SNMP (
Simple Network Management Protocol
) — это классический протокол для мониторинга и сбора информации о сетевых устройствах (сервера, сетевое оборудование, рабочие станции, принтеры и т.д.). Протокол SNMP довольно легкий, быстрый, для передачи данных использует UDP порты 161 и 162. В этой статье мы рассмотрим, как установить и настроить службу SNMP в Windows Server 2022/2019 и Windows 10/11.
Содержание:
- Установка службы SNMP в Windows Server 2022/2019
- Установка SNMP агента в Windows Server Core
- Установка службы SNMP в Windows 10/11
- Настройка службы SNMP в Windows Server и Windows 10/11
Установка службы SNMP в Windows Server 2022/2019
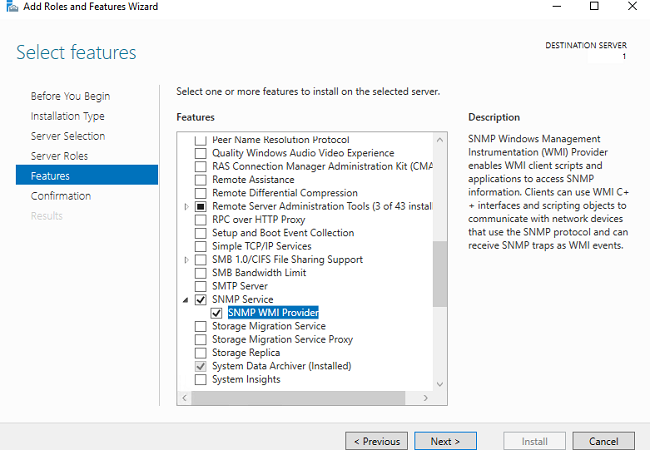
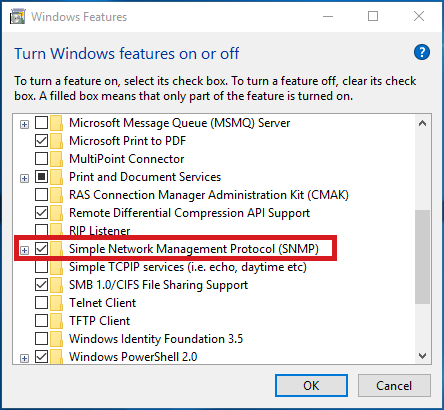
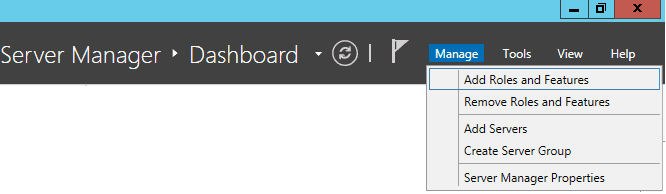
В Windows Server службу SNMP можно установить с помощью Server Manager.
