMD. 2 Способ.
Теперь рассмотрим ещё одну ситуацию, когда могут возникнуть проблемы с кодировкой в CMD.
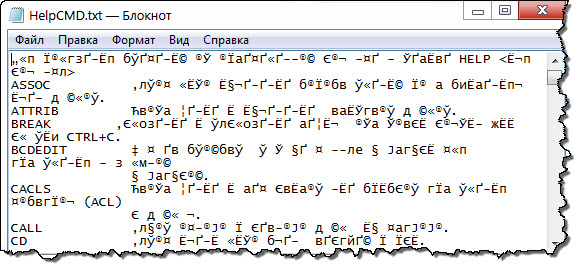
Допустим, ситуация требует сохранить результат выполнения той или иной команды в обычный «TXT» файл. В приделах этого поста возьмём для примера команду «HELP».
Задача: Сохранить справку CMD в файл «HelpCMD.txt. Для этого создайте Bat файл и запишите в него следующие строки.
|
@Echo off Help > C:HelpCMD.txt Pause |
После выполнения Bat файла в корне диска «C:» появится файл «HelpCMD.txt» и вместо справки получится вот что:
Естественно, такой вариант не кому не понравится и что бы сохранить справку в понятном для человека виде, допишите в Bat файл строку.
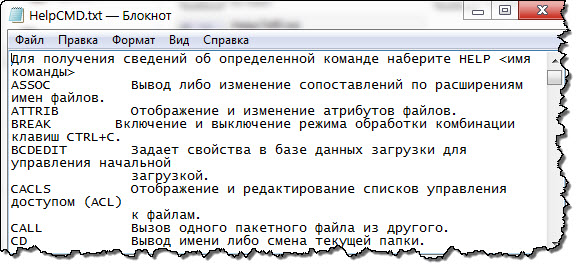
Теперь содержимое кода будет такое.
|
@Echo off chcp 1251 >nul Help > C:HelpCMD.txt Pause |
После выполнения «Батника» результат будет такой:
Вот так на много лучше, правда?
Пожалуй, на этом я закончу пост. Добавить больше нечего. Если у Вас имеются какие-то соображения по данной теме, буду рад Вашему комментарию к посту.
Дополнительно из комментариев то Garric
Автор очень хорошо описал принцип. ! Но это неудобно.
Нужно бы добавить. Если автор добавит это в статью то это будет Good.
Создаём файл .reg следующего содержания:
——
Windows Registry Editor Version 5.00
[HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT.batShellNew]
«FileName»=»BATНастроенная кодировка.bat»
——
Выполняем.
——
Топаем в %SystemRoot%SHELLNEW
Создаём там файл «BATНастроенная кодировка.bat»
Открываем в Notepad++
Вводим любой текст. (нужно!) Сохраняемся.
Удаляем текст. Меняем кодировку как сказано в статье. Сохраняемся.
———-
Щёлкаем правой кнопкой мыши по Рабочему столу. Нажимаем «Создать» — «Пакетный файл Windows».
Переименовываем. Открываем в Notepad++. Пишем батник.
В дальнейшем при работе с файлом не нажимаем ничего кроме как просто «Сохранить». Никаких «Сохранить как».
Yes, it’s frustrating—sometimes type and other programs
print gibberish, and sometimes they do not.
First of all, Unicode characters will only display if the
current console font contains the characters. So use
a TrueType font like Lucida Console instead of the default Raster Font.
But if the console font doesn’t contain the character you’re trying to display,
you’ll see question marks instead of gibberish. When you get gibberish,
there’s more going on than just font settings.
When programs use standard C-library I/O functions like printf, the
program’s output encoding must match the console’s output encoding, or
you will get gibberish. chcp shows and sets the current codepage. All
output using standard C-library I/O functions is treated as if it is in the
codepage displayed by chcp.
Matching the program’s output encoding with the console’s output encoding
can be accomplished in two different ways:
-
A program can get the console’s current codepage using
chcpor
GetConsoleOutputCP, and configure itself to output in that encoding, or -
You or a program can set the console’s current codepage using
chcpor
SetConsoleOutputCPto match the default output encoding of the program.
However, programs that use Win32 APIs can write UTF-16LE strings directly
to the console with
WriteConsoleW.
This is the only way to get correct output without setting codepages. And
even when using that function, if a string is not in the UTF-16LE encoding
to begin with, a Win32 program must pass the correct codepage to
MultiByteToWideChar.
Also, WriteConsoleW will not work if the program’s output is redirected;
more fiddling is needed in that case.
type works some of the time because it checks the start of each file for
a UTF-16LE Byte Order Mark
(BOM), i.e. the bytes 0xFF 0xFE.
If it finds such a
mark, it displays the Unicode characters in the file using WriteConsoleW
regardless of the current codepage. But when typeing any file without a
UTF-16LE BOM, or for using non-ASCII characters with any command
that doesn’t call WriteConsoleW—you will need to set the
console codepage and program output encoding to match each other.
How can we find this out?
Here’s a test file containing Unicode characters:
ASCII abcde xyz
German äöü ÄÖÜ ß
Polish ąęźżńł
Russian абвгдеж эюя
CJK 你好
Here’s a Java program to print out the test file in a bunch of different
Unicode encodings. It could be in any programming language; it only prints
ASCII characters or encoded bytes to stdout.
import java.io.*;
public class Foo {
private static final String BOM = "ufeff";
private static final String TEST_STRING
= "ASCII abcde xyzn"
+ "German äöü ÄÖÜ ßn"
+ "Polish ąęźżńłn"
+ "Russian абвгдеж эюяn"
+ "CJK 你好n";
public static void main(String[] args)
throws Exception
{
String[] encodings = new String[] {
"UTF-8", "UTF-16LE", "UTF-16BE", "UTF-32LE", "UTF-32BE" };
for (String encoding: encodings) {
System.out.println("== " + encoding);
for (boolean writeBom: new Boolean[] {false, true}) {
System.out.println(writeBom ? "= bom" : "= no bom");
String output = (writeBom ? BOM : "") + TEST_STRING;
byte[] bytes = output.getBytes(encoding);
System.out.write(bytes);
FileOutputStream out = new FileOutputStream("uc-test-"
+ encoding + (writeBom ? "-bom.txt" : "-nobom.txt"));
out.write(bytes);
out.close();
}
}
}
}
The output in the default codepage? Total garbage!
