Azure AD Toolkit
The Azure AD Toolkit is a PowerShell module that providers helper cmdlets to manage the credentials of your application or service principal.
Installing the module
Install-Module AzureADToolkit
Using the module
Connecting to your tenant
Connect to the user’s default tenant.
Specify the Tenant ID if the user signing in has access to multiple Azure Active Directory tenants.
Connect-AADToolkit -TenantId 344b8aab-389c-4e4a-8fa1-4c1ae2c0a60d
Exporting a list of all the Service Principals and Applications having credentials
Get-AADToolkitApplicationCredentials | Export-Csv -Path '.AppPermissions.csv' -NoTypeInformation
Interactively removing and rolling over the certificates and secrets of a Service Principal or Application
This command provides a menu drive interface to view the credentials of an application and allows the user to remove or roll them over.
Update-AADToolkitApplicationCredentials
Exporting a list of Service Principals and Applications with privilege scores (requires external module to generate Excel Workbook)
It is recommended that you use Connect-MgGraph -Scopes Application.Read.All to connect to Microsoft Graph PowerShell for this report. The minimum administrative role necessary to consent to this permission is Application Administrator.
Connect to Microsoft Graph PowerShell with the appropriate permissions:
Install-Module ImportExcel Install-Module Microsoft.Graph Connect-MgGragh -Scopes Application.Read.All
This example will export the report to an Excel workbook:
Build-AzureADAppConsentGrantReport -ReportOutputType ExcelWorkbook -ExcelWorkbookPath C:tempexport.xlsx
This example will retrieve the data and store it in PowerShell objects instead of exporting to Excel:
Build-AzureADAppConsentGrantReport -ReportOutputType PowerShellObjects
List all users with admin roles and their strong authentication status
Find Users with Admin Roles that are not registered for MFA by evaluating their authentication methods registered for MFA and their sign-in activity.
Connect-MgGraph -Scopes RoleManagement.Read.Directory,UserAuthenticationMethod.Read.All,AuditLog.Read.All,User.Read.All,Group.Read.All,Application.Read.All
Select-MgProfile -name Beta
Find-UnprotectedUsersWithAdminRoles -Verbose -IncludeSignIns | Export-Csv ./admins.csv
Disconnecting from your tenant
Disconnect-AzureADToolkit
Contributing
This project welcomes contributions and suggestions. Most contributions require you to agree to a
Contributor License Agreement (CLA) declaring that you have the right to, and actually do, grant us
the rights to use your contribution. For details, visit https://cla.opensource.microsoft.com.
When you submit a pull request, a CLA bot will automatically determine whether you need to provide
a CLA and decorate the PR appropriately (e.g., status check, comment). Simply follow the instructions
provided by the bot. You will only need to do this once across all repos using our CLA.
This project has adopted the Microsoft Open Source Code of Conduct.
For more information see the Code of Conduct FAQ or
contact opencode@microsoft.com with any additional questions or comments.
Trademarks
This project may contain trademarks or logos for projects, products, or services. Authorized use of Microsoft
trademarks or logos is subject to and must follow
Microsoft’s Trademark & Brand Guidelines.
Use of Microsoft trademarks or logos in modified versions of this project must not cause confusion or imply Microsoft sponsorship.
Any use of third-party trademarks or logos are subject to those third-party’s policies.
В этой статье мы рассмотрим, как установить PowerShell модуль для подключения к Azure AD, подключится к своему тенанту и получить различную информацию из Azure. Сейчас Microsoft разрешает использовать два PowerShell модуля для подключения к Azure:
- MS Online (MSOnline) – старый модуль для работы с Azure/Office 365 из PowerShell, который появился около 6 лет назад и сейчас не развивается Microsoft;
- Azure Active Directory PowerShell for Graph (AzureAD) – современный PowerShell модуль для работы с инфраструктурой Azure. Модуль активно развивается, в него добавляется новый функционал (в нем доступны почти все аналоги командлетов MSOnline за небольшим исключением)
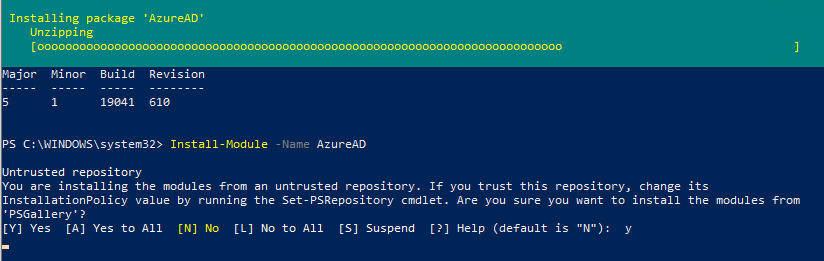
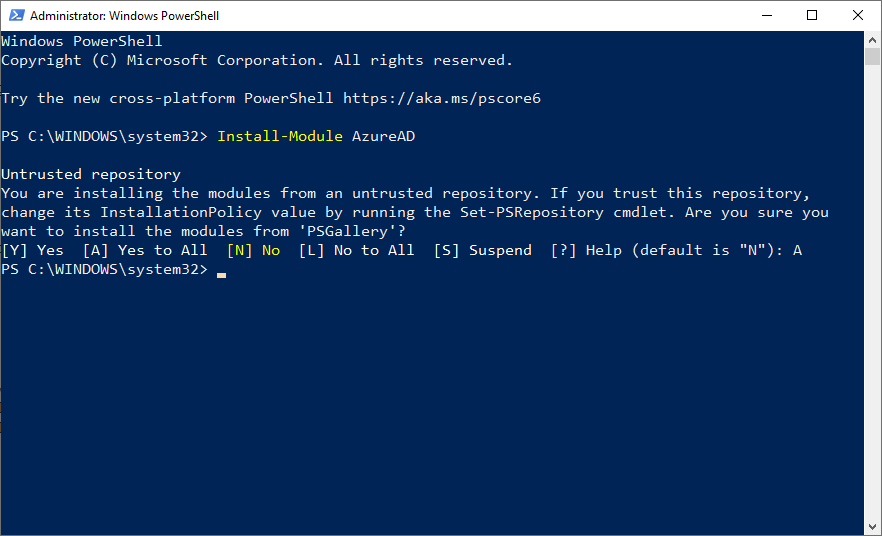
Теперь можно установить модуль Azure PowerShell из PowerShell Gallery. Запустите консоль PowerShell с правами администратора и выполните команду:
Install-Module -Name AzureAD
Появится сообщение:
Untrusted repository. You are installing the modules from an untrusted repository. If you trust this repository, change its InstallationPolicy value by running the Set-PSRepository cmdlet.
