В этой статье мы рассмотрим, как получить и проанализировать логи RDP подключений в Windows. Логи RDP подключений позволяют администраторам терминальных RDS серверов/ферм получить информацию о том, какие пользователи подключались к серверу, когда был выполнен вход и когда сеанс завершен, с какого устройства (имя или IP адрес) подключался пользователь.
Описанные методики получения и исследования RDP логов применима как к Windows Server 2022/2019/2016/2012R2, так и для десктопных версий Windows 11, 10, 8.1 c.
Содержание:
- События RDP подключений в журналах Windows (Event Viewer)
- Получаем логи RDP подключений в Windows с помощью PowerShell
- Логи RDP подключений на клиентах Windows
События RDP подключений в журналах Windows (Event Viewer)
Когда пользователь удаленно подключается к RDS серверу или удаленному столу Windows (RDP), информация об этих событиях сохраняется в журналы Windows. Рассмотрим основные этапы RDP подключения и связанные с ними события в Event Viewer.
- Network Connection
- Authentication
- Logon
- Session Disconnect/Reconnect
- Logoff
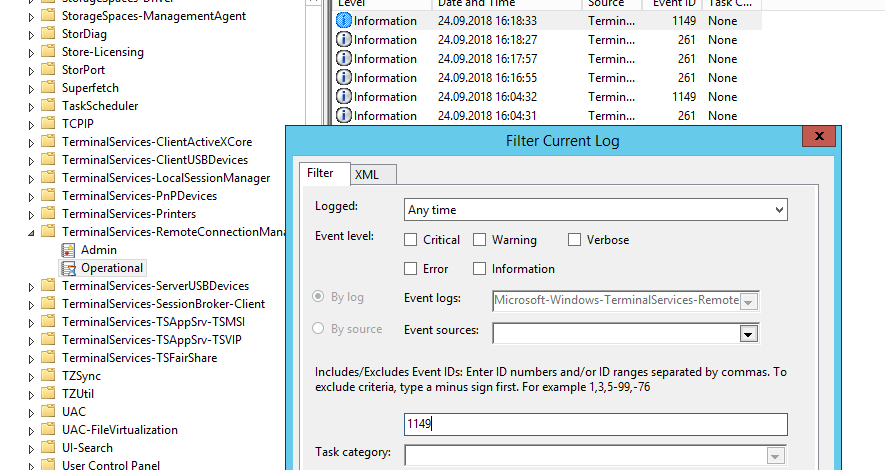
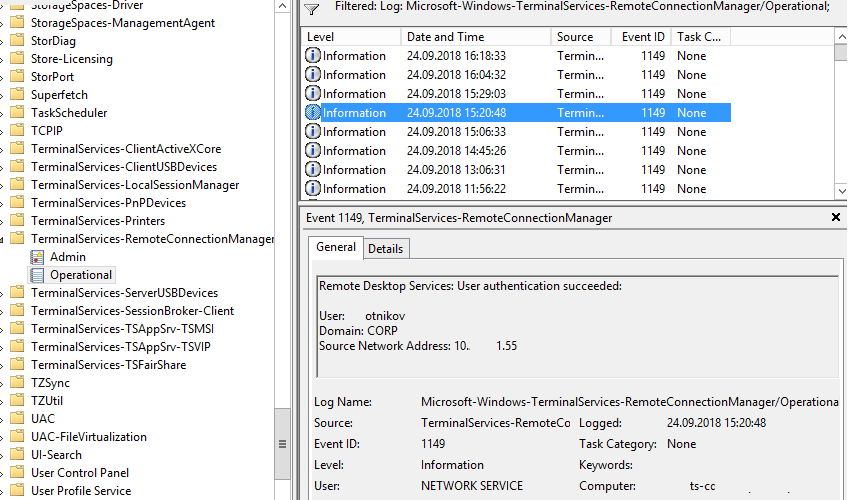
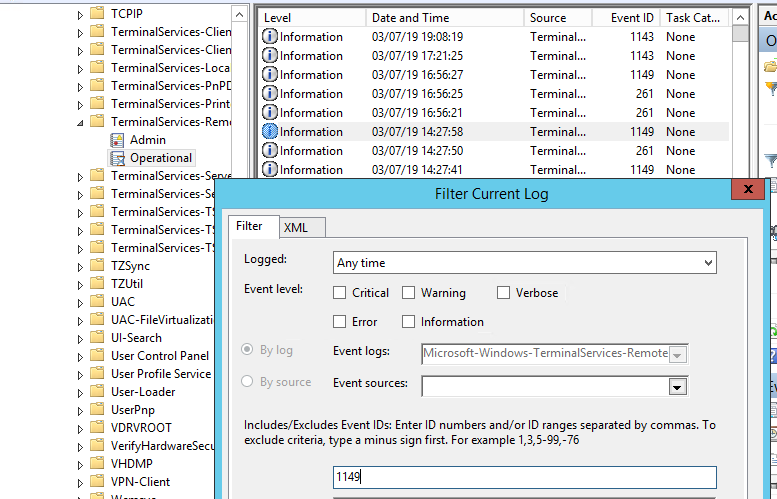
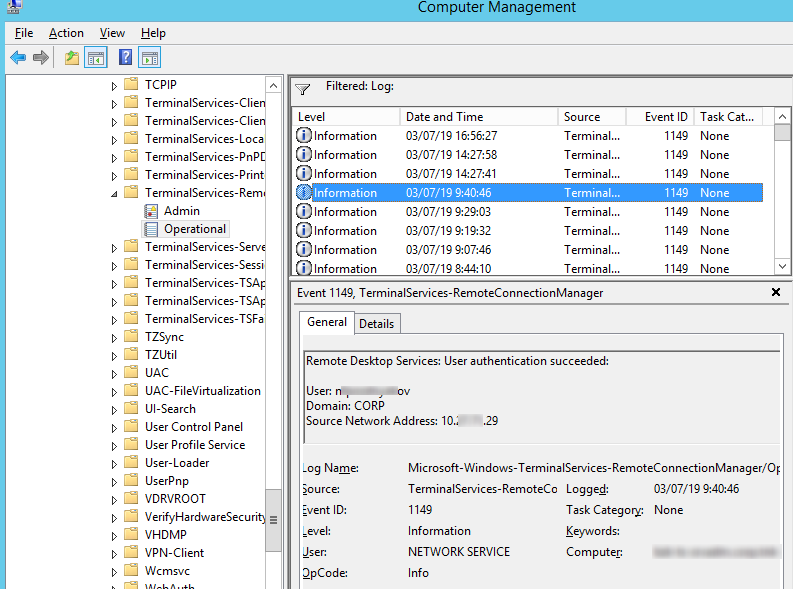
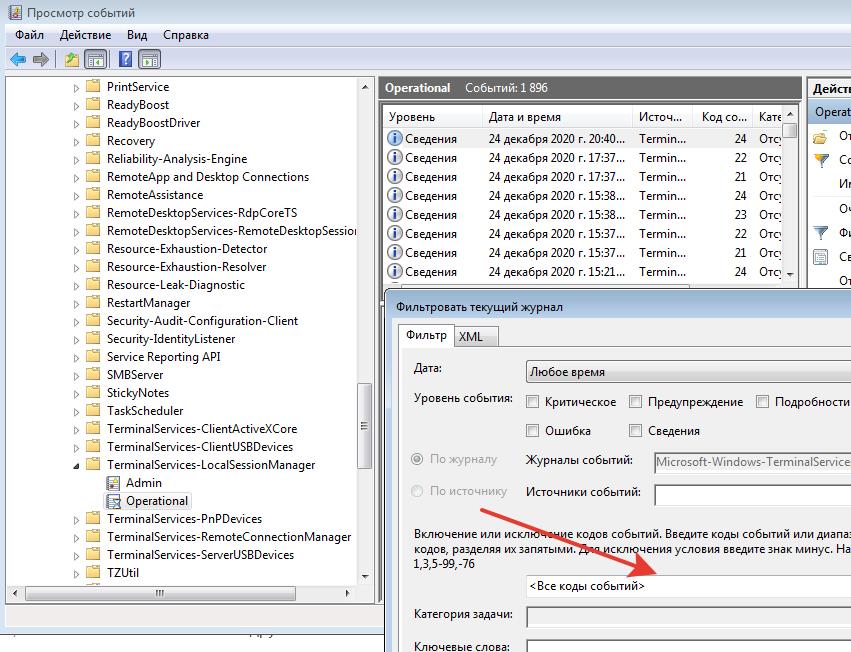
Network Connection: – событие установления сетевого подключение к серверу от RDP клиента пользователя. Событие с EventID – 1149 (Remote Desktop Services: User authentication succeeded). Наличие этого события не свидетельствует об успешной аутентификации пользователя. Этот журнал находится в разделе Applications and Services Logs -> Microsoft -> Windows -> Terminal-Services-RemoteConnectionManager -> Operational. Включите фильтр по данному событию (ПКМ по журналу-> Filter Current Log -> EventId 1149).
