Обновлено 04.04.2022
Добрый день уважаемые читатели, сегодня статья опять посвящена десятке, как вы помните с ее релиза уже прошло почти полтора года, и количество глюков связанных с новыми обновлениями, которые клепают сотрудники Microsoft, только растет и людей которые раньше с радостью переходили с 7 или 8 на свежую операционную систему, при этом хая старые версии, вынуждены признать, что десятка далека от идеала и переходят обратно на привычные себе ос. Сегодня мы с вами разберем вопрос как запретить обновления Windows 10, я конечно за установку обновлений безопасности, но например бывают случаи когда их установка только во вред, и требует обновления по верх нового обновления, которые выходят ой как не сразу.
Почему я могу выключить автоматическое обновление Windows 10 и выше
- В виду санкций, которые наложены на РФ, есть опасение, что в новом обновлении будет некая диверсия, с такой ситуацией уже столкнулись многие пользователи и администраторы, кто использует открытое программное обеспечение. Где после очередного обновления у людей ломалась система, или были всплывающие окна с некими призывами.
- Новое обновление принесло мне синий экран смерти, примером может служить синий экран whea uncorrectable error, согласитесь не очень круто когда закрывая очередной глюк MS вам создает другой
- Не работает какое либо из устройств, примерами могут служить случаи, что после обновления windows 10 не работает камера или Не работает звук на windows 10, я думаю у любого человека сразу отпадет желание, что либо обновлять, особенно у клиентов, зачем лишний геморрой.
- Перестали работать игры или программы, у моего приятеля например есть крутая мышка и например в anniversary update специальная утилита под нее работала, а уже в redstone не работает, а про игры я вообще молчу, особенно у тех людей кто привык ставить крякнутые версии.
Так, что как видите причин не любить десятку и запрещать ее обновления у народа есть.
Какие службы отвечают за обновление в Windows
Прежде, чем я вам покажу все методы, я хочу, чтобы у вас было больше знаний по устройству Windows, а именно я покажу, какие именно службы отвечают за весь процесс скачивания и установки обновлений:
- Центр обновления Windows (Wuauserv)
- dosvc
- WaaSMedicSvc
- Служба оркестратора обновления для Центра обновления Windows (UsoSvc)
- Фоновая интеллектуальная служба передачи (BITS)
Как отключить обновления Windows через Windows Update Blocker
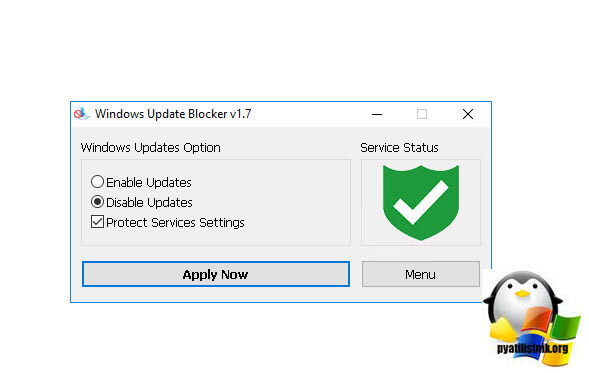
Да есть программа запрещающая обновление windows 10, Windows 11 и Windows Server, я если честно не сторонник таких вещей, если все можно реализовать штатными и встроенными средствами самой операционной системы, НО для пользователя это про чем правка реестра или манипуляции с редактором политик. Что вам необходимо, это скачать портативную версию данной утилиты, она полностью бесплатная.
Данный метод будет очень полезен для пользователей операционных систем Windows 11 «Домашняя (Home)» и Windows 10 «Домашняя (Home)»
Далее вы просто запускаете Wub_x64.exe. Все, что от вас требуется, это нажать на пункт «Disable Updates» и удостовериться, что проставилась галка «Protect Services Settings«. Как только это выполнено, смело нажимайте кнопку «Apply Now«.
Вы увидите, что статус службы стал красным, это будет означать, что вы полностью отключили обновление Windows 10 навсегда, как бы пафосно это не звучало.

Как отключить обновления Windows 10 (Выше) через реестр (Без отключения служб Windows)
Данный метод актуален на текущий момент апрель 2022 года, я протестировал его и на Windows 10 и на Windows 11. Хоть я и не сторонник того, чтобы люди лезли в реестр Windows, когда это можно обойти ,но плюс у данного метода, то что вы делаете свою систему сервером обновления, по сути он сам у себя будет их запрашивать. Так же вам не потребуется играться с автозапуском служб, редактировать на них права или запускать сторонний софт.
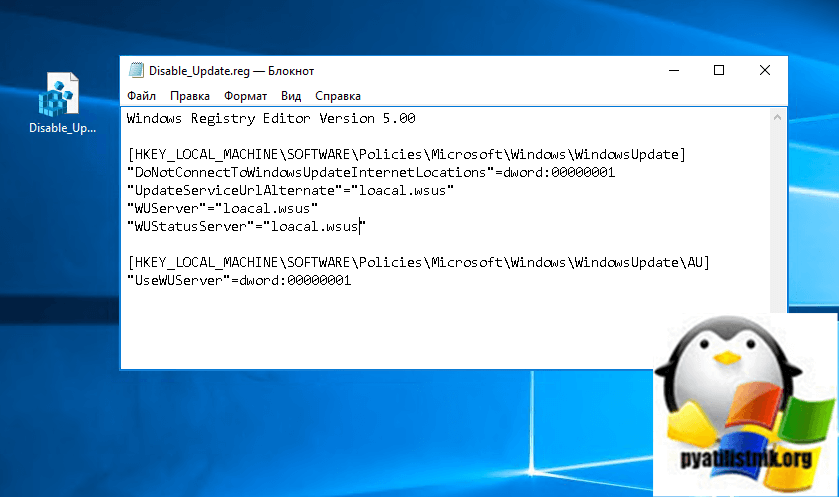
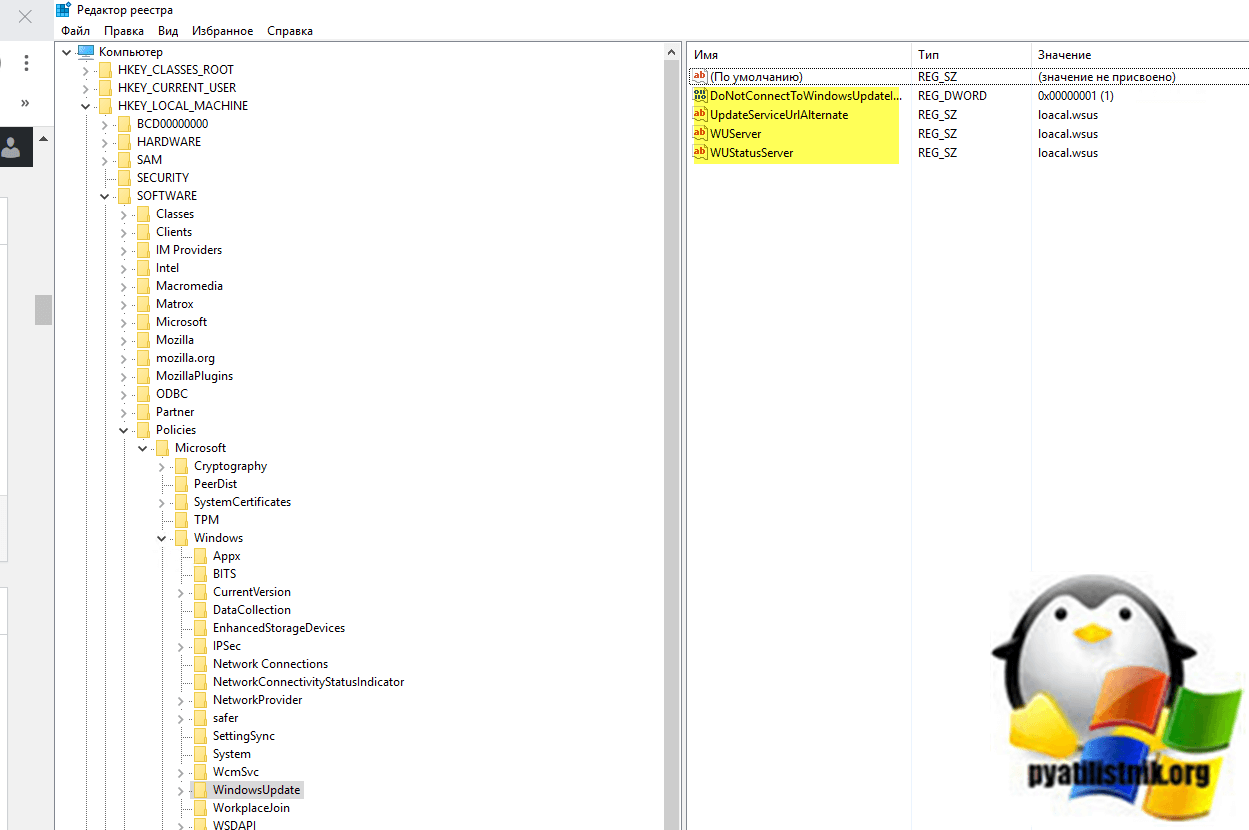
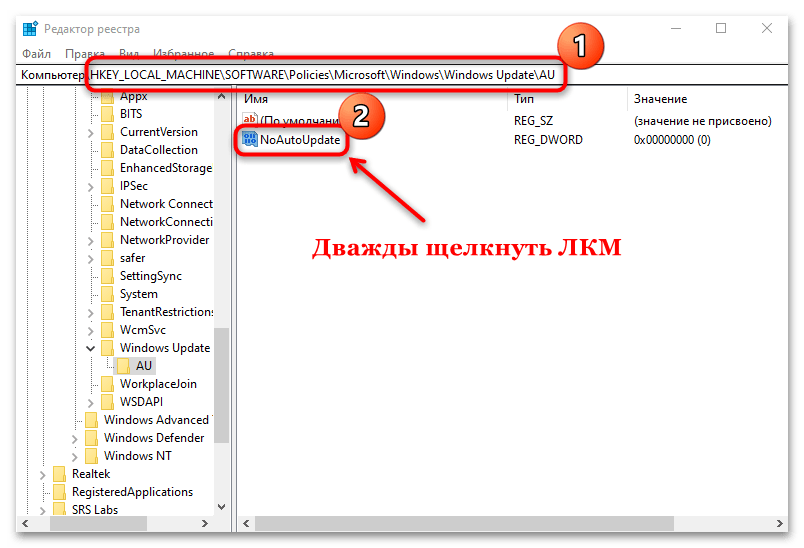
Чтобы отключить обновления Windows 10 этим методом, вам необходимо через текстовый редактор создать reg-файл, в котором будут меняться ключи реестра. Просто откройте блокнот Windows, вставьте в него текст, сохраните файл и отредактируйте его расширение с txt на reg.
Windows Registry Editor Version 5.00
[HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINESOFTWAREPoliciesMicrosoft WindowsWindowsUpdate]
«DoNotConnectToWindowsUpdateInternetLocations»=dword:00000001
«UpdateServiceUrlAlternate»=»loacal.wsus»
«WUServer»=»loacal.wsus»
«WUStatusServer»=»loacal.wsus»
[HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINESOFTWAREPoliciesMicrosoft WindowsWindowsUpdateAU]
«UseWUServer»=dword:00000001
Скачать готовый eg-файл по запрету обновлений Windows
Запускаем его и соглашаемся с применением изменений вносимых в реестр.
В результате у вас в разделе реестра «HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINESOFTWAREPoliciesMicrosoft WindowsWindowsUpdate» появятся 4 ключа.
Чтобы откатить все запретные действия, просто удалите эти 4 ключа реестра:
- DoNotConnectToWindowsUpdateInternetLocations
- UpdateServiceUrlAlternate
- WUServer
- WUStatusServer
Из раздела реестра HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINESOFTWAREPoliciesMicrosoft WindowsWindowsUpdateAU удалите параметр UseWUServer. При попытке установить обновление вы получите ошибку:
Нам не удалось подключиться к службе обновления. Мы повторим попытку позже. Кроме того, вы можете проверить наличие обновлений сейчас. Если это завершится неудачей, убедитесь, что вы подключены к Интернету.
Как отключить обновления Windows через групповую политику (Массово)
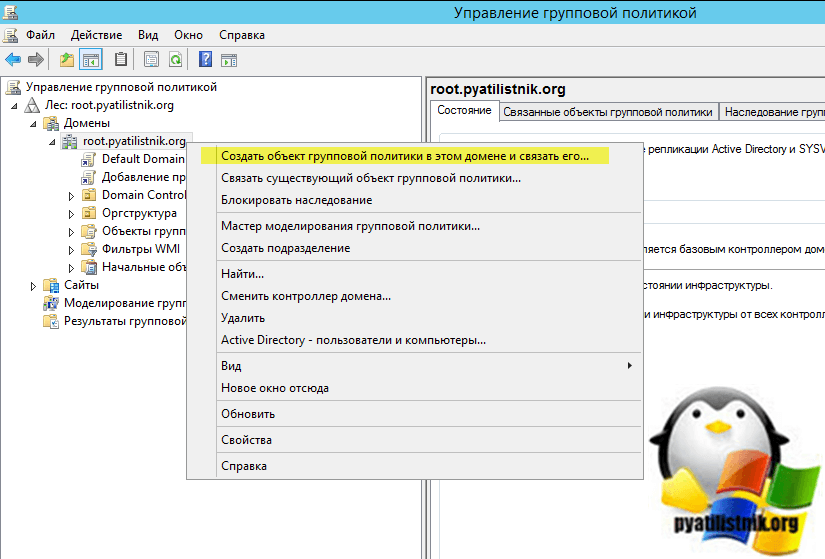
Когда мы говорим, о корпоративных средах, то там все действия желательно делать централизовано на всех сразу, чтобы можно было покрыть нужной настройкой все компьютеры. Чаще всего корпоративная инфраструктура построена на базе домена Active Directory, в которой централизованным механизмом управления выступает групповая политика.
В своем примере я буду отключать обновления для Windows 10 и Windows Server, но все действия подойдут и для других версий. Откройте редактор групповой политики, выберите нужную организационную единицу, я буду это делать на уровне корня домена. Щелкаем правым кликом и создаем новую групповую политику.
Задаем нужное имя вашей GPO политики, в моем примере будет «Отключение обновления Windows».
Переходим в раздел:
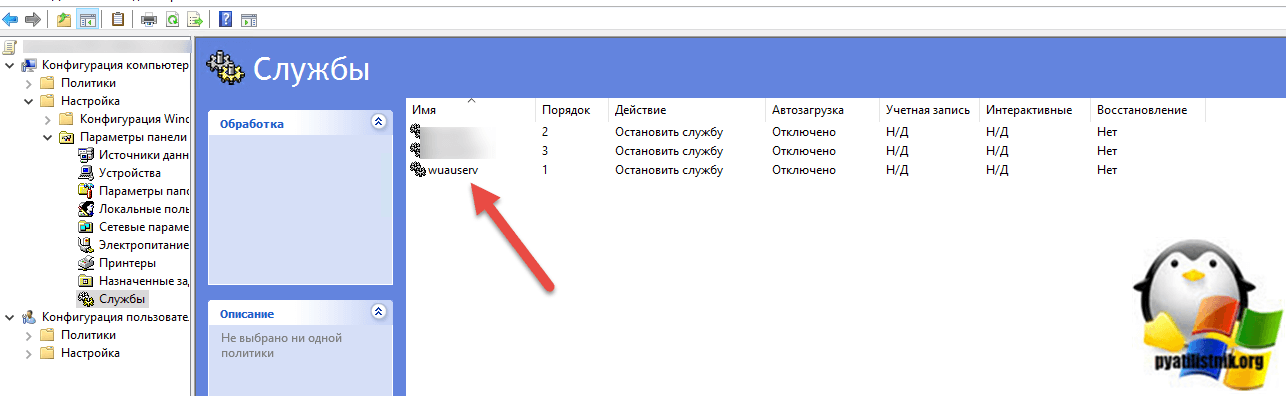
Конфигурация компьютера — Настройка — Параметры панели управления — Службы (Computer Configuration — Settings — Control Panel Options — Services)
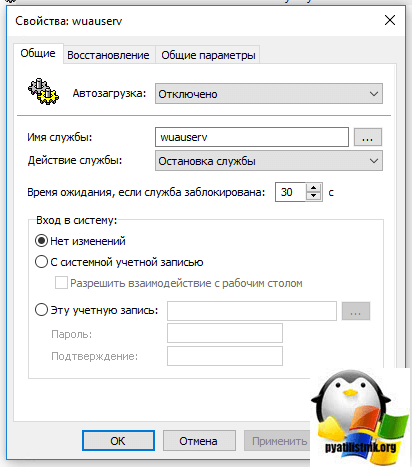
Щелкаем правым кликом и создаем службу wuauserv. Выставляем настройки:
- Автозагрузка — Отключено
- Имя службы — wuauserv
- Действие службы — остановка службы
- Вход в систему — Нет изменений
Сохраняем, хоть мы и отключили автоматический запуск службы «Центр обновления Windows», которая отвечает за установку обновлений Windows, но ее при наличии прав в системе можно запустить, что может и попытаться сделать ОС. Чтобы этого не произошло в этой же политике перейдите в раздел:
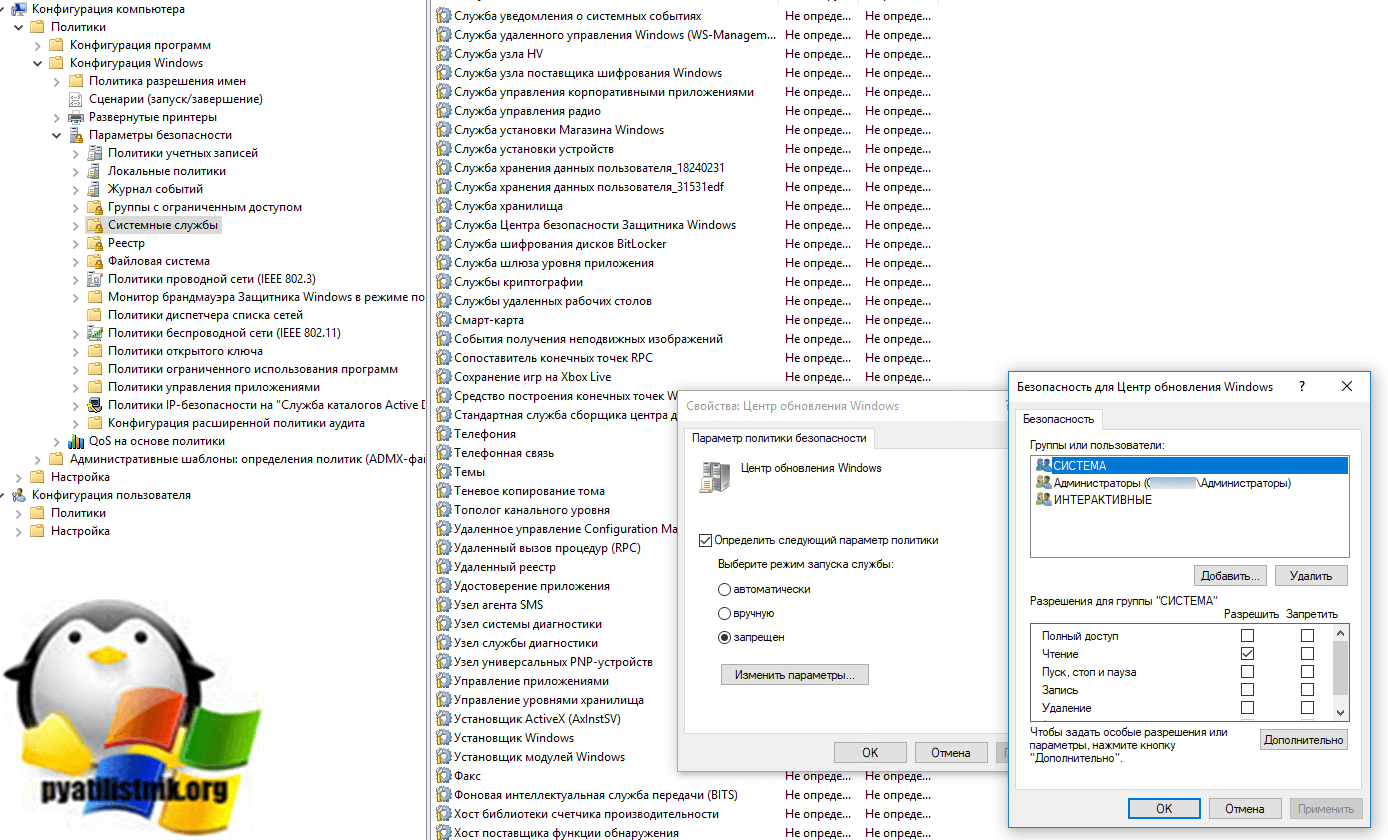
Конфигурация компьютера — Политики — Конфигурация Windows — Параметры безопасности — Системные службы (Computer Configuration — Policies — Windows Configuration — Security Options — System Services)
Найдите там службы «Центр обновления Windows (wuauserv)». Откройте ее свойства. Выставите тип запуска «Запрещен» и далее кнопку «Изменить параметры». Тут вам необходимо отнять права на запуск ее у системы и администраторов компьютера.