Нажмите Y -> Enter
Вы можете добавить галерею PowerShell в доверенные хосты с помощью команды:
Set-PSRepository -Name PSGallery -InstallationPolicy Trusted
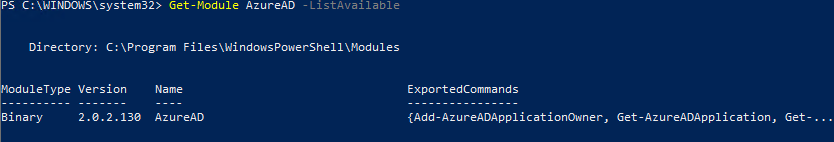
После окончания установки, можно проверить версию модуля AzureAD:
Get-Module AzureAD –ListAvailable
В нашем случае это 2.0.2.130
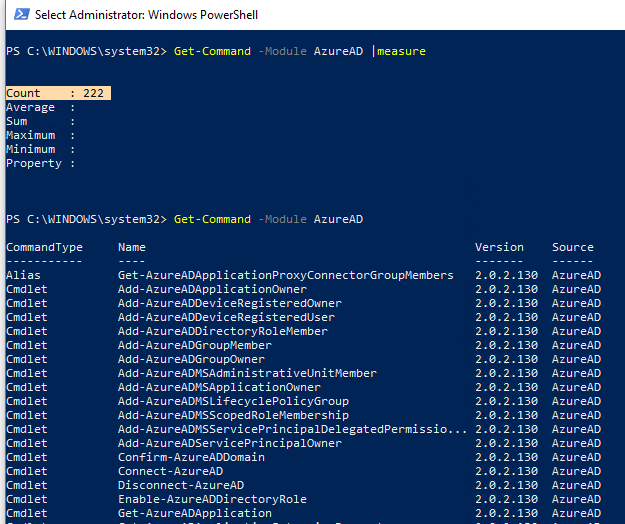
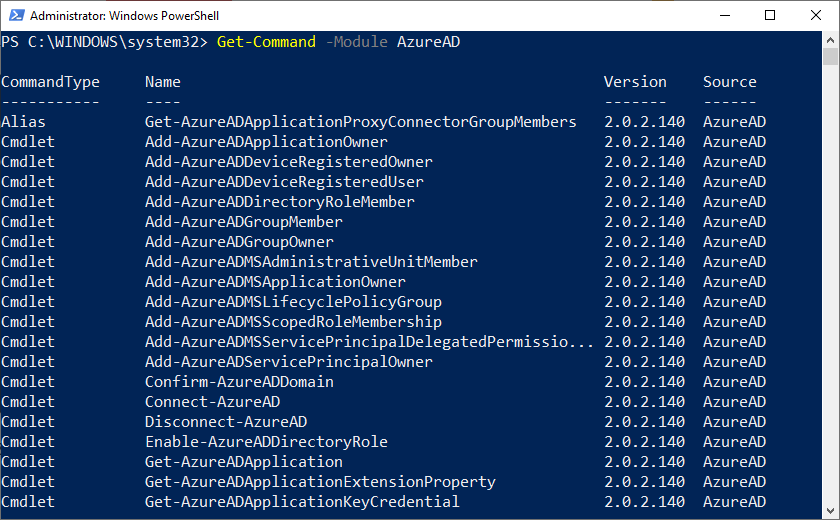
В этой версии модуля AzureAD доступно 222 командлета, которые содержат в названии *-AzureAD*. Список доступных команды можно вывести так:
Get-Command –Module AzureAD
Если у вас установлена более старая версия модуля AzureAD, ее можно обновить:
Update-Module -Name AzureAD
Если нужно установить определенную версию модуля, выполните:
Update-Module -Name AzureAD -RequiredVersion 2.0.2.120
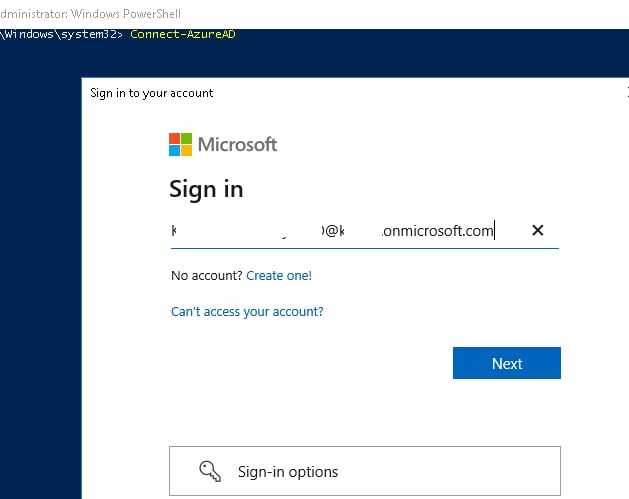
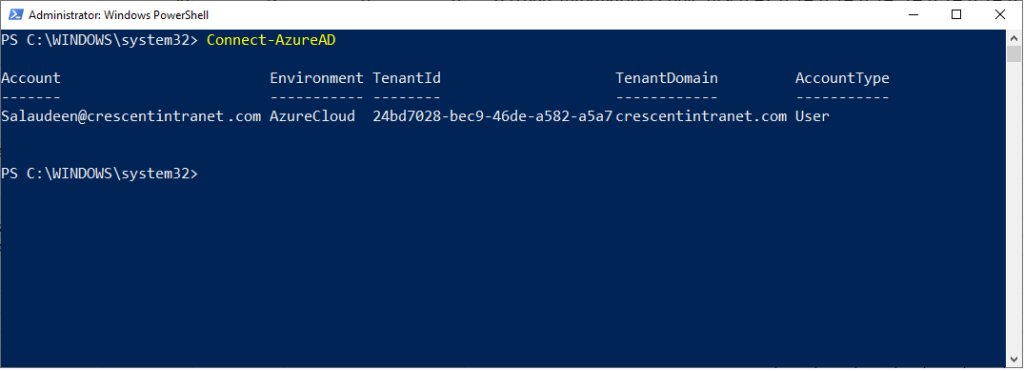
Теперь можно подключиться в Azure с помощью вашего аккаунта:
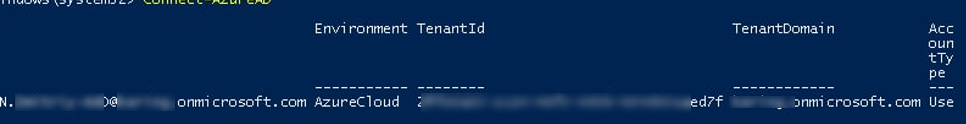
Connect-AzureAD
Командлет запросит ввести учетные данные, которые вы хотите использовать для доступа к каталогу AzureAD. В этом примере для доступа к моему тенанту я использую учетную запись [email protected]
