Network segmentation is a great way to compartmentalize the various networks you need to run in your environment. This provides many benefits from both a management and security perspective. When segmenting your networks, one of the things that you have to consider and take care of is IP addressing. Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) is an age-old standard that has been used in the enterprise for handing out IP addresses to clients on the network. DHCP requires its own broadcast domain, which in turn requires VLANs. Many organizations are using Windows Server for DHCP on their networks. In this post, we will take a look at Windows Server DHCP VLAN configuration. These steps work for Windows Server 2012, 2016, 2019, and Windows Server 2022.wind
Why are VLANs needed for DHCP?
When a client is provisioned on a network segment and is set up to have IP addressing configured automatically using DHCP, the client makes broadcast queries on the network segment to notify the DHCP server configured that it needs an IP address. The DHCP server responds with the appropriate IP address for the network segment and the additional configuration for network connectivity on the segment.
VLANs (Virtual Local Area Networks) allow taking a physical network switch and logically segmenting the physical network environment into multiple network segments. This makes much more efficient use of network hardware since additional segments do not require additional physical network switches. By introducing VLANs, you can provision multiple network segments on the same switch.
When you spin up a new network segment IP address range, you want to pair this with a new VLAN or logical network segment. VLANs control broadcast ranges. Within each VLAN, clients can initiate the broadcast for a network IP address from a DHCP server. There are many different ways to have a Windows Server participate in a VLAN network segment. Before we look at the specifics related to DHCP VLAN configuration, let’s take a look at the multiple options for connecting the Windows host into a VLAN-backed network.

Connecting Windows Server to Multiple VLANs
There are many different ways to connect Windows Server to multiple VLANs. This includes the following:
- Additional network interfaces Untagged for VLAN traffic
- A single network interface with Tagged VLAN frames
- Routed Layer 3 connectivity to VLAN-backed subnets
Additional network interfaces Untagged for VLAN traffic
With VLANs, you hear two different terms tossed out there related to the VLAN you are working with – untagged, and tagged. When you talk about untagged frames, this means the Windows host is not tagging the Ethernet frames originating from the host with VLAN information. Instead, it is relying on the upstream switch it is plumbed into to handle that configuration.
So, essentially, the Windows Server is unaware of the VLAN and doesn’t care. It simply relies on its physical uplink to do any VLAN tagging for it to communicate appropriately. However, this means that if you want to have a Windows Server to be a part of multiple VLANs, it means you need a physical uplink for each separate VLAN, since it is relying on the switch to tag the traffic appropriately for a specific VLAN.
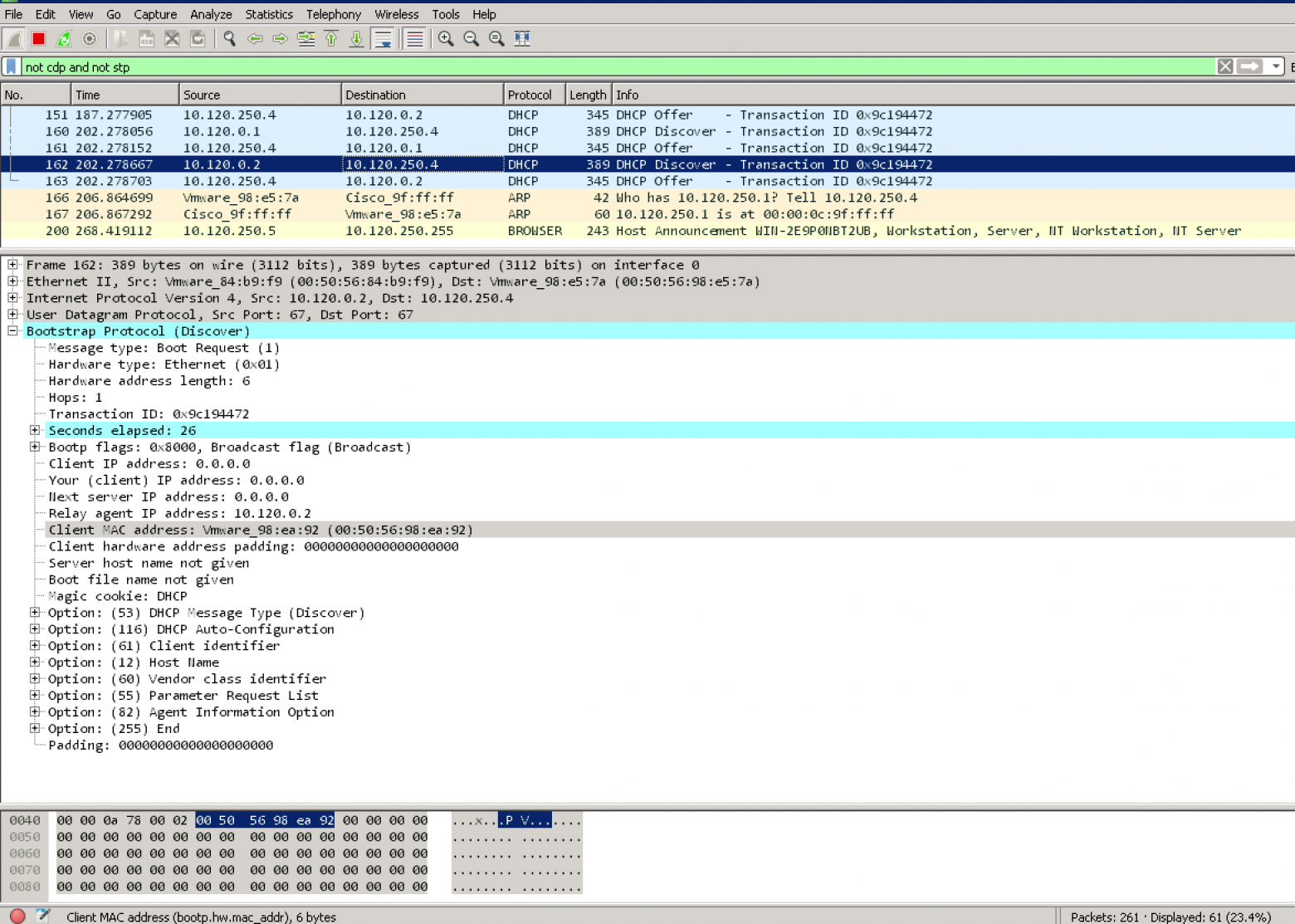
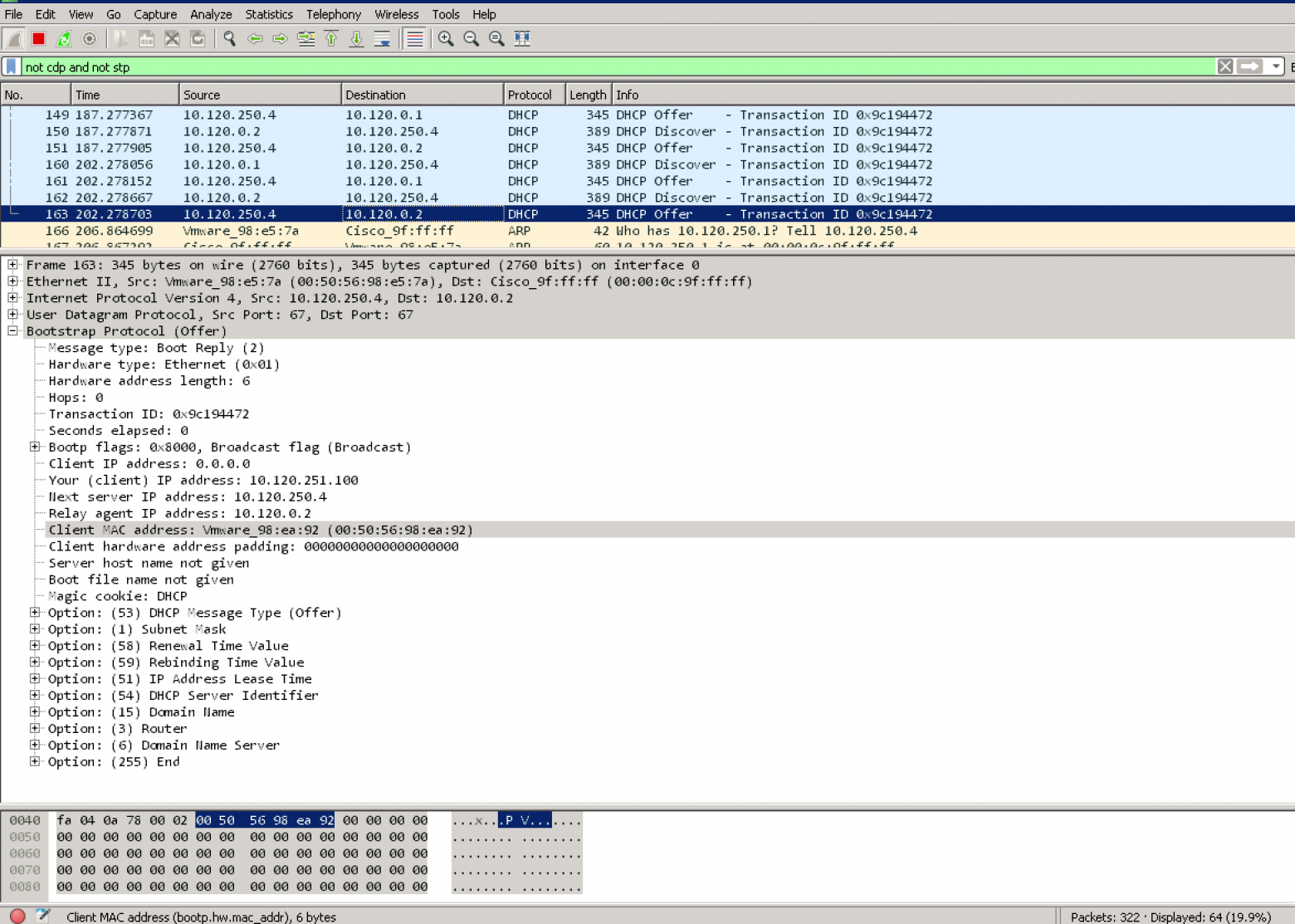
As shown below on a Windows Server 2019 server, you can specify the Bindings for the Windows DHCP Server so that it knows which interfaces to “listen” for DHCP on.

A single network interface with Tagged VLAN frames
While there may be reasons that you use multiple physical uplinks with untagged frames for communicating with different VLANs, a more efficient approach is to use Tagged VLAN frames on a single network connection. When you use tagged frames, the Windows Server tags the frames appropriately for each VLAN it is associated with. The ability to Tag frames generally needs vendor-specific driver sets to be loaded, such as the Intel Pro Set drivers using Intel-based cards.

Routed Layer 3 connectivity to VLAN-backed subnets
The third option is simply relying on routing to take care of connectivity to the VLAN-backed subnets they need to communicate with. This technically does not connect the Windows Server into the VLAN as that would mean it would have the ability to be in the broadcast domain which is a Layer 2 VLAN construct. Instead, you are relying on Layer 3 connectivity to IP addresses. For many type of communication, including Windows Server 2012 DHCP VLAN configuration, this is all that is needed.
You can use all three of the methods above for Windows Server 2012, 2016, 2019, and Windows Server 2022 DHCP VLAN configuration. You can add multiple network adapters to each VLAN and have each scope listen on that specific network interface for DHCP requests. You can also use the tagging method listed above that allows adding multiple VLANs to a single network interface which allows keeping a single network adapter and connecting that physical network uplink to multiple VLANs.
You might assume the third option, since it is not connecting the uplink to the physical broadcast domain, would not be able to answer the broadcast DHCP request from the client on a specific VLAN. However, even though the DHCP server is not on the same broadcast domain/VLAN, there are really only two pieces of information the DHCP servers need to know to allocate an IP address on a particular subnet. This includes:
- Source subnet of the client
- MAC address of the client
You will note that the Windows Server DHCP server being a part of the VLAN is not a requirement for a successful DHCP request being made to the Windows Server. The third option is typically the option that I steer towards unless there are requirements for multiple physical uplinks for compliance or other security-based reasons. So, how does the Windows DHCP Server respond to a DHCP broadcast request if it is not on the same VLAN to take part in the broadcast traffic?
IP Helper Address, DHCP Relay, DHCP Proxy Address
This is made possible by the IP Helper Address which is sometimes referred to as DHCP Relay, or DHCP proxy address. Using an IP helper address, DHCP Relay, or DHCP proxy address allows the special DHCP broadcast messages to be forwarded from VLAN they originated from and forwarded to the DHCP server. This role is typically handled by a firewall or router device that is able to take the DHCP broadcast message and forward these to the DHCP server.
How does this work? When the DHCP client issues the DHCP broadcast request packet, is as of yet has no IP address configured. This being the case, it uses a broadcast with an all zero source address – 0.0.0.0. It also has no way to get to the DHCP Server with the lack of IP configuration. With this being the case, the client uses a general broadcast address of 255.255.255.255 as the destination with the DHCP request packet.
The device handling the DHCP proxy functionality receives the DHCP request packet from the client, replaces the destination address of 255.255.255.255 with the configured address of the server that was configured in the IP helper-address configuration. The client’s MAC address is included in the DHCP request so the receiving DHCP server knows the required MAC address of the client. This information is then forwarded to the DHCP server from the router, firewall, or another device in the role of the DHCP proxy.
The DHCP server issues an address now that it knows the subnet the client resides on along with the MAC address. It sends the DHCP response back to the DHCP Proxy device. The DHCP Proxy device then forwards the response to the correct MAC address of the requesting client and it is able to be configured with the IP address allowing network communication on the subnet.
The configuration of DHCP Relay is generally simple but can vary depending on the vendor of router, firewall, or other device you might be using to perform this function. Below is the configuration of DHCP Relay on a Palo Alto firewall. You simply have to select the Interface and the DHCP Server IP Address you want to use for the target of DHCP requests.

Windows Server DHCP VLAN configuration for Virtual Machine DHCP servers
The principles still apply to Windows Server DHCP servers running inside a Windows Server virtual machine. The one method that is more difficult is the tagging of a single interface with multiple VLANs as this is not a feature that you can carry out with VMware Tools drivers that I am aware of. You can add multiple virtual NICs to a single VM and connect the virtual machine to different VLAN-backed port groups for each connection.
This will essentially place the Windows Server virtual machine on the same network segments as the clients that need addresses. Or, you can use the preferred method of using an IP Helper Address to forward the DHCP requests from all the other VLAN-backed subnets to the DHCP server and have the addresses issued by the server using only the single network connection.
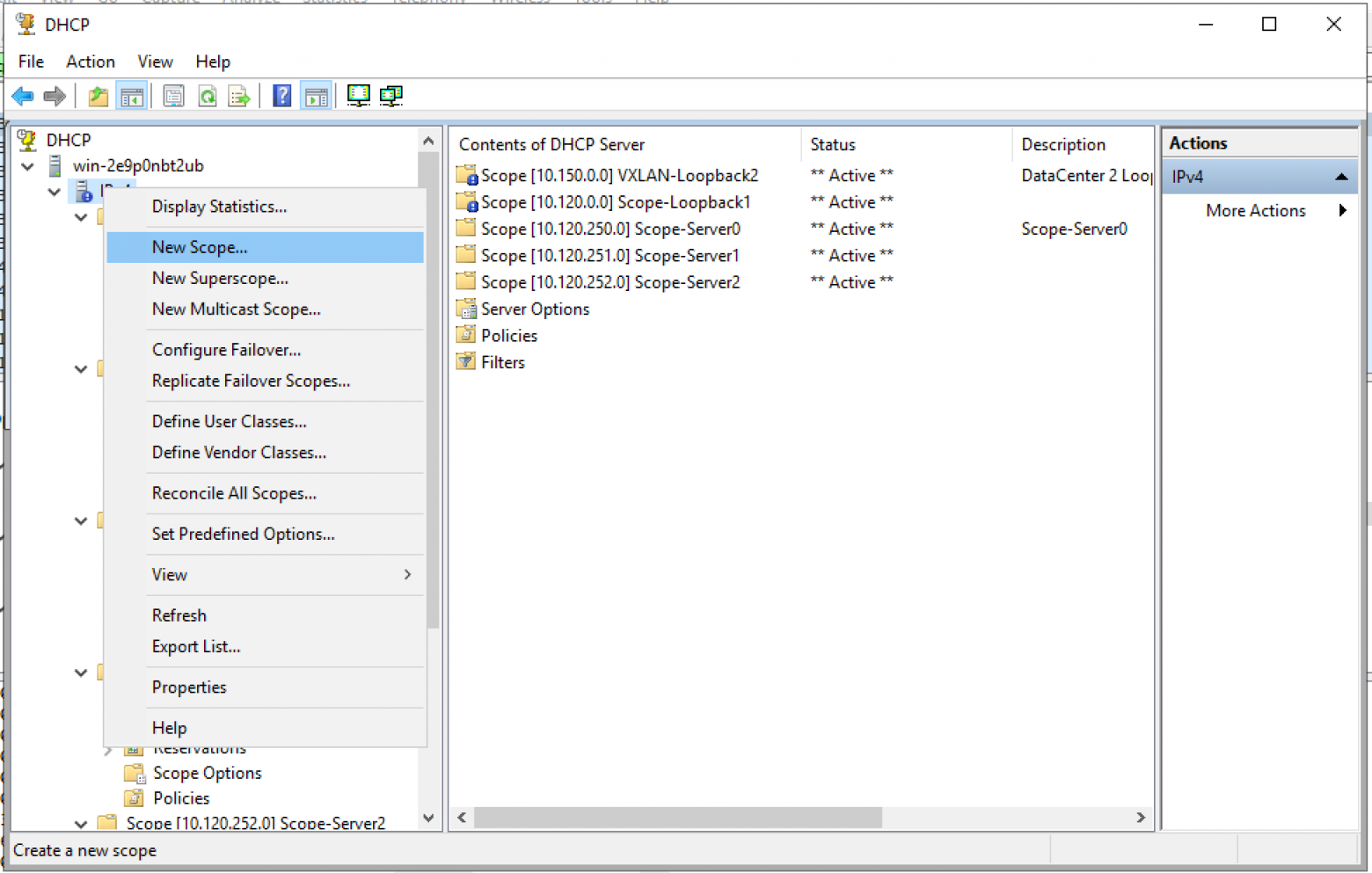
Creating a Windows Server DHCP scope for a different VLAN
As detailed by the explanation above, the actual work of the Windows Server DHCP VLAN configuration takes place with the IP Helper Address/DHCP proxy device. Creating a Windows Server DHCP scope for a different VLAN is the same as creating a scope for the native VLAN network where the DHCP Server itself is located. Non-intuitively, you won’t see any part of the scope creation wizard that has you define the VLAN configuration. However, this is not needed in any of the configurations mentioned. With IP Helper Address, the packets are forwarded by the DHCP proxy to the DHCP server. If you are using different interfaces or tagged interfaces, the DHCP server will receive the DHCP broadcasts as normal.

