Windows XP (Whistler — кодовое название при разработке) — операционная система (ОС) семейства Windows NT корпорации Microsoft. Была выпущена 25 октября 2001 года и является развитием Windows 2000 Professional.
Название XP происходит от англ. experience (опыт, впечатления). Внутренняя версия — Windows NT 5.1
Содержание
- Системные требования для Microsoft Windows XP Home и Professional Editions x86
- Платформа — x86:
- Системные требования для Microsoft Windows XP Professional x64
- Платформа: x64
- Окончание поддержки Windows XP
Системные требования для Microsoft Windows XP Home и Professional Editions x86
Платформа — x86:
- Процессор — 233 МГц (Рекомендуемые — 300 МГц);
- Оперативная память — 64 Мб (могут быть ограничены некоторые возможности) (Рекомендуемые — 128 Мб);
- Видеоадаптер и монитор — Super VGA (800X600);
- Свободное место на жестком диске — 1.5 Гб (Рекомендуемые — более 1.5 Гб);
- Оптические накопители — CD-ROM (Рекомендуемые — CD-ROM или DVD-ROM);
- Устройства ввода — Клавиатура (Рекомендуемые — Клавиатура и мышь);
- Другие устройства — Звуковая карта, колонки и/или наушники;
В дополнение к этим требованиям, для установки Service Pack 2 необходимо наличие на жёстком диске не менее 2 ГБ свободного места во время установки. А уже для SP 3 требуется 2.3 ГБ жёсткого диска при установке.
Системные требования для Microsoft Windows XP Professional x64
Платформа: x64
- Процессор: AMD Athlon 64, AMD Opteron, Intel Xeon с поддержкой Intel Extended Memory 64 Technology (EM64T), Intel Pentium 4 с Intel EM64T и другие 64-разрядные;
- Оперативная память: 256 Мб или больше;
- Видеоадаптер и монитор: Super VGA (800 x 600) или большее разрешение;
- Свободное место на HDD: 1.5 Гб или выше;
- CD-ROM или DVD-ROM, клавиатура и мышь.
Корпорация Майкрософт в течение 12 лет предоставляла поддержку для Windows XP. Теперь для нас и наших партнеров настало время инвестировать в более современные технологии, которые позволят нам и дальше разрабатывать и развивать новые эффективные способы работы.
В результате техническая поддержка по Windows XP больше не доступна. Это относится и к автоматическим обновлениям, которые повышают защиту компьютера.
Также корпорация Майкрософт прекратила предоставлять Microsoft Security Essentials для загрузки в Windows XP. Если у вас уже установлены эти компоненты, в течение некоторого времени вы будете получать обновления антивредоносных сигнатур.
Однако помните, что эффективность Microsoft Security Essentials (или любых других антивирусных программ) будет ограничена на компьютерах без последних обновлений для системы безопасности. Это значит, что компьютеры под управлением Windows XP будут незащищенными и находиться под угрозой заражения.
Загрузка …
( 13 оценок, среднее 4.08 из 5 )

Windows XP (внутренняя версия — Windows NT 5.1) — операционная система семейства Windows NT корпорации Microsoft. Дата выпуска 25 октября 2001 года. Является развитием версии Windows 2000 Professional.
Варианты Windows XP:
- Windows XP Professional Edition разработана для предприятий и предпринимателей и содержит такие функции, как удалённый доступ к рабочему столу компьютера, шифрование файлов, центральное управление правами доступа и поддержка многопроцессорных систем.
- Windows XP Home Edition — система для домашнего применения. Выпускается как недорогая «урезанная» версия Professional Edition.
- Windows XP Tablet PC Edition базируется на Professional Edition и содержит специальные приложения, оптимизированные для ввода данных стилусом на планшетных персональных компьютерах. Важнейшим свойством является понимание текстов, написанных от руки и адаптация графического интерфейса к поворотам дисплея. Эта версия продаётся только вместе с соответствующим компьютером.
- Windows XP Media Center Edition базируется на Professional Edition и содержит специальные мультимедийные приложения. Компьютер, как правило, оснащён ТВ-картой и пультом дистанционного управления (ПДУ).
- Windows XP Embedded — это встраиваемая компонентная операционная система на базе Windows XP Professional Edition и предназначена для применения в различных встраиваемых системах: системах промышленной автоматизации, банкоматах, медицинских приборах, кассовых терминалах, игровых автоматах, и т.п.
- Windows Embedded for Point of Service — специализированная операционная система на базе Windows XP Embedded, сконфигурированная для пунктов обслуживания и оптимизированная для розничной торговли и сферы услуг. На базе этой платформы можно создавать банкомат, платежный терминал, АЗС, кассовый аппарат и т.п.
- Windows XP Professional x64 Edition — специальная 64-разрядная версия, разработанная для процессоров с технологией AMD64 Opteron и Athlon 64 от фирмы AMD и процессоров с технологией EM64T от фирмы Intel. Эта система не поддерживает процессоры других производителей, а также не работает с процессором Intel Itanium. Основным достоинством системы является быстрая работа с большими числами (Long Integer и Double Float). Таким образом, эта система очень эффективна, например, при выполнении вычислений, использующих числа с плавающей запятой, необходимых в таких областях, как создание спецэффектов для кинофильмов и трёхмерной анимации, а также разработка технических и научных приложений. Данная система поддерживает смешанный режим, то есть одновременную работу 32- и 64-разрядных приложений.
- Windows XP Edition N — система без Windows Media Player и других мультимедиа-приложений. В настоящее время этот дистрибутив рассчитан на развивающиеся страны. При желании пользователь может бесплатно загрузить все недостающие приложения с веб-сайта Microsoft.
- Windows XP Starter Edition — функционально ограниченная версия для развивающихся стран. В этой версии возможна одновременная работа только 3 приложений, и каждое приложение может создать не более 3 окон.
- Windows Fundamentals for Legacy PCs — урезанная версия Microsoft Windows XP Embedded Service Pack 2 предназначенная для устаревших компьютеров.
Графическое оформление:
- Выделение в Windows Explorer осуществляется прозрачным синим прямоугольником.
- Падающая тень от ярлыков на рабочем столе.
- Боковая ориентированная на выполнение задач вспомогательная панель в окне проводника («common tasks»).
- Группирование кнопок одного приложения на панели задач в одну кнопку, при определённом количестве разных запущенных приложений, что позволяет часто избегать необходимости её «прокрутки».
- Цветовое выделения элементов в меню «Пуск», принадлежащих недавно добавленным программам.
- Меню отбрасывают тени.
- Windows XP анализирует производительность системы с определёнными визуальными эффектами и в зависимости от этого активирует их или нет.
- В Windows XP появилась возможность изменять графический интерфейс пользователя.
Системные требования операционной системы Windows XP Home и Windows XP Professional.
| Ресурсы | Минимальные | Рекомендуемые |
|---|---|---|
| Процессор | 233 MHz | 300 MHz или выше |
| Оперативная память | 64 Мб RAM (могут быть ограничены некоторые возможности) | 128 Мб RAM или выше |
| Видеоадаптер и монитор | VGA (640 x 480) | Super VGA (800 x 600) или бо́льшее разрешение |
| Свободное место на HDD | 1.5 Гб | 1.5 Гб или выше |
| Оптические накопители | CD-ROM (требуется для установки) | CD-ROM или DVD-ROM |
| Устройства взаимодействия с пользователем | клавиатура | клавиатура и мышь |
| Другие устройства | Звуковая карта, колонки и/или наушники | Звуковая карта, колонки и/или наушники |
| Service Pack 1 | Service Pack 2 | Service Pack 3 |
| Service Pack 1 (SP1) для Windows XP был выпущен 9 сентября 2002 года. Наиболее важными новшествами стали поддержка USB 2.0, утилита, позволяющая выбирать программы по умолчанию для просмотра веб, почты, обмена мгновенными сообщениями, а также различные реализации виртуальной машины Java. | Service Pack 2 (SP2) добавил в Windows XP новые возможности, поддержку Wi-Fi с мастером настройки и Bluetooth, а также улучшения в IE6 — например, возможность блокировать «всплывающие» окна. Появилась расширенная защита памяти, в частности, от атак переполнения буфера. Windows XP Service Pack 2 включает в себя Windows Security Center, который позволяет облегчить наблюдение за безопасностью системы, следя и напоминая пользователю о необходимости установить или обновить антивирус и его базы, активировать встроенный или сторонний файрволл, произвести обновление операционной системы или изменить настройки веб-браузера. Также были улучшены функции автозапуска при загрузке CD или подключении флеш-карт и подобных устройств. | Service Pack 3 (SP3) включает в себя все обновления, выпущенные после выхода Windows XP Service Pack 2, а также ряд других новых элементов. Среди них функция защиты сетевого доступа (Network Access Protection) и новая модель активации, заимствованные у Windows Vista, кроме того, появилась улучшенная функция обнаружение так называемых маршрутизаторов-«черных дыр» и др. |
Сравнение Windows XP Home Edition и Windows XP Professional.
| Возможности и средства | Windows XP Home Edition | Windows XP Professional |
|---|---|---|
| Новый интерфейс пользователя. | + | + |
| Проигрыватель Windows Media для Windows XP — поиск, воспроизведение, упорядочивание и хранение цифрового мультимедиа-материала. | + | + |
| Мастер установки сети — подключение и совместное использование компьютеров и устройств, применяемые в домашних условиях. | + | + |
| Служба сообщений Windows Messenger — средство связи и совместной работы, поддерживающее передачу немедленных сообщений, проведение голосовых и видеоконференций, а также совместное использование приложений. | + | + |
| Центр справки и поддержки — все ясно из названия. | + | + |
| Средства поддержки переносных компьютеров, включая технологии ClearType и DualView, а также усовершенствованное управление электропитанием — компьютер всегда с Вами. | + | + |
| Беспроводное подключение — автоматическая беспроводная конфигурация сети с использованием стандарта 802.1x. | + | + |
| Удаленный доступ к компьютеру — можно подключаться в удаленном режиме к ПК, работающему под управлением Windows XP Professional, с любого другого ПК, на котором установлена операционная система Windows. Таким образом можно работать со всеми приложениями и данными, издалека. | — | + |
| Автономные файлы и папки — доступ к файлам и папкам, хранящимся на общем сетевом диске даже во время отключения компьютера от сервера. | — | + |
| Быстрый запуск и усовершенствованное управление электропитанием — ускоряют загрузку системы и переход из спящего режима в рабочий. | + | + |
| Многозадачность — несколько приложений могут выполняться одновременно. | + | + |
| Масштабируемая поддержка процессора — вплоть до поддержки двусторонней многопроцессорной обработки. | — | + |
| Брандмауэр интернет-подключений — автоматически защищает подключенный к Интернету ПК от несанкционированного доступа. | + | + |
| Поддержка технологии безопасности Internet Explorer 6 — контроль использования личной информации при посещении веб-сайтов. | + | + |
| Шифрованная файловая система — защита важных данных, содержащихся в файлах, хранящихся на диске, на котором используется файловая система NTFS. | — | + |
| Управление доступом — запрещение доступа к избранным файлам, приложениям или другим ресурсам. | — | + |
| Централизованное администрирование — подключение систем, работающих под управлением Windows XP Professional, к домену Windows Server открывает доступ к многообразным эффективным средствам управления и обеспечения безопасности. | — | + |
| Групповая политика — упрощает администрирование групп пользователей и компьютеров. | — | + |
| Установка и поддержка программного обеспечения — автоматическая установка, настройка, восстановление и удаление приложений. | — | + |
| Перемещаемые профили пользователей — доступ ко всем своим документам и настройкам независимо от компьютера, используемого для входа в систему. | — | + |
| Служба удаленной установки — поддержка удаленной установки операционной системы на компьютеры, подключенные к сети. | — | + |
| Отображение текста на разных языках (технология Single Worldwide Binary) — можно вводить текст на любом языке и запускать версию приложений Win32 для любого языка, используя соответствующую версию операционной системы Windows XP. | + | + |
| Многоязычный пользовательский интерфейс — можно менять язык пользовательского интерфейса, чтобы работать с локализованными диалоговыми окнами, меню, файлами справки, словарями, средствами проверки правописания и т.д. | — | + |
P.S. На конец августа 2010 года, Windows XP — наиболее широко используемая операционная система в мире с долей на рынке, равной 53,1 %.
Поделитесь статьей в соцсетях — поддержите проект!
| Version of the Windows NT operating system | |

Screenshot of Windows XP running the Luna visual style, showing the start menu, taskbar, and My Computer window |
|
| Developer | Microsoft |
|---|---|
| Source model |
|
| Released to manufacturing |
August 24, 2001; 21 years ago[2] |
| General availability |
October 25, 2001; 21 years ago[2] |
| Final release | Service Pack 3 (5.1.2600.5512) / April 21, 2008; 14 years ago[3] |
| Marketing target | Consumer and Business |
| Update method |
|
| Platforms | IA-32, x86-64, and Itanium |
| Kernel type | Hybrid (NT) |
| Userland |
|
| License | Proprietary commercial software |
| Preceded by |
|
| Succeeded by | Windows Vista (2007) |
| Official website | Windows XP (archived at Wayback Machine) |
| Support status | |
All editions (except Windows XP Embedded, Windows XP 64-bit Edition, Windows Embedded for Point of Service, Windows Embedded Standard 2009, and Windows Embedded POSReady 2009):
Windows XP 64-bit Edition:
Windows XP Embedded:
Windows Embedded for Point of Service:
Windows Embedded Standard 2009:
Windows Embedded POSReady 2009:
|
Windows XP is a major release of Microsoft’s Windows NT operating system. It was released to manufacturing on August 24, 2001, and later to retail on October 25, 2001. It is a direct upgrade to its predecessors, Windows 2000 for high-end and business users and Windows Me for home users, and is available for any devices running Windows NT 4.0, Windows 98, Windows 2000, or Windows Me that meet the new Windows XP system requirements.
Development of Windows XP began in the late 1990s under the codename «Neptune», built on the Windows NT kernel and explicitly intended for mainstream consumer use. An updated version of Windows 2000 was also initially planned for the business market. However, in January 2000, both projects were scrapped in favor of a single OS codenamed «Whistler», which would serve as a single platform for both consumer and business markets. As a result, Windows XP is the first consumer edition of Windows not based on the Windows 95 kernel or MS-DOS. Windows XP removed support for PC-98, i486 and SGI Visual Workstation 320 and 540 and will only run on 32-bit x86 CPUs and devices that use BIOS firmware.
Upon its release, Windows XP received critical acclaim, noting increased performance and stability (especially compared to Windows Me), a more intuitive user interface, improved hardware support, and expanded multimedia capabilities. Windows XP and Windows Server 2003 were succeeded by Windows Vista and Windows Server 2008, released in 2007 and 2008, respectively.
Mainstream support for Windows XP ended on April 14, 2009, and extended support ended on April 8, 2014. Windows Embedded POSReady 2009, based on Windows XP Professional, received security updates until April 2019. After that, unofficial methods were made available to apply the updates to other editions of Windows XP. Still, Microsoft discouraged this practice, citing compatibility issues.[9] However, over eight years from the end of life date (September 2022), the majority of PCs in some countries (such as Armenia) still appeared to be running on Windows XP.[10] As of September 2022, globally, just 0.39% of Windows PCs[11] and 0.1% of all devices across all platforms continued to run Windows XP.
Development
In the late 1990s, initial development of what would become Windows XP was focused on two individual products: «Odyssey», which was reportedly intended to succeed the future Windows 2000 and «Neptune», which was reportedly a consumer-oriented operating system using the Windows NT architecture, succeeding the MS-DOS-based Windows 98.[12]
However, the projects proved to be too ambitious. In January 2000, shortly prior to the official release of Windows 2000, technology writer Paul Thurrott reported that Microsoft had shelved both Neptune and Odyssey in favor of a new product codenamed «Whistler», named after Whistler, British Columbia, as many Microsoft employees skied at the Whistler-Blackcomb ski resort.[13] The goal of Whistler was to unify both the consumer and business-oriented Windows lines under a single, Windows NT platform. Thurrott stated that Neptune had become «a black hole when all the features that were cut from Windows Me were simply re-tagged as Neptune features. And since Neptune and Odyssey would be based on the same code-base anyway, it made sense to combine them into a single project».[14]
At PDC on July 13, 2000, Microsoft announced that Whistler would be released during the second half of 2001, and also unveiled the first preview build, 2250, which featured an early implementation of Windows XP’s visual styles system and interface changes to Windows Explorer and the Control Panel.[15]
Microsoft released the first public beta build of Whistler, build 2296, on October 31, 2000. Subsequent builds gradually introduced features that users of the release version of Windows XP would recognize, such as Internet Explorer 6.0, the Microsoft Product Activation system and the Bliss desktop background.[16]
Whistler was officially unveiled during a media event on February 5, 2001, under the name Windows XP, where XP stands for «eXPerience».[17]
Release
In June 2001, Microsoft indicated that it was planning to spend at least US$1 billion on marketing and promoting Windows XP, in conjunction with Intel and other PC makers.[18] The theme of the campaign, «Yes You Can», was designed to emphasize the platform’s overall capabilities. Microsoft had originally planned to use the slogan «Prepare to Fly», but it was replaced because of sensitivity issues in the wake of the September 11 attacks.[19]
On August 24, 2001, Windows XP build 2600 was released to manufacturing (RTM). During a ceremonial media event at Microsoft Redmond Campus, copies of the RTM build were given to representatives of several major PC manufacturers in briefcases, who then flew off on decorated helicopters. While PC manufacturers would be able to release devices running XP beginning on September 24, 2001, XP was expected to reach general, retail availability on October 25, 2001. On the same day, Microsoft also announced the final retail pricing of XP’s two main editions, «Home» (as a replacement for Windows Me for home computing) and «Professional» (as a replacement for Windows 2000 for high-end users).[20]
New and updated features
User interface
While retaining some similarities to previous versions, Windows XP’s interface was overhauled with a new visual appearance, with an increased use of alpha compositing effects, drop shadows, and «visual styles», which completely changed the appearance of the operating system. The number of effects enabled are determined by the operating system based on the computer’s processing power, and can be enabled or disabled on a case-by-case basis. XP also added ClearType, a new subpixel rendering system designed to improve the appearance of fonts on liquid-crystal displays.[21] A new set of system icons was also introduced.[22] The default wallpaper, Bliss, is a photo of a landscape in the Napa Valley outside Napa, California, with rolling green hills and a blue sky with stratocumulus and cirrus clouds.[23]
The Start menu received its first major overhaul in XP, switching to a two-column layout with the ability to list, pin, and display frequently used applications, recently opened documents, and the traditional cascading «All Programs» menu. The taskbar can now group windows opened by a single application into one taskbar button, with a popup menu listing the individual windows. The notification area also hides «inactive» icons by default. A «common tasks» list was added, and Windows Explorer’s sidebar was updated to use a new task-based design with lists of common actions; the tasks displayed are contextually relevant to the type of content in a folder (e.g. a folder with music displays offers to play all the files in the folder, or burn them to a CD).[24]
The «task grouping» feature introduced in Windows XP showing both grouped and individual items
Fast user switching allows additional users to log into a Windows XP machine without existing users having to close their programs and log out. Although only one user at the time can use the console (i.e. monitor, keyboard, and mouse), previous users can resume their session once they regain control of the console.[25] Service Pack 2 and Service Pack 3 also introduced new features to Windows XP post-release, including the Windows Security Center, Bluetooth support, the executable space protection, Windows Firewall, and support for SDHC cards that are larger than 4 GB and smaller than 32 GB.[26][27][28][29]
Infrastructure
Windows XP uses prefetching to improve startup and application launch times.[30] It also became possible to revert the installation of an updated device driver, should the updated driver produce undesirable results.[31]
A copy protection system known as Windows Product Activation was introduced with Windows XP and its server counterpart, Windows Server 2003. All Windows licenses must be tied to a unique ID generated using information from the computer hardware, transmitted either via the internet or a telephone hotline. If Windows is not activated within 30 days of installation, the OS will cease to function until it is activated. Windows also periodically verifies the hardware to check for changes. If significant hardware changes are detected, the activation is voided, and Windows must be re-activated.[32]
Networking and internet functionality
Windows XP was originally bundled with Internet Explorer 6, Outlook Express 6, Windows Messenger, and MSN Explorer. New networking features were also added, including Internet Connection Firewall, Internet Connection Sharing integration with UPnP, NAT traversal APIs, Quality of Service features, IPv6 and Teredo tunneling, Background Intelligent Transfer Service, extended fax features, network bridging, peer to peer networking, support for most DSL modems, IEEE 802.11 (Wi-Fi) connections with auto configuration and roaming, TAPI 3.1, and networking over FireWire.[33] Remote Assistance and Remote Desktop were also added, which allow users to connect to a computer running Windows XP from across a network or the Internet and access their applications, files, printers, and devices or request help.[34] Improvements were also made to IntelliMirror features such as Offline Files, Roaming user profiles and Folder redirection.[35]
Backwards compatibility
To enable running software that targets or locks out specific versions of Windows, «Compatibility mode» was added. The feature allows pretending a selected earlier version of Windows to software, starting at Windows 95.[36]
While this ability was first introduced in Windows 2000 Service Pack 2, it had to be activated through the «register server» and was only available to administrator users, whereas Windows XP has it activated out of the box and also grants it to regular users.[37]
Other features
- Improved application compatibility and shims compared to Windows 2000.[38]
- DirectX 8.1, upgradeable to DirectX 9.0c.[39]
- A number of new features in Windows Explorer including task panes, thumbnails, and the option to view photos as a slideshow.[40]
- Improved imaging features such as Windows Picture and Fax Viewer.[41]
- Faster start-up, (because of improved Prefetch functions) logon, logoff, hibernation, and application launch sequences.[30]
- Numerous improvements to increase the system reliability such as improved System Restore,[42] Automated System Recovery,[43] and driver reliability improvements through Device Driver Rollback.[44]
- Hardware support improvements such as FireWire 800,[45] and improvements to multi-monitor support under the name «DualView».[46]
- Fast user switching.[47]
- The ClearType font rendering mechanism, which is designed to improve text readability on liquid-crystal display (LCD) and similar monitors, especially laptops.[21]
- Side-by-side assemblies[48] and registration-free COM.[49]
- General improvements to international support such as more locales, languages and scripts, MUI support in Terminal Services, improved Input Method Editors, and National Language Support.[50]
Removed features
Some of the programs and features that were part of the previous versions of Windows did not make it to Windows XP. Various MS-DOS commands available in its Windows 9x predecessor were removed,[51] as were the POSIX and OS/2 subsystems.[52]
In networking, NetBEUI, NWLink and NetDDE were deprecated and not installed by default.[53] Plug-and-play–incompatible communication devices (like modems and network interface cards) were no longer supported.[54]
Service Pack 2 and Service Pack 3 also removed features from Windows XP, including support for TCP half-open connections[55] and the address bar on the taskbar.[56]
Editions
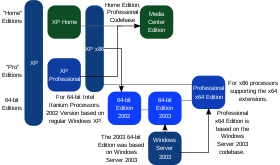
Diagram representing the main editions of Windows XP. It is based on the category of the edition (grey) and codebase (black arrow).