В ACL выберите «СИСТЕМА» и оставьте права «Чтение«, так же поступите и с группой администраторов и «ИНТЕРАКТИВНЫЕ«.
Сохраняем все изменения и просто теперь дожидаемся обновления политики или делаем это принудительно. После всех этих действий вы навсегда запретили обновление Windows 10 и других версий. Пользователь теперь даже при наличии самых больших прав не сможет изменить данную настройку, если открыть свойства службы, тут все будет не активно.
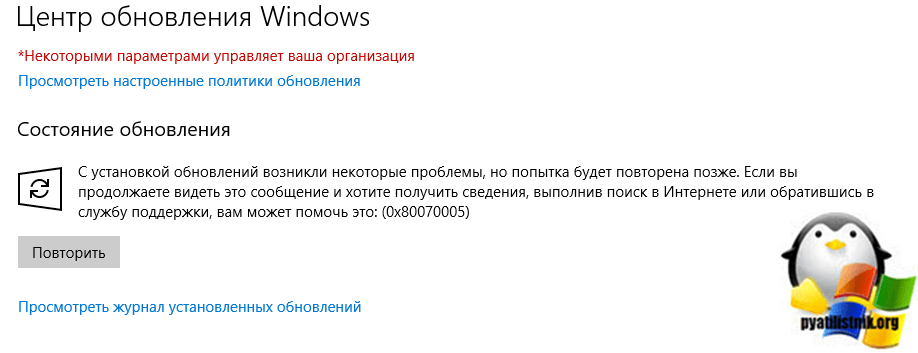
Если попытаться вручную запросить обновления, то вы получите ошибку:
С установкой обновлений возникли некоторые проблемы, но попытка будет повторена позже. Если вы продолжаете видеть это сообщение и хотите получить сведения, выполнив поиск в Интернете или обратившись в службу поддержки, вам может помочь это: (0x80070005)
Как отключить обновления в windows 10 (выше) и Windows Server через запрет службы
Да именно на всегда, пока вы явным образом не захотите сами их включить, ниже я вам подобрал все известные мне методы, некоторые из них простые другие по сложнее. Данный метод, я
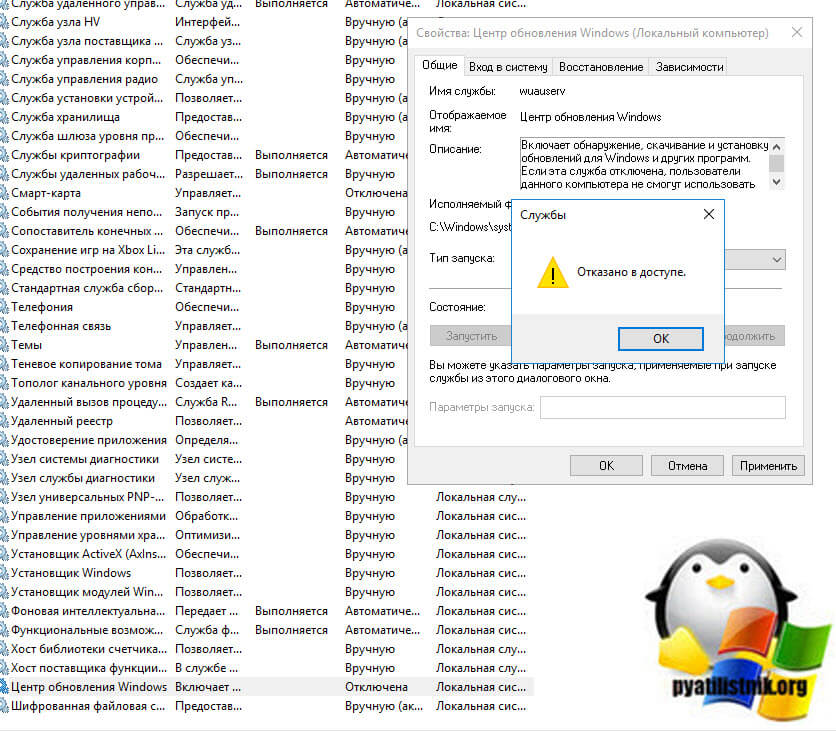
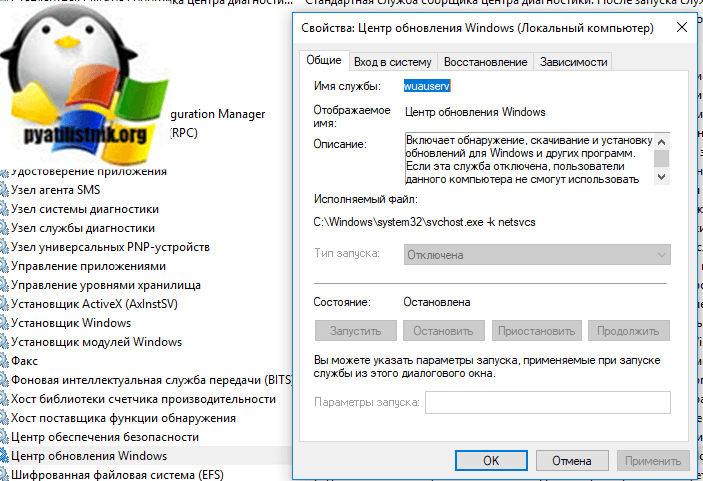
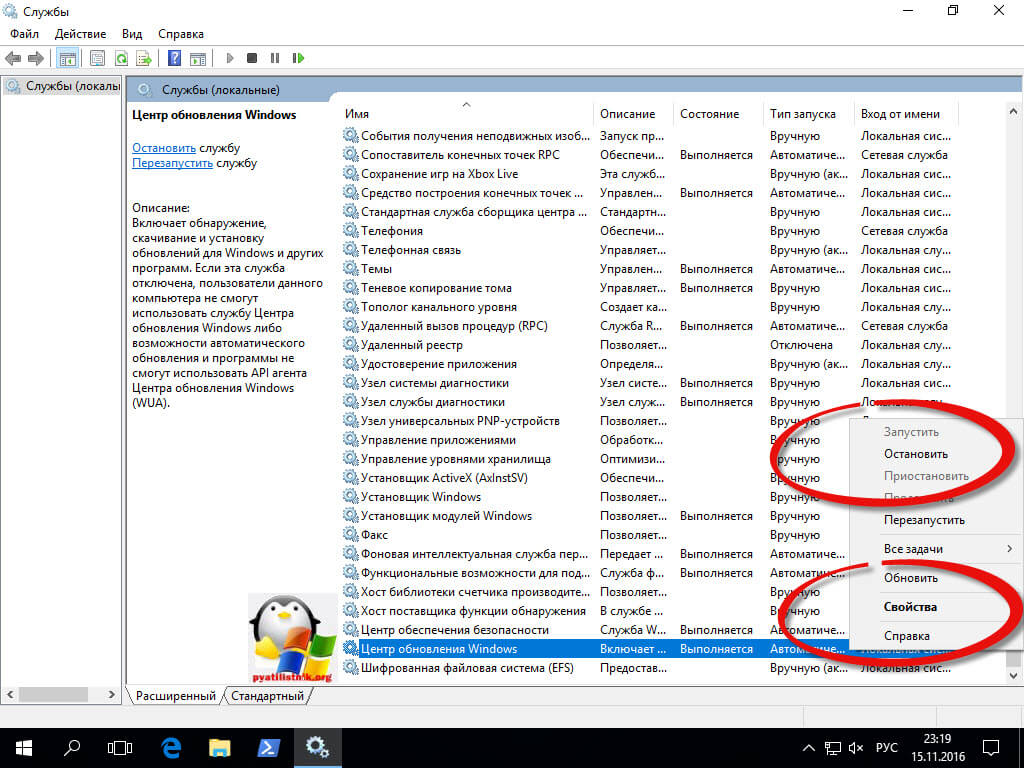
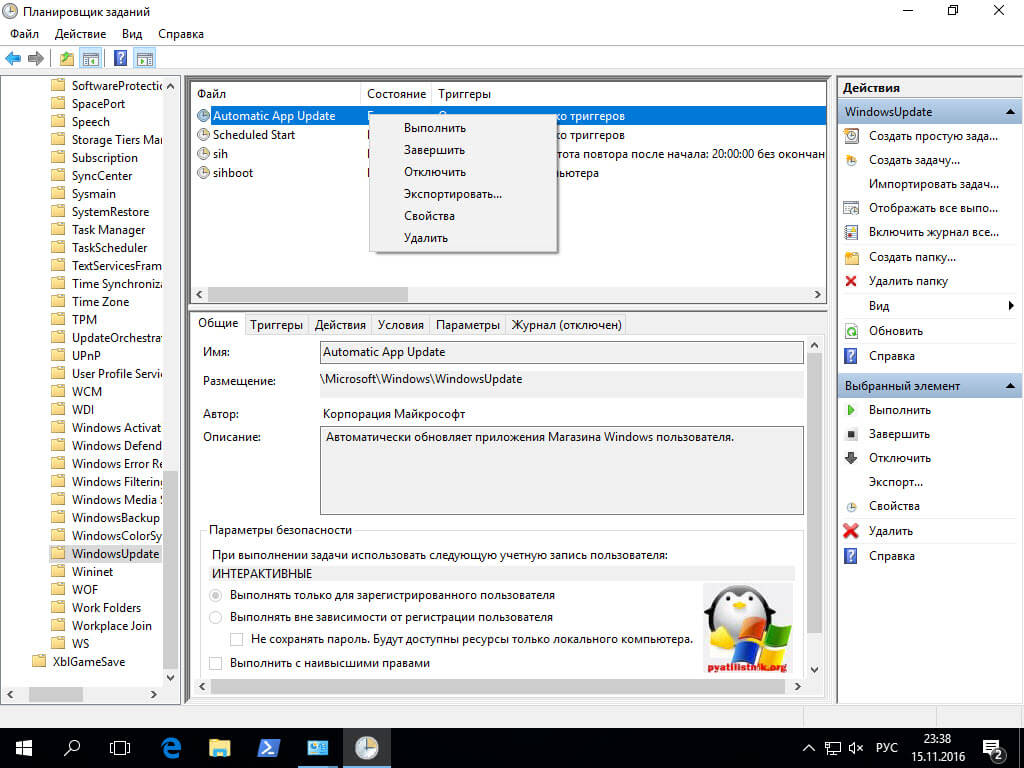
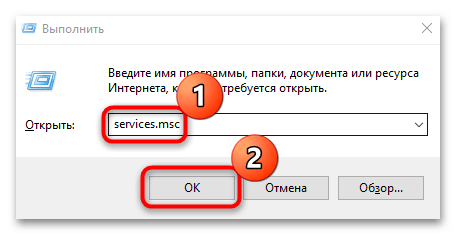
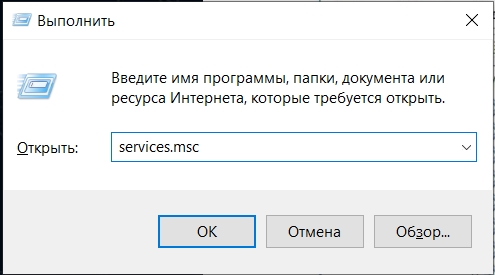
Как вы знаете в операционных системах линейки Windows есть служба под названием Центр обновления Windows, именно наличие этого процесса заставляет вашу десятку получать свежие апдейты. Самый быстрый способ отключить работающую службу. Нажимаем волшебную комбинацию горячих клавиш Win+R и в открывшемся окне выполнить пишем services.msc
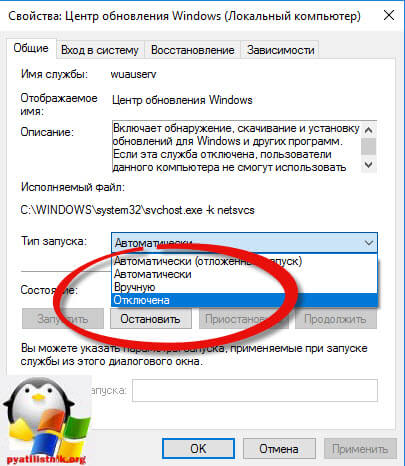
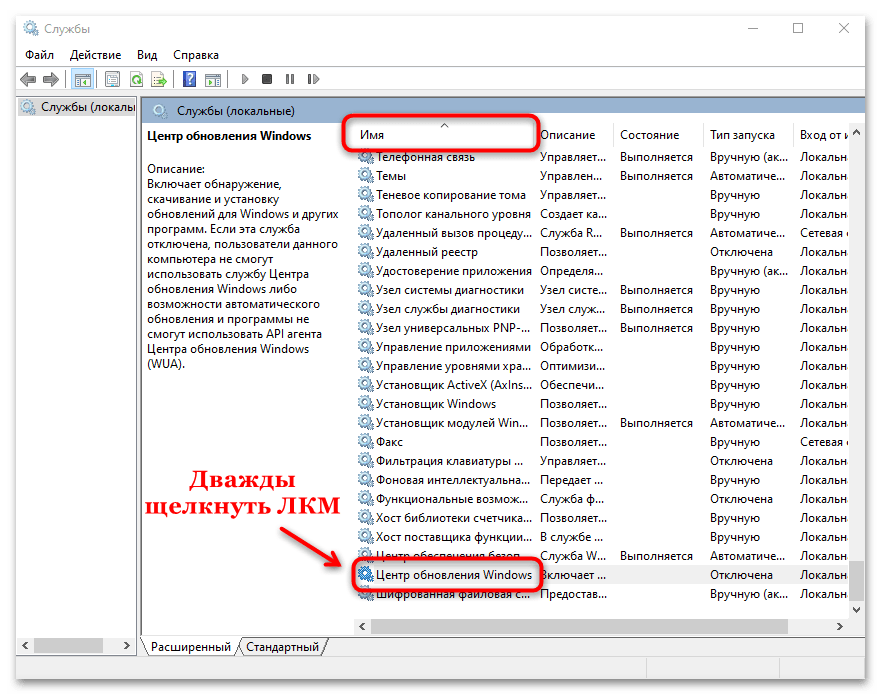
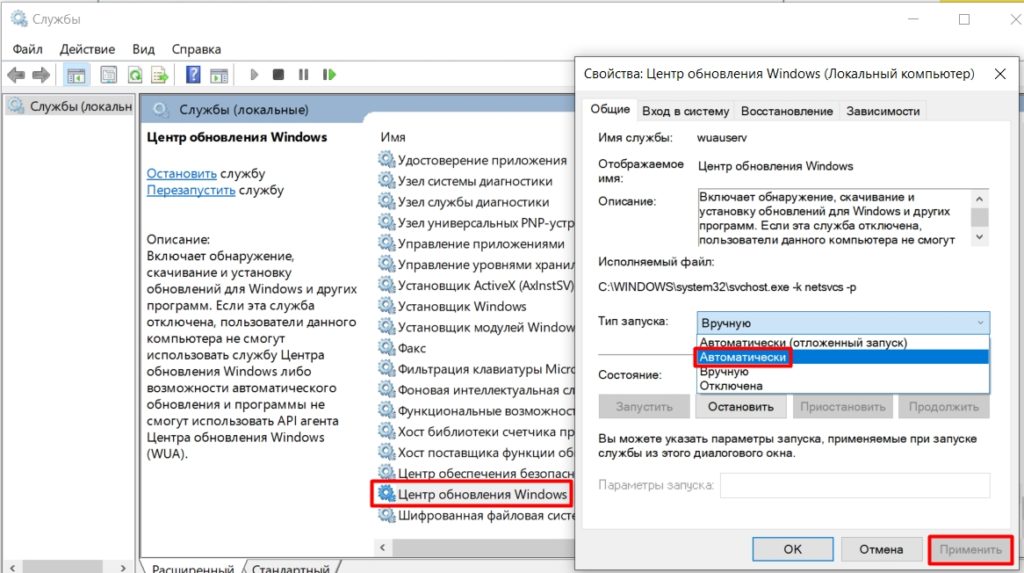
Спускаемся в самый низ и находим службу под названием Центр обновления Windows, как вы видите она работает и тип запуска у нее автоматический, это означает, что когда запускается система, служба стартует в месте с ней, нам это не нужно. Щелкаем по ней правым кликом и в начале останавливаем ее, затем переходим в свойства.
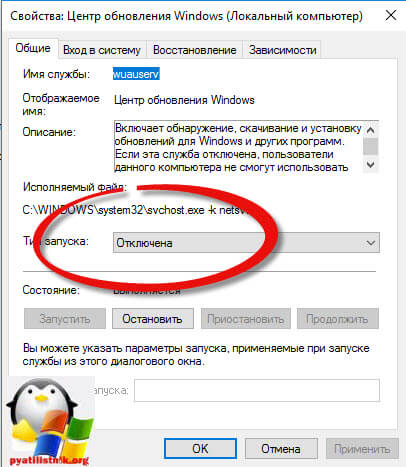
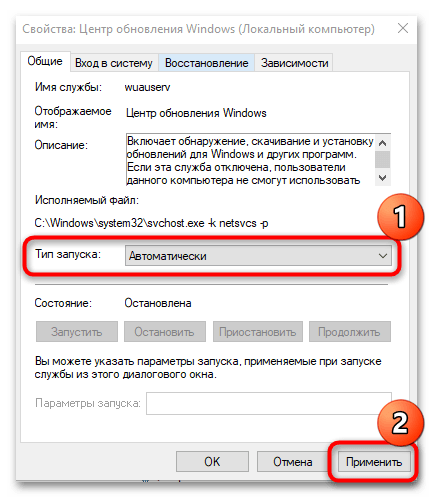
Находим поле тип запуска и выбираем там Отключена, это сто процентное запрещение, на старт службы.
Благодаря этому вам удалось отключить обновление windows 10, но есть еще маленький нюанс.
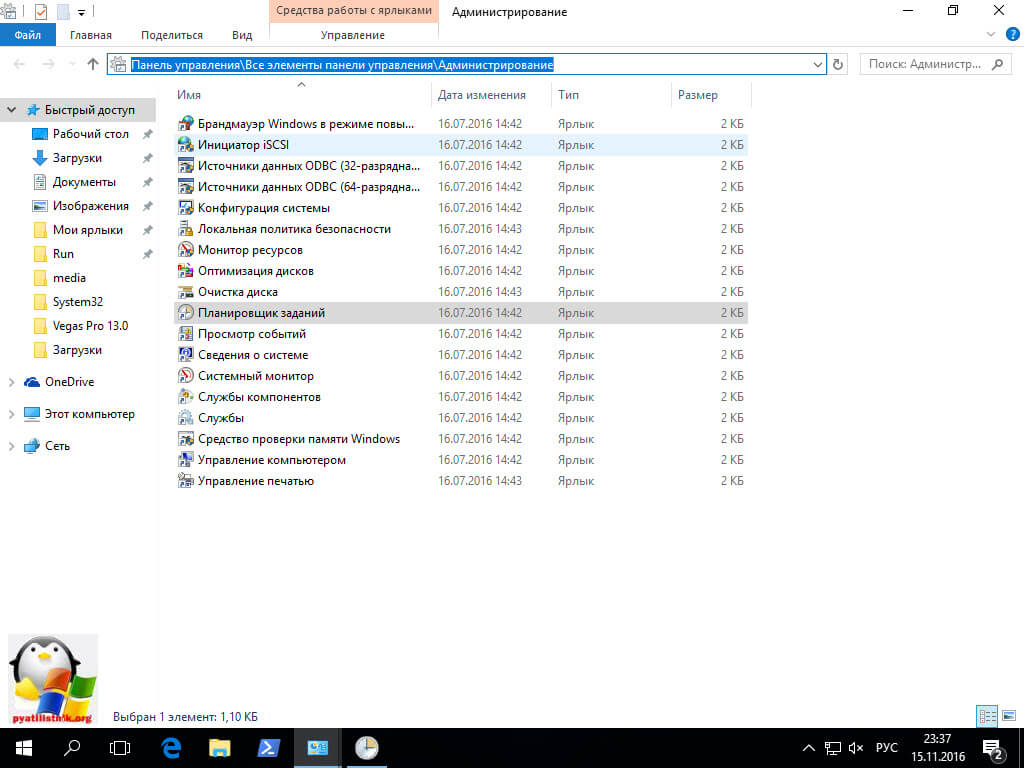
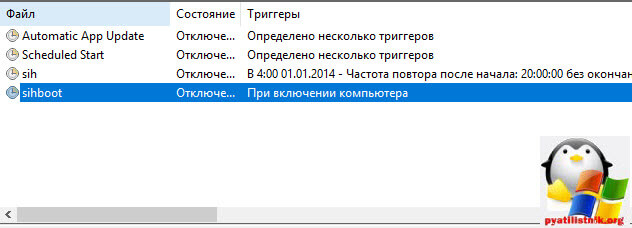
Каждую неделю Windows 10 все равно попытается найти обновления и вернуть службу обновления в рабочее состояние, делается это за счет заданий в планировщике, которые и нужно отключить
Открываем Панель управления > Администрирование > Планировщик заданий
Переходим в Библиотека планировщика > Microsoft > Windows > Windows Update и выключаем там 4 задания, через правый клик.
