I want to find out my Python installation path on Windows. For example:
C:Python25
How can I find where Python is installed?
Stevoisiak
22.1k27 gold badges119 silver badges216 bronze badges
asked Mar 15, 2009 at 9:09
Fang-Pen LinFang-Pen Lin
12.8k15 gold badges66 silver badges94 bronze badges
1
In your Python interpreter, type the following commands:
>>> import os
>>> import sys
>>> os.path.dirname(sys.executable)
'C:\Python25'
Also, you can club all these and use a single line command. Open cmd and enter following command
python -c "import os, sys; print(os.path.dirname(sys.executable))"
answered Mar 15, 2009 at 13:17
13
If you have Python in your environment variable then you can use the following command in cmd or powershell:
where python
or for Unix enviroment
which python
command line image :
answered Apr 17, 2017 at 16:04
Aekansh KansalAekansh Kansal
2,5591 gold badge14 silver badges17 bronze badges
3
It would be either of
- C:Python36
- C:Users(Your logged in User)AppDataLocalProgramsPythonPython36
answered Aug 18, 2017 at 9:52
Amol ManthalkarAmol Manthalkar
1,7901 gold badge15 silver badges16 bronze badges
5
If you need to know the installed path under Windows without starting the python interpreter, have a look in the Windows registry.
Each installed Python version will have a registry key in either:
HKLMSOFTWAREPythonPythonCoreversionnumberInstallPathHKCUSOFTWAREPythonPythonCoreversionnumberInstallPath
In 64-bit Windows, it will be under the Wow6432Node key:
HKLMSOFTWAREWow6432NodePythonPythonCoreversionnumberInstallPath
yincrash
6,2451 gold badge39 silver badges41 bronze badges
answered Mar 15, 2009 at 21:08
codeapecodeape
96.4k24 gold badges155 silver badges183 bronze badges
8
Simple way is
- open CMD
- type
where pythonin cmd
answered Jan 30, 2020 at 14:13
BigData-GuruBigData-Guru
1,0811 gold badge14 silver badges20 bronze badges
0
On my windows installation, I get these results:
>>> import sys
>>> sys.executable
'C:\Python26\python.exe'
>>> sys.platform
'win32'
>>>
(You can also look in sys.path for reasonable locations.)
answered Mar 15, 2009 at 10:18
gimelgimel
81.7k10 gold badges75 silver badges104 bronze badges
2
If you have the py command installed, which you likely do, then just use the --list-paths/-0p argument to the command:
py --list-paths
Example output:
Installed Pythons found by py Launcher for Windows
-3.8-32 C:UserscscottAppDataLocalProgramsPythonPython38-32python.exe *
-2.7-64 C:Python27python.exe
The * indicates the currently active version for scripts executed using the py command.
answered Dec 9, 2019 at 20:48
carlin.scottcarlin.scott
5,5983 gold badges27 silver badges34 bronze badges
1
Its generally
‘C:Usersuser-nameAppDataLocalProgramsPythonPython-version’
or
try using (in cmd )
where python
answered Apr 12, 2020 at 18:45
In the sys package, you can find a lot of useful information about your installation:
import sys
print sys.executable
print sys.exec_prefix
I’m not sure what this will give on your Windows system, but on my Mac executable points to the Python binary and exec_prefix to the installation root.
You could also try this for inspecting your sys module:
import sys
for k,v in sys.__dict__.items():
if not callable(v):
print "%20s: %s" % (k,repr(v))
answered Mar 15, 2009 at 9:41
Guðmundur HGuðmundur H
11.1k3 gold badges23 silver badges22 bronze badges
2
If You want the Path After successful installation then first open you CMD and type
python or python -i
It Will Open interactive shell for You and Then type
import sys
sys.executable
Hit enter and you will get path where your python is installed …
answered Oct 18, 2018 at 7:30
1
To know where Python is installed you can execute where python in your cmd.exe.
anothernode
4,86311 gold badges42 silver badges60 bronze badges
answered Jul 27, 2018 at 6:21
4
You can search for the «environmental variable for you account». If you have added the Python in the path, it’ll show as «path» in your environmental variable account.
but almost always you will find it in
«C:Users%User_name%AppDataLocalProgramsPythonPython_version»
the ‘AppData‘ folder may be hidden, make it visible from the view section of toolbar.
answered Sep 14, 2018 at 9:19
Amit GuptaAmit Gupta
2,6024 gold badges24 silver badges37 bronze badges
Make use of the Python Launcher for Windows (available as of 3.3). It is compatible with all available versions of python.
First, check if the launcher is available:
py
starts the latest installed version of Python
To see all Python versions available on your system and their path:
py -0p
or
py --list-paths
For a specific Python version path—especially useful with multiple python installations:
py -3.7 -c "import os, sys; print(os.path.dirname(sys.executable))"
python 2
py -2 -c "import os, sys; print(os.path.dirname(sys.executable))"
py installed location is C:Windowspy.exe if installed for all users, otherwise can be found at C:UsersusernameAppDataLocalProgramsPythonLauncher.
It does not require the environment PATH variable to be set if installed for all users.
answered Apr 25, 2022 at 2:23
oyeyipooyeyipo
3193 silver badges11 bronze badges
If anyone needs to do this in C# I’m using the following code:
static string GetPythonExecutablePath(int major = 3)
{
var software = "SOFTWARE";
var key = Registry.CurrentUser.OpenSubKey(software);
if (key == null)
key = Registry.LocalMachine.OpenSubKey(software);
if (key == null)
return null;
var pythonCoreKey = key.OpenSubKey(@"PythonPythonCore");
if (pythonCoreKey == null)
pythonCoreKey = key.OpenSubKey(@"Wow6432NodePythonPythonCore");
if (pythonCoreKey == null)
return null;
var pythonVersionRegex = new Regex("^" + major + @".(d+)-(d+)$");
var targetVersion = pythonCoreKey.GetSubKeyNames().
Select(n => pythonVersionRegex.Match(n)).
Where(m => m.Success).
OrderByDescending(m => int.Parse(m.Groups[1].Value)).
ThenByDescending(m => int.Parse(m.Groups[2].Value)).
Select(m => m.Groups[0].Value).First();
var installPathKey = pythonCoreKey.OpenSubKey(targetVersion + @"InstallPath");
if (installPathKey == null)
return null;
return (string)installPathKey.GetValue("ExecutablePath");
}
answered Apr 5, 2017 at 11:10
PeterPeter
36.4k38 gold badges141 silver badges196 bronze badges
2
This worked for me: C:UsersYour_user_nameAppDataLocalProgramsPython
My currently installed python version is 3.7.0
Hope this helps!
David
1,1625 gold badges13 silver badges29 bronze badges
answered Jul 16, 2018 at 6:55
Go to C:UsersUSERAppDataLocalProgramsPythonPython36
if it is not there then
open console by windows+^R
Then type cmd and hit enter
type python if installed in your local file it will show you its version from there type the following
import os
import sys
os.path.dirname(sys.executable)
answered Mar 1, 2019 at 11:34
You can find it in the Windows GUI, but you need to select “show hidden” in the menu. Directory where python is installed on my Win10 computer:
C:UsersusernameAppDataLocalProgramsPythonPython310
Very handy if you use python pip to install packages.
