Служба удаленных рабочих столов
Remote Desktop Services
Служба удаленных рабочих столов Remote Desktop Services (ранее известная, как Terminal Services) — это компонент Microsoft Windows (серверной и клиентской операционных систем), позволяющий пользователям удаленно запускать приложения или управлять сервером с любой машины, где есть клиент подключения к удаленному рабочему столу и доступ к сети. В сеансе Remote Desktop Services требует клиент наличия доступа ко всей среде удаленного компьютера или ему просто нужно запустить отдельные приложения — сервер Remote Desktop Session Host выполняет всю обработку и использует свои аппаратные ресурсы.
В простом сеансе Remote Desktop Services клиент посылает только сигналы клавиатуры и мыши и принимает видеоизображения, что требует лишь небольшой загрузки сети. Для более серьезных сеансов, которым может понадобиться доступ к локальным ресурсам, служба удаленных рабочих столов предоставляет поддержку перенаправления аудиосигналов, локального принтера, СОМ-порта, локального диска и PnP-устройств (для медиапроигрывателей и цифровых камер), чтобы облегчить пересылку данных между клиентом и сервером через единый сетевой порт. Служба удаленных рабочих столов также обеспечивает переназначение локального часового пояса, что позволяет пользователям получать отметки времени в почтовых сообщениях и файлах относительно их местоположения. Недавно служба Remote Desktop Services стала поддерживать и настольные компьютеры с высоким разрешением (до 4096×2048) и выстраивание нескольких мониторов в горизонтальный ряд, чтобы сформировать единый большой рабочий стол. С помощью компонента Client Experience пользователи могут получить настольную среду Remote Desktop Services, которая внешним видом похожа на Windows 7.
Удаленные рабочие столы
Служба удаленных рабочих столов впервые появилась в версии Windows NT 4.0 Terminal Server Edition. В последующих версиях Windows и служба удаленных рабочих столов, и ее протокол удаленных рабочих столов (Remote Desktop Protocol — RDP) были существенно усовершенствованы. Эти усовершенствования достигли своего пика в Windows Server 2008 R2 и Windows 7, где служба Terminal Services была переименована в Remote Desktop Services и была дополнена рядом новых средств.
- Поддержка управления службой удаленных рабочих столов через Windows PowerShell.
- Средством фильтрации программ RemoteApp на уровне пользователя для Remote Desktop Web Access.
- Средство Remote Desktop Virtualization Host (Узел виртуализации удаленных рабочих столов) — компонент инфраструктуры виртуальных рабочих столов Microsoft (Virtual Desktop Infrastructure — VDI).
- Средство RemoteApp and Desktop Connection (Подключение к удаленным рабочим столам и приложениям RemoteApp), предназначенные для обеспечения гладкого пользовательского взаимодействия в среде Windows 7.
- Поддержка одиночного входа (Single Sign-On) между RD Session Host и RD Web Access.
- Улучшенная поддержка воспроизведения звуковых и видеофайлов.
В настоящей главе рассматривается планирование, внедрение, управление и поддержка развертывания службы удаленных рабочих столов Windows Server 2008 R2. Здесь будут описаны не только новые возможности, добавленные в Windows Server 2008 и Windows Server 2008 R2, но и способы применения этих новых технологий для повышения качества услуг удаленного доступа как пользователям, так и сетевым администраторам.
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
| Other names | Terminal Services |
|---|---|
| Developer(s) | Microsoft |
| Operating system | Microsoft Windows |
| Service name | TermService |
| Type | Remote desktop software |
| Website | docs.microsoft.com/en-us/windows/win32/termserv/terminal-services-portal |
Remote Desktop Services (RDS), known as Terminal Services in Windows Server 2008 and earlier,[1] is one of the components of Microsoft Windows that allow a user to initiate and control an interactive session[2] on a remote computer or virtual machine over a network connection. RDS was first released in 1998 as Terminal Server in Windows NT 4.0 Terminal Server Edition, a stand-alone edition of Windows NT 4.0 Server that allowed users to log in remotely. Starting with Windows 2000, it was integrated under the name of Terminal Services as an optional component in the server editions of the Windows NT family of operating systems,[3] receiving updates and improvements with each version of Windows.[4] Terminal Services were then renamed to Remote Desktop Services with Windows Server 2008 R2[5] in 2009.
RDS is Microsoft’s implementation of thin client architecture, where Windows software, and the entire desktop of the computer running RDS, are made accessible to any remote client machine that supports Remote Desktop Protocol (RDP). User interfaces are displayed from the server onto the client system and input from the client system is transmitted to the server — where software execution takes place.[6] This is in contrast to application streaming systems, like Microsoft App-V, in which computer programs are streamed to the client on-demand and executed on the client machine.
RemoteFX was added to RDS as part of Windows Server 2008 R2 Service Pack 1.
Overview[edit]
Windows includes three client components that use RDS:
- Windows Remote Assistance – only Windows 10 and later
- Remote Desktop Connection (RDC)
- Fast user switching
The first two are individual utilities that allow a user to operate an interactive session on a remote computer over the network. In case of Remote Assistance, the remote user needs to receive an invitation and the control is cooperative. In case of RDC, however, the remote user opens a new session on the remote computer and has every power granted by its user account’s rights and restrictions.[6][7][8] Fast User Switching allows users to switch between user accounts on the local computer without quitting software and logging out. Fast User Switching is part of Winlogon and uses RDS to accomplish its switching feature.[9][10] Third-party developers have also created client software for RDS. For example, rdesktop supports Unix platforms.
Although RDS is shipped with most editions of all versions of Windows NT since Windows 2000,[3] its functionality differs in each version. Windows XP Home Edition does not accept any RDC connections at all, reserving RDS for Fast User Switching and Remote Assistance only. Other client versions of Windows only allow a maximum of one remote user to connect to the system at the cost of the user who has logged onto the console being disconnected. Windows Server allows two users to connect at the same time. This licensing scheme, called «Remote Desktop for Administration», facilitates administration of unattended or headless computers. Only by acquiring additional licenses (in addition to that of Windows) can a computer running Windows Server service multiple remote users at one time and achieve virtual desktop infrastructure.[5][9]
For an organization, RDS allows the IT department to install applications on a central server instead of multiple computers.[11] Remote users can log on and use those applications over the network. Such centralization can make maintenance and troubleshooting easier. RDS and Windows authentication systems prevent unauthorized users from accessing apps or data.
Microsoft has a long-standing agreement with Citrix to facilitate sharing of technologies and patent licensing between Microsoft Terminal Services and Citrix XenApp (formerly Citrix MetaFrame and Citrix Presentation Server). In this arrangement, Citrix has access to key source code for the Windows platform, enabling its developers to improve the security and performance of the Terminal Services platform. In late December 2004 the two companies announced a five-year renewal of this arrangement to cover Windows Vista.[12]
Server components[edit]
The key server component of RDS is Terminal Server (termdd.sys), which listens on TCP port 3389. When a Remote Desktop Protocol (RDP) client connects to this port, it is tagged with a unique SessionID and associated with a freshly spawned console session (Session 0, keyboard, mouse and character mode UI only). The login subsystem (winlogon.exe) and the GDI graphics subsystem is then initiated, which handles the job of authenticating the user and presenting the GUI. These executables are loaded in a new session, rather than the console session. When creating the new session, the graphics and keyboard/mouse device drivers are replaced with RDP-specific drivers: RdpDD.sys and RdpWD.sys. The RdpDD.sys is the device driver and it captures the UI rendering calls into a format that is transmittable over RDP. RdpWD.sys acts as keyboard and mouse driver; it receives keyboard and mouse input over the TCP connection and presents them as keyboard or mouse inputs. It also allows creation of virtual channels, which allow other devices, such as disc, audio, printers, and COM ports to be redirected, i.e., the channels act as replacement for these devices. The channels connect to the client over the TCP connection; as the channels are accessed for data, the client is informed of the request, which is then transferred over the TCP connection to the application. This entire procedure is done by the terminal server and the client, with the RDP mediating the correct transfer, and is entirely transparent to the applications.[13] RDP communications are encrypted using 128-bit RC4 encryption. Windows Server 2003 onwards, it can use a FIPS 140 compliant encryption schemes.[6]
Once a client initiates a connection and is informed of a successful invocation of the terminal services stack at the server, it loads up the device as well as the keyboard/mouse drivers. The UI data received over RDP is decoded and rendered as UI, whereas the keyboard and mouse inputs to the Window hosting the UI is intercepted by the drivers, and transmitted over RDP to the server. It also creates the other virtual channels and sets up the redirection. RDP communication can be encrypted; using either low, medium or high encryption. With low encryption, user input (outgoing data) is encrypted using a weak (40-bit RC4) cipher. With medium encryption, UI packets (incoming data) are encrypted using this weak cipher as well. The setting «High encryption (Non-export)» uses 128-bit RC4 encryption and «High encryption (Export)» uses 40-bit RC4 encryption.[14]
Terminal Server[edit]
Terminal Server is the server component of Terminal services. It handles the job of authenticating clients, as well as making the applications available remotely. It is also entrusted with the job of restricting the clients according to the level of access they have. The Terminal Server respects the configured software restriction policies, so as to restrict the availability of certain software to only a certain group of users. The remote session information is stored in specialized directories, called Session Directory which is stored at the server. Session directories are used to store state information about a session, and can be used to resume interrupted sessions. The terminal server also has to manage these directories. Terminal Servers can be used in a cluster as well.[6]
In Windows Server 2008, it has been significantly overhauled. While logging in, if the user logged on to the local system using a Windows Server Domain account, the credentials from the same sign-on can be used to authenticate the remote session. However, this requires Windows Server 2008 to be the terminal server OS, while the client OS is limited to Windows Server 2008, Windows Vista and Windows 7. In addition, the terminal server may be configured to allow connection to individual programs, rather than the entire desktop, by means of a feature named RemoteApp. Terminal Services Web Access (TS Web Access) makes a RemoteApp session invocable from the web browser. It includes the TS Web Access Web Part control which maintains the list of RemoteApps deployed on the server and keeps the list up to date. Terminal Server can also integrate with Windows System Resource Manager to throttle resource usage of remote applications.[4]
Terminal Server is managed by the Terminal Server Manager Microsoft Management Console snap-in. It can be used to configure the sign in requirements, as well as to enforce a single instance of remote session. It can also be configured by using Group Policy or Windows Management Instrumentation. It is, however, not available in client versions of Windows OS, where the server is pre-configured to allow only one session and enforce the rights of the user account on the remote session, without any customization.[6]
Remote Desktop Gateway[edit]
The Remote Desktop Gateway service component, also known as RD Gateway, can tunnel the RDP session using a HTTPS channel.[15] This increases the security of RDS by encapsulating the session with Transport Layer Security (TLS).[16] This also allows the option to use Internet Explorer as the RDP client. The official MS RDP client for macOS supports RD Gateway as of version 8. This is also available for iOS and Android.
This feature was introduced in the Windows Server 2008 and Windows Home Server products.
In October 2021, Thincast, the main contributor of the FreeRDP project, published the first Remote Desktop Gateway solution running natively on Linux.[17]
Remote Desktop HTML5 Web Client[edit]
In late 2018 Microsoft released the Remote Desktop HTML5 Web Client. The client allows users to connect to their remote apps or to their remote desktops without using an installed remote desktop client.[18][19] The web client uses the TLS secured port 443 and does not use the RD Gateway to transport traffic, instead relying solely on the remote desktop session host aspect of remote desktop services.[20][21]
Roles[edit]
- Remote Desktop Gateway
- Enables authorized users to connect to virtual desktops, Remote-App programs, and session-based desktops over a private network or the Internet.
- Remote Desktop Connection Broker Role
- Allows users to reconnect to their existing virtual desktop, RemoteApp programs, and session-based desktops. It enables even load distribution across RD Session Host servers in a session collection or across pooled virtual desktops in a pooled virtual desktop collection, and provides access to virtual desktops in a virtual desktop collection.
- Remote Desktop Session Host
- Enables a server to host RemoteApp programs as session-based desktops. Users can connect to RD Session Host servers in a session collection to run programs, save files, and use resources on those servers. Users can access Remote Desktop Session Host server by using the Remote Desktop Connection client or by using RemoteApp programs.
- Remote Desktop Virtualization Host
- Enables users to connect to virtual desktops by using RemoteApp and Desktop Connection.
- Remote Desktop Web Access
- Enables users to access RemoteApp and Desktop Connection through the Start Menu or through a web browser. RemoteApp and Desktop Connection provides users with a customized view of RemoteApp programs, session-based desktops, and virtual desktops.
- Remote Desktop Licensing
- Enables a server to manage RDS client access licenses (RDS CALs) that are required for each device or user to connect to a Remote Desktop Session Host server. RDS CALs are managed using the Remote Desktop Licensing Manager application.[22]
RemoteApp[edit]
RemoteApp (or TS RemoteApp) is a special mode of RDS, available in Windows Server 2008 R2 and later, where remote session configuration is integrated into the client operating system. The RDP 6.1 client ships with Windows XP SP3, KB952155 for Windows XP SP2 users,[23] Windows Vista SP1 and Windows Server 2008. The UI for the RemoteApp is rendered in a window over the local desktop, and is managed like any other window for local applications. The end result of this is that remote applications behave largely like local applications. The task of establishing the remote session, as well as redirecting local resources to the remote application, is transparent to the end user.[24] Multiple applications can be started in a single RemoteApp session, each with their own windows.[25]
A RemoteApp can be packaged either as a .rdp file or distributed via an .msi Windows Installer package. When packaged as an .rdp file (which contains the address of the RemoteApp server, authentication schemes to be used, and other settings), a RemoteApp can be launched by double clicking the file. It will invoke the Remote Desktop Connection client, which will connect to the server and render the UI. The RemoteApp can also be packaged in a Windows Installer database, installing which can register the RemoteApp in the Start menu as well as create shortcuts to launch it. A RemoteApp can also be registered as handler for file types or URIs. Opening a file registered with RemoteApp will first invoke Remote Desktop Connection, which will connect to the terminal server and then open the file. Any application which can be accessed over Remote Desktop can be served as a RemoteApp.[24]
Windows 7 includes built-in support for RemoteApp publishing, but it has to be enabled manually in registry, since there is no RemoteApp management console in client versions of Microsoft Windows.[26]
Windows Desktop Sharing[edit]
In Windows Vista onwards, Terminal Services also includes a multi-party desktop sharing capability known as Windows Desktop Sharing. Unlike Terminal Services, which creates a new user session for every RDP connection, Windows Desktop Sharing can host the remote session in the context of the currently logged in user without creating a new session, and make the Desktop, or a subset of it, available over RDP.[27] Windows Desktop Sharing can be used to share the entire desktop, a specific region, or a particular application.[28] Windows Desktop Sharing can also be used to share multi-monitor desktops. When sharing applications individually (rather than the entire desktop), the windows are managed (whether they are minimized or maximized) independently at the server and the client side.[28]
The functionality is only provided via a public API, which can be used by any application to provide screen sharing functionality. Windows Desktop Sharing API exposes two objects: RDPSession for the sharing session and RDPViewer for the viewer. Multiple viewer objects can be instantiated for one Session object. A viewer can either be a passive viewer, who is just able to watch the application like a screencast, or an interactive viewer, who is able to interact in real time with the remote application.[27] The RDPSession object contains all the shared applications, represented as Application objects, each with Window objects representing their on-screen windows. Per-application filters capture the application Windows and package them as Window objects.[29] A viewer must authenticate itself before it can connect to a sharing session. This is done by generating an Invitation using the RDPSession. It contains an authentication ticket and password. The object is serialized and sent to the viewers, who need to present the Invitation when connecting.[27][29]
Windows Desktop Sharing API is used by Windows Meeting Space and Windows Remote Assistance for providing application sharing functionality among network peers.[28]
Client software[edit]
Remote Desktop Connection[edit]

Remote Desktop Connection client on Windows 8 |
|
| Developer(s) | Microsoft |
|---|---|
| Operating system | Microsoft Windows |
| Type | Remote desktop software |
| Website | docs.microsoft.com/en-us/windows-server/remote/remote-desktop-services/welcome-to-rds |
Remote Desktop Connection client on macOS
Remote Desktop Connection (RDC, also called Remote Desktop or just RD,[30][31] formerly Microsoft Terminal Services Client, mstsc or tsclient)[32][33] is the client application for RDS. It allows a user to remotely log into a networked computer running the terminal services server. RDC presents the desktop interface (or application GUI) of the remote system, as if it were accessed locally.[6] In addition to regular username/password for authorizing for the remote session, RDC also supports using smart cards for authorization.[6] With RDC 6.0, the resolution of a remote session can be set independently of the settings at the remote computer.