Windows XP was released in two major editions on launch: Home Edition and Professional Edition. Both editions were made available at retail as pre-loaded software on new computers and as boxed copies. Boxed copies were sold as «Upgrade» or «Full» licenses; the «Upgrade» versions were slightly cheaper, but require an existing version of Windows to install. The «Full» version can be installed on systems without an operating system or existing version of Windows.[18] The two editions of XP were aimed at different markets: Home Edition is explicitly intended for consumer use and disables or removes certain advanced and enterprise-oriented features present on Professional, such as the ability to join a Windows domain, Internet Information Services, and Multilingual User Interface. Windows 98 or Me can be upgraded to either edition, but Windows NT 4.0 and Windows 2000 can only be upgraded to Professional.[57] Windows’ software license agreement for pre-loaded licenses allows the software to be «returned» to the OEM for a refund if the user does not wish to use it.[58] Despite the refusal of some manufacturers to honor the entitlement, it has been enforced by courts in some countries.[59]
Two specialized variants of XP were introduced in 2002 for certain types of hardware, exclusively through OEM channels as pre-loaded software. Windows XP Media Center Edition was initially designed for high-end home theater PCs with TV tuners (marketed under the term «Media Center PC»), offering expanded multimedia functionality, an electronic program guide, and digital video recorder (DVR) support through the Windows Media Center application.[60] Microsoft also unveiled Windows XP Tablet PC Edition, which contains additional pen input features, and is optimized for mobile devices meeting its Tablet PC specifications.[61] Two different 64-bit editions of XP were made available. The first, Windows XP 64-Bit Edition, was intended for IA-64 (Itanium) systems; as IA-64 usage declined on workstations in favor of AMD’s x86-64 architecture, the Itanium edition was discontinued in January 2005.[62] A new 64-bit edition supporting the x86-64 architecture, called Windows XP Professional x64 Edition, was released in April of the same year.[63]
Microsoft also targeted emerging markets with the 2004 introduction of Windows XP Starter Edition, a special variant of Home Edition intended for low-cost PCs. The OS is primarily aimed at first-time computer owners, containing heavy localization (including wallpapers and screen savers incorporating images of local landmarks), and a «My Support» area which contains video tutorials on basic computing tasks. It also removes certain «complex» features, and does not allow users to run more than three applications at a time. After a pilot program in India and Thailand, Starter was released in other emerging markets throughout 2005.[64] In 2006, Microsoft also unveiled the FlexGo initiative, which would also target emerging markets with subsidized PCs on a pre-paid, subscription basis.[65]
As a result of unfair competition lawsuits in Europe and South Korea, which both alleged that Microsoft had improperly leveraged its status in the PC market to favor its own bundled software, Microsoft was ordered to release special editions of XP in these markets that excluded certain applications. In March 2004, after the European Commission fined Microsoft €497 million (US$603 million), Microsoft was ordered to release «N» editions of XP that excluded Windows Media Player, encouraging users to pick and download their own media player software.[66] As it was sold at the same price as the edition with Windows Media Player included, certain OEMs (such as Dell, who offered it for a short period, along with Hewlett-Packard, Lenovo and Fujitsu Siemens) chose not to offer it. Consumer interest was minuscule, with roughly 1,500 units shipped to OEMs, and no reported sales to consumers.[67] In December 2005, the Korean Fair Trade Commission ordered Microsoft to make available editions of Windows XP and Windows Server 2003 that do not contain Windows Media Player or Windows Messenger.[68] The «K» and «KN» editions of Windows XP were released in August 2006, and are only available in English and Korean, and also contain links to third-party instant messenger and media player software.[69]
Service packs
A service pack is a cumulative update package that is a superset of all updates, and even service packs, that have been released before it.[70] Three service packs have been released for Windows XP. Service Pack 3 is slightly different, in that it needs at least Service Pack 1 to have been installed, in order to update a live OS.[71] However, Service Pack 3 can still be embedded into a Windows installation disc; SP1 is not reported as a prerequisite for doing so.[72]
The unique boot screens from the RTM to Service Pack 1 versions of Windows XP that identified the edition of Windows XP currently running, including a green progress bar for Home Edition and a blue progress bar for Professional, Embedded, Tablet PC Edition, and Media Center Edition were removed in Service Pack 2 of Windows XP and was replaced with a generic «Windows XP» boot screen with a blue progress bar.
Service Pack 1
Service Pack 1 (SP1) for Windows XP was released on September 9, 2002. It contained over 300 minor, post-RTM bug fixes, along with all security patches released since the original release of XP. SP1 also added USB 2.0 support, the Microsoft Java Virtual Machine, .NET Framework support, and support for technologies used by the then-upcoming Media Center and Tablet PC editions of XP.[73] The most significant change on SP1 was the addition of Set Program Access and Defaults, a settings page which allows programs to be set as default for certain types of activities (such as media players or web browsers) and for access to bundled, Microsoft programs (such as Internet Explorer or Windows Media Player) to be disabled. This feature was added to comply with the settlement of United States v. Microsoft Corp., which required Microsoft to offer the ability for OEMs to bundle third-party competitors to software it bundles with Windows (such as Internet Explorer and Windows Media Player), and give them the same level of prominence as those normally bundled with the OS.[74]
On February 3, 2003, Microsoft released Service Pack 1a (SP1a). It was the same as SP1, except, the Microsoft Java Virtual Machine was excluded.[75]
Service Pack 2
Service Pack 2 (SP2) for Windows XP Home edition and Professional edition was released on August 25, 2004.[76] Headline features included WPA encryption compatibility for Wi-Fi and usability improvements to the Wi-Fi networking user interface,[77] partial Bluetooth support,[78] and various improvements to security systems.
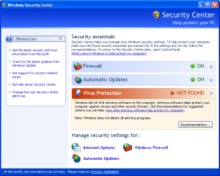
Headed by former computer hacker Window Snyder,[79][80] the service pack’s security improvements (codenamed «Springboard»,[81] as these features were intended to underpin additional changes in Longhorn) included a major revision to the included firewall (renamed Windows Firewall, and now enabled by default), and an update to Data Execution Prevention, which gained hardware support in the NX bit that can stop some forms of buffer overflow attacks. Raw socket support is removed (which supposedly limits the damage done by zombie machines) and the Windows Messenger service (which had been abused to cause pop-up advertisements to be displayed as system messages without a web browser or any additional software) became disabled by default. Additionally, security-related improvements were made to e-mail and web browsing. Service Pack 2 also added Security Center, an interface that provides a general overview of the system’s security status, including the state of the firewall and automatic updates. Third-party firewall and antivirus software can also be monitored from Security Center.[82]
In August 2006, Microsoft released updated installation media for Windows XP and Windows Server 2003 SP2 (SP2b), in order to incorporate a patch requiring ActiveX controls in Internet Explorer to be manually activated before a user may interact with them. This was done so that the browser would not violate a patent owned by Eolas.[83] Microsoft has since licensed the patent, and released a patch reverting the change in April 2008.[84] In September 2007, another minor revision known as SP2c was released for XP Professional, extending the number of available product keys for the operating system to «support the continued availability of Windows XP Professional through the scheduled system builder channel end-of-life (EOL) date of January 31, 2009.»[85]
Windows XP Service Pack 2 was later included in Windows Embedded for Point of Service and Windows Fundamentals for Legacy PCs.
Service Pack 3
The third and final Service Pack, SP3, was released through different channels between April[3] and June 2008,[86] about a year after the release of Windows Vista, and about a year before the release of Windows 7. Service Pack 3 was not available for Windows XP x64 Edition, which was based on the Windows Server 2003 kernel and, as a result, used its service packs[87] rather than the ones for the other editions.[88]
It began being automatically pushed out to Automatic Updates users on July 10, 2008.[89] A feature set overview which detailed new features available separately as stand-alone updates to Windows XP, as well as backported features from Windows Vista, was posted by Microsoft.[90] A total of 1,174 fixes are included in SP3.[91] Service Pack 3 could be installed on systems with Internet Explorer up to and including version 8; Internet Explorer 7 was not included as part of SP3.[92] It also did not include Internet Explorer 8, but instead was included in Windows 7, which was released one year after XP SP3.
Service Pack 3 included security enhancements over and above those of SP2, including APIs allowing developers to enable Data Execution Prevention for their code, independent of system-wide compatibility enforcement settings,[93] the Security Support Provider Interface,[94] improvements to WPA2 security,[95] and an updated version of the Microsoft Enhanced Cryptographic Provider Module that is FIPS 140-2 certified.[96]
In incorporating all previously released updates not included in SP2, Service Pack 3 included many other key features. Windows Imaging Component allowed camera vendors to integrate their own proprietary image codecs with the operating system’s features, such as thumbnails and slideshows.[97] In enterprise features, Remote Desktop Protocol 6.1 included support for ClearType and 32-bit color depth over RDP,[98] while improvements made to Windows Management Instrumentation in Windows Vista to reduce the possibility of corruption of the WMI repository were backported to XP SP3.[99]
In addition, SP3 contains updates to the operating system components of Windows XP Media Center Edition (MCE) and Windows XP Tablet PC Edition, and security updates for .NET Framework version 1.0, which is included in these editions. However, it does not include update rollups for the Windows Media Center application in Windows XP MCE 2005.[100] SP3 also omits security updates for Windows Media Player 10, although the player is included in Windows XP MCE 2005.[100] The Address Bar DeskBand on the Taskbar is no longer included because of antitrust violation concerns.[101]
Unofficial SP3 ZIP download packages were released on a now-defunct website called The Hotfix from 2005 to 2007.[102][103] The owner of the website, Ethan C. Allen, was a former Microsoft employee in Software Quality Assurance and would comb through the Microsoft Knowledge Base articles daily and download new hotfixes Microsoft would put online within the articles. The articles would have a «kbwinxppresp3fix» and/or «kbwinxpsp3fix» tag, thus allowing Allen to easily find and determine which fixes were planned for the official SP3 release to come. Microsoft publicly stated at the time that the SP3 pack was unofficial and advised users to not install it.[104][105] Allen also released a Vista SP1 package in 2007, for which Allen received a cease-and-desist email from Microsoft.[106]
Windows XP Service Pack 3 was later included in Windows Embedded Standard 2009 and Windows Embedded POSReady 2009.
System requirements
System requirements for Windows XP are as follows:
| Minimum | Recommended | |
|---|---|---|
| Home/Professional Edition[A] | ||
| CPU |
|
|
| Memory | 64 MB[E][F] | 128 MB |
| Free space |
|
|
| Media | CD-ROM drive or compatible | |
| Display | Super VGA (800 × 600) | |
| Sound hardware | N/A | Sound card plus speakers/headphones |
| Input device(s) | Keyboard, mouse | |
| Professional x64 Edition[J] | ||
| CPU |
|
|
| Memory | 256 MB | |
| Free space |
|
|
| Media | CD-ROM drive or compatible | |
| Display | Super VGA (800 × 600) | |
| Sound hardware | N/A | Sound card plus speakers/headphones |
| Input device(s) | Keyboard, mouse | |
| 64-Bit Edition[K] | ||
| CPU | Itanium 733 MHz | Itanium 800 MHz |
| Memory | 1 GB | |
| Free space | 6 GB | |
| Media | CD-ROM drive or compatible | |
| Display | Super VGA (800 × 600) | |
| Input device(s) | Keyboard, mouse |
Notes
- ^ «System requirements for Windows XP operating systems». April 28, 2005. Archived from the original on August 6, 2011. Retrieved March 12, 2007.
- ^ Even though this is Microsoft’s stated minimum processor speed for Windows XP, it is possible to install and run the operating system on early IA-32 processors such as a P5 Pentium without MMX instructions. Windows XP is not compatible with processors older than Pentium (such as 486) or the Cyrix 6×86 because it requires
CMPXCHG8B(see Pentium F00F bug) instructions. - ^ «Windows XP Minimal Requirement Test». Winhistory.de. September 9, 2011. Archived from the original on December 21, 2011. Retrieved January 1, 2012.
- ^ a b c d e «Windows XP: Required firmware and partition mapping scheme of hard disk drive». Support.microsoft.com. June 26, 2013. Archived from the original on April 27, 2017. Retrieved June 16, 2014.
- ^ A Microsoft TechNet paper from Summer 2001 (before Windows XP’s actual release), states that: «A computer with 64 MB of RAM will have sufficient resources to run Windows XP and a few applications with moderate memory requirements.» (Emphasis added.) These were said to be office productivity applications, e-mail programs, and web browsers (of the time). With such a configuration, user interface enhancements and fast user switching are turned off by default. For comparable workloads, 64 MB of RAM was then regarded as providing an equal or better user experience on Windows XP with similar settings than it would with Windows Me on the same hardware. In a later section of the paper, superior performance over Windows Me was noted with 128 MB of RAM or more, and with computers that exceed the minimum hardware requirements.
- ^ Sechrest, Stuart; Fortin, Michael (June 1, 2001). «Windows XP Performance». Microsoft TechNet. Archived from the original on July 27, 2010. Retrieved April 8, 2008.
- ^ «Hard disk space requirements for Windows XP Service Pack 1». Microsoft. October 29, 2007. Archived from the original on April 21, 2012. Retrieved April 6, 2012.
- ^ «The hard disk space requirements for Windows XP Service Pack 2». Microsoft. April 18, 2005. Archived from the original on November 24, 2010. Retrieved December 1, 2010.
- ^ «Windows XP – End of Support, Migration Guide, Download – TechNet». technet.microsoft.com. 2007. Archived from the original on May 13, 2008.
- ^ «Windows XP Professional x64 Edition SP2 VL EN (MSDN-TechNet)». Programmer Stuffs. March 23, 2011. Archived from the original on July 14, 2014. Retrieved May 2, 2012.
- ^ «Microsoft Windows XP 64-Bit Edition». Microsoft TechNet. Microsoft. August 15, 2001. Archived from the original on April 19, 2012. Retrieved May 2, 2012.
Physical memory limits
The maximum amount of RAM that Windows XP can support varies depending on the product edition and the processor architecture. All 32-bit editions of XP support up to 4 GB, except the Windows XP Starter edition, which supports up to 512 MB of RAM.[107] 64-bit editions support up to 128 GB.[108]
Processor limits
Windows XP Professional supports up to two physical processors;[109]
Windows XP Home Edition supports only one.[110]
However, XP supports a greater number of logical processors:
32-bit editions support up to 32 logical processors,[111] and 64-bit editions support up to 64 logical processors.[112]
Upgradeability
Several Windows XP components are upgradable to the latest versions, which include new versions introduced in later versions of Windows, and other major Microsoft applications are available. These latest versions for Windows XP include:
- ActiveSync 4.5
- DirectX 9.0c (June 7, 2010, Redistributable)
- Internet Explorer 8 on Windows XP Service Packs 2 and 3 (Internet Explorer 6 SP1 and Outlook Express 6 SP1 on Windows XP before SP2.)
- Windows Media Format Runtime and Windows Media Player 11 on Windows XP Service Packs 2 and 3 (and Windows Media Player 10 on Windows XP original release.)
- Microsoft Virtual PC 2004 and 2007
- .NET Framework up to and including version 4.0 (4.5 and higher versions are not supported.)
- Visual Studio 2005 on Windows XP versions below SP2, Visual Studio 2008 on Windows XP SP2 and Visual Studio 2010 on Windows XP SP3
- Windows Script Host 5.7
- Windows Installer 4.5
- Microsoft NetMeeting 3.02
- Office 2010 was the last version of Microsoft Office to be compatible with Windows XP.
- The Windows Services for UNIX subsystem can be installed to allow certain Unix-based applications to run on the operating system.
Support lifecycle
| Expiration date | |
|---|---|
| Mainstream support | April 14, 2009[4] |
| Extended support | April 8, 2014[4] The official exceptions ended in April 2019. |
| Applicable XP editions: | |
| Home Edition, Professional Edition, Professional x64 Edition, Professional for Embedded Systems, Media Center Editions (all), Starter Edition, Tablet PC Edition and Tablet PC Edition 2005,[4] as well as Windows Fundamentals for Legacy PCs.[113] | |
| Exceptions | |
| Windows XP 64-Bit Edition (Itanium edition, including Version 2003) | Unsupported as of June 30, 2005[5] |
| Windows XP Embedded | Mainstream support ended on January 11, 2011[4] Extended support ended on January 12, 2016[4] |
| Windows Embedded for Point of Service | Mainstream support ended on April 12, 2011[6] Extended support ended on April 12, 2016[6] |
| Windows Embedded Standard 2009 | Mainstream support ended on January 14, 2014 Extended support ended on January 8, 2019[7] |
| Windows Embedded POSReady 2009 | Mainstream support ended on April 8, 2014 Extended support ended on April 9, 2019[8] |
Support for the original release of Windows XP (without a service pack) ended on August 30, 2005.[4] Both Windows XP Service Pack 1 and 1a were retired on October 10, 2006,[4] and both Windows 2000 and Windows XP SP2 reached their end of support on July 13, 2010, about 24 months after the launch of Windows XP Service Pack 3.[4] The company stopped general licensing of Windows XP to OEMs and terminated retail sales of the operating system on June 30, 2008, 17 months after the release of Windows Vista.[114] However, an exception was announced on April 3, 2008, for OEMs producing what it defined as «ultra low-cost personal computers», particularly netbooks, until one year after the availability of Windows 7 on October 22, 2009. Analysts felt that the move was primarily intended to compete against Linux-based netbooks, although Microsoft’s Kevin Hutz stated that the decision was due to apparent market demand for low-end computers with Windows.[115]
Variants of Windows XP for embedded systems have different support policies: Windows XP Embedded SP3 and Windows Embedded for Point of Service SP3 were supported until January and April 2016, respectively. Windows Embedded Standard 2009, which was succeeded by Windows Embedded Standard 7, and Windows Embedded POSReady 2009, which was succeeded by Windows Embedded POSReady 7, were supported until January and April 2019, respectively.[116] These updates, while intended for the embedded editions, could also be downloaded on standard Windows XP with a registry hack, which enabled unofficial patches until April 2019. However, Microsoft advised Windows XP users against installing these fixes, citing incompatibility issues.[9][117]
End of support
On April 14, 2009, Windows XP exited mainstream support and entered the extended support phase; Microsoft continued to provide security updates every month for Windows XP, however, free technical support, warranty claims, and design changes were no longer being offered. Extended support ended on April 8, 2014, over 12 years after the release of Windows XP; normally Microsoft products have a support life cycle of only 10 years.[118] Beyond the final security updates released on April 8, no more security patches or support information are provided for XP free-of-charge; «critical patches» will still be created, and made available only to customers subscribing to a paid «Custom Support» plan.[119] As it is a Windows component, all versions of Internet Explorer for Windows XP also became unsupported.[120]
In January 2014, it was estimated that more than 95% of the 3 million automated teller machines in the world were still running Windows XP (which largely replaced IBM’s OS/2 as the predominant operating system on ATMs); ATMs have an average lifecycle of between seven and ten years, but some have had lifecycles as long as 15. Plans were being made by several ATM vendors and their customers to migrate to Windows 7-based systems over the course of 2014, while vendors have also considered the possibility of using Linux-based platforms in the future to give them more flexibility for support lifecycles, and the ATM Industry Association (ATMIA) has since endorsed Windows 10 as a further replacement.[121] However, ATMs typically run the embedded variant of Windows XP, which was supported through January 2016.[122] As of May 2017, around 60% of the 220,000 ATMs in India still run Windows XP.[123]
Furthermore, at least 49% of all computers in China still ran XP at the beginning of 2014. These holdouts were influenced by several factors; prices of genuine copies of later versions of Windows in the country are high, while Ni Guangnan of the Chinese Academy of Sciences warned that Windows 8 could allegedly expose users to surveillance by the United States government,[124] and the Chinese government banned the purchase of Windows 8 products for government use in May 2014 in protest of Microsoft’s inability to provide «guaranteed» support.[125] The government also had concerns that the impending end of support could affect their anti-piracy initiatives with Microsoft, as users would simply pirate newer versions rather than purchasing them legally. As such, government officials formally requested that Microsoft extend the support period for XP for these reasons. While Microsoft did not comply with their requests, a number of major Chinese software developers, such as Lenovo, Kingsoft and Tencent, will provide free support and resources for Chinese users migrating from XP.[126] Several governments, in particular those of the Netherlands and the United Kingdom, elected to negotiate «Custom Support» plans with Microsoft for their continued, internal use of Windows XP; the British government’s deal lasted for a year, and also covered support for Office 2003 (which reached end-of-life the same day) and cost £5.5 million.[127]
On March 8, 2014, Microsoft deployed an update for XP that, on the 8th of each month, displays a pop-up notification to remind users about the end of support; however, these notifications may be disabled by the user.[128] Microsoft also partnered with Laplink to provide a special «express» version of its PCmover software to help users migrate files and settings from XP to a computer with a newer version of Windows.[129]
An electroencephalograph running on Windows XP. The medical industry’s continued use of Windows XP is partly due to medical applications being incompatible with later versions of Windows.
