На днях мне в руки попал экземпляр Windows Server 2016 Essentials. Для тех, кто не в курсе, Essentials — это редакция Windows Server, специально предназначенная для использования в небольших организациях. Она входит в линейку серверных операционных систем Microsoft, однако имеет некоторые особенности, о которых мы сегодня и поговорим.
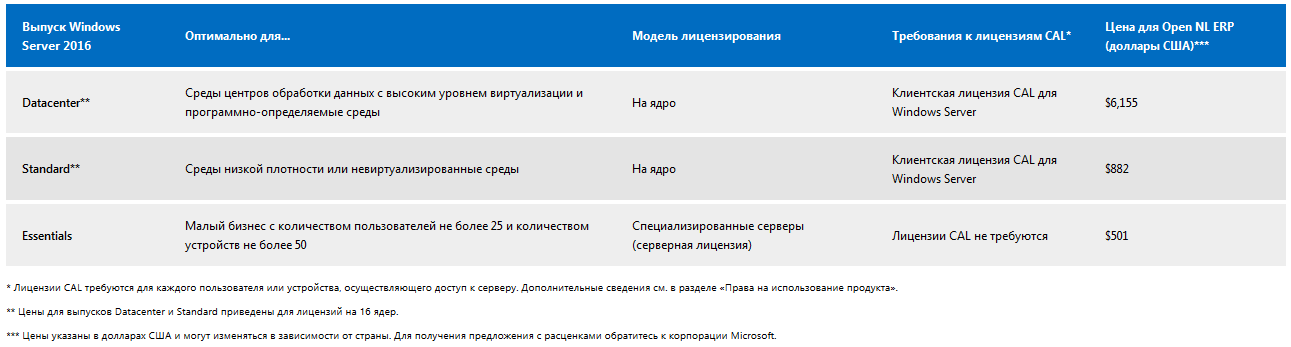
Для наглядности рассмотрим таблицу сравнения основных редакций Windows Server 2016, взятую с сайта Microsoft. Как видно из нее, ключевое отличие Essentials заключается в схеме лицензирования:
• Редакции Standard и Datacenter лицензируются по количеству физических ядер процессора, а для доступа к серверу требуются клиентские лицензии CAL;
• Редакция Essentials лицензируется на сервер и не требует наличия клиентских лицензий, а на количество подключений действует фиксированное ограничение в 25 пользователей50 устройств.
Есть несколько сценариев использования Windows Server Essentials. Предполагаемый по умолчанию — это первый (и единственный) сервер в небольшой организации. С него и начнем.
Установка в качестве первого сервера
Установка Essentials возможна как на физический сервер, так и в качестве виртуальной машины на Hyper-V. Независимо от варианта установки на сервере должно быть не более 2-х физических процессоров и максимум 64 Гб оперативной памяти.
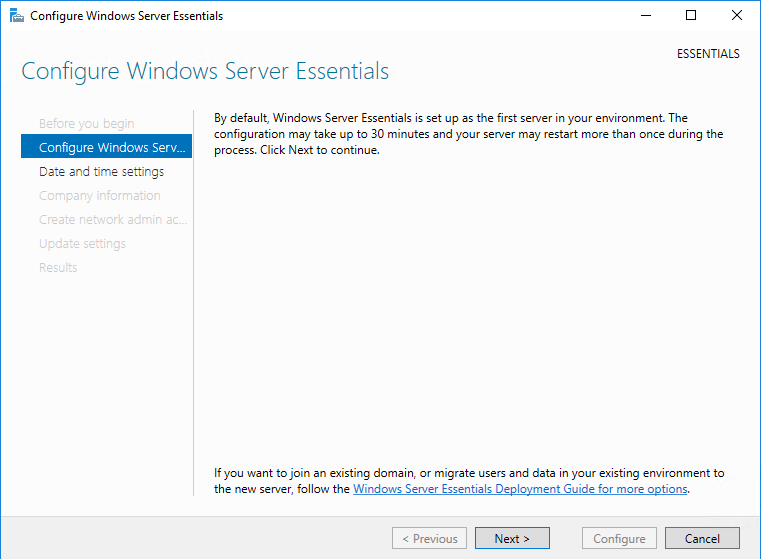
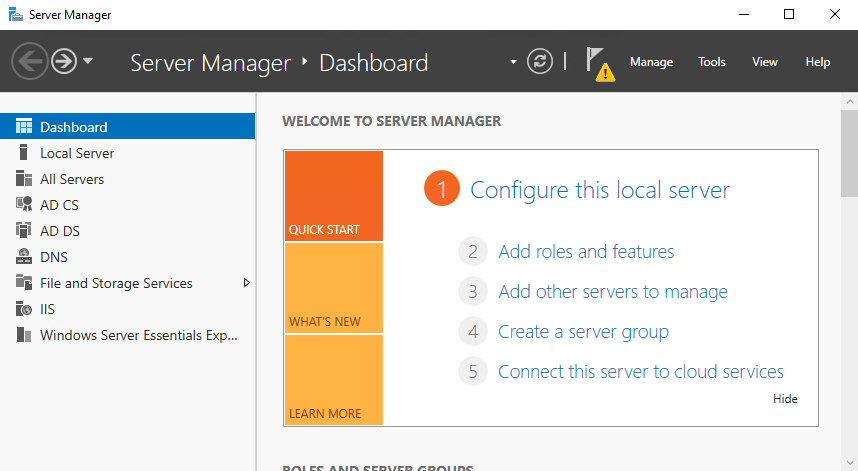
Сама процедура установки операционной системы ничем не отличается от обычной, все самое интересное начинается позднее. Сразу после установки автоматически запускается мастер настройки, с помощью которого и происходит превращение обычного сервера в Windows Server Essentials.
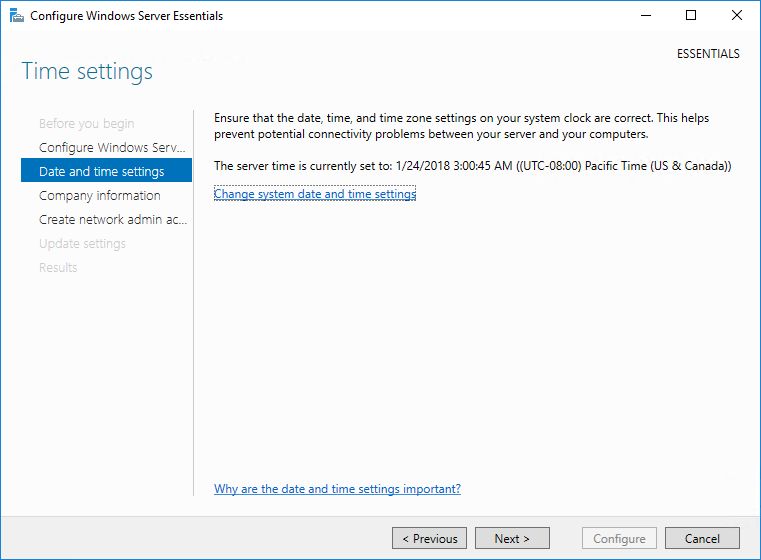
Первым делом мастер предлагает настроить дату, время и выбрать часовой пояс.
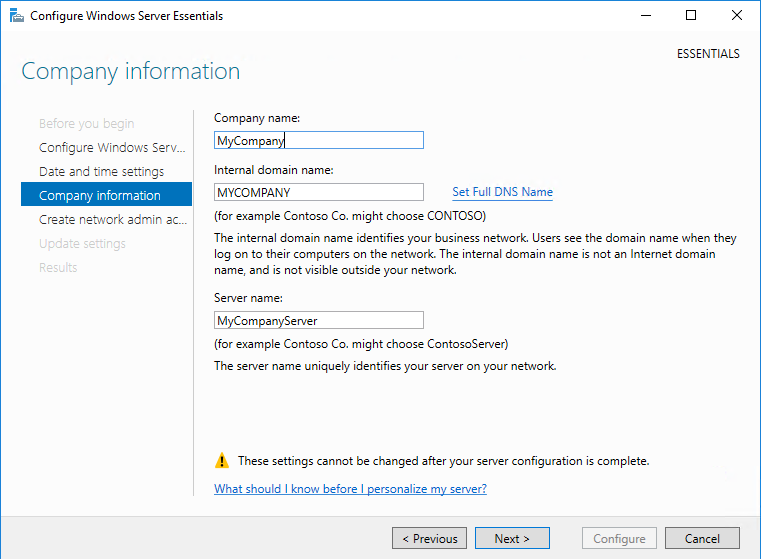
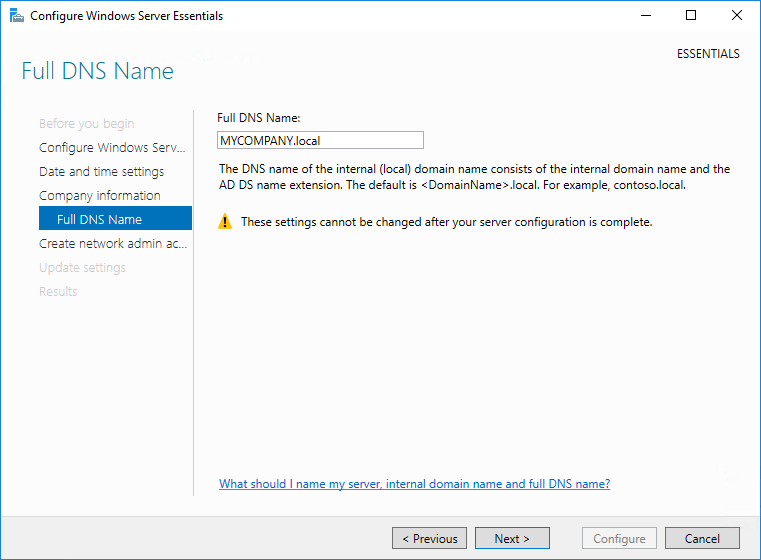
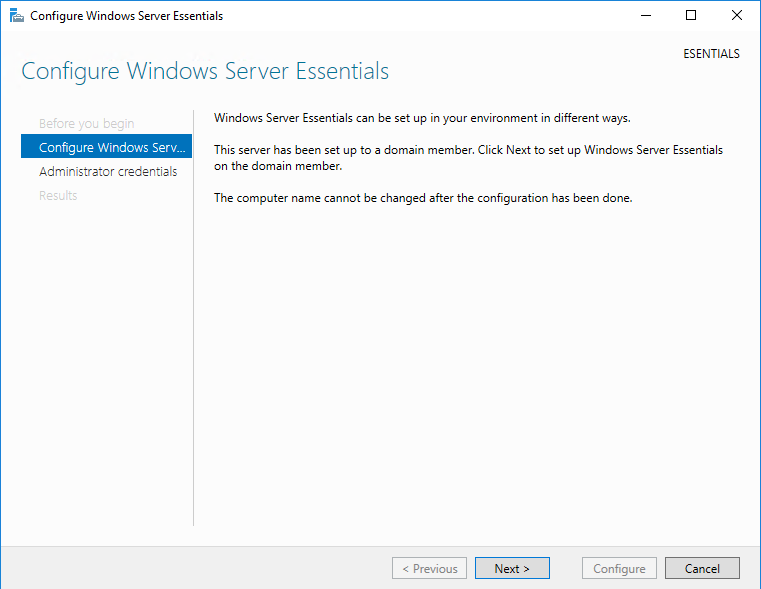
В следующем окне надо ввести информацию о компании. Этот этап очень важен, поскольку в процессе подготовки будет создан домен Active Directory, а указанное имя будет выбрано в качестве имени домена. Изменить эти настройки позже не получится, поэтому к выбору имени надо подходить серьезно.
Если нажать на ссылку «Set Full DNS Name», то появится дополнительное окно для указания полного доменного имени. По умолчанию используется имя DomainName.local.
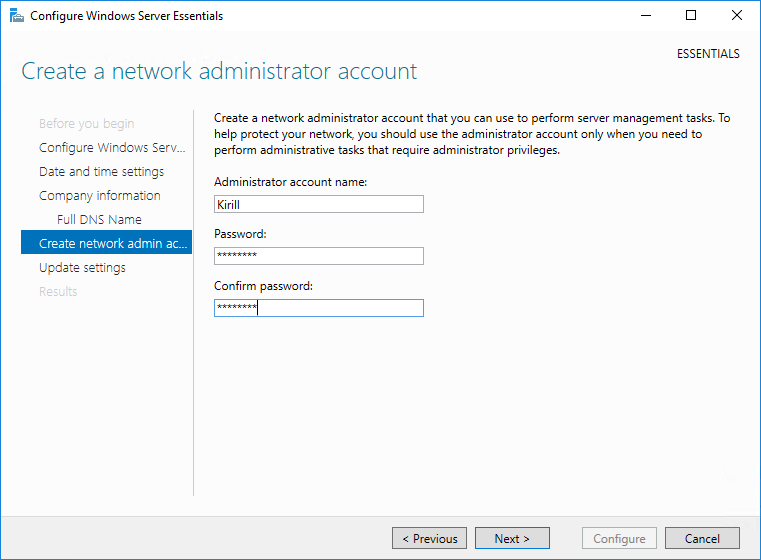
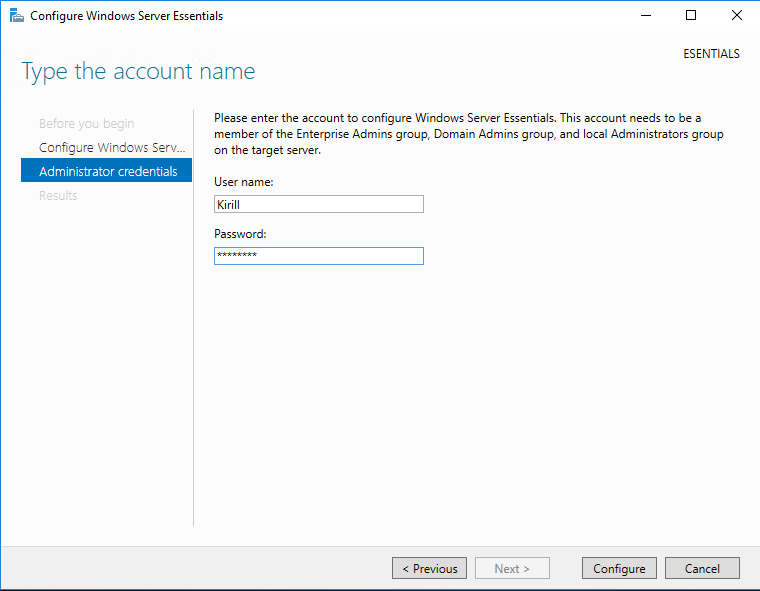
Затем надо задать учетные данные пользователя, который будет иметь административные права на сервере. Обратите внимание, что после окончания работы мастера все ранее созданные на сервере пользователи будут недоступны.
