7
Операционная система– это
совокупность программ для организации
диалога пользователя с компьютером,
для управления аппаратными средствами
и ресурсами, для запуска программ и
выполнения некоторых других функций.
В настоящее время наибольшее распространение
в нашей стране получили различные версии
графической операционной системы
WindowsфирмыMicrosoft – Windows – 95,Windows – 98,Windows – NT,Windows –2000,Windows – XP.
Во всех версиях интерфейс пользователя
и приемы работы с дисками, папками и
файлами практически не отличаются.
ОС Windows загружается
автоматическипри включениипитаниякомпьютера.
При работе в операционной системе
Windows широко применяется манипулятор
мышь. Указатель мыши в зависимости
от конкретной ситуации может иметь
различный вид.
Основные приемы управления с помощью
мыши:
-
однократныйщелчоклевойкнопкой мыши — выделение объектов,
выбор команды меню, кнопки панели
инструментов, установка и снятие флажка; -
однократный щелчокправойкнопкой мыши – вызов контекстного
меню; -
двойнойщелчоклевойкнопкой мыши по объекту – открытие
объекта (запуск приложений, открытие
документов, папок); -
задержкауказателя мыши на
объекте — вызов всплывающих
подсказок; -
протягивание при нажатой левой
кнопке мыши — изменение размеров
объектов, выделение фрагментов
документов.
Пользовательский интерфейс ос Windows
Пользовательский интерфейс-это методы
и средства, предоставляемые ОС пользователю
для взаимодействия с ней.
ОС Windows
имеет удобный графический
интерфейс пользователя.
Ниже перечислены основные
элементы пользовательского интерфейса
Windows:
-
рабочий стол;
-
меню;
-
панели инструментов;
-
программные окна;
-
диалоговые окна;
-
вторичные окна.
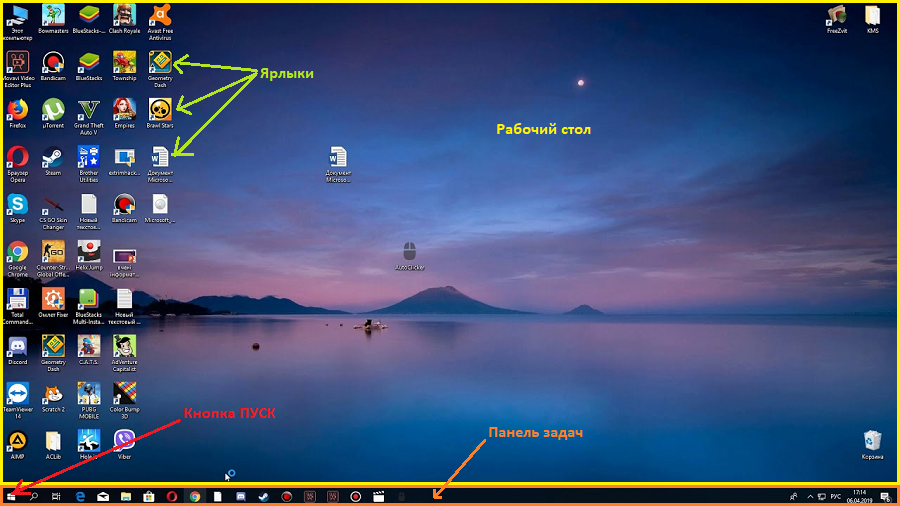
Р
стол— это экран, появляющийся после
загрузки Windows. (рис. 1).
Рис. 1. Рабочий стол.
Ниже содержится обзор объектов, являющихся
составными частями рабочего стола.
Папкав Windows— этосредствоорганизации и представления системных
ресурсов ПК (каталогов, файлов, дисковых
накопителей и т. д.).
Папка может содержать другие папки
(вложенные папки), а также такие объекты,
как, например, файлы, принтеры, диски.
Объекты в папке представляются значками,
и каждый значок имеет название,
расположенное ниже него. Для того чтобы
открыть папку, запустить программу,
открыть документ или активизировать и
открыть объект любого другого типа в
папке, достаточно дважды щелкнуть
на соответствующем значке.
По умолчанию рабочий стол содержит
следующие специальные папки:
-
Мой компьютер,
-
Сетевое окружение,
-
Корзина.
Значок Мой компьютерпредставляет
наРабочем столепапку, как бы
содержащую весь компьютер целиком.
ПапкаМой компьютерсодержит
значки всех дисковых накопителей ПК,
включая жесткие диски, накопители на
гибких и компакт-дисках и подсоединенные
сетевые диски.
Значок Сетевое окружениеобеспечивает быстрый доступ к сетевым
ресурсам, если данный ПК подсоединен к
сети. Эти сетевые ресурсы включают диски
и принтеры, общие для всех компьютеров
в сети. Чтобы просмотреть список
компьютеров, входящих в рабочую группу,
или структуру сети в целом, необходимо
дважды щелкнуть этот значок.
Корзинапредназначена для
временного хранения удаленных файлов,
папок и ярлыков. Она позволяет восстановить
объекты, удаленные по ошибке. При
переполнении корзины объекты, находящиеся
в ней дольше всех, удаляются безвозвратно.
По внешнему виду корзины видно — пуста
она или нет. Конкретную информацию о
перенесенных в корзину объектах можно
получить, перейдя в режим просмотра
корзины (двойной щелчок левой кнопкой
мыши или щелчок правой кнопкой и в
контекстном меню выбрать команду
Открыть).
Ярлык – ссылка на другой объект
Windows. Таким объектом может быть файл,
папка, устройство (диск, принтер). Это
файл специального вида, в котором
хранится путь к объекту. В отличие от
файлов, ярлыки имеют на своем значке в
левом нижнем углуизогнутую стрелку.
Используется ярлык для быстрого доступа
к объекту (быстрого открытия объекта).
Для этого достаточно дваждыщелкнуть
левой кнопкой на ярлыке.
Соседние файлы в предмете [НЕСОРТИРОВАННОЕ]
- #
- #
- #
- #
- #
- #
- #
- #
- #
- #
- #
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
(Redirected from Windows Time)
The following is a list of Microsoft Windows components.
Configuration and maintenance[edit]
| Component | Description | Introduced |
|---|---|---|
| Settings | Allows users to change system settings, similar to the Control Panel, but has less options[1] | Windows 8 |
| Control Panel | ||
| Control Panel | Allows users to view and change basic system settings and controls, such as adding hardware, adding and removing software, controlling user accounts, and changing accessibility options | Windows 1.0 |
| Device Manager | Allows the user to display and control the hardware attached to the computer, and control what device drivers are used | Windows 95 |
| Windows Mobility Center | Centralizes the most relevant information related to mobile computing | Windows Vista |
| Security and Maintenance | Centralizes and reports on the status of anti-virus, Automatic Updates, Windows Firewall, and other security-related components of the operating system | Windows XP SP2 |
| Administrative Tools | ||
| Microsoft Management Console | Provides system administrators and advanced users with a flexible interface through which they may configure and monitor the system | Windows NT 4.0 Option Pack |
| Windows System Assessment Tool | Built-in benchmarking tool that analyzes the different subsystems (graphics, memory, etc.), and uses the results to allow for comparison to other Windows Vista systems, and for software optimizations. It rates the computer’s performance using the Windows Experience Index. | Windows Vista |
| System Restore | Allows for the rolling back of system files, registry keys, installed apps, etc., to a previous state in the event of a system failure | Windows Me |
| Windows Recovery Environment | Helps diagnose and recover from serious errors which may prevent Windows from booting successfully, or restore the computer to a previous state using System Restore or a backup image | Windows Vista |
| Microsoft Drive Optimizer | Rearranges files stored on a hard disk to occupy contiguous storage locations in order to optimize computer performance | Windows 95, Windows 2000 |
| Event Viewer | Lets administrators and users view the event logs on a local or remote machine | Windows NT 3.1 |
| Resource Monitor (previously Reliability and Performance Monitor) |
Lets administrators view current system reliability and performance trends over time | Windows Vista |
| Logical Disk Manager | Logical volume manager developed by Microsoft in conjunction with Veritas Software | Windows NT 4.0 (Separate Tool), Windows 2000 |
| Registry Editor | Allows users to browse and edit the Windows registry | Windows 3.1 |
| Task Scheduler | Allows users to script tasks for running during scheduled intervals | Microsoft Plus! for Windows 95 |
| Software installation and deployment | ||
| Windows Update | An online service providing updates such as service packs, critical updates and device drivers. A variation called Microsoft Update also provides software updates for other Microsoft products. | Windows 98 |
| Windows Installer | An engine for the management of software installation. Includes a GUI framework, automatic generation of the uninstallation sequence and deployment capabilities for corporate networks. | Windows 2000 |
| ClickOnce | Technology for deploying .NET Framework-based software via web pages, with automatic update capabilities. Intended for per-user only applications. | .NET Framework 2.0 |
User interface[edit]
| Component | Description | Introduced |
|---|---|---|
| Action Center | View notifications sent from apps and change common settings | Windows 10 Version 1507 |
| Command Prompt | Text-based shell (command line interpreter) that provides a command line interface to the operating system | Windows NT 3.1 |
| Windows PowerShell | Command-line shell and scripting framework. | Windows XP |
| Windows Shell | The most visible and recognizable aspect of Microsoft Windows. The shell provides the container inside of which the entire graphical user interface is presented, including the taskbar, the desktop, Windows Explorer, as well as many of the dialog boxes and interface controls. In Windows Vista, a new compositing glass-like user interface called Windows Aero has been shown. | Windows 95 |
| File Explorer (previously Windows Explorer) |
Provides an interface for accessing the file systems, launching applications, and performing common tasks such as viewing and printing pictures | Windows 95 |
| Windows Search | Starting with Windows Vista, search is a tightly shell-integrated component of Windows. A downloadable Windows Desktop Search software is available for Windows XP and older versions. | Windows Vista, downloadable for older versions |
| Search Folders | Virtual folders that retrieve items based on queries rather than hierarchical folder trees on disk. | Windows Vista |
| Special Folders | Folders which are presented to the user through an interface as an abstract concept, instead of an absolute path. This makes it possible for an application to locate where certain kinds of files can be found, regardless of what version or language of operating system is being used. See also Windows Shell namespace. | Windows 95 |
| Start menu | Serves as the central launching point for applications. It provides a customizable, nested list of apps for the user to launch, as well as a list of most recently opened documents, a way to find files and get help, and access to the system settings. By default, the Start Button is visible at all times in the lower left-hand corner of the screen. | Windows 95 |
| Taskbar | The application desktop bar which is used to launch and monitor applications | Windows 95 |
| Task View | Displays all open windows and activities (via timeline) at a glance and switch between virtual desktops, starting in version 2004, users can now rename desktops
|
Windows 10 Version 1507 |
| File associations | Used to open a file with the appropriate app. Users can assign file associations uniquely to specific actions, known as verbs. | Windows 1.0 |
Applications and utilities[edit]
| Component | Description | Introduced |
|---|---|---|
| Easy Transfer | Used to transfer many files at once from one computer to another | Windows Vista |
| Contacts | Keeps a single list of contacts that can be shared by multiple apps | Windows Vista |
| Camera | Allows the user to take pictures or record video[2] | Windows 8 |
| Calculator | Calculation application | Windows 1.0 |
| Calendar | Calendaring application | Windows Vista |
| Character Map | Utility to view and search characters in a font, copy them to the clipboard and view their Windows Alt keycodes and Unicode names | Windows 3.1 |
| Cortana | Digital personal assistant | Windows 10 Version 1507 |
| Edge | Web browser | Windows 10 Version 1507 |
| Feedback Hub | Platform for exchanging communication with Windows Insiders and developers | Windows 10 Version 1607 |
| Groove Music (previously Xbox Music) |
Digital media player and media library application that is used for playing audio. In addition to being a media player, Groove includes the ability to copy music to compact discs, synchronize content with a digital audio player (MP3 player) or other mobile devices, and let users purchase or rent music from the Windows Store. | Windows 8 |
| Movies & TV (previously Xbox Video) |
Digital media player and media library application that is used for playing video. In addition to being a media player, Movies & TV lets users purchase or rent movies and TV episodes from the Windows Store. | Windows 8 |
| OneDrive (previously SkyDrive) |
Freemium cloud storage folder and sync service | Windows 8 |
| OneNote | Integrated note-taking app, based on the Microsoft Office product of the same name | Windows 8 |
| On-Screen Keyboard (osk.exe) | Virtual keyboard | |
| Paint 3D | Simple graphics painting app | Windows 10 Version 1703 |
| Photos | Simple image viewer | Windows 8 |
| Steps Recorder (called Problem Steps Recorder in Windows 7) |
Utility that allows the user to capture steps they took to reproduce a problem | Windows 7 |
| Windows To Go | Utility to create bootable versions of Windows 8 and above | Windows 8 |
| Notepad | Simple text editor | Windows 1.0 |
| Narrator | Screen reader utility that reads dialog boxes and window controls in a number of the more basic applications for Windows | Windows 2000 |
| Sound Recorder | Simple audio recording app that can record from a microphone or headset, and save the results in WAVE format and Windows Media Audio format in some Windows versions | Windows 3.0 Multimedia Extensions |
| Skype | Messaging and calling service | Windows 8.1, downloadable for previous versions |
| Sticky Notes | Tool for jotting notes on the desktop | Windows XP Tablet PC Edition |
| WordPad | Simple word processor that is more advanced than Notepad. It has facilities to format and print text, but lacks intermediate features such as a spell checker and thesaurus. | Windows 95 |
| Private Character Editor | Utility to create private use characters as defined under Unicode and various East Asian encoding schemes | Windows 3.1 East Asian editions |
| Remote Desktop Connection | Client implementation of the Remote Desktop Protocol; allows a user to securely connect to a computer running Terminal Services (Remote Desktop on Windows XP and Server 2003) and interact with a full desktop environment on that machine, including support for remoting of printers, audio, and drives. | Windows XP, downloadable for previous Windows versions |
| Remote Assistance | Allows a user to temporarily take over a remote computer over a network or the internet to offer help with and resolve issues | Windows XP |
| Mobility Center | Allows a user to adjust settings related to mobile computing | Windows Vista |
| Speech Recognition | Allows a user to input voice commands | Windows Vista |
| IExpress | Allows users to create self-extracting, self-installing INF installation-based packages | Internet Explorer 6 |
| Xbox Console Companion (previously Xbox and Xbox Games) |
Account manager for Xbox Live user accounts and a screen recording tool | Windows 8 |
| Xbox Game Bar | Provides a overlay for compatible games allowing for screen capture, chatting over the Xbox network, showing the frame rate of games, and playing music via Spotify[3][4] | Windows 10 May 2019 Update (Version 1903)[5] |
| Magnifier | Screen enlargement app | Windows 98 |
| Fax and Scan | Integrated faxing and image scanning application | Windows Vista, older faxing and scanning applications were present in previous Windows versions |
| Photo Viewer | Simple image viewer that can play a simple slideshow | Windows 7 |
| Email aggregator | Windows 8 | |
| Maps | Map viewer that allows users to look for locations, plan routes, and store offline maps | Windows 8 |
| Media Center | Designed to serve as a home-entertainment hub, to be viewed from a distance up to 3 meters (~10 feet) and controlled by specially designed remote controls. Lets users browse and view pictures, videos, and music from local hard drives, optical drives, and network locations, along with viewing, recording and deferred-playing live TV. Features an interactive TV guide with scheduled recording capabilities. Can also be used for visualization of other information (like sports scores) within the interface. | Windows XP Media Center Edition |
| Task Manager | Provides information about computer performance and displays details about running applications, processes, network activity, logged-in users, and system services | Windows 3.0 |
| Disk Cleanup | Utility for compacting rarely used files and removing files that are no longer required | Windows 98 |
| Snipping Tool | Screen-capture tool that allows for taking screenshots (called snips) | Experience Pack for Windows XP Tablet PC Edition 2005 |
| Microsoft Store (previously Windows Store) |
Initially known as Windows Store, it started as an app store for Windows 8. In Windows 10, it expanded into a broad digital distribution platform for apps, games, music, digital video and e-books. In 2017, it was renamed Microsoft Store and started offering hardware in United States, Canada and United Kingdom. | Windows 8 |
| MSN apps | Provide information from MSN web services | Windows 8 |
| Alarms & Clock(pre Alarms) | App that allows Windows users to set alarms, stopwatches, timers, and view a world clock | Windows 8 |
| Windows Security (previously Windows Defender Security Center) |
Antivirus | Windows 10 Version 1703 |
| Solitaire Collection | Set of solitaire card games | Windows 10 Version 1507, downloadable for Windows 8.x |
Windows Server components[edit]
| Component | Description | Supported by |
|---|---|---|
| Active Directory | A set of technologies introduced with Windows 2000 that allows administrators to assign enterprise-wide policies, deploy apps to many computers, and apply critical updates to an entire organization. Active Directory stores information and settings relating to an organization in a central, organized, accessible database. Networks can vary from a small installation with a few objects, to global-scale directories with millions of objects. Related topics: Domain controller, Flexible single master operation |
Windows 2000 and later server versions |
| Group Policy | Provides centralized management of user and computer settings in an Active Directory environment. Group policy can control a target object’s registry, NTFS security, audit and security policy, software installation, logon/logoff scripts, folder redirection, and Internet Explorer settings. Policy settings are stored in Group Policy Objects (GPOs), and may be linked to one or more sites, domains or organizational units. Related topics: Administrative Templates |
Windows 2000 and later |
| Internet Information Services | Web server | Windows NT family |
File systems[edit]
| Component | Description | Supported by |
|---|---|---|
| FAT12, FAT16 | The original file systems used with MS-DOS. The standard file systems used with Windows 1.0 through Windows 95. | All versions |
| FAT32 | Extensions to FAT supporting larger disk sizes. The standard file system for Windows 98 and Me. | Windows 95 OSR2 and later versions |
| NTFS | Standard file system of Windows NT; supports security via access control lists, as well as file system journaling and file-system metadata. Windows 2000 added support for reparse points (making NTFS junction points and Single instance storage possible), Hard links, file compression, and Sparse files. Encryption of data is provided by Encrypting File System. Symbolic links and transactioning of file operations via Transactional NTFS are features new to Windows Vista.