Если у вас включен Azure MFA, подтвердите в вход в аккаунт на устройстве.
Также можно запросить имя и пароль для подключения и сохранить их в переменную:
$AzureADcreds = Get-Credential
И затем использовать их для подключения:
Connect-AzureAD -Credential $AzureADcreds
Вы можете использовать сохраненный пароль во внешнем хранилище с помощью PowerShell модуля SecretManagement (поддерживаются почти все популярные vault провайдеры: Bitwarden, Azure Key Vault, KeePass, LastPass, HashiCorp Vault, Windows Credential Manager и т.д). Для подключения к Azure AD с паролем из хранилища используется такая команда PowerShell:
Connect-AzureAD -Credential (Get-Secret -Vault MyPersonalVault -Name azadm_kbuldogov)
Командлет возвращает подтверждение, показывающее, что сеанс был успешно подключен к каталогу. В строке будет указано окружение AzureCloud, TenantID и TenantDomain.
Для подключения к некоторым специализированным облакам AzureOffice 365 нужно указывать параметр -AzureEnvironmentName.
Connect-AzureAD -AzureEnvironmentName AzureChinaCloud
Connect-AzureAD -AzureEnvironmentName AzureGermanyCloud
Connect-AzureAD -AzureEnvironmentName AzureUSGovernment
По умолчанию модуль подключается к облаку Worldwide.