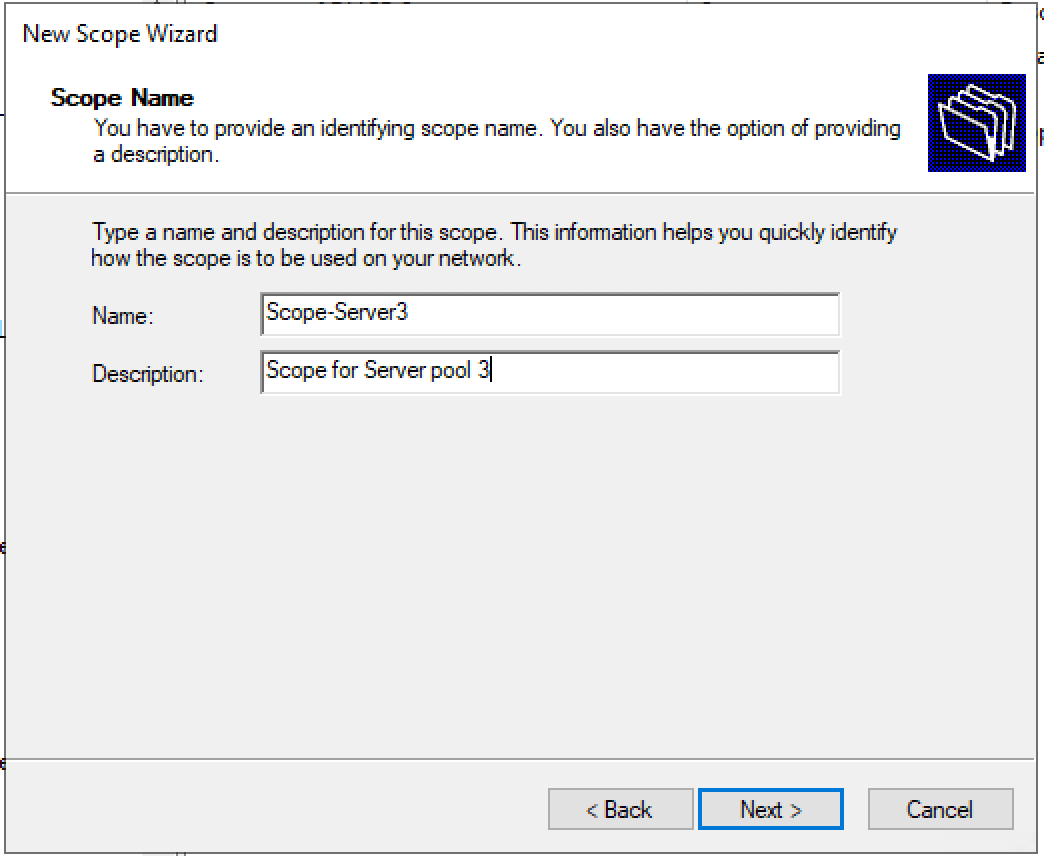
Set the name and description (optional) of the new DHCP scope.

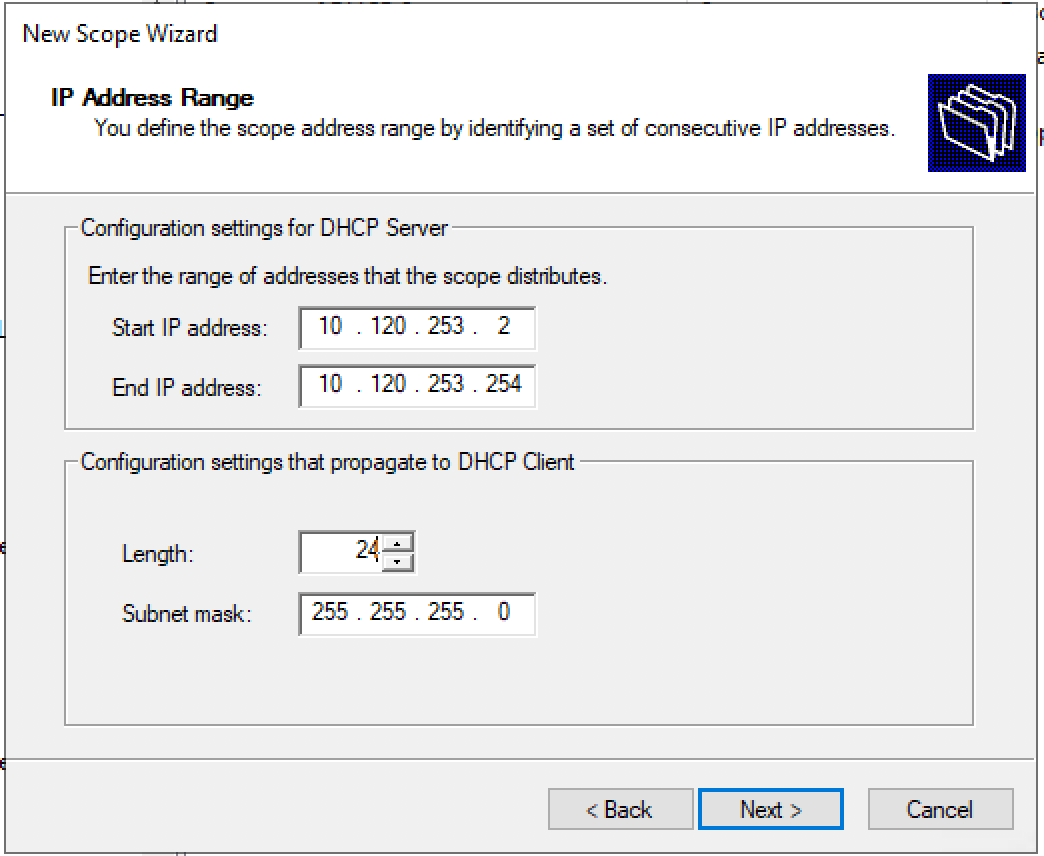
Specify the new DHCP address range.

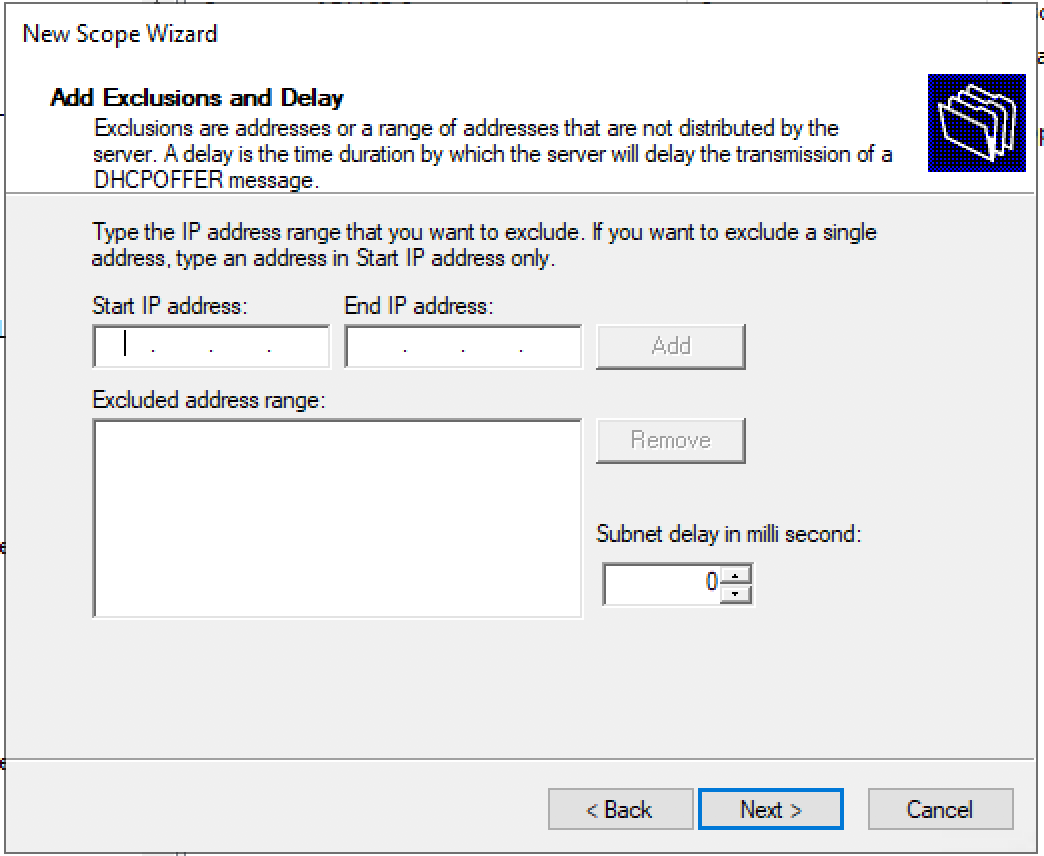
Set the exclusion range for the DHCP scope.

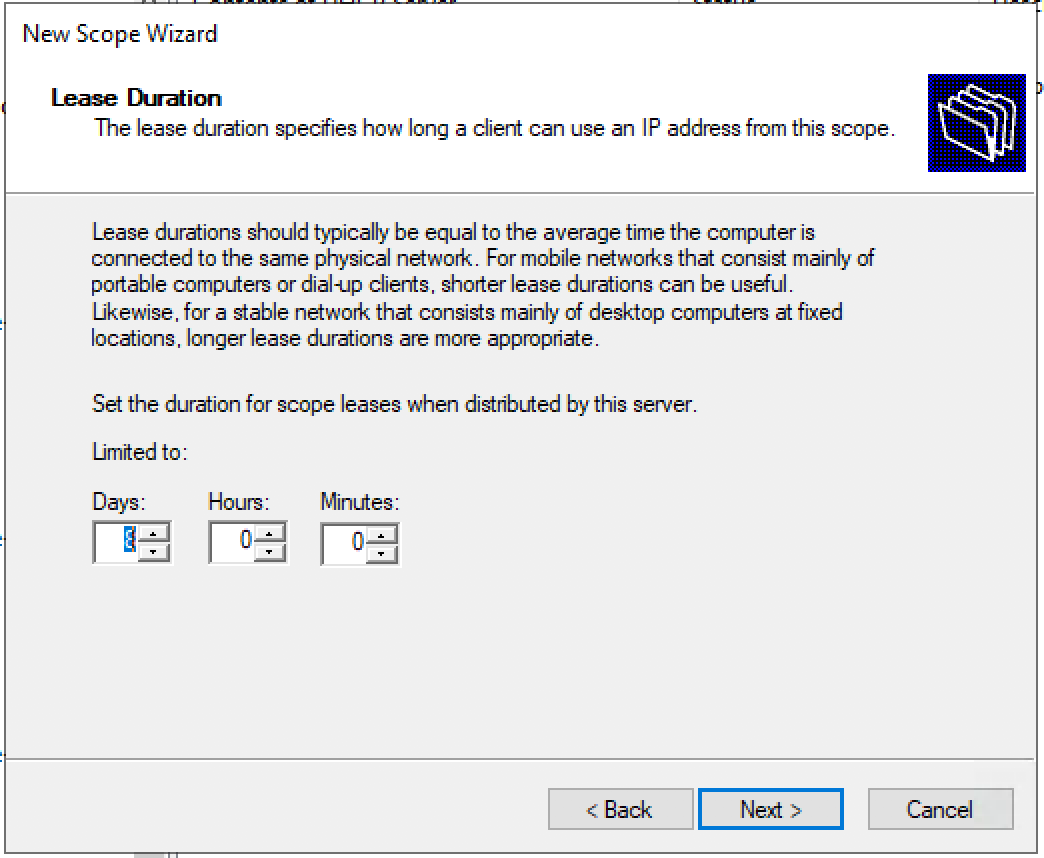
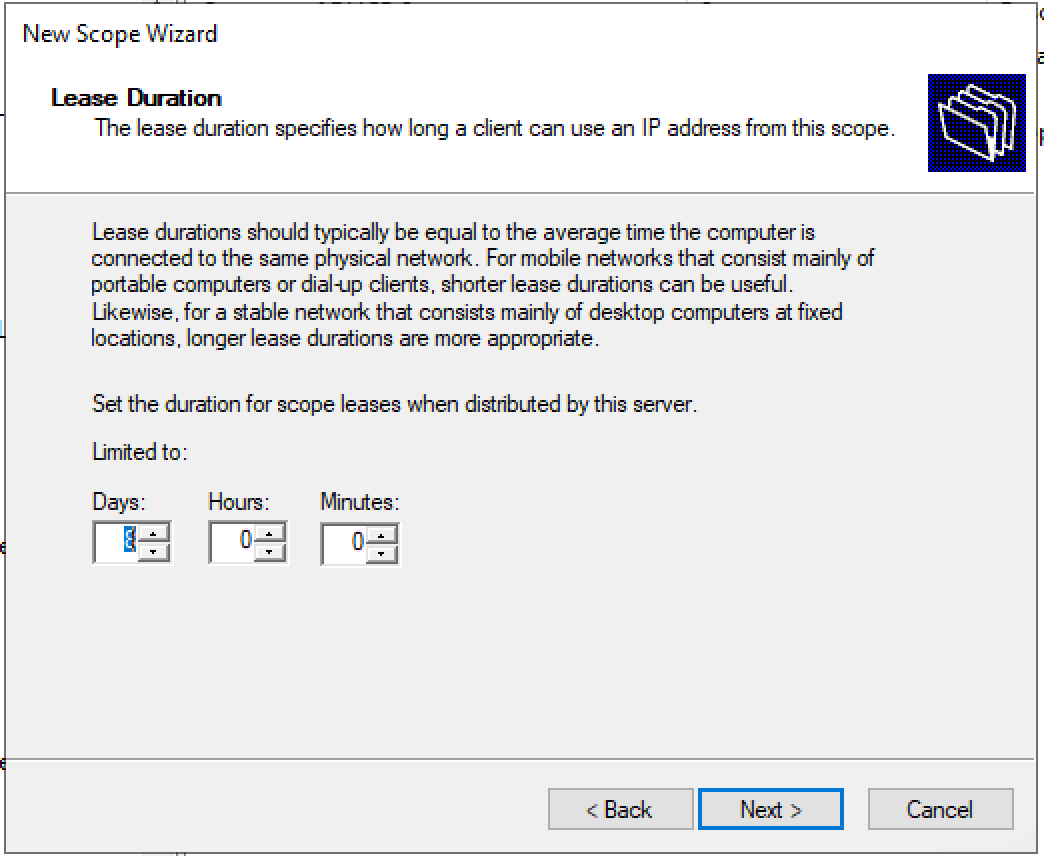
Specify the lease duration.

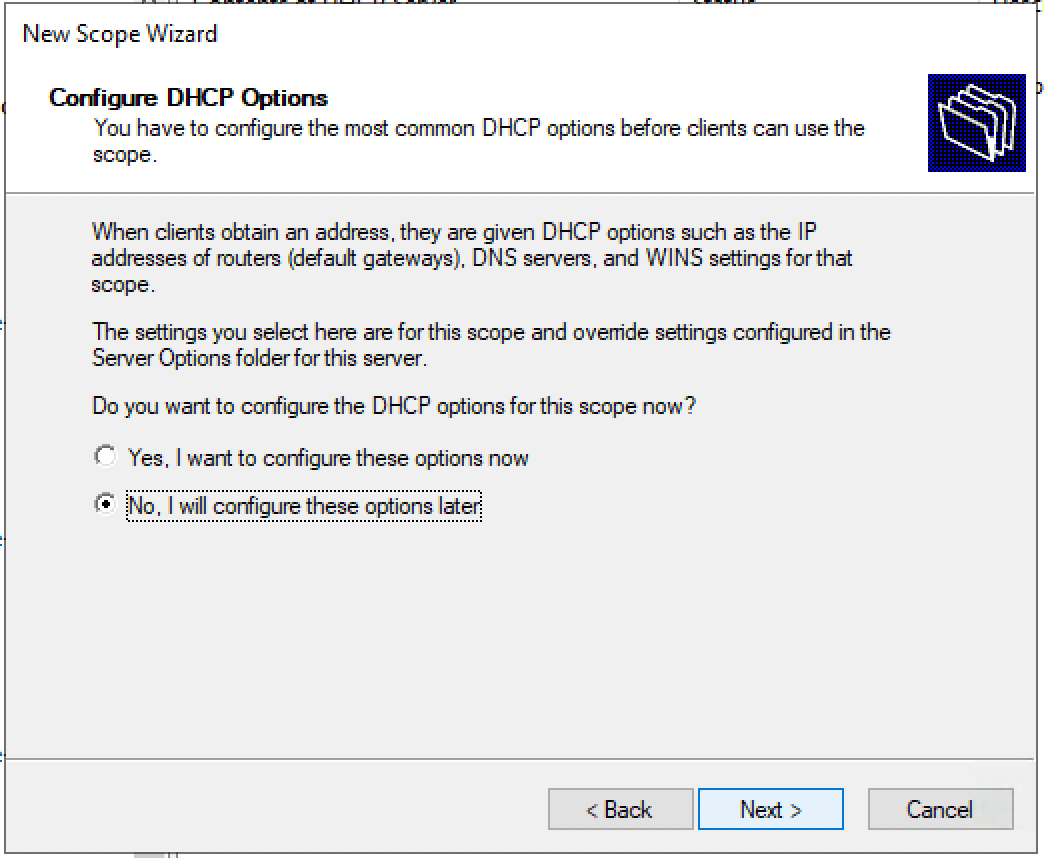
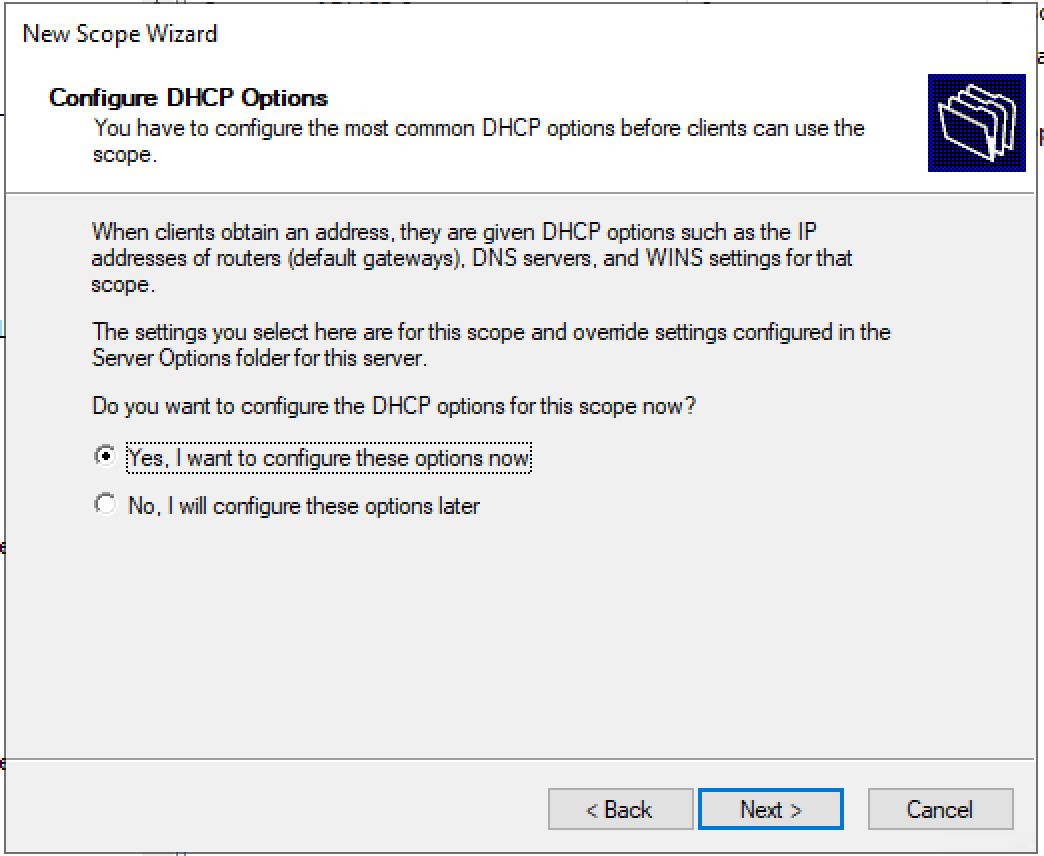
Configure the DHCP options for the new DHCP scope.