Although Windows 9x operating systems cannot read or write NTFS formatted disks, they can access the data over a network if it is shared by a computer running Windows NT. |
Windows NT (all versions) |
| ISO 9660 (CDFS) | The predominant file system for CD-ROM and DVD-ROM media. Windows includes support for Joliet extensions and the ISO 9660:1999 standard. ISO 9660:1999 is supported since Windows XP. | MS-DOS and Windows 9x via extensions, such as MSCDEX.EXE (Microsoft CDROM Extension), natively in Windows NT |
| Universal Disk Format (UDF) | A file system for storing files on optical media. It is an implementation of the ISO/IEC 13346 standard (also known as ECMA-167). It is considered to be a replacement of ISO 9660. Successive versions of Windows have supported newer versions of UDF. | Windows 98, Windows 2000, Windows XP, Windows Server 2003, Windows Vista |
| HPFS | High-Performance File system, used on OS/2 computers. Read and write capability in Windows 95 (where it also listed network computer NTFS-formatted drives as «HPFS», even though it had no direct NTFS capabilities). HPFS write support was dropped in Windows NT 4.0 and Windows 98, and dropped altogether shortly before the release of Windows 2000. | Windows 95 (Read/write), Windows 98, Windows NT (read), 3.1/3.51 (read/write/boot) |
| ReFS | A newer file system, based on NTFS. This system adds built-in integrity checking and removes the need for chkdsk, among other features. The maximum partition size is 1 YB. | Windows Server 2012, Windows 8.1 |
Core components[edit]
| Component | Acronym | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Windows kernel (Windows NT)
Main article: Architecture of the Windows NT operating system line |
||
| Ntoskrnl.exe | The Windows kernel image. Provides the kernel and executive layers of the kernel architecture, and is responsible for services such as hardware virtualization, process and memory management, etc. | |
| hal.dll | HAL | Provides and handles the interaction between software and hardware via the Hardware Abstraction Layer. |
| kernel32.dll | This application provides kernel operations to apps in the Win32 mode, like memory management, I/Os, process creation, etc. | |
| Core processes (Windows NT) | ||
| System idle process | SIP | A counter which measures how much idle capacity the CPU has at any given time. The process runs in the background and monitors processing bandwidth, occupied memory and the Windows virtual paging file. |
| Session Manager Subsystem | SMSS | Performs several critical boot-time operations, such as the creation of environment variables, starting CSRSS, and performing file-copy operations that were queued up from before the system was booted (pending file rename operations). During system operation, it handles Windows File Protection and the creation of logon sessions via Winlogon. |
| Client/Server Runtime Subsystem | CSRSS | User-mode side of the Win32 subsystem. Provides the capability for applications to use the Windows API. |
| Local Security Authority Subsystem Service | LSASS | Responsible for enforcing the security policy on the system. Verifies users logging on to the computer and creates security tokens. |
| Winlogon | Responsible for handling the secure attention key, loading the user profile on logon, and optionally locking the computer when a screensaver is running. On Windows NT systems prior to Windows Vista, Winlogon is also responsible for loading GINA libraries which are responsible collecting logon credentials from the user. | |
| Svchost.exe | A generic host process name for services that run from dynamic-link libraries (DLLs). Several Svchost processes are typically present on a Windows machine, each running in a different security context, depending on what privileges the contained services require. | |
| Windows on Windows and WOW64 | WoW | An abstraction layer that allows legacy code to operate on more modern versions of Windows; typically this means running 16-bit Windows applications on 32-bit Windows, and 32-bit applications on 64-bit Windows. |
| Virtual DOS machine | NTVDM | Allows MS-DOS apps to run on Intel 80386 or higher computers when there is already another operating system running and controlling the hardware. Introduced in Windows 2.1; not available in any 64-bit edition of Windows. |
| System startup (Windows NT)
Main articles: Windows NT Startup Process and Windows Vista Startup Process |
||
| NTLDR, IA64ldr, Winload | The boot loader; performs basic system initialization options such as loading the hardware abstraction layer and boot-time device drivers, prior to passing control to the Windows kernel. In versions prior to Vista, NTLDR and IA64ldr also display menus to the user if multiple operating systems are defined in boot.ini, or if F8 is pressed. | |
| Recovery Console | Provides the means for administrators to perform a limited range of tasks using a command line interface, primarily to aid in recovering from situations where Windows does not boot successfully. | |
| ntdetect.com | Used during the boot process to detect basic hardware components that may be required during the boot process | |
| Windows Boot Manager | In Windows Vista and later operating systems, displays boot menus to the user if multiple operating systems are configured in the system’s Boot Configuration Data. | |
| Graphical subsystem | ||
| Desktop Window Manager | DWM | The compositing manager introduced in Windows Vista that handles compositing and manages special effects on screen objects in a graphical user interface |
| Graphics Device Interface | GDI/GDI+ | The kernel graphics component for representing graphical objects and transmitting them to output devices such as monitors and printers |
| Windows USER | The Windows USER component provides core user interface, messaging and visual elements |
Services[edit]
This list is not all-inclusive.
| Display name | Service key name | Description | Introduced |
|---|---|---|---|
| Active Directory Service | NTDS | Network Authentication Management | Windows 2000 Server |
| Alerter service | Alerter | Sends administrative alerts over the network to client computers, administrators and users | Windows NT |
| Application Layer Gateway service |
ALG | Provides support for plugins that allow network protocols to pass through Windows Firewall and work behind Internet Connection Sharing | Windows 2000 |
| Application Experience service | Processes application compatibility cache requests for applications as they launch[6] | ||
| Application Management | AppMgmt | Processes requests to enumerate, install, and remove applications that are installed on the computer or deployed through an organization’s network | Windows 2000 |
| Background Intelligent Transfer Service |
BITS | Transfers files between machines using idle network bandwidth. Used by Windows Update, Windows Server Update Services, and Systems Management Server to deliver software updates to clients, as well as by Windows Messenger. | Windows XP |
| Computer Browser | Browser | Crawls neighboring computers on the network and locates shared resources. One of the computers acts as the Master Browser and supplies this information to other computers designated as browsers.[7] | Windows for Workgroups |
| Delivery Optimization | DoSvc | A peer-to-peer distribution service that downloads Windows updates and Microsoft Store apps from the local network or Internet peers, and redistributes them to others. Can be configured using either the Settings app or Group Policy. The Settings app can turn it on or off, and specify whether the service operates on the local network only, downloads from and uploads to the Internet peers as well. Group Policy allows finer control.[8][9] Delivery Optimization relies on a centralized web service that does not index contents under 10 MB. Computers without Internet access cannot use Delivery Optimization.[10] | Windows 10 Anniversary Update[8] |
| Distributed Link Tracking | TrkWks, TrkSrv | Used to track links to files on NTFS volumes. Windows uses these services to find linked files if they are renamed or moved (locally or to another machine).[11] | Windows 2000 |
| Distributed Transaction Coordinator |
MSDTC | Allows transactional components to be configured through COM+ by coordinating transactions that are distributed across multiple computers and/or resource managers, such as databases, message queues, file systems, and other transaction–based resource managers.[12] | Windows 2000 and later NT-based |
| DNS Client | DNSCache | Resolves and caches domain names (e.g. “en.wikipedia.org”) to IP addresses | Windows 2000 |
| Event Log | EventLog | Stores and retrieves events that can be viewed in the event viewer. Part of services.exe.[13] | Windows NT |
| Extensible Authentication Protocol | EAPHost | Provides EAP authentication to connecting clients | Windows 2000 |
| Indexing Service | CISVC | Indexes contents and properties of files on local and remote computers; provides rapid access to files through flexible querying language.[14] | Windows 2000 and later NT-based |
| Interactive Services Detection | UI0Detect | For compatibility; when a service-displayed user interface is detected, it gives the user an option to switch to Session0 to see it | Windows Vista |
| Internet Connection Sharing (ICS) | SharedAccess | When enabled, it allows other computers on the local network to access an internet connection that is available to the host computer | Windows 2000;[15] Windows Vista onward[16] |
| Network Location Awareness | NLA | Manages network configurations and information, and notifies applications of changes | Windows XP |
| Network Store Interface Service | NSIS | Collects routing information of active network interfaces, shares this with other services and notifies applications of changes | Windows XP |
| NTLM Security Support Provider | NTLMSSP | Uses the NTLM MS-CHAP protocol to encapsulate and negotiate options in order to provide signed and sealed communication. Deprecated now in favor of Kerberos authentication. | Windows NT |
| Peer Name Resolution Protocol | PNRPSvc | Resolves domain names using Peer Name Resolution Protocol | Windows XP |
| Plug and Play | PlugPlay | Enables autodetection and configuration of hardware | Windows 2000 |
| Windows Print spooler [fr] | Spooler | Manages printer devices and moves files into memory for printing | Windows 95, Windows NT |
| Remote Procedure Call (RPC) | RpcSs | Provides Remote Procedure Call features via remotely accessible Named Pipes | Windows NT family |
| Routing and Remote Access Service | RRAS | API and server software that enables applications to administer the routing and remote-access service capabilities of the operating system, to function as a network router. | Windows 2000 |
| Secondary Logon | SecLogon | Allows users to run apps with a different account than the one they logged in with. Allows non-administrative accounts to perform administrative tasks.[17] | |
| Security Accounts Manager | SamSs | Manages user account security information | Windows NT family |
| System Event Notification Service | SENS | Monitors system events, such as network, power, logon, logoff, terminal services session connection and disconnection, and delivers these to applications and other system components.[18] | Windows 2000 |
| Superfetch | SysMain | Monitors file usage patterns and boosts system speed by caching frequently accessed files to RAM[19] | Windows Vista |
| Task Scheduler | Schedule | Lets users setup and schedule automated tasks | Microsoft Plus! for Windows 95 |
| TCP/IP NetBIOS Helper | LmHosts | Enables support for NetBIOS over TCP/IP (NetBT) service and NetBIOS name resolution | Windows NT family |
| Volume Shadow Copy | VSS | Creates multiple versions of files that change. The ability to store persistent snapshots was added in Windows Server 2003.[20] | Windows XP |
| Windows Audio | AudioSrv | Manages audio devices for Windows-based apps. Controls all audio functions. | Windows XP |
| Windows Error Reporting | WERSvc | Generates error logs and reports errors. On Windows Vista and later, it notifies of solutions. | Windows XP |
| Windows Firewall | MpsSvc | Blocks unauthorized network connections to and from the computer | Windows Vista |
| Windows Firewall(née Internet Connection Sharing) | SharedAccess | Provides a simple firewall feature which was introduced in Windows XP. It also shares the internet on the local network, if the internet connection sharing feature is turned on.[21] | Windows XP only[22][23] |
| Windows Image Acquisition (WIA) | STISvc | Handles scanner and camera inputs | Windows Me |
| Windows Time | W32Time | Synchronizes the system time with external time servers. From Windows Server 2003 forward, full and compliant NTP support is provided.[24] | Windows 2000 |
| Windows Update | WUAUServ | Provides updates for the operating system and its installed components | Windows XP |
| Wireless Zero Configuration | WZCSvc (XP), WLANSvc | Configures and manages 802.11 wireless adapters | Windows XP, Server 2003 only |
| Windows Messenger service | Messenger | Allows users to send pop-up messages to other computers over the network | Windows NT family |
| WebClient[25] | Enables Windows-based apps to create and interact with Internet-based files | Windows XP |
DirectX[edit]
- Direct3D
- DirectDraw
- DirectInput
- DirectMusic
- DirectPlay
- DirectShow
- DirectSound
- DirectX Media Objects
- DirectX plugin
- DirectX Video Acceleration
Networking[edit]
- Administrative share
- Distributed File System
- My Network Places (formerly Network Neighborhood)
- Network Access Protection
- Remote Installation Services
- Server Message Block
- Windows Rights Management Services
Scripting and command-line[edit]
- Batch file
- CHKDSK
- Cmd.exe
- ComSpec
- Ipconfig
- Net / Net Send
- Netdom.exe: Windows Domain Manager
- Netsh
- Netstat
- QBasic
- Regsvr32
- Robocopy
- Win32 console
- Windows Script Host
- Windows PowerShell
- XCOPY
Kernel[edit]
- Commit charge
- Kernel Transaction Manager
- Win32 Thread Information Block
.NET Framework[edit]
- Assembly
- CLI Languages
- Metadata
- .NET Remoting
- ADO.NET
- ASP.NET
- Base Class Library
- Common Intermediate Language
- Common Language Infrastructure
- Common Language Runtime
- Common Type System
- Virtual Execution System
- Windows CardSpace
- Windows Communication Foundation
- Windows Forms
- Windows Presentation Foundation
- Windows Workflow Foundation
Security[edit]
| Component | Description | Introduced |
|---|---|---|
| AppLocker | Policy-based component that enables or disables execution of software based on rules such as location, properties and digital signature | Windows 7 Professional, Enterprise and Ultimate editions Windows Server 2008 R2 |
| BitLocker Drive Encryption | Disk encryption software, designed to protect data by providing encryption for entire volumes | Windows Vista Enterprise and Ultimate editions, Windows Server 2008 |
| Credential Guard | Virtualization-based isolation of stored credentials to prevent theft and pass-the-hash attacks. | Windows 10 Enterprise, Education, IoT Enterprise, or , Windows Server 2016 |