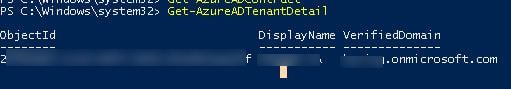
Информацию о текущем тенанте Azure можно вывести так:
Get-AzureADTenantDetail
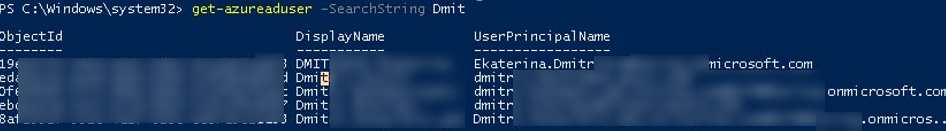
Теперь вы можете использовать командлеты модуля AzureAD для получения различной информации из домена. Найдем пользователей, чьи имена начинаются с Dmit:
get-azureaduser -SearchString Dmit
Или список облачных групп в AzureAD:
Get-AzureADGroup
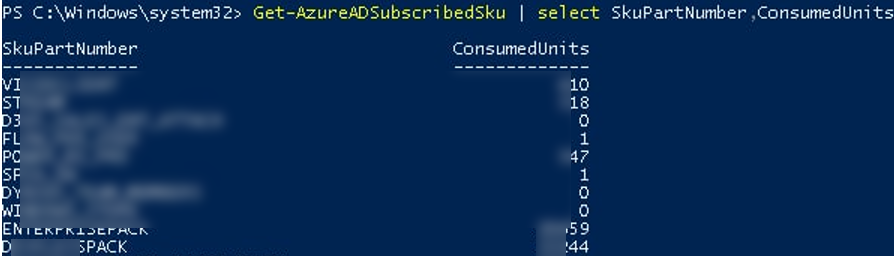
Чтобы получить список доступных лицензий, которые доступны в вашей подписке Office 365 используется командлет:
Get-AzureADSubscribedSku | select SkuPartNumber, ConsumedUnits
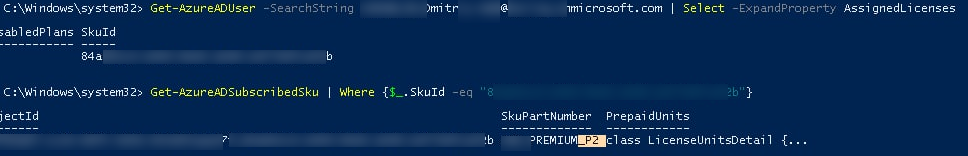
Можно определить, какая лицензия назначена определенному аккаунту:
Get-AzureADUser -SearchString [email protected] | Select -ExpandProperty AssignedLicenses
Затем по полученному SkuID можно узнать имя лицензии:
Get-AzureADSubscribedSku | Where {$_.SkuId -eq "6123434-b223-4332-babcd-1e9231231235"}
Подрообнее про управление лицензиями в Azure AD через PowerShell рассказано в статье.
Чтобы в сессии PowerShell отключится от Azure, выполните:
Disconnect-AzureAD
When you want to use PowerShell to interact with your Azure AD environment you will need to install the Azure AD Module. This module allows you to manage your whole Azure Active Directory with PowerShell.
Good to know up front is that the Azure AD Module isn’t supported in PowerShell 7. Also, Microsoft is planning to deprecate Azure AD Graph (the endpoint that the Azure AD Module uses) after June 30, 2022.
In this article, I will explain how you can install and update the Azure AD Module in PowerShell.
To install the Azure Module we will be using PowerShell. For production environments, is recommended to use the General Availability (GA) version. If you want to test out new features, then you could also install the Public Preview version of the module.
Time needed: 5 minutes.
- Open PowerShell with Elevated permissions
– Right-click on your Start menu (or press Windows key + X)
– Choose Windows PowerShell (admin) or Windows Terminal (admin) on Windows 11 - Install Azure AD Module
Type the following command in PowerShell:
Install-Module AzureADType Y to install the NuGet provider when requested
- Access Untrusted Repository
After NuGet is installed you will get the question if you want to install from an Untrusted Repository. Press Y to install the Azure AD Module
- Connect to AzureAD
The AzureAD module is now installed in PowerShell. You can test the module by connecting to Azure AD using the following command
Connect-AzureAD
Install the AzureADPreview Module
To install the preview version of the module you can follow the same steps. Only replace the module name with AzureADPreview:
Install-Module AzureADPreview
Update the Azure AD Module
Updating the Azure AD Module is basically a re-install of the module in PowerShell. We can first check the version that you have currently installed with the Get-Module cmdlet
Get-Module -Name AzureADPreview
And then check the available version in the repository of PSGallery:
Find-module -Name AzureADPreview -Repository psgallery
If you have an older version installed then it’s a good idea to update the module. This way you will have access to the latest cmdlets of the module.
We are going to use the Update-Module cmdlet to update the module:
Update-Module -Name AzureADPreview
Again press Y to install the module from an untrusted source
Wrapping Up
For now, is the Azure AD module still the easiest way to go to manage our Azure Active Directory users with PowerShell. But keep in mind that the module may stop working after June 2022.
Read more about the new module, Microsoft Graph SDK, in this article.
If you have any questions, just drop a comment below.
Related Posts

The Windows Azure Active Directory team regularly updates the Azure Active Directory PowerShell Module with new features and functionality. Not all additions are applicable to all audiences.
This article is designed to help you keep track of the versions that have been released since calendar year 2014, and to understand whether you need to update to the newest version or not, while also providing you access to all previously released versions.
Table of Contents
- Related FAQ
- How can I determine what version of AAD PowerShell I have?
- Where can I find the latest version of AAD PowerShell?
- Installing PowerShell V2 from the PowerShell Gallery
- What can I do if AAD PowerShell doesn’t work as expected after upgrading to the latest version?
- Release overview
- Version 2.0.0.17 (PowerShell V2 Public Preview)
- Version 2.0.0.7 (PowerShell V2 Public Preview)
- Version 1.1.166.0 (PowerShell V1 General Availability)
- Version 1.1.143.0 (PowerShell V2 Public Preview)
- Some changes
- New functionality in AzureAD PowerShell
- Download link
- Version 9031.1
- Version 8362.1
- Version 8262.2
- Version 8073.4
- Version 8000.119
- Preview Versions of MSOL PowerShell
- Version 8808.1 (Public Preview v2)
- Version 8806.11 (Public Preview v1)
↑ Back to top
Related FAQ
How can I determine what version of AAD PowerShell I have?
You can run the get-item cmdlet to check the version of the DLL files of the module that you have currently installed:
(get-item C:WindowsSystem32WindowsPowerShellv1.0ModulesMSOnlineMicrosoft.Online.Administration.Automation.PSModule.dll).VersionInfo.FileVersion
Where can I find the latest version of AAD PowerShell?