Despite the approaching end of support, there were still notable holdouts that had not migrated past XP; many users elected to remain on XP because of the poor reception of Windows Vista, sales of newer PCs with newer versions of Windows declined because of the Great Recession and the effects of Vista, and deployments of new versions of Windows in enterprise environments require a large amount of planning, which includes testing applications for compatibility (especially those that are dependent on Internet Explorer 6, which is not compatible with newer versions of Windows).[130] Major security software vendors (including Microsoft itself) planned to continue offering support and definitions for Windows XP past the end of support to varying extents, along with the developers of Google Chrome, Mozilla Firefox, and Opera web browsers;[120] despite these measures, critics similarly argued that users should eventually migrate from XP to a supported platform.[131] The United States’ Computer Emergency Readiness Team released an alert in March 2014 advising users of the impending end of support, and informing them that using XP after April 8 may prevent them from meeting US government information security requirements.[132]
Microsoft continued to provide Security Essentials virus definitions and updates for its Malicious Software Removal Tool (MSRT) for XP until July 14, 2015.[133] As the end of extended support approached, Microsoft began to increasingly urge XP customers to migrate to newer versions such as Windows 7 or 8 in the interest of security, suggesting that attackers could reverse engineer security patches for newer versions of Windows and use them to target equivalent vulnerabilities in XP.[134] Windows XP is remotely exploitable by numerous security holes that were discovered after Microsoft stopped supporting it.[135][136]
Similarly, specialized devices that run XP, particularly medical devices, must have any revisions to their software—even security updates for the underlying operating system—approved by relevant regulators before they can be released. For this reason, manufacturers often did not allow any updates to devices’ operating systems, leaving them open to security exploits and malware.[137]
Despite the end of support for Windows XP, Microsoft has released three emergency security updates for the operating system to patch major security vulnerabilities:
- A patch released in May 2014 to address recently discovered vulnerabilities in Internet Explorer 6 through 11 on all versions of Windows.[138]
- A patch released in May 2017 to address a vulnerability that was being leveraged by the WannaCry ransomware attack.[139]
- A patch released in May 2019 to address a critical code execution vulnerability in Remote Desktop Services which can be exploited in a similar way as the WannaCry vulnerability.[140][141]
Researchers reported in August 2019 that Windows 10 users may be at risk for «critical» system compromise because of design flaws of hardware device drivers from multiple providers.[142] In the same month, computer experts reported that the BlueKeep security vulnerability, CVE-2019-0708, that potentially affects older unpatched Microsoft Windows versions via the program’s Remote Desktop Protocol, allowing for the possibility of remote code execution, may now include related flaws, collectively named DejaBlue, affecting newer Windows versions (i.e., Windows 7 and all recent versions) as well.[143] In addition, experts reported a Microsoft security vulnerability, CVE-2019-1162, based on legacy code involving Microsoft CTF and ctfmon (ctfmon.exe), that affects all Windows versions from the older Windows XP version to the most recent Windows 10 versions; a patch to correct the flaw is currently available.[144]
Microsoft announced in July 2019 that the Microsoft Internet Games services on Windows XP and Windows Me would end on July 31, 2019 (and for Windows 7 on January 22, 2020).[145] Others, such as Steam, had done the same, ending support for Windows XP and Windows Vista in January 2019.[146]
In 2020, Microsoft announced that it would disable the Windows Update service for SHA-1 endpoints; since Windows XP did not get an update for SHA-2, Windows Update Services are no longer available on the OS as of late July 2020.[147] However, as of October 2021, the old updates for Windows XP are still available on the Microsoft Update Catalog,[148] or through Legacy Update, a community-driven third party replacement for the Windows XP update servers.
Reception
On release, Windows XP received critical acclaim. CNET described the operating system as being «worth the hype», considering the new interface to be «spiffier» and more intuitive than previous versions, but feeling that it may «annoy» experienced users with its «hand-holding». XP’s expanded multimedia support and CD burning functionality were also noted, along with its streamlined networking tools. The performance improvements of XP in comparison to 2000 and Me were also praised, along with its increased number of built-in device drivers in comparison to 2000. The software compatibility tools were also praised, although it was noted that some programs, particularly older MS-DOS software, may not work correctly on XP because of its differing architecture. They panned Windows XP’s new licensing model and product activation system, considering it to be a «slightly annoying roadblock», but acknowledged Microsoft’s intent for the changes.[149] PC Magazine provided similar praise, although noting that a number of its online features were designed to promote Microsoft-owned services, and that aside from quicker boot times, XP’s overall performance showed little difference over Windows 2000.[150] Windows XP’s default theme, Luna, was criticized by some users for its childish look.[151][152]
Despite extended support for Windows XP ending in 2014, many users – including some enterprises – were reluctant to move away from an operating system they viewed as a stable known quantity despite the many security and functionality improvements in subsequent releases of Windows. Windows XP’s longevity was viewed as testament to its stability and Microsoft’s successful attempts to keep it up to date, but also as an indictment of its direct successor’s perceived failings.[153]
According to web analytics data generated by Net Applications, Windows XP was the most widely used operating system until August 2012, when Windows 7 overtook it (later overtaken by Windows 10),[154] while StatCounter indicates it happening almost a year earlier.[155] In January 2014, Net Applications reported a market share of 29.23%[156] of «desktop operating systems» for XP (when XP was introduced there was not a separate mobile category to track), while W3Schools reported a share of 11.0%.[157]
As of September 2022, in most regions or continents, Windows XP market share on PCs, as a fraction of the total Windows share, has gone below 1% (0.5% in Africa[158]). XP still has a double-digit market share in a few countries, such as Armenia at over 50%,[159][160][161][162] at 57%, where Windows 7 was highest ranked, and with it being replaced by Windows 10, Windows XP got highest ranked for the longest time, and had over 60% share on some weekends in the summer of 2019.[163][164]
Source code leak
On September 23, 2020, source code for Windows XP with Service Pack 1 and Windows Server 2003 was leaked onto the imageboard 4chan by an unknown user. Anonymous users managed to compile the code, as well as a Twitter user who posted videos of the process on YouTube proving that the code was genuine.[165] The videos were later removed on copyright grounds by Microsoft. The leak was incomplete as it was missing the Winlogon source code and some other components.[166][167] The original leak itself was spread using magnet links and torrent files whose payload originally included Server 2003 and XP source code and which was later updated with additional files, among which were previous leaks of Microsoft products, its patents, media about conspiracy theories on Bill Gates by anti-vaccination movements and an assortment of PDF files on different topics.[168]
Microsoft issued a statement stating that it was investigating the leaks.[167][169][170]
See also
- BlueKeep (security vulnerability)
- Comparison of operating systems
- History of operating systems
- List of operating systems
References
- ^ «Windows Licensing Programs». Microsoft. Archived from the original on December 16, 2008. Retrieved September 21, 2008.
- ^ a b «An Inside Look at the Months-long Process of Getting Windows XP Ready for Release to Manufacturing | Stories». Microsoft Stories. Microsoft. August 24, 2001. Archived from the original on August 5, 2019. Retrieved June 24, 2018.
- ^ a b Kelly, Gordon (April 16, 2008). «Windows XP SP3 Release Date(s) Confirmed». Trusted Reviews. Trusted Reviews. Archived from the original on June 23, 2018. Retrieved June 23, 2018.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l «Microsoft Product Lifecycle Search: Windows XP». Microsoft Support. Microsoft. Archived from the original on July 20, 2012. Retrieved May 14, 2022.
- ^ a b «Microsoft Security Bulletin MS05-036 – Critical». July 12, 2015. Archived from the original on April 26, 2018. Retrieved April 26, 2018.
- ^ a b c d Mackie, Kurt (February 19, 2014). «Windows XP Embedded Supported for Two or More Years». Redmond Magazine. 1105 Media. Archived from the original on February 20, 2017. Retrieved June 23, 2018.
- ^ a b c «Microsoft Product Lifecycle Search: Windows Embedded Standard 2009». Microsoft Support. Microsoft. Archived from the original on July 13, 2015. Retrieved October 13, 2012.
- ^ a b c «Microsoft Product Lifecycle Search: Windows Embedded POSReady 2009». Microsoft Support. Microsoft. Archived from the original on October 10, 2014. Retrieved October 13, 2012.
- ^ a b Seltzer, Larry (May 26, 2014). «Registry hack enables continued updates for Windows XP». ZDNet. Archived from the original on January 26, 2021. Retrieved January 30, 2021.
[UPDATE:] Late Monday we received a statement from a Microsoft spokesperson: We recently became aware of a hack that purportedly aims to provide security updates to Windows XP customers. The security updates that could be installed are intended for Windows Embedded and Windows Server 2003 customers and do not fully protect Windows XP customers. Windows XP customers also run a significant risk of functionality issues with their machines if they install these updates, as they are not tested against Windows XP. The best way for Windows XP customers to protect their systems is to upgrade to a more modern operating system, like Windows 7 or Windows 8.1.
- ^ «Desktop Windows Version Market Share in Armenia — September 2022». September 30, 2022. Retrieved October 10, 2022.
- ^ «Desktop Windows Version Market Share Worldwide | StatCounter Global Stats». gs.statcounter.com. Statcounter. Archived from the original on April 20, 2019. Retrieved May 8, 2022.
- ^ Miles, Stephanie (January 24, 2000). «Microsoft consolidates Windows development efforts». CNET. CNET Networks. Archived from the original on February 1, 2014. Retrieved January 23, 2014.
- ^ «Windows «Longhorn» FAQ». Paul Thurrott’s SuperSite for Windows. Penton Media. June 22, 2005. Archived from the original on April 4, 2008. Retrieved April 4, 2008.
- ^ Thurrott, Paul (October 6, 2010). «The Road to Gold: The development of Windows XP Reviewed». Paul Thurrott’s Supersite for Windows. Penton Media. Archived from the original on February 2, 2014. Retrieved January 23, 2014.
- ^ Thurrott, Paul (July 17, 2000). «Introducing the Whistler Preview, Build 2250». Windows IT Pro. Penton Media. Archived from the original on June 12, 2018. Retrieved June 9, 2018.
- ^ Thurrott, Paul (October 6, 2010). «The Road to Gold (Part Two)». Paul Thurrott’s SuperSite for Windows. Penton Media. Archived from the original on February 2, 2014. Retrieved January 23, 2014.
- ^ «Microsoft to christen Windows, Office with new name». CNET. CNET Networks. February 5, 2001. Archived from the original on February 1, 2014. Retrieved January 23, 2014.
- ^ a b «Windows XP marketing tab to hit $1 billion». CNET. CNET Networks. January 2, 2002. Archived from the original on February 1, 2014. Retrieved January 23, 2014.
- ^ «Microsoft changes XP slogan in wake of US attacks». Computerworld NZ. IDG. Archived from the original on September 5, 2015. Retrieved August 7, 2015.
- ^ Thurrott, Paul (October 15, 2001). «The Road to Gold (Part Three)». Paul Thurrott’s Supersite for Windows. Penton Media. Archived from the original on August 29, 2017. Retrieved March 11, 2017.
- ^ a b «HOW TO: Use ClearType to Enhance Screen Fonts in Windows XP». Support. Microsoft. October 27, 2002. Archived from the original on August 5, 2011. Retrieved August 8, 2011.
- ^ Esposito, Dino (November 2001). «New Graphical Interface: Enhance Your Programs with New Windows XP Shell Features». MSDN. Microsoft. Archived from the original on August 9, 2011. Retrieved August 8, 2011.
- ^ Turner, Paul (February 22, 2004). «No view of Palouse from Windows». The Spokesman-Review. Spokane. Archived from the original on May 11, 2011. Retrieved September 19, 2012.
- ^ Fitzpatrick, Jason (August 6, 2015). «The Start Menu Should Be Sacred (But It’s Still a Disaster in Windows 10)». How-To Geek. Archived from the original on March 13, 2017. Retrieved July 30, 2016.
- ^ «How To Use the Fast User Switching Feature in Windows XP (Revision 1.5)». Microsoft Support. Microsoft. March 27, 2007. Archived from the original on August 12, 2011. Retrieved August 8, 2011.
- ^ «Bluetooth Wireless Technology FAQ». Archived from the original on December 23, 2018. Retrieved August 8, 2011.
- ^ «Manually Configuring Windows Firewall in Windows XP Service Pack 2». Archived from the original on August 26, 2017. Retrieved August 26, 2017.
- ^ «Description of the Windows Firewall feature in Windows XP SP2». Archived from the original on September 17, 2009. Retrieved September 18, 2009.
- ^ «Hotfix for Windows XP that adds support for SDHC cards that have a capacity of more than 4 GB». Support (5.0 ed.). May 22, 2013. Archived from the original on February 5, 2014. Retrieved June 18, 2019.
- ^ a b «Kernel Enhancements for Windows XP». Windows Hardware Developer Center (WHDC). Microsoft. January 13, 2003. Archived from the original on March 7, 2008. Retrieved August 8, 2011.
- ^ «HOW TO: Use the Driver Roll Back Feature to Restore a Previous Version of a Device Driver in Windows XP». Microsoft. October 27, 2002. Archived from the original on February 18, 2006.
- ^ Fisher, Ken (February 2, 2001). «Windows Product Activation: an early look». Ars Technica. Archived from the original on December 5, 2011. Retrieved February 22, 2017.
- ^ «Windows XP Networking Features and Enhancements». Microsoft TechNet. Microsoft. August 8, 2001. Archived from the original on July 26, 2011. Retrieved August 8, 2011.
- ^ «Frequently Asked Questions About Remote Desktop». Microsoft. Archived from the original on July 4, 2007.
- ^ Otey, Michael (October 2001). «Discover Windows XP». Microsoft Developer. Archived from the original on April 20, 2012. Retrieved June 21, 2018.
- ^ «Windows XP Program Compatibility Wizard». ServerWatch. March 12, 2002. Archived from the original on November 13, 2021. Retrieved November 13, 2021.
- ^ «How to Enable Application Compatibility-Mode Technology in Windows 2000 Service Pack 2». Active Win. 2000. Archived from the original on August 18, 2001. Retrieved November 13, 2021.
- ^ Proffit, Brian (September 2, 2002). «Old Apps Find A New Home On Windows XP». PC Magazine. Ziff Davis. Archived from the original on June 10, 2020. Retrieved July 10, 2018.
- ^ Karp, David; O’Reilly, Tim; Mott, Troy (2005). Windows XP in a Nutshell : [a desktop quick reference] (2nd ed.). Beijing [u.a.]: O’Reilly. p. 141. ISBN 978-0-596-00900-7.
- ^ Richtmyer, Richard (August 23, 2001). «Opening up Windows XP». CNN Money. CNN. Archived from the original on December 23, 2017. Retrieved June 24, 2018.
- ^ «Windows Picture and Fax Viewer overview». Windows XP Professional Product Documentation. Microsoft Corporation. Archived from the original on 2 December 2010. Retrieved 23 November 2010.
- ^ Harder, Bobbie (April 2001). «Microsoft Windows XP System Restore». Microsoft. Archived from the original on February 4, 2005.
- ^ Petri, Daniel (January 8, 2009). «What is ASR in Windows XP and Windows Server 2003?». Petri. Blue Whale Web Media Group. Archived from the original on March 12, 2017. Retrieved June 24, 2018.
- ^ Columbus, Louis (June 29, 2001). Exploring Windows XP’s Device Driver Rollback and System Restore. InformIT. Pearson Education. Archived from the original on January 5, 2014. Retrieved June 24, 2018.
- ^ Norton, Peter; Mueller, John Paul (2002). Peter Norton’s Complete Guide to Windows XP. Pearson Education. p. N/A. ISBN 9780132715386. Archived from the original on April 15, 2021. Retrieved July 10, 2018.
- ^ McNamee, Kieran (June 27, 2003). «Setting up dual monitors using Windows XP Home». PC World. Archived from the original on February 5, 2017. Retrieved June 24, 2018.
- ^ «Architecture of Fast User Switching». Microsoft Knowledgebase. Microsoft. January 15, 2006. Archived from the original on August 2, 2009. Retrieved June 24, 2018.
- ^ Satran, Michael (May 31, 2018). «About Side-by-Side Assemblies». docs.microsoft.com. Microsoft. Archived from the original on June 24, 2018. Retrieved June 24, 2018.
- ^ Wienholt, Nick (August 14, 2006). «Simplify Application Deployment with Registration-Free COM — Developer.com». www.developer.com. QuinStreet Enterprise. Archived from the original on December 16, 2010. Retrieved June 24, 2018.
- ^ Honeycutt, Jerry (2003). Introducing Microsoft Windows Server 2003. Redmond, Wash.: Microsoft. pp. 293–298. ISBN 9780735615700.
- ^ «New ways to do familiar tasks». Windows XP Product Documentation. Microsoft. Archived from the original on May 3, 2006. Retrieved May 21, 2014.
- ^ «Kernel Enhancements for Windows XP». MSDN. Microsoft. January 13, 2003. Archived from the original on March 6, 2013. Retrieved April 16, 2014.
- ^ Pittsley, Steven (June 13, 2002). «Easy install guide for NetBEUI and IPX in Windows XP Pro». TechRepublic. CBS Interactive. Archived from the original on April 11, 2017. Retrieved June 24, 2018.
- ^ «Non-Plug and Play Network Device Support in Windows XP». Support. Microsoft. October 18, 2001. Archived from the original on October 30, 2004. Retrieved November 8, 2012.
- ^ «TCP/IP Raw Sockets (Windows)». MSDN. Microsoft. Archived from the original on January 28, 2013. Retrieved November 7, 2012.
- ^ Pash, Adam (April 29, 2008). «Field Guide to Windows XP SP3». Lifehacker. Univision Communications. Archived from the original on January 15, 2018. Retrieved June 24, 2018.
- ^ «Differences with Windows XP Home Edition». TechNet. Microsoft. September 11, 2009. Archived from the original on February 9, 2014. Retrieved January 26, 2014.
- ^ Marti, Don (November 6, 2006). «Dell customer gets Windows refund». LinuxWorld. IDG. Archived from the original on September 27, 2008. Retrieved September 13, 2008.
- ^ «HP must reimburse Italian PC buyer the amount paid for Microsoft software». Heise online. October 29, 2007. Archived from the original on October 15, 2008. Retrieved September 13, 2008.
- ^ Wilcox, Joe (July 16, 2002). «Microsoft reveals media XP details». CNET. CNET Networks. Archived from the original on February 7, 2015. Retrieved January 26, 2014.
- ^ Wilcox, Joe; Junnarkar, Sandeep (November 7, 2002). «Microsoft launches tablet PC drive». CNET. CNET Networks. Archived from the original on February 7, 2015. Retrieved January 26, 2014.
- ^ Evers, Joris (January 5, 2005). «Microsoft nixes Windows XP for Itanium». Computerworld. IDG. Archived from the original on February 2, 2014. Retrieved January 26, 2014.
- ^ «Microsoft Raises the Speed Limit with the Availability of 64-Bit Editions of Windows Server 2003 and Windows XP Professional» (Press release). Microsoft. April 25, 2005. Archived from the original on February 25, 2015. Retrieved September 10, 2015.
- ^ Thurrott, Paul (January 3, 2005). «Windows XP Starter Edition». Paul Thurrott’s SuperSite for Windows. Penton Media. Archived from the original on August 28, 2013. Retrieved April 12, 2008.
- ^ Fried, Ina (May 23, 2006). «Microsoft pitches pay-as-you-go PCs». CNET. CNET Networks. Archived from the original on February 7, 2015. Retrieved January 26, 2014.
- ^ «Microsoft and EU reach agreement». BBC. March 28, 2005. Archived from the original on September 22, 2015.
- ^ Bishop, Todd (December 24, 2004). «Europe gets ‘reduced’ Windows». Seattle Post-Intelligencer. Hearst Corporation. Archived from the original on October 6, 2021. Retrieved November 30, 2018.
- ^ Anderson, Nate (December 7, 2005). «South Korea fines Microsoft for antitrust abuses». Ars Technica. Condé Nast Publications. Archived from the original on April 22, 2008. Retrieved April 12, 2008.
- ^ «Changes to Windows XP Home Edition K and Windows XP Professional K from earlier versions of Windows XP (MSKB 922474)». Microsoft Support. Microsoft. September 15, 2006. Archived from the original on December 19, 2013. Retrieved January 26, 2014.
- ^ «Service Pack and Update Center». Support. Microsoft. September 10, 2016. Archived from the original on August 31, 2017.
- ^ «Installing Windows XP Service Pack 3 (SP3)». Microsoft. Microsoft. November 18, 2011. Archived from the original on August 22, 2017. Retrieved August 22, 2017.
- ^ Purdy, Kevin. «Slipstream Service Pack 3 into Your Windows XP Installation CD». Lifehacker. Archived from the original on August 22, 2017. Retrieved August 22, 2017.
- ^ «Windows XP SP1 Irons out the Wrinkles». PC Magazine. Archived from the original on February 26, 2014. Retrieved January 26, 2014.
- ^ Mendelson, Edward. «Microsoft Windows XP Service Pack 1 review». CNET. CNET Networks. Archived from the original on February 9, 2008. Retrieved January 26, 2014.
- ^ «Differences Between Windows XP SP1 and Windows XP SP1a». February 3, 2003. Archived from the original on January 27, 2007. Retrieved September 21, 2007.
- ^ «How to obtain the latest Windows XP service pack». March 26, 2007. Archived from the original on October 14, 2004. Retrieved September 21, 2007.
- ^ Shinder, Deb (August 26, 2004). «Windows XP Service Pack 2: How it affects wireless networking». TechRepublic. CBS Interactive. Archived from the original on June 13, 2017. Retrieved June 24, 2018.
- ^ «Bluetooth Wireless Technology FAQ – 2010». July 24, 2012. Archived from the original on March 3, 2016. Retrieved November 4, 2012.
- ^ Menn, Joseph (2019). Cult of the Dead Cow: How the Original Hacking Supergroup Might Just Save the World. New York: Public Affairs. p. 49–50.
- ^ Grimes, Roger A. (2017). «46 — Profile: Window Snyder». Hacking the hacker : learn from the experts who take down hackers. Indianapolis, IN: Wiley. ISBN 978-1-119-39626-0. OCLC 983465946.
- ^ Thurrott, Paul (October 15, 2003). «Windows XP SP2 to be ‘Springboard’ to Longhorn». Windows IT Pro. Archived from the original on June 23, 2018.
- ^ «Windows XP Service Pack 2 information». Microsoft. August 4, 2004. Archived from the original on October 16, 2007.
- ^ Mux, Victor (August 21, 2006). «Why Windows XP SP2b and Windows Server 2003 SP2a?». Microsoft. Archived from the original on August 12, 2009.
- ^ Fletcher, Jefferson (April 8, 2008). «IE Automatic Component Activation Now Available». IEBlog. Microsoft. Archived from the original on April 11, 2008. Retrieved April 11, 2008.
- ^ Mux, Victor (August 9, 2007). «Microsoft Windows XP Professional Service Pack 2c Release». MSDN. Microsoft. Archived from the original on February 2, 2014. Retrieved January 26, 2014.
- ^ Emil Protalinski — April 29, 2008, 1:35 pm UTC (April 29, 2008). «Microsoft releases the long-anticipated Windows XP SP3 (updated)». Ars Technica. Archived from the original on January 15, 2022. Retrieved February 10, 2022.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ «Release Notes for Microsoft Windows Server 2003 Service Pack 2». Archived from the original on November 11, 2019. Retrieved November 11, 2019.
- ^ Oiaga, Marius (December 14, 2007). «64-Bit Windows XP Service Pack 3?». Softpedia. SoftNews NET. Archived from the original on May 8, 2018. Retrieved June 24, 2018.
- ^ Keizer, Gregg (July 8, 2008). «Microsoft sets XP SP3 automatic download for Thursday». Computerworld. IDG. Archived from the original on July 9, 2008. Retrieved July 8, 2008.
- ^ «Windows XP Service Pack 3 Overview». Microsoft. May 6, 2008. Archived from the original on May 6, 2008. Retrieved May 7, 2008.
- ^ «List of fixes that are included in Windows XP Service Pack 3». Microsoft. May 6, 2008. Archived from the original on May 9, 2008. Retrieved June 23, 2018.
- ^ Oiaga, Marius (December 14, 2007). «No, Internet Explorer 7 Will Not(!) Be a Part of Windows XP SP3». SoftNews NET. Archived from the original on January 18, 2012.
