| Version of the Windows NT operating system | |

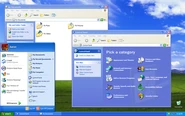
Screenshot of Windows XP running the Luna visual style, showing the start menu, taskbar, and My Computer window |
|
| Developer | Microsoft |
|---|---|
| Source model |
|
| Released to manufacturing |
August 24, 2001; 21 years ago[2] |
| General availability |
October 25, 2001; 21 years ago[2] |
| Final release | Service Pack 3 (5.1.2600.5512) / April 21, 2008; 14 years ago[3] |
| Marketing target | Consumer and Business |
| Update method |
|
| Platforms | IA-32, x86-64, and Itanium |
| Kernel type | Hybrid (NT) |
| Userland |
|
| License | Proprietary commercial software |
| Preceded by |
|
| Succeeded by | Windows Vista (2007) |
| Official website | Windows XP (archived at Wayback Machine) |
| Support status | |
All editions (except Windows XP Embedded, Windows XP 64-bit Edition, Windows Embedded for Point of Service, Windows Embedded Standard 2009, and Windows Embedded POSReady 2009):
Windows XP 64-bit Edition:
Windows XP Embedded:
Windows Embedded for Point of Service:
Windows Embedded Standard 2009:
Windows Embedded POSReady 2009:
|
Windows XP is a major release of Microsoft’s Windows NT operating system. It was released to manufacturing on August 24, 2001, and later to retail on October 25, 2001. It is a direct upgrade to its predecessors, Windows 2000 for high-end and business users and Windows Me for home users, and is available for any devices running Windows NT 4.0, Windows 98, Windows 2000, or Windows Me that meet the new Windows XP system requirements.
Development of Windows XP began in the late 1990s under the codename «Neptune», built on the Windows NT kernel and explicitly intended for mainstream consumer use. An updated version of Windows 2000 was also initially planned for the business market. However, in January 2000, both projects were scrapped in favor of a single OS codenamed «Whistler», which would serve as a single platform for both consumer and business markets. As a result, Windows XP is the first consumer edition of Windows not based on the Windows 95 kernel or MS-DOS. Windows XP removed support for PC-98, i486 and SGI Visual Workstation 320 and 540 and will only run on 32-bit x86 CPUs and devices that use BIOS firmware.
Upon its release, Windows XP received critical acclaim, noting increased performance and stability (especially compared to Windows Me), a more intuitive user interface, improved hardware support, and expanded multimedia capabilities. Windows XP and Windows Server 2003 were succeeded by Windows Vista and Windows Server 2008, released in 2007 and 2008, respectively.
Mainstream support for Windows XP ended on April 14, 2009, and extended support ended on April 8, 2014. Windows Embedded POSReady 2009, based on Windows XP Professional, received security updates until April 2019. After that, unofficial methods were made available to apply the updates to other editions of Windows XP. Still, Microsoft discouraged this practice, citing compatibility issues.[9] However, over eight years from the end of life date (September 2022), the majority of PCs in some countries (such as Armenia) still appeared to be running on Windows XP.[10] As of September 2022, globally, just 0.39% of Windows PCs[11] and 0.1% of all devices across all platforms continued to run Windows XP.
Development
In the late 1990s, initial development of what would become Windows XP was focused on two individual products: «Odyssey», which was reportedly intended to succeed the future Windows 2000 and «Neptune», which was reportedly a consumer-oriented operating system using the Windows NT architecture, succeeding the MS-DOS-based Windows 98.[12]
However, the projects proved to be too ambitious. In January 2000, shortly prior to the official release of Windows 2000, technology writer Paul Thurrott reported that Microsoft had shelved both Neptune and Odyssey in favor of a new product codenamed «Whistler», named after Whistler, British Columbia, as many Microsoft employees skied at the Whistler-Blackcomb ski resort.[13] The goal of Whistler was to unify both the consumer and business-oriented Windows lines under a single, Windows NT platform. Thurrott stated that Neptune had become «a black hole when all the features that were cut from Windows Me were simply re-tagged as Neptune features. And since Neptune and Odyssey would be based on the same code-base anyway, it made sense to combine them into a single project».[14]
At PDC on July 13, 2000, Microsoft announced that Whistler would be released during the second half of 2001, and also unveiled the first preview build, 2250, which featured an early implementation of Windows XP’s visual styles system and interface changes to Windows Explorer and the Control Panel.[15]
Microsoft released the first public beta build of Whistler, build 2296, on October 31, 2000. Subsequent builds gradually introduced features that users of the release version of Windows XP would recognize, such as Internet Explorer 6.0, the Microsoft Product Activation system and the Bliss desktop background.[16]
Whistler was officially unveiled during a media event on February 5, 2001, under the name Windows XP, where XP stands for «eXPerience».[17]
Release
In June 2001, Microsoft indicated that it was planning to spend at least US$1 billion on marketing and promoting Windows XP, in conjunction with Intel and other PC makers.[18] The theme of the campaign, «Yes You Can», was designed to emphasize the platform’s overall capabilities. Microsoft had originally planned to use the slogan «Prepare to Fly», but it was replaced because of sensitivity issues in the wake of the September 11 attacks.[19]
On August 24, 2001, Windows XP build 2600 was released to manufacturing (RTM). During a ceremonial media event at Microsoft Redmond Campus, copies of the RTM build were given to representatives of several major PC manufacturers in briefcases, who then flew off on decorated helicopters. While PC manufacturers would be able to release devices running XP beginning on September 24, 2001, XP was expected to reach general, retail availability on October 25, 2001. On the same day, Microsoft also announced the final retail pricing of XP’s two main editions, «Home» (as a replacement for Windows Me for home computing) and «Professional» (as a replacement for Windows 2000 for high-end users).[20]
New and updated features
User interface
While retaining some similarities to previous versions, Windows XP’s interface was overhauled with a new visual appearance, with an increased use of alpha compositing effects, drop shadows, and «visual styles», which completely changed the appearance of the operating system. The number of effects enabled are determined by the operating system based on the computer’s processing power, and can be enabled or disabled on a case-by-case basis. XP also added ClearType, a new subpixel rendering system designed to improve the appearance of fonts on liquid-crystal displays.[21] A new set of system icons was also introduced.[22] The default wallpaper, Bliss, is a photo of a landscape in the Napa Valley outside Napa, California, with rolling green hills and a blue sky with stratocumulus and cirrus clouds.[23]
The Start menu received its first major overhaul in XP, switching to a two-column layout with the ability to list, pin, and display frequently used applications, recently opened documents, and the traditional cascading «All Programs» menu. The taskbar can now group windows opened by a single application into one taskbar button, with a popup menu listing the individual windows. The notification area also hides «inactive» icons by default. A «common tasks» list was added, and Windows Explorer’s sidebar was updated to use a new task-based design with lists of common actions; the tasks displayed are contextually relevant to the type of content in a folder (e.g. a folder with music displays offers to play all the files in the folder, or burn them to a CD).[24]
The «task grouping» feature introduced in Windows XP showing both grouped and individual items
Fast user switching allows additional users to log into a Windows XP machine without existing users having to close their programs and log out. Although only one user at the time can use the console (i.e. monitor, keyboard, and mouse), previous users can resume their session once they regain control of the console.[25] Service Pack 2 and Service Pack 3 also introduced new features to Windows XP post-release, including the Windows Security Center, Bluetooth support, the executable space protection, Windows Firewall, and support for SDHC cards that are larger than 4 GB and smaller than 32 GB.[26][27][28][29]
Infrastructure
Windows XP uses prefetching to improve startup and application launch times.[30] It also became possible to revert the installation of an updated device driver, should the updated driver produce undesirable results.[31]
A copy protection system known as Windows Product Activation was introduced with Windows XP and its server counterpart, Windows Server 2003. All Windows licenses must be tied to a unique ID generated using information from the computer hardware, transmitted either via the internet or a telephone hotline. If Windows is not activated within 30 days of installation, the OS will cease to function until it is activated. Windows also periodically verifies the hardware to check for changes. If significant hardware changes are detected, the activation is voided, and Windows must be re-activated.[32]
Networking and internet functionality
Windows XP was originally bundled with Internet Explorer 6, Outlook Express 6, Windows Messenger, and MSN Explorer. New networking features were also added, including Internet Connection Firewall, Internet Connection Sharing integration with UPnP, NAT traversal APIs, Quality of Service features, IPv6 and Teredo tunneling, Background Intelligent Transfer Service, extended fax features, network bridging, peer to peer networking, support for most DSL modems, IEEE 802.11 (Wi-Fi) connections with auto configuration and roaming, TAPI 3.1, and networking over FireWire.[33] Remote Assistance and Remote Desktop were also added, which allow users to connect to a computer running Windows XP from across a network or the Internet and access their applications, files, printers, and devices or request help.[34] Improvements were also made to IntelliMirror features such as Offline Files, Roaming user profiles and Folder redirection.[35]
Backwards compatibility
To enable running software that targets or locks out specific versions of Windows, «Compatibility mode» was added. The feature allows pretending a selected earlier version of Windows to software, starting at Windows 95.[36]
While this ability was first introduced in Windows 2000 Service Pack 2, it had to be activated through the «register server» and was only available to administrator users, whereas Windows XP has it activated out of the box and also grants it to regular users.[37]
Other features
- Improved application compatibility and shims compared to Windows 2000.[38]
- DirectX 8.1, upgradeable to DirectX 9.0c.[39]
- A number of new features in Windows Explorer including task panes, thumbnails, and the option to view photos as a slideshow.[40]
- Improved imaging features such as Windows Picture and Fax Viewer.[41]
- Faster start-up, (because of improved Prefetch functions) logon, logoff, hibernation, and application launch sequences.[30]
- Numerous improvements to increase the system reliability such as improved System Restore,[42] Automated System Recovery,[43] and driver reliability improvements through Device Driver Rollback.[44]
- Hardware support improvements such as FireWire 800,[45] and improvements to multi-monitor support under the name «DualView».[46]
- Fast user switching.[47]
- The ClearType font rendering mechanism, which is designed to improve text readability on liquid-crystal display (LCD) and similar monitors, especially laptops.[21]
- Side-by-side assemblies[48] and registration-free COM.[49]
- General improvements to international support such as more locales, languages and scripts, MUI support in Terminal Services, improved Input Method Editors, and National Language Support.[50]
Removed features
Some of the programs and features that were part of the previous versions of Windows did not make it to Windows XP. Various MS-DOS commands available in its Windows 9x predecessor were removed,[51] as were the POSIX and OS/2 subsystems.[52]
In networking, NetBEUI, NWLink and NetDDE were deprecated and not installed by default.[53] Plug-and-play–incompatible communication devices (like modems and network interface cards) were no longer supported.[54]
Service Pack 2 and Service Pack 3 also removed features from Windows XP, including support for TCP half-open connections[55] and the address bar on the taskbar.[56]
Editions
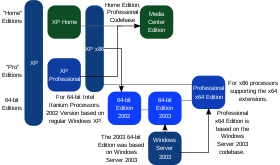
Diagram representing the main editions of Windows XP. It is based on the category of the edition (grey) and codebase (black arrow).
Windows XP was released in two major editions on launch: Home Edition and Professional Edition. Both editions were made available at retail as pre-loaded software on new computers and as boxed copies. Boxed copies were sold as «Upgrade» or «Full» licenses; the «Upgrade» versions were slightly cheaper, but require an existing version of Windows to install. The «Full» version can be installed on systems without an operating system or existing version of Windows.[18] The two editions of XP were aimed at different markets: Home Edition is explicitly intended for consumer use and disables or removes certain advanced and enterprise-oriented features present on Professional, such as the ability to join a Windows domain, Internet Information Services, and Multilingual User Interface. Windows 98 or Me can be upgraded to either edition, but Windows NT 4.0 and Windows 2000 can only be upgraded to Professional.[57] Windows’ software license agreement for pre-loaded licenses allows the software to be «returned» to the OEM for a refund if the user does not wish to use it.[58] Despite the refusal of some manufacturers to honor the entitlement, it has been enforced by courts in some countries.[59]
Two specialized variants of XP were introduced in 2002 for certain types of hardware, exclusively through OEM channels as pre-loaded software. Windows XP Media Center Edition was initially designed for high-end home theater PCs with TV tuners (marketed under the term «Media Center PC»), offering expanded multimedia functionality, an electronic program guide, and digital video recorder (DVR) support through the Windows Media Center application.[60] Microsoft also unveiled Windows XP Tablet PC Edition, which contains additional pen input features, and is optimized for mobile devices meeting its Tablet PC specifications.[61] Two different 64-bit editions of XP were made available. The first, Windows XP 64-Bit Edition, was intended for IA-64 (Itanium) systems; as IA-64 usage declined on workstations in favor of AMD’s x86-64 architecture, the Itanium edition was discontinued in January 2005.[62] A new 64-bit edition supporting the x86-64 architecture, called Windows XP Professional x64 Edition, was released in April of the same year.[63]
Microsoft also targeted emerging markets with the 2004 introduction of Windows XP Starter Edition, a special variant of Home Edition intended for low-cost PCs. The OS is primarily aimed at first-time computer owners, containing heavy localization (including wallpapers and screen savers incorporating images of local landmarks), and a «My Support» area which contains video tutorials on basic computing tasks. It also removes certain «complex» features, and does not allow users to run more than three applications at a time. After a pilot program in India and Thailand, Starter was released in other emerging markets throughout 2005.[64] In 2006, Microsoft also unveiled the FlexGo initiative, which would also target emerging markets with subsidized PCs on a pre-paid, subscription basis.[65]
As a result of unfair competition lawsuits in Europe and South Korea, which both alleged that Microsoft had improperly leveraged its status in the PC market to favor its own bundled software, Microsoft was ordered to release special editions of XP in these markets that excluded certain applications. In March 2004, after the European Commission fined Microsoft €497 million (US$603 million), Microsoft was ordered to release «N» editions of XP that excluded Windows Media Player, encouraging users to pick and download their own media player software.[66] As it was sold at the same price as the edition with Windows Media Player included, certain OEMs (such as Dell, who offered it for a short period, along with Hewlett-Packard, Lenovo and Fujitsu Siemens) chose not to offer it. Consumer interest was minuscule, with roughly 1,500 units shipped to OEMs, and no reported sales to consumers.[67] In December 2005, the Korean Fair Trade Commission ordered Microsoft to make available editions of Windows XP and Windows Server 2003 that do not contain Windows Media Player or Windows Messenger.[68] The «K» and «KN» editions of Windows XP were released in August 2006, and are only available in English and Korean, and also contain links to third-party instant messenger and media player software.[69]
Service packs
A service pack is a cumulative update package that is a superset of all updates, and even service packs, that have been released before it.[70] Three service packs have been released for Windows XP. Service Pack 3 is slightly different, in that it needs at least Service Pack 1 to have been installed, in order to update a live OS.[71] However, Service Pack 3 can still be embedded into a Windows installation disc; SP1 is not reported as a prerequisite for doing so.[72]
The unique boot screens from the RTM to Service Pack 1 versions of Windows XP that identified the edition of Windows XP currently running, including a green progress bar for Home Edition and a blue progress bar for Professional, Embedded, Tablet PC Edition, and Media Center Edition were removed in Service Pack 2 of Windows XP and was replaced with a generic «Windows XP» boot screen with a blue progress bar.
Service Pack 1
Service Pack 1 (SP1) for Windows XP was released on September 9, 2002. It contained over 300 minor, post-RTM bug fixes, along with all security patches released since the original release of XP. SP1 also added USB 2.0 support, the Microsoft Java Virtual Machine, .NET Framework support, and support for technologies used by the then-upcoming Media Center and Tablet PC editions of XP.[73] The most significant change on SP1 was the addition of Set Program Access and Defaults, a settings page which allows programs to be set as default for certain types of activities (such as media players or web browsers) and for access to bundled, Microsoft programs (such as Internet Explorer or Windows Media Player) to be disabled. This feature was added to comply with the settlement of United States v. Microsoft Corp., which required Microsoft to offer the ability for OEMs to bundle third-party competitors to software it bundles with Windows (such as Internet Explorer and Windows Media Player), and give them the same level of prominence as those normally bundled with the OS.[74]
On February 3, 2003, Microsoft released Service Pack 1a (SP1a). It was the same as SP1, except, the Microsoft Java Virtual Machine was excluded.[75]
Service Pack 2
Service Pack 2 (SP2) for Windows XP Home edition and Professional edition was released on August 25, 2004.[76] Headline features included WPA encryption compatibility for Wi-Fi and usability improvements to the Wi-Fi networking user interface,[77] partial Bluetooth support,[78] and various improvements to security systems.
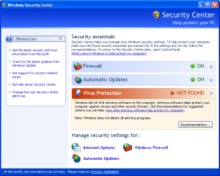
Headed by former computer hacker Window Snyder,[79][80] the service pack’s security improvements (codenamed «Springboard»,[81] as these features were intended to underpin additional changes in Longhorn) included a major revision to the included firewall (renamed Windows Firewall, and now enabled by default), and an update to Data Execution Prevention, which gained hardware support in the NX bit that can stop some forms of buffer overflow attacks. Raw socket support is removed (which supposedly limits the damage done by zombie machines) and the Windows Messenger service (which had been abused to cause pop-up advertisements to be displayed as system messages without a web browser or any additional software) became disabled by default. Additionally, security-related improvements were made to e-mail and web browsing. Service Pack 2 also added Security Center, an interface that provides a general overview of the system’s security status, including the state of the firewall and automatic updates. Third-party firewall and antivirus software can also be monitored from Security Center.[82]
In August 2006, Microsoft released updated installation media for Windows XP and Windows Server 2003 SP2 (SP2b), in order to incorporate a patch requiring ActiveX controls in Internet Explorer to be manually activated before a user may interact with them. This was done so that the browser would not violate a patent owned by Eolas.[83] Microsoft has since licensed the patent, and released a patch reverting the change in April 2008.[84] In September 2007, another minor revision known as SP2c was released for XP Professional, extending the number of available product keys for the operating system to «support the continued availability of Windows XP Professional through the scheduled system builder channel end-of-life (EOL) date of January 31, 2009.»[85]
Windows XP Service Pack 2 was later included in Windows Embedded for Point of Service and Windows Fundamentals for Legacy PCs.
Service Pack 3
The third and final Service Pack, SP3, was released through different channels between April[3] and June 2008,[86] about a year after the release of Windows Vista, and about a year before the release of Windows 7. Service Pack 3 was not available for Windows XP x64 Edition, which was based on the Windows Server 2003 kernel and, as a result, used its service packs[87] rather than the ones for the other editions.[88]
It began being automatically pushed out to Automatic Updates users on July 10, 2008.[89] A feature set overview which detailed new features available separately as stand-alone updates to Windows XP, as well as backported features from Windows Vista, was posted by Microsoft.[90] A total of 1,174 fixes are included in SP3.[91] Service Pack 3 could be installed on systems with Internet Explorer up to and including version 8; Internet Explorer 7 was not included as part of SP3.[92] It also did not include Internet Explorer 8, but instead was included in Windows 7, which was released one year after XP SP3.
Service Pack 3 included security enhancements over and above those of SP2, including APIs allowing developers to enable Data Execution Prevention for their code, independent of system-wide compatibility enforcement settings,[93] the Security Support Provider Interface,[94] improvements to WPA2 security,[95] and an updated version of the Microsoft Enhanced Cryptographic Provider Module that is FIPS 140-2 certified.[96]
In incorporating all previously released updates not included in SP2, Service Pack 3 included many other key features. Windows Imaging Component allowed camera vendors to integrate their own proprietary image codecs with the operating system’s features, such as thumbnails and slideshows.[97] In enterprise features, Remote Desktop Protocol 6.1 included support for ClearType and 32-bit color depth over RDP,[98] while improvements made to Windows Management Instrumentation in Windows Vista to reduce the possibility of corruption of the WMI repository were backported to XP SP3.[99]
In addition, SP3 contains updates to the operating system components of Windows XP Media Center Edition (MCE) and Windows XP Tablet PC Edition, and security updates for .NET Framework version 1.0, which is included in these editions. However, it does not include update rollups for the Windows Media Center application in Windows XP MCE 2005.[100] SP3 also omits security updates for Windows Media Player 10, although the player is included in Windows XP MCE 2005.[100] The Address Bar DeskBand on the Taskbar is no longer included because of antitrust violation concerns.[101]
Unofficial SP3 ZIP download packages were released on a now-defunct website called The Hotfix from 2005 to 2007.[102][103] The owner of the website, Ethan C. Allen, was a former Microsoft employee in Software Quality Assurance and would comb through the Microsoft Knowledge Base articles daily and download new hotfixes Microsoft would put online within the articles. The articles would have a «kbwinxppresp3fix» and/or «kbwinxpsp3fix» tag, thus allowing Allen to easily find and determine which fixes were planned for the official SP3 release to come. Microsoft publicly stated at the time that the SP3 pack was unofficial and advised users to not install it.[104][105] Allen also released a Vista SP1 package in 2007, for which Allen received a cease-and-desist email from Microsoft.[106]
Windows XP Service Pack 3 was later included in Windows Embedded Standard 2009 and Windows Embedded POSReady 2009.
System requirements
System requirements for Windows XP are as follows:
| Minimum | Recommended | |
|---|---|---|
| Home/Professional Edition[A] | ||
| CPU |
|
|
| Memory | 64 MB[E][F] | 128 MB |
| Free space |
|
|
| Media | CD-ROM drive or compatible | |
| Display | Super VGA (800 × 600) | |
| Sound hardware | N/A | Sound card plus speakers/headphones |
| Input device(s) | Keyboard, mouse | |
| Professional x64 Edition[J] | ||
| CPU |
|
|
| Memory | 256 MB | |
| Free space |
|
|
| Media | CD-ROM drive or compatible | |
| Display | Super VGA (800 × 600) | |
| Sound hardware | N/A | Sound card plus speakers/headphones |
| Input device(s) | Keyboard, mouse | |
| 64-Bit Edition[K] | ||
| CPU | Itanium 733 MHz | Itanium 800 MHz |
| Memory | 1 GB | |
| Free space | 6 GB | |
| Media | CD-ROM drive or compatible | |
| Display | Super VGA (800 × 600) | |
| Input device(s) | Keyboard, mouse |
Notes
- ^ «System requirements for Windows XP operating systems». April 28, 2005. Archived from the original on August 6, 2011. Retrieved March 12, 2007.
- ^ Even though this is Microsoft’s stated minimum processor speed for Windows XP, it is possible to install and run the operating system on early IA-32 processors such as a P5 Pentium without MMX instructions. Windows XP is not compatible with processors older than Pentium (such as 486) or the Cyrix 6×86 because it requires
CMPXCHG8B(see Pentium F00F bug) instructions. - ^ «Windows XP Minimal Requirement Test». Winhistory.de. September 9, 2011. Archived from the original on December 21, 2011. Retrieved January 1, 2012.
- ^ a b c d e «Windows XP: Required firmware and partition mapping scheme of hard disk drive». Support.microsoft.com. June 26, 2013. Archived from the original on April 27, 2017. Retrieved June 16, 2014.
- ^ A Microsoft TechNet paper from Summer 2001 (before Windows XP’s actual release), states that: «A computer with 64 MB of RAM will have sufficient resources to run Windows XP and a few applications with moderate memory requirements.» (Emphasis added.) These were said to be office productivity applications, e-mail programs, and web browsers (of the time). With such a configuration, user interface enhancements and fast user switching are turned off by default. For comparable workloads, 64 MB of RAM was then regarded as providing an equal or better user experience on Windows XP with similar settings than it would with Windows Me on the same hardware. In a later section of the paper, superior performance over Windows Me was noted with 128 MB of RAM or more, and with computers that exceed the minimum hardware requirements.
- ^ Sechrest, Stuart; Fortin, Michael (June 1, 2001). «Windows XP Performance». Microsoft TechNet. Archived from the original on July 27, 2010. Retrieved April 8, 2008.
- ^ «Hard disk space requirements for Windows XP Service Pack 1». Microsoft. October 29, 2007. Archived from the original on April 21, 2012. Retrieved April 6, 2012.
- ^ «The hard disk space requirements for Windows XP Service Pack 2». Microsoft. April 18, 2005. Archived from the original on November 24, 2010. Retrieved December 1, 2010.
- ^ «Windows XP – End of Support, Migration Guide, Download – TechNet». technet.microsoft.com. 2007. Archived from the original on May 13, 2008.
- ^ «Windows XP Professional x64 Edition SP2 VL EN (MSDN-TechNet)». Programmer Stuffs. March 23, 2011. Archived from the original on July 14, 2014. Retrieved May 2, 2012.
- ^ «Microsoft Windows XP 64-Bit Edition». Microsoft TechNet. Microsoft. August 15, 2001. Archived from the original on April 19, 2012. Retrieved May 2, 2012.
Physical memory limits
The maximum amount of RAM that Windows XP can support varies depending on the product edition and the processor architecture. All 32-bit editions of XP support up to 4 GB, except the Windows XP Starter edition, which supports up to 512 MB of RAM.[107] 64-bit editions support up to 128 GB.[108]
Processor limits
Windows XP Professional supports up to two physical processors;[109]
Windows XP Home Edition supports only one.[110]
However, XP supports a greater number of logical processors:
32-bit editions support up to 32 logical processors,[111] and 64-bit editions support up to 64 logical processors.[112]
Upgradeability
Several Windows XP components are upgradable to the latest versions, which include new versions introduced in later versions of Windows, and other major Microsoft applications are available. These latest versions for Windows XP include:
- ActiveSync 4.5
- DirectX 9.0c (June 7, 2010, Redistributable)
- Internet Explorer 8 on Windows XP Service Packs 2 and 3 (Internet Explorer 6 SP1 and Outlook Express 6 SP1 on Windows XP before SP2.)
- Windows Media Format Runtime and Windows Media Player 11 on Windows XP Service Packs 2 and 3 (and Windows Media Player 10 on Windows XP original release.)
- Microsoft Virtual PC 2004 and 2007
- .NET Framework up to and including version 4.0 (4.5 and higher versions are not supported.)
- Visual Studio 2005 on Windows XP versions below SP2, Visual Studio 2008 on Windows XP SP2 and Visual Studio 2010 on Windows XP SP3
- Windows Script Host 5.7
- Windows Installer 4.5
- Microsoft NetMeeting 3.02
- Office 2010 was the last version of Microsoft Office to be compatible with Windows XP.
- The Windows Services for UNIX subsystem can be installed to allow certain Unix-based applications to run on the operating system.
Support lifecycle
| Expiration date | |
|---|---|
| Mainstream support | April 14, 2009[4] |
| Extended support | April 8, 2014[4] The official exceptions ended in April 2019. |
| Applicable XP editions: | |
| Home Edition, Professional Edition, Professional x64 Edition, Professional for Embedded Systems, Media Center Editions (all), Starter Edition, Tablet PC Edition and Tablet PC Edition 2005,[4] as well as Windows Fundamentals for Legacy PCs.[113] | |
| Exceptions | |
| Windows XP 64-Bit Edition (Itanium edition, including Version 2003) | Unsupported as of June 30, 2005[5] |
| Windows XP Embedded | Mainstream support ended on January 11, 2011[4] Extended support ended on January 12, 2016[4] |
| Windows Embedded for Point of Service | Mainstream support ended on April 12, 2011[6] Extended support ended on April 12, 2016[6] |
| Windows Embedded Standard 2009 | Mainstream support ended on January 14, 2014 Extended support ended on January 8, 2019[7] |
| Windows Embedded POSReady 2009 | Mainstream support ended on April 8, 2014 Extended support ended on April 9, 2019[8] |
Support for the original release of Windows XP (without a service pack) ended on August 30, 2005.[4] Both Windows XP Service Pack 1 and 1a were retired on October 10, 2006,[4] and both Windows 2000 and Windows XP SP2 reached their end of support on July 13, 2010, about 24 months after the launch of Windows XP Service Pack 3.[4] The company stopped general licensing of Windows XP to OEMs and terminated retail sales of the operating system on June 30, 2008, 17 months after the release of Windows Vista.[114] However, an exception was announced on April 3, 2008, for OEMs producing what it defined as «ultra low-cost personal computers», particularly netbooks, until one year after the availability of Windows 7 on October 22, 2009. Analysts felt that the move was primarily intended to compete against Linux-based netbooks, although Microsoft’s Kevin Hutz stated that the decision was due to apparent market demand for low-end computers with Windows.[115]
Variants of Windows XP for embedded systems have different support policies: Windows XP Embedded SP3 and Windows Embedded for Point of Service SP3 were supported until January and April 2016, respectively. Windows Embedded Standard 2009, which was succeeded by Windows Embedded Standard 7, and Windows Embedded POSReady 2009, which was succeeded by Windows Embedded POSReady 7, were supported until January and April 2019, respectively.[116] These updates, while intended for the embedded editions, could also be downloaded on standard Windows XP with a registry hack, which enabled unofficial patches until April 2019. However, Microsoft advised Windows XP users against installing these fixes, citing incompatibility issues.[9][117]
End of support
On April 14, 2009, Windows XP exited mainstream support and entered the extended support phase; Microsoft continued to provide security updates every month for Windows XP, however, free technical support, warranty claims, and design changes were no longer being offered. Extended support ended on April 8, 2014, over 12 years after the release of Windows XP; normally Microsoft products have a support life cycle of only 10 years.[118] Beyond the final security updates released on April 8, no more security patches or support information are provided for XP free-of-charge; «critical patches» will still be created, and made available only to customers subscribing to a paid «Custom Support» plan.[119] As it is a Windows component, all versions of Internet Explorer for Windows XP also became unsupported.[120]
In January 2014, it was estimated that more than 95% of the 3 million automated teller machines in the world were still running Windows XP (which largely replaced IBM’s OS/2 as the predominant operating system on ATMs); ATMs have an average lifecycle of between seven and ten years, but some have had lifecycles as long as 15. Plans were being made by several ATM vendors and their customers to migrate to Windows 7-based systems over the course of 2014, while vendors have also considered the possibility of using Linux-based platforms in the future to give them more flexibility for support lifecycles, and the ATM Industry Association (ATMIA) has since endorsed Windows 10 as a further replacement.[121] However, ATMs typically run the embedded variant of Windows XP, which was supported through January 2016.[122] As of May 2017, around 60% of the 220,000 ATMs in India still run Windows XP.[123]
Furthermore, at least 49% of all computers in China still ran XP at the beginning of 2014. These holdouts were influenced by several factors; prices of genuine copies of later versions of Windows in the country are high, while Ni Guangnan of the Chinese Academy of Sciences warned that Windows 8 could allegedly expose users to surveillance by the United States government,[124] and the Chinese government banned the purchase of Windows 8 products for government use in May 2014 in protest of Microsoft’s inability to provide «guaranteed» support.[125] The government also had concerns that the impending end of support could affect their anti-piracy initiatives with Microsoft, as users would simply pirate newer versions rather than purchasing them legally. As such, government officials formally requested that Microsoft extend the support period for XP for these reasons. While Microsoft did not comply with their requests, a number of major Chinese software developers, such as Lenovo, Kingsoft and Tencent, will provide free support and resources for Chinese users migrating from XP.[126] Several governments, in particular those of the Netherlands and the United Kingdom, elected to negotiate «Custom Support» plans with Microsoft for their continued, internal use of Windows XP; the British government’s deal lasted for a year, and also covered support for Office 2003 (which reached end-of-life the same day) and cost £5.5 million.[127]
On March 8, 2014, Microsoft deployed an update for XP that, on the 8th of each month, displays a pop-up notification to remind users about the end of support; however, these notifications may be disabled by the user.[128] Microsoft also partnered with Laplink to provide a special «express» version of its PCmover software to help users migrate files and settings from XP to a computer with a newer version of Windows.[129]
An electroencephalograph running on Windows XP. The medical industry’s continued use of Windows XP is partly due to medical applications being incompatible with later versions of Windows.