| Data Execution Prevention | Security feature that is intended to prevent an application or service from executing code from a non-executable memory region | Windows XP Service Pack 2 |
| Encrypting File System | File system driver that provides file system-level encryption | Windows 2000 |
| Security Account Manager | Database stored as a registry file | Windows NT 3.1 |
| SYSKEY | Utility that encrypts the hashed password information in a SAM database using a 128-bit encryption key | Windows NT 4.0 Service Pack 3 |
| User Account Control | Technology and security infrastructure utility that aims to improve the security of Microsoft Windows by limiting application software to standard user privileges until an administrator authorizes an increase | Windows Vista, Windows Server 2008 |
| Windows Firewall | Utility designed to block unauthorized access while permitting authorized communications. An earlier edition known as Internet Connection Firewall that was disabled by default was included with the original Windows XP release. | Windows XP Service Pack 2 |
| Windows Defender | Security utility to prevent, remove and quarantine malware (viruses, Trojan horses, etc.) | Downloadable for Windows XP and Windows Server 2003 |
| Windows Resource Protection | Protects Registry keys and folders in addition to critical system files | Windows Vista |
Deprecated components and apps[edit]
| Component | Description | Category | Introduced | Last OS included | Superseded by |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3D Pinball | Pinball game | Game | Plus! 95 for Windows 95 | Windows XP | — |
| ActiveMovie | Streaming media technology | API | Windows 95 | Windows Me | DirectShow |
| Cardfile | Personal information manager | Personal organizer | Windows 1.0 | Windows Me | Outlook Express, Windows Mail, or Windows Live Mail |
| Chess Titans | Chess game | Game | Windows Vista | Windows 7 | Microsoft Chess |
| DriveSpace | Disk compression utility | Data compression | MS-DOS | Windows Me | — |
| Windows DVD Maker | DVD authoring software | Video | Windows Vista | Windows 7 | — |
| File Manager | File manager app | File manager | Windows 3.0 | Windows Me | Windows Explorer |
| FreeCell | FreeCell game | Game | Win32s | Windows 7 | Microsoft Solitaire Collection |
| Hearts | Version of the Hearts game using Black Lady scoring | Game | Windows for Workgroups 3.11 | Windows 7 | Microsoft Hearts |
| Insider Hub | Windows 10 Version 1507 | Windows 10 Version 1511 | Feedback Hub | ||
| Windows Help and Support | Online and offline reference manual for troubleshooting. | Utility | Windows Me | Windows 8.1 | Microsoft Tips or Get Started |
| HyperTerminal | Communication utility based on a low end version of HyperACCESS | Communication | Windows 95 | Windows XP | — |
| Hold ‘Em | Version of the Texas hold ’em game | Game | Windows Vista | Windows Vista | — |
| Hover! | Video game in a combination of bumper cars and capture the flag | Game | Windows 95 | Windows 95 | — |
| InkBall | Game where the user tries to get colored balls into the correct holes | Game | Windows XP Tablet PC Edition | Windows Vista | — |
| Internet Explorer | Web browser | Web browser and FTP client. See also: Internet Explorer versions, Features, History, Removal, Browser Helper Objects | Microsoft Plus! for Windows 95 | Windows 10 | Microsoft Edge |
| Mahjong Titans | Version of the Mahjong solitaire game | Game | Windows Vista | Windows 7 | Microsoft Mahjong |
| Windows Mail | E-mail client | Windows Vista | Windows Vista | Mail (Windows) | |
| Internet Mail and News | E-mail and news client | Windows 95 | Windows 95 | Outlook Express, Windows Mail, or Windows Live Mail | |
| Minesweeper | Version of the minesweeper game | Game | Microsoft Entertainment Pack, Windows 3.1 | Windows 7 | Microsoft Minesweeper |
| Media Control Interface | An app that can play media files and record sound by passing commands as strings. | API | Windows 3.0 | Windows Me | — |
| Windows Media Player | Digital media player app | Media player | Windows 3.0 Multimedia Extensions | Windows 10 | Windows Media Player, Movies & TV, or Groove Music |
| Microsoft Calendar | Calendaring app | Personal organizer | Windows 1.0 | Windows 3.1 | Windows Calendar, Windows Live Mail, or the Calendar app for Windows |
| Microsoft Diagnostics | Tool that provides detailed technical information about user’s software and hardware | Diagnostics | MS-DOS | Plus! 95 for Windows 95 | Microsoft System Information |
| Microsoft Fax | Faxing app | Fax | Windows 95 | Windows XP | Windows Fax and Scan |
| Microsoft Private Folder | Tool to protect private data | Personal organizer | Windows XP | Windows XP | |
| Windows Help | Documentation browser that used a proprietary format | Online help | Windows 3.0 | Windows XP | Microsoft Help |
| Windows Feedback | Windows 10 Version 1507 | Windows 10 Version 1511 | Feedback Hub | ||
| NTBackup | Built-in backup app | Backup | Downloadable for Windows NT 4.0 | Windows XP, Windows Server 2003 | Backup and Restore, Windows Server Backup |
| Outlook Express | E-mail client | Internet Explorer 4 | Windows XP | Windows Mail or Windows Live Mail | |
| Paint | Simple graphics painting app | Application | Windows 1.0 | — | — |
| Program Manager | Shell composed of a task-oriented graphical user interface, consisting of icons (shortcuts for apps) arranged into app groups. | GUI | Windows 3.0 | Windows XP | Windows Explorer |
| Purble Place | Educational game for children, teaching pattern recognition, shapes, and colors | Game | Windows Vista | Windows 7 | — |
| Reader | e-book reader | e-book reader | Windows 8 | Windows 10 Creators Update | Microsoft Edge (PDF), XPS Viewer (XPS), Photos (TIFF)[26] |
| Reversi | Version of Reversi. | Game | Windows 1.0 | Windows 3.0 | Internet Reversi only on Windows Me and Windows XP |
| Solitaire | Klondike Solitaire game | Game | Windows 3.0 | Windows 7 | Microsoft Solitaire Collection |
| Spider Solitaire | Spider Solitaire game | Game | Microsoft Plus! 98 | Windows 7 | Microsoft Solitaire Collection |
| System File Checker | Utility that allows users to scan for and restore corruptions in Windows system files | Security | Windows 98 | Windows Server 2003 | Windows Resource Protection |
| Tinker | Puzzle game in which the player controls a robot through various mazes and obstacle courses | Game | Windows Vista | Windows Vista | — |
| Video for Windows | Multimedia framework | API | Windows 3.1 | Windows 95 | DirectShow |
| Windows Address Book | List of contacts that can be shared by multiple apps | Contact manager | Internet Explorer 3 | Windows XP | Windows Contacts, People, or Windows Live Mail |
| Windows Desktop Gadgets | Widget engine for Microsoft Gadgets | User interface | Windows Vista | Windows 7 | Live tiles |
| Windows File Protection | Sub-system in the operating system, aims to prevent apps from replacing critical Windows system files. | Security | Windows Me as System File Protection | Windows XP | Windows Resource Protection |
| Windows Journal | Notetaking application that allows for the creation of handwritten notes | Accessories | Windows XP Tablet PC Edition | Windows 10 Threshold 2 | General improvements in Ink API |
| Windows Messaging | E-mail client | Windows 95 | Windows 95 | Internet Mail and News, Windows Mail, or Windows Live Mail | |
| Windows Messenger | Instant messaging client | Internet messaging | Windows XP | Windows XP, Windows Server 2003 | Windows Live Messenger or Skype |
| Windows Movie Maker | Non-linear video editing software | Video | Windows Me | Windows Vista | Windows Live Movie Maker or Microsoft Photos |
| Windows NetMeeting | Video conferencing client | Web conference | Windows 95 OSR2 | Windows XP | Windows Meeting Space |
| Windows Photo Gallery | Image organizer | Photo | Windows Vista | Windows Vista | Windows Live Photo Gallery or Microsoft Photos |
| Windows Picture and Fax Viewer | Image viewer | Photo | Windows XP | Windows XP | Windows Photo Gallery, Windows Fax and Scan, Windows Live Photo Gallery, Windows Photo Viewer, or Microsoft Photos |
| Windows Write | Simple word processor | Word processor | Windows 1.0 | Windows NT 3.51 | WordPad |
APIs[edit]
- ClearType
- Media Foundation
- Windows Driver Foundation
- Windows Imaging Component
- Windows Management Instrumentation
Miscellaneous (to be categorized)[edit]
- ActiveSync
- Compatibility Appraiser collects telemetry information.[27]
- DMRC (Device Metadata Retrieval Client) interfaces to metadata about devices from Windows 7 onwards.[28]
- I/O technologies
- Macro Recorder
- Microsoft Agent
- Prefetcher
- ReadyBoost
- Sync Center
- Text Services Framework
- Universal Audio Architecture
- Windows Color System
- Windows Diagnostic Infrastructure (WDI)[29]
- Windows Mobile Device Center
- Windows Rally
- Windows Registry
- Windows Speech Recognition
- XML Paper Specification
See also[edit]
- Outline of Microsoft
- List of Unix daemons
- List of games included with Windows
References[edit]
- ^ Shultz, Greg (February 28, 2015). «Control Panel and Settings: Why are both still UI options in Windows 10?». TechRepublic. Retrieved October 7, 2022.
- ^ «Get $Windows Camera from the Microsoft Store». apps.microsoft.com. Retrieved October 7, 2022.
- ^ «Xbox Support». support.xbox.com. Retrieved October 7, 2022.
- ^ Hoffman, Chris. «How to See FPS in Any Windows 10 Game (Without Extra Software)». How-To Geek. Retrieved October 7, 2022.
- ^ The Xbox Game Bar Team (May 22, 2019). «Introducing the New Xbox Game Bar». Xbox Wire. Microsoft. Archived from the original on September 21, 2019. Retrieved August 21, 2019.
- ^ «System Services». technet.microsoft.com. Microsoft. 2014. Archived from the original on November 5, 2017. Retrieved September 2, 2014.
The Application Experience service (AELookupSvc) is a part of the Application Compatibility Administrator. It processes application compatibility lookup requests for applications as they are started, provides support for Windows Server 2008 and Windows Vista–based computers running apps in compatibility mode, reports on compatibility issues, and automatically applies software updates to apps.
- ^ «Description of the Microsoft Computer Browser Service». Microsoft. Archived from the original on January 1, 2015. Retrieved November 3, 2017.
- ^ a b Mackie, Kurt (August 16, 2016). «Microsoft Clarifies Windows 10 ‘Delivery Optimization’«. Redmond Magazine. 1105 Enterprise Computing Group. Archived from the original on February 13, 2020. Retrieved January 27, 2018.
- ^ Hachman, Mark (March 29, 2017). «How Delivery Optimization in Windows 10 Creators Update helps avoid data overage fees». PCWorld. IDG. Archived from the original on August 25, 2017. Retrieved January 27, 2018.
- ^ Halfin, Dani; Poggemeyer, Liza; Lich, Brian; Kieselbach, Oliver; Childs, Andrew (April 30, 2018). «Configure Delivery Optimization for Windows 10 updates». docs.microsoft.com. Microsoft. Archived from the original on July 23, 2018. Retrieved July 23, 2018.
- ^ «Distributed Link Tracking on Windows-based domain controllers». Microsoft. Archived from the original on February 25, 2015. Retrieved October 28, 2008.
- ^ «Distributed Transaction Coordinator (MSDTC)». Microsoft. Archived from the original on September 10, 2016. Retrieved June 27, 2008.
- ^ «Event Log». Microsoft. Archived from the original on September 10, 2016. Retrieved June 27, 2008.
- ^ «What is Indexing Service?». Microsoft. Archived from the original on January 1, 2011. Retrieved June 27, 2008.
- ^ «Windows 2000 Professional and Server Service Pack 4 Services Configuration by Black Viper» Archived December 17, 2019, at the Wayback Machine, notice that the service is listed on this page. Retrieved April 2013
- ^ «Windows Firewall» Archived February 13, 2020, at the Wayback Machine. Retrieved April 2013
- ^ «Secondary Logon (Run As): Starting Programs and Tools in Local Administrative Context». Microsoft Corporation. Archived from the original on March 6, 2015. Retrieved October 28, 2008.
- ^ «System Event Notification Service». The Elder Geek. Archived from the original on October 26, 2008. Retrieved June 27, 2008.
- ^ «Myth Busted: Why Disabling SuperFetch on Vista and Windows 7 Is a Bad Idea», retrieved April 2013
- ^ «What Is Volume Shadow Copy Service?: Data Recovery». Microsoft Corporation. Archived from the original on August 26, 2017. Retrieved October 28, 2008.
- ^ «Windows Firewall/Internet Connection Sharing (ICS)» Archived September 10, 2016, at the Wayback Machine, Retrieved April 2013
- ^ «Windows 2000 Professional and Server Service Pack 4 Services Configuration by Black Viper» Archived December 17, 2019, at the Wayback Machine, Notice the absence of the service on this page. Retrieved April 2013
- ^ «Windows Firewall/Internet Connection Sharing (ICS)» Archived February 13, 2020, at the Wayback Machine, Notice that XP is the operating system listed. Retrieved April 2013
- ^ «How Windows Time Service Works: Windows Time Service». Microsoft Corporation. Archived from the original on April 22, 2016. Retrieved October 28, 2008.
- ^ Minasi, Mark; Layfield, Rhonda; Justice, Lisa (2006). Mastering Windows Server 2003: upgrade edition for SP1 and R2 (12 ed.). John Wiley & Sons. p. 56. ISBN 978-0-470-05645-5. Archived from the original on September 21, 2019. Retrieved July 21, 2010.
There is also a client piece for WebDAV built into XP, 2003, R2, and Vista, called the WebClient Service.
- ^ «Microsoft replaces standalone PDF reader app with Edge». MSPoweruser. November 26, 2017. Archived from the original on August 19, 2019. Retrieved August 19, 2019.
- ^ Leonhard, Woody (April 20, 2015). «KB 2952664 triggers daily telemetry run in Windows 7 — and may be snooping on users: Microsoft bills the ‘compatibility update’ as way to ease the upgrade process to Windows 10 — but it’s collecting data daily». Operating Systems. InfoWorld. InfoWorld, Inc. Archived from the original on June 2, 2017. Retrieved August 23, 2016.
The Microsoft Compatibility Appraiser task runs %windir%system32rundll32.exe appraiser.dll,DoScheduledTelemetryRun with the description ‘Collects program telemetry information if opted-in to the Microsoft Customer Experience Improvement Program.’
- ^ Compare: Tulloch, Mitch; Northrup, Tony; Honeycutt, Jerry; Wilson, Ed (2010). Windows 7 Resource Kit. Windows 7 Resource Kit, Microsoft Corporation. Vol. 1. Microsoft Press. p. 708. ISBN 9780735627000. Archived from the original on January 11, 2022. Retrieved August 18, 2016.
The DMRC [(Device Metadata Retrieval Client)] checks the computer’s local metadata cache and metadata store for metadata that applies to the device.
- ^ Solomon, David A.; Russinovich, Mark E.; Ionescu, Alex (June 17, 2009). Windows Internals. Developer Reference (5 ed.). Microsoft Press (published 2009). ISBN 9780735637962. Archived from the original on September 21, 2019. Retrieved October 24, 2016.
The Windows Diagnostic Infrastructure (WDI) helps to detect, diagnose, and resolve common problem scenarios with minimal user intervention.
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
(Redirected from Windows Time)
The following is a list of Microsoft Windows components.