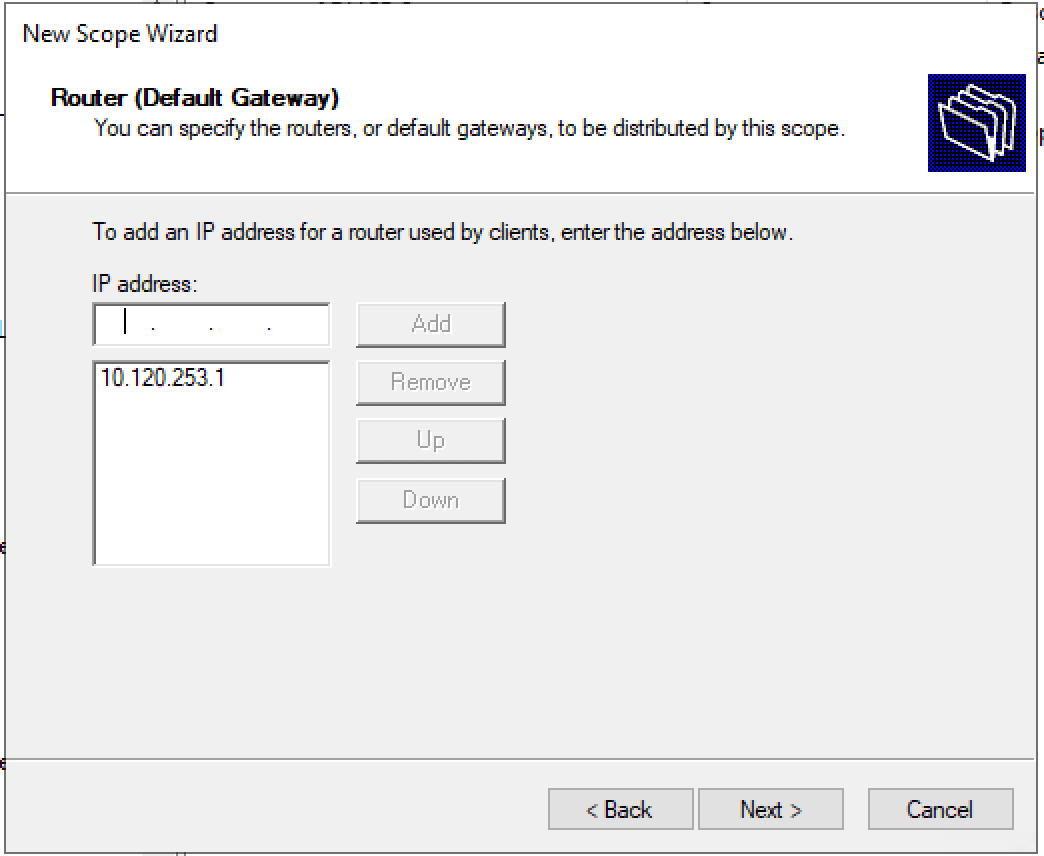
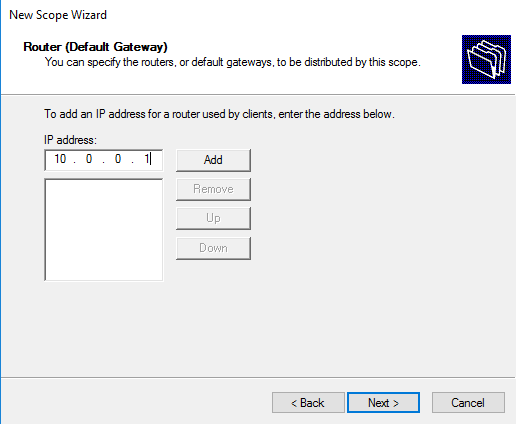
Define the default gateway of the new Windows Server DHCP VLAN configuration.

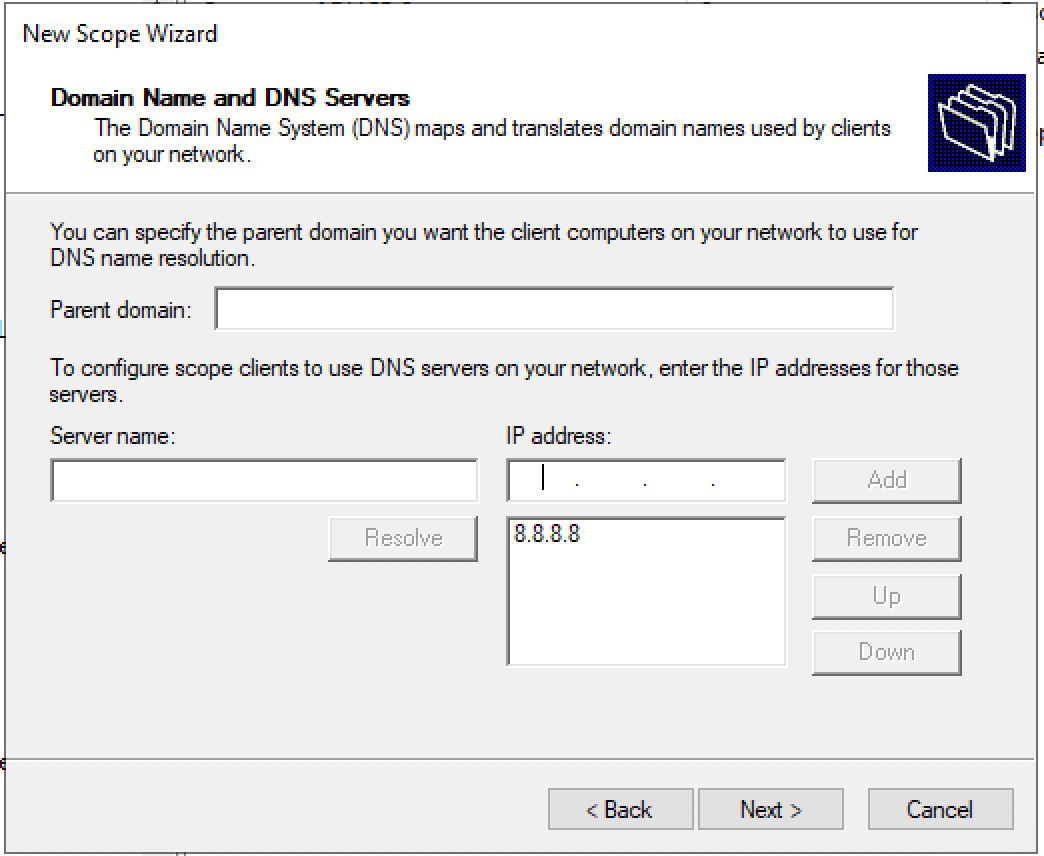
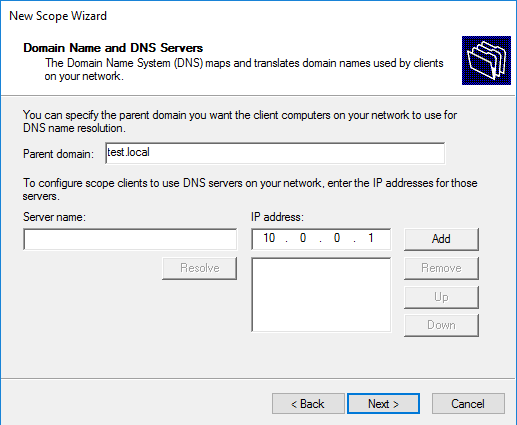
Configure domain name and DNS servers.

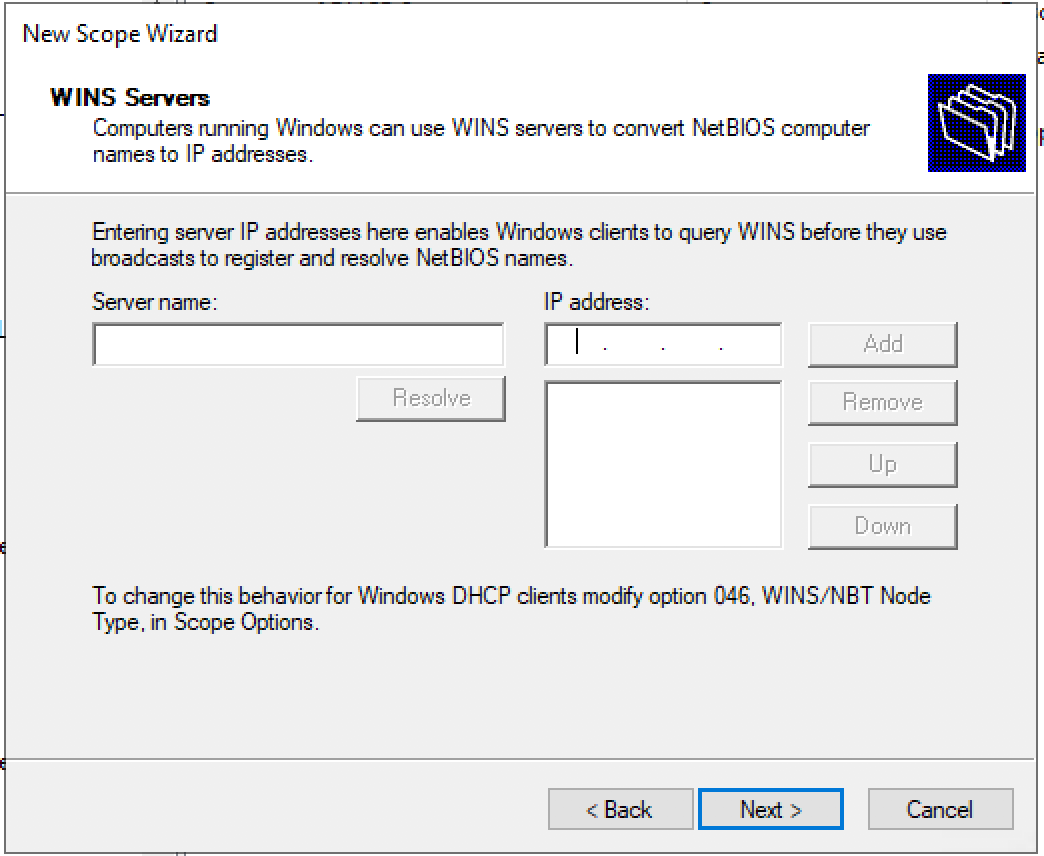
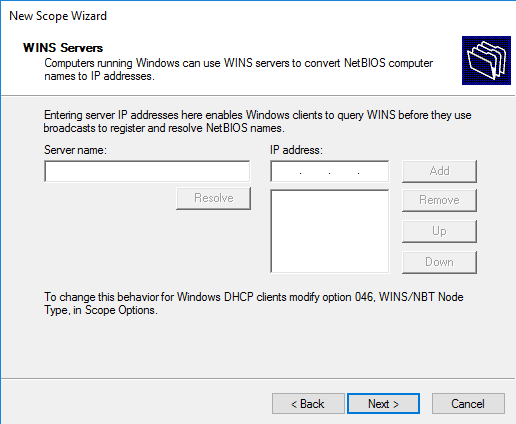
Setup any WINS server addresses.

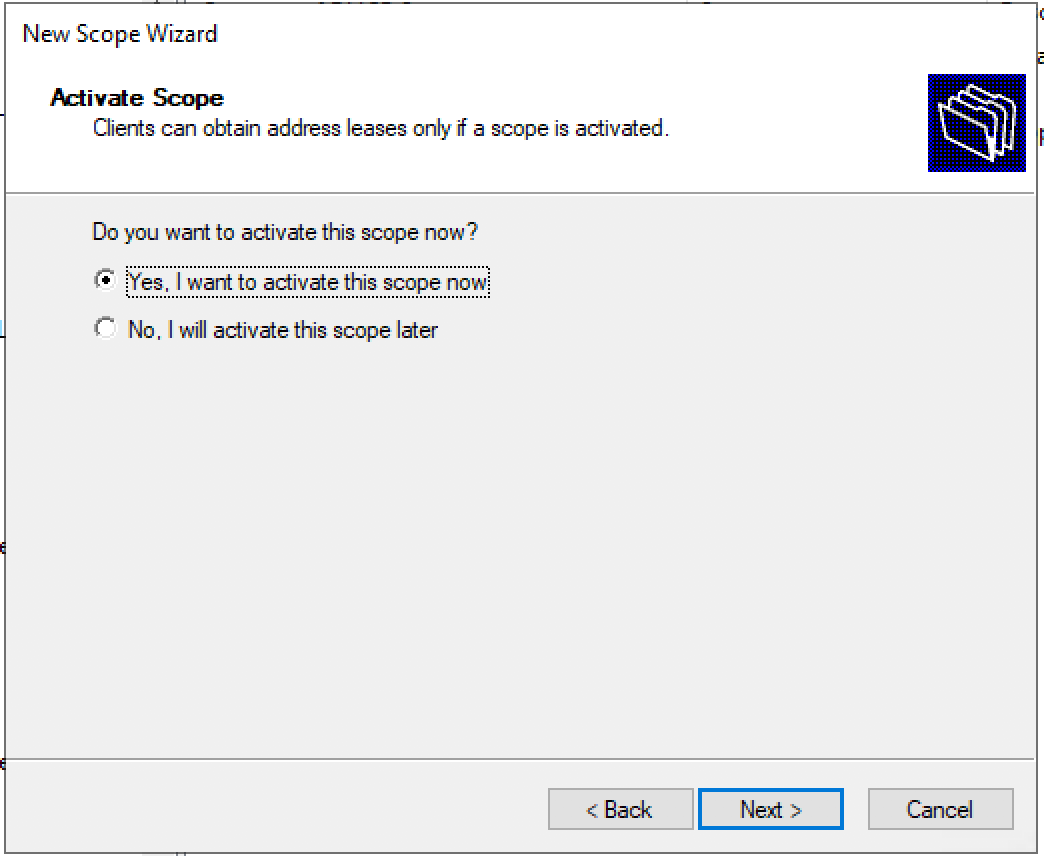
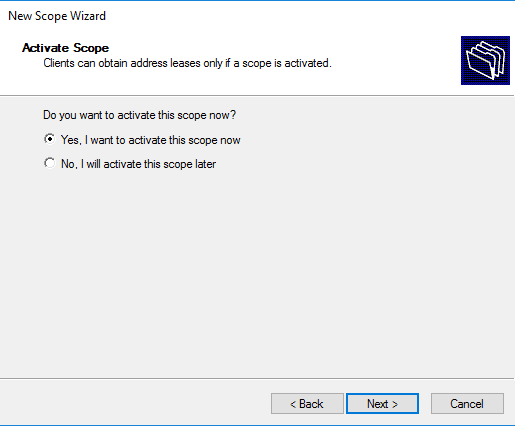
Activate the new DHCP scope.

Complete the new DHCP scope wizard.

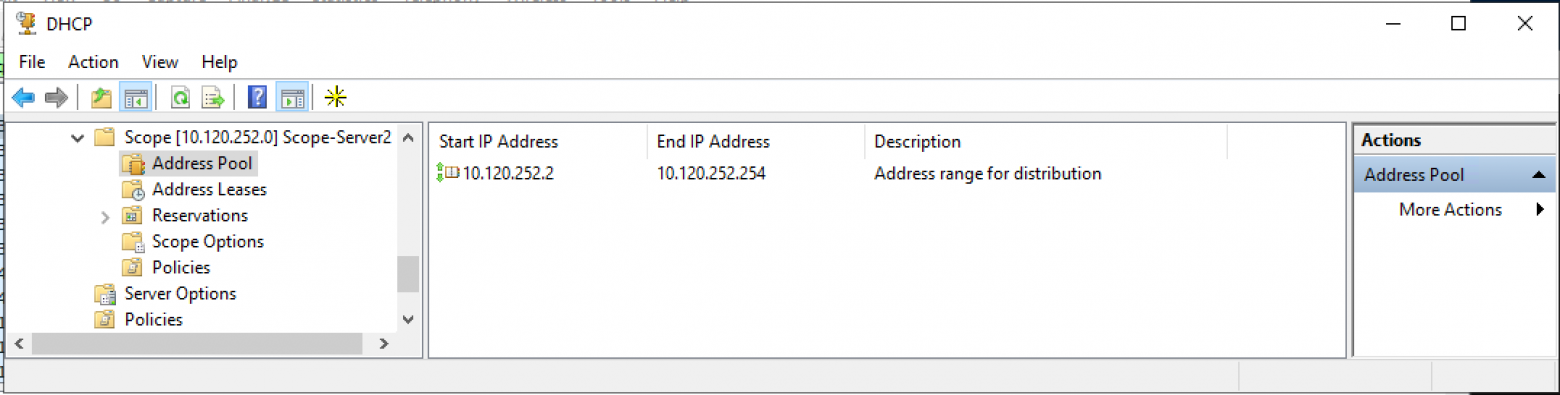
Below is an example of how my DHCP server looks after creating two different scopes for address leasing.
- 192.168.1.0/24 – associated with VLAN 10, which is not where the Windows Server DHCP server resides.
- 10.1.149.0/24 – associated with VLAN 149. This is the VLAN where the DHCP server resides.