- The following fwlinks should always point to the most current version of AAD PowerShell
- Azure Active Directory Module for Windows PowerShell V2 (64-bit version)
- Azure Active Directory Module for Windows PowerShell V1 (64-bit version)
Installing PowerShell V2 from the PowerShell Gallery
The AzureAD PowerShell V2 module can be downloaded and installed from the PowerShell Gallery,
www.powershellgallery.com. The gallery uses the PowerShellGet module.
The PowerShellGet module requires PowerShell 3.0 or newer.
Therefore, PowerShellGet requires one of the following operating systems:
- Windows 10
- Windows 8.1 Pro
- Windows 8.1 Enterprise
- Windows 7 SP1
- Windows Server 2016 TP5
- Windows Server 2012 R2
- Windows Server 2008 R2 SP1
PowerShellGet also requires .NET Framework 4.5 or above. You can install .NET Framework 4.5 or above from
here.
For more information, please refer to
https://msdn.microsoft.com/powershell/gallery/readme
What can I do if AAD PowerShell doesn’t work as expected after upgrading to the latest version?
Please use the download links below to reinstall a previous version of the AAD PowerShell Module to unblock any issues you may be facing, and then make a post to the
Azure Active Directory Forum, describing your issue, and how to reproduce the problems.
↑ Back to top
Release overview
Version 2.0.0.17 (PowerShell V2 Public Preview)
This is a public preview release of the new AzureAD PowerShell V2 cmdlets. The following changes are included in this release:
- New cmdlets New-AzureADMSGroup, Set-AzureADMSGroup and Remove-AzureADMSGroup added. These cmdlets can be used to manage Office 365 groups and dynamic groups in your directory
- New cmdlets to revoke a user’s Refresh Tokens added: Revoke-AzureADSignedInUserAllRefreshTokens and Revoke-AzureADUserAllRefreshTokens
- Connect-AzureAD no longer requires -Force
- Naming convention change for cmdlets that call Microsoft Graph
- Going forward, all cmdlets that call Microsoft Graph will have “MS” in their cmdlet names, as in “Get-AzureADMSGroup”. The cmdlets that call Azure AD Graph will not change, so there is also a “Get-AzureADGroup” cmdlet.
Download link
Version 2.0.0.7 (PowerShell V2 Public Preview)
This is a public preview release of the new AzureAD PowerShell V2 cmdlets. The following changes are included in this release:
- New cmdlets to manage Policy objects have been added
- New cmdlets to manage Device owner and user have been added
- More inline help is a added
- Domain cmdlet parameter is changed
- Connect cmdlet parameter is changed
- A Native app creation bug is fixed
- A User creation/update bug fixed
- There is improved reliability on link related cmdlets.
Download link
Version 1.1.166.0 (PowerShell V1 General Availability)
This is the general availability release of the V1 version («MSOnline») of Azure Active Directory PowerShell cmdlets. The following cmdlets have been added:
- Get-MsolCompanyAllowedDataLocation
- Set-MsolCompanyMultiNationalEnabled
- Set-MsolCompanyAllowedDataLocation
The following cmdlets are not available in this release.
- Get-MSOLAllSettings, Get-MSOLSetting, New-MSOLSetting, Remove-MSOLSetting, Set-MSOLSetting
- Get-AllSettingTemplate, Get-SettingTemplate
Please note that the Settings cmdlets that were published in the preview release of the MSOL module are no longer available in this module. This functionality can now be found in the newer
Azure AD PowerShell V2 Preview module, which can be installed from here: https://www.powershellgallery.com/packages/AzureADPreview
More information about how to use the new cmdlets for Settings can be found here: https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/active-directory/active-directory-accessmanagement-groups-settings-cmdlets
More information about the Azure AD PowerShell V2 module can be found here: https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/powershell/azuread/
Download link
64-bit
Version 1.1.143.0 (PowerShell V2 Public Preview)
This the public preview of the new V2 version of Azure Active Directory PowerShell cmdlets. This preview release marks a first step on a journey to renew the existing MSOL PowerShell cmdlets which you are so familiar with. One of the key features of this
release is a close alignment of the PowerShell functionality with the Graph API capabilities. We are also moving towards a faster and more agile release process for new or updated functionality of these cmdlets.
The new PowerShell cmdlets provide more functionality in several areas, most notably for Modern Authentication and MFA, and includes management of Applications and Certificate Authority through PowerShell.
Over time, we will fully replace the existing MSOL cmdlets. You will see regular new functionality updates to this preview release until the complete replacement is available.
Some changes
As you will notice, some things have changed when compared to the existing MSOL library. First of all – we have updated the names of all cmdlets to conform with the Azure PowerShell naming conventions. Since we’re publishing a new module for these cmdlets,
the name of the module has changed as well: the existing module’s name was “MSOL”, the new module is call “AzureAD”. So where e.g. an existing cmdlet was named “New-MSOLUser”, which adds a new user to the directory, the new cmdlet’s name is “New-AzureADUser.
Secondly – the parameters for the new cmdlets sometimes changed as well. As we are developing cmdlets in close alignment with the Graph API functionality, we’re also keeping the names of objects and parameters as close as possible to what is used in Graph
API.