- ^ Howard, Michael (January 29, 2008). «New NX APIs added to Windows Vista SP1, Windows XP SP3 and Windows Server 2008». Michael Howard’s Web Log. Microsoft. Archived from the original on August 25, 2011. Retrieved August 8, 2011.
- ^ «Description of the Credential Security Support Provider (CredSSP) in Windows XP Service Pack 3». Microsoft. May 6, 2008. Archived from the original on October 9, 2009. Retrieved June 23, 2018.
- ^ Enterprise IT Planet Staff (May 13, 2005). «Upgraded Wi-Fi Security for Windows XP SP2». Wi-Fi Planet. QuinStreet Enterprise. Archived from the original on June 23, 2018. Retrieved June 23, 2018.
- ^ «Overview of Windows XP Service Pack 3» (PDF). Archived (PDF) from the original on January 17, 2009.
- ^ «Information about Windows Imaging Component». Microsoft. August 13, 2002. Archived from the original on May 10, 2011.
- ^ Nanjappa, Ashwin (January 27, 2010). «Windows: ClearType on RDP». CodeYarns.com. Archived from the original on November 17, 2015. Retrieved June 16, 2014.
- ^ «A hotfix is available that improves the stability of the Windows Management Instrumentation repository in Windows XP». Support. Microsoft. October 8, 2011. Archived from the original on March 5, 2013. Retrieved January 20, 2013.
- ^ a b «FAQs regarding SP3 RTM». Microsoft. April 22, 2008. Archived from the original on August 24, 2011. Retrieved June 23, 2018.
- ^ Kaelin, Mark (May 8, 2008). «How do I… Return the Address bar Windows XP SP3 removed?». TechRepublic. CBS Interactive. Archived from the original on September 5, 2015. Retrieved May 5, 2015.
- ^ «Windows XP SP3 preview surfaces on Web». PC World. IDG. October 6, 2005. Archived from the original on October 31, 2020. Retrieved October 29, 2020.
- ^ «Sneak preview of Windows XP SP3 surfaces». Ars Technica. Ars Technica. October 6, 2005. Archived from the original on November 4, 2020. Retrieved October 29, 2020.
- ^ «Microsoft employee blasts ‘fake’ service pack». PC World. IDG. October 14, 2005. Archived from the original on October 31, 2020. Retrieved October 29, 2020.
- ^ «Windows XP SP3 preview a fake». Ars Technica. Ars Technica. October 15, 2005. Archived from the original on October 31, 2020. Retrieved October 29, 2020.
- ^ «Microsoft leans on Vista SP1 site». PC World. IDG. October 4, 2007. Archived from the original on May 18, 2017. Retrieved October 29, 2020.
- ^ «What is the maximum amount of RAM the Windows operating system can handle?». Crucial. Archived from the original on May 11, 2011. Retrieved June 25, 2010.
- ^ «Physical Memory Limits: Windows XP». Memory Limits for Windows Releases. Microsoft. Archived from the original on January 6, 2014. Retrieved January 14, 2014.
- ^ «Processor and memory capabilities of Windows XP Professional x64 Edition and of the x64-based versions of Windows Server 2003 (Revision 7.0)». Microsoft Support. Microsoft. December 20, 2010. Archived from the original on August 12, 2011. Retrieved August 8, 2011.
- ^ Kumar, I. Suuresh (October 25, 2010). «Multi-core processor and multiprocessor limit for Windows XP». Microsoft Answers. Microsoft. Archived from the original on April 19, 2014. Retrieved April 18, 2014.
- ^ «Processor Affinity Under WOW64». MSDN. Microsoft. January 27, 2011. Archived from the original on May 6, 2011. Retrieved August 8, 2011.
- ^ «Maximum quantity of logical processors in a PC supported by Microsoft Windows XP professional, x64 edition». Support. Microsoft. December 20, 2010. Archived from the original on January 11, 2013. Retrieved January 20, 2013.
- ^ «Microsoft Product Lifecycle Search: Windows Fundamentals for Legacy PCs». Microsoft Support. Microsoft. Archived from the original on October 5, 2014. Retrieved October 13, 2012.
- ^ Fried, Ina (September 27, 2007). «Microsoft extends Windows XP’s stay». CNET. CBS Interactive. Archived from the original on August 30, 2008. Retrieved June 5, 2008.
- ^ Lai, Eric (March 3, 2008). «Microsoft to keep Windows XP alive—but only for Eee PCs and wannabes». Computerworld. IDG. Archived from the original on April 8, 2008. Retrieved April 8, 2008.
- ^ Tung, Liam (February 18, 2014). «Microsoft: ‘Remember, some XP-based embedded systems to get support to 2019’«. ZDNet. CBS Interactive. Archived from the original on April 4, 2014. Retrieved April 6, 2014.
- ^ Newman, Jared (August 27, 2014). «Enthusiast developer keeps Windows XP alive with unofficial ‘Service Pack 4’«. PCWorld. Archived from the original on October 26, 2018. Retrieved October 26, 2018.
- ^ Satherley, Dan (April 9, 2013). «Businesses urged to ditch XP». 3 News NZ. Archived from the original on July 13, 2014. Retrieved June 28, 2019.
- ^ Keizer, Gregg (August 26, 2013). «Microsoft will craft XP patches after April ’14, but not for you». Computerworld. IDG. Archived from the original on October 20, 2013. Retrieved December 12, 2013.
- ^ a b Keizer, Gregg (March 11, 2014). «US-CERT urges XP users to dump IE». Computerworld. IDG. Archived from the original on June 28, 2019. Retrieved June 28, 2019.
- ^ ATM Industry Association (collectively) (June 1, 2015). «ATMIA position paper recommending migration to Windows 10». www.atmia.com (Press release). ATM Industry Association. Archived from the original on May 25, 2017.
- ^ Summers, Nick (January 16, 2014). «ATMs Face Deadline to Upgrade From Windows XP». Bloomberg Businessweek. Bloomberg L.P. Archived from the original on January 16, 2014. Retrieved January 17, 2014.
- ^ «Wannacry ransomware cyber attack: Indian ATMs could be at high risk as most run on Windows XP». Business Today. May 15, 2017. Archived from the original on May 17, 2017. Retrieved May 18, 2017.
- ^ «Windows 8 a ‘threat’ to China’s security». BBC. June 5, 2014. Archived from the original on October 8, 2018. Retrieved October 8, 2018.
- ^ Kan, Michael (May 20, 2014). «China bans government purchases of Windows 8». PCWorld. IDG. Archived from the original on May 20, 2014. Retrieved May 20, 2014.
- ^ «Microsoft Partners Lenovo, Tencent to Offer XP Tech Support in China». Voanews.com. Reuters. April 9, 2014. Archived from the original on April 13, 2014. Retrieved April 16, 2014.
- ^ Gallagher, Sean (April 6, 2014). «Not dead yet: Dutch, British governments pay to keep Windows XP alive». Ars Technica. Condé Nast Publications. Archived from the original on October 14, 2019. Retrieved October 15, 2019.
- ^ Foley, Mary Jo (March 3, 2014). «Microsoft to start nagging Windows XP users about April 8 end-of-support date». ZDNet. CBS Interactive. Archived from the original on October 14, 2019. Retrieved October 15, 2019.
- ^ Yegulalp, Serdar (March 3, 2014). «Microsoft: Use Laplink’s Windows XP migration tools, not ours». Infoworld. Archived from the original on October 15, 2019.
- ^ Ward, Mark (March 5, 2014). «XP – the operating system that will not die». BBC News. Archived from the original on March 24, 2014. Retrieved March 25, 2014.
- ^ Egan, Matt (April 7, 2014). «What should XP users do when Microsoft ends support? Upgrade to Windows 8, buy a new PC, keep running XP?». PC Advisor. Archived from the original on February 14, 2014. Retrieved April 6, 2014.
- ^ «Alert (TA14-069A): Microsoft Ending Support for Windows XP and Office 2003». March 11, 2014. Archived from the original on March 16, 2014. Retrieved April 6, 2014.
- ^ Keizer, Gregg (January 19, 2014). «Microsoft will furnish malware assassin to XP users until mid-2015». Computerworld. IDG. Archived from the original on January 22, 2014.
- ^ «Microsoft Warns of Permanent Zero-Day Exploits for Windows XP». Infosecurity. Reed Exhibitions. August 20, 2013. Archived from the original on August 26, 2013. Retrieved August 27, 2013.
- ^ «Microsoft Security Bulletin MS15-011 JASBUG». February 10, 2015. Archived from the original on August 11, 2015. Retrieved September 18, 2015.
- ^ Freeman, Robert (November 11, 2014). «IBM X-Force Researcher Finds Significant Vulnerability in Microsoft Windows». Securityintelligence.com. Archived from the original on July 3, 2015. Retrieved September 18, 2015.
- ^ Talbot, David (October 17, 2012). «Computer Viruses Are «Rampant» on Medical Devices in Hospitals». MIT Technology Review. Archived from the original on October 19, 2016. Retrieved April 6, 2014.
- ^ Goodin, Dan (May 1, 2014). «Emergency patch for critical IE 0-day throws lifeline to XP laggards, too». Ars Technica. Conde Nast. Archived from the original on May 17, 2017. Retrieved May 26, 2017.
- ^ Warren, Tom (May 13, 2017). «Microsoft issues ‘highly unusual’ Windows XP patch to prevent massive ransomware attack». The Verge. Vox Media. Archived from the original on May 14, 2017. Retrieved May 13, 2017.
- ^ Warren, Tom (May 14, 2019). «Microsoft warns of major WannaCry-like Windows security exploit, releases XP patches». The Verge. Vox Media. Archived from the original on September 2, 2019. Retrieved May 16, 2019.
- ^ «Prevent a worm by updating Remote Desktop Services (CVE-2019-0708) – MSRC». blogs.technet.microsoft.com. May 14, 2019. Archived from the original on May 14, 2019. Retrieved May 16, 2019.
- ^ Winder, Davey (August 11, 2019). «Critical Windows 10 Warning: Millions Of Users At Risk». Forbes. Archived from the original on August 11, 2019. Retrieved August 11, 2019.
- ^ Greenberg, Andy (August 13, 2019). «DejaBlue: New BlueKeep-Style Bugs Renew The Risk Of A Windows worm». wired. Archived from the original on April 13, 2021. Retrieved August 15, 2019.
- ^ Seals, Tara (August 14, 2019). «20-Year-Old Bug in Legacy Microsoft Code Plagues All Windows Users». ThreatPost.com. Archived from the original on April 17, 2021. Retrieved August 15, 2019.
- ^ «Farewell to Microsoft Internet Games on Windows XP, Windows ME, and Windows 7». answers.microsoft.com. Archived from the original on July 14, 2019. Retrieved August 4, 2019.
- ^ «Windows XP and Windows Vista Support – Steam – Knowledge Base – Steam Support». support.steampowered.com. Archived from the original on August 12, 2019. Retrieved August 4, 2019.
- ^ «Windows Update SHA-1 based endpoints discontinued for older Windows devices». support.microsoft.com. Archived from the original on April 17, 2021. Retrieved April 6, 2021.
- ^ «Microsoft Update Catalog». www.catalog.update.microsoft.com. Archived from the original on April 15, 2021. Retrieved April 6, 2021.
- ^ Lake, Matt (October 10, 2002). «Microsoft Windows XP – Home Edition review». CNET. Archived from the original on May 31, 2007. Retrieved March 25, 2014.
- ^ Mendelson, Edward (September 3, 2001). «Microsoft Ships Its Biggest OS Upgrade Ever—Early!». PC Magazine. Archived from the original on March 25, 2014. Retrieved March 25, 2014.
- ^ Manes, Stephen (August 26, 2004). «Full Disclosure: Your Take on Windows’ Worst Irritations». PCWorld. IDG. Archived from the original on October 8, 2009.
- ^ Bright, Peter (April 10, 2014). «Memory lane: Before everyone loved Windows XP, they hated it». Ars Technica. Condé Nast. Archived from the original on April 24, 2014. Retrieved June 20, 2014.
- ^ Bright, Peter (October 25, 2011). «Ten years of Windows XP: how longevity became a curse». Ars Technica. WIRED Media Group. Archived from the original on June 12, 2018. Retrieved June 9, 2018.
- ^ «Operating system market share». September 9, 2012. Archived from the original on September 9, 2012. Retrieved September 8, 2018.
- ^ «Desktop Windows Version Market Share Worldwide». StatCounter Global Stats. Archived from the original on April 20, 2019. Retrieved July 2, 2019.
- ^ Crothers, Brooke (February 2, 2014). «Oops, Windows XP gains in January but so does Windows 8.1». CNET. CBS Interactive. Archived from the original on February 21, 2014. Retrieved March 16, 2014.
- ^ «OS Platform Statistics». w3schools. Archived from the original on September 17, 2015. Retrieved September 14, 2015.
- ^ «Desktop Windows Version Market Share Africa». StatCounter Global Stats. Archived from the original on September 22, 2022. Retrieved September 22, 2022.
- ^ «Desktop Windows Version Market Share Armenia». StatCounter Global Stats. Archived from the original on September 4, 2018. Retrieved December 11, 2021.
- ^ «Desktop Windows Version Market Share Armenia». StatCounter Global Stats. Archived from the original on September 4, 2018. Retrieved December 11, 2021.
- ^ «Desktop Windows Version Market Share Armenia». StatCounter Global Stats. Archived from the original on September 4, 2018. Retrieved July 10, 2021.
- ^ «Desktop Windows Version Market Share Armenia». StatCounter Global Stats. Archived from the original on September 4, 2018. Retrieved March 2, 2021.
- ^ «Desktop Windows Version Market Share Armenia». StatCounter Global Stats. Archived from the original on September 4, 2018. Retrieved July 2, 2020.
- ^ «Desktop Windows Version Market Share Armenia». StatCounter Global Stats. Archived from the original on September 4, 2018. Retrieved July 2, 2020.
- ^ Cimpanu, Catalin. «Windows XP leak confirmed after user compiles the leaked code into a working OS». ZDNet. Archived from the original on September 30, 2020. Retrieved October 1, 2020.
- ^ Warren, Tom (September 25, 2020). «Windows XP source code leaks online». The Verge. Archived from the original on September 29, 2021. Retrieved October 1, 2020.
- ^ a b Alcorn, Paul (September 30, 2020). «Windows XP Source Code Leaked, Posted to 4chan (Update, It Works)». Tom’s Hardware. Archived from the original on October 6, 2021. Retrieved October 1, 2020.
- ^ «Windows XP Source Code Leaked By Apparent Bill Gates Conspiracist». Gizmodo. September 25, 2020. Archived from the original on October 1, 2020. Retrieved October 1, 2020.
- ^ «The Windows XP and Windows Server 2003 source code leaks online». Graham Cluley. September 25, 2020. Archived from the original on September 26, 2020. Retrieved September 29, 2020.
- ^ «Windows XP source code leaked online». www.computing.co.uk. September 28, 2020. Archived from the original on October 2, 2020. Retrieved September 29, 2020.
Further reading
- Joyce, Jerry; Moon, Marianne (2004). Microsoft Windows XP Plain & Simple. Microsoft Press. ISBN 978-0-7356-2112-1.
External links
- Windows XP End of Support
- Security Update for Windows XP SP3 (KB4012598)
| Version of the Windows NT operating system | |

Screenshot of Windows XP running the Luna visual style, showing the start menu, taskbar, and My Computer window |
|
| Developer | Microsoft |
|---|---|
| Source model |
|
| Released to manufacturing |
August 24, 2001; 21 years ago[2] |
| General availability |
October 25, 2001; 21 years ago[2] |
| Final release | Service Pack 3 (5.1.2600.5512) / April 21, 2008; 14 years ago[3] |
| Marketing target | Consumer and Business |
| Update method |
|
| Platforms | IA-32, x86-64, and Itanium |
| Kernel type | Hybrid (NT) |
| Userland |
|
| License | Proprietary commercial software |
| Preceded by |
|
| Succeeded by | Windows Vista (2007) |
| Official website | Windows XP (archived at Wayback Machine) |
| Support status | |
All editions (except Windows XP Embedded, Windows XP 64-bit Edition, Windows Embedded for Point of Service, Windows Embedded Standard 2009, and Windows Embedded POSReady 2009):
Windows XP 64-bit Edition:
Windows XP Embedded:
Windows Embedded for Point of Service:
Windows Embedded Standard 2009:
Windows Embedded POSReady 2009:
|
Windows XP is a major release of Microsoft’s Windows NT operating system. It was released to manufacturing on August 24, 2001, and later to retail on October 25, 2001. It is a direct upgrade to its predecessors, Windows 2000 for high-end and business users and Windows Me for home users, and is available for any devices running Windows NT 4.0, Windows 98, Windows 2000, or Windows Me that meet the new Windows XP system requirements.
Development of Windows XP began in the late 1990s under the codename «Neptune», built on the Windows NT kernel and explicitly intended for mainstream consumer use. An updated version of Windows 2000 was also initially planned for the business market. However, in January 2000, both projects were scrapped in favor of a single OS codenamed «Whistler», which would serve as a single platform for both consumer and business markets. As a result, Windows XP is the first consumer edition of Windows not based on the Windows 95 kernel or MS-DOS. Windows XP removed support for PC-98, i486 and SGI Visual Workstation 320 and 540 and will only run on 32-bit x86 CPUs and devices that use BIOS firmware.
Upon its release, Windows XP received critical acclaim, noting increased performance and stability (especially compared to Windows Me), a more intuitive user interface, improved hardware support, and expanded multimedia capabilities. Windows XP and Windows Server 2003 were succeeded by Windows Vista and Windows Server 2008, released in 2007 and 2008, respectively.
Mainstream support for Windows XP ended on April 14, 2009, and extended support ended on April 8, 2014. Windows Embedded POSReady 2009, based on Windows XP Professional, received security updates until April 2019. After that, unofficial methods were made available to apply the updates to other editions of Windows XP. Still, Microsoft discouraged this practice, citing compatibility issues.[9] However, over eight years from the end of life date (September 2022), the majority of PCs in some countries (such as Armenia) still appeared to be running on Windows XP.[10] As of September 2022, globally, just 0.39% of Windows PCs[11] and 0.1% of all devices across all platforms continued to run Windows XP.
Development
In the late 1990s, initial development of what would become Windows XP was focused on two individual products: «Odyssey», which was reportedly intended to succeed the future Windows 2000 and «Neptune», which was reportedly a consumer-oriented operating system using the Windows NT architecture, succeeding the MS-DOS-based Windows 98.[12]
However, the projects proved to be too ambitious. In January 2000, shortly prior to the official release of Windows 2000, technology writer Paul Thurrott reported that Microsoft had shelved both Neptune and Odyssey in favor of a new product codenamed «Whistler», named after Whistler, British Columbia, as many Microsoft employees skied at the Whistler-Blackcomb ski resort.[13] The goal of Whistler was to unify both the consumer and business-oriented Windows lines under a single, Windows NT platform. Thurrott stated that Neptune had become «a black hole when all the features that were cut from Windows Me were simply re-tagged as Neptune features. And since Neptune and Odyssey would be based on the same code-base anyway, it made sense to combine them into a single project».[14]
At PDC on July 13, 2000, Microsoft announced that Whistler would be released during the second half of 2001, and also unveiled the first preview build, 2250, which featured an early implementation of Windows XP’s visual styles system and interface changes to Windows Explorer and the Control Panel.[15]
Microsoft released the first public beta build of Whistler, build 2296, on October 31, 2000. Subsequent builds gradually introduced features that users of the release version of Windows XP would recognize, such as Internet Explorer 6.0, the Microsoft Product Activation system and the Bliss desktop background.[16]
Whistler was officially unveiled during a media event on February 5, 2001, under the name Windows XP, where XP stands for «eXPerience».[17]
Release
In June 2001, Microsoft indicated that it was planning to spend at least US$1 billion on marketing and promoting Windows XP, in conjunction with Intel and other PC makers.[18] The theme of the campaign, «Yes You Can», was designed to emphasize the platform’s overall capabilities. Microsoft had originally planned to use the slogan «Prepare to Fly», but it was replaced because of sensitivity issues in the wake of the September 11 attacks.[19]
On August 24, 2001, Windows XP build 2600 was released to manufacturing (RTM). During a ceremonial media event at Microsoft Redmond Campus, copies of the RTM build were given to representatives of several major PC manufacturers in briefcases, who then flew off on decorated helicopters. While PC manufacturers would be able to release devices running XP beginning on September 24, 2001, XP was expected to reach general, retail availability on October 25, 2001. On the same day, Microsoft also announced the final retail pricing of XP’s two main editions, «Home» (as a replacement for Windows Me for home computing) and «Professional» (as a replacement for Windows 2000 for high-end users).[20]
New and updated features
User interface
While retaining some similarities to previous versions, Windows XP’s interface was overhauled with a new visual appearance, with an increased use of alpha compositing effects, drop shadows, and «visual styles», which completely changed the appearance of the operating system. The number of effects enabled are determined by the operating system based on the computer’s processing power, and can be enabled or disabled on a case-by-case basis. XP also added ClearType, a new subpixel rendering system designed to improve the appearance of fonts on liquid-crystal displays.[21] A new set of system icons was also introduced.[22] The default wallpaper, Bliss, is a photo of a landscape in the Napa Valley outside Napa, California, with rolling green hills and a blue sky with stratocumulus and cirrus clouds.[23]
The Start menu received its first major overhaul in XP, switching to a two-column layout with the ability to list, pin, and display frequently used applications, recently opened documents, and the traditional cascading «All Programs» menu. The taskbar can now group windows opened by a single application into one taskbar button, with a popup menu listing the individual windows. The notification area also hides «inactive» icons by default. A «common tasks» list was added, and Windows Explorer’s sidebar was updated to use a new task-based design with lists of common actions; the tasks displayed are contextually relevant to the type of content in a folder (e.g. a folder with music displays offers to play all the files in the folder, or burn them to a CD).[24]
The «task grouping» feature introduced in Windows XP showing both grouped and individual items
Fast user switching allows additional users to log into a Windows XP machine without existing users having to close their programs and log out. Although only one user at the time can use the console (i.e. monitor, keyboard, and mouse), previous users can resume their session once they regain control of the console.[25] Service Pack 2 and Service Pack 3 also introduced new features to Windows XP post-release, including the Windows Security Center, Bluetooth support, the executable space protection, Windows Firewall, and support for SDHC cards that are larger than 4 GB and smaller than 32 GB.[26][27][28][29]
Infrastructure
Windows XP uses prefetching to improve startup and application launch times.[30] It also became possible to revert the installation of an updated device driver, should the updated driver produce undesirable results.[31]
A copy protection system known as Windows Product Activation was introduced with Windows XP and its server counterpart, Windows Server 2003. All Windows licenses must be tied to a unique ID generated using information from the computer hardware, transmitted either via the internet or a telephone hotline. If Windows is not activated within 30 days of installation, the OS will cease to function until it is activated. Windows also periodically verifies the hardware to check for changes. If significant hardware changes are detected, the activation is voided, and Windows must be re-activated.[32]
Networking and internet functionality
Windows XP was originally bundled with Internet Explorer 6, Outlook Express 6, Windows Messenger, and MSN Explorer. New networking features were also added, including Internet Connection Firewall, Internet Connection Sharing integration with UPnP, NAT traversal APIs, Quality of Service features, IPv6 and Teredo tunneling, Background Intelligent Transfer Service, extended fax features, network bridging, peer to peer networking, support for most DSL modems, IEEE 802.11 (Wi-Fi) connections with auto configuration and roaming, TAPI 3.1, and networking over FireWire.[33] Remote Assistance and Remote Desktop were also added, which allow users to connect to a computer running Windows XP from across a network or the Internet and access their applications, files, printers, and devices or request help.[34] Improvements were also made to IntelliMirror features such as Offline Files, Roaming user profiles and Folder redirection.[35]
Backwards compatibility
To enable running software that targets or locks out specific versions of Windows, «Compatibility mode» was added. The feature allows pretending a selected earlier version of Windows to software, starting at Windows 95.[36]
While this ability was first introduced in Windows 2000 Service Pack 2, it had to be activated through the «register server» and was only available to administrator users, whereas Windows XP has it activated out of the box and also grants it to regular users.[37]
Other features
- Improved application compatibility and shims compared to Windows 2000.[38]
- DirectX 8.1, upgradeable to DirectX 9.0c.[39]
- A number of new features in Windows Explorer including task panes, thumbnails, and the option to view photos as a slideshow.[40]
- Improved imaging features such as Windows Picture and Fax Viewer.[41]
- Faster start-up, (because of improved Prefetch functions) logon, logoff, hibernation, and application launch sequences.[30]
- Numerous improvements to increase the system reliability such as improved System Restore,[42] Automated System Recovery,[43] and driver reliability improvements through Device Driver Rollback.[44]
- Hardware support improvements such as FireWire 800,[45] and improvements to multi-monitor support under the name «DualView».[46]
- Fast user switching.[47]
- The ClearType font rendering mechanism, which is designed to improve text readability on liquid-crystal display (LCD) and similar monitors, especially laptops.[21]
- Side-by-side assemblies[48] and registration-free COM.[49]
- General improvements to international support such as more locales, languages and scripts, MUI support in Terminal Services, improved Input Method Editors, and National Language Support.[50]
Removed features
Some of the programs and features that were part of the previous versions of Windows did not make it to Windows XP. Various MS-DOS commands available in its Windows 9x predecessor were removed,[51] as were the POSIX and OS/2 subsystems.[52]
In networking, NetBEUI, NWLink and NetDDE were deprecated and not installed by default.[53] Plug-and-play–incompatible communication devices (like modems and network interface cards) were no longer supported.[54]
Service Pack 2 and Service Pack 3 also removed features from Windows XP, including support for TCP half-open connections[55] and the address bar on the taskbar.[56]
Editions
Diagram representing the main editions of Windows XP. It is based on the category of the edition (grey) and codebase (black arrow).
