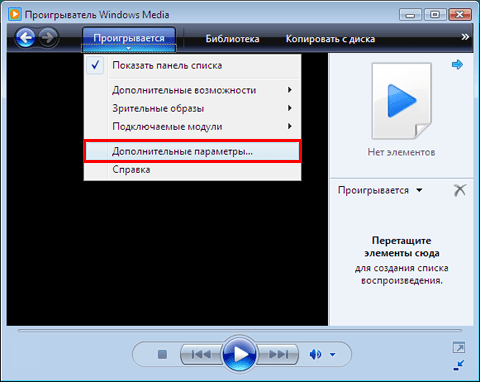
-
Форматы Windows Media (ASF, WMA, WMV, WM)
-
Метафайлы Windows Media (.asx, .wax, .wvx, .wmx, .wpl)
-
Microsoft Digital Video Recording (DVR-MS)
-
Пакет Windows Media Download (WMD)
-
Audio Visual Interleave (AVI)
-
Moving Pictures Experts Group (MPG, MPEG, M1V, MP2, MP3, MPA, MPE, M3U)
-
Musical Instrument Digital Interface (MID, MIDI, RMI)
-
Audio Interchange File Format (AIF, AIFC, AIFF)
-
Sun Microsystems и NeXT (AU, SND)
-
Аудио Windows (WAV)
-
CD Audio Track (CDA)
-
Indeo Video Technology (IVF)
-
Обложки проигрывателя Windows Media (WMZ, WMS)
-
Файл фильма QuickTime (MOV)
-
Аудиофайл MP4 (M4A)
-
Видеофайл MP4 (MP4, M4V, MP4V, 3G2, 3GP2, 3GP, 3GPP)
-
Аудиофайл Windows (AAC, ADT, ADTS)
-
Видеофайл MPEG-2 TS (M2TS)
-
Free Lossless Audio Codec (FLAC)
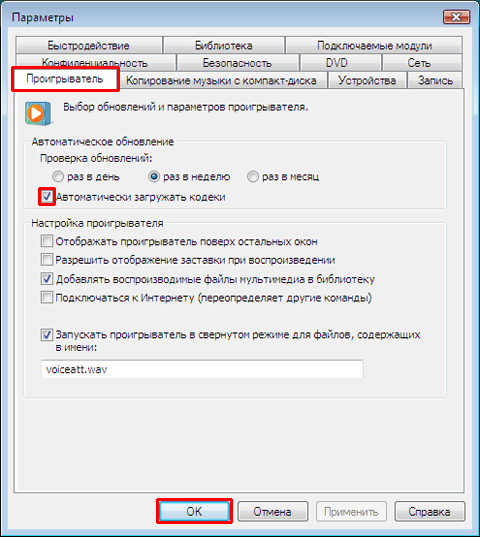
Подробные сведения о поддерживаемых форматах файлов
Формат Advanced Systems (.asf)
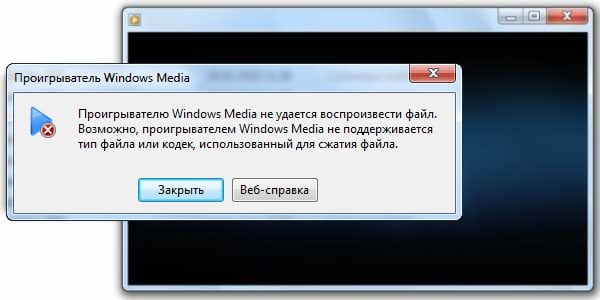
Формат Advanced Systems Format (ASF) является предпочтительным форматом файлов Windows Media. Если на компьютере установлены соответствующие кодеки, то, используя проигрыватель Windows Media, можно воспроизводить видео-, аудио- и смешанные записи, сжатые с помощью этих кодеков и сохраненные в файле ASF. Кроме того, эти записи можно преобразовать в потоковый файл с помощью служб Windows Media или сжать с помощью диспетчера Windows Media Rights Manager.
Формат ASF является расширяемым форматом, предназначенным для хранения синхронизированных данных мультимедиа. Данные в формате ASF могут передаваться по сетям различных типов при помощи различных протоколов, а также воспроизводиться с локального компьютера. Формат ASF поддерживает такие возможности, как использование расширяемых типов носителей, загрузка компонентов, использование масштабируемых типов носителей, определение важности потока, заданной автором, многоязыковая поддержка, а также широкие возможности управления содержимым и документами.
Как правило, файлы в формате ASF, которые содержат звуковые записи, упакованные с помощью кодека Windows Media Audio (WMA), имеют расширение WMA. Аналогично, файлы в формате ASF, содержащие аудио-, видео- или смешанные записи, которые упакованы с помощью кодеков Windows Media Audio (WMA) и Windows Media Video (WMV), имеют расширение WMV. Если содержимое файла упаковано с помощью другого кодека, то файл имеет расширение ASF. Дополнительные сведения о формате ASF см. на веб-сайте корпорации Microsoft:
Файлы формата Advanced Systems (.asf)
Windows Media Audio (.wma)
Файлы Windows Media Audio (WMA) являются файлами в формате Advanced Systems Format (ASF), содержащими аудиозаписи, которые упакованы с помощью кодека Windows Media Audio (WMA). Использование отдельного расширения позволяет установить на компьютер несколько проигрывателей и использовать часть из них для воспроизведения только звуковых файлов с расширением .wma.
Windows Media Video (.wmv, .wm)
Файлы Windows Media Video (WMV) являются файлами в формате Advanced Systems Format (ASF), содержащими аудио-, видео- или смешанные записи, упакованные с помощью кодеков Windows Media Audio (WMA) и Windows Media Video (WMV). Использование отдельного расширения позволяет установить на компьютер несколько проигрывателей и использовать часть из них для воспроизведения только звуковых и видеофайлов с расширением .wmw.
Advanced Stream Redirector (.asx)
Файлы в формате Advanced Stream Redirector (ASX), также называемые метафайлами Windows Media, являются текстовыми файлами, содержащими информацию о потоке и его представлении. Файлы ASX используются для создания списков воспроизведения и хранения информации о представлении элементов списка.
Метафайлы Windows Media основываются на синтаксисе XML и используют кодировку ANSI или UNICODE (UTF-8). Они состоят из множества элементов, их тегов и атрибутов. Каждый элемент в метафайле Windows Media определяет отдельный параметр или действие проигрывателя Windows Media.
Файлы ASX могут ссылаться на файлы любого формата, поддерживаемого проигрывателем Windows Media.
Дополнительные сведения о метафайлах Windows Media см. на следующем веб-сайте Microsoft:
Метафвйлы Windows Media
Windows Media Audio Redirector (.wax)
Файлы Redirector Windows Media Audio (.wax) — это метафайлы Windows Media, ссылающиеся на файлы Windows Media Audio (.wma).
Windows Media Video Redirector (.wvx)
Файлы Redirector Windows Media (.wvx) — это метафайлы Windows Media, ссылающиеся на файлы Windows Media Video (.wmv)
Windows Media Redirector (.wmx)
Данный формат файлов поддерживается следующими версиями проигрывателя Windows Media. Файлы Redirector Windows Media (.wmx) — это метафайлы Windows Media, ссылающиеся на файлы Windows Media Audio (.wma), Windows Media Video (WMV) или на те и другие.
Метафайлы Windows Media Playlist (.wpl)
Файлы в формате Windows Media Player Playlist (WPL) — это клиентская часть списков воспроизведения, записанных в специальном формате. Данный формат файлов появился в проигрывателе Windows Media 9. В отличие от форматов ASX и M3U, формат WPL позволяет создавать динамические списки воспроизведения. В проигрывателе Windows Media 9 в режиме автоматического формирования списка воспроизведения используется формат WPL. Формат .wpl — это формат файла по умолчанию, используемый для плейлистов в проигрывателе Windows Media 9.
В Microsoft Windows XP Media Center Edition корпорация Microsoft представила формат файла *.dvr-ms для хранения записанных телевизионных материалов. Файлы DVR-MS позволяют использовать такие возможности программы Personal Video Recorder (PVR), как воспроизведение с задержкой, включение функции живой паузы, одновременная запись и воспроизведение. Видеозаписи, содержащиеся в файлах DVR-MS, представляют собой видеопоток стандарта MPEG-2, а аудиозаписи — аудиопоток стандарта MPEG-1 Layer II.
Для воспроизведения незащищенных файлов формата DVR-MS на компьютере под управлением Windows XP должны быть установлены следующие компоненты.
-
Операционная система Windows XP с пакетом обновления 1 (SP1) или более поздней версии.
-
Обновление,
Дополнительные сведения см. в следующей статье базы знаний Майкрософт:810243 Поддержка воспроизведения DirectShow для файлов, записанных с помощью Windows XP Media Center Edition
-
Декодер DVD, совместимый с Windows XP.
Дополнительные сведения о файлах формата *.dvr-ms см. на веб-сайте Microsoft:
О формате файла dvr-ms
Пакеты Windows Media Download (WMD) объединяют обложки проигрывателя Windows Media, списки воспроизведения и мультимедийные данные в единый загружаемый файл с расширением WMD. Например, пакет WMD может включать несколько клипов с рекламными вставками и ссылками на веб-узлы распространителей музыкальных произведений.
Чтобы загрузить с веб-узла пакет WMD, необходимо щелкнуть ссылку на требуемый пакет. После загрузки пакета на компьютер проигрыватель Windows Media автоматически извлекает содержащиеся в пакете файлы, списки воспроизведения и мультимедийные данные, отображает обложку в
окне Сейчас играет проигрывателя Windows Media (в полноэкранном режиме) и затем воспроизводит первый элемент в списке воспроизведения. Дополнительные сведения о файлах .wmd см. на веб-сайте Microsoft:
Создание пакета скачивания Windows Media (не рекомендуется)
Формат Audio Video Interleave (AVI) является частным случаем формата Resource Interchange File Format (RIFF). Формат AVI разработан корпорацией Майкрософт. Формат AVI является наиболее распространенным форматом представления видео- и звуковых данных для компьютера.
Если на компьютере установлены соответствующие кодеки, то, используя проигрыватель Windows Media, можно воспроизводить видео- и аудио- записи, сжатые с помощью этих кодеков и сохраненные в файле AVI. В файлах AVI часто используются следующие видеокодеки.
-
Кодек DivX.
Дополнительные сведения см. на следующем веб-сайте DivX:
DivX
-
Кодек Cinepak.
Дополнительные сведения см. на следующем веб-сайте Cinepak:
Cinepak
-
Кодек Indeo.
Дополнительные сведения см. на следующем веб-сайте Ligos:
Ligos Corporation
-
Кодек DV.
-
Кодек MJPEG.
-
Кодек несжатых данных RGB или YUY2.
В файлах AVI часто используются следующие аудиокодеки:
-
Кодек MP3.
-
Кодек MS ADPCM (Microsoft Adaptive Differential Pulse Code Modulation).
-
Кодек PCM (Uncompressed Pulse Code Modulation).
Стандарты Moving Picture Experts Group (MPEG) разработаны компанией Moving Picture Experts Group. Это развивающийся набор стандартов сжатия аудио- и видеоданных.
MPEG-1 (.mpeg, .mpg, .m1v)
Данный стандарт позволяет кодировать видеоданные со скоростью передачи около 1,5 миллиона бит в секунду (bps). Этот формат был разработан специально для использования на компакт-дисках форматов Video-CD и CD-i. Большинство реализаций стандарта MPEG-1 обеспечивают воспроизведение с разрешением 352×240 точек и скоростью 30 кадров в секунду (fps). При использовании этого стандарта получено изображение по качеству несколько хуже, чем получаемое с помощью обычного видеомагнитофона.
Как правило, файл с расширением M1V — это поток в стандарте MPEG-1, содержащий только видеоданные. Файлы с расширением MPG или MPEG являются, как правило, потоками в формате MPEG-1, содержащими видеоданные в формате MPEG-1 и аудиоданные в формате MPEG-1 Layer II (MP2).
Расширения MPG и MPEG также часто используются потоками MPEG-2, содержащими видеоданные, упакованные по стандарту MPEG-2. Поскольку операционные системы Windows содержат декодер только для видеоданных формата MPEG-1, то для воспроизведения потоков в формате MPEG-2 с помощью проигрывателя Windows Media необходим дополнительный декодер данных в формате MPEG-2 (также называемый декодером DVD). Дополнительную информацию о наборах декодеров для DVD можно найти на сайте Microsoft:
Загрузки для Windows
MPEG Audio Layer III (.mp3)
Данный стандарт также разработан группой MPEG. Он представляет собой технологию сжатия звуковых данных, являющуюся частью спецификаций MPEG-1 и MPEG-2. Институт Fraunhofer разработал MP3 в Германии в 1991 году. MP3 использует перцептивное аудиокодирование для сжатия CD-звука практически с такой же точностью воспроизведения звука.
MPEG Audio Layer II (.mp2, .mpa)
Стандарт MPEG Audio Layer II был разработан как часть стандарта MPEG-1 и доработан при разработке стандарта MPEG-2.
M3U (.m3u)
Файл с расширением M3U — это список воспроизведения, ссылающийся на файлы с расширением MP3 и хранящий дополнительные метаданные для элементов списка.
Формат Musical Instrument Digital Interface (MIDI) — это стандартный протокол обмена информацией между музыкальными инструментами, синтезаторами и компьютерами. Он определяет коды таких событий, как начало воспроизведения ноты, ее высоту, длительность звучания, громкость и прочие атрибуты. Это также определяет коды для различных кнопок, шкал и педалей, используемых на синтезаторах.
Данный формат был разработан компанией Apple Computer. Этот формат можно использовать для хранения высококачественных аудио сэмплов и информации о музыкальных инструментах.
Звуковые файлы Unix Audio (AU) создаются операционной системой UNIX.
Файлы с расширением SND — это звуковые файлы в формате, используемом компьютерами Sun, NeXt и Silicon Graphics. Файл обычно содержит необработанные звуковые данные, сопровождаемыми текстовым идентификатором.
Файлы в формате Wave Form Audio (WAV) используются операционными системами Windows для хранения звуков путем сохранения формы сигнала. Чтобы с помощью импульсно-кодовой модуляции записать одну минуту звучания, требуется от 644 КБ до 27 МБ дискового пространства. Этот объем зависит от частоты дискретизации, типа звука (моно или стерео) и разрядности данных при оцифровке.
Подобно форматам AVI и ASF, файл формата WAV является просто хранилищем. Если на компьютере установлены соответствующие кодеки, то, используя проигрыватель Windows Media, можно воспроизводить аудиозаписи, сжатые с помощью этих кодеков и сохраненные в файле WAV. К числу наиболее распространенных аудиокодеков, используемых в файлах WAV, относятся кодек MS ADPCM (Microsoft Adaptive Differential Pulse Code Modulation) и кодек несжатой модуляции PCM (Pulse Code Modulation).