Z:andrewprojectssx1259084>chcp
Active code page: 850
Z:andrewprojectssx1259084>java Foo
== UTF-8
= no bom
ASCII abcde xyz
German ├ñ├Â├╝ ├ä├û├£ ├ƒ
Polish ąęźżńł
Russian ð░ð▒ð▓ð│ð┤ðÁð ÐìÐÄÐÅ
CJK õ¢áÕÑ¢
= bom
´╗┐ASCII abcde xyz
German ├ñ├Â├╝ ├ä├û├£ ├ƒ
Polish ąęźżńł
Russian ð░ð▒ð▓ð│ð┤ðÁð ÐìÐÄÐÅ
CJK õ¢áÕÑ¢
== UTF-16LE
= no bom
A S C I I a b c d e x y z
G e r m a n õ ÷ ³ ─ Í ▄ ▀
P o l i s h ♣☺↓☺z☺|☺D☺B☺
R u s s i a n 0♦1♦2♦3♦4♦5♦6♦ M♦N♦O♦
C J K `O}Y
= bom
■A S C I I a b c d e x y z
G e r m a n õ ÷ ³ ─ Í ▄ ▀
P o l i s h ♣☺↓☺z☺|☺D☺B☺
R u s s i a n 0♦1♦2♦3♦4♦5♦6♦ M♦N♦O♦
C J K `O}Y
== UTF-16BE
= no bom
A S C I I a b c d e x y z
G e r m a n õ ÷ ³ ─ Í ▄ ▀
P o l i s h ☺♣☺↓☺z☺|☺D☺B
R u s s i a n ♦0♦1♦2♦3♦4♦5♦6 ♦M♦N♦O
C J K O`Y}
= bom
■ A S C I I a b c d e x y z
G e r m a n õ ÷ ³ ─ Í ▄ ▀
P o l i s h ☺♣☺↓☺z☺|☺D☺B
R u s s i a n ♦0♦1♦2♦3♦4♦5♦6 ♦M♦N♦O
C J K O`Y}
== UTF-32LE
= no bom
A S C I I a b c d e x y z
G e r m a n õ ÷ ³ ─ Í ▄ ▀
P o l i s h ♣☺ ↓☺ z☺ |☺ D☺ B☺
R u s s i a n 0♦ 1♦ 2♦ 3♦ 4♦ 5♦ 6♦ M♦ N
♦ O♦
C J K `O }Y
= bom
■ A S C I I a b c d e x y z
G e r m a n õ ÷ ³ ─ Í ▄ ▀
P o l i s h ♣☺ ↓☺ z☺ |☺ D☺ B☺
R u s s i a n 0♦ 1♦ 2♦ 3♦ 4♦ 5♦ 6♦ M♦ N
♦ O♦
C J K `O }Y
== UTF-32BE
= no bom
A S C I I a b c d e x y z
G e r m a n õ ÷ ³ ─ Í ▄ ▀
P o l i s h ☺♣ ☺↓ ☺z ☺| ☺D ☺B
R u s s i a n ♦0 ♦1 ♦2 ♦3 ♦4 ♦5 ♦6 ♦M ♦N
♦O
C J K O` Y}
= bom
■ A S C I I a b c d e x y z
G e r m a n õ ÷ ³ ─ Í ▄ ▀
P o l i s h ☺♣ ☺↓ ☺z ☺| ☺D ☺B
R u s s i a n ♦0 ♦1 ♦2 ♦3 ♦4 ♦5 ♦6 ♦M ♦N
♦O
C J K O` Y}
However, what if we type the files that got saved? They contain the exact
same bytes that were printed to the console.
Z:andrewprojectssx1259084>type *.txt
uc-test-UTF-16BE-bom.txt
■ A S C I I a b c d e x y z
G e r m a n õ ÷ ³ ─ Í ▄ ▀
P o l i s h ☺♣☺↓☺z☺|☺D☺B
R u s s i a n ♦0♦1♦2♦3♦4♦5♦6 ♦M♦N♦O
C J K O`Y}
uc-test-UTF-16BE-nobom.txt
A S C I I a b c d e x y z
G e r m a n õ ÷ ³ ─ Í ▄ ▀
P o l i s h ☺♣☺↓☺z☺|☺D☺B
R u s s i a n ♦0♦1♦2♦3♦4♦5♦6 ♦M♦N♦O
C J K O`Y}
uc-test-UTF-16LE-bom.txt
ASCII abcde xyz
German äöü ÄÖÜ ß
Polish ąęźżńł
Russian абвгдеж эюя
CJK 你好
uc-test-UTF-16LE-nobom.txt
A S C I I a b c d e x y z
G e r m a n õ ÷ ³ ─ Í ▄ ▀
P o l i s h ♣☺↓☺z☺|☺D☺B☺
R u s s i a n 0♦1♦2♦3♦4♦5♦6♦ M♦N♦O♦
C J K `O}Y
uc-test-UTF-32BE-bom.txt
■ A S C I I a b c d e x y z
G e r m a n õ ÷ ³ ─ Í ▄ ▀
P o l i s h ☺♣ ☺↓ ☺z ☺| ☺D ☺B
R u s s i a n ♦0 ♦1 ♦2 ♦3 ♦4 ♦5 ♦6 ♦M ♦N
♦O
C J K O` Y}
uc-test-UTF-32BE-nobom.txt
A S C I I a b c d e x y z
G e r m a n õ ÷ ³ ─ Í ▄ ▀
P o l i s h ☺♣ ☺↓ ☺z ☺| ☺D ☺B
R u s s i a n ♦0 ♦1 ♦2 ♦3 ♦4 ♦5 ♦6 ♦M ♦N
♦O
C J K O` Y}
uc-test-UTF-32LE-bom.txt
A S C I I a b c d e x y z
G e r m a n ä ö ü Ä Ö Ü ß
P o l i s h ą ę ź ż ń ł
R u s s i a n а б в г д е ж э ю я
C J K 你 好
uc-test-UTF-32LE-nobom.txt
A S C I I a b c d e x y z
G e r m a n õ ÷ ³ ─ Í ▄ ▀
P o l i s h ♣☺ ↓☺ z☺ |☺ D☺ B☺
R u s s i a n 0♦ 1♦ 2♦ 3♦ 4♦ 5♦ 6♦ M♦ N
♦ O♦
C J K `O }Y
uc-test-UTF-8-bom.txt
´╗┐ASCII abcde xyz
German ├ñ├Â├╝ ├ä├û├£ ├ƒ
Polish ąęźżńł
Russian ð░ð▒ð▓ð│ð┤ðÁð ÐìÐÄÐÅ
CJK õ¢áÕÑ¢
uc-test-UTF-8-nobom.txt
ASCII abcde xyz
German ├ñ├Â├╝ ├ä├û├£ ├ƒ
Polish ąęźżńł
Russian ð░ð▒ð▓ð│ð┤ðÁð ÐìÐÄÐÅ
CJK õ¢áÕÑ¢
The only thing that works is UTF-16LE file, with a BOM, printed to the
console via type.