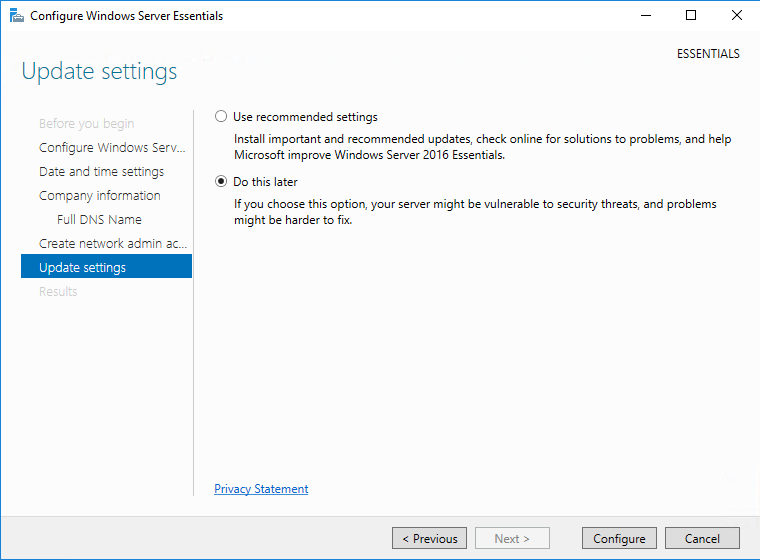
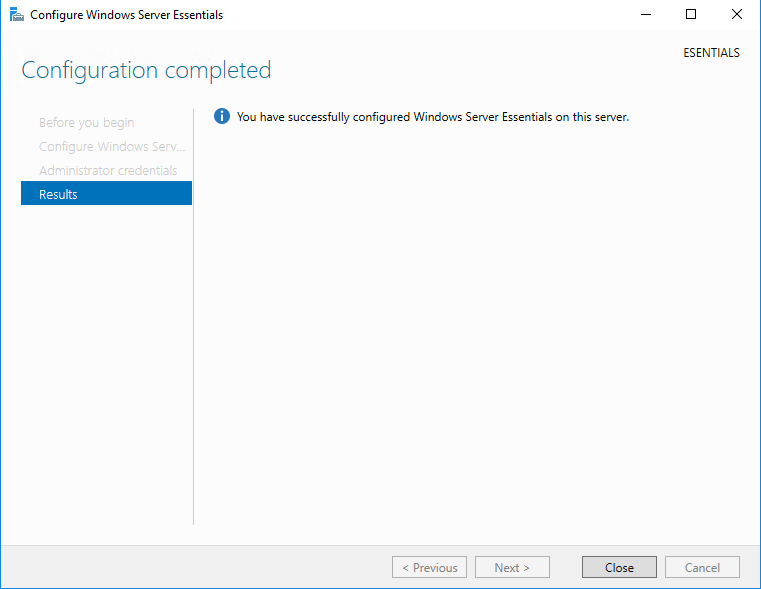
В завершение требуется выбрать настройки автоматического обновления. Здесь можно просто согласиться с рекомендованными параметрами или отложить настройку на потом. На этом этапе можно вернуться назад и поменять введенные настройки, например изменить имя домена или учетные данные администратора. Если же вы уверены в своих действиях, то надо нажать кнопку «Configure»
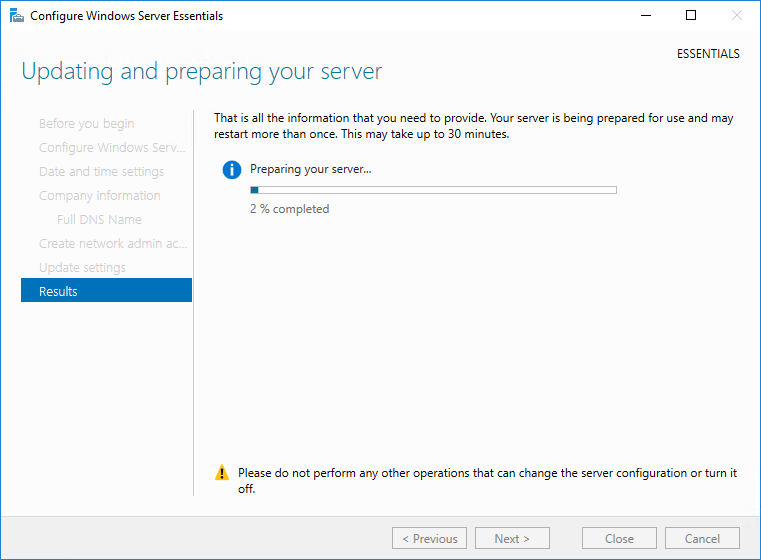
и дождаться окончания настройки. Процесс достаточно длительный и занимает от 10 до 30 минут, в зависимости от быстродействия сервера. В процессе сервер несколько раз перезагружается.
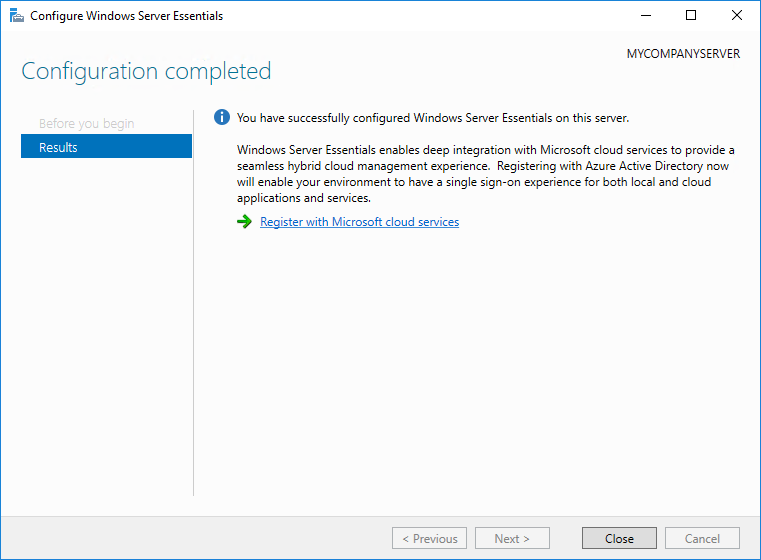
По окончании настройки можно сразу зарегистрировать сервер в облачных сервисах Microsoft.
Процедура настройки выглядит несерьезной, но это только на первый взгляд. На самом деле в процессе настройки на сервер устанавливаются роли доменного контроллера, сервера DNS, центра сертификации, файлового сервера, веб-сервера, роль Windows Server Essentials Experience и еще много всего по мелочи. Что примечательно, изменить набор устанавливаемых компонентов невозможно.
Установка в качестве рядового сервера в домене
Если у вас уже имеется домен Active Directory и вы зачем то хотите установить Windows Server Essentials в качестве рядового сервера, то сначала необходимо добавить сервер в домен и только после этого запускать мастер настройки. При этом процедура настройки сокращается до минимума.
Надо только указать учетные данные пользователя для подключения к домену и запустить настройку. Обратите внимание, что указанный пользователь должен быть членом группы Enterprise Admins.
При таком варианте настройки на сервер устанавливаются все те-же компоненты, кроме роли доменного контроллера и DNS-сервера.
Панель управления
Кроме стандартных оснасток в Windows Server Essentials имеется специальная панель Windows Server Essentials Dashboard, которая становится доступной после завершения работы мастера. Эта панель предназначена для управления сервером и является отличительной чертой Essentials, поэтому рассмотрим ее поподробнее.
Внешне панель напоминает оснастку Server Manager, однако по своей сути кардинально от нее отличается. Предполагается, что редакция Essentials будет использоваться в небольших компаниях или филиалах, где зачастую отсутствуют квалифицированные системные администраторы, а управление сервером осуществляет сотрудник, более-менее знакомый с IT. Поэтому задача панели управления — предоставить максимально простой и быстрый доступ к наиболее важным функциям сервера.
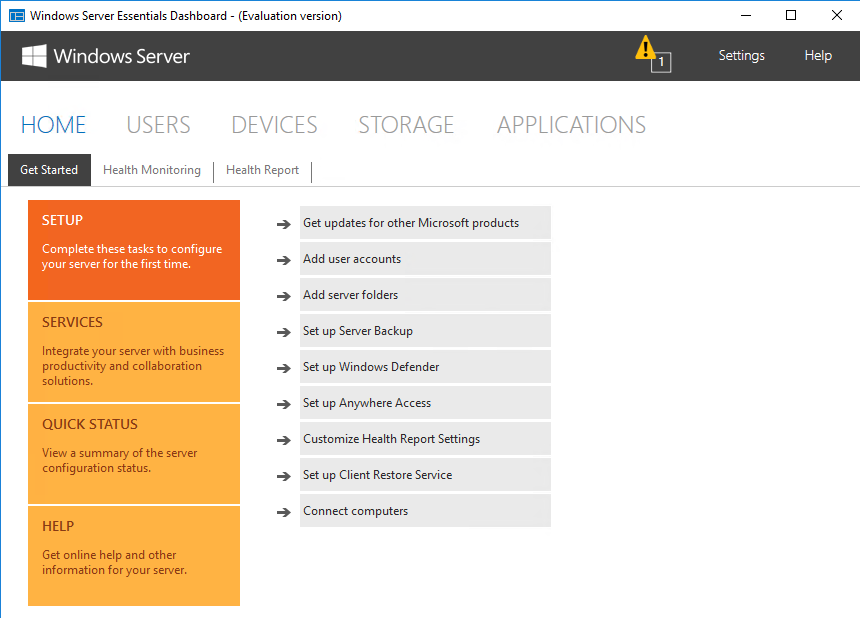
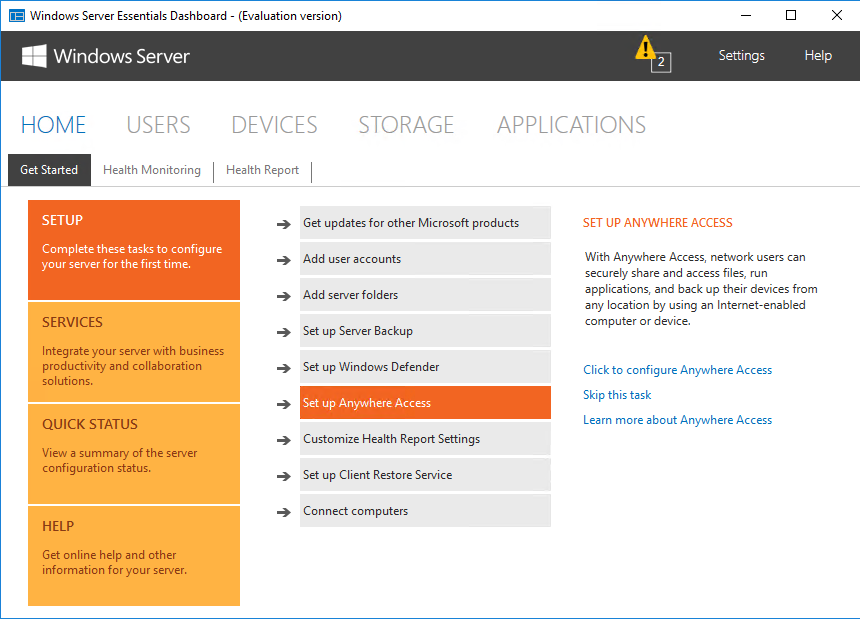
Панель состоит из нескольких основных разделов. Большинство разделов пересекаются между собой и ссылаются друг на друга. При запуски панели открывается домашний раздел, в котором имеется несколько вкладок. На вкладке «Setup» находятся ссылки на некоторые базовые настройки сервера. Все настройки производятся с помощью мастеров, достаточно только перейти на нужную вкладку и нажать на ссылку.