Файлы CD Audio (CDA) — это звуковые файлы, хранящиеся на компакт-диске. Они могут быть проиграны только с компакт-диска. Поэтому образец такого файла не включен в данную статью. При возникновении проблем с воспроизведением файла CDA следует попытаться воспроизвести другой файл CDA с этого же компакт-диска или файл CDA с другого компакт-диска. Файлы CDA представляют собой звуковые дорожки компакт-диска и не содержат фактических значений импульсно-кодовой модуляции. Файл нельзя воспроизвести, скопировав файл .cda с компакт-диска на жесткий диск.
Файлы Indeo Video Files (IVF) — это видеофайлы, упакованные с помощью кодека, разработанного компанией Ligos Corporation. Стандарты Indeo часто обновляются. Чтобы воспроизводить файлы, сжатые с помощью этого кодека, следует убедиться в наличии последней версии пакета Indeo. Для этого необходимо обратиться в компанию Ligos Corporation. Для этого посетите следующий веб-сайт Ligos:
Ligos Corporation
Чтобы воспроизвести файл .ivf, загрузите файл на жесткий диск перед его воспроизведением. Для этого выполните следующие действия:
-
Щелкните правой кнопкой ссылку на требуемый файл .ivf и выберите
Сохранить объект как. -
Укажите, где на жестком диске должен быть сохранен файл.
-
Дважды щелкните файл, чтобы воспроизвести его.
Дополнительные сведения см. в следующей статье базы знаний Майкрософт:
281919 При воспроизведении файла IVF появляется сообщение об ошибке «Неизвестная ошибка»
Файл описания обложки проигрывателя Windows Media (WMS) — это документ в формате XML, описывающий элементы, из которых состоит обложка, их назначение и взаимосвязь. Разработчик сценариев создает файл описания обложки (WMS) и связанные с ним файлы сценариев JScript (JS), объединяющие элементы и добавляющие возможности к обложке.
Файл с расширением WMZ — это архив формата Zip, содержащий файл описания обложки проигрывателя Windows Media, связанные файлы Jscript и требуемые графические файлы.
Формат QuickTime был разработан компанией Apple Computer для создания, редактирования, просмотра и публикации мультимедийных файлов. Файлы в формате QuickTime могут содержать видео- и аудиозаписи, анимацию, графические изображения, трехмерные объекты и объекты виртуальной реальности. Проигрыватель Windows Media может воспроизводить только файлы в формате QuickTime версии 2.0 или более ранней. Более поздние версии данного формата требуют наличия проигрывателя Apple QuickTime. Дополнительные сведения см. на следующем веб-сайте Apple:
Поддержка QuickTime Player
.m4a (только аудио) часто сжимается с использованием кодирования AAC (с потерями), но также может быть в формате Apple Lossless (без потерь).
Формат MPEG-4 является стандартом Международной организации по стандартизации (ISO), описывающим различные аспекты представления мультимедийных данных, включая их создание, сжатие и передачу. При этом, хотя сжатие и конейнеризация данных в файле описываются двумя различными независимыми частями стандарта MPEG-4, многие неправильно думают, что они взаимозаменяемы. Таким образом, можно лишь частично реализовать требования стандарта и при этом остаться в него рамках.
В соответствии со стандартом MPEG-4, файлы формата MPEG-4 содержат видеоданные, сжатые с помощью методов MPEG-4, и звуковые данные, сжатые с помощью метода Advanced Audio Coding (AAC). Как правило, эти файлы имеют расширение MP4. Проигрыватель Windows Media не поддерживает воспроизведение таких файлов. Для воспроизведения файлов MP4 с помощью проигрывателя Windows Media необходимо установить декодер MPEG-4, совместимый с DirectShow. Такие декодеры включены в пакеты Ligos LSX-MPEG Player и EnvivioTV.
Дополнительные сведения о проигрывателе Ligos LSX-MPEG см. на следующем сайте Ligos:
Ligos Corporation
Дополнительные сведения об EnvivioTV см. на следующем сайте Envivio:
Портфолио Ericsson
Корпорация Microsoft решила использовать сжатие видео стандарта MPEG-4. и в настоящее время выпускает следующие кодеки на основе MPEG-4.
-
Microsoft MPEG-4 версии 1
-
Microsoft MPEG-4 версии 2
-
Microsoft MPEG-4 версии 3
-
ISO MPEG-4 версии 1
С помощью программ Windows Media Tools и Windows Media Encoder можно сохранять видеоданные формата MPEG-4 в файле формата ASF. В дальнейшем можно воспроизводить эти файлы с помощью проигрывателя Windows Media. Дополнительные сведения о Microsoft и поддержке MPEG-4 см. на сайте корпорации Microsoft:
Получить Windows Media Player
Формат файла m4v — это формат видеофайла, который очень близок к формату MP4. Он был разработан Apple. Среди отличий — необязательная защита копии с помощью компонента DRM корпорации Apple и обработка звуковых данных AC3 (Dolby Digital), которые не стандартизованы для контейнера MP4.
MP4V — это видеофайл MPEG-4.
3GP (формат файла 3GPP) — это формат мультимедийного контейнера, разработанный компанией Third Generation Partnership Project (3GPP) для мультимедийных служб 3G UMTS. Он используется на мобильных телефонах 3G, а также может воспроизводиться на некоторых телефонах 2G и 4G.
3G2 (формат файла 3GPP2) — это формат мультимедийного контейнера, разработанный компанией 3GPP2 для мультимедийных служб 3G CDMA2000. Он очень похож на формат файла 3GP, однако имеет немного другие расширения и ограничения.
Тип файла .3gp2 связан главным образом с «3GPP2» .
Advanced Audio Coding (.aac) — это стандартизированная схема кодирования цифрового звука с потерей сжатия. Разработанный для замены формата MP3, формат AAC, как правило, обеспечивает лучшее качество звука при одинаковой скорости потока по сравнению с его предшественником.
Потоковая передача аудиоданных(adts) используется, если данные передаются в потоке передачи MPEG-2, состоящем из серии кадров. У каждого кадра есть заголовок с аудио информацией AAC.
m2ts — это расширение файла, используемое для формата файла контейнера Blu-ray Disc Audio-Video (BDAV) MPEG-2 Transport Stream (M2TS). Он предназначен для мультиплексирования потоков аудио-, видео- и других данных. Формат основан на контейнере потоковой передачи данных MPEG-2. Обычно этот формат контейнера используется для передачи видео высокой четкости на диске Blu-ray и видеозаписи AVCHD.
Дополнительная информация
В этой статье упомянуты программные продукты независимых производителей. Корпорация Майкрософт не предоставляет каких-либо гарантий, подразумеваемых или иных, относительно производительности и надежности этих продуктов.
Нужна дополнительная помощь?
This article is about the original version used prior to Windows 8. For the successor version, see Media Player (Windows 11).

Windows Media Player 12 Legacy running on Windows 11 2022 Update |
|
| Developer(s) | Microsoft |
|---|---|
| Stable release | 12.0.22621.457 (September 20, 2022; 4 months ago) [±] |
| Preview release | 12.0.25120.1000 (May 18, 2022; 8 months ago) [±] |
| Operating system |
|
| Included with |
|
| Predecessor | ActiveMovie Control, CD Player, DVD Player (Win32 version) |
| Successor | Microsoft Movies & TV, Groove Music, Media Player (Windows 11) |
| Type | Media player |
| Website | support.microsoft.com/en-gb/windows/windows-media-player-d10303a5-896c-2ce2-53d4-5bd5b9fd888b |
Windows Media Player (WMP) is the first media player and media library application that was developed by Microsoft for playing audio, video and viewing images on personal computers running the Microsoft Windows operating system, as well as on Pocket PC and Windows Mobile-based devices. Editions of Windows Media Player were also released for classic Mac OS, Mac OS X, and Solaris but development of these has since been discontinued.
Windows Media Player was eventually replaced in Windows 8 with Groove Music. Groove Music persisted in Windows 8.1 and Windows 10, before being replaced in turn with the Media Player in Windows 11.
In addition to being a media player, the application has the ability to rip audio file from and copy to compact discs, burn recordable discs in Audio CD format or as data discs with playlists such as an MP3 CD, synchronize content with a digital audio player (MP3 player) or other mobile devices, and enable users to purchase or rent music from a number of online music stores.
Windows Media Player 11 was made available for Windows XP and included in Windows Vista and Windows Server 2008. The default file formats are Windows Media Video (WMV), Windows Media Audio (WMA), and Advanced Systems Format (ASF), and its own XML based playlist format called Windows Playlist (WPL). The player is also able to utilize a digital rights management service in the form of Windows Media DRM.
Windows Media Player 12 is the most recent version of Windows Media Player prior to Windows 11. It was released on October 22, 2009, along with Windows 7[b] and has not been made available for previous versions of Windows nor has it been updated since for Windows 8, Windows 8.1, Windows 10, and Windows 11.[2][3] Windows 8 and later instead use Groove Music (for audio) and Microsoft Movies & TV (for video) as the default playback applications for most media; As of October 2021, Windows Media Player is still included as a Windows component. Windows RT does not run Windows Media Player.
On November 16, 2021, Microsoft announced that it would replace Groove Music with the new Media Player application, though the legacy Windows Media Player will continue to be optionally available with Windows 11.[4]
History[edit]
Media Player 5 running in Windows 2000.
The first version of Windows Media Player appeared in 1991, when Windows 3.0 with Multimedia Extensions was released.[5] Originally called Media Player, this component was included with «Multimedia PC»-compatible machines but not available for retail sale. It was capable of playing .mmm animation files, and could be extended to support other formats.[6] It used MCI to handle media files. Being a component of Windows, Media Player shows the same version number as that of the version Windows with which it was included.
WMP running in Windows 8.
Microsoft continually produced new programs to play media files. In November of the following year, Video for Windows was introduced with the ability to play digital video files in an AVI container format,[7] with codec support for RLE and Video1, and support for playing uncompressed files. Indeo 3.2 was added in a later release. Video for Windows was first available as a free add-on to Windows 3.1, and later integrated into Windows 95 and Windows NT 4.0. In 1995, Microsoft released ActiveMovie with DirectX Media SDK. ActiveMovie incorporates a new way of dealing with media files, and adds support for streaming media (which the original Media Player could not handle). In 1996, ActiveMovie was renamed DirectShow.[8] However, Media Player continued to come with Windows until Windows XP, in which it was officially renamed Windows Media Player v5.1.[9] («v5.1» is the version number of Windows XP).
In 1999, Windows Media Player’s versioning broke away from that of Windows itself. Windows Media Player 6.4 came as an out-of-band update for Windows 95-98 and Windows NT 4.0 that co-existed with Media Player and became a built-in component of Windows 2000, Windows ME, and Windows XP with an mplayer2.exe stub allowing to use this built-in instead of newer versions.[10] Windows Media Player 7.0 and its successors also came in the same fashion, replacing each other but leaving Media Player and Windows Media Player 6.4 intact. Windows XP is the only operating system to have three different versions of Windows Media Player (v5.1, v6.4, and v8) side by side. All versions branded Windows Media Player (instead of simply Media Player) support DirectShow codecs. Windows Media Player version 7 was a large revamp, with a new user interface, visualizations and increased functionality. Windows Vista, however, dropped older versions of Windows Media Player in favor of v11, which included the removal of the Windows Media Source Filter (DirectShow codec).
In 2004, Microsoft launched digital music store MSN Music for new Windows Media Player 10 to compete with Apple iTunes.[11][12]
However, MSN Music was discontinued already in 2006 with the launch of Zune music players.[13]
Beginning with Windows Vista, Windows Media Player supports the Media Foundation framework besides DirectShow; as such it plays certain types of media using Media Foundation as well as some types of media using DirectShow.[14] Windows Media Player 12 was released with Windows 7. It included support for more media formats and added new features. With Windows 8, however, the player did not receive an upgrade.
On April 16, 2012, Microsoft announced that Windows Media Player would not be included in Windows RT, the line of Windows designed to run on ARM-based devices.[15]
Windows 11[edit]
A different app called Media Player is the successor to Groove Music for Windows 10 (previously Xbox Music) and Windows Media Player. Media Player started to be offered to all Windows 11 users on February 15, 2022.[16]
The new Media Player can also play video, as part of Groove’s rebranding from a music streaming service to a media player.[17] Other changes include the album cover view being in fullscreen, and a refresh to the mini player.[18] Accessibility has also been optimized, with some improved keyboard shortcuts and hotkey support for keyboard users and with other assistive technologies.[19]
Features[edit]
Core playback and library functions[edit]
Windows Media Player supports playback of audio, video and pictures, along with fast forward, reverse, file markers (if present) and variable playback speed (seek & time compression/dilation introduced in WMP 9 Series). It supports local playback, streaming playback with multicast streams and progressive downloads. Items in a playlist can be skipped over temporarily at playback time without removing them from the playlist. Full keyboard-based operation is possible in the player.
Windows Media Player supports full media management, via the integrated media library introduced first in version 7, which offers cataloguing and searching of media and viewing media metadata. Media can be arranged according to album, artist, genre, date et al. Windows Media Player 9 Series introduced Quick Access Panel to browse and navigate the entire library through a menu. The Quick Access Panel was also added to the mini mode in version 10 but was entirely removed in version 11. WMP 9 Series also introduced ratings and Auto Ratings. Windows Media Player 10 introduced support for aggregating pictures, Recorded TV shows, and other media into the library. A fully featured tag editor was featured in versions 9-11 of WMP, called the Advanced Tag Editor. However, the feature was removed in Windows Media Player 12. Since WMP 9 Series, the player features dynamically updated Auto Playlists based on criteria. Auto Playlists are updated every time users open them. WMP 9 Series and later also supports Auto Ratings which automatically assigns ratings based on the number of times a song is played. Pre-populated auto playlists are included in Windows Media Player 9 Series. Custom Auto Playlists can be created only on Windows XP and later.
In Windows Media Player 11, the Quick Access Panel was removed and replaced with an Explorer-style navigation pane on the left which can be customized for each library to show the user selected media or metadata categories, with contents appearing on the right, in a graphical manner with thumbnails featuring album art or other art depicting the item. Missing album art can be added directly to the placeholders in the Library itself (though the program re-renders all album art imported this way into 1×1 pixel ratio, 200×200 resolution JPEGs). There are separate Tiles, Icons, Details or Extended Tiles views for Music, Pictures, Video and Recorded TV which can be set individually from the navigation bar. Entries for Pictures and Video show their thumbnails. Version 11 also introduced the ability to search and display results on-the-fly as characters are being entered, without waiting for Enter key to be hit. Incremental search results are refined based on further characters that are typed. Stacking allows graphical representations of how many albums there are in a specific category or folder. The pile appears larger as the category contains more albums. The List pane includes an option to prompt the user to remove items skipped in a playlist upon save or skip them only during playback.