If we use anything other than type to print the file, we get garbage:
Z:andrewprojectssx1259084>copy uc-test-UTF-16LE-bom.txt CON
■A S C I I a b c d e x y z
G e r m a n õ ÷ ³ ─ Í ▄ ▀
P o l i s h ♣☺↓☺z☺|☺D☺B☺
R u s s i a n 0♦1♦2♦3♦4♦5♦6♦ M♦N♦O♦
C J K `O}Y
1 file(s) copied.
From the fact that copy CON does not display Unicode correctly, we can
conclude that the type command has logic to detect a UTF-16LE BOM at the
start of the file, and use special Windows APIs to print it.
We can see this by opening cmd.exe in a debugger when it goes to type
out a file:
After type opens a file, it checks for a BOM of 0xFEFF—i.e., the bytes
0xFF 0xFE in little-endian—and if there is such a BOM, type sets an
internal fOutputUnicode flag. This flag is checked later to decide
whether to call WriteConsoleW.
But that’s the only way to get type to output Unicode, and only for files
that have BOMs and are in UTF-16LE. For all other files, and for programs
that don’t have special code to handle console output, your files will be
interpreted according to the current codepage, and will likely show up as
gibberish.
You can emulate how type outputs Unicode to the console in your own programs like so:
#include <stdio.h>
#define UNICODE
#include <windows.h>
static LPCSTR lpcsTest =
"ASCII abcde xyzn"
"German äöü ÄÖÜ ßn"
"Polish ąęźżńłn"
"Russian абвгдеж эюяn"
"CJK 你好n";
int main() {
int n;
wchar_t buf[1024];
HANDLE hConsole = GetStdHandle(STD_OUTPUT_HANDLE);
n = MultiByteToWideChar(CP_UTF8, 0,
lpcsTest, strlen(lpcsTest),
buf, sizeof(buf));
WriteConsole(hConsole, buf, n, &n, NULL);
return 0;
}
This program works for printing Unicode on the Windows console using the
default codepage.
For the sample Java program, we can get a little bit of correct output by
setting the codepage manually, though the output gets messed up in weird ways:
Z:andrewprojectssx1259084>chcp 65001
Active code page: 65001
Z:andrewprojectssx1259084>java Foo
== UTF-8
= no bom
ASCII abcde xyz
German äöü ÄÖÜ ß
Polish ąęźżńł
Russian абвгдеж эюя
CJK 你好
ж эюя
CJK 你好
你好
好
�
= bom
ASCII abcde xyz
German äöü ÄÖÜ ß
Polish ąęźżńł
Russian абвгдеж эюя
CJK 你好
еж эюя
CJK 你好
你好
好
�
== UTF-16LE
= no bom
A S C I I a b c d e x y z
…
However, a C program that sets a Unicode UTF-8 codepage:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <windows.h>
int main() {
int c, n;
UINT oldCodePage;
char buf[1024];
oldCodePage = GetConsoleOutputCP();
if (!SetConsoleOutputCP(65001)) {
printf("errorn");
}
freopen("uc-test-UTF-8-nobom.txt", "rb", stdin);
n = fread(buf, sizeof(buf[0]), sizeof(buf), stdin);
fwrite(buf, sizeof(buf[0]), n, stdout);
SetConsoleOutputCP(oldCodePage);
return 0;
}
does have correct output:
Z:andrewprojectssx1259084>.test
ASCII abcde xyz
German äöü ÄÖÜ ß
Polish ąęźżńł
Russian абвгдеж эюя
CJK 你好
The moral of the story?
typecan print UTF-16LE files with a BOM regardless of your current codepage- Win32 programs can be programmed to output Unicode to the console, using
WriteConsoleW. - Other programs which set the codepage and adjust their output encoding accordingly can print Unicode on the console regardless of what the codepage was when the program started
- For everything else you will have to mess around with
chcp, and will probably still get weird output.
Yes, it’s frustrating—sometimes type and other programs
print gibberish, and sometimes they do not.
First of all, Unicode characters will only display if the
current console font contains the characters. So use
a TrueType font like Lucida Console instead of the default Raster Font.
But if the console font doesn’t contain the character you’re trying to display,
you’ll see question marks instead of gibberish. When you get gibberish,
there’s more going on than just font settings.
When programs use standard C-library I/O functions like printf, the
program’s output encoding must match the console’s output encoding, or
you will get gibberish. chcp shows and sets the current codepage. All
output using standard C-library I/O functions is treated as if it is in the
codepage displayed by chcp.
Matching the program’s output encoding with the console’s output encoding
can be accomplished in two different ways:
-
A program can get the console’s current codepage using
chcpor
GetConsoleOutputCP, and configure itself to output in that encoding, or -
You or a program can set the console’s current codepage using
chcpor
SetConsoleOutputCPto match the default output encoding of the program.
However, programs that use Win32 APIs can write UTF-16LE strings directly
to the console with
WriteConsoleW.
This is the only way to get correct output without setting codepages. And
even when using that function, if a string is not in the UTF-16LE encoding
to begin with, a Win32 program must pass the correct codepage to
MultiByteToWideChar.
Also, WriteConsoleW will not work if the program’s output is redirected;
more fiddling is needed in that case.
type works some of the time because it checks the start of each file for
a UTF-16LE Byte Order Mark
(BOM), i.e. the bytes 0xFF 0xFE.
If it finds such a
mark, it displays the Unicode characters in the file using WriteConsoleW
regardless of the current codepage. But when typeing any file without a
UTF-16LE BOM, or for using non-ASCII characters with any command
that doesn’t call WriteConsoleW—you will need to set the
console codepage and program output encoding to match each other.
How can we find this out?
Here’s a test file containing Unicode characters:
ASCII abcde xyz
German äöü ÄÖÜ ß
Polish ąęźżńł
Russian абвгдеж эюя
CJK 你好
Here’s a Java program to print out the test file in a bunch of different
Unicode encodings. It could be in any programming language; it only prints
ASCII characters or encoded bytes to stdout.
import java.io.*;
public class Foo {
private static final String BOM = "ufeff";
private static final String TEST_STRING
= "ASCII abcde xyzn"
+ "German äöü ÄÖÜ ßn"
+ "Polish ąęźżńłn"
+ "Russian абвгдеж эюяn"
+ "CJK 你好n";
public static void main(String[] args)
throws Exception
{
String[] encodings = new String[] {
"UTF-8", "UTF-16LE", "UTF-16BE", "UTF-32LE", "UTF-32BE" };
for (String encoding: encodings) {
System.out.println("== " + encoding);
for (boolean writeBom: new Boolean[] {false, true}) {
System.out.println(writeBom ? "= bom" : "= no bom");
String output = (writeBom ? BOM : "") + TEST_STRING;
byte[] bytes = output.getBytes(encoding);
System.out.write(bytes);
FileOutputStream out = new FileOutputStream("uc-test-"
+ encoding + (writeBom ? "-bom.txt" : "-nobom.txt"));
out.write(bytes);
out.close();
}
}
}
}
The output in the default codepage? Total garbage!