Configuration and maintenance[edit]
| Component | Description | Introduced |
|---|---|---|
| Settings | Allows users to change system settings, similar to the Control Panel, but has less options[1] | Windows 8 |
| Control Panel | ||
| Control Panel | Allows users to view and change basic system settings and controls, such as adding hardware, adding and removing software, controlling user accounts, and changing accessibility options | Windows 1.0 |
| Device Manager | Allows the user to display and control the hardware attached to the computer, and control what device drivers are used | Windows 95 |
| Windows Mobility Center | Centralizes the most relevant information related to mobile computing | Windows Vista |
| Security and Maintenance | Centralizes and reports on the status of anti-virus, Automatic Updates, Windows Firewall, and other security-related components of the operating system | Windows XP SP2 |
| Administrative Tools | ||
| Microsoft Management Console | Provides system administrators and advanced users with a flexible interface through which they may configure and monitor the system | Windows NT 4.0 Option Pack |
| Windows System Assessment Tool | Built-in benchmarking tool that analyzes the different subsystems (graphics, memory, etc.), and uses the results to allow for comparison to other Windows Vista systems, and for software optimizations. It rates the computer’s performance using the Windows Experience Index. | Windows Vista |
| System Restore | Allows for the rolling back of system files, registry keys, installed apps, etc., to a previous state in the event of a system failure | Windows Me |
| Windows Recovery Environment | Helps diagnose and recover from serious errors which may prevent Windows from booting successfully, or restore the computer to a previous state using System Restore or a backup image | Windows Vista |
| Microsoft Drive Optimizer | Rearranges files stored on a hard disk to occupy contiguous storage locations in order to optimize computer performance | Windows 95, Windows 2000 |
| Event Viewer | Lets administrators and users view the event logs on a local or remote machine | Windows NT 3.1 |
| Resource Monitor (previously Reliability and Performance Monitor) |
Lets administrators view current system reliability and performance trends over time | Windows Vista |
| Logical Disk Manager | Logical volume manager developed by Microsoft in conjunction with Veritas Software | Windows NT 4.0 (Separate Tool), Windows 2000 |
| Registry Editor | Allows users to browse and edit the Windows registry | Windows 3.1 |
| Task Scheduler | Allows users to script tasks for running during scheduled intervals | Microsoft Plus! for Windows 95 |
| Software installation and deployment | ||
| Windows Update | An online service providing updates such as service packs, critical updates and device drivers. A variation called Microsoft Update also provides software updates for other Microsoft products. | Windows 98 |
| Windows Installer | An engine for the management of software installation. Includes a GUI framework, automatic generation of the uninstallation sequence and deployment capabilities for corporate networks. | Windows 2000 |
| ClickOnce | Technology for deploying .NET Framework-based software via web pages, with automatic update capabilities. Intended for per-user only applications. | .NET Framework 2.0 |
User interface[edit]
| Component | Description | Introduced |
|---|---|---|
| Action Center | View notifications sent from apps and change common settings | Windows 10 Version 1507 |
| Command Prompt | Text-based shell (command line interpreter) that provides a command line interface to the operating system | Windows NT 3.1 |
| Windows PowerShell | Command-line shell and scripting framework. | Windows XP |
| Windows Shell | The most visible and recognizable aspect of Microsoft Windows. The shell provides the container inside of which the entire graphical user interface is presented, including the taskbar, the desktop, Windows Explorer, as well as many of the dialog boxes and interface controls. In Windows Vista, a new compositing glass-like user interface called Windows Aero has been shown. | Windows 95 |
| File Explorer (previously Windows Explorer) |
Provides an interface for accessing the file systems, launching applications, and performing common tasks such as viewing and printing pictures | Windows 95 |
| Windows Search | Starting with Windows Vista, search is a tightly shell-integrated component of Windows. A downloadable Windows Desktop Search software is available for Windows XP and older versions. | Windows Vista, downloadable for older versions |
| Search Folders | Virtual folders that retrieve items based on queries rather than hierarchical folder trees on disk. | Windows Vista |
| Special Folders | Folders which are presented to the user through an interface as an abstract concept, instead of an absolute path. This makes it possible for an application to locate where certain kinds of files can be found, regardless of what version or language of operating system is being used. See also Windows Shell namespace. | Windows 95 |
| Start menu | Serves as the central launching point for applications. It provides a customizable, nested list of apps for the user to launch, as well as a list of most recently opened documents, a way to find files and get help, and access to the system settings. By default, the Start Button is visible at all times in the lower left-hand corner of the screen. | Windows 95 |
| Taskbar | The application desktop bar which is used to launch and monitor applications | Windows 95 |
| Task View | Displays all open windows and activities (via timeline) at a glance and switch between virtual desktops, starting in version 2004, users can now rename desktops | Windows 10 Version 1507 |
| File associations | Used to open a file with the appropriate app. Users can assign file associations uniquely to specific actions, known as verbs. | Windows 1.0 |
Applications and utilities[edit]
| Component | Description | Introduced |
|---|---|---|
| Easy Transfer | Used to transfer many files at once from one computer to another | Windows Vista |
| Contacts | Keeps a single list of contacts that can be shared by multiple apps | Windows Vista |
| Camera | Allows the user to take pictures or record video[2] | Windows 8 |
| Calculator | Calculation application | Windows 1.0 |
| Calendar | Calendaring application | Windows Vista |
| Character Map | Utility to view and search characters in a font, copy them to the clipboard and view their Windows Alt keycodes and Unicode names | Windows 3.1 |
| Cortana | Digital personal assistant | Windows 10 Version 1507 |
| Edge | Web browser | Windows 10 Version 1507 |
| Feedback Hub | Platform for exchanging communication with Windows Insiders and developers | Windows 10 Version 1607 |
| Groove Music (previously Xbox Music) |
Digital media player and media library application that is used for playing audio. In addition to being a media player, Groove includes the ability to copy music to compact discs, synchronize content with a digital audio player (MP3 player) or other mobile devices, and let users purchase or rent music from the Windows Store. | Windows 8 |
| Movies & TV (previously Xbox Video) |
Digital media player and media library application that is used for playing video. In addition to being a media player, Movies & TV lets users purchase or rent movies and TV episodes from the Windows Store. | Windows 8 |
| OneDrive (previously SkyDrive) |
Freemium cloud storage folder and sync service | Windows 8 |
| OneNote | Integrated note-taking app, based on the Microsoft Office product of the same name | Windows 8 |
| On-Screen Keyboard (osk.exe) | Virtual keyboard | |
| Paint 3D | Simple graphics painting app | Windows 10 Version 1703 |
| Photos | Simple image viewer | Windows 8 |
| Steps Recorder (called Problem Steps Recorder in Windows 7) |
Utility that allows the user to capture steps they took to reproduce a problem | Windows 7 |
| Windows To Go | Utility to create bootable versions of Windows 8 and above | Windows 8 |
| Notepad | Simple text editor | Windows 1.0 |
| Narrator | Screen reader utility that reads dialog boxes and window controls in a number of the more basic applications for Windows | Windows 2000 |
| Sound Recorder | Simple audio recording app that can record from a microphone or headset, and save the results in WAVE format and Windows Media Audio format in some Windows versions | Windows 3.0 Multimedia Extensions |
| Skype | Messaging and calling service | Windows 8.1, downloadable for previous versions |
| Sticky Notes | Tool for jotting notes on the desktop | Windows XP Tablet PC Edition |
| WordPad | Simple word processor that is more advanced than Notepad. It has facilities to format and print text, but lacks intermediate features such as a spell checker and thesaurus. | Windows 95 |
| Private Character Editor | Utility to create private use characters as defined under Unicode and various East Asian encoding schemes | Windows 3.1 East Asian editions |
| Remote Desktop Connection | Client implementation of the Remote Desktop Protocol; allows a user to securely connect to a computer running Terminal Services (Remote Desktop on Windows XP and Server 2003) and interact with a full desktop environment on that machine, including support for remoting of printers, audio, and drives. | Windows XP, downloadable for previous Windows versions |
| Remote Assistance | Allows a user to temporarily take over a remote computer over a network or the internet to offer help with and resolve issues | Windows XP |
| Mobility Center | Allows a user to adjust settings related to mobile computing | Windows Vista |
| Speech Recognition | Allows a user to input voice commands | Windows Vista |
| IExpress | Allows users to create self-extracting, self-installing INF installation-based packages | Internet Explorer 6 |
| Xbox Console Companion (previously Xbox and Xbox Games) |
Account manager for Xbox Live user accounts and a screen recording tool | Windows 8 |
| Xbox Game Bar | Provides a overlay for compatible games allowing for screen capture, chatting over the Xbox network, showing the frame rate of games, and playing music via Spotify[3][4] | Windows 10 May 2019 Update (Version 1903)[5] |
| Magnifier | Screen enlargement app | Windows 98 |
| Fax and Scan | Integrated faxing and image scanning application | Windows Vista, older faxing and scanning applications were present in previous Windows versions |
| Photo Viewer | Simple image viewer that can play a simple slideshow | Windows 7 |
| Email aggregator | Windows 8 | |
| Maps | Map viewer that allows users to look for locations, plan routes, and store offline maps | Windows 8 |
| Media Center | Designed to serve as a home-entertainment hub, to be viewed from a distance up to 3 meters (~10 feet) and controlled by specially designed remote controls. Lets users browse and view pictures, videos, and music from local hard drives, optical drives, and network locations, along with viewing, recording and deferred-playing live TV. Features an interactive TV guide with scheduled recording capabilities. Can also be used for visualization of other information (like sports scores) within the interface. | Windows XP Media Center Edition |
| Task Manager | Provides information about computer performance and displays details about running applications, processes, network activity, logged-in users, and system services | Windows 3.0 |
| Disk Cleanup | Utility for compacting rarely used files and removing files that are no longer required | Windows 98 |
| Snipping Tool | Screen-capture tool that allows for taking screenshots (called snips) | Experience Pack for Windows XP Tablet PC Edition 2005 |
| Microsoft Store (previously Windows Store) |
Initially known as Windows Store, it started as an app store for Windows 8. In Windows 10, it expanded into a broad digital distribution platform for apps, games, music, digital video and e-books. In 2017, it was renamed Microsoft Store and started offering hardware in United States, Canada and United Kingdom. | Windows 8 |
| MSN apps | Provide information from MSN web services | Windows 8 |
| Alarms & Clock(pre Alarms) | App that allows Windows users to set alarms, stopwatches, timers, and view a world clock | Windows 8 |
| Windows Security (previously Windows Defender Security Center) |
Antivirus | Windows 10 Version 1703 |
| Solitaire Collection | Set of solitaire card games | Windows 10 Version 1507, downloadable for Windows 8.x |
Windows Server components[edit]
| Component | Description | Supported by |
|---|---|---|
| Active Directory | A set of technologies introduced with Windows 2000 that allows administrators to assign enterprise-wide policies, deploy apps to many computers, and apply critical updates to an entire organization. Active Directory stores information and settings relating to an organization in a central, organized, accessible database. Networks can vary from a small installation with a few objects, to global-scale directories with millions of objects. Related topics: Domain controller, Flexible single master operation |
Windows 2000 and later server versions |
| Group Policy | Provides centralized management of user and computer settings in an Active Directory environment. Group policy can control a target object’s registry, NTFS security, audit and security policy, software installation, logon/logoff scripts, folder redirection, and Internet Explorer settings. Policy settings are stored in Group Policy Objects (GPOs), and may be linked to one or more sites, domains or organizational units. Related topics: Administrative Templates |
Windows 2000 and later |
| Internet Information Services | Web server | Windows NT family |
File systems[edit]
| Component | Description | Supported by |
|---|---|---|
| FAT12, FAT16 | The original file systems used with MS-DOS. The standard file systems used with Windows 1.0 through Windows 95. | All versions |
| FAT32 | Extensions to FAT supporting larger disk sizes. The standard file system for Windows 98 and Me. | Windows 95 OSR2 and later versions |
| NTFS | Standard file system of Windows NT; supports security via access control lists, as well as file system journaling and file-system metadata. Windows 2000 added support for reparse points (making NTFS junction points and Single instance storage possible), Hard links, file compression, and Sparse files. Encryption of data is provided by Encrypting File System. Symbolic links and transactioning of file operations via Transactional NTFS are features new to Windows Vista.
Although Windows 9x operating systems cannot read or write NTFS formatted disks, they can access the data over a network if it is shared by a computer running Windows NT. |
Windows NT (all versions) |
| ISO 9660 (CDFS) | The predominant file system for CD-ROM and DVD-ROM media. Windows includes support for Joliet extensions and the ISO 9660:1999 standard. ISO 9660:1999 is supported since Windows XP. | MS-DOS and Windows 9x via extensions, such as MSCDEX.EXE (Microsoft CDROM Extension), natively in Windows NT |
| Universal Disk Format (UDF) | A file system for storing files on optical media. It is an implementation of the ISO/IEC 13346 standard (also known as ECMA-167). It is considered to be a replacement of ISO 9660. Successive versions of Windows have supported newer versions of UDF. | Windows 98, Windows 2000, Windows XP, Windows Server 2003, Windows Vista |
| HPFS | High-Performance File system, used on OS/2 computers. Read and write capability in Windows 95 (where it also listed network computer NTFS-formatted drives as «HPFS», even though it had no direct NTFS capabilities). HPFS write support was dropped in Windows NT 4.0 and Windows 98, and dropped altogether shortly before the release of Windows 2000. | Windows 95 (Read/write), Windows 98, Windows NT (read), 3.1/3.51 (read/write/boot) |
| ReFS | A newer file system, based on NTFS. This system adds built-in integrity checking and removes the need for chkdsk, among other features. The maximum partition size is 1 YB. | Windows Server 2012, Windows 8.1 |
Core components[edit]
| Component | Acronym | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Windows kernel (Windows NT)
Main article: Architecture of the Windows NT operating system line |
||
| Ntoskrnl.exe | The Windows kernel image. Provides the kernel and executive layers of the kernel architecture, and is responsible for services such as hardware virtualization, process and memory management, etc. | |
| hal.dll | HAL | Provides and handles the interaction between software and hardware via the Hardware Abstraction Layer. |
| kernel32.dll | This application provides kernel operations to apps in the Win32 mode, like memory management, I/Os, process creation, etc. | |
| Core processes (Windows NT) | ||
| System idle process | SIP | A counter which measures how much idle capacity the CPU has at any given time. The process runs in the background and monitors processing bandwidth, occupied memory and the Windows virtual paging file. |
| Session Manager Subsystem | SMSS | Performs several critical boot-time operations, such as the creation of environment variables, starting CSRSS, and performing file-copy operations that were queued up from before the system was booted (pending file rename operations). During system operation, it handles Windows File Protection and the creation of logon sessions via Winlogon. |
| Client/Server Runtime Subsystem | CSRSS | User-mode side of the Win32 subsystem. Provides the capability for applications to use the Windows API. |
| Local Security Authority Subsystem Service | LSASS | Responsible for enforcing the security policy on the system. Verifies users logging on to the computer and creates security tokens. |
| Winlogon | Responsible for handling the secure attention key, loading the user profile on logon, and optionally locking the computer when a screensaver is running. On Windows NT systems prior to Windows Vista, Winlogon is also responsible for loading GINA libraries which are responsible collecting logon credentials from the user. | |
| Svchost.exe | A generic host process name for services that run from dynamic-link libraries (DLLs). Several Svchost processes are typically present on a Windows machine, each running in a different security context, depending on what privileges the contained services require. | |
| Windows on Windows and WOW64 | WoW | An abstraction layer that allows legacy code to operate on more modern versions of Windows; typically this means running 16-bit Windows applications on 32-bit Windows, and 32-bit applications on 64-bit Windows. |
| Virtual DOS machine | NTVDM | Allows MS-DOS apps to run on Intel 80386 or higher computers when there is already another operating system running and controlling the hardware. Introduced in Windows 2.1; not available in any 64-bit edition of Windows. |
| System startup (Windows NT)
Main articles: Windows NT Startup Process and Windows Vista Startup Process |
||
| NTLDR, IA64ldr, Winload | The boot loader; performs basic system initialization options such as loading the hardware abstraction layer and boot-time device drivers, prior to passing control to the Windows kernel. In versions prior to Vista, NTLDR and IA64ldr also display menus to the user if multiple operating systems are defined in boot.ini, or if F8 is pressed. | |
| Recovery Console | Provides the means for administrators to perform a limited range of tasks using a command line interface, primarily to aid in recovering from situations where Windows does not boot successfully. | |
| ntdetect.com | Used during the boot process to detect basic hardware components that may be required during the boot process | |
| Windows Boot Manager | In Windows Vista and later operating systems, displays boot menus to the user if multiple operating systems are configured in the system’s Boot Configuration Data. | |
| Graphical subsystem | ||
| Desktop Window Manager | DWM | The compositing manager introduced in Windows Vista that handles compositing and manages special effects on screen objects in a graphical user interface |
| Graphics Device Interface | GDI/GDI+ | The kernel graphics component for representing graphical objects and transmitting them to output devices such as monitors and printers |
| Windows USER | The Windows USER component provides core user interface, messaging and visual elements |
Services[edit]
This list is not all-inclusive.