Visualizations[edit]
Windows Media Player 11 running in mini mode (in Windows XP MCE) showing the «Bars and Waves» visualization
While playing music, Windows Media Player can show visualizations. The current three visualizations are Alchemy, which was first introduced in version 9, Bars and Waves, which has been used since version 7, and Battery, introduced version 8. «Musical Colors» was removed starting with version 9, but is retained if Windows Media Player was upgraded from version 7 or 8. Version 11 and above refrains from having the former «Ambience,” «Particle,” «Plenoptic,” and «Spikes» visualizations. The «Battery» visualization was similarly removed in later editions of version 12. The reason for their removal was that the visualizations do not support full screen controls (either the visualization gets shifted to the left while there is a thick black bar to the right side of the screen, that there are no full screen controls, or that the visualization have DXE Problems). More visualizations such as «BlazingColors,” «ColorCubes,” «Softie the Snowman,» and «Yule Log» used to be downloadable however, the downloads from Microsoft’s website have mostly been taken down and it’s available on the WMP Goodies site.
Format support[edit]
The player includes intrinsic support for Windows Media codecs and also WAV and MP3 media formats. On Windows XP and above with WMP 9 Series and later, the Windows Media Audio Professional codec is included which supports multichannel audio at up to 24-bit 192 kHz resolution. Windows Media Player 11 includes the Windows Media Format 11 runtime which adds low bitrate support (below 128 kbit/s for WMA Pro), support for ripping music to WMA Pro 10 and updates the original WMA to version 9.2.[citation needed]
Support for any media codec and container format can be added using specific DirectShow filters or Media Foundation codecs (Media Foundation codecs only in Windows Vista and later). The player will not play MP3 files that contain compressed ID3 headers («tags»), trying to do so results in a «The input media file is invalid» error message. MP3 playback support was built-in beginning with version 6.1 and audio CD playback was natively supported with version 7.[citation needed]
DVD playback features minus the necessary decoders were integrated into Windows Media Player 8 for Windows XP. The player activates DVD and Blu-ray playback functionality with support for menus, titles and chapters, parental controls and audio track language selection if compatible decoders are installed. MPEG-2 and Dolby Digital (AC-3) decoders were included beginning with Windows Media Player 11 on Windows Vista (Home Premium and Ultimate editions only) and Windows 7 (Home Premium, Ultimate, or Enterprise editions) to allow DVD playback without additional software. However, the decoders were subsequently removed in Windows 8 and Windows 10 due to licensing costs.[20]
Windows Media Player 12 adds native support for H.264 and MPEG-4 Part 2 video formats, ALAC, AAC audio[21] and 3GP[clarification needed got no codec available for 3GP], MP4 and MOV container formats.[22] Windows Media Player 12 is also able to play AVCHD formats (.M2TS and .mts).[23]
As of Windows 10 version 1507, Windows Media Player 12 can play FLAC, HEVC, and SubRip subtitle, and Matroska container formats.[24] Although the WebM file type is not officially associated with Windows Media Player 12 (the default player is Microsoft Movies & TV), playback of VP9 video in WebM container is possible on Windows 10 version 1809 and later.[25]
Windows Media Player Mobile[edit]
Windows Media Player Mobile 10 on Windows Mobile 6.5 supports MP3, ASF, WMA, and WMV using WMV or MPEG-4 codecs.[26]
Disc burning, ripping, and playback[edit]
Windows Media Player features integrated Audio CD-burning support since version 7 as well as data CD burning support since Windows Media Player 9 Series on Windows XP and later. Data CDs can have any of the media formats supported by the player. While burning Data CDs, the media can, optionally, be transcoded into WMA format and playlists can be added to the CD as well. Starting with WMP 9 Series, audio CDs can be burnt with volume leveling.
Audio CDs can be ripped as WMA or WMA 10 Pro (WMA 10 Pro in WMP 11 and later) at 48, 64, 96, 128, 160, and 192 kbit/s, WMA lossless (470 to 940 kbit/s) (9 Series on XP and later), WMA variable bitrate (from 40 to 75 kbit/s up to 240-355 kbit/s), MP3 at 128, 192, 256, and 320 kbit/s, or uncompressed WAV (WAV ripping in WMP 11 and later). Since WMP 9 Series, 20 bit high-resolution CDs (HDCDs) are also supported, if capable audio hardware is present. Audio can be ripped using error correction and ripped audio can be protected with Windows Media DRM. Ripping to MP3 is supported only in Windows Media Player 8 for Windows XP and later if a compatible MP3 encoder is installed. Windows Media Player 10 included the Fraunhofer MP3 Professional encoder. Information on CDs such as album name, artist and track listings can optionally be automatically downloaded from the online Windows Media database when the CD is inserted. Version 11 added support for ripping audio CDs to WAV and WMA 10 Pro formats. With their 2015 implementation in Windows 10, Version 12 also added lossless FLAC and ALAC formats for ripping and playback. For burning, version 11 shows a graphical bar indicating how much space will be used on the disc and introduced Disc spanning which splits a burn list onto multiple discs in case the content does not fit on one disc.
Portable device sync[edit]
Windows Media Player allows the user to connect, share and sync data with portable handheld devices and game consoles since version 7. Media can be optionally transcoded to a format better suited for the target device, automatically, when synchronizing. When deleting playlists from devices, Windows Media Player can automatically remove their contents. Devices can be formatted using Windows Media Player 9 Series and later. Version 10 and later support the Media Transfer Protocol and Auto Sync. Auto Sync allows users to specify criteria such as recently added music or highest rated songs, by which media will be automatically synchronized with the portable device and other advanced features like setting the clock on the portable device automatically, communicating with the device to retrieve the user’s preferences. Windows Media Player 10 also introduced the UMDF-based Windows Portable Devices API.
Version 11 has improved synchronization features for loading content onto PlaysForSure-compatible portable players. WMP 11 supports reverse-synchronization, by which media present on the portable device can be replicated back to the PC. Shuffle Sync can be used to randomize content synced with the portable device, Multi PC Sync to synchronize portable device content across multiple PCs and Guest Sync to synchronize different content from multiple PCs with the portable device. Portable devices appear in the navigation pane of the library where their content can be browsed and searched.
Windows Media Player’s ‘Sync’ function has options that allow it to be set to automatically down-convert (transcode) high bit-rate song files to a lower bit-rate. This down-conversion function is switched on by default. This is useful for providing low bit-rate files to those portable devices that need them, and to save space on portable devices with smaller storage capacities. For high bit-rate capable devices with sufficient storage capabilities, the down conversion process can be omitted.
In versions 11 (2006) and 12 (2009), the Quality settings that the user has selected in the Windows Media Player settings for Sync, for that specific portable device, are used to control the quality (bit-rate) of files that are copied to the portable device. Leaving the Quality settings to Automatic will often result in 192kbs files being copied to the portable device. Manual settings can also be made. 192kbs is the highest quality down-conversion bit-rate that can be manually selected when the Sync function’s down-conversion function is turned on. Lower bit-rates can also be selected.
For portable devices that can handle high bit-rate files, the best quality files are obtained by leaving the down-conversion process switched off (unchecked) for that specific device. In Windows Media Player Version 11, switching off the down-conversion function is done in the Quality tab of the Advanced Options of the Sync settings for the device. In Windows Media Player Version 12, switching off the down-conversion function is done in the Quality tab of the Properties for the device in the Select Settings for the device in the Sync Options menu.
When set up in such a way, Windows Media Player’s ‘Sync’ function can be used to sync unchanged high bit-rate song files to suitable portable devices (i.e. those capable of using file formats such as WMA Lossless, mp3-360kbs, etc.). For example, some users have created large song libraries on their PCs containing .wma formatted song files using the high bit-rate WMA Lossless (WMA-LL) protocol, or using other high bit-rate song file formats. The WMA-LL protocol is selectable in Windows Media Player as an option when ripping songs from CDs. The resulting bit-rates seen on ripped WMA-LL files are often 3 to 6 times higher than 192kbs, and can typically fall anywhere in the range of 600kbs to 1200kbs, depending on the quality of the source file that was present on the CD in the first place. The sound quality is much improved over the default rate, although the file size is larger.
At the time that Versions 11 and 12 were released, the capabilities and capacities of portable devices typically required down-conversion of the bit-rates of the files placed on the portable devices. Thus, Sync down-conversion was turned on by default. This was to ensure playability of the files and to ensure that the file sizes were small enough to efficiently fit a reasonably large selection of songs on the portable device.
In recent years (circa 2012), portable devices became available that could natively play these Windows Media Player produced high bit-rate WMA-LL files (and others), and that have storage capacities suitable for large collections of high bit-rate song files. This made it much more practicable and desirable to use software programs such as Windows Media Player to synchronize previously PC-bound libraries of high bit-rate songs to these new portable devices.
Enhanced playback features[edit]
Windows Media Player features universal brightness, contrast, saturation and hue adjustments and pixel aspect ratio for supported video formats. It also includes a 10-band graphic equalizer with presets and SRS WOW audio post-processing system. Windows Media Player can also have attached audio and video DSP plug-ins which process the output audio or video data. Video Smoothing was introduced in WMP 9 Series (Windows XP and later only) which upscales frame-rate by interpolating added frames, in effect giving a smoother playback on low-framerate videos. The player supports subtitles and closed-captioning for local media, video on demand streaming or live streaming scenarios. Typically Windows Media captions support the SAMI file format but can also carry embedded closed caption data.
The player can use video overlays or VMR (Video Mixing Renderer) surfaces, if the video card supports them. In Windows XP, it uses VMR7 by default, but can also be made to use the more advanced YUV mixing mode by enabling the «Use high quality mode» option in Advanced Performance settings. This turns on deinterlacing, scaling and improved color accuracy.[27] WMP 9 Series introduced native playback for deinterlacing for TV output. Version 9 introduced DXVA accelerated playback. Version 11 introduced improved support for DirectX accelerated decoding of WMV video (DXVA decoding). Up to version 11, it supported static lyrics and «Synchronized Lyrics,” by which different lines of lyrics can be time-stamped, so that they display only at those times. Synchronized Lyrics also were accessible through the Advanced Tag Editor which was removed in version 12.
Since Windows Media Player 9 Series, the player supports crossfading, audio dynamic range (Quiet Mode) for WMA Pro and WMA Lossless, and auto volume leveling for certain media which includes volume level/gain information such as MP3 or Windows Media. The player also supports extensive configurable privacy and security settings.
Shell integration[edit]
The player has Windows Explorer shell integration to add files and playlist to the Now Playing pane and other playlists can be controlled from the Windows Explorer shell itself, via right-click menu. The My Music folder also includes a separate My Playlists folder where playlists are maintained. When the player is closed and reopened, simply clicking the play button restores the last playlist even if it was not saved. Starting with Windows Media Player 10, the playlist pane is also visible from the Library view. AutoPlay handlers in Windows expose various Windows Media Player tasks.
Windows Media Player 11 running in mini mode in Windows Vista and Windows XP respectively. Notice the difference in the logo.
Up to version 11, it featured a taskbar-mounted Mini mode in which the most common media control buttons are presented as a toolbar on the Windows taskbar. Flyout windows can display media information, the active visualization or the video being played back. Mini-mode was introduced as a shell player powertoy for Windows Media Player 8 in Windows XP and integrated later into WMP 9 Series. Mini-mode has been removed in Windows Media Player 12 in favor of controls in the taskbar’s interactive thumbnail preview which lacks volume control, a progress bar and information displayed whenever a new song is played.
The user interface has been redesigned in Windows Media Player 12 such that the Now Playing view plays media in a separate minimalist window with floating playback controls, and also gives access to the current playlist, visualizations, and enhancements.[21] Enhancements are housed in individual undocked windows. The library view includes the rest of the media management functions. It also can preview songs from the library when users hover over the media file and click the Preview button.[21] Windows Media Player 12 can play unprotected songs from the iTunes library. The taskbar-integrated Mini-player has been replaced with controls in the taskbar’s interactive thumbnail preview (called the Thumbnail Toolbar),[28] albeit minus the volume control function, track and album information shown whenever a new song is played and the progress bar. The taskbar icon also supports jump lists introduced in Windows 7.
The thumbnail viewer of Windows Media Player 12 in Windows 7 Home Premium
Extensibility[edit]
The player has had skinning support since Windows Media Player (WMP) 7 and includes a color chooser since the WMP 9 Series. Not all functions are usually exposed in skin mode. Windows Media Player 10 allows setting the video border color. Color chooser has been removed in WMP 12. It supports visualizations and Info Center View (Info Center View in WMP 9 Series and later) which displays media metadata fetched from the internet. Full screen visualizations are supported in WMP 9 Series and later. It supports Background plug-ins, window plug-ins and Now Playing plug-ins to control media playback besides DSP and renderer plug-ins. Plug-in support was introduced in WMP 9 Series.
Online features[edit]
The player integrates web-browsing support to browse online music stores, shop for music and tune to internet radio stations since version 7. It provides an embeddable ActiveX control for Internet Explorer so that developers can play Windows Media on web pages. Windows Media Player 10 and later feature integration with a large number of online music stores and selecting a music store switches the Info Center view, radio and other online features to use services from that store. Purchased music from a particular store appears in a separate library node under the respective category.
Media streaming[edit]
Previously, Microsoft had released Windows Media Connect for Windows XP to stream media content with its built-in UPnP media server. With version 11 of Windows Media Player, Media Sharing was integrated and allows content (Music, Pictures, Video) to be streamed to and from Universal Plug and Play (UPnP) AV enabled devices such as the PS3, Xbox 360, and Roku SoundBridge. This includes DRM protected PlaysForSure content. WMP 11 on Windows Vista can also act as a client to connect to remote media libraries using this feature; this is not available on the Windows XP version.