Z:andrewprojectssx1259084>chcp
Active code page: 850
Z:andrewprojectssx1259084>java Foo
== UTF-8
= no bom
ASCII abcde xyz
German ├ñ├Â├╝ ├ä├û├£ ├ƒ
Polish ąęźżńł
Russian ð░ð▒ð▓ð│ð┤ðÁð ÐìÐÄÐÅ
CJK õ¢áÕÑ¢
= bom
´╗┐ASCII abcde xyz
German ├ñ├Â├╝ ├ä├û├£ ├ƒ
Polish ąęźżńł
Russian ð░ð▒ð▓ð│ð┤ðÁð ÐìÐÄÐÅ
CJK õ¢áÕÑ¢
== UTF-16LE
= no bom
A S C I I a b c d e x y z
G e r m a n õ ÷ ³ ─ Í ▄ ▀
P o l i s h ♣☺↓☺z☺|☺D☺B☺
R u s s i a n 0♦1♦2♦3♦4♦5♦6♦ M♦N♦O♦
C J K `O}Y
= bom
■A S C I I a b c d e x y z
G e r m a n õ ÷ ³ ─ Í ▄ ▀
P o l i s h ♣☺↓☺z☺|☺D☺B☺
R u s s i a n 0♦1♦2♦3♦4♦5♦6♦ M♦N♦O♦
C J K `O}Y
== UTF-16BE
= no bom
A S C I I a b c d e x y z
G e r m a n õ ÷ ³ ─ Í ▄ ▀
P o l i s h ☺♣☺↓☺z☺|☺D☺B
R u s s i a n ♦0♦1♦2♦3♦4♦5♦6 ♦M♦N♦O
C J K O`Y}
= bom
■ A S C I I a b c d e x y z
G e r m a n õ ÷ ³ ─ Í ▄ ▀
P o l i s h ☺♣☺↓☺z☺|☺D☺B
R u s s i a n ♦0♦1♦2♦3♦4♦5♦6 ♦M♦N♦O
C J K O`Y}
== UTF-32LE
= no bom
A S C I I a b c d e x y z
G e r m a n õ ÷ ³ ─ Í ▄ ▀
P o l i s h ♣☺ ↓☺ z☺ |☺ D☺ B☺
R u s s i a n 0♦ 1♦ 2♦ 3♦ 4♦ 5♦ 6♦ M♦ N
♦ O♦
C J K `O }Y
= bom
■ A S C I I a b c d e x y z
G e r m a n õ ÷ ³ ─ Í ▄ ▀
P o l i s h ♣☺ ↓☺ z☺ |☺ D☺ B☺
R u s s i a n 0♦ 1♦ 2♦ 3♦ 4♦ 5♦ 6♦ M♦ N
♦ O♦
C J K `O }Y
== UTF-32BE
= no bom
A S C I I a b c d e x y z
G e r m a n õ ÷ ³ ─ Í ▄ ▀
P o l i s h ☺♣ ☺↓ ☺z ☺| ☺D ☺B
R u s s i a n ♦0 ♦1 ♦2 ♦3 ♦4 ♦5 ♦6 ♦M ♦N
♦O
C J K O` Y}
= bom
■ A S C I I a b c d e x y z
G e r m a n õ ÷ ³ ─ Í ▄ ▀
P o l i s h ☺♣ ☺↓ ☺z ☺| ☺D ☺B
R u s s i a n ♦0 ♦1 ♦2 ♦3 ♦4 ♦5 ♦6 ♦M ♦N
♦O
C J K O` Y}
However, what if we type the files that got saved? They contain the exact
same bytes that were printed to the console.
Z:andrewprojectssx1259084>type *.txt
uc-test-UTF-16BE-bom.txt
■ A S C I I a b c d e x y z
G e r m a n õ ÷ ³ ─ Í ▄ ▀
P o l i s h ☺♣☺↓☺z☺|☺D☺B
R u s s i a n ♦0♦1♦2♦3♦4♦5♦6 ♦M♦N♦O
C J K O`Y}
uc-test-UTF-16BE-nobom.txt
A S C I I a b c d e x y z
G e r m a n õ ÷ ³ ─ Í ▄ ▀
P o l i s h ☺♣☺↓☺z☺|☺D☺B
R u s s i a n ♦0♦1♦2♦3♦4♦5♦6 ♦M♦N♦O
C J K O`Y}
uc-test-UTF-16LE-bom.txt
ASCII abcde xyz
German äöü ÄÖÜ ß
Polish ąęźżńł
Russian абвгдеж эюя
CJK 你好
uc-test-UTF-16LE-nobom.txt
A S C I I a b c d e x y z
G e r m a n õ ÷ ³ ─ Í ▄ ▀
P o l i s h ♣☺↓☺z☺|☺D☺B☺
R u s s i a n 0♦1♦2♦3♦4♦5♦6♦ M♦N♦O♦
C J K `O}Y
uc-test-UTF-32BE-bom.txt
■ A S C I I a b c d e x y z
G e r m a n õ ÷ ³ ─ Í ▄ ▀
P o l i s h ☺♣ ☺↓ ☺z ☺| ☺D ☺B
R u s s i a n ♦0 ♦1 ♦2 ♦3 ♦4 ♦5 ♦6 ♦M ♦N
♦O
C J K O` Y}
uc-test-UTF-32BE-nobom.txt
A S C I I a b c d e x y z
G e r m a n õ ÷ ³ ─ Í ▄ ▀
P o l i s h ☺♣ ☺↓ ☺z ☺| ☺D ☺B
R u s s i a n ♦0 ♦1 ♦2 ♦3 ♦4 ♦5 ♦6 ♦M ♦N
♦O
C J K O` Y}
uc-test-UTF-32LE-bom.txt
A S C I I a b c d e x y z
G e r m a n ä ö ü Ä Ö Ü ß
P o l i s h ą ę ź ż ń ł
R u s s i a n а б в г д е ж э ю я
C J K 你 好
uc-test-UTF-32LE-nobom.txt
A S C I I a b c d e x y z
G e r m a n õ ÷ ³ ─ Í ▄ ▀
P o l i s h ♣☺ ↓☺ z☺ |☺ D☺ B☺
R u s s i a n 0♦ 1♦ 2♦ 3♦ 4♦ 5♦ 6♦ M♦ N
♦ O♦
C J K `O }Y
uc-test-UTF-8-bom.txt
´╗┐ASCII abcde xyz
German ├ñ├Â├╝ ├ä├û├£ ├ƒ
Polish ąęźżńł
Russian ð░ð▒ð▓ð│ð┤ðÁð ÐìÐÄÐÅ
CJK õ¢áÕÑ¢
uc-test-UTF-8-nobom.txt
ASCII abcde xyz
German ├ñ├Â├╝ ├ä├û├£ ├ƒ
Polish ąęźżńł
Russian ð░ð▒ð▓ð│ð┤ðÁð ÐìÐÄÐÅ
CJK õ¢áÕÑ¢
The only thing that works is UTF-16LE file, with a BOM, printed to the
console via type.