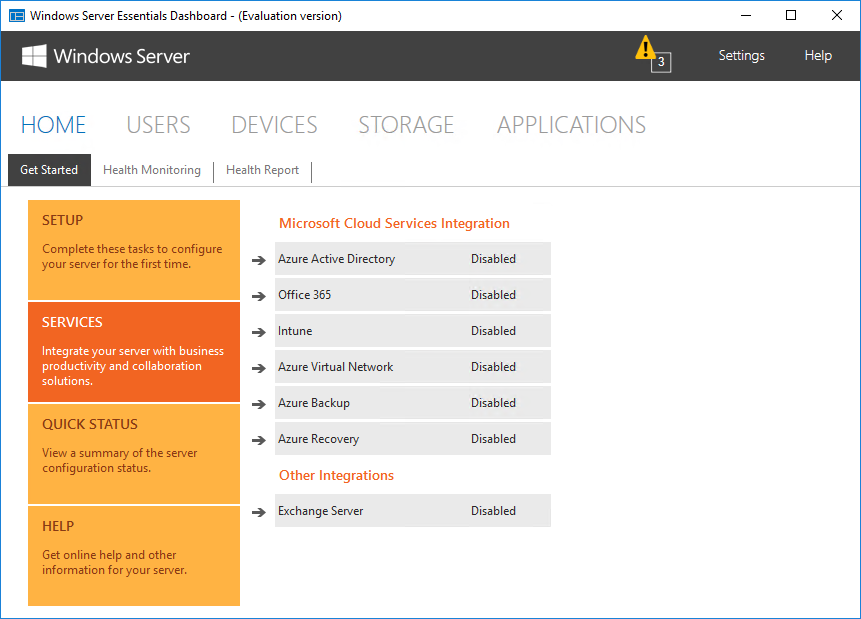
Windows Server 2016 Essentials можно интегрировать с облачными сервисами Microsoft, такими как Azure или Office 365. На вкладке «Services» показано состояние этих служб и отсюда же можно подключиться к нужной службе, при наличии активной подписки. После подключения службой можно управлять напрямую из консоли управления, это является особенностью Essentials.
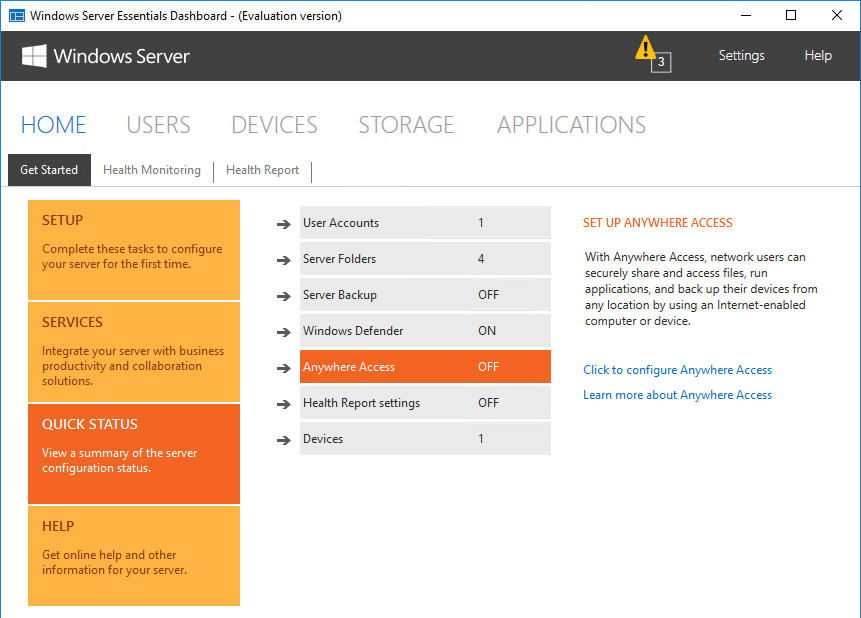
На вкладке «Quick Status» можно оперативно посмотреть текущее состояние сервера — количество пользователей и устройств, общие папки, состояние резервного копирования и т.п.
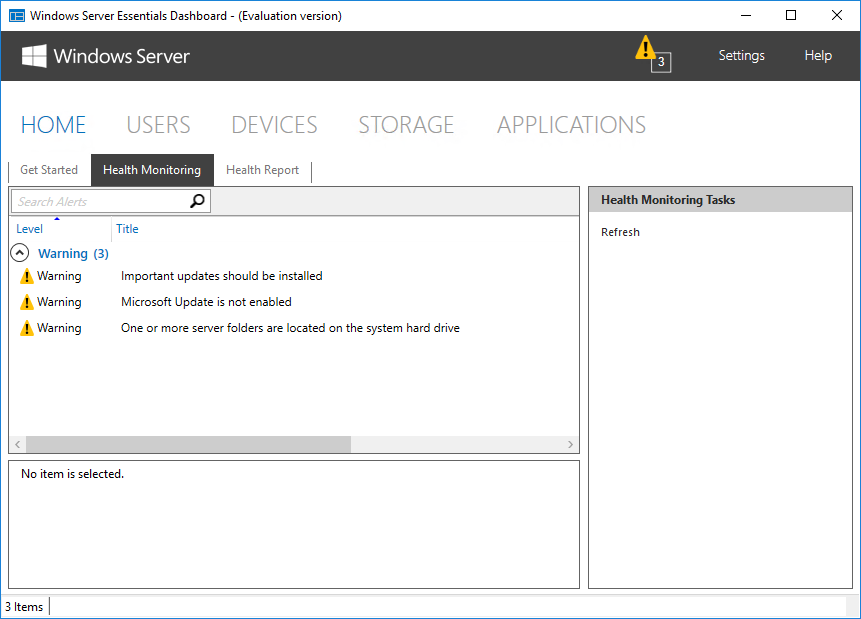
В подразделе «Health Monitoring» показаны сообщения системы о наличии проблем в работе сервера.
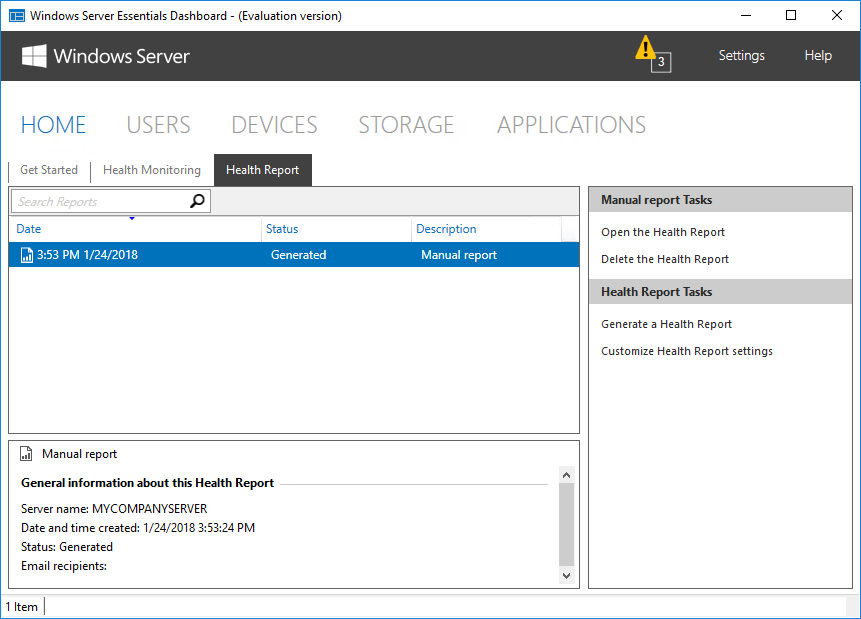
А в подразделе «Health Report» есть возможность получить отчет о состоянии сервера. В отчет входят в основном сообщения из предыдущего раздела, но с более подробным описанием. Отчет можно сгенерировать вручную или настроить создание по расписанию. Также при необходимости готовый отчет может отправляться на указанные адреса e-mail.
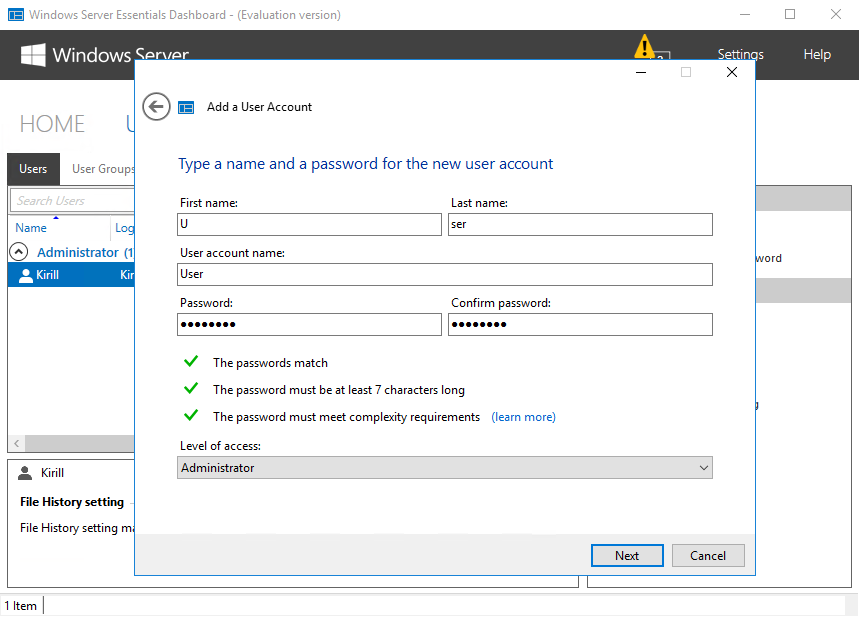
Переходим к следующему разделу «Users». Из этого раздела можно управлять пользователями и группами (создавать, удалять и т.п.) а также настраивать политику паролей (длина, сложность и т.п.).
Надо сказать, что поскольку интерфейс управления рассчитан на ″неискушенного″ пользователя и сильно упрощен, некоторые важные моменты в нем просто отсутствуют. К примеру при создании нового пользователя доступно только два уровня доступа — Standard User и Administrator. При этом Administrator означает, что пользователь будет добавлен не куда нибудь, а в группу администраторов домена.
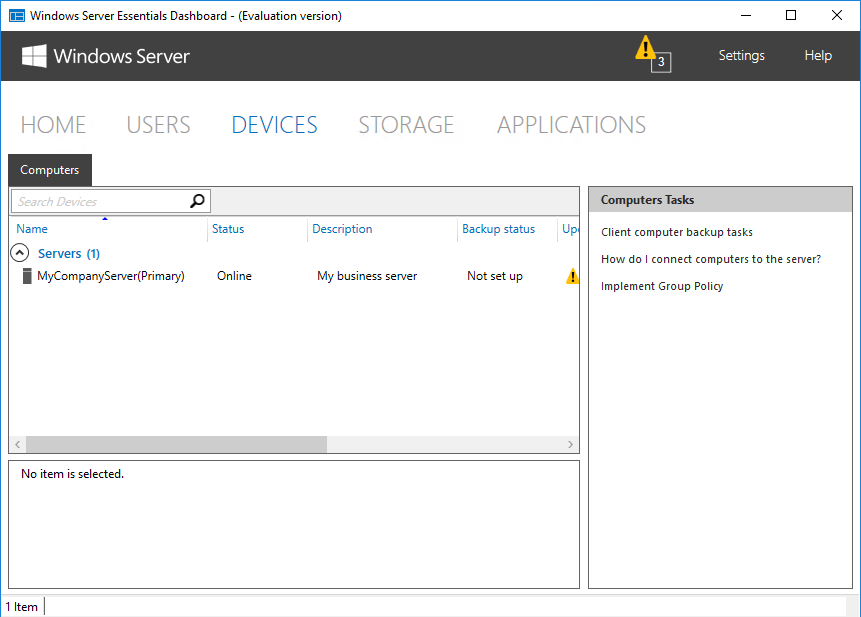
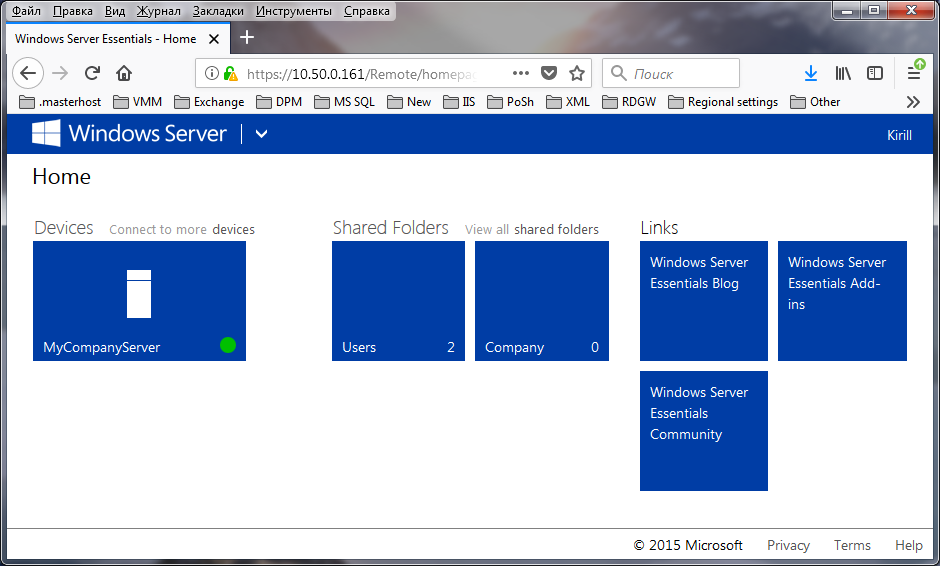
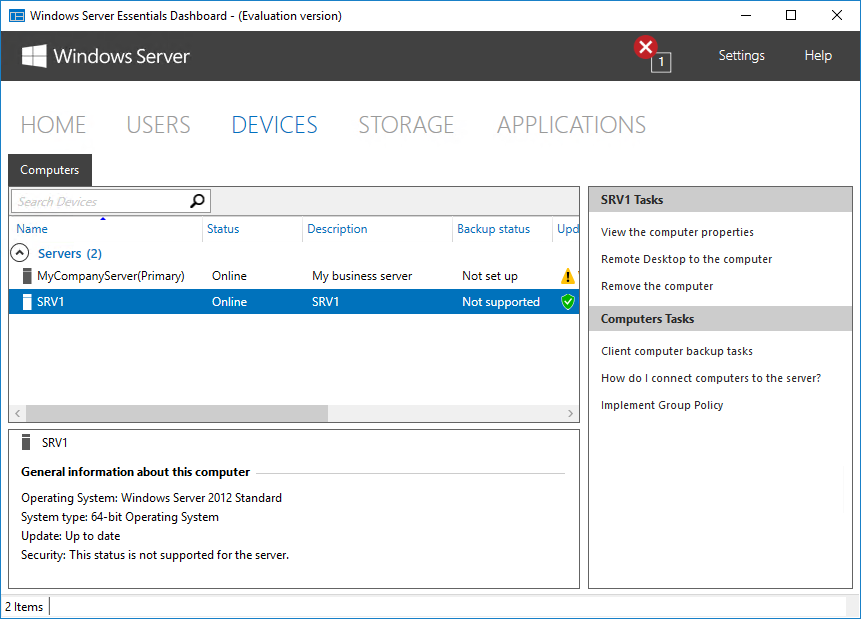
В разделе «Devices» отображаются компьютеры, подключенные к данному серверу. Чуть позже я расскажу о том, что представляет из себя процедура подключения.