С помощью PowerShell можно вывести список всех попыток RDP подключений:
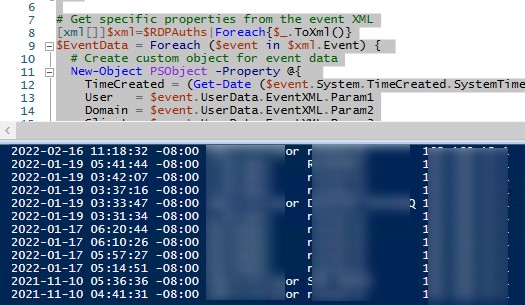
$RDPAuths = Get-WinEvent -LogName 'Microsoft-Windows-TerminalServices-RemoteConnectionManager/Operational' -FilterXPath '<QueryList><Query Id="0"><Select>*[System[EventID=1149]]</Select></Query></QueryList>'
[xml[]]$xml=$RDPAuths|Foreach{$_.ToXml()}
$EventData = Foreach ($event in $xml.Event)
{ New-Object PSObject -Property @{
TimeCreated = (Get-Date ($event.System.TimeCreated.SystemTime) -Format 'yyyy-MM-dd hh:mm:ss K')
User = $event.UserData.EventXML.Param1
Domain = $event.UserData.EventXML.Param2
Client = $event.UserData.EventXML.Param3
}
} $EventData | FT
В результате у вас получится список с историей всех сетевых RDP подключений к данному серверу. В событии содержится имя пользователя, домен (если используется NLA аутентификация, при отключенном NLA текст события выглядит иначе) и IP адрес компьютера пользователя.
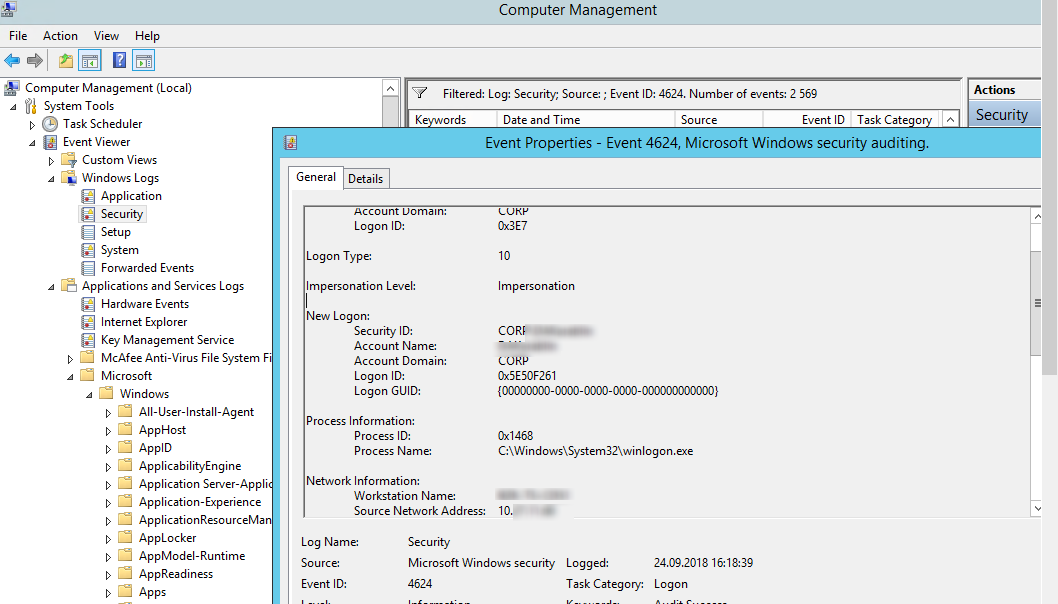
Authentication: – успешная или неудачная аутентификация пользователя на сервере. Журнал Windows -> Security. Здесь нас могут интересовать события с EventID – 4624 (успешная аутентификация — An account was successfully logged on) или 4625 (ошибка аутентификации — An account failed to log on). Обратите внимание на значение LogonType в событии.
- LogonType = 10 или 3 — при входе через терминальную службу RDP —.
- LogonType = 7, значит выполнено переподключение к уже существующему RDP сеансу.
- LogonType = 5 – событие RDP подключения к консоли сервера (в режиме mstsc.exe /admin)
Вы можете использовать события с ошибками аутентификации для защиты от удаленного перебора паролей через RDP. СВы можете автоматически блокировать на файерволе IP адреса, с которых выполняется подбор пароля, простым PowerShell скриптом (см. статью).
При этом имя пользователя содержится в описании события в поле Account Name, имя компьютера в Workstation Name, а имя пользователя в Source Network Address.
Обратите внимание на значение поля LogonID – это уникальный идентификатор сессии пользователя, с помощью которого можно отслеживать дальнейшую активность данного пользователя. Но при отключении от RDP сессии (disconnect) и повторного переподключения к той же сессии, пользователю будет выдан новый TargetLogonID (хотя RDP сессия осталась той же самой).
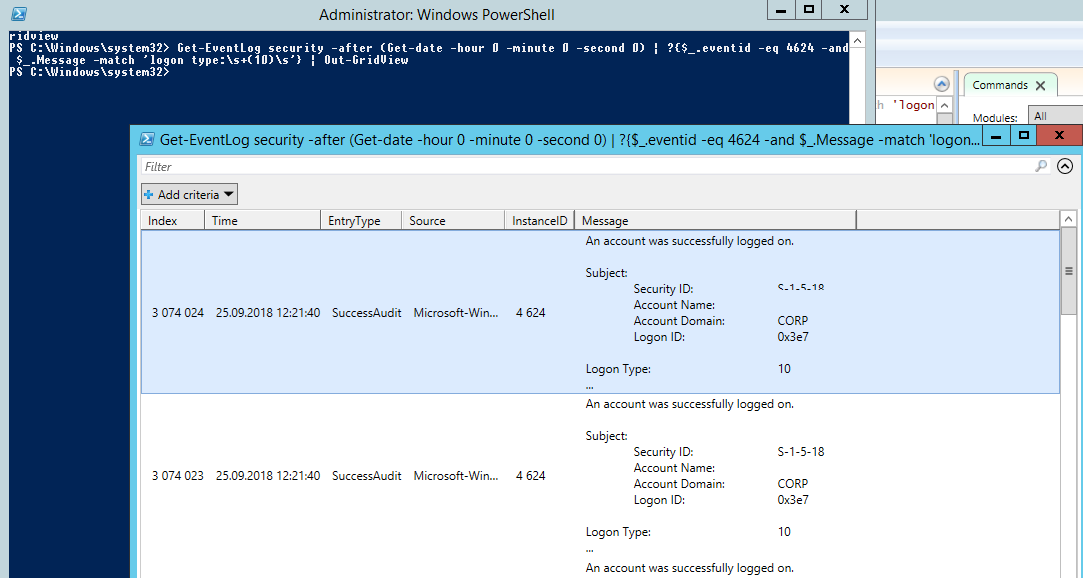
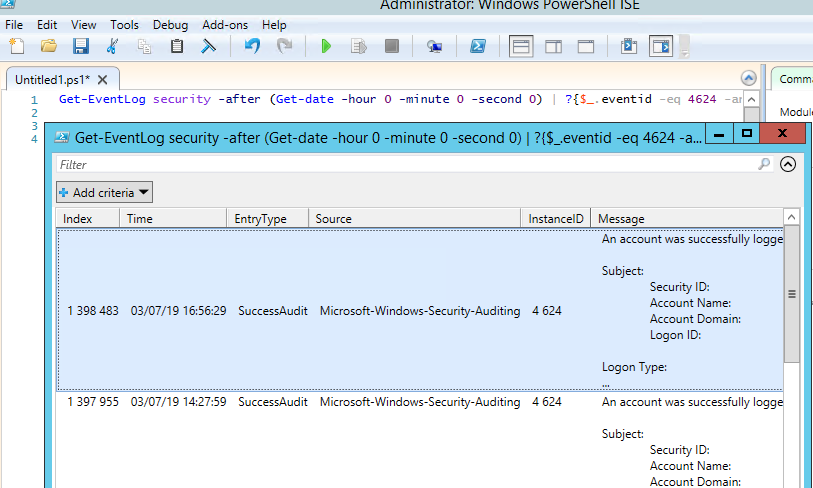
Вы можете получить список событий успешных авторизаций по RDP (событие 4624) с помощью такой команды PowerShell.
Get-EventLog security -after (Get-date -hour 0 -minute 0 -second 0) | ?{$_.eventid -eq 4624 -and $_.Message -match 'logon type:s+(10)s'} | Out-GridView
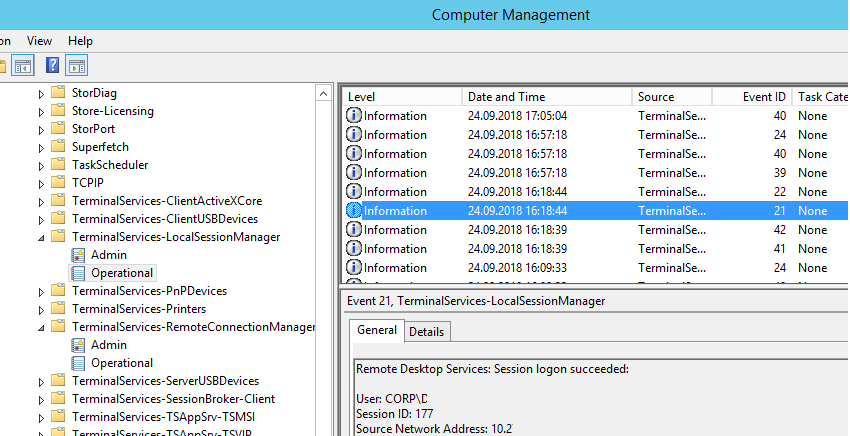
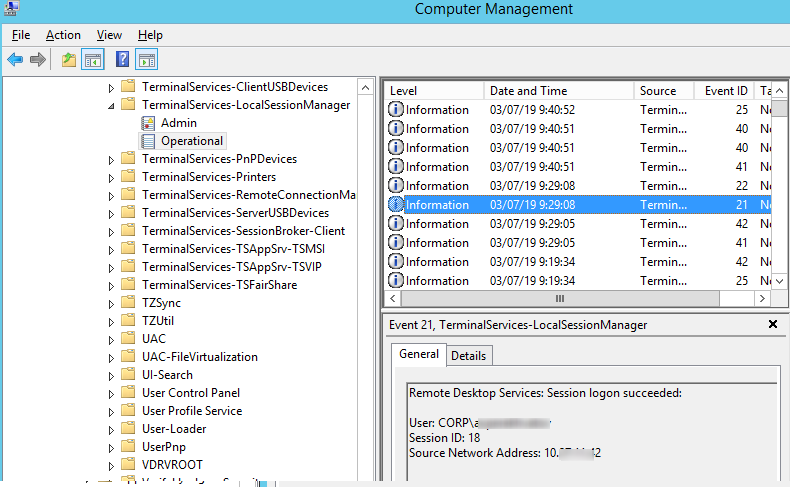
Logon: – RDP вход в систему, EventID – 21 (Remote Desktop Services: Session logon succeeded. Это событие появляется после успешной аутентификации пользователя. Этот журнал находится в разделе Applications and Services Logs -> Microsoft -> Windows -> TerminalServices-LocalSessionManager -> Operational. Как вы видите, здесь можно узнать идентификатор RDP сессии для пользователя — Session ID.