Должно получиться вот так.
Ниже мы рассмотрим второй метод как отключить автоматическое обновление windows 10.
Как отключить автоматические обновления Windows 10 через локальный редактор политик
Первым метод мы разобрали, расскажу еще про один, но он подойдет далеко не всем пользователям, так как работает он только в Windows 10 Pro и Enterprise, в виду того, что в них есть такой компонент как редактор локальной групповой политики. Он по сути помогает отключить обновления windows 10 в реестре, так как все изменяемые настройки в нем, это просто GUI интерфейс реестра Windows.
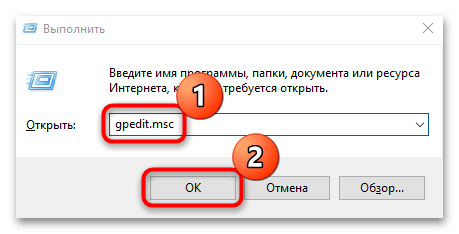
Снова нажимаем Win+R и вводим gpedit.msc.
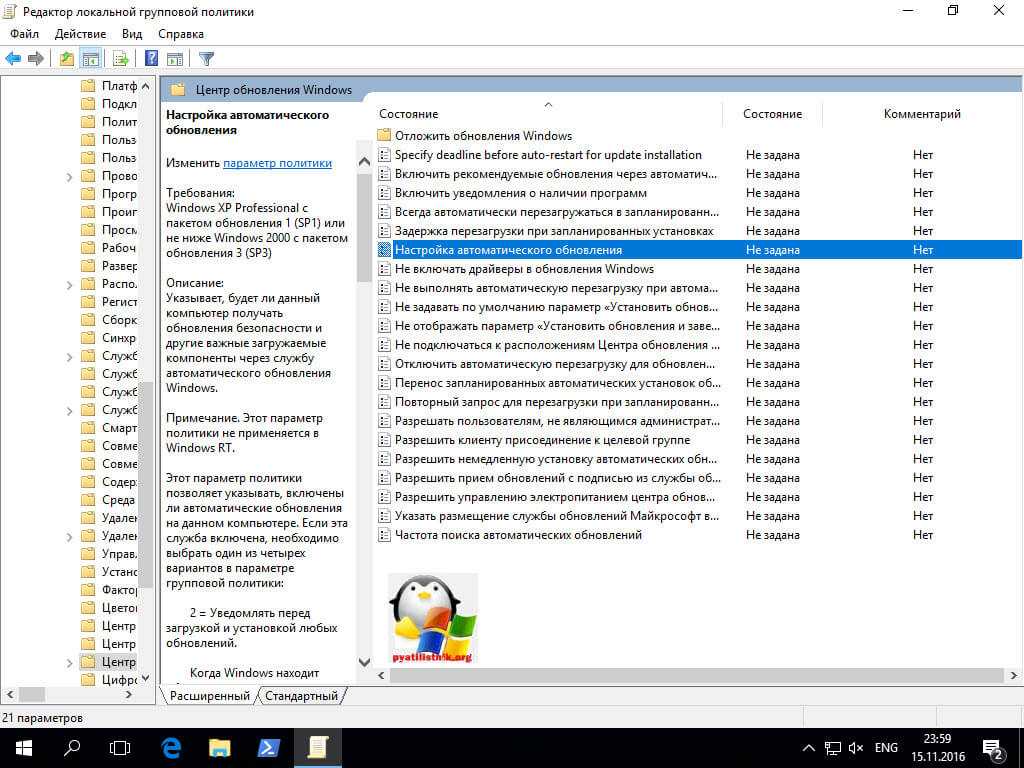
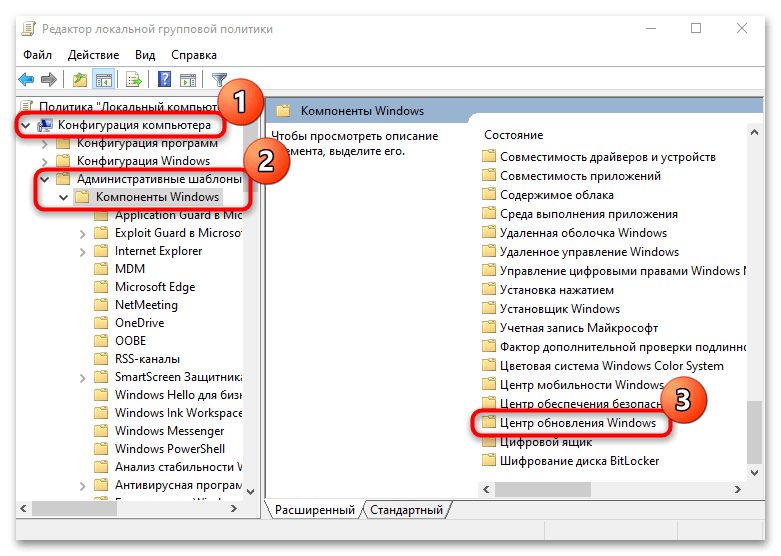
Тут редактор редактор локальной групповой политики, содержит два раздела, на пользователя и на компьютер, нас будет интересовать второй. Переходим по пути:
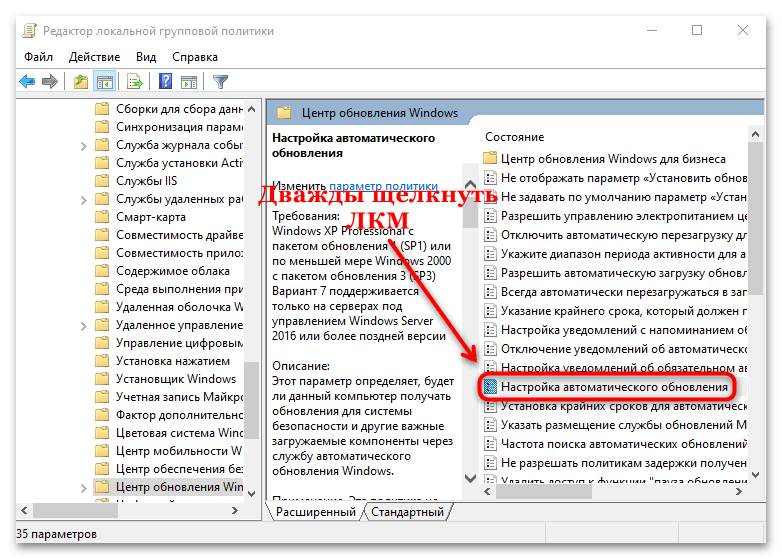
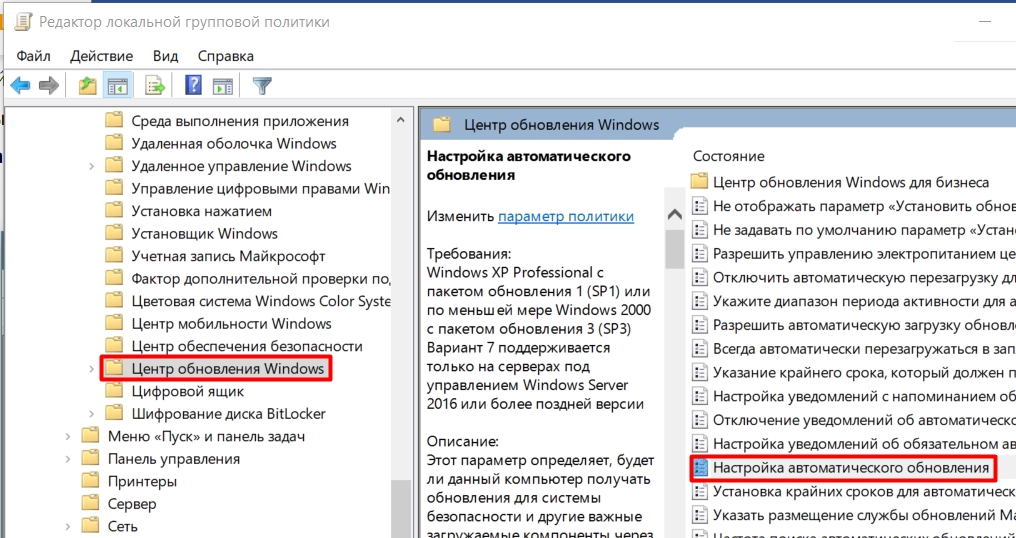
Конфигурация компьютера > Административные шаблоны > Компоненты Windows > Центр обновления Windows > Настройка автоматического обновления
Именно это пункт поможет отключить обновления windows 10 в реестре, щелкаем по нему двойным кликом. Ставим переключатель в положение Отключено, этим вы делаете запрет автоматического обновления Windows 10 навсегда.
Выше я рассказывал, про планировщик заданий, так же проверьте выключены ли они
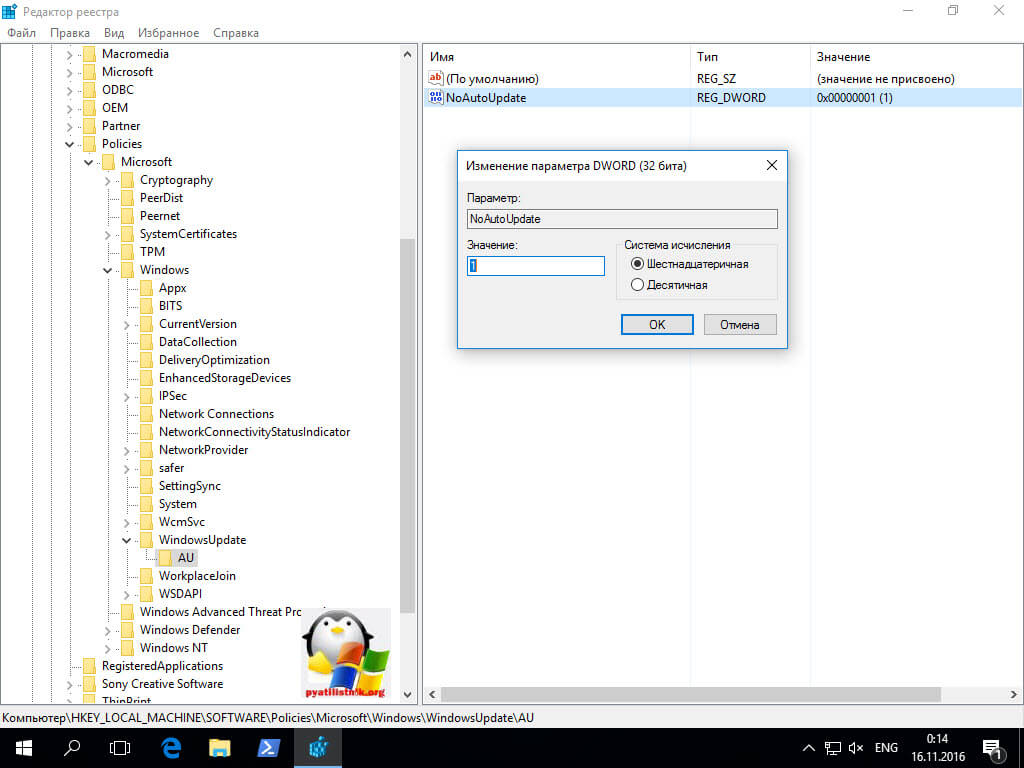
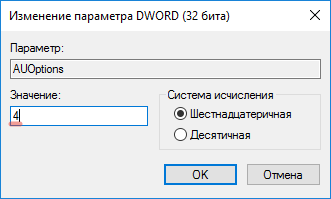
для людей кто хочет все контролировать и сам создать нужные ключи в реестре, делаем следующее. Нужно запустить редактор реестра windows, переходим во в такую ветку:
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE SOFTWARE Policies Microsoft Windows WindowsUpdate AU
тут вам через правый клик нужно создать DWORD 32 бита параметр в шеснадцатеричном виде со значением 1.
Вот это два самых действенных метода запретить обновления в windows 10 redstone, ниже я покажу еще пару дополнительных настроек, которые так же в той или иной степени дополнят первые методы.
Использование лимитного подключения
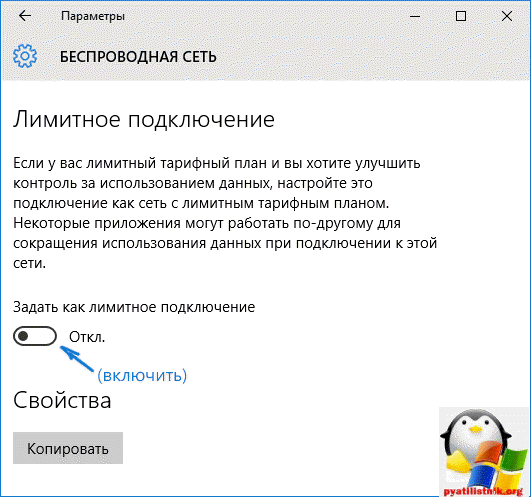
Операционная система Windows 10 имеет в себе такой функционал как лимитное подключение, благодаря ему можно сделать так, что она не будет загружать апдейты автоматически, если используется это подключение. Задав так для WiFi лимитное подключение (логично что в локальной сети это не прокатит), вы отключите установку апдейтов.
Нажимаем Win+I, у вас откроются Параметры Windows 10.
зайдите в Сеть и Интернет — Wi-Fi и ниже списка беспроводных сетей нажмите Дополнительные параметры. Ставим отключить ползунок на Задать как лимитное подключение.
Теперь десятка не будет автоматически загружать и устанавливать новые обновления до тех пор, пока ваше подключение к интернету значится как лимитное.
Если у вас еще остались вопросы о том как как запретить обновления в windows 10, то пишите их в комментариях.
Windows 10 — актуальная версия операционной системы (ОС) от Microsoft. По словам разработчика, дистрибутив будет иметь длительную поддержку, что означает выпуск апдейтов на долгосрочной основе. Пользователям рекомендуется обновить Windows 10 до последней версии и настроить систему автоматической установки пакетов. Это гарантирует безопасность программного обеспечения и своевременное получение всех новых функций.
Содержание
- Проверка обновлений через параметры системы
- Включение обновлений Windows 10
- Службы
- Командная строка
- Настройка автоматического обновления
- Редактор локальной групповой политики
- Системный реестр
- Сторонние программы для запуска обновлений
- Заключение
Проверка обновлений через параметры системы
По умолчанию в системы активированы все службы, отвечающие за проверку и автоматическую инсталляцию последних апдейтов. При необходимости можно посмотреть новые релизы вручную, через параметры системы:
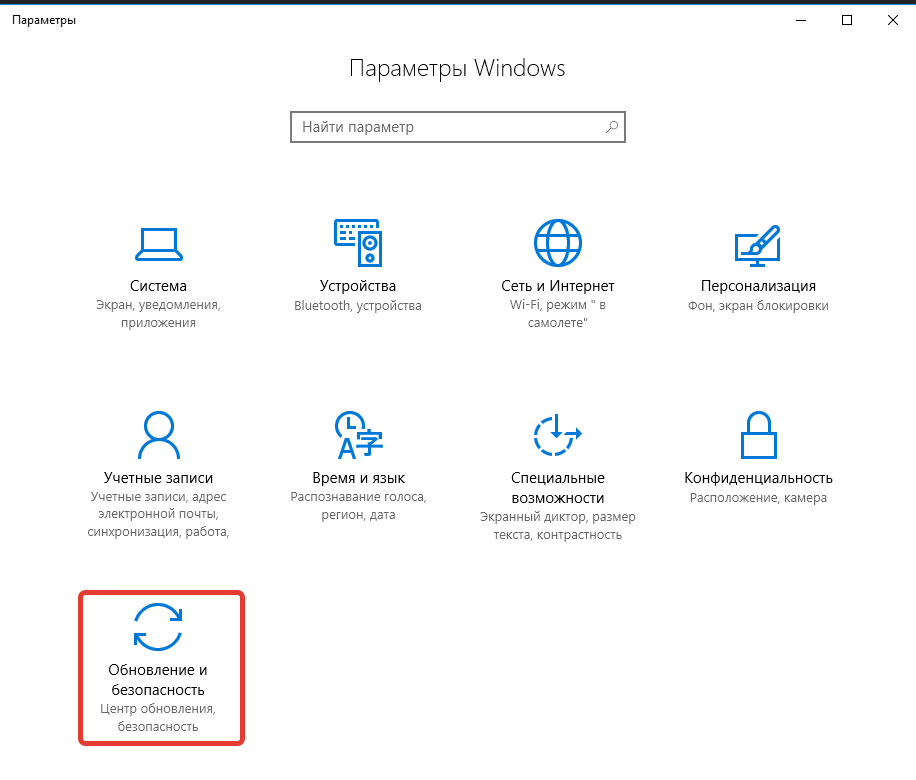
- Развернуть меню «Пуск», нажать Параметры.
- Перейти «Обновление и безопасность».
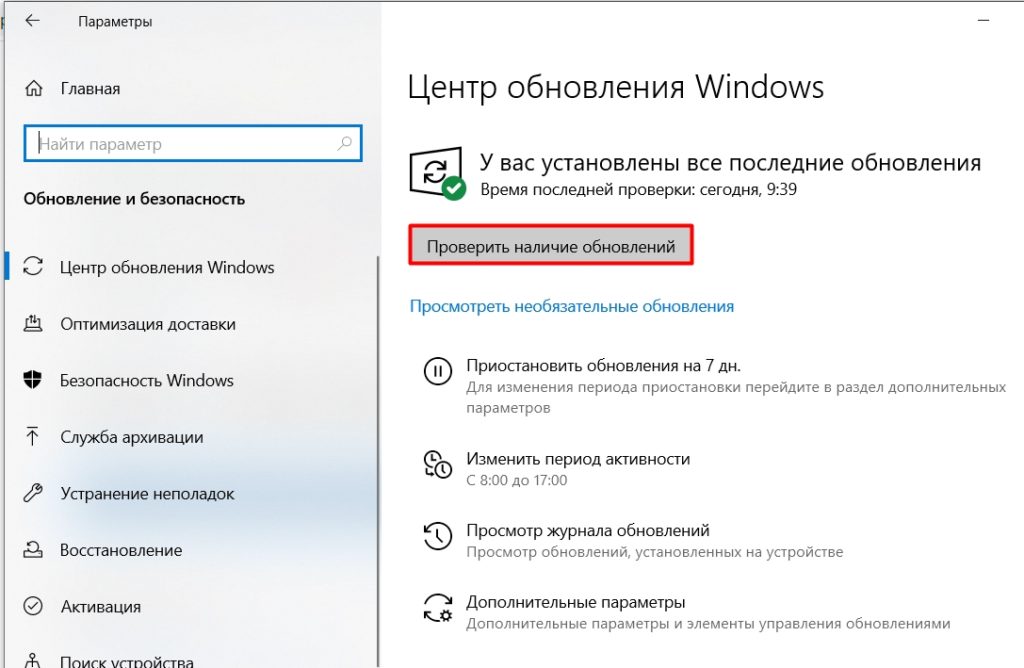
- Во вкладке «Центр обновления Windows» щелкнуть по Проверить наличие обновлений.
Обратите внимание! Если пакеты данных были загружены системой автоматически, на странице отобразится перечень. Там же можно обновиться.
Обновить Windows 10 не удастся, если в системе отключена соответствующая служба. Для активации потребуется воспользоваться специальной утилитой или выполнить действие через «Командную строку».
Службы
За проверку, загрузку и инсталляцию апдейтов отвечает служба «Центр обновления Windows». Чтобы включить этот процесс, нужно:
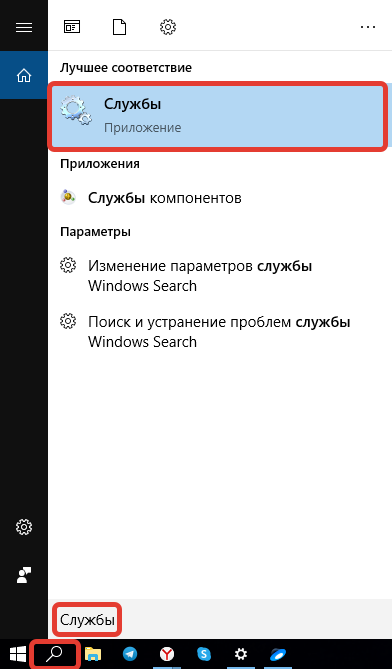
- Воспользовавшись поиском в левой стороне «Панели задач», ввести запрос «Службы» и кликнуть по одноименному пункту в результатах выдачи.