With version 12, media streaming was further improved. While previous versions streamed media to UPnP compliant devices (Digital Media Server role) and could play media by fetching it from a network share (Digital Media Player role),[29] Windows Media Player 12 can access media from the shared media libraries on the network or HomeGroup, stream media to DLNA 1.5 compliant devices and allows itself (once the remote control option is turned on) to be remotely controlled by Digital Media Controller devices which stream media (Digital Media Renderer role).[29] Similarly, the Play To feature once enabled for remote PCs, by turning on remote control of the player, allows compliant devices and computers to be discovered and controlled remotely from a computer running Windows Media Player 12 (Digital Media Controller role).[29] If the devices do not support the streamed format, Windows Media Player 12 transcodes the format on-the-fly. Media from a home network can also be streamed over the internet using an Online ID Provider service, which handles discovery of the computer’s IP address, authorization, security, connectivity and Quality of Service issues.[29]
Skin Mode[edit]
Windows Media Player also features skins. Currently, Windows Media Player has two default skins: «Corporate,” which was first introduced in version 8, and «Revert,” which first shipped with version 9. In versions 7 and 8, there were many unusual skins such as «Heart,” «Headspace,” «Canvas,” «Goo,” and «Atomic,” which were removed starting with version 9, but are retained if the player is upgraded, although some can still be downloaded from an archive of the Microsoft website.[30] In versions 7, 8, 9, and 10 there were many usual skins such as «9SeriesDefault,” «Atomic,” «Bluesky,” «Canvas,” «Classic,” «Compact,” «goo,” «Headspace,” «heart,” «iconic,” «Miniplayer,” «Optic,” «Pyrite,” «QuickSilver,” «Radio,” «Roundlet,” «Rusty,” «splat,” «Toothy,” «Windows Classic,” and «Windows XP,” which were removed starting with version 11. This Corporate skin is not deletable.
Security issues[edit]
Microsoft Windows Media Runtime in Windows 2000, Windows XP, Windows Vista and Windows Server contained a bug that permitted «remote code execution if a user opened a specially crafted media file». Such a file would allow the attacker to «then install programs; view, change, or delete data; or create new accounts with full user rights», if the account on which the file was played had administrator privileges.[31] The problem was addressed in a critical update issued on September 8, 2009.[32]
Other versions[edit]
Microsoft has also released versions of Windows Media Player for other platforms including Windows Mobile, classic Mac OS, Mac OS X, Palm-size PC, Handheld PC, and Solaris. Of these, only the Windows Mobile edition continues to be actively developed and supported by Microsoft. Version 1 of the Zune software was also based on Windows Media Player; later versions are not.
Windows Mobile[edit]
Windows Media Player 10.3 Mobile on a Windows Mobile Professional device
Windows Media Player for Pocket PC was first announced on January 6, 2000, and has been revised on a schedule roughly similar to that of the Windows version.[33] Currently known as «Media Player 10 Mobile,” this edition (released in October 2004) closely resembles the capabilities of the Windows version of WMP 10, including playlist capabilities, a media library, album art, WMA Lossless playback, support for DRM-protected media, video playback at 640×480 with stereo sound, and the same Energy Blue interface aesthetics also seen in Windows XP Media Center Edition 2005. It also supports synchronization with the desktop version of WMP 10, and additionally supports synchronizing and transcoding of recorded television shows from Media Center. Media Player 10 Mobile is not available as a download from Microsoft, distribution is done solely through OEM partners, and is typically included on devices based on Windows Mobile.
Windows Mobile 6 includes a copy of Windows Media Player 10 Mobile, but with a similar (but not quite identical) theme as Windows Media Player 11.
Mac OS X[edit]
Version 9 was the final version of Windows Media Player to be released for Mac OS X before development was canceled by Microsoft. It was developed by the Windows Media team at Microsoft instead of the Macintosh Business Unit and released in 2003. On release the application lacked many basic features that were found in other media players such as Apple’s iTunes and QuickTime.[citation needed] It also lacked support for many media formats that version 9 of the Windows counterpart supported on release 10 months earlier.
The Mac version supported only Windows Media encoded media (up to version 9) enclosed in the ASF format, lacking support for all other formats such as MP4, MPEG, and Microsoft’s own AVI format. On the user interface front, it did not prevent screensavers from running during playback, it did not support file drag-and-drop, nor did it support playlists. While Windows Media Player 9 had added support for some files that use the WMV9 codec (also known as the WMV3 codec by the FourCC), in other aspects it was seen as having degraded in features from previous versions.
On January 12, 2006, Microsoft announced it had ceased development of Windows Media Player for Mac. Microsoft now distributes a third-party plugin called WMV Player (produced and maintained by Flip4Mac) which allows some forms of Windows Media to be played within Apple’s QuickTime Player and other QuickTime-aware applications.[34]
European Commission case[edit]
In March 2004, the European Commission in the European Union Microsoft antitrust case fined Microsoft €497 million and ordered the company to provide a version of Windows without Windows Media Player, claiming Microsoft «broke European Union competition law by leveraging its near monopoly in the market for PC operating systems onto the markets for work group server operating systems and for media players.” The company has made available a compliant version of its flagship operating system under the negotiated name «Windows XP N,” though the product has not been very successful. Windows Vista, Windows 7 and Windows 8 are also available in «N» editions. However, it is possible to either install Windows Media Player (XP/Vista)[35] or the Media Restore Pack through Windows Update (Vista) to add the media player.
Release history[edit]
Prior to the release of Windows Media Player in Windows 98 Second Edition, separate programs, CD Player, Deluxe CD Player, DVD Player and Media Player, were included in old versions of Microsoft Windows for playback of media files.
| Version | Original release | Included with | Available for | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Microsoft Windows | ||||
| Media Player | February 15, 2022 | Windows 11 | — | |
| Windows Media Player 12 | July 22, 2009 | Windows 7 Windows 8 Windows 8.1 Windows 10 Windows 11 Windows Server 2008 R2 Windows Server 2012 Windows Server 2012 R2 Windows Server 2016 Windows Server 2019 Windows Server 2022 |
— | 
|
| Windows Media Player 11 | October 18, 2006 | Windows Vista Windows Server 2008 |
Windows XP (SP2+) Windows XP x64 Edition |
|
| Windows Media Player 10 | August 25, 2004 | Windows XP x64 Edition Windows XP Media Center Edition 2005 Windows Server 2003 (SP1+) |
Windows Server 2003 Windows XP[37] |
|
| Windows Media Player 9 Series | January 7, 2003[38] | Windows XP (SP2+) Windows Server 2003 (RTM) |
Windows XP Windows ME Windows 2000 Windows 98 SE[39] |
|
Windows Media Player for Windows XP (version  |
August 24, 2001 | Windows XP (RTM & SP1) | — | |
| Windows Media Player 7.1 | May 16, 2001 | Windows 2000 (SP2+) | Windows ME Windows 2000 Windows 98[39][40] |
|
| Windows Media Player 7.0 | June 19, 2000[41] | Windows ME | Windows 2000 Windows 98 Windows 95 |
|
| Windows Media Player 6.4[c] | September 15, 1999 | Windows 2000 Windows ME (hidden) Windows XP (hidden) Windows Server 2003 (hidden) Internet Explorer 5.01 Internet Explorer 5.5 Internet Explorer 6.0 |
Windows 98 Windows NT 4.0 Windows 95 |
|
| Windows Media Player 6.1 | March 1999 | Windows 98 SE Internet Explorer 5.0 |
Windows 98 Windows NT 4.0 Windows 95 |
|
| Microsoft Media Player 5.1 | 2001 | Windows XP (hidden) | — | |
| Media Player 5.0 | 1999 | Windows 2000 (hidden) | — | |
| Media Player 4.9 | 2000 | Windows ME (hidden) | — | |
| Media Player 4.1 | 1998 | Windows 98 Windows 98 SE (hidden) |
— | |
| Media Player 4.0 | 1995 | Windows 95 Windows NT 4.0 |
— | |
| Media Player 3.51 | 1995 | Windows NT 3.51 | — | |
| Media Player 3.5 | 1994 | Windows NT 3.5 | — | |
| Media Player 3.15 | 1992 | — | Windows 3.1 with Video for Windows | |
| Media Player 3.1 | 1992 | Windows 3.1 Windows NT 3.1 |
— | |
| Media Player 3.0 | 1991 | — | Windows 3.0 with Multimedia Extension | |
| Windows Mobile | ||||
| Windows Media Player 10.3 Mobile | February 12, 2007 (Windows Mobile 6) | Windows Mobile 6.1 Windows Mobile 6 |
Windows Mobile 5.0 | 
|
| Windows Media Player 10.2 Mobile | ? | Windows Mobile 5.0 | — | |
| Windows Media Player 10.1 Mobile | May 10, 2005 | Windows Mobile 5.0 | — | |
| Windows Media Player 10 Mobile | October 12, 2004 | Windows Mobile 2003 SE | — | |
| Windows Media Player 9.0.1 | March 24, 2004 | Windows Mobile 2003 SE | — | |
| Windows Media Player 9 Series | June 23, 2003 | Windows Mobile 2003 | — | |
| Windows Media Player 8.5 | October 11, 2002 | Pocket PC 2002 | — | |
| Windows Media Player 8.01 | July 2002 | Pocket PC 2002 | — | |
| Windows Media Player 8 | October 4, 2001 (Pocket PC) | Pocket PC 2002 Smartphone 2002 |
— | |
| Windows Media Player 7.1 | May 21, 2001 | Pocket PC 2000 | — | |
| Windows Media Player 7 | December 12, 2000 | Pocket PC 2000 | — | |
| Windows Media Player 1.2 | September 7, 2000 | Handheld PC 2000 | — | |
| Windows Media Player 1.1 | ? | Palm-size PC CE 2.11 | — | |
| Windows Media Player | April 19, 2000 | Pocket PC 2000 | — | |
| Mac | ||||
| Windows Media Player 9 Series | November 7, 2003 | — | Mac OS X | |
| Windows Media Player 7 | July 24, 2001 | Mac OS 9 | Mac OS 8.x | |
| Windows Media Player 6.3 | July 17, 2000 | Mac OS 8 | Mac OS 7.x | |
| Solaris | ||||
| Windows Media Player 6.3 | July 17, 2000 | — | Solaris |
See also[edit]
- Comparison of media players
- Comparison of video player software
- Groove Music
- Media Player Classic, a media player that mimics the appearance of Windows Media Player 6.4
- Media Transfer Protocol
- Windows Media Encoder
- Windows Media Services
Footnotes[edit]
- ^ Except for «N» and «KN» editions of Windows, as well as Windows RT
- ^ N and KN versions of Windows 7 do not include Windows Media Player by default.[1]
- ^ Windows Media Player 6.4 was shipped side-by-side with later versions of WMP in Windows ME and Windows XP
References[edit]
- ^ «Microsoft Documentation Page». Microsoft Docs. October 22, 2020. Archived from the original on February 9, 2021.
- ^ LeBlanc, Brandon (July 22, 2009). «Windows 7 Has Been Released to Manufacturing». Blogging Windows. Microsoft. Archived from the original on September 26, 2015. Retrieved December 21, 2020.
- ^ «Windows Media Player 12 — Windows 7 features». Windows. Microsoft. Archived from the original on September 22, 2009. Retrieved June 15, 2011.
- ^ Hachman, Mark (2021-11-16). «Windows Media Player is getting a long-overdue upgrade». PCWorld.
- ^ «Windows Version History». Support (4.0 ed.). Microsoft. September 23, 2011. Archived from the original on February 26, 2015. Retrieved May 2, 2009.
- ^ Lineback, Nathan. «Windows 3.0 with Multimedia Extensions». Toasty Tech. Archived from the original on April 15, 2009. Retrieved May 2, 2009.
- ^ «Video for Windows». PC Tech Guide. Archived from the original on April 10, 2009. Retrieved May 2, 2009.
- ^ Blome, Michael; Wasson, Mike (July 2002). «DirectShow: Core Media Technology in Windows XP Empowers You to Create Custom Audio/Video Processing Components». MSDN Magazine. Microsoft. Archived from the original on September 14, 2008. Retrieved May 1, 2009.
- ^
C:Windowssystem32myplay32.exe. Windows XP. Microsoft Corporation. - ^ «MPLAYER2.EXE Is Linked to Missing Export MSDXM.OCX». Support. Microsoft. April 25, 2006. Archived from the original on March 14, 2007. Retrieved February 13, 2015.
- ^ «MSN Music to offer free songs». Archived from the original on 2020-09-21. Retrieved 2020-05-21.
- ^ «MSN Launches Preview Release of Music Download Service». September 2004. Archived from the original on 2020-08-06. Retrieved 2020-05-21.
- ^ «MSN Music Shutting Down for Zune». Archived from the original on 2020-08-13. Retrieved 2020-05-21.
- ^ «DSP Plug-in Packaging». MSDN. Microsoft. Archived from the original on 2010-11-05. Retrieved 2010-04-08.
- ^ LeBlanc, Brandon (April 16, 2012). «Windows Announcing the Windows 8 Editions». The Windows Blog. Archived from the original on April 18, 2012.
- ^ «Media Player is available for Windows 11». 16 November 2021.
- ^ «Microsoft is replacing Windows Media Player with Media Player for Windows 11». Engadget. Retrieved 2021-11-18.
- ^ «Full screen album art». 16 November 2021.
- ^ «Optimized accessibility». 16 November 2021.
- ^ «DVD playback options for Windows». Windows help & learning.
- ^ a b c Peter Bright (October 30, 2008). «Hands on: Windows Media Player 12’s surprising new features». ArsTechnica. Condé Nast Digital. Archived from the original on March 27, 2009. Retrieved March 25, 2009.
- ^ «Windows 7 RC to natively support .mov files». Chakkaradeep Chandran. Neowin.net. February 26, 2009. Archived from the original on July 3, 2012. Retrieved March 25, 2009.
- ^ «Windows 7 next generation camera support». Download Center. Microsoft. Archived from the original (PPTX) on December 27, 2008.
- ^ «Native MKV, FLAC And HEVC Support In Windows 10». Lifehacker Australia. 29 November 2014.
- ^ «Windows 10 1809 Built-In Apps: What to Keep». Vacuum Breather.
- ^ «Formats supported by Windows Media Player Mobile». MSDN. Microsoft. April 8, 2010. Archived from the original on November 18, 2012. Retrieved November 7, 2012.
- ^ «Windows Media Player manual». Download Center. Microsoft. September 1, 2004. Archived from the original (DOC) on June 7, 2005.
- ^ Kiriaty, Yochay; Goldshtein, Sasha (July 2009). «Introducing The Taskbar APIs». MSDN Magazine. Microsoft. Thumbnail Toolbars. Archived from the original on 2015-03-25. Retrieved 2015-04-23.
- ^ a b c d Sinofsky, Steven (May 12, 2009). «Media Streaming with Windows 7». Engineering Windows 7. Microsoft. Archived from the original on July 12, 2011. Retrieved April 23, 2015.
- ^ «Skins for Windows Media Player». Windows. Microsoft. Archived from the original on June 9, 2016.