With version 6.0, if the Desktop Experience component is plugged into the remote server, remote application user interface elements (e.g., application windows borders, Maximize, Minimize, and Close buttons etc.) will take on the same appearance of local applications. In this scenario, the remote applications will use the Aero theme if the user connects to the server from a Windows Vista machine running Aero.[4] Later versions of the protocol also support rendering the UI in full 32-bit color, as well as resource redirection for printers, COM ports, disk drives, mice and keyboards. With resource redirection, remote applications can use the resources of the local computer. Audio is also redirected, so that any sounds generated by a remote application are played back at the client system.[6][4] Moreover, a remote session can also span multiple monitors at the client system, independent of the multi-monitor settings at the server. RDC can also be used to connect to Windows Media Center (WMC) remote sessions; however, since WMC does not stream video using RDP, only the applications can be viewed this way, not any media.
RDC prioritizes UI data as well as keyboard and mouse inputs, as opposed to print jobs or file transfers. so as to make the applications more responsive. It redirects plug and play devices such as cameras, portable music players, and scanners, so that input from these devices can be used by the remote applications as well.[4] RDC can also be used to connect to computers which are exposed via Windows Home Server RDP Gateway over the Internet.[34] Finally, few shortcuts that will be handy
- To achieve Ctrl+Alt+Del effect on remote desktop, you can use the Ctrl+Alt+End key combination.
- To alternate between the full screen and window mode of remote desktop, you can use Ctrl+Alt+Break ( Ctrl+Fn+Alt+⇧ Shift on certain HP laptops).
Other clients[edit]
Microsoft produces an official client for a variety of non Windows platforms:
- Windows Mobile[35][36]
- MacOS: Microsoft Remote Desktop for Mac
- Android: Microsoft Remote Desktop
- iOS and iPadOS: Microsoft Remote Desktop
There have been numerous non-Microsoft implementations of clients that implement subsets of the Microsoft functionality for a range of platforms. The most common are:
- FreeRDP — Open Source under Apache license
- rdesktop for Linux/Unix and Microsoft Windows
- Remmina for Linux (based on FreeRDP)
- CoRD for macOS (Discontinued in April 2020)
- Thincast Client for Linux, macOS and Windows
See also[edit]
- BlueKeep (security vulnerability)
- Windows MultiPoint Server
- Microsoft NetMeeting, a discontinued Microsoft product also provides Shared-desktop feature, in the similar time-frame of Windows NT Terminal Services Edition
- Virtual Network Computing
References[edit]
- ^ «Windows Remote Desktop Services spotlight». Retrieved 2010-11-18.
- ^ QuinnRadich. «Remote Desktop Sessions — Win32 apps». docs.microsoft.com. Retrieved 2022-07-09.
- ^ a b «Remote Desktop Connection». PC World. IDG. 17 August 2011.
- ^ a b c d e «Whats new in Terminal Services in Windows Server 2008». Retrieved 2007-07-23.
- ^ a b Russel, Charlie; Zacker, Craig (2009). «4: Remote Desktop Services and VDI: Centralizing Desktop and Application Management» (PDF). Introducing Windows Server 2008 R2. Redmond, WA: Microsoft Press. Archived from the original (PDF) on 29 August 2017. Retrieved 11 January 2014.
- ^ a b c d e f g h «Technical Overview of Terminal Services in Windows Server 2003». Microsoft. Archived from the original on 2003-01-26. Retrieved 2007-07-23.
- ^
«How to change the listening port for Remote Desktop». Retrieved 2010-11-18. - ^
«Frequently Asked Questions about Remote Desktop». Microsoft. Retrieved 2007-07-23. - ^ a b
Russinovich, Mark; Solomon, David A.; Ionescu, Alex (2012). Windows Internals (6th ed.). Redmond, WA: Microsoft Press. pp. 20–21. ISBN 978-0-7356-4873-9. - ^
«Architecture of Fast User Switching». Support. Microsoft. 15 January 2006. Retrieved 11 January 2014. - ^ «Remote Services». Log me in 123.
- ^ «Citrix and Microsoft Sign Technology Collaboration and Licensing Agreement». Citrix. 2004-12-21. Archived from the original on 2011-07-05. Retrieved 2012-04-13.
- ^
«How Terminal Services Works». Microsoft. 2003-03-28. Retrieved 2007-07-23. - ^ «Connection Configuration in Terminal Server». Support (5.0 ed.). Microsoft. 22 June 2014.
- ^ «Terminal Services Gateway (TS Gateway)». Microsoft TechNet. Retrieved 2009-09-10.
- ^ «Remote Desktop Protocol». Microsoft Developer Network (MSDN). Retrieved 2009-09-10.
- ^ «RD Gateway Documentation». Thincast. Retrieved 2021-10-17.
- ^ Waggoner, Rob. «Microsoft Has Released the HTML5-Based RDP Web Client». blog.mycloudit.com. Retrieved 2020-05-10.
- ^ «Remote Desktop HTML5 client on Windows Server 2019». msfreaks. 2018-10-06. Retrieved 2020-05-10.
- ^ «RD Web Client (HTML5) – New Features In 1.0.11». www.rdsgurus.com. Retrieved 2020-05-10.
- ^ Berson, Freek (2018-01-12). «The Microsoft Platform: HTML5 client for Microsoft Remote Desktop Services 2016: Remote Desktop Web Client». The Microsoft Platform. Retrieved 2020-05-10.
- ^ TechNet: Remote Desktop Licensing
- ^ «Description of the Remote Desktop Connection 6.1 client update for Terminal Services in Windows XP Service Pack 2». Retrieved 2010-11-18.
- ^ a b «Terminal Services RemoteApp (TS RemoteApp)». Retrieved 2007-07-23.
- ^ «Terminal Services RemoteApp Session Termination Logic». Retrieved 2007-10-02.
- ^ «How to enable RemoteApp (via RDP 7.0) within VirtualBox or VMWare running Windows 7, Vista SP1+ or Windows XP SP3». Retrieved 2010-11-18.
- ^ a b c «Windows Desktop Sharing». Retrieved 2007-10-11.
- ^ a b c «Windows Desktop Sharing API». Retrieved 2007-10-11.
- ^ a b «About Windows Desktop Sharing». Retrieved 2007-10-11.
- ^ «Remote Desktop Services — Access from anywhere». Microsoft.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: url-status (link) - ^ «Get started with the Android client». Microsoft.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: url-status (link) - ^ «Why doesn’t the New Folder command work in the root of a redirected drive resource in a Remote Desktop session?». The Old New Thing. Microsoft. 17 December 2013. Retrieved 18 December 2013.
- ^ Savill, John (1 October 2008). The Complete Guide to Windows Server 2008. Pearson Education. p. 1752. ISBN 978-0-13-279758-0. Retrieved 1 June 2012.
Windows XP, Windows Server 2003, Windows Vista, and Windows Server 2008 all contain the RDC tool,
mstsc.exe[…] MSTSC in the filenamemstsc.exestands for Microsoft Terminal Services Client. - ^ «Remote Desktop Connection». Remote Support.
- ^ Drager, Dave (27 March 2008). «How to Remotely Control your Mobile Phone from Desktop». MakeUseOf. Retrieved 27 January 2022.
- ^ Miniman, Brandon (2009-03-16). «Tutorial: Setting up Remote Desktop in Windows Mobile». PocketNow. Archived from the original on 2009-08-01. Retrieved 27 January 2022.
External links[edit]
- Welcome to Remote Desktop Services
- Download Chrome Remote Desktop
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
| Other names | Terminal Services |
|---|---|
| Developer(s) | Microsoft |
| Operating system | Microsoft Windows |
| Service name | TermService |
| Type | Remote desktop software |
| Website | docs.microsoft.com/en-us/windows/win32/termserv/terminal-services-portal |
Remote Desktop Services (RDS), known as Terminal Services in Windows Server 2008 and earlier,[1] is one of the components of Microsoft Windows that allow a user to initiate and control an interactive session[2] on a remote computer or virtual machine over a network connection. RDS was first released in 1998 as Terminal Server in Windows NT 4.0 Terminal Server Edition, a stand-alone edition of Windows NT 4.0 Server that allowed users to log in remotely. Starting with Windows 2000, it was integrated under the name of Terminal Services as an optional component in the server editions of the Windows NT family of operating systems,[3] receiving updates and improvements with each version of Windows.[4] Terminal Services were then renamed to Remote Desktop Services with Windows Server 2008 R2[5] in 2009.
RDS is Microsoft’s implementation of thin client architecture, where Windows software, and the entire desktop of the computer running RDS, are made accessible to any remote client machine that supports Remote Desktop Protocol (RDP). User interfaces are displayed from the server onto the client system and input from the client system is transmitted to the server — where software execution takes place.[6] This is in contrast to application streaming systems, like Microsoft App-V, in which computer programs are streamed to the client on-demand and executed on the client machine.
RemoteFX was added to RDS as part of Windows Server 2008 R2 Service Pack 1.
Overview[edit]
Windows includes three client components that use RDS:
- Windows Remote Assistance – only Windows 10 and later
- Remote Desktop Connection (RDC)
- Fast user switching
The first two are individual utilities that allow a user to operate an interactive session on a remote computer over the network. In case of Remote Assistance, the remote user needs to receive an invitation and the control is cooperative. In case of RDC, however, the remote user opens a new session on the remote computer and has every power granted by its user account’s rights and restrictions.[6][7][8] Fast User Switching allows users to switch between user accounts on the local computer without quitting software and logging out. Fast User Switching is part of Winlogon and uses RDS to accomplish its switching feature.[9][10] Third-party developers have also created client software for RDS. For example, rdesktop supports Unix platforms.
Although RDS is shipped with most editions of all versions of Windows NT since Windows 2000,[3] its functionality differs in each version. Windows XP Home Edition does not accept any RDC connections at all, reserving RDS for Fast User Switching and Remote Assistance only. Other client versions of Windows only allow a maximum of one remote user to connect to the system at the cost of the user who has logged onto the console being disconnected. Windows Server allows two users to connect at the same time. This licensing scheme, called «Remote Desktop for Administration», facilitates administration of unattended or headless computers. Only by acquiring additional licenses (in addition to that of Windows) can a computer running Windows Server service multiple remote users at one time and achieve virtual desktop infrastructure.[5][9]
For an organization, RDS allows the IT department to install applications on a central server instead of multiple computers.[11] Remote users can log on and use those applications over the network. Such centralization can make maintenance and troubleshooting easier. RDS and Windows authentication systems prevent unauthorized users from accessing apps or data.
Microsoft has a long-standing agreement with Citrix to facilitate sharing of technologies and patent licensing between Microsoft Terminal Services and Citrix XenApp (formerly Citrix MetaFrame and Citrix Presentation Server). In this arrangement, Citrix has access to key source code for the Windows platform, enabling its developers to improve the security and performance of the Terminal Services platform. In late December 2004 the two companies announced a five-year renewal of this arrangement to cover Windows Vista.[12]
Server components[edit]
The key server component of RDS is Terminal Server (termdd.sys), which listens on TCP port 3389. When a Remote Desktop Protocol (RDP) client connects to this port, it is tagged with a unique SessionID and associated with a freshly spawned console session (Session 0, keyboard, mouse and character mode UI only). The login subsystem (winlogon.exe) and the GDI graphics subsystem is then initiated, which handles the job of authenticating the user and presenting the GUI. These executables are loaded in a new session, rather than the console session. When creating the new session, the graphics and keyboard/mouse device drivers are replaced with RDP-specific drivers: RdpDD.sys and RdpWD.sys. The RdpDD.sys is the device driver and it captures the UI rendering calls into a format that is transmittable over RDP. RdpWD.sys acts as keyboard and mouse driver; it receives keyboard and mouse input over the TCP connection and presents them as keyboard or mouse inputs. It also allows creation of virtual channels, which allow other devices, such as disc, audio, printers, and COM ports to be redirected, i.e., the channels act as replacement for these devices. The channels connect to the client over the TCP connection; as the channels are accessed for data, the client is informed of the request, which is then transferred over the TCP connection to the application. This entire procedure is done by the terminal server and the client, with the RDP mediating the correct transfer, and is entirely transparent to the applications.[13] RDP communications are encrypted using 128-bit RC4 encryption. Windows Server 2003 onwards, it can use a FIPS 140 compliant encryption schemes.[6]
Once a client initiates a connection and is informed of a successful invocation of the terminal services stack at the server, it loads up the device as well as the keyboard/mouse drivers. The UI data received over RDP is decoded and rendered as UI, whereas the keyboard and mouse inputs to the Window hosting the UI is intercepted by the drivers, and transmitted over RDP to the server. It also creates the other virtual channels and sets up the redirection. RDP communication can be encrypted; using either low, medium or high encryption. With low encryption, user input (outgoing data) is encrypted using a weak (40-bit RC4) cipher. With medium encryption, UI packets (incoming data) are encrypted using this weak cipher as well. The setting «High encryption (Non-export)» uses 128-bit RC4 encryption and «High encryption (Export)» uses 40-bit RC4 encryption.[14]
Terminal Server[edit]
Terminal Server is the server component of Terminal services. It handles the job of authenticating clients, as well as making the applications available remotely. It is also entrusted with the job of restricting the clients according to the level of access they have. The Terminal Server respects the configured software restriction policies, so as to restrict the availability of certain software to only a certain group of users. The remote session information is stored in specialized directories, called Session Directory which is stored at the server. Session directories are used to store state information about a session, and can be used to resume interrupted sessions. The terminal server also has to manage these directories. Terminal Servers can be used in a cluster as well.[6]
In Windows Server 2008, it has been significantly overhauled. While logging in, if the user logged on to the local system using a Windows Server Domain account, the credentials from the same sign-on can be used to authenticate the remote session. However, this requires Windows Server 2008 to be the terminal server OS, while the client OS is limited to Windows Server 2008, Windows Vista and Windows 7. In addition, the terminal server may be configured to allow connection to individual programs, rather than the entire desktop, by means of a feature named RemoteApp. Terminal Services Web Access (TS Web Access) makes a RemoteApp session invocable from the web browser. It includes the TS Web Access Web Part control which maintains the list of RemoteApps deployed on the server and keeps the list up to date. Terminal Server can also integrate with Windows System Resource Manager to throttle resource usage of remote applications.[4]
Terminal Server is managed by the Terminal Server Manager Microsoft Management Console snap-in. It can be used to configure the sign in requirements, as well as to enforce a single instance of remote session. It can also be configured by using Group Policy or Windows Management Instrumentation. It is, however, not available in client versions of Windows OS, where the server is pre-configured to allow only one session and enforce the rights of the user account on the remote session, without any customization.[6]
Remote Desktop Gateway[edit]
The Remote Desktop Gateway service component, also known as RD Gateway, can tunnel the RDP session using a HTTPS channel.[15] This increases the security of RDS by encapsulating the session with Transport Layer Security (TLS).[16] This also allows the option to use Internet Explorer as the RDP client. The official MS RDP client for macOS supports RD Gateway as of version 8. This is also available for iOS and Android.