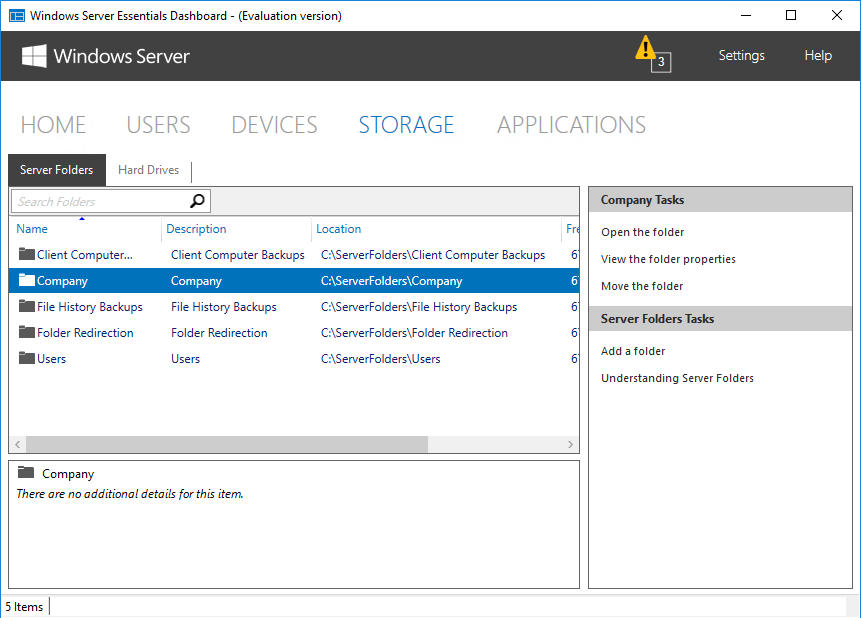
В разделе «Storage» показаны общие папки и жесткие диски, имеющиеся на сервере. Поддерживается технология Storage Spaces и при наличии на сервере нескольких физических дисков на базе Windows Server Essentials можно собрать отказоустойчивое файловое хранилище.
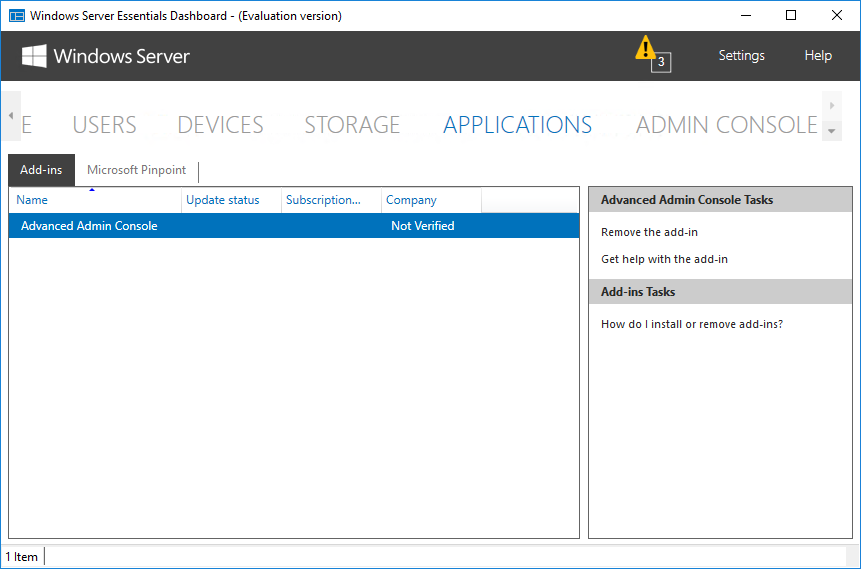
В разделе «Applications» должны отображаться специальные приложения, установленные на сервере.
Приложения эти представляют из себя дополнения для стандартного функционала для Windows Server Essentials. Их можно найти в Центре партнеров Microsoft (бывший Microsoft Pinpoint), на сайтах разработчиков либо написать самому, с помощью Windows Server Essentials SDK.
В качестве примера я установил приложение Advanced Admin Console, предназначенное для администрирования сервера. Как видите, приложения интегрируются в консоль управления и расширяют ее функциональность.
Удаленный доступ
Одна из интересных возможностей Windows Server Essentials является функция под ″скромным″ названием повсеместный доступ (Anywhere Access). Эта функция обеспечивает удаленный доступ к данным и приложениям с помощью веб-браузера. По умолчанию Anywhere Access не включен и перед тем, как его использовать, необходимо произвести настройку. Настройка осуществляется с помощью мастера, который запускается по ссылке на вкладке «Setup».
Примечание. Для настройки Anywhere Access в обязательном порядке требуется наличие SSL-сертификата.
Подключение снаружи осуществляется по адресу https://DomainName/Remote, а при подключении внутри локальной сети https://ServerName/Remote.
Надо сказать, что веб-консоль не особо функциональна, в основном ее можно использовать для управления файлами и папками, находящимися на сервере. Однако большим плюсом консоли является то, что доступ к файлам можно осуществить практически с любого устройства, на котором имеется подключение к сети и веб-браузер.
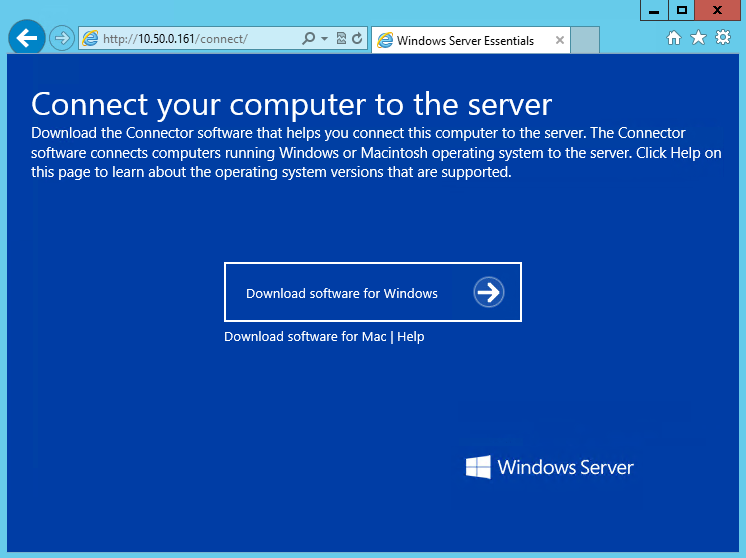
Подключение компьютера
Подключение компьютера — одна из эксклюзивных функций Essentials. Подключить можно клиентские и серверные ОС Windows, а также MacOS. Для подключения необходимо зайти по адресу http://ServerName/connect, загрузить коннектор и установить его на подключаемый компьютер.
После установки и настройки коннектора подключенный компьютер появляется в панели управления и мы можем посмотреть его свойства и состояние некоторых компонентов. Также для каждого подключенного устройства автоматически настраивается резервное копирование. Ну и еще можно подключиться к выбранному компьютеру по RDP прямо из панели управления.
А теперь рассмотрим некоторые интересные моменты, которые отсутствуют в официальной документации.
Без настройки
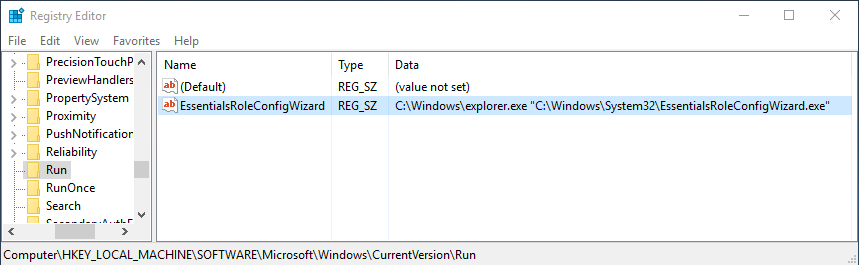
Первый вопрос, который возник у меня — можно ли использовать Windows Server Essentials как обычный сервер? Технически можно, для этого достаточно отменить процедуру настройки. Мастер настройки представляет собой обычный исполняемый файл с именем EssentialsRoleConfigurationVizard.exe, находящийся в папке C:WindowsSystem32. Автоматический запуск мастера обеспечивается с помощью ключа реестра EssentialsRoleConfigurationVizard в разделе HKLMSoftwareMicrosoftWindowsCurrentVersionRun и для отмены запуска достаточно удалить этот ключ.
После этого сервером вполне можно пользоваться, но без настройки не запустится панель управления и, соответственно, все эксклюзивные возможности Windows Server Essentials будут недоступны. Кроме того возможно, что подобное поведение нарушает лицензионное соглашение.
Ограничения
Редакция Essentials отличается от остальных редакций Windows наличием некоторых ограничений. Это очень важный момент, поэтому рассмотрим эти ограничения поподробнее.
Приложения
Windows Server Essentials никак не ограничена в установке приложений и на данную редакцию вполне можно устанавливать такие серверные приложения как Exchange, SQL Server и т.п. Однако при этом необходимо помнить, что редакция Essentials поддерживает не более 2-х физических процессоров и максимум 64 Гб оперативной памяти. Если лимит на процессоры не особо ограничивает сервер по производительности, то с памятью все гораздо хуже. 64 Гб ОЗУ для сервера это крайне мало, поэтому на базе Essentials не получится создать более-менее производительное решение. Обойти это ограничение невозможно, сколько бы памяти не было установлено в сервере, доступно системе будет не более 64Гб.
Роли сервера
В Windows Server 2016 Essentials доступен весь базовый функционал Windows Server. Отсутствуют все новые фичи виртуализации, такие как контейнеры или нано-сервер, но роль Hyper-V установить можно. Хотя при ограничении на количество памяти использование Essentials как сервер виртуализации не имеет особого смысла.
Отдельно стоит упомянуть о ролях RDS (Remote Desktop Services). Эти роли доступны для выбора и их все можно установить на сервер. Однако редакция Essentials ограничена всего 2 подключениями по RDP и это ограничение никак нельзя обойти. Даже если установить на сервер роль RDP-сервера и навесить на него терминальные лицензии, количество возможных подключений не увеличится.
Дело в том, что для подключения по RDP необходимо наличие клиентских лицензий (CAL), а Essentials не использует клиентские лицензии. Это обстоятельство исключает возможность использования Windows Server Essentials в качестве сервера RDS.
Пользователи и устройства
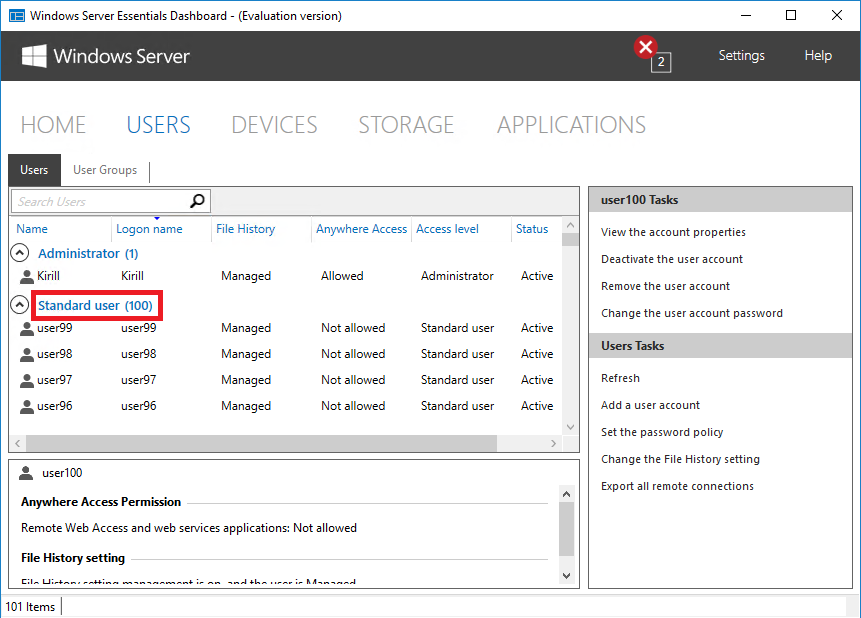
Редакция Essentials отличается наличием ограничения на 25 пользователей50 устройств. Но что именно означают эти ограничения и можно ли их обойти?