Событие с EventID – 21 (Remote Desktop Services: Shell start notification received) означает успешный запуск оболочки Explorer (появление окна рабочего стола в RDP сессии).
Session Disconnect/Reconnect – события отключения и переподключения к сессии имеют разные коды в зависимости от того, что вызвало отключение пользователя (отключение по неактивности, заданному в таймаутах для RDP сессий; выбор пункта Disconnect в сессии; завершение RDP сессии другим пользователем или администратором и т.д.). Эти события находятся в разделе журналов Applications and Services Logs -> Microsoft -> Windows -> TerminalServices-LocalSessionManager -> Operational. Рассмотрим RDP события, которые могут быть полезными:
- EventID – 24 (Remote Desktop Services: Session has been disconnected) – пользователь отключился от RDP сессии.
- EventID – 25 (Remote Desktop Services: Session reconnection succeeded) – пользователь переподключился к своей имеющейся RDP сессии на сервере.
- EventID – 39 (Session <A> has been disconnected by session <B>) – пользователь сам отключился от своей RDP сессии, выбрав соответствующий пункт меню (а не просто закрыл окно RDP клиента). Если идентификаторы сессий разные, значит пользователя отключил другой пользователь (или администратор).
- EventID – 40 (Session <A> has been disconnected, reason code <B>). Здесь нужно смотреть на код причины отключения в событии. Например:
- reason code 0 (No additional information is available) – обычно говорит о том, что пользователь просто закрыл окно RDP клиента.
- reason code 5 (The client’s connection was replaced by another connection) – пользователь переподключился к своей старой сессии.
- reason code 11 (User activity has initiated the disconnect) – пользователь сам нажал на кнопку Disconnect в меню.
Событие с EventID – 4778 в журнале Windows -> Security (A session was reconnected to a Window Station). Пользователь переподключился к RDP сессии (пользователю выдается новый LogonID).
Событие с EventID 4779 в журнале Windows -> Security (A session was disconnected from a Window Station). Отключение от RDP сеанса.
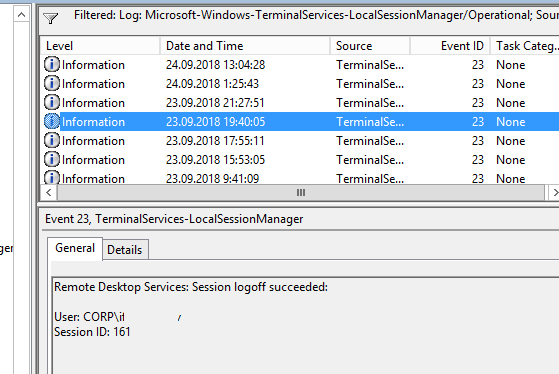
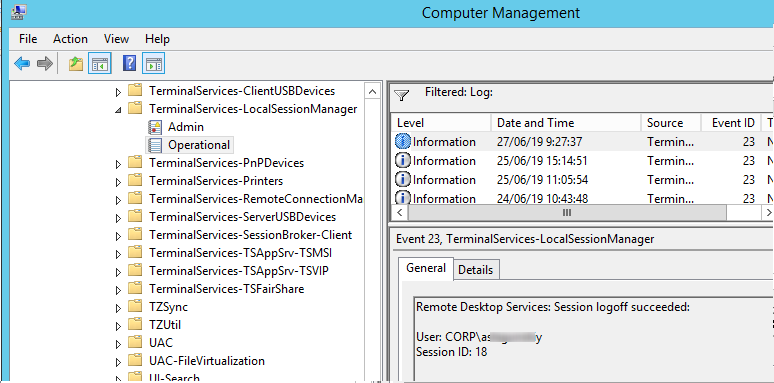
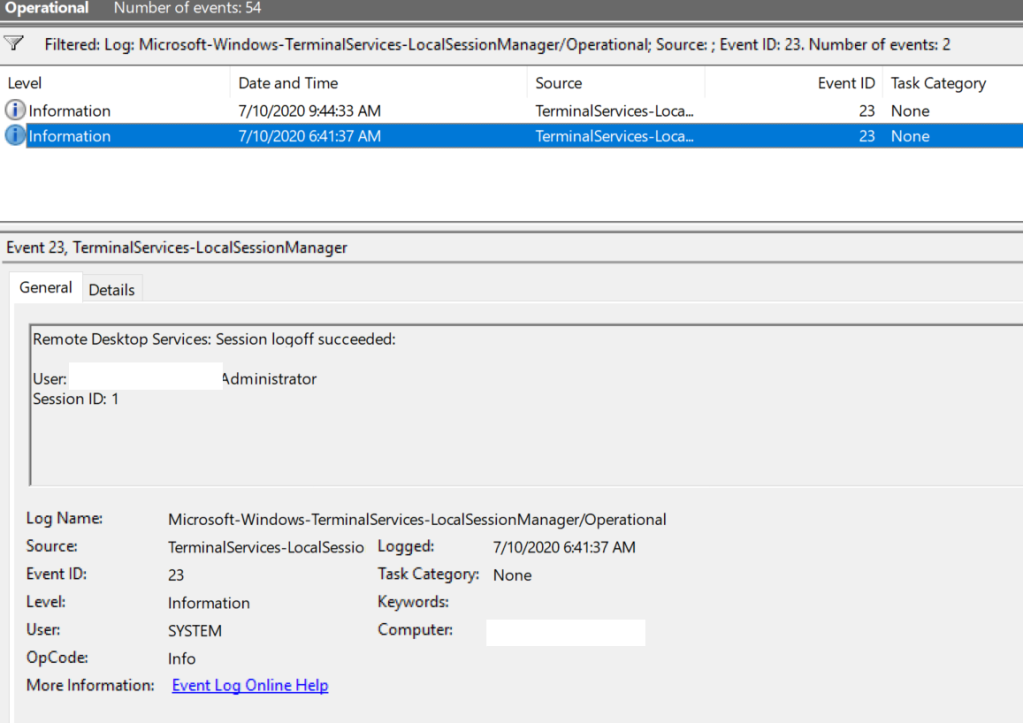
Logoff: – выход пользователя из системы. При этом в журнале Applications and Services Logs -> Microsoft -> Windows -> TerminalServices-LocalSessionManager -> Operational регистрируется событие с EventID 23 (Remote Desktop Services: Session logoff succeeded).
При этом в журнале Security нужно смотреть событие EventID 4634 (An account was logged off).
Событие Event 9009 (The Desktop Window Manager has exited with code (<X>) в журнале System говорит о том, что пользователь инициировал завершение RDP сессии, и окно и графический shell пользователя был завершен.