- ^ «Microsoft Security Bulletin MS09-047: Critical Vulnerabilities in Windows Media Format Could Allow Remote Code Execution». Microsoft TechNet. Microsoft. September 8, 2009. Archived from the original on July 31, 2010. Retrieved June 5, 2010.
- ^ «MS09-047: Description of the security update for Windows Media Format Runtime, Windows Media Services, and Media Foundation: September 8, 2009». Support. Microsoft. September 10, 2009. Archived from the original on May 19, 2010. Retrieved June 5, 2010.
- ^ «Microsoft Unveils Windows Media Player for Palm-Size and Pocket PCs». News Center. Microsoft. January 6, 2000. Archived from the original on August 6, 2020. Retrieved January 31, 2017.
- ^ «Windows Media Components for QuickTime». Microsoft. Archived from the original on January 12, 2006. Retrieved March 30, 2007.
- ^ Microsoft. Download Center Archived 2017-07-25 at the Wayback Machine. «be used to restore Windows Media Player and related technologies to N and KN editions of Windows Vista.» Retrieved July 26, 2008
- ^ «Get Windows Media Player». Windows. Microsoft. Archived from the original on August 25, 2010. Retrieved November 5, 2011.
- ^ «MS09-037: Description of the security update for Windows Media Player: August 11, 2009». Support. Microsoft. May 8, 2012. Archived from the original on September 21, 2013. Retrieved August 12, 2013.
- ^ «Final Release of Windows Media 9 Series Starts Next Wave of Digital Media». News Center. Microsoft. January 7, 2003. Archived from the original on February 3, 2016. Retrieved September 29, 2015.
- ^ a b Petri, Daniel (2009-01-08). «Download Windows Media Player 9». Petri. Archived from the original on 2019-02-13. Retrieved 2019-02-12.
- ^ «Windows Media Player 7.1 for Windows 98, 2000, and Me 7.1 — BumperSoft». www.bumpersoft.com. Archived from the original on 2019-02-13. Retrieved 2019-02-12.
- ^ «Microsoft Windows Media Player 7 Brings Click and Play Digital Media To Millions Around the Globe». News Center. Microsoft. July 17, 2000. Archived from the original on May 27, 2015. Retrieved June 15, 2011.
Further reading[edit]
- Liron, Marc (2004). «A Little Windows Media Player History…» Windows XP Media Player — The Best There Is?. Archived from the original on January 18, 2008. Retrieved October 7, 2011.
- «The default codecs that are included with Windows Media Player 9 and with Windows Media Player 10 (Revision 1.1)». Microsoft Support Center. Microsoft Corporation. August 4, 2005. Archived from the original on November 20, 2011. Retrieved October 7, 2011.
External links[edit]
- Official website
- The Vintage Windows Media Player
- wmplugins.com — The place to find and share plug-ins, skins and visualizations.
This article is about the original version used prior to Windows 8. For the successor version, see Media Player (Windows 11).

Windows Media Player 12 Legacy running on Windows 11 2022 Update |
|
| Developer(s) | Microsoft |
|---|---|
| Stable release | 12.0.22621.457 (September 20, 2022; 4 months ago) [±] |
| Preview release | 12.0.25120.1000 (May 18, 2022; 8 months ago) [±] |
| Operating system |
|
| Included with |
|
| Predecessor | ActiveMovie Control, CD Player, DVD Player (Win32 version) |
| Successor | Microsoft Movies & TV, Groove Music, Media Player (Windows 11) |
| Type | Media player |
| Website | support.microsoft.com/en-gb/windows/windows-media-player-d10303a5-896c-2ce2-53d4-5bd5b9fd888b |
Windows Media Player (WMP) is the first media player and media library application that was developed by Microsoft for playing audio, video and viewing images on personal computers running the Microsoft Windows operating system, as well as on Pocket PC and Windows Mobile-based devices. Editions of Windows Media Player were also released for classic Mac OS, Mac OS X, and Solaris but development of these has since been discontinued.
Windows Media Player was eventually replaced in Windows 8 with Groove Music. Groove Music persisted in Windows 8.1 and Windows 10, before being replaced in turn with the Media Player in Windows 11.
In addition to being a media player, the application has the ability to rip audio file from and copy to compact discs, burn recordable discs in Audio CD format or as data discs with playlists such as an MP3 CD, synchronize content with a digital audio player (MP3 player) or other mobile devices, and enable users to purchase or rent music from a number of online music stores.
Windows Media Player 11 was made available for Windows XP and included in Windows Vista and Windows Server 2008. The default file formats are Windows Media Video (WMV), Windows Media Audio (WMA), and Advanced Systems Format (ASF), and its own XML based playlist format called Windows Playlist (WPL). The player is also able to utilize a digital rights management service in the form of Windows Media DRM.
Windows Media Player 12 is the most recent version of Windows Media Player prior to Windows 11. It was released on October 22, 2009, along with Windows 7[b] and has not been made available for previous versions of Windows nor has it been updated since for Windows 8, Windows 8.1, Windows 10, and Windows 11.[2][3] Windows 8 and later instead use Groove Music (for audio) and Microsoft Movies & TV (for video) as the default playback applications for most media; As of October 2021, Windows Media Player is still included as a Windows component. Windows RT does not run Windows Media Player.
On November 16, 2021, Microsoft announced that it would replace Groove Music with the new Media Player application, though the legacy Windows Media Player will continue to be optionally available with Windows 11.[4]
History[edit]
Media Player 5 running in Windows 2000.
The first version of Windows Media Player appeared in 1991, when Windows 3.0 with Multimedia Extensions was released.[5] Originally called Media Player, this component was included with «Multimedia PC»-compatible machines but not available for retail sale. It was capable of playing .mmm animation files, and could be extended to support other formats.[6] It used MCI to handle media files. Being a component of Windows, Media Player shows the same version number as that of the version Windows with which it was included.
WMP running in Windows 8.
Microsoft continually produced new programs to play media files. In November of the following year, Video for Windows was introduced with the ability to play digital video files in an AVI container format,[7] with codec support for RLE and Video1, and support for playing uncompressed files. Indeo 3.2 was added in a later release. Video for Windows was first available as a free add-on to Windows 3.1, and later integrated into Windows 95 and Windows NT 4.0. In 1995, Microsoft released ActiveMovie with DirectX Media SDK. ActiveMovie incorporates a new way of dealing with media files, and adds support for streaming media (which the original Media Player could not handle). In 1996, ActiveMovie was renamed DirectShow.[8] However, Media Player continued to come with Windows until Windows XP, in which it was officially renamed Windows Media Player v5.1.[9] («v5.1» is the version number of Windows XP).
In 1999, Windows Media Player’s versioning broke away from that of Windows itself. Windows Media Player 6.4 came as an out-of-band update for Windows 95-98 and Windows NT 4.0 that co-existed with Media Player and became a built-in component of Windows 2000, Windows ME, and Windows XP with an mplayer2.exe stub allowing to use this built-in instead of newer versions.[10] Windows Media Player 7.0 and its successors also came in the same fashion, replacing each other but leaving Media Player and Windows Media Player 6.4 intact. Windows XP is the only operating system to have three different versions of Windows Media Player (v5.1, v6.4, and v8) side by side. All versions branded Windows Media Player (instead of simply Media Player) support DirectShow codecs. Windows Media Player version 7 was a large revamp, with a new user interface, visualizations and increased functionality. Windows Vista, however, dropped older versions of Windows Media Player in favor of v11, which included the removal of the Windows Media Source Filter (DirectShow codec).
In 2004, Microsoft launched digital music store MSN Music for new Windows Media Player 10 to compete with Apple iTunes.[11][12]
However, MSN Music was discontinued already in 2006 with the launch of Zune music players.[13]
Beginning with Windows Vista, Windows Media Player supports the Media Foundation framework besides DirectShow; as such it plays certain types of media using Media Foundation as well as some types of media using DirectShow.[14] Windows Media Player 12 was released with Windows 7. It included support for more media formats and added new features. With Windows 8, however, the player did not receive an upgrade.
On April 16, 2012, Microsoft announced that Windows Media Player would not be included in Windows RT, the line of Windows designed to run on ARM-based devices.[15]
Windows 11[edit]
A different app called Media Player is the successor to Groove Music for Windows 10 (previously Xbox Music) and Windows Media Player. Media Player started to be offered to all Windows 11 users on February 15, 2022.[16]
The new Media Player can also play video, as part of Groove’s rebranding from a music streaming service to a media player.[17] Other changes include the album cover view being in fullscreen, and a refresh to the mini player.[18] Accessibility has also been optimized, with some improved keyboard shortcuts and hotkey support for keyboard users and with other assistive technologies.[19]
Features[edit]
Core playback and library functions[edit]
Windows Media Player supports playback of audio, video and pictures, along with fast forward, reverse, file markers (if present) and variable playback speed (seek & time compression/dilation introduced in WMP 9 Series). It supports local playback, streaming playback with multicast streams and progressive downloads. Items in a playlist can be skipped over temporarily at playback time without removing them from the playlist. Full keyboard-based operation is possible in the player.
Windows Media Player supports full media management, via the integrated media library introduced first in version 7, which offers cataloguing and searching of media and viewing media metadata. Media can be arranged according to album, artist, genre, date et al. Windows Media Player 9 Series introduced Quick Access Panel to browse and navigate the entire library through a menu. The Quick Access Panel was also added to the mini mode in version 10 but was entirely removed in version 11. WMP 9 Series also introduced ratings and Auto Ratings. Windows Media Player 10 introduced support for aggregating pictures, Recorded TV shows, and other media into the library. A fully featured tag editor was featured in versions 9-11 of WMP, called the Advanced Tag Editor. However, the feature was removed in Windows Media Player 12. Since WMP 9 Series, the player features dynamically updated Auto Playlists based on criteria. Auto Playlists are updated every time users open them. WMP 9 Series and later also supports Auto Ratings which automatically assigns ratings based on the number of times a song is played. Pre-populated auto playlists are included in Windows Media Player 9 Series. Custom Auto Playlists can be created only on Windows XP and later.
In Windows Media Player 11, the Quick Access Panel was removed and replaced with an Explorer-style navigation pane on the left which can be customized for each library to show the user selected media or metadata categories, with contents appearing on the right, in a graphical manner with thumbnails featuring album art or other art depicting the item. Missing album art can be added directly to the placeholders in the Library itself (though the program re-renders all album art imported this way into 1×1 pixel ratio, 200×200 resolution JPEGs). There are separate Tiles, Icons, Details or Extended Tiles views for Music, Pictures, Video and Recorded TV which can be set individually from the navigation bar. Entries for Pictures and Video show their thumbnails. Version 11 also introduced the ability to search and display results on-the-fly as characters are being entered, without waiting for Enter key to be hit. Incremental search results are refined based on further characters that are typed. Stacking allows graphical representations of how many albums there are in a specific category or folder. The pile appears larger as the category contains more albums. The List pane includes an option to prompt the user to remove items skipped in a playlist upon save or skip them only during playback.
Visualizations[edit]
Windows Media Player 11 running in mini mode (in Windows XP MCE) showing the «Bars and Waves» visualization
While playing music, Windows Media Player can show visualizations. The current three visualizations are Alchemy, which was first introduced in version 9, Bars and Waves, which has been used since version 7, and Battery, introduced version 8. «Musical Colors» was removed starting with version 9, but is retained if Windows Media Player was upgraded from version 7 or 8. Version 11 and above refrains from having the former «Ambience,” «Particle,” «Plenoptic,” and «Spikes» visualizations. The «Battery» visualization was similarly removed in later editions of version 12. The reason for their removal was that the visualizations do not support full screen controls (either the visualization gets shifted to the left while there is a thick black bar to the right side of the screen, that there are no full screen controls, or that the visualization have DXE Problems). More visualizations such as «BlazingColors,” «ColorCubes,” «Softie the Snowman,» and «Yule Log» used to be downloadable however, the downloads from Microsoft’s website have mostly been taken down and it’s available on the WMP Goodies site.
Format support[edit]
The player includes intrinsic support for Windows Media codecs and also WAV and MP3 media formats. On Windows XP and above with WMP 9 Series and later, the Windows Media Audio Professional codec is included which supports multichannel audio at up to 24-bit 192 kHz resolution. Windows Media Player 11 includes the Windows Media Format 11 runtime which adds low bitrate support (below 128 kbit/s for WMA Pro), support for ripping music to WMA Pro 10 and updates the original WMA to version 9.2.[citation needed]
Support for any media codec and container format can be added using specific DirectShow filters or Media Foundation codecs (Media Foundation codecs only in Windows Vista and later). The player will not play MP3 files that contain compressed ID3 headers («tags»), trying to do so results in a «The input media file is invalid» error message. MP3 playback support was built-in beginning with version 6.1 and audio CD playback was natively supported with version 7.[citation needed]
DVD playback features minus the necessary decoders were integrated into Windows Media Player 8 for Windows XP. The player activates DVD and Blu-ray playback functionality with support for menus, titles and chapters, parental controls and audio track language selection if compatible decoders are installed. MPEG-2 and Dolby Digital (AC-3) decoders were included beginning with Windows Media Player 11 on Windows Vista (Home Premium and Ultimate editions only) and Windows 7 (Home Premium, Ultimate, or Enterprise editions) to allow DVD playback without additional software. However, the decoders were subsequently removed in Windows 8 and Windows 10 due to licensing costs.[20]
Windows Media Player 12 adds native support for H.264 and MPEG-4 Part 2 video formats, ALAC, AAC audio[21] and 3GP[clarification needed got no codec available for 3GP], MP4 and MOV container formats.[22] Windows Media Player 12 is also able to play AVCHD formats (.M2TS and .mts).[23]
As of Windows 10 version 1507, Windows Media Player 12 can play FLAC, HEVC, and SubRip subtitle, and Matroska container formats.[24] Although the WebM file type is not officially associated with Windows Media Player 12 (the default player is Microsoft Movies & TV), playback of VP9 video in WebM container is possible on Windows 10 version 1809 and later.[25]
Windows Media Player Mobile[edit]
Windows Media Player Mobile 10 on Windows Mobile 6.5 supports MP3, ASF, WMA, and WMV using WMV or MPEG-4 codecs.[26]
Disc burning, ripping, and playback[edit]
Windows Media Player features integrated Audio CD-burning support since version 7 as well as data CD burning support since Windows Media Player 9 Series on Windows XP and later. Data CDs can have any of the media formats supported by the player. While burning Data CDs, the media can, optionally, be transcoded into WMA format and playlists can be added to the CD as well. Starting with WMP 9 Series, audio CDs can be burnt with volume leveling.