This feature was introduced in the Windows Server 2008 and Windows Home Server products.
In October 2021, Thincast, the main contributor of the FreeRDP project, published the first Remote Desktop Gateway solution running natively on Linux.[17]
Remote Desktop HTML5 Web Client[edit]
In late 2018 Microsoft released the Remote Desktop HTML5 Web Client. The client allows users to connect to their remote apps or to their remote desktops without using an installed remote desktop client.[18][19] The web client uses the TLS secured port 443 and does not use the RD Gateway to transport traffic, instead relying solely on the remote desktop session host aspect of remote desktop services.[20][21]
Roles[edit]
- Remote Desktop Gateway
- Enables authorized users to connect to virtual desktops, Remote-App programs, and session-based desktops over a private network or the Internet.
- Remote Desktop Connection Broker Role
- Allows users to reconnect to their existing virtual desktop, RemoteApp programs, and session-based desktops. It enables even load distribution across RD Session Host servers in a session collection or across pooled virtual desktops in a pooled virtual desktop collection, and provides access to virtual desktops in a virtual desktop collection.
- Remote Desktop Session Host
- Enables a server to host RemoteApp programs as session-based desktops. Users can connect to RD Session Host servers in a session collection to run programs, save files, and use resources on those servers. Users can access Remote Desktop Session Host server by using the Remote Desktop Connection client or by using RemoteApp programs.
- Remote Desktop Virtualization Host
- Enables users to connect to virtual desktops by using RemoteApp and Desktop Connection.
- Remote Desktop Web Access
- Enables users to access RemoteApp and Desktop Connection through the Start Menu or through a web browser. RemoteApp and Desktop Connection provides users with a customized view of RemoteApp programs, session-based desktops, and virtual desktops.
- Remote Desktop Licensing
- Enables a server to manage RDS client access licenses (RDS CALs) that are required for each device or user to connect to a Remote Desktop Session Host server. RDS CALs are managed using the Remote Desktop Licensing Manager application.[22]
RemoteApp[edit]
RemoteApp (or TS RemoteApp) is a special mode of RDS, available in Windows Server 2008 R2 and later, where remote session configuration is integrated into the client operating system. The RDP 6.1 client ships with Windows XP SP3, KB952155 for Windows XP SP2 users,[23] Windows Vista SP1 and Windows Server 2008. The UI for the RemoteApp is rendered in a window over the local desktop, and is managed like any other window for local applications. The end result of this is that remote applications behave largely like local applications. The task of establishing the remote session, as well as redirecting local resources to the remote application, is transparent to the end user.[24] Multiple applications can be started in a single RemoteApp session, each with their own windows.[25]
A RemoteApp can be packaged either as a .rdp file or distributed via an .msi Windows Installer package. When packaged as an .rdp file (which contains the address of the RemoteApp server, authentication schemes to be used, and other settings), a RemoteApp can be launched by double clicking the file. It will invoke the Remote Desktop Connection client, which will connect to the server and render the UI. The RemoteApp can also be packaged in a Windows Installer database, installing which can register the RemoteApp in the Start menu as well as create shortcuts to launch it. A RemoteApp can also be registered as handler for file types or URIs. Opening a file registered with RemoteApp will first invoke Remote Desktop Connection, which will connect to the terminal server and then open the file. Any application which can be accessed over Remote Desktop can be served as a RemoteApp.[24]
Windows 7 includes built-in support for RemoteApp publishing, but it has to be enabled manually in registry, since there is no RemoteApp management console in client versions of Microsoft Windows.[26]
Windows Desktop Sharing[edit]
In Windows Vista onwards, Terminal Services also includes a multi-party desktop sharing capability known as Windows Desktop Sharing. Unlike Terminal Services, which creates a new user session for every RDP connection, Windows Desktop Sharing can host the remote session in the context of the currently logged in user without creating a new session, and make the Desktop, or a subset of it, available over RDP.[27] Windows Desktop Sharing can be used to share the entire desktop, a specific region, or a particular application.[28] Windows Desktop Sharing can also be used to share multi-monitor desktops. When sharing applications individually (rather than the entire desktop), the windows are managed (whether they are minimized or maximized) independently at the server and the client side.[28]
The functionality is only provided via a public API, which can be used by any application to provide screen sharing functionality. Windows Desktop Sharing API exposes two objects: RDPSession for the sharing session and RDPViewer for the viewer. Multiple viewer objects can be instantiated for one Session object. A viewer can either be a passive viewer, who is just able to watch the application like a screencast, or an interactive viewer, who is able to interact in real time with the remote application.[27] The RDPSession object contains all the shared applications, represented as Application objects, each with Window objects representing their on-screen windows. Per-application filters capture the application Windows and package them as Window objects.[29] A viewer must authenticate itself before it can connect to a sharing session. This is done by generating an Invitation using the RDPSession. It contains an authentication ticket and password. The object is serialized and sent to the viewers, who need to present the Invitation when connecting.[27][29]
Windows Desktop Sharing API is used by Windows Meeting Space and Windows Remote Assistance for providing application sharing functionality among network peers.[28]
Client software[edit]
Remote Desktop Connection[edit]

Remote Desktop Connection client on Windows 8 |
|
| Developer(s) | Microsoft |
|---|---|
| Operating system | Microsoft Windows |
| Type | Remote desktop software |
| Website | docs.microsoft.com/en-us/windows-server/remote/remote-desktop-services/welcome-to-rds |
Remote Desktop Connection client on macOS
Remote Desktop Connection (RDC, also called Remote Desktop or just RD,[30][31] formerly Microsoft Terminal Services Client, mstsc or tsclient)[32][33] is the client application for RDS. It allows a user to remotely log into a networked computer running the terminal services server. RDC presents the desktop interface (or application GUI) of the remote system, as if it were accessed locally.[6] In addition to regular username/password for authorizing for the remote session, RDC also supports using smart cards for authorization.[6] With RDC 6.0, the resolution of a remote session can be set independently of the settings at the remote computer.
With version 6.0, if the Desktop Experience component is plugged into the remote server, remote application user interface elements (e.g., application windows borders, Maximize, Minimize, and Close buttons etc.) will take on the same appearance of local applications. In this scenario, the remote applications will use the Aero theme if the user connects to the server from a Windows Vista machine running Aero.[4] Later versions of the protocol also support rendering the UI in full 32-bit color, as well as resource redirection for printers, COM ports, disk drives, mice and keyboards. With resource redirection, remote applications can use the resources of the local computer. Audio is also redirected, so that any sounds generated by a remote application are played back at the client system.[6][4] Moreover, a remote session can also span multiple monitors at the client system, independent of the multi-monitor settings at the server. RDC can also be used to connect to Windows Media Center (WMC) remote sessions; however, since WMC does not stream video using RDP, only the applications can be viewed this way, not any media.
RDC prioritizes UI data as well as keyboard and mouse inputs, as opposed to print jobs or file transfers. so as to make the applications more responsive. It redirects plug and play devices such as cameras, portable music players, and scanners, so that input from these devices can be used by the remote applications as well.[4] RDC can also be used to connect to computers which are exposed via Windows Home Server RDP Gateway over the Internet.[34] Finally, few shortcuts that will be handy
- To achieve Ctrl+Alt+Del effect on remote desktop, you can use the Ctrl+Alt+End key combination.
- To alternate between the full screen and window mode of remote desktop, you can use Ctrl+Alt+Break ( Ctrl+Fn+Alt+⇧ Shift on certain HP laptops).
Other clients[edit]
Microsoft produces an official client for a variety of non Windows platforms:
- Windows Mobile[35][36]
- MacOS: Microsoft Remote Desktop for Mac
- Android: Microsoft Remote Desktop
- iOS and iPadOS: Microsoft Remote Desktop
There have been numerous non-Microsoft implementations of clients that implement subsets of the Microsoft functionality for a range of platforms. The most common are:
- FreeRDP — Open Source under Apache license
- rdesktop for Linux/Unix and Microsoft Windows
- Remmina for Linux (based on FreeRDP)
- CoRD for macOS (Discontinued in April 2020)
- Thincast Client for Linux, macOS and Windows
See also[edit]
- BlueKeep (security vulnerability)
- Windows MultiPoint Server
- Microsoft NetMeeting, a discontinued Microsoft product also provides Shared-desktop feature, in the similar time-frame of Windows NT Terminal Services Edition
- Virtual Network Computing
References[edit]
- ^ «Windows Remote Desktop Services spotlight». Retrieved 2010-11-18.
- ^ QuinnRadich. «Remote Desktop Sessions — Win32 apps». docs.microsoft.com. Retrieved 2022-07-09.
- ^ a b «Remote Desktop Connection». PC World. IDG. 17 August 2011.
- ^ a b c d e «Whats new in Terminal Services in Windows Server 2008». Retrieved 2007-07-23.
- ^ a b Russel, Charlie; Zacker, Craig (2009). «4: Remote Desktop Services and VDI: Centralizing Desktop and Application Management» (PDF). Introducing Windows Server 2008 R2. Redmond, WA: Microsoft Press. Archived from the original (PDF) on 29 August 2017. Retrieved 11 January 2014.
- ^ a b c d e f g h «Technical Overview of Terminal Services in Windows Server 2003». Microsoft. Archived from the original on 2003-01-26. Retrieved 2007-07-23.
- ^
«How to change the listening port for Remote Desktop». Retrieved 2010-11-18. - ^
«Frequently Asked Questions about Remote Desktop». Microsoft. Retrieved 2007-07-23. - ^ a b
Russinovich, Mark; Solomon, David A.; Ionescu, Alex (2012). Windows Internals (6th ed.). Redmond, WA: Microsoft Press. pp. 20–21. ISBN 978-0-7356-4873-9. - ^
«Architecture of Fast User Switching». Support. Microsoft. 15 January 2006. Retrieved 11 January 2014. - ^ «Remote Services». Log me in 123.
- ^ «Citrix and Microsoft Sign Technology Collaboration and Licensing Agreement». Citrix. 2004-12-21. Archived from the original on 2011-07-05. Retrieved 2012-04-13.
- ^
«How Terminal Services Works». Microsoft. 2003-03-28. Retrieved 2007-07-23. - ^ «Connection Configuration in Terminal Server». Support (5.0 ed.). Microsoft. 22 June 2014.
- ^ «Terminal Services Gateway (TS Gateway)». Microsoft TechNet. Retrieved 2009-09-10.
- ^ «Remote Desktop Protocol». Microsoft Developer Network (MSDN). Retrieved 2009-09-10.
- ^ «RD Gateway Documentation». Thincast. Retrieved 2021-10-17.
- ^ Waggoner, Rob. «Microsoft Has Released the HTML5-Based RDP Web Client». blog.mycloudit.com. Retrieved 2020-05-10.
- ^ «Remote Desktop HTML5 client on Windows Server 2019». msfreaks. 2018-10-06. Retrieved 2020-05-10.
- ^ «RD Web Client (HTML5) – New Features In 1.0.11». www.rdsgurus.com. Retrieved 2020-05-10.
- ^ Berson, Freek (2018-01-12). «The Microsoft Platform: HTML5 client for Microsoft Remote Desktop Services 2016: Remote Desktop Web Client». The Microsoft Platform. Retrieved 2020-05-10.
- ^ TechNet: Remote Desktop Licensing
- ^ «Description of the Remote Desktop Connection 6.1 client update for Terminal Services in Windows XP Service Pack 2». Retrieved 2010-11-18.
- ^ a b «Terminal Services RemoteApp (TS RemoteApp)». Retrieved 2007-07-23.
- ^ «Terminal Services RemoteApp Session Termination Logic». Retrieved 2007-10-02.
- ^ «How to enable RemoteApp (via RDP 7.0) within VirtualBox or VMWare running Windows 7, Vista SP1+ or Windows XP SP3». Retrieved 2010-11-18.
- ^ a b c «Windows Desktop Sharing». Retrieved 2007-10-11.
- ^ a b c «Windows Desktop Sharing API». Retrieved 2007-10-11.
- ^ a b «About Windows Desktop Sharing». Retrieved 2007-10-11.
- ^ «Remote Desktop Services — Access from anywhere». Microsoft.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: url-status (link) - ^ «Get started with the Android client». Microsoft.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: url-status (link) - ^ «Why doesn’t the New Folder command work in the root of a redirected drive resource in a Remote Desktop session?». The Old New Thing. Microsoft. 17 December 2013. Retrieved 18 December 2013.
- ^ Savill, John (1 October 2008). The Complete Guide to Windows Server 2008. Pearson Education. p. 1752. ISBN 978-0-13-279758-0. Retrieved 1 June 2012.
Windows XP, Windows Server 2003, Windows Vista, and Windows Server 2008 all contain the RDC tool,
mstsc.exe[…] MSTSC in the filenamemstsc.exestands for Microsoft Terminal Services Client. - ^ «Remote Desktop Connection». Remote Support.
- ^ Drager, Dave (27 March 2008). «How to Remotely Control your Mobile Phone from Desktop». MakeUseOf. Retrieved 27 January 2022.
- ^ Miniman, Brandon (2009-03-16). «Tutorial: Setting up Remote Desktop in Windows Mobile». PocketNow. Archived from the original on 2009-08-01. Retrieved 27 January 2022.
External links[edit]
- Welcome to Remote Desktop Services
- Download Chrome Remote Desktop
Обновлено 23.06.2019

Постановка задачи
Разобрать все методы, позволяющие вам включать RDP доступ на Windows системах, понимать какие ключи реестра за это отвечают и как это можно применять на практике.