New functionality in AzureAD PowerShell
Managing Certificate Authority using Powershell for Azure AD
These are the new cmdlets that are used to manage Certificate Authority:
- New-AzureADTrustedCertificateAuthority — Adds a new certificate authority for the tenant
- Get-AzureADTrustedCertificateAuthorities — Retrieves the list of certificate authority for the tenant
- Remove-AzureADTrustedCertificateAuthority — Removes a certificate authority for the tenant
- Set-AzureADTrustedCertificateAuthority — Modifying a certificate authority for the tenant
Managing Applications in Azure AD using PowerShell
Several new cmdlets have been added to enable management of Applications in Azure AD using PowerShell. There is a set of cmdlets to create, modify and remove Applications:
- New-AzureADApplication
- Remove-AzureADApplication
- Set-AzureADApplication
- We also offer capabilities to manage Directory Extensions in PowerShell:
- Get-AzureADApplicationExtensionProperty
- New-AzureADApplicationExtensionProperty
- Remove-AzureADApplicationExtensionProperty
There are new cmdlets to manage Owners for an Application:
- Add-AzureADApplicationOwner
- Get-AzureADApplicationOwner
- Remove-AzureADApplicationOwner
And finally, we’re offering new capabilities to manage credentials for Applications in PowerShell:
- Get-AzureADApplicationKeyCredential
- New-AzureADApplicationKeyCredential
- Remove-AzureADApplicationKeyCredential
- Get-AzureADApplicationPasswordCredential
- New-AzureADApplicationPasswordCredential
- Remove-AzureADApplicationPasswordCredential
Download link
PowerShell Gallery
↑ Back to top
Version 9031.1
| Released | 3/10/2016 | |
|---|---|---|
| New Features |
|
|
|
Download Link (EN) |
32-Bit |
64-Bit |
↑ Back to top
Version 8362.1
| Released | 1/19/2015 | |
|---|---|---|
| New Features |
|
|
| Download Link (EN) |
32-Bit |
64-Bit |
↑ Back to top
Version 8262.2
| Released | 12/15/2014 | |
|---|---|---|
| New Features |
|
|
| Download Link (EN) |
32-Bit |
64-Bit |
↑ Back to top
Version 8073.4
| Released | 11/5/2014 | |
|---|---|---|
| New Features |
|
|
| Download Link (EN) |
32-Bit |
64-Bit |
↑ Back to top
Version 8000.119
| Released | 09/10/2014 | |
|---|---|---|
| New Features |
|
|
| Download Link (EN) |
32-Bit |
64-Bit |
↑ Back to top
Preview Versions of MSOL PowerShell
Version 8808.1 (Public Preview v2)
| Released | 10/30/2015 | |
|---|---|---|
| New Features |
|
|
| Download Link (EN) |
32-Bit |
64-Bit |
↑ Back to top
Version 8806.11 (Public Preview v1)
| Released | 9/25/2015 | |
|---|---|---|
| New Features |
See blogpost |
|
| Download Link (EN) |
32-Bit |
64-Bit |
↑ Back to top
How to install the Azure Active Directory PowerShell Module
In order to connect to manage users and organisation settings in Office 365 via Powershell, you need to install the Azure Active Directory PowerShell Module. This can be simply installed via PowerShell itself.
Why do you need the Azure Active Directory PowerShell Module?
This module allows you to perform a lot of the Office 365 user and organisation administration tasks via PowerShell. It’s great for bulk tasks like password resets, password policies, license management/reporting etc.
If you’re a Microsoft Partner, and are managing your customers Office 365 tenants via delegated administration, this module gives you a secure way to perform admin tasks using your own credentials. See our guide here for more info.
Importantly, this module doesn’t give you the ability to manage the features of Exchange Online, Skype for Business, SharePoint/OneDrive etc. These require a separate PowerShell connection method or PowerShell module.
How to Install the Azure Active Directory PowerShell Module via PowerShell
- Open the Start menu on your computer and search for ‘Powershell’
- Right-click on Windows PowerShell and choose ‘Run as administrator’
- Type the following command and press enter.
Install-Module -Name MSOnline
- Type “Y” to install and import the NuGet provider
- Type “Y” again to trust the provider
- Wait for the package to install, then type the following to enter your Office 365 admin credentials and connect to Azure Active Directory via PowerShell:
Connect-MsolService
- Once the Azure Active Directory PowerShell module has been installed, you only need to run the Connect-MsolService command to connect to the Azure AD service on this PC.
To perform Exchange Online Administration tasks, you’ll need to set up a separate connection to Exchange Online via PowerShell. Follow our quick guide here for more info.

Elliot Munro
Need additional help? Want to be across Microsoft 365 updates and GCITS articles when they’re released? Connect with Elliot Munro on LinkedIn here. If you have an Office 365 or Azure issue that you’d like us to take a look at (or have a request for a useful script) send Elliot an email at [email protected]
In this Azure AD tutorial, we will discuss how to connect to azure in PowerShell. We will also see how to install the Azure Active Directory PowerShell Module to work with Azure AD using PowerShell.
Table of Contents
- How to Connect to Azure in PowerShell (And Azure AD)
- Connect to Azure and Azure AD from PowerShell – Video Tutorial
- Connect to Azure PowerShell
- Install Azure Active Directory PowerShell Module in Windows 10 (AzureAD)
- Install Azure AD PowerShell for Graph module (AzureADPreview)
- Install Azure Active Directory PowerShell Module (MSOnline)
Well, let’s discuss how to Connect to Azure in PowerShell (And Azure AD)
Also, you may like following Azure tutorials:
- What is Microsoft Azure and How does Microsoft Azure Works?