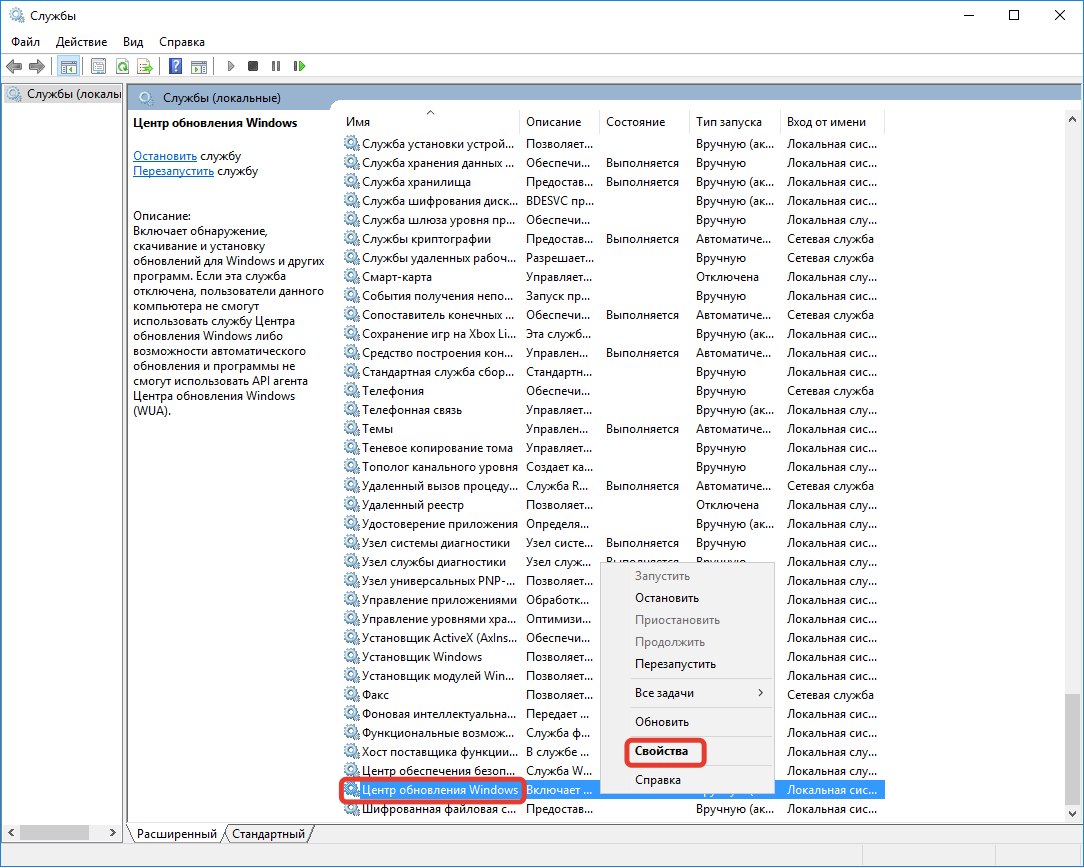
- В перечне всех процессов отыскать «Центр обновления Windows», нажать по названию правой кнопкой мыши (ПКМ) и щелкнуть по строке «Свойства».
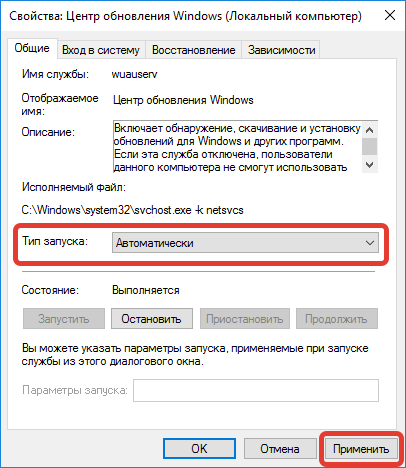
- Из выпадающего меню «Тип запуска» выбрать значение «Автоматически», нажать Применить.
Важно! Если состояние процесса отображается как «Остановлена», предварительно требуется нажать Запустить.
После выполнения всех действий окно службы можно закрыть. Чтобы внесенные изменения применились, рекомендуется перезапустить компьютер.
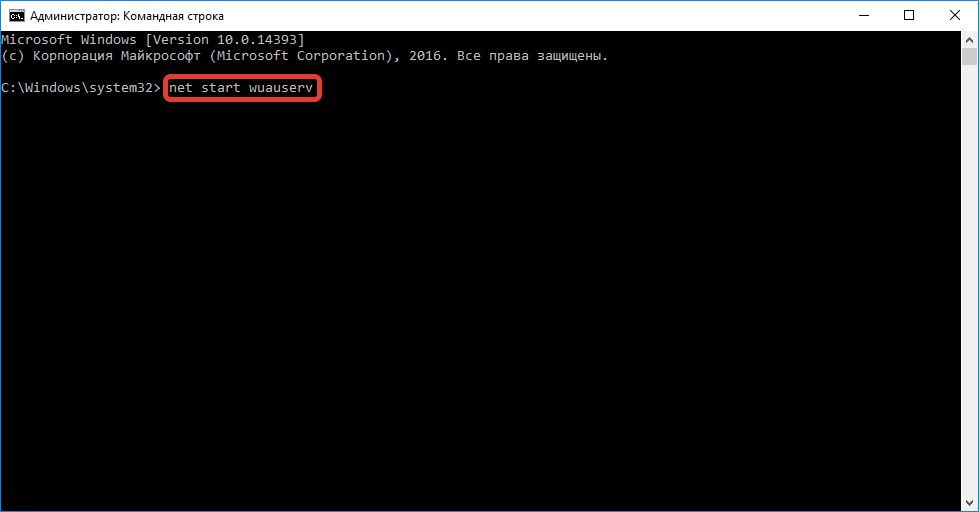
Командная строка
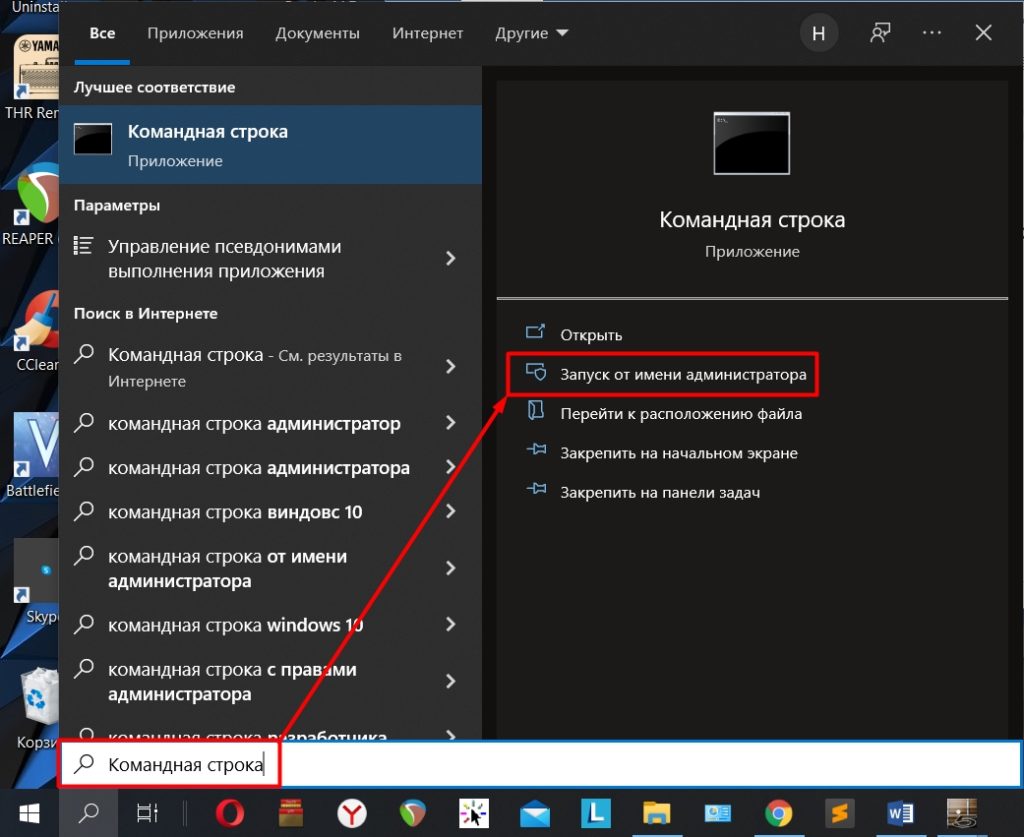
Включить обновление Windows 10 можно через консоль, запущенную с правами суперпользователя. Пошаговое руководство:
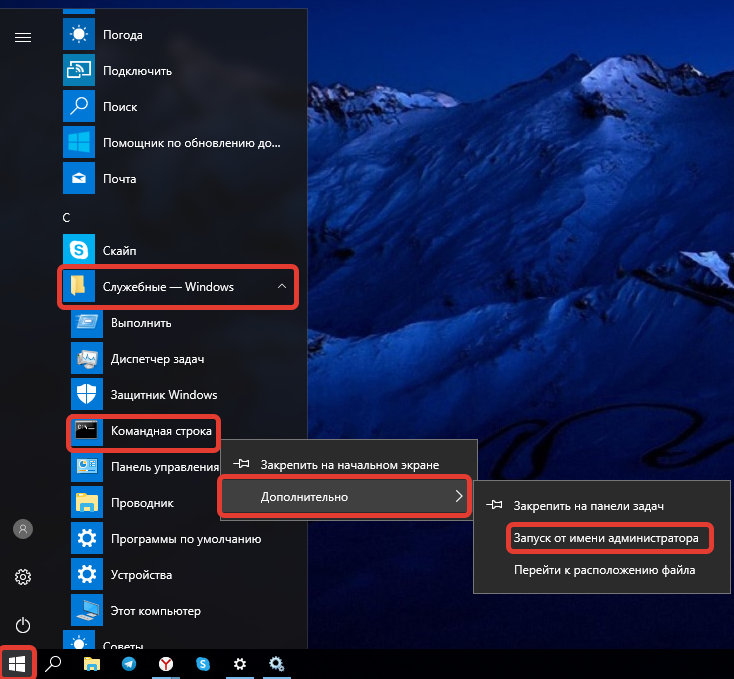
- Развернуть меню «Пуск», в списке программ открыть директорию «Служебные — Windows».
- Нажать ПКМ по пункту «Командная строка», выбрать «Дополнительно» → «Запуск от имени администратора».
- Подтвердить инициализацию, нажав Да.
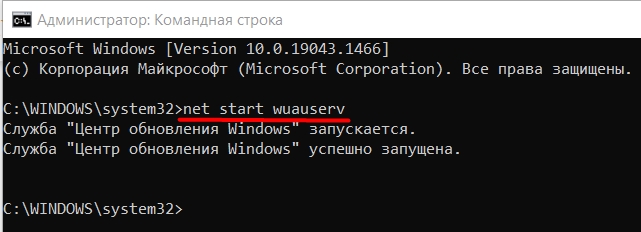
- В консоли ввести команду net start wuauserv, нажать Enter.
В случае успешного выполнения операции, отобразится надпись соответствующего содержания — окно можно закрывать.
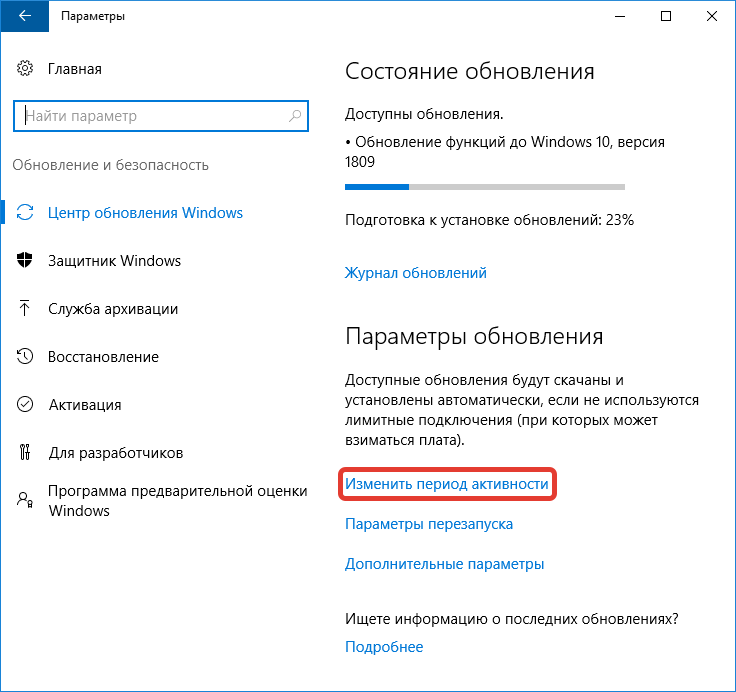
Настройка автоматического обновления
Изменить конфигурацию автообновления можно в меню параметров ОС, для этого понадобится:
- Зайти в «Пуск», кликнуть по Параметры.
- Перейти в «Обновление и безопасность».
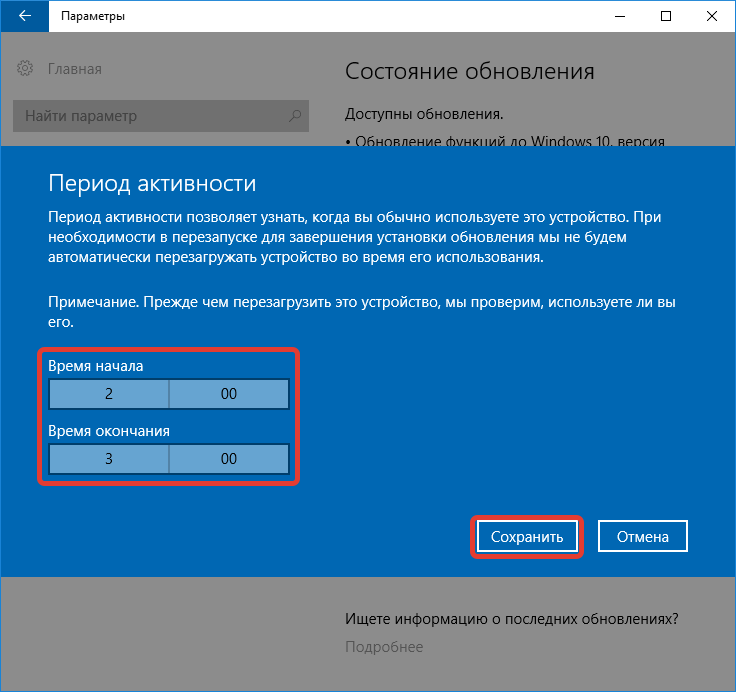
- Во вкладке «Центр обновления Windows» нажать по пункту «Изменить период активности».
- Кликнуть по ссылке «Изменить» и выбрать период активности, в момент которого апдейты будут загружаться, но не устанавливаться.
Выполнить подобную настройку можно через другие средства ОС: редактора групповой политики и системного реестра.
Редактор локальной групповой политики
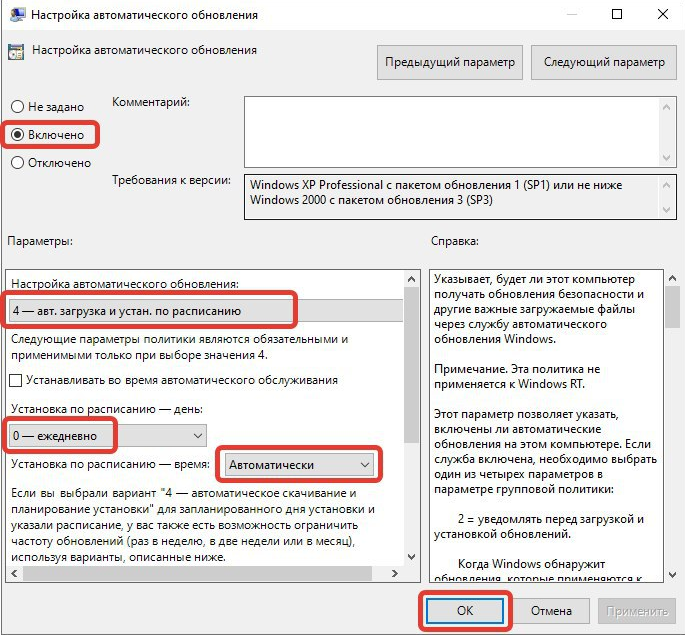
В десятой версии ОС присутствует специальное средство, позволяющее выполнять настройку отдельных компонентов. Для изменения конфигурации автообновления потребуется:
- Нажать Win + R, выполнить команду gpedit.msc.
- Используя древовидную структуру каталогов на боковой панели, перейти по пути «Конфигурация компьютера» → «Административные шаблоны» → «Компоненты Windows» → «Центр обновления Windows».
- В списке файлов найти и открыть «Настройка автоматического обновления».
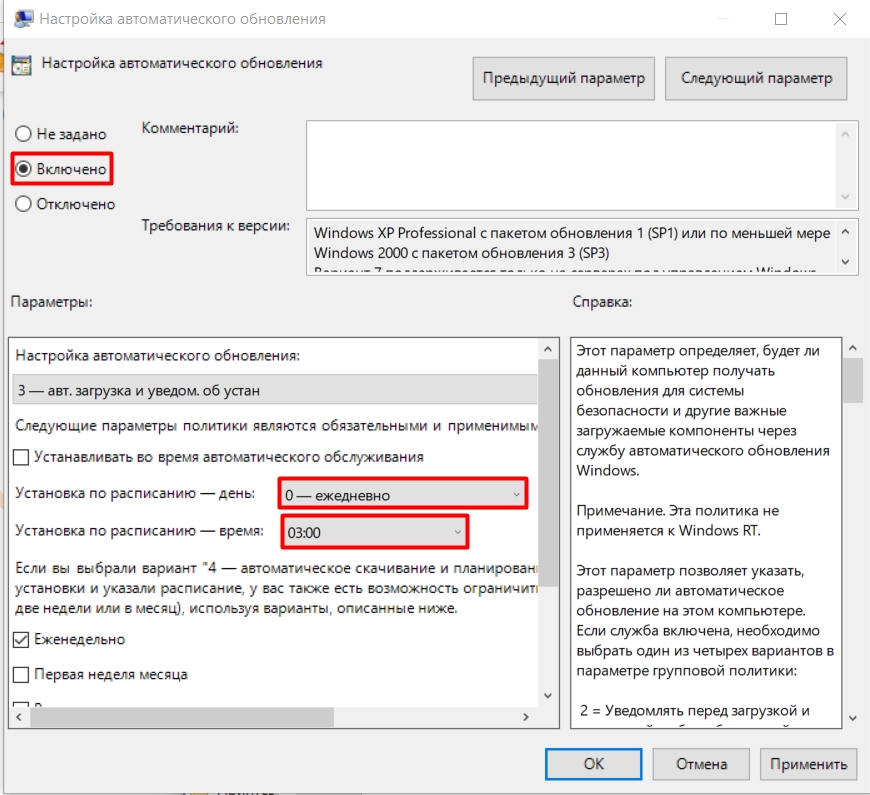
- Установить отметку напротив пункта «Включено».
- Из выпадающего списка выбрать «4 — авт. загрузка и устан. по расписанию».
- Задать установку по расписанию «0 — ежедневно» и «Автоматически», как указано на изображении ниже.
- Нажать ОК, закрыть окно.
Важно! Воспользоваться методом можно только в редакции Pro.
Системный реестр
Задать аналогичную конфигурацию можно в редакторе реестра, для этого необходимо:
- Нажать Win + R, выполнить команду regedit.
- Перейти по пути HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINESOFTWAREPoliciesMicrosoftWindowsWindowsUpdateAU.
- Используя контекстное меню, создать следующие параметры DWORD:
- AUOptions — 4;
- NoAutoUpdate — 0;
- ScheduledInstallDay — 0;
- ScheduledInstallEveryWeek — 1;
- ScheduledInstallTime — 24.
Важно! Если на пути следования к указанному адресу отсутствует определенная директория, необходимо создать папку самостоятельно.
Добавление параметра DWORD происходит следующим образом:
- Нажать ПКМ по свободной области в правой части интерфейса.
- Выбрать «Создать» → «Параметр DWORD (32 бита)».
- Задать новое имя, после чего дважды кликнуть для настройки.
- Вписать в поле «Значение» соответствующее названию параметра число.
После выполнения инструкций окно реестра нужно закрыть, а компьютер перезапустить.
Сторонние программы для запуска обновлений
У штатных средств Windows 10 повышена сложность интерфейса, за счет чего неопытный пользователь может не разобраться во всех нюансах обновления ОС. Рекомендуется обратить внимание на продукты от сторонних разработчиков, например:
- Winaero Tweaker;
- Windows Update MiniTool;
- WAU Manager.
Каждое приложение обладает интуитивно понятным интерфейсом и имеет дополнительные функции при работе с обновлениями. Для инсталляции рекомендуется использовать установщик, загруженный на официальном ресурсе разработчика.
Заключение
В рамках ОС Windows 10 предусмотрены инструменты для выполнения проверки, загрузки и инсталляции обновлений. Неопытным юзерам рекомендуется использовать меню в параметрах системы. В качестве альтернативы подойдут решения от сторонних разработчиков. Для осуществления гибкой настройки автообновления ОС следует прибегнуть к использованию редактора групповой политики. Опытные пользователи могут создавать соответствующие параметры в системном реестре.