Suraj Rao
29.3k11 gold badges96 silver badges103 bronze badges
answered Dec 31, 2021 at 14:35
You could have many versions of Python installed on your machine. So if you’re in Windows at a command prompt, entering something like this…
py --version
…should tell you what version you’re using at the moment. (Maybe replace py with python or python3 if py doesn’t work). Anyway you’d see something like
Python 3.10.2
If you then create a virtual environment using something like this…
py -m venv venv
…that environment will also use that Python version. To verify, activate the environment…
venvscriptsactivate.bat
You’ll see the name of the command prompt. Now if execute:
where python
…it will show you which Python executable that virtual environment uses. It will be a copy of Python.exe what’s actually in the Scripts subfolder of the virtual environment folder. Of course to see which version that is, again use py --version.
answered Jan 26, 2022 at 15:55
if you still stuck or you get this
C:\Users\name of your\AppData\Local\Programs\Python\Python36
simply do this replace 2 with one
C:UsersakshayAppDataLocalProgramsPythonPython36
Kos
4,7809 gold badges38 silver badges41 bronze badges
answered Jun 2, 2018 at 16:48
I installed 2 and 3 and had the same problem finding 3. Fortunately, typing path at the windows path let me find where I had installed it. The path was an option when I installed Python which I just forgot. If you didn’t select setting the path when you installed Python 3 that probably won’t work — unless you manually updated the path when you installed it.
In my case it was at c:Program FilesPython37python.exe
answered Feb 3, 2019 at 16:39
If you use anaconda navigator on windows, you can go too enviornments and scroll over the enviornments, the root enviorment will indicate where it is installed. It can help if you want to use this enviorment when you need to connect this to other applications, where you want to integrate some python code.
answered Jun 6, 2019 at 10:01
PV8PV8
5,4075 gold badges41 silver badges76 bronze badges
Option 1 : Check System Environment Variables > Path
Option 2 : C:UsersAsusAppDataLocalProgramsPython (By default Path)
answered Oct 1, 2022 at 10:09
I want to find out my Python installation path on Windows. For example:
C:Python25
How can I find where Python is installed?
Stevoisiak
22.1k27 gold badges119 silver badges216 bronze badges
asked Mar 15, 2009 at 9:09
Fang-Pen LinFang-Pen Lin
12.8k15 gold badges66 silver badges94 bronze badges
1
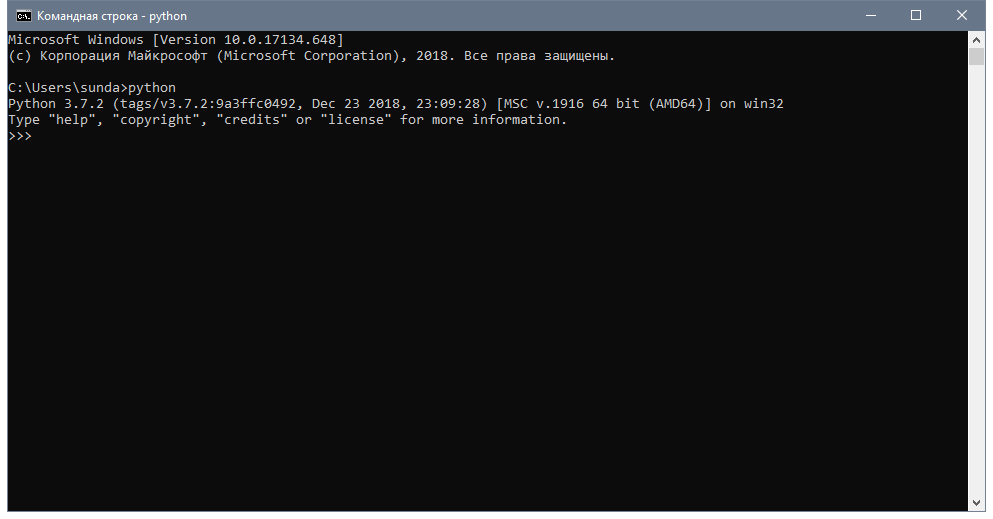
In your Python interpreter, type the following commands:
>>> import os
>>> import sys
>>> os.path.dirname(sys.executable)
'C:\Python25'
Also, you can club all these and use a single line command. Open cmd and enter following command
python -c "import os, sys; print(os.path.dirname(sys.executable))"
answered Mar 15, 2009 at 13:17
13
If you have Python in your environment variable then you can use the following command in cmd or powershell:
where python
or for Unix enviroment
which python
command line image :
answered Apr 17, 2017 at 16:04
Aekansh KansalAekansh Kansal
2,5591 gold badge14 silver badges17 bronze badges
3
It would be either of
- C:Python36
- C:Users(Your logged in User)AppDataLocalProgramsPythonPython36
answered Aug 18, 2017 at 9:52
Amol ManthalkarAmol Manthalkar
1,7901 gold badge15 silver badges16 bronze badges
5
If you need to know the installed path under Windows without starting the python interpreter, have a look in the Windows registry.
Each installed Python version will have a registry key in either:
HKLMSOFTWAREPythonPythonCoreversionnumberInstallPathHKCUSOFTWAREPythonPythonCoreversionnumberInstallPath
In 64-bit Windows, it will be under the Wow6432Node key:
HKLMSOFTWAREWow6432NodePythonPythonCoreversionnumberInstallPath
yincrash
6,2451 gold badge39 silver badges41 bronze badges
answered Mar 15, 2009 at 21:08
codeapecodeape
96.4k24 gold badges155 silver badges183 bronze badges
8
Simple way is
- open CMD
- type
where pythonin cmd
answered Jan 30, 2020 at 14:13
BigData-GuruBigData-Guru
1,0811 gold badge14 silver badges20 bronze badges
0
On my windows installation, I get these results:
>>> import sys
>>> sys.executable
'C:\Python26\python.exe'
>>> sys.platform
'win32'
>>>
(You can also look in sys.path for reasonable locations.)
answered Mar 15, 2009 at 10:18
gimelgimel
81.7k10 gold badges75 silver badges104 bronze badges
2
If you have the py command installed, which you likely do, then just use the --list-paths/-0p argument to the command:
py --list-paths
Example output:
Installed Pythons found by py Launcher for Windows
-3.8-32 C:UserscscottAppDataLocalProgramsPythonPython38-32python.exe *
-2.7-64 C:Python27python.exe
The * indicates the currently active version for scripts executed using the py command.
answered Dec 9, 2019 at 20:48
carlin.scottcarlin.scott
5,5983 gold badges27 silver badges34 bronze badges
1
Its generally
‘C:Usersuser-nameAppDataLocalProgramsPythonPython-version’
or
try using (in cmd )
where python
answered Apr 12, 2020 at 18:45
In the sys package, you can find a lot of useful information about your installation:
import sys
print sys.executable
print sys.exec_prefix
I’m not sure what this will give on your Windows system, but on my Mac executable points to the Python binary and exec_prefix to the installation root.
You could also try this for inspecting your sys module:
import sys
for k,v in sys.__dict__.items():
if not callable(v):
print "%20s: %s" % (k,repr(v))
answered Mar 15, 2009 at 9:41
Guðmundur HGuðmundur H
11.1k3 gold badges23 silver badges22 bronze badges
2
If You want the Path After successful installation then first open you CMD and type
python or python -i
It Will Open interactive shell for You and Then type
import sys
sys.executable
Hit enter and you will get path where your python is installed …
answered Oct 18, 2018 at 7:30
1
To know where Python is installed you can execute where python in your cmd.exe.
anothernode
4,86311 gold badges42 silver badges60 bronze badges
answered Jul 27, 2018 at 6:21
4
You can search for the «environmental variable for you account». If you have added the Python in the path, it’ll show as «path» in your environmental variable account.
but almost always you will find it in
«C:Users%User_name%AppDataLocalProgramsPythonPython_version»
the ‘AppData‘ folder may be hidden, make it visible from the view section of toolbar.
answered Sep 14, 2018 at 9:19
Amit GuptaAmit Gupta
2,6024 gold badges24 silver badges37 bronze badges
Make use of the Python Launcher for Windows (available as of 3.3). It is compatible with all available versions of python.