Audio CDs can be ripped as WMA or WMA 10 Pro (WMA 10 Pro in WMP 11 and later) at 48, 64, 96, 128, 160, and 192 kbit/s, WMA lossless (470 to 940 kbit/s) (9 Series on XP and later), WMA variable bitrate (from 40 to 75 kbit/s up to 240-355 kbit/s), MP3 at 128, 192, 256, and 320 kbit/s, or uncompressed WAV (WAV ripping in WMP 11 and later). Since WMP 9 Series, 20 bit high-resolution CDs (HDCDs) are also supported, if capable audio hardware is present. Audio can be ripped using error correction and ripped audio can be protected with Windows Media DRM. Ripping to MP3 is supported only in Windows Media Player 8 for Windows XP and later if a compatible MP3 encoder is installed. Windows Media Player 10 included the Fraunhofer MP3 Professional encoder. Information on CDs such as album name, artist and track listings can optionally be automatically downloaded from the online Windows Media database when the CD is inserted. Version 11 added support for ripping audio CDs to WAV and WMA 10 Pro formats. With their 2015 implementation in Windows 10, Version 12 also added lossless FLAC and ALAC formats for ripping and playback. For burning, version 11 shows a graphical bar indicating how much space will be used on the disc and introduced Disc spanning which splits a burn list onto multiple discs in case the content does not fit on one disc.
Portable device sync[edit]
Windows Media Player allows the user to connect, share and sync data with portable handheld devices and game consoles since version 7. Media can be optionally transcoded to a format better suited for the target device, automatically, when synchronizing. When deleting playlists from devices, Windows Media Player can automatically remove their contents. Devices can be formatted using Windows Media Player 9 Series and later. Version 10 and later support the Media Transfer Protocol and Auto Sync. Auto Sync allows users to specify criteria such as recently added music or highest rated songs, by which media will be automatically synchronized with the portable device and other advanced features like setting the clock on the portable device automatically, communicating with the device to retrieve the user’s preferences. Windows Media Player 10 also introduced the UMDF-based Windows Portable Devices API.
Version 11 has improved synchronization features for loading content onto PlaysForSure-compatible portable players. WMP 11 supports reverse-synchronization, by which media present on the portable device can be replicated back to the PC. Shuffle Sync can be used to randomize content synced with the portable device, Multi PC Sync to synchronize portable device content across multiple PCs and Guest Sync to synchronize different content from multiple PCs with the portable device. Portable devices appear in the navigation pane of the library where their content can be browsed and searched.
Windows Media Player’s ‘Sync’ function has options that allow it to be set to automatically down-convert (transcode) high bit-rate song files to a lower bit-rate. This down-conversion function is switched on by default. This is useful for providing low bit-rate files to those portable devices that need them, and to save space on portable devices with smaller storage capacities. For high bit-rate capable devices with sufficient storage capabilities, the down conversion process can be omitted.
In versions 11 (2006) and 12 (2009), the Quality settings that the user has selected in the Windows Media Player settings for Sync, for that specific portable device, are used to control the quality (bit-rate) of files that are copied to the portable device. Leaving the Quality settings to Automatic will often result in 192kbs files being copied to the portable device. Manual settings can also be made. 192kbs is the highest quality down-conversion bit-rate that can be manually selected when the Sync function’s down-conversion function is turned on. Lower bit-rates can also be selected.
For portable devices that can handle high bit-rate files, the best quality files are obtained by leaving the down-conversion process switched off (unchecked) for that specific device. In Windows Media Player Version 11, switching off the down-conversion function is done in the Quality tab of the Advanced Options of the Sync settings for the device. In Windows Media Player Version 12, switching off the down-conversion function is done in the Quality tab of the Properties for the device in the Select Settings for the device in the Sync Options menu.
When set up in such a way, Windows Media Player’s ‘Sync’ function can be used to sync unchanged high bit-rate song files to suitable portable devices (i.e. those capable of using file formats such as WMA Lossless, mp3-360kbs, etc.). For example, some users have created large song libraries on their PCs containing .wma formatted song files using the high bit-rate WMA Lossless (WMA-LL) protocol, or using other high bit-rate song file formats. The WMA-LL protocol is selectable in Windows Media Player as an option when ripping songs from CDs. The resulting bit-rates seen on ripped WMA-LL files are often 3 to 6 times higher than 192kbs, and can typically fall anywhere in the range of 600kbs to 1200kbs, depending on the quality of the source file that was present on the CD in the first place. The sound quality is much improved over the default rate, although the file size is larger.
At the time that Versions 11 and 12 were released, the capabilities and capacities of portable devices typically required down-conversion of the bit-rates of the files placed on the portable devices. Thus, Sync down-conversion was turned on by default. This was to ensure playability of the files and to ensure that the file sizes were small enough to efficiently fit a reasonably large selection of songs on the portable device.
In recent years (circa 2012), portable devices became available that could natively play these Windows Media Player produced high bit-rate WMA-LL files (and others), and that have storage capacities suitable for large collections of high bit-rate song files. This made it much more practicable and desirable to use software programs such as Windows Media Player to synchronize previously PC-bound libraries of high bit-rate songs to these new portable devices.
Enhanced playback features[edit]
Windows Media Player features universal brightness, contrast, saturation and hue adjustments and pixel aspect ratio for supported video formats. It also includes a 10-band graphic equalizer with presets and SRS WOW audio post-processing system. Windows Media Player can also have attached audio and video DSP plug-ins which process the output audio or video data. Video Smoothing was introduced in WMP 9 Series (Windows XP and later only) which upscales frame-rate by interpolating added frames, in effect giving a smoother playback on low-framerate videos. The player supports subtitles and closed-captioning for local media, video on demand streaming or live streaming scenarios. Typically Windows Media captions support the SAMI file format but can also carry embedded closed caption data.
The player can use video overlays or VMR (Video Mixing Renderer) surfaces, if the video card supports them. In Windows XP, it uses VMR7 by default, but can also be made to use the more advanced YUV mixing mode by enabling the «Use high quality mode» option in Advanced Performance settings. This turns on deinterlacing, scaling and improved color accuracy.[27] WMP 9 Series introduced native playback for deinterlacing for TV output. Version 9 introduced DXVA accelerated playback. Version 11 introduced improved support for DirectX accelerated decoding of WMV video (DXVA decoding). Up to version 11, it supported static lyrics and «Synchronized Lyrics,” by which different lines of lyrics can be time-stamped, so that they display only at those times. Synchronized Lyrics also were accessible through the Advanced Tag Editor which was removed in version 12.
Since Windows Media Player 9 Series, the player supports crossfading, audio dynamic range (Quiet Mode) for WMA Pro and WMA Lossless, and auto volume leveling for certain media which includes volume level/gain information such as MP3 or Windows Media. The player also supports extensive configurable privacy and security settings.
Shell integration[edit]
The player has Windows Explorer shell integration to add files and playlist to the Now Playing pane and other playlists can be controlled from the Windows Explorer shell itself, via right-click menu. The My Music folder also includes a separate My Playlists folder where playlists are maintained. When the player is closed and reopened, simply clicking the play button restores the last playlist even if it was not saved. Starting with Windows Media Player 10, the playlist pane is also visible from the Library view. AutoPlay handlers in Windows expose various Windows Media Player tasks.
Windows Media Player 11 running in mini mode in Windows Vista and Windows XP respectively. Notice the difference in the logo.
Up to version 11, it featured a taskbar-mounted Mini mode in which the most common media control buttons are presented as a toolbar on the Windows taskbar. Flyout windows can display media information, the active visualization or the video being played back. Mini-mode was introduced as a shell player powertoy for Windows Media Player 8 in Windows XP and integrated later into WMP 9 Series. Mini-mode has been removed in Windows Media Player 12 in favor of controls in the taskbar’s interactive thumbnail preview which lacks volume control, a progress bar and information displayed whenever a new song is played.
The user interface has been redesigned in Windows Media Player 12 such that the Now Playing view plays media in a separate minimalist window with floating playback controls, and also gives access to the current playlist, visualizations, and enhancements.[21] Enhancements are housed in individual undocked windows. The library view includes the rest of the media management functions. It also can preview songs from the library when users hover over the media file and click the Preview button.[21] Windows Media Player 12 can play unprotected songs from the iTunes library. The taskbar-integrated Mini-player has been replaced with controls in the taskbar’s interactive thumbnail preview (called the Thumbnail Toolbar),[28] albeit minus the volume control function, track and album information shown whenever a new song is played and the progress bar. The taskbar icon also supports jump lists introduced in Windows 7.
The thumbnail viewer of Windows Media Player 12 in Windows 7 Home Premium
Extensibility[edit]
The player has had skinning support since Windows Media Player (WMP) 7 and includes a color chooser since the WMP 9 Series. Not all functions are usually exposed in skin mode. Windows Media Player 10 allows setting the video border color. Color chooser has been removed in WMP 12. It supports visualizations and Info Center View (Info Center View in WMP 9 Series and later) which displays media metadata fetched from the internet. Full screen visualizations are supported in WMP 9 Series and later. It supports Background plug-ins, window plug-ins and Now Playing plug-ins to control media playback besides DSP and renderer plug-ins. Plug-in support was introduced in WMP 9 Series.
Online features[edit]
The player integrates web-browsing support to browse online music stores, shop for music and tune to internet radio stations since version 7. It provides an embeddable ActiveX control for Internet Explorer so that developers can play Windows Media on web pages. Windows Media Player 10 and later feature integration with a large number of online music stores and selecting a music store switches the Info Center view, radio and other online features to use services from that store. Purchased music from a particular store appears in a separate library node under the respective category.
Media streaming[edit]
Previously, Microsoft had released Windows Media Connect for Windows XP to stream media content with its built-in UPnP media server. With version 11 of Windows Media Player, Media Sharing was integrated and allows content (Music, Pictures, Video) to be streamed to and from Universal Plug and Play (UPnP) AV enabled devices such as the PS3, Xbox 360, and Roku SoundBridge. This includes DRM protected PlaysForSure content. WMP 11 on Windows Vista can also act as a client to connect to remote media libraries using this feature; this is not available on the Windows XP version.
With version 12, media streaming was further improved. While previous versions streamed media to UPnP compliant devices (Digital Media Server role) and could play media by fetching it from a network share (Digital Media Player role),[29] Windows Media Player 12 can access media from the shared media libraries on the network or HomeGroup, stream media to DLNA 1.5 compliant devices and allows itself (once the remote control option is turned on) to be remotely controlled by Digital Media Controller devices which stream media (Digital Media Renderer role).[29] Similarly, the Play To feature once enabled for remote PCs, by turning on remote control of the player, allows compliant devices and computers to be discovered and controlled remotely from a computer running Windows Media Player 12 (Digital Media Controller role).[29] If the devices do not support the streamed format, Windows Media Player 12 transcodes the format on-the-fly. Media from a home network can also be streamed over the internet using an Online ID Provider service, which handles discovery of the computer’s IP address, authorization, security, connectivity and Quality of Service issues.[29]
Skin Mode[edit]
Windows Media Player also features skins. Currently, Windows Media Player has two default skins: «Corporate,” which was first introduced in version 8, and «Revert,” which first shipped with version 9. In versions 7 and 8, there were many unusual skins such as «Heart,” «Headspace,” «Canvas,” «Goo,” and «Atomic,” which were removed starting with version 9, but are retained if the player is upgraded, although some can still be downloaded from an archive of the Microsoft website.[30] In versions 7, 8, 9, and 10 there were many usual skins such as «9SeriesDefault,” «Atomic,” «Bluesky,” «Canvas,” «Classic,” «Compact,” «goo,” «Headspace,” «heart,” «iconic,” «Miniplayer,” «Optic,” «Pyrite,” «QuickSilver,” «Radio,” «Roundlet,” «Rusty,” «splat,” «Toothy,” «Windows Classic,” and «Windows XP,” which were removed starting with version 11. This Corporate skin is not deletable.
Security issues[edit]
Microsoft Windows Media Runtime in Windows 2000, Windows XP, Windows Vista and Windows Server contained a bug that permitted «remote code execution if a user opened a specially crafted media file». Such a file would allow the attacker to «then install programs; view, change, or delete data; or create new accounts with full user rights», if the account on which the file was played had administrator privileges.[31] The problem was addressed in a critical update issued on September 8, 2009.[32]
Other versions[edit]
Microsoft has also released versions of Windows Media Player for other platforms including Windows Mobile, classic Mac OS, Mac OS X, Palm-size PC, Handheld PC, and Solaris. Of these, only the Windows Mobile edition continues to be actively developed and supported by Microsoft. Version 1 of the Zune software was also based on Windows Media Player; later versions are not.
Windows Mobile[edit]
Windows Media Player 10.3 Mobile on a Windows Mobile Professional device
Windows Media Player for Pocket PC was first announced on January 6, 2000, and has been revised on a schedule roughly similar to that of the Windows version.[33] Currently known as «Media Player 10 Mobile,” this edition (released in October 2004) closely resembles the capabilities of the Windows version of WMP 10, including playlist capabilities, a media library, album art, WMA Lossless playback, support for DRM-protected media, video playback at 640×480 with stereo sound, and the same Energy Blue interface aesthetics also seen in Windows XP Media Center Edition 2005. It also supports synchronization with the desktop version of WMP 10, and additionally supports synchronizing and transcoding of recorded television shows from Media Center. Media Player 10 Mobile is not available as a download from Microsoft, distribution is done solely through OEM partners, and is typically included on devices based on Windows Mobile.
Windows Mobile 6 includes a copy of Windows Media Player 10 Mobile, but with a similar (but not quite identical) theme as Windows Media Player 11.
Mac OS X[edit]
Version 9 was the final version of Windows Media Player to be released for Mac OS X before development was canceled by Microsoft. It was developed by the Windows Media team at Microsoft instead of the Macintosh Business Unit and released in 2003. On release the application lacked many basic features that were found in other media players such as Apple’s iTunes and QuickTime.[citation needed] It also lacked support for many media formats that version 9 of the Windows counterpart supported on release 10 months earlier.
The Mac version supported only Windows Media encoded media (up to version 9) enclosed in the ASF format, lacking support for all other formats such as MP4, MPEG, and Microsoft’s own AVI format. On the user interface front, it did not prevent screensavers from running during playback, it did not support file drag-and-drop, nor did it support playlists. While Windows Media Player 9 had added support for some files that use the WMV9 codec (also known as the WMV3 codec by the FourCC), in other aspects it was seen as having degraded in features from previous versions.