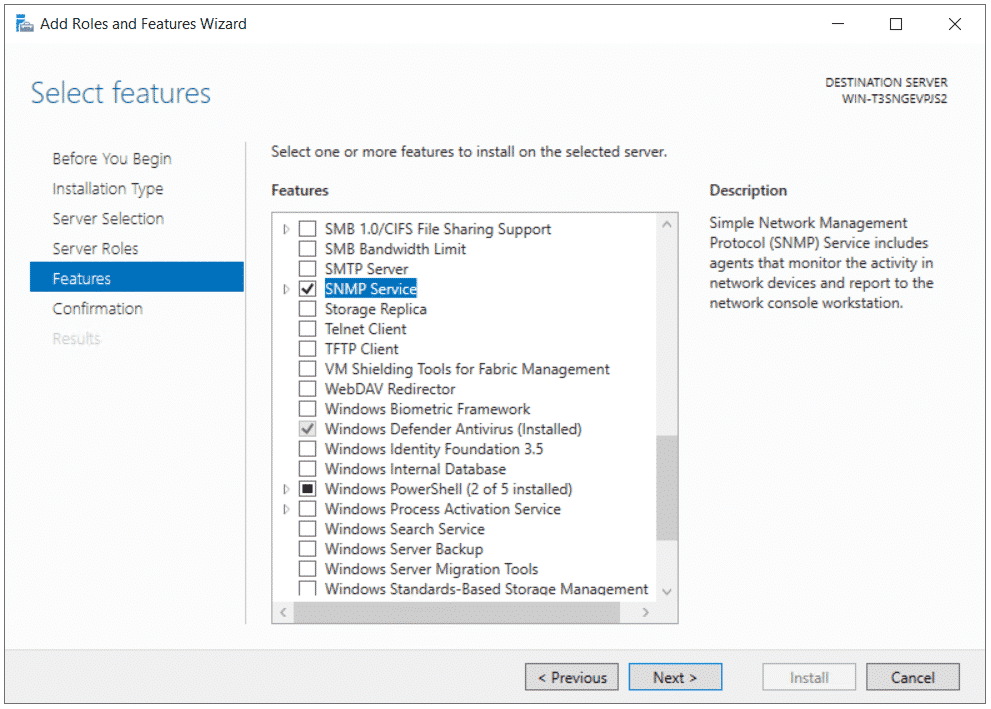
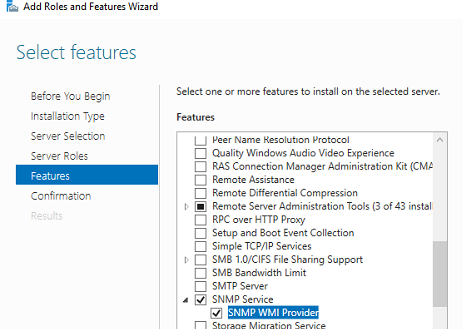
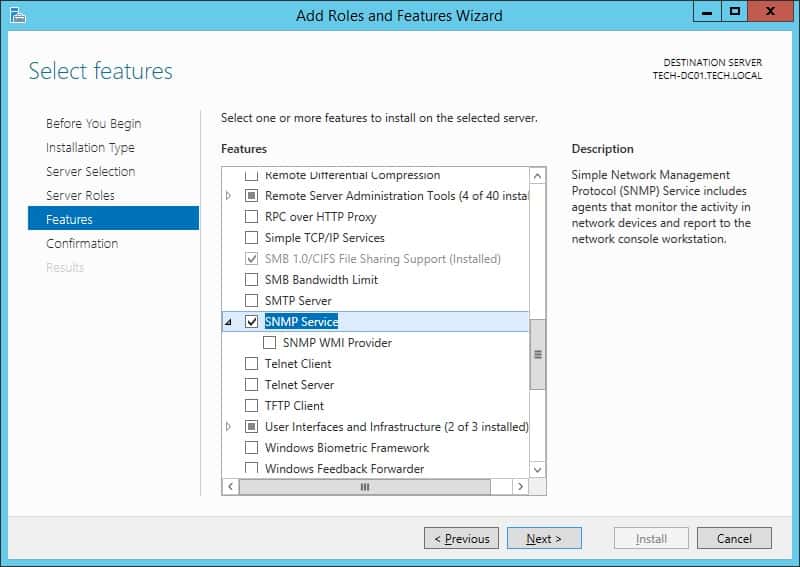
Выберите Add roles and features -> Features. Выберите SNMP Service (если нужно отметьте также SNMP WMI Providers).
Служба SNMP WMI Provider позволяет опрашивать SNMP устройство через WMI.
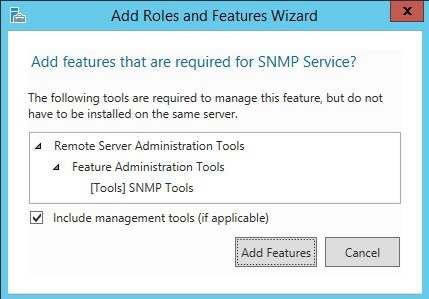
Нажмите Next -> Install и дождитесь окончания установки.
Установка SNMP агента в Windows Server Core
В Windows Server Core можно установить SNMP с помощью веб-интерфеса Windows Admin Center и PowerShell.