EventID 4647 — User-initiated logoff
Получаем логи RDP подключений в Windows с помощью PowerShell
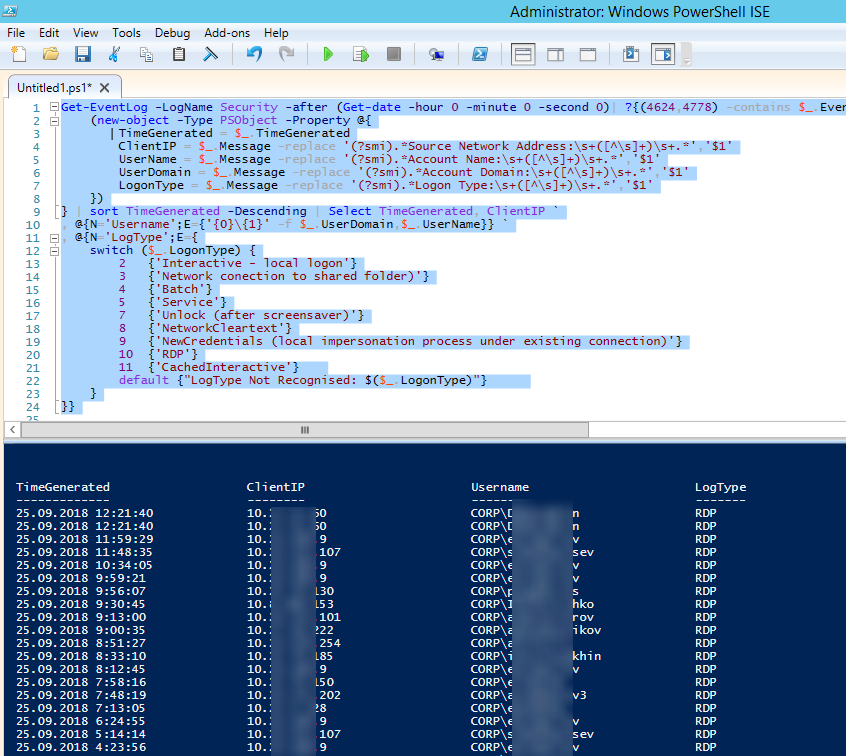
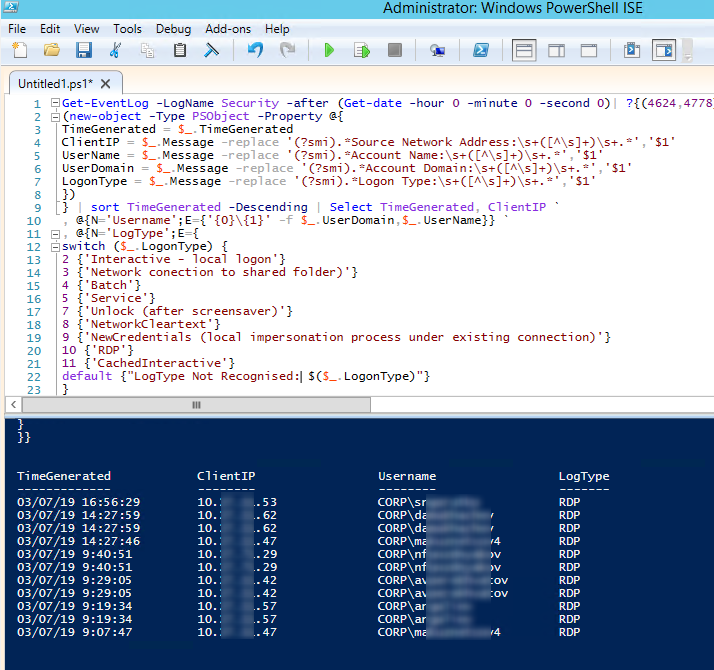
Ниже представлен небольшой PowerShell скрипт, который выгружает из журналов терминального RDS сервера историю всех RDP подключений за текущий день. В полученной таблице указано время подключения, IP адрес клиента и имя пользователя (при необходимости вы можете включить в отчет другие типы входов).
Get-EventLog -LogName Security -after (Get-date -hour 0 -minute 0 -second 0)| ?{(4624,4778) -contains $_.EventID -and $_.Message -match 'logon type:s+(10)s'}| %{
(new-object -Type PSObject -Property @{
TimeGenerated = $_.TimeGenerated
ClientIP = $_.Message -replace '(?smi).*Source Network Address:s+([^s]+)s+.*','$1'
UserName = $_.Message -replace '(?smi).*ssAccount Name:s+([^s]+)s+.*','$1'
UserDomain = $_.Message -replace '(?smi).*ssAccount Domain:s+([^s]+)s+.*','$1'
LogonType = $_.Message -replace '(?smi).*Logon Type:s+([^s]+)s+.*','$1'
})
} | sort TimeGenerated -Descending | Select TimeGenerated, ClientIP `
, @{N='Username';E={'{0}{1}' -f $_.UserDomain,$_.UserName}} `
, @{N='LogType';E={
switch ($_.LogonType) {
2 {'Interactive - local logon'}
3 {'Network conection to shared folder)'}
4 {'Batch'}
5 {'Service'}
7 {'Unlock (after screensaver)'}
8 {'NetworkCleartext'}
9 {'NewCredentials (local impersonation process under existing connection)'}
10 {'RDP'}
11 {'CachedInteractive'}
default {"LogType Not Recognised: $($_.LogonType)"}
}
}}
Можно экспортировать логи RDP подключений из журнала в CSV файл (для дальнейшего анализа в таблице Excel). Экспорт журнала можно выполнить из консоли Event Viewer (при условии что логи не очищены) или через командную строку:
WEVTUtil query-events Security > c:pssecurity_log.txt
Или с помощью PowerShell:
get-winevent -logname "Microsoft-Windows-TerminalServices-LocalSessionManager/Operational" | Export-Csv c:psrdp-log.csv -Encoding UTF8
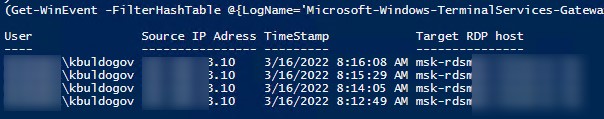
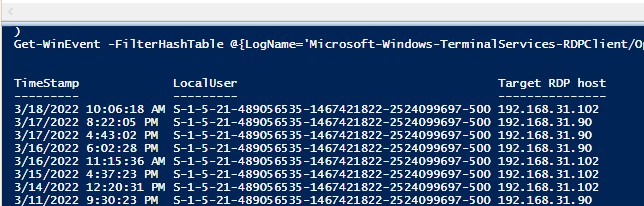
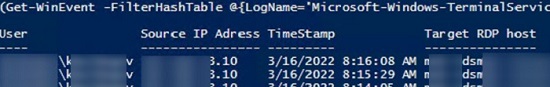
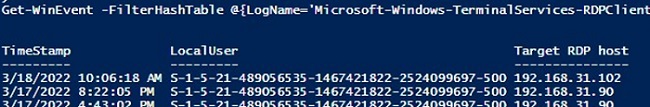
Если ваши пользователи подключаются к RDS серверам через шлюз удаленных рабочих столов Remote Desktop Gateway, вы можете обрабатывать логи подключений пользователей по журналу Microsoft-Windows-TerminalServices-Gateway по EventID 302. Например, следующий PowerShell скрипт выведет полную историю подключений через RD Gateway указанного пользователя:
$rdpusername="kbuldogov"
$properties = @(
@{n='User';e={$_.Properties[0].Value}},
@{n='Source IP Adress';e={$_.Properties[1].Value}},
@{n='TimeStamp';e={$_.TimeCreated}}
@{n='Target RDP host';e={$_.Properties[3].Value}}
)
(Get-WinEvent -FilterHashTable @{LogName='Microsoft-Windows-TerminalServices-Gateway/Operational';ID='302'} | Select-Object $properties) -match $rdpusername
Другие события, связанные с подключениями пользователей на RD Gateway в журнале Microsoft-Windows-TerminalServices-Gateway:
- 300 —
The user %1, on client computer %2, met resource authorization policy requirements and was therefore authorized to connect to resource %4 - 302 —
The user %1, on client computer %2, connected to resource %4 - 303 —
The user %1, on client computer %2, disconnected from the following network resource: %4. Before the user disconnected, the client transferred %6 bytes and received %5 bytes. The client session duration was %7 seconds.
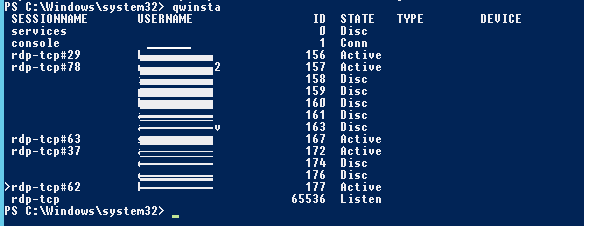
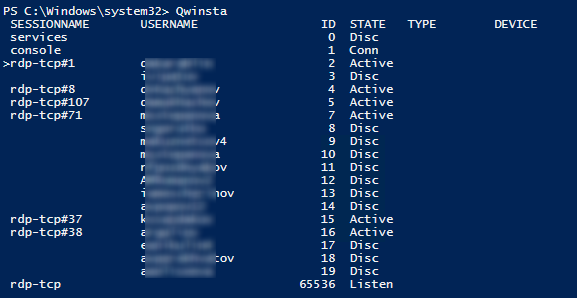
Список текущих RDP сессий на сервере можно вывести командой:
qwinsta
Команда возвращает как идентификатор сессии (ID), имя пользователя (USERNAME)и состояние (Active/Disconnect). Эту команду удобна использовать, когда нужно определить ID RDP сессии пользователя при теневом подключении.
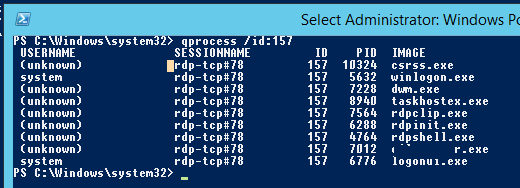
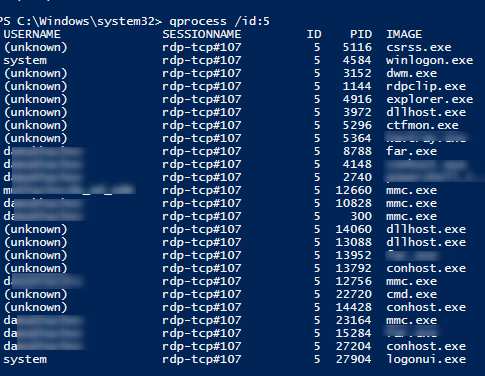
Список запущенных процессов в конкретной RDP сессии (указывается ID сессии):
qprocess /id:157
Логи RDP подключений на клиентах Windows
Также вы можете изучать логи исходящих подключений на стороне RDP клиента. Они доступны в журнале событий Application and Services Logs -> Microsoft -> Windows -> TerminalServices-ClientActiveXCore -> Microsoft-Windows-TerminalServices-RDPClient -> Operation.