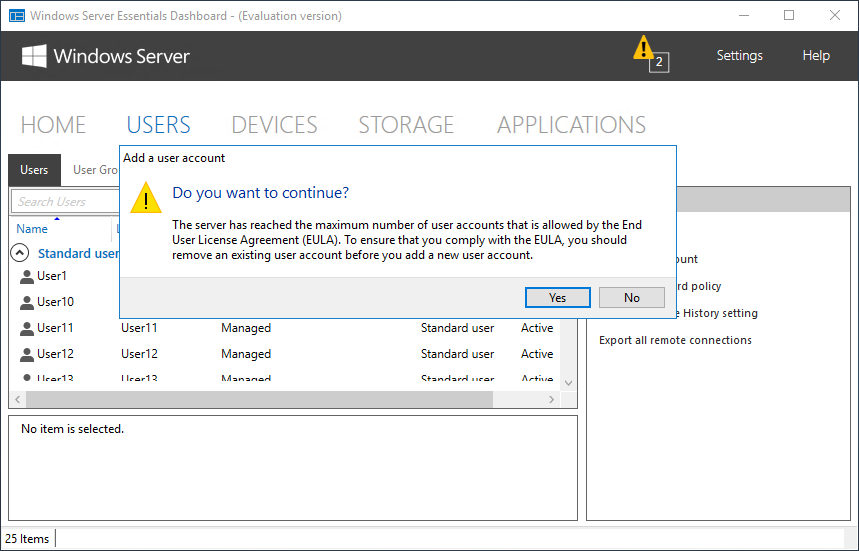
Для примера возьмем ограничение в 25 пользователей и попробуем его превысить. И действительно, при попытке создать пользователя сверх лимита будет выдано сообщение о нарушении лицензионного соглашения, а сам процесс создания завершится ошибкой. Но это только при создании пользователя из панели управления.
Используя оснастку ADUC или PowerShell можно без проблем создать любое количество пользователей. Т.е. ограничение не техническое и при необходимости его можно легко обойти, хотя это и будет нарушением лицензионного соглашения.
Что касается 50 устройств, то тут ограничение работает, но только на количество подключенных устройств. Т.е. количество учетных записей компьютеров в Active Directory не ограничено и их также можно создавать в любом количестве.
Смена редакции
При выборе Windows Server Essentials необходимо четко понимать все ограничения этой операционной системы и быть уверенным в том, что они не станут препятствием для роста компании в будущем. Однако если это уже произошло, то отчаиваться не стоит. Конечно, изменить лимиты невозможно, но можно изменить саму редакцию операционной системы.
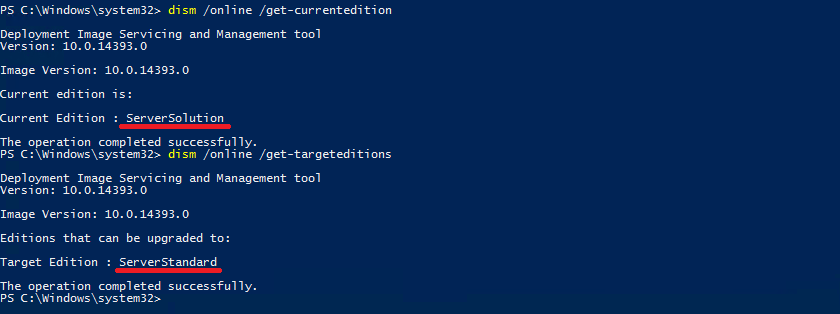
Сделать это можно с помощью утилиты dism. Например так можно посмотреть текущую редакцию:
Dism /Online /Get-CurrentEdition
А так — определить редакцию, на которую можно перейти:
Dism /Online /Get-TargetEditions
Как видите, с Essentials можно перейти на редакцию Standard. Для этого достаточно выполнить такую команду:
Dism /Online /Set-Edition:ServerStandard /AcceptEula /ProductKey:xxxxx-xxxxx-xxxxx-xxxxx-xxxxx
Что примечательно, после апгрейда настройки и установленные роли сервера остаются неизменными, при этом снимаются все ограничения редакции Essentials. Конечно после этой операции потребуется раскошелится на клиентские лицензии, а также пересчитать количество серверных лицензий в соответствии с ядрами процессора.
Заключение
В заключение рассмотрим плюсы и минусы Windows Server Essentials. К плюсам можно отнести:
+ Экономия на покупке клиентских и серверных лицензий;
+ Простота настройки и использования;
+ Интеграция с облачными службами;
+ Возможность без особых потерь перейти на полноценную редакцию Windows Server.
Ну и минусы, как же без них:
– Лимит на количество пользователейустройств;
– Ограничение на количество процессоров и максимальный размер памяти;
– Невозможность использования в качестве сервера удаленных рабочих столов;
– Непрозрачная процедура настройки, не позволяющая выбрать только необходимый функционал;
– Очень грубые и примитивные (на мой взгляд) настройки в консоли управления.
Минусов получилось больше, хотя в целом Windows Server Essentials неплохая система, вполне подходящая для своих целей. Главное при выборе четко понимать все ее особенности и быть уверенным в своем выборе.
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia

Windows Server 2019 Essentials displaying the Windows Server Essentials Server Manager |
|
| Developer(s) | Microsoft |
|---|---|
| Final release |
2019 |
| Type | Operating system |
| License | Commercial proprietary software |
| Website | microsoft.com/windows-server/ |
Windows Server Essentials (formerly Small Business Server or SBS)[2] is an integrated server suite from Microsoft for businesses with no more than 25 users or 50 devices. It includes Windows Server, Exchange Server, Windows SharePoint Services, and Microsoft Outlook. Application server technologies are tightly integrated to provide and offer management benefits such as integrated setup, enhanced monitoring, Remote Web Workplace, a unified management console, and remote access.
Windows Server Essentials 2019 was the last release of this product. Microsoft has since discontinued this suite in favor of Microsoft 365 and Microsoft Azure. Those holding an «Essentials» license receive an activation key for Windows Server 2022 instead.
History[edit]
As Small Business Server[edit]
Initially, Microsoft marketed the Small Business Server (SBS) an edition of Microsoft BackOffice Server. With the release of Windows 2000, however, Microsoft spun off Small Business Server 2000 as a separate offering. Until this point, the Premium editions of SBS included SQL Server, ISA Server, and FrontPage. SBS 2003 and later all bear the «Windows» brand and are editions of Windows Server.
SBS 2008 came with an edition of Windows Server 2008 bears the name Windows Server 2008 for Windows Essential Server Solutions («WinWESS»), also known as Windows Server 2008 Standard FE.[3] This edition of Windows Server 2008 is available outside the product suite, supporting a maximum of 15 Client Access Licenses.[4] SBS 2008 Premium edition does not include ISA Server but includes SQL Server 2008. Those upgrading to SBS 2008 Premium edition via Software Assurance were compensated with a free license for the latest version of ISA Server.[5] In December 2008, Microsoft also introduced a Windows Essential Business Server product aimed at medium-sized businesses, but this was discontinued in June 2010 due to low demand.
SBS 2011 was available in Essentials, Standard, and Premium editions. The Essentials edition is a scaled down version for 1 to 25 users; the other editions are based on the Windows Server codebase and include Exchange Server, Windows SharePoint Services, and Microsoft Outlook in addition to what comes with Window Server.
As Windows Server Essentials[edit]
Starting with Windows Server 2012, Microsoft renamed SBS to Windows Server Essentials. Four versions of Windows Server Essentials were released along with their Windows Server siblings: 2012, 2012 R2,[6] 2016, and 2019.[7] Windows Server 2019 Essentials removed many features found in previous versions of Windows Server Essentials because the «Windows Server Essentials Experience» role was not included in any of the Windows Server 2019 SKUs. This includes Essentials Connector, Client PC Backup, Office 365 integration, Remote Web Access, and the Windows Server Essentials Dashboard.[8][9]
Discontinuation[edit]
In September 2018, the Windows Server hinted that Windows Server Essentials 2019 might be the last version of this product.[10] Following the release of Windows Server 2022, Microsoft announced that their Windows Server Essentials 2022 offering is merely a customized licensing scheme for the Standard edition of Windows Server 2022.[11]
At the time of discontinuation, Microsoft offered the same software as part of its Microsoft 365 and Microsoft Azure plans.
Versions[edit]
- October 22, 1997 – BackOffice Small Business Server 4.0
- Consists of Windows NT Server 4.0 SP3 and includes Exchange Server 5.0 SP1, Internet Information Services 3.0, SQL Server 6.5 SP3, Proxy Server 1.0, Internet Explorer 3.02 or 4.01, and Outlook 97; allows 25 client licenses.
- May 24, 1999 – BackOffice Small Business Server 4.5
- Consists of Windows NT Server 4.0 SP4 and includes Exchange Server 5.5 SP2, IIS 4.0, SQL Server 7.0, Proxy Server 2.0, Internet Explorer 5.0, Outlook 2000, and FrontPage 2000; allows 50 client licenses.
- February 21, 2001 – Microsoft Small Business Server 2000
- Consists of Windows 2000 Server (including Internet Explorer 5.0 and IIS 5.0) and includes Exchange 2000 Server, SQL Server 2000 Standard Edition, Internet Security & Acceleration Server 2000, Outlook 2000 and FrontPage 2000; allows 50 client licenses.
- October 9, 2003 – Windows Small Business Server 2003 (codenamed Bobcat)
- Consists of Windows Server 2003 and includes Microsoft Exchange Server 2003, Microsoft Outlook 2003, Windows SharePoint Services 2.0, and optionally Microsoft SQL Server 2000, ISA Server 2000 (upgrade to ISA Server 2004 in Small Business Server Premium SP1), and Microsoft FrontPage 2003 in Premium edition; allows 75 client licenses. Service Pack 1 for Windows Small Business Server 2003 was released on July 25, 2005.[12]
- July 29, 2006 – Windows Small Business Server 2003 R2
- Consists of Windows Server 2003 and includes Microsoft Exchange Server 2003, Microsoft Outlook 2003, Windows SharePoint Services 2.0, and optionally Microsoft SQL Server 2005 Workgroup Edition, ISA Server 2004, and Microsoft FrontPage 2003 in Premium edition; allows 75 client licenses. A major addition is a built-in patch management tool optimized for small businesses, based on Microsoft Windows Server Update Services. Exchange database size limit is set to 18 GB by default but can be expanded to 75 GB using a registry key.
- August 21, 2008[13] – Windows Small Business Server 2008 (codenamed Cougar)
- Consists of Windows Server 2008 and includes Microsoft Exchange Server 2007, Windows SharePoint Services 3.0 and 120-day trial subscriptions of new security products from Microsoft, namely, Forefront Security for Exchange and Windows Live OneCare for Server.[14][15] The standard edition of SBS 2008 will be a single server product for small businesses. The premium edition will contain a license for Windows Server 2008 and SQL Server 2008 Standard Edition, with the option to run SQL Server on either the main SBS server, or a second server. The premium edition will therefore be targeted at dual-server scenarios such as terminal services application sharing, line of business applications, edge security, secondary domain controllers, and virtualization.[16] In addition to features present in previous versions, new features include:
- A streamlined administration and management console that is designed around tasks to be accomplished rather than underlying technologies[17]
- Built-in support for registering and configuring domain name and DNS records via multiple registrars
- Monitoring reports that gather data from both servers and clients on the network, including Security Center status (anti-virus, spyware, and client firewall) from all the clients
- New features in the Remote Web Workplace, such as the ability to define default and allowed PCs for each user
- Office Live Small Business integration for and configuring a public web site or extranet
- New server backup features, based on the incremental block-based backup technology in Windows Server 2008 (tape backup no longer supported via native tools, but continues to be supported via third parties)
- SBS 2008 requires installation behind a separate network firewall device. In contrast with SBS 2003, it does not support being installed directly on the edge of the network, ISA Server is no longer bundled and a dual-NIC configuration is not possible.[18]
- Migration of 32-bit SBS 2003 versions to 64-bit SBS 2008 and SBS2011 has no in place upgrade and can be problematic.[19][20][21] Inability to upgrade Sharepoint[22] (WSS 2.0) by WSS 3.0 or SharePoint 2010 Foundation.
- SBS 2008 was released to manufacturing on August 21, 2008[23] and was launched on November 12, 2008.[24] Windows Small Business Server 2008 supports organizations with up to 75 users or devices.[15] A notable change from SBS 2003 is that CALs are not enforced electronically.[25]
- December 13, 2010 – Windows Small Business Server 2011
- Microsoft announced two successors to the SBS series during WPC 2010, both based on Windows Server 2008 R2. One successor (code name «Aurora») supports a maximum of 25 users, does not include Exchange, SharePoint and Windows Server Update Services (WSUS), and is oriented to attach cloud services. The other successor (code name «SBS 7») is the more direct successor of SBS 2008, and continues to support a maximum of 75 users, and includes Exchange, SharePoint and WSUS.
- Late in 2010, Microsoft announced the official branding for the 2011 wave: SBS «7» became «Windows Small Business Server 2011 Standard,» and «Aurora» was christened «Windows Small Business Server 2011 Essentials.» Whereas formerly, the premium edition of SBS was packaged as a superset of the standard edition, in the 2011 wave, it was be available as an add-on, containing standalone copies of SQL Server 2008 R2 and Windows Server 2008 R2. It could be added to either SBS 2011 Essentials or Standard.
- In mid-December, Microsoft released SBS 2011 Standard to TechNet and MSDN subscribers for evaluation. Microsoft released SBS 2011 Standard to volume licensing customers in early January and as a trial in mid-January. SBS 2011 requires an Internet connection.
- October 10, 2012 – Windows Server 2012 Essentials
- In July 2012, Microsoft announced that there would not be another SBS product. Rather, Windows Server 2012 Essentials succeeded SBS Essentials.[26] Windows Server 2012 Essentials does not include Microsoft Exchange Server, which is used for messaging and collaboration, including the ability to host email. Windows Server Essentials and its successors were designed for small businesses with up to 25 users and 50 devices.
- September 9, 2013 – Windows Server 2012 R2 Essentials
- October 12, 2016 – Windows Server 2016 Essentials
- November 13, 2018 – Windows Server 2019 Essentials
- Windows Server 2019 Essentials removed many features found in previous versions of Windows Server Essentials, including Remote Web Access, Essentials Connector, Client PC Backup, Office 365 integration and the Windows Server Essentials Dashboard.[8][9] It is the last version of Windows Server Essentials.