If we use anything other than type to print the file, we get garbage:
Z:andrewprojectssx1259084>copy uc-test-UTF-16LE-bom.txt CON
■A S C I I a b c d e x y z
G e r m a n õ ÷ ³ ─ Í ▄ ▀
P o l i s h ♣☺↓☺z☺|☺D☺B☺
R u s s i a n 0♦1♦2♦3♦4♦5♦6♦ M♦N♦O♦
C J K `O}Y
1 file(s) copied.
From the fact that copy CON does not display Unicode correctly, we can
conclude that the type command has logic to detect a UTF-16LE BOM at the
start of the file, and use special Windows APIs to print it.
We can see this by opening cmd.exe in a debugger when it goes to type
out a file:
After type opens a file, it checks for a BOM of 0xFEFF—i.e., the bytes
0xFF 0xFE in little-endian—and if there is such a BOM, type sets an
internal fOutputUnicode flag. This flag is checked later to decide
whether to call WriteConsoleW.
But that’s the only way to get type to output Unicode, and only for files
that have BOMs and are in UTF-16LE. For all other files, and for programs
that don’t have special code to handle console output, your files will be
interpreted according to the current codepage, and will likely show up as
gibberish.
You can emulate how type outputs Unicode to the console in your own programs like so:
#include <stdio.h>
#define UNICODE
#include <windows.h>
static LPCSTR lpcsTest =
"ASCII abcde xyzn"
"German äöü ÄÖÜ ßn"
"Polish ąęźżńłn"
"Russian абвгдеж эюяn"
"CJK 你好n";
int main() {
int n;
wchar_t buf[1024];
HANDLE hConsole = GetStdHandle(STD_OUTPUT_HANDLE);
n = MultiByteToWideChar(CP_UTF8, 0,
lpcsTest, strlen(lpcsTest),
buf, sizeof(buf));
WriteConsole(hConsole, buf, n, &n, NULL);
return 0;
}
This program works for printing Unicode on the Windows console using the
default codepage.
For the sample Java program, we can get a little bit of correct output by
setting the codepage manually, though the output gets messed up in weird ways:
Z:andrewprojectssx1259084>chcp 65001
Active code page: 65001
Z:andrewprojectssx1259084>java Foo
== UTF-8
= no bom
ASCII abcde xyz
German äöü ÄÖÜ ß
Polish ąęźżńł
Russian абвгдеж эюя
CJK 你好
ж эюя
CJK 你好
你好
好
�
= bom
ASCII abcde xyz
German äöü ÄÖÜ ß
Polish ąęźżńł
Russian абвгдеж эюя
CJK 你好
еж эюя
CJK 你好
你好
好
�
== UTF-16LE
= no bom
A S C I I a b c d e x y z
…
However, a C program that sets a Unicode UTF-8 codepage:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <windows.h>
int main() {
int c, n;
UINT oldCodePage;
char buf[1024];
oldCodePage = GetConsoleOutputCP();
if (!SetConsoleOutputCP(65001)) {
printf("errorn");
}
freopen("uc-test-UTF-8-nobom.txt", "rb", stdin);
n = fread(buf, sizeof(buf[0]), sizeof(buf), stdin);
fwrite(buf, sizeof(buf[0]), n, stdout);
SetConsoleOutputCP(oldCodePage);
return 0;
}
does have correct output:
Z:andrewprojectssx1259084>.test
ASCII abcde xyz
German äöü ÄÖÜ ß
Polish ąęźżńł
Russian абвгдеж эюя
CJK 你好
The moral of the story?
typecan print UTF-16LE files with a BOM regardless of your current codepage- Win32 programs can be programmed to output Unicode to the console, using
WriteConsoleW. - Other programs which set the codepage and adjust their output encoding accordingly can print Unicode on the console regardless of what the codepage was when the program started
- For everything else you will have to mess around with
chcp, and will probably still get weird output.
Yes, it’s frustrating—sometimes type and other programs
print gibberish, and sometimes they do not.
First of all, Unicode characters will only display if the
current console font contains the characters. So use
a TrueType font like Lucida Console instead of the default Raster Font.
But if the console font doesn’t contain the character you’re trying to display,
you’ll see question marks instead of gibberish. When you get gibberish,
there’s more going on than just font settings.
When programs use standard C-library I/O functions like printf, the
program’s output encoding must match the console’s output encoding, or
you will get gibberish. chcp shows and sets the current codepage. All
output using standard C-library I/O functions is treated as if it is in the
codepage displayed by chcp.
Matching the program’s output encoding with the console’s output encoding
can be accomplished in two different ways:
-
A program can get the console’s current codepage using
chcpor
GetConsoleOutputCP, and configure itself to output in that encoding, or -
You or a program can set the console’s current codepage using
chcpor
SetConsoleOutputCPto match the default output encoding of the program.
However, programs that use Win32 APIs can write UTF-16LE strings directly
to the console with
WriteConsoleW.
This is the only way to get correct output without setting codepages. And
even when using that function, if a string is not in the UTF-16LE encoding
to begin with, a Win32 program must pass the correct codepage to
MultiByteToWideChar.
Also, WriteConsoleW will not work if the program’s output is redirected;
more fiddling is needed in that case.
type works some of the time because it checks the start of each file for
a UTF-16LE Byte Order Mark
(BOM), i.e. the bytes 0xFF 0xFE.
If it finds such a
mark, it displays the Unicode characters in the file using WriteConsoleW
regardless of the current codepage. But when typeing any file without a
UTF-16LE BOM, or for using non-ASCII characters with any command
that doesn’t call WriteConsoleW—you will need to set the
console codepage and program output encoding to match each other.