First, check if the launcher is available:
py
starts the latest installed version of Python
To see all Python versions available on your system and their path:
py -0p
or
py --list-paths
For a specific Python version path—especially useful with multiple python installations:
py -3.7 -c "import os, sys; print(os.path.dirname(sys.executable))"
python 2
py -2 -c "import os, sys; print(os.path.dirname(sys.executable))"
py installed location is C:Windowspy.exe if installed for all users, otherwise can be found at C:UsersusernameAppDataLocalProgramsPythonLauncher.
It does not require the environment PATH variable to be set if installed for all users.
answered Apr 25, 2022 at 2:23
oyeyipooyeyipo
3193 silver badges11 bronze badges
If anyone needs to do this in C# I’m using the following code:
static string GetPythonExecutablePath(int major = 3)
{
var software = "SOFTWARE";
var key = Registry.CurrentUser.OpenSubKey(software);
if (key == null)
key = Registry.LocalMachine.OpenSubKey(software);
if (key == null)
return null;
var pythonCoreKey = key.OpenSubKey(@"PythonPythonCore");
if (pythonCoreKey == null)
pythonCoreKey = key.OpenSubKey(@"Wow6432NodePythonPythonCore");
if (pythonCoreKey == null)
return null;
var pythonVersionRegex = new Regex("^" + major + @".(d+)-(d+)$");
var targetVersion = pythonCoreKey.GetSubKeyNames().
Select(n => pythonVersionRegex.Match(n)).
Where(m => m.Success).
OrderByDescending(m => int.Parse(m.Groups[1].Value)).
ThenByDescending(m => int.Parse(m.Groups[2].Value)).
Select(m => m.Groups[0].Value).First();
var installPathKey = pythonCoreKey.OpenSubKey(targetVersion + @"InstallPath");
if (installPathKey == null)
return null;
return (string)installPathKey.GetValue("ExecutablePath");
}
answered Apr 5, 2017 at 11:10
PeterPeter
36.4k38 gold badges141 silver badges196 bronze badges
2
This worked for me: C:UsersYour_user_nameAppDataLocalProgramsPython
My currently installed python version is 3.7.0
Hope this helps!
David
1,1625 gold badges13 silver badges29 bronze badges
answered Jul 16, 2018 at 6:55
Go to C:UsersUSERAppDataLocalProgramsPythonPython36
if it is not there then
open console by windows+^R
Then type cmd and hit enter
type python if installed in your local file it will show you its version from there type the following
import os
import sys
os.path.dirname(sys.executable)
answered Mar 1, 2019 at 11:34
You can find it in the Windows GUI, but you need to select “show hidden” in the menu. Directory where python is installed on my Win10 computer:
C:UsersusernameAppDataLocalProgramsPythonPython310
Very handy if you use python pip to install packages.
Suraj Rao
29.3k11 gold badges96 silver badges103 bronze badges
answered Dec 31, 2021 at 14:35
You could have many versions of Python installed on your machine. So if you’re in Windows at a command prompt, entering something like this…
py --version
…should tell you what version you’re using at the moment. (Maybe replace py with python or python3 if py doesn’t work). Anyway you’d see something like
Python 3.10.2
If you then create a virtual environment using something like this…
py -m venv venv
…that environment will also use that Python version. To verify, activate the environment…
venvscriptsactivate.bat
You’ll see the name of the command prompt. Now if execute:
where python
…it will show you which Python executable that virtual environment uses. It will be a copy of Python.exe what’s actually in the Scripts subfolder of the virtual environment folder. Of course to see which version that is, again use py --version.
answered Jan 26, 2022 at 15:55
if you still stuck or you get this
C:\Users\name of your\AppData\Local\Programs\Python\Python36
simply do this replace 2 with one
C:UsersakshayAppDataLocalProgramsPythonPython36
Kos
4,7809 gold badges38 silver badges41 bronze badges
answered Jun 2, 2018 at 16:48
I installed 2 and 3 and had the same problem finding 3. Fortunately, typing path at the windows path let me find where I had installed it. The path was an option when I installed Python which I just forgot. If you didn’t select setting the path when you installed Python 3 that probably won’t work — unless you manually updated the path when you installed it.
In my case it was at c:Program FilesPython37python.exe
answered Feb 3, 2019 at 16:39
If you use anaconda navigator on windows, you can go too enviornments and scroll over the enviornments, the root enviorment will indicate where it is installed. It can help if you want to use this enviorment when you need to connect this to other applications, where you want to integrate some python code.
answered Jun 6, 2019 at 10:01
PV8PV8
5,4075 gold badges41 silver badges76 bronze badges
Option 1 : Check System Environment Variables > Path
Option 2 : C:UsersAsusAppDataLocalProgramsPython (By default Path)
answered Oct 1, 2022 at 10:09
Windows не содержит Python в списке предустановленных программ. Вы можете скачать его и установить дополнительно. Во время первой установки Python 3 на Windows могут возникнуть трудности, поэтому мы создали этот туториал. Просто следуйте инструкции и у вас все получится.
Какую версию Python скачать — 2 или 3?
Больше 10 лет назад вышла новая версия python, которая разделила сообщество на 2 части. Сразу это вызывало много споров, новичкам приходилось выбирать: python 2 или python 3. Сегодня большая часть обучается третей версии. На этой версии мы и покажем как установить язык программирования python на Windows.
На этой странице вы можете скачать python для Windows.
В вверху разработчики предлагают выбрать версию.
Если вы не планируете работать с проектом, который написан на Python 2, а таких довольно много. Скачайте python 2+. Для веб разработки, анализа данных и многих других целей лучшим вариантом будет python 3 версии.
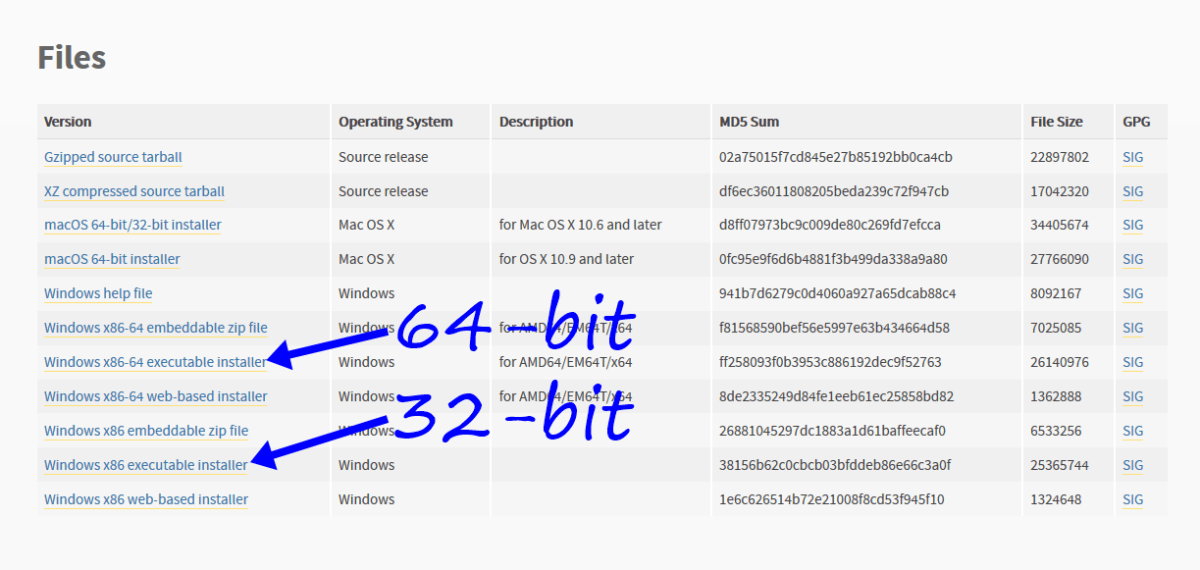
Внизу страницы версии ссылки на скачивание установщиков. Есть возможность скачать python под 64-битную и 32-битную Windows.