| Display name | Service key name | Description | Introduced |
|---|---|---|---|
| Active Directory Service | NTDS | Network Authentication Management | Windows 2000 Server |
| Alerter service | Alerter | Sends administrative alerts over the network to client computers, administrators and users | Windows NT |
| Application Layer Gateway service |
ALG | Provides support for plugins that allow network protocols to pass through Windows Firewall and work behind Internet Connection Sharing | Windows 2000 |
| Application Experience service | Processes application compatibility cache requests for applications as they launch[6] | ||
| Application Management | AppMgmt | Processes requests to enumerate, install, and remove applications that are installed on the computer or deployed through an organization’s network | Windows 2000 |
| Background Intelligent Transfer Service |
BITS | Transfers files between machines using idle network bandwidth. Used by Windows Update, Windows Server Update Services, and Systems Management Server to deliver software updates to clients, as well as by Windows Messenger. | Windows XP |
| Computer Browser | Browser | Crawls neighboring computers on the network and locates shared resources. One of the computers acts as the Master Browser and supplies this information to other computers designated as browsers.[7] | Windows for Workgroups |
| Delivery Optimization | DoSvc | A peer-to-peer distribution service that downloads Windows updates and Microsoft Store apps from the local network or Internet peers, and redistributes them to others. Can be configured using either the Settings app or Group Policy. The Settings app can turn it on or off, and specify whether the service operates on the local network only, downloads from and uploads to the Internet peers as well. Group Policy allows finer control.[8][9] Delivery Optimization relies on a centralized web service that does not index contents under 10 MB. Computers without Internet access cannot use Delivery Optimization.[10] | Windows 10 Anniversary Update[8] |
| Distributed Link Tracking | TrkWks, TrkSrv | Used to track links to files on NTFS volumes. Windows uses these services to find linked files if they are renamed or moved (locally or to another machine).[11] | Windows 2000 |
| Distributed Transaction Coordinator |
MSDTC | Allows transactional components to be configured through COM+ by coordinating transactions that are distributed across multiple computers and/or resource managers, such as databases, message queues, file systems, and other transaction–based resource managers.[12] | Windows 2000 and later NT-based |
| DNS Client | DNSCache | Resolves and caches domain names (e.g. “en.wikipedia.org”) to IP addresses | Windows 2000 |
| Event Log | EventLog | Stores and retrieves events that can be viewed in the event viewer. Part of services.exe.[13] | Windows NT |
| Extensible Authentication Protocol | EAPHost | Provides EAP authentication to connecting clients | Windows 2000 |
| Indexing Service | CISVC | Indexes contents and properties of files on local and remote computers; provides rapid access to files through flexible querying language.[14] | Windows 2000 and later NT-based |
| Interactive Services Detection | UI0Detect | For compatibility; when a service-displayed user interface is detected, it gives the user an option to switch to Session0 to see it | Windows Vista |
| Internet Connection Sharing (ICS) | SharedAccess | When enabled, it allows other computers on the local network to access an internet connection that is available to the host computer | Windows 2000;[15] Windows Vista onward[16] |
| Network Location Awareness | NLA | Manages network configurations and information, and notifies applications of changes | Windows XP |
| Network Store Interface Service | NSIS | Collects routing information of active network interfaces, shares this with other services and notifies applications of changes | Windows XP |
| NTLM Security Support Provider | NTLMSSP | Uses the NTLM MS-CHAP protocol to encapsulate and negotiate options in order to provide signed and sealed communication. Deprecated now in favor of Kerberos authentication. | Windows NT |
| Peer Name Resolution Protocol | PNRPSvc | Resolves domain names using Peer Name Resolution Protocol | Windows XP |
| Plug and Play | PlugPlay | Enables autodetection and configuration of hardware | Windows 2000 |
| Windows Print spooler [fr] | Spooler | Manages printer devices and moves files into memory for printing | Windows 95, Windows NT |
| Remote Procedure Call (RPC) | RpcSs | Provides Remote Procedure Call features via remotely accessible Named Pipes | Windows NT family |
| Routing and Remote Access Service | RRAS | API and server software that enables applications to administer the routing and remote-access service capabilities of the operating system, to function as a network router. | Windows 2000 |
| Secondary Logon | SecLogon | Allows users to run apps with a different account than the one they logged in with. Allows non-administrative accounts to perform administrative tasks.[17] | |
| Security Accounts Manager | SamSs | Manages user account security information | Windows NT family |
| System Event Notification Service | SENS | Monitors system events, such as network, power, logon, logoff, terminal services session connection and disconnection, and delivers these to applications and other system components.[18] | Windows 2000 |
| Superfetch | SysMain | Monitors file usage patterns and boosts system speed by caching frequently accessed files to RAM[19] | Windows Vista |
| Task Scheduler | Schedule | Lets users setup and schedule automated tasks | Microsoft Plus! for Windows 95 |
| TCP/IP NetBIOS Helper | LmHosts | Enables support for NetBIOS over TCP/IP (NetBT) service and NetBIOS name resolution | Windows NT family |
| Volume Shadow Copy | VSS | Creates multiple versions of files that change. The ability to store persistent snapshots was added in Windows Server 2003.[20] | Windows XP |
| Windows Audio | AudioSrv | Manages audio devices for Windows-based apps. Controls all audio functions. | Windows XP |
| Windows Error Reporting | WERSvc | Generates error logs and reports errors. On Windows Vista and later, it notifies of solutions. | Windows XP |
| Windows Firewall | MpsSvc | Blocks unauthorized network connections to and from the computer | Windows Vista |
| Windows Firewall(née Internet Connection Sharing) | SharedAccess | Provides a simple firewall feature which was introduced in Windows XP. It also shares the internet on the local network, if the internet connection sharing feature is turned on.[21] | Windows XP only[22][23] |
| Windows Image Acquisition (WIA) | STISvc | Handles scanner and camera inputs | Windows Me |
| Windows Time | W32Time | Synchronizes the system time with external time servers. From Windows Server 2003 forward, full and compliant NTP support is provided.[24] | Windows 2000 |
| Windows Update | WUAUServ | Provides updates for the operating system and its installed components | Windows XP |
| Wireless Zero Configuration | WZCSvc (XP), WLANSvc | Configures and manages 802.11 wireless adapters | Windows XP, Server 2003 only |
| Windows Messenger service | Messenger | Allows users to send pop-up messages to other computers over the network | Windows NT family |
| WebClient[25] | Enables Windows-based apps to create and interact with Internet-based files | Windows XP |
DirectX[edit]
- Direct3D
- DirectDraw
- DirectInput
- DirectMusic
- DirectPlay
- DirectShow
- DirectSound
- DirectX Media Objects
- DirectX plugin
- DirectX Video Acceleration
Networking[edit]
- Administrative share
- Distributed File System
- My Network Places (formerly Network Neighborhood)
- Network Access Protection
- Remote Installation Services
- Server Message Block
- Windows Rights Management Services
Scripting and command-line[edit]
- Batch file
- CHKDSK
- Cmd.exe
- ComSpec
- Ipconfig
- Net / Net Send
- Netdom.exe: Windows Domain Manager
- Netsh
- Netstat
- QBasic
- Regsvr32
- Robocopy
- Win32 console
- Windows Script Host
- Windows PowerShell
- XCOPY
Kernel[edit]
- Commit charge
- Kernel Transaction Manager
- Win32 Thread Information Block
.NET Framework[edit]
- Assembly
- CLI Languages
- Metadata
- .NET Remoting
- ADO.NET
- ASP.NET
- Base Class Library
- Common Intermediate Language
- Common Language Infrastructure
- Common Language Runtime
- Common Type System
- Virtual Execution System
- Windows CardSpace
- Windows Communication Foundation
- Windows Forms
- Windows Presentation Foundation
- Windows Workflow Foundation
Security[edit]
| Component | Description | Introduced |
|---|---|---|
| AppLocker | Policy-based component that enables or disables execution of software based on rules such as location, properties and digital signature | Windows 7 Professional, Enterprise and Ultimate editions Windows Server 2008 R2 |
| BitLocker Drive Encryption | Disk encryption software, designed to protect data by providing encryption for entire volumes | Windows Vista Enterprise and Ultimate editions, Windows Server 2008 |
| Credential Guard | Virtualization-based isolation of stored credentials to prevent theft and pass-the-hash attacks. | Windows 10 Enterprise, Education, IoT Enterprise, or , Windows Server 2016 |
| Data Execution Prevention | Security feature that is intended to prevent an application or service from executing code from a non-executable memory region | Windows XP Service Pack 2 |
| Encrypting File System | File system driver that provides file system-level encryption | Windows 2000 |
| Security Account Manager | Database stored as a registry file | Windows NT 3.1 |
| SYSKEY | Utility that encrypts the hashed password information in a SAM database using a 128-bit encryption key | Windows NT 4.0 Service Pack 3 |
| User Account Control | Technology and security infrastructure utility that aims to improve the security of Microsoft Windows by limiting application software to standard user privileges until an administrator authorizes an increase | Windows Vista, Windows Server 2008 |
| Windows Firewall | Utility designed to block unauthorized access while permitting authorized communications. An earlier edition known as Internet Connection Firewall that was disabled by default was included with the original Windows XP release. | Windows XP Service Pack 2 |
| Windows Defender | Security utility to prevent, remove and quarantine malware (viruses, Trojan horses, etc.) | Downloadable for Windows XP and Windows Server 2003 |
| Windows Resource Protection | Protects Registry keys and folders in addition to critical system files | Windows Vista |
Deprecated components and apps[edit]
| Component | Description | Category | Introduced | Last OS included | Superseded by |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3D Pinball | Pinball game | Game | Plus! 95 for Windows 95 | Windows XP | — |
| ActiveMovie | Streaming media technology | API | Windows 95 | Windows Me | DirectShow |
| Cardfile | Personal information manager | Personal organizer | Windows 1.0 | Windows Me | Outlook Express, Windows Mail, or Windows Live Mail |
| Chess Titans | Chess game | Game | Windows Vista | Windows 7 | Microsoft Chess |
| DriveSpace | Disk compression utility | Data compression | MS-DOS | Windows Me | — |
| Windows DVD Maker | DVD authoring software | Video | Windows Vista | Windows 7 | — |
| File Manager | File manager app | File manager | Windows 3.0 | Windows Me | Windows Explorer |
| FreeCell | FreeCell game | Game | Win32s | Windows 7 | Microsoft Solitaire Collection |
| Hearts | Version of the Hearts game using Black Lady scoring | Game | Windows for Workgroups 3.11 | Windows 7 | Microsoft Hearts |
| Insider Hub | Windows 10 Version 1507 | Windows 10 Version 1511 | Feedback Hub | ||
| Windows Help and Support | Online and offline reference manual for troubleshooting. | Utility | Windows Me | Windows 8.1 | Microsoft Tips or Get Started |
| HyperTerminal | Communication utility based on a low end version of HyperACCESS | Communication | Windows 95 | Windows XP | — |
| Hold ‘Em | Version of the Texas hold ’em game | Game | Windows Vista | Windows Vista | — |
| Hover! | Video game in a combination of bumper cars and capture the flag | Game | Windows 95 | Windows 95 | — |
| InkBall | Game where the user tries to get colored balls into the correct holes | Game | Windows XP Tablet PC Edition | Windows Vista | — |
| Internet Explorer | Web browser | Web browser and FTP client. See also: Internet Explorer versions, Features, History, Removal, Browser Helper Objects | Microsoft Plus! for Windows 95 | Windows 10 | Microsoft Edge |
| Mahjong Titans | Version of the Mahjong solitaire game | Game | Windows Vista | Windows 7 | Microsoft Mahjong |
| Windows Mail | E-mail client | Windows Vista | Windows Vista | Mail (Windows) | |
| Internet Mail and News | E-mail and news client | Windows 95 | Windows 95 | Outlook Express, Windows Mail, or Windows Live Mail | |
| Minesweeper | Version of the minesweeper game | Game | Microsoft Entertainment Pack, Windows 3.1 | Windows 7 | Microsoft Minesweeper |
| Media Control Interface | An app that can play media files and record sound by passing commands as strings. | API | Windows 3.0 | Windows Me | — |
| Windows Media Player | Digital media player app | Media player | Windows 3.0 Multimedia Extensions | Windows 10 | Windows Media Player, Movies & TV, or Groove Music |
| Microsoft Calendar | Calendaring app | Personal organizer | Windows 1.0 | Windows 3.1 | Windows Calendar, Windows Live Mail, or the Calendar app for Windows |
| Microsoft Diagnostics | Tool that provides detailed technical information about user’s software and hardware | Diagnostics | MS-DOS | Plus! 95 for Windows 95 | Microsoft System Information |
| Microsoft Fax | Faxing app | Fax | Windows 95 | Windows XP | Windows Fax and Scan |
| Microsoft Private Folder | Tool to protect private data | Personal organizer | Windows XP | Windows XP | |
| Windows Help | Documentation browser that used a proprietary format | Online help | Windows 3.0 | Windows XP | Microsoft Help |
| Windows Feedback | Windows 10 Version 1507 | Windows 10 Version 1511 | Feedback Hub | ||
| NTBackup | Built-in backup app | Backup | Downloadable for Windows NT 4.0 | Windows XP, Windows Server 2003 | Backup and Restore, Windows Server Backup |
| Outlook Express | E-mail client | Internet Explorer 4 | Windows XP | Windows Mail or Windows Live Mail | |
| Paint | Simple graphics painting app | Application | Windows 1.0 | — | — |
| Program Manager | Shell composed of a task-oriented graphical user interface, consisting of icons (shortcuts for apps) arranged into app groups. | GUI | Windows 3.0 | Windows XP | Windows Explorer |
| Purble Place | Educational game for children, teaching pattern recognition, shapes, and colors | Game | Windows Vista | Windows 7 | — |
| Reader | e-book reader | e-book reader | Windows 8 | Windows 10 Creators Update | Microsoft Edge (PDF), XPS Viewer (XPS), Photos (TIFF)[26] |
| Reversi | Version of Reversi. | Game | Windows 1.0 | Windows 3.0 | Internet Reversi only on Windows Me and Windows XP |
| Solitaire | Klondike Solitaire game | Game | Windows 3.0 | Windows 7 | Microsoft Solitaire Collection |
| Spider Solitaire | Spider Solitaire game | Game | Microsoft Plus! 98 | Windows 7 | Microsoft Solitaire Collection |
| System File Checker | Utility that allows users to scan for and restore corruptions in Windows system files | Security | Windows 98 | Windows Server 2003 | Windows Resource Protection |
| Tinker | Puzzle game in which the player controls a robot through various mazes and obstacle courses | Game | Windows Vista | Windows Vista | — |
| Video for Windows | Multimedia framework | API | Windows 3.1 | Windows 95 | DirectShow |
| Windows Address Book | List of contacts that can be shared by multiple apps | Contact manager | Internet Explorer 3 | Windows XP | Windows Contacts, People, or Windows Live Mail |
| Windows Desktop Gadgets | Widget engine for Microsoft Gadgets | User interface | Windows Vista | Windows 7 | Live tiles |
| Windows File Protection | Sub-system in the operating system, aims to prevent apps from replacing critical Windows system files. | Security | Windows Me as System File Protection | Windows XP | Windows Resource Protection |
| Windows Journal | Notetaking application that allows for the creation of handwritten notes | Accessories | Windows XP Tablet PC Edition | Windows 10 Threshold 2 | General improvements in Ink API |
| Windows Messaging | E-mail client | Windows 95 | Windows 95 | Internet Mail and News, Windows Mail, or Windows Live Mail | |
| Windows Messenger | Instant messaging client | Internet messaging | Windows XP | Windows XP, Windows Server 2003 | Windows Live Messenger or Skype |
| Windows Movie Maker | Non-linear video editing software | Video | Windows Me | Windows Vista | Windows Live Movie Maker or Microsoft Photos |
| Windows NetMeeting | Video conferencing client | Web conference | Windows 95 OSR2 | Windows XP | Windows Meeting Space |
| Windows Photo Gallery | Image organizer | Photo | Windows Vista | Windows Vista | Windows Live Photo Gallery or Microsoft Photos |
| Windows Picture and Fax Viewer | Image viewer | Photo | Windows XP | Windows XP | Windows Photo Gallery, Windows Fax and Scan, Windows Live Photo Gallery, Windows Photo Viewer, or Microsoft Photos |
| Windows Write | Simple word processor | Word processor | Windows 1.0 | Windows NT 3.51 | WordPad |
APIs[edit]
- ClearType
- Media Foundation
- Windows Driver Foundation
- Windows Imaging Component
- Windows Management Instrumentation
Miscellaneous (to be categorized)[edit]
- ActiveSync
- Compatibility Appraiser collects telemetry information.[27]
- DMRC (Device Metadata Retrieval Client) interfaces to metadata about devices from Windows 7 onwards.[28]
- I/O technologies
- Macro Recorder
- Microsoft Agent
- Prefetcher
- ReadyBoost
- Sync Center
- Text Services Framework
- Universal Audio Architecture
- Windows Color System
- Windows Diagnostic Infrastructure (WDI)[29]
- Windows Mobile Device Center
- Windows Rally
- Windows Registry
- Windows Speech Recognition
- XML Paper Specification
See also[edit]
- Outline of Microsoft
- List of Unix daemons
- List of games included with Windows
References[edit]
- ^ Shultz, Greg (February 28, 2015). «Control Panel and Settings: Why are both still UI options in Windows 10?». TechRepublic. Retrieved October 7, 2022.