Despite the approaching end of support, there were still notable holdouts that had not migrated past XP; many users elected to remain on XP because of the poor reception of Windows Vista, sales of newer PCs with newer versions of Windows declined because of the Great Recession and the effects of Vista, and deployments of new versions of Windows in enterprise environments require a large amount of planning, which includes testing applications for compatibility (especially those that are dependent on Internet Explorer 6, which is not compatible with newer versions of Windows).[130] Major security software vendors (including Microsoft itself) planned to continue offering support and definitions for Windows XP past the end of support to varying extents, along with the developers of Google Chrome, Mozilla Firefox, and Opera web browsers;[120] despite these measures, critics similarly argued that users should eventually migrate from XP to a supported platform.[131] The United States’ Computer Emergency Readiness Team released an alert in March 2014 advising users of the impending end of support, and informing them that using XP after April 8 may prevent them from meeting US government information security requirements.[132]
Microsoft continued to provide Security Essentials virus definitions and updates for its Malicious Software Removal Tool (MSRT) for XP until July 14, 2015.[133] As the end of extended support approached, Microsoft began to increasingly urge XP customers to migrate to newer versions such as Windows 7 or 8 in the interest of security, suggesting that attackers could reverse engineer security patches for newer versions of Windows and use them to target equivalent vulnerabilities in XP.[134] Windows XP is remotely exploitable by numerous security holes that were discovered after Microsoft stopped supporting it.[135][136]
Similarly, specialized devices that run XP, particularly medical devices, must have any revisions to their software—even security updates for the underlying operating system—approved by relevant regulators before they can be released. For this reason, manufacturers often did not allow any updates to devices’ operating systems, leaving them open to security exploits and malware.[137]
Despite the end of support for Windows XP, Microsoft has released three emergency security updates for the operating system to patch major security vulnerabilities:
- A patch released in May 2014 to address recently discovered vulnerabilities in Internet Explorer 6 through 11 on all versions of Windows.[138]
- A patch released in May 2017 to address a vulnerability that was being leveraged by the WannaCry ransomware attack.[139]
- A patch released in May 2019 to address a critical code execution vulnerability in Remote Desktop Services which can be exploited in a similar way as the WannaCry vulnerability.[140][141]
Researchers reported in August 2019 that Windows 10 users may be at risk for «critical» system compromise because of design flaws of hardware device drivers from multiple providers.[142] In the same month, computer experts reported that the BlueKeep security vulnerability, CVE-2019-0708, that potentially affects older unpatched Microsoft Windows versions via the program’s Remote Desktop Protocol, allowing for the possibility of remote code execution, may now include related flaws, collectively named DejaBlue, affecting newer Windows versions (i.e., Windows 7 and all recent versions) as well.[143] In addition, experts reported a Microsoft security vulnerability, CVE-2019-1162, based on legacy code involving Microsoft CTF and ctfmon (ctfmon.exe), that affects all Windows versions from the older Windows XP version to the most recent Windows 10 versions; a patch to correct the flaw is currently available.[144]
Microsoft announced in July 2019 that the Microsoft Internet Games services on Windows XP and Windows Me would end on July 31, 2019 (and for Windows 7 on January 22, 2020).[145] Others, such as Steam, had done the same, ending support for Windows XP and Windows Vista in January 2019.[146]
In 2020, Microsoft announced that it would disable the Windows Update service for SHA-1 endpoints; since Windows XP did not get an update for SHA-2, Windows Update Services are no longer available on the OS as of late July 2020.[147] However, as of October 2021, the old updates for Windows XP are still available on the Microsoft Update Catalog,[148] or through Legacy Update, a community-driven third party replacement for the Windows XP update servers.
Reception
On release, Windows XP received critical acclaim. CNET described the operating system as being «worth the hype», considering the new interface to be «spiffier» and more intuitive than previous versions, but feeling that it may «annoy» experienced users with its «hand-holding». XP’s expanded multimedia support and CD burning functionality were also noted, along with its streamlined networking tools. The performance improvements of XP in comparison to 2000 and Me were also praised, along with its increased number of built-in device drivers in comparison to 2000. The software compatibility tools were also praised, although it was noted that some programs, particularly older MS-DOS software, may not work correctly on XP because of its differing architecture. They panned Windows XP’s new licensing model and product activation system, considering it to be a «slightly annoying roadblock», but acknowledged Microsoft’s intent for the changes.[149] PC Magazine provided similar praise, although noting that a number of its online features were designed to promote Microsoft-owned services, and that aside from quicker boot times, XP’s overall performance showed little difference over Windows 2000.[150] Windows XP’s default theme, Luna, was criticized by some users for its childish look.[151][152]
Despite extended support for Windows XP ending in 2014, many users – including some enterprises – were reluctant to move away from an operating system they viewed as a stable known quantity despite the many security and functionality improvements in subsequent releases of Windows. Windows XP’s longevity was viewed as testament to its stability and Microsoft’s successful attempts to keep it up to date, but also as an indictment of its direct successor’s perceived failings.[153]
According to web analytics data generated by Net Applications, Windows XP was the most widely used operating system until August 2012, when Windows 7 overtook it (later overtaken by Windows 10),[154] while StatCounter indicates it happening almost a year earlier.[155] In January 2014, Net Applications reported a market share of 29.23%[156] of «desktop operating systems» for XP (when XP was introduced there was not a separate mobile category to track), while W3Schools reported a share of 11.0%.[157]
As of September 2022, in most regions or continents, Windows XP market share on PCs, as a fraction of the total Windows share, has gone below 1% (0.5% in Africa[158]). XP still has a double-digit market share in a few countries, such as Armenia at over 50%,[159][160][161][162] at 57%, where Windows 7 was highest ranked, and with it being replaced by Windows 10, Windows XP got highest ranked for the longest time, and had over 60% share on some weekends in the summer of 2019.[163][164]
Source code leak
On September 23, 2020, source code for Windows XP with Service Pack 1 and Windows Server 2003 was leaked onto the imageboard 4chan by an unknown user. Anonymous users managed to compile the code, as well as a Twitter user who posted videos of the process on YouTube proving that the code was genuine.[165] The videos were later removed on copyright grounds by Microsoft. The leak was incomplete as it was missing the Winlogon source code and some other components.[166][167] The original leak itself was spread using magnet links and torrent files whose payload originally included Server 2003 and XP source code and which was later updated with additional files, among which were previous leaks of Microsoft products, its patents, media about conspiracy theories on Bill Gates by anti-vaccination movements and an assortment of PDF files on different topics.[168]
Microsoft issued a statement stating that it was investigating the leaks.[167][169][170]
See also
- BlueKeep (security vulnerability)
- Comparison of operating systems
- History of operating systems
- List of operating systems
References
- ^ «Windows Licensing Programs». Microsoft. Archived from the original on December 16, 2008. Retrieved September 21, 2008.
- ^ a b «An Inside Look at the Months-long Process of Getting Windows XP Ready for Release to Manufacturing | Stories». Microsoft Stories. Microsoft. August 24, 2001. Archived from the original on August 5, 2019. Retrieved June 24, 2018.
- ^ a b Kelly, Gordon (April 16, 2008). «Windows XP SP3 Release Date(s) Confirmed». Trusted Reviews. Trusted Reviews. Archived from the original on June 23, 2018. Retrieved June 23, 2018.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l «Microsoft Product Lifecycle Search: Windows XP». Microsoft Support. Microsoft. Archived from the original on July 20, 2012. Retrieved May 14, 2022.
- ^ a b «Microsoft Security Bulletin MS05-036 – Critical». July 12, 2015. Archived from the original on April 26, 2018. Retrieved April 26, 2018.
- ^ a b c d Mackie, Kurt (February 19, 2014). «Windows XP Embedded Supported for Two or More Years». Redmond Magazine. 1105 Media. Archived from the original on February 20, 2017. Retrieved June 23, 2018.
- ^ a b c «Microsoft Product Lifecycle Search: Windows Embedded Standard 2009». Microsoft Support. Microsoft. Archived from the original on July 13, 2015. Retrieved October 13, 2012.
- ^ a b c «Microsoft Product Lifecycle Search: Windows Embedded POSReady 2009». Microsoft Support. Microsoft. Archived from the original on October 10, 2014. Retrieved October 13, 2012.
- ^ a b Seltzer, Larry (May 26, 2014). «Registry hack enables continued updates for Windows XP». ZDNet. Archived from the original on January 26, 2021. Retrieved January 30, 2021.
[UPDATE:] Late Monday we received a statement from a Microsoft spokesperson: We recently became aware of a hack that purportedly aims to provide security updates to Windows XP customers. The security updates that could be installed are intended for Windows Embedded and Windows Server 2003 customers and do not fully protect Windows XP customers. Windows XP customers also run a significant risk of functionality issues with their machines if they install these updates, as they are not tested against Windows XP. The best way for Windows XP customers to protect their systems is to upgrade to a more modern operating system, like Windows 7 or Windows 8.1.
- ^ «Desktop Windows Version Market Share in Armenia — September 2022». September 30, 2022. Retrieved October 10, 2022.
- ^ «Desktop Windows Version Market Share Worldwide | StatCounter Global Stats». gs.statcounter.com. Statcounter. Archived from the original on April 20, 2019. Retrieved May 8, 2022.
- ^ Miles, Stephanie (January 24, 2000). «Microsoft consolidates Windows development efforts». CNET. CNET Networks. Archived from the original on February 1, 2014. Retrieved January 23, 2014.
- ^ «Windows «Longhorn» FAQ». Paul Thurrott’s SuperSite for Windows. Penton Media. June 22, 2005. Archived from the original on April 4, 2008. Retrieved April 4, 2008.
- ^ Thurrott, Paul (October 6, 2010). «The Road to Gold: The development of Windows XP Reviewed». Paul Thurrott’s Supersite for Windows. Penton Media. Archived from the original on February 2, 2014. Retrieved January 23, 2014.
- ^ Thurrott, Paul (July 17, 2000). «Introducing the Whistler Preview, Build 2250». Windows IT Pro. Penton Media. Archived from the original on June 12, 2018. Retrieved June 9, 2018.
- ^ Thurrott, Paul (October 6, 2010). «The Road to Gold (Part Two)». Paul Thurrott’s SuperSite for Windows. Penton Media. Archived from the original on February 2, 2014. Retrieved January 23, 2014.
- ^ «Microsoft to christen Windows, Office with new name». CNET. CNET Networks. February 5, 2001. Archived from the original on February 1, 2014. Retrieved January 23, 2014.
- ^ a b «Windows XP marketing tab to hit $1 billion». CNET. CNET Networks. January 2, 2002. Archived from the original on February 1, 2014. Retrieved January 23, 2014.
- ^ «Microsoft changes XP slogan in wake of US attacks». Computerworld NZ. IDG. Archived from the original on September 5, 2015. Retrieved August 7, 2015.
- ^ Thurrott, Paul (October 15, 2001). «The Road to Gold (Part Three)». Paul Thurrott’s Supersite for Windows. Penton Media. Archived from the original on August 29, 2017. Retrieved March 11, 2017.
- ^ a b «HOW TO: Use ClearType to Enhance Screen Fonts in Windows XP». Support. Microsoft. October 27, 2002. Archived from the original on August 5, 2011. Retrieved August 8, 2011.
- ^ Esposito, Dino (November 2001). «New Graphical Interface: Enhance Your Programs with New Windows XP Shell Features». MSDN. Microsoft. Archived from the original on August 9, 2011. Retrieved August 8, 2011.
- ^ Turner, Paul (February 22, 2004). «No view of Palouse from Windows». The Spokesman-Review. Spokane. Archived from the original on May 11, 2011. Retrieved September 19, 2012.
- ^ Fitzpatrick, Jason (August 6, 2015). «The Start Menu Should Be Sacred (But It’s Still a Disaster in Windows 10)». How-To Geek. Archived from the original on March 13, 2017. Retrieved July 30, 2016.
- ^ «How To Use the Fast User Switching Feature in Windows XP (Revision 1.5)». Microsoft Support. Microsoft. March 27, 2007. Archived from the original on August 12, 2011. Retrieved August 8, 2011.
- ^ «Bluetooth Wireless Technology FAQ». Archived from the original on December 23, 2018. Retrieved August 8, 2011.
- ^ «Manually Configuring Windows Firewall in Windows XP Service Pack 2». Archived from the original on August 26, 2017. Retrieved August 26, 2017.
- ^ «Description of the Windows Firewall feature in Windows XP SP2». Archived from the original on September 17, 2009. Retrieved September 18, 2009.
- ^ «Hotfix for Windows XP that adds support for SDHC cards that have a capacity of more than 4 GB». Support (5.0 ed.). May 22, 2013. Archived from the original on February 5, 2014. Retrieved June 18, 2019.
- ^ a b «Kernel Enhancements for Windows XP». Windows Hardware Developer Center (WHDC). Microsoft. January 13, 2003. Archived from the original on March 7, 2008. Retrieved August 8, 2011.
- ^ «HOW TO: Use the Driver Roll Back Feature to Restore a Previous Version of a Device Driver in Windows XP». Microsoft. October 27, 2002. Archived from the original on February 18, 2006.
- ^ Fisher, Ken (February 2, 2001). «Windows Product Activation: an early look». Ars Technica. Archived from the original on December 5, 2011. Retrieved February 22, 2017.
- ^ «Windows XP Networking Features and Enhancements». Microsoft TechNet. Microsoft. August 8, 2001. Archived from the original on July 26, 2011. Retrieved August 8, 2011.
- ^ «Frequently Asked Questions About Remote Desktop». Microsoft. Archived from the original on July 4, 2007.
- ^ Otey, Michael (October 2001). «Discover Windows XP». Microsoft Developer. Archived from the original on April 20, 2012. Retrieved June 21, 2018.
- ^ «Windows XP Program Compatibility Wizard». ServerWatch. March 12, 2002. Archived from the original on November 13, 2021. Retrieved November 13, 2021.
- ^ «How to Enable Application Compatibility-Mode Technology in Windows 2000 Service Pack 2». Active Win. 2000. Archived from the original on August 18, 2001. Retrieved November 13, 2021.
- ^ Proffit, Brian (September 2, 2002). «Old Apps Find A New Home On Windows XP». PC Magazine. Ziff Davis. Archived from the original on June 10, 2020. Retrieved July 10, 2018.
- ^ Karp, David; O’Reilly, Tim; Mott, Troy (2005). Windows XP in a Nutshell : [a desktop quick reference] (2nd ed.). Beijing [u.a.]: O’Reilly. p. 141. ISBN 978-0-596-00900-7.
- ^ Richtmyer, Richard (August 23, 2001). «Opening up Windows XP». CNN Money. CNN. Archived from the original on December 23, 2017. Retrieved June 24, 2018.
- ^ «Windows Picture and Fax Viewer overview». Windows XP Professional Product Documentation. Microsoft Corporation. Archived from the original on 2 December 2010. Retrieved 23 November 2010.
- ^ Harder, Bobbie (April 2001). «Microsoft Windows XP System Restore». Microsoft. Archived from the original on February 4, 2005.
- ^ Petri, Daniel (January 8, 2009). «What is ASR in Windows XP and Windows Server 2003?». Petri. Blue Whale Web Media Group. Archived from the original on March 12, 2017. Retrieved June 24, 2018.
- ^ Columbus, Louis (June 29, 2001). Exploring Windows XP’s Device Driver Rollback and System Restore. InformIT. Pearson Education. Archived from the original on January 5, 2014. Retrieved June 24, 2018.
- ^ Norton, Peter; Mueller, John Paul (2002). Peter Norton’s Complete Guide to Windows XP. Pearson Education. p. N/A. ISBN 9780132715386. Archived from the original on April 15, 2021. Retrieved July 10, 2018.
- ^ McNamee, Kieran (June 27, 2003). «Setting up dual monitors using Windows XP Home». PC World. Archived from the original on February 5, 2017. Retrieved June 24, 2018.
- ^ «Architecture of Fast User Switching». Microsoft Knowledgebase. Microsoft. January 15, 2006. Archived from the original on August 2, 2009. Retrieved June 24, 2018.
- ^ Satran, Michael (May 31, 2018). «About Side-by-Side Assemblies». docs.microsoft.com. Microsoft. Archived from the original on June 24, 2018. Retrieved June 24, 2018.
- ^ Wienholt, Nick (August 14, 2006). «Simplify Application Deployment with Registration-Free COM — Developer.com». www.developer.com. QuinStreet Enterprise. Archived from the original on December 16, 2010. Retrieved June 24, 2018.
- ^ Honeycutt, Jerry (2003). Introducing Microsoft Windows Server 2003. Redmond, Wash.: Microsoft. pp. 293–298. ISBN 9780735615700.
- ^ «New ways to do familiar tasks». Windows XP Product Documentation. Microsoft. Archived from the original on May 3, 2006. Retrieved May 21, 2014.
- ^ «Kernel Enhancements for Windows XP». MSDN. Microsoft. January 13, 2003. Archived from the original on March 6, 2013. Retrieved April 16, 2014.
- ^ Pittsley, Steven (June 13, 2002). «Easy install guide for NetBEUI and IPX in Windows XP Pro». TechRepublic. CBS Interactive. Archived from the original on April 11, 2017. Retrieved June 24, 2018.
- ^ «Non-Plug and Play Network Device Support in Windows XP». Support. Microsoft. October 18, 2001. Archived from the original on October 30, 2004. Retrieved November 8, 2012.
- ^ «TCP/IP Raw Sockets (Windows)». MSDN. Microsoft. Archived from the original on January 28, 2013. Retrieved November 7, 2012.
- ^ Pash, Adam (April 29, 2008). «Field Guide to Windows XP SP3». Lifehacker. Univision Communications. Archived from the original on January 15, 2018. Retrieved June 24, 2018.
- ^ «Differences with Windows XP Home Edition». TechNet. Microsoft. September 11, 2009. Archived from the original on February 9, 2014. Retrieved January 26, 2014.
- ^ Marti, Don (November 6, 2006). «Dell customer gets Windows refund». LinuxWorld. IDG. Archived from the original on September 27, 2008. Retrieved September 13, 2008.
- ^ «HP must reimburse Italian PC buyer the amount paid for Microsoft software». Heise online. October 29, 2007. Archived from the original on October 15, 2008. Retrieved September 13, 2008.
- ^ Wilcox, Joe (July 16, 2002). «Microsoft reveals media XP details». CNET. CNET Networks. Archived from the original on February 7, 2015. Retrieved January 26, 2014.
- ^ Wilcox, Joe; Junnarkar, Sandeep (November 7, 2002). «Microsoft launches tablet PC drive». CNET. CNET Networks. Archived from the original on February 7, 2015. Retrieved January 26, 2014.
- ^ Evers, Joris (January 5, 2005). «Microsoft nixes Windows XP for Itanium». Computerworld. IDG. Archived from the original on February 2, 2014. Retrieved January 26, 2014.
- ^ «Microsoft Raises the Speed Limit with the Availability of 64-Bit Editions of Windows Server 2003 and Windows XP Professional» (Press release). Microsoft. April 25, 2005. Archived from the original on February 25, 2015. Retrieved September 10, 2015.
- ^ Thurrott, Paul (January 3, 2005). «Windows XP Starter Edition». Paul Thurrott’s SuperSite for Windows. Penton Media. Archived from the original on August 28, 2013. Retrieved April 12, 2008.
- ^ Fried, Ina (May 23, 2006). «Microsoft pitches pay-as-you-go PCs». CNET. CNET Networks. Archived from the original on February 7, 2015. Retrieved January 26, 2014.
- ^ «Microsoft and EU reach agreement». BBC. March 28, 2005. Archived from the original on September 22, 2015.
- ^ Bishop, Todd (December 24, 2004). «Europe gets ‘reduced’ Windows». Seattle Post-Intelligencer. Hearst Corporation. Archived from the original on October 6, 2021. Retrieved November 30, 2018.
- ^ Anderson, Nate (December 7, 2005). «South Korea fines Microsoft for antitrust abuses». Ars Technica. Condé Nast Publications. Archived from the original on April 22, 2008. Retrieved April 12, 2008.
- ^ «Changes to Windows XP Home Edition K and Windows XP Professional K from earlier versions of Windows XP (MSKB 922474)». Microsoft Support. Microsoft. September 15, 2006. Archived from the original on December 19, 2013. Retrieved January 26, 2014.
- ^ «Service Pack and Update Center». Support. Microsoft. September 10, 2016. Archived from the original on August 31, 2017.
- ^ «Installing Windows XP Service Pack 3 (SP3)». Microsoft. Microsoft. November 18, 2011. Archived from the original on August 22, 2017. Retrieved August 22, 2017.
- ^ Purdy, Kevin. «Slipstream Service Pack 3 into Your Windows XP Installation CD». Lifehacker. Archived from the original on August 22, 2017. Retrieved August 22, 2017.
- ^ «Windows XP SP1 Irons out the Wrinkles». PC Magazine. Archived from the original on February 26, 2014. Retrieved January 26, 2014.
- ^ Mendelson, Edward. «Microsoft Windows XP Service Pack 1 review». CNET. CNET Networks. Archived from the original on February 9, 2008. Retrieved January 26, 2014.
- ^ «Differences Between Windows XP SP1 and Windows XP SP1a». February 3, 2003. Archived from the original on January 27, 2007. Retrieved September 21, 2007.
- ^ «How to obtain the latest Windows XP service pack». March 26, 2007. Archived from the original on October 14, 2004. Retrieved September 21, 2007.
- ^ Shinder, Deb (August 26, 2004). «Windows XP Service Pack 2: How it affects wireless networking». TechRepublic. CBS Interactive. Archived from the original on June 13, 2017. Retrieved June 24, 2018.
- ^ «Bluetooth Wireless Technology FAQ – 2010». July 24, 2012. Archived from the original on March 3, 2016. Retrieved November 4, 2012.
- ^ Menn, Joseph (2019). Cult of the Dead Cow: How the Original Hacking Supergroup Might Just Save the World. New York: Public Affairs. p. 49–50.
- ^ Grimes, Roger A. (2017). «46 — Profile: Window Snyder». Hacking the hacker : learn from the experts who take down hackers. Indianapolis, IN: Wiley. ISBN 978-1-119-39626-0. OCLC 983465946.
- ^ Thurrott, Paul (October 15, 2003). «Windows XP SP2 to be ‘Springboard’ to Longhorn». Windows IT Pro. Archived from the original on June 23, 2018.
- ^ «Windows XP Service Pack 2 information». Microsoft. August 4, 2004. Archived from the original on October 16, 2007.
- ^ Mux, Victor (August 21, 2006). «Why Windows XP SP2b and Windows Server 2003 SP2a?». Microsoft. Archived from the original on August 12, 2009.
- ^ Fletcher, Jefferson (April 8, 2008). «IE Automatic Component Activation Now Available». IEBlog. Microsoft. Archived from the original on April 11, 2008. Retrieved April 11, 2008.
- ^ Mux, Victor (August 9, 2007). «Microsoft Windows XP Professional Service Pack 2c Release». MSDN. Microsoft. Archived from the original on February 2, 2014. Retrieved January 26, 2014.
- ^ Emil Protalinski — April 29, 2008, 1:35 pm UTC (April 29, 2008). «Microsoft releases the long-anticipated Windows XP SP3 (updated)». Ars Technica. Archived from the original on January 15, 2022. Retrieved February 10, 2022.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ «Release Notes for Microsoft Windows Server 2003 Service Pack 2». Archived from the original on November 11, 2019. Retrieved November 11, 2019.
- ^ Oiaga, Marius (December 14, 2007). «64-Bit Windows XP Service Pack 3?». Softpedia. SoftNews NET. Archived from the original on May 8, 2018. Retrieved June 24, 2018.
- ^ Keizer, Gregg (July 8, 2008). «Microsoft sets XP SP3 automatic download for Thursday». Computerworld. IDG. Archived from the original on July 9, 2008. Retrieved July 8, 2008.
- ^ «Windows XP Service Pack 3 Overview». Microsoft. May 6, 2008. Archived from the original on May 6, 2008. Retrieved May 7, 2008.
- ^ «List of fixes that are included in Windows XP Service Pack 3». Microsoft. May 6, 2008. Archived from the original on May 9, 2008. Retrieved June 23, 2018.
- ^ Oiaga, Marius (December 14, 2007). «No, Internet Explorer 7 Will Not(!) Be a Part of Windows XP SP3». SoftNews NET. Archived from the original on January 18, 2012.
- ^ Howard, Michael (January 29, 2008). «New NX APIs added to Windows Vista SP1, Windows XP SP3 and Windows Server 2008». Michael Howard’s Web Log. Microsoft. Archived from the original on August 25, 2011. Retrieved August 8, 2011.
- ^ «Description of the Credential Security Support Provider (CredSSP) in Windows XP Service Pack 3». Microsoft. May 6, 2008. Archived from the original on October 9, 2009. Retrieved June 23, 2018.
- ^ Enterprise IT Planet Staff (May 13, 2005). «Upgraded Wi-Fi Security for Windows XP SP2». Wi-Fi Planet. QuinStreet Enterprise. Archived from the original on June 23, 2018. Retrieved June 23, 2018.
- ^ «Overview of Windows XP Service Pack 3» (PDF). Archived (PDF) from the original on January 17, 2009.
- ^ «Information about Windows Imaging Component». Microsoft. August 13, 2002. Archived from the original on May 10, 2011.
- ^ Nanjappa, Ashwin (January 27, 2010). «Windows: ClearType on RDP». CodeYarns.com. Archived from the original on November 17, 2015. Retrieved June 16, 2014.
- ^ «A hotfix is available that improves the stability of the Windows Management Instrumentation repository in Windows XP». Support. Microsoft. October 8, 2011. Archived from the original on March 5, 2013. Retrieved January 20, 2013.
- ^ a b «FAQs regarding SP3 RTM». Microsoft. April 22, 2008. Archived from the original on August 24, 2011. Retrieved June 23, 2018.
- ^ Kaelin, Mark (May 8, 2008). «How do I… Return the Address bar Windows XP SP3 removed?». TechRepublic. CBS Interactive. Archived from the original on September 5, 2015. Retrieved May 5, 2015.
- ^ «Windows XP SP3 preview surfaces on Web». PC World. IDG. October 6, 2005. Archived from the original on October 31, 2020. Retrieved October 29, 2020.
- ^ «Sneak preview of Windows XP SP3 surfaces». Ars Technica. Ars Technica. October 6, 2005. Archived from the original on November 4, 2020. Retrieved October 29, 2020.
- ^ «Microsoft employee blasts ‘fake’ service pack». PC World. IDG. October 14, 2005. Archived from the original on October 31, 2020. Retrieved October 29, 2020.
- ^ «Windows XP SP3 preview a fake». Ars Technica. Ars Technica. October 15, 2005. Archived from the original on October 31, 2020. Retrieved October 29, 2020.
- ^ «Microsoft leans on Vista SP1 site». PC World. IDG. October 4, 2007. Archived from the original on May 18, 2017. Retrieved October 29, 2020.
- ^ «What is the maximum amount of RAM the Windows operating system can handle?». Crucial. Archived from the original on May 11, 2011. Retrieved June 25, 2010.
- ^ «Physical Memory Limits: Windows XP». Memory Limits for Windows Releases. Microsoft. Archived from the original on January 6, 2014. Retrieved January 14, 2014.
- ^ «Processor and memory capabilities of Windows XP Professional x64 Edition and of the x64-based versions of Windows Server 2003 (Revision 7.0)». Microsoft Support. Microsoft. December 20, 2010. Archived from the original on August 12, 2011. Retrieved August 8, 2011.
- ^ Kumar, I. Suuresh (October 25, 2010). «Multi-core processor and multiprocessor limit for Windows XP». Microsoft Answers. Microsoft. Archived from the original on April 19, 2014. Retrieved April 18, 2014.
- ^ «Processor Affinity Under WOW64». MSDN. Microsoft. January 27, 2011. Archived from the original on May 6, 2011. Retrieved August 8, 2011.
- ^ «Maximum quantity of logical processors in a PC supported by Microsoft Windows XP professional, x64 edition». Support. Microsoft. December 20, 2010. Archived from the original on January 11, 2013. Retrieved January 20, 2013.
- ^ «Microsoft Product Lifecycle Search: Windows Fundamentals for Legacy PCs». Microsoft Support. Microsoft. Archived from the original on October 5, 2014. Retrieved October 13, 2012.
- ^ Fried, Ina (September 27, 2007). «Microsoft extends Windows XP’s stay». CNET. CBS Interactive. Archived from the original on August 30, 2008. Retrieved June 5, 2008.