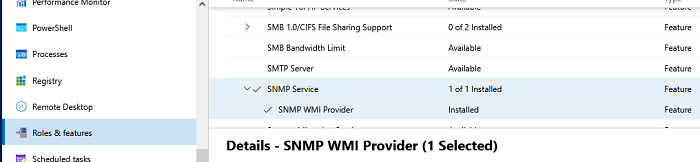
Если вы используете Windows Admin Center, подключитесь к хосту Windows Server, выберите Roles and Features -> SNMP Service.
Т.к. в Windows Server Core отсутствует графический интерфейс, а для его управления используется командная строка, вы можете установить службу SNMP из командной строки PowerShell.
Для установки ролей в Windows Server из PowerShell используется командлет Install-WindowsFeature.
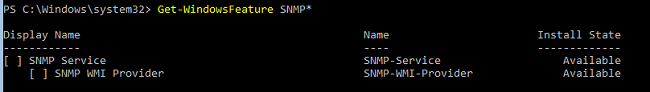
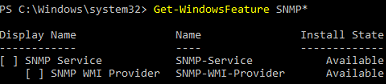
Проверьте, что служба SNMP не установлена:
Get-WindowsFeature SNMP*
Установите роль SNMP и WMI провайдер:
Install-WindowsFeature SNMP-Service,SNMP-WMI-Provider -IncludeManagementTools
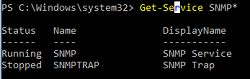
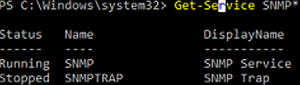
Проверьте, что службы SNMP запущены:
Get-Service SNMP*
В нашем примере SNMP служба запущена, а SNMPTRAP остановлена.
Установка службы SNMP в Windows 10/11
Вы можете использовать службу SNMP не только в Windows Server, но и в десктопных редакциях Windows 10 и 11.
В Windows 10/11 служба SNMP, вынесена в отдельный компонент Feature On Demand (как RSAT и OpenSSH).
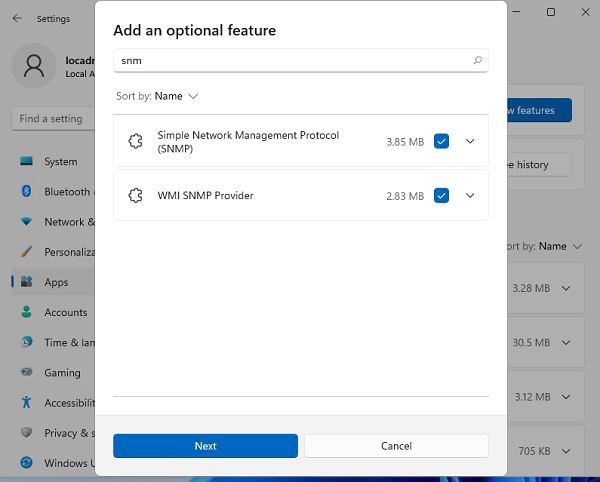
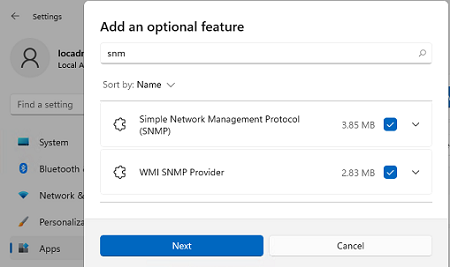
Вы можете установить SNMP через панель Settings. Перейдите в Apps -> Optional features -> Add an optional feature -> View features.
В списке доступных компонентов выберите Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) и WMI SNMP Provider. Для начала установки нажмите Next (понадобится интернет подключение к серверам Microsoft).
Для установки службы SNMP через PowerShell, используйте команду:
Add-WindowsCapability -Online -Name SNMP.Client~~~~0.0.1.0
Для установки службы SNMP без подключения к интернету, вам понадобится скачать ISO образ Windows 10/11 Features on Demand из личного кабинета на сайте лицензирования Volume Licensing Service Center (VLSC).