- ^ «Get $Windows Camera from the Microsoft Store». apps.microsoft.com. Retrieved October 7, 2022.
- ^ «Xbox Support». support.xbox.com. Retrieved October 7, 2022.
- ^ Hoffman, Chris. «How to See FPS in Any Windows 10 Game (Without Extra Software)». How-To Geek. Retrieved October 7, 2022.
- ^ The Xbox Game Bar Team (May 22, 2019). «Introducing the New Xbox Game Bar». Xbox Wire. Microsoft. Archived from the original on September 21, 2019. Retrieved August 21, 2019.
- ^ «System Services». technet.microsoft.com. Microsoft. 2014. Archived from the original on November 5, 2017. Retrieved September 2, 2014.
The Application Experience service (AELookupSvc) is a part of the Application Compatibility Administrator. It processes application compatibility lookup requests for applications as they are started, provides support for Windows Server 2008 and Windows Vista–based computers running apps in compatibility mode, reports on compatibility issues, and automatically applies software updates to apps.
- ^ «Description of the Microsoft Computer Browser Service». Microsoft. Archived from the original on January 1, 2015. Retrieved November 3, 2017.
- ^ a b Mackie, Kurt (August 16, 2016). «Microsoft Clarifies Windows 10 ‘Delivery Optimization’«. Redmond Magazine. 1105 Enterprise Computing Group. Archived from the original on February 13, 2020. Retrieved January 27, 2018.
- ^ Hachman, Mark (March 29, 2017). «How Delivery Optimization in Windows 10 Creators Update helps avoid data overage fees». PCWorld. IDG. Archived from the original on August 25, 2017. Retrieved January 27, 2018.
- ^ Halfin, Dani; Poggemeyer, Liza; Lich, Brian; Kieselbach, Oliver; Childs, Andrew (April 30, 2018). «Configure Delivery Optimization for Windows 10 updates». docs.microsoft.com. Microsoft. Archived from the original on July 23, 2018. Retrieved July 23, 2018.
- ^ «Distributed Link Tracking on Windows-based domain controllers». Microsoft. Archived from the original on February 25, 2015. Retrieved October 28, 2008.
- ^ «Distributed Transaction Coordinator (MSDTC)». Microsoft. Archived from the original on September 10, 2016. Retrieved June 27, 2008.
- ^ «Event Log». Microsoft. Archived from the original on September 10, 2016. Retrieved June 27, 2008.
- ^ «What is Indexing Service?». Microsoft. Archived from the original on January 1, 2011. Retrieved June 27, 2008.
- ^ «Windows 2000 Professional and Server Service Pack 4 Services Configuration by Black Viper» Archived December 17, 2019, at the Wayback Machine, notice that the service is listed on this page. Retrieved April 2013
- ^ «Windows Firewall» Archived February 13, 2020, at the Wayback Machine. Retrieved April 2013
- ^ «Secondary Logon (Run As): Starting Programs and Tools in Local Administrative Context». Microsoft Corporation. Archived from the original on March 6, 2015. Retrieved October 28, 2008.
- ^ «System Event Notification Service». The Elder Geek. Archived from the original on October 26, 2008. Retrieved June 27, 2008.
- ^ «Myth Busted: Why Disabling SuperFetch on Vista and Windows 7 Is a Bad Idea», retrieved April 2013
- ^ «What Is Volume Shadow Copy Service?: Data Recovery». Microsoft Corporation. Archived from the original on August 26, 2017. Retrieved October 28, 2008.
- ^ «Windows Firewall/Internet Connection Sharing (ICS)» Archived September 10, 2016, at the Wayback Machine, Retrieved April 2013
- ^ «Windows 2000 Professional and Server Service Pack 4 Services Configuration by Black Viper» Archived December 17, 2019, at the Wayback Machine, Notice the absence of the service on this page. Retrieved April 2013
- ^ «Windows Firewall/Internet Connection Sharing (ICS)» Archived February 13, 2020, at the Wayback Machine, Notice that XP is the operating system listed. Retrieved April 2013
- ^ «How Windows Time Service Works: Windows Time Service». Microsoft Corporation. Archived from the original on April 22, 2016. Retrieved October 28, 2008.
- ^ Minasi, Mark; Layfield, Rhonda; Justice, Lisa (2006). Mastering Windows Server 2003: upgrade edition for SP1 and R2 (12 ed.). John Wiley & Sons. p. 56. ISBN 978-0-470-05645-5. Archived from the original on September 21, 2019. Retrieved July 21, 2010.
There is also a client piece for WebDAV built into XP, 2003, R2, and Vista, called the WebClient Service.
- ^ «Microsoft replaces standalone PDF reader app with Edge». MSPoweruser. November 26, 2017. Archived from the original on August 19, 2019. Retrieved August 19, 2019.
- ^ Leonhard, Woody (April 20, 2015). «KB 2952664 triggers daily telemetry run in Windows 7 — and may be snooping on users: Microsoft bills the ‘compatibility update’ as way to ease the upgrade process to Windows 10 — but it’s collecting data daily». Operating Systems. InfoWorld. InfoWorld, Inc. Archived from the original on June 2, 2017. Retrieved August 23, 2016.
The Microsoft Compatibility Appraiser task runs %windir%system32rundll32.exe appraiser.dll,DoScheduledTelemetryRun with the description ‘Collects program telemetry information if opted-in to the Microsoft Customer Experience Improvement Program.’
- ^ Compare: Tulloch, Mitch; Northrup, Tony; Honeycutt, Jerry; Wilson, Ed (2010). Windows 7 Resource Kit. Windows 7 Resource Kit, Microsoft Corporation. Vol. 1. Microsoft Press. p. 708. ISBN 9780735627000. Archived from the original on January 11, 2022. Retrieved August 18, 2016.
The DMRC [(Device Metadata Retrieval Client)] checks the computer’s local metadata cache and metadata store for metadata that applies to the device.
- ^ Solomon, David A.; Russinovich, Mark E.; Ionescu, Alex (June 17, 2009). Windows Internals. Developer Reference (5 ed.). Microsoft Press (published 2009). ISBN 9780735637962. Archived from the original on September 21, 2019. Retrieved October 24, 2016.
The Windows Diagnostic Infrastructure (WDI) helps to detect, diagnose, and resolve common problem scenarios with minimal user intervention.

Introducing Microsoft Surface Studio 2

Windows 8
Microsoft Windows — семейство проприетарных операционных систем корпорации Microsoft, ориентированных на применение графического интерфейса при управлении. Изначально Windows была всего лишь графической надстройкой для MS-DOS. По состоянию на август 2014 года под управлением операционных систем семейства Windows по данным ресурса NetMarketShare работает более 91% персональных компьютеров. Windows работает на платформах x86, x86-64, IA-64 и ARM. Существовали также версии для DEC Alpha, MIPS, PowerPC и SPARC.
Основные статьи: История логотипов Windows, История логотипов Windows 1985-2015
Версии[]
| Версии Microsoft Windows | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Дата выхода | Название | Последняя версия | Дата прекращения поддержки | Последняя версия встроенного браузера |
| 20 ноября 1985 | Windows 1.0x | 1.04 (апрель 1987) | 31 декабря 2001 | Нет браузеров |
| 1 ноября 1987 | Windows 2.x Windows 2.1x |
2.11 (13 марта 1989) | 31 декабря 2001 | |
| 22 мая 1990 | Windows 3.x | 3.00a (31 октября 1990) | 31 декабря 2001 [1] | |
| 18 марта 1992 | Windows 3.1 | 3.1 | 31 декабря 2001 | Internet Explorer 5 |
| 1 октября 1992 | Windows для рабочих групп 3.1 | 3.11 (31 декабря 1993) | 31 декабря 2001 | |
| 27 июля 1993 | Windows NT 3.1 | 3.10.528 SP3 (10 ноября 1994) | 31 декабря 2000 | |
| 21 сентября 1994 | Windows NT 3.5 | 3.50.807 SP3 (21 июня 1995) | 31 декабря 2001 | |
| 30 мая 1995 | Windows NT 3.51 | 3.51.1057 SP5 (19 сентября 1996) | 31 декабря 2001 | |
| 24 августа 1995 | Windows 95 | 4.00.950C (4.03.1214) (26 ноября 1997) | 31 декабря 2000 (осн.) (Retail); 31 декабря 2001 (SBL) (ext) | Internet Explorer 5.5 |
| 29 июля 1996 | Windows NT 4.0 | 4.00.1381 / SP6a SRP (26 июля 2001) | 20 июня 2002 (осн.); 30 июня 2003 (SBL); 31 декабря 2004 (ext) | Internet Explorer 6 |
| 25 июня 1998 | Windows 98 | 4.10.2222A (SE) (5 мая 1999) | 30 июня 2002 (осн.); 31 марта 2004 (SBL); 11 июля 2006 (ext) | |
| 20 апреля 2000 | Windows 2000 | 5.0.2195 / 5.0 SP4 Rollup 1 v2 (13 сентября 2005) | 31 марта 2004 (retail); 31 марта 2005 (SBL); 30 июня 2005 (осн); 13 июля 2010 (ext) | |
| 14 сентября 2000 | Windows ME | 4.90.9000 (14 сентября 2000) | 31 декабря 2003 (осн.); 30 июня 2004 (SBL) (Retail); 11 июля 2006 (ext) | |
| 24 августа 2001 (RTM) 25 октября 2001 (продажи) |
Windows XP | 5.1.2600.5512 SP3 (21 апреля 2008) | 30 сентября 2004 (RTM); 10 сентября 2006 (SP1/SP1a); 30 июня 2008 (retail); 14 апреля 2009 (SP2/SP3 осн.); 13 июля 2010 (SP2); 22 октября 2010 (SBL); 8 апреля 2014 (ext) | Internet Explorer 8 |
| 28 марта 2003 | Windows XP 64-bit Edition | 5.2.3790 | 25 июля 2006 | |
| 24 апреля 2003 | Windows Server 2003 | 5.2.3790.3959 SP2 (13 марта 2007) | 30 июня 2009 (RTM); 13 июля 2010 (осн.); 14 июля 2015 (ext) | |
| 25 апреля 2005 | Windows XP Professional x64 Edition | 5.2.3790.3959 SP2 (13 марта 2007) | 30 июня 2008 (retail); 31 января 2009 (SBL) | |
| 8 ноября 2006 (RTM) 30 января 2007 (продажи) |
Windows Vista | 6.0.6001 / SP2 Build 6002 (25 мая 2009) | 13 апреля 2010 (RTM); 22 октября 2010 (retail); 12 июля 2011 (SP1); 22 октября 2011 (SBL); 10 апреля 2012 (осн.); 11 апреля 2017 (ext) | Internet Explorer 9 |
| 16 июля 2007 | Windows Home Server | 5.2.4500 (16 июля 2007) | 8 января 2013 (осн.) | |
| 27 февраля 2008 | Windows Server 2008 | 6.0.6002 / SP2 build 6002 (25 мая 2009) | 12 июля 2011 (SP1), 9 июля 2015 (осн.), 10 июля 2018 (ext) | |
| 13 июля 2009 (RTM) 22 октября 2009 (продажи) |
Windows 7 | 6.1.7601 / SP1 Build 7601 (22 февраля 2011) | 9 апреля 2013 (RTM), 13 января 2015 (осн), 14 января 2020 (ext) | Internet Explorer 11 |
| 13 июля 2009 (RTM) 22 октября 2009 (продажи) |
Windows Server 2008 R2 или Windows Server 7 | 6.1.7601 / SP1 Build 7601 (22 февраля 2011) | 9 июля 2015 (осн.), 10 июля 2018 (ext) | |
| 6 апреля 2011 | Windows Home Server 2011 | 6.1.8400 | 12 апреля 2016 (осн.) | |
| 1 августа 2012 (RTM) 4 сентября 2012 (продажи) |
Windows Server 2012 | 6.2.9200 (26 октября 2012) | 12 января 2016(осн), 10 января 2018 (ext) | |
| 1 августа 2012 (RTM) 26 октября 2012 (продажи) |
Windows 8 | 6.2.9200 (26 октября 2012) | 12 января 2016 (осн) 10 января 2018 (ext) | |
| 21 августа 2013 (RTM) 17 октября 2013 (продажи) |
Windows Server 2012 R2 | 6.3.9600 (17 октября 2013) | 9 января 2018 (осн) 10 января 2023 (ext) | |
| 21 августа 2013 (RTM) 17 октября 2013 (продажи) |
Windows 8.1 | 6.3.9600 (17 октября 2013) | 9 января 2018 (осн) 10 января 2023 (ext) | |
| 15 июля 2015 (RTM) 29 июля 2015 (продажи) |
Windows 10 | 10.0.10586 (12 ноября 2015) | 13 октября 2020 (осн.), 14 октября 2025 (ext.) | Microsoft Edge / Internet Explorer 11(оставлен для совместимости) |
| 5 октября 2021 | Windows 11 | 10.0.22000.778 | не анонсирована | |
| Условные обозначения: | ||||
| Оболочка для MS-DOS | Windows 9x | Windows NT | Windows Server | |
| Поддержка прекращена | ||||
| осн. — окончание действия лицензии для первого (основного) релиза | SBL — окончание срока лицензии для производителей[2] | retail — окончание срока лицензии для розничных покупателей | SPx — окончание срока лицензии для различных дополнений (сервис-паков) к системе | ext — полное окончание поддержки системы |
Графические интерфейсы и расширения для DOS[]
Логотип первых Windows
Первые версии Windows не были полноценными операционными системами, а являлись надстройками к операционной системе DOS и были по сути многофункциональным расширением, добавляя поддержку новых режимов работы процессора, поддержку многозадачности, обеспечивая стандартизациюинтерфейсов аппаратного обеспечения и единообразие для пользовательских интерфейсов программ. Предоставляли встроенные средства GDI и USER для создания графического интерфейса. Первые версии Windows вообще состояли из трёх модулей — KERNEL, GDI и USER. Первый из них предоставлял вызовы управления памятью, запуском .EXE-файлов и загрузкой .DLL-файлов, второй — графику, третий — окна. Они работали с процессорами начиная с Intel 8086.
- Windows 1.0 (1985)
- Windows 2.0 (1987)
- Windows 2.1 (Windows 386, 1987) — в системе появилась возможность запуска DOS-приложений в графических окнах, причём каждому приложению предоставлялись полные 640 Кб памяти. Полная поддержка процессора 80286. Появилась поддержка процессоров 80386.
- Windows 3.0 (1990) — улучшена поддержка процессоров 80386 и защищённого режима.
- Windows 3.1 (1992) — серьёзно переработанная Windows 3.0; устранены UAE (фатальные ошибки прикладных программ), добавлен механизм OLE, печать в режиме WYSIWYG («что видите, то и получите»), шрифты TrueType, изменён диспетчер файлов, добавлены мультимедийные функции.
- Windows для рабочих групп (Windows for Workgroups) 3.1/3.11 — первая версия ОС семейства с поддержкой локальных сетей. В системе также испытывались отдельные усовершенствования ядра, применённые позднее в Windows 95.
Семейство Windows 9x[]
Основная статья: Windows 9x
Логотип первой системы семейства Windows 95
Первая система данного семейства Windows 95 была выпущена в 1995 году. Её отличительными особенностями являлись: новый пользовательский интерфейс, поддержка длинных имён файлов, автоматическое определение и конфигурация периферийных устройств Plug and Play, способность исполнять 32-битные приложения и наличие поддержки TCP/IP прямо в системе. Windows 95 использовала вытесняющую многозадачность и выполняла каждое 32-битное приложение в своём адресном пространстве. К данному семейству относятся также Windows 98 и Windows ME.