- ^ Lai, Eric (March 3, 2008). «Microsoft to keep Windows XP alive—but only for Eee PCs and wannabes». Computerworld. IDG. Archived from the original on April 8, 2008. Retrieved April 8, 2008.
- ^ Tung, Liam (February 18, 2014). «Microsoft: ‘Remember, some XP-based embedded systems to get support to 2019’«. ZDNet. CBS Interactive. Archived from the original on April 4, 2014. Retrieved April 6, 2014.
- ^ Newman, Jared (August 27, 2014). «Enthusiast developer keeps Windows XP alive with unofficial ‘Service Pack 4’«. PCWorld. Archived from the original on October 26, 2018. Retrieved October 26, 2018.
- ^ Satherley, Dan (April 9, 2013). «Businesses urged to ditch XP». 3 News NZ. Archived from the original on July 13, 2014. Retrieved June 28, 2019.
- ^ Keizer, Gregg (August 26, 2013). «Microsoft will craft XP patches after April ’14, but not for you». Computerworld. IDG. Archived from the original on October 20, 2013. Retrieved December 12, 2013.
- ^ a b Keizer, Gregg (March 11, 2014). «US-CERT urges XP users to dump IE». Computerworld. IDG. Archived from the original on June 28, 2019. Retrieved June 28, 2019.
- ^ ATM Industry Association (collectively) (June 1, 2015). «ATMIA position paper recommending migration to Windows 10». www.atmia.com (Press release). ATM Industry Association. Archived from the original on May 25, 2017.
- ^ Summers, Nick (January 16, 2014). «ATMs Face Deadline to Upgrade From Windows XP». Bloomberg Businessweek. Bloomberg L.P. Archived from the original on January 16, 2014. Retrieved January 17, 2014.
- ^ «Wannacry ransomware cyber attack: Indian ATMs could be at high risk as most run on Windows XP». Business Today. May 15, 2017. Archived from the original on May 17, 2017. Retrieved May 18, 2017.
- ^ «Windows 8 a ‘threat’ to China’s security». BBC. June 5, 2014. Archived from the original on October 8, 2018. Retrieved October 8, 2018.
- ^ Kan, Michael (May 20, 2014). «China bans government purchases of Windows 8». PCWorld. IDG. Archived from the original on May 20, 2014. Retrieved May 20, 2014.
- ^ «Microsoft Partners Lenovo, Tencent to Offer XP Tech Support in China». Voanews.com. Reuters. April 9, 2014. Archived from the original on April 13, 2014. Retrieved April 16, 2014.
- ^ Gallagher, Sean (April 6, 2014). «Not dead yet: Dutch, British governments pay to keep Windows XP alive». Ars Technica. Condé Nast Publications. Archived from the original on October 14, 2019. Retrieved October 15, 2019.
- ^ Foley, Mary Jo (March 3, 2014). «Microsoft to start nagging Windows XP users about April 8 end-of-support date». ZDNet. CBS Interactive. Archived from the original on October 14, 2019. Retrieved October 15, 2019.
- ^ Yegulalp, Serdar (March 3, 2014). «Microsoft: Use Laplink’s Windows XP migration tools, not ours». Infoworld. Archived from the original on October 15, 2019.
- ^ Ward, Mark (March 5, 2014). «XP – the operating system that will not die». BBC News. Archived from the original on March 24, 2014. Retrieved March 25, 2014.
- ^ Egan, Matt (April 7, 2014). «What should XP users do when Microsoft ends support? Upgrade to Windows 8, buy a new PC, keep running XP?». PC Advisor. Archived from the original on February 14, 2014. Retrieved April 6, 2014.
- ^ «Alert (TA14-069A): Microsoft Ending Support for Windows XP and Office 2003». March 11, 2014. Archived from the original on March 16, 2014. Retrieved April 6, 2014.
- ^ Keizer, Gregg (January 19, 2014). «Microsoft will furnish malware assassin to XP users until mid-2015». Computerworld. IDG. Archived from the original on January 22, 2014.
- ^ «Microsoft Warns of Permanent Zero-Day Exploits for Windows XP». Infosecurity. Reed Exhibitions. August 20, 2013. Archived from the original on August 26, 2013. Retrieved August 27, 2013.
- ^ «Microsoft Security Bulletin MS15-011 JASBUG». February 10, 2015. Archived from the original on August 11, 2015. Retrieved September 18, 2015.
- ^ Freeman, Robert (November 11, 2014). «IBM X-Force Researcher Finds Significant Vulnerability in Microsoft Windows». Securityintelligence.com. Archived from the original on July 3, 2015. Retrieved September 18, 2015.
- ^ Talbot, David (October 17, 2012). «Computer Viruses Are «Rampant» on Medical Devices in Hospitals». MIT Technology Review. Archived from the original on October 19, 2016. Retrieved April 6, 2014.
- ^ Goodin, Dan (May 1, 2014). «Emergency patch for critical IE 0-day throws lifeline to XP laggards, too». Ars Technica. Conde Nast. Archived from the original on May 17, 2017. Retrieved May 26, 2017.
- ^ Warren, Tom (May 13, 2017). «Microsoft issues ‘highly unusual’ Windows XP patch to prevent massive ransomware attack». The Verge. Vox Media. Archived from the original on May 14, 2017. Retrieved May 13, 2017.
- ^ Warren, Tom (May 14, 2019). «Microsoft warns of major WannaCry-like Windows security exploit, releases XP patches». The Verge. Vox Media. Archived from the original on September 2, 2019. Retrieved May 16, 2019.
- ^ «Prevent a worm by updating Remote Desktop Services (CVE-2019-0708) – MSRC». blogs.technet.microsoft.com. May 14, 2019. Archived from the original on May 14, 2019. Retrieved May 16, 2019.
- ^ Winder, Davey (August 11, 2019). «Critical Windows 10 Warning: Millions Of Users At Risk». Forbes. Archived from the original on August 11, 2019. Retrieved August 11, 2019.
- ^ Greenberg, Andy (August 13, 2019). «DejaBlue: New BlueKeep-Style Bugs Renew The Risk Of A Windows worm». wired. Archived from the original on April 13, 2021. Retrieved August 15, 2019.
- ^ Seals, Tara (August 14, 2019). «20-Year-Old Bug in Legacy Microsoft Code Plagues All Windows Users». ThreatPost.com. Archived from the original on April 17, 2021. Retrieved August 15, 2019.
- ^ «Farewell to Microsoft Internet Games on Windows XP, Windows ME, and Windows 7». answers.microsoft.com. Archived from the original on July 14, 2019. Retrieved August 4, 2019.
- ^ «Windows XP and Windows Vista Support – Steam – Knowledge Base – Steam Support». support.steampowered.com. Archived from the original on August 12, 2019. Retrieved August 4, 2019.
- ^ «Windows Update SHA-1 based endpoints discontinued for older Windows devices». support.microsoft.com. Archived from the original on April 17, 2021. Retrieved April 6, 2021.
- ^ «Microsoft Update Catalog». www.catalog.update.microsoft.com. Archived from the original on April 15, 2021. Retrieved April 6, 2021.
- ^ Lake, Matt (October 10, 2002). «Microsoft Windows XP – Home Edition review». CNET. Archived from the original on May 31, 2007. Retrieved March 25, 2014.
- ^ Mendelson, Edward (September 3, 2001). «Microsoft Ships Its Biggest OS Upgrade Ever—Early!». PC Magazine. Archived from the original on March 25, 2014. Retrieved March 25, 2014.
- ^ Manes, Stephen (August 26, 2004). «Full Disclosure: Your Take on Windows’ Worst Irritations». PCWorld. IDG. Archived from the original on October 8, 2009.
- ^ Bright, Peter (April 10, 2014). «Memory lane: Before everyone loved Windows XP, they hated it». Ars Technica. Condé Nast. Archived from the original on April 24, 2014. Retrieved June 20, 2014.
- ^ Bright, Peter (October 25, 2011). «Ten years of Windows XP: how longevity became a curse». Ars Technica. WIRED Media Group. Archived from the original on June 12, 2018. Retrieved June 9, 2018.
- ^ «Operating system market share». September 9, 2012. Archived from the original on September 9, 2012. Retrieved September 8, 2018.
- ^ «Desktop Windows Version Market Share Worldwide». StatCounter Global Stats. Archived from the original on April 20, 2019. Retrieved July 2, 2019.
- ^ Crothers, Brooke (February 2, 2014). «Oops, Windows XP gains in January but so does Windows 8.1». CNET. CBS Interactive. Archived from the original on February 21, 2014. Retrieved March 16, 2014.
- ^ «OS Platform Statistics». w3schools. Archived from the original on September 17, 2015. Retrieved September 14, 2015.
- ^ «Desktop Windows Version Market Share Africa». StatCounter Global Stats. Archived from the original on September 22, 2022. Retrieved September 22, 2022.
- ^ «Desktop Windows Version Market Share Armenia». StatCounter Global Stats. Archived from the original on September 4, 2018. Retrieved December 11, 2021.
- ^ «Desktop Windows Version Market Share Armenia». StatCounter Global Stats. Archived from the original on September 4, 2018. Retrieved December 11, 2021.
- ^ «Desktop Windows Version Market Share Armenia». StatCounter Global Stats. Archived from the original on September 4, 2018. Retrieved July 10, 2021.
- ^ «Desktop Windows Version Market Share Armenia». StatCounter Global Stats. Archived from the original on September 4, 2018. Retrieved March 2, 2021.
- ^ «Desktop Windows Version Market Share Armenia». StatCounter Global Stats. Archived from the original on September 4, 2018. Retrieved July 2, 2020.
- ^ «Desktop Windows Version Market Share Armenia». StatCounter Global Stats. Archived from the original on September 4, 2018. Retrieved July 2, 2020.
- ^ Cimpanu, Catalin. «Windows XP leak confirmed after user compiles the leaked code into a working OS». ZDNet. Archived from the original on September 30, 2020. Retrieved October 1, 2020.
- ^ Warren, Tom (September 25, 2020). «Windows XP source code leaks online». The Verge. Archived from the original on September 29, 2021. Retrieved October 1, 2020.
- ^ a b Alcorn, Paul (September 30, 2020). «Windows XP Source Code Leaked, Posted to 4chan (Update, It Works)». Tom’s Hardware. Archived from the original on October 6, 2021. Retrieved October 1, 2020.
- ^ «Windows XP Source Code Leaked By Apparent Bill Gates Conspiracist». Gizmodo. September 25, 2020. Archived from the original on October 1, 2020. Retrieved October 1, 2020.
- ^ «The Windows XP and Windows Server 2003 source code leaks online». Graham Cluley. September 25, 2020. Archived from the original on September 26, 2020. Retrieved September 29, 2020.
- ^ «Windows XP source code leaked online». www.computing.co.uk. September 28, 2020. Archived from the original on October 2, 2020. Retrieved September 29, 2020.
Further reading
- Joyce, Jerry; Moon, Marianne (2004). Microsoft Windows XP Plain & Simple. Microsoft Press. ISBN 978-0-7356-2112-1.
External links
- Windows XP End of Support
- Security Update for Windows XP SP3 (KB4012598)
| Version of the Windows NT operating system | |

Screenshot of Windows XP running the Luna visual style, showing the start menu, taskbar, and My Computer window |
|
| Developer | Microsoft |
|---|---|
| Source model |
|
| Released to manufacturing |
August 24, 2001; 21 years ago[2] |
| General availability |
October 25, 2001; 21 years ago[2] |
| Final release | Service Pack 3 (5.1.2600.5512) / April 21, 2008; 14 years ago[3] |
| Marketing target | Consumer and Business |
| Update method |
|
| Platforms | IA-32, x86-64, and Itanium |
| Kernel type | Hybrid (NT) |
| Userland |
|
| License | Proprietary commercial software |
| Preceded by |
|
| Succeeded by | Windows Vista (2007) |
| Official website | Windows XP (archived at Wayback Machine) |
| Support status | |
All editions (except Windows XP Embedded, Windows XP 64-bit Edition, Windows Embedded for Point of Service, Windows Embedded Standard 2009, and Windows Embedded POSReady 2009):
Windows XP 64-bit Edition:
Windows XP Embedded:
Windows Embedded for Point of Service:
Windows Embedded Standard 2009:
Windows Embedded POSReady 2009:
|
Windows XP is a major release of Microsoft’s Windows NT operating system. It was released to manufacturing on August 24, 2001, and later to retail on October 25, 2001. It is a direct upgrade to its predecessors, Windows 2000 for high-end and business users and Windows Me for home users, and is available for any devices running Windows NT 4.0, Windows 98, Windows 2000, or Windows Me that meet the new Windows XP system requirements.
Development of Windows XP began in the late 1990s under the codename «Neptune», built on the Windows NT kernel and explicitly intended for mainstream consumer use. An updated version of Windows 2000 was also initially planned for the business market. However, in January 2000, both projects were scrapped in favor of a single OS codenamed «Whistler», which would serve as a single platform for both consumer and business markets. As a result, Windows XP is the first consumer edition of Windows not based on the Windows 95 kernel or MS-DOS. Windows XP removed support for PC-98, i486 and SGI Visual Workstation 320 and 540 and will only run on 32-bit x86 CPUs and devices that use BIOS firmware.
Upon its release, Windows XP received critical acclaim, noting increased performance and stability (especially compared to Windows Me), a more intuitive user interface, improved hardware support, and expanded multimedia capabilities. Windows XP and Windows Server 2003 were succeeded by Windows Vista and Windows Server 2008, released in 2007 and 2008, respectively.
Mainstream support for Windows XP ended on April 14, 2009, and extended support ended on April 8, 2014. Windows Embedded POSReady 2009, based on Windows XP Professional, received security updates until April 2019. After that, unofficial methods were made available to apply the updates to other editions of Windows XP. Still, Microsoft discouraged this practice, citing compatibility issues.[9] However, over eight years from the end of life date (September 2022), the majority of PCs in some countries (such as Armenia) still appeared to be running on Windows XP.[10] As of September 2022, globally, just 0.39% of Windows PCs[11] and 0.1% of all devices across all platforms continued to run Windows XP.
Development
In the late 1990s, initial development of what would become Windows XP was focused on two individual products: «Odyssey», which was reportedly intended to succeed the future Windows 2000 and «Neptune», which was reportedly a consumer-oriented operating system using the Windows NT architecture, succeeding the MS-DOS-based Windows 98.[12]
However, the projects proved to be too ambitious. In January 2000, shortly prior to the official release of Windows 2000, technology writer Paul Thurrott reported that Microsoft had shelved both Neptune and Odyssey in favor of a new product codenamed «Whistler», named after Whistler, British Columbia, as many Microsoft employees skied at the Whistler-Blackcomb ski resort.[13] The goal of Whistler was to unify both the consumer and business-oriented Windows lines under a single, Windows NT platform. Thurrott stated that Neptune had become «a black hole when all the features that were cut from Windows Me were simply re-tagged as Neptune features. And since Neptune and Odyssey would be based on the same code-base anyway, it made sense to combine them into a single project».[14]
At PDC on July 13, 2000, Microsoft announced that Whistler would be released during the second half of 2001, and also unveiled the first preview build, 2250, which featured an early implementation of Windows XP’s visual styles system and interface changes to Windows Explorer and the Control Panel.[15]
Microsoft released the first public beta build of Whistler, build 2296, on October 31, 2000. Subsequent builds gradually introduced features that users of the release version of Windows XP would recognize, such as Internet Explorer 6.0, the Microsoft Product Activation system and the Bliss desktop background.[16]
Whistler was officially unveiled during a media event on February 5, 2001, under the name Windows XP, where XP stands for «eXPerience».[17]
Release
In June 2001, Microsoft indicated that it was planning to spend at least US$1 billion on marketing and promoting Windows XP, in conjunction with Intel and other PC makers.[18] The theme of the campaign, «Yes You Can», was designed to emphasize the platform’s overall capabilities. Microsoft had originally planned to use the slogan «Prepare to Fly», but it was replaced because of sensitivity issues in the wake of the September 11 attacks.[19]
On August 24, 2001, Windows XP build 2600 was released to manufacturing (RTM). During a ceremonial media event at Microsoft Redmond Campus, copies of the RTM build were given to representatives of several major PC manufacturers in briefcases, who then flew off on decorated helicopters. While PC manufacturers would be able to release devices running XP beginning on September 24, 2001, XP was expected to reach general, retail availability on October 25, 2001. On the same day, Microsoft also announced the final retail pricing of XP’s two main editions, «Home» (as a replacement for Windows Me for home computing) and «Professional» (as a replacement for Windows 2000 for high-end users).[20]
New and updated features
User interface
While retaining some similarities to previous versions, Windows XP’s interface was overhauled with a new visual appearance, with an increased use of alpha compositing effects, drop shadows, and «visual styles», which completely changed the appearance of the operating system. The number of effects enabled are determined by the operating system based on the computer’s processing power, and can be enabled or disabled on a case-by-case basis. XP also added ClearType, a new subpixel rendering system designed to improve the appearance of fonts on liquid-crystal displays.[21] A new set of system icons was also introduced.[22] The default wallpaper, Bliss, is a photo of a landscape in the Napa Valley outside Napa, California, with rolling green hills and a blue sky with stratocumulus and cirrus clouds.[23]
The Start menu received its first major overhaul in XP, switching to a two-column layout with the ability to list, pin, and display frequently used applications, recently opened documents, and the traditional cascading «All Programs» menu. The taskbar can now group windows opened by a single application into one taskbar button, with a popup menu listing the individual windows. The notification area also hides «inactive» icons by default. A «common tasks» list was added, and Windows Explorer’s sidebar was updated to use a new task-based design with lists of common actions; the tasks displayed are contextually relevant to the type of content in a folder (e.g. a folder with music displays offers to play all the files in the folder, or burn them to a CD).[24]
The «task grouping» feature introduced in Windows XP showing both grouped and individual items
Fast user switching allows additional users to log into a Windows XP machine without existing users having to close their programs and log out. Although only one user at the time can use the console (i.e. monitor, keyboard, and mouse), previous users can resume their session once they regain control of the console.[25] Service Pack 2 and Service Pack 3 also introduced new features to Windows XP post-release, including the Windows Security Center, Bluetooth support, the executable space protection, Windows Firewall, and support for SDHC cards that are larger than 4 GB and smaller than 32 GB.[26][27][28][29]
Infrastructure
Windows XP uses prefetching to improve startup and application launch times.[30] It also became possible to revert the installation of an updated device driver, should the updated driver produce undesirable results.[31]
A copy protection system known as Windows Product Activation was introduced with Windows XP and its server counterpart, Windows Server 2003. All Windows licenses must be tied to a unique ID generated using information from the computer hardware, transmitted either via the internet or a telephone hotline. If Windows is not activated within 30 days of installation, the OS will cease to function until it is activated. Windows also periodically verifies the hardware to check for changes. If significant hardware changes are detected, the activation is voided, and Windows must be re-activated.[32]
Networking and internet functionality
Windows XP was originally bundled with Internet Explorer 6, Outlook Express 6, Windows Messenger, and MSN Explorer. New networking features were also added, including Internet Connection Firewall, Internet Connection Sharing integration with UPnP, NAT traversal APIs, Quality of Service features, IPv6 and Teredo tunneling, Background Intelligent Transfer Service, extended fax features, network bridging, peer to peer networking, support for most DSL modems, IEEE 802.11 (Wi-Fi) connections with auto configuration and roaming, TAPI 3.1, and networking over FireWire.[33] Remote Assistance and Remote Desktop were also added, which allow users to connect to a computer running Windows XP from across a network or the Internet and access their applications, files, printers, and devices or request help.[34] Improvements were also made to IntelliMirror features such as Offline Files, Roaming user profiles and Folder redirection.[35]
Backwards compatibility
To enable running software that targets or locks out specific versions of Windows, «Compatibility mode» was added. The feature allows pretending a selected earlier version of Windows to software, starting at Windows 95.[36]
While this ability was first introduced in Windows 2000 Service Pack 2, it had to be activated through the «register server» and was only available to administrator users, whereas Windows XP has it activated out of the box and also grants it to regular users.[37]
Other features
- Improved application compatibility and shims compared to Windows 2000.[38]
- DirectX 8.1, upgradeable to DirectX 9.0c.[39]
- A number of new features in Windows Explorer including task panes, thumbnails, and the option to view photos as a slideshow.[40]
- Improved imaging features such as Windows Picture and Fax Viewer.[41]
- Faster start-up, (because of improved Prefetch functions) logon, logoff, hibernation, and application launch sequences.[30]
- Numerous improvements to increase the system reliability such as improved System Restore,[42] Automated System Recovery,[43] and driver reliability improvements through Device Driver Rollback.[44]
- Hardware support improvements such as FireWire 800,[45] and improvements to multi-monitor support under the name «DualView».[46]
- Fast user switching.[47]
- The ClearType font rendering mechanism, which is designed to improve text readability on liquid-crystal display (LCD) and similar monitors, especially laptops.[21]
- Side-by-side assemblies[48] and registration-free COM.[49]
- General improvements to international support such as more locales, languages and scripts, MUI support in Terminal Services, improved Input Method Editors, and National Language Support.[50]
Removed features
Some of the programs and features that were part of the previous versions of Windows did not make it to Windows XP. Various MS-DOS commands available in its Windows 9x predecessor were removed,[51] as were the POSIX and OS/2 subsystems.[52]
In networking, NetBEUI, NWLink and NetDDE were deprecated and not installed by default.[53] Plug-and-play–incompatible communication devices (like modems and network interface cards) were no longer supported.[54]
Service Pack 2 and Service Pack 3 also removed features from Windows XP, including support for TCP half-open connections[55] and the address bar on the taskbar.[56]
Editions
Diagram representing the main editions of Windows XP. It is based on the category of the edition (grey) and codebase (black arrow).
Windows XP was released in two major editions on launch: Home Edition and Professional Edition. Both editions were made available at retail as pre-loaded software on new computers and as boxed copies. Boxed copies were sold as «Upgrade» or «Full» licenses; the «Upgrade» versions were slightly cheaper, but require an existing version of Windows to install. The «Full» version can be installed on systems without an operating system or existing version of Windows.[18] The two editions of XP were aimed at different markets: Home Edition is explicitly intended for consumer use and disables or removes certain advanced and enterprise-oriented features present on Professional, such as the ability to join a Windows domain, Internet Information Services, and Multilingual User Interface. Windows 98 or Me can be upgraded to either edition, but Windows NT 4.0 and Windows 2000 can only be upgraded to Professional.[57] Windows’ software license agreement for pre-loaded licenses allows the software to be «returned» to the OEM for a refund if the user does not wish to use it.[58] Despite the refusal of some manufacturers to honor the entitlement, it has been enforced by courts in some countries.[59]
Two specialized variants of XP were introduced in 2002 for certain types of hardware, exclusively through OEM channels as pre-loaded software. Windows XP Media Center Edition was initially designed for high-end home theater PCs with TV tuners (marketed under the term «Media Center PC»), offering expanded multimedia functionality, an electronic program guide, and digital video recorder (DVR) support through the Windows Media Center application.[60] Microsoft also unveiled Windows XP Tablet PC Edition, which contains additional pen input features, and is optimized for mobile devices meeting its Tablet PC specifications.[61] Two different 64-bit editions of XP were made available. The first, Windows XP 64-Bit Edition, was intended for IA-64 (Itanium) systems; as IA-64 usage declined on workstations in favor of AMD’s x86-64 architecture, the Itanium edition was discontinued in January 2005.[62] A new 64-bit edition supporting the x86-64 architecture, called Windows XP Professional x64 Edition, was released in April of the same year.[63]
Microsoft also targeted emerging markets with the 2004 introduction of Windows XP Starter Edition, a special variant of Home Edition intended for low-cost PCs. The OS is primarily aimed at first-time computer owners, containing heavy localization (including wallpapers and screen savers incorporating images of local landmarks), and a «My Support» area which contains video tutorials on basic computing tasks. It also removes certain «complex» features, and does not allow users to run more than three applications at a time. After a pilot program in India and Thailand, Starter was released in other emerging markets throughout 2005.[64] In 2006, Microsoft also unveiled the FlexGo initiative, which would also target emerging markets with subsidized PCs on a pre-paid, subscription basis.[65]
As a result of unfair competition lawsuits in Europe and South Korea, which both alleged that Microsoft had improperly leveraged its status in the PC market to favor its own bundled software, Microsoft was ordered to release special editions of XP in these markets that excluded certain applications. In March 2004, after the European Commission fined Microsoft €497 million (US$603 million), Microsoft was ordered to release «N» editions of XP that excluded Windows Media Player, encouraging users to pick and download their own media player software.[66] As it was sold at the same price as the edition with Windows Media Player included, certain OEMs (such as Dell, who offered it for a short period, along with Hewlett-Packard, Lenovo and Fujitsu Siemens) chose not to offer it. Consumer interest was minuscule, with roughly 1,500 units shipped to OEMs, and no reported sales to consumers.[67] In December 2005, the Korean Fair Trade Commission ordered Microsoft to make available editions of Windows XP and Windows Server 2003 that do not contain Windows Media Player or Windows Messenger.[68] The «K» and «KN» editions of Windows XP were released in August 2006, and are only available in English and Korean, and also contain links to third-party instant messenger and media player software.[69]
Service packs
A service pack is a cumulative update package that is a superset of all updates, and even service packs, that have been released before it.[70] Three service packs have been released for Windows XP. Service Pack 3 is slightly different, in that it needs at least Service Pack 1 to have been installed, in order to update a live OS.[71] However, Service Pack 3 can still be embedded into a Windows installation disc; SP1 is not reported as a prerequisite for doing so.[72]
The unique boot screens from the RTM to Service Pack 1 versions of Windows XP that identified the edition of Windows XP currently running, including a green progress bar for Home Edition and a blue progress bar for Professional, Embedded, Tablet PC Edition, and Media Center Edition were removed in Service Pack 2 of Windows XP and was replaced with a generic «Windows XP» boot screen with a blue progress bar.
Service Pack 1
Service Pack 1 (SP1) for Windows XP was released on September 9, 2002. It contained over 300 minor, post-RTM bug fixes, along with all security patches released since the original release of XP. SP1 also added USB 2.0 support, the Microsoft Java Virtual Machine, .NET Framework support, and support for technologies used by the then-upcoming Media Center and Tablet PC editions of XP.[73] The most significant change on SP1 was the addition of Set Program Access and Defaults, a settings page which allows programs to be set as default for certain types of activities (such as media players or web browsers) and for access to bundled, Microsoft programs (such as Internet Explorer or Windows Media Player) to be disabled. This feature was added to comply with the settlement of United States v. Microsoft Corp., which required Microsoft to offer the ability for OEMs to bundle third-party competitors to software it bundles with Windows (such as Internet Explorer and Windows Media Player), and give them the same level of prominence as those normally bundled with the OS.[74]
On February 3, 2003, Microsoft released Service Pack 1a (SP1a). It was the same as SP1, except, the Microsoft Java Virtual Machine was excluded.[75]
Service Pack 2
Service Pack 2 (SP2) for Windows XP Home edition and Professional edition was released on August 25, 2004.[76] Headline features included WPA encryption compatibility for Wi-Fi and usability improvements to the Wi-Fi networking user interface,[77] partial Bluetooth support,[78] and various improvements to security systems.
Headed by former computer hacker Window Snyder,[79][80] the service pack’s security improvements (codenamed «Springboard»,[81] as these features were intended to underpin additional changes in Longhorn) included a major revision to the included firewall (renamed Windows Firewall, and now enabled by default), and an update to Data Execution Prevention, which gained hardware support in the NX bit that can stop some forms of buffer overflow attacks. Raw socket support is removed (which supposedly limits the damage done by zombie machines) and the Windows Messenger service (which had been abused to cause pop-up advertisements to be displayed as system messages without a web browser or any additional software) became disabled by default. Additionally, security-related improvements were made to e-mail and web browsing. Service Pack 2 also added Security Center, an interface that provides a general overview of the system’s security status, including the state of the firewall and automatic updates. Third-party firewall and antivirus software can also be monitored from Security Center.[82]
In August 2006, Microsoft released updated installation media for Windows XP and Windows Server 2003 SP2 (SP2b), in order to incorporate a patch requiring ActiveX controls in Internet Explorer to be manually activated before a user may interact with them. This was done so that the browser would not violate a patent owned by Eolas.[83] Microsoft has since licensed the patent, and released a patch reverting the change in April 2008.[84] In September 2007, another minor revision known as SP2c was released for XP Professional, extending the number of available product keys for the operating system to «support the continued availability of Windows XP Professional through the scheduled system builder channel end-of-life (EOL) date of January 31, 2009.»[85]
Windows XP Service Pack 2 was later included in Windows Embedded for Point of Service and Windows Fundamentals for Legacy PCs.
Service Pack 3
The third and final Service Pack, SP3, was released through different channels between April[3] and June 2008,[86] about a year after the release of Windows Vista, and about a year before the release of Windows 7. Service Pack 3 was not available for Windows XP x64 Edition, which was based on the Windows Server 2003 kernel and, as a result, used its service packs[87] rather than the ones for the other editions.[88]
It began being automatically pushed out to Automatic Updates users on July 10, 2008.[89] A feature set overview which detailed new features available separately as stand-alone updates to Windows XP, as well as backported features from Windows Vista, was posted by Microsoft.[90] A total of 1,174 fixes are included in SP3.[91] Service Pack 3 could be installed on systems with Internet Explorer up to and including version 8; Internet Explorer 7 was not included as part of SP3.[92] It also did not include Internet Explorer 8, but instead was included in Windows 7, which was released one year after XP SP3.