Wrapping Up
Hopefully, this Windows Server DHCP VLAN Configuration: Detailed Guide will help any who may be trying to wrap their heads around the configuration of DHCP services for different VLANs and network segments in their network. By understanding the different means you have available to hand out IP addresses from a Windows DHCP Server you can effectively segment your network and easily handle IP addressing for all clients in the network, regardless of the VLAN they reside on.
Назначение этой статьи – упростить настройку DHCP сервиса для фабрики VXLAN BGP EVPN and DFA с использованием Microsoft Windows Server 2016/2019.
В официальной документации DHCP сервис на базе Microsoft Windows Server 2012 для фабрики настраивается как SuperScope, содержащий пул Loopback (в данном пуле – изюминка это исключение из пула всех IP адресов пула (excluded IP address = pool)) и пулы выдачи IP адресов для реальный сетей (здесь изюминка – настраиваются policy – в которых фильтруются DHCP Relay Circuit ID и этот DHCP relay Circuit ID содержит VNI для сети, т. е. для другого пула этот DHCP Relay Circuit ID будет чуть другим).
To configure DHCP on Windows server.
1. Create a super scope. Within the super scope, create scope B, S1, S2, S3, …, Sn for the subnet B and the subnets for each segment.
2. In scope B, specify the 'Exclusion Range' to be the entire address range (so that the offered address range must not be from this scope).
3. For every segment scope Si, specify a policy that matches on Agent Circuit ID with value of '0108000600XXXXXX', where '0108000600' is a fixed value for all segments, the 6 numbers "XXXXXX" is the segment ID value in hexadecimal. Also ensure to check the Append wildcard(*) check box.
4. Set the policy address range to the entire range of the scope.Данная статья содержит ответы на следующие вопросы:
- Почему не поддерживаются Microsoft Windows Server 2000/2003/2008?
- Почему в Microsoft Windows Server 2012 настройка такая сложная?
- Как упрощается настройка в Microsoft Windows Server 2016/2019?
Содержание
- Введение
- Как настраивается DHCP Relay на фабрике VXLAN BGP EVPN
- RFC которые используются в DHCP Relay с фабрики VXLAN BGP EVPN
- Эволюция документации Cisco в части настройки DHCP на Microsoft Windows Server 2012
- DHCP в Microsoft Windows Server (superscope & policy)
- Основная часть
- Почему не поддерживается Microsoft Windows Server 2000/2003/2008?
- Почему в Microsoft Windows Server 2012 настройка такая сложная?
- Как упрощается настройка в Microsoft Windows Server 2016/2019?
- Пример
- Настройка DHCP сервиса на Microsoft Windows Server 2019
- Заключение
- Список источников
Введение
В этой части кратко перечислены все исходные данные: Инструкции по настройке сетевого оборудования, RFC используемые в DHCP пакетах в фабриках eVPN, справочно приведена эволюция настроек DHCP сервера на Microsoft Windows Server 2012 в документации Cisco. А также краткие сведения о Superscope и Policy в сервисе DHCP на серверах Microsoft Windows Server.
Как настраивается DHCP Relay на фабрике VXLAN BGP EVPN, DFA
Настройка DHCP Relay на фабрике VXLAN BGP EVPN не является основной темой этой статьи, т. к. она достаточно простая. Привожу ссылки на документацию и спойлер по настройкам на сетевом оборудовании.
- Nexus 9000 VXLAN Configuration Guide 7.X
- Nexus 9000 VXLAN Configuration Guide 9.3
- DFA (Cisco Dynamic Fabric Automation)
Пример настройки DHCP Relay на Nexus 9000V v9.2(3)
service dhcp
ip dhcp relay
ip dhcp relay information option
ip dhcp relay information option vpn
interface loopback10
vrf member VRF1
ip address 10.120.0.1/32 tag 1234567
interface Vlan12
no shutdown
vrf member VRF1
no ip redirects
ip address 10.120.251.1/24 tag 1234567
no ipv6 redirects
fabric forwarding mode anycast-gateway
ip dhcp relay address 10.0.0.5
ip dhcp relay source-interface loopback10
RFC которые реализованы в работе сервиса DHCP Relay в фабриках VXLAN BGP EVPN
- Список RFC, для Nexus 9000 v9.3
- Список RFC, Nexus 9000 v7.x
RFC#6607: Sub-option 151(0x97) — Virtual Subnet Selection
• Sub-option 151(0x97) - Virtual Subnet Selection (Defined in RFC#6607)
Used to convey VRF related information to the DHCP server in an MPLS-VPN and VXLAN EVPN multi-tenant environment.Передается «имя» VRF в котором находиться клиент.
RFC#5107: Sub-option 11(0xb) — Server ID Override
• Sub-option 11(0xb) - Server ID Override (Defined in RFC#5107.)
The server identifier (server ID) override sub-option allows the DHCP relay agent to specify a new value for the server ID option, which is inserted by the DHCP server in the reply packet. This sub-option allows the DHCP relay agent to act as the actual DHCP server such that the renew requests will come to the relay agent rather than the DHCP server directly. The server ID override sub-option contains the incoming interface IP address, which is the IP address on the relay agent that is accessible from the client. Using this information, the DHCP client sends all renew and release request packets to the relay agent. The relay agent adds all of the appropriate sub-options and then forwards the renew and release request packets to the original DHCP server. For this function, Cisco’s proprietary implementation is sub-option 152(0x98). You can use the ip dhcp relay sub-option type cisco command to manage the function.Опция используется для того, чтобы клиент посылал запрос о перепродлении аренды адреса на IP адрес используемый в этой опции. (В Cisco VXLAN BGP EVPN – это Anycast адрес шлюза по умолчанию для клиента.)
RFC#3527: Sub-option 5(0x5) — Link Selection
Sub-option 5(0x5) - Link Selection (Defined in RFC#3527.)
The link selection sub-option provides a mechanism to separate the subnet/link on which the DHCP client resides from the gateway address (giaddr), which can be used to communicate with the relay agent by the DHCP server. The relay agent will set the sub-option to the correct subscriber subnet and the DHCP server will use that value to assign an IP address rather than the giaddr value. The relay agent will set the giaddr to its own IP address so that DHCP messages are able to be forwarded over the network. For this function, Cisco’s proprietary implementation is sub-option 150(0x96). You can use the ip dhcp relay sub-option type ciscocommand to manage the function.Адрес сети, из которой клиенту необходим IP адрес.
Эволюция документации Cisco в части настройки DHCP на Microsoft Windows Server 2012
Включил этот раздел потому, что прослеживается положительная тенденция со стороны вендора:
Nexus 9000 VXLAN Configuration Guide 7.3
В документации приведена только настройка DHCP Relay на сетевом оборудовании.
Для настройки DHCP на Windows Server 2012 использовалась другая статья:
Configuring Microsoft Windows Server 2012 to provide DHCP services in an eVPN Scenario (VXLAN, Cisco One Fabric, etc)
В этой статье указывается, что для каждой сети/VNI необходима своя связка SuperScope и свой собственный набор Loopback адресов:
If multiple DHCP Scopes are required for multiple subnets, you need to create one LoopbackX per subnet/vlan on all LEAFS and create a superscope with a loopbackX range scope and actual client IP subnet scope per vlan.Nexus 9000 VXLAN Configuration Guide 9.3
Добавили настройки Windows 2012 Server в документацию по настройке сетевого оборудования. Для всех используемых пулов адресов необходим один SuperScope на ЦОД и этот SuperScope является границей ЦОД:
Create Superscope for all scopes you want to use for Option 82-based policies.
Note
The Superscope should combine all scopes and act as the administrative boundary.Cisco Dynamic Fabric Automation
Очень емко рассказано обо всем:
Let us assume the switch is using the address from subnet B (it can be the backbone subnet, management subnet, or any customer designated subnet for this purpose) to communicate with the Windows DHCP server. In DFA we have subnets S1, S2, S3, …, Sn for segment s1, s2, s3, …, sn.
To configure DHCP on Windows server.
1. Create a super scope. Within the super scope, create scope B, S1, S2, S3, …, Sn for the subnet B and the subnets for each segment.
2. In scope B, specify the 'Exclusion Range' to be the entire address range (so that the offered address range must not be from this scope).