Логотип второй системы семейства Windows 98
Операционные системы этого семейства не являлись безопасными многопользовательскими системами как Windows NT, поскольку из соображений совместимости вся подсистема пользовательского интерфейса и графики оставалась 16-битной и мало отличалась от той, что в Windows 3.x. Так как этот код не был потокобезопасным, все вызовы в подсистему оборачивались в мьютекс по имени Win16Lock, который, кроме того, ещё и находился всегда в захваченном состоянии во время исполнения 16-битного приложения. Таким образом, «повисание» 16-битного приложения немедленно блокировало всю ОС. Но уже в 1999 году вышло второе исправленное издание. Программный интерфейс был подмножеством Win32 API, поддерживаемым Windows NT, но имел поддержку юникода в очень ограниченном объёме[3]. Также в нём не было должного обеспечения безопасности (списков доступа к объектам и понятия «администратор»). В составе Windows 95 присутствовал MS-DOS 7.0, однако его роль сводилась к обеспечению процесса загрузки и исполнению 16-битных DOS приложений. Исследователи заметили, что ядро Windows 95 — VMM — обращается к DOS под собой, но таких обращений довольно мало, главнейшая функция ядра DOS — файловая система FAT — не использовалась. В целом же интерфейс между VMM и нижележащей DOS никогда не публиковался, и DOS была замечена Эндрю Шульманом (книга Недокументированный Windows 95) в наличии недокументированных вызовов только для поддержки VMM.
Семейство Windows NT[]
Основная статья: Windows NT
Логотип семейства Windows NT
Операционные системы этого семейства в настоящее время работают на процессорах с архитектурами x86, x86-64, и Itanium, ARM. Ранние версии (до 4.0 включительно) также поддерживали некоторые RISC-процессоры: Alpha, MIPS, и Power PC. Все операционные системы этого семейства являются полностью 32- или 64- битными операционными системами, и не нуждаются в MS-DOS даже для загрузки.
Только в этом семействе представлены операционные системы для серверов. До версии Windows 2000 включительно они выпускались под тем же названием, что и аналогичная версия для рабочих станций, но с добавлением суффикса, например, «Windows NT 4.0 Server» и «Windows 2000 Datacenter Server». Начиная с Windows Server 2003 серверные операционные системы называются добавлением суффикса «Server» и года выпуска.
Логотип Windows 7 Логотип Windows 8
- Windows NT 3.1 (1993)
- Windows NT 3.5 (1994)
- Windows NT 3.51 (1995)
- Windows NT 4.0 (1996)
- Windows 2000 — Windows NT 5.0 (2000)
- Windows XP — Windows NT 5.1 (2001)
- Windows XP 64-bit Edition — Windows NT 5.2 (2003)
- Windows Server 2003 — Windows NT 5.2 (2003)
- Windows XP Professional x64 Edition — Windows NT 5.2 (2005)
- Windows Vista — Windows NT 6.0 (2006)
- Windows Home Server — Windows NT 5.2 (2007)
- Windows Server 2008 — Windows NT 6.0 (2008)
- Windows Small Business Server — Windows NT 6.0 (2008)
- Windows 7 — Windows NT 6.1 (2009)
- Windows Server 2008 R2 — Windows NT 6.1 (2009)
- Windows Home Server 2011 — Windows NT 6.1 (2011)
- Windows 8 — Windows NT 6.2 (2012)
- Windows Server 2012 — Windows NT 6.2 (2012)
- Windows 8.1 — Windows NT 6.3 (2013)
- Windows Server 2012 R2 — Windows NT 6.3 (2013)
- Windows 9 — Windows NT 6.4 (2015)
В основу семейства Windows NT положено разделение адресных пространств между процессами. Каждый процесс имеет возможность работать с выделенной ему памятью. Однако он не имеет прав для записи в память других процессов, драйверов и системного кода.
Семейство Windows NT относится к операционным системам с вытесняющей многозадачностью. Разделение процессорного времени между потоками происходит по принципу «карусели». Ядро операционной системы выделяет квант времени (в Windows 2000 квант равен примерно 20 мс) каждому из потоков по очереди при условии, что все потоки имеют одинаковый приоритет. Поток может отказаться от выделенного ему кванта времени. В этом случае система перехватывает у него управление (даже если выделенный квант времени не закончен) и передаёт управление другому потоку. При передаче управления другому потоку система сохраняет состояние всех регистров процессора в особой структуре в оперативной памяти. Эта структура называется контекстом потока. Сохранения контекста потока достаточно для последующего возобновления его работы.
Семейство ОС для смартфонов[]
Основная статья: Windows Phone
Логотип Windows Phone
Это семейство операционных систем реального времени было специально разработано для мобильных устройств. Поддерживаются процессоры ARM, MIPS, SuperH и x86. В отличие от остальных операционных систем Windows, операционные системы этого семейства продаются только в составе готовых устройств, таких как смартфоны, карманные компьютеры, GPS-навигаторы, MP3-проигрыватели и другие. В настоящее время под термином «Windows CE» понимают только ядро операционной системы. Например, Windows Mobile 5.0 включает в себя ядро Windows CE 5.0.
- Windows CE
- Windows Mobile
- Windows Phone
- Windows 10 Mobile
Семейство встраиваемых ОС Windows Embedded[]
Основная статья: Windows Embedded
Логотип Windows Embedded
Windows Embedded — это семейство операционных систем реального времени, было специально разработано для применения в различных встраиваемых системах. Ядро системы имеет общее с семейством ОС Windows CE и поддерживает процессоры ARM, MIPS, SuperH и x86.
Windows Embedded включает дополнительные функции по встраиванию, среди которых фильтр защиты от записи (EWF и FBWF), загрузка с флеш-памяти,CD-ROM, сети, использование собственной оболочки системы и т. п.
В отличие от операционных систем Windows, операционные системы этого семейства продаются только в составе готовых устройств, таких как: банкоматы,медицинские приборы, навигационное оборудование, «тонкие» клиенты, VoIP-терминалы, медиапроигрыватели, цифровые рамки (альбомы), кассовые терминалы, платёжные терминалы, роботы, игровые автоматы, музыкальные автоматы и другие.
В настоящее время выпускаются следующие варианты ОС Windows Embedded[4]:
- Windows Embedded CE,
- Windows Embedded Standard,
- Windows Embedded POSReady,
- Windows Embedded Enterprise,
- Windows Embedded NavReady,
- Windows Embedded Server.
Интегрированные программные продукты[]
Пакет Windows включает в себя «стандартные» приложения[5], такие как браузер (Internet Explorer), почтовый клиент (Outlook Express или Почта Windows), музыкальный и видеопроигрыватель (Проигрыватель Windows Media). С помощью технологий COM и OLE их компоненты могут быть использованы в приложениях сторонних производителей. Эти продукты бесплатны и могут быть свободно скачаны с официального сайта Microsoft, однако для установки некоторых из них необходимо иметь лицензионную версию Windows (верно только для ранних версий до Windows, начиная с Windows 98 являются неотъемлемой частью системы). Запуск этих программ под другими операционными системами возможен только с помощью эмуляторов среды Windows (Wine).
Вокруг факта включения таких «стандартных» продуктов в ОС Windows разгорается много дискуссий и юридических споров, по мнению сторонних разработчиков, это ведёт к отсутствию конкуренции и создает препятствия для распространения конкурирующих продуктов, они же часто ставят под сомнение качество браузера Internet Explorer, объясняя его популярность вхождением в пакет Windows и плохой осведомленностью пользователей о наличии альтернатив.
В 1997 году компания Sun Microsystems подала в суд на компанию за нарушение лицензии на использование технологий Java. В 2001 году Microsoft выплатила штраф и исключила не совместимую с лицензированной виртуальную машину Java из состава своих продуктов[6].
Распространённость[]
В настоящее время Windows установлена на 91% персональных компьютеров и рабочих станций. По данным компании Net Applications, на август 2014 года рыночная доля Windows составила ▲91,68%.
Среди различных версий Windows по данным W3Schools с августа 2011 года наиболее популярна Windows 7[7] (около 50%).
| «GoStats.ru»,
июнь 2011[8] |
«Net Market Share»,
июнь 2011[9] |
«GoStats.ru»,
август 2014[10] |
«Net Market Share»,
август 2014[11] |
«GoStats.ru»,
август 2015[12] |
|
| Все версии | 94.70 % | 93.32 % | 90.46% | 91.68% | 84.76% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Windows 10 | — | — | — | — | 2.87% |
| Windows 8 | — | — | 2,4% | 12,48% | 33,67% |
| Windows 7 | 25.89 % | 28.68 % | 76.72% | 51.22% | 40.63% |
| Windows XP | 55.44 % | 54.04 % | — | 23.89% | 6.55% |
<nowiki>
Комментарии[]
Windows 7 — умершая легенда (Ghast88)
| Хронология ОС Windows | |
|---|---|
| Основные версии | MS-DOS: Windows 1.0x • Windows 2.x (Windows 2.1x) • Windows 3.x Windows 9x: Windows 95 • Windows 98 • Windows ME Windows NT: Windows NT 3.1 • Windows NT 3.5 • Windows NT 3.51 • Windows NT 4.0 • Windows 2000 • Windows XP • Windows Vista • Windows 7 • Windows 8 • Windows 8.1 • Windows 10 |
| Windows Server | Windows Server 2003 • Windows Home Server (Windows Home Server 2011) • Windows Server 2008 (Windows HPC Server 2008 • Windows Server 2008 R2) • Windows Essential Business Server • Windows MultiPoint Server • Windows Small Business Server • Windows Server 2012 (Windows Server 2012 R2) • Windows Server 2016 |
| Специализированные | Windows Embedded (Windows Embedded Automotive • Windows Embedded POSReady) • Среда предустановки Windows • Windows Fundamentals for Legacy PCs |
| Мобильные | Windows CE (Windows CE 1.0 • Windows CE 2.0 • Windows CE 3.0 • Windows CE 4.0 • Windows CE 5.0 • Windows CE 6.0 • Windows Embedded Compact 7 • Windows Embedded Compact 2013) • Windows Mobile • Windows Phone • Windows RT • Windows 10 Mobile |
| Другие проекты | Открытые: Xenix • OS/2 • Microsoft Singularity • Midori Закрытые: Windows Neptune • Windows Nashville • Windows Odyssey • Windows Cairo • Windows Longhorn • Windows 10x |
| Альтернативные реализации | ReactOS • Wine |
| |
|
|---|---|
| Основные |
Aero • |
| Службы управления |
Архивация и восстановление • |
| Приложения |
Контакты • |
| Игры |
Chess Titans • |
| Ядро ОС |
Ntoskrnl.exe • |
| Службы |
Autorun.inf • |
| Файловые системы |
ReFS • |
| Сервер |
Active Directory • |
| Архитектура |
NT • |
| Безопасность |
BitLocker • |
| Совместимость |
Подсистема UNIX (Interix) • |
- ↑ Microsoft Support Lifecycle Шаблон:Ref-en
- ↑ Лицензирование для сборщиков систем OEM
Содержание
- Национальная библиотека им. Н. Э. Баумана Bauman National Library
- Персональные инструменты
- Microsoft Windows
- Содержание
- Основные графические интерфейсы и расширения для DOS
- Windows 1.0
- Windows 2.0
- Windows 3.0
- Windows 3.1
- Семейство Windows 9x
- Windows 95
- Windows 98
- 2001-20016 годы
- Windows 7
- Windows 8
- Windows 10
Национальная библиотека им. Н. Э. Баумана
Bauman National Library
Персональные инструменты
Microsoft Windows
Разработчик Microsoft Написана на Закрытый исходный код / Shared source Дата выхода на
производство 20 November 1985 года ; 35 years ago ( 1985-11-20 ) Последний релиз 10.0.10586.218 (по разработчикам 1511) Платформы x86, x86-64, IA-64, ARM Ядро (тип) Windows NT По умолчанию
пользовательский
интерфейс Metro (интерфейс) и Windows USER[d] Лицензия Пользовательское соглашение Официальный веб-сайт windows.com
Microsoft Windows — семейство проприетарных операционных систем корпорации Microsoft, ориентированных на применение графического интерфейса при управлении. Изначально Windows была всего лишь графической надстройкой для MS-DOS. По состоянию на август 2014 года под управлением операционных систем семейства Windows по данным ресурса Net Applications работает около 89% персональных компьютеров. Windows работает на платформах x86, x86-64, IA-64 и ARM. Существовали также версии для DEC Alpha, MIPS, PowerPC и SPARC.
Содержание
Основные графические интерфейсы и расширения для DOS
Первые версии Windows не были полноценными операционными системами, а являлись надстройками к операционной системе DOS и были по сути многофункциональным расширением, добавляя поддержку новых режимов работы процессора, поддержку многозадачности, обеспечивая стандартизацию интерфейсов аппаратного обеспечения и единообразие для пользовательских интерфейсов программ. Предоставляли встроенные средства GDI и USER для создания графического интерфейса. Первые версии Windows вообще состояли из трёх модулей — KERNEL, GDI и USER. Первый из них предоставлял вызовы управления памятью, запуском .EXE-файлов и загрузкой .DLL-файлов, второй — графику, третий — окна. Они работали с процессорами начиная с Intel 8086.
Windows 1.0
Microsoft Windows 1.0 — графический интерфейс пользователя компании Microsoft для операционной системы MS-DOS, использующий принцип фреймового менеджера окон, созданный для облегчения диалога с последней, унификации внешнего вида приложений и оптимизации работы с периферийными устройствами (например, с принтером). Система официально анонсирована Биллом Гейтсом 10 ноября 1983 года в Нью-Йорке, однако была выпущена лишь спустя два года. В течение этих лет над продуктом работали 24 разработчика. Наконец, 20 ноября 1985 года были начаты поставки системы в сети розничной торговли. Для ускорения доставки комплектов программы в магазины была использована пересылка по почте. На следующий день продукт был официально представлен на пресс-конференции. Объявленная стоимость в США составляла 99 долларов, в Германии — 399 немецких марок. Очевидным минусом продукта являлось то, что для полноценного использования нужно было приобретать такое дорогостоящие оборудование, как мышь, память большего объёма и новую модель процессора.
Windows 2.0
Выход состоялся 2 апреля 1987 года. Microsoft воспользовалась скоростными характеристиками процессора Intel 286, возможностью расширения памяти и взаимодействия приложений с использованием DDE. Пользователи этой ОС могли применять комбинации клавиш для быстрого осуществления системных операций. Windows 2.0 использовала многооконную среду Presentation Manager и имела собственный API-код, но могла задействовать только 640 Кб памяти MS-DOS и расширенную память. Однако несмотря на то, что многие разработчики принялись писать программное обеспечение под Windows 2.x (а это было существенным признаком грядущего успеха ОС), она не получила широкого распространения, поскольку слабая аппаратная часть и значительные программные ограничения затрудняли использование многооконного интерфейса.
Windows 3.0
Появившаяся 22 мая 1990 года система первой получила по-настоящему массовое распространение. Произошло это во многом за счёт того, что она предустанавливалась производителями на продаваемые компьютеры. С выходом Windows 3.0, операционная система от Microsoft немедленно становится доминирующим продуктом на рынке благодаря предварительной установке на новых компьютерах и широкой поддержке со стороны независимых поставщиков аппаратных средств и программного обеспечения.
В Windows 3.0 программисты Microsoft заменили файловую оболочку DOS собственным «Диспетчером Программ» и специальной надстройкой, предназначенной для навигации по диску – «Диспетчер Файлов». Окна, функциональные кнопки и другие элементы интерфейса имели псевдотрехмерное оформление и использовали расширенную цветовую палитру VGA, благодаря чему выглядели очень красиво и вполне современно.
Операционная система включала полнофункциональную «Панель Управления», позволявшую оперировать практически всеми возможными настройками Windows, в том числе, открывавшую новую возможность — установки любого графического изображения в формате bmp в качестве «подложки» основного рабочего пространства системы. Кроме того, система помощи в Windows 3.0 была реализована с использованием языка HTML и содержала гиперссылки, ведущие к различным тематическим разделам подсказки, а само окно интерактивной помощи имело интерфейс стандартного веб-браузера.