Service Pack 3 included security enhancements over and above those of SP2, including APIs allowing developers to enable Data Execution Prevention for their code, independent of system-wide compatibility enforcement settings,[93] the Security Support Provider Interface,[94] improvements to WPA2 security,[95] and an updated version of the Microsoft Enhanced Cryptographic Provider Module that is FIPS 140-2 certified.[96]
In incorporating all previously released updates not included in SP2, Service Pack 3 included many other key features. Windows Imaging Component allowed camera vendors to integrate their own proprietary image codecs with the operating system’s features, such as thumbnails and slideshows.[97] In enterprise features, Remote Desktop Protocol 6.1 included support for ClearType and 32-bit color depth over RDP,[98] while improvements made to Windows Management Instrumentation in Windows Vista to reduce the possibility of corruption of the WMI repository were backported to XP SP3.[99]
In addition, SP3 contains updates to the operating system components of Windows XP Media Center Edition (MCE) and Windows XP Tablet PC Edition, and security updates for .NET Framework version 1.0, which is included in these editions. However, it does not include update rollups for the Windows Media Center application in Windows XP MCE 2005.[100] SP3 also omits security updates for Windows Media Player 10, although the player is included in Windows XP MCE 2005.[100] The Address Bar DeskBand on the Taskbar is no longer included because of antitrust violation concerns.[101]
Unofficial SP3 ZIP download packages were released on a now-defunct website called The Hotfix from 2005 to 2007.[102][103] The owner of the website, Ethan C. Allen, was a former Microsoft employee in Software Quality Assurance and would comb through the Microsoft Knowledge Base articles daily and download new hotfixes Microsoft would put online within the articles. The articles would have a «kbwinxppresp3fix» and/or «kbwinxpsp3fix» tag, thus allowing Allen to easily find and determine which fixes were planned for the official SP3 release to come. Microsoft publicly stated at the time that the SP3 pack was unofficial and advised users to not install it.[104][105] Allen also released a Vista SP1 package in 2007, for which Allen received a cease-and-desist email from Microsoft.[106]
Windows XP Service Pack 3 was later included in Windows Embedded Standard 2009 and Windows Embedded POSReady 2009.
System requirements
System requirements for Windows XP are as follows:
| Minimum | Recommended | |
|---|---|---|
| Home/Professional Edition[A] | ||
| CPU |
|
|
| Memory | 64 MB[E][F] | 128 MB |
| Free space |
|
|
| Media | CD-ROM drive or compatible | |
| Display | Super VGA (800 × 600) | |
| Sound hardware | N/A | Sound card plus speakers/headphones |
| Input device(s) | Keyboard, mouse | |
| Professional x64 Edition[J] | ||
| CPU |
|
|
| Memory | 256 MB | |
| Free space |
|
|
| Media | CD-ROM drive or compatible | |
| Display | Super VGA (800 × 600) | |
| Sound hardware | N/A | Sound card plus speakers/headphones |
| Input device(s) | Keyboard, mouse | |
| 64-Bit Edition[K] | ||
| CPU | Itanium 733 MHz | Itanium 800 MHz |
| Memory | 1 GB | |
| Free space | 6 GB | |
| Media | CD-ROM drive or compatible | |
| Display | Super VGA (800 × 600) | |
| Input device(s) | Keyboard, mouse |
Notes
- ^ «System requirements for Windows XP operating systems». April 28, 2005. Archived from the original on August 6, 2011. Retrieved March 12, 2007.
- ^ Even though this is Microsoft’s stated minimum processor speed for Windows XP, it is possible to install and run the operating system on early IA-32 processors such as a P5 Pentium without MMX instructions. Windows XP is not compatible with processors older than Pentium (such as 486) or the Cyrix 6×86 because it requires
CMPXCHG8B(see Pentium F00F bug) instructions. - ^ «Windows XP Minimal Requirement Test». Winhistory.de. September 9, 2011. Archived from the original on December 21, 2011. Retrieved January 1, 2012.
- ^ a b c d e «Windows XP: Required firmware and partition mapping scheme of hard disk drive». Support.microsoft.com. June 26, 2013. Archived from the original on April 27, 2017. Retrieved June 16, 2014.
- ^ A Microsoft TechNet paper from Summer 2001 (before Windows XP’s actual release), states that: «A computer with 64 MB of RAM will have sufficient resources to run Windows XP and a few applications with moderate memory requirements.» (Emphasis added.) These were said to be office productivity applications, e-mail programs, and web browsers (of the time). With such a configuration, user interface enhancements and fast user switching are turned off by default. For comparable workloads, 64 MB of RAM was then regarded as providing an equal or better user experience on Windows XP with similar settings than it would with Windows Me on the same hardware. In a later section of the paper, superior performance over Windows Me was noted with 128 MB of RAM or more, and with computers that exceed the minimum hardware requirements.
- ^ Sechrest, Stuart; Fortin, Michael (June 1, 2001). «Windows XP Performance». Microsoft TechNet. Archived from the original on July 27, 2010. Retrieved April 8, 2008.
- ^ «Hard disk space requirements for Windows XP Service Pack 1». Microsoft. October 29, 2007. Archived from the original on April 21, 2012. Retrieved April 6, 2012.
- ^ «The hard disk space requirements for Windows XP Service Pack 2». Microsoft. April 18, 2005. Archived from the original on November 24, 2010. Retrieved December 1, 2010.
- ^ «Windows XP – End of Support, Migration Guide, Download – TechNet». technet.microsoft.com. 2007. Archived from the original on May 13, 2008.
- ^ «Windows XP Professional x64 Edition SP2 VL EN (MSDN-TechNet)». Programmer Stuffs. March 23, 2011. Archived from the original on July 14, 2014. Retrieved May 2, 2012.
- ^ «Microsoft Windows XP 64-Bit Edition». Microsoft TechNet. Microsoft. August 15, 2001. Archived from the original on April 19, 2012. Retrieved May 2, 2012.
Physical memory limits
The maximum amount of RAM that Windows XP can support varies depending on the product edition and the processor architecture. All 32-bit editions of XP support up to 4 GB, except the Windows XP Starter edition, which supports up to 512 MB of RAM.[107] 64-bit editions support up to 128 GB.[108]
Processor limits
Windows XP Professional supports up to two physical processors;[109]
Windows XP Home Edition supports only one.[110]
However, XP supports a greater number of logical processors:
32-bit editions support up to 32 logical processors,[111] and 64-bit editions support up to 64 logical processors.[112]
Upgradeability
Several Windows XP components are upgradable to the latest versions, which include new versions introduced in later versions of Windows, and other major Microsoft applications are available. These latest versions for Windows XP include:
- ActiveSync 4.5
- DirectX 9.0c (June 7, 2010, Redistributable)
- Internet Explorer 8 on Windows XP Service Packs 2 and 3 (Internet Explorer 6 SP1 and Outlook Express 6 SP1 on Windows XP before SP2.)
- Windows Media Format Runtime and Windows Media Player 11 on Windows XP Service Packs 2 and 3 (and Windows Media Player 10 on Windows XP original release.)
- Microsoft Virtual PC 2004 and 2007
- .NET Framework up to and including version 4.0 (4.5 and higher versions are not supported.)
- Visual Studio 2005 on Windows XP versions below SP2, Visual Studio 2008 on Windows XP SP2 and Visual Studio 2010 on Windows XP SP3
- Windows Script Host 5.7
- Windows Installer 4.5
- Microsoft NetMeeting 3.02
- Office 2010 was the last version of Microsoft Office to be compatible with Windows XP.
- The Windows Services for UNIX subsystem can be installed to allow certain Unix-based applications to run on the operating system.
Support lifecycle
| Expiration date | |
|---|---|
| Mainstream support | April 14, 2009[4] |
| Extended support | April 8, 2014[4] The official exceptions ended in April 2019. |
| Applicable XP editions: | |
| Home Edition, Professional Edition, Professional x64 Edition, Professional for Embedded Systems, Media Center Editions (all), Starter Edition, Tablet PC Edition and Tablet PC Edition 2005,[4] as well as Windows Fundamentals for Legacy PCs.[113] | |
| Exceptions | |
| Windows XP 64-Bit Edition (Itanium edition, including Version 2003) | Unsupported as of June 30, 2005[5] |
| Windows XP Embedded | Mainstream support ended on January 11, 2011[4] Extended support ended on January 12, 2016[4] |
| Windows Embedded for Point of Service | Mainstream support ended on April 12, 2011[6] Extended support ended on April 12, 2016[6] |
| Windows Embedded Standard 2009 | Mainstream support ended on January 14, 2014 Extended support ended on January 8, 2019[7] |
| Windows Embedded POSReady 2009 | Mainstream support ended on April 8, 2014 Extended support ended on April 9, 2019[8] |
Support for the original release of Windows XP (without a service pack) ended on August 30, 2005.[4] Both Windows XP Service Pack 1 and 1a were retired on October 10, 2006,[4] and both Windows 2000 and Windows XP SP2 reached their end of support on July 13, 2010, about 24 months after the launch of Windows XP Service Pack 3.[4] The company stopped general licensing of Windows XP to OEMs and terminated retail sales of the operating system on June 30, 2008, 17 months after the release of Windows Vista.[114] However, an exception was announced on April 3, 2008, for OEMs producing what it defined as «ultra low-cost personal computers», particularly netbooks, until one year after the availability of Windows 7 on October 22, 2009. Analysts felt that the move was primarily intended to compete against Linux-based netbooks, although Microsoft’s Kevin Hutz stated that the decision was due to apparent market demand for low-end computers with Windows.[115]
Variants of Windows XP for embedded systems have different support policies: Windows XP Embedded SP3 and Windows Embedded for Point of Service SP3 were supported until January and April 2016, respectively. Windows Embedded Standard 2009, which was succeeded by Windows Embedded Standard 7, and Windows Embedded POSReady 2009, which was succeeded by Windows Embedded POSReady 7, were supported until January and April 2019, respectively.[116] These updates, while intended for the embedded editions, could also be downloaded on standard Windows XP with a registry hack, which enabled unofficial patches until April 2019. However, Microsoft advised Windows XP users against installing these fixes, citing incompatibility issues.[9][117]
End of support
On April 14, 2009, Windows XP exited mainstream support and entered the extended support phase; Microsoft continued to provide security updates every month for Windows XP, however, free technical support, warranty claims, and design changes were no longer being offered. Extended support ended on April 8, 2014, over 12 years after the release of Windows XP; normally Microsoft products have a support life cycle of only 10 years.[118] Beyond the final security updates released on April 8, no more security patches or support information are provided for XP free-of-charge; «critical patches» will still be created, and made available only to customers subscribing to a paid «Custom Support» plan.[119] As it is a Windows component, all versions of Internet Explorer for Windows XP also became unsupported.[120]
In January 2014, it was estimated that more than 95% of the 3 million automated teller machines in the world were still running Windows XP (which largely replaced IBM’s OS/2 as the predominant operating system on ATMs); ATMs have an average lifecycle of between seven and ten years, but some have had lifecycles as long as 15. Plans were being made by several ATM vendors and their customers to migrate to Windows 7-based systems over the course of 2014, while vendors have also considered the possibility of using Linux-based platforms in the future to give them more flexibility for support lifecycles, and the ATM Industry Association (ATMIA) has since endorsed Windows 10 as a further replacement.[121] However, ATMs typically run the embedded variant of Windows XP, which was supported through January 2016.[122] As of May 2017, around 60% of the 220,000 ATMs in India still run Windows XP.[123]
Furthermore, at least 49% of all computers in China still ran XP at the beginning of 2014. These holdouts were influenced by several factors; prices of genuine copies of later versions of Windows in the country are high, while Ni Guangnan of the Chinese Academy of Sciences warned that Windows 8 could allegedly expose users to surveillance by the United States government,[124] and the Chinese government banned the purchase of Windows 8 products for government use in May 2014 in protest of Microsoft’s inability to provide «guaranteed» support.[125] The government also had concerns that the impending end of support could affect their anti-piracy initiatives with Microsoft, as users would simply pirate newer versions rather than purchasing them legally. As such, government officials formally requested that Microsoft extend the support period for XP for these reasons. While Microsoft did not comply with their requests, a number of major Chinese software developers, such as Lenovo, Kingsoft and Tencent, will provide free support and resources for Chinese users migrating from XP.[126] Several governments, in particular those of the Netherlands and the United Kingdom, elected to negotiate «Custom Support» plans with Microsoft for their continued, internal use of Windows XP; the British government’s deal lasted for a year, and also covered support for Office 2003 (which reached end-of-life the same day) and cost £5.5 million.[127]
On March 8, 2014, Microsoft deployed an update for XP that, on the 8th of each month, displays a pop-up notification to remind users about the end of support; however, these notifications may be disabled by the user.[128] Microsoft also partnered with Laplink to provide a special «express» version of its PCmover software to help users migrate files and settings from XP to a computer with a newer version of Windows.[129]
An electroencephalograph running on Windows XP. The medical industry’s continued use of Windows XP is partly due to medical applications being incompatible with later versions of Windows.
Despite the approaching end of support, there were still notable holdouts that had not migrated past XP; many users elected to remain on XP because of the poor reception of Windows Vista, sales of newer PCs with newer versions of Windows declined because of the Great Recession and the effects of Vista, and deployments of new versions of Windows in enterprise environments require a large amount of planning, which includes testing applications for compatibility (especially those that are dependent on Internet Explorer 6, which is not compatible with newer versions of Windows).[130] Major security software vendors (including Microsoft itself) planned to continue offering support and definitions for Windows XP past the end of support to varying extents, along with the developers of Google Chrome, Mozilla Firefox, and Opera web browsers;[120] despite these measures, critics similarly argued that users should eventually migrate from XP to a supported platform.[131] The United States’ Computer Emergency Readiness Team released an alert in March 2014 advising users of the impending end of support, and informing them that using XP after April 8 may prevent them from meeting US government information security requirements.[132]
Microsoft continued to provide Security Essentials virus definitions and updates for its Malicious Software Removal Tool (MSRT) for XP until July 14, 2015.[133] As the end of extended support approached, Microsoft began to increasingly urge XP customers to migrate to newer versions such as Windows 7 or 8 in the interest of security, suggesting that attackers could reverse engineer security patches for newer versions of Windows and use them to target equivalent vulnerabilities in XP.[134] Windows XP is remotely exploitable by numerous security holes that were discovered after Microsoft stopped supporting it.[135][136]
Similarly, specialized devices that run XP, particularly medical devices, must have any revisions to their software—even security updates for the underlying operating system—approved by relevant regulators before they can be released. For this reason, manufacturers often did not allow any updates to devices’ operating systems, leaving them open to security exploits and malware.[137]
Despite the end of support for Windows XP, Microsoft has released three emergency security updates for the operating system to patch major security vulnerabilities:
- A patch released in May 2014 to address recently discovered vulnerabilities in Internet Explorer 6 through 11 on all versions of Windows.[138]
- A patch released in May 2017 to address a vulnerability that was being leveraged by the WannaCry ransomware attack.[139]
- A patch released in May 2019 to address a critical code execution vulnerability in Remote Desktop Services which can be exploited in a similar way as the WannaCry vulnerability.[140][141]
Researchers reported in August 2019 that Windows 10 users may be at risk for «critical» system compromise because of design flaws of hardware device drivers from multiple providers.[142] In the same month, computer experts reported that the BlueKeep security vulnerability, CVE-2019-0708, that potentially affects older unpatched Microsoft Windows versions via the program’s Remote Desktop Protocol, allowing for the possibility of remote code execution, may now include related flaws, collectively named DejaBlue, affecting newer Windows versions (i.e., Windows 7 and all recent versions) as well.[143] In addition, experts reported a Microsoft security vulnerability, CVE-2019-1162, based on legacy code involving Microsoft CTF and ctfmon (ctfmon.exe), that affects all Windows versions from the older Windows XP version to the most recent Windows 10 versions; a patch to correct the flaw is currently available.[144]
Microsoft announced in July 2019 that the Microsoft Internet Games services on Windows XP and Windows Me would end on July 31, 2019 (and for Windows 7 on January 22, 2020).[145] Others, such as Steam, had done the same, ending support for Windows XP and Windows Vista in January 2019.[146]
In 2020, Microsoft announced that it would disable the Windows Update service for SHA-1 endpoints; since Windows XP did not get an update for SHA-2, Windows Update Services are no longer available on the OS as of late July 2020.[147] However, as of October 2021, the old updates for Windows XP are still available on the Microsoft Update Catalog,[148] or through Legacy Update, a community-driven third party replacement for the Windows XP update servers.
Reception
On release, Windows XP received critical acclaim. CNET described the operating system as being «worth the hype», considering the new interface to be «spiffier» and more intuitive than previous versions, but feeling that it may «annoy» experienced users with its «hand-holding». XP’s expanded multimedia support and CD burning functionality were also noted, along with its streamlined networking tools. The performance improvements of XP in comparison to 2000 and Me were also praised, along with its increased number of built-in device drivers in comparison to 2000. The software compatibility tools were also praised, although it was noted that some programs, particularly older MS-DOS software, may not work correctly on XP because of its differing architecture. They panned Windows XP’s new licensing model and product activation system, considering it to be a «slightly annoying roadblock», but acknowledged Microsoft’s intent for the changes.[149] PC Magazine provided similar praise, although noting that a number of its online features were designed to promote Microsoft-owned services, and that aside from quicker boot times, XP’s overall performance showed little difference over Windows 2000.[150] Windows XP’s default theme, Luna, was criticized by some users for its childish look.[151][152]
Despite extended support for Windows XP ending in 2014, many users – including some enterprises – were reluctant to move away from an operating system they viewed as a stable known quantity despite the many security and functionality improvements in subsequent releases of Windows. Windows XP’s longevity was viewed as testament to its stability and Microsoft’s successful attempts to keep it up to date, but also as an indictment of its direct successor’s perceived failings.[153]
According to web analytics data generated by Net Applications, Windows XP was the most widely used operating system until August 2012, when Windows 7 overtook it (later overtaken by Windows 10),[154] while StatCounter indicates it happening almost a year earlier.[155] In January 2014, Net Applications reported a market share of 29.23%[156] of «desktop operating systems» for XP (when XP was introduced there was not a separate mobile category to track), while W3Schools reported a share of 11.0%.[157]
As of September 2022, in most regions or continents, Windows XP market share on PCs, as a fraction of the total Windows share, has gone below 1% (0.5% in Africa[158]). XP still has a double-digit market share in a few countries, such as Armenia at over 50%,[159][160][161][162] at 57%, where Windows 7 was highest ranked, and with it being replaced by Windows 10, Windows XP got highest ranked for the longest time, and had over 60% share on some weekends in the summer of 2019.[163][164]
Source code leak
On September 23, 2020, source code for Windows XP with Service Pack 1 and Windows Server 2003 was leaked onto the imageboard 4chan by an unknown user. Anonymous users managed to compile the code, as well as a Twitter user who posted videos of the process on YouTube proving that the code was genuine.[165] The videos were later removed on copyright grounds by Microsoft. The leak was incomplete as it was missing the Winlogon source code and some other components.[166][167] The original leak itself was spread using magnet links and torrent files whose payload originally included Server 2003 and XP source code and which was later updated with additional files, among which were previous leaks of Microsoft products, its patents, media about conspiracy theories on Bill Gates by anti-vaccination movements and an assortment of PDF files on different topics.[168]
Microsoft issued a statement stating that it was investigating the leaks.[167][169][170]
See also
- BlueKeep (security vulnerability)
- Comparison of operating systems
- History of operating systems
- List of operating systems
References
- ^ «Windows Licensing Programs». Microsoft. Archived from the original on December 16, 2008. Retrieved September 21, 2008.
- ^ a b «An Inside Look at the Months-long Process of Getting Windows XP Ready for Release to Manufacturing | Stories». Microsoft Stories. Microsoft. August 24, 2001. Archived from the original on August 5, 2019. Retrieved June 24, 2018.
- ^ a b Kelly, Gordon (April 16, 2008). «Windows XP SP3 Release Date(s) Confirmed». Trusted Reviews. Trusted Reviews. Archived from the original on June 23, 2018. Retrieved June 23, 2018.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l «Microsoft Product Lifecycle Search: Windows XP». Microsoft Support. Microsoft. Archived from the original on July 20, 2012. Retrieved May 14, 2022.
- ^ a b «Microsoft Security Bulletin MS05-036 – Critical». July 12, 2015. Archived from the original on April 26, 2018. Retrieved April 26, 2018.
- ^ a b c d Mackie, Kurt (February 19, 2014). «Windows XP Embedded Supported for Two or More Years». Redmond Magazine. 1105 Media. Archived from the original on February 20, 2017. Retrieved June 23, 2018.
- ^ a b c «Microsoft Product Lifecycle Search: Windows Embedded Standard 2009». Microsoft Support. Microsoft. Archived from the original on July 13, 2015. Retrieved October 13, 2012.
- ^ a b c «Microsoft Product Lifecycle Search: Windows Embedded POSReady 2009». Microsoft Support. Microsoft. Archived from the original on October 10, 2014. Retrieved October 13, 2012.
- ^ a b Seltzer, Larry (May 26, 2014). «Registry hack enables continued updates for Windows XP». ZDNet. Archived from the original on January 26, 2021. Retrieved January 30, 2021.
[UPDATE:] Late Monday we received a statement from a Microsoft spokesperson: We recently became aware of a hack that purportedly aims to provide security updates to Windows XP customers. The security updates that could be installed are intended for Windows Embedded and Windows Server 2003 customers and do not fully protect Windows XP customers. Windows XP customers also run a significant risk of functionality issues with their machines if they install these updates, as they are not tested against Windows XP. The best way for Windows XP customers to protect their systems is to upgrade to a more modern operating system, like Windows 7 or Windows 8.1.
- ^ «Desktop Windows Version Market Share in Armenia — September 2022». September 30, 2022. Retrieved October 10, 2022.
- ^ «Desktop Windows Version Market Share Worldwide | StatCounter Global Stats». gs.statcounter.com. Statcounter. Archived from the original on April 20, 2019. Retrieved May 8, 2022.
- ^ Miles, Stephanie (January 24, 2000). «Microsoft consolidates Windows development efforts». CNET. CNET Networks. Archived from the original on February 1, 2014. Retrieved January 23, 2014.
- ^ «Windows «Longhorn» FAQ». Paul Thurrott’s SuperSite for Windows. Penton Media. June 22, 2005. Archived from the original on April 4, 2008. Retrieved April 4, 2008.
- ^ Thurrott, Paul (October 6, 2010). «The Road to Gold: The development of Windows XP Reviewed». Paul Thurrott’s Supersite for Windows. Penton Media. Archived from the original on February 2, 2014. Retrieved January 23, 2014.
- ^ Thurrott, Paul (July 17, 2000). «Introducing the Whistler Preview, Build 2250». Windows IT Pro. Penton Media. Archived from the original on June 12, 2018. Retrieved June 9, 2018.
- ^ Thurrott, Paul (October 6, 2010). «The Road to Gold (Part Two)». Paul Thurrott’s SuperSite for Windows. Penton Media. Archived from the original on February 2, 2014. Retrieved January 23, 2014.
- ^ «Microsoft to christen Windows, Office with new name». CNET. CNET Networks. February 5, 2001. Archived from the original on February 1, 2014. Retrieved January 23, 2014.
- ^ a b «Windows XP marketing tab to hit $1 billion». CNET. CNET Networks. January 2, 2002. Archived from the original on February 1, 2014. Retrieved January 23, 2014.
- ^ «Microsoft changes XP slogan in wake of US attacks». Computerworld NZ. IDG. Archived from the original on September 5, 2015. Retrieved August 7, 2015.
- ^ Thurrott, Paul (October 15, 2001). «The Road to Gold (Part Three)». Paul Thurrott’s Supersite for Windows. Penton Media. Archived from the original on August 29, 2017. Retrieved March 11, 2017.
- ^ a b «HOW TO: Use ClearType to Enhance Screen Fonts in Windows XP». Support. Microsoft. October 27, 2002. Archived from the original on August 5, 2011. Retrieved August 8, 2011.
- ^ Esposito, Dino (November 2001). «New Graphical Interface: Enhance Your Programs with New Windows XP Shell Features». MSDN. Microsoft. Archived from the original on August 9, 2011. Retrieved August 8, 2011.
- ^ Turner, Paul (February 22, 2004). «No view of Palouse from Windows». The Spokesman-Review. Spokane. Archived from the original on May 11, 2011. Retrieved September 19, 2012.
- ^ Fitzpatrick, Jason (August 6, 2015). «The Start Menu Should Be Sacred (But It’s Still a Disaster in Windows 10)». How-To Geek. Archived from the original on March 13, 2017. Retrieved July 30, 2016.
- ^ «How To Use the Fast User Switching Feature in Windows XP (Revision 1.5)». Microsoft Support. Microsoft. March 27, 2007. Archived from the original on August 12, 2011. Retrieved August 8, 2011.
- ^ «Bluetooth Wireless Technology FAQ». Archived from the original on December 23, 2018. Retrieved August 8, 2011.
- ^ «Manually Configuring Windows Firewall in Windows XP Service Pack 2». Archived from the original on August 26, 2017. Retrieved August 26, 2017.
- ^ «Description of the Windows Firewall feature in Windows XP SP2». Archived from the original on September 17, 2009. Retrieved September 18, 2009.
- ^ «Hotfix for Windows XP that adds support for SDHC cards that have a capacity of more than 4 GB». Support (5.0 ed.). May 22, 2013. Archived from the original on February 5, 2014. Retrieved June 18, 2019.
- ^ a b «Kernel Enhancements for Windows XP». Windows Hardware Developer Center (WHDC). Microsoft. January 13, 2003. Archived from the original on March 7, 2008. Retrieved August 8, 2011.
- ^ «HOW TO: Use the Driver Roll Back Feature to Restore a Previous Version of a Device Driver in Windows XP». Microsoft. October 27, 2002. Archived from the original on February 18, 2006.
- ^ Fisher, Ken (February 2, 2001). «Windows Product Activation: an early look». Ars Technica. Archived from the original on December 5, 2011. Retrieved February 22, 2017.
- ^ «Windows XP Networking Features and Enhancements». Microsoft TechNet. Microsoft. August 8, 2001. Archived from the original on July 26, 2011. Retrieved August 8, 2011.
- ^ «Frequently Asked Questions About Remote Desktop». Microsoft. Archived from the original on July 4, 2007.
- ^ Otey, Michael (October 2001). «Discover Windows XP». Microsoft Developer. Archived from the original on April 20, 2012. Retrieved June 21, 2018.
- ^ «Windows XP Program Compatibility Wizard». ServerWatch. March 12, 2002. Archived from the original on November 13, 2021. Retrieved November 13, 2021.
- ^ «How to Enable Application Compatibility-Mode Technology in Windows 2000 Service Pack 2». Active Win. 2000. Archived from the original on August 18, 2001. Retrieved November 13, 2021.
- ^ Proffit, Brian (September 2, 2002). «Old Apps Find A New Home On Windows XP». PC Magazine. Ziff Davis. Archived from the original on June 10, 2020. Retrieved July 10, 2018.
- ^ Karp, David; O’Reilly, Tim; Mott, Troy (2005). Windows XP in a Nutshell : [a desktop quick reference] (2nd ed.). Beijing [u.a.]: O’Reilly. p. 141. ISBN 978-0-596-00900-7.
- ^ Richtmyer, Richard (August 23, 2001). «Opening up Windows XP». CNN Money. CNN. Archived from the original on December 23, 2017. Retrieved June 24, 2018.
- ^ «Windows Picture and Fax Viewer overview». Windows XP Professional Product Documentation. Microsoft Corporation. Archived from the original on 2 December 2010. Retrieved 23 November 2010.
- ^ Harder, Bobbie (April 2001). «Microsoft Windows XP System Restore». Microsoft. Archived from the original on February 4, 2005.
- ^ Petri, Daniel (January 8, 2009). «What is ASR in Windows XP and Windows Server 2003?». Petri. Blue Whale Web Media Group. Archived from the original on March 12, 2017. Retrieved June 24, 2018.
- ^ Columbus, Louis (June 29, 2001). Exploring Windows XP’s Device Driver Rollback and System Restore. InformIT. Pearson Education. Archived from the original on January 5, 2014. Retrieved June 24, 2018.
- ^ Norton, Peter; Mueller, John Paul (2002). Peter Norton’s Complete Guide to Windows XP. Pearson Education. p. N/A. ISBN 9780132715386. Archived from the original on April 15, 2021. Retrieved July 10, 2018.
- ^ McNamee, Kieran (June 27, 2003). «Setting up dual monitors using Windows XP Home». PC World. Archived from the original on February 5, 2017. Retrieved June 24, 2018.
- ^ «Architecture of Fast User Switching». Microsoft Knowledgebase. Microsoft. January 15, 2006. Archived from the original on August 2, 2009. Retrieved June 24, 2018.
- ^ Satran, Michael (May 31, 2018). «About Side-by-Side Assemblies». docs.microsoft.com. Microsoft. Archived from the original on June 24, 2018. Retrieved June 24, 2018.
- ^ Wienholt, Nick (August 14, 2006). «Simplify Application Deployment with Registration-Free COM — Developer.com». www.developer.com. QuinStreet Enterprise. Archived from the original on December 16, 2010. Retrieved June 24, 2018.
- ^ Honeycutt, Jerry (2003). Introducing Microsoft Windows Server 2003. Redmond, Wash.: Microsoft. pp. 293–298. ISBN 9780735615700.
- ^ «New ways to do familiar tasks». Windows XP Product Documentation. Microsoft. Archived from the original on May 3, 2006. Retrieved May 21, 2014.
- ^ «Kernel Enhancements for Windows XP». MSDN. Microsoft. January 13, 2003. Archived from the original on March 6, 2013. Retrieved April 16, 2014.
- ^ Pittsley, Steven (June 13, 2002). «Easy install guide for NetBEUI and IPX in Windows XP Pro». TechRepublic. CBS Interactive. Archived from the original on April 11, 2017. Retrieved June 24, 2018.
- ^ «Non-Plug and Play Network Device Support in Windows XP». Support. Microsoft. October 18, 2001. Archived from the original on October 30, 2004. Retrieved November 8, 2012.
- ^ «TCP/IP Raw Sockets (Windows)». MSDN. Microsoft. Archived from the original on January 28, 2013. Retrieved November 7, 2012.
- ^ Pash, Adam (April 29, 2008). «Field Guide to Windows XP SP3». Lifehacker. Univision Communications. Archived from the original on January 15, 2018. Retrieved June 24, 2018.
- ^ «Differences with Windows XP Home Edition». TechNet. Microsoft. September 11, 2009. Archived from the original on February 9, 2014. Retrieved January 26, 2014.
- ^ Marti, Don (November 6, 2006). «Dell customer gets Windows refund». LinuxWorld. IDG. Archived from the original on September 27, 2008. Retrieved September 13, 2008.