Методы активации доступа по RDP
Я могу выделить вот такие способы:
- Классический метод с использованием оснастки свойств системы Windows
- С помощью оболочки и командлетов PowerShell
- Удаленное включение, через реестр Windows
- Через GPO политику
Как удаленно включить RDP
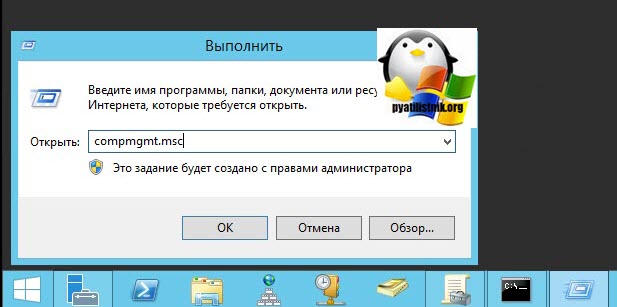
И так начну с более интересного метода. Предположим, что у вас есть сервер или компьютер, от которого у вас есть учетные данные для входа, но не активен вход через удаленный рабочий стол. И вам хотели бы его активировать. Делается все это просто. Тут мы воспользуемся удаленным доступом через консоль. Откройте окно выполнить (Сочетание клавиш WIN и R одновременно) и в открывшемся окне введите:
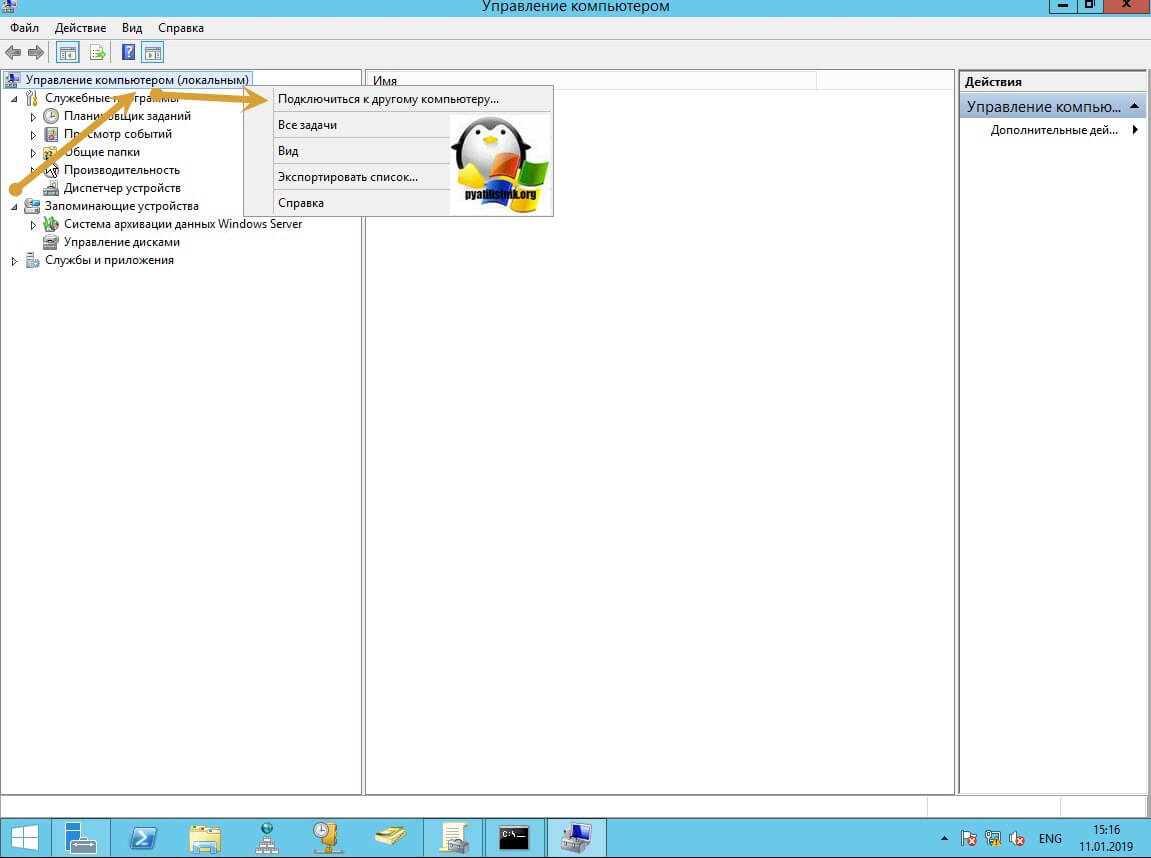
Далее щелкаете по корню «Управление компьютера (локальным)» правым кликом и в открывшемся окне выберите пункт «Подключиться к другому компьютеру»
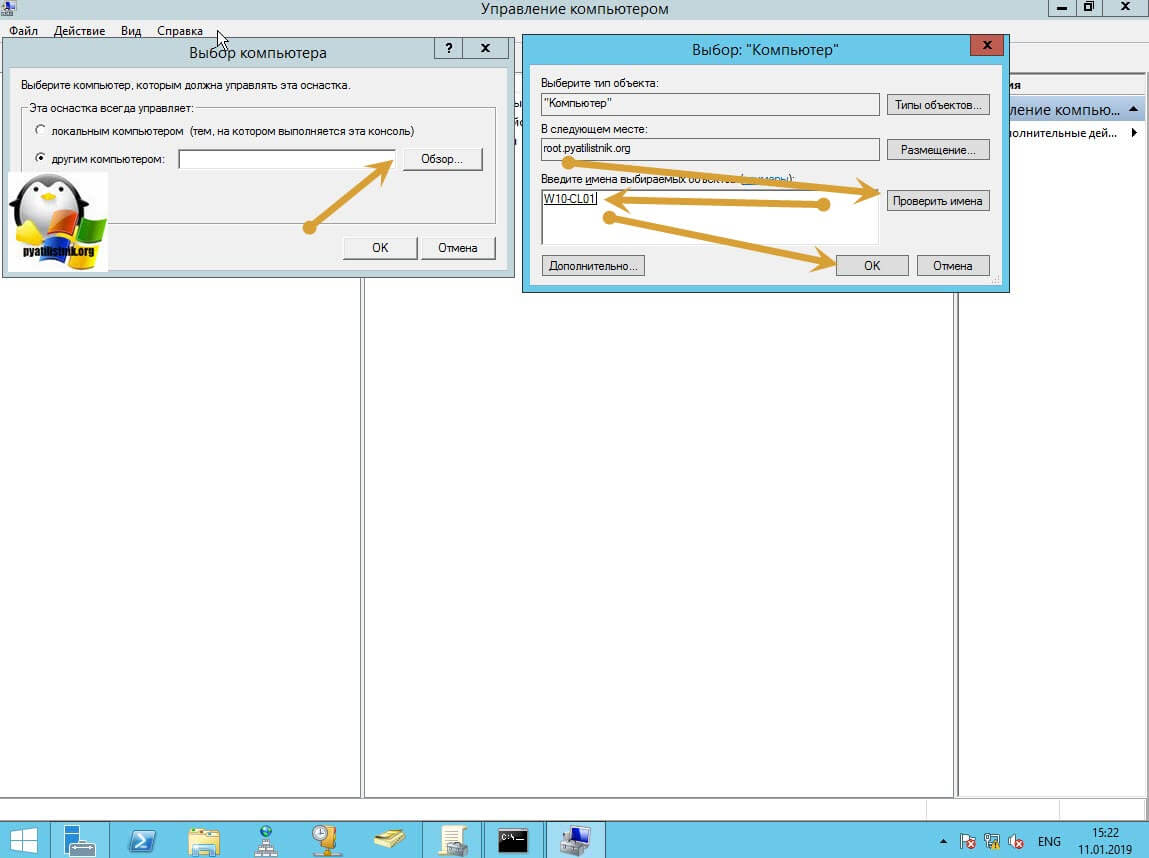
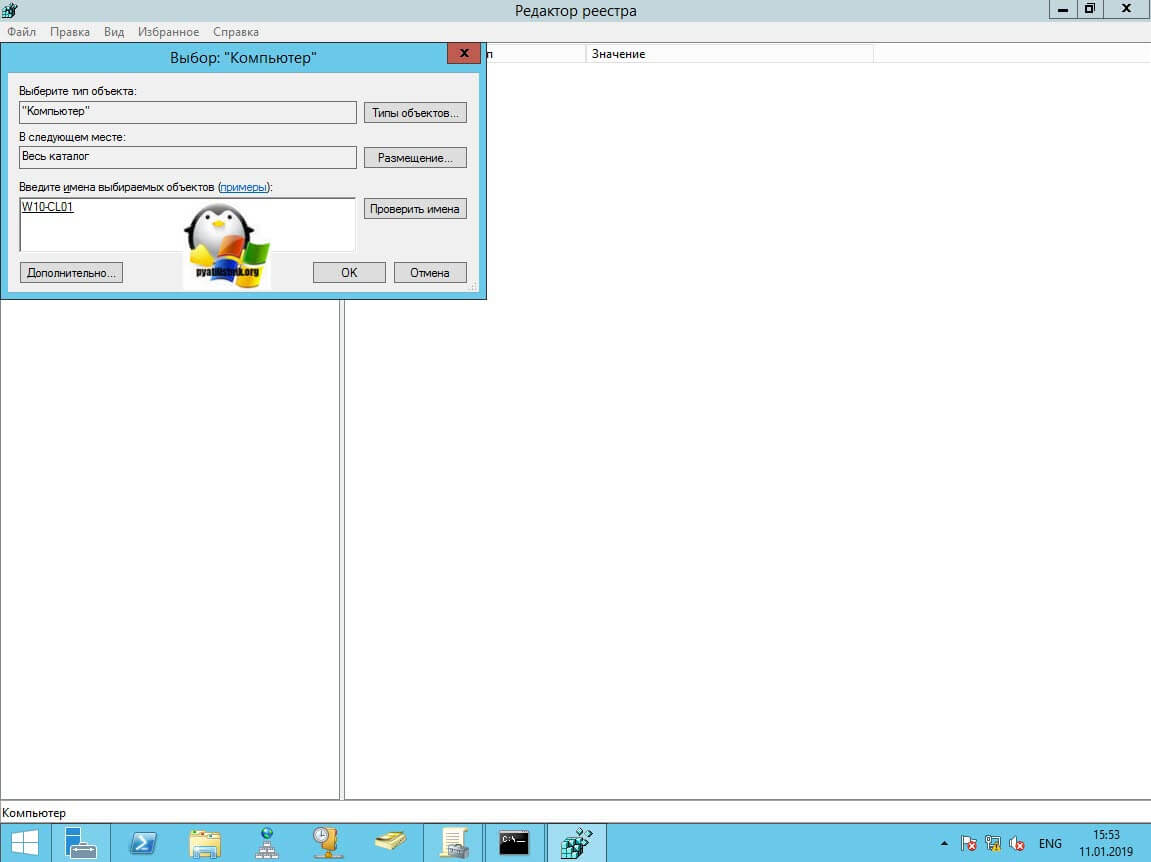
В окне выбора компьютера, вам необходимо нажать кнопку «Обзор», которое откроет второе окошко, где нужно выбрать необходимый компьютер, так как у меня доменная сеть, то мне еще проще. В моем примере это будет компьютер с операционной системой Windows 10 под DNS-именем W10-CL01. Нажимаем ок.
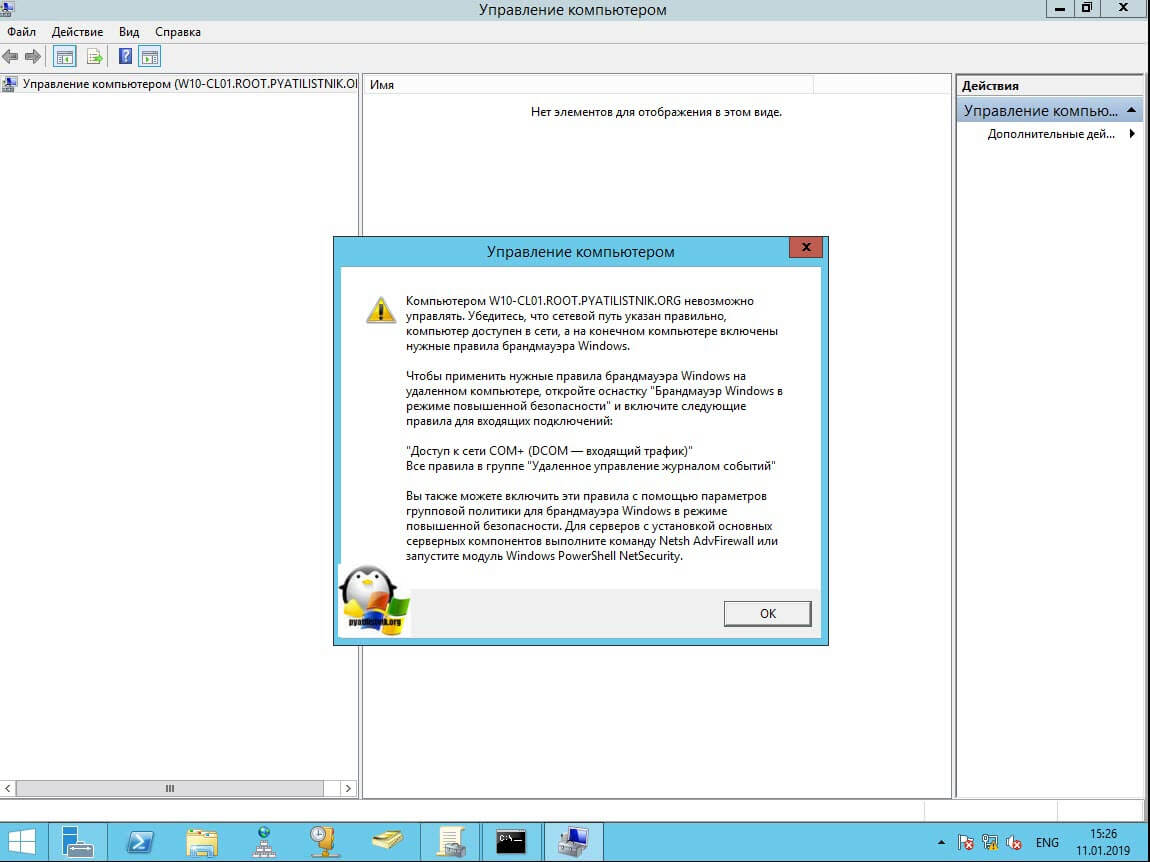
У вас будет произведено подключение к данному компьютеру. Если у вас выскочит ошибка:
Компьютером невозможно управлять. Убедитесь, что сетевой путь указан правильно, компьютер доступен в сети, а на конечном компьютере включены нужные правила брандмауэра Windows
В данном случае, нужно проверить две вещи:
- Доступен ли компьютер по сети, для этого проведите элементарный ping компьютера.
- Это нужно на этом компьютере в брандмауэре Windows разрешить «Удаленное управление журналом событий»
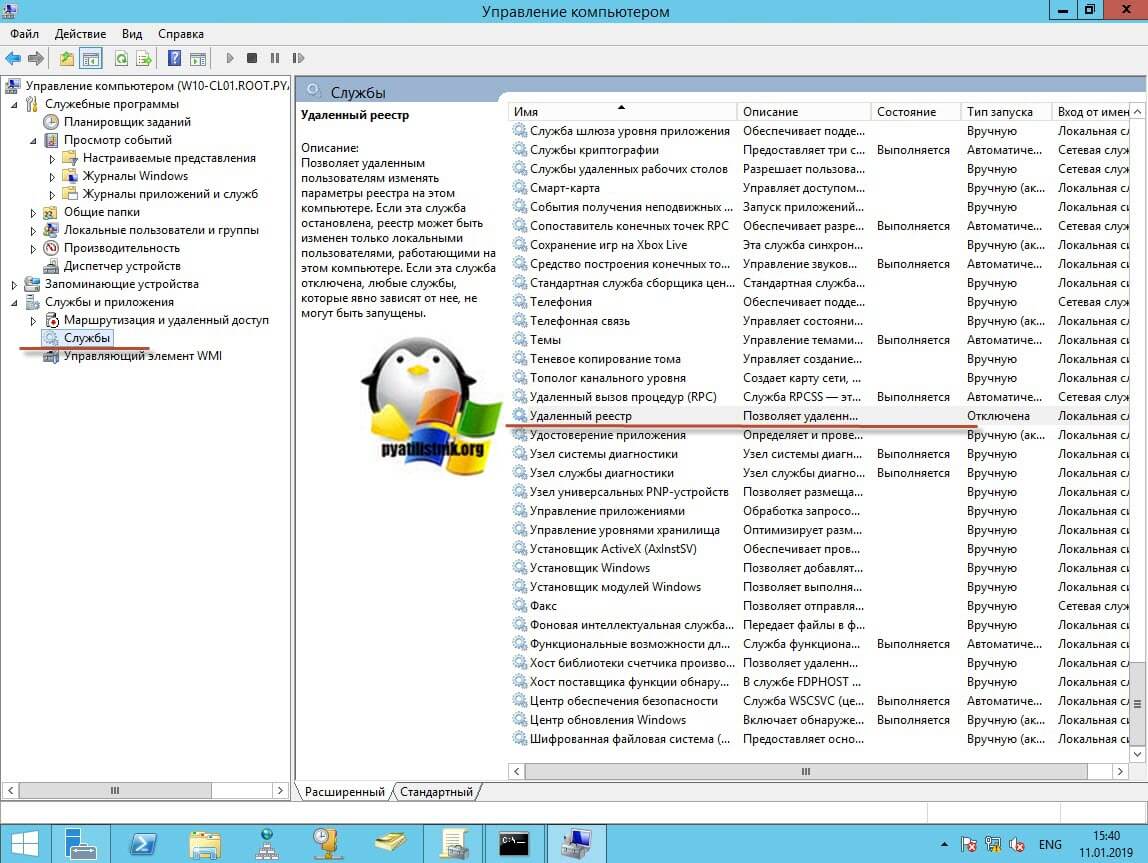
Про то как локально разрешать в брандмауэре службы и порты я говорил, посмотрите по ссылке. Если доступа нет, сделать, это локально, то ниже я приведу пример, как это сделать удаленно. Когда вы подключились к нужному компьютеру или серверу, вам необходимо перед удаленным включением RDP доступа, удостовериться, что у вас на вкладке службы, в активном состоянии запущен сервис «Удаленный реестр».