3. For every segment scope Si, specify a policy that matches on Agent Circuit ID with value of '0108000600XXXXXX', where '0108000600' is a fixed value for all segments, the 6 numbers "XXXXXX" is the segment ID value in hexadecimal. Also ensure to check the Append wildcard(*) check box.
4. Set the policy address range to the entire range of the scope.
DHCP в Microsoft Windows Server (superscope & policy)
SuperScope
Superscope is an administrative feature of a DHCP server that can be used to group multiple scopes as a single administrative entity. Superscope allows a DHCP server to provide leases from more than one scope to clients on a single physical network. Scopes added to a superscope are called member scopes.Что такое SuperScope – это функционал, позволяющий объединить несколько пулов IP адресов в одну административную единицу. Чтобы анонсировать пользователям в одной физической сети (в одном VLAN) ip адреса из нескольких пулов. Если запрос пришел к пулу адресов в составе SuperScope, то выдать клиенту адрес можно из другого Scope входящего в этот SuperScope.
Policy
The DHCP Server role in Windows Server 2012 introduces a new feature that allows you to create IPv4 policies that specify custom IP address and option assignments for DHCP clients based on a set of conditions.
The policy based assignment (PBA) feature allows you to group DHCP clients by specific attributes based on fields contained in the DHCP client request packet. PBA enables targeted administration and greater control of the configuration parameters delivered to network devices with DHCP.Политики – позволяют назначать пользователям IP адреса в зависимости от типа пользователя или параметра. Инженеры Cisco используют политики в Windows Server 2012 для фильтрации по VNI (Virtual Network Identifier).
Основная часть
В данном разделены проведены результаты исследований, почему не поддерживается, как это работает (логика), что нового и как это новое нам поможет.
Почему не поддерживается Microsoft Windows Server 2000/2003/2008?
Microsoft Windows Server 2008 и более ранние версии не обрабатывают опцию 82 (Option 82) и обратный пакет отправляют без опции 82.
Win2k8 R2 DHCP problem with Option82
- Запрос от клиента отправляется Broadcast (DHCP Discover).
- Оборудование (Nexus) отправляет пакет к DHCP серверу (DHCP Discover + Option 82).
- DHCP Сервер принимает пакет обрабатывает, отправляет обратно, но без опции 82. (DHCP Offer – without option 82)
- Оборудование (Nexus) принимает пакет от DHCP сервера. (DHCP Offer) Но не отправляет этот пакет к конечному пользователю.
Данные снифера — на Windows Server 2008 и на клиенте DHCP
Windows Server 2008 получает запрос от сетевого оборудования. (Option 82 присутствует в списке)
Windows Server 2008 отправляет ответ к сетевому оборудованию. (Option 82 отсутствует в списке опций в пакете)
Запрос от клиента – присутствуют DHCP Discover и отсутствуют DHCP Offer
Статистика на сетевом оборудовании:
NEXUS-9000V-SW-1# show ip dhcp relay statistics
----------------------------------------------------------------------
Message Type Rx Tx Drops
----------------------------------------------------------------------
Discover 8 8 0
Offer 8 8 0
Request(*) 0 0 0
Ack 0 0 0
Release(*) 0 0 0
Decline 0 0 0
Inform(*) 0 0 0
Nack 0 0 0
----------------------------------------------------------------------
Total 16 16 0
----------------------------------------------------------------------
DHCP L3 FWD:
Total Packets Received : 0
Total Packets Forwarded : 0
Total Packets Dropped : 0
Non DHCP:
Total Packets Received : 0
Total Packets Forwarded : 0
Total Packets Dropped : 0
DROP:
DHCP Relay not enabled : 0
Invalid DHCP message type : 0
Interface error : 0
Tx failure towards server : 0
Tx failure towards client : 0
Unknown output interface : 0
Unknown vrf or interface for server : 0
Max hops exceeded : 0
Option 82 validation failed : 0
Packet Malformed : 0
Relay Trusted port not configured : 0
DHCP Request dropped on MCT : 0
* - These counters will show correct value when switch
receives DHCP request packet with destination ip as broadcast
address. If request is unicast it will be HW switched
NEXUS-9000V-SW-1#Почему в Microsoft Windows Server 2012 настройка такая сложная?
В Microsoft Windows Server 2012 еще не поддерживается RFC#3527 (Option 82 Sub-option 5(0x5) — Link Selection)
Но уже реализован функционал Policy.
Как это работает:
- Microsoft Windows Server 2012 есть супер-пул (SuperScope) в котором есть адреса Loopback и пулы для реальных сетей.
- Выбор пула для выдачи IP адреса попадает в SuperScope, т. к. ответ пришел от DHCP Relay с Source адреса Loopback, входящего в SuperScope.
- Используя Policy запрос выбирает из Superscope тот member scope, VNI которого содержится в Option 82 Suboption 1 Agent Circuit ID. (“0108000600”+ 24 бита VNI + 24 бита значения которых мне неизвестно, но сниффер показывает значения 0 в этом поле.)
Как упрощается настройка в Microsoft Windows Server 2016/2019?
В Microsoft Windows Server 2016 реализован функционал RFC#3527. Т. е. Windows Server 2016 умеет распознавать правильную сеть из атрибута Option 82 Sub-option 5(0x5) — Link Selection
Возникают сразу 3 вопроса:
- Можем ли обойтись без Superscope?
- Можем ли обойтись без Policy и перевода VNI в 16-тиричный вид?
- Можем ли обойтись без Scope для Loopback адресов DHCP Source?
Q. Можем ли обойтись без Superscope?
A. Да, scope можно создавать сразу в области IPv4 адресов.
Q. Можем ли обойтись без Policy и перевода VNI в 16-тиричный вид?
A. Да, выбор сети происходит на основе Option 82 Suboption 0x5,
Q. Можем ли обойтись без Scope для Loopback адресов DHCP Source?
A. Нет, не можем. Т. к. в Microsoft Windows Server 2016/2019 действует защита от злонамеренных DHCP запросов. Т. е. все запросы с адресов, которых нет в пуле DHCP сервера считаются злонамеренными.
DHCP Subnet Selection Options
Note
All relay agent IP addresses (GIADDR) must be part of an active DHCP scope IP address range. Any GIADDR outside of the DHCP scope IP address ranges is considered a rogue relay and Windows DHCP Server will not acknowledge DHCP client requests from those relay agents.
A special scope can be created to "authorize" relay agents. Create a scope with the GIADDR (or multiple if the GIADDR's are sequential IP addresses), exclude the GIADDR address(es) from distribution, and then activate the scope. This will authorize the relay agents while preventing the GIADDR addresses from being assigned.Т.е. для настройки на Microsoft Windows Server 2016/2019 DHCP пула для VXLAN BGP EVPN фабрики необходимо только:
- Создать пул для Source адресов Relay.
- Создать пул для клиентских сетей
Что не является необходимым (но можно настроить и это будет работать, и не будет мешать работать):
- Создавать Policy
- Создавать SuperScope
Пример
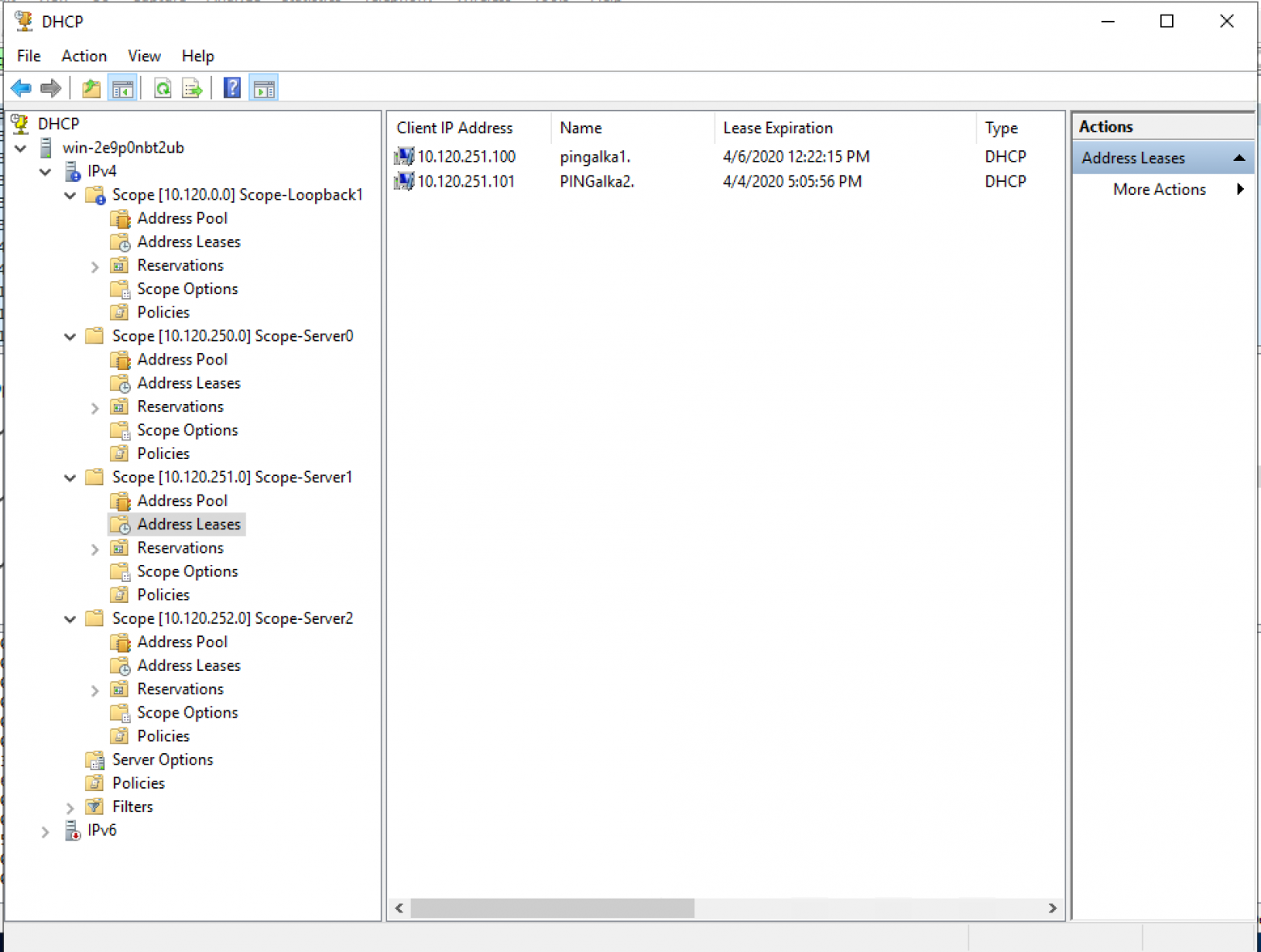
Пример настройки DHCP сервера (присутствуют 2 реальных клиента DHCP — клиенты подключены к VXLAN фабрике)
Пример настройки пользовательского пула:
Пример настройки пользовательского пула (выбраны политики — для доказательства что политики не использовались для корректной работы пула):
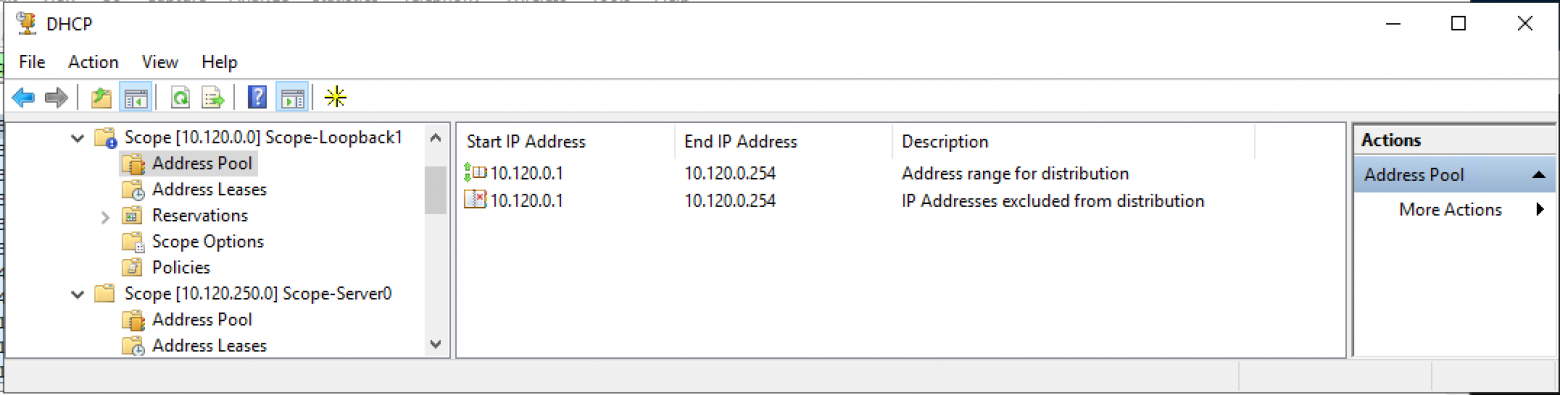
Пример настройки пула для Source адресов DHCP Relay (диапазон адресов для выдачи полностью соответствует исключению из пула адресов):
Настройка DHCP сервиса на Microsoft Windows Server 2019
Настройка пула для Loopback адресов (source) для DHCP Relay.
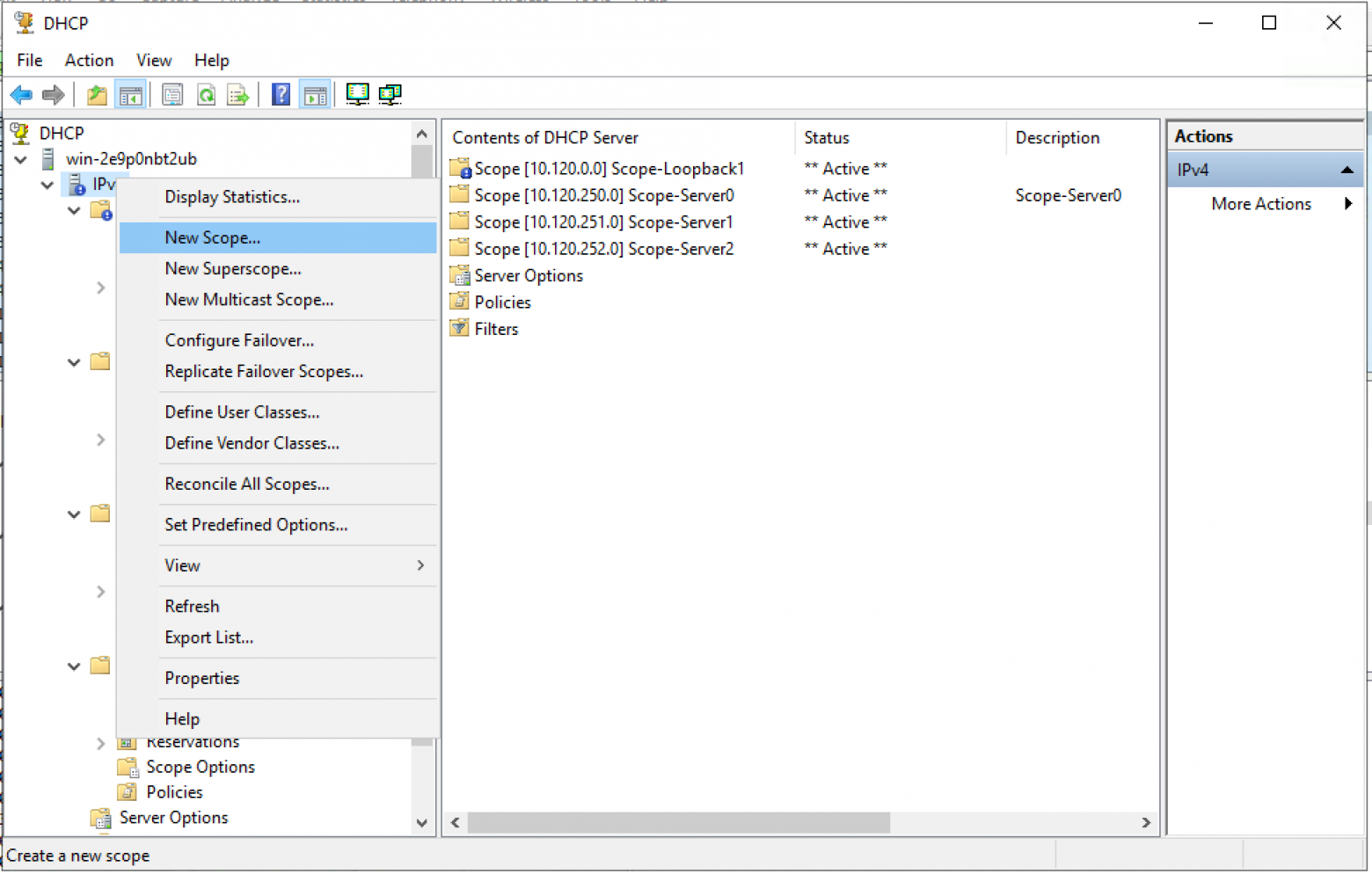
Создаем новый пул (Scope) в пространстве IPv4.
Мастер создания пула. «Next >»
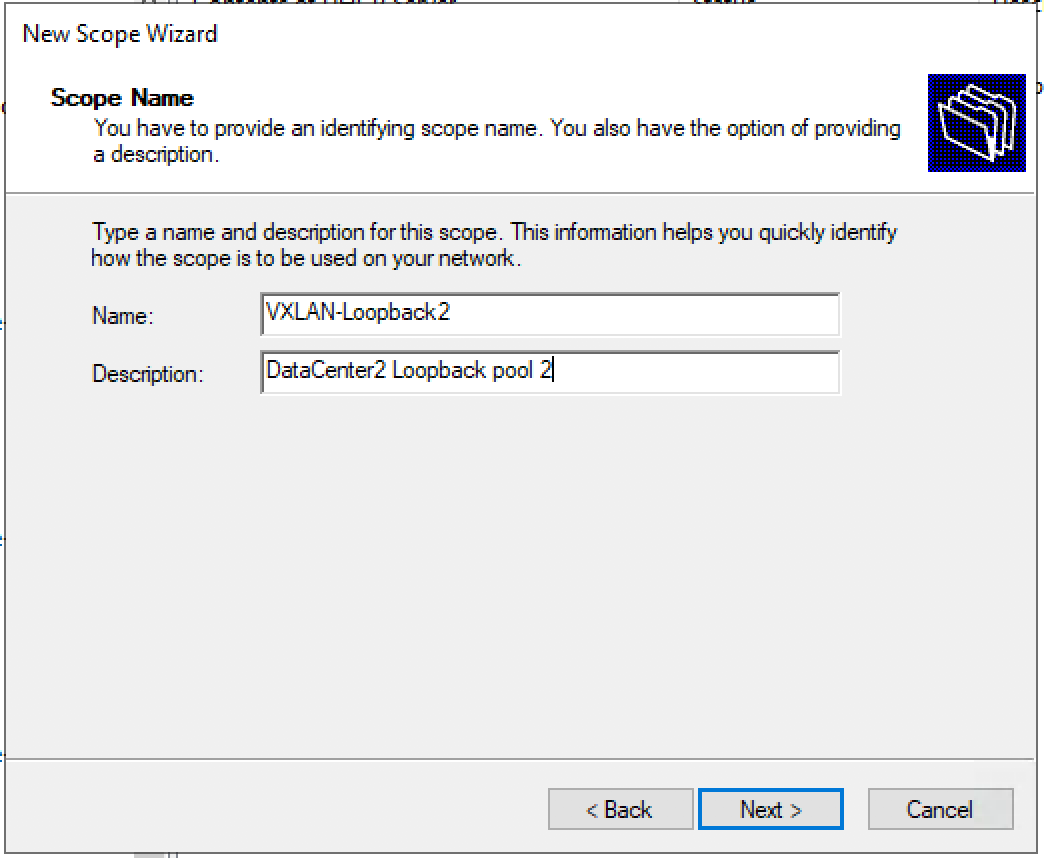
Настраиваем имя пула и описание (Description) пула.
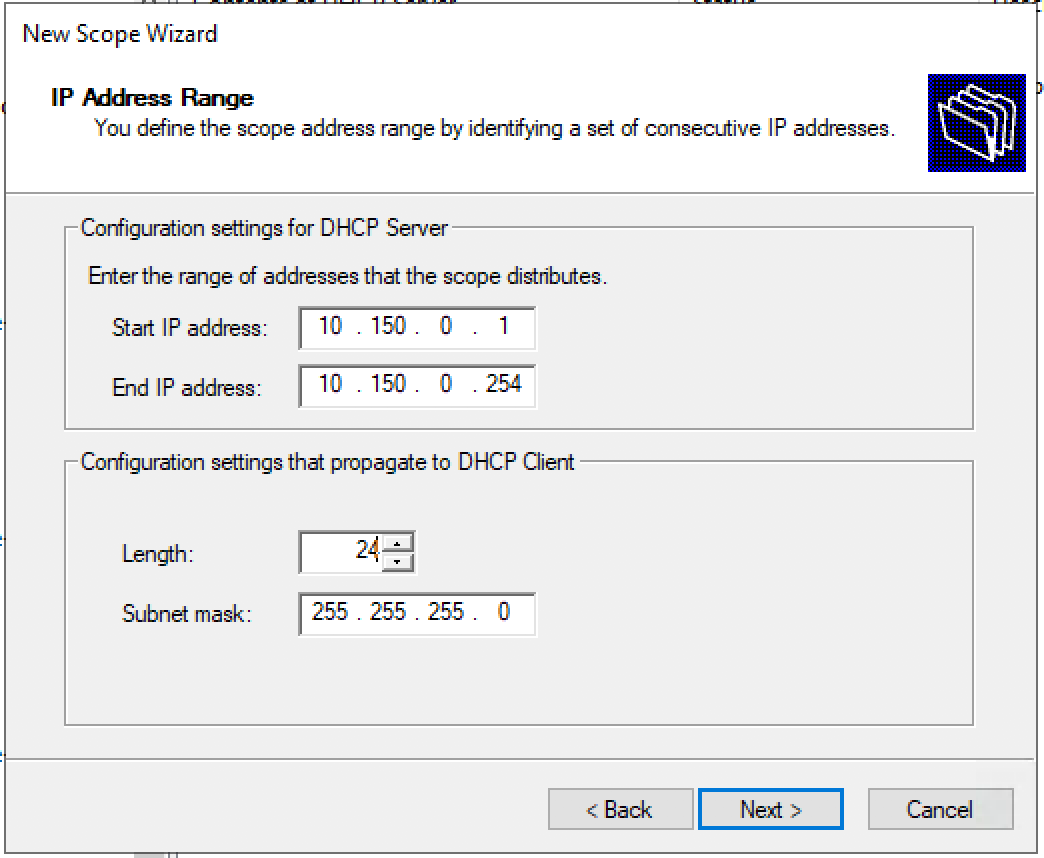
Задаем диапазон IP адресов для Loopback и маску для пула.
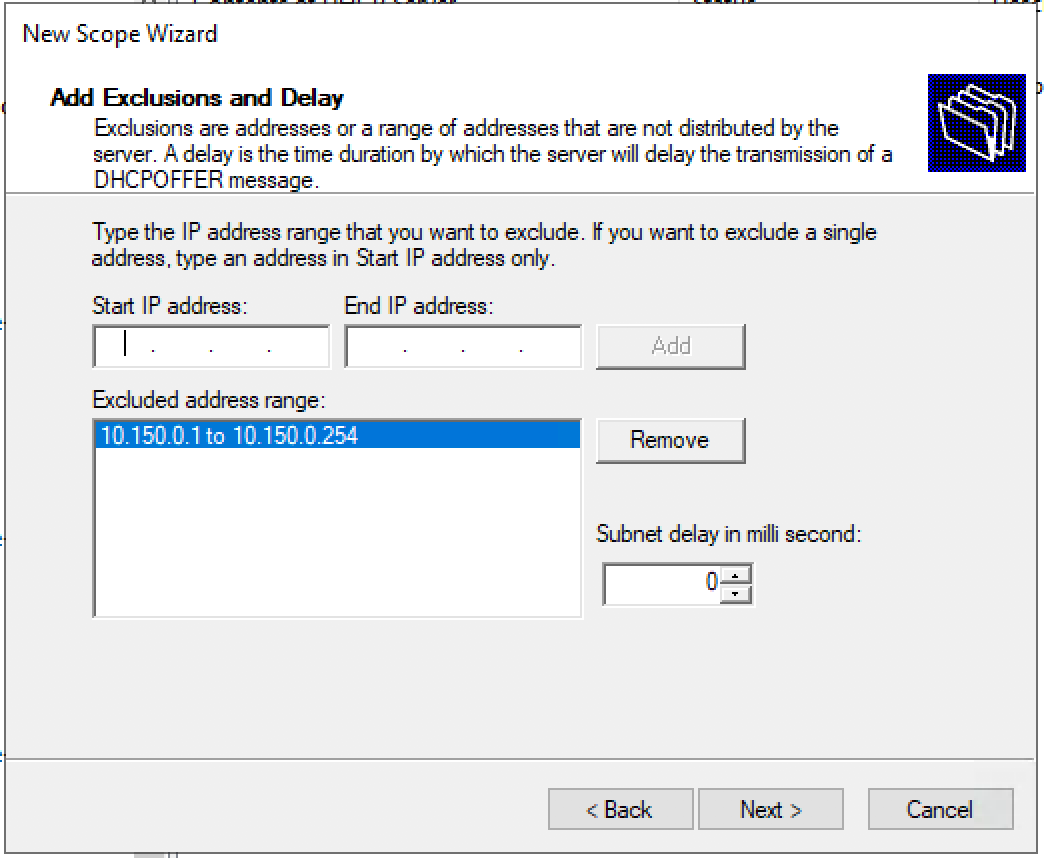
Добавляем исключения. Диапазон исключений должен полностью совпадать с диапазоном пула.
Время аренды. «Next >»
Запрос: Будете настраивать DHCP опции сейчас (DNS, WINS, Gateway, Domain) или сделаете это позже. Быстрее будет ответить нет, и после активировать пул вручную. Либо пройти до конца не заполняя ни какую информацию и в конце мастера активировать пул.
Подтверждаем, что опции не настроены, пул не активирован. «Finish»
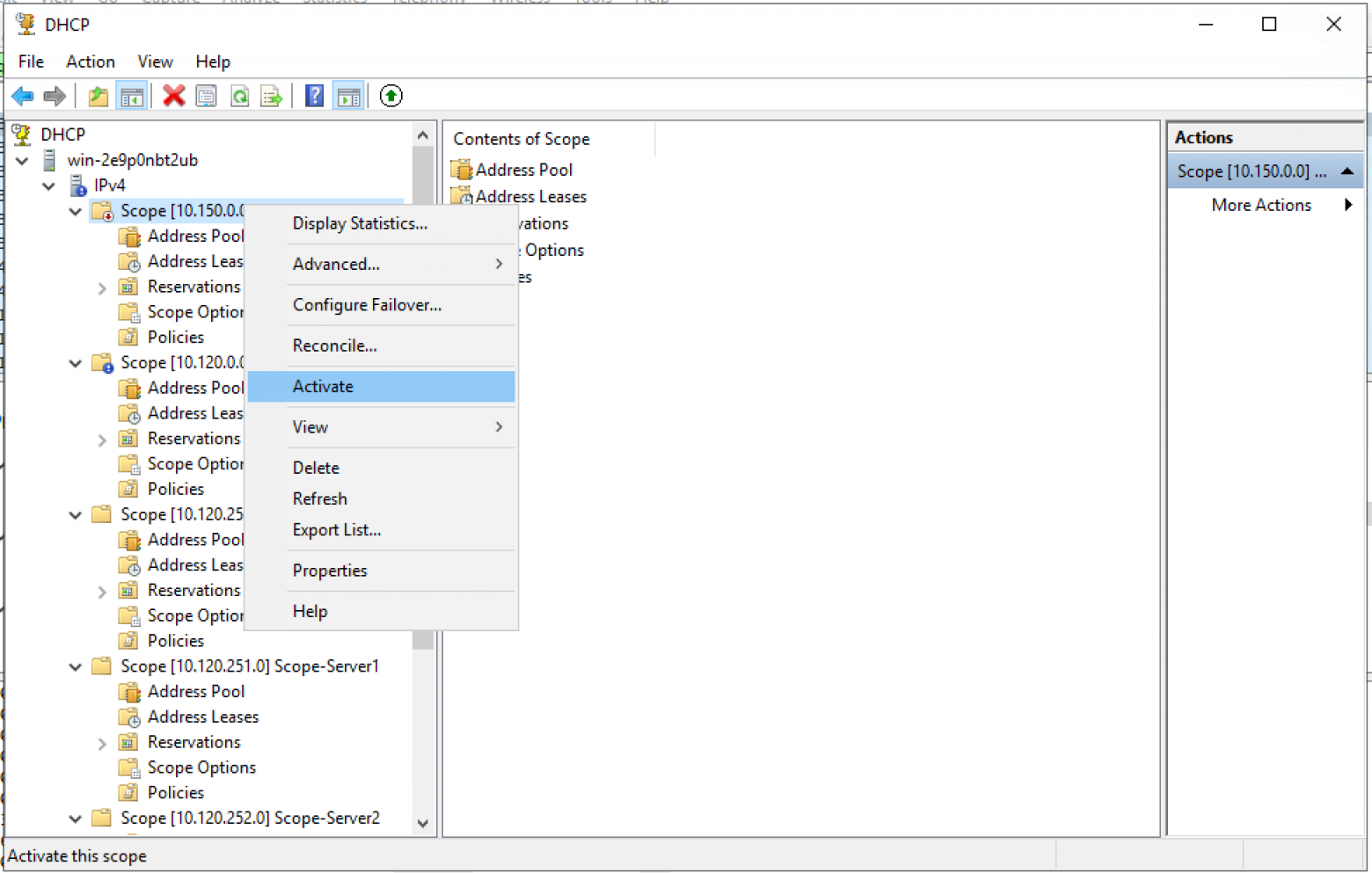
Активируем пул вручную. — Выбираем Scope и в контекстном меню — выбираем «Activate».
Создаем пул для пользователей/серверов.
Создаем новый пул.
Мастер создания пула. «Next >»