- ^ «HP must reimburse Italian PC buyer the amount paid for Microsoft software». Heise online. October 29, 2007. Archived from the original on October 15, 2008. Retrieved September 13, 2008.
- ^ Wilcox, Joe (July 16, 2002). «Microsoft reveals media XP details». CNET. CNET Networks. Archived from the original on February 7, 2015. Retrieved January 26, 2014.
- ^ Wilcox, Joe; Junnarkar, Sandeep (November 7, 2002). «Microsoft launches tablet PC drive». CNET. CNET Networks. Archived from the original on February 7, 2015. Retrieved January 26, 2014.
- ^ Evers, Joris (January 5, 2005). «Microsoft nixes Windows XP for Itanium». Computerworld. IDG. Archived from the original on February 2, 2014. Retrieved January 26, 2014.
- ^ «Microsoft Raises the Speed Limit with the Availability of 64-Bit Editions of Windows Server 2003 and Windows XP Professional» (Press release). Microsoft. April 25, 2005. Archived from the original on February 25, 2015. Retrieved September 10, 2015.
- ^ Thurrott, Paul (January 3, 2005). «Windows XP Starter Edition». Paul Thurrott’s SuperSite for Windows. Penton Media. Archived from the original on August 28, 2013. Retrieved April 12, 2008.
- ^ Fried, Ina (May 23, 2006). «Microsoft pitches pay-as-you-go PCs». CNET. CNET Networks. Archived from the original on February 7, 2015. Retrieved January 26, 2014.
- ^ «Microsoft and EU reach agreement». BBC. March 28, 2005. Archived from the original on September 22, 2015.
- ^ Bishop, Todd (December 24, 2004). «Europe gets ‘reduced’ Windows». Seattle Post-Intelligencer. Hearst Corporation. Archived from the original on October 6, 2021. Retrieved November 30, 2018.
- ^ Anderson, Nate (December 7, 2005). «South Korea fines Microsoft for antitrust abuses». Ars Technica. Condé Nast Publications. Archived from the original on April 22, 2008. Retrieved April 12, 2008.
- ^ «Changes to Windows XP Home Edition K and Windows XP Professional K from earlier versions of Windows XP (MSKB 922474)». Microsoft Support. Microsoft. September 15, 2006. Archived from the original on December 19, 2013. Retrieved January 26, 2014.
- ^ «Service Pack and Update Center». Support. Microsoft. September 10, 2016. Archived from the original on August 31, 2017.
- ^ «Installing Windows XP Service Pack 3 (SP3)». Microsoft. Microsoft. November 18, 2011. Archived from the original on August 22, 2017. Retrieved August 22, 2017.
- ^ Purdy, Kevin. «Slipstream Service Pack 3 into Your Windows XP Installation CD». Lifehacker. Archived from the original on August 22, 2017. Retrieved August 22, 2017.
- ^ «Windows XP SP1 Irons out the Wrinkles». PC Magazine. Archived from the original on February 26, 2014. Retrieved January 26, 2014.
- ^ Mendelson, Edward. «Microsoft Windows XP Service Pack 1 review». CNET. CNET Networks. Archived from the original on February 9, 2008. Retrieved January 26, 2014.
- ^ «Differences Between Windows XP SP1 and Windows XP SP1a». February 3, 2003. Archived from the original on January 27, 2007. Retrieved September 21, 2007.
- ^ «How to obtain the latest Windows XP service pack». March 26, 2007. Archived from the original on October 14, 2004. Retrieved September 21, 2007.
- ^ Shinder, Deb (August 26, 2004). «Windows XP Service Pack 2: How it affects wireless networking». TechRepublic. CBS Interactive. Archived from the original on June 13, 2017. Retrieved June 24, 2018.
- ^ «Bluetooth Wireless Technology FAQ – 2010». July 24, 2012. Archived from the original on March 3, 2016. Retrieved November 4, 2012.
- ^ Menn, Joseph (2019). Cult of the Dead Cow: How the Original Hacking Supergroup Might Just Save the World. New York: Public Affairs. p. 49–50.
- ^ Grimes, Roger A. (2017). «46 — Profile: Window Snyder». Hacking the hacker : learn from the experts who take down hackers. Indianapolis, IN: Wiley. ISBN 978-1-119-39626-0. OCLC 983465946.
- ^ Thurrott, Paul (October 15, 2003). «Windows XP SP2 to be ‘Springboard’ to Longhorn». Windows IT Pro. Archived from the original on June 23, 2018.
- ^ «Windows XP Service Pack 2 information». Microsoft. August 4, 2004. Archived from the original on October 16, 2007.
- ^ Mux, Victor (August 21, 2006). «Why Windows XP SP2b and Windows Server 2003 SP2a?». Microsoft. Archived from the original on August 12, 2009.
- ^ Fletcher, Jefferson (April 8, 2008). «IE Automatic Component Activation Now Available». IEBlog. Microsoft. Archived from the original on April 11, 2008. Retrieved April 11, 2008.
- ^ Mux, Victor (August 9, 2007). «Microsoft Windows XP Professional Service Pack 2c Release». MSDN. Microsoft. Archived from the original on February 2, 2014. Retrieved January 26, 2014.
- ^ Emil Protalinski — April 29, 2008, 1:35 pm UTC (April 29, 2008). «Microsoft releases the long-anticipated Windows XP SP3 (updated)». Ars Technica. Archived from the original on January 15, 2022. Retrieved February 10, 2022.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ «Release Notes for Microsoft Windows Server 2003 Service Pack 2». Archived from the original on November 11, 2019. Retrieved November 11, 2019.
- ^ Oiaga, Marius (December 14, 2007). «64-Bit Windows XP Service Pack 3?». Softpedia. SoftNews NET. Archived from the original on May 8, 2018. Retrieved June 24, 2018.
- ^ Keizer, Gregg (July 8, 2008). «Microsoft sets XP SP3 automatic download for Thursday». Computerworld. IDG. Archived from the original on July 9, 2008. Retrieved July 8, 2008.
- ^ «Windows XP Service Pack 3 Overview». Microsoft. May 6, 2008. Archived from the original on May 6, 2008. Retrieved May 7, 2008.
- ^ «List of fixes that are included in Windows XP Service Pack 3». Microsoft. May 6, 2008. Archived from the original on May 9, 2008. Retrieved June 23, 2018.
- ^ Oiaga, Marius (December 14, 2007). «No, Internet Explorer 7 Will Not(!) Be a Part of Windows XP SP3». SoftNews NET. Archived from the original on January 18, 2012.
- ^ Howard, Michael (January 29, 2008). «New NX APIs added to Windows Vista SP1, Windows XP SP3 and Windows Server 2008». Michael Howard’s Web Log. Microsoft. Archived from the original on August 25, 2011. Retrieved August 8, 2011.
- ^ «Description of the Credential Security Support Provider (CredSSP) in Windows XP Service Pack 3». Microsoft. May 6, 2008. Archived from the original on October 9, 2009. Retrieved June 23, 2018.
- ^ Enterprise IT Planet Staff (May 13, 2005). «Upgraded Wi-Fi Security for Windows XP SP2». Wi-Fi Planet. QuinStreet Enterprise. Archived from the original on June 23, 2018. Retrieved June 23, 2018.
- ^ «Overview of Windows XP Service Pack 3» (PDF). Archived (PDF) from the original on January 17, 2009.
- ^ «Information about Windows Imaging Component». Microsoft. August 13, 2002. Archived from the original on May 10, 2011.
- ^ Nanjappa, Ashwin (January 27, 2010). «Windows: ClearType on RDP». CodeYarns.com. Archived from the original on November 17, 2015. Retrieved June 16, 2014.
- ^ «A hotfix is available that improves the stability of the Windows Management Instrumentation repository in Windows XP». Support. Microsoft. October 8, 2011. Archived from the original on March 5, 2013. Retrieved January 20, 2013.
- ^ a b «FAQs regarding SP3 RTM». Microsoft. April 22, 2008. Archived from the original on August 24, 2011. Retrieved June 23, 2018.
- ^ Kaelin, Mark (May 8, 2008). «How do I… Return the Address bar Windows XP SP3 removed?». TechRepublic. CBS Interactive. Archived from the original on September 5, 2015. Retrieved May 5, 2015.
- ^ «Windows XP SP3 preview surfaces on Web». PC World. IDG. October 6, 2005. Archived from the original on October 31, 2020. Retrieved October 29, 2020.
- ^ «Sneak preview of Windows XP SP3 surfaces». Ars Technica. Ars Technica. October 6, 2005. Archived from the original on November 4, 2020. Retrieved October 29, 2020.
- ^ «Microsoft employee blasts ‘fake’ service pack». PC World. IDG. October 14, 2005. Archived from the original on October 31, 2020. Retrieved October 29, 2020.
- ^ «Windows XP SP3 preview a fake». Ars Technica. Ars Technica. October 15, 2005. Archived from the original on October 31, 2020. Retrieved October 29, 2020.
- ^ «Microsoft leans on Vista SP1 site». PC World. IDG. October 4, 2007. Archived from the original on May 18, 2017. Retrieved October 29, 2020.
- ^ «What is the maximum amount of RAM the Windows operating system can handle?». Crucial. Archived from the original on May 11, 2011. Retrieved June 25, 2010.
- ^ «Physical Memory Limits: Windows XP». Memory Limits for Windows Releases. Microsoft. Archived from the original on January 6, 2014. Retrieved January 14, 2014.
- ^ «Processor and memory capabilities of Windows XP Professional x64 Edition and of the x64-based versions of Windows Server 2003 (Revision 7.0)». Microsoft Support. Microsoft. December 20, 2010. Archived from the original on August 12, 2011. Retrieved August 8, 2011.
- ^ Kumar, I. Suuresh (October 25, 2010). «Multi-core processor and multiprocessor limit for Windows XP». Microsoft Answers. Microsoft. Archived from the original on April 19, 2014. Retrieved April 18, 2014.
- ^ «Processor Affinity Under WOW64». MSDN. Microsoft. January 27, 2011. Archived from the original on May 6, 2011. Retrieved August 8, 2011.
- ^ «Maximum quantity of logical processors in a PC supported by Microsoft Windows XP professional, x64 edition». Support. Microsoft. December 20, 2010. Archived from the original on January 11, 2013. Retrieved January 20, 2013.
- ^ «Microsoft Product Lifecycle Search: Windows Fundamentals for Legacy PCs». Microsoft Support. Microsoft. Archived from the original on October 5, 2014. Retrieved October 13, 2012.
- ^ Fried, Ina (September 27, 2007). «Microsoft extends Windows XP’s stay». CNET. CBS Interactive. Archived from the original on August 30, 2008. Retrieved June 5, 2008.
- ^ Lai, Eric (March 3, 2008). «Microsoft to keep Windows XP alive—but only for Eee PCs and wannabes». Computerworld. IDG. Archived from the original on April 8, 2008. Retrieved April 8, 2008.
- ^ Tung, Liam (February 18, 2014). «Microsoft: ‘Remember, some XP-based embedded systems to get support to 2019’«. ZDNet. CBS Interactive. Archived from the original on April 4, 2014. Retrieved April 6, 2014.
- ^ Newman, Jared (August 27, 2014). «Enthusiast developer keeps Windows XP alive with unofficial ‘Service Pack 4’«. PCWorld. Archived from the original on October 26, 2018. Retrieved October 26, 2018.
- ^ Satherley, Dan (April 9, 2013). «Businesses urged to ditch XP». 3 News NZ. Archived from the original on July 13, 2014. Retrieved June 28, 2019.
- ^ Keizer, Gregg (August 26, 2013). «Microsoft will craft XP patches after April ’14, but not for you». Computerworld. IDG. Archived from the original on October 20, 2013. Retrieved December 12, 2013.
- ^ a b Keizer, Gregg (March 11, 2014). «US-CERT urges XP users to dump IE». Computerworld. IDG. Archived from the original on June 28, 2019. Retrieved June 28, 2019.
- ^ ATM Industry Association (collectively) (June 1, 2015). «ATMIA position paper recommending migration to Windows 10». www.atmia.com (Press release). ATM Industry Association. Archived from the original on May 25, 2017.
- ^ Summers, Nick (January 16, 2014). «ATMs Face Deadline to Upgrade From Windows XP». Bloomberg Businessweek. Bloomberg L.P. Archived from the original on January 16, 2014. Retrieved January 17, 2014.
- ^ «Wannacry ransomware cyber attack: Indian ATMs could be at high risk as most run on Windows XP». Business Today. May 15, 2017. Archived from the original on May 17, 2017. Retrieved May 18, 2017.
- ^ «Windows 8 a ‘threat’ to China’s security». BBC. June 5, 2014. Archived from the original on October 8, 2018. Retrieved October 8, 2018.
- ^ Kan, Michael (May 20, 2014). «China bans government purchases of Windows 8». PCWorld. IDG. Archived from the original on May 20, 2014. Retrieved May 20, 2014.
- ^ «Microsoft Partners Lenovo, Tencent to Offer XP Tech Support in China». Voanews.com. Reuters. April 9, 2014. Archived from the original on April 13, 2014. Retrieved April 16, 2014.
- ^ Gallagher, Sean (April 6, 2014). «Not dead yet: Dutch, British governments pay to keep Windows XP alive». Ars Technica. Condé Nast Publications. Archived from the original on October 14, 2019. Retrieved October 15, 2019.
- ^ Foley, Mary Jo (March 3, 2014). «Microsoft to start nagging Windows XP users about April 8 end-of-support date». ZDNet. CBS Interactive. Archived from the original on October 14, 2019. Retrieved October 15, 2019.
- ^ Yegulalp, Serdar (March 3, 2014). «Microsoft: Use Laplink’s Windows XP migration tools, not ours». Infoworld. Archived from the original on October 15, 2019.
- ^ Ward, Mark (March 5, 2014). «XP – the operating system that will not die». BBC News. Archived from the original on March 24, 2014. Retrieved March 25, 2014.
- ^ Egan, Matt (April 7, 2014). «What should XP users do when Microsoft ends support? Upgrade to Windows 8, buy a new PC, keep running XP?». PC Advisor. Archived from the original on February 14, 2014. Retrieved April 6, 2014.
- ^ «Alert (TA14-069A): Microsoft Ending Support for Windows XP and Office 2003». March 11, 2014. Archived from the original on March 16, 2014. Retrieved April 6, 2014.
- ^ Keizer, Gregg (January 19, 2014). «Microsoft will furnish malware assassin to XP users until mid-2015». Computerworld. IDG. Archived from the original on January 22, 2014.
- ^ «Microsoft Warns of Permanent Zero-Day Exploits for Windows XP». Infosecurity. Reed Exhibitions. August 20, 2013. Archived from the original on August 26, 2013. Retrieved August 27, 2013.
- ^ «Microsoft Security Bulletin MS15-011 JASBUG». February 10, 2015. Archived from the original on August 11, 2015. Retrieved September 18, 2015.
- ^ Freeman, Robert (November 11, 2014). «IBM X-Force Researcher Finds Significant Vulnerability in Microsoft Windows». Securityintelligence.com. Archived from the original on July 3, 2015. Retrieved September 18, 2015.
- ^ Talbot, David (October 17, 2012). «Computer Viruses Are «Rampant» on Medical Devices in Hospitals». MIT Technology Review. Archived from the original on October 19, 2016. Retrieved April 6, 2014.
- ^ Goodin, Dan (May 1, 2014). «Emergency patch for critical IE 0-day throws lifeline to XP laggards, too». Ars Technica. Conde Nast. Archived from the original on May 17, 2017. Retrieved May 26, 2017.
- ^ Warren, Tom (May 13, 2017). «Microsoft issues ‘highly unusual’ Windows XP patch to prevent massive ransomware attack». The Verge. Vox Media. Archived from the original on May 14, 2017. Retrieved May 13, 2017.
- ^ Warren, Tom (May 14, 2019). «Microsoft warns of major WannaCry-like Windows security exploit, releases XP patches». The Verge. Vox Media. Archived from the original on September 2, 2019. Retrieved May 16, 2019.
- ^ «Prevent a worm by updating Remote Desktop Services (CVE-2019-0708) – MSRC». blogs.technet.microsoft.com. May 14, 2019. Archived from the original on May 14, 2019. Retrieved May 16, 2019.
- ^ Winder, Davey (August 11, 2019). «Critical Windows 10 Warning: Millions Of Users At Risk». Forbes. Archived from the original on August 11, 2019. Retrieved August 11, 2019.
- ^ Greenberg, Andy (August 13, 2019). «DejaBlue: New BlueKeep-Style Bugs Renew The Risk Of A Windows worm». wired. Archived from the original on April 13, 2021. Retrieved August 15, 2019.
- ^ Seals, Tara (August 14, 2019). «20-Year-Old Bug in Legacy Microsoft Code Plagues All Windows Users». ThreatPost.com. Archived from the original on April 17, 2021. Retrieved August 15, 2019.
- ^ «Farewell to Microsoft Internet Games on Windows XP, Windows ME, and Windows 7». answers.microsoft.com. Archived from the original on July 14, 2019. Retrieved August 4, 2019.
- ^ «Windows XP and Windows Vista Support – Steam – Knowledge Base – Steam Support». support.steampowered.com. Archived from the original on August 12, 2019. Retrieved August 4, 2019.
- ^ «Windows Update SHA-1 based endpoints discontinued for older Windows devices». support.microsoft.com. Archived from the original on April 17, 2021. Retrieved April 6, 2021.
- ^ «Microsoft Update Catalog». www.catalog.update.microsoft.com. Archived from the original on April 15, 2021. Retrieved April 6, 2021.
- ^ Lake, Matt (October 10, 2002). «Microsoft Windows XP – Home Edition review». CNET. Archived from the original on May 31, 2007. Retrieved March 25, 2014.
- ^ Mendelson, Edward (September 3, 2001). «Microsoft Ships Its Biggest OS Upgrade Ever—Early!». PC Magazine. Archived from the original on March 25, 2014. Retrieved March 25, 2014.
- ^ Manes, Stephen (August 26, 2004). «Full Disclosure: Your Take on Windows’ Worst Irritations». PCWorld. IDG. Archived from the original on October 8, 2009.
- ^ Bright, Peter (April 10, 2014). «Memory lane: Before everyone loved Windows XP, they hated it». Ars Technica. Condé Nast. Archived from the original on April 24, 2014. Retrieved June 20, 2014.
- ^ Bright, Peter (October 25, 2011). «Ten years of Windows XP: how longevity became a curse». Ars Technica. WIRED Media Group. Archived from the original on June 12, 2018. Retrieved June 9, 2018.
- ^ «Operating system market share». September 9, 2012. Archived from the original on September 9, 2012. Retrieved September 8, 2018.
- ^ «Desktop Windows Version Market Share Worldwide». StatCounter Global Stats. Archived from the original on April 20, 2019. Retrieved July 2, 2019.
- ^ Crothers, Brooke (February 2, 2014). «Oops, Windows XP gains in January but so does Windows 8.1». CNET. CBS Interactive. Archived from the original on February 21, 2014. Retrieved March 16, 2014.
- ^ «OS Platform Statistics». w3schools. Archived from the original on September 17, 2015. Retrieved September 14, 2015.
- ^ «Desktop Windows Version Market Share Africa». StatCounter Global Stats. Archived from the original on September 22, 2022. Retrieved September 22, 2022.
- ^ «Desktop Windows Version Market Share Armenia». StatCounter Global Stats. Archived from the original on September 4, 2018. Retrieved December 11, 2021.
- ^ «Desktop Windows Version Market Share Armenia». StatCounter Global Stats. Archived from the original on September 4, 2018. Retrieved December 11, 2021.
- ^ «Desktop Windows Version Market Share Armenia». StatCounter Global Stats. Archived from the original on September 4, 2018. Retrieved July 10, 2021.
- ^ «Desktop Windows Version Market Share Armenia». StatCounter Global Stats. Archived from the original on September 4, 2018. Retrieved March 2, 2021.
- ^ «Desktop Windows Version Market Share Armenia». StatCounter Global Stats. Archived from the original on September 4, 2018. Retrieved July 2, 2020.
- ^ «Desktop Windows Version Market Share Armenia». StatCounter Global Stats. Archived from the original on September 4, 2018. Retrieved July 2, 2020.
- ^ Cimpanu, Catalin. «Windows XP leak confirmed after user compiles the leaked code into a working OS». ZDNet. Archived from the original on September 30, 2020. Retrieved October 1, 2020.
- ^ Warren, Tom (September 25, 2020). «Windows XP source code leaks online». The Verge. Archived from the original on September 29, 2021. Retrieved October 1, 2020.
- ^ a b Alcorn, Paul (September 30, 2020). «Windows XP Source Code Leaked, Posted to 4chan (Update, It Works)». Tom’s Hardware. Archived from the original on October 6, 2021. Retrieved October 1, 2020.
- ^ «Windows XP Source Code Leaked By Apparent Bill Gates Conspiracist». Gizmodo. September 25, 2020. Archived from the original on October 1, 2020. Retrieved October 1, 2020.
- ^ «The Windows XP and Windows Server 2003 source code leaks online». Graham Cluley. September 25, 2020. Archived from the original on September 26, 2020. Retrieved September 29, 2020.
- ^ «Windows XP source code leaked online». www.computing.co.uk. September 28, 2020. Archived from the original on October 2, 2020. Retrieved September 29, 2020.
Further reading
- Joyce, Jerry; Moon, Marianne (2004). Microsoft Windows XP Plain & Simple. Microsoft Press. ISBN 978-0-7356-2112-1.
External links
- Windows XP End of Support
- Security Update for Windows XP SP3 (KB4012598)
Windows XP (кодовое название при разработке — Whistler; внутренняя версия — Windows NT 5.1) — операционная система (ОС) семейства Windows NT корпорации Microsoft. Была выпущена 25 октября 2001 года и является развитием Windows 2000 Professional. Название XP происходит от англ. experience («опыт», «впечатления»[1]).
В отличие от предыдущей системы Windows 2000, которая поставлялась как в серверном, так и в клиентском вариантах, Windows XP является исключительно клиентской системой. Её серверным аналогом является Windows Server 2003. Хотя Windows Server 2003 и построен на базе того же кода, что и Windows XP, почти всецело наследуя интерфейс её пользовательской части, Windows Server 2003 всё же использует более новую и переработанную версию ядра NT 5.2; появившаяся позже Windows XP Professional x64 Edition имела то же ядро, что и Windows Server 2003, и получала те же обновления безопасности, вследствие чего можно было говорить о том, что их развитие шло одинаково. Windows XP, получила совершенно новый пользовательский интерфейс, который значительно отличается от ставшего уже привычным по предыдущим версиям, таких как Windows 95, 98 и Me. Впоследствии Windows XP стала самой популярной на долгие годы. Благодаря невысоким системным требованиям и хорошей поддержке как нового, так и старого аппаратного обеспечения, обеспечивала высокую производительность на широком спектре конфигураций.
По оценкам веб-аналитики NetMarketShare Windows XP была самой используемой операционной системой для доступа к Интернету в мире, с максимальной долей в 76,1 % в январе 2007 года. С августа 2011 года Windows 7 обогнала Windows XP. По состоянию на вторую половину 2015 года, Windows XP находится на третьем месте после Windows 8 и Windows 7 с долей около 11-12%. [2]. Согласно статистическим данным W3Schools доля Windows XP в ноябре 2015, составила 2.2%.
В настоящее время, многие современные программы уже не работают в среде Windows XP. Для большинства современного оборудования отсутствуют драйверы, способные обеспечить функционирование в среде Windows XP. Из-за ряда технических ограничений по причине сильного устаревания, данная операционная система становится «узким местом» для новых систем, не позволяющей в полной мере реализовать потенциальные возможности аппаратного обеспечения. Поддержка Windows XP корпорацией Microsoft прекращена 8 апреля 2014.
Варианты[]
Windows XP выпускалась в следующих вариантах
- Windows XP Professional Edition была разработана для предприятий и предпринимателей и содержит такие функции, как удалённый доступ к рабочему столу компьютера, шифрование файлов (при помощи Encrypting FIle System), центральное управление правами доступа и поддержка многопроцессорных систем.
- Windows XP Home Edition — система для домашнего применения. Выпускается как недорогая «урезанная» версия Professional Edition, но базируется на том же ядре.
- Windows XP Tablet PC Edition базируется на Professional Edition и содержит специальные приложения, оптимизированные для ввода данных стилусом на планшетных персональных компьютерах. Важнейшим свойством является понимание текстов, написанных от руки и адаптация графического интерфейса к поворотам дисплея. Эта версия продаётся только вместе с соответствующим компьютером.
- Windows XP Media Center Edition базируется на Professional Edition и содержит специальные мультимедийные приложения. Компьютер, как правило, оснащён ТВ-картой и пультом дистанционного управления (ПДУ). Важнейшим свойством является возможность подключения к телевизору и управление компьютером через ПДУ благодаря упрощённой системе управления Windows. Эта система содержит также функции для приёма УКВ-радио.
- Улучшения в подсистеме EFS, заключающиеся в необязательности агента восстановления, более безопасного сохранения ключей. Шифруемые файлы теперь не просто удаляются, а перезаписываются нулями, что гораздо надёжнее. Начиная с SP1 становится возможным использовать (он и используется по умолчанию) алгоритм AES, наряду с DESX и 3-DES.
- Настраиваемые панели инструментов, с помощью которых можно оптимизировать доступ к файлам, папкам и ресурсам Интернета. Достаточно разместить их на краю Рабочего стола (наподобие боковой панели) или на Панели задач (в форме ссылки).
- Частичное использование сборок (Шаблон:Lang-en).
Графический интерфейс пользователя[]
Файл:RoyaleXP2.PNG Англоязычное стартовое меню в новом виде при использовании темы Royale
- Выделение в Windows Explorer осуществляется прозрачным синим прямоугольником.
- Падающая тень от ярлыков на рабочем столе.
- Боковая панель, ориентированная на выполнение задач в окне проводника («common tasks»).
- Группирование кнопок одного приложения на панели задач в одну кнопку, при определённом количестве разных запущенных приложений, что позволяет часто избегать необходимости её «прокрутки».
- Появилась возможность заблокировать панель задач и вспомогательные панели, во избежание их случайного изменения.
- Цветовое выделения элементов в меню «Пуск», принадлежащих недавно добавленным программам.
- Меню отбрасывают тени (в Windows 2000 тень отбрасывал указатель мыши, но не элементы меню).
Windows XP анализирует производительность системы с определёнными визуальными эффектами и в зависимости от этого активирует их или нет, учитывая возможное падение или рост производительности. Пользователи также могут изменять данные параметры, используя диалоговые окна настройки, при этом можно либо гибко выбрать активность тех или иных визуальных эффектов, либо отдать это на управление системе или же выбрать максимальную производительность или лучший вид графического интерфейса.[3]
Некоторые эффекты, такие как полупрозрачность и т. п., требуют наличия производительной графической подсистемы, на старых видеокартах производительность может сильно упасть и Microsoft рекомендует отключить эти возможности в таком случае.[4]
В Windows XP появилась возможность использовать Visual Styles, позволяющие изменить графический интерфейс пользователя. Luna — новый стиль графического интерфейса, входящий в поставку XP и являющийся интерфейсом по умолчанию для компьютеров, имеющих более 64 мегабайт оперативной памяти. Возможно использовать и другие Visual Styles, но они должны быть подписаны цифровой подписью Microsoft (так как имеют важное значение в функционировании системы). Один из интерфейсов доступен на версии Windows XP Black Edition by Spa.
Для обхода этого ограничения некоторые пользователи используют специальное программное обеспечение, такое, как TGTSoft’s StyleXP, а иногда и изменённую версию библиотеки uxtheme.dll.
Также существует стиль «классический», повторяющий стиль интерфейса Windows 2000 (который использует на 4 МБ меньше памяти, чем Luna), а также многочисленные стили, созданные сторонними разработчиками. Для версии Media Center Microsoft разработала «визуальный стиль» Royale, который включён в эту версию Windows XP и доступен для установки в других версиях XP.[5]
Для Windows XP были созданы более 100 значков компанией The Iconfactory, известной своим набором бесплатных значков для операционной системы Mac OS X[6]
Интерфейс командной строки (CLI)[]
Windows XP также имеет интерфейс командной строки (CLI, «консоль»), cmd.exe, для управления системой командами из консоли или запуска сценариев, называемых «командными файлами» (с расширениями cmd), основанными на пакетных файлах MS-DOS. Синтаксис Windows XP CLI достаточно хорошо задокументирован во встроенной системе помощи (файл справки ntcmds.chm). Более подробную общую информацию можно получить, набрав в командной строке help для получения общих сведений о доступных командах и «имя команды» /?. Интерфейс командной строки доступен как в виде окна, так и в полноэкранном виде (переключение между ними осуществляется нажатием Шаблон:Key), предпочитаемый вид можно указать в соответствующем диалоге настройки, наряду с такими параметрами, как размер и тип шрифтов и т. д. При работе в данном режиме пользователь может вызывать предыдущие команды (так, клавиша Шаблон:Key возвращает предыдущую команду, а Шаблон:Key выводит меню со списком вводившихся команд; Шаблон:Key вызывает из этого списка команду по номеру), использовать автодополнение имён файлов и каталогов (Шаблон:Key), а также команд; доступно вызываемое правым кликом контекстное меню в том числе с работой с буфером обмена. Многие действия по управлению операционной системой можно выполнить, используя интерфейс CLI. Наиболее важными из них являются команды:
netс подкомандами, позволяющая управлять локальными пользователями и группами (net user /?иnet localgroup /?), аккаунтами, общим доступом к ресурсам на ПК (net share /?) и в сети (net view /?) и т. д.- команды просмотра и управления процессами
tasklist /?иtaskkill /? - команда управления разрешениями файлов
cacls /?, позволяющая просматривать и изменять права доступа к файлам и папкам; в Шаблон:Lang-en2 — это единственная возможность гибко изменять права, так как соответствующий графический инструмент доступен только в безопасном режиме - команды, аналогичные командам MS-DOS, позволяющие копировать, перемещать и удалять файлы и каталоги и т. д.