Вы так же можете из локальной оснастки «Службы», подключиться к удаленной, для этого в окне «Выполнить» введите services.msc и в открывшемся окне щелкните по корню правым кликом, где выберите соответствующий пункт
В моем примере я подключился к удаленным службам, через управление компьютером.
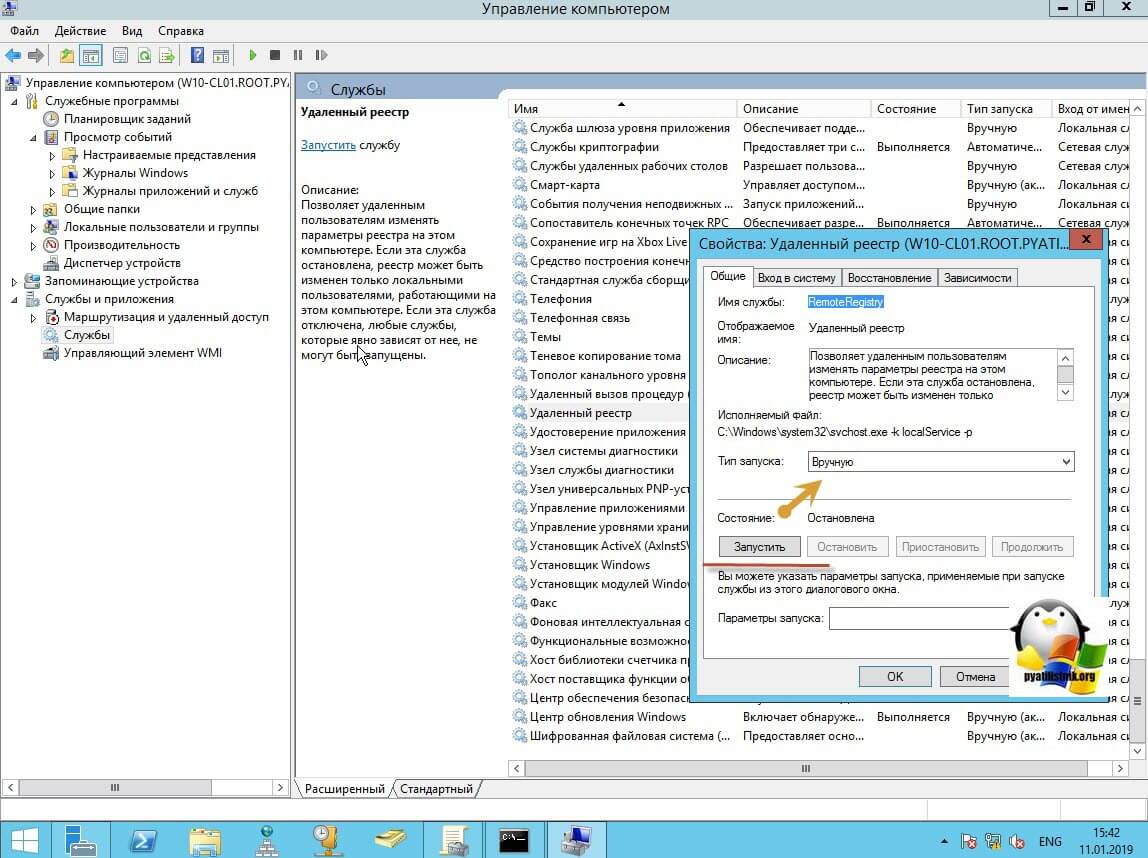
Если этого не сделать, то подключиться к реестру не получиться, и вы не сможете включить RDP по сети. Переходим в свойства данной службы и в типе запуска выставите вручную, после чего нажмите применить. После этого у вас станет активной кнопка запуска, нажимаем ее и проверяем, что сервис стартанул. После этого переходим к редактированию реестра по локальной сети.
В окне выполнить введите regedit и у вас откроется реестр Windows .
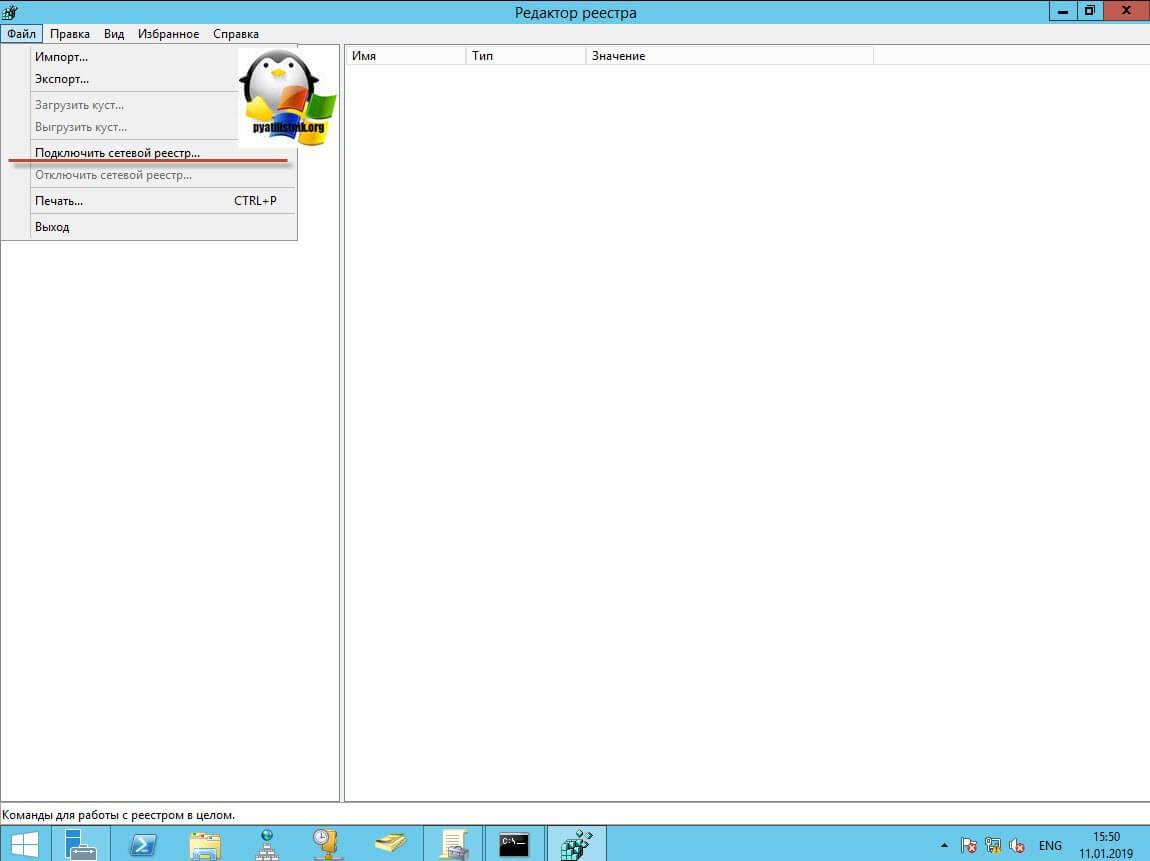
В самом верху есть меню файл, открыв его вам необходимо найти пункт «Подключить сетевой реестр».
У вас откроется окно поиска, где вам необходимо найти нужный вам сетевой компьютер или сервер, после чего нажать ок.
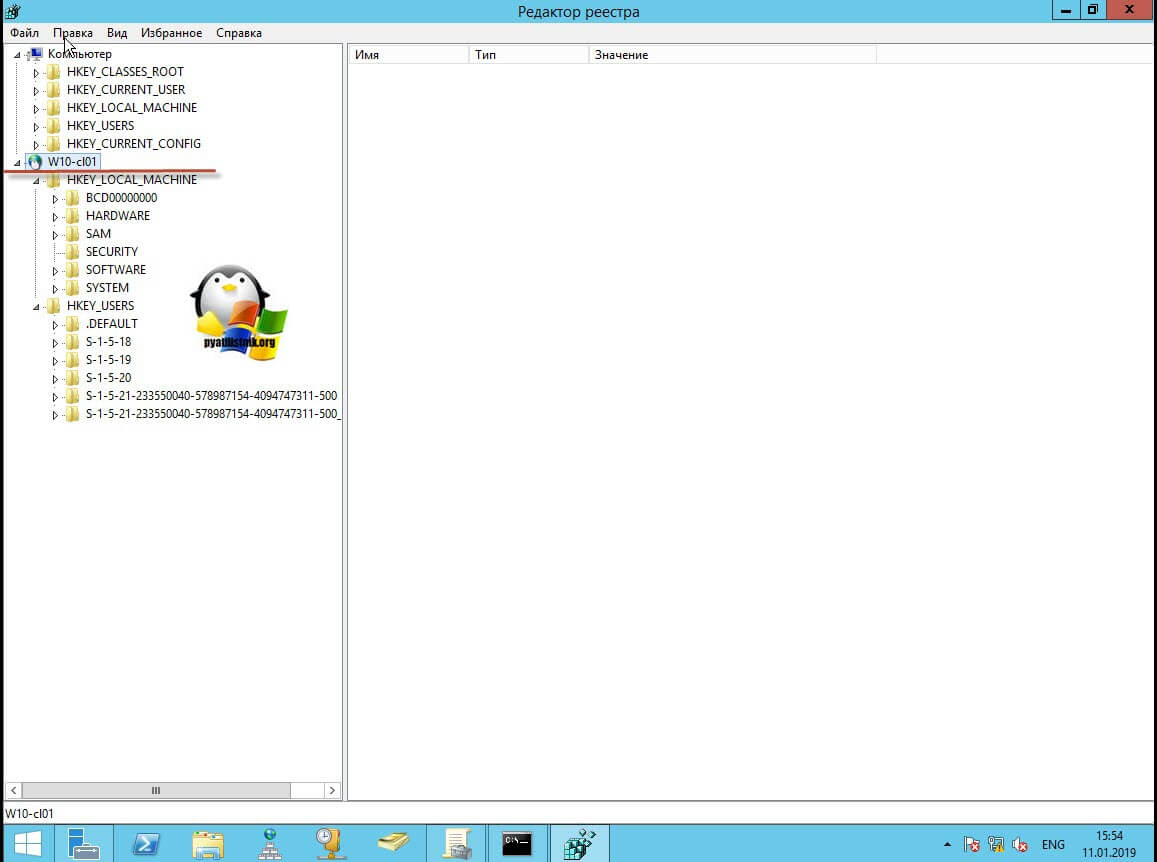
В итоге у вас в окне редактора реестра Windows появится еще один куст. Именно через данный реестр вы включите RDP службу на удаленной системе.
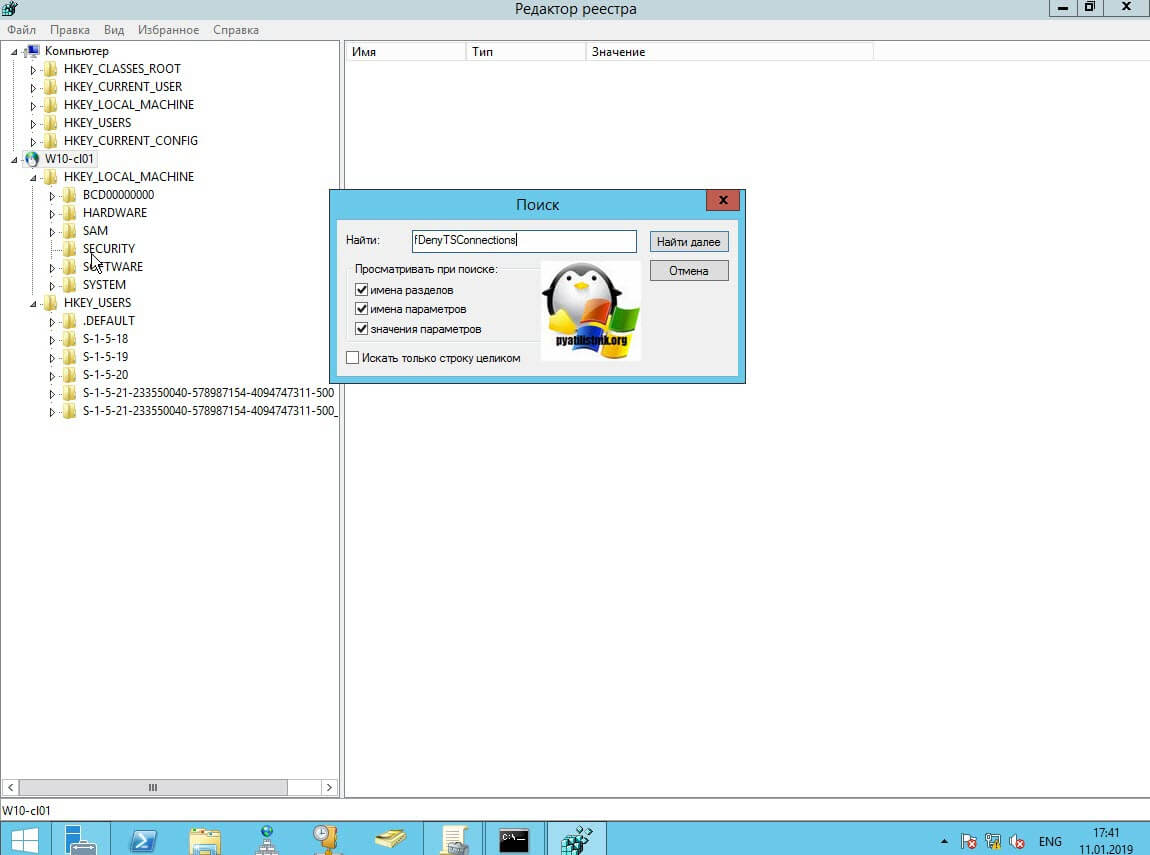
Теперь выбираем корень сетевого реестра Windows и нажимаем кнопку CTRL+F, у вас откроется форма поиска по нему. Тут вам необходимо найти ключ fDenyTSConnections.