Настраиваем имя пула и описание (Description) пула.
Задаем диапазон IP адресов для Loopback и маску для пула.
Добавляем исключения. (По умолчанию исключений не требуется) «Next >»
Время аренды. «Next >»
Запрос: Будете настраивать DHCP опции сейчас (DNS, WINS, Gateway, Domain) или сделаете это позже. Да настроим сейчас.
Настраиваем адрес шлюза по умолчанию.
Настраиваем домен и адреса DNS серверов.
Настраиваем IP адреса WINS серверов.
Активация Scope.
Пул настроен. «Finish»
Заключение
Использование Windows Server 2016/2019 уменьшает сложность настройки DHCP сервера для VXLAN фабрики (или любой другой фабрики). (Не требуется передача IT специалистам специальные связки: Network/Agent Circuit ID для прописывания фильтров.)
Будет ли работать конфигурация для Windows Server 2012 на новых серверах 2016/2019 – да будет работать.
В данном документе приведены ссылки на 2 версии: 7.X и 9.3. Это связано с тем, что версия 7.0(3)I7(7) — Cisco Suggested release, а версия 9.3 — является самой инновационной (вплоть до поддержки Multicast через VXLAN Multisite).
Список источников
- Nexus 9000 VXLAN Configuration Guide 7.x
- Nexus 9000 VXLAN Configuration Guide 9.3
- DFA (Cisco Dynamic Fabric Automation)
- Configuring Microsoft Windows Server 2012 to provide DHCP services in an eVPN Scenario (VXLAN, Cisco One Fabric, etc)
- 3.4 DHCP Superscopes
- Introduction to DHCP Policies
- Win2k8 R2 DHCP problem with Option82
- DHCP Subnet Selection Options
Here is an example of the network topology I am trying to create.
There is the standard router — Netgear Genie. It can link each port to a VLAN, and the Wifi can be on the vlan, but my thought was to leave this agnostic of VLAN and just route traffic. It is also a DHCP — ideally just for the Guest network.
The switch is a smart switch and supports VLAN,
There are two WAPS which are HP and can also broadcast multiple SSID each on a VLAN.
In the «Company» network, there is a Windows Server 2016, which is the AD, DNS, DHCP etc for the company network. (Company — small business from home…)
The «Guest» network would be for non business users who do not need access to the Company network and should not be able to see.
(There is also CCTV, and this would be useful to segment on it’s own VLAN too. but this is an issue for another day)
I have two questions:
1) Is is possible to have the DHCP server on the router level, or does it need to reside within VLAN 101. (so they are both separate to each other)
2) What VLAN tagging and PVID settings are required for the switch.
Many thanks in advance.
- Remove From My Forums
-
Question
-
DHCP for multiple VLANs
We have multiple VLANS. We have Windows Server 2016. Not sure the best way to approach our vlans as we want DHCP on each VLAN.
Do we have to have multiple nics with a dedicated one for each vlan?
Can you have multiple vlans on 1 DHCP server for Windows 2016 or would we have to set up a virtual machine for each — I have no idea?
-
Moved by
Monday, October 30, 2017 4:55 PM
Not a multipoint question
-
Moved by
Answers
-
-
Proposed as answer by
frank_songMicrosoft contingent staff
Tuesday, October 31, 2017 6:24 AM -
Marked as answer by
Technomage18
Friday, November 3, 2017 5:16 PM
-
Proposed as answer by
Данная статья описывает процедуру установки и настройки DHCP сервера на базе Windows Server 2019. В статье описаны особенности установки и настройки DHCP роли, создания областей DHCP, настройки их параметров и резервации статических адресов. Мы рассмотрим как привычный способ настройки параметров DHCP сервера через графическую консоль, так и настройку DHCP из командной строки PowerShell.
Протокол DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol) используется для автоматического назначения сетевых настроек (IP адрес, маска подсети, шлюз, DNS сервера и т.д.) устройствам в вашей сети (компьютеры, ноутбуки, сканеры, принтеры и т.д.). Также DHCP сервер позволяет более эффективно использовать адресное пространство, избегать конфликта IP адресов в сети и централизованно управлять сетевыми параметрами на клиентских устройствах.
Содержание:
- Установка роли DHCP сервера в Windows Server 2019/2016
- Настройка DHCP областей в Windows Server
- Резервация IP адресов на DHCP сервере
- Настройка и управление DHCP сервером с помощью PowerShell
Установка роли DHCP сервера в Windows Server 2019/2016
В этом примере мы установим DHCP сервер на хосте с Windows Server 2019 и IP адресом 192.168.13.4. Вы можете использовать как Server Core версию, так и Full GUI. В маленькой инфраструктуре допустимо устанавливать DHCP сервер на сервер с ролью контроллера домена Active Directory.
Обязательно назначьте статический IP адрес серверу с ролью DHCP сервер. При установке роли DHCP из консоли PowerShell на сервере с автоматическим получением IP адреса появляется предупреждение:
Configure at least one static IP address on your computer before installing DHCP. WARNING: The following recommended condition is not met for DHCP: No static IP addresses were found on this computer. If the IP address changes, clients might not be able to contact this server. Please configure a static IP address before installing DHCP Server.
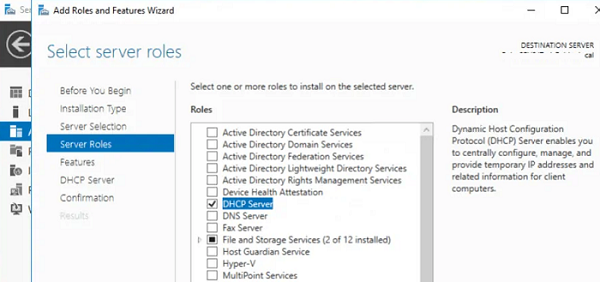
Установить роль DHCP Server можно из консоли Server Manager (Add Roles and Features -> Server Roles).
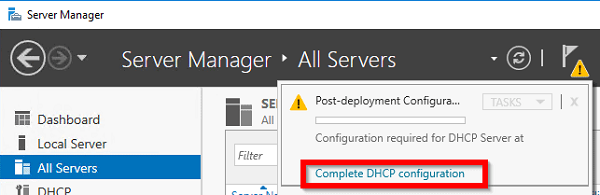
После установки роли DHCP роли нужно выполнить Post-Deployment Configuration. Для этого в консоли Server Manager щелкните по уведомлению и выберите Complete DHCP configuration.
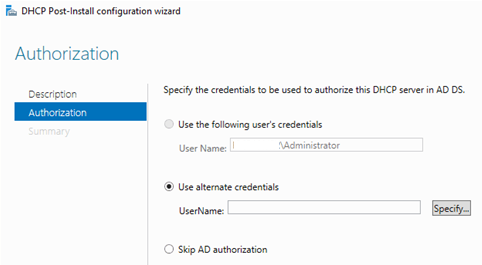
Вам будет предложено аутентифицировать новый DHCP сервер в Active Directory (экран Authorization). Для авторизации DHCP сервера в AD учетная запись должна состоять в доменной группе Enterprise Admins.
Если у вас нет прав на авторизацию DHCP в AD, вы можете указать, чтобы ваш DHCP сервер запускался без проверки авторизации в домене:
Set-ItemProperty -Path "HKLM:SYSTEMCurrentControlSetServicesDHCPServerParameters" -Name DisableRogueDetection -Value 1 -Force
Также вы можете установить и настроить DHCP роль в Windows Server из консоли PowerShell.
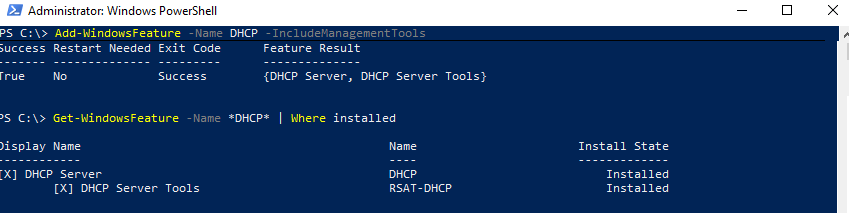
Установка роли DHCP:
Install-WindowsFeature DHCP –IncludeManagementTools
Проверьте, что роль и инструменты управления RSAT-DHCP установлены:
Get-WindowsFeature -Name *DHCP*| Where Installed
Авторизуйте DHCP сервер в Active Directory (укажите DNS имя сервера и IP адрес, который будет использоваться DHCP клиентами):
Add-DhcpServerInDC -DnsName hq-dc01.contoso.com -IPAddress 192.168.13.4
Создайте локальные группы безопасности DHCP сервера:
Add-DhcpServerSecurityGroup
Чтобы Server Manager перестал показывать уведомление о том, что DHCP роль требует настройки, выполните команду:
Set-ItemProperty -Path HKLM:SOFTWAREMicrosoftServerManagerRoles12 -Name ConfigurationState -Value 2
Перезапустите службу DHCPServer:
Restart-Service -Name DHCPServer -Force
База данных и логи DHCP сервера находятся в каталоге
%systemroot%system32dhcp
.
- dhcp.mdb — файл базы данных сервера DHCP’;
- j50.log – транзакционный журнал (используется при восстановлении конфигурации DHCP);
- j50.chk — файл контрольной точки;
- tmp.edb — временный рабочий файл DHCP-сервера.
Настройка DHCP областей в Windows Server
После установки роли DHCP вам нужно создать DHCP области (Scopes), которые описывают диапазоны IP адресов и другие настройки, выдающиеся сервером клиентам.
Для управления сервером DHCP используется консоль dhcpmgmt.msc (вы можете управлять DHCP сервером локально или с удаленного компьютера с установленным RSAT). Запустите консоль DHCP, разверните ваш сервер -> IPv4.
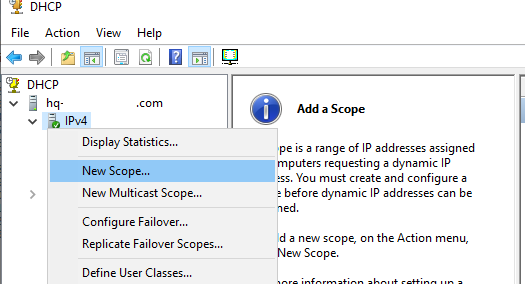
Чтобы создать новую область выберите New Scope.
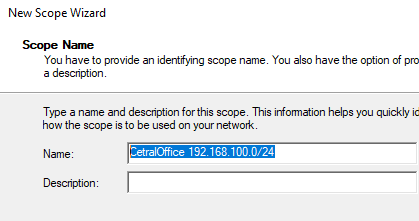
Укажите название DHCP области.
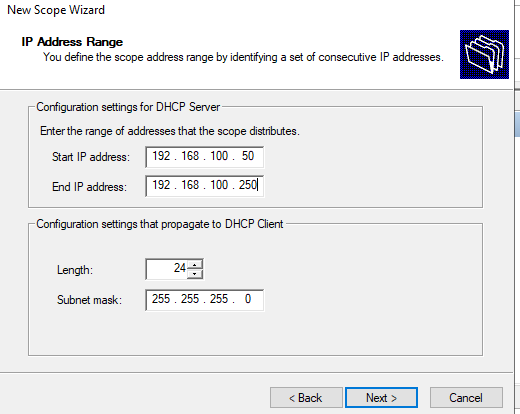
Укажите диапазон IP адресов, который будет выдаваться этой областью и маску сети. В этом примере я хочу использовать эту DHCP область для обслуживания подсети 192.168.100.0/24. В рамках этой сети DHCP сервером будет назначаться динамические IP адреса из диапазона 192.168.100.50 — 192.168.100.250. В следующем окне можно добавить исключения в этот диапазон (Add Exclusions and Delay).
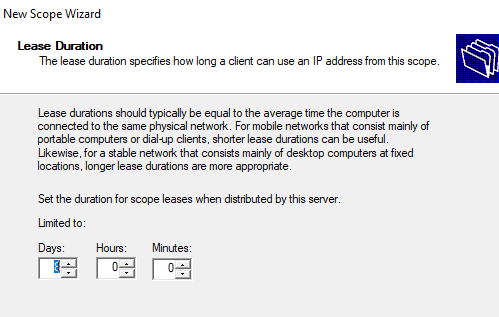
Далее нужно указать длительность аренды (Lease Duration) IP адреса DHCP клиентом (по умолчанию 8 дней, менять без особой необходимости не нужно).