Windows XP was released in two major editions on launch: Home Edition and Professional Edition. Both editions were made available at retail as pre-loaded software on new computers and as boxed copies. Boxed copies were sold as «Upgrade» or «Full» licenses; the «Upgrade» versions were slightly cheaper, but require an existing version of Windows to install. The «Full» version can be installed on systems without an operating system or existing version of Windows.[18] The two editions of XP were aimed at different markets: Home Edition is explicitly intended for consumer use and disables or removes certain advanced and enterprise-oriented features present on Professional, such as the ability to join a Windows domain, Internet Information Services, and Multilingual User Interface. Windows 98 or Me can be upgraded to either edition, but Windows NT 4.0 and Windows 2000 can only be upgraded to Professional.[57] Windows’ software license agreement for pre-loaded licenses allows the software to be «returned» to the OEM for a refund if the user does not wish to use it.[58] Despite the refusal of some manufacturers to honor the entitlement, it has been enforced by courts in some countries.[59]
Two specialized variants of XP were introduced in 2002 for certain types of hardware, exclusively through OEM channels as pre-loaded software. Windows XP Media Center Edition was initially designed for high-end home theater PCs with TV tuners (marketed under the term «Media Center PC»), offering expanded multimedia functionality, an electronic program guide, and digital video recorder (DVR) support through the Windows Media Center application.[60] Microsoft also unveiled Windows XP Tablet PC Edition, which contains additional pen input features, and is optimized for mobile devices meeting its Tablet PC specifications.[61] Two different 64-bit editions of XP were made available. The first, Windows XP 64-Bit Edition, was intended for IA-64 (Itanium) systems; as IA-64 usage declined on workstations in favor of AMD’s x86-64 architecture, the Itanium edition was discontinued in January 2005.[62] A new 64-bit edition supporting the x86-64 architecture, called Windows XP Professional x64 Edition, was released in April of the same year.[63]
Microsoft also targeted emerging markets with the 2004 introduction of Windows XP Starter Edition, a special variant of Home Edition intended for low-cost PCs. The OS is primarily aimed at first-time computer owners, containing heavy localization (including wallpapers and screen savers incorporating images of local landmarks), and a «My Support» area which contains video tutorials on basic computing tasks. It also removes certain «complex» features, and does not allow users to run more than three applications at a time. After a pilot program in India and Thailand, Starter was released in other emerging markets throughout 2005.[64] In 2006, Microsoft also unveiled the FlexGo initiative, which would also target emerging markets with subsidized PCs on a pre-paid, subscription basis.[65]
As a result of unfair competition lawsuits in Europe and South Korea, which both alleged that Microsoft had improperly leveraged its status in the PC market to favor its own bundled software, Microsoft was ordered to release special editions of XP in these markets that excluded certain applications. In March 2004, after the European Commission fined Microsoft €497 million (US$603 million), Microsoft was ordered to release «N» editions of XP that excluded Windows Media Player, encouraging users to pick and download their own media player software.[66] As it was sold at the same price as the edition with Windows Media Player included, certain OEMs (such as Dell, who offered it for a short period, along with Hewlett-Packard, Lenovo and Fujitsu Siemens) chose not to offer it. Consumer interest was minuscule, with roughly 1,500 units shipped to OEMs, and no reported sales to consumers.[67] In December 2005, the Korean Fair Trade Commission ordered Microsoft to make available editions of Windows XP and Windows Server 2003 that do not contain Windows Media Player or Windows Messenger.[68] The «K» and «KN» editions of Windows XP were released in August 2006, and are only available in English and Korean, and also contain links to third-party instant messenger and media player software.[69]
Service packs
A service pack is a cumulative update package that is a superset of all updates, and even service packs, that have been released before it.[70] Three service packs have been released for Windows XP. Service Pack 3 is slightly different, in that it needs at least Service Pack 1 to have been installed, in order to update a live OS.[71] However, Service Pack 3 can still be embedded into a Windows installation disc; SP1 is not reported as a prerequisite for doing so.[72]
The unique boot screens from the RTM to Service Pack 1 versions of Windows XP that identified the edition of Windows XP currently running, including a green progress bar for Home Edition and a blue progress bar for Professional, Embedded, Tablet PC Edition, and Media Center Edition were removed in Service Pack 2 of Windows XP and was replaced with a generic «Windows XP» boot screen with a blue progress bar.
Service Pack 1
Service Pack 1 (SP1) for Windows XP was released on September 9, 2002. It contained over 300 minor, post-RTM bug fixes, along with all security patches released since the original release of XP. SP1 also added USB 2.0 support, the Microsoft Java Virtual Machine, .NET Framework support, and support for technologies used by the then-upcoming Media Center and Tablet PC editions of XP.[73] The most significant change on SP1 was the addition of Set Program Access and Defaults, a settings page which allows programs to be set as default for certain types of activities (such as media players or web browsers) and for access to bundled, Microsoft programs (such as Internet Explorer or Windows Media Player) to be disabled. This feature was added to comply with the settlement of United States v. Microsoft Corp., which required Microsoft to offer the ability for OEMs to bundle third-party competitors to software it bundles with Windows (such as Internet Explorer and Windows Media Player), and give them the same level of prominence as those normally bundled with the OS.[74]
On February 3, 2003, Microsoft released Service Pack 1a (SP1a). It was the same as SP1, except, the Microsoft Java Virtual Machine was excluded.[75]
Service Pack 2
Service Pack 2 (SP2) for Windows XP Home edition and Professional edition was released on August 25, 2004.[76] Headline features included WPA encryption compatibility for Wi-Fi and usability improvements to the Wi-Fi networking user interface,[77] partial Bluetooth support,[78] and various improvements to security systems.
Headed by former computer hacker Window Snyder,[79][80] the service pack’s security improvements (codenamed «Springboard»,[81] as these features were intended to underpin additional changes in Longhorn) included a major revision to the included firewall (renamed Windows Firewall, and now enabled by default), and an update to Data Execution Prevention, which gained hardware support in the NX bit that can stop some forms of buffer overflow attacks. Raw socket support is removed (which supposedly limits the damage done by zombie machines) and the Windows Messenger service (which had been abused to cause pop-up advertisements to be displayed as system messages without a web browser or any additional software) became disabled by default. Additionally, security-related improvements were made to e-mail and web browsing. Service Pack 2 also added Security Center, an interface that provides a general overview of the system’s security status, including the state of the firewall and automatic updates. Third-party firewall and antivirus software can also be monitored from Security Center.[82]
In August 2006, Microsoft released updated installation media for Windows XP and Windows Server 2003 SP2 (SP2b), in order to incorporate a patch requiring ActiveX controls in Internet Explorer to be manually activated before a user may interact with them. This was done so that the browser would not violate a patent owned by Eolas.[83] Microsoft has since licensed the patent, and released a patch reverting the change in April 2008.[84] In September 2007, another minor revision known as SP2c was released for XP Professional, extending the number of available product keys for the operating system to «support the continued availability of Windows XP Professional through the scheduled system builder channel end-of-life (EOL) date of January 31, 2009.»[85]
Windows XP Service Pack 2 was later included in Windows Embedded for Point of Service and Windows Fundamentals for Legacy PCs.
Service Pack 3
The third and final Service Pack, SP3, was released through different channels between April[3] and June 2008,[86] about a year after the release of Windows Vista, and about a year before the release of Windows 7. Service Pack 3 was not available for Windows XP x64 Edition, which was based on the Windows Server 2003 kernel and, as a result, used its service packs[87] rather than the ones for the other editions.[88]
It began being automatically pushed out to Automatic Updates users on July 10, 2008.[89] A feature set overview which detailed new features available separately as stand-alone updates to Windows XP, as well as backported features from Windows Vista, was posted by Microsoft.[90] A total of 1,174 fixes are included in SP3.[91] Service Pack 3 could be installed on systems with Internet Explorer up to and including version 8; Internet Explorer 7 was not included as part of SP3.[92] It also did not include Internet Explorer 8, but instead was included in Windows 7, which was released one year after XP SP3.
Service Pack 3 included security enhancements over and above those of SP2, including APIs allowing developers to enable Data Execution Prevention for their code, independent of system-wide compatibility enforcement settings,[93] the Security Support Provider Interface,[94] improvements to WPA2 security,[95] and an updated version of the Microsoft Enhanced Cryptographic Provider Module that is FIPS 140-2 certified.[96]
In incorporating all previously released updates not included in SP2, Service Pack 3 included many other key features. Windows Imaging Component allowed camera vendors to integrate their own proprietary image codecs with the operating system’s features, such as thumbnails and slideshows.[97] In enterprise features, Remote Desktop Protocol 6.1 included support for ClearType and 32-bit color depth over RDP,[98] while improvements made to Windows Management Instrumentation in Windows Vista to reduce the possibility of corruption of the WMI repository were backported to XP SP3.[99]
In addition, SP3 contains updates to the operating system components of Windows XP Media Center Edition (MCE) and Windows XP Tablet PC Edition, and security updates for .NET Framework version 1.0, which is included in these editions. However, it does not include update rollups for the Windows Media Center application in Windows XP MCE 2005.[100] SP3 also omits security updates for Windows Media Player 10, although the player is included in Windows XP MCE 2005.[100] The Address Bar DeskBand on the Taskbar is no longer included because of antitrust violation concerns.[101]
Unofficial SP3 ZIP download packages were released on a now-defunct website called The Hotfix from 2005 to 2007.[102][103] The owner of the website, Ethan C. Allen, was a former Microsoft employee in Software Quality Assurance and would comb through the Microsoft Knowledge Base articles daily and download new hotfixes Microsoft would put online within the articles. The articles would have a «kbwinxppresp3fix» and/or «kbwinxpsp3fix» tag, thus allowing Allen to easily find and determine which fixes were planned for the official SP3 release to come. Microsoft publicly stated at the time that the SP3 pack was unofficial and advised users to not install it.[104][105] Allen also released a Vista SP1 package in 2007, for which Allen received a cease-and-desist email from Microsoft.[106]
Windows XP Service Pack 3 was later included in Windows Embedded Standard 2009 and Windows Embedded POSReady 2009.
System requirements
System requirements for Windows XP are as follows:
| Minimum | Recommended | |
|---|---|---|
| Home/Professional Edition[A] | ||
| CPU |
|
|
| Memory | 64 MB[E][F] | 128 MB |
| Free space |
|
|
| Media | CD-ROM drive or compatible | |
| Display | Super VGA (800 × 600) | |
| Sound hardware | N/A | Sound card plus speakers/headphones |
| Input device(s) | Keyboard, mouse | |
| Professional x64 Edition[J] | ||
| CPU |
|
|
| Memory | 256 MB | |
| Free space |
|
|
| Media | CD-ROM drive or compatible | |
| Display | Super VGA (800 × 600) | |
| Sound hardware | N/A | Sound card plus speakers/headphones |
| Input device(s) | Keyboard, mouse | |
| 64-Bit Edition[K] | ||
| CPU | Itanium 733 MHz | Itanium 800 MHz |
| Memory | 1 GB | |
| Free space | 6 GB | |
| Media | CD-ROM drive or compatible | |
| Display | Super VGA (800 × 600) | |
| Input device(s) | Keyboard, mouse |
Notes
- ^ «System requirements for Windows XP operating systems». April 28, 2005. Archived from the original on August 6, 2011. Retrieved March 12, 2007.
- ^ Even though this is Microsoft’s stated minimum processor speed for Windows XP, it is possible to install and run the operating system on early IA-32 processors such as a P5 Pentium without MMX instructions. Windows XP is not compatible with processors older than Pentium (such as 486) or the Cyrix 6×86 because it requires
CMPXCHG8B(see Pentium F00F bug) instructions. - ^ «Windows XP Minimal Requirement Test». Winhistory.de. September 9, 2011. Archived from the original on December 21, 2011. Retrieved January 1, 2012.
- ^ a b c d e «Windows XP: Required firmware and partition mapping scheme of hard disk drive». Support.microsoft.com. June 26, 2013. Archived from the original on April 27, 2017. Retrieved June 16, 2014.
- ^ A Microsoft TechNet paper from Summer 2001 (before Windows XP’s actual release), states that: «A computer with 64 MB of RAM will have sufficient resources to run Windows XP and a few applications with moderate memory requirements.» (Emphasis added.) These were said to be office productivity applications, e-mail programs, and web browsers (of the time). With such a configuration, user interface enhancements and fast user switching are turned off by default. For comparable workloads, 64 MB of RAM was then regarded as providing an equal or better user experience on Windows XP with similar settings than it would with Windows Me on the same hardware. In a later section of the paper, superior performance over Windows Me was noted with 128 MB of RAM or more, and with computers that exceed the minimum hardware requirements.
- ^ Sechrest, Stuart; Fortin, Michael (June 1, 2001). «Windows XP Performance». Microsoft TechNet. Archived from the original on July 27, 2010. Retrieved April 8, 2008.
- ^ «Hard disk space requirements for Windows XP Service Pack 1». Microsoft. October 29, 2007. Archived from the original on April 21, 2012. Retrieved April 6, 2012.
- ^ «The hard disk space requirements for Windows XP Service Pack 2». Microsoft. April 18, 2005. Archived from the original on November 24, 2010. Retrieved December 1, 2010.
- ^ «Windows XP – End of Support, Migration Guide, Download – TechNet». technet.microsoft.com. 2007. Archived from the original on May 13, 2008.
- ^ «Windows XP Professional x64 Edition SP2 VL EN (MSDN-TechNet)». Programmer Stuffs. March 23, 2011. Archived from the original on July 14, 2014. Retrieved May 2, 2012.
- ^ «Microsoft Windows XP 64-Bit Edition». Microsoft TechNet. Microsoft. August 15, 2001. Archived from the original on April 19, 2012. Retrieved May 2, 2012.
Physical memory limits
The maximum amount of RAM that Windows XP can support varies depending on the product edition and the processor architecture. All 32-bit editions of XP support up to 4 GB, except the Windows XP Starter edition, which supports up to 512 MB of RAM.[107] 64-bit editions support up to 128 GB.[108]
Processor limits
Windows XP Professional supports up to two physical processors;[109]
Windows XP Home Edition supports only one.[110]
However, XP supports a greater number of logical processors:
32-bit editions support up to 32 logical processors,[111] and 64-bit editions support up to 64 logical processors.[112]
Upgradeability
Several Windows XP components are upgradable to the latest versions, which include new versions introduced in later versions of Windows, and other major Microsoft applications are available. These latest versions for Windows XP include:
- ActiveSync 4.5
- DirectX 9.0c (June 7, 2010, Redistributable)
- Internet Explorer 8 on Windows XP Service Packs 2 and 3 (Internet Explorer 6 SP1 and Outlook Express 6 SP1 on Windows XP before SP2.)
- Windows Media Format Runtime and Windows Media Player 11 on Windows XP Service Packs 2 and 3 (and Windows Media Player 10 on Windows XP original release.)
- Microsoft Virtual PC 2004 and 2007
- .NET Framework up to and including version 4.0 (4.5 and higher versions are not supported.)
- Visual Studio 2005 on Windows XP versions below SP2, Visual Studio 2008 on Windows XP SP2 and Visual Studio 2010 on Windows XP SP3
- Windows Script Host 5.7
- Windows Installer 4.5
- Microsoft NetMeeting 3.02
- Office 2010 was the last version of Microsoft Office to be compatible with Windows XP.
- The Windows Services for UNIX subsystem can be installed to allow certain Unix-based applications to run on the operating system.
Support lifecycle
| Expiration date | |
|---|---|
| Mainstream support | April 14, 2009[4] |
| Extended support | April 8, 2014[4] The official exceptions ended in April 2019. |
| Applicable XP editions: | |
| Home Edition, Professional Edition, Professional x64 Edition, Professional for Embedded Systems, Media Center Editions (all), Starter Edition, Tablet PC Edition and Tablet PC Edition 2005,[4] as well as Windows Fundamentals for Legacy PCs.[113] | |
| Exceptions | |
| Windows XP 64-Bit Edition (Itanium edition, including Version 2003) | Unsupported as of June 30, 2005[5] |
| Windows XP Embedded | Mainstream support ended on January 11, 2011[4] Extended support ended on January 12, 2016[4] |
| Windows Embedded for Point of Service | Mainstream support ended on April 12, 2011[6] Extended support ended on April 12, 2016[6] |
| Windows Embedded Standard 2009 | Mainstream support ended on January 14, 2014 Extended support ended on January 8, 2019[7] |
| Windows Embedded POSReady 2009 | Mainstream support ended on April 8, 2014 Extended support ended on April 9, 2019[8] |
Support for the original release of Windows XP (without a service pack) ended on August 30, 2005.[4] Both Windows XP Service Pack 1 and 1a were retired on October 10, 2006,[4] and both Windows 2000 and Windows XP SP2 reached their end of support on July 13, 2010, about 24 months after the launch of Windows XP Service Pack 3.[4] The company stopped general licensing of Windows XP to OEMs and terminated retail sales of the operating system on June 30, 2008, 17 months after the release of Windows Vista.[114] However, an exception was announced on April 3, 2008, for OEMs producing what it defined as «ultra low-cost personal computers», particularly netbooks, until one year after the availability of Windows 7 on October 22, 2009. Analysts felt that the move was primarily intended to compete against Linux-based netbooks, although Microsoft’s Kevin Hutz stated that the decision was due to apparent market demand for low-end computers with Windows.[115]
Variants of Windows XP for embedded systems have different support policies: Windows XP Embedded SP3 and Windows Embedded for Point of Service SP3 were supported until January and April 2016, respectively. Windows Embedded Standard 2009, which was succeeded by Windows Embedded Standard 7, and Windows Embedded POSReady 2009, which was succeeded by Windows Embedded POSReady 7, were supported until January and April 2019, respectively.[116] These updates, while intended for the embedded editions, could also be downloaded on standard Windows XP with a registry hack, which enabled unofficial patches until April 2019. However, Microsoft advised Windows XP users against installing these fixes, citing incompatibility issues.[9][117]
End of support
On April 14, 2009, Windows XP exited mainstream support and entered the extended support phase; Microsoft continued to provide security updates every month for Windows XP, however, free technical support, warranty claims, and design changes were no longer being offered. Extended support ended on April 8, 2014, over 12 years after the release of Windows XP; normally Microsoft products have a support life cycle of only 10 years.[118] Beyond the final security updates released on April 8, no more security patches or support information are provided for XP free-of-charge; «critical patches» will still be created, and made available only to customers subscribing to a paid «Custom Support» plan.[119] As it is a Windows component, all versions of Internet Explorer for Windows XP also became unsupported.[120]
In January 2014, it was estimated that more than 95% of the 3 million automated teller machines in the world were still running Windows XP (which largely replaced IBM’s OS/2 as the predominant operating system on ATMs); ATMs have an average lifecycle of between seven and ten years, but some have had lifecycles as long as 15. Plans were being made by several ATM vendors and their customers to migrate to Windows 7-based systems over the course of 2014, while vendors have also considered the possibility of using Linux-based platforms in the future to give them more flexibility for support lifecycles, and the ATM Industry Association (ATMIA) has since endorsed Windows 10 as a further replacement.[121] However, ATMs typically run the embedded variant of Windows XP, which was supported through January 2016.[122] As of May 2017, around 60% of the 220,000 ATMs in India still run Windows XP.[123]
Furthermore, at least 49% of all computers in China still ran XP at the beginning of 2014. These holdouts were influenced by several factors; prices of genuine copies of later versions of Windows in the country are high, while Ni Guangnan of the Chinese Academy of Sciences warned that Windows 8 could allegedly expose users to surveillance by the United States government,[124] and the Chinese government banned the purchase of Windows 8 products for government use in May 2014 in protest of Microsoft’s inability to provide «guaranteed» support.[125] The government also had concerns that the impending end of support could affect their anti-piracy initiatives with Microsoft, as users would simply pirate newer versions rather than purchasing them legally. As such, government officials formally requested that Microsoft extend the support period for XP for these reasons. While Microsoft did not comply with their requests, a number of major Chinese software developers, such as Lenovo, Kingsoft and Tencent, will provide free support and resources for Chinese users migrating from XP.[126] Several governments, in particular those of the Netherlands and the United Kingdom, elected to negotiate «Custom Support» plans with Microsoft for their continued, internal use of Windows XP; the British government’s deal lasted for a year, and also covered support for Office 2003 (which reached end-of-life the same day) and cost £5.5 million.[127]
On March 8, 2014, Microsoft deployed an update for XP that, on the 8th of each month, displays a pop-up notification to remind users about the end of support; however, these notifications may be disabled by the user.[128] Microsoft also partnered with Laplink to provide a special «express» version of its PCmover software to help users migrate files and settings from XP to a computer with a newer version of Windows.[129]
An electroencephalograph running on Windows XP. The medical industry’s continued use of Windows XP is partly due to medical applications being incompatible with later versions of Windows.