- Azure active directory premium features
- Microsoft Azure Free Training (Get a free voucher for AZ-900 Certification)
We will see two ways to connect to Azure using PowerShell.
Connect to Azure and Azure AD from PowerShell – Video Tutorial
Subscribe to Our YouTube Channel for more videos
Connect to Azure PowerShell
To connect to Azure PowerShell, first we need to install Azure PowerShell on Windows using MSI installer.
To work with Azure PowerShell, you should have:
- Windows PowerShell 5.1 (Update Link)
- .NET Framework 4.7.2 or later. (Download Link)
Note: The PowerShell MSI installer works on having PowerShell versions 5.1 or higher. You can check the current PowerShell version by using the below command:
$PSVersionTable.PSVersionIf you are using the Widows 10 OS, then you will be having already the PowerShell 5.1 version.

Now, you can download Azure PowerShell MSI package from GitHub.
Once downloaded, run the setup to install Microsoft Azure PowerShell. Click on Install like below:

Now, you can see in the screen, it is installing Azure PowerShell.

Then it will show a successful message like below:

Click on the Finish button and then you can connect to Microsoft Azure from PowerShell.
Open Windows PowerShell in Administration mode and run the below command.
Connect-AzAccountWe can use Connect-AzAccount command to connect to Microsoft Azure from PowerShell.

Once you enter the credentials, it will display the Azure details like Account, subscriptionname, tenant id, environment like below:

This is how we can connect to Microsoft Azure from PowerShell.
- How to create a user in Azure active directory
Install Azure Active Directory PowerShell Module in Windows 10 (AzureAD)
Now, we will see how to install Azure active directory PowerShell Module in Windows 10.
Open PowerShell in Admin mode like below:
Then run the below command:
Install-Module AzureADThis will install the Azure AD PowerShell module like below:

You can also check what are the modules installed by running the below command.
Get-InstalledModule
or
Get-Module -Listavailable
Then you can run the below command to connect to Azure AD.
Connect-AzureADOnce you run the command, it will ask you the user name and password (Azure AD administrator) and then it will connect to Azure AD.
Then you can retrieve all users from the Azure AD using PowerShell by running the below command. (You can add the code in Windows PowerShell ISE)
Connect-AzureAD
Get-AzADUserYou can see it will display all the users from the azure active directory.

- The term ‘connect-azuread’ is not recognized as the name of a cmdlet function Azure
Optional Content
Once you install this, then you will see few dlls will be there in the below folder:
C:Program FilesWindowsPowerShellModulesAzureAD2.0.2.76
Here 2.0.2.76 is the version, may be varies depending on the version you are installing.
Here find the Microsoft.Open.AzureAD16.Graph.Client.dll
Here, we need to add the above dlls references.
The full code will looks like below: (You can add the code in Windows PowerShell ISE)
Here I am retrieving get Azure AD users using PowerShell.
Add-Type -Path 'C:Program FilesWindowsPowerShellModulesAzureAD2.0.2.76Microsoft.Open.AzureAD16.Graph.Client.dll'
Connect-AzureAD
Get-AzADUserYou can see the Azure active directory users like below:

Install Azure AD PowerShell for Graph module (AzureADPreview)
We can install Azure AD PowerShell for Graph module which is known as AzureADPreview.
If you have already installed AzureAD, then you can uninstall AzureAD before installalling AzureADPreview.
Below are the useful command to work with AzureADPreview.
Check which AzureAD module in installed
You can run the below command to check which AzureAD module has been installed in the system.
Get-Module -ListAvailable AzureAD*Uninstall AzureAD module
If you have already installed AzureAD module, then uninstall the AzureAD module before installing AzureADPreview module.
Uninstall-Module AzureADInstall AzureADPreview module
You can run the below command to install AzureADPreview module.
Install-Module AzureADPreviewInstall the latest version of AzureADPreview module
Anytime, you can uninstall the AzureADPreview module and install the latest version of the AzureADPreview module by running the below command.
Uninstall-Module AzureADPreview
Install-Module AzureADPreview
This is how we can install AzureADPreview PowerShell for Graph module.
Install Azure Active Directory PowerShell Module (MSOnline)
Now, we will see how to install the Azure Active Directory PowerShell Module. So that you can work with Azure Active directory from PowerShell.
You can also manage users or organization’s information in Office 365 via PowerShell.
Open Windows PowerShell and Run as administrator.
Note: You can also use Windows PowerShell ISE.
Then run the below command which will install the Azure Active Directory PowerShell Module:
Install-Module -Name MSOnlineSelect Y, when it ask for NuGet provider is required to continue. And again press Y for the trusted provider.
Finally, you can see the Azure AD PowerShell module will be installed like below:

Once installed successfully, you can connect to Azure AD from PowerShell by running the below command:
Connect-MSOlService
This is how you can connect to Azure AD from PowerShell.
Then you can run the below command to get all the users from the Azure active directory.
Get-AzADUser- the term ‘get-aduser’ is not recognized as the name of a cmdlet powershell
In this tutorial, we discuss how to Microsoft Azure from PowerShell. Also we saw:
- Install Azure Active Directory PowerShell Module in Windows 10
- Install Azure Active Directory PowerShell Module
Requirement: Connect to Azure AD with PowerShell.
How to Connect to Azure Active Directory using PowerShell?