( 1 оценка, среднее 5 из 5 )
Содержание
- Способ 1: «Службы»
- Способ 2: «Командная строка»
- Способ 3: «Редактор реестра»
- Способ 4: «Редактор локальной групповой политики»
- Способ 5: «Диспетчер задач»
- Способ 6: Сторонний софт
- Возобновление обновлений
- Вопросы и ответы
Способ 1: «Службы»
Если автоматические обновления отключены, то можно вручную их активировать, перезапустив соответствующую службу:
- Откройте приложение «Службы». Для этого одновременным нажатием на клавиши «Win + R» вызовите диалоговое окно «Выполнить» и пропишите команду
services.msc. - В списке служб найдите «Центр обновления Windows» и дважды щелкните левой кнопкой мыши по названию. Если необходимо, можно нажать на вкладку «Имя» и упорядочить службы по алфавиту, чтобы было проще отыскать строку по имени.
- В новом окошке в меню «Тип запуска» выберите пункт «Автоматически». Нажмите на кнопку «Применить».
- Если служба выключена, то кликните по кнопке «Запустить», затем по «ОК».
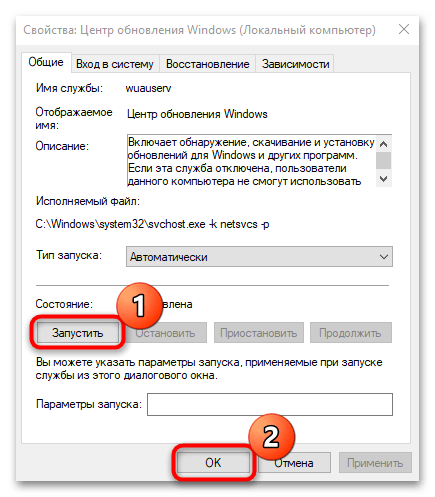
Служба автоматического поиска и установки обновлений для операционной системы, программных компонентов и продуктов компании теперь активирована.
Способ 2: «Командная строка»
Включить автообновление в Виндовс 10 можно с помощью специальной команды, введенной в интерфейсе консоли «Командная строка», которая запущена с расширенными правами:
- Откройте средство, введя соответствующий запрос в системной строке поиска. В результате запросов выберите пункт «Запуск от имени администратора».
- В интерфейсе терминала вставьте команду
net start wuauserv, затем нажмите на клавишу «Enter».
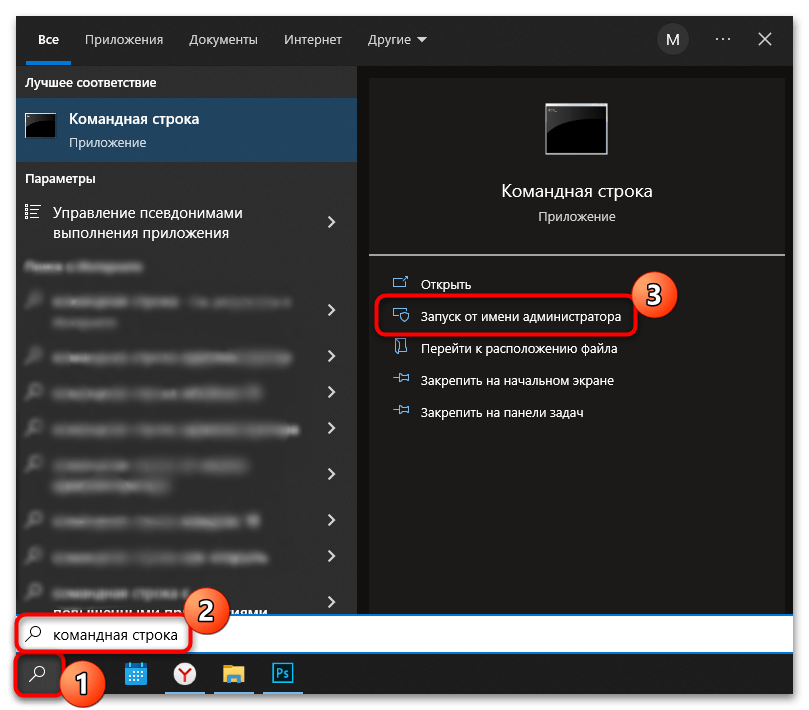
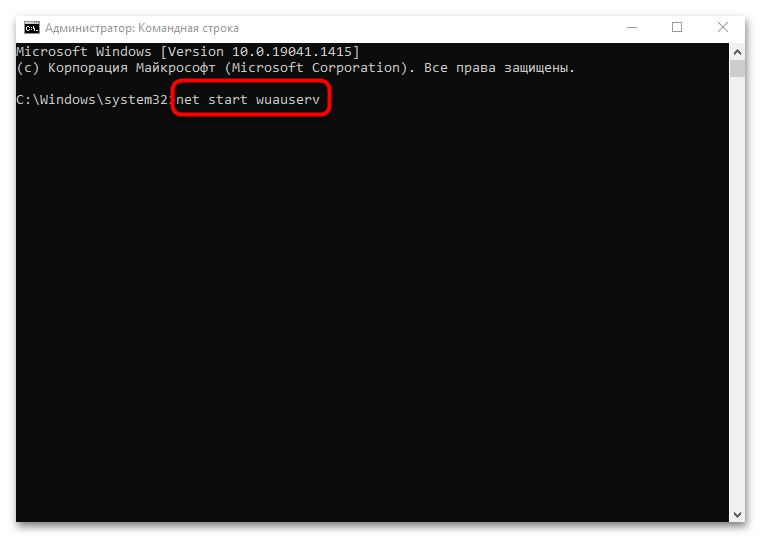
В окне консоли отобразится уведомление, что служба успешно активировалась, и она будет действовать в автоматическом режиме.
Способ 3: «Редактор реестра»
Еще один метод активации служб автоматического обновления Windows 10 – это внесение изменений в системный реестр. Следует отметить, что невнимательно выполненные действия могут привести к нарушению работоспособности системы, поэтому можно создать контрольную точку для восстановления состояния, если что-то пошло не так после редактирования.
Читайте также: Инструкция по созданию точки восстановления Windows 10
- Откройте приложение «Редактор реестра». Быстрее всего оно запускается через вызов приложения «Выполнить» (клавиши Win + R) и команду
regedit. - Разверните ветки:
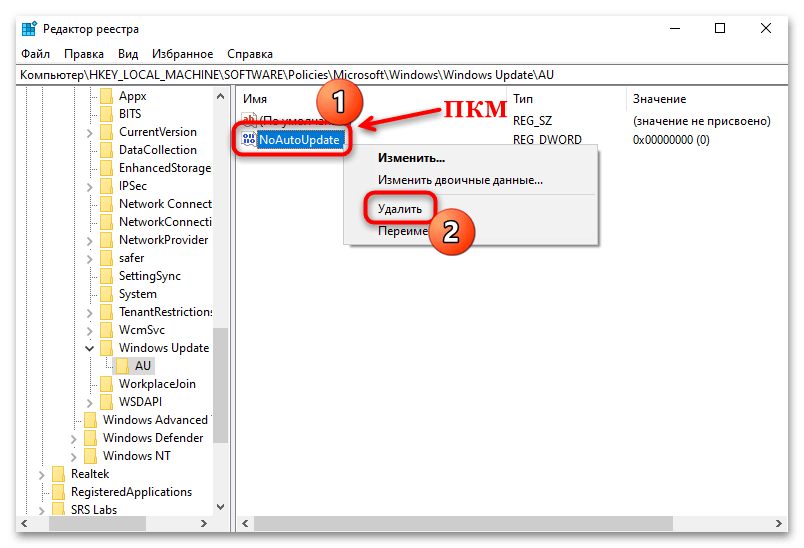
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINESOFTWAREPoliciesMicrosoftWindowsWindowsUpdateAU. В каталоге «AU» отыщите параметр «NoAutoUpdate» и дважды кликните по нему, чтобы перейти в окно с настройкой. - В поле «Значение» введите «0» и щелкните по кнопке «ОК».
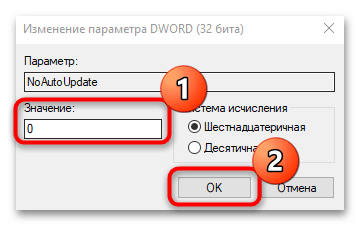
Также можно полностью удалить параметр, кликнув по нему правой кнопкой мыши и выбрав соответствующий пункт.
Способ 4: «Редактор локальной групповой политики»
Настройка автоматического обновления через «Редактор локальной групповой политики» подойдет для редакций Pro и Enterprise. Используя средство, можно включить загрузку и установку апдейтов без вмешательства пользователя:
- Через диалоговое окно «Выполнить» перейдите в приложение «Редактор локальной групповой политики», вставив команду
gpedit.msc. - На панели слева раскройте меню «Конфигурация компьютера», затем выберите «Административные шаблоны». В разделе «Компоненты Windows» найдите каталог «Центр обновления Windows». Нажмите на него.
- В главном окне отыщите функцию «Настройка автоматического обновления». Кликните по ней два раза левой кнопкой мыши.
- В новом окне поставьте отметку у пункта «Включено», затем нажмите на кнопку «ОК» для подтверждения действия.
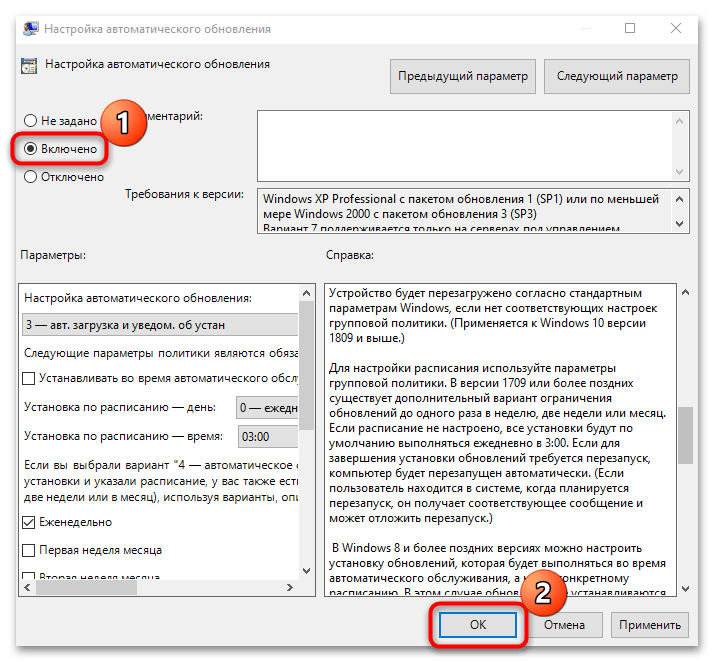
Помимо активации автоматического обновления операционной системы, в окне с настройками можно задать период и время для загрузки апдейтов, определить подходящий вариант обновлений, откладывать процедуру на определенное время.
Способ 5: «Диспетчер задач»
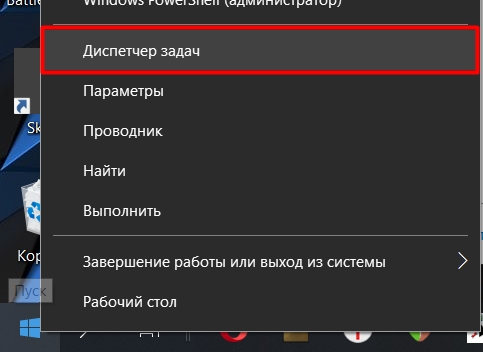
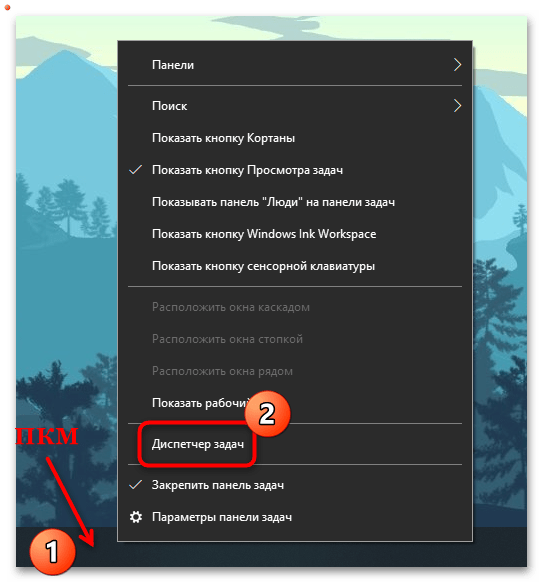
Можно попробовать активировать службу автообновления в Windows 10 через средство «Диспетчер задач», где пользователь может контролировать процессы и управлять ими:
- Запустите «Диспетчер задач». Обычно достаточно щелкнуть правой кнопкой мыши по нижней рабочей панели и выбрать нужное средство в меню.
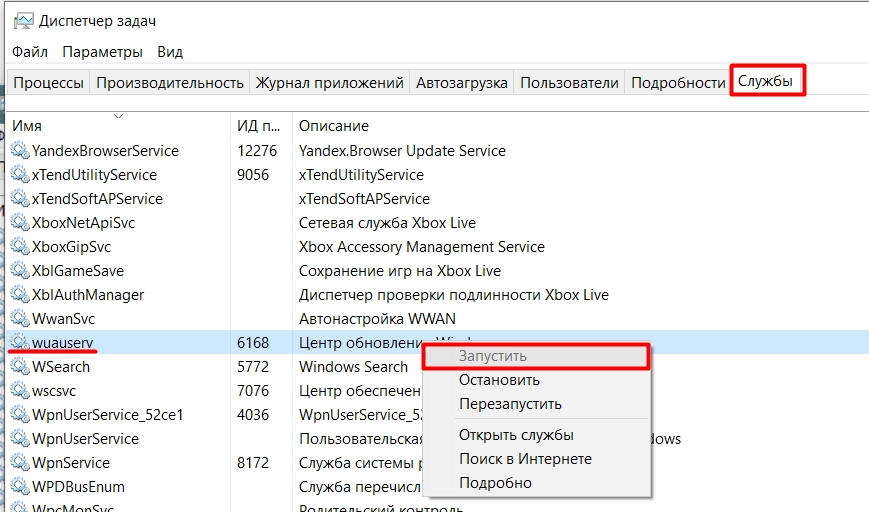
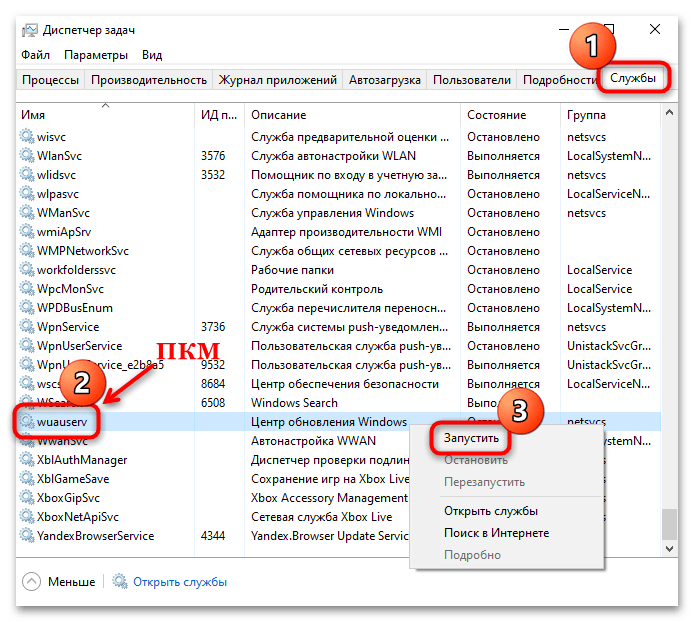
- Откройте вкладку «Службы» и найдите «wuauserv», отвечающую за «Центр обновления Windows». Работает ли служба, можно посмотреть в столбике «Состояние». Чтобы включить ее, кликните по названию правой кнопкой мыши и выберите пункт «Запустить».
Способ 6: Сторонний софт
Для управления обновлениями используются сторонние утилиты, с помощью которых можно быстро, без ручного редактирования реестра или использования команд, как приостановить, так и включить автообновления в Windows 10. Одним из таких инструментов является бесплатная программа Win Update Stop с простым интерфейсом.
Скачать Win Update Stop с официального сайта
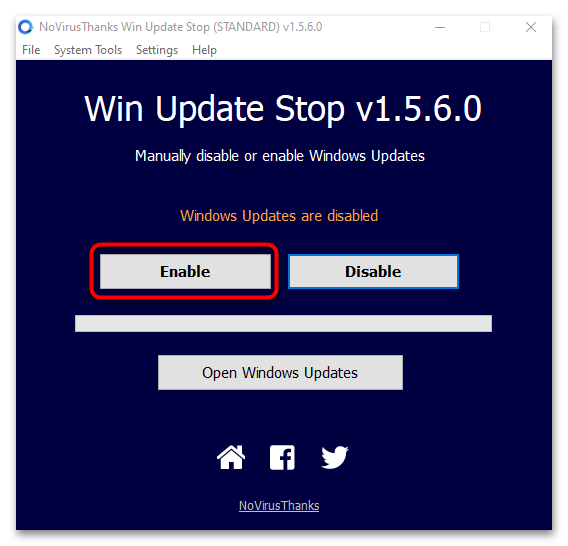
- Скачайте и установите утилиту. После запуска в интерфейсе можно увидеть две кнопки, где «Enable» обозначает включение обновлений операционной системы.
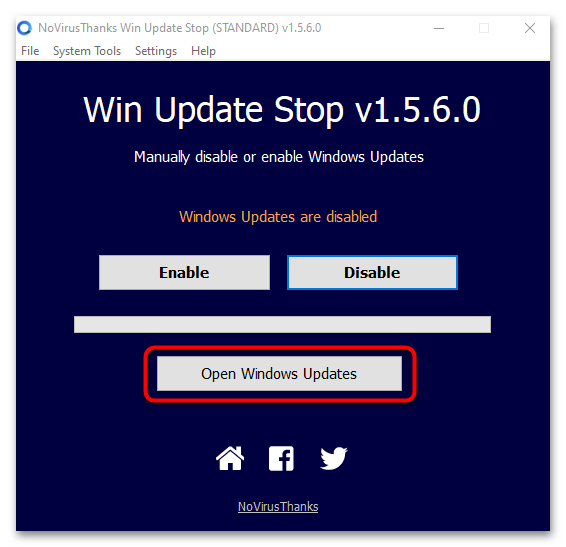
- Принцип работы программы заключается в изменении параметров «Центра обновления Windows». Перейти в раздел «Параметров» можно, нажав на кнопку «Open Windows Updates».
Возобновление обновлений
Через приложение «Параметры» можно не только посмотреть наличие апдейтов, но и настроить автоматическое обновление операционной системы. Если загрузка и установка новых программных компонентов временно отключена, то ее можно возобновить в несколько кликов:
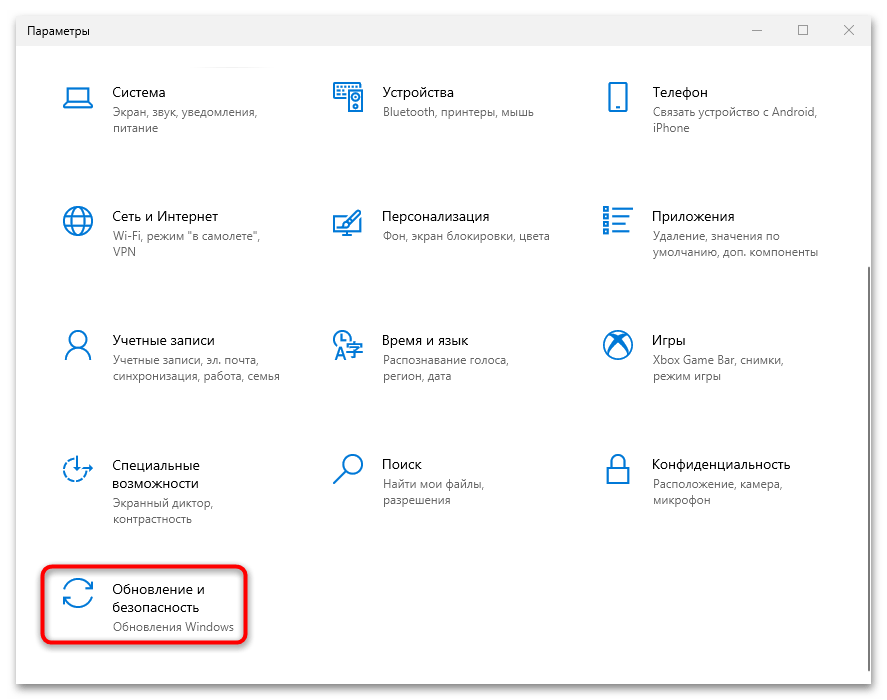
- Щелкните по значку Windows на нижней рабочей панели, затем в меню выберите пункт в виде шестеренки – «Параметры».
- В новом окне перейдите в раздел «Обновление и безопасность».