How can we find this out?
Here’s a test file containing Unicode characters:
ASCII abcde xyz
German äöü ÄÖÜ ß
Polish ąęźżńł
Russian абвгдеж эюя
CJK 你好
Here’s a Java program to print out the test file in a bunch of different
Unicode encodings. It could be in any programming language; it only prints
ASCII characters or encoded bytes to stdout.
import java.io.*;
public class Foo {
private static final String BOM = "ufeff";
private static final String TEST_STRING
= "ASCII abcde xyzn"
+ "German äöü ÄÖÜ ßn"
+ "Polish ąęźżńłn"
+ "Russian абвгдеж эюяn"
+ "CJK 你好n";
public static void main(String[] args)
throws Exception
{
String[] encodings = new String[] {
"UTF-8", "UTF-16LE", "UTF-16BE", "UTF-32LE", "UTF-32BE" };
for (String encoding: encodings) {
System.out.println("== " + encoding);
for (boolean writeBom: new Boolean[] {false, true}) {
System.out.println(writeBom ? "= bom" : "= no bom");
String output = (writeBom ? BOM : "") + TEST_STRING;
byte[] bytes = output.getBytes(encoding);
System.out.write(bytes);
FileOutputStream out = new FileOutputStream("uc-test-"
+ encoding + (writeBom ? "-bom.txt" : "-nobom.txt"));
out.write(bytes);
out.close();
}
}
}
}
The output in the default codepage? Total garbage!
Z:andrewprojectssx1259084>chcp
Active code page: 850
Z:andrewprojectssx1259084>java Foo
== UTF-8
= no bom
ASCII abcde xyz
German ├ñ├Â├╝ ├ä├û├£ ├ƒ
Polish ąęźżńł
Russian ð░ð▒ð▓ð│ð┤ðÁð ÐìÐÄÐÅ
CJK õ¢áÕÑ¢
= bom
´╗┐ASCII abcde xyz
German ├ñ├Â├╝ ├ä├û├£ ├ƒ
Polish ąęźżńł
Russian ð░ð▒ð▓ð│ð┤ðÁð ÐìÐÄÐÅ
CJK õ¢áÕÑ¢
== UTF-16LE
= no bom
A S C I I a b c d e x y z
G e r m a n õ ÷ ³ ─ Í ▄ ▀
P o l i s h ♣☺↓☺z☺|☺D☺B☺
R u s s i a n 0♦1♦2♦3♦4♦5♦6♦ M♦N♦O♦
C J K `O}Y
= bom
■A S C I I a b c d e x y z
G e r m a n õ ÷ ³ ─ Í ▄ ▀
P o l i s h ♣☺↓☺z☺|☺D☺B☺
R u s s i a n 0♦1♦2♦3♦4♦5♦6♦ M♦N♦O♦
C J K `O}Y
== UTF-16BE
= no bom
A S C I I a b c d e x y z
G e r m a n õ ÷ ³ ─ Í ▄ ▀
P o l i s h ☺♣☺↓☺z☺|☺D☺B
R u s s i a n ♦0♦1♦2♦3♦4♦5♦6 ♦M♦N♦O
C J K O`Y}
= bom
■ A S C I I a b c d e x y z
G e r m a n õ ÷ ³ ─ Í ▄ ▀
P o l i s h ☺♣☺↓☺z☺|☺D☺B
R u s s i a n ♦0♦1♦2♦3♦4♦5♦6 ♦M♦N♦O
C J K O`Y}
== UTF-32LE
= no bom
A S C I I a b c d e x y z
G e r m a n õ ÷ ³ ─ Í ▄ ▀
P o l i s h ♣☺ ↓☺ z☺ |☺ D☺ B☺
R u s s i a n 0♦ 1♦ 2♦ 3♦ 4♦ 5♦ 6♦ M♦ N
♦ O♦
C J K `O }Y
= bom
■ A S C I I a b c d e x y z
G e r m a n õ ÷ ³ ─ Í ▄ ▀
P o l i s h ♣☺ ↓☺ z☺ |☺ D☺ B☺
R u s s i a n 0♦ 1♦ 2♦ 3♦ 4♦ 5♦ 6♦ M♦ N
♦ O♦
C J K `O }Y
== UTF-32BE
= no bom
A S C I I a b c d e x y z
G e r m a n õ ÷ ³ ─ Í ▄ ▀
P o l i s h ☺♣ ☺↓ ☺z ☺| ☺D ☺B
R u s s i a n ♦0 ♦1 ♦2 ♦3 ♦4 ♦5 ♦6 ♦M ♦N
♦O
C J K O` Y}
= bom
■ A S C I I a b c d e x y z
G e r m a n õ ÷ ³ ─ Í ▄ ▀
P o l i s h ☺♣ ☺↓ ☺z ☺| ☺D ☺B
R u s s i a n ♦0 ♦1 ♦2 ♦3 ♦4 ♦5 ♦6 ♦M ♦N
♦O
C J K O` Y}
However, what if we type the files that got saved? They contain the exact
same bytes that were printed to the console.