Вне зависимости от версии и страны, python на английском языке. Вы не сможете скачать python на русском с официального сайта (и с любого другого).
Скачайте и запустите установщик Python 3, он называется “python-3.****.exe”.
Если на компьютере уже установлена python 2, нет необходимости удалять его. На установку Python 3 она не повлияет.
На первом экране отметьте пункт “Add Python 3.7 to PATH” и нажмите “Install Now”.
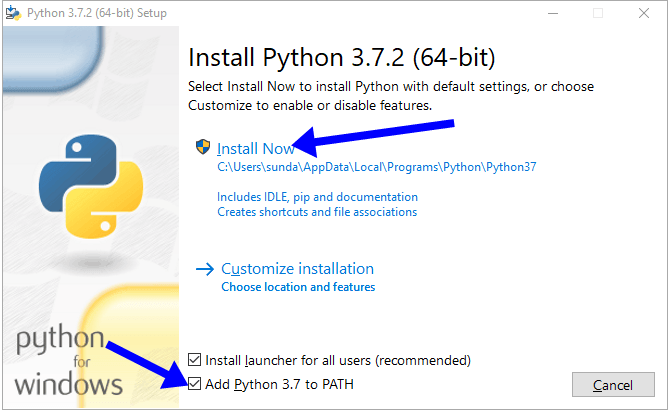
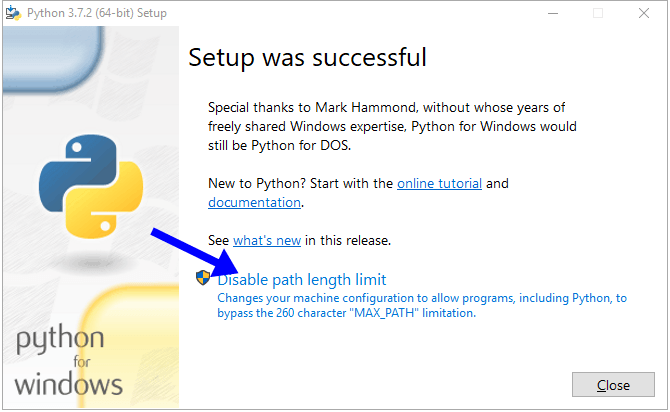
MAX_PATH. В системах Linux этих ограничений нет. Проигнорировав этот пункт, вы можете столкнуться с проблемой совместимости в будущем. Код созданный на Linux не запустится на Windows.
Как проверить уставился ли python
Самый быстрый и простой способ узнать, есть ли интерпретатор python на компьютере — через командную строку.
- Запустите
cmd.exeчерез диспетчер задач или поиск. - Введите
python
В результате командная строка выведет версию python, которая установлена в системе.
Если версия python 2 или вы получили ошибку:
"python" не является внутренней или внешней
командой, исполняемой программой или пакетным файлом.
Следуйте инструкциям ниже. Это легко исправить.
Как добавить python в переменную PATH (ADD to PATH)
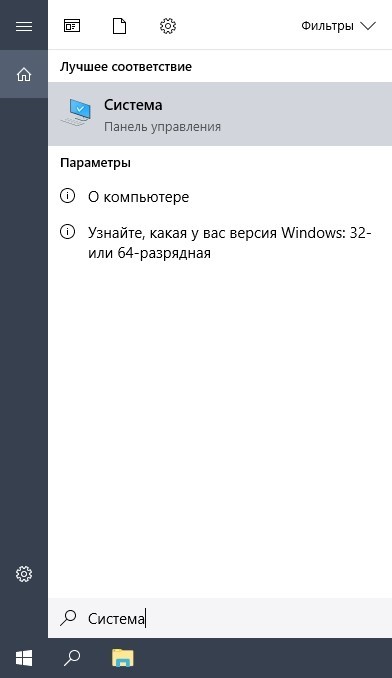
Откройте окно “Система” с помощью поиска.
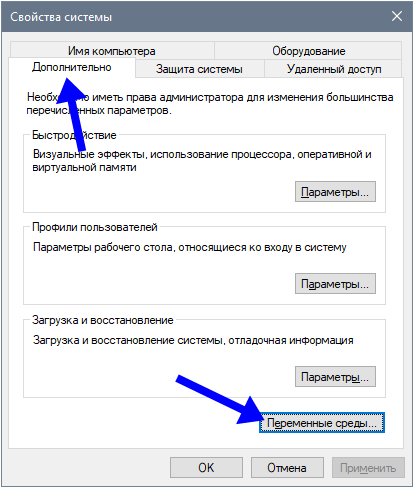
В окне “Система”, нажмите “Дополнительные параметры системы”. Откроется “Свойства системы”. Во вкладке “Дополнительно”, нажимайте “Переменные среды” как на фото ниже.
В открывшемся окне выберите Path -> “Изменить”. Откроется новое окно, куда вы должны добавить путь к интерпретатору python.
Путь у каждого свой, похож на C:UsersUserNameAppDataLocalProgramsPythonPython37. Где Python37 — папка с python.
Нажмите “Создать” и добавьте 2 пути. К папке python и pythonScripts
Как создать отдельную команду для python 2 и python 3
Чтобы использовать обе версии python, измените python.exe на python2.exe, в папке с python 2. А в папке с python 3 , python.exe на python3.exe.
Теперь проверьте обе версии:
>python2 -V
Python 2.7.14
>python3 -V
Python 3.7.2
После этих не сложных действий, python установлен на вашем Windows и готов к работе в любом текстовом редакторе.
Попробуйте создать свою первую программу:
Первая программа на Python «Hello world»
Установка Python доступна на самых разных платформах, включая Linux и Mac OS X. Давайте разберемся, как установить среду Python.
Установка локальной среды
Откройте окно терминала и введите «python», чтобы узнать, установлен ли он уже и если да, то какая версия установлена.
- Unix (Solaris, Linux, FreeBSD, AIX, HP/UX, SunOS, IRIX и т. д.)
- Windows 9x/NT/2000
- Macintosh (Intel, PPC, 68K)
- OS/2
- DOS (несколько версий)
- PalmOS
- Мобильные телефоны Nokia
- Windows CE
- Acorn/RISC OS
- BeOS
- Amiga
- VMS/OpenVMS
- QNX
- VxWorks
- Psion
- Python также был перенесен на виртуальные машины Java и .NET.
Самый последний и актуальный исходный код, двоичные файлы, документация, новости и т. д. доступны на официальном сайте Python https://www.python.org/.
Вы можете загрузить документацию Python, перейдя по адресу https://www.python.org/doc/. Документация доступна в форматах HTML, PDF и PostScript.