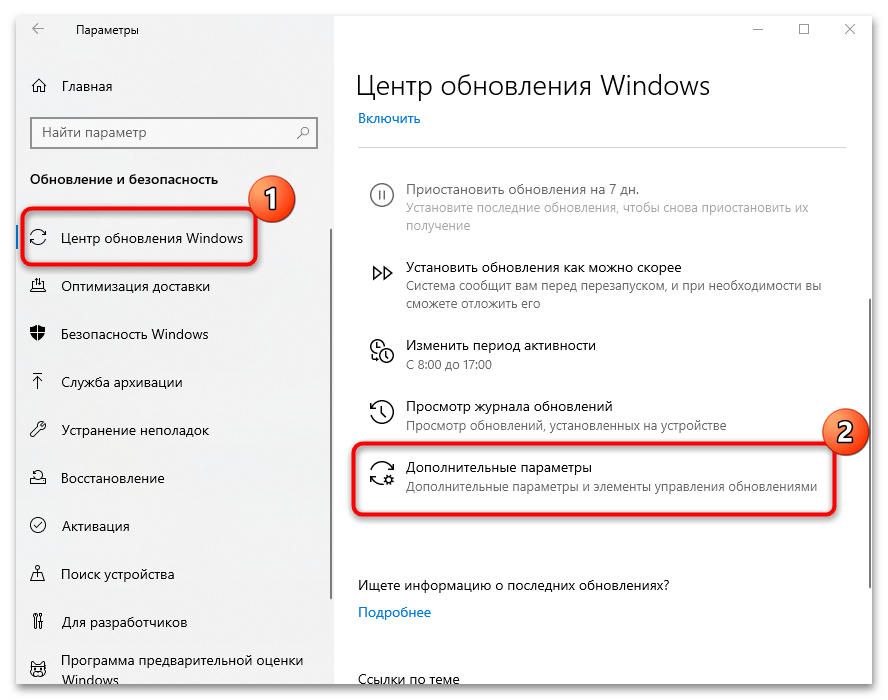
- На вкладке «Центр обновления Windows» выберите функцию возобновления автообновлений. Также можно настроить автоматические обновления, убрав лимитное подключение или изменив другие настройки. Для этого кликните по строке «Дополнительные параметры».
- Если на компьютере установлены другие продукты компании Microsoft, например Word, то для автоматического обновления программ отметьте соответствующую опцию. Если используется интернет с ограниченным трафиком, то лучше отключить скачивание обновлений через лимитные подключения.

Читайте также: Решение проблем с работоспособностью Центра обновлений Windows 10
Еще статьи по данной теме:
Помогла ли Вам статья?
Центр обновления Windows зависит от нескольких других служб, которые также должны быть запущены на вашем компьютере.
…
Проверьте отображение услуг справа на предмет названий:
- Фоновая интеллектуальная служба передачи.
- Криптографические службы.
- Автоматические обновления.
- Журнал событий.
Что такое помощник по обновлению Windows 10 и нужен ли он мне?
Помощник по обновлению Windows 10 — это инструмент управления обновлениями в Windows 10, который используется для предоставления последних обновлений функций Windows, уведомления пользователей об управлении последними обновлениями и обеспечения безопасности вашей системы Windows 10.
Безопасно ли отключать службу Центра обновления Windows?
Мы не рекомендуем вам отключить автоматическое обновление Windows in Windows 10. Если на вашем компьютере все в порядке с загрузками в фоновом режиме и это не влияет на вашу работу, делать это не рекомендуется.
Выпускает ли Microsoft Windows 11?
Операционная система Microsoft для настольных ПК следующего поколения, Windows 11, уже доступна в бета-версии и будет официально выпущена Октябрь 5th.
Можно ли удалить Помощник по обновлению Windows 10?
Так что да, вы совершенно правы, удалив Update Assistant. в Настройки> Приложения> Приложения и функции. В этом больше нет необходимости, да и вообще в этом нет необходимости.
Что произойдет, если я удалю Помощник по обновлению Windows 10?
Помощник по обновлению Windows 10 будет мертв навсегда и вы можете использовать свой идеально работающий компьютер как есть неограниченное время без перебоев.
Как я могу бесплатно обновить Windows?
Посетите страницу загрузки Windows 10. Это официальная страница Microsoft, которая может позволить вам выполнить обновление бесплатно. Когда вы окажетесь там, откройте Windows 10 Media Creation Tool (нажмите «Загрузить инструмент сейчас») и выберите «Обновить этот компьютер сейчас».
Что происходит во время обновления Windows?
В процессе обновления Windows Update Orchestrator работает в фоновом режиме для сканирования, загрузки и установки обновлений. Он выполняет эти действия автоматически, в соответствии с вашими настройками, и беззвучно, чтобы не мешать работе вашего компьютера.
SCCM лучше WSUS?
WSUS может удовлетворить потребности сети только для Windows на самом базовом уровне, в то время как SCCM предлагает расширенный набор инструментов для большего контроля над развертыванием исправлений и видимостью конечных точек. SCCM также предлагает способы исправления альтернативных ОС и сторонних приложений, но в целом он все еще оставляет желать лучшего. много желать лучшего.
Центр обновления Windows 10 – это программная утилита операционной системы, которая отвечает за скачивание и установку всех внутренних компонентов Windows. Если в самом начале ОС была достаточно сырая, то сейчас это одна из самых продвинутых систем во всем мире. Для чего нужно производить регулярное обновление:
- Оптимизация и ускорение работы всей системы.
- Улучшение безопасности.
- Исправление ошибок и дыр в безопасности.
- Обнова модуля встроенного антивируса.
- Оптимизация работы с программами и драйверами.
- Исправление глобальных и мелких ошибок ОС.
Компания Microsoft советует регулярно обновлять систему, и с ней я в этом полностью согласен. В свое время я работал инженеров в одной крупной конторе. Как-то раз всю компанию поразил вирус «WannaCry», несмотря на то что на всех компах стоял антивирусник. А все дело было в том, что операционные системы не обновлялись из-за кривой настройки центра обновления. И как итог – почти вся информация была удалена с компов сотрудников. И если бы система была бы вовремя обновлена, то одна из дыр безопасности, через которую проник вирус – просто отсутствовала, и подобная проблема не возникла.
В статье ниже я расскажу, как выполнить и включить обновление (или автообновление) Windows 10, и как это же обновление настроить. Также я рассмотрю ситуацию, когда служба в ОС отключена. Она может быть отключена в нескольких случаях. Когда пользователь сам сделал это, или была установлена определенная сборка.
Содержание
- Запуск и настройка
- Включение службы
- Способ 1: Службы
- Способ 2: Командная строка
- Способ 3: Диспетчер задач
- Нет службы центр обновления Windows 10
- Настройка автоматического обновления по расписанию
- Задать вопрос автору статьи
Запуск и настройка
В этой главе я расскажу вам, как выполнить поиск обновлений, как выключить эту процедуру, чтобы она не выполнялась автоматически, а также рассмотрим дополнительные настройки.
- Откройте «Пуск» – «Параметры».
- Перейдите в «Обновление и безопасность».
- Вы можете сразу выполнить проверку наличия обновы для вашей системы.
- После этого начнется установка обязательных компонентов системы. Некоторые компоненты могут быть установлены только после перезагрузки компьютера.
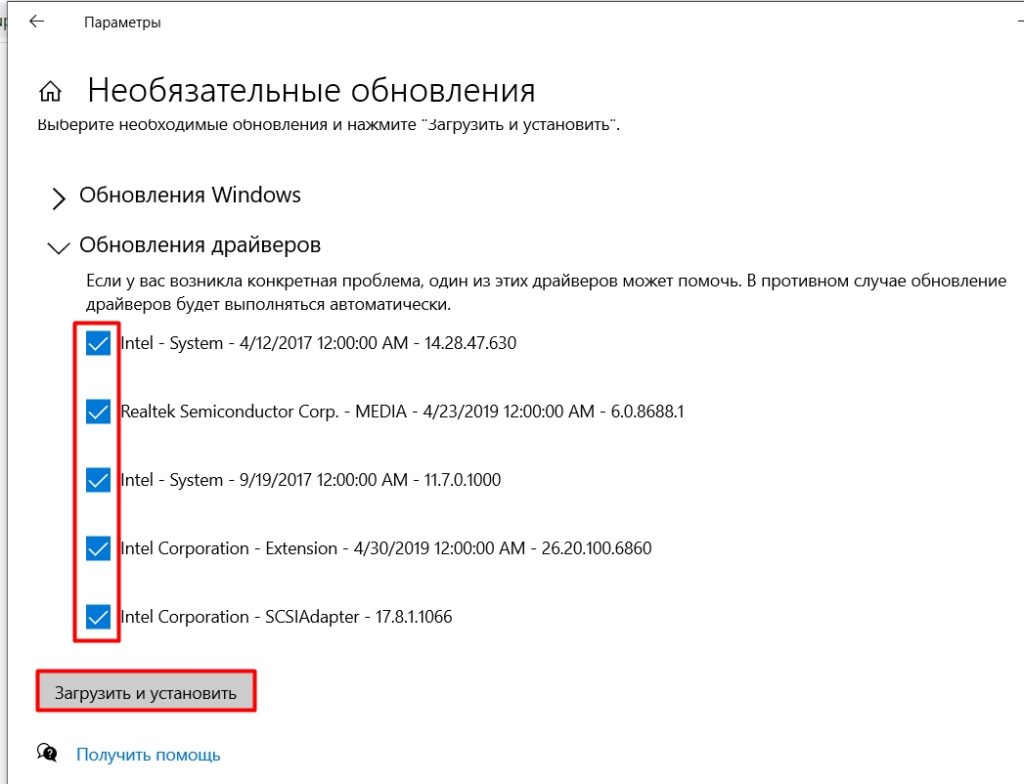
- Если нажать по ссылке «Необязательные обновления», то тут можно обновить драйвера. Нужно понимать, что они будут скачены с серверов Microsoft, а там, как правило, есть не все свежие драйвера. Поэтому я всегда советую обновлять их вручную – об этом подробно написано тут.
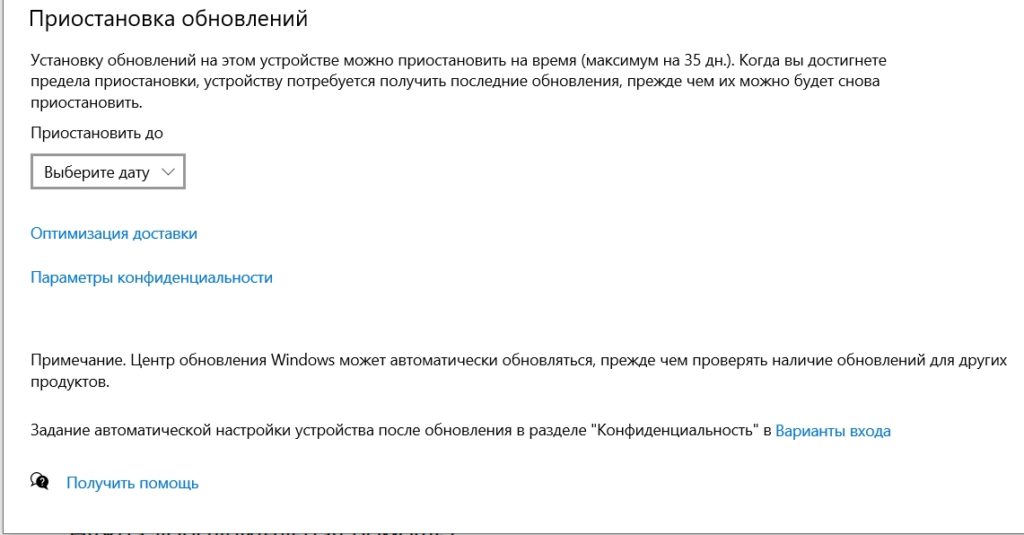
- Перейдите на один шаг назад. Давайте рассмотрим дополнительные настройки. Первая кнопка – вы можете приостановить скачивание хоть каких-то обновлений на 7 дней. Можно изменить период вашей активности – в этот период никаких скачиваний не происходит. Журнал мы рассматривать не будем, так как там особо ничего интересного нет.
Перейдите в «Дополнительные параметры». Если у вас установлена Microsoft Word или другие программные продукты от данной компании, то можно установить галочку для автоматического обновления и этих программ. Если вы используете интернет с ограничением по трафику, то тут можно установить лимитное подключение. Третью галочку устанавливать не рекомендую, так как в таком случае комп будет сам перезагружаться в момент установки новых пакетов.
В самом низу можно отложить обновление, но на максимальный срок – до 35 дней.
Включение службы
В этой главе мы рассмотрим, именно включение самой службы центра обновления Windows 10. Рассмотрим несколько вариантов. Они все делают одно и тоже, поэтому просто выберите тот, который вам больше всего понравится.
Способ 1: Службы
- Найдите на клавиатуре две кнопки и R и нажмите на них, чтобы вызвать вспомогательную программы по выполнению системных утилит.
- Вписываем команду:
services.msc
ПРИМЕЧАНИЕ! В службы вы можете попасть и через поиск системы – просто вбейте туда это же название.
- В списке находим «Центр обновления Windows», открываем его и устанавливаем тип запуска в «Автоматическом» режиме. Применяем настройку.
- Перезагружаем комп.
Способ 2: Командная строка
Запускаем командную строку с правами администратора. Вы можете сделать это любым способом, но проще всего найти консоль через поиск Виндовс, вбив название в поисковую строку. Если вы не видите поиск, найдите значок лупы в левом нижнем углу и нажмите на него.
Далее внимательно вводим команду:
net start wuauserv
Чтобы применить команду, нажмите на клавишу «Enter» на клавиатуре. Далее вы должны увидеть сообщение, что служба успешно запущена.
Способ 3: Диспетчер задач
Зайдите в «Диспетчер задач» – для этого нажмите правой кнопкой мыши по кнопке «Пуск» или по пустой области нижней полоски основной панели.
Перейдите на вкладку «Службы». Найдите службу под названием:
wuauserv
Опять жмем правой кнопкой и из выпадающего списка выбираем «Запустить». Если вы не можете найти эту службу, то вы можете отсортировать службы по алфавитному порядку, для этого нажмите по верхнему названию столбца – «Имя».
Нет службы центр обновления Windows 10
Если вы столкнулись с тем, что служба куда-то пропала, то вот несколько рекомендаций, которые должны помочь:
- Выполните откат системы до определенной точки.
- Выполните проверку и восстановление целостности системных файлов.
- Проверьте ОС антивирусной программой.
- Если вы установили пиратскую сборку, то советую выполнить нормальную установку официальной версии Виндовс 10 – об этом подробно написано тут.
Настройка автоматического обновления по расписанию
Вы можете включить автоматическую скачку обновы. Вы можете установить конкретное время скачивания обновления. Это удобно для тех, кто не хочет, чтобы данная процедура проходила в фоновом режиме и тормозила компьютер и интернет. Давайте рассмотрим способ через редактор локальной групповой политики.
- Используем наши клавиши + R и вписываем:
gpedit.msc
ВЫЛЕЗЛА ОШИБКА! В таком случае у вас установлена домашняя версия Виндовс 10, в которой нет редактора локальной групповой политики.
- Открываем основной раздел «Конфигурация компьютера». В ней находим подраздел «Административные шаблоны». Далее раскрываем папку «Компоненты Windows» и находим там «Центр обновления Windows» (ветку раскрывать не нужно, просто один раз на неё нажмите). Теперь смотрим в правый блок и находим там «Настройку автоматического обновления».
- Сначала включаем конфигурацию. Теперь устанавливаем дни, а также время обновления. Можно также установить расписание обновления – один раз в несколько недель.
- Перезагружаем комп.

Windows Update on Windows 11 |
|
| Other names | Microsoft Update |
|---|---|
| Developer(s) | Microsoft |
| Operating system |
|
| Included with |
|
| Service name | Windows Update |
| Type | Network service |
| Website | support.microsoft.com/en-us/windows/windows-update-faq |
Windows Update is a Microsoft service for the Windows 9x and Windows NT families of operating system, which automates downloading and installing Microsoft Windows software updates over the Internet. The service delivers software updates for Windows, as well as the various Microsoft antivirus products, including Windows Defender and Microsoft Security Essentials. Since its inception, Microsoft has introduced two extensions of the service: Microsoft Update and Windows Update for Business. The former expands the core service to include other Microsoft products, such as Microsoft Office and Microsoft Expression Studio. The latter is available to business editions of Windows 10 and permits postponing updates or receiving updates only after they have undergone rigorous testing.
As the service has evolved over the years, so has its client software. For a decade, the primary client component of the service was the Windows Update web app that could only be run on Internet Explorer. Starting with Windows Vista, the primary client component became Windows Update Agent, an integral component of the operating system.
The service provides several kinds of updates. Security updates or critical updates mitigate vulnerabilities against security exploits against Microsoft Windows. Cumulative updates are updates that bundle multiple updates, both new and previously released updates. Cumulative updates were introduced with Windows 10 and have been backported to Windows 7 and Windows 8.1.
Microsoft routinely releases updates on the second Tuesday of each month (known as the Patch Tuesday), but can provide them whenever a new update is urgently required to prevent a newly discovered or prevalent exploit. System administrators can configure Windows Update to install critical updates for Microsoft Windows automatically, so long as the computer has an Internet connection.
In Windows 10 and Windows 11, the use of Windows Update is mandatory, however, the software agreement states that users may stop receiving updates on their device by disconnecting their device from the Internet.[1][2]
Clients[edit]
Windows Update web app[edit]
The Windows Update web app, version 4, in Windows Me
Windows Update was introduced as a web app with the launch of Windows 98 and offered additional desktop themes, games, device driver updates, and optional components such as NetMeeting.[3] Windows 95 and Windows NT 4.0 were retroactively given the ability to access the Windows Update website and download updates designed for those operating systems, starting with the release of Internet Explorer 4. The initial focus of Windows Update was free add-ons and new technologies for Windows. Security fixes for Outlook Express, Internet Explorer and other programs appeared later, as did access to beta versions of upcoming Microsoft software, e.g. Internet Explorer 5. Fixes to Windows 98 to resolve the Year 2000 problem were distributed using Windows Update in December 1998. Microsoft attributed the sales success of Windows 98 in part to Windows Update.[4]
The Windows Update web app requires either Internet Explorer or a third-party web browser that supports the ActiveX technology. The first version of the web app, version 3, does not send any personally-identifiable information to Microsoft. Instead, the app downloads a full list of every available update and chooses which one to download and install. But the list grew so large that the performance impact of processing became a concern. Arie Slob, writing for the Windows-help.net newsletter in March 2003, noted that the size of the update list had exceeded 400 KB, which caused delays of more than a minute for dial-up users.[5] Windows Update v4, released in 2001 in conjunction with Windows XP, changed this. This version of the app makes an inventory of the system’s hardware and Microsoft software and sends them to the service, thus offloading the processing burden to Microsoft servers.[5]
Critical Update Notification Utility[edit]
Critical Update Notification Utility (initially Critical Update Notification Tool) is a background process that checks the Windows Update web site on a regular schedule for new updates that have been marked as «Critical». It was released shortly after Windows 98.
By default, this check occurs every five minutes, plus when Internet Explorer starts; however, the user could configure the next check to occur only at certain times of the day or on certain days of the week. The tool queries the Microsoft server for a file called «cucif.cab«, which contained a list of all the critical updates released for the operating system. The tool then compares this list with the list of installed updates on its machine and displays an update availability notification. Once the check is executed, any custom schedule defined by the user is reverted to the default. Microsoft stated that this ensures that users received notification of critical updates in a timely manner.[6]
An analysis done by security researcher H. D. Moore in early 1999 was critical of this approach, describing it as «horribly inefficient» and susceptible to attacks. In a posting to BugTraq, he explained that, «every single Windows 98 computer that wishes to get an update has to rely on a single host for the security. If that one server got compromised one day, or an attacker cracks the [Microsoft] DNS server again, there could be millions of users installing trojans every hour. The scope of this attack is big enough to attract crackers who actually know what they are doing…»[7]
Microsoft continued to promote the tool through 1999 and the first half of 2000. Initial releases of Windows 2000 shipped with the tool. The tool did not support Windows 95 and Windows NT 4.0.
Automatic Updates[edit]
Automatic Updates is the successor of the Critical Update Notification Utility. It was released in 2000, along with Windows Me. It supports Windows 2000 SP3 as well.
Unlike its predecessor, Automatic Updates can download and install updates. Instead of the five-minute schedule used by its predecessor, Automatic Updates checks the Windows Update servers once a day. After Windows Me is installed, a notification balloon prompts the user to configure the Automatic Updates client. The user can choose from three notification schemes: Being notified before downloading the update, being notified before installing the update, or both. If new updates are ready to be installed, the user may install them before turning off the computer. A shield icon will be displayed on the Shutdown button during this time.
Windows XP and Windows 2000 SP3 include Background Intelligent Transfer Service, a Windows service for transferring files in the background without user interaction. As a system component, it is capable of monitoring the user’s Internet usage, and throttling its own bandwidth usage in order to prioritize user-initiated activities. The Automatic Updates client for these operating systems was updated to use this system service.