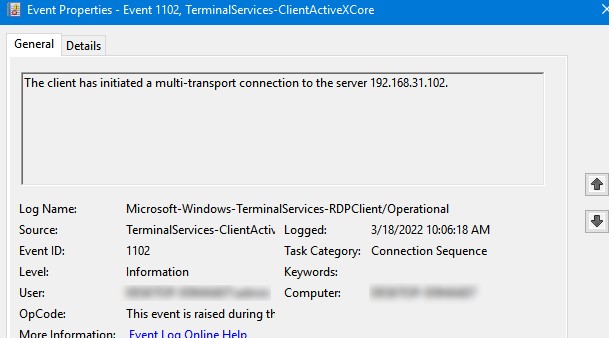
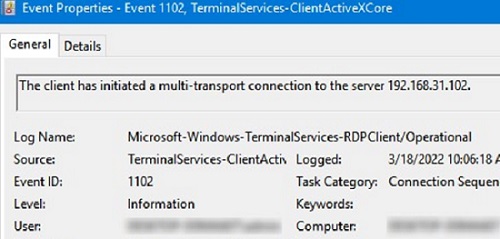
Например, событие с Event ID 1102 появляется, когда компьютер устанавливает подключение с удаленным RDS хостом Windows Server или компьютером с Windows 10/11 с включенной службой RDP (десктопные версии Windows также поддерживают несколько одновременных rdp подключений).
The client has initiated a multi-transport connection to the server 192.168.31.102.
Следующий RDP скрипт выведет историю RDP подключений на указанном компьютере (для получения событий Event Log используется командлет Get-WinEvent):
$properties = @(
@{n='TimeStamp';e={$_.TimeCreated}}
@{n='LocalUser';e={$_.UserID}}
@{n='Target RDP host';e={$_.Properties[1].Value}}
)
Get-WinEvent -FilterHashTable @{LogName='Microsoft-Windows-TerminalServices-RDPClient/Operational';ID='1102'} | Select-Object $properties
Скрипт возвращает SID пользователей, которые инициировали RDP подключения на этом компьютере и DNS имена/IP адреса серверов, к которым подключались пользователи. Вы можете преобразовать SID в имена пользователей.
Также история RDP подключений пользователя хранится в реестре.
I’ve been through most of the free/affordable answers on this page as well as searching elsewhere (for days, including reading the Event logs mentioned by Andy Bichler) and here’s an alternate free RDP monitoring and blocking tool:
http://www.tweaking.com/content/page/remote_desktop_ip_monitor_blocker.html
I haven’t tested it extensively, but downloaded and scanned it (the portable version) and although the UI is a bit on the ugly side, it’s working on a 2012 R2 server without issue thus far. It’s «hands on,» but a no-brainer as well and beats deciphering the event logs.
There is also ts_block which allows you to automatically block IPs that are brute forcing your server’s RDP (which I’m guessing would have some log of RDP attempts):
https://github.com/EvanAnderson/ts_block
As you can see in that link, the author is a serverfault user. I have not tested it as it’s basically a vbscript that I would need to dissect before using. But, it seems promising.
The problem with the event logs mentioned by Andy above is that they are not very clear or descriptive as to who’s doing what… at least in a malicious sense. You can find IP Addresses, but then it’s hard to tell if they are related to all the unsuccessful login attempts. So, another tool other than the inherent logs seems almost mandatory if you’re server is internet facing and you have any concerns about security.
In this article, we’ll describe how to get and audit the RDP connection logs in Windows. The RDP connection logs allow RDS terminal servers administrators to get information about which users logged on to the server when a specific RDP user logged on and ended up the session, and from which device (DNS name or IP address) the user logged on.
Contents:
- RDP Connection Events in Windows Event Viewer
- Getting Remote Desktop Login History with PowerShell
- Outgoing RDP Connection Logs in Windows
The article is applicable when analyzing RDP logs for both Windows Server 2022/2019/2016/2012R2 and to desktop editions (Windows 11, 10, and 8.1).
RDP Connection Events in Windows Event Viewer
When a user connects to a Remote Desktop-enabled or RDS host, information about these events is stored in the Event Viewer logs (eventvwr.msc). Consider the main stages of RDP connection and related events in the Event Viewer, which may be of interest to the administrator
- Network Connection;
- Authentication;
- Logon;
- Session Disconnect/Reconnect;
- Logoff.
Network Connection – establishing a network connection to a server from the user’s RDP client. It is the event with the EventID 1149 (Remote Desktop Services: User authentication succeeded). If this event is found, it doesn’t mean that user authentication has been successful. This log is located in “Applications and Services Logs -> Microsoft -> Windows -> Terminal-Services-RemoteConnectionManager > Operational”. Enable the log filter for this event (right-click the log -> Filter Current Log -> EventId 1149).
You can list all RDP connection attempts with PowerShell:
$RDPAuths = Get-WinEvent -LogName 'Microsoft-Windows-TerminalServices-RemoteConnectionManager/Operational' -FilterXPath '<QueryList><Query Id="0"><Select>*[System[EventID=1149]]</Select></Query></QueryList>'
[xml[]]$xml=$RDPAuths|Foreach{$_.ToXml()}
$EventData = Foreach ($event in $xml.Event)
{ New-Object PSObject -Property @{
TimeCreated = (Get-Date ($event.System.TimeCreated.SystemTime) -Format 'yyyy-MM-dd hh:mm:ss K')
User = $event.UserData.EventXML.Param1
Domain = $event.UserData.EventXML.Param2
Client = $event.UserData.EventXML.Param3
}
} $EventData | FT
Then you will get an event list with the history of all RDP connections to this server. The logs provide a username, a domain (in this case the Network Level Authentication is used; if NLA is disabled, the event description looks differently), and the IP address of the user’s computer.
Authentication shows whether an RDP user has been successfully authenticated on the server or not. The log is located under Windows -> Security. So, you may be interested in the events with the EventID 4624 (An account was successfully logged on) or 4625 (An account failed to log on).
Please, pay attention to the LogonType value in the event description.
- LogonType = 10 or 3 — if the Remote Desktop service has been used to create a new session during log on;
- LogonType = 7, means that a user has reconnected to the existing RDP session;
- LogonType = 5 – RDP connection to the server console (in the mstsc.exe /admin mode).
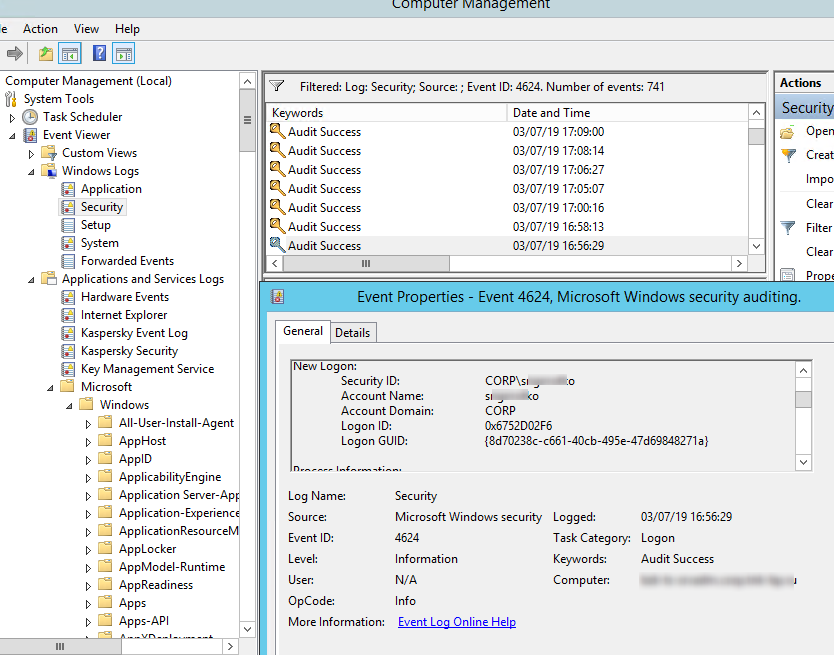
In this case, the user name is contained in the event description in the Account Name field, the computer name in the Workstation Name, and the user IP in the Source Network Address.
Please, note the value of the LogonID field. This is a unique user RDP session identifier that helps track the user’s further activity. However, if an RDP session is disconnected and a user reconnects to it, the user will be assigned a new LogonID (although the RDP session remains the same).
You can get a list of successful RDP authentication events (EventID 4624) using this PowerShell command:
Get-EventLog security -after (Get-date -hour 0 -minute 0 -second 0) | ?{$_.eventid -eq 4624 -and $_.Message -match 'logon type:s+(10)s'} | Out-GridView
Logon refers to an RDP login to Windows. EventID 21 – this event appears after a user has been successfully authenticated (Remote Desktop Services: Session logon succeeded). This events are located in the “Applications and Services Logs -> Microsoft -> Windows -> TerminalServices-LocalSessionManager -> Operational”. As you can see, here you can find the ID of a user RDP session — Session ID.
EventID – 21 (Remote Desktop Services: Shell start notification received) indicates that the Explorer shell has been successfully started (the Windows desktop appears in the user’s RDP session).
Session Disconnect/Reconnect – session disconnection and reconnection events have different IDs depending on what caused the user disconnection (disconnection due to inactivity set in timeouts for RDP sessions, Disconnect option has been selected by the user in the session, RDP session ended by another user or an administrator, etc.). You can find these events in the Event Viewer under “Applications and Services Logs -> Microsoft -> Windows -> TerminalServices-LocalSessionManager -> Operational”. Let’s consider the RDP Event IDs that might be useful:
- EventID – 24 (
Remote Desktop Services: Session has been disconnected) –a user has disconnected from the RDP session; - EventID – 25 (
Remote Desktop Services: Session reconnection succeeded) – a user has reconnected to the existing RDP session on the server; - EventID – 39 (
Session <A> has been disconnected by session <B>) – a user has disconnected from the RDP session by selecting the corresponding menu option (instead of just closing the RDP client window). If the session IDs are different, a user has been disconnected by another user (or administrator); - EventID – 40 (
Session <A> has been disconnected, reason code <B>). Here you must check the disconnection reason code in the event description. For example:- reason code 0 (
No additional information is available) means that a user has just closed the RDP client window; - reason code 5 (
The client’s connection was replaced by another connection) means that a user has reconnected to the previous RDP session; - reason code 11 (
User activity has initiated the disconnect) a user has clicked the Disconnect button in the start menu.