Azure Active Directory (Azure AD) is Microsoft’s cloud-based identity and access management service. Azure AD allows you to manage user identities and access rights to your applications, whether on-premises or in the cloud. With the Power of PowerShell, we can automate tasks, access settings that are not available in the web user interface, Filter and query data, generate reports, make configuration changes to the objects, etc. This blog post will show you how to connect to Azure AD using PowerShell and demonstrate some of the basics of working with Azure AD for Office 365 using PowerShell!
Step 1: Install the Azure AD PowerShell Module
To start with Azure AD PowerShell, You have to install the Microsoft Azure Active Directory module on your local computer. To check if you have the Azure AD PowerShell module already installed, use:
Get-Module AzureAD -ListAvailable
You can also use the “Get-InstalledModule” cmdlet to get a list of installed modules on your local computer.
Assuming you have an x64 bit operating system at least Windows 7 Sp1/Windows Server 2008 R2 SP1 or later, And have at least a PowerShell version 5.1 installed (Check your current PowerShell version with the command: $PSVersionTable.PSVersion) on your computer, here are the steps to install the AzureAD PowerShell module:
- Type “PowerShell” from the start menu >> Right-click on Windows PowerShell and choose “Run as administrator”
- Type “Install-Module AzureAD” and hit Enter.
- You’ll be asked to confirm the installation from the PSGallery. Type “A” to select “Yes to All” and hit the Enter key.
Install-Module -Name AzureAD
This will download and install the PowerShell module for Azure Active Directory to your local computer. (AKA: Azure Active Directory PowerShell for Graph)
Want to suppress the confirmation prompt: You are installing the modules from an untrusted repository. If you trust this repository, change its InstallationPolicy value by running the Set-PSRepository cmdlet. Are you sure you want to install the modules from ‘PSGallery’? It’s a good idea to trust PowerShell Gallery so that you won’t get this confirmation prompt! Use:
Set-PSRepository -Name PSGallery -InstallationPolicy Trusted
To update the existing Azure AD module to the latest version, run the following command as admin:
Update-Module -Name AzureAD
Step 2: Connect to Azure AD using Connect-AzureAD cmdlet
The next step is to connect to Azure AD from PowerShell. Type Connect-AzureAD cmdlet and hit the enter key. You’ll be prompted to login to Azure AD, which is Multi-factor authentication (MFA) aware. Ensure you have administrator access to Azure Active Directory before executing these cmdlets.
You can also get the credentials prompt to enter the username and password of an admin account and connect to Azure AD:
Connect-AzureAD -Credential (Get-Credential)
There are more parameters you can pass to the above cmdlet, such as TenantID, AccountID (UserPrincipleName), etc. How about connecting with a saved user name and password?
#Parameter $AdminUserName = "[email protected]" $AdminPassword = "Password goes here" #Variable for Pscredential object $SecurePassword = ConvertTo-SecureString $AdminPassword -AsPlainText -Force $Credential = New-Object System.Management.Automation.PSCredential -argumentlist $AdminUserName, $SecurePassword #Connect to Azure Active Directory Connect-AzureAD –Credential $Credential
But the above two methods don’t support two-factor authentication!
Step 3: Start using cmdlets from Azure AD PowerShell Module.
Once connected, you can start using PowerShell cmdlets available for Azure AD to interact with your tenant. To get all cmdlets from the AzureAD module, use:
Get-Command -Module AzureAD
This will list all PowerShell cmdlets for Azure AD
The Azure AD PowerShell Module allows us to manage users and groups, applications, and domains on Office 365 and Azure with activities such as automating tasks, generate reports, export data, Performing bulk operations, etc. The Azure AD PowerShell module can be installed in client operating systems such as Windows 10 or Server operating systems like Windows 2016.
Once connected, You can start using the cmdlets in your PowerShell script, such as: To list all users in your tenant, use:
To disconnect from Azure in your PowerShell session, run the below command:
How to Install the AzureADPreview module?
The azureADPreview module is where new updates are shipped first. E.g., the cmdlet Get-AzureADAuditSignInLogs is available only in the Azure AD Preview module as of today. To install the preview version of the module, you can replace the module name with AzureADPreview in the Install-Module cmdlet.
Install-Module -Name AzureADPreview
Install Azure AD PowerShell Module V1
For some backward compatibility, If you need the V1 of the Azure AD PowerShell module (AKA: MSOnline), here is how to install and connect to Microsoft Azure Active Directory with Connect-MSOLService cmdlet:
#Install the MSOnline Module Install-Module -Name MSOnline #Connect to Azure Active Directory Connect-MsolService #Start executing cmdlets Get-MsolUser
How do I Connect to Exchange Online with PowerShell?
To connect to Exchange Online with PowerShell, you need to first install the PowerShell Module for Exchange Online Management using “Install-Module ExchangeOnlineManagement”. And then, you can connect to Exchange Online using the Connect-ExchangeOnline cmdlet.
More info: Connect to Exchange Online PowerShell
How do I connect to SharePoint Online from PowerShell?
You must first download and install the SharePoint Online Management Shell or SharePoint Online PowerShell Module. Then you can connect to SharePoint Online through PowerShell using the Connect-SPOService cmdlet.
More info: Connect to SharePoint Online PowerShell
How do I connect to a Microsoft team using PowerShell?
Connecting to teams from PowerShell is a two-step process: First, Install Microsoft Teams PowerShell Module using “Install-Module MicrosoftTeams”. Next, Connect to Microsoft Teams using the PowerShell cmdlet “Connect-MicrosoftTeams”
More info: Connect to Teams PowerShell