Despite the approaching end of support, there were still notable holdouts that had not migrated past XP; many users elected to remain on XP because of the poor reception of Windows Vista, sales of newer PCs with newer versions of Windows declined because of the Great Recession and the effects of Vista, and deployments of new versions of Windows in enterprise environments require a large amount of planning, which includes testing applications for compatibility (especially those that are dependent on Internet Explorer 6, which is not compatible with newer versions of Windows).[130] Major security software vendors (including Microsoft itself) planned to continue offering support and definitions for Windows XP past the end of support to varying extents, along with the developers of Google Chrome, Mozilla Firefox, and Opera web browsers;[120] despite these measures, critics similarly argued that users should eventually migrate from XP to a supported platform.[131] The United States’ Computer Emergency Readiness Team released an alert in March 2014 advising users of the impending end of support, and informing them that using XP after April 8 may prevent them from meeting US government information security requirements.[132]
Microsoft continued to provide Security Essentials virus definitions and updates for its Malicious Software Removal Tool (MSRT) for XP until July 14, 2015.[133] As the end of extended support approached, Microsoft began to increasingly urge XP customers to migrate to newer versions such as Windows 7 or 8 in the interest of security, suggesting that attackers could reverse engineer security patches for newer versions of Windows and use them to target equivalent vulnerabilities in XP.[134] Windows XP is remotely exploitable by numerous security holes that were discovered after Microsoft stopped supporting it.[135][136]
Similarly, specialized devices that run XP, particularly medical devices, must have any revisions to their software—even security updates for the underlying operating system—approved by relevant regulators before they can be released. For this reason, manufacturers often did not allow any updates to devices’ operating systems, leaving them open to security exploits and malware.[137]
Despite the end of support for Windows XP, Microsoft has released three emergency security updates for the operating system to patch major security vulnerabilities:
- A patch released in May 2014 to address recently discovered vulnerabilities in Internet Explorer 6 through 11 on all versions of Windows.[138]
- A patch released in May 2017 to address a vulnerability that was being leveraged by the WannaCry ransomware attack.[139]
- A patch released in May 2019 to address a critical code execution vulnerability in Remote Desktop Services which can be exploited in a similar way as the WannaCry vulnerability.[140][141]
Researchers reported in August 2019 that Windows 10 users may be at risk for «critical» system compromise because of design flaws of hardware device drivers from multiple providers.[142] In the same month, computer experts reported that the BlueKeep security vulnerability, CVE-2019-0708, that potentially affects older unpatched Microsoft Windows versions via the program’s Remote Desktop Protocol, allowing for the possibility of remote code execution, may now include related flaws, collectively named DejaBlue, affecting newer Windows versions (i.e., Windows 7 and all recent versions) as well.[143] In addition, experts reported a Microsoft security vulnerability, CVE-2019-1162, based on legacy code involving Microsoft CTF and ctfmon (ctfmon.exe), that affects all Windows versions from the older Windows XP version to the most recent Windows 10 versions; a patch to correct the flaw is currently available.[144]
Microsoft announced in July 2019 that the Microsoft Internet Games services on Windows XP and Windows Me would end on July 31, 2019 (and for Windows 7 on January 22, 2020).[145] Others, such as Steam, had done the same, ending support for Windows XP and Windows Vista in January 2019.[146]
In 2020, Microsoft announced that it would disable the Windows Update service for SHA-1 endpoints; since Windows XP did not get an update for SHA-2, Windows Update Services are no longer available on the OS as of late July 2020.[147] However, as of October 2021, the old updates for Windows XP are still available on the Microsoft Update Catalog,[148] or through Legacy Update, a community-driven third party replacement for the Windows XP update servers.
Reception
On release, Windows XP received critical acclaim. CNET described the operating system as being «worth the hype», considering the new interface to be «spiffier» and more intuitive than previous versions, but feeling that it may «annoy» experienced users with its «hand-holding». XP’s expanded multimedia support and CD burning functionality were also noted, along with its streamlined networking tools. The performance improvements of XP in comparison to 2000 and Me were also praised, along with its increased number of built-in device drivers in comparison to 2000. The software compatibility tools were also praised, although it was noted that some programs, particularly older MS-DOS software, may not work correctly on XP because of its differing architecture. They panned Windows XP’s new licensing model and product activation system, considering it to be a «slightly annoying roadblock», but acknowledged Microsoft’s intent for the changes.[149] PC Magazine provided similar praise, although noting that a number of its online features were designed to promote Microsoft-owned services, and that aside from quicker boot times, XP’s overall performance showed little difference over Windows 2000.[150] Windows XP’s default theme, Luna, was criticized by some users for its childish look.[151][152]
Despite extended support for Windows XP ending in 2014, many users – including some enterprises – were reluctant to move away from an operating system they viewed as a stable known quantity despite the many security and functionality improvements in subsequent releases of Windows. Windows XP’s longevity was viewed as testament to its stability and Microsoft’s successful attempts to keep it up to date, but also as an indictment of its direct successor’s perceived failings.[153]
According to web analytics data generated by Net Applications, Windows XP was the most widely used operating system until August 2012, when Windows 7 overtook it (later overtaken by Windows 10),[154] while StatCounter indicates it happening almost a year earlier.[155] In January 2014, Net Applications reported a market share of 29.23%[156] of «desktop operating systems» for XP (when XP was introduced there was not a separate mobile category to track), while W3Schools reported a share of 11.0%.[157]
As of September 2022, in most regions or continents, Windows XP market share on PCs, as a fraction of the total Windows share, has gone below 1% (0.5% in Africa[158]). XP still has a double-digit market share in a few countries, such as Armenia at over 50%,[159][160][161][162] at 57%, where Windows 7 was highest ranked, and with it being replaced by Windows 10, Windows XP got highest ranked for the longest time, and had over 60% share on some weekends in the summer of 2019.[163][164]
Source code leak
On September 23, 2020, source code for Windows XP with Service Pack 1 and Windows Server 2003 was leaked onto the imageboard 4chan by an unknown user. Anonymous users managed to compile the code, as well as a Twitter user who posted videos of the process on YouTube proving that the code was genuine.[165] The videos were later removed on copyright grounds by Microsoft. The leak was incomplete as it was missing the Winlogon source code and some other components.[166][167] The original leak itself was spread using magnet links and torrent files whose payload originally included Server 2003 and XP source code and which was later updated with additional files, among which were previous leaks of Microsoft products, its patents, media about conspiracy theories on Bill Gates by anti-vaccination movements and an assortment of PDF files on different topics.[168]
Microsoft issued a statement stating that it was investigating the leaks.[167][169][170]
See also
- BlueKeep (security vulnerability)
- Comparison of operating systems
- History of operating systems
- List of operating systems
References
- ^ «Windows Licensing Programs». Microsoft. Archived from the original on December 16, 2008. Retrieved September 21, 2008.
- ^ a b «An Inside Look at the Months-long Process of Getting Windows XP Ready for Release to Manufacturing | Stories». Microsoft Stories. Microsoft. August 24, 2001. Archived from the original on August 5, 2019. Retrieved June 24, 2018.
- ^ a b Kelly, Gordon (April 16, 2008). «Windows XP SP3 Release Date(s) Confirmed». Trusted Reviews. Trusted Reviews. Archived from the original on June 23, 2018. Retrieved June 23, 2018.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l «Microsoft Product Lifecycle Search: Windows XP». Microsoft Support. Microsoft. Archived from the original on July 20, 2012. Retrieved May 14, 2022.
- ^ a b «Microsoft Security Bulletin MS05-036 – Critical». July 12, 2015. Archived from the original on April 26, 2018. Retrieved April 26, 2018.
- ^ a b c d Mackie, Kurt (February 19, 2014). «Windows XP Embedded Supported for Two or More Years». Redmond Magazine. 1105 Media. Archived from the original on February 20, 2017. Retrieved June 23, 2018.
- ^ a b c «Microsoft Product Lifecycle Search: Windows Embedded Standard 2009». Microsoft Support. Microsoft. Archived from the original on July 13, 2015. Retrieved October 13, 2012.
- ^ a b c «Microsoft Product Lifecycle Search: Windows Embedded POSReady 2009». Microsoft Support. Microsoft. Archived from the original on October 10, 2014. Retrieved October 13, 2012.
- ^ a b Seltzer, Larry (May 26, 2014). «Registry hack enables continued updates for Windows XP». ZDNet. Archived from the original on January 26, 2021. Retrieved January 30, 2021.
[UPDATE:] Late Monday we received a statement from a Microsoft spokesperson: We recently became aware of a hack that purportedly aims to provide security updates to Windows XP customers. The security updates that could be installed are intended for Windows Embedded and Windows Server 2003 customers and do not fully protect Windows XP customers. Windows XP customers also run a significant risk of functionality issues with their machines if they install these updates, as they are not tested against Windows XP. The best way for Windows XP customers to protect their systems is to upgrade to a more modern operating system, like Windows 7 or Windows 8.1.
- ^ «Desktop Windows Version Market Share in Armenia — September 2022». September 30, 2022. Retrieved October 10, 2022.
- ^ «Desktop Windows Version Market Share Worldwide | StatCounter Global Stats». gs.statcounter.com. Statcounter. Archived from the original on April 20, 2019. Retrieved May 8, 2022.
- ^ Miles, Stephanie (January 24, 2000). «Microsoft consolidates Windows development efforts». CNET. CNET Networks. Archived from the original on February 1, 2014. Retrieved January 23, 2014.
- ^ «Windows «Longhorn» FAQ». Paul Thurrott’s SuperSite for Windows. Penton Media. June 22, 2005. Archived from the original on April 4, 2008. Retrieved April 4, 2008.
- ^ Thurrott, Paul (October 6, 2010). «The Road to Gold: The development of Windows XP Reviewed». Paul Thurrott’s Supersite for Windows. Penton Media. Archived from the original on February 2, 2014. Retrieved January 23, 2014.
- ^ Thurrott, Paul (July 17, 2000). «Introducing the Whistler Preview, Build 2250». Windows IT Pro. Penton Media. Archived from the original on June 12, 2018. Retrieved June 9, 2018.
- ^ Thurrott, Paul (October 6, 2010). «The Road to Gold (Part Two)». Paul Thurrott’s SuperSite for Windows. Penton Media. Archived from the original on February 2, 2014. Retrieved January 23, 2014.
- ^ «Microsoft to christen Windows, Office with new name». CNET. CNET Networks. February 5, 2001. Archived from the original on February 1, 2014. Retrieved January 23, 2014.
- ^ a b «Windows XP marketing tab to hit $1 billion». CNET. CNET Networks. January 2, 2002. Archived from the original on February 1, 2014. Retrieved January 23, 2014.
- ^ «Microsoft changes XP slogan in wake of US attacks». Computerworld NZ. IDG. Archived from the original on September 5, 2015. Retrieved August 7, 2015.
- ^ Thurrott, Paul (October 15, 2001). «The Road to Gold (Part Three)». Paul Thurrott’s Supersite for Windows. Penton Media. Archived from the original on August 29, 2017. Retrieved March 11, 2017.
- ^ a b «HOW TO: Use ClearType to Enhance Screen Fonts in Windows XP». Support. Microsoft. October 27, 2002. Archived from the original on August 5, 2011. Retrieved August 8, 2011.
- ^ Esposito, Dino (November 2001). «New Graphical Interface: Enhance Your Programs with New Windows XP Shell Features». MSDN. Microsoft. Archived from the original on August 9, 2011. Retrieved August 8, 2011.
- ^ Turner, Paul (February 22, 2004). «No view of Palouse from Windows». The Spokesman-Review. Spokane. Archived from the original on May 11, 2011. Retrieved September 19, 2012.
- ^ Fitzpatrick, Jason (August 6, 2015). «The Start Menu Should Be Sacred (But It’s Still a Disaster in Windows 10)». How-To Geek. Archived from the original on March 13, 2017. Retrieved July 30, 2016.
- ^ «How To Use the Fast User Switching Feature in Windows XP (Revision 1.5)». Microsoft Support. Microsoft. March 27, 2007. Archived from the original on August 12, 2011. Retrieved August 8, 2011.
- ^ «Bluetooth Wireless Technology FAQ». Archived from the original on December 23, 2018. Retrieved August 8, 2011.
- ^ «Manually Configuring Windows Firewall in Windows XP Service Pack 2». Archived from the original on August 26, 2017. Retrieved August 26, 2017.
- ^ «Description of the Windows Firewall feature in Windows XP SP2». Archived from the original on September 17, 2009. Retrieved September 18, 2009.
- ^ «Hotfix for Windows XP that adds support for SDHC cards that have a capacity of more than 4 GB». Support (5.0 ed.). May 22, 2013. Archived from the original on February 5, 2014. Retrieved June 18, 2019.
- ^ a b «Kernel Enhancements for Windows XP». Windows Hardware Developer Center (WHDC). Microsoft. January 13, 2003. Archived from the original on March 7, 2008. Retrieved August 8, 2011.
- ^ «HOW TO: Use the Driver Roll Back Feature to Restore a Previous Version of a Device Driver in Windows XP». Microsoft. October 27, 2002. Archived from the original on February 18, 2006.
- ^ Fisher, Ken (February 2, 2001). «Windows Product Activation: an early look». Ars Technica. Archived from the original on December 5, 2011. Retrieved February 22, 2017.
- ^ «Windows XP Networking Features and Enhancements». Microsoft TechNet. Microsoft. August 8, 2001. Archived from the original on July 26, 2011. Retrieved August 8, 2011.
- ^ «Frequently Asked Questions About Remote Desktop». Microsoft. Archived from the original on July 4, 2007.
- ^ Otey, Michael (October 2001). «Discover Windows XP». Microsoft Developer. Archived from the original on April 20, 2012. Retrieved June 21, 2018.
- ^ «Windows XP Program Compatibility Wizard». ServerWatch. March 12, 2002. Archived from the original on November 13, 2021. Retrieved November 13, 2021.
- ^ «How to Enable Application Compatibility-Mode Technology in Windows 2000 Service Pack 2». Active Win. 2000. Archived from the original on August 18, 2001. Retrieved November 13, 2021.
- ^ Proffit, Brian (September 2, 2002). «Old Apps Find A New Home On Windows XP». PC Magazine. Ziff Davis. Archived from the original on June 10, 2020. Retrieved July 10, 2018.
- ^ Karp, David; O’Reilly, Tim; Mott, Troy (2005). Windows XP in a Nutshell : [a desktop quick reference] (2nd ed.). Beijing [u.a.]: O’Reilly. p. 141. ISBN 978-0-596-00900-7.
- ^ Richtmyer, Richard (August 23, 2001). «Opening up Windows XP». CNN Money. CNN. Archived from the original on December 23, 2017. Retrieved June 24, 2018.
- ^ «Windows Picture and Fax Viewer overview». Windows XP Professional Product Documentation. Microsoft Corporation. Archived from the original on 2 December 2010. Retrieved 23 November 2010.
- ^ Harder, Bobbie (April 2001). «Microsoft Windows XP System Restore». Microsoft. Archived from the original on February 4, 2005.
- ^ Petri, Daniel (January 8, 2009). «What is ASR in Windows XP and Windows Server 2003?». Petri. Blue Whale Web Media Group. Archived from the original on March 12, 2017. Retrieved June 24, 2018.
- ^ Columbus, Louis (June 29, 2001). Exploring Windows XP’s Device Driver Rollback and System Restore. InformIT. Pearson Education. Archived from the original on January 5, 2014. Retrieved June 24, 2018.
- ^ Norton, Peter; Mueller, John Paul (2002). Peter Norton’s Complete Guide to Windows XP. Pearson Education. p. N/A. ISBN 9780132715386. Archived from the original on April 15, 2021. Retrieved July 10, 2018.
- ^ McNamee, Kieran (June 27, 2003). «Setting up dual monitors using Windows XP Home». PC World. Archived from the original on February 5, 2017. Retrieved June 24, 2018.
- ^ «Architecture of Fast User Switching». Microsoft Knowledgebase. Microsoft. January 15, 2006. Archived from the original on August 2, 2009. Retrieved June 24, 2018.
- ^ Satran, Michael (May 31, 2018). «About Side-by-Side Assemblies». docs.microsoft.com. Microsoft. Archived from the original on June 24, 2018. Retrieved June 24, 2018.
- ^ Wienholt, Nick (August 14, 2006). «Simplify Application Deployment with Registration-Free COM — Developer.com». www.developer.com. QuinStreet Enterprise. Archived from the original on December 16, 2010. Retrieved June 24, 2018.
- ^ Honeycutt, Jerry (2003). Introducing Microsoft Windows Server 2003. Redmond, Wash.: Microsoft. pp. 293–298. ISBN 9780735615700.
- ^ «New ways to do familiar tasks». Windows XP Product Documentation. Microsoft. Archived from the original on May 3, 2006. Retrieved May 21, 2014.
- ^ «Kernel Enhancements for Windows XP». MSDN. Microsoft. January 13, 2003. Archived from the original on March 6, 2013. Retrieved April 16, 2014.
- ^ Pittsley, Steven (June 13, 2002). «Easy install guide for NetBEUI and IPX in Windows XP Pro». TechRepublic. CBS Interactive. Archived from the original on April 11, 2017. Retrieved June 24, 2018.
- ^ «Non-Plug and Play Network Device Support in Windows XP». Support. Microsoft. October 18, 2001. Archived from the original on October 30, 2004. Retrieved November 8, 2012.
- ^ «TCP/IP Raw Sockets (Windows)». MSDN. Microsoft. Archived from the original on January 28, 2013. Retrieved November 7, 2012.
- ^ Pash, Adam (April 29, 2008). «Field Guide to Windows XP SP3». Lifehacker. Univision Communications. Archived from the original on January 15, 2018. Retrieved June 24, 2018.
- ^ «Differences with Windows XP Home Edition». TechNet. Microsoft. September 11, 2009. Archived from the original on February 9, 2014. Retrieved January 26, 2014.
- ^ Marti, Don (November 6, 2006). «Dell customer gets Windows refund». LinuxWorld. IDG. Archived from the original on September 27, 2008. Retrieved September 13, 2008.
- ^ «HP must reimburse Italian PC buyer the amount paid for Microsoft software». Heise online. October 29, 2007. Archived from the original on October 15, 2008. Retrieved September 13, 2008.
- ^ Wilcox, Joe (July 16, 2002). «Microsoft reveals media XP details». CNET. CNET Networks. Archived from the original on February 7, 2015. Retrieved January 26, 2014.
- ^ Wilcox, Joe; Junnarkar, Sandeep (November 7, 2002). «Microsoft launches tablet PC drive». CNET. CNET Networks. Archived from the original on February 7, 2015. Retrieved January 26, 2014.
- ^ Evers, Joris (January 5, 2005). «Microsoft nixes Windows XP for Itanium». Computerworld. IDG. Archived from the original on February 2, 2014. Retrieved January 26, 2014.
- ^ «Microsoft Raises the Speed Limit with the Availability of 64-Bit Editions of Windows Server 2003 and Windows XP Professional» (Press release). Microsoft. April 25, 2005. Archived from the original on February 25, 2015. Retrieved September 10, 2015.
- ^ Thurrott, Paul (January 3, 2005). «Windows XP Starter Edition». Paul Thurrott’s SuperSite for Windows. Penton Media. Archived from the original on August 28, 2013. Retrieved April 12, 2008.
- ^ Fried, Ina (May 23, 2006). «Microsoft pitches pay-as-you-go PCs». CNET. CNET Networks. Archived from the original on February 7, 2015. Retrieved January 26, 2014.
- ^ «Microsoft and EU reach agreement». BBC. March 28, 2005. Archived from the original on September 22, 2015.
- ^ Bishop, Todd (December 24, 2004). «Europe gets ‘reduced’ Windows». Seattle Post-Intelligencer. Hearst Corporation. Archived from the original on October 6, 2021. Retrieved November 30, 2018.
- ^ Anderson, Nate (December 7, 2005). «South Korea fines Microsoft for antitrust abuses». Ars Technica. Condé Nast Publications. Archived from the original on April 22, 2008. Retrieved April 12, 2008.
- ^ «Changes to Windows XP Home Edition K and Windows XP Professional K from earlier versions of Windows XP (MSKB 922474)». Microsoft Support. Microsoft. September 15, 2006. Archived from the original on December 19, 2013. Retrieved January 26, 2014.
- ^ «Service Pack and Update Center». Support. Microsoft. September 10, 2016. Archived from the original on August 31, 2017.
- ^ «Installing Windows XP Service Pack 3 (SP3)». Microsoft. Microsoft. November 18, 2011. Archived from the original on August 22, 2017. Retrieved August 22, 2017.
- ^ Purdy, Kevin. «Slipstream Service Pack 3 into Your Windows XP Installation CD». Lifehacker. Archived from the original on August 22, 2017. Retrieved August 22, 2017.
- ^ «Windows XP SP1 Irons out the Wrinkles». PC Magazine. Archived from the original on February 26, 2014. Retrieved January 26, 2014.
- ^ Mendelson, Edward. «Microsoft Windows XP Service Pack 1 review». CNET. CNET Networks. Archived from the original on February 9, 2008. Retrieved January 26, 2014.
- ^ «Differences Between Windows XP SP1 and Windows XP SP1a». February 3, 2003. Archived from the original on January 27, 2007. Retrieved September 21, 2007.
- ^ «How to obtain the latest Windows XP service pack». March 26, 2007. Archived from the original on October 14, 2004. Retrieved September 21, 2007.
- ^ Shinder, Deb (August 26, 2004). «Windows XP Service Pack 2: How it affects wireless networking». TechRepublic. CBS Interactive. Archived from the original on June 13, 2017. Retrieved June 24, 2018.
- ^ «Bluetooth Wireless Technology FAQ – 2010». July 24, 2012. Archived from the original on March 3, 2016. Retrieved November 4, 2012.
- ^ Menn, Joseph (2019). Cult of the Dead Cow: How the Original Hacking Supergroup Might Just Save the World. New York: Public Affairs. p. 49–50.