- reason code 0 (
EventID 4778 in Windows -> Security log (A session was reconnected to a Window Station). A user has reconnected to an RDP session (a user is assigned a new LogonID).
EventID 4779 in “Windows -> Security” log (A session was disconnected from a Window Station). A user has been disconnected from an RDP session.
Logoff refers to the end of a user session. It is logged as the event with the EventID 23 (Remote Desktop Services: Session logoff succeeded) under “Applications and Services Logs -> Microsoft -> Windows -> TerminalServices-LocalSessionManager -> Operational”.
At the same time the EventID 4634 (An account was logged off) appears in the Security log.
The EventID 9009 (The Desktop Window Manager has exited with code <X>) in the System log means that a user has initiated logoff from the RDP session with both the window and the graphic shell of the user have been terminated.
EventID 4647 — User-initiated logoff
Getting Remote Desktop Login History with PowerShell
Here is a short PowerShell script that lists the history of all RDP connections for the current day from the terminal RDS server event logs. The resulting table shows the connection time, the client’s IP address (DNS computername), and the remote user name (if necessary, you can include other LogonTypes in the report).
Get-EventLog -LogName Security -after (Get-date -hour 0 -minute 0 -second 0)| ?{(4624,4778) -contains $_.EventID -and $_.Message -match 'logon type:s+(10)s'}| %{
(new-object -Type PSObject -Property @{
TimeGenerated = $_.TimeGenerated
ClientIP = $_.Message -replace '(?smi).*Source Network Address:s+([^s]+)s+.*','$1'
UserName = $_.Message -replace '(?smi).*ssAccount Name:s+([^s]+)s+.*','$1'
UserDomain = $_.Message -replace '(?smi).*ssAccount Domain:s+([^s]+)s+.*','$1'
LogonType = $_.Message -replace '(?smi).*Logon Type:s+([^s]+)s+.*','$1'
})
} | sort TimeGenerated -Descending | Select TimeGenerated, ClientIP `
, @{N='Username';E={'{0}{1}' -f $_.UserDomain,$_.UserName}} `
, @{N='LogType';E={
switch ($_.LogonType) {
2 {'Interactive - local logon'}
3 {'Network connection to shared folder)'}
4 {'Batch'}
5 {'Service'}
7 {'Unlock (after screensaver)'}
8 {'NetworkCleartext'}
9 {'NewCredentials (local impersonation process under existing connection)'}
10 {'RDP'}
11 {'CachedInteractive'}
default {"LogType Not Recognised: $($_.LogonType)"}
}
}}
This method allows you to collect and parse RDP connection logs on a standalone RDSH server. If you have multiple servers in the RDS farm, you can query each of them with this script, or get logs from a management server with the Remote Desktop Connection Broker role.
You can export RDP connection logs from the Event Viewer to a CSV file (for further analysis in an Excel spreadsheet). You can export the log from the Event Viewer GUI (assuming Event Viewer logs are not cleared) or via the command prompt:
WEVTUtil query-events Security > c:psrdp_security_log.txt
Or with PowerShell:
get-winevent -logname "Microsoft-Windows-TerminalServices-LocalSessionManager/Operational" | Export-Csv c:psrdp_connection_log.txt -Encoding UTF8
If your users connect to corporate RDS hosts through the Remote Desktop Gateway, you can check the user connection logs in the Microsoft-Windows-TerminalServices-Gateway log by the EventID 302. For example, the following PowerShell script will display the specified user’s connection history through RD Gateway:
$rdpusername="b.smith"
$properties = @(
@{n='User';e={$_.Properties[0].Value}},
@{n='Source IP Adress';e={$_.Properties[1].Value}},
@{n='TimeStamp';e={$_.TimeCreated}}
@{n='Target RDP host';e={$_.Properties[3].Value}}
)
(Get-WinEvent -FilterHashTable @{LogName='Microsoft-Windows-TerminalServices-Gateway/Operational';ID='302'} | Select-Object $properties) -match $rdpusername
You can check the following RD Gateway user connection events in the Microsoft-Windows-TerminalServices-Gateway event log:
- 300 — The user NAME, on client computer DEVICE, met resource authorization policy requirements and was therefore authorized to connect to resource RDPHOST;
- 302 — The user NAME, on client computer DEVICE, connected to resource RDPHOST;
- 303 — The user NAME, on client computer DEVICE, disconnected from the following network resource: RDPHOST. Before the user disconnected, the client transferred X bytes and received X bytes. The client session duration was X seconds.
You can display the list of current remote sessions on your RDS host with the command:
qwinsta
The command returns the session ID, the USERNAME, and the session state (Active/Disconnect). This command is useful when you need to get the user’s RDP session ID when using shadow Remote Desktop connections.
You can display the list of the running processes in the specific RDP session (the session ID is specified):
qprocess /id:5
Outgoing RDP Connection Logs in Windows
You can also view outgoing RDP connection logs on the client side. They are available in the following event log: Application and Services Logs -> Microsoft -> Windows -> TerminalServices-ClientActiveXCore -> Microsoft-Windows-TerminalServices-RDPClient -> Operational.
For example, EventID 1102 occurs when a user connects to a remote Windows Server RDS host or a Windows 10/11 computer with RDP enabled (desktop Windows editions also support multiple simultaneous RDP connections).
The client has initiated a multi-transport connection to the server 192.168.13.201.
The following RDP script will display the history of RDP client connections on the current computer:
$properties = @(
@{n='TimeStamp';e={$_.TimeCreated}}
@{n='LocalUser';e={$_.UserID}}
@{n='Target RDP host';e={$_.Properties[1].Value}}
)
Get-WinEvent -FilterHashTable @{LogName='Microsoft-Windows-TerminalServices-RDPClient/Operational';ID='1102'} | Select-Object $properties
The script returns the SIDs of the users who initiated RDP connections on this computer, as well as the DNS names/IP addresses of the Remote Desktop hosts that the users connected to. You can convert SIDs to usernames as follows.
- Remove From My Forums
-
Question
-
Hello,
I need to know WHO (IP Address) and WHEN accessed my computer (with remote desktop). is there any log file ? (Windows 7)
Regards
— Mreza
Answers
-
Also take a look here.
Regards, Dave Patrick ….
Microsoft Certified Professional
Microsoft MVP [Windows]Disclaimer: This posting is provided «AS IS» with no warranties or guarantees , and confers no rights.
-
Marked as answer by
MohammadReza Taesiri
Saturday, June 16, 2012 7:08 PM
-
Marked as answer by
All replies
-
Thanks for reply. but i think your link is broken!
Actually there is a computer in front of my eyes, and someone thinks someone else accessed to this computer via Remote Desktop. Is there any log file?
Can I use Event viewer (Windows Logs > Application) to prove someone had access to this computer on specific time (with remote desktop connection).
— Mreza
-
Also take a look here.
Regards, Dave Patrick ….
Microsoft Certified Professional
Microsoft MVP [Windows]Disclaimer: This posting is provided «AS IS» with no warranties or guarantees , and confers no rights.
-
Marked as answer by
MohammadReza Taesiri
Saturday, June 16, 2012 7:08 PM
-
Marked as answer by
-
Thank you very much!
— Mreza
-
You’re welcome.
Regards, Dave Patrick ….
Microsoft Certified Professional
Microsoft MVP [Windows]Disclaimer: This posting is provided «AS IS» with no warranties or guarantees , and confers no rights.
-
Hello.
Is there any similar log in WinXP?
-
Thanks Mike! Working like a charm, and that saved me a lot of headaches, to easily get a simple but informative summary of RDP-sessions.
-
Nice script Mike — thanks.
-
spot on, exactly what I was after!
-
Hi Mike! This is the first script I ran in PowerShell. I just right clicked on the downloaded file and selected Run with PowerShell. How do I retrieve the csv output?
-
I guess you already found it, but in favor of those others who will read this thread later on:
The csv file is saved to the current users desktop on the computer you run the script on.
-
Tnx Dave. this was very useful and helpful
-
Hopefully I can get an answer.
I tried the script but in my output csv file, the ServerName column it lists all the servers I added in the script and not individually. i.e.
ServerName IPAddress
server01, server02, server03 10.1.0.10
I would like it to look like this
User ServerName IPAddress
JohnA Server01 10.1.25.10
SueB server02 10.1.33.10
JackJ server03 10.1.28.10
SueB server01 10.1.33.10
What am I doing wrong with the script, or can I not get this type of format with the script
Update: never mind I figured it out.
-
Edited by
Mrs.PTCruiser
Thursday, October 4, 2018 4:11 PM
-
Edited by
-
Thanks this really helped. I was able to tell the coworker to use a different tool to see the machine. You saved a ton of work.
-
Thanks for the info. My activity log does not show any User name or IP address. What is the solutions for this ?
-
Now this is what I call an answer! I’ve been searching for years for such a solution.
Thank you very much, Mike.
Включаем шифрование RDP
Сессии RDP поддерживают четыре типа шифрования
- RDP Low Encryption — по умолчанию (самый старый режим). Может согласовать шифрование на базе 56-ти битового DES или 40-ка битового RC2. Очень плохой вариант. Например, если включить его, то не включится TLS.