Licensing[edit]
Normally, Microsoft licenses its on-premises server products on a per-seat or per-user basis, i.e., the licensing cost depends on how many users or computers use these products. Businesses that install them require to obtain client access licenses (CALs). Windows Server 2012 Essentials and later do not need any CALs. However, this has not always been the case. Earlier versions – Windows Small Business Server (SBS) – had their own types of CAL, and included the user CALs for Windows Server, Exchange Server, and eventually SQL Server. The SBS CALs cost more than the Windows Server CALs, but less than the sum of separate access licenses for the two or three servers.
Windows Small Business Server has the following design restrictions:[27]
- Only one computer in the domain can run SBS. The domain supports multiple servers (including additional domain controllers) running any other operating system, such as Windows Server, but only one SBS.
- SBS must be the root of the Active Directory forest.
- SBS cannot establish a trust relationship with any other domains or have sub-domains.
- SBS is limited to 75 users or devices depending on the type of CAL.
- SBS 2003 and earlier are limited to no more than 4 GB of RAM. SBS 2008 supports a maximum of 32GB. It requires a minimum of 4GB for installation, but needs more for performance.
- SBS 2003 R2 and earlier are only available for the IA-32 (32-bit) architecture.
- SBS 2008 is only available for the x86-64 architecture.
- The SQL Server that comes with SBS 2008 is «SQL Server 2008 Standard Edition for Small Business.».[28][29] It cannot be installed outside a network that has a domain controller, and must have fewer than 75 PCs or users (depending on the CAL.)
- Remote Desktop Services on SBS is restricted to two simultaneous sessions. (Change from SBS 2000 policy)[30] Terminal Services in application sharing mode needs to be run on a second server running a separately obtained copy of Windows Server.
To remove these restrictions and upgrade to regular editions of Windows Server, Exchange Server, SQL Server and ISA Server, there was a Windows Small Business Server 2003 R2 Transition Pack.[31]
References[edit]
- ^ «What’s New in Windows Server 2019 Essentials». Windows Server Essentials documentations. Microsoft – via Microsoft Docs.
- ^ «Frequently Asked Questions» (PDF). Windows Server Essentials portal. Microsoft. October 5, 2012. p. 1. Retrieved July 11, 2013.
Q: Why did Microsoft change the name of Windows Small Business Server Essentials to Windows Server Essentials? A: […]
- ^ «Windows Small Business Server 2008 Technical FAQ». Microsoft Technet. Microsoft Corporation. Retrieved June 9, 2010.
Windows Server 2008 Standard FE is the shortened name for Windows Server 2008 for Windows Essential Server Solutions. When you run the Winver tool you will see this reference.
- ^ «Managing Licenses in Windows Server 2008 for Windows Essential Server Solutions». Technet.microsoft.com. March 10, 2009. Retrieved August 30, 2012.
- ^ «SBS 2008 RC1 and EBS 2008 RC1 finalised». Geekzone.co.nz. Retrieved August 30, 2012.
- ^ «Windows Server Essentials». Microsoft Technet. Microsoft. Retrieved February 10, 2013.
- ^ «Update on Windows Server 2019 availability». Windows Server Blog. Microsoft. November 13, 2018.
- ^ a b eross-msft. «What’s New in Windows Server 2019 Essentials». docs.microsoft.com. Retrieved December 17, 2020.
- ^ a b «Windows Server 2019 — end of an era». The Office Maven. September 7, 2018.
- ^ Pivovarova, Irina; Apolinario, Vinicius (September 5, 2018). «Windows Server 2019 Essentials update». Microsoft Windows Server Blog. Microsoft.
All of this led to our decision to offer yet another version of on-premises server for small businesses – Windows Server 2019 Essentials. This edition will be released along with the other editions of Windows Server 2019 later this year. There is a strong possibility that this could be the last edition of Windows Server Essentials.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: url-status (link) - ^ «Get started with Windows Server Essentials». Windows Server Essentials documentations. Microsoft. September 3, 2021.
With Windows Server 2022, the Essentials edition is available to purchase from OEMs only, however there is no specific installation media. Instead, an Essentials edition product key is used to activate the Standard edition of Windows Server 2022 and means you get all the same features.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: url-status (link) - ^ «Windows Small Business Server 2003 Service Pack 1». Download Center. Microsoft. August 18, 2012.
- ^ Paron, Dean (October 21, 2008). «SBS 2008: Released to Manufacturing!». The Windows Server Essentials and Small Business Server Blog. Microsoft – via Blog Archive.
- ^ «SBS 2008 editions». microsoft.com. Microsoft. Archived from the original on February 25, 2008.
- ^ a b «Introducing the Windows Essential Server Solutions Family of Products». Blogs.technet.com. February 20, 2008. Retrieved August 30, 2012.
- ^ SBS Server #1 is required to be 64-bit; SBS Server #2 will provide the option to run as either 32-bit or 64-bit. Microsoft unveils new Small Business Server
- ^ «Windows SBS Console». Microsoft. August 17, 2008. Archived from the original on August 17, 2008. Retrieved March 26, 2021.
- ^ «Preparing your Network for Small Business Server 2008». Sbs.seandaniel.com. May 1, 2008. Retrieved August 30, 2012.
- ^ «Migrate to Windows Small Business Server 2008 from Windows Small Business Server 2003». Technet.microsoft.com. Retrieved August 30, 2012.
- ^ «Migrate to Windows Small Business Server 2011 Standard from Windows Small Business Server 2003». Technet.microsoft.com. Retrieved August 30, 2012.
- ^ e.g. Migration Tool has increased default 7 day Active Directory coexistence period to 21 days to address this
- ^ «Installing Windows SharePoint Services 3.0 on a Server Running Windows Small Business Server 2003». Technet.microsoft.com. April 27, 2009. Retrieved August 30, 2012.
- ^ «Small Business Server 2008 (SBS 2008) Released to Manufacturing». Geekzone.co.nz. Retrieved August 30, 2012.
- ^ «Microsoft SMB Community Blog». Blogs.msdn.com. Retrieved August 30, 2012.
- ^ «SBS 2008 and the usage of CAL’s». Social.technet.microsoft.com. Retrieved August 30, 2012.
- ^ Windows Small Business Server Essentials becomes Windows Server 2012 Essentials
- ^ «Windows Small Business Server 2003 R2: Frequently Asked Questions». Microsoft. July 11, 2006. Retrieved September 2, 2006.
- ^ «Microsoft SQL Server Editions | The Cloud Ready Information Platform». Microsoft.com. Retrieved August 30, 2012.
- ^ «Microsoft Windows Small Business Server (SBS) Features». Microsoft.com. Retrieved August 30, 2012.
- ^ «Licensing – Windows Small Business Server 2003 R2: Frequently Asked Questions». Microsoft. Retrieved September 2, 2006.
- ^ «Windows Small Business Server 2003 R2 Transition Pack». Microsoft.com. Retrieved August 30, 2012.
External links[edit]
- The Windows Server Essentials and Small Business Server Blog in Microsoft Blog Archive
- SBSFaq.com, an independent blog
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia

Windows Server 2019 Essentials displaying the Windows Server Essentials Server Manager |
|
| Developer(s) | Microsoft |
|---|---|
| Final release |
2019 |
| Type | Operating system |
| License | Commercial proprietary software |
| Website | microsoft.com/windows-server/ |
Windows Server Essentials (formerly Small Business Server or SBS)[2] is an integrated server suite from Microsoft for businesses with no more than 25 users or 50 devices. It includes Windows Server, Exchange Server, Windows SharePoint Services, and Microsoft Outlook. Application server technologies are tightly integrated to provide and offer management benefits such as integrated setup, enhanced monitoring, Remote Web Workplace, a unified management console, and remote access.
Windows Server Essentials 2019 was the last release of this product. Microsoft has since discontinued this suite in favor of Microsoft 365 and Microsoft Azure. Those holding an «Essentials» license receive an activation key for Windows Server 2022 instead.
History[edit]
As Small Business Server[edit]
Initially, Microsoft marketed the Small Business Server (SBS) an edition of Microsoft BackOffice Server. With the release of Windows 2000, however, Microsoft spun off Small Business Server 2000 as a separate offering. Until this point, the Premium editions of SBS included SQL Server, ISA Server, and FrontPage. SBS 2003 and later all bear the «Windows» brand and are editions of Windows Server.
SBS 2008 came with an edition of Windows Server 2008 bears the name Windows Server 2008 for Windows Essential Server Solutions («WinWESS»), also known as Windows Server 2008 Standard FE.[3] This edition of Windows Server 2008 is available outside the product suite, supporting a maximum of 15 Client Access Licenses.[4] SBS 2008 Premium edition does not include ISA Server but includes SQL Server 2008. Those upgrading to SBS 2008 Premium edition via Software Assurance were compensated with a free license for the latest version of ISA Server.[5] In December 2008, Microsoft also introduced a Windows Essential Business Server product aimed at medium-sized businesses, but this was discontinued in June 2010 due to low demand.
SBS 2011 was available in Essentials, Standard, and Premium editions. The Essentials edition is a scaled down version for 1 to 25 users; the other editions are based on the Windows Server codebase and include Exchange Server, Windows SharePoint Services, and Microsoft Outlook in addition to what comes with Window Server.
As Windows Server Essentials[edit]
Starting with Windows Server 2012, Microsoft renamed SBS to Windows Server Essentials. Four versions of Windows Server Essentials were released along with their Windows Server siblings: 2012, 2012 R2,[6] 2016, and 2019.[7] Windows Server 2019 Essentials removed many features found in previous versions of Windows Server Essentials because the «Windows Server Essentials Experience» role was not included in any of the Windows Server 2019 SKUs. This includes Essentials Connector, Client PC Backup, Office 365 integration, Remote Web Access, and the Windows Server Essentials Dashboard.[8][9]
Discontinuation[edit]
In September 2018, the Windows Server hinted that Windows Server Essentials 2019 might be the last version of this product.[10] Following the release of Windows Server 2022, Microsoft announced that their Windows Server Essentials 2022 offering is merely a customized licensing scheme for the Standard edition of Windows Server 2022.[11]
At the time of discontinuation, Microsoft offered the same software as part of its Microsoft 365 and Microsoft Azure plans.
Versions[edit]
- October 22, 1997 – BackOffice Small Business Server 4.0
- Consists of Windows NT Server 4.0 SP3 and includes Exchange Server 5.0 SP1, Internet Information Services 3.0, SQL Server 6.5 SP3, Proxy Server 1.0, Internet Explorer 3.02 or 4.01, and Outlook 97; allows 25 client licenses.
- May 24, 1999 – BackOffice Small Business Server 4.5
- Consists of Windows NT Server 4.0 SP4 and includes Exchange Server 5.5 SP2, IIS 4.0, SQL Server 7.0, Proxy Server 2.0, Internet Explorer 5.0, Outlook 2000, and FrontPage 2000; allows 50 client licenses.
- February 21, 2001 – Microsoft Small Business Server 2000
- Consists of Windows 2000 Server (including Internet Explorer 5.0 and IIS 5.0) and includes Exchange 2000 Server, SQL Server 2000 Standard Edition, Internet Security & Acceleration Server 2000, Outlook 2000 and FrontPage 2000; allows 50 client licenses.
- October 9, 2003 – Windows Small Business Server 2003 (codenamed Bobcat)
- Consists of Windows Server 2003 and includes Microsoft Exchange Server 2003, Microsoft Outlook 2003, Windows SharePoint Services 2.0, and optionally Microsoft SQL Server 2000, ISA Server 2000 (upgrade to ISA Server 2004 in Small Business Server Premium SP1), and Microsoft FrontPage 2003 in Premium edition; allows 75 client licenses. Service Pack 1 for Windows Small Business Server 2003 was released on July 25, 2005.[12]
- July 29, 2006 – Windows Small Business Server 2003 R2
- Consists of Windows Server 2003 and includes Microsoft Exchange Server 2003, Microsoft Outlook 2003, Windows SharePoint Services 2.0, and optionally Microsoft SQL Server 2005 Workgroup Edition, ISA Server 2004, and Microsoft FrontPage 2003 in Premium edition; allows 75 client licenses. A major addition is a built-in patch management tool optimized for small businesses, based on Microsoft Windows Server Update Services. Exchange database size limit is set to 18 GB by default but can be expanded to 75 GB using a registry key.
- August 21, 2008[13] – Windows Small Business Server 2008 (codenamed Cougar)
- Consists of Windows Server 2008 and includes Microsoft Exchange Server 2007, Windows SharePoint Services 3.0 and 120-day trial subscriptions of new security products from Microsoft, namely, Forefront Security for Exchange and Windows Live OneCare for Server.[14][15] The standard edition of SBS 2008 will be a single server product for small businesses. The premium edition will contain a license for Windows Server 2008 and SQL Server 2008 Standard Edition, with the option to run SQL Server on either the main SBS server, or a second server. The premium edition will therefore be targeted at dual-server scenarios such as terminal services application sharing, line of business applications, edge security, secondary domain controllers, and virtualization.[16] In addition to features present in previous versions, new features include:
- A streamlined administration and management console that is designed around tasks to be accomplished rather than underlying technologies[17]
- Built-in support for registering and configuring domain name and DNS records via multiple registrars
- Monitoring reports that gather data from both servers and clients on the network, including Security Center status (anti-virus, spyware, and client firewall) from all the clients
- New features in the Remote Web Workplace, such as the ability to define default and allowed PCs for each user
- Office Live Small Business integration for and configuring a public web site or extranet
- New server backup features, based on the incremental block-based backup technology in Windows Server 2008 (tape backup no longer supported via native tools, but continues to be supported via third parties)
- SBS 2008 requires installation behind a separate network firewall device. In contrast with SBS 2003, it does not support being installed directly on the edge of the network, ISA Server is no longer bundled and a dual-NIC configuration is not possible.[18]
- Migration of 32-bit SBS 2003 versions to 64-bit SBS 2008 and SBS2011 has no in place upgrade and can be problematic.[19][20][21] Inability to upgrade Sharepoint[22] (WSS 2.0) by WSS 3.0 or SharePoint 2010 Foundation.