On January 12, 2006, Microsoft announced it had ceased development of Windows Media Player for Mac. Microsoft now distributes a third-party plugin called WMV Player (produced and maintained by Flip4Mac) which allows some forms of Windows Media to be played within Apple’s QuickTime Player and other QuickTime-aware applications.[34]
European Commission case[edit]
In March 2004, the European Commission in the European Union Microsoft antitrust case fined Microsoft €497 million and ordered the company to provide a version of Windows without Windows Media Player, claiming Microsoft «broke European Union competition law by leveraging its near monopoly in the market for PC operating systems onto the markets for work group server operating systems and for media players.” The company has made available a compliant version of its flagship operating system under the negotiated name «Windows XP N,” though the product has not been very successful. Windows Vista, Windows 7 and Windows 8 are also available in «N» editions. However, it is possible to either install Windows Media Player (XP/Vista)[35] or the Media Restore Pack through Windows Update (Vista) to add the media player.
Release history[edit]
Prior to the release of Windows Media Player in Windows 98 Second Edition, separate programs, CD Player, Deluxe CD Player, DVD Player and Media Player, were included in old versions of Microsoft Windows for playback of media files.
| Version | Original release | Included with | Available for | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Microsoft Windows | ||||
| Media Player | February 15, 2022 | Windows 11 | — | |
| Windows Media Player 12 | July 22, 2009 | Windows 7 Windows 8 Windows 8.1 Windows 10 Windows 11 Windows Server 2008 R2 Windows Server 2012 Windows Server 2012 R2 Windows Server 2016 Windows Server 2019 Windows Server 2022 |
— | 
|
| Windows Media Player 11 | October 18, 2006 | Windows Vista Windows Server 2008 |
Windows XP (SP2+) Windows XP x64 Edition |
|
| Windows Media Player 10 | August 25, 2004 | Windows XP x64 Edition Windows XP Media Center Edition 2005 Windows Server 2003 (SP1+) |
Windows Server 2003 Windows XP[37] |
|
| Windows Media Player 9 Series | January 7, 2003[38] | Windows XP (SP2+) Windows Server 2003 (RTM) |
Windows XP Windows ME Windows 2000 Windows 98 SE[39] |
|
Windows Media Player for Windows XP (version  |
August 24, 2001 | Windows XP (RTM & SP1) | — | |
| Windows Media Player 7.1 | May 16, 2001 | Windows 2000 (SP2+) | Windows ME Windows 2000 Windows 98[39][40] |
|
| Windows Media Player 7.0 | June 19, 2000[41] | Windows ME | Windows 2000 Windows 98 Windows 95 |
|
| Windows Media Player 6.4[c] | September 15, 1999 | Windows 2000 Windows ME (hidden) Windows XP (hidden) Windows Server 2003 (hidden) Internet Explorer 5.01 Internet Explorer 5.5 Internet Explorer 6.0 |
Windows 98 Windows NT 4.0 Windows 95 |
|
| Windows Media Player 6.1 | March 1999 | Windows 98 SE Internet Explorer 5.0 |
Windows 98 Windows NT 4.0 Windows 95 |
|
| Microsoft Media Player 5.1 | 2001 | Windows XP (hidden) | — | |
| Media Player 5.0 | 1999 | Windows 2000 (hidden) | — | |
| Media Player 4.9 | 2000 | Windows ME (hidden) | — | |
| Media Player 4.1 | 1998 | Windows 98 Windows 98 SE (hidden) |
— | |
| Media Player 4.0 | 1995 | Windows 95 Windows NT 4.0 |
— | |
| Media Player 3.51 | 1995 | Windows NT 3.51 | — | |
| Media Player 3.5 | 1994 | Windows NT 3.5 | — | |
| Media Player 3.15 | 1992 | — | Windows 3.1 with Video for Windows | |
| Media Player 3.1 | 1992 | Windows 3.1 Windows NT 3.1 |
— | |
| Media Player 3.0 | 1991 | — | Windows 3.0 with Multimedia Extension | |
| Windows Mobile | ||||
| Windows Media Player 10.3 Mobile | February 12, 2007 (Windows Mobile 6) | Windows Mobile 6.1 Windows Mobile 6 |
Windows Mobile 5.0 | 
|
| Windows Media Player 10.2 Mobile | ? | Windows Mobile 5.0 | — | |
| Windows Media Player 10.1 Mobile | May 10, 2005 | Windows Mobile 5.0 | — | |
| Windows Media Player 10 Mobile | October 12, 2004 | Windows Mobile 2003 SE | — | |
| Windows Media Player 9.0.1 | March 24, 2004 | Windows Mobile 2003 SE | — | |
| Windows Media Player 9 Series | June 23, 2003 | Windows Mobile 2003 | — | |
| Windows Media Player 8.5 | October 11, 2002 | Pocket PC 2002 | — | |
| Windows Media Player 8.01 | July 2002 | Pocket PC 2002 | — | |
| Windows Media Player 8 | October 4, 2001 (Pocket PC) | Pocket PC 2002 Smartphone 2002 |
— | |
| Windows Media Player 7.1 | May 21, 2001 | Pocket PC 2000 | — | |
| Windows Media Player 7 | December 12, 2000 | Pocket PC 2000 | — | |
| Windows Media Player 1.2 | September 7, 2000 | Handheld PC 2000 | — | |
| Windows Media Player 1.1 | ? | Palm-size PC CE 2.11 | — | |
| Windows Media Player | April 19, 2000 | Pocket PC 2000 | — | |
| Mac | ||||
| Windows Media Player 9 Series | November 7, 2003 | — | Mac OS X | |
| Windows Media Player 7 | July 24, 2001 | Mac OS 9 | Mac OS 8.x | |
| Windows Media Player 6.3 | July 17, 2000 | Mac OS 8 | Mac OS 7.x | |
| Solaris | ||||
| Windows Media Player 6.3 | July 17, 2000 | — | Solaris |
See also[edit]
- Comparison of media players
- Comparison of video player software
- Groove Music
- Media Player Classic, a media player that mimics the appearance of Windows Media Player 6.4
- Media Transfer Protocol
- Windows Media Encoder
- Windows Media Services
Footnotes[edit]
- ^ Except for «N» and «KN» editions of Windows, as well as Windows RT
- ^ N and KN versions of Windows 7 do not include Windows Media Player by default.[1]
- ^ Windows Media Player 6.4 was shipped side-by-side with later versions of WMP in Windows ME and Windows XP
References[edit]
- ^ «Microsoft Documentation Page». Microsoft Docs. October 22, 2020. Archived from the original on February 9, 2021.
- ^ LeBlanc, Brandon (July 22, 2009). «Windows 7 Has Been Released to Manufacturing». Blogging Windows. Microsoft. Archived from the original on September 26, 2015. Retrieved December 21, 2020.
- ^ «Windows Media Player 12 — Windows 7 features». Windows. Microsoft. Archived from the original on September 22, 2009. Retrieved June 15, 2011.
- ^ Hachman, Mark (2021-11-16). «Windows Media Player is getting a long-overdue upgrade». PCWorld.
- ^ «Windows Version History». Support (4.0 ed.). Microsoft. September 23, 2011. Archived from the original on February 26, 2015. Retrieved May 2, 2009.
- ^ Lineback, Nathan. «Windows 3.0 with Multimedia Extensions». Toasty Tech. Archived from the original on April 15, 2009. Retrieved May 2, 2009.
- ^ «Video for Windows». PC Tech Guide. Archived from the original on April 10, 2009. Retrieved May 2, 2009.
- ^ Blome, Michael; Wasson, Mike (July 2002). «DirectShow: Core Media Technology in Windows XP Empowers You to Create Custom Audio/Video Processing Components». MSDN Magazine. Microsoft. Archived from the original on September 14, 2008. Retrieved May 1, 2009.
- ^
C:Windowssystem32myplay32.exe. Windows XP. Microsoft Corporation. - ^ «MPLAYER2.EXE Is Linked to Missing Export MSDXM.OCX». Support. Microsoft. April 25, 2006. Archived from the original on March 14, 2007. Retrieved February 13, 2015.
- ^ «MSN Music to offer free songs». Archived from the original on 2020-09-21. Retrieved 2020-05-21.
- ^ «MSN Launches Preview Release of Music Download Service». September 2004. Archived from the original on 2020-08-06. Retrieved 2020-05-21.
- ^ «MSN Music Shutting Down for Zune». Archived from the original on 2020-08-13. Retrieved 2020-05-21.
- ^ «DSP Plug-in Packaging». MSDN. Microsoft. Archived from the original on 2010-11-05. Retrieved 2010-04-08.
- ^ LeBlanc, Brandon (April 16, 2012). «Windows Announcing the Windows 8 Editions». The Windows Blog. Archived from the original on April 18, 2012.
- ^ «Media Player is available for Windows 11». 16 November 2021.
- ^ «Microsoft is replacing Windows Media Player with Media Player for Windows 11». Engadget. Retrieved 2021-11-18.
- ^ «Full screen album art». 16 November 2021.
- ^ «Optimized accessibility». 16 November 2021.
- ^ «DVD playback options for Windows». Windows help & learning.
- ^ a b c Peter Bright (October 30, 2008). «Hands on: Windows Media Player 12’s surprising new features». ArsTechnica. Condé Nast Digital. Archived from the original on March 27, 2009. Retrieved March 25, 2009.
- ^ «Windows 7 RC to natively support .mov files». Chakkaradeep Chandran. Neowin.net. February 26, 2009. Archived from the original on July 3, 2012. Retrieved March 25, 2009.
- ^ «Windows 7 next generation camera support». Download Center. Microsoft. Archived from the original (PPTX) on December 27, 2008.
- ^ «Native MKV, FLAC And HEVC Support In Windows 10». Lifehacker Australia. 29 November 2014.
- ^ «Windows 10 1809 Built-In Apps: What to Keep». Vacuum Breather.
- ^ «Formats supported by Windows Media Player Mobile». MSDN. Microsoft. April 8, 2010. Archived from the original on November 18, 2012. Retrieved November 7, 2012.
- ^ «Windows Media Player manual». Download Center. Microsoft. September 1, 2004. Archived from the original (DOC) on June 7, 2005.
- ^ Kiriaty, Yochay; Goldshtein, Sasha (July 2009). «Introducing The Taskbar APIs». MSDN Magazine. Microsoft. Thumbnail Toolbars. Archived from the original on 2015-03-25. Retrieved 2015-04-23.
- ^ a b c d Sinofsky, Steven (May 12, 2009). «Media Streaming with Windows 7». Engineering Windows 7. Microsoft. Archived from the original on July 12, 2011. Retrieved April 23, 2015.
- ^ «Skins for Windows Media Player». Windows. Microsoft. Archived from the original on June 9, 2016.
- ^ «Microsoft Security Bulletin MS09-047: Critical Vulnerabilities in Windows Media Format Could Allow Remote Code Execution». Microsoft TechNet. Microsoft. September 8, 2009. Archived from the original on July 31, 2010. Retrieved June 5, 2010.
- ^ «MS09-047: Description of the security update for Windows Media Format Runtime, Windows Media Services, and Media Foundation: September 8, 2009». Support. Microsoft. September 10, 2009. Archived from the original on May 19, 2010. Retrieved June 5, 2010.
- ^ «Microsoft Unveils Windows Media Player for Palm-Size and Pocket PCs». News Center. Microsoft. January 6, 2000. Archived from the original on August 6, 2020. Retrieved January 31, 2017.
- ^ «Windows Media Components for QuickTime». Microsoft. Archived from the original on January 12, 2006. Retrieved March 30, 2007.
- ^ Microsoft. Download Center Archived 2017-07-25 at the Wayback Machine. «be used to restore Windows Media Player and related technologies to N and KN editions of Windows Vista.» Retrieved July 26, 2008
- ^ «Get Windows Media Player». Windows. Microsoft. Archived from the original on August 25, 2010. Retrieved November 5, 2011.
- ^ «MS09-037: Description of the security update for Windows Media Player: August 11, 2009». Support. Microsoft. May 8, 2012. Archived from the original on September 21, 2013. Retrieved August 12, 2013.
- ^ «Final Release of Windows Media 9 Series Starts Next Wave of Digital Media». News Center. Microsoft. January 7, 2003. Archived from the original on February 3, 2016. Retrieved September 29, 2015.
- ^ a b Petri, Daniel (2009-01-08). «Download Windows Media Player 9». Petri. Archived from the original on 2019-02-13. Retrieved 2019-02-12.
- ^ «Windows Media Player 7.1 for Windows 98, 2000, and Me 7.1 — BumperSoft». www.bumpersoft.com. Archived from the original on 2019-02-13. Retrieved 2019-02-12.
- ^ «Microsoft Windows Media Player 7 Brings Click and Play Digital Media To Millions Around the Globe». News Center. Microsoft. July 17, 2000. Archived from the original on May 27, 2015. Retrieved June 15, 2011.
Further reading[edit]
- Liron, Marc (2004). «A Little Windows Media Player History…» Windows XP Media Player — The Best There Is?. Archived from the original on January 18, 2008. Retrieved October 7, 2011.
- «The default codecs that are included with Windows Media Player 9 and with Windows Media Player 10 (Revision 1.1)». Microsoft Support Center. Microsoft Corporation. August 4, 2005. Archived from the original on November 20, 2011. Retrieved October 7, 2011.
External links[edit]
- Official website
- The Vintage Windows Media Player
- wmplugins.com — The place to find and share plug-ins, skins and visualizations.
Обзор программного обеспечения
Основные функции
- Поддерживает популярные видео и аудио форматы, такие как WMV и MPEG
- Позволяет настроить организацию медиафайлов
- Позволяет передавать потоки между различными компьютерами и устройствами в одной сети.
- Воспроизведение и запись аудио на компакт-диски
Снимок экрана с Microsoft Windows Media Player 12
Основные функции
Microsoft Windows Media Player — это приложение медиабиблиотеки, используемое для воспроизведения видео и аудио и для просмотра изображений. Приложение поставляется в комплекте с операционной системой Windows.
Windows Media Player поддерживает множество популярных аудио и видео форматов, таких как WMV, MOV, MPEG, WAV, ASF, MIDI и AIFF. Плеер также поддерживает видео H.264, Xvid и DivX. Существует большое количество бесплатных плагинов, которые расширяют возможности Windows Media Player. В проигрывателе Windows Media вы также можете передавать медиафайлы с других устройств в вашей сети, синхронизировать носитель с портативными устройствами и записывать аудио на компакт-диск.
Проигрыватель Windows Media позволяет настраивать мультимедийный интерфейс. Он позволяет настраивать навигационную панель, сортировать медиа по категориям, таким как жанр и рейтинг, и редактировать скин плеера. Проигрыватель Windows Media также позволяет создавать свои собственные плейлисты и создавать списки воспроизведения на основе ваших критериев.