Automatic Updates in Windows XP gained notoriety for repeatedly interrupting the user while working on their computer. Every time an update requiring a reboot was installed, Automatic Updates would prompt the user with a dialog box that allowed the user to restart immediately or dismiss the dialog box, which would reappear in ten minutes; a behavior that Jeff Atwood described as «perhaps the naggiest dialog box ever.»[8]
In 2013, it was observed that shortly after the startup process, Automatic Updates (wuauclt.exe) and Service Host (svchost.exe) in Windows XP would claim 100% of a computer’s CPU capacity for extended periods of time (between ten minutes to two hours), making affected computers unusable. According to Woody Leonhart of InfoWorld, early reports of this issue could be seen in Microsoft TechNet forums in late May 2013, although Microsoft first received large number of complaints about this issue in September 2013. The cause was an exponential algorithm in the evaluation of superseded updates which had grown large over the decade following the release of Windows XP. Microsoft’s attempts to fix the issue in October, November and December proved futile, causing the issue to be escalated to the top priority.[9][10]
Windows Update Agent[edit]
Starting with Windows Vista and Windows Server 2008, Windows Update Agent replaces both the Windows Update web app and the Automatic Updates client.[11][12] It is in charge of downloading and installing software update from Windows Update, as well as the on-premises servers of Windows Server Updates Services or System Center Configuration Manager.[13][14]
Windows Update Agent can be managed through a Control Panel applet, as well as Group Policy, Microsoft Intune and Windows PowerShell. It can also be set to automatically download and install both important and recommended updates. In prior versions of Windows, such updates were only available through the Windows Update web site. Additionally, Windows Update in Windows Vista supports downloading Windows Ultimate Extras, optional software for Windows Vista Ultimate Edition.
Unlike Automatic Updates in Windows XP, Windows Update Agent in Windows Vista and Windows 7 allows the user to postpone the mandatory restart (required for the update process to complete) for up to four hours. The revised dialog box that prompts for the restart appears under other windows, instead of on top of them. However, standard user accounts only have 15 minutes to respond to this dialog box. This was changed with Windows 8: Users have 3 days (72 hours) before the computer reboots automatically after installing automatic updates that require a reboot. Windows 8 also consolidates the restart requests for non-critical updates into just one per month. Additionally, the login screen notifies them of the restart requirements.[15]
Windows Update Agent makes use of the Transactional NTFS feature introduced with Windows Vista to apply updates to Windows system files. This feature helps Windows recover cleanly in the event of an unexpected failure, as file changes are committed atomically.[16]
Windows 10 contains major changes to Windows Update Agent operations; it no longer allows the manual, selective installation of updates. All updates, regardless of type (this includes hardware drivers), are downloaded and installed automatically, and users are only given the option to choose whether their system would reboot automatically to install updates when the system is inactive, or be notified to schedule a reboot.[17][18] Microsoft offers a diagnostic tool that can be used to hide troublesome device drivers and prevent them from being reinstalled, but only after they had been already installed, then uninstalled without rebooting the system.[19][20]
Windows Update Agent on Windows 10 supports peer-to-peer distribution of updates; by default, systems’ bandwidth is used to distribute previously downloaded updates to other users, in combination with Microsoft servers. Users may optionally change Windows Update to only perform peer-to-peer updates within their local area network.[21]
Windows 10 also introduced cumulative updates. For example, if Microsoft released updates KB00001 in July, KB00002 in August, and KB00003 in September, Microsoft would release cumulative update KB00004 which packs KB00001, KB00002, and KB00003 together. Installing KB00004 will also install KB00001, KB00002 and KB00003, mitigating the need for multiple restarts and reducing the number of downloads needed. KB00004 may also include other fixes with their own KB-number that were not separately released.[22] A disadvantage of cumulative updates is that downloading and installing updates that fix individual problems is no longer possible. KB stands for knowledge base as in Microsoft Knowledge Base.
Windows Update for Business[edit]
Windows Update for Business is a term for a set of features in the Pro, Enterprise and Education editions of Windows 10, intended to ease the administration of Windows across organizations. It enables IT pros to:[23][24][25]
- Switch between the standard and the deferred release branches of Windows 10. This feature has since been removed as Microsoft retired the deferred branch.[26]
- Defer automatic installation of ordinary updates for 30 days. Starting with Windows 10 version 20H1, this feature is more difficult to access.[27]
- Defer automatic installation of Windows upgrades (a.k.a. «feature updates») for 365 days. Starting with Windows 10 version 20H1, these updates are no longer automatically offered.[27]
These features were added in Windows 10 version 1511.[28] They are intended for large organizations with many computers, so they can logically group their computers for gradual deployment. Microsoft recommends a small set of pilot computers to receive the updates almost immediately, while the set of most critical computers to receive them after every other group has done so, and has experienced their effects.[29]
Other Microsoft update management solutions, such as Windows Server Update Services or System Center Configuration Manager, do not override Windows Update for Business. Rather, they force Windows 10 into the «dual scan mode». This can cause confusion for administrators who do not comprehend the full ramifications of the dual scan mode.[30]
Complementary software and services[edit]
As organizations continued to use more computers, the per-machine Windows Update clients started to become unwieldy and insufficient. In response to the need of organizations for deploying updates to many machines, Microsoft introduced Software Update Services (SUS), which was later renamed Windows Server Update Services (WSUS). A component of the Windows Server family of operating systems, WSUS downloads updates for Microsoft products to a server computer on which it is running and redistributes them to the computers within the organization over a local area network (LAN). One of the benefits of this method is a reduction in the consumption of Internet bandwidth, equal to (N-1)×S, where N is the number of computers in the organization and S is the size made by the updates. Additionally, WSUS permits administrators to test updates on a small group of test computers before deploying them to all systems, in order to ensure that business continuity is not disrupted because of the changes of the updates. For very large organizations, multiple WSUS servers can be chained together hierarchically. Only one server in this hierarchy downloads from the Internet.
Update packages distributed via the Windows Update service can be individually downloaded from Microsoft Update Catalog. These updates can be installed on computers without internet access (e.g. via USB flash drive) or slipstreamed with a Windows installation. In case of the former, Windows Update Agent (wusa.exe) can install these files. In case of the latter, Microsoft deployment utilities such as DISM, WADK and MDT can consume these packages.
Microsoft offers System Center Configuration Manager for very complex deployment and servicing scenarios. The product integrates with all of the aforesaid tools (WSUS, DISM, WADK, MDT) to automate the process.
A number of tools have been created by independent software vendors which provide the ability for Windows Updates to be automatically downloaded for, or added to, an online or offline system. One common use for offline updates is to ensure a system is fully patched against security vulnerabilities before being connected to the Internet or another network. A second use is that downloads can be very large, but may be dependent on a slow or unreliable network connection, or the same updates may be needed for more than one machine. AutoPatcher, WSUS Offline Update, PortableUpdate, and Windows Updates Downloader are examples of such tools.[31]
Service[edit]
At the beginning of 2005, Windows Update was being accessed by about 150 million people,[32] with about 112 million of those using Automatic Updates.[33] As of 2008, Windows Update had about 500 million clients, processed about 350 million unique scans per day, and maintained an average of 1.5 million simultaneous connections to client machines. On Patch Tuesday, the day Microsoft typically releases new software updates, outbound traffic could exceed 500 gigabits per second.[34] Approximately 90% of all clients used automatic updates to initiate software updates, with the remaining 10% using the Windows Update web site. The web site is built using ASP.NET, and processes an average of 90,000 page requests per second.
Traditionally, the service provided each patch in its own proprietary archive file. Occasionally, Microsoft released service packs which bundled all updates released over the course of years for a certain product. Starting with Windows 10, however, all patches are delivered in cumulative packages.[35] On 15 August 2016, Microsoft announced that effective October 2016, all future patches to Windows 7 and 8.1 would become cumulative as with Windows 10. The ability to download and install individual updates would be removed as existing updates are transitioned to this model.[36] This has resulted in increasing download sizes of each monthly update. An analysis done by Computerworld determined that the download size for Windows 7 x64 has increased from 119.4MB in October 2016 to 203MB in October 2017.[37] Initially, Microsoft was very vague about specific changes within each cumulative update package.[35] However, since early 2016, Microsoft has begun releasing more detailed information on the specific changes.[38]
In 2011, the update service was decommissioned for Windows 98, 98 SE, ME and NT4 and the old updates for those systems were removed from its servers.[39][40]
On August 3, 2020, the update service was decommissioned for Windows 2000, XP, Server 2003 and Vista due to Microsoft discontinuing SHA-1 updates. The old updates are still available on the Microsoft Update Catalog.[41]
Microsoft Update[edit]
At the February 2005 RSA Conference, Microsoft announced the first beta of Microsoft Update, an optional replacement for Windows Update that provides security patches, service packs and other updates for both Windows and other Microsoft software.[42] The initial release in June 2005 provided support for Microsoft Office 2003, Exchange 2003, and SQL Server 2000, running on Windows 2000, XP, and Server 2003. Over time, the list has expanded to include other Microsoft products, such as Windows Live, Windows Defender, Visual Studio, runtimes and redistributables, Zune Software, Virtual PC and Virtual Server, CAPICOM, Microsoft Lync, Microsoft Expression Studio, and other server products. It also offers Silverlight and Windows Media Player as optional downloads if applicable to the operating system.
Office Update[edit]
Office Update is a free online service that allows users to detect and install updates for certain Microsoft Office products.
The original update service supported Office 2000, Office XP, Office 2003 and Office 2007. On 1 August 2009 Microsoft decommissioned the Office Update service, merging it with Microsoft Update.[43] Microsoft Update does not support Office 2000.
With the introduction of the Office 365 licensing program, however, Microsoft once again activated a separate Office update service.[44][45]
References[edit]
- ^ «Microsoft License Terms». www.microsoft.com. Section 13b. Retrieved 30 March 2020.
- ^ «MICROSOFT SOFTWARE LICENSE TERMS». www.microsoft.com. Retrieved 20 July 2022.
Canada. You may stop receiving updates on your device by turning off Internet access. If and when you re-connect to the Internet, the software will resume checking for and installing updates.
- ^ Gartner, John (24 August 1995). «Taking Windows 98 For A Test-Drive». TechWeb. CMP Net. Archived from the original on 3 December 1998.
- ^ «Strong Holiday Sales Make Windows 98 Best-Selling Software of 1998». PressPass (Press release). Microsoft. 9 February 1999. Archived from the original on 6 March 2012. Retrieved 29 July 2008.
- ^ a b Slob, Arie (22 March 2003). «Windows Update is Spying on You!». Windows-Help.NET. InfiniSource. Archived from the original on 14 January 2018. Retrieved 12 September 2019.
- ^ «Description of the Windows Critical Update Notification utility». Support. Microsoft. 5 December 2007. Archived from the original on 26 July 2020. Retrieved 22 November 2018.
- ^ Moore, H. D. (29 January 1999). «How the MS Critical Update Notification works…» BugTraq mailing list archive. Archived from the original on 21 June 2009. Retrieved 30 July 2008 – via seclists.org.
- ^ Atwood, Jeff (13 May 2005). «XP Automatic Update Nagging». Coding Horror: Programming and Human Factors. Archived from the original on 9 November 2021. Retrieved 12 September 2019.
- ^ Bright, Peter (16 December 2013). «Exponential algorithm making Windows XP miserable could be fixed». Ars Technica. Condé Nast. Archived from the original on 6 May 2021. Retrieved 12 September 2019.
- ^ Leonhard, Woody (16 December 2013). «Microsoft promises to fix Windows XP SVCHOST redlining ‘as soon as possible’«. InfoWorld. IDG. Archived from the original on 30 March 2019. Retrieved 12 September 2019.
- ^ «How to update the Windows Update Agent to the latest version». Support. Microsoft. 6 June 2017. Archived from the original on 4 September 2020. Retrieved 22 November 2018.
- ^ «Windows Update Agent». TechNet. Microsoft. 13 December 2007. Archived from the original on 14 January 2018. Retrieved 22 November 2018.
- ^ «How to Install the Windows Update Agent on Client Computers». TechNet. Microsoft. 2007. Archived from the original on 11 October 2018. Retrieved 22 November 2018.
- ^ Rouse, Margaret (May 2014). «Microsoft Windows Update Agent». TechTarget. Archived from the original on 27 January 2021. Retrieved 22 November 2018.
- ^ Savov, Vlad (15 November 2011). «Windows 8 auto-update will consolidate restarts into one per month, give you three days to do it». The Verge. Vox Media. Archived from the original on 29 August 2021. Retrieved 22 November 2018.
- ^ «NTFS Beta Chat Transcript (July 12, 2006)». Storage at Microsoft. Microsoft. 12 July 2006. Archived from the original on 20 April 2019. Retrieved 22 November 2018.
- ^ «Windows 10 lets you schedule Windows Update restarts». CNET. Archived from the original on 19 February 2015. Retrieved 4 August 2015.
- ^ «Did Microsoft Just Backtrack On Forced Updates For Windows 10?». CRN.com. 27 July 2015. Archived from the original on 28 July 2015. Retrieved 4 August 2015.
- ^ «On the road to Windows 10: Nvidia driver tests KB 3073930 patch blocker». InfoWorld. 27 July 2015. Archived from the original on 20 June 2017. Retrieved 31 July 2015.
- ^ «On the road to Windows 10: Problems with forced updates and KB 3073930». InfoWorld. 22 July 2015. Archived from the original on 20 June 2017. Retrieved 31 July 2015.
- ^ «How to stop Windows 10 from using your PC’s bandwidth to update strangers’ systems». PC World. IDG. Archived from the original on 5 August 2015. Retrieved 4 August 2015.
- ^ «User can’t log on to a POP/IMAP account by using NTLM authentication in Exchange Server 2013». Archived from the original on 10 February 2021. Retrieved 24 March 2020.
To resolve this issue, install Cumulative Update 21
- ^ Hammoudi, Samir (15 November 2015). «Windows Update for Business explained». beanexpert. Microsoft. Archived from the original on 19 April 2019. Retrieved 14 January 2018.
- ^ Azzarello, Pat (10 May 2017). «What is Windows Update for Business?». Windows for IT Pros. Microsoft. Archived from the original on 11 June 2018. Retrieved 14 January 2018.
Windows Update for Business is intended for machines running Windows 10 or later, and Windows 10 Education, Professional, or Enterprise editions managed in organizations.
- ^ Halfin, Danni; Brower, Nick; Lich, Brian; Poggemeyer, Liza (13 October 2017). «Deploy updates using Windows Update for Business». Microsoft Docs. Microsoft. Archived from the original on 22 October 2021. Retrieved 22 November 2018.
- ^ «Microsoft changes Windows Update for Business options — gHacks Tech News». www.ghacks.net. 15 February 2019. Archived from the original on 6 October 2021. Retrieved 3 November 2020.
- ^ a b «Microsoft removes Setting to defer feature updates from Windows 10 version 2004 — gHacks Tech News». www.ghacks.net. 25 June 2020. Archived from the original on 27 August 2021. Retrieved 3 November 2020.
- ^ Bott, Ed (17 January 2018). «How to take control of Windows 10 updates and upgrades (even if you don’t own a business)». ZDNet. CBS Interactive. Archived from the original on 12 November 2021. Retrieved 22 November 2018.
- ^ Halfin, Danni; Lich, Brian (27 July 2017). «Build deployment rings for Windows 10 updates». Microsoft Docs. Microsoft. Archived from the original on 24 May 2021. Retrieved 22 November 2018.
- ^ Rasheed, Shadab (9 January 2017). «Why WSUS and SCCM managed clients are reaching out to Microsoft Online». Windows Server Blog. Microsoft. Archived from the original on 14 January 2018. Retrieved 22 November 2018.
- ^ «4 Tools to Update Windows Offline and install Hotfixes from a Local Source». raymond.cc. 14 November 2005. Archived from the original on 20 October 2021. Retrieved 22 November 2018.
- ^ «RSA Conference 2005: «Security: Raising the Bar» (speech transcript)». PressPass. Microsoft. 15 February 2005. Archived from the original on 8 March 2009. Retrieved 30 July 2008.
- ^ «Microsoft Announces Availability of New Solutions to Help Protect Customers Against Spyware and Viruses». PressPass. Microsoft. 6 January 2005. Archived from the original on 2 April 2012. Retrieved 30 July 2008.
- ^ «Introducing the Microsoft.com Engineering Operations Team». Microsoft TechNet. Microsoft. 2008. Archived from the original on 26 August 2017. Retrieved 31 May 2012.
- ^ a b «Windows 10 users beg Microsoft for more info on updates». Computerworld. IDG. 14 September 2015. Archived from the original on 14 September 2015. Retrieved 30 September 2015.
- ^ «Windows 7, 8.1 moving to Windows 10’s cumulative update model». Ars Technica. Conde Nast Digital. 15 August 2016. Archived from the original on 14 February 2017. Retrieved 16 August 2016.
- ^ Gregg Keizer (14 December 2017). «Why Windows 7 updates are getting bigger». Computerworld. Archived from the original on 22 November 2018. Retrieved 22 November 2018.
- ^ «Windows 10 update details». Windows 10 update history. Microsoft. Archived from the original on 5 March 2016. Retrieved 4 March 2016.
- ^ «I can’t access Windows Update v4 — Windows 9x/ME — MSFN». msfn.org. Archived from the original on 9 November 2021. Retrieved 25 April 2021.
- ^ «Where is Windows Update for Win98? — BetaArchive». www.betaarchive.com. Archived from the original on 8 November 2021. Retrieved 25 April 2021.
- ^ «Windows Update SHA-1 based endpoints discontinued for older Windows devices». Archived from the original on 18 December 2020. Retrieved 5 August 2020.
- ^ «Microsoft Update Site Launched». helpwithwindows.com. 10 June 2005. Archived from the original on 22 November 2018. Retrieved 30 July 2008.
- ^ «About Office Update». office.microsoft.com. Microsoft. Archived from the original on 28 May 2010.
- ^ «Install Office updates». support.office.com. Microsoft. Archived from the original on 23 May 2020. Retrieved 4 December 2017.
- ^ «Check for Office for Mac updates automatically». support.office.com. Microsoft. Archived from the original on 9 August 2018. Retrieved 4 December 2017.
External links[edit]
- Microsoft Update website
- Microsoft Technical Security Notifications

Windows Update on Windows 11 |
|
| Other names | Microsoft Update |
|---|---|
| Developer(s) | Microsoft |
| Operating system |
|
| Included with |
|
| Service name | Windows Update |
| Type | Network service |
| Website | support.microsoft.com/en-us/windows/windows-update-faq |
Windows Update is a Microsoft service for the Windows 9x and Windows NT families of operating system, which automates downloading and installing Microsoft Windows software updates over the Internet. The service delivers software updates for Windows, as well as the various Microsoft antivirus products, including Windows Defender and Microsoft Security Essentials. Since its inception, Microsoft has introduced two extensions of the service: Microsoft Update and Windows Update for Business. The former expands the core service to include other Microsoft products, such as Microsoft Office and Microsoft Expression Studio. The latter is available to business editions of Windows 10 and permits postponing updates or receiving updates only after they have undergone rigorous testing.
As the service has evolved over the years, so has its client software. For a decade, the primary client component of the service was the Windows Update web app that could only be run on Internet Explorer. Starting with Windows Vista, the primary client component became Windows Update Agent, an integral component of the operating system.
The service provides several kinds of updates. Security updates or critical updates mitigate vulnerabilities against security exploits against Microsoft Windows. Cumulative updates are updates that bundle multiple updates, both new and previously released updates. Cumulative updates were introduced with Windows 10 and have been backported to Windows 7 and Windows 8.1.
Microsoft routinely releases updates on the second Tuesday of each month (known as the Patch Tuesday), but can provide them whenever a new update is urgently required to prevent a newly discovered or prevalent exploit. System administrators can configure Windows Update to install critical updates for Microsoft Windows automatically, so long as the computer has an Internet connection.
In Windows 10 and Windows 11, the use of Windows Update is mandatory, however, the software agreement states that users may stop receiving updates on their device by disconnecting their device from the Internet.[1][2]
Clients[edit]
Windows Update web app[edit]
The Windows Update web app, version 4, in Windows Me
Windows Update was introduced as a web app with the launch of Windows 98 and offered additional desktop themes, games, device driver updates, and optional components such as NetMeeting.[3] Windows 95 and Windows NT 4.0 were retroactively given the ability to access the Windows Update website and download updates designed for those operating systems, starting with the release of Internet Explorer 4. The initial focus of Windows Update was free add-ons and new technologies for Windows. Security fixes for Outlook Express, Internet Explorer and other programs appeared later, as did access to beta versions of upcoming Microsoft software, e.g. Internet Explorer 5. Fixes to Windows 98 to resolve the Year 2000 problem were distributed using Windows Update in December 1998. Microsoft attributed the sales success of Windows 98 in part to Windows Update.[4]
The Windows Update web app requires either Internet Explorer or a third-party web browser that supports the ActiveX technology. The first version of the web app, version 3, does not send any personally-identifiable information to Microsoft. Instead, the app downloads a full list of every available update and chooses which one to download and install. But the list grew so large that the performance impact of processing became a concern. Arie Slob, writing for the Windows-help.net newsletter in March 2003, noted that the size of the update list had exceeded 400 KB, which caused delays of more than a minute for dial-up users.[5] Windows Update v4, released in 2001 in conjunction with Windows XP, changed this. This version of the app makes an inventory of the system’s hardware and Microsoft software and sends them to the service, thus offloading the processing burden to Microsoft servers.[5]
Critical Update Notification Utility[edit]
Critical Update Notification Utility (initially Critical Update Notification Tool) is a background process that checks the Windows Update web site on a regular schedule for new updates that have been marked as «Critical». It was released shortly after Windows 98.