Системные требования[]
Файл:DesignedforWinXPlogo.PNG Логотип Designed for Windows XP (Совместимо с Windows XP)
Системные требования операционных систем Windows XP Home и Professional Editions следующие:[7]
| Минимальные(Официально) | Рекомендуемые | |
|---|---|---|
| Процессор | 233 МГц | 300 МГц или выше |
| Оперативная память | 64 МБ (могут быть ограничены некоторые возможности) | 128 МБ или выше |
| Видеоадаптер и монитор | Super VGA (800×600) | |
| Свободное место на жёстком диске | 1,5 ГБ или больше | |
| Оптические накопители | CD-ROM | CD-ROM или DVD-ROM |
| Устройства взаимодействия с пользователем | Клавиатура | Клавиатура и мышь |
| Другие устройства | Звуковая карта, колонки и/или наушники |
В дополнение к этим требованиям, для установки Service Pack 2 необходимо наличие на жёстком диске не менее 2 ГБ свободного места во время установки.
А уже для SP 3 требуется 2.3 ГБ жёсткого диска при установке.
[8]
Пакеты обновлений и поддержка[]
Microsoft периодически выпускает пакеты обновлений (service packs) своих операционных систем, устраняющие выявленные проблемы и добавляющие новые возможности.
Windows XP Gold[]
Поддержка Windows XP без установленных пакетов обновлений закончилась 30 сентября 2004 года.[9]
Пакет обновлений 1[]
Пакет обновлений 1 (SP1) для Windows XP был выпущен 9 сентября 2002 года. Наиболее важными новшествами стали поддержка USB 2.0, возможность выбирать программы по умолчанию для просмотра Интернета, почты, обмена мгновенными сообщениями, а также различные реализации виртуальной машины Java. Шифрующая файловая система EFS получила возможность использовать алгоритм шифрования AES с 256-битным ключом. По умолчанию включена поддержка LBA-48, позволяющая операционной системе работать с жёсткими дисками ёмкостью более 137 Гб.
Пакет обновлений 1a был выпущен 3 февраля 2003 года и удалял виртуальную машину Java из системы. Корпорация Майкрософт не рекомендовала пользователям, уже установившим пакет обновлений SP1, устанавливать пакет SP1а.
Поддержка Windows XP Service Pack 1 и 1a закончилась 10 октября 2006 года.[10]
Пакет обновлений 2[]
Пакет обновлений 2 (Service Pack 2, SP2) (кодовое название Springboard) был выпущен 6 августа 2004 года. SP2 добавил в Windows XP новые возможности, включая улучшенный файрволл; поддержку Wi-Fi с мастером настройки и Bluetooth, а также улучшения в Internet Explorer 6 — например, возможность блокировать «всплывающие» окна. Данный сервис-пак внёс значительные изменения в безопасность Windows XP. Так, значительным изменениям подвергся встроенный файрволл, который был переименован в Брандмауэр Windows и теперь активирован для всех создаваемых соединений по умолчанию. Появилась расширенная защита памяти, в частности, от атак переполнения буфера как с использованием технологии «NX-бит», так и рядом других приемов. Изменения коснулись и сервисов — такие сервисы, как telnet и служба сообщений, отключены по умолчанию, ряд сервисов запускаются с пониженными правами и т. д. Изменения в области безопасности затронули и почтовую программу Outlook Express и браузер Internet Explorer. Windows XP Service Pack 2 включает в себя Центр обеспечения безопасности, который позволяет облегчить наблюдение за безопасностью системы, следя и напоминая пользователю о необходимости установить или обновить антивирус и его базы, активировать встроенный или сторонний файрволл, произвести обновление операционной системы или изменить настройки веб-браузера. Сторонние антивирусы и файрволлы имеют возможность взаимодействовать с ним с помощью интерфейса API. Также были улучшены функции автозапуска при вставке компакт-диска или подключении флеш-карт и подобных устройств.
При загрузке системы исчезли подзаголовки с названием редакции; полоса загрузки в редакциях Home и Embedded сменила зелёный и жёлтый цвета на синий цвет, как в редакции Professional.
Поддержка Windows XP Service Pack 2 закончилась 13 июля 2010 года.[11][12]
Пакет обновлений 3[]
В начале августа 2007 года Microsoft начала бета-тестирование SP3[13] среди ограниченной группы бета-тестеров. Несмотря на то, что бета-версия была передана только избранным, её дистрибутив появился в пиринговых сетях. С 12 декабря 2007 года версия RC1 SP3 доступна для загрузки и тестирования всем желающим.[14]
Окончательная версия Пакета обновлений 3 была представлена 21 апреля 2008 года, но только для бизнес-клиентов, таких как производители оригинального оборудования и подписчики MSDN и TechNet. Остальные пользователи смогли получить третий сервис-пак 6 мая.
Пакет может быть установлен только поверх пакета Service Pack 1 (SP1) или Service Pack 2 (SP2), и доступен только для 32-битной версии.[15]
Включает в себя все обновления, выпущенные после выхода Windows XP Service Pack 2, а также ряд других новых элементов. Среди них функция защиты сетевого доступа (Network Access Protection) и новая модель активации, заимствованные у Windows Vista, кроме того, появилась улучшенная функция обнаружения так называемых маршрутизаторов-«чёрных дыр» и др.
С 1 июля 2008 года Microsoft прекратила продажи Windows XP SP2 своим поставщикам.[16] До середины 2010 года Windows XP SP3 поставлялась в OEM и BOX поставках[16], для Windows Vista Business возможен бесплатный «даунгрейд», а также в продаже находится Get Genuine Kit Windows XP SP3, предназначенный для лицензирования установленного пиратского ПО, в рамках корпоративного лицензирования пакет Get Genuine Solution Windows XP.
Windows XP Service Pack 3 также распространяется как часть опционального компонента Windows 7 Windows XP Mode.[17][18]
Неофициальный выпуск[]
В 2014 году силами энтузиастов был создан «Service Pack 4» на основе POSReady — варианта для XP.[19] Данная версия является не официальной и нарушающей лицензионное соглашение, т.к. обновления изначально предназначены для другой версии Windows XP (POSReady).
Завершение поддержки[]
Поддержка Windows XP Service Pack 3 завершилась 8 апреля 2014 года, следом и поддержка сети.[20] В этот же день Microsoft выпустила обновление для современной операционной системы — Windows 8.1 .
На момент прекращения официальной всеобщей поддержки (8 апреля 2014 года) Windows XP было 12,5 лет. Этот срок поддержки стал самым долгим за всю историю Windows, за отдельную плату он мог быть продлён ещё на 5 лет.
24 сентября 2014 года компания Microsoft выпустила патч для ряда операционных систем, в их числе оказалась и Windows XP Embedded.[21] В отношении версии для ПК было сделано заявление: «ещё есть пользователи, работающие на Windows XP, поддержка которой закончилась в апреле 2014 года, а также на пиратском ПО. Таким пользователям не доступны обновления системы безопасности и другие критичные обновления. Лучшим решением для них является миграция на современные лицензионные продукты Microsoft».[21]. Но есть еще патч в реестр, который давал возможность получать обновления для Windows XP до 2019 года, поддержка банкоматов на Windows XP продлилась до 2019 года. [22]
Поддержка Windows Embedded POSReady 2009 завершилась 9 апреля 2019 года.
Критика[]
Несмотря на некоторые преимущества перед Windows Vista и даже Windows 7 в быстродействии на устаревших компьютерах, за что её так ценят пользователи, Windows XP (SP1, SP2, SP3) имеет характерный недостаток:при установке системы пользователю предлагается создать для работы учётную запись с правами администратора, что приводит к потенциальной уязвимости системы к вирусам. Несмотря на то, что есть возможность использовать учётную запись с ограниченными правами, многие пользователи не используют данный подход по различным причинам (по незнанию, или потому что часть программ не работала нормально без прав администратора). Есть возможность запускать наиболее уязвимые программы (например, браузер) с пониженными правами[23]. В последующих версиях (Windows Vista и последующей доработкой в Windows 7 и старше) проблема уязвимости системы перед вирусными атаками была частично решена компонентом User Account Control, где система уже явно запрашивала повышение привилегий. Также заявления «о меньшей безопасности Windows XP» в настоящее время стали менее актуальны, чем на момент выхода Vista, в силу развития антивирусов и их эвристических способностей.
Интересные факты[]
- Презентация Windows XP происходила в Нью-Йорке всего через полтора месяца после атаки на башни-близнецы и началась с того, что хор Евангелической церкви спел «America the Beautiful».
См. также[]
- Windows XP 64-bit Edition
- Windows XP Professional x64 Edition
- Безмятежность
Примечания[]
- ↑ Lingvo: experience
- ↑ Windows XP Market Share on Desktop. Net Applications. Проверено 5 сентября 2015.
- ↑ Change Windows visual effects. Microsoft. Проверено ???. Архивировано из первоисточника 19 ноября 2012.
- ↑ Computer Slows When You Click Multiple Icons in Windows XP. Microsoft (Шаблон:HumanizeDate). Проверено ???. Архивировано из первоисточника 19 ноября 2012.
- ↑ Download Royale Theme for WinXP — Official Free — A new theme, potentially destined for Windows XP. Freeware — Softpedia
- ↑ Iconfactory Design: Windows Icon Design. The Iconfactory. Проверено 22 мая 2006. Архивировано из первоисточника 25 августа 2011.
- ↑ System requirements for Windows XP operating systems (Шаблон:HumanizeDate). Проверено 12 марта 2007. Архивировано из первоисточника 25 августа 2011.
- ↑ System Requirements for Windows XP Service Pack 2. Microsoft (Шаблон:HumanizeDate). Проверено 19 августа 2007. Архивировано из первоисточника 25 августа 2011.
- ↑ Lifecycle Supported Service Packs. Microsoft. Проверено 19 июня 2007.
- ↑ End of support for Windows 98, Windows Me, и Windows XP Service Pack 1 (Шаблон:HumanizeDate). Проверено 27 июня 2006. Архивировано из первоисточника 25 августа 2011.
- ↑ Поиск сведений о жизненном цикле продуктов корпорации Майкрософт — Windows XP
- ↑ http://old.computerra.ru/vision/546303/ «Поддержка Windows XP с пакетом обновления SP2 завершится 13 июля 2010 года.»
- ↑ WinBeta.org Beta News and Reviews
- ↑ Новости Software — 3DNews — Daily Digital Digest
- ↑ http://windows.microsoft.com/ru-ru/windows/help/learn-how-to-install-windows-xp-service-pack-3-sp3 Способы установки пакета обновления 3 (SP3) для Windows XP — Microsoft
- ↑ 16,0 16,1 Microsoft прекратила продажу Windows XP
- ↑ «is a fully licensed version of Windows XP with Service Pack 3» // Install and use Windows XP Mode in Windows 7Шаблон:Ref-en
- ↑ List of fixes that are included in Windows XP Service Pack 3
- ↑ Windows XP получила неофициальное обновление SP4
- ↑ Поддержка Windows XP SP3 и Office 2003 г.. Microsoft. Архивировано из первоисточника 30 мая 2012.
- ↑ 21,0 21,1 Microsoft поможет пользователям перейти на зимнее время. Microsoft (Шаблон:HumanizeDate). Проверено 20 октября 2014.
- ↑ Поддержку Windows XP можно продлить
- ↑ Утилита Dropmyrights от Microsoft
Литература[]
- Шаблон:±. Microsoft Windows XP SP2 для «чайников». Полный справочник = Windows XP All-in-One Desk Reference For Dummies. — 2-е изд. — Шаблон:Указание места в библиоссылке: Диалектика, 2007. — 720 с. — ISBN 0-7645-7463-9.
- Шаблон:±. Microsoft Windows XP SP2. Полное руководство = Microsoft Windows XP Unleashed. — Шаблон:Указание места в библиоссылке: Вильямс, 2006. — 880 с. — ISBN 0-672-32833-X.
- Шаблон:±. Windows XP. Самоучитель. — Шаблон:Указание места в библиоссылке: КУДИЦ-ПРЕСС, 2006. — ISBN 5-91136-021-7.
Ссылки[]
Шаблон:Внешние ссылки нежелательны
- Сайт проверки легальности копии Windows XP
- Windows XP — Справочник
- Windows XP
Windows XP — это операционная система, разработанная Microsoft для использования на персональных компьютерах, включая настольные и домашние компьютеры, ноутбуки и терминалы.
Впервые он был выпущен производителям компьютеров 24 августа 2001 года, а широкой публике — 25 октября 2001 года.
Это одна из самых популярных версий Windows, основанная на установленной пользовательской базе. Название «XP» сокращенно означает «eXPerience», что подчеркивает расширенные возможности для пользователя.
Windows XP предшествовал Windows 2000 и Windows Me, а затем Windows Vista.
8 апреля 2014 года Microsoft выпустила последние обновления для Windows XP. Таким образом, эта версия Windows больше не поддерживается Microsoft. Тем не менее, Windows XP остается популярной операционной системой среди многих пользователей, которые любят эту версию. Tckb ds bcgjkmpetnt ОС Linux, то вам может быть интересно прочитать про основные различия между Linux и Windows
Версии Windows XP
Microsoft предоставила семь выпусков Windows XP. Тем не менее, только первые два из списка ниже были широко доступны для обычного пользователя:
- Windows XP Professional
- Windows XP Home
- Windows XP Media Center Edition (MCE)
- Windows XP Tablet PC Edition
- Windows XP Starter Edition
- Windows XP Home Edition ULCPC
- Windows XP Professional x64 Edition
Домашняя версия предназначена для среднего пользователя и для более дешевых компьютеров. Windows XP Home ориентирована на начинающих пользователей компьютеров.
Профессиональная версия более ориентирована на предприятия и имеет возможность присоединиться к домену Windows, информационным службам интернета и многоязычному пользовательскому интерфейсу.
Основные функции в Windows XP
Как мы уже говорили, Windows XP — это простая в использовании операционная система. Тот факт, что он интуитивно понятен и удобен для пользователя, делает его одной из самых популярных версий Windows.
Первой новой функцией для Windows XP является интерфейс, полностью отличающийся от предыдущих версий, таких как Windows 2000 или Windows Me. Microsoft разработала новый привлекательный и удобный внешний вид с визуальными стилями и различными эффектами.
Кроме того, в Windows XP существовал огромный и разнообразный набор инструментов и программ, что делает Windows XP более безопасной, надежной и стабильной операционной системой, чем предыдущие версии.
Список новых функций в Windows XP:
- Пользовательский интерфейс
- Встроенный CD-рекордер
- Доступные драйверы устройств
- Брандмауэр подключения к Интернету
Обновления в Windows XP
Обновления в Windows XP предоставлялись в виде пакетов обновления. Пакет обновления представляет собой накопительные программные ресурсы, аналогичные в Windows 10. Тем не менее, в отличие от Windows 10, обновления для Windows XP меньше, но больше.
Например, переход с Windows XP с пакетом обновления 1 на Windows XP с пакетом обновления 2 является более масштабным и сложным, чем переход с Windows 10 версии 1809 на Windows 10 версии 1903. Если вы пользователь macOS, то вам может быть полезно прочитать про сравнение безопасности macOS и Windows.
Microsoft выпустила 3 пакета обновления. Третий и последний, SP3, был опубликован 6 мая 2008 года.
Минимальные требования для Windows XP
- Жесткий диск: 1,5 ГБ свободного места (5 ГБ Windows XP SP3)
- Оперативная память: 64 МБ (рекомендуется 128 МБ)
- Процессор: 233 МГц (рекомендуется 300 МГц)
- Видеокарта: 800 × 600 или выше
- Привод CD-ROM или DVD-ROM
К счастью, на рынке нет компьютеров, которые бы не соответствовали этим крайне скромным характеристикам.
Так что, если вы испытываете ностальгию, современный ПК будет работать под управлением Windows XP без проблем.
Поддержка Windows XP
8 апреля 2014 года Microsoft прекратила поддержку Windows XP — спустя 12 лет после ее выхода. Для этой версии Windows больше не выходят обновления безопасности и не предоставляется техническая поддержка. Следующей крупной версией ОС после Windows XP стала Windows Vista.
2.1. Назначение и возможности операционной системы MicrosoftWindowsXpProfessional
Microsoft
Windows XP (символы
XP являются сокращением от английского
eXPerience
— опыт,
знания)
– 32-разрядная операционная система с
приоритетной многозадачностью и
улучшенной реализацией работы с памятью,
основанной на ядре NT
(New Technology),
ориентированная на решение разнообразных
задач с использованием компьютеров
различного класса (от переносных ПК до
мощных серверов).
Отличительными
чертами Windows XPявляются: простота управления, повышенная
надежность, использование механизмов
защиты данных и программ, возможность
работы в локальных и глобальных сетях,
реализация удаленного доступа и др.
В
состав семейства WindowsХР
входят следующие версии:
-
Windows
XP Home
Edition– ОС для работы
с цифровыми мультимедийными материалами
на домашних компьютерах; -
Windows
XP Professional– ОС, предназначенная для корпоративных
пользователей и обеспечивающая высокий
уровень масштабируемости и надежности; -
Windows
XP 64-Bit Edition– ОС для работы на рабочих
станциях и серверах, оснащенных
64-разрядными микропроцессорами семействаIntel Itanium.
Система
содержит целый ряд хорошо интегрированных
функциональных средств, которые ранее
были доступны только как продукты
независимых фирм (архиватор WinZip;
универсальный проигрыватель Windows
Media Player; ПО
для записи компакт-дисков и др.).
С
выпуском этой ОС Microsoft еще более
приблизилась к созданию универсальной
системы, в которой объединены возможности,
рассчитанные на массового потребителя
(например, совместимость с играми,
мультимедийные возможности), и функции
корпоративного уровня, заимствованные
из Windows 2000
и предназначенные для сетей и обеспечения
безопасности. Благодаря большему списку
совместимых устройств и большей
библиотеке встроенных драйверов Windows
XP стала
значительно удобнее для домашнего
пользователя нежели предыдущие версии
Windows.
Windows
XP представляет
собой комплекс программ, обеспечивающих
взаимосвязь отдельных устройств
компьютера, а также связь с этими
устройствами. Она является промежуточным
звеном между устройствами компьютера
и работающими на нем программами.
Основной частью ОС является ядро,
которое определяет общие возможности
системы. Ядро содержит базовый набор
механизмов, на основе которых строятся
уже все остальные.
С
точки зрения пользователя ОС нужна для
удобного общения человека с устройствами
компьютера и установленными на нем
программами, т.е. для предоставления
удобного интерфейса к различным
программам и ресурсам компьютера.
Интерфейс
ОС должен обеспечивать удобный доступ
к файлам и папкам, запуску программ, к
настройкам, к выполнению этих настроек
и т.д.
Интерфейсом
называется совокупность инструментов,
которые можно использовать для обмена
информацией, т.е. для получения доступа
к чему-либо или для выполнения каких-либо
действий. Рабочий стол Windows XP
является примером интерфейса (подобные
интерфейсы называются пользовательскими
графическими интерфейсами).
С
другой стороны, термин «интерфейс»
применяется к набору команд, используемых
для обмена информацией с внешним
устройством, например с модемом. Такие
интерфейсы называют аппаратными.
Кроме
того, совокупность параметров, передаваемых
программе, и механизм вызова отдельных
ее частей называется программным
интерфейсом.
Таким
образом, ОС можно представить как
совокупность механизмов для предоставления
программных и пользовательских
интерфейсов, а также преобразования
аппаратных интерфейсов в программные
(эта функция реализуется драйверами)
(рис 2.1).
Рис. 2.1.Логическая
схема взаимодействие компьютера,
операционной системы и пользователя
Судить
о том, «хорошая» операционная система
или «плохая», следует по тому, насколько
стабильно работает компьютер, насколько
эффективно происходит управление
ресурсами компьютера, каковы принципы
обеспечения безопасности информации
на компьютере и т.д.
От
предшественниц Windows XP отличают следующие
качества:
-
Существенно
упрощена установки и настройка системы. -
Использование
более наглядного пользовательского
графического интерфейса. -
Поддержка
быстрого подключения к компьютеру
различных устройств. -
Значительно
сокращено количество ситуаций, требующих
перезагрузки компьютера при инсталляции
ОС. -
Достаточно
хорошо реализована многозадачность.
ОС стабильно и эффективно управляет
работой компьютера при одновременном
выполнении нескольких программ. -
Существенно
улучшена поддержка файловой системы
NTFS, которая позволяет шифровать данные,
что делает более надежной их защиту,
непосредственно управлять доступом к
тем или иным файлам, разрешая или
запрещая доступ к ним другим пользователям
и/или группам пользователей. -
Поддержка
больших объемов оперативной памяти
(до 4 Гбайт) и возможности использования
нескольких процессоров, что позволяет
наращивать мощность компьютера. -
Встроенная
поддержка записи дисков CD-R и CD-RW. -
Наличие
встроенного механизма автоматического
восстановления (System
Restore). -
Улучшенные
механизмы защиты системных файлов
Windows XP, от которых зависит работа ОС.
При этом защита производится по двум
направлениям:
-
Защита
системных файлов Windows XP — на основные
системные файлы ОС налагается запрет
перезаписи. Если же таковая произойдет
(например, при установке новой программы),
то служба защиты файлов восстановит
файл в первоначальном виде из специально
хранящейся для этого резервной копии. -
Блокирование
драйверов, содержащих ошибки. На
официальном сайте Microsoft размещен
постоянно обновляемый каталог драйверов,
в которых были замечены неполадки. А
функция блокирования некачественных
драйверов (Defective
Driver Blocking),
используемая в Windows XP, не допускает
установки драйверов, о которых известно,
что они вызывают появление ошибок.
-
Появление
новых инструментов администрирования
пользователей. -
Наличие
развитой возможности управления
удаленным рабочим столом. -
Среди
положительных качеств Windows XP можно
также отметить:
-
поддержку
Multimedia
Extensions (MMX),
благодаря чему существенно улучшается
работа мультимедиа; -
встроенную
программу дефрагментации диска; -
поддержку
новых технологий, UPnP
(Universal Plag and
Play) и ClearType
(повышает качество отображения текстовой
информации на жидкокристаллическом
мониторе, экране ноутбука), DualView
(позволяет использовать 2 монитора на
одном компьютере); -
поддержку
известных стандартов оборудования
IrDA
(Infrared Data
Association), USB
(Universal Serial
Bus) и
высокоскоростной шины IEEE
1394; -
улучшенную
поддержку сетевых устройств и еще
многое другое.
Использование
ОС Windows XP
Professionalпозволяет
достичь нового уровня эффективности и
надежности вычислительных систем
благодаря ее возможностям, которые
приведены в табл.2.1.
Таблица
2.1.
Характерные свойства ОС Windows
ХР Professional
|
Возможность |
Описание |
|
Надежность |
|
|
Ядро |
В |
|
Усовершенствованные |
Средство |
|
Существенное |
Устранена |
|
Улучшенная |
Критически |
|
Поддержка |
Механизм, |
|
Защита |
Предохраняет |
|
Программа |
Системная |
|
Усовершенствованные |
Предоставляет |
|
Быстродействие |
|
|
Многозадачность |
Допускается |
|
Масштабируемая |
Поддерживается |
|
Защита |
|
|
Шифрованная |
Все |
|
IP-безопасность |
Позволяет |
|
Поддержка |
Надежное |
|
Поддержка |
В |
|
Удобство |
|
|
Новое |
Обновленный |
|
Адаптированная |
ОС |
|
Контекстные |
При |
|
Встроенное |
В |
|
Средства |
Проигрыватель
|
|
Упрощенная |
Файлы |
|
Работа |
Рабочий |
|
Средства |
Предоставление |
Кроме
того, ОС Windows XP
Professionalобеспечивает
быстрый доступ к передовым инструментальным
средствам цифровой эры благодаря:
-
принципиально
новым методам работы с удаленными
системами (использование удаленного
рабочего стола, реализуемого протоколом
RDP(Remote Desktop Protocol)); -
обеспечению
безопасного доступа к беспроводным
сетям; -
наличию
улучшенной справочной системы и
технической поддержки посредством
удаленного управления; -
развитым
средствам поддержки сетевых технологий; -
совместимости
с приложениями, разработанными для
ранних версий Windows; -
поддержке
новейших стандартов (чтения DVD-дисков
UDF 2.01и форматирования записываемых
DVD для файловой системыFAT32, поддержка
интерфейсаDirectX 8и стандартовInfrared Data Association(IrDA),Universal Serial
Bus(USB), а также быстродействующей
шиныIEEE 1394) и др.
Windows XP оставалась флагманской операционной системой Microsoft дольше, чем любая другая версия Windows, с 25 октября 2001 г. по 30 января 2007 г., когда ей на смену пришла Windows Vista. … Последующие версии такие же, но с обновленным Windows Media Center.
На младшей компьютерной системе Windows XP превосходит Windows Vista в большинстве проверенных областей. Сетевая производительность ОС Windows зависит от размера пакета и используемого протокола. Однако в целом Windows Vista по сравнению с Windows XP показывает лучшую производительность сети, особенно для пакетов среднего размера.
Что появилось после Windows Vista?
Windows 7 (Октябрь 2009 г.)
Windows 7 была выпущена Microsoft 22 октября 2009 года как последняя из линейки операционных систем Windows 25-летней давности и как преемница Windows Vista.
Windows XP — это то же самое, что Vista?
Ключевое отличие: Windows Vista — это более новая операционная система от Microsoft. Он предназначен для большей экономии времени и удобен для пользователя, чем XP. Vista требует большей аппаратной поддержки, чем XP. Windows XP и Vista являются операционными системами Microsoft..
Какая версия Windows XP или 2000 новее?
XP новее 2000.
Кто-нибудь еще пользуется Windows Vista?
Microsoft прекратила поддержку Windows Vista. Это означает, что больше не будет никаких дополнительных исправлений безопасности или исправлений ошибок для Vista, а также технической помощи. Операционные системы, которые больше не поддерживаются, более уязвимы для злонамеренных атак, чем более новые операционные системы.
Когда вышла Windows 11?
Microsoft не сообщил нам точную дату выпуска для Windows 11 пока что, но некоторые просочившиеся изображения в прессе указали, что дата выпуска is от Microsoft на официальной веб-странице написано, что «появится позже в этом году».
Какие операционные системы 5?
Пять самых распространенных операционных систем: Microsoft Windows, Apple macOS, Linux, Android и iOS от Apple.
Можно ли будет использовать Windows XP в 2019 году?
Впервые запущенный еще в 2001 году, долгое время Microsoftнесуществующая операционная система Windows XP все еще жива по данным NetMarketShare, среди некоторых групп пользователей. По состоянию на прошлый месяц 1.26% всех ноутбуков и настольных компьютеров в мире все еще работали на ОС 19-летней давности.
Какая Windows XP самая лучшая?
Первоначальный ответ: Какая версия Windows лучше всего: Windows XP, 7, 8, 8.1 или 10? правда трогать другие операционки не захочется. Xp обеспечивает наилучшее изображение и качество звука. Если хочешь отличной внешности, тогда Стекло Windows XP Super самый лучший
Windows 2000 — это то же самое, что и XP?
На смену Windows 2000 и Windows 2000 Server пришла Windows XP (выпущен в октябре 2001 г.) и Windows Server 2003 (выпущен в апреле 2003 г.) соответственно.
Почему не было Windows 9?
Оказывается, что Microsoft могла пропустить Windows 9 и сразу перешел к 10 по причине, которая восходит к эпохе 2 года. … По сути, существует давний сокращенный код, предназначенный для различения Windows 95 и 98, который не понимает, что теперь существует Windows 9.
Выпускает ли Microsoft Windows 11?
Операционная система Microsoft для настольных ПК следующего поколения, Windows 11, уже доступна в бета-версии и будет официально выпущена Октябрь 5th.
| Windows XP | |
 |
|
 Windows XP Service Pack 3 |
|
| Разработчик |
Microsoft Corporation |
|---|---|
| Семейство ОС |
Windows NT |
| Первый выпуск |
25 октября 2001 (инфо) |
| Последняя версия |
5.1.2600.5687 Service Pack 3 — 21 апреля 2008 [1] |
| Тип ядра |
гибридное ядро |
| Интерфейс |
Luna |
| Лицензия |
Microsoft EULA |
| Состояние |
Общая поддержка прекращена 14 апреля 2009 года[2]
|
| Веб-сайт |
http://www.microsoft.com |
Windows XP (кодовое название при разработке — Whistler; внутренняя версия — Windows NT 5.1) — операционная система (ОС) семейства Windows NT корпорации Microsoft. Она была выпущена 25 октября 2001 года и является развитием Windows 2000 Professional. Название XP происходит от англ. eXPerience (опыт).
В отличие от предыдущей системы Windows 2000, которая поставлялась как в серверном, так и в клиентском вариантах, Windows XP является исключительно клиентской системой. Её серверным аналогом является Windows Server 2003. Хотя Windows Server 2003 и построен на базе того же кода, что и Windows XP, почти всецело наследуя интерфейс её пользовательской части, Windows Server 2003 всё же использует более новую и переработанную версию ядра NT 5.2; появившаяся позже Windows XP Professional x64 Edition имела то же ядро, что и Windows Server 2003, и получала те же обновления безопасности, вследствие чего можно было говорить о том, что их развитие шло одинаково.
По данным веб-аналитики от W3Schools (англ.) с сентября 2003 по июль 2011 года Windows XP была самой используемой операционной системой для доступа к Интернету в мире. На октябрь 2012 года Windows XP находилась на втором месте после Windows 7 с долей ▼22,1 %. Максимум этого значения составлял 76,1 % и был достигнут в январе 2007 года.[3]
Содержание
- 1 Варианты
- 2 Новое в сравнении с Windows 2000
- 3 Графический интерфейс пользователя
- 4 Интерфейс командной строки (CLI)
- 5 Системные требования
- 6 Пакеты обновлений и поддержка
- 6.1 Windows XP Gold/SP0
- 6.2 Пакет обновлений 1
- 6.3 Пакет обновлений 2
- 6.4 Пакет обновлений 3
- 7 Критика
- 8 Интересные факты
- 9 См. также
- 10 Примечания
- 11 Литература
- 12 Ссылки
Варианты
Windows XP выпускалась во многих вариантах:
- Windows XP Professional Edition была разработана для предприятий и предпринимателей и содержит такие функции, как удалённый доступ к рабочему столу компьютера, шифрование файлов (при помощи Encrypting File System), центральное управление правами доступа и поддержка многопроцессорных систем.