Установка Python
Дистрибутив Python доступен для самых разных платформ. Вам необходимо загрузить только двоичный код, подходящий для вашей платформы, и установить Python.
Если двоичный код для вашей платформы недоступен, вам понадобится компилятор C для компиляции исходного кода вручную. Компиляция исходного кода обеспечивает большую гибкость с точки зрения выбора функций, необходимых для вашей установки.
Ниже приведен краткая инструкция по установке Python на различных платформах.
Установка версии для Unix и Linux
Выполните следующие шаги по установке Python на устройстве Unix/Linux.
- Откройте веб-браузер и перейдите по адресу https://www.python.org/downloads/
- Перейдите по ссылке, чтобы загрузить заархивированный исходный код, доступный для Unix/Linux.
- Загрузите и распакуйте файлы.
- Отредактируйте файл Modules/Setup, если вы хотите настроить некоторые параметры.
- Запустите скрипт ./configure
- Выполните
- Выполните установку Python
Python установится в стандартную директорию /usr/local/bin, а его библиотеки в /usr/local/lib/pythonXX, где XX – это версия Python.
Установка Python на Windows
Выполните следующие шаги по установке Python на ОС Windows.
- Откройте веб-браузер и перейдите по адресу https://www.python.org/downloads/
- Перейдите по ссылке на файл python-XYZ.msi установщика Windows, где XYZ – это версия, которую необходимо установить.
- Чтобы использовать этот установщик python-XYZ.msi, система Windows должна поддерживать Microsoft Installer 2.0. Сохраните файл установщика на компьютере, а затем запустите его, чтобы узнать, поддерживает ли ваш компьютер MSI.
- Запустите скачанный файл, после чего откроется мастер установки и настройки Python, который делает процесс установки максимально простым. Просто примите настройки по умолчанию и дождитесь завершения установки.
Установка версии для Macintosh
Последние Mac поставляются с установленным Python, но его версия может быть устаревшей. Смотрите инструкции по получению текущей версии вместе с дополнительными инструментами для поддержки разработки на Mac на странице http://www.python.org/download/mac/. Для версий Mac OS до Mac OS X 10.3 (выпущенных в 2003 году) доступен MacPython.
Он поддерживается Джеком Янсеном, и вы можете получить полный доступ ко всей документации на его веб-сайте — http://www.cwi.nl/~jack/macpython.html. Также там вы можете получить полную информацию об установке версии для Mac OS.
Настройка PATH
Программы и другие исполняемые файлы могут находиться во многих каталогах, поэтому операционные системы предоставляют путь поиска, в котором перечислены каталоги, в которых ОС ищет исполняемые файлы.
Путь хранится в переменной среде, которая представляет собой именованную строку, поддержива емую операционной системой. Эта переменная содержит информацию, доступную для командной оболочки и других программ.
Переменная пути называется PATH в Unix или Path в Windows (Unix чувствителен к регистру; Windows — нет).
В Mac OS установщик обрабатывает сведения о пути. Чтобы вызвать интерпретатор Python из любого конкретного каталога, вы должны добавить каталог Python в свой путь.
Настройка пути в Unix/Linux
Чтобы добавить директорию Python к пути для определенного сеанса в Unix:
- В командной оболочке csh введите setenv PATH «$PATH:/usr/local/bin/python» и нажмите Enter.
- В командной оболочке bash (Linux) введите export PATH=»$PATH:/usr/local/bin/python» и нажмите Enter.
- В командной оболочке sh или ksh введите PATH=»$PATH:/usr/local/bin/python» и нажмите Enter.
- Примечание: /usr/local/bin/python – это путь к каталогу Python.
Настройка пути в Windows
Чтобы добавить каталог Python к пути для определенного сеанса в Windows:
В командной строке введите path %path%;C:Python и нажмите Enter.
Примечание: C:Python – это путь к каталогу Python.
Переменные среды Python
В таблице приведены важные переменные среды, которые может распознавать Python:
| № п/п | Переменная и описание |
| 1 | PYTHONPATH Роль данной переменной аналогична PATH. Эта переменная сообщает интерпретатору Python, где найти файлы модуля, импортированные в программу. Переменная должна включать каталог исходной библиотеки Python и каталоги, содержащие исходный код Python. PYTHONPATH иногда задается установщиком Python. |
| 2 | PYTHONSTARTUP Содержит путь к файлу инициализации, содержащему исходный код Python. Выполняется каждый раз при запуске интерпретатора. В Unix называется .pythonrc.py и содержит команды, которые загружают утилиты или изменяют PYTHONPATH. |
| 3 | PYTHONCASEOK Используется в Windows, чтобы указать Python найти первое совпадение без учета регистра в операторе импорта. Задайте для этой переменной любое значение, чтобы активировать ее. |
| 4 | PYTHONHOME Это альтернативный путь поиска модуля. Обычно встраивается в каталоги PYTHONSTARTUP или PYTHONPATH для упрощения переключения библиотек модулей. |
Запуск Python
Есть три разных способа запуска Python.
Интерактивный интерпретатор
Вы можете запустить Python из Unix, DOS или любой другой системы, которая предоставляет вам интерпретатор командной строки или командное окно.
Введите python в командной строке.
Начните писать код прямо в интерактивном интерпретаторе.
$python # Unix/Linux
или
python% # Unix/Linux
или
C:> python # Windows/DOS
В таблице приведен список всех доступных параметров командной строки:
| № п/п | Опции и описание |
|
1 |
-d Обеспечивает вывод отладки. |
|
2 |
-O Генерирует оптимизированный байт-код (в результате создаются файлы .pyo). |
|
3 |
-S Не запускает импорт местоположения для поиска путей Python при запуске. |
|
4 |
-v Подробный вывод (подробная трассировка операторов импорта). |
|
5 |
-X Отключает встроенные исключения на основе классов (используйте только строки); устарело, начиная с версии 1.6. |
|
6 |
-c cmd Запускает скрипт Python, отправленный в качестве строки cmd |
|
7 |
file Запускает скрипт Python из заданного файла |
Скрипт из командной строки
Сценарий Python может быть выполнен из командной строки, вызвав интерпретатор в вашем приложении, как показано ниже:
$python script.py # Unix/Linux
или
python% script.py # Unix/Linux
или
C: >python script.py # Windows/DOS
Примечание: убедитесь, что режим разрешений для файла позволяет выполнение.
Интегрированная среда разработки
Вы также можете запустить Python из среды графического интерфейса пользователя (GUI), если в вашей системе установлено приложение с графическим интерфейсом, которое поддерживает Python.
- Unix — IDLE является первой Unix IDE для Python.
- Windows — PythonWin является первым интерфейсом Windows для Python, представляющий собой IDE с графическим интерфейсом.
- Macintosh — версия Python для Macintosh вместе с IDLE IDE доступна с основного веб-сайта и может быть загружена в виде файлов MacBinary или BinHex’d.
Если вы не можете правильно настроить среду, обратитесь за помощью к системному администратору. Убедитесь, что среда Python правильно настроена и работает нормально.
Примечание: все примеры, приведенные в последующих главах, выполняются с версией Python 2.4.3, доступной в версии CentOS Linux.
Мы провели настройку окружения онлайн-среды программирования Python, так что вы можете выполнять все доступные примеры онлайн одновременно, когда изучаете теорию. Не стесняйтесь изменять любой пример и выполнять его онлайн.
You may need to add Python to PATH if you’ve installed Python, but typing python on the command line doesn’t seem to work. You may be getting a message saying that the term python isn’t recognized, or you may end up with the wrong version of Python running.