Для офлайн установки службы SNMP с такого ISO образа используется команда:
Add-WindowsCapability -Online -Name SNMP.Client~~~~0.0.1.0 -LimitAccess -Source \msk-fs01DistrWindows-FODWin11
Настройка службы SNMP в Windows Server и Windows 10/11
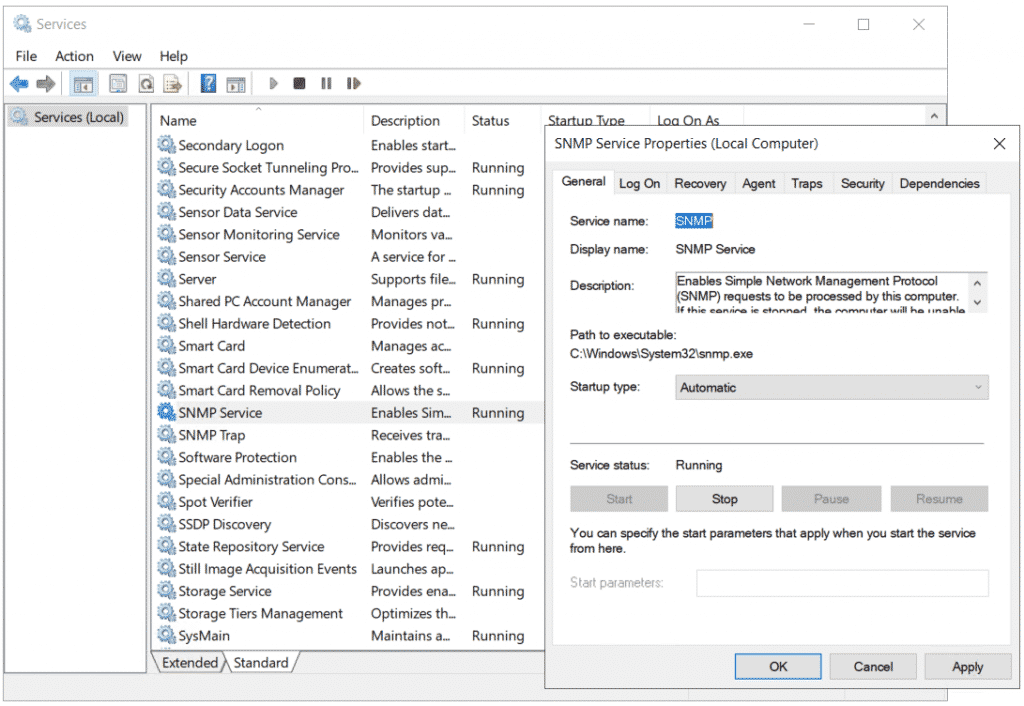
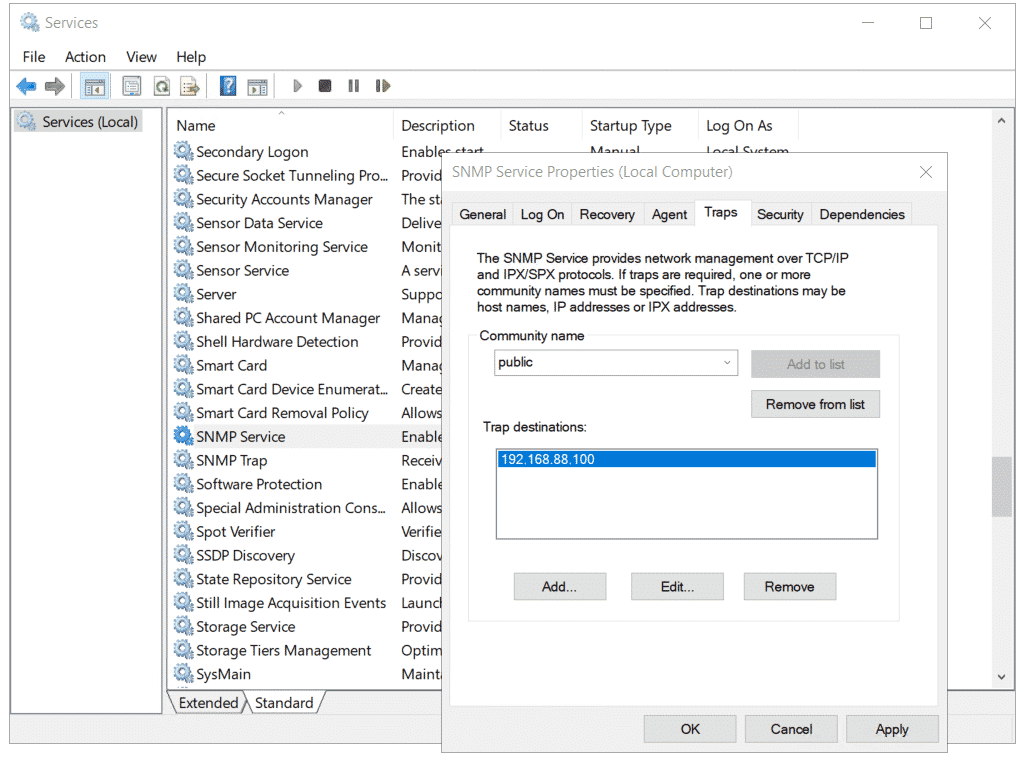
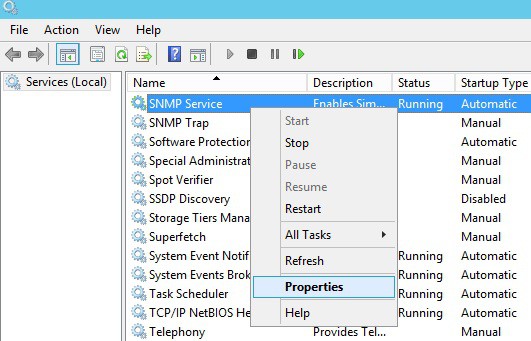