- SBS 2008 was released to manufacturing on August 21, 2008[23] and was launched on November 12, 2008.[24] Windows Small Business Server 2008 supports organizations with up to 75 users or devices.[15] A notable change from SBS 2003 is that CALs are not enforced electronically.[25]
- December 13, 2010 – Windows Small Business Server 2011
- Microsoft announced two successors to the SBS series during WPC 2010, both based on Windows Server 2008 R2. One successor (code name «Aurora») supports a maximum of 25 users, does not include Exchange, SharePoint and Windows Server Update Services (WSUS), and is oriented to attach cloud services. The other successor (code name «SBS 7») is the more direct successor of SBS 2008, and continues to support a maximum of 75 users, and includes Exchange, SharePoint and WSUS.
- Late in 2010, Microsoft announced the official branding for the 2011 wave: SBS «7» became «Windows Small Business Server 2011 Standard,» and «Aurora» was christened «Windows Small Business Server 2011 Essentials.» Whereas formerly, the premium edition of SBS was packaged as a superset of the standard edition, in the 2011 wave, it was be available as an add-on, containing standalone copies of SQL Server 2008 R2 and Windows Server 2008 R2. It could be added to either SBS 2011 Essentials or Standard.
- In mid-December, Microsoft released SBS 2011 Standard to TechNet and MSDN subscribers for evaluation. Microsoft released SBS 2011 Standard to volume licensing customers in early January and as a trial in mid-January. SBS 2011 requires an Internet connection.
- October 10, 2012 – Windows Server 2012 Essentials
- In July 2012, Microsoft announced that there would not be another SBS product. Rather, Windows Server 2012 Essentials succeeded SBS Essentials.[26] Windows Server 2012 Essentials does not include Microsoft Exchange Server, which is used for messaging and collaboration, including the ability to host email. Windows Server Essentials and its successors were designed for small businesses with up to 25 users and 50 devices.
- September 9, 2013 – Windows Server 2012 R2 Essentials
- October 12, 2016 – Windows Server 2016 Essentials
- November 13, 2018 – Windows Server 2019 Essentials
- Windows Server 2019 Essentials removed many features found in previous versions of Windows Server Essentials, including Remote Web Access, Essentials Connector, Client PC Backup, Office 365 integration and the Windows Server Essentials Dashboard.[8][9] It is the last version of Windows Server Essentials.
Licensing[edit]
Normally, Microsoft licenses its on-premises server products on a per-seat or per-user basis, i.e., the licensing cost depends on how many users or computers use these products. Businesses that install them require to obtain client access licenses (CALs). Windows Server 2012 Essentials and later do not need any CALs. However, this has not always been the case. Earlier versions – Windows Small Business Server (SBS) – had their own types of CAL, and included the user CALs for Windows Server, Exchange Server, and eventually SQL Server. The SBS CALs cost more than the Windows Server CALs, but less than the sum of separate access licenses for the two or three servers.
Windows Small Business Server has the following design restrictions:[27]
- Only one computer in the domain can run SBS. The domain supports multiple servers (including additional domain controllers) running any other operating system, such as Windows Server, but only one SBS.
- SBS must be the root of the Active Directory forest.
- SBS cannot establish a trust relationship with any other domains or have sub-domains.
- SBS is limited to 75 users or devices depending on the type of CAL.
- SBS 2003 and earlier are limited to no more than 4 GB of RAM. SBS 2008 supports a maximum of 32GB. It requires a minimum of 4GB for installation, but needs more for performance.
- SBS 2003 R2 and earlier are only available for the IA-32 (32-bit) architecture.
- SBS 2008 is only available for the x86-64 architecture.
- The SQL Server that comes with SBS 2008 is «SQL Server 2008 Standard Edition for Small Business.».[28][29] It cannot be installed outside a network that has a domain controller, and must have fewer than 75 PCs or users (depending on the CAL.)
- Remote Desktop Services on SBS is restricted to two simultaneous sessions. (Change from SBS 2000 policy)[30] Terminal Services in application sharing mode needs to be run on a second server running a separately obtained copy of Windows Server.
To remove these restrictions and upgrade to regular editions of Windows Server, Exchange Server, SQL Server and ISA Server, there was a Windows Small Business Server 2003 R2 Transition Pack.[31]
References[edit]
- ^ «What’s New in Windows Server 2019 Essentials». Windows Server Essentials documentations. Microsoft – via Microsoft Docs.
- ^ «Frequently Asked Questions» (PDF). Windows Server Essentials portal. Microsoft. October 5, 2012. p. 1. Retrieved July 11, 2013.
Q: Why did Microsoft change the name of Windows Small Business Server Essentials to Windows Server Essentials? A: […]
- ^ «Windows Small Business Server 2008 Technical FAQ». Microsoft Technet. Microsoft Corporation. Retrieved June 9, 2010.
Windows Server 2008 Standard FE is the shortened name for Windows Server 2008 for Windows Essential Server Solutions. When you run the Winver tool you will see this reference.
- ^ «Managing Licenses in Windows Server 2008 for Windows Essential Server Solutions». Technet.microsoft.com. March 10, 2009. Retrieved August 30, 2012.
- ^ «SBS 2008 RC1 and EBS 2008 RC1 finalised». Geekzone.co.nz. Retrieved August 30, 2012.
- ^ «Windows Server Essentials». Microsoft Technet. Microsoft. Retrieved February 10, 2013.
- ^ «Update on Windows Server 2019 availability». Windows Server Blog. Microsoft. November 13, 2018.
- ^ a b eross-msft. «What’s New in Windows Server 2019 Essentials». docs.microsoft.com. Retrieved December 17, 2020.
- ^ a b «Windows Server 2019 — end of an era». The Office Maven. September 7, 2018.
- ^ Pivovarova, Irina; Apolinario, Vinicius (September 5, 2018). «Windows Server 2019 Essentials update». Microsoft Windows Server Blog. Microsoft.
All of this led to our decision to offer yet another version of on-premises server for small businesses – Windows Server 2019 Essentials. This edition will be released along with the other editions of Windows Server 2019 later this year. There is a strong possibility that this could be the last edition of Windows Server Essentials.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: url-status (link) - ^ «Get started with Windows Server Essentials». Windows Server Essentials documentations. Microsoft. September 3, 2021.
With Windows Server 2022, the Essentials edition is available to purchase from OEMs only, however there is no specific installation media. Instead, an Essentials edition product key is used to activate the Standard edition of Windows Server 2022 and means you get all the same features.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: url-status (link) - ^ «Windows Small Business Server 2003 Service Pack 1». Download Center. Microsoft. August 18, 2012.
- ^ Paron, Dean (October 21, 2008). «SBS 2008: Released to Manufacturing!». The Windows Server Essentials and Small Business Server Blog. Microsoft – via Blog Archive.
- ^ «SBS 2008 editions». microsoft.com. Microsoft. Archived from the original on February 25, 2008.
- ^ a b «Introducing the Windows Essential Server Solutions Family of Products». Blogs.technet.com. February 20, 2008. Retrieved August 30, 2012.
- ^ SBS Server #1 is required to be 64-bit; SBS Server #2 will provide the option to run as either 32-bit or 64-bit. Microsoft unveils new Small Business Server
- ^ «Windows SBS Console». Microsoft. August 17, 2008. Archived from the original on August 17, 2008. Retrieved March 26, 2021.
- ^ «Preparing your Network for Small Business Server 2008». Sbs.seandaniel.com. May 1, 2008. Retrieved August 30, 2012.
- ^ «Migrate to Windows Small Business Server 2008 from Windows Small Business Server 2003». Technet.microsoft.com. Retrieved August 30, 2012.
- ^ «Migrate to Windows Small Business Server 2011 Standard from Windows Small Business Server 2003». Technet.microsoft.com. Retrieved August 30, 2012.
- ^ e.g. Migration Tool has increased default 7 day Active Directory coexistence period to 21 days to address this
- ^ «Installing Windows SharePoint Services 3.0 on a Server Running Windows Small Business Server 2003». Technet.microsoft.com. April 27, 2009. Retrieved August 30, 2012.
- ^ «Small Business Server 2008 (SBS 2008) Released to Manufacturing». Geekzone.co.nz. Retrieved August 30, 2012.
- ^ «Microsoft SMB Community Blog». Blogs.msdn.com. Retrieved August 30, 2012.
- ^ «SBS 2008 and the usage of CAL’s». Social.technet.microsoft.com. Retrieved August 30, 2012.
- ^ Windows Small Business Server Essentials becomes Windows Server 2012 Essentials
- ^ «Windows Small Business Server 2003 R2: Frequently Asked Questions». Microsoft. July 11, 2006. Retrieved September 2, 2006.
- ^ «Microsoft SQL Server Editions | The Cloud Ready Information Platform». Microsoft.com. Retrieved August 30, 2012.
- ^ «Microsoft Windows Small Business Server (SBS) Features». Microsoft.com. Retrieved August 30, 2012.
- ^ «Licensing – Windows Small Business Server 2003 R2: Frequently Asked Questions». Microsoft. Retrieved September 2, 2006.
- ^ «Windows Small Business Server 2003 R2 Transition Pack». Microsoft.com. Retrieved August 30, 2012.
External links[edit]
- The Windows Server Essentials and Small Business Server Blog in Microsoft Blog Archive
- SBSFaq.com, an independent blog
Решил написать подробную инструкцию по установке и настройке нового Windows server 2016 Essentials, а заодно и сделать небольшой обзор новых возможностей этой серверной «оси».
Почему собственно Essentials ?
Многие малые компании начинают свою работу с покупки Windows server standard.
И зря тратят деньги!
Ведь если в вашей компании, например, планируется работа до 25 пользователей в 1С Предприятии, тогда Вам идеально подойдет именно Essentials!
Минус, на мой взгляд, здесь только один:
Нет, возможность поднять службу терминалов для удаленной работы пользователей на этом сервере в 1С (Использовать обычный всем нам знакомый удаленный рабочий стол).
Эта версия лицензируется по количеству процессоров на сервере и главное не требует CAL лицензий! (клиентские лицензии на подключение).
Но большинству малых предприятий с уверенностью можно рекомендовать редакцию Essentials.
Экономия здесь очевидна:
Например, редакция —
Microsoft Windows Server 2012 R2 Standard Edition x64 Russian 2CPU/2VM DVD ОЕМ —
Обойдется примерно в ~ 43 000 руб. + CAL на каждого пользователя еще примерно ~1500 руб.
(20 пользователей = 30 000 руб).
Итого: ~ 73 000 руб.
Тогда как Microsoft Windows Server Essentials 2016 Single Multilanguage
Обойдется нам примерно в ~ 26 000 руб!
Если сравнивать редакции Essentials и Standard, на предмет функционала, то с уверенностью можно казать что Essentials почти не уступает Standard, все нужные основные компоненты и роли там также доступны, а сама операционная система идеально подойдет начинающим системным администраторам, так как многие функции, можно реализовать двумя, тремя кликами мышкой.
Много нового появилось в этой версии, и действительно есть, что рассказать, но об этом позже, пока скачаем дистрибутив Windows server 2016 Essentials и установим его.
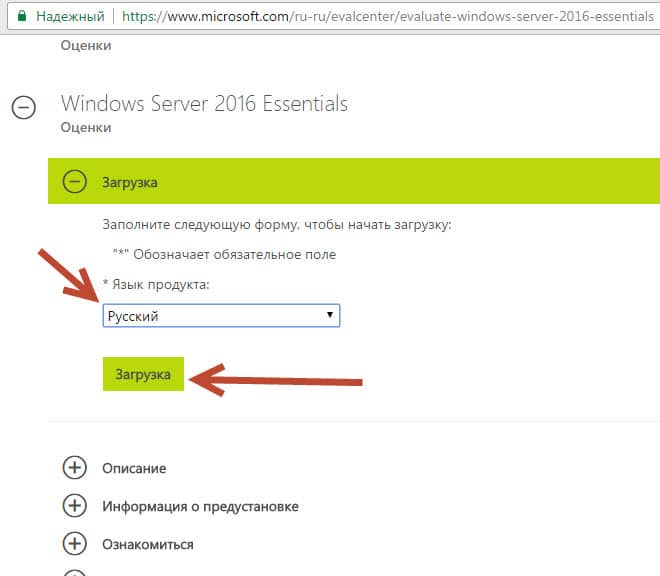
Скачать бесплатно пакет установки рекомендую на сайте Microsoft.
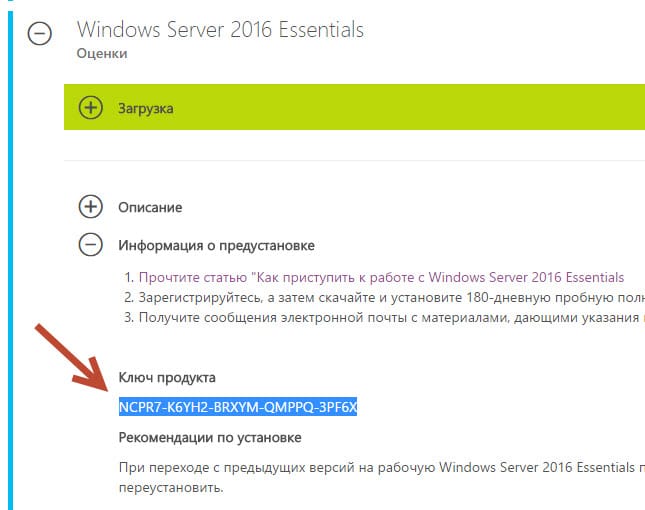
Установка и настройка Windows server 2016 Essentials
Там же бесплатно получим ключик на 180 дней. За этот период мы успеем его хорошо протестировать и связаться с партнерами Microsoft для получения лицензии.