- Windows XP Home Edition — система для домашнего применения. Выпускается как недорогая «урезанная» версия Professional Edition, но базируется на том же ядре.
- Windows XP Tablet PC Edition базируется на Professional Edition и содержит специальные приложения, оптимизированные для ввода данных стилусом на планшетных персональных компьютерах. Важнейшим свойством является понимание текстов, написанных от руки и адаптация графического интерфейса к поворотам дисплея. Эта версия продаётся только вместе с соответствующим компьютером.
- Windows XP Media Center Edition базируется на Professional Edition и содержит специальные мультимедийные приложения. Компьютер, как правило, оснащён ТВ-картой и пультом дистанционного управления (ПДУ). Важнейшим свойством является возможность подключения к телевизору и управление компьютером через ПДУ благодаря упрощённой системе управления Windows. Эта система содержит также функции для приёма УКВ-радио.
- Windows XP Embedded — это встраиваемая компонентная операционная система на базе Windows XP Professional Edition и предназначена для применения в различных встраиваемых системах: системах промышленной автоматизации, банкоматах, медицинских приборах, кассовых терминалах, игровых автоматах, VoIP-компонентах и т. п. Windows XP Embedded включает дополнительные функции по встраиванию, среди которых фильтр защиты от записи (EWF и FBWF), загрузка с флеш-памяти, CD-ROM, сети, использование собственной оболочки системы и т. п.
- Windows Embedded POSReady — специализированная операционная система на базе Windows XP Embedded, сконфигурированная для пунктов обслуживания и оптимизированная для розничной торговли и сферы услуг. На базе этой платформы можно создавать банкомат, платёжный терминал, АЗС, кассовый аппарат и т. п. Дополнительно Windows Embedded for Point of Service включает технологию POS for .NET для быстрой разработки торговых приложений и поддержки торгового периферийного оборудования.
- Windows XP Professional x64 Edition — специальная 64-разрядная версия, разработанная для процессоров с технологией AMD64 Opteron и Athlon 64 от фирмы AMD и процессоров с технологией EM64T от фирмы Intel. Эта система не поддерживает процессоры других производителей, а также не работает с процессором Intel Itanium. Хотя первые 64-разрядные процессоры появились в 2003 году, Windows XP Professional x64 Edition вышла в свет только в апреле 2005 года. Основным достоинством системы является быстрая работа с большими числами (Long Integer и Double Float). Таким образом, эта система очень эффективна, например, при выполнении вычислений, использующих числа с плавающей запятой, необходимых в таких областях, как создание спецэффектов для кинофильмов и трёхмерной анимации, а также разработка технических и научных приложений. Данная система поддерживает смешанный режим, то есть одновременную работу 32- и 64-разрядных приложений, однако для этого все драйверы должны быть в 64-разрядном исполнении. Это означает, что большинство 32-разрядных приложений могут работать и в этой системе. Исключение составляют лишь те приложения, которые сильно зависят от аппаратного обеспечения компьютера, например, антивирусы и дефрагментаторы.
- Windows XP 64-bit Edition — это издание разрабатывалось специально для рабочих станций с архитектурой IA-64 и микропроцессорами Itanium. Это издание Windows XP более не развивается с 2005 года, после того, как HP прекратил разработку рабочих станций с микропроцессорами Itanium. Поддержка этой архитектуры осталась в серверных версиях операционной системы Windows.
- Windows XP Edition N — система без Windows Media Player и других мультимедиа-приложений. Эти версии созданы под давлением Европейской Антимонопольной Комиссии, которая требовала «облегчить» Windows XP. В настоящее время этот дистрибутив рассчитан на развивающиеся страны. При желании пользователь может бесплатно загрузить все недостающие приложения с веб-сайта Microsoft. Существует как в Home, так и в Professional вариантах.
- Windows XP Starter Edition — сильно функционально ограниченная версия для развивающихся стран и финансово слабых регионов. В этой версии возможна одновременная работа только 3 приложений, и каждое приложение может создать не более 3 окон. В системе полностью отсутствуют сетевые функции, не поддерживается высокая разрешающая способность, а также не допускается использование более 512 мегабайт оперативной памяти или жёсткого диска объёмом более 120 гигабайт. Система может работать на процессорах уровня Intel Celeron или AMD Duron.
- Windows Fundamentals for Legacy PCs — урезанная версия Microsoft Windows XP Embedded Service Pack 2, предназначенная для устаревших компьютеров.
Новое в сравнении с Windows 2000
Некоторыми из наиболее заметных улучшений в Windows XP по сравнению с Windows 2000 являются:
- Новое оформление графического интерфейса, включая более округлые формы и плавные цвета; а также дополнительные функциональные улучшения (такие, как возможность представления папки в виде слайд-шоу в проводнике Windows).
- Поддержка метода сглаживания текста ClearType, улучшающего отображение текста на ЖК-дисплеях (по умолчанию отключена).
- Возможность быстрого переключения пользователей, позволяющая временно прервать работу одного пользователя и выполнить вход в систему под именем другого пользователя, оставляя при этом приложения, запущенные первым пользователем, включёнными.
- Функция «удалённый помощник», позволяющая опытным пользователям и техническому персоналу подключаться к компьютеру с системой Windows XP по сети для разрешения проблем. При этом помогающий пользователь может видеть содержимое экрана, вести беседу и (с позволения удалённого пользователя) брать управление в свои руки.
- Программа восстановления системы, предназначенная для возвращения системы в определённое предшествующее состояние (эта функция является развитием аналогичной программы, включённой в Windows ME), а также улучшение других способов восстановления системы. Так, при загрузке последней удачной конфигурации загружается также и прежний набор драйверов, что позволяет в ряде случаев легко восстановить систему при проблемах, возникших в результате установки драйверов; возможность отката драйверов и т. д.
- Улучшенная совместимость со старыми программами и играми. Специальный мастер совместимости позволяет эмулировать для отдельной программы поведение одной из предыдущих версий ОС (начиная с Windows 95). Впрочем, функция совместимости присутствует в Windows 2000 с пакетом обновления 2.[4]
- Возможность удалённого доступа к рабочей станции благодаря включению в систему миниатюрного сервера терминалов (только в издании Professional).
- Более развитые функции управления системой из командной строки.
- Поддержка проводником Windows цифровых фотоформатов и аудиофайлов (автоматическое отображение метаданных для аудиофайлов, например, тегов ID3 для MP3-файлов).
- Windows XP включает технологии, разработанные фирмой Roxio, которые позволяют производить прямую запись CD из проводника, не устанавливая дополнительное ПО, а работа с перезаписываемыми компакт-дисками становится подобной работе с дискетами или жёсткими дисками. Также в Media Player включена возможность производить запись аудио-дисков. Возможности работы с образами дисков не предусмотрено.
- Windows XP может работать с архивами ZIP и CAB без установки дополнительного ПО. Работа с архивами данного типа возможна в проводнике как с обычными папками, которые можно создавать и удалять, заходить в архив, добавлять/удалять файлы подобно работе с обычными папками. Также возможна установка пароля на архив. При необходимости можно назначить для работы с этими архивами любое стороннее программное обеспечение.
- Улучшения в подсистеме EFS, заключающиеся в необязательности агента восстановления, более безопасного сохранения ключей. Шифруемые файлы теперь не просто удаляются, а перезаписываются нулями, что гораздо надёжнее. Начиная с SP1 становится возможным использовать (он и используется по умолчанию) алгоритм AES, наряду с DESX и 3-DES.
- Настраиваемые панели инструментов, с помощью которых можно оптимизировать доступ к файлам, папкам и ресурсам Интернета. Достаточно разместить их на краю Рабочего стола (наподобие боковой панели) или на Панели задач (в форме ссылки).
- Частичное использование сборок (англ. Side-by-side assembly, (SxS)).
Графический интерфейс пользователя
Стартовое меню в новом виде при использовании темы Royale
- Выделение в Windows Explorer осуществляется прозрачным синим прямоугольником.
- Падающая тень от ярлыков на рабочем столе.
- Боковая панель, ориентированная на выполнение задач в окне проводника («common tasks»).
- Группирование кнопок одного приложения на панели задач в одну кнопку, при определённом количестве разных запущенных приложений, что позволяет часто избегать необходимости её «прокрутки».
- Появилась возможность заблокировать панель задач и вспомогательные панели, во избежание их случайного изменения.
- Цветовое выделения элементов в меню «Пуск», принадлежащих недавно добавленным программам.
- Меню отбрасывают тени (в Windows 2000 тень отбрасывал указатель мыши, но не элементы меню).
Windows XP анализирует производительность системы с определёнными визуальными эффектами и в зависимости от этого активирует их или нет, учитывая возможное падение или рост производительности. Пользователи также могут изменять данные параметры, используя диалоговые окна настройки, при этом можно либо гибко выбрать активность тех или иных визуальных эффектов, либо отдать это на управление системе или же выбрать максимальную производительность или лучший вид графического интерфейса.[5]
Некоторые эффекты, такие как полупрозрачность и т. п., требуют наличия производительной графической подсистемы, на старых видеокартах производительность может сильно упасть и Microsoft рекомендует отключить эти возможности в таком случае.[6]
В Windows XP появилась возможность использовать Visual Styles, позволяющие изменить графический интерфейс пользователя. Luna — новый стиль графического интерфейса, входящий в поставку XP и являющийся интерфейсом по умолчанию для компьютеров, имеющих более 64 мегабайт оперативной памяти. Возможно использовать и другие Visual Styles, но они должны быть подписаны цифровой подписью Microsoft (так как имеют важное значение в функционировании системы).
Для обхода этого ограничения некоторые пользователи используют специальное программное обеспечение, такое, как TGTSoft’s StyleXP, а иногда и изменённую версию библиотеки uxtheme.dll.
Также существует стиль «классический», повторяющий стиль интерфейса Windows 2000 (который использует на 4 МБ меньше памяти, чем Luna), а также многочисленные стили, созданные сторонними разработчиками. Для версии Media Center Microsoft разработала «визуальный стиль» Royale, который включён в эту версию Windows XP и доступен для установки в других версиях XP.[7]
Для Windows XP были созданы более 100 значков компанией The Iconfactory, известной своим набором бесплатных значков для операционной системы Mac OS X[8]
Интерфейс командной строки (CLI)
Windows XP также имеет интерфейс командной строки (CLI, «консоль»), cmd.exe, для управления системой командами из консоли или запуска сценариев, называемых «командными файлами» (с расширениями cmd), основанными на пакетных файлах MS-DOS. Синтаксис Windows XP CLI достаточно хорошо задокументирован во встроенной системе помощи (файл справки ntcmds.chm). Более подробную общую информацию можно получить, набрав в командной строке «help» для получения общих сведений о доступных командах и «имя команды /?». Интерфейс командной строки доступен как в виде окна, так и в полноэкранном виде (переключение между ними осуществляется нажатием Alt + ↵ Enter ), предпочитаемый вид можно указать в соответствующем диалоге настройки, наряду с такими параметрами, как размер и тип шрифтов и т. д. При работе в данном режиме пользователь может вызывать предыдущие команды (так, клавиша ↑ возвращает предыдущую команду, а F7 выводит меню со списком вводившихся команд), использовать автодополнение имён файлов и каталогов, а также команд. Многие действия по управлению операционной системой можно выполнить, используя интерфейс CLI. Наиболее важными из них являются команды:
- «net» с подкомандами, позволяющая управлять локальными пользователями и группами («net user /?» и «net localgroup /?»), аккаунтами, общим доступом к ресурсам на ПК («net share /?») и в сети («net view /?») и т. д.
- Команды просмотра и управления процессами «tasklist /?» и «taskkill /?»
- Команда управления разрешениями файлов «cacls /?», позволяющая просматривать и изменять права доступа к файлам и папкам (в Home Edition — это единственная возможность гибко изменять права, так как соответствующий графический инструмент доступен только в безопасном режиме)
- А также команды, аналогичные командам MS-DOS, позволяющие копировать, перемещать и удалять файлы и каталоги и т. д.
Системные требования
Логотип Designed for Windows XP
Системные требования операционных систем Windows XP Home и Professional editions следующие:[9]
| Декларируемые как минимальные | Рекомендуемые | |
|---|---|---|
| Процессор | 233 МГц | 300 МГц или выше |
| Оперативная память | 64 Мб (могут быть ограничены некоторые возможности) | 128 Мб или выше |
| Видеоадаптер и монитор | Super VGA (800×600) | |
| Свободное место на жёстком диске | 1,5 Гб или больше | |
| Оптические накопители | CD-ROM (требуется для установки) | CD-ROM или DVD-ROM |
| Устройства взаимодействия с пользователем | Клавиатура | Клавиатура и мышь |
| Другие устройства | Звуковая карта, колонки и/или наушники |
В дополнение к этим требованиям, для установки Service Pack 2 необходимо наличие на жёстком диске не менее 1,8 ГБ свободного места во время установки.[10]
Пакеты обновлений и поддержка
Microsoft периодически выпускает пакеты обновлений (service packs) своих операционных систем, устраняющие выявленные проблемы и добавляющие новые возможности.
Windows XP Gold/SP0
Поддержка Windows XP без установленных пакетов обновлений (Gold/SP0) закончилась 30 сентября 2004 года.[11]
Пакет обновлений 1
Пакет обновлений 1 (SP1) для Windows XP был выпущен 9 сентября 2002 года. Наиболее важными новшествами стали поддержка USB 2.0, утилита, позволяющая выбирать программы по умолчанию для просмотра Интернета, почты, обмена мгновенными сообщениями, а также различные реализации виртуальной машины Java. Начиная с SP1 шифрующая файловая система EFS получила возможность использовать алгоритм шифрования AES с 256-битным ключом.
Начиная с SP1 по умолчанию включена поддержка LBA-48, позволяющая операционной системе работать с жёсткими дисками ёмкостью более 137 Гб.
Пакет обновлений 1a был выпущен 3 февраля 2003 года и удалял виртуальную машину Java из системы. Корпорация Майкрософт не рекомендовала пользователям, уже установившим пакет обновлений SP1, устанавливать пакет SP1а.
Поддержка Windows XP Service Pack 1 и 1a закончилась 10 октября 2006 года.[12]
Пакет обновлений 2
Пакет обновлений 2 (Service Pack 2, SP2) (кодовое название Springboard) был выпущен 6 августа 2004 года. SP2 добавил в Windows XP новые возможности, включая улучшенный файрволл; поддержку Wi-Fi с мастером настройки и Bluetooth, а также улучшения в Internet Explorer 6 — например, возможность блокировать «всплывающие» окна. Данный сервис-пак внёс значительные изменения в безопасность Windows XP. Так, значительным изменениям подвергся встроенный файрволл, который был переименован в Брандмауэр Windows и теперь активирован для всех создаваемых соединений по умолчанию. Появилась расширенная защита памяти, в частности, от атак переполнения буфера как с использованием технологии «NX-бит», так и рядом других приемов. Изменения коснулись и сервисов — такие сервисы, как telnet и служба сообщений, отключены по умолчанию, ряд сервисов запускаются с пониженными правами и т. д. Изменения в области безопасности затронули и почтовую программу Outlook Express и браузер Internet Explorer. Windows XP Service Pack 2 включает в себя Центр обеспечения безопасности, который позволяет облегчить наблюдение за безопасностью системы, следя и напоминая пользователю о необходимости установить или обновить антивирус и его базы, активировать встроенный или сторонний файрволл, произвести обновление операционной системы или изменить настройки веб-браузера. Сторонние антивирусы и файрволлы имеют возможность взаимодействовать с ним с помощью интерфейса API. Также были улучшены функции автозапуска при вставке компакт-диска или подключении флеш-карт и подобных устройств.
При загрузке системы исчезли подзаголовки с названием редакции; полоса загрузки в редакциях Home и Embedded сменила зелёный и жёлтый цвета на синий цвет, как в редакции Professional.
Поддержка Windows XP Service Pack 2 закончилась 13 июля 2010 года.[2]
Пакет обновлений 3
В начале августа 2007 года Microsoft начала бета-тестирование SP3[13] среди ограниченной группы бета-тестеров. Несмотря на то, что бета-версия была передана только избранным, её дистрибутив появился в пиринговых сетях. С 12 декабря 2007 года версия RC1 SP3 доступна для загрузки и тестирования всем желающим.[14]
Окончательная версия Пакета обновлений 3 для Windows XP была представлена 21 апреля 2008 года, но только для бизнес-клиентов, таких как производители оригинального оборудования и подписчики MSDN и TechNet. Остальные пользователи смогли получить третий сервис-пак с онлайн-сервиса Windows Update или через центр загрузки Microsoft 6 мая, а также с помощью сервиса автоматического обновления в начале лета.
Пакет может быть установлен только поверх пакета Service Pack 1 (SP1) или Service Pack 2 (SP2), и доступен только для 32-битной версии.[15]
Пакет включает в себя все обновления, выпущенные после выхода Windows XP Service Pack 2 в августе 2004 года, а также ряд других новых элементов. Среди них функция защиты сетевого доступа (Network Access Protection) и новая модель активации, заимствованные у Windows Vista, кроме того, появилась улучшенная функция обнаружения так называемых маршрутизаторов-«чёрных дыр» и др.
С 1 июля 2008 года Microsoft прекратила продажи Windows XP SP2 своим поставщикам.[16] До середины 2010 года Windows XP SP3 поставлялась в OEM и BOX поставках[16], для Windows Vista Business возможен бесплатный «даунгрейд», а также в продаже находится Get Genuine Kit Windows XP SP3, предназначенный для лицензирования установленного пиратского ПО, в рамках корпоративного лицензирования пакет Get Genuine Solution Windows XP.
Windows XP Service Pack 3 также распространяется как часть опционального компонента Windows 7 Windows XP Mode.[17][18]
Поддержка Windows XP Service Pack 3 завершается 8 апреля 2014 года.[19]
Критика
|
|
Несмотря на некоторые преимущества перед Windows Vista и даже Windows 7 в быстродействии, за что её так ценят пользователи, Windows XP (SP1, SP2, SP3) имеет характерный недостаток:
- При установке системы пользователю предлагается создать для работы учётную запись с правами администратора, что приводит к потенциальной уязвимости системы к вирусам. Несмотря на то, что эта проблема решается созданием и использованием отдельной учётной записи с ограниченными правами, многие пользователи не используют данный подход по различным причинам, в том числе по незнанию. В последующих версиях (Vista и старше) данная проблема была решена компонентом User Account Control. Также заявления «о меньшей безопасности Windows XP» в настоящее время стали менее актуальны, чем на момент выхода Vista, в силу развития антивирусов и их эвристических способностей.
Интересные факты
- Презентация Windows XP происходила в Нью-Йорке всего через полтора месяца после атаки на башни-близнецы и началась с того, что хор Евангелической церкви спел «America the Beautiful».
- Есть возможность запустить Windows XP на смартфонах или КПК с помощью BOCHS (Android) и QEMU (Windows Mobile), но ресурсов устройства будет недостаточно для быстрой работы.
- На момент прекращения поддержки (8 апреля 2014 года) Windows XP исполнится чуть менее 13 лет. Это будет самый долгий срок за всю историю Windows.
См. также
- Безмятежность
- nLite
Примечания
- ↑ Not Authorized
- ↑ 1 2 3 4 Поиск сведений о жизненном цикле продуктов корпорации Майкрософт — Windows XP
- ↑ OS Platform Statistics. w3schools (???). Архивировано из первоисточника 21 августа 2011. Проверено 3 сентября 2010.
- ↑ Активация технологии режима совместимости приложений в Windows 2000 с пакетами обновлений 2 (SP2) и 3 (SP3)
- ↑ Change Windows visual effects. Microsoft. Архивировано из первоисточника 19 ноября 2012. Проверено ???.
- ↑ Computer Slows When You Click Multiple Icons in Windows XP. Microsoft (15 января 2006). Архивировано из первоисточника 19 ноября 2012. Проверено ???.
- ↑ Download Royale Theme for WinXP — Official Free — A new theme, potentially destined for Windows XP. Freeware — Softpedia
- ↑ Iconfactory Design: Windows Icon Design. The Iconfactory. Архивировано из первоисточника 25 августа 2011. Проверено 22 мая 2006.
- ↑ System requirements for Windows XP operating systems (28 апреля 2005). Архивировано из первоисточника 25 августа 2011. Проверено 12 марта 2007.
- ↑ System Requirements for Windows XP Service Pack 2. Microsoft (20 августа 2004). Архивировано из первоисточника 25 августа 2011. Проверено 19 августа 2007.
- ↑ Lifecycle Supported Service Packs. Microsoft. Проверено 19 июня 2007.
- ↑ End of support for Windows 98, Windows Me, и Windows XP Service Pack 1 (6 января 2006). Архивировано из первоисточника 25 августа 2011. Проверено 27 июня 2006.
- ↑ WinBeta.org Beta News and Reviews
- ↑ Новости Software — 3DNews — Daily Digital Digest
- ↑ http://windows.microsoft.com/ru-ru/windows/help/learn-how-to-install-windows-xp-service-pack-3-sp3 Способы установки пакета обновления 3 (SP3) для Windows XP — Microsoft
- ↑ 1 2 Microsoft прекратила продажу Windows XP
- ↑ «is a fully licensed version of Windows XP with Service Pack 3» // Install and use Windows XP Mode in Windows 7 (англ.)
- ↑ List of fixes that are included in Windows XP Service Pack 3
- ↑ Поддержка Windows XP SP3 и Office 2003 завершается 8 апреля 2014 г.. Microsoft. Архивировано из первоисточника 30 мая 2012.
Литература
- Вуди Леонард. Microsoft Windows XP SP2 для «чайников». Полный справочник = Windows XP All-in-One Desk Reference For Dummies. — 2-е изд. — М.: Диалектика, 2007. — 720 с. — ISBN 0-7645-7463-9
- Пол Мак-Федрис. Microsoft Windows XP SP2. Полное руководство = Microsoft Windows XP Unleashed. — М.: Вильямс, 2006. — 880 с. — ISBN 0-672-32833-X
- Проффит Брайан. Windows XP. Самоучитель. — М.: КУДИЦ-ПРЕСС, 2006.
Ссылки
- Windows XP Home Page
- Сайт проверки легальности копии Windows XP
- Windows XP — Справочник
- Windows XP
| |
||
|---|---|---|
|
Оболочки над MS-DOS: 1.0 • 2.x • 3.x • Windows 9x: 95 • 98 • ME • Windows NT: NT 3.1 • NT 3.5 • NT 3.51 • NT 4.0 • 2000 • XP • Vista • 7 • 8 |
||
| Windows Server |
2003 • Home (2011) • 2008 (HPC 2008 • R2) • Essential Business • MultiPoint • Small Business • 2012 |
 |
| Специализированные |
Embedded (Automotive • POSReady) • PE • FLP |
|
| Мобильные |
Windows CE (1.0 • 2.0 • 3.0 • 4.0 • 5.0 • 6.0 • 7.0) • Mobile • Phone • RT |
|
| Другие проекты |
Xenix • OS/2 • Singularity • Midori • Закрытые: Neptune • Nashville • Odyssey • Cairo |
|
| Альтернативные реализации |
ReactOS • Wine |


Данная статья представляет краткий обзор всех версий операционной системы Windows.
Версия Вашей системы: Windows 7
Версии для настольных компьютеров
| Логотип | Версия | Год | Статус |
|---|---|---|---|
 |
Windows 1 | 1985 | Не поддерживается Не используется |
 |
Windows 2 | 1987 | |
 |
Windows 3 | 1990 | |
 |
Windows NT 3.1 | 1993 | |
 |
Windows NT 3.5 Workstation | 1994 | |
 |
Windows NT 3.51 | 1995 | |
 |
Windows 95 | 1995 | |
 |
Windows NT 4.0 | 1996 | |
 |
Windows 98 | 1998 | |
 |
Windows Millenium | 2000 | |
 |
Windows 2000 (NT 5.0) | 2000 | |
 |
Windows XP (NT 5.1) | 2001 | Не поддерживается Встречается редко |
 |
Windows Vista (NT 6.0) | 2006 | Не поддерживается Почти, не используется |
 |
Windows 7 (NT 6.1) | 2009 | Не поддерживается Пока используется |
 |
Windows 8 (NT 6.2) | 2012 | Не поддерживается Почти, не используется |
 |
Windows 8.1 (NT 6.3) | 2013 | Поддерживается Почти, не используется |
 |
Windows 10 (NT 10) | 2015 | Поддерживается Активно используется |
 |
Windows 11 (NT 10) | 2021 | Поддерживается Начинает применяться |
Серверные Windows
| Логотип | Версия | Год | Статус |
|---|---|---|---|
 |
Windows NT 3.1 Advanced Server | 1993 | Не поддерживается Как правило, не используется |
 |
Windows NT 3.5 Server | 1994 | |
 |
Windows NT 3.51 Server | 1995 | |
 |
Windows NT 4.0 Server | 1996 | |
 |
Windows 2000 Server | 2000 | |
 |
Windows Server 2003 | 2003 | |
 |
Windows Server 2003 R2 | 2005 | |
 |
Windows Server 2008 | 2008 | |
 |
Windows Server 2008 R2 | 2009 | Не поддерживается Пока еще используется |
 |
Windows Server 2012 | 2012 | Поддерживается Активно используется |
 |
Windows Server 2012 R2 | 2013 | |
 |
Windows Server 2016 | 2016 | |
 |
Windows Server 2019 | 2018 | |
 |
Windows Server 2022 | 2021 | Начало использования |
Все версии Windows по линейкам + хронология
| Линейка | Годы | Перечисление версий |
|---|---|---|
| 16 бит | 1985 — 1995 | Windows 1 / 2 / 3 |
| 32 бита (9x) |
1995 — 2001 | Windows 95 / 98 / ME |
| NT (32 и 64 бита) |
с 1993 | Windows NT 3.1 / NT 3.5 / NT 3.51 / NT 4.0 Workstation / 2000 / XP / Vista / 7 / 8 / 8.1 / 10 |
| NT Servers (32 и 64 бита) |
с 1993 | Windows NT 3.1 / NT 3.5 / NT 3.51 / NT 4.0 Server / 2000 Server / 2003 / 2003 R2 / 2008 / 2008 R2 / 2012 / 2012 R2 / 2016 / 2019 / 2022 |
История успеха
Данная история успеха отражает частоту использования системы; количество глюков, с которыми столкнулись пользователи; отзывы.
 |
Windows 1 | Неудача |
 |
Windows 2 | Нейтрально |
 |
Windows 3 | Успех |
 |
Windows 95 | Неудача |
 |
Windows 98 | Успех |
 |
Windows Millenium | Провал |
 |
Windows 2000 | Нейтрально |
 |
Windows XP | Большой успех |
 |
Windows Vista | Провал |
 |
Windows 7 | Успех |
 |
Windows 8 | Провал |
 |
Windows 8.1 | Неудача |
 |
Windows 10 | Успех |
 |
Windows 11 | Нейтрально |
* несмотря на провал некоторых версий операционной системы, они несли новые функции, которые перешли в уже успешные версии. Например, в миллениум появились красивые иконки и окна, которые перешли в Windows 2000. Поэтому провал не стоит оценивать, как неудачную работу.
 Windows 1
Windows 1
Годы поддержки: 1985 — 2001. Ветка: 16 бит.
Издания: —
Что нового
До Windows 1 был MS-DOS, поэтому самое главное новшество — графический интерфейс и возможность управления при помощи мыши.
Системные требования
| Процессор | 8088 |
|---|---|
| Оперативная память | 256 Кбайт |
| Объем жесткого диска | 3 Мб |
 Windows 2
Windows 2
Годы поддержки: 1989 — 2001. Ветка: 16 бит.
Издания: —
Что нового
- Возможность использования сочетания клавиш.
- Появились перекрывающиеся окна.
- Возможность увеличить и уменьшить окно.
Системные требования
| Процессор | 8088 |
|---|---|
| Оперативная память | 256 Кбайт |
| Объем жесткого диска | 3 Мб |
 Windows 3
Windows 3
Годы поддержки: 1990 — 2008. Ветка: 16 бит.
Издания: —
Что нового
- Первый (от Microsoft) удобный для пользователя интерфейс.
- Появление диспетчера программ.
- Появление мультимедийных возможностей.
- Поддержка сети (с 3.1).
Системные требования
| Минимальные | Рекомендуемые | |
|---|---|---|
| Процессор | 8086/8088 | 80486DX 33 МГц |
| Оперативная память | 640 Кбайт | 4 Мб |
| Объем жесткого диска | 6,5 Мб | 60 Мб |
 Windows NT 3.1
Windows NT 3.1
Годы поддержки: 1993 — 2001. Ветка: NT. Разрядность: 16, 32 и 64 бита.
Издания: —
Что нового
- Первая система на базе ядра NT.
- Поддержка файловой системы NTFS.
Системные требования
| Процессор | Intel 80386 |
|---|---|
| Оперативная память | 2 Мб |
| Объем жесткого диска | 8 Мб |
 Windows NT 3.5 Workstation
Windows NT 3.5 Workstation
Годы поддержки: 1994 — 2001. Ветка: NT. Разрядность: 16, 32 и 64 бита.
Издания: —
Что нового
- Встроенная поддержка Winsock и TCP/IP.
- Появление сервера и клиента DHCP и WINS.
- Предоставление общего доступа к файлам и принтерам.
- Поддержка VFAT.
Системные требования
| Процессор | 33 МГц |
|---|---|
| Оперативная память | 12 Мб |
| Объем жесткого диска | 70 Мб |
 Windows NT 3.51 Workstation
Windows NT 3.51 Workstation
Годы поддержки: 1995 — 2001. Ветка: NT. Разрядность: 16, 32 и 64 бита.
Издания: —
Системные требования
| Процессор | 33 МГц |
|---|---|
| Оперативная память | 12 Мб |
| Объем жесткого диска | 70 Мб |
 Windows 95
Windows 95
Годы поддержки: 1995 — 2001. Ветка: 9x (32 бита).
Системные требования
| Минимальные | Рекомендуемые | |
|---|---|---|
| Процессор | 80386 DX | Pentium |
| Оперативная память | 4 Мб | 8 Мб |
| Объем жесткого диска | 50 Мб | 100 Мб |
 Windows NT 4.0 Workstation
Windows NT 4.0 Workstation
Годы поддержки: 1996 — 2004. Ветка: NT. Разрядность: 32 и 64 бита.