- ^ Grimes, Roger A. (2017). «46 — Profile: Window Snyder». Hacking the hacker : learn from the experts who take down hackers. Indianapolis, IN: Wiley. ISBN 978-1-119-39626-0. OCLC 983465946.
- ^ Thurrott, Paul (October 15, 2003). «Windows XP SP2 to be ‘Springboard’ to Longhorn». Windows IT Pro. Archived from the original on June 23, 2018.
- ^ «Windows XP Service Pack 2 information». Microsoft. August 4, 2004. Archived from the original on October 16, 2007.
- ^ Mux, Victor (August 21, 2006). «Why Windows XP SP2b and Windows Server 2003 SP2a?». Microsoft. Archived from the original on August 12, 2009.
- ^ Fletcher, Jefferson (April 8, 2008). «IE Automatic Component Activation Now Available». IEBlog. Microsoft. Archived from the original on April 11, 2008. Retrieved April 11, 2008.
- ^ Mux, Victor (August 9, 2007). «Microsoft Windows XP Professional Service Pack 2c Release». MSDN. Microsoft. Archived from the original on February 2, 2014. Retrieved January 26, 2014.
- ^ Emil Protalinski — April 29, 2008, 1:35 pm UTC (April 29, 2008). «Microsoft releases the long-anticipated Windows XP SP3 (updated)». Ars Technica. Archived from the original on January 15, 2022. Retrieved February 10, 2022.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ «Release Notes for Microsoft Windows Server 2003 Service Pack 2». Archived from the original on November 11, 2019. Retrieved November 11, 2019.
- ^ Oiaga, Marius (December 14, 2007). «64-Bit Windows XP Service Pack 3?». Softpedia. SoftNews NET. Archived from the original on May 8, 2018. Retrieved June 24, 2018.
- ^ Keizer, Gregg (July 8, 2008). «Microsoft sets XP SP3 automatic download for Thursday». Computerworld. IDG. Archived from the original on July 9, 2008. Retrieved July 8, 2008.
- ^ «Windows XP Service Pack 3 Overview». Microsoft. May 6, 2008. Archived from the original on May 6, 2008. Retrieved May 7, 2008.
- ^ «List of fixes that are included in Windows XP Service Pack 3». Microsoft. May 6, 2008. Archived from the original on May 9, 2008. Retrieved June 23, 2018.
- ^ Oiaga, Marius (December 14, 2007). «No, Internet Explorer 7 Will Not(!) Be a Part of Windows XP SP3». SoftNews NET. Archived from the original on January 18, 2012.
- ^ Howard, Michael (January 29, 2008). «New NX APIs added to Windows Vista SP1, Windows XP SP3 and Windows Server 2008». Michael Howard’s Web Log. Microsoft. Archived from the original on August 25, 2011. Retrieved August 8, 2011.
- ^ «Description of the Credential Security Support Provider (CredSSP) in Windows XP Service Pack 3». Microsoft. May 6, 2008. Archived from the original on October 9, 2009. Retrieved June 23, 2018.
- ^ Enterprise IT Planet Staff (May 13, 2005). «Upgraded Wi-Fi Security for Windows XP SP2». Wi-Fi Planet. QuinStreet Enterprise. Archived from the original on June 23, 2018. Retrieved June 23, 2018.
- ^ «Overview of Windows XP Service Pack 3» (PDF). Archived (PDF) from the original on January 17, 2009.
- ^ «Information about Windows Imaging Component». Microsoft. August 13, 2002. Archived from the original on May 10, 2011.
- ^ Nanjappa, Ashwin (January 27, 2010). «Windows: ClearType on RDP». CodeYarns.com. Archived from the original on November 17, 2015. Retrieved June 16, 2014.
- ^ «A hotfix is available that improves the stability of the Windows Management Instrumentation repository in Windows XP». Support. Microsoft. October 8, 2011. Archived from the original on March 5, 2013. Retrieved January 20, 2013.
- ^ a b «FAQs regarding SP3 RTM». Microsoft. April 22, 2008. Archived from the original on August 24, 2011. Retrieved June 23, 2018.
- ^ Kaelin, Mark (May 8, 2008). «How do I… Return the Address bar Windows XP SP3 removed?». TechRepublic. CBS Interactive. Archived from the original on September 5, 2015. Retrieved May 5, 2015.
- ^ «Windows XP SP3 preview surfaces on Web». PC World. IDG. October 6, 2005. Archived from the original on October 31, 2020. Retrieved October 29, 2020.
- ^ «Sneak preview of Windows XP SP3 surfaces». Ars Technica. Ars Technica. October 6, 2005. Archived from the original on November 4, 2020. Retrieved October 29, 2020.
- ^ «Microsoft employee blasts ‘fake’ service pack». PC World. IDG. October 14, 2005. Archived from the original on October 31, 2020. Retrieved October 29, 2020.
- ^ «Windows XP SP3 preview a fake». Ars Technica. Ars Technica. October 15, 2005. Archived from the original on October 31, 2020. Retrieved October 29, 2020.
- ^ «Microsoft leans on Vista SP1 site». PC World. IDG. October 4, 2007. Archived from the original on May 18, 2017. Retrieved October 29, 2020.
- ^ «What is the maximum amount of RAM the Windows operating system can handle?». Crucial. Archived from the original on May 11, 2011. Retrieved June 25, 2010.
- ^ «Physical Memory Limits: Windows XP». Memory Limits for Windows Releases. Microsoft. Archived from the original on January 6, 2014. Retrieved January 14, 2014.
- ^ «Processor and memory capabilities of Windows XP Professional x64 Edition and of the x64-based versions of Windows Server 2003 (Revision 7.0)». Microsoft Support. Microsoft. December 20, 2010. Archived from the original on August 12, 2011. Retrieved August 8, 2011.
- ^ Kumar, I. Suuresh (October 25, 2010). «Multi-core processor and multiprocessor limit for Windows XP». Microsoft Answers. Microsoft. Archived from the original on April 19, 2014. Retrieved April 18, 2014.
- ^ «Processor Affinity Under WOW64». MSDN. Microsoft. January 27, 2011. Archived from the original on May 6, 2011. Retrieved August 8, 2011.
- ^ «Maximum quantity of logical processors in a PC supported by Microsoft Windows XP professional, x64 edition». Support. Microsoft. December 20, 2010. Archived from the original on January 11, 2013. Retrieved January 20, 2013.
- ^ «Microsoft Product Lifecycle Search: Windows Fundamentals for Legacy PCs». Microsoft Support. Microsoft. Archived from the original on October 5, 2014. Retrieved October 13, 2012.
- ^ Fried, Ina (September 27, 2007). «Microsoft extends Windows XP’s stay». CNET. CBS Interactive. Archived from the original on August 30, 2008. Retrieved June 5, 2008.
- ^ Lai, Eric (March 3, 2008). «Microsoft to keep Windows XP alive—but only for Eee PCs and wannabes». Computerworld. IDG. Archived from the original on April 8, 2008. Retrieved April 8, 2008.
- ^ Tung, Liam (February 18, 2014). «Microsoft: ‘Remember, some XP-based embedded systems to get support to 2019’«. ZDNet. CBS Interactive. Archived from the original on April 4, 2014. Retrieved April 6, 2014.
- ^ Newman, Jared (August 27, 2014). «Enthusiast developer keeps Windows XP alive with unofficial ‘Service Pack 4’«. PCWorld. Archived from the original on October 26, 2018. Retrieved October 26, 2018.
- ^ Satherley, Dan (April 9, 2013). «Businesses urged to ditch XP». 3 News NZ. Archived from the original on July 13, 2014. Retrieved June 28, 2019.
- ^ Keizer, Gregg (August 26, 2013). «Microsoft will craft XP patches after April ’14, but not for you». Computerworld. IDG. Archived from the original on October 20, 2013. Retrieved December 12, 2013.
- ^ a b Keizer, Gregg (March 11, 2014). «US-CERT urges XP users to dump IE». Computerworld. IDG. Archived from the original on June 28, 2019. Retrieved June 28, 2019.
- ^ ATM Industry Association (collectively) (June 1, 2015). «ATMIA position paper recommending migration to Windows 10». www.atmia.com (Press release). ATM Industry Association. Archived from the original on May 25, 2017.
- ^ Summers, Nick (January 16, 2014). «ATMs Face Deadline to Upgrade From Windows XP». Bloomberg Businessweek. Bloomberg L.P. Archived from the original on January 16, 2014. Retrieved January 17, 2014.
- ^ «Wannacry ransomware cyber attack: Indian ATMs could be at high risk as most run on Windows XP». Business Today. May 15, 2017. Archived from the original on May 17, 2017. Retrieved May 18, 2017.
- ^ «Windows 8 a ‘threat’ to China’s security». BBC. June 5, 2014. Archived from the original on October 8, 2018. Retrieved October 8, 2018.
- ^ Kan, Michael (May 20, 2014). «China bans government purchases of Windows 8». PCWorld. IDG. Archived from the original on May 20, 2014. Retrieved May 20, 2014.
- ^ «Microsoft Partners Lenovo, Tencent to Offer XP Tech Support in China». Voanews.com. Reuters. April 9, 2014. Archived from the original on April 13, 2014. Retrieved April 16, 2014.
- ^ Gallagher, Sean (April 6, 2014). «Not dead yet: Dutch, British governments pay to keep Windows XP alive». Ars Technica. Condé Nast Publications. Archived from the original on October 14, 2019. Retrieved October 15, 2019.
- ^ Foley, Mary Jo (March 3, 2014). «Microsoft to start nagging Windows XP users about April 8 end-of-support date». ZDNet. CBS Interactive. Archived from the original on October 14, 2019. Retrieved October 15, 2019.
- ^ Yegulalp, Serdar (March 3, 2014). «Microsoft: Use Laplink’s Windows XP migration tools, not ours». Infoworld. Archived from the original on October 15, 2019.
- ^ Ward, Mark (March 5, 2014). «XP – the operating system that will not die». BBC News. Archived from the original on March 24, 2014. Retrieved March 25, 2014.
- ^ Egan, Matt (April 7, 2014). «What should XP users do when Microsoft ends support? Upgrade to Windows 8, buy a new PC, keep running XP?». PC Advisor. Archived from the original on February 14, 2014. Retrieved April 6, 2014.
- ^ «Alert (TA14-069A): Microsoft Ending Support for Windows XP and Office 2003». March 11, 2014. Archived from the original on March 16, 2014. Retrieved April 6, 2014.
- ^ Keizer, Gregg (January 19, 2014). «Microsoft will furnish malware assassin to XP users until mid-2015». Computerworld. IDG. Archived from the original on January 22, 2014.
- ^ «Microsoft Warns of Permanent Zero-Day Exploits for Windows XP». Infosecurity. Reed Exhibitions. August 20, 2013. Archived from the original on August 26, 2013. Retrieved August 27, 2013.
- ^ «Microsoft Security Bulletin MS15-011 JASBUG». February 10, 2015. Archived from the original on August 11, 2015. Retrieved September 18, 2015.
- ^ Freeman, Robert (November 11, 2014). «IBM X-Force Researcher Finds Significant Vulnerability in Microsoft Windows». Securityintelligence.com. Archived from the original on July 3, 2015. Retrieved September 18, 2015.
- ^ Talbot, David (October 17, 2012). «Computer Viruses Are «Rampant» on Medical Devices in Hospitals». MIT Technology Review. Archived from the original on October 19, 2016. Retrieved April 6, 2014.
- ^ Goodin, Dan (May 1, 2014). «Emergency patch for critical IE 0-day throws lifeline to XP laggards, too». Ars Technica. Conde Nast. Archived from the original on May 17, 2017. Retrieved May 26, 2017.
- ^ Warren, Tom (May 13, 2017). «Microsoft issues ‘highly unusual’ Windows XP patch to prevent massive ransomware attack». The Verge. Vox Media. Archived from the original on May 14, 2017. Retrieved May 13, 2017.
- ^ Warren, Tom (May 14, 2019). «Microsoft warns of major WannaCry-like Windows security exploit, releases XP patches». The Verge. Vox Media. Archived from the original on September 2, 2019. Retrieved May 16, 2019.
- ^ «Prevent a worm by updating Remote Desktop Services (CVE-2019-0708) – MSRC». blogs.technet.microsoft.com. May 14, 2019. Archived from the original on May 14, 2019. Retrieved May 16, 2019.
- ^ Winder, Davey (August 11, 2019). «Critical Windows 10 Warning: Millions Of Users At Risk». Forbes. Archived from the original on August 11, 2019. Retrieved August 11, 2019.
- ^ Greenberg, Andy (August 13, 2019). «DejaBlue: New BlueKeep-Style Bugs Renew The Risk Of A Windows worm». wired. Archived from the original on April 13, 2021. Retrieved August 15, 2019.
- ^ Seals, Tara (August 14, 2019). «20-Year-Old Bug in Legacy Microsoft Code Plagues All Windows Users». ThreatPost.com. Archived from the original on April 17, 2021. Retrieved August 15, 2019.
- ^ «Farewell to Microsoft Internet Games on Windows XP, Windows ME, and Windows 7». answers.microsoft.com. Archived from the original on July 14, 2019. Retrieved August 4, 2019.
- ^ «Windows XP and Windows Vista Support – Steam – Knowledge Base – Steam Support». support.steampowered.com. Archived from the original on August 12, 2019. Retrieved August 4, 2019.
- ^ «Windows Update SHA-1 based endpoints discontinued for older Windows devices». support.microsoft.com. Archived from the original on April 17, 2021. Retrieved April 6, 2021.
- ^ «Microsoft Update Catalog». www.catalog.update.microsoft.com. Archived from the original on April 15, 2021. Retrieved April 6, 2021.
- ^ Lake, Matt (October 10, 2002). «Microsoft Windows XP – Home Edition review». CNET. Archived from the original on May 31, 2007. Retrieved March 25, 2014.
- ^ Mendelson, Edward (September 3, 2001). «Microsoft Ships Its Biggest OS Upgrade Ever—Early!». PC Magazine. Archived from the original on March 25, 2014. Retrieved March 25, 2014.
- ^ Manes, Stephen (August 26, 2004). «Full Disclosure: Your Take on Windows’ Worst Irritations». PCWorld. IDG. Archived from the original on October 8, 2009.
- ^ Bright, Peter (April 10, 2014). «Memory lane: Before everyone loved Windows XP, they hated it». Ars Technica. Condé Nast. Archived from the original on April 24, 2014. Retrieved June 20, 2014.
- ^ Bright, Peter (October 25, 2011). «Ten years of Windows XP: how longevity became a curse». Ars Technica. WIRED Media Group. Archived from the original on June 12, 2018. Retrieved June 9, 2018.
- ^ «Operating system market share». September 9, 2012. Archived from the original on September 9, 2012. Retrieved September 8, 2018.
- ^ «Desktop Windows Version Market Share Worldwide». StatCounter Global Stats. Archived from the original on April 20, 2019. Retrieved July 2, 2019.
- ^ Crothers, Brooke (February 2, 2014). «Oops, Windows XP gains in January but so does Windows 8.1». CNET. CBS Interactive. Archived from the original on February 21, 2014. Retrieved March 16, 2014.
- ^ «OS Platform Statistics». w3schools. Archived from the original on September 17, 2015. Retrieved September 14, 2015.
- ^ «Desktop Windows Version Market Share Africa». StatCounter Global Stats. Archived from the original on September 22, 2022. Retrieved September 22, 2022.
- ^ «Desktop Windows Version Market Share Armenia». StatCounter Global Stats. Archived from the original on September 4, 2018. Retrieved December 11, 2021.
- ^ «Desktop Windows Version Market Share Armenia». StatCounter Global Stats. Archived from the original on September 4, 2018. Retrieved December 11, 2021.
- ^ «Desktop Windows Version Market Share Armenia». StatCounter Global Stats. Archived from the original on September 4, 2018. Retrieved July 10, 2021.
- ^ «Desktop Windows Version Market Share Armenia». StatCounter Global Stats. Archived from the original on September 4, 2018. Retrieved March 2, 2021.
- ^ «Desktop Windows Version Market Share Armenia». StatCounter Global Stats. Archived from the original on September 4, 2018. Retrieved July 2, 2020.
- ^ «Desktop Windows Version Market Share Armenia». StatCounter Global Stats. Archived from the original on September 4, 2018. Retrieved July 2, 2020.
- ^ Cimpanu, Catalin. «Windows XP leak confirmed after user compiles the leaked code into a working OS». ZDNet. Archived from the original on September 30, 2020. Retrieved October 1, 2020.
- ^ Warren, Tom (September 25, 2020). «Windows XP source code leaks online». The Verge. Archived from the original on September 29, 2021. Retrieved October 1, 2020.
- ^ a b Alcorn, Paul (September 30, 2020). «Windows XP Source Code Leaked, Posted to 4chan (Update, It Works)». Tom’s Hardware. Archived from the original on October 6, 2021. Retrieved October 1, 2020.
- ^ «Windows XP Source Code Leaked By Apparent Bill Gates Conspiracist». Gizmodo. September 25, 2020. Archived from the original on October 1, 2020. Retrieved October 1, 2020.
- ^ «The Windows XP and Windows Server 2003 source code leaks online». Graham Cluley. September 25, 2020. Archived from the original on September 26, 2020. Retrieved September 29, 2020.
- ^ «Windows XP source code leaked online». www.computing.co.uk. September 28, 2020. Archived from the original on October 2, 2020. Retrieved September 29, 2020.
Further reading
- Joyce, Jerry; Moon, Marianne (2004). Microsoft Windows XP Plain & Simple. Microsoft Press. ISBN 978-0-7356-2112-1.
External links
- Windows XP End of Support
- Security Update for Windows XP SP3 (KB4012598)
- Минимальные
- Рекомендуемые
Минимальные системные требования
- Разрядность: x86 (32-bit)
- ЦП [CPU]: Pentium 233 MHz
- Видеоадаптер [GPU]: Встроенная или дискретная
- Винчестер [HDD]: 1.5 Gb
- Оперативная память [RAM]: 64 Mb
- Аудиокарта [AUDIO]: Любая
- Контроллер: Клавиатура, Мышь
- Разрешение экрана: VGA 640×480
- Дополнительно: DVD/CD привод
Рекомендуемые системные требования
- Разрядность: x86 (32-bit)
- ЦП [CPU]: Pentiun III, Pentium IV
- Видеоадаптер [GPU]: Дискретная
- Винчестер [HDD]: 1.5 Gb
- Оперативная память [RAM]: 128 Mb
- Аудиокарта [AUDIO]: Любая
- Контроллер: Клавиатура, Мышь Microsoft Mouse
- Разрешение экрана: SVGA 800×600
Для того, чтобы нужная операционная система Виндовс ХР полноценно функционировала ПК, его минимальные системные требования должны быть примерно такими как написано ниже: Центральный процессор обязан обладать 32-bit разрядностью и скоростью не ниже 233 мегагерц. «Оперативки» нормальным сочетанием будет 128 мегабайт, это позволит гулять по интернет а также выполнять другие задачи. Свободное место вашего HDD должно быть не меньше 1.5 Gb.
Содержание
- Рекомендованные системные требования для ОС Windows XP (x86/x64)
- Системные требования для Microsoft Windows XP Home и Professional Editions x86
- Платформа — x86:
- Системные требования для Microsoft Windows XP Professional x64
- Платформа: x64
- Окончание поддержки Windows XP
- Спецификация и системные требования
- Новый интерфейс
- Безопасность и стабильность
- Программы
- Резюме
- Windows XP: системные требования, сравнение версий
- Windows XP
- Windows XP
- Разработчик
- Семейство ОС
- Основана на
- Исходный код
- Первый выпуск
- Последняя версия
- Поддерживаемые языки
- Поддерживаемые платформы
- Тип ядра
- Интерфейс
- Лицензия
- Состояние
- Содержание
- Варианты [ ]
- Новое в сравнении с Windows 2000 [ ]
- Графический интерфейс пользователя [ ]
- Интерфейс командной строки (CLI ) [ ]
- Системные требования [ ]
- Пакеты обновлений и поддержка [ ]
- Windows XP Gold [ ]
- Пакет обновлений 1 [ ]
- Пакет обновлений 2 [ ]
- Пакет обновлений 3 [ ]
- Неофициальный выпуск [ ]
- Завершение поддержки [ ]
- Критика [ ]
- Система Windows XP и основные ее характеристики
- Дата выхода Windows XP
- Версии Windows XP
- Основные функции в Windows XP
- Обновления в Windows XP
- Минимальные требования для Windows XP
- Поддержка Windows XP
Рекомендованные системные требования для ОС Windows XP (x86/x64)
Windows XP (Whistler — кодовое название при разработке) — операционная система (ОС) семейства Windows NT корпорации Microsoft. Была выпущена 25 октября 2001 года и является развитием Windows 2000 Professional.
Название XP происходит от англ. experience (опыт, впечатления). Внутренняя версия — Windows NT 5.1
Системные требования для Microsoft Windows XP Home и Professional Editions x86
Платформа — x86:
В дополнение к этим требованиям, для установки Service Pack 2 необходимо наличие на жёстком диске не менее 2 ГБ свободного места во время установки. А уже для SP 3 требуется 2.3 ГБ жёсткого диска при установке.
Системные требования для Microsoft Windows XP Professional x64
Платформа: x64
Окончание поддержки Windows XP
Корпорация Майкрософт в течение 12 лет предоставляла поддержку для Windows XP. Теперь для нас и наших партнеров настало время инвестировать в более современные технологии, которые позволят нам и дальше разрабатывать и развивать новые эффективные способы работы. В результате техническая поддержка по Windows XP больше не доступна. Это относится и к автоматическим обновлениям, которые повышают защиту компьютера.
Также корпорация Майкрософт прекратила предоставлять Microsoft Security Essentials для загрузки в Windows XP. Если у вас уже установлены эти компоненты, в течение некоторого времени вы будете получать обновления антивредоносных сигнатур. Однако помните, что эффективность Microsoft Security Essentials (или любых других антивирусных программ) будет ограничена на компьютерах без последних обновлений для системы безопасности. Это значит, что компьютеры под управлением Windows XP будут незащищенными и находиться под угрозой заражения.
Источник

Спецификация и системные требования
Данная операционная система поставлялась на рынок в двух вариантах – Windows XP Home Edition и всем полюбившаяся Windows XP Professional. Обе конфигурации являются полноценными программными продуктами и отлично подходят для работы на современных, мощных ПК. Windows XP Home Edition разрабатывалась как замена Win 98 и Win ME для домашних пользователей. Ее основное предназначение – просмотр мультимедийных файлов, работа с документами, серфинг в глобальной сети, игры, развлечения и многое другое. Windows XP Professional, по задумке разработчиков компании Microsoft, должна стать заменой Win 2000 и Win NT как профессиональный инструмент для работы. Предполагаемая область использования – рабочие станции, корпоративные компьютеры. Эта версия дополнительно поддерживает такие функции, как:
Как мы видим, эти, а также ряд других функций, присутствующих в Windows XP Professional, вряд ли будут полезны домашним пользователям.