By default, this check occurs every five minutes, plus when Internet Explorer starts; however, the user could configure the next check to occur only at certain times of the day or on certain days of the week. The tool queries the Microsoft server for a file called «cucif.cab«, which contained a list of all the critical updates released for the operating system. The tool then compares this list with the list of installed updates on its machine and displays an update availability notification. Once the check is executed, any custom schedule defined by the user is reverted to the default. Microsoft stated that this ensures that users received notification of critical updates in a timely manner.[6]
An analysis done by security researcher H. D. Moore in early 1999 was critical of this approach, describing it as «horribly inefficient» and susceptible to attacks. In a posting to BugTraq, he explained that, «every single Windows 98 computer that wishes to get an update has to rely on a single host for the security. If that one server got compromised one day, or an attacker cracks the [Microsoft] DNS server again, there could be millions of users installing trojans every hour. The scope of this attack is big enough to attract crackers who actually know what they are doing…»[7]
Microsoft continued to promote the tool through 1999 and the first half of 2000. Initial releases of Windows 2000 shipped with the tool. The tool did not support Windows 95 and Windows NT 4.0.
Automatic Updates[edit]
Automatic Updates is the successor of the Critical Update Notification Utility. It was released in 2000, along with Windows Me. It supports Windows 2000 SP3 as well.
Unlike its predecessor, Automatic Updates can download and install updates. Instead of the five-minute schedule used by its predecessor, Automatic Updates checks the Windows Update servers once a day. After Windows Me is installed, a notification balloon prompts the user to configure the Automatic Updates client. The user can choose from three notification schemes: Being notified before downloading the update, being notified before installing the update, or both. If new updates are ready to be installed, the user may install them before turning off the computer. A shield icon will be displayed on the Shutdown button during this time.
Windows XP and Windows 2000 SP3 include Background Intelligent Transfer Service, a Windows service for transferring files in the background without user interaction. As a system component, it is capable of monitoring the user’s Internet usage, and throttling its own bandwidth usage in order to prioritize user-initiated activities. The Automatic Updates client for these operating systems was updated to use this system service.
Automatic Updates in Windows XP gained notoriety for repeatedly interrupting the user while working on their computer. Every time an update requiring a reboot was installed, Automatic Updates would prompt the user with a dialog box that allowed the user to restart immediately or dismiss the dialog box, which would reappear in ten minutes; a behavior that Jeff Atwood described as «perhaps the naggiest dialog box ever.»[8]
In 2013, it was observed that shortly after the startup process, Automatic Updates (wuauclt.exe) and Service Host (svchost.exe) in Windows XP would claim 100% of a computer’s CPU capacity for extended periods of time (between ten minutes to two hours), making affected computers unusable. According to Woody Leonhart of InfoWorld, early reports of this issue could be seen in Microsoft TechNet forums in late May 2013, although Microsoft first received large number of complaints about this issue in September 2013. The cause was an exponential algorithm in the evaluation of superseded updates which had grown large over the decade following the release of Windows XP. Microsoft’s attempts to fix the issue in October, November and December proved futile, causing the issue to be escalated to the top priority.[9][10]
Windows Update Agent[edit]
Starting with Windows Vista and Windows Server 2008, Windows Update Agent replaces both the Windows Update web app and the Automatic Updates client.[11][12] It is in charge of downloading and installing software update from Windows Update, as well as the on-premises servers of Windows Server Updates Services or System Center Configuration Manager.[13][14]
Windows Update Agent can be managed through a Control Panel applet, as well as Group Policy, Microsoft Intune and Windows PowerShell. It can also be set to automatically download and install both important and recommended updates. In prior versions of Windows, such updates were only available through the Windows Update web site. Additionally, Windows Update in Windows Vista supports downloading Windows Ultimate Extras, optional software for Windows Vista Ultimate Edition.
Unlike Automatic Updates in Windows XP, Windows Update Agent in Windows Vista and Windows 7 allows the user to postpone the mandatory restart (required for the update process to complete) for up to four hours. The revised dialog box that prompts for the restart appears under other windows, instead of on top of them. However, standard user accounts only have 15 minutes to respond to this dialog box. This was changed with Windows 8: Users have 3 days (72 hours) before the computer reboots automatically after installing automatic updates that require a reboot. Windows 8 also consolidates the restart requests for non-critical updates into just one per month. Additionally, the login screen notifies them of the restart requirements.[15]
Windows Update Agent makes use of the Transactional NTFS feature introduced with Windows Vista to apply updates to Windows system files. This feature helps Windows recover cleanly in the event of an unexpected failure, as file changes are committed atomically.[16]
Windows 10 contains major changes to Windows Update Agent operations; it no longer allows the manual, selective installation of updates. All updates, regardless of type (this includes hardware drivers), are downloaded and installed automatically, and users are only given the option to choose whether their system would reboot automatically to install updates when the system is inactive, or be notified to schedule a reboot.[17][18] Microsoft offers a diagnostic tool that can be used to hide troublesome device drivers and prevent them from being reinstalled, but only after they had been already installed, then uninstalled without rebooting the system.[19][20]
Windows Update Agent on Windows 10 supports peer-to-peer distribution of updates; by default, systems’ bandwidth is used to distribute previously downloaded updates to other users, in combination with Microsoft servers. Users may optionally change Windows Update to only perform peer-to-peer updates within their local area network.[21]
Windows 10 also introduced cumulative updates. For example, if Microsoft released updates KB00001 in July, KB00002 in August, and KB00003 in September, Microsoft would release cumulative update KB00004 which packs KB00001, KB00002, and KB00003 together. Installing KB00004 will also install KB00001, KB00002 and KB00003, mitigating the need for multiple restarts and reducing the number of downloads needed. KB00004 may also include other fixes with their own KB-number that were not separately released.[22] A disadvantage of cumulative updates is that downloading and installing updates that fix individual problems is no longer possible. KB stands for knowledge base as in Microsoft Knowledge Base.
Windows Update for Business[edit]
Windows Update for Business is a term for a set of features in the Pro, Enterprise and Education editions of Windows 10, intended to ease the administration of Windows across organizations. It enables IT pros to:[23][24][25]
- Switch between the standard and the deferred release branches of Windows 10. This feature has since been removed as Microsoft retired the deferred branch.[26]
- Defer automatic installation of ordinary updates for 30 days. Starting with Windows 10 version 20H1, this feature is more difficult to access.[27]
- Defer automatic installation of Windows upgrades (a.k.a. «feature updates») for 365 days. Starting with Windows 10 version 20H1, these updates are no longer automatically offered.[27]
These features were added in Windows 10 version 1511.[28] They are intended for large organizations with many computers, so they can logically group their computers for gradual deployment. Microsoft recommends a small set of pilot computers to receive the updates almost immediately, while the set of most critical computers to receive them after every other group has done so, and has experienced their effects.[29]
Other Microsoft update management solutions, such as Windows Server Update Services or System Center Configuration Manager, do not override Windows Update for Business. Rather, they force Windows 10 into the «dual scan mode». This can cause confusion for administrators who do not comprehend the full ramifications of the dual scan mode.[30]
Complementary software and services[edit]
As organizations continued to use more computers, the per-machine Windows Update clients started to become unwieldy and insufficient. In response to the need of organizations for deploying updates to many machines, Microsoft introduced Software Update Services (SUS), which was later renamed Windows Server Update Services (WSUS). A component of the Windows Server family of operating systems, WSUS downloads updates for Microsoft products to a server computer on which it is running and redistributes them to the computers within the organization over a local area network (LAN). One of the benefits of this method is a reduction in the consumption of Internet bandwidth, equal to (N-1)×S, where N is the number of computers in the organization and S is the size made by the updates. Additionally, WSUS permits administrators to test updates on a small group of test computers before deploying them to all systems, in order to ensure that business continuity is not disrupted because of the changes of the updates. For very large organizations, multiple WSUS servers can be chained together hierarchically. Only one server in this hierarchy downloads from the Internet.
Update packages distributed via the Windows Update service can be individually downloaded from Microsoft Update Catalog. These updates can be installed on computers without internet access (e.g. via USB flash drive) or slipstreamed with a Windows installation. In case of the former, Windows Update Agent (wusa.exe) can install these files. In case of the latter, Microsoft deployment utilities such as DISM, WADK and MDT can consume these packages.
Microsoft offers System Center Configuration Manager for very complex deployment and servicing scenarios. The product integrates with all of the aforesaid tools (WSUS, DISM, WADK, MDT) to automate the process.
A number of tools have been created by independent software vendors which provide the ability for Windows Updates to be automatically downloaded for, or added to, an online or offline system. One common use for offline updates is to ensure a system is fully patched against security vulnerabilities before being connected to the Internet or another network. A second use is that downloads can be very large, but may be dependent on a slow or unreliable network connection, or the same updates may be needed for more than one machine. AutoPatcher, WSUS Offline Update, PortableUpdate, and Windows Updates Downloader are examples of such tools.[31]
Service[edit]
At the beginning of 2005, Windows Update was being accessed by about 150 million people,[32] with about 112 million of those using Automatic Updates.[33] As of 2008, Windows Update had about 500 million clients, processed about 350 million unique scans per day, and maintained an average of 1.5 million simultaneous connections to client machines. On Patch Tuesday, the day Microsoft typically releases new software updates, outbound traffic could exceed 500 gigabits per second.[34] Approximately 90% of all clients used automatic updates to initiate software updates, with the remaining 10% using the Windows Update web site. The web site is built using ASP.NET, and processes an average of 90,000 page requests per second.
Traditionally, the service provided each patch in its own proprietary archive file. Occasionally, Microsoft released service packs which bundled all updates released over the course of years for a certain product. Starting with Windows 10, however, all patches are delivered in cumulative packages.[35] On 15 August 2016, Microsoft announced that effective October 2016, all future patches to Windows 7 and 8.1 would become cumulative as with Windows 10. The ability to download and install individual updates would be removed as existing updates are transitioned to this model.[36] This has resulted in increasing download sizes of each monthly update. An analysis done by Computerworld determined that the download size for Windows 7 x64 has increased from 119.4MB in October 2016 to 203MB in October 2017.[37] Initially, Microsoft was very vague about specific changes within each cumulative update package.[35] However, since early 2016, Microsoft has begun releasing more detailed information on the specific changes.[38]
In 2011, the update service was decommissioned for Windows 98, 98 SE, ME and NT4 and the old updates for those systems were removed from its servers.[39][40]
On August 3, 2020, the update service was decommissioned for Windows 2000, XP, Server 2003 and Vista due to Microsoft discontinuing SHA-1 updates. The old updates are still available on the Microsoft Update Catalog.[41]
Microsoft Update[edit]
At the February 2005 RSA Conference, Microsoft announced the first beta of Microsoft Update, an optional replacement for Windows Update that provides security patches, service packs and other updates for both Windows and other Microsoft software.[42] The initial release in June 2005 provided support for Microsoft Office 2003, Exchange 2003, and SQL Server 2000, running on Windows 2000, XP, and Server 2003. Over time, the list has expanded to include other Microsoft products, such as Windows Live, Windows Defender, Visual Studio, runtimes and redistributables, Zune Software, Virtual PC and Virtual Server, CAPICOM, Microsoft Lync, Microsoft Expression Studio, and other server products. It also offers Silverlight and Windows Media Player as optional downloads if applicable to the operating system.
Office Update[edit]
Office Update is a free online service that allows users to detect and install updates for certain Microsoft Office products.
The original update service supported Office 2000, Office XP, Office 2003 and Office 2007. On 1 August 2009 Microsoft decommissioned the Office Update service, merging it with Microsoft Update.[43] Microsoft Update does not support Office 2000.
With the introduction of the Office 365 licensing program, however, Microsoft once again activated a separate Office update service.[44][45]
References[edit]
- ^ «Microsoft License Terms». www.microsoft.com. Section 13b. Retrieved 30 March 2020.
- ^ «MICROSOFT SOFTWARE LICENSE TERMS». www.microsoft.com. Retrieved 20 July 2022.
Canada. You may stop receiving updates on your device by turning off Internet access. If and when you re-connect to the Internet, the software will resume checking for and installing updates.
- ^ Gartner, John (24 August 1995). «Taking Windows 98 For A Test-Drive». TechWeb. CMP Net. Archived from the original on 3 December 1998.
- ^ «Strong Holiday Sales Make Windows 98 Best-Selling Software of 1998». PressPass (Press release). Microsoft. 9 February 1999. Archived from the original on 6 March 2012. Retrieved 29 July 2008.
- ^ a b Slob, Arie (22 March 2003). «Windows Update is Spying on You!». Windows-Help.NET. InfiniSource. Archived from the original on 14 January 2018. Retrieved 12 September 2019.
- ^ «Description of the Windows Critical Update Notification utility». Support. Microsoft. 5 December 2007. Archived from the original on 26 July 2020. Retrieved 22 November 2018.
- ^ Moore, H. D. (29 January 1999). «How the MS Critical Update Notification works…» BugTraq mailing list archive. Archived from the original on 21 June 2009. Retrieved 30 July 2008 – via seclists.org.
- ^ Atwood, Jeff (13 May 2005). «XP Automatic Update Nagging». Coding Horror: Programming and Human Factors. Archived from the original on 9 November 2021. Retrieved 12 September 2019.
- ^ Bright, Peter (16 December 2013). «Exponential algorithm making Windows XP miserable could be fixed». Ars Technica. Condé Nast. Archived from the original on 6 May 2021. Retrieved 12 September 2019.
- ^ Leonhard, Woody (16 December 2013). «Microsoft promises to fix Windows XP SVCHOST redlining ‘as soon as possible’«. InfoWorld. IDG. Archived from the original on 30 March 2019. Retrieved 12 September 2019.
- ^ «How to update the Windows Update Agent to the latest version». Support. Microsoft. 6 June 2017. Archived from the original on 4 September 2020. Retrieved 22 November 2018.
- ^ «Windows Update Agent». TechNet. Microsoft. 13 December 2007. Archived from the original on 14 January 2018. Retrieved 22 November 2018.
- ^ «How to Install the Windows Update Agent on Client Computers». TechNet. Microsoft. 2007. Archived from the original on 11 October 2018. Retrieved 22 November 2018.
- ^ Rouse, Margaret (May 2014). «Microsoft Windows Update Agent». TechTarget. Archived from the original on 27 January 2021. Retrieved 22 November 2018.
- ^ Savov, Vlad (15 November 2011). «Windows 8 auto-update will consolidate restarts into one per month, give you three days to do it». The Verge. Vox Media. Archived from the original on 29 August 2021. Retrieved 22 November 2018.
- ^ «NTFS Beta Chat Transcript (July 12, 2006)». Storage at Microsoft. Microsoft. 12 July 2006. Archived from the original on 20 April 2019. Retrieved 22 November 2018.
- ^ «Windows 10 lets you schedule Windows Update restarts». CNET. Archived from the original on 19 February 2015. Retrieved 4 August 2015.
- ^ «Did Microsoft Just Backtrack On Forced Updates For Windows 10?». CRN.com. 27 July 2015. Archived from the original on 28 July 2015. Retrieved 4 August 2015.
- ^ «On the road to Windows 10: Nvidia driver tests KB 3073930 patch blocker». InfoWorld. 27 July 2015. Archived from the original on 20 June 2017. Retrieved 31 July 2015.
- ^ «On the road to Windows 10: Problems with forced updates and KB 3073930». InfoWorld. 22 July 2015. Archived from the original on 20 June 2017. Retrieved 31 July 2015.
- ^ «How to stop Windows 10 from using your PC’s bandwidth to update strangers’ systems». PC World. IDG. Archived from the original on 5 August 2015. Retrieved 4 August 2015.
- ^ «User can’t log on to a POP/IMAP account by using NTLM authentication in Exchange Server 2013». Archived from the original on 10 February 2021. Retrieved 24 March 2020.
To resolve this issue, install Cumulative Update 21
- ^ Hammoudi, Samir (15 November 2015). «Windows Update for Business explained». beanexpert. Microsoft. Archived from the original on 19 April 2019. Retrieved 14 January 2018.
- ^ Azzarello, Pat (10 May 2017). «What is Windows Update for Business?». Windows for IT Pros. Microsoft. Archived from the original on 11 June 2018. Retrieved 14 January 2018.
Windows Update for Business is intended for machines running Windows 10 or later, and Windows 10 Education, Professional, or Enterprise editions managed in organizations.
- ^ Halfin, Danni; Brower, Nick; Lich, Brian; Poggemeyer, Liza (13 October 2017). «Deploy updates using Windows Update for Business». Microsoft Docs. Microsoft. Archived from the original on 22 October 2021. Retrieved 22 November 2018.
- ^ «Microsoft changes Windows Update for Business options — gHacks Tech News». www.ghacks.net. 15 February 2019. Archived from the original on 6 October 2021. Retrieved 3 November 2020.
- ^ a b «Microsoft removes Setting to defer feature updates from Windows 10 version 2004 — gHacks Tech News». www.ghacks.net. 25 June 2020. Archived from the original on 27 August 2021. Retrieved 3 November 2020.
- ^ Bott, Ed (17 January 2018). «How to take control of Windows 10 updates and upgrades (even if you don’t own a business)». ZDNet. CBS Interactive. Archived from the original on 12 November 2021. Retrieved 22 November 2018.
- ^ Halfin, Danni; Lich, Brian (27 July 2017). «Build deployment rings for Windows 10 updates». Microsoft Docs. Microsoft. Archived from the original on 24 May 2021. Retrieved 22 November 2018.
- ^ Rasheed, Shadab (9 January 2017). «Why WSUS and SCCM managed clients are reaching out to Microsoft Online». Windows Server Blog. Microsoft. Archived from the original on 14 January 2018. Retrieved 22 November 2018.
- ^ «4 Tools to Update Windows Offline and install Hotfixes from a Local Source». raymond.cc. 14 November 2005. Archived from the original on 20 October 2021. Retrieved 22 November 2018.
- ^ «RSA Conference 2005: «Security: Raising the Bar» (speech transcript)». PressPass. Microsoft. 15 February 2005. Archived from the original on 8 March 2009. Retrieved 30 July 2008.
- ^ «Microsoft Announces Availability of New Solutions to Help Protect Customers Against Spyware and Viruses». PressPass. Microsoft. 6 January 2005. Archived from the original on 2 April 2012. Retrieved 30 July 2008.
- ^ «Introducing the Microsoft.com Engineering Operations Team». Microsoft TechNet. Microsoft. 2008. Archived from the original on 26 August 2017. Retrieved 31 May 2012.
- ^ a b «Windows 10 users beg Microsoft for more info on updates». Computerworld. IDG. 14 September 2015. Archived from the original on 14 September 2015. Retrieved 30 September 2015.
- ^ «Windows 7, 8.1 moving to Windows 10’s cumulative update model». Ars Technica. Conde Nast Digital. 15 August 2016. Archived from the original on 14 February 2017. Retrieved 16 August 2016.
- ^ Gregg Keizer (14 December 2017). «Why Windows 7 updates are getting bigger». Computerworld. Archived from the original on 22 November 2018. Retrieved 22 November 2018.
- ^ «Windows 10 update details». Windows 10 update history. Microsoft. Archived from the original on 5 March 2016. Retrieved 4 March 2016.
- ^ «I can’t access Windows Update v4 — Windows 9x/ME — MSFN». msfn.org. Archived from the original on 9 November 2021. Retrieved 25 April 2021.
- ^ «Where is Windows Update for Win98? — BetaArchive». www.betaarchive.com. Archived from the original on 8 November 2021. Retrieved 25 April 2021.
- ^ «Windows Update SHA-1 based endpoints discontinued for older Windows devices». Archived from the original on 18 December 2020. Retrieved 5 August 2020.
- ^ «Microsoft Update Site Launched». helpwithwindows.com. 10 June 2005. Archived from the original on 22 November 2018. Retrieved 30 July 2008.
- ^ «About Office Update». office.microsoft.com. Microsoft. Archived from the original on 28 May 2010.
- ^ «Install Office updates». support.office.com. Microsoft. Archived from the original on 23 May 2020. Retrieved 4 December 2017.
- ^ «Check for Office for Mac updates automatically». support.office.com. Microsoft. Archived from the original on 9 August 2018. Retrieved 4 December 2017.
External links[edit]
- Microsoft Update website
- Microsoft Technical Security Notifications