- RDP Client Compatible Encryption — Попробует до 128 бит RC4, но сразу согласится на DES/RC2. Очень плохой вариант. Тоже не совместим с TLS.
- RDP High Encryption — Минимально допустимый режим. Потребует хотя бы 128-ми битовый RC4. Работает со всеми серверами, начиная с Windows 2000 Server w/HEP.
- RDP FIPS140-1 Encryption — Будет поддерживать современные симметричные алгоритмы и в явном виде не будет поддерживать RC2, RC4, одиночный DES, а также будет заставлять использовать для вычисления целостности (Message Authentication Code – MAC) алгоритм SHA-1, а не MD5
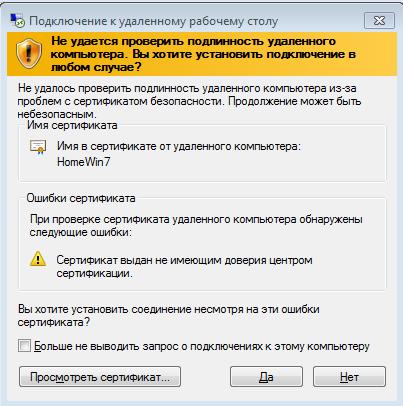
Но в полном объеме шифрование не заработает:
- нет валидного сертификата SSL (самоподписанный сертификат)
- будет ругаться RDP при подключении
- будет ругаться сисадмин в офисе
Но мы делаем временный доступ на две недели и надеемся, что злые боты нас не найдут за это время.
RDP ругается на сертификат…
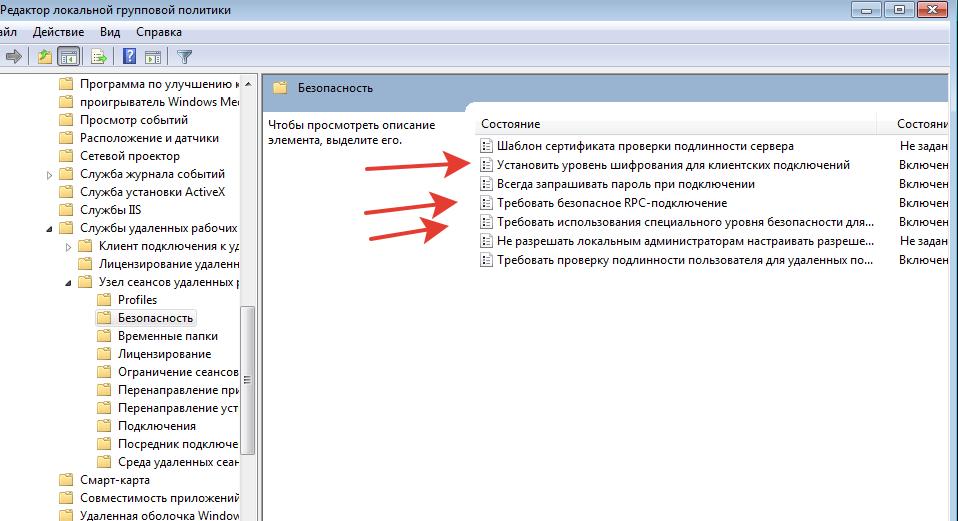
Конфигурация компьютера —> Административные шаблоны —> Компоненты Windows —> Службы удаленных рабочих столов —> Узел сеансов удаленных рабочих столов—>Безопасность
«Установить уровень шифрования для клиентских подключений». Включаем и выбираем «Высокий» уровень. Это нам даст 128-битное шифрование.
Включаем параметр «Требовать безопасное RPC-подключение»
Устанавливаем параметр «Требовать использования специального уровня безопасности для удаленных подключений по методу RDP» в значение «Включено» и Уровень безопасности в значение «SSL TLS 1.0»
Самый максимальный уровень шифрования обеспечивается стандартом FIPS 140-1 (для Windows 7).
Federal Information Processing Standards (FIPS) — Федеральный стандарты по обработке информации. Стандарт компьютерной безопасности правительства США. В настоящее время принят FIPS 140-2.
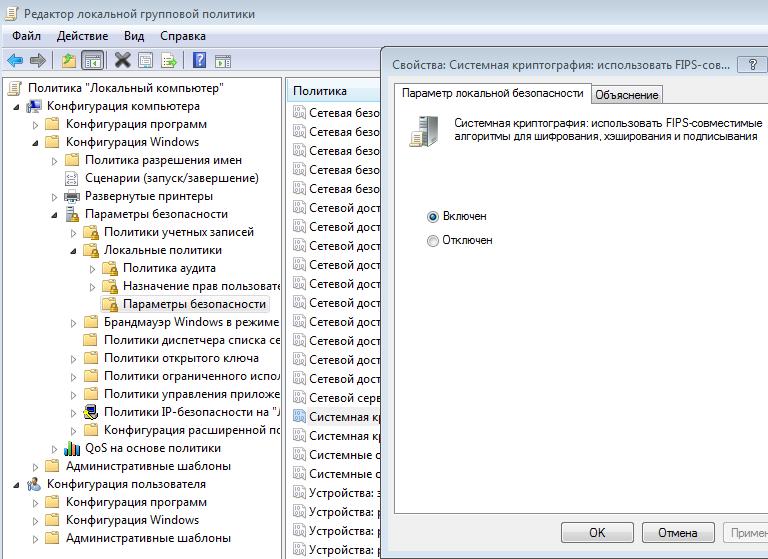
Конфигурация компьютера —> Конфигурация Windows —> Параметры безопасности —> Локальные политики —> Параметры безопасности
Чтобы включить использование FIPS 140-1 — включаем параметр «Системная криптография: использовать FIPS-совместимые алгоритмы для шифрования, хэширования и подписывания»
ВАЖНО: если Вы подключаетесь из Windows XP (или к Windows XP) — не включайте это шифрование, Windows XP ничего не знает про FISP
Подключаем RDP Windows XP из Windows 7
Просмотр логов подключения RDP
Да, Windows ведет подробные логи подключения, только они сильно спрятаны в настройках и немного не очевидны.
Администрирование —> Просмотр событий —> Журналы приложений и служб —> Microsoft —> Windows —> TerminalServices-LocalSessionManager —> Operational
И это общий лог. Для получения списка по конкретным событиям нужно отфильтровать по коду события… Правой клавишей мышки по Operational —> «Фильтр»
- EventID – 21 (Remote Desktop Services: Shell start notification received) означает успешный запуск оболочки Explorer (появление окна рабочего стола в RDP сессии
- EventID – 24 (Remote Desktop Services: Session has been disconnected) – пользователь отключился от RDP сессии.
- EventID – 25 (Remote Desktop Services: Session reconnection succeeded) – пользователь переподключился к своей имеющейся RDP сессии на сервере.
- EventID – 39 (Session <A> has been disconnected by session <B>) – пользователь сам отключился от своей RDP сессии, выбрав соответствующий пункт меню (а не просто закрыл окно RDP клиента). Если идентификаторы сессий разные, значит пользователя отключил другой пользователь (или администратор).
- EventID – 40 (Session <A> has been disconnected, reason code <B>). Здесь нужно смотреть на код причины отключения в событии. Например:
- reason code 0 (No additional information is available)– обычно говорит о том, что пользователь просто закрыл окно RDP клиента.
- reason code 5 (The client’s connection was replaced by another connection) – пользователь переподключился к своей старой сессии.