Он также по сути должен лежать по пути:
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINESYSTEMCurrentControlSetControlTerminal ServerfDenyTSсonnections
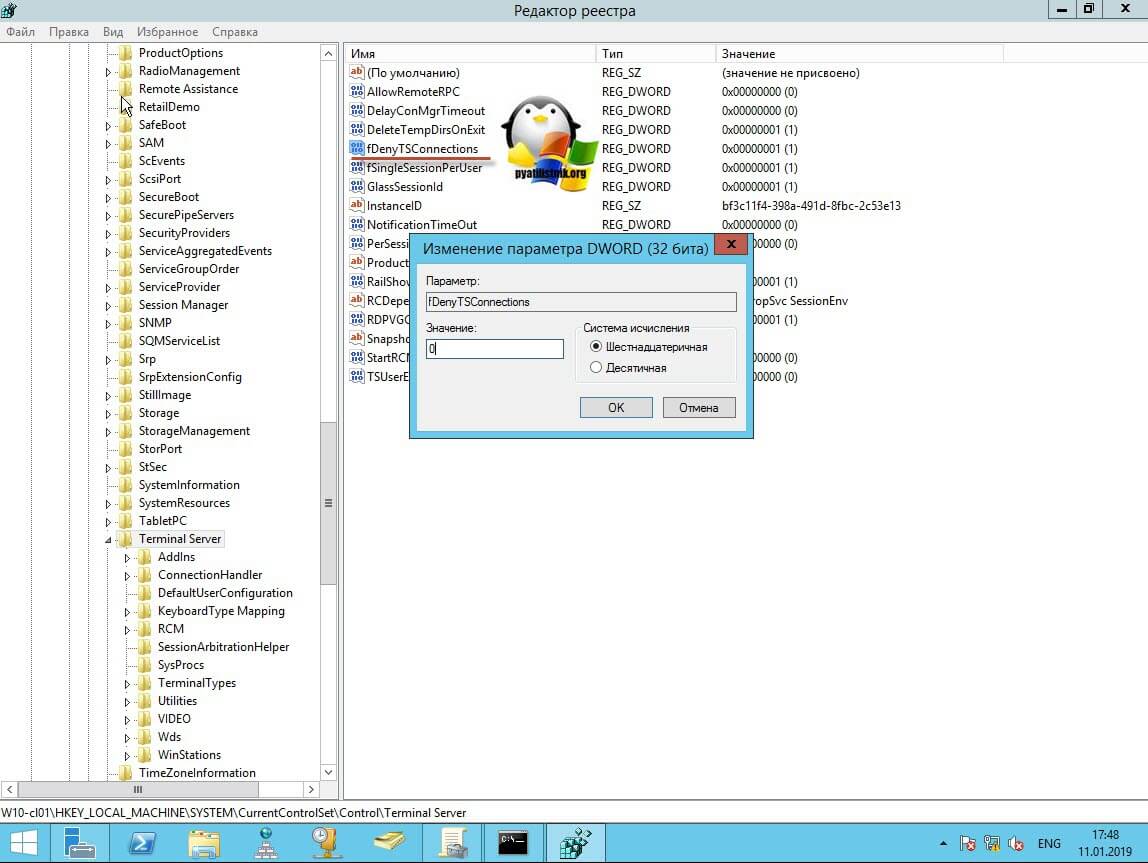
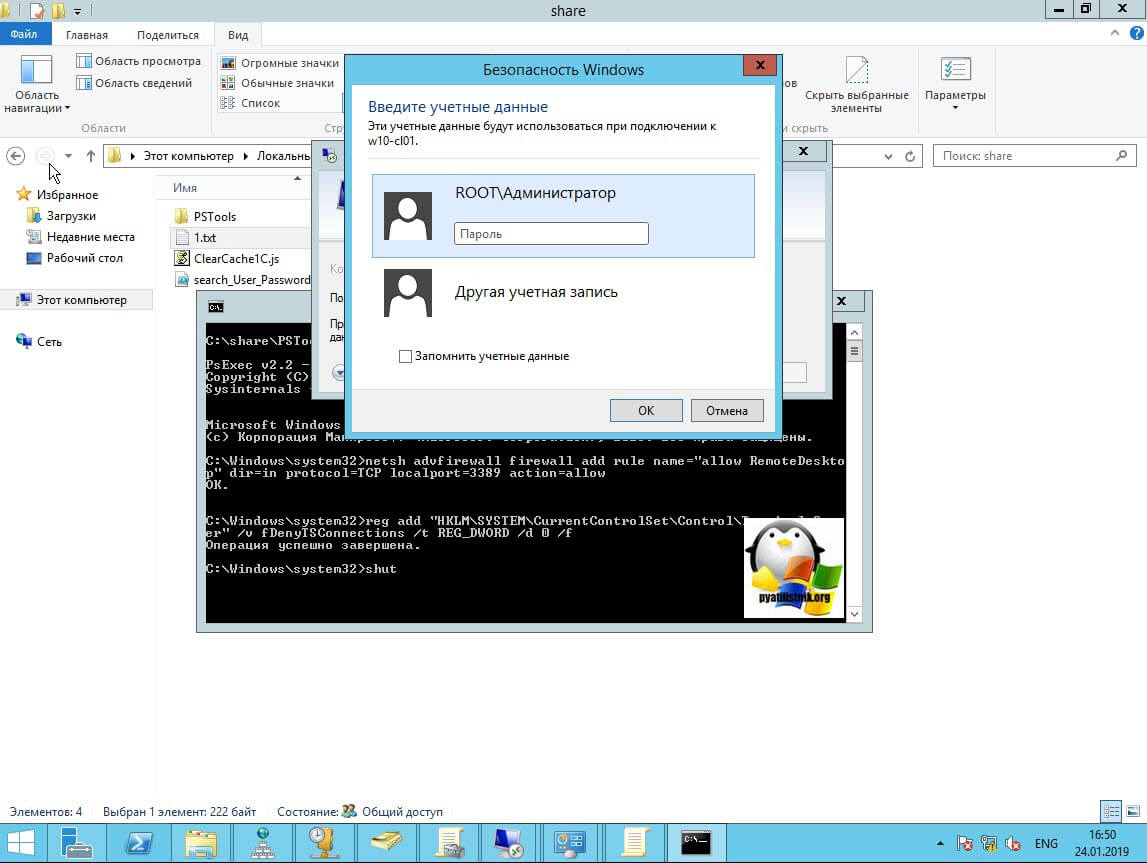
Где ключу fDenyTSConnections вам необходимо изменить значение с 1 на 0, чтобы включить RDP доступ к удаленному компьютеру.
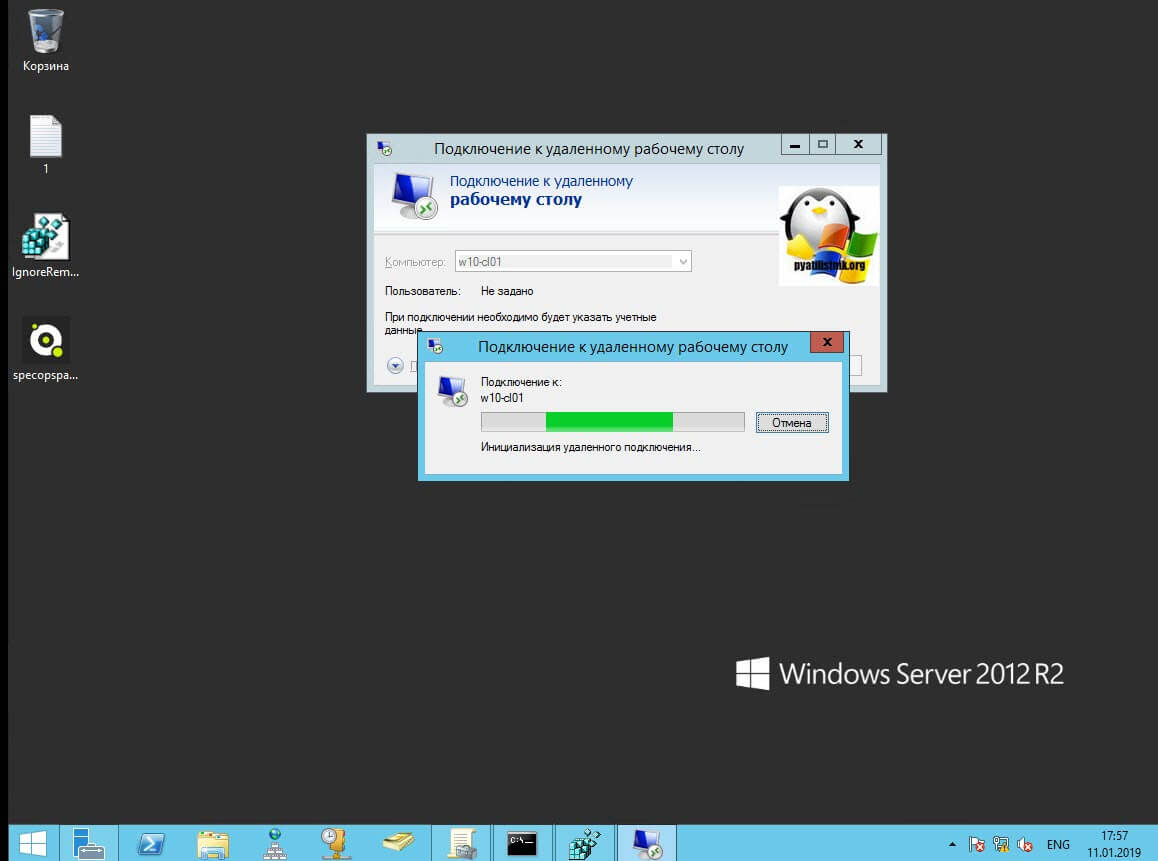
Пробуем произвести подключение, для этого откройте клиента подключения к удаленному рабочему столу (mstsc) и смотрим результат.
Если у вас будут закрыты порты, то вы увидите вот такую картину. При попытке подключиться у вас будет висеть инициализация удаленного подключения.
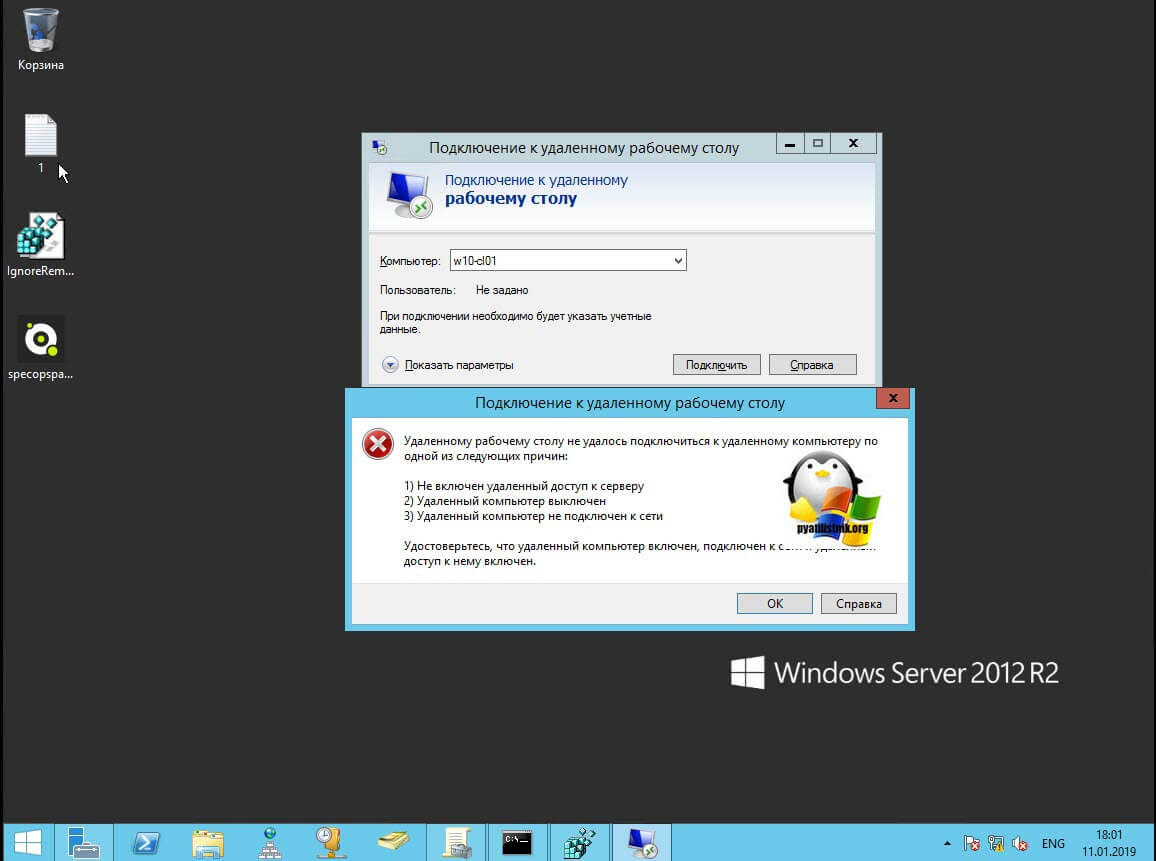
После чего вы увидите ошибку:
- Удаленному рабочему столу не удается подключиться к удаленному компьютеру по одной из следующих причин:
Не включен удаленный доступ к серверу - Удаленный компьютер выключен
- Удаленный компьютер не подключен к сети
Удостоверьтесь, что удаленный компьютер включен, подключен к сети и удаленный доступ к нему включен
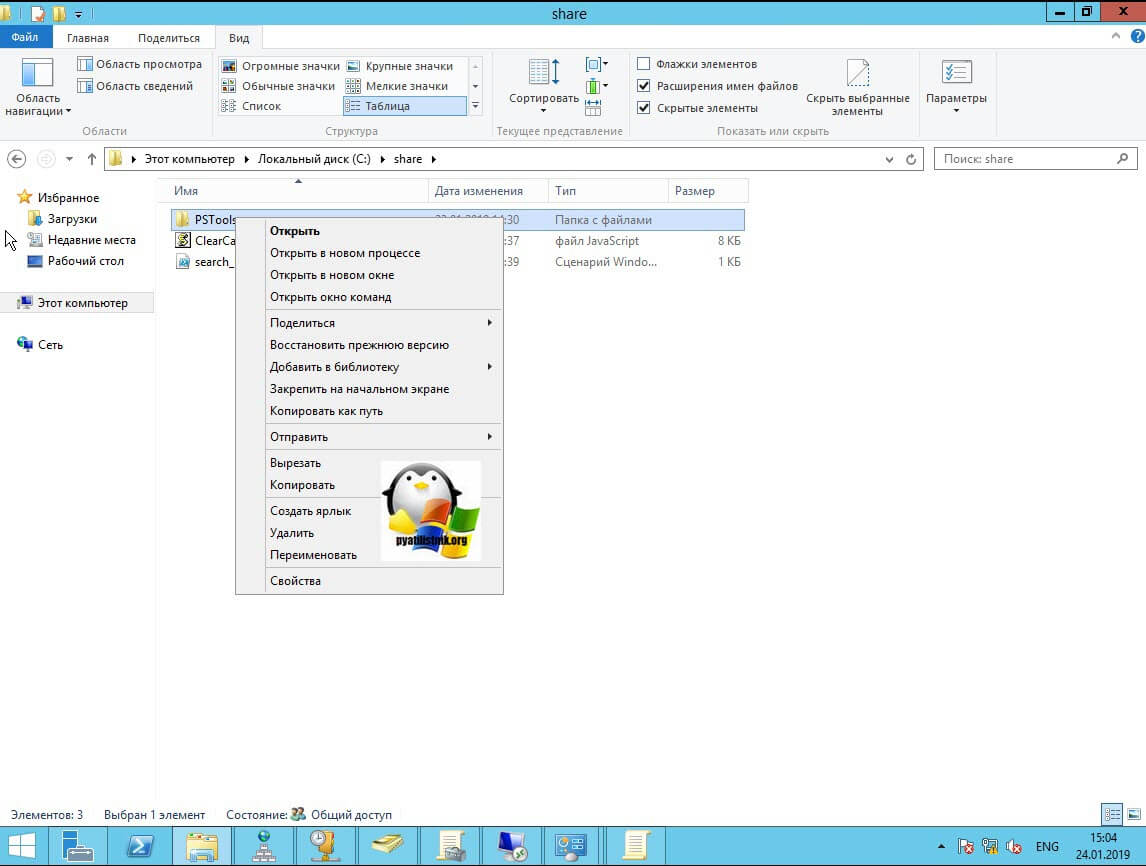
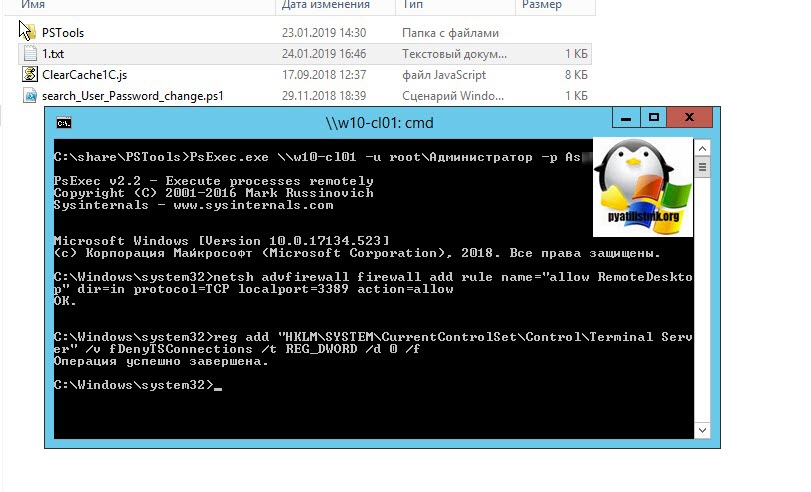
Напоминаю, что вы можете проверить доступность порта , через утилиту Telnet. Проверять нам нужно порт 3389. Вероятнее всего он не ответит. Как я и писал выше откроем порты и создадим правило в брандмауэре. Для этого мы воспользуемся утилитой PSTools.