Набор поставляемого вместе с системой программного обеспечения также был значительно расширен: помимо текстовых редакторов Notepad и Wordpad, графического редактора Paintbrush, инструментов удаленного доступа к сети и многих других утилит, Windows 3.0 содержала также комплект игр: «Пасьянс-Косынка», «Пасьянс Свободная Ячейка» и «Сапер». Система поддерживала несколько режимов памяти, включая 16-разрядный Real Mode для компьютеров с более ранними процессорами, нежели Intel 80286, и 32-разрядный Enhanced Mode для более производительных процессоров 80386. Релиз Windows 3.0 позволил Microsoft на равных конкурировать в плане удобства работы с Apple Macintosh. В частности, в Windows 3.0 появилась панель управления и система окон. Требования к аппаратному обеспечению у системы были следующие:
- Процессоры 8086/8088 или более современные.
- 384 Кб памяти в режиме Real Mode, 1 Мб в режиме Standart Mode и 2 Мб в режиме Enhanced Mode.
- 6-7 Мб свободного пространства на жёстком диске.
- Графические карты CGA/EGA/VGA/Hercules/8514/A/XGA и совместимый монитор.
- MS-DOS 3.1 или новее.
- Также рекомендовалось использовать совместимую с продуктом Microsoft мышь.
Windows 3.1
Следующим этапом в развитии Windows стала Windows 3.1. Появившаяся на рынке в апреле 1992 года она была первой платформой семейства Windows, имевшей русскую локализацию и получившей широкое распространение в нашей стране. По большому счету, Windows 3.1 представляла собой лишь улучшенную модификацию Windows 3.0, она обладала расширенными функциями настройки параметров рабочей среды и улучшенным графическим интерфейсом, было исправлено множество ошибок, повышена стабильность, добавлены масштабируемые шрифты TrueType и др.
Семейство Windows 9x
Windows 95
Windows 95 (кодовое название — Chicago) — графическая многозадачная операционная система корпорации Microsoft. Была официально представлена 24 августа 1995 года. Российская версия поступила в продажу 10 ноября 1995 года.
Windows 95 предназначалась в основном для домашнего и SOHO сегментов. Система являлась гибридной — поддерживала исполнение 16- и 32-разрядного кода. Новшества интерфейса Windows 95 активно использовались во всех последующих версиях Windows: в ней появились такие элементы графического интерфейса, как рабочий стол со значками, панель задач и меню «Пуск». Поддержка Windows 95 прекращена 31 декабря 2001 года. На современных системах, запуск возможен только на некоторых виртуальных машинах, которым в свою очередь нередко требуются определенные настройки и драйверы.
Windows 98
Официально Windows 98 появилась 25 июня 1998 года, по истечении почти годового периода бета-тестирования и ровно через два года и десять месяцев после появления своей предшественницы. В новой системе улучшилась поддержка AGP, доработаны драйверы USB, добавлена поддержка работы с несколькими мониторами и поддержка WebTV. В интерфейс системы интегрирован браузер Internet Explorer 4.
Спустя год, 5 мая 1999 была выпущена обновленная версия Windows 98 Second Edition, которая включала множество исправлений, добавляла поддержку DVD, но в тоже время и увеличивала системные требования к ПК. Помимо этого, Internet Explorer 4 был заменен на новый, более быстрый Internet Explorer 5.
В феврале 2000 года Microsoft выпустила Windows 2000 (NT 5.0). По сравнению с предыдущей версией — NT 4.0, в Windows 2000 появилась поддержка службы каталогов Active Directory, службы IIS версии 5.0, файловой системы NTFS 3.0, а также обновлен интерфейс. Чуть позже, в сентябре этого же года, вышла новая ОС из семейства Windows 9x — Windows ME (Millennium Edition). Новая система приобрела ряд новых возможностей. Прежде всего, это улучшенная работа со средствами мультимедиа, возможность записывать не только аудио, но и видеоинформацию, средства восстановления информации после сбоев и др. Кроме того, одним из наиболее заметных изменений в новой системе стало отсутствие реального режима MS-DOS. Системные требования для Windows 98: процессор 486DX/66 MHz или лучше, 16 Мб ОЗУ и по крайней мере 195 Мб свободного дискового пространства при стандартной установке.
2001-20016 годы
25 октября 2001 года была выпущена Windows XP, объединяющая в себе две линейки операционных систем, существовавших до сих пор раздельно — «домашние» Windows 9х/МЕ и «корпоративные» Windows NT/2000. Среди наиболее заметных улучшений Windows XP можно отметить новый графический интерфейс, возможность удаленного управления, быстрая смена пользователей, улучшенная функция восстановления системы и др.
В 2003 году вышла серверный вариант операционной системы Windows XP — Windows Server 2003. Новая серверная ОС в основном развивала функции предшественника – Windows 2000. Кроме того, по заявлениям Microsoft, в Windows Server 2003 большое внимание было уделено безопасности системы.
В июле 2006 года появилась ОС для маломощных ПК основанная на Windows XP — Windows Fundamentals for Legacy PCs (FLP). В конце ноября 2006 года Microsoft официально выпустила Windows Vista, но только для корпоративных клиентов, у рядовых пользователей появилась возможность приобрести новую операционную систему 30 января 2007 года. В Windows Vista появились новые возможности оформления пользовательского интерфейса, обновлена подсистема управления памятью и вводом-выводом, появился режим «гибернации», улучшена безопасность и др.
7 января 2007 года Билл Гейтс анонсировал серверную операционную систему для использования в домашних сетях Windows Home Server, спустя примерно полгода она стала доступной пользователям.
27 февраля 2008 года состоялся релиз новой серверной ОС — Windows Server 2008, которая должна стать заменой Windows Server 2003.
Windows 7
Операционная система поступила в продажу 22 октября 2009 года — меньше, чем через три года после выпуска предыдущей операционной системы Windows Vista. Партнёрам и клиентам, обладающим лицензией Volume Licensing, доступ к RTM был предоставлен 24 июля 2009 года. В интернете оригинальные установочные образы финальной версии системы были доступны с 21 июля 2009 года.
Основные особенности и нововведения:
- реализована поддержка Unicode 5.1
- Данная ОС обладает поддержкой мультитач-управления
- Все версии ОС включают 50 новых шрифтов. А существующие шрифты доработаны для корректного отображения всех символов.
- Реализована поддержка псевдонимов для папок на внутреннем уровне.
- Более тесная интеграция с производителями драйверов.
- Улучшена совместимость со старыми приложениями, некоторые из которых было невозможно запустить на Windows Vista.
- Проигрыватель Windows Media Player 12 получил новый интерфейс.
- Функция Удалённого рабочего стола потерпела следующие изменения. Была введена поддержка интерфейса Aero Peek, Direct 2D и Direct3D 10.1, поддержка нескольких мониторов, расширений мультимедиа, DirectShow, а также возможность воспроизведения звука с низкими задержками.
Windows 8
Поступила в продажу 26 октября 2012 года. По состоянию на февраль 2015 года доля операционной системы Windows 8 среди используемых в мире для доступа к сети Интернет составляет 21,3 % и занимает второе место после Windows 7. Серверной версией является Windows Server 2012.
- Учётная запись Майкрософт и синхронизация параметров: Возможность войти в Windows с помощью Windows Live ID|Live ID. Это позволит войти в профиль пользователя и загрузить настройки через интернет, а также добавляет интеграцию с OneDrive.
- Магазин приложений Windows Store: единственный способ покупки и загрузки Metro-приложений, а также приложений для рабочего стола в Windows RT.
- Два новых метода для аутентификации пользователя: картинка-пароль, позволяющая пользователю войти в систему при помощи трех касаний, и четырёхзначный PIN-код, а также встроенная поддержка биометрических устройств. Пароль нелокальной учетной записи пользователя соответствует паролю учетной записи Майкрософт.
- Internet Explorer 10. IE 10 в Windows 8 включен в настольном и сенсорном вариантах. Последний не поддерживает плагины или ActiveX, но включает в себя версию проигрывателя Adobe Flash Player, который оптимизирован для сенсорного управления.
- Проводник. Включает в себя Ribbon-ленту (наподобие ленты в Microsoft Office и Windows Essentials) и улучшения в способах разрешения конфликтов при переносе или копировании файлов.
- Восстановление системы. Добавлено две новые функции: Восстановление и Сброс. Восстановление для Windows возвращает все системные файлы в исходное состояние, сохраняя при этом все настройки, пользовательские файлы и приложения. Сброс же возвращает компьютер к заводским настройкам.
- Новый диспетчер задач. В Windows 8 диспетчер задач был полностью изменен. Добавлены новые графики производительности, оптимизировано управление выполняющимися приложениями, фоновыми процессами и службами на единой вкладке «Производительность». Также в диспетчер задач было перенесено управление автозагрузками из «Конфигурации системы».
- Функция «Семейная безопасность» была встроена в Windows, управление семейной безопасностью осуществляется в панели управления.
- Персонализация: после запуска на экране появляется картинка с текущим временем и датой. Для начала работы нужно нажать любую кнопку, открыв экран приветствия. Саму картинку можно сменить в настройках. Добавлено автоопределение цвета в темах для рабочего стола.
- Новая панель управления в стиле Metro UI, которая позволяет быстро изменить некоторые настройки системы.
- Усовершенствованный поиск: На начальном экране нужно лишь нажать любую клавишу для начала поиска по приложениям, параметрам и т. п.
- Переключение раскладки клавиатуры: менять раскладку клавиатуры можно также с помощью сочетаний клавиш Windows + Space либо Shift + Alt.
Windows 10
Официальная дата релиза 29 июля 2015 года.
Основные отличия от предыдущих версий:
- Модифицированное меню «Пуск», позволяющее просматривать наиболее часто используемые приложения и файлы, заниматься их настройкой. Появилась возможность убирать или закреплять плитки.
- Изменение размера «Пуск» в один клик мышки, которое возможно с версии 10056.
- Установленные пользователем игры и программы располагаются в середине меню «Пуск», а не отображаются с подсветкой при открытии вкладки «Приложения».
- Открыть Магазин Windows теперь возможно при помощи оконного режима, развернув его на полный экран.
- Центр уведомлений заменил панель волшебных кнопок.
- При нажатии на знак сетевого подключения оно откроется в маленьком окошке, как в Windows 7.
- Появилось новое оформление батарейного индикатора.
- Обновленный календарь и часы.
- Окна, перерисованные под современный стиль, имеют новую анимацию.
- Изменен интерфейс рамок окон.
- Обновлён экран блокировки и приветствия.
Здравствуйте, начинающие пользователи компьютера! Вместе с вами постараемся разобраться в том, что такое Windows и зачем оно нам нужно.
Windows — это операционная система, сделанная корпорацией Microsoft (Майкрософт). Операционная система (ОС) — это главная программа, которая запускается при включении компьютера. Она позволяет пользователям компьютера работать с файлами, пользоваться Интернетом и запускать в окошках другие программы, игры, фильмы, музыку. Windows переводится как «окна».
Операционная система Windows платная. Если вы покупаете компьютер с уже установленной Windows, то часть денег вы платите за операционную систему. Для подтверждения того, что вы являетесь владельцем Windows, может потребоваться лицензионный ключ. Такое бывает, например, если вы переустановили Windows. Лицензионный ключ это набор символов вида «XXXXX-XXXXX-YYYYY-YYYYY-ZZZZZ». Он может быть указан в наклейке на корпусе вашего компьютера или на диске с Windows. Перепишите лицензионный ключ на листок и сохраните, может пригодиться. Наклейка выглядит примерно так:
Вместе с Windows на компьютер устанавливается набор программ, необходимых для повседневного использования:
- Калькулятор.
- Редактор Notepad (блокнот) для работы с текстовыми файлами.
- Редактор WordPad для работы с документами.
- Редактор картинок Paint.
- Браузер Edge или Internet Explorer для работы в Интернет.
- Проигрыватель видео и музыки.
- Антивирус от Microsoft (защитник).
- другие программы и даже игры.
Можно устанавливать другие программы и игры из Интернета или с дисков. Такие программы также могут быть платные.
История и разновидности Windows
Даты выхода ОС Windows для персональных компьютеров (ПК):
- Windows 1.0 (1985)
- Windows 2.0 — 2.1 (1987-1988)
- Windows 3.0 — 3.2 (1990-1994)
- Windows NT 3.1 — 3.51 (1993-1995)
- Windows 95 — Windows 4.0 (1995)
- Windows NT 4.0 (1996)
- Windows 98 — Windows 4.1 (1998)
- Windows 2000 — Windows NT 5.0 (1999)
- Windows ME — Windows 4.9 (2000)
- Windows XP — Windows NT 5.1 — 5.2 (2001-2005)
- Windows Vista — Windows NT 6.0 (2006)
- Windows 7 — Windows NT 6.1 (2009)
- Windows 8 — Windows NT 6.2 (2012)
- Windows 8.1 — Windows NT 6.3 (2013)
- Windows 10 — Windows NT 10.0 (2015)
- Windows 11 — Windows NT 10.0 (2021)
В последних версиях Windows есть сборки, отличающиеся функционалом и ценой:
- Home Edition — сборка для домашнего использования с простой конфигурацией.
- Professional — сборка с дополнительным функционалом для более продвинутых пользователей.
- Enterprise — корпоративная версия для организаций.
Интерфейс Windows
Интерфейс — это внешний вид операционной системы. У отдельных частей интерфейса есть свои названия.
- Рабочий стол — основное место, занимает большую часть экрана. Здесь можно располагать ярлыки.
- Панель задач — здесь можно закреплять программы, с которыми вы чаще всего работаете. Здесь же показываются открытые в данный момент программы, выбранный язык, дата и время.
- Кнопка ПУСК — при нажатии открывается меню для быстрого доступа к программам.
- Ярлык — картинка, при нажатии на которые открывается соответствующая программа или документ.
Кнопка ПУСК может также находиться на вашей клавиатуре.
Внешний вид меню ПУСК:
Ссылки
Linux — что это такое?
Разновидности операционных систем
Рассмотрим какие ещё бывают операционные системы, кроме Windows. Речь пойдёт об операционных системах для персональных компьютеров. Не будем акцентировать внимание на операционных системах для серверов, мобильных телефонов и специализированной техники.
- MacOS — операционная система от компании Apple. Установлена как основная операционная система на продуктах компании. Платная.
- Linux — операционная система распространяется бесплатно. Сложна в освоении, поэтому мало распространена. Имеет несколько разновидностей (модификаций), которые поддерживаются различными компаниями и сообществами, например:
- Ubuntu
- Fedora
- Elementary OS
- Chrome OS
- OpenSuse
- Linux Mint
- Mageia
- PCLinuxOS
- Manjaro
- Arch
- Puppy
- и ещё много других
- FreeBSD — современная операционная система семейства UNIX, распространяется свободно.
Интересные факты об операционных системах
На одном компьютере может быть установлено одновременно несколько операционных систем. В этом случае при включении компьютера вас спросят, какую операционную систему нужно загрузить.
Microsoft Windows и ядро Linux могут быть запущены одновременно на одной и той же машине с помощью специального программного обеспечения CoLinux. В windows 10 уже появилась встроенная подсистема linux.
Для обучения пользователей обращению с мышкой в Microsoft разработали и внедрили в Windows компьютерную версию игры Reversi. Таким образом пользователи привыкали использовать мышь, кликая с её помощью на фишки. Задумайтесь, для чего сделана игра «сапёр»?
На рекламу Windows 95 было потрачено более 300 миллионов долларов.
В Windows нельзя создать папку с названиями con, prn, aux, nul. Это ограничение восходит относят к временам операционной системы MS-DOS. Некоторые слова были зарезервированы для обозначения устройств ввода-вывода, поэтому нельзя создать папки с такими именами.
Линус Торвальдс использовал операционную систему Minix, однако был недоволен многими ограничениями в ней и решил написать свою систему. Когда была выпущена более-менее стабильная версия, интерес Торвальдса к проекту угас, и он был готов его забросить. Но в тот же период он случайно испортил раздел на жёстком диске, где стояла Minix, и вместо её переустановки Торвальдс решил всё-таки закончить начатое. Так благодаря случайности появилось ядро Linux и впоследствии ОС GNU/Linux.
На данный момент более 75% серверов обеспечивающие надежную работу Интернет работают под управлением Linux.
MenuetOS — самая маленькая операционная система. Написана на ассемблере и помещается на дискету.