- reason code 11 (User activity has initiated the disconnect) – пользователь сам нажал на кнопку Disconnect в меню
Что бы посмотреть все входы RDP — в фильтре пишем 21,25
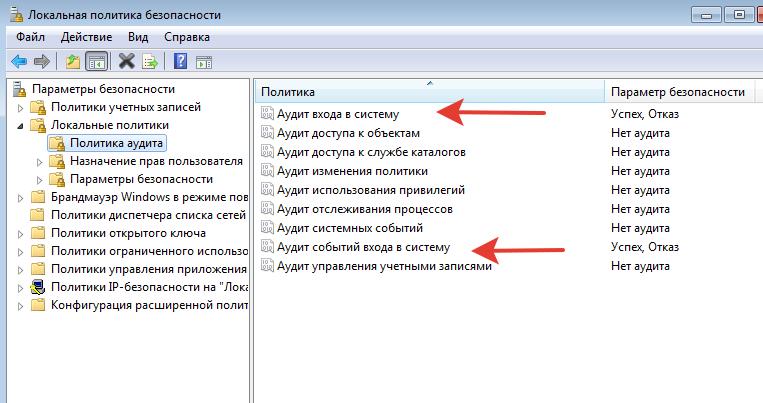
Так, а где IP входа? По умолчанию аудит IP отключен. Идем в настройки политик безопасности secpol.msc
Включаем регистрацию Успеха и Отказа
Вот тут читаем подробнее (+защита от перебора IPBan для Wondows)
Защищаем RDP сервер от перебора паролей с блокировкой по IP
Для создания сложностей ботам (подбор паролей на порту 3389) используем
Классический вход в Windows
Почитать в разделе
RDP

Версия 7 (вышла в составе Windows 7, поддерживается в Windows XP, где по умолчанию в данной версии установлена 6.1)
Версия 7.1…
(Читать полностью…)
- Всего статей в разделе: 8
- Показано статей в списке: 7
- Сортировка: название по алфавиту
Борьба с “крестиком” терминального сеанса RDP
Вообще убрать панель от пользователя – в настройках при создании удаленного рабочего стола (выход только через завершение сеанса) Убрать сам “крестик” (выход только через завершение сеанса)
Есть специальная программа, которая крестик убирает. Смотреть здесь. И будет вот так 
(пункты 1 и 2 могут…
(Читать полностью…)
Как включить звук при подключении RDP
Настройки звука на целевом компьютере RDP
Для начала нам необходима служба
Проверка работы службы Windows Audio
«Пуск» — «Администрирование» — «Службы», в списке находите «Windows Audio» и два раза кликаем по ней. В настройках службы нужно установить «Тип запуска — Автоматически», «применить» и затем и можно сразу же запустить службу с помощью соответствующей кнопки ВАЖНО: если служба Windows Audio не запускается — убедитесь, что включены и запущены…
(Читать полностью…)
Настраиваем RDP (remote desktop protocol)

Порты сервера и их основная защита Для долговременной удаленной работы необходимо использовать: или создать VPN-тунель и уже внутри него подключаться через RDP
или использовать профессиональные средства сервер-клиент типа RAdmin Для быстрого подключения из дома к ПК на работе читаем статью Подключаем компьютер к рабочему ПК…
(Читать полностью…)
Переключение языков при RDP
языковая раскладка Проблема возникает, если язык клиентской машины перед подключением к RDP не совпадает с языком по умолчанию в серверной машине. Например вводите пароль из английских букв и не переключая языка конектитесь к серверу терминалов, на котором по умолчанию русский язык — получите необходимость «двойного» переключения языка и раскладки. Можно…
(Читать полностью…)
Подключаем RDP Windows XP из Windows 7
Для подключения через RDP нам нужна Windows XP Professional SP3
Да, на форумах полно советов, как из Home сделать Professional. Не верьте. Все советы касаются изменений в реестре. И да — система будет показывать, что она теперь Professional — но это только…
(Читать полностью…)
Подключаем компьютер к рабочему ПК через RDP (Windows 7)

некоторые провайдеры меняют IP один раз в месяц В крайнем случае (если очень надо) — можно купить услугу «выделенный IP» и адрес от провайдера не будет меняться. А наш домашний ПК — он там, за интернетом — в свой локальной сети. Можно подключиться из дома к рабочему компьютеру в локальной сети офиса через RDP: …
(Читать полностью…)
Формат файла RDP

Структура файла RDP
screen mode id:i: — 1 — удаленный сеанс выполняется в оконном режиме, 2 — в полноэкранном. Редактируется на вкладке ”Экран” окна ”Параметры” средства ”Подключение к удаленному рабочему столу”. use multimon:i: — 0 — запрет поддержки нескольких мониторов, 1 — разрешение поддержки…
(Читать полностью…)
In this article we will take a look at the features of Remote Desktop Protocol (RDP) connection auditing and log analysis in Windows. Typically, it is useful when investigating various incidents on Windows servers when a system administrator is required to provide information about what users logged on to the server, when he logged on and off, and from which device (name or IP address) the RDP user was connecting.
Remote Desktop Connection Events
Like other events, the Windows RDP connection logs are stored in the event logs. The Windows logs contain a lot of information, but it can be difficult to find the right event quickly. When a user remotely connects to a Windows server, many events are generated in the Windows logs. We will take a look at the following:
- Network Connection
- Authentication
- Logon
- Session Disconnect/Reconnect
- Logoff
Network Connection Events
Network Connection connects user’s RDP client with the Windows server. That logs EventID – 1149 (Remote Desktop Services: User authentication succeeded). The presence of this event does not indicate successful user authentication. This log can be found at Applications and Services Logs ⇒ Microsoft ⇒ Windows ⇒ Terminal-Services-RemoteConnectionManager ⇒ Operational. You can filter this log by right clicking on Operational log ⇒ Selecting “Filter Current Log” and type in EventID 1149.
The result is a list with the history of all network RDP connections to this server. As you can see, the log file contains the username, domain (When Network Level Authentication (NLA) authentication is used), and IP address of the computer from which the RDP connection is made.
Authentication Events
User authentication can be successful or unsuccessful on the server. Navigate to Windows logs ⇒ Security. We are interested in logs with EventID – 4624 (An account was successfully logged on) or 4625 (An account failed to log on). Pay attention to the LogonType value in the event. LogonType – 10 or 3 indicates a new logon to the system. If LogonType is 7, it indicates re-connection to an existing RDP session.
The username of the connecting account is written in the Account Name field, his computer name is written in Workstation Name, and the IP address in Source Network Address.
Take a look at TargetLogonID field, which is a unique user session identifier that can be used to track further activity of this user. However, if a user disconnects from the RDP session and reconnects to the session again, the user will be issued a new TargetLogonID (although the RDP session remains the same).
You can get a list of successful authentication events over RDP (EventID 4624) using the following PowerShell command:
Get-EventLog security -after (Get-date -hour 0 -minute 0 -second 0) | ?{$_.eventid -eq 4624 -and $_.Message -match 'logon type:s+(10)s'} | Out-GridView
Logon Events
RDP logon is the event that appears after successful user authentication. Log entry with EventID – 21 (Remote Desktop Services: Session logon succeeded). This log can be found in Applications and Services Logs ⇒ Microsoft ⇒ Windows ⇒ TerminalServices-LocalSessionManager ⇒ Operational. As you can see here you can see the RDP Session ID for the user.
“Remote Desktop Services: Shell start received” details in EventID 21 means that the Explorer shell has been successfully launched in the RDP session.
Session Disconnect and Reconnect Events
Session Disconnect/Reconnect events have different codes depending on what caused the user to end the session, for example disable by inactivity, selecting “Disconnect” in Start menu, RDP session drop by another user or administrator, etc. These events can be found in Applications and Services Logs ⇒ Microsoft ⇒ Windows ⇒ TerminalServices-LocalSessionManager ⇒ Operational. Let’s take a look at the RDP events that may be of interest:
- EventID – 24 (Remote Desktop Services: Session has been disconnected) – the user has disconnected from the RDP session.
- EventID – 25 (Remote Desktop Services: Session reconnection succeeded) – The user has reconnected to his existing RDP session on the server.
- EventID – 39 (Session A has been disconnected by session B) – user disconnected from his RDP session by selecting the appropriate menu item (not just closed the RDP client window by clicking on “x” in the top right corner). If the session IDs are different, then the user has been disconnected by another user or administrator.
- EventID – 40 (Session A has been disconnected, reason code B). Here you should look at the reason code for the disconnection in the event. For example:
- Reason code 0 (No additional information is available) – usually indicates that the user just closed the RDP client window.
- Reason code 5 (The client’s connection was replaced by another connection) – the user re-connected to his old session.
- Reason code 11 (User activity has the disconnect) – the user clicked the Disconnect button on the menu.
- EventID – 4778 in Windows log ⇒ Security (A session was reconnected to a Window Station). The user re-connected to an RDP session (the user is given a new LogonID).
- EventID 4799 in Windows Logon ⇒ Security (A session was reconnected to a Window Station). Disconnection from an RDP session.
Logoff Events
Logoff logs track the user disconnection from the system. In the Applications and Services Logs ⇒ Microsoft ⇒ Windows ⇒ TerminalServices-LocalSessionManager ⇒ Operational logs we can find EventID 23. In this case in Security log we need to search for EventID 4634 (An account was logged off).
Event 9009 (The Desktop Window Manager has exited with code (x)) in the System log shows that the user initiated the end of the RDP session and the user’s window and graphical shell were terminated. Below is a small PowerShell that uploads the history of all RDP connections for the current day from the Remote Desktop Service server. The table below shows the connection time, client IP address, and RDP username (you can include other logon types in the report if necessary).
Get-EventLog -LogName Security -after (Get-date -hour 0 -minute 0 -second 0)| ?{(4624,4778) -contains $_.EventID -and $_.Message -match 'logon type:s+(10)s'}| %{
(new-object -Type PSObject -Property @{
TimeGenerated = $_.TimeGenerated
ClientIP = $_.Message -replace '(?smi).*Source Network Address:s+([^s]+)s+.*','$1'
UserName = $_.Message -replace '(?smi).*Account Name:s+([^s]+)s+.*','$1'
UserDomain = $_.Message -replace '(?smi).*Account Domain:s+([^s]+)s+.*','$1'
LogonType = $_.Message -replace '(?smi).*Logon Type:s+([^s]+)s+.*','$1'
})
} | sort TimeGenerated -Descending | Select TimeGenerated, ClientIP `
, @{N='Username';E={'{0}{1}' -f $_.UserDomain,$_.UserName}} `
, @{N='LogType';E={
switch ($_.LogonType) {
2 {'Interactive - local logon'}
3 {'Network conection to shared folder)'}
4 {'Batch'}
5 {'Service'}
7 {'Unlock (after screensaver)'}
8 {'NetworkCleartext'}
9 {'NewCredentials (local impersonation process under existing connection)'}
10 {'RDP'}
11 {'CachedInteractive'}
default {"LogType Not Recognised: $($_.LogonType)"}
}
}}
Exporting RDP logs
Sometimes it is needed to export RDP logs into Excel table, in this case you can upload any Windows log to a text file and afterwards import it into Excel. You can export the log from the Event Viewer console or from the command line:
WEVTUtil query-events Security > c:pssecurity_log.txt
Or:
get-winevent -logname "Microsoft-Windows-TerminalServices-LocalSessionManager/Operational" | Export-Csv c:psrdp-log.txt -Encoding UTF8
A list of the current RDP sessions on the server can be displayed as a command “Qwinsta”
The command returns as session identifier, username and status (Active/Disconnect). This command is useful when you need to determine the RDP session ID of a user during a shadow connection.
After defining a Session ID you can list running processes in a particular RDP session:
So here are the most common ways to view RDP connection logs in Windows.