скачать PSTools с сайта Microsoft https://technet.microsoft.com/ru-ru/sysinternals/pstools.aspx?f=255&MSPPError=-2147217396
На выходе у вас будет архив с утилитами, который нужно будет распаковать через архиватор. Когда вы распакуйте его, зажмите клавишу Shift и кликните правым кликом по папке PSTools. Из контекстного меню выберите пункт «Открыть окно команд».
Введите вот такую команду:
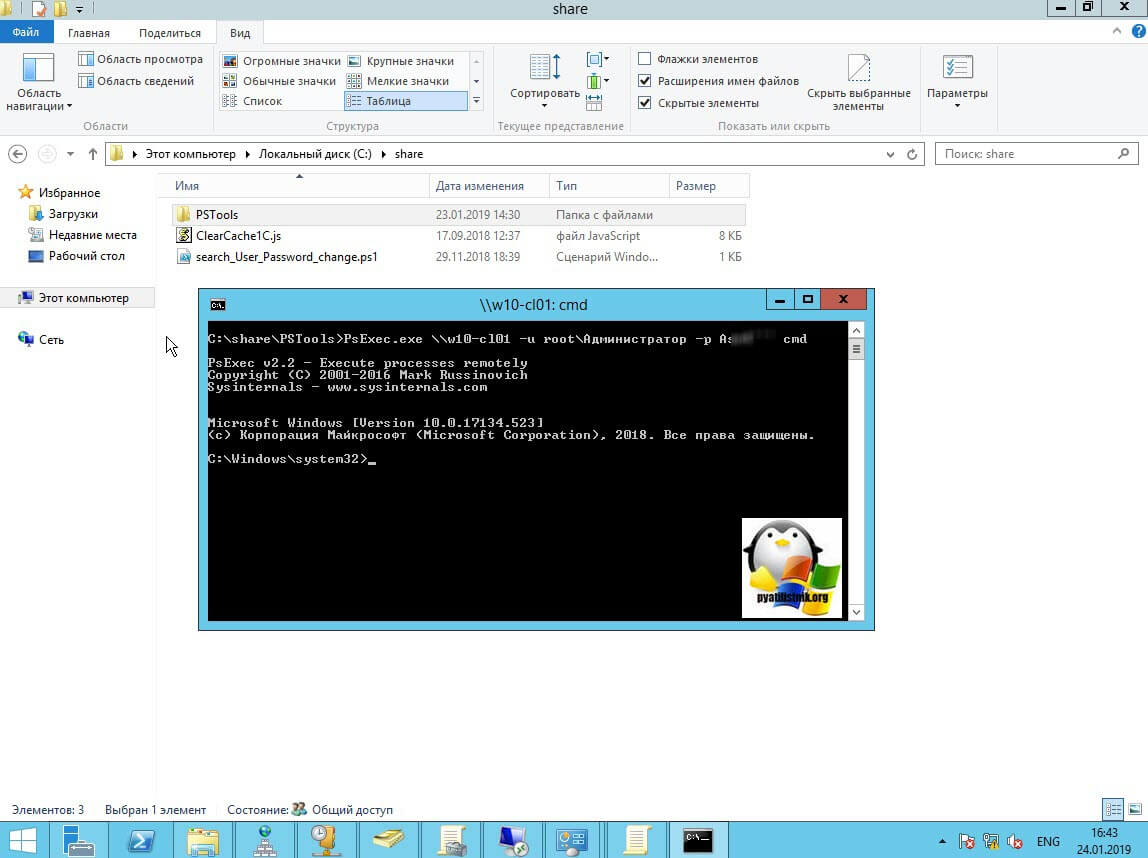
PsExec.exe \IP-адрес или DNS-имя компьютера -u domainлогин -p пароль cmd
Мой пример: PsExec.exe \w10-cl01 -u rootАдминистратор -p пароль cmd
В итоге у вас будет произведено подключение к удаленному компьютеру, вы увидите в заголовке \dns-имя: cmd. Это означает, что вы успешно подключены.
Далее вступает утилита командной строки netsh, благодаря ей мы создадим правило разрешающее входящие подключения по RDP.
netsh advfirewall firewall add rule name=»allow RemoteDesktop» dir=in protocol=TCP localport=3389 action=allow
Если вы до этого не включали через реестр доступ к удаленному рабочему столу, то так же это можно выполнить в PsExec.exe:
reg add «HKLMSYSTEMCurrentControlSetControlTerminal Server» /v fDenyTSConnections /t REG_DWORD /d 0 /f
По идее все должно работать сразу и без перезагрузки, но если она требуется, то выполните команду:
Классический метод включения удаленного рабочего стола
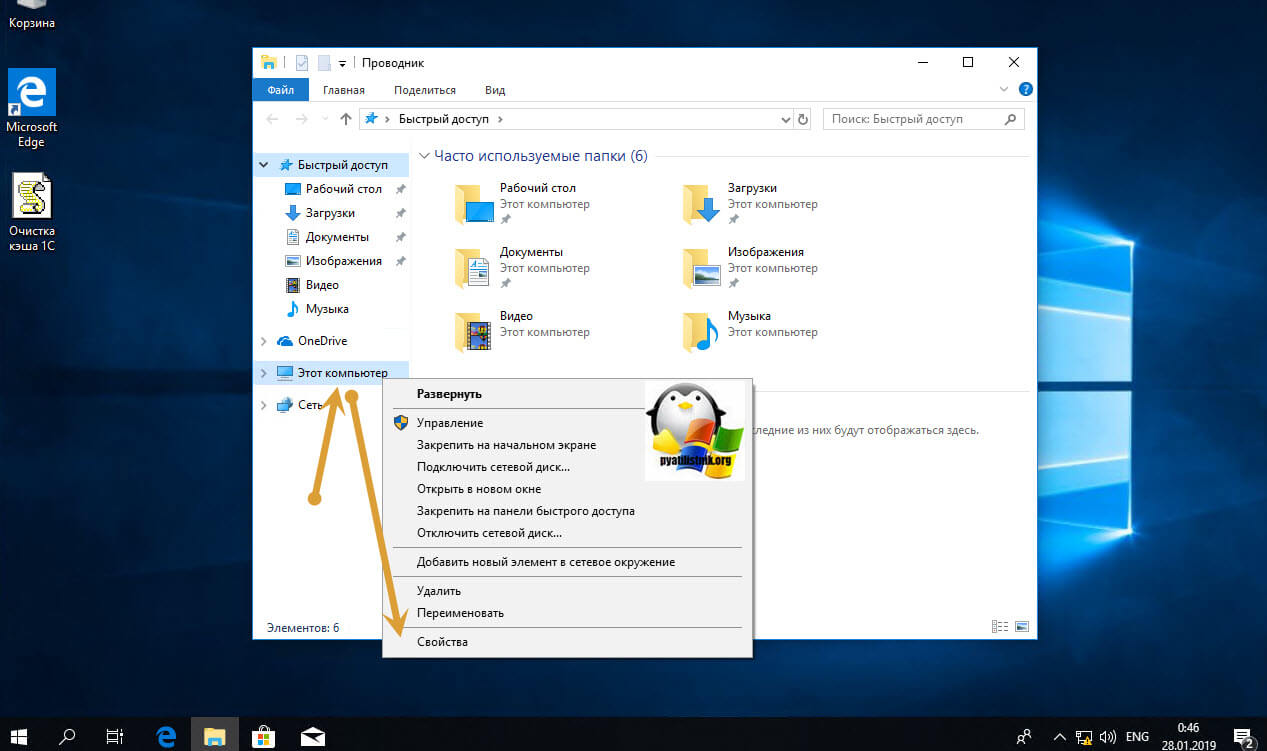
С удаленным включением служб RDP мы разобрались, теперь напомню для новичков, как можно локально его активировать. По умолчанию данная служба, как я и писал не работает. Чтобы это исправить есть два метода. Универсальный метод для любой версии Windows, я буду показывать на десятке, но для семерки, восьмерки, все будет одинаково. Откройте проводник Windows. Найдите в левой части объект «Этот компьютер (Мой компьютер)». Кликните по нему правым кликом и из контекстного меню перейдите в пункт «Свойства».
У вас откроется окно система. В правой части нажмите пункт «Настройка удаленного доступа», которое вызовет окно свойств системы. НА вкладке «Удаленный доступ», чтобы активировать службы удаленных рабочих столов Windows, вам нужно активировать пункт «Разрешить удаленные подключения к этому компьютеру». После этого у вас в системе сразу будет работать RDP доступ.
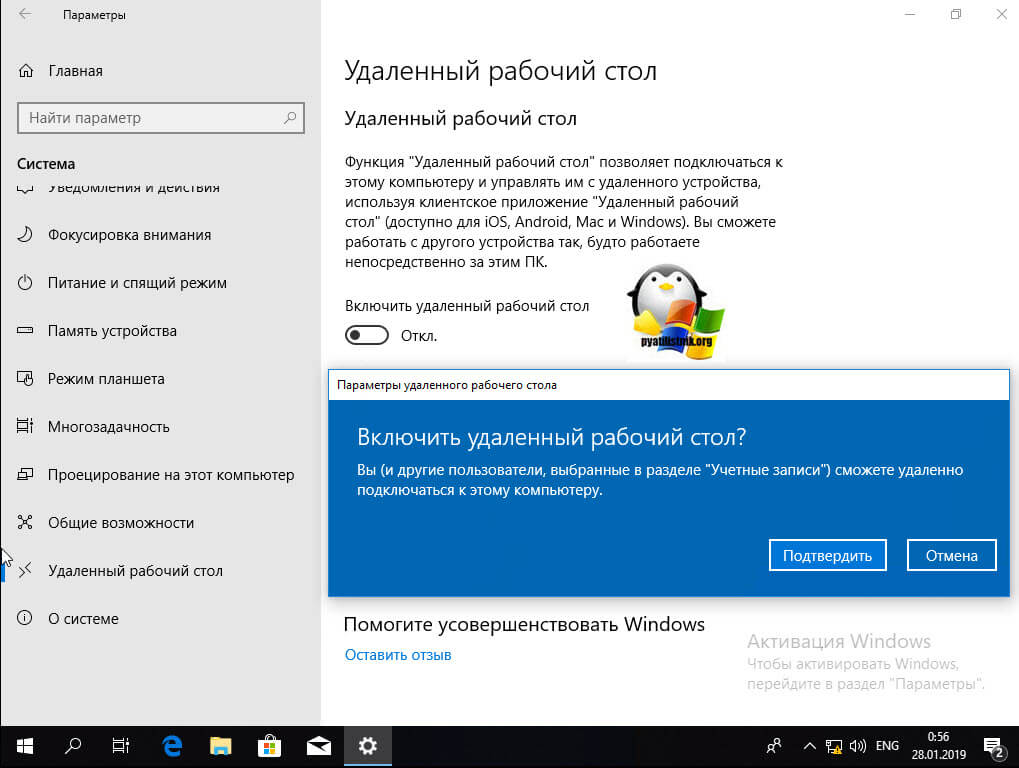
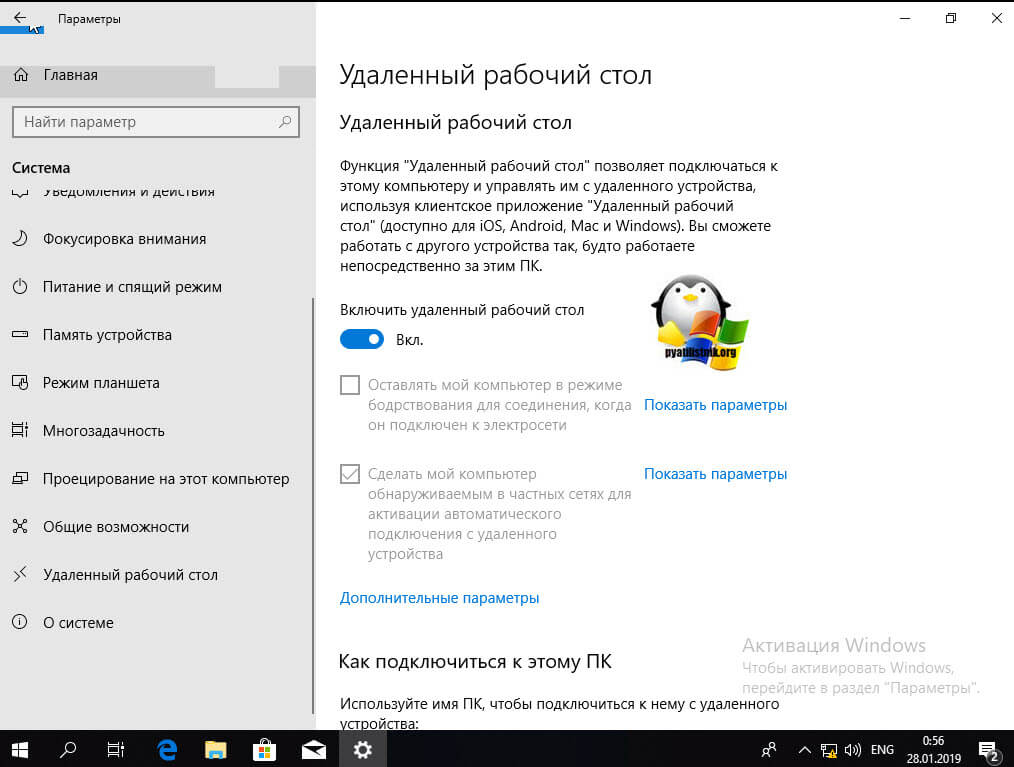
А вот метод исключительно для Windows 10 или Windows Server 2016 и выше. Вы открываете параметры Windows. Переходите в пункт система. В системе будет пункт «Удаленный рабочий стол». Активируем ползунок «Включить удаленный рабочий стол». Выскочит окно с подтверждением, говорим «Подтвердить».
Все функционал RDP активен, можно подключаться с других компьютеров. Данный метод по сути ставит все тужу галку, что мы видели и в классическом окне системы.
Этот подход можно с натяжкой назвать удаленным методом включения RDP, так как на той стороне вам потребуются руки которыми вы будите управлять по телефоны.
Как включить удаленный рабочий стол (RDP) через PowerShell
Открываем на компьютере, где необходимо включить RDP службу оснастку PowerShell.