Издания: —
Системные требования
| Минимальные | Рекомендуемые | |
|---|---|---|
| Процессор | 486/25 | 486DX2/50 |
| Оперативная память | 12 Мб | 24 Мб |
| Объем жесткого диска | 128 Мб | 1 Гб |
 Windows 98
Windows 98
Годы поддержки: 1998 — 2006. Ветка: 9x (32 бита).
Системные требования
| Минимальные | Рекомендуемые | |
|---|---|---|
| Процессор | 486DX 66 МГц | Pentium |
| Оперативная память | 16 Мб | 24 Мб |
| Объем жесткого диска | 200 Мб | 500 Мб |
 Windows Millenium
Windows Millenium
Годы поддержки: 2000 — 2006. Ветка: 9x (32 бита).
Системные требования
| Минимальные | Рекомендуемые | |
|---|---|---|
| Процессор | 150 МГц | 300 МГц |
| Оперативная память | 32 Мб | 128 Мб |
| Объем жесткого диска | 200 Мб | 500 Мб |
 Windows 2000
Windows 2000
Годы поддержки: 2000 — 2010. Ветка: NT.
Системные требования
| Минимальные | Рекомендуемые | |
|---|---|---|
| Процессор | 133 МГц | 1 ГГц |
| Оперативная память | 32 Мб | 128 Мб |
| Объем жесткого диска | 2 Гб | 20 Гб |
 Windows XP
Windows XP
Годы поддержки: 2000 — 2010. Ветка: NT. Разрядность: 32 и 64 бита.
Редакции: XP, XP Professional
Системные требования
| Минимальные | Рекомендуемые | |
|---|---|---|
| Процессор | 233 МГц | 300 МГц |
| Оперативная память | 64 Мб | 128 Мб |
| Объем жесткого диска | 1,5 Гб | от 1,5 Гб |
 Windows Vista
Windows Vista
Годы поддержки: 2006 — 2017. Ветка: NT. Разрядность: 32 и 64 бита.
Издания: Начальная (Starter), Домашняя базовая (Basic), Домашняя расширенная (Premium), Бизнес (Business), Корпоративная (Enterprise), Максимальная (Ultimate)
Системные требования
| Минимальные | Рекомендуемые | |
|---|---|---|
| Процессор | 800 МГц | 1 ГГц |
| Оперативная память | 512 Мб | 1 Гб |
| Объем жесткого диска | 20 Гб | 40 Гб |
 Windows 7
Windows 7
Годы поддержки: 2009 — 2020. Ветка: NT. Разрядность: 32 и 64 бита.
Издания: Начальная (Starter), Домашняя базовая (Home Basic), Домашняя расширенная (Home Premium), Профессиональная (Professional), Корпоративная (Enterprise), Максимальная (Ultimate)
Системные требования
| Минимальные | Рекомендуемые | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Архитектура | 32-бит | 64-бит | 32-бит | 64-бит |
| Процессор | 1 ГГц | |||
| Оперативная память | 1 Гб | 2 Гб | 4 Гб | |
| Объем жесткого диска | 16 Гб | 20 Гб | 16 Гб | 20 Гб |
 Windows 8
Windows 8
Годы поддержки: 2012 — 2016. Ветка: NT. Разрядность: 32 и 64 бита.
Издания: 8, 8 Профессиональная (Pro), 8 Корпоративная (Enterprise)
Системные требования
| Минимальные | Рекомендуемые | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Архитектура | 32-бит | 64-бит | 32-бит | 64-бит |
| Процессор | 1 ГГц | |||
| Оперативная память | 1 Гб | 2 Гб | 4 Гб | |
| Объем жесткого диска | 16 Гб | 20 Гб | 16 Гб | 20 Гб |
 Windows 8.1
Windows 8.1
Годы поддержки: 2013 — 2023. Ветка: NT. Разрядность: 32 и 64 бита.
Издания: 8, 8 Профессиональная (Pro), 8 Корпоративная (Enterprise)
Системные требования
| Минимальные | Рекомендуемые | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Архитектура | 32-бит | 64-бит | 32-бит | 64-бит |
| Процессор | 1 ГГц | |||
| Оперативная память | 1 Гб | 2 Гб | 4 Гб | |
| Объем жесткого диска | 16 Гб | 20 Гб | 16 Гб | 20 Гб |
 Windows 10
Windows 10
Годы поддержки: 2015 — 2025. Ветка: NT. Разрядность: 32 и 64 бита.
Издания
- Домашняя (Home). Для большинства домашних компьютеров. Нет возможности настроить удаленный рабочий стол для того, чтобы к систему можно было подключиться удаленно; нет возможности использования групповых политик и присоединения к домену.
- Профессиональная (Pro). Содержит все функции домашней версии + возможность присоединения к домену, использования групповых политик, возможность подключения к компьютеру с использованием удаленного рабочего стола.
- Корпоративная (Enterprise). Урезаны некоторые функции домашней версии. Есть все дополнительные функции версии Pro + DirectAccess, AppLocker.
- S. Является урезанной версией; предустановлена на некоторые устройства. Не поддерживает стандартную установку приложений — возможна установка только из магазина Windows.
Что нового
Windows 10 претерпевает сильные изменения с выходом новых билдов. Поэтому нововведения будем рассматривать исходя из этого.
Билд 1507 (ноябрь 2015):
- Улучшенная производительность.
- Новый встроенный браузер Microsoft Edge.
- Автоматическое сжимание соседнего окна, при прижимании активного окна в одной из сторон рабочего стола.
- «Все приложения» в «Пуск» поддерживают отображение в 2048 элементов (раньше только 512).
- Принудительная установка обновлений.
- Использование виртуального голосового помощника Кортана.
- Обновленный меню пуск — представляет из себя гибрид предыдущих версий и Windows 8 (вернулся старый вариант раскрытия, а в правой части появились плитки).
- Возможность создания нескольких рабочих столов.
- Отказ от плиточной системы Windows 8.
1607 (август 2016):
- Возможность рукописного ввода (Windows Ink).
- Идентификация с помощью веб-камеры.
- Синхронизация с мобильного устройства уведомлений.
- Изменение меню параметров системы.
1703 (апрель 2017):
- Встроенная поддержка шлемов виртуальной реальности.
- Игровой режим
- По умолчанию предлагается командная строка в Powershell.
- Доступ к классической панели управления скрыт из контекстного меню. Теперь его можно вызвать командой control.
- Улучшение работы встроенного антивируса.
- Идентификация с помощью веб-камеры для Active Directory.
- Возможность создавать скриншот с выделением области с помощью сочетания клавиш Win + Shaft + S.
- Поддержка шрифта Брайля.
- Увеличенное время работы от батареи.
1709 (октябрь 2017):
- Возможность работы Cortana на одном устройстве и окончание работы на другом.
- Отключение протокола SMBv1. Включить можно вручную.
- Появление панели «Люди».
- Информация о GPU в диспетчере задач.
- Полноэкранный режим Microsoft Edge
- Увеличенное время работы от батареи (функция Power Throttling).
- Появление панели эмодзи.
- Выборочная синхронизация OneDrive.
- Исправление проблемы торможения в играх.
1803 (апрель 2018):
- Возможность восстановить пароль с помощью контрольных вопросов.
1809 (октябрь 2018):
- Темная тема для проводника.
- Возможность получения доступа к сообщениям с телефона (функция «Ваш телефон»).
1903 (май 2019):
- Изолированный рабочий стол для безопасного запуска приложений.
1909 (ноябрь 2019):
- Универсальный поиск в Проводнике.
- Улучшение производительности.
2004 (май 2020):
- Функция «Загрузка из облака» для переустановки Windows 10.
- Регулирование пропускной способности для обновлений Windows.
- Отображение температуры видеоядра в Диспетчере задач.
- Возможность удаления Блокнот, Paint, WordPad.
- Возможность использование Windows без пароля.
* данный список содержит часть нововведений. Полный список на странице в Википедии.
Системные требования
| Минимальные | Рекомендуемые | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Архитектура | 32-бит | 64-бит | 32-бит | 64-бит |
| Процессор | 1 ГГц | |||
| Оперативная память | 1 Гб | 2 Гб | 4 Гб | |
| Объем жесткого диска | 16 Гб | 20 Гб | 16 Гб | 20 Гб |
 Windows 11 (последняя для настольных компьютеров)
Windows 11 (последняя для настольных компьютеров)
Годы поддержки: 2021 — 2031. Ветка: NT. Разрядность: только 64 бита.
Основные издания: Домашняя (Home), Профессиональная (Pro), 8 Корпоративная (Enterprise).
Дополнительные издания: для обучения (Education), для облаков (Cloud).
Системные требования
| Процессор | 2 ядра, 1 ГГц |
|---|---|
| Оперативная память | 4 Гб |
| Объем жесткого диска | 64 Гб |
| БИОС (прошивка) | UEFI |
| Видеоадаптер | Совместимый с DirectX 12 / WDDM 2.x |
| Интернет | Для Home необходим вход под учетной записью Microsoft. |
 Windows NT 3.1 Advanced Server
Windows NT 3.1 Advanced Server
Годы поддержки: 1993 — 2001. Ветка: NT. Разрядность: 16, 32 и 64 бита.
Издания: —
Системные требования
| Процессор | Intel 80386 |
|---|---|
| Оперативная память | 2 Мб |
| Объем жесткого диска | 8 Мб |
 Windows NT 3.5 Server
Windows NT 3.5 Server
Годы поддержки: 1994 — 2001. Ветка: NT. Разрядность: 16, 32 и 64 бита.
Издания: —
Что нового
- Встроенная поддержка Winsock и TCP/IP.
- Появление сервера DHCP и WINS.
- Предоставление общего доступа к файлам и принтерам.
- Поддержка VFAT.
Системные требования
| Процессор | 33 МГц |
|---|---|
| Оперативная память | 16 Мб |
| Объем жесткого диска | 70 Мб |
 Windows NT 3.51 Server
Windows NT 3.51 Server
Годы поддержки: 1995 — 2001. Ветка: NT. Разрядность: 16, 32 и 64 бита.
Издания: —
Системные требования
| Процессор | 33 МГц |
|---|---|
| Оперативная память | 16 Мб |
| Объем жесткого диска | 70 Мб |
 Windows NT 4.0 Server
Windows NT 4.0 Server
Годы поддержки: 1996 — 2004. Ветка: NT. Разрядность: 32 и 64 бита.
Издания: Server, Enterprise Edition, Terminal Server
Системные требования
| Минимальные | Рекомендуемые | |
|---|---|---|
| Процессор | 486/25 | 486DX2/50 |
| Оперативная память | 16 Мб | 24 Мб |
| Объем жесткого диска | 128 Мб | 1 Гб |
 Windows 2000 Server
Windows 2000 Server
Годы поддержки: 2000 — 2010. Ветка: NT. Разрядность: 32 и 64 бита.
Издания: Server, Advanced Server и Datacenter Server
Системные требования
| Минимальные | Рекомендуемые | |
|---|---|---|
| Процессор | 133 МГц | 1 ГГц |
| Оперативная память | 32 Мб | 128 Мб |
| Объем жесткого диска | 2 Гб | 20 Гб |
 Windows Server 2003
Windows Server 2003
Годы поддержки: 2003 — 2015. Ветка: NT. Разрядность: 32 и 64 бита.
Издания: Web, Standard, Enterprise, Datacenter
Системные требования
Web, Standard, Enterprise:
| Минимальные | Рекомендуемые | |
|---|---|---|
| Процессор | 133 МГц | 550 МГц |
| Оперативная память | 128 Мб | 256 Мб |
| Объем жесткого диска | 1,5 Гб | 2 Гб |
Datacenter Edition:
| Минимальные | Рекомендуемые | |
|---|---|---|
| Процессор | 400 МГц | 733 МГц |
| Оперативная память | 512 Мб | 1 Гб |
| Объем жесткого диска | 1,5 Гб | 2 Гб |
 Windows Server 2003 R2
Windows Server 2003 R2
Годы поддержки: 2005 — 2015. Ветка: NT. Разрядность: 32 и 64 бита.
Издания: Standard, Enterprise, Datacenter
Системные требования
Standard, Enterprise:
| Минимальные | Рекомендуемые | |
|---|---|---|
| Процессор | 133 МГц | 550 МГц |
| Оперативная память | 128 Мб | 256 Мб |
| Объем жесткого диска | 1,2 Гб | 2 Гб |
Datacenter Edition:
| Минимальные | Рекомендуемые | |
|---|---|---|
| Процессор | 400 МГц | 733 МГц |
| Оперативная память | 512 Мб | 1 Гб |
| Объем жесткого диска | 1,2 Гб | 2 Гб |
 Windows Server 2008
Windows Server 2008
Годы поддержки: 2008 — 2020. Ветка: NT. Разрядность: 32 и 64 бита.
Издания: Web, Standard, Enterprise, Datacenter, HPC, Storage, Itanium
Системные требования
| Минимальные | Рекомендуемые | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Архитектура | 32-бит | 64-бит | 32-бит | 64-бит |
| Процессор | 1 ГГц | 1.4 ГГц | 2 ГГц | |
| Оперативная память | 512 Мб | 2 Гб | ||
| Объем жесткого диска | 10 Гб | 40 Гб |
 Windows Server 2008 R2
Windows Server 2008 R2
Годы поддержки: 2009 — 2020. Ветка: NT. Разрядность: 64 бита.
Издания: Foundation, Small Business, Web, Standard, Enterprise, Datacenter, HPC, Itanium
Системные требования
| Минимальные | Рекомендуемые | |
|---|---|---|
| Процессор | 1.4 ГГц | 2 ГГц |
| Оперативная память | 512 Мб | 2 Гб |
| Объем жесткого диска | 10 Гб | 40 Гб |
 Windows Server 2012
Windows Server 2012
Годы поддержки: 2012 — 2023. Ветка: NT. Разрядность: 64 бита.
Издания: Foundation, Essentials, Standard, Datacenter
Системные требования
| Минимальные | Рекомендуемые | |
|---|---|---|
| Процессор | 1.4 ГГц | 2 ГГц |
| Оперативная память | 2 Гб | 4 Гб |
| Объем жесткого диска | 32 Гб | 60 Гб |
 Windows Server 2012 R2
Windows Server 2012 R2
Годы поддержки: 2013 — 2023. Ветка: NT. Разрядность: 64 бита.
Издания: Foundation, Essentials, Standard, Datacenter
Системные требования
| Минимальные | Рекомендуемые | |
|---|---|---|
| Процессор | 1.4 ГГц | 2 ГГц |
| Оперативная память | 2 Гб | 4 Гб |
| Объем жесткого диска | 32 Гб | 60 Гб |
 Windows Server 2016
Windows Server 2016
Годы поддержки: 2016 — 2026. Ветка: NT. Разрядность: 64 бита.
Издания: Essentials, Standard, Datacenter
Что нового
- Лицензирование на физические ядра процессора (минимум 16).
- Новый режим установки — Nano.
- Появление контейнерной виртуализации.
- OpenGL и OpenCL для RDP.
- Шифрование виртуальных машин и внутреннего сетевого трафика.
- Блочная репликация файловых хранилищ.
Системные требования
| Минимальные | Рекомендуемые | |
|---|---|---|
| Процессор | 1.4 ГГц | 3.1 ГГц |
| Оперативная память | 2 Гб | 4 Гб |
| Объем жесткого диска | 32 Гб | 60 Гб |
Более подробно в обзоре Windows Server 2016.
 Windows Server 2019
Windows Server 2019
Годы поддержки: 2018 — 2029. Ветка: NT. Разрядность: 64 бита.
Издания: Standard, Datacenter
Что нового
- Улучшенная безопасность — встроенные технологии Defender ATP и Defender Exploit Guard.
- Windows Subsystem Linux (WSL) — контейнеры для поддержки приложений Linux.
- Для построения кластера с четным количеством узлов в качестве диска-свидетеля может выступать USB-диск.
Системные требования
| Минимальные | Рекомендуемые | |
|---|---|---|
| Процессор | 1.4 ГГц | 3.1 ГГц |
| Оперативная память | 512 Мб (Nano) 2 Гб (GUI) |
4 Гб |
| Объем жесткого диска | 32 Гб | 60 Гб |
 Windows Server 2022 (последняя для серверов)
Windows Server 2022 (последняя для серверов)
Годы поддержки: 2021 — 2031. Ветка: NT. Разрядность: 64 бита.
Издания: Standard, Datacenter
Что нового
- Улучшенная безопасность.
- Больше возможностей для работы с облаками, особенно, Microsoft Azure.
Системные требования
| Минимальные | Рекомендуемые | |
|---|---|---|
| Процессор | 1.4 ГГц | 3.1 ГГц |
| Оперативная память | 512 Мб (Nano) 2 Гб (GUI) Поддержка ECC |
4 Гб
Поддержка ECC |
| Объем жесткого диска | 32 Гб | 60 Гб |
| Сетевой адаптер | 1 гигабит в секунду |
Самые популярные настольные ОС с 2004 по 2019. XP доминировала до лета 2011.
Рабочий стол и панель управления Windows XP
Windows XP — легендарная операционная система от Microsoft. Выпущена 25 октября 2001 года, в середине нулевых добралась до России, похоронена разработчиками 8 апреля 2014. Впрочем, остаётся немало любителей, которые пользуются ей до сих пор — в силу разных причин: кто-то просто фанат, а кто-то пожилой пенсионер/экономит копейку. Вместе с браузером IE в 2000-е была своеобразной классикой в компьютерной отрасли. Вплоть до середины 2010-х годов была самой распространённой ОС в России.
История[править]
Выживание под Windows XP SP0 в 2018 году
Пустить ностальгическую слезу
Windows XP появилась на свет 25 октября 2001 года. В Россию начала попадать после 2003, где-то к 2006-7 году подавляющее большинство пользователей перешли на неё. К концу 2000-х наблюдалось полное доминирование этой системы в компьютерной сфере, в этой связи ее не смогла заменить плоходоработанная Windows Vista.
Поддержка прекращена 8 апреля 2014 года, с тех пор популярность снизилась, и XP сейчас перешла в разряд стремительно вымирающих операционных систем. Поддержка для всяких банкоматов и прочих некомпьютерных устройств завершилась только в 2019 году.
Жизненный цикл составил почти 13 лет для физлиц и 18 лет для предприятий, пока что этот рекорд держится. Следующей массовой ОС стала Windows 7. Её поддержка завершена 14 января 2020 года, таким образом, она не смогла побить рекорд XP.
Windows XP пришла к нам в эпоху модемов, флоппи-дисков, ЭЛТ-экранов и Pentium IV, а ушла уже во время высокоскоростных соединений, облачных хранилищ, VR-шлемов и Pentium VII.
Сравнение с Windows 2000[править]
В Windows XP появились обновления, которых не было в Windows 2000:
- Новый интерфейс ‘Luna’. Но по желанию можно вернуть и старый интерфейс из Windows 2000.
- Возможность использования компьютера несколькими пользователями — блокировка с временным выходом из системы.
- Режим совместимости для программ — если программа работала в старых версиях Windows, но не работает в новой, можно попробовать запустить в режиме совместимости. Иногда помогает.
- Более новые версии стандартных программ: Internet Explorer, Windows Media Player и другие.
Преимущества[править]
Одним из преимуществ «чистых» версий Windows XP является высокая скорость работы. Системой можно пользоваться сразу после запуска, в отличие от более новых версий, которым нужна пара минут на «прогрев».
Также система получила популярность благодаря приемлемым системным требованиям:
- Процессор от 233 МГц
- ОЗУ от 64 МБайт
- Дисковое пространство от 2,1 ГБайт
С такими минимальными требованиями она спокойно встаёт на компьютеры конца 90-х. Если вы некромант ретрокомпьютерщик не по годам, но хотите пользоваться относительно современным ПО, то Windows 2000 для этих целей уже не подходит, а XP всё ещё можно использовать. Можно завести её в качестве параллельной ОС: для игр и ретро-ПО более старую версию, а для интернета и современного ПО использовать XP.
В отличие от Windows 7, 8 и тем более 10, XP не так сильно расходует ресурсы машины на поддержание самой себя. На слабосильных компьютерах это ощутимый плюс.
Windows Vista требовала больших (по меркам 2007 года) мощностей оборудования, не все были готовы его покупать. Это стало причиной низкой популярности Vista, народ продолжал сидеть на XP ещё несколько лет.
По сравнению с Windows 98 и ME главный плюс — высокая стабильность работы. У автора правки XP ни разу с 2007 не вылетала в BSOD. Впрочем, то же можно сказать и про остальные NT-версии, начиная с 2000. Так как очень многие пользователи пересаживались на XP сразу с 98 или (реже) 95, минуя NT4, ME и 2000, то они заметили ощутимую разницу. Больше не приходилось переустанавливать Windows раз в полгода, а синий экран стал менее частым гостем. А если ещё и установочный диск легальный, и нормальный антивирус, и обновления вовремя скачивать…
Недостатки[править]
Главный недостаток Windows XP — это её возраст. Как ни грустно, поддержка прекратилась, и производители ПО больше не делают совместимых с ней программ, либо скоро перестанут.
Ещё один недостаток — платность. Раньше можно было легальным способом получить бесплатную дистрибутиву по студенческой программе Microsoft, причём в любом исполнении и с любым service-pack’ом. Когда в 2014 завершилась поддержка, то и возможность скачки закрыли. Вариант с условно-бесплатным получением — купить компьютер с предустановленной XP (обычно Home Basic), но сейчас их тоже нигде не достать. В те времена покупка ПК в магазине ещё и не гарантировала подлинность Windows. Нелегальный обход — скачка с торрентов, со всеми рисками наткнуться на нерабочую версию, говносборку и вирусы.
Говносборки — ныне явление почти исчезло, но в дремучие времена было популярным. «Народные умельцы» делали свои версии Windows с пакетами предустановленного ПО и кучами ошибок. Естественно, риск получить троян при скачивании говносборки в разы выше, чем чистой версии. Наиболее известные говносборки — ZverCD и ZverDVD. Желающие обмазаться могут посмотреть канал белорусского видеоблогера Алексея Лещенко (умер в 2021 году), который делал обзоры на подобные вещи. Ещё существовали кряки, подменявшие файл logon.exe, в котором сидит регистрация.
Windows XP отличалась крайне низкой безопасностью и защищённостью. В эпоху XP многие пользователи сидели под админской учётной записью, а это значит, что вирусы могли нанести серьёзный ущерб при проникновении. Сейчас это остаётся актуальным. Более того, обновления безопасности в последний раз выпускались 9 мая 2019, и будут ли они ещё — неизвестно. Вирусы под XP до сих пор не вымерли, так что будьте бдительны.
В руках неопытного пользователя операционка быстро загаживалась. Раньше народ мало заботился о подлинности ПО, часто скачивали взломанные версии. Таким образом на компьютер пользователя попадали трояны, adware, браузеры «Амиго» и другие прелести говнософта. Система начинала тормозить, область уведомлений и меню «Пуск» светились аки новогодняя ёлка. Без нормального антивируса и умения чистить реестр это лечилось путём переустановки. Какое-то время компьютер работал быстро, затем в неумелых руках через несколько месяцев он возвращался к прежнему состоянию. Это справедливо и для более новых версий Windows.
Кто использует?[править]
- Обладатели старых и слабых компьютеров. Хотя XP с каждым годом пользоваться всё труднее, но это пока что можно назвать полноценной жизнью, а не выживанием. XP проще и удобнее в использовании, чем Ubuntu, AntiX Linux, Q4OS Linux и прочие свободные ОС для слабых машин.
- Пользователи специализированного ПО. Особенно сюда относится софт для лабораторий, станков, банкоматов и для коммерческих задач. Писать или покупать программы для новых ОС зачастую оказывается дороже, чем продолжать поддержку старых ОС. Для коммерческих целей продолжалась поддержка XP Embedded POSReady 2009 вплоть до 9 апреля 2019.
- Близкая категория — любители ретро-игр. Игры, выпущенные после 2000 года, обычно запускаются и на современных ОС вплоть до Windows 10, а вот в игры для более ранних версий Windows без костылей сейчас уже не поиграть. Сюда же относятся и игры для DOS и Windows 3.x. В XP это всё работает «из коробки».
- «Утята» и ностальгирующие. Для многих из нас XP — это символ того самого 2007 года, со всеми его преимуществами и недостатками. Некоторые упорно продолжают пользоваться старыми версиями программ, потому что «раньше было лучше», а на новое переучиваться нет желания.
- Пенсионеры и технически неграмотные люди. Могут и не знать, что поддержка давно прекращена и что вышли новые версии Windows.
- Пользователи изолированных компьютеров. По какой-то причине компьютер стоит много лет без интернета, а в обновлении ОС не было необходимости. С годами такие машины переходят в разряд аутентичных ретрокомпьютеров.
- Разумные пользователи, которые знают, что после обновления ОС ничего не изменится, кроме обоев.
Актуальные версии популярного ПО[править]
По возможности лучше всего скачивать софт (особенно браузеры) с официальных сайтов, а если удалось найти легальные диски с ПО, то в идеале желательно использовать их с дальнейшим обновлением до последних версий.
По состоянию на 2022 год все приведённые ниже браузеры для Windows XP безнадёжно устарели. Поэтому рекомендуется скачать браузер Mypal или китайский браузер 360 Extreme Explorer на основе Chromium 86 и не мучаться. Ссылки для скачивания браузера Mypal: версия на основе Pale Moon, версия на основе Mozilla Firefox Quantum. Тема по браузеру 360 Extreme Explorer на форуме Ru-Board, скачать самодельные сборки браузера 360 Extreme Explorer с выпиленной китайщиной можно здесь или здесь.
- Internet Explorer — версия 8. Вот только использовать его можно разве что для скачивания другого браузера — большинство современных сайтов он уже не откроет, но всё равно он лучше дефолтного IE 6. Скачивается через Центр обновления Windows.
- Google Chrome — версия 49.0.2623.112.
- Mozilla Firefox — версия 52.
- Яндекс браузер — версия 17.4.1.
- Opera — версия 36.0.2130.65
- Microsoft Office — версия 2010 года. Несмотря на год выпуска, справляется с задачами гораздо лучше freeware-поделок. Если вы до сих пор не переучились на ленточный интерфейс, то ставьте Office 2003 с поддержкой форматов Office 2007, для большинства задач хватит и этого.
- Libre Office — версия 5.4.7.2. По функционалу почти догоняет Microsoft Office 2000.
- Adobe Photoshop — версия CS6 13.0.1 Extended Final.
- ICQ — внезапно Mail.ru сделали отдельную версию для XP, которая скачивается с официального сайта. Можно установить и невозбранно вернуться в 2007, если хоть кто-то из контактов ещё жив.
Игры по умолчанию[править]
- Косынка (Solitaire)
- Пасьянс «Паук»
- Червы — вырезали из Windows 2000, но по многочисленным просьбам трудящихся восстановили в XP.
- Солитер
- Сапёр
- Пинбол «Звёздный юнга» (Space Cadet). На ЖК-экранах пиксели неприятно размываются, поэтому рекомендуется играть на ЭЛТ.
Скриншоты[править]
-
Рабочий стол с темой по умолчанию «Luna» и обоями «Безмятежность»
-
Меню «Пуск», считается одним из лучших в серии Windows
-
Стандартные программы
-
Серебристая тема
-
Классическая тема из Windows 2000
-
Перед выключением экран становится чёрно-белым. А твоя Windows 10 так умеет?
-
| Программы | X86 • Proxifier • AutoHotInterception • AutoHotKey • ShareX • Perl • APKPure • Avast! • ΜTorrent • Opera • Windows • Python • PHP • Sublime Text • JavaScript • CSS • Операционная система • HTML • Paint • Linux • MacOS • HTTPS • Face Pay • Onfido • Id.abonent • Pickpoint • Windows 2000 • Windows XP • Drimsim • Скрепыш • От Adobe • Windows 7 • МС-21 • Калькулятор Consul War • Google Play • Apple • VIPole • ИИ Galactica • Windows 11 • Hello Asuka • Stable Diffusion • ChatGPT • Character.AI • Hello World |
| Инициативы | Tesla Phone • Подсветка компьютера • Тряпка для очистки экрана от Apple • Регистрация самолетов на Бермудах • Фейковый билет на самолет • Левая симка • Серый телефон • Онлайн-проверка автомобиля • Чек-лист осмотра автомобиля • Фейковая бронь отеля • Запрет старых автомобилей • ИВЛ • Установка NovelAI на компьютер • AlternativeTo • PythonTutor • CodeWars • DataCamp • AppleScript |
| Понятия | Место на диске • Баннермейкер • Уведомления в браузере • Повышение разрешения нейросетью • Распознавание лиц • Чистая установка • Скриншот • Аппаратное ускорение • SMS • Датамайн • Капча • Торрент • Прокси • Компьютер • Переустановка Windows • Стройка • Версия 2.0 • Ман • Код • Обфускация • Автоматизация • Рандомайзер • Нейросети • Текстовый файл • Графические артефакты |
| Техника | Умный дом • Акваланг (ядерный) • Телефон • планшет • роботизированная доставка • Смартфон • Аэрофлот • Айфон • Айпад • Huawei • Суперджет • MNP в Украине • Кошерный телефон • SIM-карта • Кнопочные телефоны • GPS-маячок • Пропаганда электромобилей |
| Мемы | Переделка фамиклона из PAL в NTSC • Работает — не трогай • ASCII-арт • Пропеллер • Теледильдоника • Дилдо с подсветкой • Инженер • Индусский код • Нескучные обои • Срок годности сим-карты • Бета-тест • За сжатие Джипега • Шкала ебучих шакалов • Ебучий шакал |
| Инновацъи | Zona • Подсветка синтаксиса кода • OpenAI • Распознавание PDF • Разбор самолётов на запчасти • Два монитора • Запрет формата APK • RuMarket • NashStore • Российские аналоги Google Play • RuStore • Российский процессор • Многоразовая туалетная бумага • Безопасные для российских самолётов страны • Сканирование дисков Google Chrome • Настройка викибота для HTTPS • Двигатель на вампире |
| Люди | Денис Кумпон • Томас Эдисон • Ламборгини Урус • Билл Гейтс • Илья Кантор • Юрий Ключевский |