A common fix for these problems is adding Python to the PATH environment variable. In this tutorial, you’ll learn how to add Python to PATH. You’ll also learn about what PATH is and why PATH is vital for programs like the command line to be able to find your Python installation.
The steps that you’ll need to take to add something to PATH will depend significantly on your operating system (OS), so be sure to skip to the relevant section if you’re only interested in this procedure for one OS.
Note that you can use the following steps to add any program to PATH, not just Python.
How to Add Python to PATH on Windows
The first step is to locate the directory in which your target Python executable lives. The path to the directory is what you’ll be adding to the PATH environment variable.
To find the Python executable, you’ll need to look for a file called python.exe. The Python executable could be in a directory in C:Python or in your AppData folder, for instance. If the executable were in AppData, then the path would typically look something like this:
C:Users<USER>AppDataLocalProgramsPython
In your case, the <USER> part would be replaced by your currently logged-in user name.
Once you’ve found the executable, make sure it works by double-clicking it and verifying that it starts up a Python REPL in a new window.
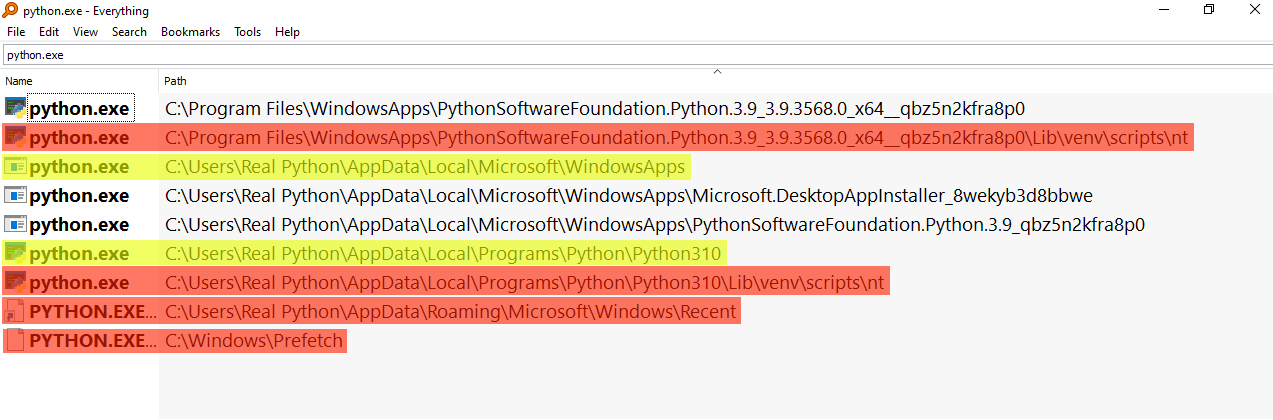
If you’re struggling to find the right executable, you can use Windows Explorer’s search feature. The issue with the built-in search is that it’s painfully slow. To perform a super-fast full system search for any file, a great alternative is Everything:
Those paths highlighted in yellow, namely those at WindowsApps and Python310, would be ideal candidates to add to PATH because they look like executables at the root level of an installation. Those highlighted in red wouldn’t be suitable because some are part of a virtual environment—you can see venv in the path—and some are shortcuts or internal Windows installations.
You may also encounter Python executables that are installed within the folder for a different program. This is due to the fact that many applications bundle their own version of Python within them. These bundled Python installations would also be unsuitable.
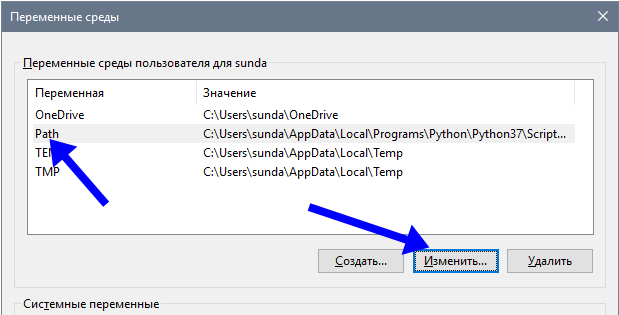
Once you’ve located your Python executable, open the Start menu and search for the Edit the system environment variables entry, which opens up a System Properties window. In the Advanced tab, click on the button Environment Variables. There you’ll see User and System variables, which you’ll be able to edit:
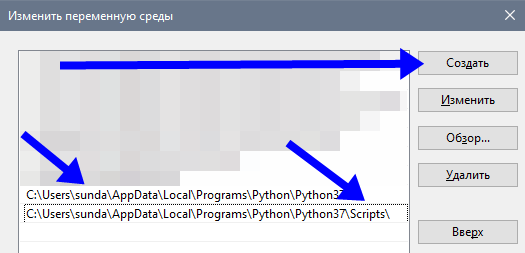
In the section entitled User Variables, double-click on the entry that says Path. Another window will pop up showing a list of paths. Click the New button and paste the path to your Python executable there. Once that’s inserted, select your newly added path and click the Move Up button until it’s at the top.
That’s it! You may need to reboot your computer for the changes to take effect, but you should now be able to call python from the command line.
For setting the PATH environment variable from the command line, check out the section on Configuring Environment Variables in the Windows Python coding setup guide. You can also find instructions in the supplemental materials:
You may also want to set up PATH on your Linux or macOS machine, or perhaps you’re using Windows Subsystem for Linux (WSL). If so, read the next section for the procedure on UNIX-based systems.
How to Add Python to PATH on Linux and macOS
Since Python typically comes pre-installed on UNIX-based systems, the most common problem on Linux and macOS is for the wrong python to run, rather than not finding any python. That said, in this section, you’ll be troubleshooting not being able to run python at all.
The first step is locating your target Python executable. It should be a program that you can run by first navigating to the containing directory and then typing ./python on the command line.
You need to prepend the call to the Python executable with its relative path in the current folder (./) because otherwise you’ll invoke whichever Python is currently recorded on your PATH. As you learned earlier, this might not be the Python interpreter that you want to run.
Often the Python executable can be found in the /bin/ folder. But if Python is already in the /bin/ folder, then it’s most likely already on PATH because /bin/ is automatically added by the system. If this is the case, then you may want to skip to the section on the order of paths within PATH.
Since you’re probably here because you’ve installed Python but it’s still not being found when you type python on the command line, though, you’ll want to search for it in another location.
That said, it might be that /bin/ has been removed from PATH altogether, in which case you might skip forward to the section on mangaging PATH.
Once you’ve located your Python executable and are sure it’s working, take note of the path for later. Now it’s time to start the process of adding it to your PATH environment variable.
First, you’ll want to navigate to your home folder to check out what configuration scripts you have available:
You should see a bunch of configuration files that begin with a period (.). These are colloquially known as dotfiles and are hidden from ls by default.
One or two dotfiles get executed whenever you log in to your system, another one or two run whenever you start a new command-line session, and most others are used by other applications for configuration settings.
You’re looking for the files that run when you start your system or a new command-line session. They’ll probably have names similar to these:
.profile.bash_profile.bash_login.zprofile.zlogin
The keywords to look for are profile and login. You should, in theory, only have one of these, but if you have more than one, you may need to read the comments in them to figure out which ones run on login. For example, .profile file on Ubuntu will typically have the following comment:
# This file is not read by bash(1), if ~/.bash_profile or ~/.bash_login
# exists.
So, if you have .profile but also .bash_profile, then you’ll want to use .bash_profile.
You can also use a .bashrc or .zshrc file, which are scripts that run whenever you start a new command-line session. Run command (rc) files are common places to put PATH configurations.