Z:andrewprojectssx1259084>type *.txt
uc-test-UTF-16BE-bom.txt
■ A S C I I a b c d e x y z
G e r m a n õ ÷ ³ ─ Í ▄ ▀
P o l i s h ☺♣☺↓☺z☺|☺D☺B
R u s s i a n ♦0♦1♦2♦3♦4♦5♦6 ♦M♦N♦O
C J K O`Y}
uc-test-UTF-16BE-nobom.txt
A S C I I a b c d e x y z
G e r m a n õ ÷ ³ ─ Í ▄ ▀
P o l i s h ☺♣☺↓☺z☺|☺D☺B
R u s s i a n ♦0♦1♦2♦3♦4♦5♦6 ♦M♦N♦O
C J K O`Y}
uc-test-UTF-16LE-bom.txt
ASCII abcde xyz
German äöü ÄÖÜ ß
Polish ąęźżńł
Russian абвгдеж эюя
CJK 你好
uc-test-UTF-16LE-nobom.txt
A S C I I a b c d e x y z
G e r m a n õ ÷ ³ ─ Í ▄ ▀
P o l i s h ♣☺↓☺z☺|☺D☺B☺
R u s s i a n 0♦1♦2♦3♦4♦5♦6♦ M♦N♦O♦
C J K `O}Y
uc-test-UTF-32BE-bom.txt
■ A S C I I a b c d e x y z
G e r m a n õ ÷ ³ ─ Í ▄ ▀
P o l i s h ☺♣ ☺↓ ☺z ☺| ☺D ☺B
R u s s i a n ♦0 ♦1 ♦2 ♦3 ♦4 ♦5 ♦6 ♦M ♦N
♦O
C J K O` Y}
uc-test-UTF-32BE-nobom.txt
A S C I I a b c d e x y z
G e r m a n õ ÷ ³ ─ Í ▄ ▀
P o l i s h ☺♣ ☺↓ ☺z ☺| ☺D ☺B
R u s s i a n ♦0 ♦1 ♦2 ♦3 ♦4 ♦5 ♦6 ♦M ♦N
♦O
C J K O` Y}
uc-test-UTF-32LE-bom.txt
A S C I I a b c d e x y z
G e r m a n ä ö ü Ä Ö Ü ß
P o l i s h ą ę ź ż ń ł
R u s s i a n а б в г д е ж э ю я
C J K 你 好
uc-test-UTF-32LE-nobom.txt
A S C I I a b c d e x y z
G e r m a n õ ÷ ³ ─ Í ▄ ▀
P o l i s h ♣☺ ↓☺ z☺ |☺ D☺ B☺
R u s s i a n 0♦ 1♦ 2♦ 3♦ 4♦ 5♦ 6♦ M♦ N
♦ O♦
C J K `O }Y
uc-test-UTF-8-bom.txt
´╗┐ASCII abcde xyz
German ├ñ├Â├╝ ├ä├û├£ ├ƒ
Polish ąęźżńł
Russian ð░ð▒ð▓ð│ð┤ðÁð ÐìÐÄÐÅ
CJK õ¢áÕÑ¢
uc-test-UTF-8-nobom.txt
ASCII abcde xyz
German ├ñ├Â├╝ ├ä├û├£ ├ƒ
Polish ąęźżńł
Russian ð░ð▒ð▓ð│ð┤ðÁð ÐìÐÄÐÅ
CJK õ¢áÕÑ¢
The only thing that works is UTF-16LE file, with a BOM, printed to the
console via type.
If we use anything other than type to print the file, we get garbage:
Z:andrewprojectssx1259084>copy uc-test-UTF-16LE-bom.txt CON
■A S C I I a b c d e x y z
G e r m a n õ ÷ ³ ─ Í ▄ ▀
P o l i s h ♣☺↓☺z☺|☺D☺B☺
R u s s i a n 0♦1♦2♦3♦4♦5♦6♦ M♦N♦O♦
C J K `O}Y
1 file(s) copied.
From the fact that copy CON does not display Unicode correctly, we can
conclude that the type command has logic to detect a UTF-16LE BOM at the
start of the file, and use special Windows APIs to print it.
We can see this by opening cmd.exe in a debugger when it goes to type
out a file:
After type opens a file, it checks for a BOM of 0xFEFF—i.e., the bytes
0xFF 0xFE in little-endian—and if there is such a BOM, type sets an
internal fOutputUnicode flag. This flag is checked later to decide
whether to call WriteConsoleW.
But that’s the only way to get type to output Unicode, and only for files
that have BOMs and are in UTF-16LE. For all other files, and for programs
that don’t have special code to handle console output, your files will be
interpreted according to the current codepage, and will likely show up as
gibberish.
You can emulate how type outputs Unicode to the console in your own programs like so:
#include <stdio.h>
#define UNICODE
#include <windows.h>
static LPCSTR lpcsTest =
"ASCII abcde xyzn"
"German äöü ÄÖÜ ßn"
"Polish ąęźżńłn"
"Russian абвгдеж эюяn"
"CJK 你好n";
int main() {
int n;
wchar_t buf[1024];
HANDLE hConsole = GetStdHandle(STD_OUTPUT_HANDLE);
n = MultiByteToWideChar(CP_UTF8, 0,
lpcsTest, strlen(lpcsTest),
buf, sizeof(buf));
WriteConsole(hConsole, buf, n, &n, NULL);
return 0;
}
This program works for printing Unicode on the Windows console using the
default codepage.
For the sample Java program, we can get a little bit of correct output by
setting the codepage manually, though the output gets messed up in weird ways:
Z:andrewprojectssx1259084>chcp 65001
Active code page: 65001
Z:andrewprojectssx1259084>java Foo
== UTF-8
= no bom
ASCII abcde xyz
German äöü ÄÖÜ ß
Polish ąęźżńł
Russian абвгдеж эюя
CJK 你好
ж эюя
CJK 你好
你好
好
�
= bom
ASCII abcde xyz
German äöü ÄÖÜ ß
Polish ąęźżńł
Russian абвгдеж эюя
CJK 你好
еж эюя
CJK 你好
你好
好
�
== UTF-16LE
= no bom
A S C I I a b c d e x y z
…
However, a C program that sets a Unicode UTF-8 codepage:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <windows.h>
int main() {
int c, n;
UINT oldCodePage;
char buf[1024];
oldCodePage = GetConsoleOutputCP();
if (!SetConsoleOutputCP(65001)) {
printf("errorn");
}
freopen("uc-test-UTF-8-nobom.txt", "rb", stdin);
n = fread(buf, sizeof(buf[0]), sizeof(buf), stdin);
fwrite(buf, sizeof(buf[0]), n, stdout);
SetConsoleOutputCP(oldCodePage);
return 0;
}
does have correct output:
Z:andrewprojectssx1259084>.test
ASCII abcde xyz
German äöü ÄÖÜ ß
Polish ąęźżńł
Russian абвгдеж эюя
CJK 你好
The moral of the story?
typecan print UTF-16LE files with a BOM regardless of your current codepage- Win32 programs can be programmed to output Unicode to the console, using
WriteConsoleW. - Other programs which set the codepage and adjust their output encoding accordingly can print Unicode on the console regardless of what the codepage was when the program started
- For everything else you will have to mess around with
chcp, and will probably still get weird output.
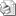
Добавил(а) microsin
Иногда по неизвестным причинам некоторые команды русскоязычной версии Windows выводят русский текст в нечитаемой кодировке, кракозябрами.