Первая команда активирует галку «Разрешить удаленные подключения к этому компьютеру»
(Get-WmiObject Win32_TerminalServiceSetting -Namespace rootcimv2TerminalServices).SetAllowTsConnections(1,1)
Вторая команда активирует галку «Разрешить подключение только с компьютеров, на которых работает удаленный рабочий стол с проверкой подлинности на уровне сети»
(Get-WmiObject -Class «Win32_TSGeneralSetting» -Namespace rootcimv2TerminalServices -Filter «TerminalName=’RDP-tcp'»).SetUserAuthenticationRequired(0)
Третья команда, включает правило в Брандмауэре
Enable-NetFirewallRule -DisplayGroup «Remote Desktop»
Данные команды вы можете собрать в скрипт и распространить его через групповую политику при включении компьютера или автологоне пользователя.
Как удаленно включить RDP через групповую политику
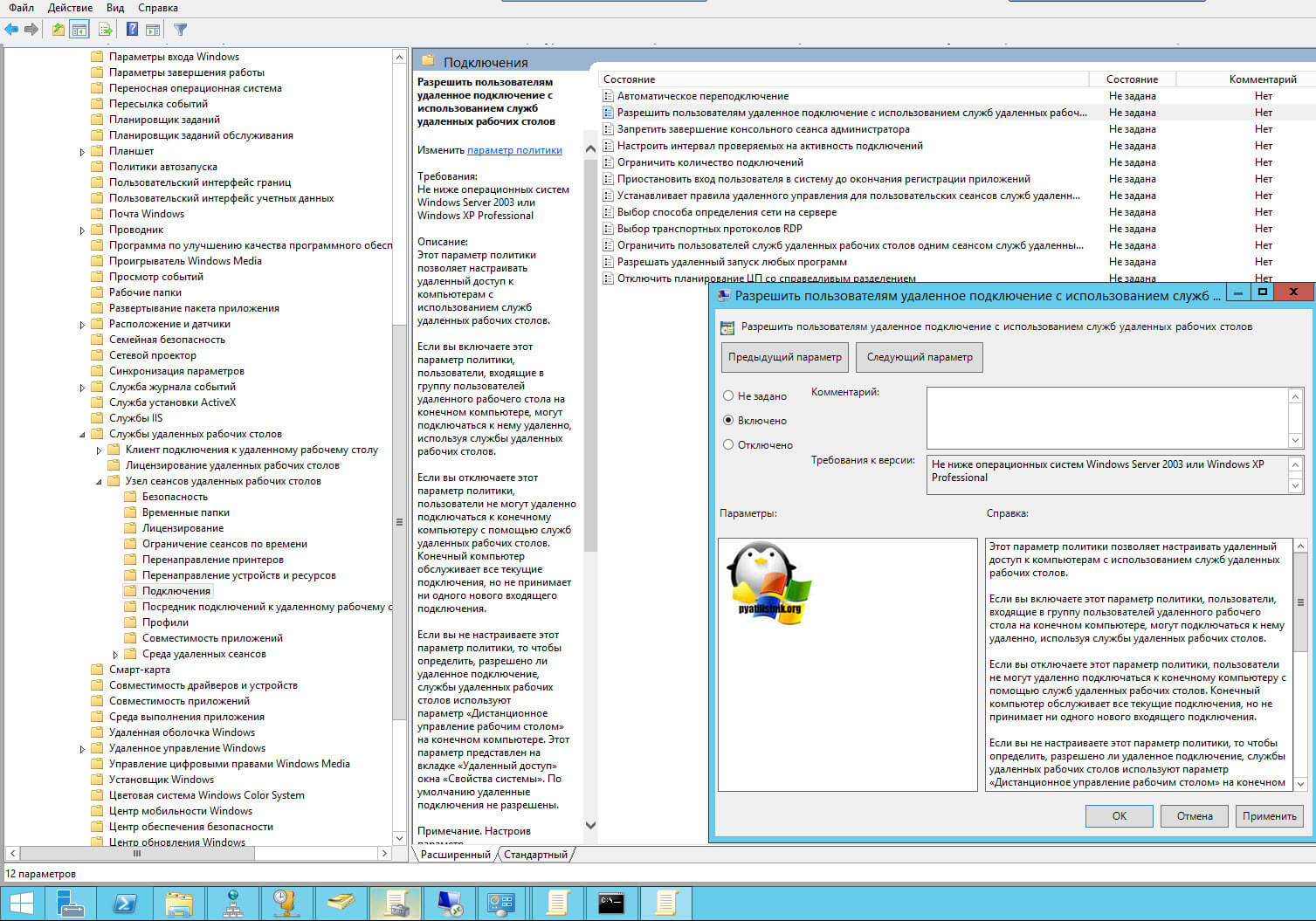
Данный метод включения удаленного рабочего стола на нужном компьютере возможен за счет домена Active Directory, благодаря централизованному управлению рабочих станций ваших сотрудников. Откройте редактор управления групповыми политиками. Создайте новую политику и прилинкуйте ее к нужному организационному подразделению, которое содержит нужный компьютер. После чего зайдите в свойства данной политики и измените ее настройки. Перейдите по пути:
Конфигурация компьютера — Политики — Административные шаблоны — Компоненты Windows — Службы удаленных рабочих столов — Узел сеансов удаленных рабочих столов — Подключения — Разрешать удаленное подключение с использованием служб удаленных рабочих столов
Откройте эту настройку и включите ее. Не забываем после этого обновить групповую политику на нужном компьютере и не забываем там открыть порт для RDP. Так же политиками или локально.
Конфигурация компьютера — Политики — Административные шаблоны — Сеть — Сетевые подключения — Брандмауэр Windows — Профиль домена — Разрешить исключения для входящих сообщений удаленного управления рабочим столом
.
Включив настройку вы можете указать конкретные ip-адреса откуда можно производить подключение или же ввести *, это будет означать, для всех.
На этом у меня все, уверен, что есть еще какие-то методы позволяющие удаленно включить RDP службу удаленных рабочих столов, но мне лень гуглить и искать их, я пользуюсь вот такими. С вами был Иван Семин, автор и создатель блога Pyatilistnik.org.
Оснастка Службы удаленных рабочих столов на Windows 7
(Remote Desktops MMC Snap-in on Windows 7)
это специальное средство для удаленного управления несколькими подключениями удаленных рабочих столов на основе протокола RDP.
В первую очередь это средство будет полезно системным администраторам. Которые часто зависают на тех или иных серверах при настройки или отладки сервисов и служб, чтении логов журналов событий и так далее.
Для того чтобы воспользоваться “Службой удаленных рабочих столов” , необходимо иметь на вашем компьютере установленный пакет, который называется “Средство удаленного администрирования сервера для Windows 7 с пакетом обновления 1” (Remote Server Administration Tools for Windows 7 with SP1), сокращенно RSAT, который позволяют ИТ-администраторам управлять ролями и компонентами, которые устанавливаются на компьютерах под управлением Windows Server® 2008 R2, Windows Server® 2008 или Windows Server® 2003, с удаленного компьютера под управлением Windows 7.
Соответственно установить этот пакет можно только на Windows 7 или Windows 7 SP1 выпусков Профессиональная, Корпоративная и Максимальная (Windows 7 Enterprise, Professional, Ultimate edition).
RSAT доступен как для 32-х, так и для 64-х битных операционных систем.
Размеры установочных файлов весят немало:
Windows6.1-KB958830-x64-RefreshPkg.msu 239.5 MB
Windows6.1-KB958830-x86-RefreshPkg.msu 230.0 MB
Размеры файлов можно объяснить наличием достаточного для удаленного администрирования количества оснасток и утилит, соответствующих библиотек поддержки и модулей справки, хотя мне кажется можно было сделать файлик размером поскромнее.
Закачать RSAT можно по следующей ссылке: http://www.microsoft.com/ru-ru/download/details.aspx?id=7887
Пакет должен установиться без каких либо проблем.
Далее необходимо зайти: Пуск – Панель управления – Удаление программы.
Для владельцев забугорной версии Windows, этот путь может быть следующим: Start — Control Panel — Programs.
В открывшемся окне необходим щёлкнуть по надписи, обведенной на картинке выше, “Включение и отключение компонентов Windows” или “Turn Windows features on or off”.
В открывшемся окне “Включение или отключение компонентов Windows” переходим в раздел “Средства удаленного администрирования сервера” – “Средства администрирования ролей” – “Средства служб удаленных рабочих столов”.
По английски будет соответственно: scroll down to the “Remote Server Administration Tools” — “Role Administration Tools” — сheck the “Remote Desktop Services Tools” checkbox.
На этом все нажимаем “ОК”, ждем пока установится выбранный компонент и закрываем все окна.
Для того чтобы запустить оснастку “Службы удаленных рабочих столов на Windows 7”, необходим выполнить следующие действия: Пуск – Администрирование — Службы удаленных рабочих столов — Удаленные рабочие столы.
Альтернативный вариант: Пуск – Выполнить — tsmmc.msc.
Откроется типовое для некоторых средства администрирования окно (терминальный сервер), в левой части которого будут отображаться наименования подключаемых компьютеров, а в правой части собственно удаленный рабочий стол выбранного элемента из левой части.
Добавление новых хостов осуществляется щелчком правой кнопкой мыши по элементу “Удаленные рабочие столы” – “Добавление нового подключения”.
В общем виде работа через оснастку “Службы удаленных рабочих столов на Windows 7” выглядит подобно изображению выше.
В общем, надо сказать, довольно удобное средство удаленного администрирования.
- Remove From My Forums
-
Вопрос
-
Кнофигурация:
Windows 2003 Server R2 + ISA 2006 Server
Проблема:
На одном из серверов в домене поднял WSUS, через некоторое время вдруг перестал работать удаленный рабочий стол на сервере с ISA 2006.
Сначала грешил на саму ISA, но потом вдруг заметил отсутствие слушающего порта 3389 на сервере, как будто служба termsrcs просто не запустилась. Проверил, сама служба Terminal Services запущена, галочка «Включить удаленный доступ к рабочему столу» стоит, логах необной ошибки. Запустил команду netstat на другой машине, нашел сервис обрабатывающий RDP запросы:
TCP 0.0.0.0:3389 0.0.0.0:0 LISTENING 2180
TermService
[svchost.exe]
А на машине с ISA такого сервиса нет. Хотя быть должна.
Очень надеюсь на Вашу помощь.
Ответы
-
Посмотрите настройки Terminal Services Configuration, например, объект RDP-TCP Connection может быть привязан к другому сетевому адаптеру. Сравните настройки с другим заведомо работающим сервером.
-
Помечено в качестве ответа
14 мая 2009 г. 11:33
-
Помечено в качестве ответа
Служба удаленных рабочих столов Remote Desktop Services (ранее известная, как Terminal Services) — это компонент Microsoft Windows (серверной и клиентской операционных систем), позволяющий пользователям удаленно запускать приложения или управлять сервером с любой машины, где есть клиент подключения к удаленному …
Как включить удаленный доступ к рабочему столу Windows 10?
Включите удаленные подключения на компьютере, к которому требуется подключиться.
- Убедитесь, что у вас установлена Windows 10 Pro. …
- Когда все готово, выберите Пуск > Параметры > Система > Удаленный рабочий стол и включите параметр Включить удаленный рабочий стол.
Как открыть службу удаленных рабочих столов?
Запустите «Диспетчер серверов» и нажмите кнопку «Добавить роли и компоненты». Откройте вкладку с названием «Роли сервера» и выберите в списке роль «Службы удаленных рабочих столов». Щелкните по кнопке «Далее».
Как запустить Remote Desktop Connection?
Запустить программу «Подключение к удаленному рабочему столу» можно из меню «Пуск» — «Все программы» — «Стандартные» — «Подключение к удаленному рабочему столу», либо же выполнив команду mstsc.exe (для этого необходимо нажать комбинацию клавиш WIN+R и вписать имя команды в появившемся окне «Выполнить»).
Почему не работает удаленный рабочий стол?
Проверьте, включен ли порт 3389. Если удаленный рабочий стол не подключается, возможно, проблема в брандмауэре. … Если этот порт включен, но проблема все еще появляется, попробуйте отключить и включить брандмауэр. Иногда быстрая перезагрузка брандмауэра может решить проблему, поэтому вы можете попробовать это.
Как разрешить удаленный доступ к компу?
Можно настроить компьютер для удаленного доступа с помощью нескольких простых действий.
- На устройстве, с которого вы собираетесь подключиться, откройте меню Пуск и щелкните значок Параметры.
- Выберите группу Система возле элемента Удаленный рабочий стол.
- Включите удаленный рабочий стол с помощью ползунка.
5.06.2018
Как подключить удаленный рабочий стол Windows 10 через VPN?
Подключение к рабочему столу Windows через VPN-подключение
- Выберите «Использовать моё подключение к Интернету (VPN)».
- Введите «Интернет-адрес» и имя назначения и нажмите «Далее».
- Заполните поля «Пользователь» и «Пароль» и нажмите «Подключить».
- После подключения нажать «Закрыть».
15.01.2014
Как добавить роль терминального сервера?
В панели быстрого запуска открываем Диспетчер серверов:
- Нажимаем Управление — Добавить роли и компоненты:
- Нажимаем Далее до «Выбор типа установки». …
- В окне «Выбор ролей сервера» выбираем Службы удаленных рабочих столов:
- Кликаем Далее, пока не появится окно «Выбор служб ролей» и выбираем следующие:
Как подключиться к VDI?
Для подключения к виртуальному рабочему столу (VDI/DaaS) через OC Windows нужно:
- Нажать комбинацию клавиш Win+R или вызвать приложение “Выполнить” (“Run”), приложение расположено в меню пуск.
- Во всплывшем окне напишите название программы, которую нужно открыть — mstsc.exe и нажмите “ОК”.
Как настроить удаленный рабочий стол на Windows Server 2012 R2?
Включение
- Открываем сведения о системе. В Windows Server 2012 R2 / 2016 или 10 кликаем правой кнопкой мыши по Пуск и выбираем Система.
- Настраиваем удаленный рабочий стол. В меню слева кликаем по Настройка удаленного доступа.
13.09.2016
Как настроить удаленный доступ к домашнему компьютеру?
В свойствах Мой компьютер во вкладке Удаленные сеансы надо поставить флажок напротив Разрешить удаленный доступ к этому компьютеру (рис. 1). Затем необходимо выбрать пользователя, который имеет право на подключение к Remote Desktop с удаленного компьютера, нажав на кнопку Выбрать удаленных пользователей.
Где находится Remote Desktop Connection?
Не важно, серверную вы используете операционную системе или нет, для подключения к удаленному рабочему столу используется одно и то же приложение — Remote Desktop Connection. Выполняемый файл называется mstsc.exe и расположен в %systemroot%/system32/mstsc.exe.
Что делать если не подключается удаленный рабочий стол?
Вы можете следовать некоторым из этих решений ниже, чтобы ваш RDP в Windows работал правильно.
- Решение 1. Измените / настройте параметры брандмауэра
- Решение 2. Разрешите подключения к удаленному рабочему столу, если это не разрешено
- Решение 3. Сбросьте учетные данные удаленного рабочего стола
- Решение 4. …
- Решение 5.
Как победить постоянно Отваливающийся удаленный рабочий стол?
Решить проблему можно следующим образом: Открыть редактор реестра, развернуть ветвь HKEY_Local_machineSystemCurrentcontrolsetControlTerminal server и изменить значение параметра fDenyTSConnections из 1 в 0. Тем самым вы разрешите службе удаленных рабочих столов принимать подключения.
Как настроить удаленный доступ через гугл?
Как настроить удаленный доступ на компьютере
- Откройте Chrome на компьютере.
- В адресной строке введите remotedesktop.google.com/access .
- Под надписью «Настройте удаленный доступ» нажмите на значок «Скачать» .
- Следуйте инструкциям на экране.