To add the Python path to the beginning of your PATH environment variable, you’re going to be executing a single command on the command line.
Use the following line, replacing <PATH_TO_PYTHON> with your actual path to the Python executable, and replace .profile with the login script for your system:
$ echo export PATH="<PATH_TO_PYTHON>:$PATH" >> ~/.profile
This command adds export PATH="<PATH_TO_PYTHON>:$PATH" to the end of .profile. The command export PATH="<PATH_TO_PYTHON>:$PATH" prepends <PATH_TO_PYTHON> to the PATH environment variable. It’s similar to the following operation in Python:
>>>
>>> PATH = "/home/realpython/apps:/bin"
>>> PATH = f"/home/realpython/python:{PATH}"
>>> PATH
'/home/realpython/python:/home/realpython/apps:/bin'
Since PATH is just a string separated by colons, prepending a value involves creating a string with the new path, a colon, then the old path. With this string, you set the new value of PATH.
To refresh your current command-line session, you can run the following command, replacing .profile with whichever login script you’ve chosen:
Now, you should be able to call python from the command line directly. The next time you log in, Python should automatically be added to PATH.
If you’re thinking this process seems a bit opaque, you’re not alone! Read on for more of a deep dive into what’s going on.
Understanding What PATH Is
PATH is an environment variable that contains a list of paths to folders. Each path in PATH is separated by a colon or a semicolon—a colon for UNIX-based systems and a semicolon for Windows. It’s like a Python variable with a long string as its value. The difference is that PATH is a variable accessible by almost all programs.
Programs like the command line use the PATH environment variable to find executables. For example, whenever you type the name of a program into the command line, the command line will search various places for the program. One of the places that the command line searches is PATH.
All the paths in PATH need to be directories—they shouldn’t be files or executables directly. Programs that use PATH take each directory in turn and search all the files within it. Subdirectories within directories in PATH don’t get searched, though. So it’s no good just adding your root path to PATH!
It’s also important to note that programs that use PATH typically don’t search for anything except executables. So, you can’t use PATH as a way to define shortcuts to commonly used files.
Understanding the Importance of Order Within PATH
If you type python into the command line, the command line will look in each folder in the PATH environment variable for a python executable. Once it finds one, it’ll stop searching. This is why you prepend the path to your Python executable to PATH. Having the newly added path first ensures that your system will find this Python executable.
A common issue is having a failed Python installation on your PATH. If the corrupted executable is the first one that the command line comes across, then the command line will try and run that and then abort any further searching. The quick fix for this is just adding your new Python directory before the old Python directory, though you’d probably want to clean your system of the bad Python installation too.
Reordering PATH on Windows is relatively straightforward. You open the GUI control panel and adjust the order using the Move Up and Move Down buttons. If you’re on a UNIX-based operating system, however, the process is more involved. Read on to learn more.
Managing Your PATH on UNIX-based Systems
Usually, your first task when managing your PATH is to see what’s in there. To see the value of any environment variable in Linux or macOS, you can use the echo command:
$ echo $PATH
/usr/local/sbin:/usr/local/bin:/usr/sbin:/home/realpython/badpython:/usr/bin:/sbin:/bin:/usr/games:/usr/local/games
Note that the $ symbol is used to tell the command line that the following identifier is a variable. The issue with this command is that it just dumps all the paths on one line, separated by colons. So you might want to take advantage of the tr command to translate colons into newlines:
$ echo $PATH | tr ":" "n"
/usr/local/sbin
/usr/local/bin
/usr/sbin
/home/realpython/badpython
/usr/bin
/sbin
/bin
/usr/games
/usr/local/games
In this example, you can see that badpython is present in PATH. The ideal course of action would be to perform some PATH archaeology and figure out where it gets added to PATH, but for now, you just want to remove it by adding something to your login script .
Since PATH is a shell string, you don’t have access to convenient methods to remove parts of it, like you would if it were a Python list. That said, you can pipe together a few shell commands to achieve something similar:
export PATH=`echo $PATH | tr ":" "n" | grep -v 'badpython' | tr "n" ":"`
This command takes the list from the previous command and feeds it into grep, which, together with the -v switch, will filter out any lines containing the substring badpython. Then you can translate the newlines back to colons, and you have a new and valid PATH string that you use right away to replace your old PATH string.
Though this can be a handy command, the ideal solution would be to figure out where that bad path gets added. You could try looking at other login scripts or examine specific files in /etc/. In Ubuntu, for instance, there’s a file called environment, which typically defines a starting path for the system. In macOS, that might be /etc/paths. There can also be profile files and folders in /etc/ that might contain startup scripts.
The main difference between configurations in /etc/ and in your home folder is that what’s in /etc/ is system-wide, while whatever’s in your home folder will be scoped to your user.
It can often involve a bit of archeology to track down where something gets added to your PATH, though. So, you may want to add a line in your login or rc script that filters out certain entries from PATH as a quick fix.
Conclusion
In this tutorial, you’ve learned how to add Python, or any other program, to your PATH environment variable on Windows, Linux, and macOS. You also learned a bit more about what PATH is and why its internal order is vital to consider. Finally, you also discovered how you might manage your PATH on a UNIX-based system, seeing as it’s more complex than managing your PATH on Windows.
Начиная с этой статьи будет запущен цикл публикаций, посвященный языку Python, с позиции его изучения. Каждая статья будет представлена в виде урока на определенную тему. Не будем отходить от канонов и первую статью посвятим установке языка Python.
В этой статье рассмотрим следующие темы:
- Версии Python (2 и 3)
- Установка Python
- Установка Anaconda
- Установка IDE PyCharm
- Проверка работоспособности
На сегодняшний день существуют две версии Python – это Python 2 и Python 3, у них отсутствует полная совместимость друг с другом. На момент написания статьи вторая версия Python ещё широко используется, но, судя по изменениям, которые происходят, со временем, он останется только для того, чтобы запускать старый код. В нашей с вами работе, мы будем использовать Python 3, и, в дальнейшем, если где-то будет встречаться слово Python, то под ним следует понимать Python 3. Случаи применения Python 2 будут специально оговариваться.
2. Установка Python
Для установки интерпретатора Python на ваш компьютер, первое, что нужно сделать – это скачать дистрибутив. Загрузить его можно с официального сайта, перейдя по ссылке https://www.python.org/downloads/
2.1 Установка Python в Windows
Для операционной системы Windows дистрибутив распространяется либо в виде исполняемого файла (с расширением exe), либо в виде архивного файла (с расширением zip). Если вы используете Windows 7, не забудьте установить Service Pack 1!
Порядок установки.
1. Запустите скачанный установочный файл.
2. Выберет способ установки.
В данном окне предлагается два варианта Install Now и Customize installation. При выборе Install Now, Python установится в папку по указанному пути. Помимо самого интерпретатора будет установлен IDLE (интегрированная среда разработки), pip (пакетный менеджер) и документация, а также будут созданы соответствующие ярлыки и установлены связи файлов, имеющие расширение .py с интерпретатором Python. Customize installation – это вариант настраиваемой установки. Опция Add python 3.5 to PATH нужна для того, чтобы появилась возможность запускать интерпретатор без указания полного пути до исполняемого файла при работе в командной строке.
3. Отметьте необходимые опций установки (доступно при выборе Customize installation)
На этом шаге нам предлагается отметить дополнения, устанавливаемые вместе с интерпретатором Python. Рекомендуем выбрать все опции.
- Documentation – установка документаций.