Установка и настройка Windows server 2016 Essentials
Итак, если образ *ISO скачали (его размер около 4500 Mb).
Запишем его на диск или сделаем «загрузочную флешку» здесь кому как удобно и приступаем к установке.
Сама установка довольно простая, и некоторые трудности могут быть лишь при настройке (первичной) редакции Essentials.
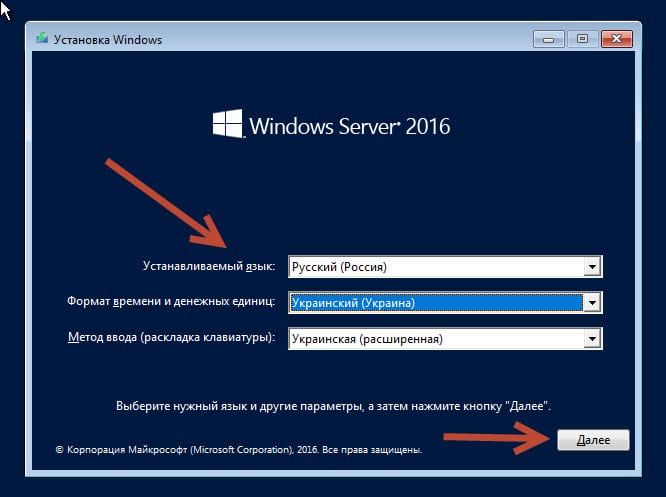
Установка и настройка Windows server 2016 Essentials
Установка и настройка Windows server 2016 Essentials
Укажем «Формат времени и денежных единиц» Ваша страна.
И выберем из списка «Метод ввода (раскладка клавиатуры)», затем клик «Далее».
Установка и настройка Windows server 2016 Essentials
Клик по кнопке «Установить». Затем в следующем окне введем «Ключ продукта» (Тот который мы получили еще на сайте Microsoft когда качали установочный пакет). Так Essentials будет активирован в тестовом периоде на 180 дней.
Если Вы хотите больше узнать о технической стороне 1С, тогда регистрируйтесь на первый бесплатный модуль курса: Администратор 1С >>>


Общее описание
Дата выхода: 29.09.2016 Платформа: NT Поддержка до: 2026 г.
Как попробовать/скачать
Пробная версия Windows Server 2016 доступна для скачивания с официального сайта. Тестовый период длится 180 дней, в течение которого доступны все функциональные возможности. После окончания данного периода необходимо купить и перевести систему на платную основу или отказаться от ее использования.
Скачанный ISO-образ позволяет развернуть Windows в 3-х вариантах:
- Полная версия — с графическим интерфейсом.
- Windows Core — с управлением из командной строки Powershell или удаленной консоли.
- Nano Server — урезанная Server Core с управлением только с удаленной консоли.
Редакции и их сравнение
Основные редакции
Standard Edition и Datacenter Edition. По сравнению с Windows Server 2012 имеют различия не только в части лицензирования виртуальных машин, но и некоторых функциональных возможностей.
| Функции | Standard | Datacenter |
|---|---|---|
| Лицензирование виртуальных машин | 2 бесплатно | Не требуется |
| Высокодоступное хранилище Storage Spaces Direct | — | + |
| Блочная репликация Storage Replica | — | + |
| Защита виртуальных машин Shielded Virtual Machines и Host Guardian Service | — | + |
| Управление сетью Network Fabric | — | + |
| SDN Microsoft Azure Stack | — | + |
| Примерная стоимость в долларах США (на 16 ядер) | $ 900 | $ 6 200 |
Дополнительные редакции
- Windows Server 2016 Essentials — разрешено использование не более чем для 25 пользователей и 50 устройств.
- MultiPoint Premium Server — для одновременной работы нескольких пользователей на одном компьютере (через KVM). Для образовательных учреждений.
- Windows Storage Server 2016 — решения для хранения данных. Доступно только для ОЕМ поставщиков.
- Hyper-V Server 2016 — бесплатная платформа для виртуализации.
Лицензирование
Лицензирование Windows Server 2016 для основных редакций претерпело некоторые изменения — теперь учет ведется по физическим ядрам процессора.
Ключевые особенности лицензирования по ядрам
- Лицензирование по физическим ядрам, а не процессорам, как в предыдущих версиях.
- Покупка дополнительных лицензий осуществляется комплектами по 2 ядра.
- Минимальное количество ядер — 16. Если используется процессор с 4 ядрами, купить нужно одну лицензию. Если используем 24 ядра — одну лицензию + 4 комплекта по 2 ядра.
- Минимальное количество ядер на процессор — 8. Если у нас 4 процессора по 4 ядра, купить нужно две лицензии по 16 ядер.
Сводная таблица лицензирования для выпусков
| Выпуск | Как лицензируется | Необходимость CAL |
|---|---|---|
| Standard | На ядра | Да |
| Datacenter | На ядра | Да |
| Essentials | На процессоры | Нет |
| MultiPoint Premium Server | На процессоры | Да + Remote Desktop Services CAL |
| Storage Server | На процессоры | Нет |
Лицензирование виртуальных машин
- Если в качестве хоста виртуализации используется Datacenter, лицензирование виртуальных машин не требуется.
- При использовании Standard Edition — не лицензируются только 2 машины. Для остальных покупаются лицензии по вышеописанной схеме.
- Для Windows Server Hyper-V и платформ других разработчиков необходимо лицензирование по ядрам (как описано выше).
Что нового
Так как Windows Server 2016 позиционируется как облачная операционная система, большая часть изменений коснулась вопросов безопасности, виртуализации и кластеризации.
Новое для виртуализации
- Появление контейнерной виртуализации.
- Более удобное управление сетью в Hyper-V — появился виртуальный сетевой контроллер.
- Повышенная защита от сбоев виртуальных машин с новым форматом виртуальных дисков — .VMCX и .VMRS
- Создание снапшотов из гостевых систем.
- Добавление оперативной памяти и Ethernet адаптеров на лету (без выключения виртуальной машины).
Новинки для кластеров
- Возможность обновления кластера без остановки.
- Блочная репликация файлов.
Другие обновления
- Дополнительный вариант установки — Nano.
- OpenGL и OpenCL для RDP.
- Встроенная поддержка HTTP/2.
Системные требования
Standard и Datacenter
| Минимум | Рекомендовано | Максимум | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Процессор | 1.4 ГГц | 2 ГГц | — |
| Оперативная память | 512 Мб (Nano) | 4 Гб | 24 Тб |
| Объем жесткого диска | 32 Гб | 60 Гб | — |
Essential
| Минимум | Рекомендовано | Максимум | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Процессор | 1.4 ГГц | 3.1 ГГц | 2 процессора |
| Оперативная память | 2 Гб | 4 Гб | 64 Гб |
| Объем жесткого диска | 32 Гб | 60 Гб | — |
Был ли полезен этот ответ?
Да Нет
Microsoft Windows Server 2016 – версия серверной операционной системы, пришедшая на смену Windows Server 2012. Финальная версия Windows Server 2016 включает в себя множество полезных обновлений и ориентирована на безопасный запуск и развертывание приложений в изолированной среде. Значительные изменения произошли среде Hyper-V. Значительно выше стал уровень защиты данных, благодаря инструменту PowerShell и функции делегирования прав доступа.
Главной особенностью Windows Server 2016 является изолированная операционная среда с применением контейнеров. По сути, реализация контейнерного типа приложений позволила значительно оптимизировать деятельность в виртуальной среде. Изолированная среда позволяет приложениям запускаться, не имея воздействия на всю операционную систему в целом. В Windows Server 2016 доступны два вида контейнеров: Windows Server и контейнеры Hyper-V. Причем в среде Hyper-V приложениям обеспечивается более полная изоляция благодаря высокому уровню оптимизации виртуальных машин.
В настоящее время продаются лицензии на актуальную версию Windows Server 2019. Корпоративные лицензии Microsoft Windows Server 2019 разрешают использование предыдущих версий продукта соответствующих редакций (правило Downgrade). При этом применяются принципы лицензирования актуальной версии.
Таким образом, вы можете использовать Windows Server 2016, купив лицензии Windows Server 2019 (но только корпоративные лицензии). Правила лицензирования продукта не изменились.
|
|
|---|
Редакции Microsoft Windows Server 2016
Существуют следующие редакции (выпуски) Microsoft Windows Server 2016:
- Datacenter – содержит полный функционал с неограниченными правами на запуск виртуальных экземпляров.
- Standard – редакция ОС с полными возможностями и правом запуска до двух виртуальных экземпляров.
- Essentials – редакция ОС для предприятий малого бизнеса (поддерживает до 25 пользователей или 50 устройств).
См. также: Сравнение различных выпусков Windows Server 2016
Выбор вида лицензии
Для Microsoft Windows Server доступно 3 основных вида лицензирования:
- Приобретение лицензии в комплекте с оборудованием (ОЕМ).
- Коробочная версия (FPP).
- Корпоративная лицензия (Open License, Open Value и т.д.).
Подробнее об этих видах лицензий можно прочитать в статье:
- В чем отличия коробочных, электронных, OEM и корпоративных лицензий на ПО Microsoft?
Принципы лицензирования
Редакции Windows Server 2016 Standard и Datacenter лицензируются по схеме «Лицензии на ядра» + «лицензия клиентского доступа CAL» + «дополнительная лицензия External Connector».
Каждая серверная лицензия выпускается на 2 физических ядра (2Lic Core). Минимальный пакет на 1 процессор – 4 лицензии 2Lic Core (8 ядер). Минимальный пакет на 1 сервер – 8 лицензий 2Lic Core (т.е нужно лицензировать как минимум 16 ядер).
При покупке лицензий Windows Server 2016 Standard или Datacenter вам понадобятся:
- серверные лицензии, для каждого сервера нужно 8 или более лицензий – это определяется количеством ядер;
- клиентские лицензии Windows Server CAL, количество которых равно числу лицензируемых клиентов – пользователей или устройств.
Клиент – это пользователь или устройство (компьютер), которые прямо или косвенно обращаются к серверному программному обеспечению. Соответственно, существуют клиентские лицензии «на пользователя» (User CAL) и «на устройство» (Device CAL). Вам нужно будет выбрать тип лицензии, который наиболее подходит (например, более экономичный). Чаще выбирают лицензии «на устройство».
Важное замечание: при увеличении числа серверов число клиентских лицензий не увеличивается. Количество клиентских лицензий зависит только от числа лицензируемых объектов – пользователей или устройств.
Например, для 1 сервера, имеющего не более 2 процессоров по 8 ядер каждый, и 20 подключенных к нему устройств у вас получится такой список лицензий для редакции Standard:
- WinSvrSTDCore 2016 SNGL OLP 2Lic NL CoreLic – 8 шт.
- WinSvrCAL 2016 SNGL OLP NL DvcCAL – 20 шт.
С 1 мая 2017 года в прайс-листе Microsoft появилась специальная позиция для покупки минимального набора серверных лицензий: пакет на 16 ядер.
Для редакции Standard:
- WinSvrSTDCore 2016 SNGL OLP 16Lic NL CoreLic
Пакеты лицензий на 2 ядра остаются доступны для заказа. Изменений в лицензионных требованиях нет, пользователи по-прежнему должны лицензировать все физические ядра серверов. Цена одной лицензии на 16 ядер не отличается от стоимости 8 лицензий на 2 ядра.
Лицензия External Connector позволяет подключаться к серверу неограниченному числу внешних пользователей. Внешними пользователями могут быть сотрудники партнерских компаний, покупатели или поставщики, просто посторонние люди (т.е. все, кроме сотрудников вашей организации). Для своих сотрудников необходимо покупать лицензии CAL.
|
|
А если не буду покупать клиентские лицензии? |
Лицензирование Windows Server 2016 Essentials не изменилось по сравнению с предыдущей версией. Редакция Essentials лицензируется, как и раньше, по числу серверов и не требует лицензий клиентского доступа.
|
|
Если у меня в офисе несколько организаций и все пользуются общими серверами – на какую организацию надо покупать лицензию? |
|
|
Как лицензируется использование сервера терминалов в Windows Server? |
Существует два типа Windows Server 20162 Remote Desktop Services CAL: клиентская лицензия на «на устройство» (Device CAL) и «на пользователя» (User CAL). Лицензия Windows Server 2016 Remote Desktop Services External Connector позволяет предоставить неограниченному количеству внешних пользователей доступ к терминальным службам на базе Windows Server.
Важное замечание: лицензии Windows Remote Desktop Services CAL приобретаются в дополнение к лицензиям Windows Server CAL. То есть в нашем примере, если 10 устройств из 20 подключенных к серверу используют терминальный доступ, необходимо приобрести 20 лицензий Windows Server CAL и 10 лицензий Windows Remote Desktop Services CAL:
- WinSvrSTDCore 2016 SNGL OLP 2Lic NL CoreLic – 8 шт.
- WinSvrCAL 2016 SNGL OLP NL DvcCAL – 20 шт.
- WinRmtDsktpSrvcsCAL 2016 SNGL OLP NL DvcCAL – 10 шт.
|
|
Можно ли к Windows Server 2016 Essentials подключаться через терминальный доступ (rdp), какие лицензии для этого нужно купить? |
См. также:
- Лицензирование для «чайников»: Windows Server 2019
- Лицензирование Microsoft Windows Server 2016
- Все, что нужно знать о корпоративных лицензиях Microsoft OLP
- Как читать прайс-лист Microsoft
- Лицензирование для «чайников»: Microsoft Windows 10
Теги:
microsoft windows server
windows server 2016
лицензирование
для чайников
Назад в список