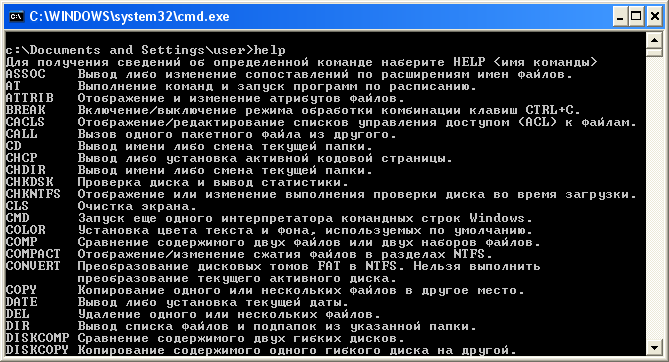
Например, команда help выводит нормальный текст:
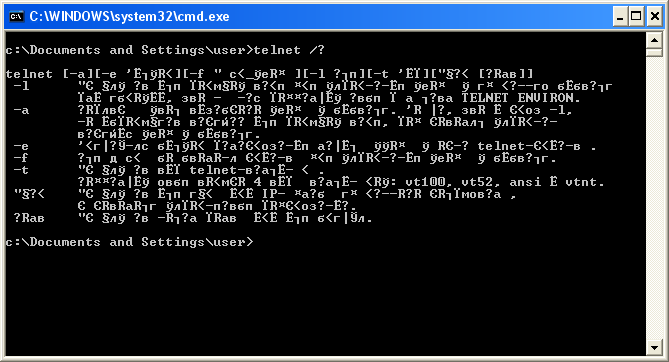
Но при этом подсказка telnet выводит в ответ кракозябры.
Так может происходить, к примеру, если текущая кодировка консоли 866, а утилита telnet.exe почему-то выводит текст в кодировке 1251. Вывести текст в нужной кодировке поможет команда chcp, которая устанавливает нужную кодировку.
Вот так можно посмотреть текущую кодировку консоли:
c:Documents and Settingsuser>chcp Текущая кодовая страница: 866 c:Documents and Settingsuser>
А вот так можно поменять кодировку на 1251, после чего вывод подсказки telnet будет отображаться нормально:
c:Documents and Settingsuser>chcp 1251 Текущая кодовая страница: 1251 c:Documents and Settingsuser>
К сожалению, заранее угадать, в какой кодировке выводится текст, невозможно, поэтому проще попробовать установить командой chcp разные кодировки, чтобы добиться правильного отображения русского текста. Обычно используются кодировки 866 (кодировка русского текста DOS), 1251 (кодировка русского текста Windows), 65001 (UTF-8).
[Шрифт cmd.exe]
Иногда кракозябры можно убрать, если выбрать в свойствах окна cmd.exe шрифт Lucida Console (по умолчанию там стоит «Точечные шрифты»).
[Ссылки]
1. Универсальный декодер — конвертер кириллицы.
Currently I’m running Windows 7 x64 and usually I want all console tools to work with UTF-8 rather than with default code page 850.
Running chcp 65001 in the command prompt prior to use of any tools helps but is there any way to set is as default code page?
Update:
Changing HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINESYSTEMCurrentControlSetControlNlsCodePageOEMCP value to 65001 appear to make the system unable to boot in my case.
Proposed change of HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINESoftwareMicrosoftCommand ProcessorAutorun to @chcp 65001>nul served just well for my purpose. (thanks to Ole_Brun)
asked Apr 12, 2011 at 10:42
7
To change the codepage for the console only, do the following:
- Start -> Run -> regedit
- Go to
[HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINESoftwareMicrosoftCommand ProcessorAutorun] - Change the value to
@chcp 65001>nul
If Autorun is not present, you can add a New String
Nabi K.A.Z.
3801 gold badge5 silver badges10 bronze badges
answered Apr 12, 2011 at 12:22
Nils Magne LundeNils Magne Lunde
2,5421 gold badge16 silver badges14 bronze badges
11
Personally, I don’t like changing the registry. This can cause a lot of problems. I created a batch file:
@ECHO OFF
REM change CHCP to UTF-8
CHCP 65001
CLS
I saved at C:WindowsSystem32 as switch.bat and created a link for cmd.exe on the Desktop.
In the properties of the cmd shortcut, changed the destination to: C:WindowsSystem32cmd.exe /k switch
Voilà, when I need to type in UTF-8, I use this link.
answered Dec 7, 2013 at 15:36
jucajuca
6095 silver badges2 bronze badges
5
In the 1809 build of Windows 10 I’ve managed to permanently solve this by going to the system’s Language settings, selecting Administrative language settings, clicking Change system locale... and checking the Beta: Use Unicode UTF-8 for worldwide language support box and then restarting my pc.
This way it applies to all applications, even those ones that I don’t start from a command prompt!
(Which was necessary for me, since I was trying to edit Agda code from Atom.)
Bob Stein
1,3371 gold badge16 silver badges23 bronze badges
answered May 11, 2019 at 14:44
Isti115Isti115
89410 silver badges11 bronze badges
7
Edit the Registry:
Windows Registry Editor Version 5.00
[HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINESYSTEMCurrentControlSetControlNlsCodePage]
"OEMCP"="65001"
Then restart. With this fix, if you are using Consolas font, it seems to lock
PowerShell into a small font size. cmd.exe still works fine. As a workaround,
you can use Lucida Console, or I switched to Cascadia Mono:
https://github.com/microsoft/cascadia-code
answered Jun 13, 2015 at 20:39
1
This can be done by creating a PowerShell profile and adding the command «chcp 65001 >$null» to it:
PS> Set-ExecutionPolicy RemoteSigned
PS> New-Item -Path $Profile -ItemType file -Force
PS> notepad $Profile
This doesn’t require editing the registry and, unlike editing a shortcut, will work if PowerShell is started in a specific folder using the Windows Explorer context menu.
answered Sep 3, 2017 at 20:56
0
The command to change the codepage is chcp <codepage>. Example: chcp 1252. You should type it in a Powershell window.
To avoid the hassle of typing it everytime (if you always have to change the codepage), you may append it to the program’s command line. To do so, follow these steps:
- Right-click the Powershell icon on Start menu and choose «More» > «Open file Location».
- Right-click the Powershell shortcut and select «Properties».
- Add the following to the end of the «Target» command line:
-NoExit -Command "chcp 1252"
Be happy.
Don’t fuss with Windows Registry unless you have no other option.
answered Nov 2, 2016 at 21:11
JColaresJColares
591 silver badge1 bronze badge
1
Open in Powershell through Explorer still didn’t work for me even though I’ve tried enabling that Beta Unicode feature in the language settings.
However, I’ve just found this worked.
[HKEY_CURRENT_USERConsole%SystemRoot%_System32_WindowsPowerShell_v1.0_powershell.exe]
"CodePage"=dword:0000fde9
From: https://www.zhihu.com/question/54724102
answered Feb 15, 2021 at 11:09
If you’re using ConEmu then:
- Open up Settings from the upper right menu
- Go to Startup -> Environment
- Add
chcp 65001on a new line. - Click «Save Settings».
- Close ConEmu and re-open it
answered May 4, 2020 at 1:22
Instead of changing the registry, you can instead create %HOMEPATH%init.cmd.
Mine reads:
@ECHO OFF
CHCP 65001 > nul
answered Jan 21 at 9:39