Укажите, что вы хотите настроить дополнительный параметры DHCP области.
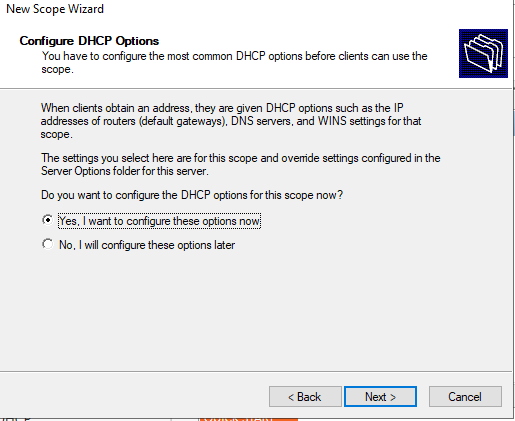
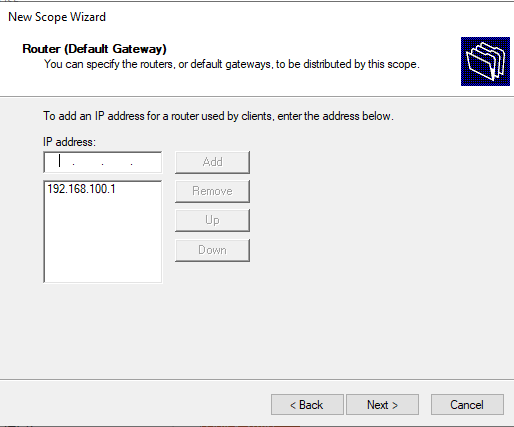
Укажите IP адрес шлюза в подсети, который должен назначаться клиентам (в нашем примере это 192.168.100.1).
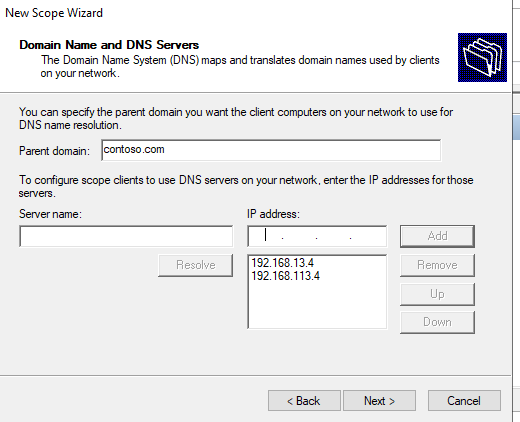
Затем укажите имя домена и адреса DNS серверов, которые будут назначены клиентам DHCP.
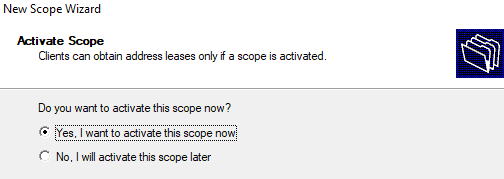
Осталось активировать DHCP область (разрешить ей обслуживать клиентов).
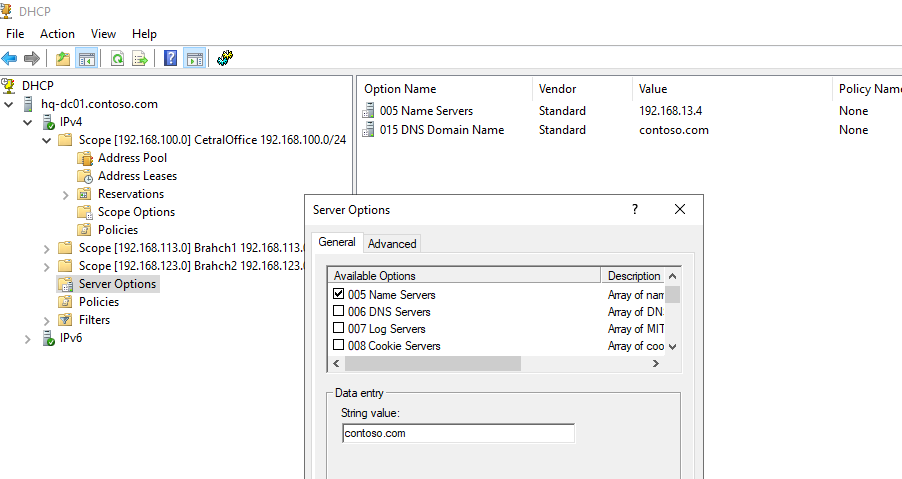
DHCP сервер может выдавать клиентам различный настройки (кроме IP адреса). Для этого используются Scope Options.
В Windows Server DHCP можно настроить глобальные настройки области или Scope Options для каждой области.
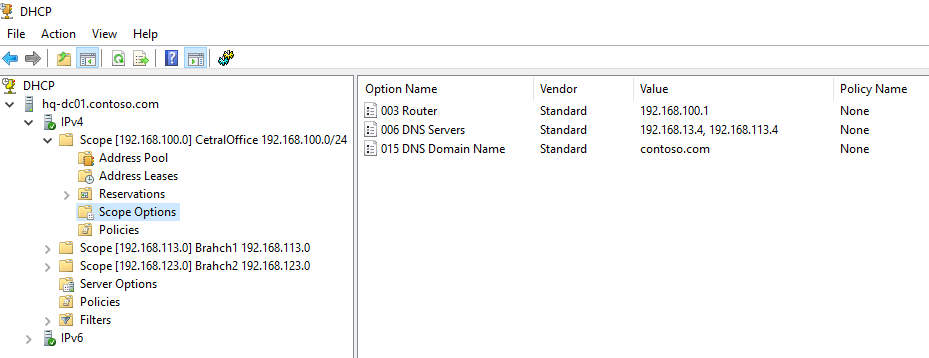
Ранее мы уже настроили три опции области:
-
003 Router -
006 DNS Server -
015 DNS Domain Name
Можно добавить и другие опции (NTP сервера, PXE и т.д.).
В разделе Server Options DHCP сервера можно настроить глобальные опции, которые будут наследуются всеми областями. Но вы можете переопределить глобальные настройки в настройках каждой области (опции области имеют приоритет над опциями сервера).
Один DHCP сервер может обслуживать сотни удаленных подсетей и VLAN. Поэтому вы можете создать на нем несколько областей. Главное, чтобы в каждой из подсетей был настроен ретранслятор (DHCP relay agent), который пересылает широковещательные DHCP-запросы на указанный DHCP сервер. В терминах Cisco DHCP ретранслятор называется ip helper. Вы можете настроить DHCP Relay даже на Windows Server.
Протокол DHCP в качестве транспорта использует протокол UDP. Пакеты от клиента к серверу передаются по порту 67 UDP, обратно через UDP 68
Резервация IP адресов на DHCP сервере
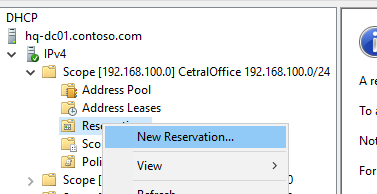
По умолчанию DCHP сервер выдает клиентам динамические адреса. Это означает что IP адрес у любого клиента может меняться. Если вы хотите, чтобы определенные устройства всегда получали от DHCP сервера один и тот же адрес, вы можете его зарезервировать (например, для сетевых принтеров, которые настроены у пользователей).
Для DHCP резервации выберите область и перейдите в секции Reservation. В меню выберите New Reservation.
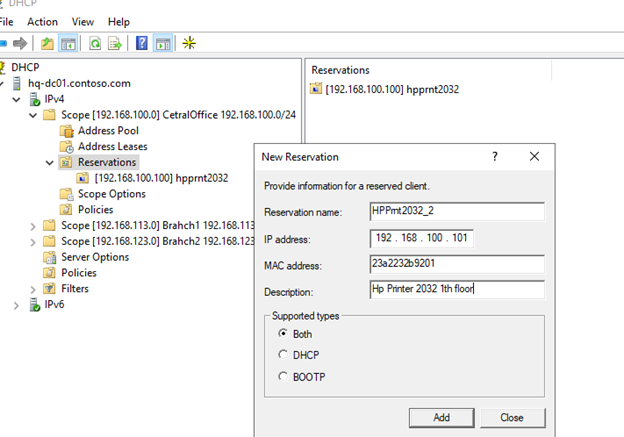
При создании резервации нужно указать IP адрес, который нужно сохранить за клиентом и его MAC адрес (уникальное значение). MAC адрес в Windows можно получить из результатов команды
ipconfig /all
или с помощью PowerShell
get-netadapter|select name,macaddress
). Опционально можно указать имя и описание устройства.
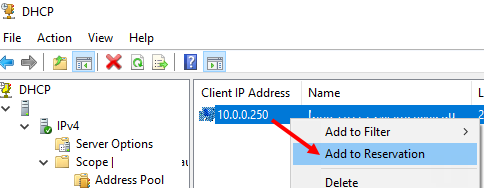
Также вы можете зарезервировать текущий динамический адрес за устройством, найдя его в разделе Address Leases. Щелкните по устройству и выберите Add to Reservation.
Настройка и управление DHCP сервером с помощью PowerShell
Все операции по настройке и управлению DHCP сервером на Windows Server 2019/2016 можно выполнять из консоли PowerShell. Рассмотрим основные команды управления DHCP. Для этого используется модуль DHCPServer. Импортируйте модуль в сессию:
Import-Module DHCPServer
Вывести полный список командлетов в моделе DHCP можно так:
Get-Command -Module DHCPServer
Следующая команда выведет список авторизованных DHCP серверов в Active Directory:
Get-DhcpServerInDC
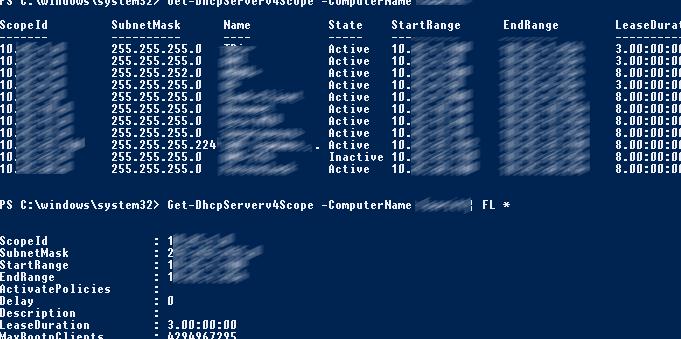
Вывести список DHCP областей на указанном сервере:
Get-DhcpServerv4Scope –ComputerName msk-dhcp1
Если нужно показать все параметры области (Delay, Description, Name и т.д.):
Get-DhcpServerv4Scope –ComputerName msk-dhcp1| FL *
Если нужно отобразить данные о IPv6 областях:
Get-DHCPServerv6Scope
Получить настройки для конкретной области:
Get-DhcpServerv4Scope –ComputerName msk-dhcp1 –ScopeID 10.10.1.0
Создадим новую (неактивную) область с диапазоном адресов с 192.168.113.50 до 192.168.113.250:
Add-DhcpServerv4Scope -Name “Brahch1 192.168.113.0” -StartRange 192.168.113.50 -EndRange 192.168.113.250 -SubnetMask 255.255.255.0 -State InActive
Настроить следующие параметры DHCP сервера: DNS сервер, домен и адрес шлюза по-умолчанию:
Set-DhcpServerv4OptionValue -ScopeID 192.168.113.0 -DnsDomain contoso.com -DnsServer 192.168.13.4 -Router 192.168.113.1
Добавить исключения в DHCP область:
Add-DhcpServerv4ExclusionRange -ScopeID 192.168.113.0 -StartRange 192.168.113.90 -EndRange 192.168.113.100
Активировать DHCP область:
Set-DhcpServerv4Scope -ScopeID 192.168.113.0 -State Active
Для удобства можно использовать такую команду PowerShell при создании новой области:
$HashArgs = @{
'Name' = 'EKB Office Scope';
'Description' = 'workstations';
'StartRange' = '192.168.140.10';
'EndRange' = '192.168.140.200';
'SubnetMask' = '255.255.255.0';
'State' = 'Active';
'LeaseDuration' = '1.00:00:00';
}
Add-DhcpServerv4Scope @HashArgs
Опции для DHCP сервера добавляется так (к примеру, WPAD):
Add-DhcpServerv4OptionDefinition -ComputerName msk-dhcp1 -Name WPAD -OptionId 252 -Type String
Вывести список настроенных опций DHCP сервера можно так:
Get-DHCPServerv4OptionValue -ComputerName msk-dhcp1 | Format-List
Выведем список настроенных параметров зоны:
Get-DHCPServerv4OptionValue -ComputerName msk-dhcp1 -ScopeId 10.10.1.0 | Format-List
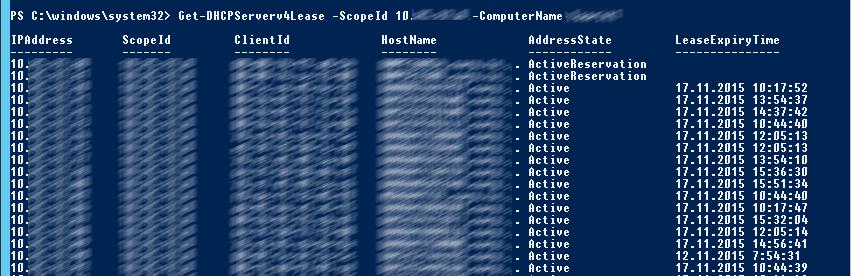
Показать текущий список арендованных адресов для области 10.10.1.0:
Get-DHCPServerv4Lease -ScopeId 10.10.1.0 -ComputerName msk-dhcp1
Создать DHCP резервацию для клиента, которому назначен динамический IP адрес 10.10.1.88 (конвертировать выданный адрес в зарезервированный):
Get-DhcpServerv4Lease -ComputerName msk-dhcp1 -IPAddress 10.10.1.88| Add-DhcpServerv4Reservation -ComputerName msk-dhcp1
Можно массово зарезервировать IP адреса для компьютеров по списку из csv файла. Для этого создайте текстовый файл в формате:
ScopeId,IPAddress,Name,ClientId,Description 10.10.1.0,10.10.1.88,Client1,ba-ab-5c-3d-4e-6f,Reservation PC-msk-s1 10.10.1.0,10.10.1.89,Client2,ba-ab-5c-5d-2e-3f,Reservation PC-msk-s2
Сохраните файл с именем
c:dhcpDHCPReservations.csv
и запустите следующую команду, которая импортирует данные из csv файла и создаст DHCP резервации для клиентов:
Import-Csv –Path c:dhcpDHCPReservations.csv | Add-DhcpServerv4Reservation -ComputerName msk-dhcp1
Отключить область на DHCP сервере:
Set-DhcpServerv4Scope -ComputerName msk-dhcp1-ScopeId 10.10.1.0-State InActive
Удалить область с DHCP сервера:
Remove-DHCPServerv4Scope -ComputerName msk-dhcp1-ScopeId 10.10.1.0 -Force
Возможно получить статистику DHCP сервера (количество областей, резерваций, процент использования адресов и пр.).
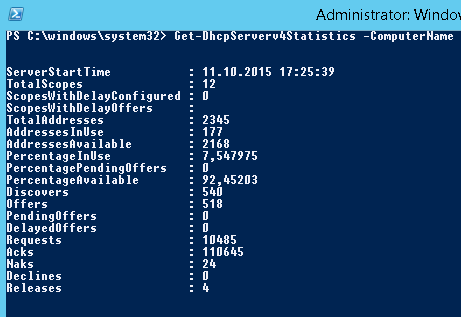
Get-DhcpServerv4Statistics -ComputerName msk-dhcp1
Аналогичная информация для конкретной области может быть получена с помощью командлета Get-DhcpServerv4ScopeStatistics.
Конфигурацию DHCP сервера можно экспортировать в указанный XML файл с помощью команды:
Export-DHCPServer -ComputerName msk-dhcp1 -File C:dhcpdhcp-export.xml
Совет. Заданием с такой командой в планировщике задач можно реализовать регулярное резервное копирование конфигурации DHCP сервера.
В дальнейшем эти настройки DHCP сервера можно импортировать (перенести) на другой DHCP сервер:
Import-DHCPServer -ComputerName msk-dhcp2 -File C:dhcpdhcp-export.xml -BackupPath C:dhcpbackup
CharlesHTN
This person is a verified professional.
Verify your account
to enable IT peers to see that you are a professional.
datil
General Networking Expert
-
check
31
Best Answers -
thumb_up
144
Helpful Votes -
format_list_bulleted
1
How-to
Is your HP 2920 switch doing the routing? If so, like others mentioned, you need a IP Helper statement on VLAN 2, which will tell the switch where to send DHCP request packets for clients.
I’m not sure exactly how to put that in from the GUI, but from the CLI, you would do:
- config t
- vlan 2
- ip helper-address w.x.y.z
- exit
- exit
Don’t forget to save changes afterwards (AFTER testing and verifying you didn’t break things!!!). From the CLI, you can just «write memory», or «wr mem» for short.
Of course, w.x.y.z would be the IP of whatever device is acting as the DHCP server. Note that the IP Helper statement is only needed if the DHCP server is on a different subnet/vlan. You could place a DHCP server directly on that VLAN, and then you wouldn’t need the IP Helper setting.