Если вы пользователь Windows, Windows Media Player является хорошим вариантом для организации и воспроизведения ваших медиа. Он поддерживает множество популярных аудио- и видеоформатов, позволяет настраивать организацию медиафайлов и позволяет записывать аудио на компакт-диск. Microsoft Windows Media Player является надежным решением для ваших нужд воспроизведения мультимедиа.
Обновлено: 18 сентября 2017 г.
▶ Первичное расширение файла
.wmv
– Windows Media Video File
▶ Другие расширения файлов, используемые Microsoft Windows Media Player 12
| Поддерживаемые типы файлов | |
|---|---|
| .AVI | Audio Video Interleave File |
| .MP3 | MP3 Audio File |
| .AC3 | Audio Codec 3 File |
| .ASF | Advanced Systems Format File |
| .AIFC | Compressed Audio Interchange File |
| .AIF | Audio Interchange File Format |
| .DVR | Microsoft Recorded TV Show |
| .H264 | H.264 Encoded Video File |
| .JPG | JPEG Image |
| .M4V | iTunes Video File |
| .MPEG4 | MPEG-4 File |
| .M4B | MPEG-4 Audio Book File |
| .MOV | Apple QuickTime Movie |
| .M4A | MPEG-4 Audio File |
| .MKV | Matroska Video File |
| .MIDI | MIDI File |
| .MPG | MPEG Video File |
| .MTS | AVCHD Video File |
| .MP4 | MPEG-4 Video File |
| .OGG | Ogg Vorbis Audio File |
| .PNG | Portable Network Graphic |
| .SND | Sound File |
| .VC1 | VC-1 Video File |
| .VFW | Video for Windows |
| .VOB | DVD Video Object File |
| .XVID | Xvid-Encoded Video File |
| .WMA | Windows Media Audio File |
| .WM | Windows Media File |
| .WPL | Windows Media Player Playlist |
| .WMS | Windows Media Skin |
| .WAV | WAVE Audio File |
| .WEBM | WebM Video File |
| Дополнительные связанные форматы файлов | |
|---|---|
| .BIK | Bink Video File |
| .APL | Monkey’s Audio Track Information File |
| .AIFF | Audio Interchange File Format |
| .ALAC | ALAC Encoded Audio File |
| .ADT | ADTS Audio File |
| .ASX | Microsoft ASF Redirector File |
| .AX | DirectShow Filter |
| .AU | Audio File |
| .EVO | HD DVD Video File |
| .CDA | CD Audio Track Shortcut |
| .DVR-MS | Microsoft Digital Video Recording |
| .DMB | Digital Multimedia Broadcasting File |
| .DVF | Sony Digital Voice File |
| .HDMOV | QuickTime HD Movie File |
| .IVF | Indeo Video Format File |
| .ICS | IC Recorder Sound File |
| .K3G | 3GP Mobile Phone Video File |
| .M2V | MPEG-2 Video |
| .MP2 | MPEG Layer II Compressed Audio File |
| .MPGA | MPEG-1 Layer 3 Audio File |
| .MPV2 | MPEG-2 Video Stream |
| .MP4V | MPEG-4 Video |
| .MP4.INFOVID | Parrot AR Drone and Gyro Flyer Video |
| .M1A | MPEG-1 Audio File |
| .MID | MIDI File |
| .M3U | Media Playlist File |
| .M3U8 | UTF-8 M3U Playlist File |
| .MPV | MPEG Elementary Stream Video File |
| .M2T | HDV Video File |
| .MP2V | MPEG-2 Video File |
| .MPA | MPEG-2 Audio File |
| .MPG2 | MPEG-2 Video File |
| .MSV | Memory Stick Voice File |
| .MPE | MPEG Movie File |
| .MOB | MOBTV Video File |
| .M2A | MPEG-1 Layer 2 Audio File |
| .M2P | MPEG-2 Program Stream File |
| .MPEG | MPEG Movie |
| .M2TS | Blu-ray BDAV Video File |
| .OGX | Ogg Vorbis Multiplexed Media File |
| .NAP | Napster Secured Music File |
| .PRX | Windows Media Profile File |
| .RBS | MP3 Ringtone File |
| .RV | Real Video File |
| .RECORD | GarageBand Records Audio File |
| .RMI | RMID MIDI File |
| .TTA | True Audio File |
| .T3D | TicTacTi Advertisement Definition File |
| .U | AU Audio File |
| .SHN | Shorten Compressed Audio File |
| .SRT | SubRip Subtitle File |
| .SPX | Ogg Vorbis Speex File |
| .SMI | SAMI Subtitles File |
| .SCM | Super Chain Media File |
| .VP3 | On2 Streaming Video File |
| .VP6 | TrueMotion VP6 Video File |
| .VP7 | TrueMotion VP7 Video File |
| .VID | Generic Video File |
| .V | Subsampled Raw YUV Image |
| .WMDB | Windows Media Database File |
| .WAVE | WAVE Sound File |
| .WMZ | Compressed Windows Media Player Skin |
| .WDF | Wonderland Adventures Media File |
| .WAX | Windows Media Audio Redirect |
| .WVX | Windows Media Video Redirector |
| .WMX | Windows Media Redirector File |
| .WMD | Windows Media Download Package |
| .Y | Subsampled Raw YUV Image |
| .ZVR | SAFA Media Audio File |
Какие файлы может воспроизводить Windows Media Center
Обновлено: 2021-05-18
Медиацентр можно даже сделать проигрывателем по умолчанию для определенных типов файлов открываться в Windows Media, когда их дважды щелкнуть. Дополнительные сведения см. Изменение проигрывателя музыки и видео по умолчанию.
Чтобы открыть в Windows Media, медиацентра сначала нужно указать расположение, в котором хранятся файлы. Чтобы узнать, как это сделать, см. Добавление цифровых медиафайлов в Windows Media Center.
После установки новых кодеков в Windows, возможно, поддерживаться дополнительные форматы файлов.
В таблице приведены типы музыкальных файлов поддерживает медиацентр.
|
Типы музыкальных файлов (формат) |
Расширения имен файлов |
|---|---|
|
Файл Windows Media Audio |
.asx, .wm, .wma и .wmx |
|
Звуковой файл Windows |
.wav |
|
Звуковой файл MP3 |
.mp3 и .m3u |
|
Расширенное кодирование аудио |
.aac |
Типы видеофайлов
В таблице ниже приведены типы видеофайлов, поддерживает медиацентр.
|
Типы видеофайлов (формат) |
Расширения имен файлов |
|---|---|
|
Мультимедиа Windows |
.wm и .asf |
|
Файл Windows Media Video |
.wmv |
|
Видеофайл Windows |
.avi |
|
Файл телепередач (Windows) |
.wtv |
|
Файл записанных телепрограм (Microsoft) |
.dvr-ms |
|
Файл фильмов |
.mpeg, .mpg, .mpe, .m1v, .mp2, .mpv2 и .vob |
Типы файлов изображений
В таблице ниже приведены типы файлов изображений, которые поддерживает медиацентр.
|
Типы файлов изображений (формат) |
Расширения имен файлов |
|---|---|
|
JPEG |
.jpg и .jpeg |
|
JPEG XR |
.hdp и .wdp |
|
TIFF |
.tif и .tiff |
|
Формат RAW |
.raw |
|
GIF |
.gif |
|
Точечный рисунок |
.bmp |
|
Portable Network Graphics (Мобильная сетевая графика) |
.png |
Примечания:
- Медиацентр не поддерживает цифровые изображения, созданные с помощью цифровой камеры и сохраненные в формате RAW.
- Анимированные файлы в формате GIF поддерживаются частично. Для этого формата можно просматривать статические изображения, но не анимацию.
Стандартный мультимедиа проигрыватель, который по умолчанию включен в состав программ операционной системы Microsoft Windows. Также известен как Windows Media Player. Используется для воспроизведения аудио- и видеофайлов, потокового мультимедиа, просмотра изображений в виде слайд-шоу.
Проигрыватель Windows Media имеет понятный интерфейс и является доступным каждому пользователю вариантом для организации и воспроизведения мультимедиа на компьютере: музыки, фильмов, клипов, роликов, прочих аудио- и видеозаписей.
Программа помогает упорядочить коллекцию мультимедиа в виде библиотеки, автоматически загружает из интернета обложки музыкальных альбомов и сведения о композициях, сортируя треки по исполнителям, альбомам, жанрам и другим параметрам. Поддерживает функцию копирования музыки с компакт-диска на компьютер и записи аудиотреков на CD-диск.
Проигрыватель Windows Media предоставляет стандартные инструменты управления воспроизведением мультимедиа и создания плейлистов (списков воспроизведения). Из дополнительных возможностей можно отметить синхронизацию музыки, видео и фотографий с мобильными устройствами, приобретение цифрового медиаконтента в интернет-магазинах, передачу потокового мультимедиа на другие устройства сети, например, телевизор.
Основным расширением файла, ассоциированным с Проигрывателем Windows, является WMV – Windows Media Video File (Видеофайл Windows Media). По умолчанию Проигрыватель способен воспроизводить мультимедиа многих популярных форматов, среди которых WMA, MP3, AVI, WAV, MPEG. Перечень поддерживаемых медиаформатов можно расширить, скачав из интернета и установив на компьютер необходимый пакет кодеков. Как правило, это решает проблему с невозможностью воспроизведения того или иного файла.
До недавнего времени Проигрыватель Windows Media позволял просматривать видео с DVD-дисков, однако в Windows 8.1 и 10 эта возможность не поддерживается. Также не поддерживается воспроизведение дисков формата Blu-ray. Для этого необходимо использовать другие программы.
Если вы довольно долго пользуетесь операционной системой Windows, то наверняка вы уже не первый раз сталкиваетесь с проблемой, когда проигрыватель Windows Media не воспроизводит музыкальные или видео файлы. Чаще всего возникает сообщение «Проигрывателю Windows Media не удается воспроизвести файл» при переустановке системы или замене ее на другую версию. Как сделать, чтобы плеер вновь работал – об этом я расскажу вам далее в этой статье.
Содержание
- Причины проблемы с Windows Media
- Форматы и файлы, которые поддерживает Виндовс Медиа
- Устраняем ошибку проигрывателя при воспроизведении видео
- Что такое кодек?
Ошибка в Windows Media может иметь различные причины:
- Файл, который вы пытаетесь воспроизвести поврежден.
- Файл не поддерживается проигрывателем Windows Media. Например, файлы VIV нельзя открывать плеером, он не понимает их. Поэтому будет возникать подобная ошибка.
- В вашей операционной системе нет нужного кодека, который необходим для воспроизведения видео данного формата.
- Файл отсутствует на диске. Такое иногда случается, например, когда ярлык файла находится на рабочем столе, но сам файл был удален ранее.
- Проигрыватель не поддерживает данный кодек, который нужен для воспроизведения музыкального или видео файла.
Среди всех перечисленных причин чаще всего ошибка «Проигрывателю Виндовс Медиа не удается воспроизвести файл» возникает по причине отсутствия того или иного кодека. Чтобы не устанавливать различные пакеты кодеков и другое ПО вслепую, необходимо знать какие именно форматы поддерживает проигрыватель. Возможно вы просто пытаетесь воспроизвести не поддерживаемый формат файла.
Форматы и файлы, которые поддерживает Виндовс Медиа
Плеер поддерживает следующие форматы:
- MPE, MPG, M3U, MPEG (Moving Picture Experts Group), MPV2, MPA, MP3, M1V.
- Следующие форматы: WAV, WAX, WM, ASF, ASX, WMV, WMA.
- MIDI форматы (цифровой интерфейс музыкальных инструментов) RMI, MIDI, MID.
- Форматы UNIX – SND и AU.
Проигрыватель не поддерживает AVI-файлы, которые были созданы с помощью MPEG4v3. Эти файлы поддерживаются лишь в потоковом формате ASF. Есть только один способ воспроизвести файл – это перекодировать его в один из поддерживающих форматов. Это можно сделать при помощи кодировщика Windows Media.
Устраняем ошибку проигрывателя при воспроизведении видео
Чтобы убедиться в том, что файл не поврежден, попробуйте воспроизвести другой файл с таким же расширением. Если другие файлы воспроизводятся – значит файл, который вызывает ошибку поврежден. Если другие файлы тоже вызывают ошибку «Проигрывателю Windows Media не удается воспроизвести файл», попробуйте переустановить проигрыватель.
Если переустановка не дала результата, вам понадобиться установить пакет специальных кодеков. Для этого перейдите на сайт https://www.codecguide.com/download_kl.htm и выберите нужный пакет из списка. Лучше всего скачайте самый полный пакет кодеков (Full), он весит около 56 Мб. Для этого прокрутите главную страницу в самый низ и выберите ссылку «Download Full».
Если же вы не хотите этого делать вручную, можно установить в настройках плеера, чтобы он самостоятельно загружал все необходимые кодеки из Интернета. Для этого запустите проигрыватель, обычно он находится в меню «Пуск», в списке «Все программы».
- Нажмите на проигрывателе «Проигрывается» и выберите «Дополнительные параметры».
- Затем выберите вкладку «Проигрыватель».
- Поставьте галочку на пункте «Автоматически загружать кодеки» и нажмите «Применить», затем «Ок».
Поставьте галочку в пункте «Автоматически загружать кодеки»
Рекомендую: При воспроизведении видео нет звука.
Что такое кодек?
Кодек – это специальная программа, которая умеет преобразовывать сигналы и данные. Для того, чтобы передать или зашифровать любой поток или количество данных, его кодируют при помощи кодека, а для воспроизведения или преобразования – декодируют. Чаще всего кодеки задействованы в области цифрового видео и звука.
При преобразовании данных в кодеке могут быть использованы 2 вида сжатия – без потерь данных и с потерями. Практически все аудио- и видео кодеки используют способ с потерями данных при сжатии. Это дает возможность уменьшить объем конечного файла, что является положительным моментом для хранения этих данных. Но все же такой способ ведет к потере качества при воспроизведении. У аудио кодеков есть хорошее свойство – их можно настраивать таким образом, что потеря качества практически не распознается человеческим слухом. Это нужно знать для исправления дисфункции «Проигрывателю Windows Media не удается воспроизвести файл».
Если неприемлема потеря качества, используют другой способ сжатия – без потерь. Это может применяться в случаях, когда планируется последующее редактирования файла, иначе с потерями качество первичного файла будет значительно ухудшаться при каждом сохранении.
Если говорить о кодеках простым языком – то это программы-посредники между нами и компьютером. Если вы столкнулись с проблемой, когда проигрыватель Windows Media не воспроизводит файлы, то в первую очередь попробуйте установить пакет кодеков.