Минимальными системными требованиями для Windows XP названа следующая конфигурация ПК: ЦПУ 233 МГц, 64Мбайт оперативной памяти (не используемой видеокартой), 1.5 Гбайт свободного места на HDD.
Новый интерфейс
Для Windows XP был разработан новый графический интерфейс под названием Luna. Он пришелся по вкусу пользователям, поскольку выгодно отличается от графического оформления других операционных систем компании Microsoft. На смену прямым линиям и строгим формам пришли округлые контуры, тени, анимированные эффекты и прозрачные элементы, которые делают картинку более живой и приятной. Кроме того, разработчики позаботились о создании более удобной в использовании и понятной неподготовленному пользователю концепции работы с операционной системой.
В Windows XP была значительно расширена функциональность Главного меню и Панели задач. В Главном меню пользователи могут найти ссылки на часто используемые программы и папки. Панель задач теперь умеет скрывать редко используемые ярлыки в системном трее, а ссылки на несколько открытых одновременно окон одного приложения – размещать друг над другом, тем самым экономя экранное пространство.
Безопасность и стабильность
Windows XP заслуженно считается самой надежной, стабильной и безопасной операционной системой от компании Microsoft. Она содержит ряд революционных инноваций, которые позволили ей встать на качественно новый уровень по сравнению с предшественницами. Безусловно, самым главным нововведением в вопросах безопасности стало введение системы администрирования пользователей и контроля доступа. Теперь можно потребовать от пользователей регистрации при входе. Таким способом можно четко определить возможности каждого пользователя по редактированию и удалению файлов, а также работе с программами.
Кроме того, в Windows XP существует три типа пользователей: Администраторы, Гости и Лимитированные. Каждый из типов имеет свои, строго ограниченные возможности по контролю за конфигурацией системы, которые, к тому же, могут быть изменены Администратором. Такая гибкость в работе позволяет обеспечить сохранность данных и безопасность системы без необходимости осуществлять постоянный контроль за работой пользователей.
Кроме того, Windows XP имеет встроенный сетевой брэндмауэр начального уровня, который обеспечивает приемлемый уровень безопасности при работе в интернете. Также имеется возможность при помощи групповых политик ограничивать права определенных программ, запрещать установку ПО, не имеющего цифрового сертификата и многое другое. Помимо прочего, большой вклад в обеспечение общей стабильности вносит функция восстановления системы. Стоит отметить, что безопасность операционной системы увеличивается с каждым новым выходом крупного пакета обновлений под названием Service Pack. На сегодняшний день, самой стабильной и безопасной является Windows XP SP3.
Программы
Windows XP может похвастаться большим набором встроенного программного обеспечения на все случаи жизни. Для работы с интернетом пользователям предлагается браузер Internet Explorer 6, который был значительно усовершенствован по сравнению с предыдущей версией. Он имеет поддержку ряда новых web-стандартов, таких как Р3Р, новую панель обозревателя и навигационные значки. Пользователям, которые активно общаются в сети, пригодится программа Windows Messenger, которая позволяет не просто обмениваться текстовыми сообщениями, но и организовывать настоящие видеоконференции.
Для работы с мультимедиа в состав операционной системы входят программы Windows Media Player 8 а так же знакомый нам по более ранним версиям Windows Movie Maker. Последняя представляет собой несложный видеоредактор, при помощи которого пользователи могут монтировать домашние видеозаписи, добавлять к ним различные эффекты. Windows Media Player позволяет просматривать видеофайлы наиболее популярных форматов, а также содержит востребованную функцию записи CD и DVD-дисков.
Резюме
Windows XP на момент своего выхода стала отличным решением для всех пользователей, чьи компьютеры по своим характеристикам позволяли установить данную операционную систему. Она принесла на домашние компьютеры недоступный до сих пор уровень надежности, стабильности и безопасности. Кроме того, она установила новый стандарт удобного и дружественного интерфейса, призванного сделать работу за компьютером приятной даже для новичка.
Источник
Windows XP: системные требования, сравнение версий

Windows XP (внутренняя версия — Windows NT 5.1) — операционная система семейства Windows NT корпорации Microsoft. Дата выпуска 25 октября 2001 года. Является развитием версии Windows 2000 Professional.
Варианты Windows XP:
Графическое оформление:
Системные требования операционной системы Windows XP Home и Windows XP Professional.
| Ресурсы | Минимальные | Рекомендуемые |
|---|---|---|
| Процессор | 233 MHz | 300 MHz или выше |
| Оперативная память | 64 Мб RAM (могут быть ограничены некоторые возможности) | 128 Мб RAM или выше |
| Видеоадаптер и монитор | VGA (640 x 480) | Super VGA (800 x 600) или бо́льшее разрешение |
| Свободное место на HDD | 1.5 Гб | 1.5 Гб или выше |
| Оптические накопители | CD-ROM (требуется для установки) | CD-ROM или DVD-ROM |
| Устройства взаимодействия с пользователем | клавиатура | клавиатура и мышь |
| Другие устройства | Звуковая карта, колонки и/или наушники | Звуковая карта, колонки и/или наушники |
| Service Pack 1 | Service Pack 2 | Service Pack 3 |
| Service Pack 1 (SP1) для Windows XP был выпущен 9 сентября 2002 года. Наиболее важными новшествами стали поддержка USB 2.0, утилита, позволяющая выбирать программы по умолчанию для просмотра веб, почты, обмена мгновенными сообщениями, а также различные реализации виртуальной машины Java. | Service Pack 2 (SP2) добавил в Windows XP новые возможности, поддержку Wi-Fi с мастером настройки и Bluetooth, а также улучшения в IE6 — например, возможность блокировать «всплывающие» окна. Появилась расширенная защита памяти, в частности, от атак переполнения буфера. Windows XP Service Pack 2 включает в себя Windows Security Center, который позволяет облегчить наблюдение за безопасностью системы, следя и напоминая пользователю о необходимости установить или обновить антивирус и его базы, активировать встроенный или сторонний файрволл, произвести обновление операционной системы или изменить настройки веб-браузера. Также были улучшены функции автозапуска при загрузке CD или подключении флеш-карт и подобных устройств. | Service Pack 3 (SP3) включает в себя все обновления, выпущенные после выхода Windows XP Service Pack 2, а также ряд других новых элементов. Среди них функция защиты сетевого доступа (Network Access Protection) и новая модель активации, заимствованные у Windows Vista, кроме того, появилась улучшенная функция обнаружение так называемых маршрутизаторов-«черных дыр» и др. |
Сравнение Windows XP Home Edition и Windows XP Professional.
Источник
Windows XP
Windows XP (кодовое название при разработке — Whistler; внутренняя версия — Windows NT 5.1) — операционная система (ОС) семейства Windows NT корпорации Microsoft. Была выпущена 25 октября 2001 года и является развитием Windows 2000 Professional. Название XP происходит от англ. experience («опыт», «впечатления» [1] ).
Windows XP
Разработчик
Семейство ОС
Основана на
Исходный код
Первый выпуск
Последняя версия
Поддерживаемые языки
Поддерживаемые платформы
Тип ядра
Интерфейс
Лицензия
Состояние
В настоящее время, многие современные программы уже не работают в среде Windows XP. Для большинства современного оборудования отсутствуют драйверы, способные обеспечить функционирование в среде Windows XP. Из-за ряда технических ограничений по причине сильного устаревания, данная операционная система становится «узким местом» для новых систем, не позволяющей в полной мере реализовать потенциальные возможности аппаратного обеспечения. Поддержка Windows XP корпорацией Microsoft прекращена 8 апреля 2014.

Содержание
Варианты [ ]
Windows XP выпускалась в следующих вариантах
Новое в сравнении с Windows 2000 [ ]
Некоторыми из наиболее заметных улучшений в Windows XP по сравнению с Windows 2000 являются:
Графический интерфейс пользователя [ ]
Англоязычное стартовое меню в новом виде при использовании темы Royale
Windows XP анализирует производительность системы с определёнными визуальными эффектами и в зависимости от этого активирует их или нет, учитывая возможное падение или рост производительности. Пользователи также могут изменять данные параметры, используя диалоговые окна настройки, при этом можно либо гибко выбрать активность тех или иных визуальных эффектов, либо отдать это на управление системе или же выбрать максимальную производительность или лучший вид графического интерфейса. [4]
Некоторые эффекты, такие как полупрозрачность и т. п., требуют наличия производительной графической подсистемы, на старых видеокартах производительность может сильно упасть и Microsoft рекомендует отключить эти возможности в таком случае. [5]
В Windows XP появилась возможность использовать Visual Styles, позволяющие изменить графический интерфейс пользователя. Luna — новый стиль графического интерфейса, входящий в поставку XP и являющийся интерфейсом по умолчанию для компьютеров, имеющих более 64 мегабайт оперативной памяти. Возможно использовать и другие Visual Styles, но они должны быть подписаны цифровой подписью Microsoft (так как имеют важное значение в функционировании системы). Один из интерфейсов доступен на версии Windows XP Black Edition by Spa.
Интерфейс командной строки (CLI ) [ ]
Системные требования [ ]
Логотип Designed for Windows XP (Совместимо с Windows XP)
Системные требования операционных систем Windows XP Home и Professional Editions следующие: [8]
В дополнение к этим требованиям, для установки Service Pack 2 необходимо наличие на жёстком диске не менее 2 ГБ свободного места во время установки. А уже для SP 3 требуется 2.3 ГБ жёсткого диска при установке. [9]
Пакеты обновлений и поддержка [ ]
Microsoft периодически выпускает пакеты обновлений (service packs) своих операционных систем, устраняющие выявленные проблемы и добавляющие новые возможности.
Windows XP Gold [ ]
Пакет обновлений 1 [ ]
Пакет обновлений 1a был выпущен 3 февраля 2003 года и удалял виртуальную машину Java из системы. Корпорация Майкрософт не рекомендовала пользователям, уже установившим пакет обновлений SP1, устанавливать пакет SP1а.
Пакет обновлений 2 [ ]
При загрузке системы исчезли подзаголовки с названием редакции; полоса загрузки в редакциях Home и Embedded сменила зелёный и жёлтый цвета на синий цвет, как в редакции Professional.
Пакет обновлений 3 [ ]
Окончательная версия Пакета обновлений 3 была представлена 21 апреля 2008 года, но только для бизнес-клиентов, таких как производители оригинального оборудования и подписчики MSDN и TechNet. Остальные пользователи смогли получить третий сервис-пак 6 мая.
Пакет может быть установлен только поверх пакета Service Pack 1 (SP1) или Service Pack 2 (SP2), и доступен только для 32-битной версии. [16]
Неофициальный выпуск [ ]
В 2014 году силами энтузиастов был создан «Service Pack 4» на основе POSReady — варианта для XP. [20] Данная версия является не официальной и нарушающей лицензионное соглашение, т.к. обновления изначально предназначены для другой версии Windows XP (POSReady).
Завершение поддержки [ ]
На момент прекращения официальной всеобщей поддержки (8 апреля 2014 года) Windows XP было 12,5 лет. Этот срок поддержки стал самым долгим за всю историю Windows, за отдельную плату он мог быть продлён ещё на 5 лет.
Поддержка Windows Embedded POSReady 2009 завершилась 9 апреля 2019 года.
Критика [ ]
Источник
Система Windows XP и основные ее характеристики
Дата выхода Windows XP
Это одна из самых популярных версий Windows, основанная на установленной пользовательской базе. Название «XP» сокращенно означает «eXPerience», что подчеркивает расширенные возможности для пользователя.
Windows XP предшествовал Windows 2000 и Windows Me, а затем Windows Vista.
8 апреля 2014 года Microsoft выпустила последние обновления для Windows XP. Таким образом, эта версия Windows больше не поддерживается Microsoft. Тем не менее, Windows XP остается популярной операционной системой среди многих пользователей, которые любят эту версию. Tckb ds bcgjkmpetnt ОС Linux, то вам может быть интересно прочитать про основные различия между Linux и Windows
Версии Windows XP
Microsoft предоставила семь выпусков Windows XP. Тем не менее, только первые два из списка ниже были широко доступны для обычного пользователя:
Домашняя версия предназначена для среднего пользователя и для более дешевых компьютеров. Windows XP Home ориентирована на начинающих пользователей компьютеров.
Профессиональная версия более ориентирована на предприятия и имеет возможность присоединиться к домену Windows, информационным службам интернета и многоязычному пользовательскому интерфейсу.
Основные функции в Windows XP
Первой новой функцией для Windows XP является интерфейс, полностью отличающийся от предыдущих версий, таких как Windows 2000 или Windows Me. Microsoft разработала новый привлекательный и удобный внешний вид с визуальными стилями и различными эффектами.
Кроме того, в Windows XP существовал огромный и разнообразный набор инструментов и программ, что делает Windows XP более безопасной, надежной и стабильной операционной системой, чем предыдущие версии.
Список новых функций в Windows XP:
Обновления в Windows XP
Обновления в Windows XP предоставлялись в виде пакетов обновления. Пакет обновления представляет собой накопительные программные ресурсы, аналогичные в Windows 10. Тем не менее, в отличие от Windows 10, обновления для Windows XP меньше, но больше.
Например, переход с Windows XP с пакетом обновления 1 на Windows XP с пакетом обновления 2 является более масштабным и сложным, чем переход с Windows 10 версии 1809 на Windows 10 версии 1903. Если вы пользователь macOS, то вам может быть полезно прочитать про сравнение безопасности macOS и Windows.
Microsoft выпустила 3 пакета обновления. Третий и последний, SP3, был опубликован 6 мая 2008 года.
Минимальные требования для Windows XP
К счастью, на рынке нет компьютеров, которые бы не соответствовали этим крайне скромным характеристикам.
Так что, если вы испытываете ностальгию, современный ПК будет работать под управлением Windows XP без проблем.
Поддержка Windows XP
Источник
Microsoft® Windows® XP Professional: требования к системе
— Рекомендуется компьютер с процессором, тактовая частота которого составляет не менее 300 МГц; допустимый минимум — 233 МГц (система с одним или двумя процессорами);* использоваться могут процессоры семейств Intel Pentium/Celeron, AMD K6/Athlon/Duron, или другие совместимые процессоры.
— Рекомендуется не менее 128 МБ ОЗУ (допустимый минимум — 64 МБ, при этом быстродействие и некоторые возможности операционной системы могут быть ограничены).
— 1,5 ГБ свободного места на жестком диске*.
— Видеоплата и монитор Super VGA, с разрешением не менее 800×600 точек.
— Дисковод для компакт-дисков или дисков DVD.
— Клавиатура и мышь Microsoft Mouse, или совместимое устройство ввода.
Дополнительные элементы и службы, необходимые для использования некоторых возможностей Windows XP
Доступ к интернету
— Для пользования всемирной сетью необходимо подключение к интернету, учетная запись цифрового паспорта Microsoft .NET Passport и внесение своевременной платы интернет-провайдеру. Также может потребоваться оплата услуг местной или междугородной телефонной связи.
— Модем со скоростью передачи не менее 14,4 Кбит/с.
Создание сети
— Сетевая плата, соответствующая типу локальной, глобальной, беспроводной или домашней сети, к которой планируется подключить компьютер, а также доступ к соответствующей сетевой инфраструктуре. Для доступа к сетям независимых компаний может потребоваться внесение дополнительной платы.
Передача мгновенных сообщений, проведение голосовых и видеоконференций, совместное использование приложений. Обеим сторонам необходимы следующие элементы:
— Учетная запись цифрового паспорта Microsoft .NET Passport и доступ к интернету, или учетная запись службы мгновенных сообщений Exchange 2000 Server и доступ к сети (для некоторых конфигураций может потребоваться загрузка дополнительных компонентов).
Проведение голосовых и видеоконференций. Обеим сторонам необходимы следующие элементы:
— Модем со скоростью передачи не менее 33,6 Кбит/с, или сетевое подключение.
— Микрофон и звуковая плата с динамиками, или головная телефонная гарнитура.
Организация видеоконференций. Обеим сторонам необходимы следующие элементы:
— Камера для видеоконференций.
— Компьютеры обеих сторон должны работать под управлением операционной системы Windows XP.
Совместное использование приложений. Обеим сторонам необходимы следующие элементы:
— Модем со скоростью передачи не менее 33,6 Кбит/с, или сетевое подключение.
— Компьютеры обеих сторон должны работать под управлением операционной системы Windows XP.
Использование удаленной технической поддержки
— Компьютеры обеих сторон должны быть подключены к сети.
— Компьютеры обеих сторон должны работать под управлением операционной системы Windows XP.
Удаленное управление рабочим столом
— Компьютер под управлением операционной системы Windows 95, или более поздней версии.
— Оба компьютера должны быть подключены к сети.
Работа со звуком
— Звуковая плата и динамики, или наушники.
Воспроизведение DVD-фильмов
— Дисковод DVD и плата, или программное обеспечение DVD-декодера.
— Не менее 8 МБ видеопамяти.
Работа с приложением Windows Movie Maker
— Для использования функций видеозаписи требуется соответствующее цифровое или аналоговое устройство видеозаписи.
— Процессор с частотой не менее 400 МГц для записи видео с помощью цифровой видеокамеры.
* Реальные требования могут меняться в зависимости от конфигурации системы и устанавливаемых приложений и функций. Если установка осуществляется по сети, может потребоваться дополнительное место на жестком диске.
Релиз опубликован: 2001-10-26
Данный материал является частной записью члена сообщества Club.CNews.
Редакция CNews не несет ответственности за его содержание.
Системные требования (официальные)
Системные требования (официальные)
Рассмотрим, какое аппаратное обеспечение нужно иметь для работы системы Windows XP.
• Процессор с частотой не ниже 233 МГц (рекомендуется от 300 МГц и выше).
• 128 Мбайт оперативной памяти (при 64 Мбайт быстродействие может быть ограничено).
• Монитор и видеокарта, поддерживающие разрешение 800 ? 600 или выше.
• Привод компакт-дисков или DVD.
Совет.
Если вы хотите на компьютере не только пользоваться текстовым редактором Word, а еще и запускать игры, работать с графикой, создавать анимации, сочинять музыку, то вам понадобится, как минимум, процессор с частотой 1200 МГц и 256 Мбайт оперативной памяти. Но поверьте, Windows XP того стоит.
Данный текст является ознакомительным фрагментом.
Читайте также
Системные требования
Системные требования
Минимальные требования, которым должны отвечать технические характеристики хост-компьютера, предназначенного для установки Virtual PC 2004, существенно зависят от номенклатуры гостевых ОС, устанавливаемых на виртуальные машины. Это и понятно — ведь
Системные требования
Системные требования
Минимальные требования, которым должны отвечать технические характеристики хост-компьютера, предназначенного для установки VMware, зависят от номенклатуры гостевых ОС для виртуальных машин.Для работы же собственно VMware Workstation необходимы следующие
Системные требования
Системные требования
Для работы Parallels Workstation необходимы следующие вычислительные ресурсы:? процессор с архитектурой х86 (AMD Duron или Intel Pentium II) и тактовой частотой от 400 МГц (рекомендуемая частота — не менее 1,5 ГГц); если используемый процессор поддерживает режим
Системные требования
Системные требования
Перед установкой необходимо ознакомиться со списком требований Windows Vista к оборудованию. Минимальная конфигурация аппаратных средств, необходимых для установки Windows Vista, следующая.• Современный процессор Intel или AMD. Для комфортной работы
Системные требования
Системные требования
Для успешной работы в программе Skype понадобятся следующие технические компоненты:? персональный компьютер с операционной системой Windows 2000 или XP (использование Windows 2000 требует установки DirectX 9.0 для видеоданных);? соединение с Интернетом
Минимальные системные требования
Минимальные системные требования
Radmin — довольно скромная программа, если речь идет о требованиях к аппаратной части компьютера. Ее можно запускать даже на машине с 386 процессором, имеющей 8 Мбайт оперативной памяти. Другими словами, если вы смогли установить на
1.1.1. Системные требования
1.1.1. Системные требования
Fedora 8 можно установить на любой современный (и не очень) компьютер. Основное требование — это 256 Мбайт (можно и больше!) оперативной памяти и как минимум 3 Гбайт свободного места на жестком диске.Если у вас меньше 256 Мбайт оперативной памяти, то вы вес
1.4. Системные требования
1.4. Системные требования
Как и любой другой программный продукт, операционная система Windows 7 для своей установки и безотказной работы выдвигает определенные требования к мощности компьютера. В табл. 1.2 приведен список требований к системным ресурсам.Таблица 1.2. Системные
Системные требования
Системные требования
Для успешной эксплуатации операционной системы Windows 7 компьютер должен отвечать следующим минимальным требованиям:• Тактовая частота процессора – 1 ГГц. Он может быть как 32–разрядным (х86), так и 64–разрядным (х64).• Объем оперативной памяти – 1 Гб
Отнесенные к ПО системные требования
Отнесенные к ПО системные требования
Установленные для ПО системные требования обычно называются в СММ «установленными требованиями». Они представляют собой подгруппу системных требований, которые необходимо реализовать в программных компонентах системы.
Системные требования
Системные требования
Для пользования данной программой существуют следующие системные требования.• ПК с процессором Intel Pentium 200 или выше.• Операционная система Microsoft Windows XP/2000, Windows 98SE/ME (для работы с русским интерфейсом операционная система должна поддерживать
Системные требования
Системные требования
Память на сервере (все платформы)
Оценка памяти сервера включает множество факторов.* Работа сервера Firebird. Сервер Firebird осуществляет эффективное использование ресурсов сервера. Суперсервер (Superserver) после старта использует приблизительно 2 Мбайта
1.6. Системные требования Ubuntu
1.6. Системные требования Ubuntu
Системные требования Ubuntu совсем невелики, особенно на фоне Windows 7, которой для более или менее нормальной работы требуются 1 Гбайт оперативной памяти и почти 20 Гбайт свободного места на жестком диске. Ubuntu в этом плане существенно скромнее. Для
Системные требования к компьютеру
Системные требования к компьютеру
Каждое программное обеспечение предъявляет свои требования к оборудованию, обеспечивающему его нормальную работу. Можно, конечно, ухитриться использовать компьютеры и с более скромными возможностями, но в этом случае вы лишь
Системные требования
Системные требования
Если у вас, к примеру, кассетный видеомагнитофон, вы никогда не купите к нему DVD диск, потому что знаете – магнитофон ваш «питается» только кассетами и диски попросту не «переваривает». Точно так же дело обстоит и с играми для вашего компьютера.
2.2. Системные требования
2.2. Системные требования
Когда появилась Windows Vista, ее часто ругали за слишком высокие системные требования. Так оно и было. Вспоминаю по себе: тогда у меня был компьютер с 768 Мбайт оперативной памяти. Я все же установил на него Vista, но производительность оставляла желать