- pip – установка пакетного менеджера pip.
- tcl/tk and IDLE – установка интегрированной среды разработки (IDLE) и библиотеки для построения графического интерфейса (tkinter).
4. Выберете место установки (доступно при выборе Customize installation)
Помимо указания пути, данное окно позволяет внести дополнительные изменения в процесс установки с помощью опций:
- Install for all users – Установить для всех пользователей. Если не выбрать данную опцию, то будет предложен вариант инсталляции в папку пользователя, устанавливающего интерпретатор.
- Associate files with Python – Связать файлы, имеющие расширение .py, с Python. При выборе данной опции будут внесены изменения в Windows, позволяющие запускать Python скрипты по двойному щелчку мыши.
- Create shortcuts for installed applications – Создать ярлыки для запуска приложений.
- Add Python to environment variables – Добавить пути до интерпретатора Python в переменную PATH.
- Precomple standard library – Провести прекомпиляцию стандартной библиотеки.
Последние два пункта связаны с загрузкой компонентов для отладки, их мы устанавливать не будем.
5. После успешной установки вас ждет следующее сообщение.
2.2 Установка Python в Linux
Чаще всего интерпретатор Python уже в входит в состав дистрибутива. Это можно проверить набрав в терминале
> python
или
> python3
В первом случае, вы запустите Python 2 во втором – Python 3. В будущем, скорее всего, во всех дистрибутивах Linux, включающих Python, будет входить только третья версия. Если у вас, при попытке запустить Python, выдается сообщение о том, что он не установлен, или установлен, но не тот, что вы хотите, то у вас есть два пути: а) собрать Python из исходников; б) взять из репозитория.
Для установки из репозитория в Ubuntu воспользуйтесь командой
> sudo apt-get install python3
Сборку из исходников в данной статье рассматривать не будем.
3. Установка Anaconda
Для удобства запуска примеров и изучения языка Python, советуем установить на свой ПК пакет Anaconda. Этот пакет включает в себя интерпретатор языка Python (есть версии 2 и 3), набор наиболее часто используемых библиотек и удобную среду разработки и исполнения, запускаемую в браузере.
Для установки этого пакета, предварительно нужно скачать дистрибутив https://www.continuum.io/downloads.
Есть варианты под Windows, Linux и MacOS.
3.1 Установка Anaconda в Windows
1. Запустите скачанный инсталлятор. В первом появившемся окне необходимо нажать “Next”.
2. Далее следует принять лицензионное соглашение.
3. Выберете одну из опций установки:
- Just Me – только для пользователя, запустившего установку;
- All Users – для всех пользователей.
4. Укажите путь, по которому будет установлена Anaconda.
5. Укажите дополнительные опции:
- Add Anaconda to the system PATH environment variable – добавить Anaconda в системную переменную PATH
- Register Anaconda as the system Python 3.5 – использовать Anaconda, как интерпретатор Python 3.5 по умолчанию.
Для начала установки нажмите на кнопку “Install”.
5. После этого будет произведена установка Anaconda на ваш компьютер.
3.2 Установка Anaconda в Linux
- Скачайте дистрибутив Anaconda для Linux, он будет иметь расширение .sh, и запустите установку командой:
> bash имя_дистрибутива.sh
В результате вы увидите приглашение к установке. Для продолжения процессе нажмите “Enter”.
2. Прочитайте лицензионное соглашение, его нужно пролистать до конца.
Согласитесь с ним, для этого требуется набрать в командной строке “yes”, в ответе на вопрос инсталлятора:
Do you approve the license terms? [yes|no]
3. Выберете место установки. Можно выбрать один из следующих вариантов:
- Press ENTER to confirm the location – нажмите ENTER для принятия предложенного пути установки. Путь по умолчанию для моей машины: /home/tester/anaconda3, он представлен чуть выше данного меню.
- Press CTRL-C to abort the installation – нажмите CTRL-C для отмены установки.
- Or specify a different location below – или укажите другой путь в строке ниже.
Нажмите ENTER.
4. После этого начнется установка.
4. Установка PyCharm
Если в процессе разработки вам необходим отладчик и вообще вы привыкли работать в IDE, а не в текстовом редакторе, то тогда одним из лучших вариантов будет IDE PyCharm от JetBrains. Для скачивания данного продукта нужно перейти по ссылке https://www.jetbrains.com/pycharm/download/
IDE доступна для Windows, Linux и MacOS. Существуют два вида лицензии PyCharm – это Professional и Community. Мы будем использовать версию Community, так как она бесплатна и её функционала более чем достаточно для наших задач.
4.1 Установка PyCharm в Windows
1. Запустите скачанный дистрибутив PyCharm.
2. Выберете путь установки программы.
3. Укажите ярлыки, которые нужно создать на рабочем столе (запуск 32-х и 64-х разрядной версии PyCharm) и отметить опцию из блока Create associations если требуется связать файлы с расширением .py с PyCharm.
4. Выберете имя для папки в меню Пуск.
5. Далее PyCharm будет установлен на ваш компьютер.
4.2 Установка PyCharm в Linux
1. Скачайте с сайта дистрибутив на компьютер.
2. Распакуйте архивный файл, для этого можно воспользоваться командой:
> tar xvf имя_архива.tar.gz
Перейдите в каталог, который был создан после распаковки дистрибутива, найдите в нем подкаталог bin и зайдите в него. Запустите pycharm.sh командой:
> ./pycharm.sh
В результате должен запуститься PyCharm.
5. Проверка работоспособности
Теперь проверим работоспособность всего того, что мы установили.
5.1 Проверка интерпретатора Python
Для начала протестируем интерпретатор в командном режиме. Если вы работаете в Windows, то нажмите сочетание Win+R и в появившемся окне введите python. В Linux откройте окно терминала и в нем введите python3 (или python).
В результате Python запустится в командном режиме, выглядеть это будет примерно так (картинка приведена для Windows, в Linux результат будет аналогичным):
В окне введите:
print("Hello, World!")
Результат должен быть следующий:
5.2 Проверка Anaconda
Здесь и далее будем считать, что пакет Anaconda установлен в Windows, в папку C:Anaconda3, в Linux, вы его можно найти в каталоге, который выбрали при установке.
Перейдите в папку Scripts и введите в командной строке:
ipython notebook
Если вы находитесь в Windows и открыли папку C:Anaconda3Scripts через проводник, то для запуска интерпретатора командной строки для этой папки в поле адреса введите cmd.
В результате запустится веб-сервер и среда разработки в браузере.
Создайте ноутбук для разработки, для этого нажмите на кнопку New (в правом углу окна) и в появившемся списке выберете Python.
В результате будет создана новая страница в браузере с ноутбуком. Введите в первой ячейке команду
print("Hello, World!")
и нажмите Alt+Enter на клавиатуре. Ниже ячейки должна появиться соответствующая надпись.
5.3 Проверка PyCharm
Запустите PyCharm и выберете Create New Project в появившемся окне.
Укажите путь до проекта Python и интерпретатор, который будет использоваться для запуска и отладки.
Добавьте Python файл в проект.
Введите код программы.
Запустите программу.
В результате должно открыться окно с выводом программы.
На этом первый урок закончен.
P.S.
Если вам интересна тема анализа данных, то мы рекомендуем ознакомиться с библиотекой Pandas. На нашем сайте вы можете найти вводные уроки по этой теме. Все уроки по библиотеке Pandas собраны в книге “Pandas. Работа с данными”.
Спасибо за внимание!
Python. Урок 2. Запуск программ на Python >>>