As others have mentioned, using the Windows Server to provide DHCP/DNS services to your guest network is probably a bad idea. Personally, I let my firewall handle DHCP on my Guest networks, and have it point clients to Goooooooooogle DNS. My Windows Servers handle DHCP/DNS for everything internal.
1 found this helpful
thumb_up
thumb_down
И снова о DHCP. В предыдущей статье мы рассмотрели базовые принципы работы этого протокола. Сегодня перейдем к практике и настроим DHCP-сервер на базе Windows Server 2016.
Служба DHCP входит в состав Windows Server и является одной из серверных ролей, поэтому первое, что нам надо сделать — эту роль установить.
Установка
Открываем оснастку Server Manager, запускаем мастер добавления ролей и компонентов (Add Roles and Features Wizard) и выбираем тип установки «Role-based or feature-based installation».
Указываем сервер, на котором будет производиться установка.
В разделе «Server Roles» отмечаем отмечаем для установки пункт «DHCP Server».
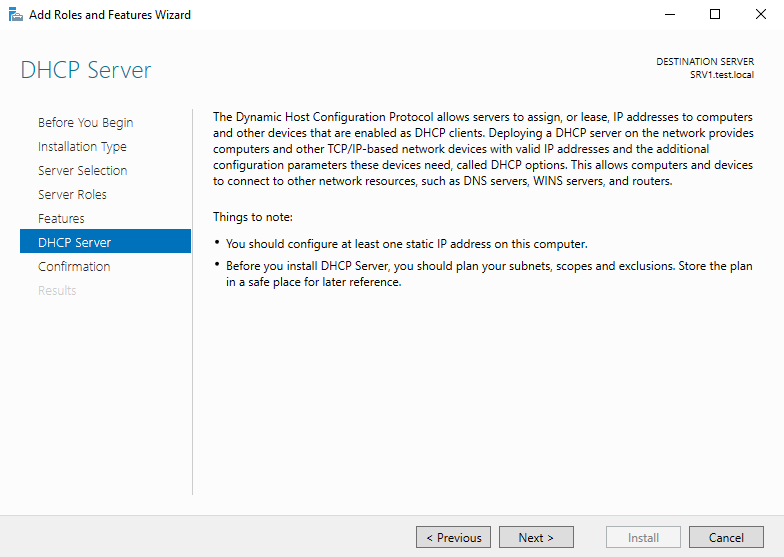
В процессе установки мастер напомнит о необходимости заранее спланировать структуру сети, а также о том, что для работы DHCP на сервере должен быть хотя бы один статический IP адрес.
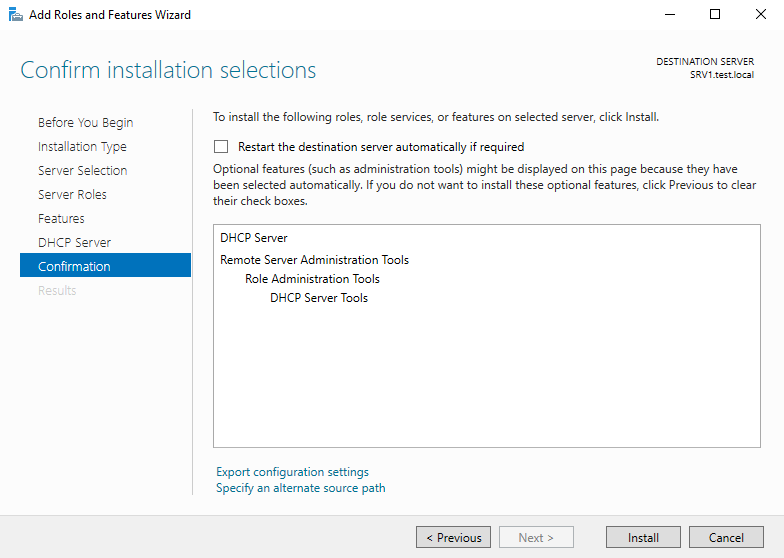
Проверяем список устанавливаемых компонентов и и запускаем установку.
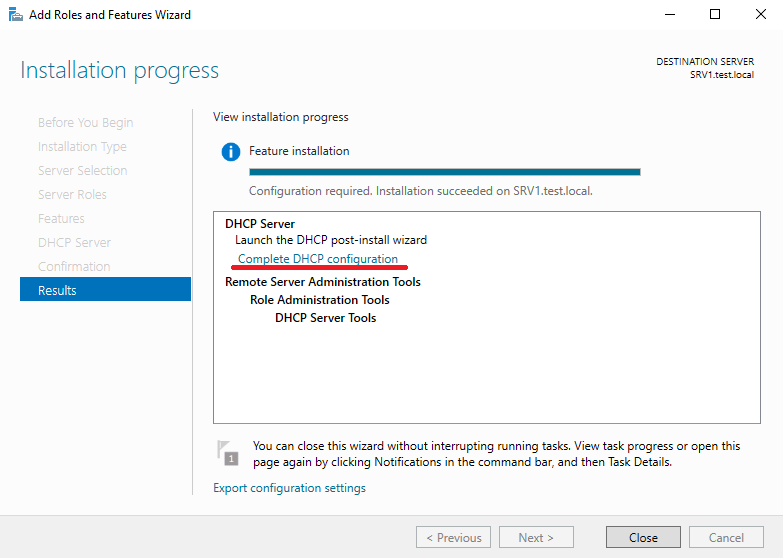
По завершении установки не надо сразу закрывать окно мастера, поскольку в нем будет предложено произвести первоначальную настройку DHCP. Для этого надо кликнуть по ссылке «Complete DHCP configuration».
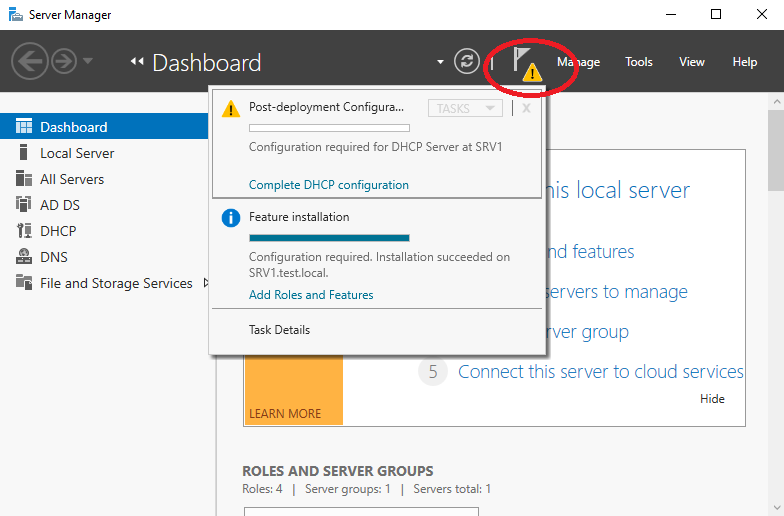
Если же вы поторопились и закрыли окно, то найти ссылку можно в главном окне Server Manager, кликнув на значок уведомления.
Переход по ссылке запускает еще один мастер первоначальной настройки DHCP (DHCP Post-Install configuration wizard). В процессе первоначальной настройки производится два действия:
1. Создание групп безопасности, которым будет разрешено управлять данным DHCP сервером. Всего создаются 2 группы:
DHCP Administrators — члены этой группы имеют полные права на DHCP сервер и могут изменять его настройки;
DHCP Users — членам этой группы даны права только на чтение. Они могут просматривать текущие настройки DHCP и статистику подключений.
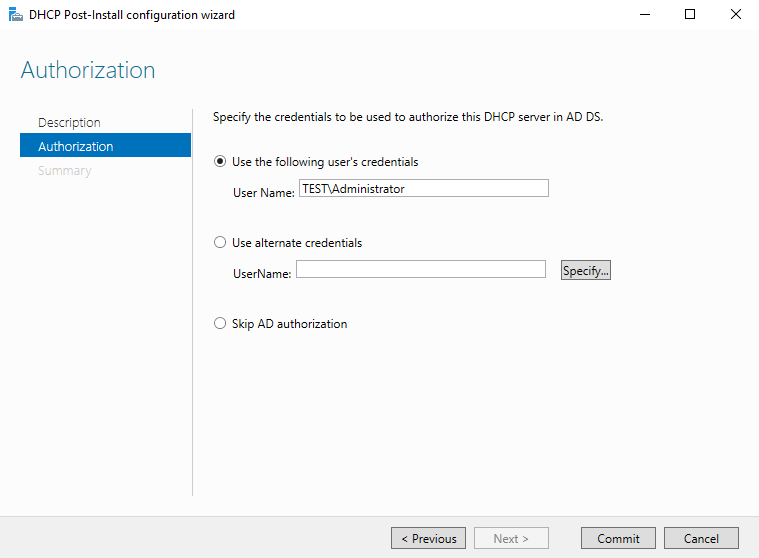
2. Авторизация DHCP сервера в домене Active Directory. Авторизация необходима для того, чтобы предотвратить появление в сети ″левых″ DHCP серверов. Если сервер является членом домена, то при запуске служба DHCP обращается к AD для того, чтобы просмотреть список авторизованных серверов. Если она не обнаруживает в списке свой адрес, то считает себя неавторизованной и останавливает работу. Таким образом, пока сервер не пройдет авторизацию, служба DHCP на нем просто не запустится.
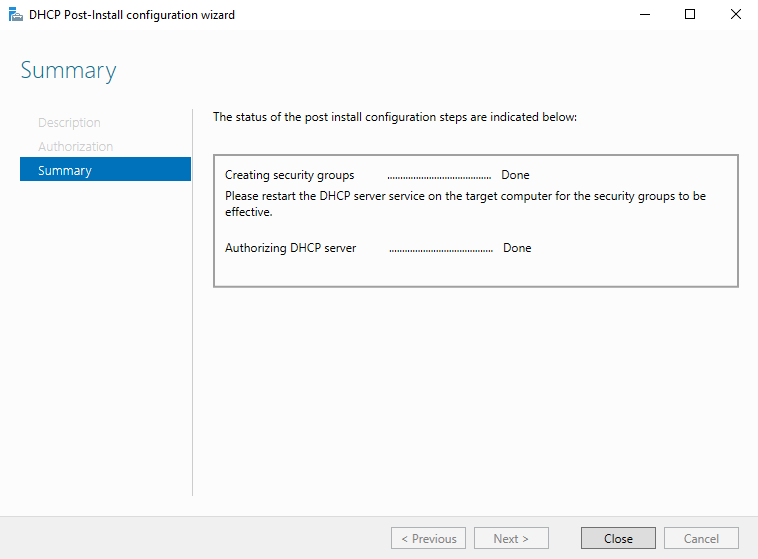
Сама процедура настройки заключается в том, чтобы указать учетные данные пользователя, от имени которого будет производится настройка, нажать кнопку «Commit»
и дождаться завершения процесса.
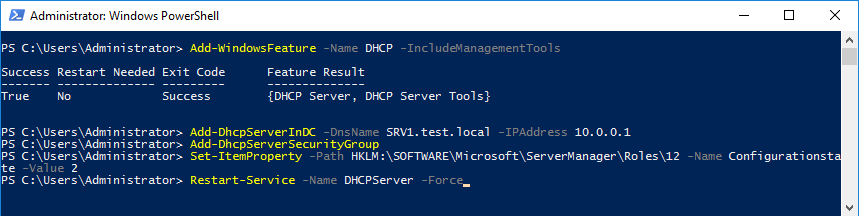
Все то же самое можно сделать с помощью PowerShell, нужно выполнить всего несколько команд. Установка роли DHCP:
Add-WindowsFeature -Name DHCP -IncludeManagementTools
Авторизация в AD. Здесь указываем DNS-имя сервера и IP-адрес, с которого он будет обслуживать клиентов:
Add-DhcpServerInDC -DnsName SRV1.test.local -IPAddress 10.0.0.1
Создание групп безопасности:
Add-DhcpSecurityGroup
Изменение состояния конфигурации сервера. Без этого он считается несконфигурированным и Server Manager будет постоянно выдавать предупреждение о необходимости настройки:
Set-ItemProperty -Path HKLM:SOFTWAREMicrosoftServerManagerRoles12 -Name ConfigurationState -Value 2
Ну и в завершение необходимо рестартовать службу DHCP:
Restart-Service -Name DHCPServer -Force
Примечание. По умолчанию авторизовывать DHCP сервера в AD имеют право только члены группы Администраторы предприятия (Enterprise Admins). Поэтому пользователь, от имени которого производится настройка, должен входить в группу Enterprise Admins, иначе будет выдана ошибка с отказом в доступе.
Настройка
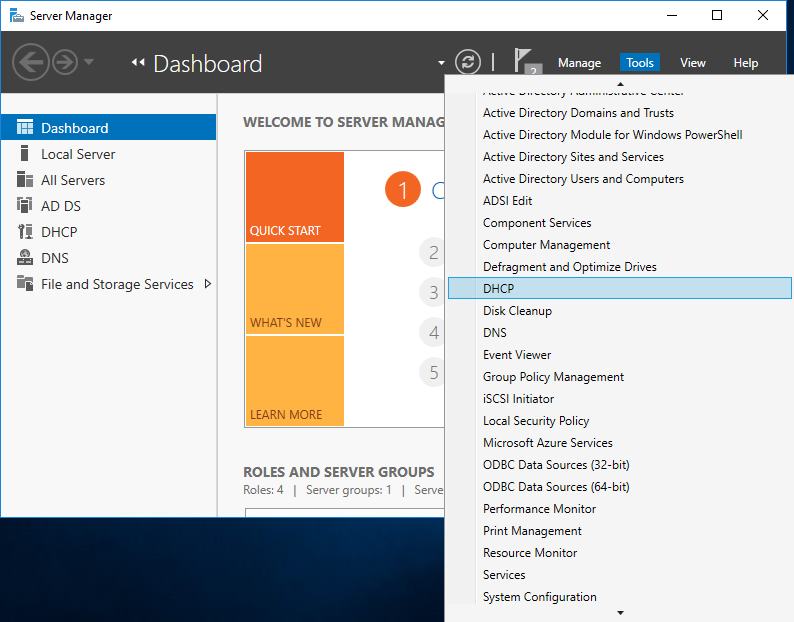
Для настройки сервера нам понадобится оснастка DHCP. Запустить ее можно из меню «Tools» в Server Manager, либо нажав клавиши Win+R и выполнив команду dhcpmgmt.msc.
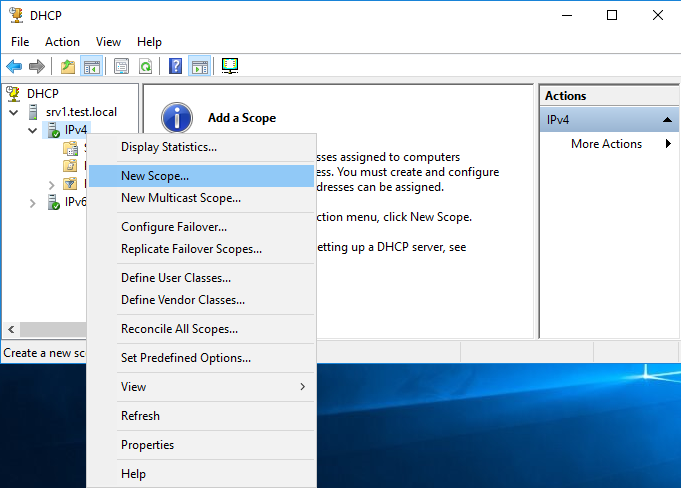
Первым делом нам надо создать область (Scope) — диапазон IP-адресов, которые будут выдаваться клиентам. Поскольку наш DHCP-сервер будет выдавать только IPv4 адреса, то переходим к разделу IPv4, кликаем по нему правой клавишей мыши и в открывшемся меню выбираем пункт «New Scope».
Запускается очередной мастер.
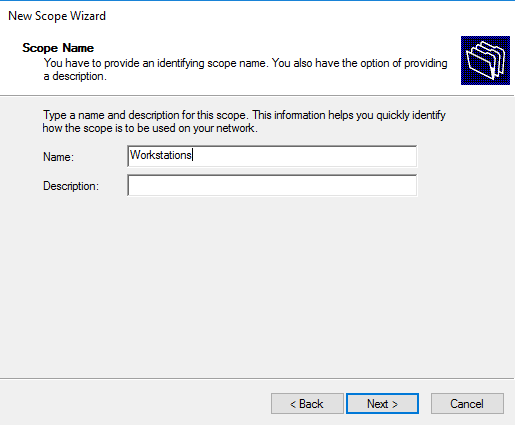
Задаем имя области и, при необходимости, ее описание.
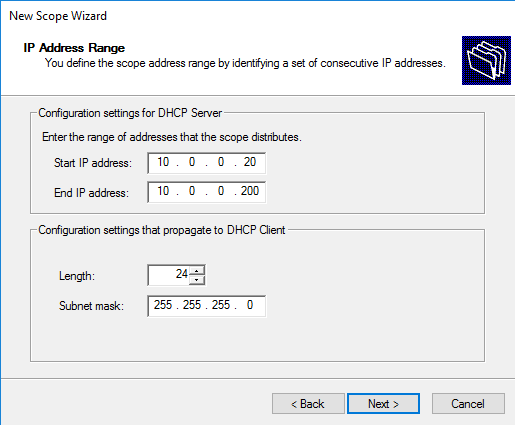
Затем указываем диапазон IP адресов и префиксмаску подсети. На всякий случай напомню, что маска определяет возможное количество адресов в сети, например сеть с префиксом 24 содержит 254 адреса. Кстати, вовсе не обязательно выделять под область все имеющиеся адреса, можно оставить десяток-другой на всякий случай, например для серверов или сетевых устройств.
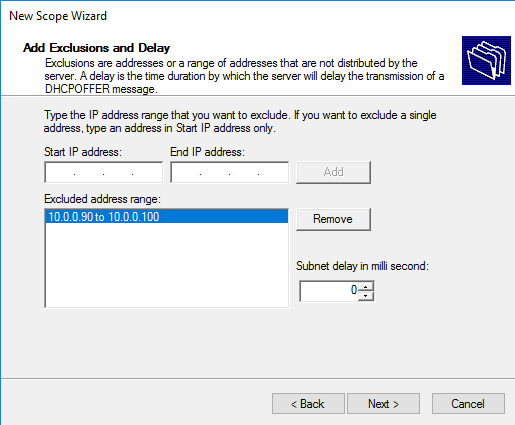
При необходимости можно исключить один или несколько IP-адресов из создаваемой области, добавив их в исключения (Exclusions). Исключения могут потребоваться в том случае, если в указанной подсети уже имеются адреса, выданные вручную.
Здесь же можно задать задержку ответа DHCP-сервера — количество миллисекунд, которое выжидает сервер перед тем, как ответить на запрос клиента.
Примечание. В DHCP существует понятие раздельной области, когда одна область разбита на две части (обычно в соотношении 80/20) и обслуживается двумя DHCP-серверами. Такая конфигурация нужна для того, чтобы в случае недоступности первого сервера второй продолжал выдачу адресов из данной области. Но поскольку необходимо, чтобы все запросы по возможности обслуживал первый (основной) сервер, на втором выставляется задержка, чтобы он не смог ответить раньше первого.
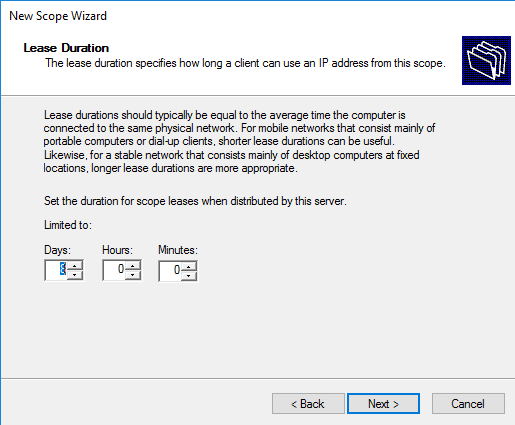
На следующем шаге указываем время аренды (Lease Duration) — срок, на который клиенту выдается IP адрес. Выбор этого параметра напрямую зависит от особенностей обслуживаемой сети, так при наличии большого числа часто меняющихся клиентов (напр. публичная сеть) время аренды нужно сделать поменьше, а если сеть статична и редко изменяется (сеть предприятия), то время аренды можно увеличить. По умолчанию в Windows установлено 8 дней.
Теперь перейдем к настройке дополнительных параметров области.
Сначала указываем адрес шлюза по умолчанию (Default Gateway).
Затем вводим имя домена и добавляем DNS-сервера. Для добавления можно указать имя сервера и нажать «Resolve», либо указать IP адрес.
По аналогии с DNS можно добавить WINS сервера, если конечно они у вас есть.
Можем сразу активировать область, либо отложить это действие.
На этом настройка DHCP сервера завершена, остается только проверить работу сервера.
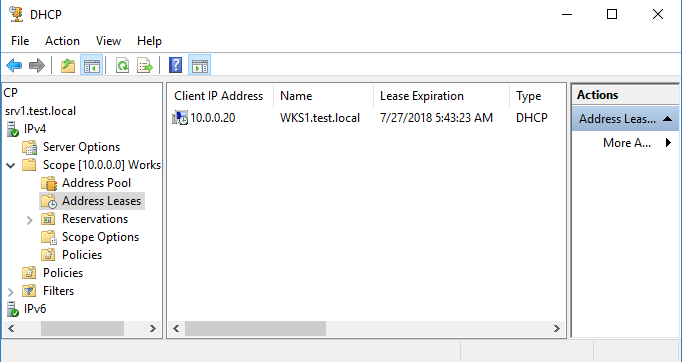
Посмотреть клиентов, получивших адреса из данной области, можно в разделе «Address Leases». В моей тестовой сети есть всего один клиент, который успешно получил свой IP адрес.
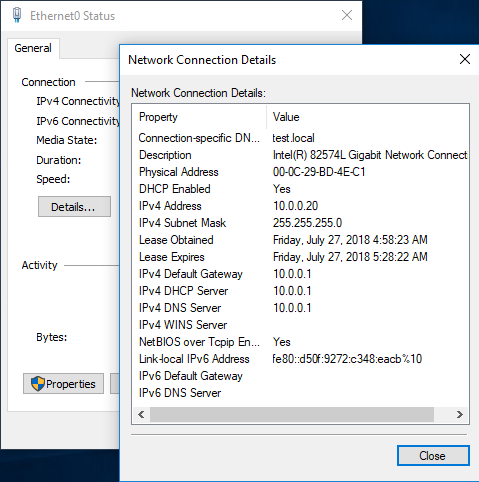
Ну и на всякий случай зайдем на клиента и проверим, что он успешно получил свой адрес.
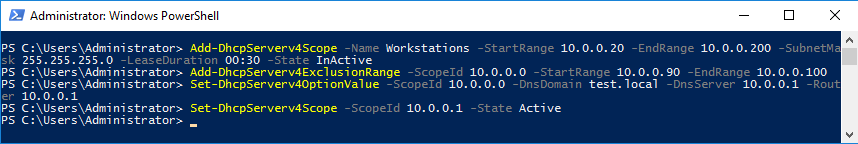
Все настройки можно произвести с помощью PowerShell. Cоздаем область (неактивную):
Add-DhcpServerv4Scope -Name Workstations -StartRange 10.0.0.20 -EndRange 10.0.0.200 -SubnetMask 255.255.255.0 -LeaseDuration 00:30 -State InActive
Добавляем исключения:
Add-DhcpServerv4ExclusionRange -ScopeID 10.0.0.0 -StartRange 10.0.0.90 -EndRange 10.0.0.100
Добавляем доп. опции (DNS, gateway и т.п.):
Set-DhcpServerv4OptionValue -ScopeID 10.0.0.0 -DnsDomain test.local -DnsServer 10.0.0.1 -Router 10.0.0.1
И активируем область:
Set-DhcpServerv4Scope -ScopeID 10.0.0.0 -State Active
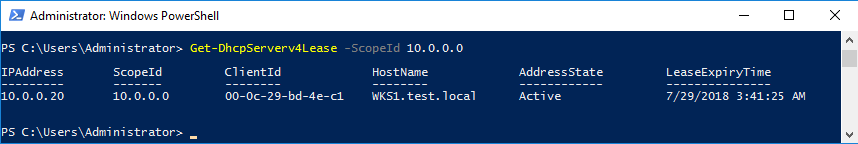
Посмотреть список клиентов можно также из консоли, командой:
Get-DhcpServerv4Lease -ScopeID 10.0.0.0
Стоит уточнить, что хотя в статье использовался Windows Server 2016, настройка для Windows Server 2008-2012 ничем особо не отличается.
На этом все, на сегодня. А в следующей статье мы рассмотрим развертывание двух DHCP-серверов в отказоустойчивой конфигурации.