Вы можете настроить параметры службы SNMP в консоли services.msc. Найдите службу SNMP Services в списке и откройте ее свойства.
Обратите внимание, что у службы SNMP есть несколько дополнительных вкладок:
- Agent
- Traps
- Security
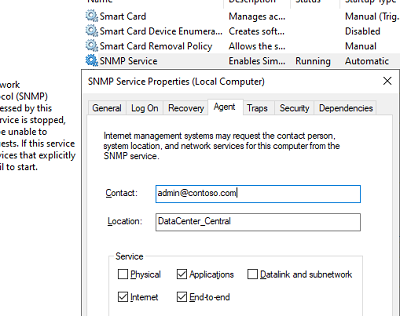
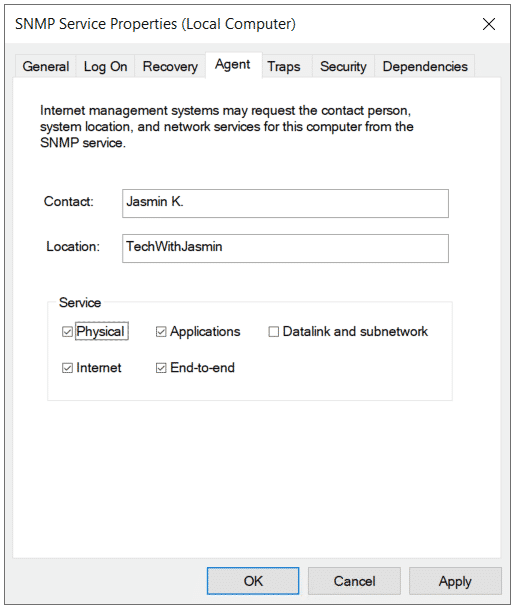
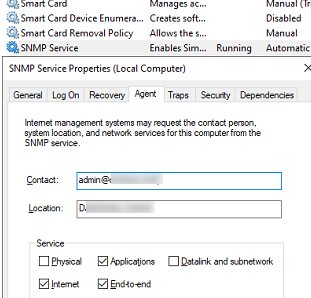
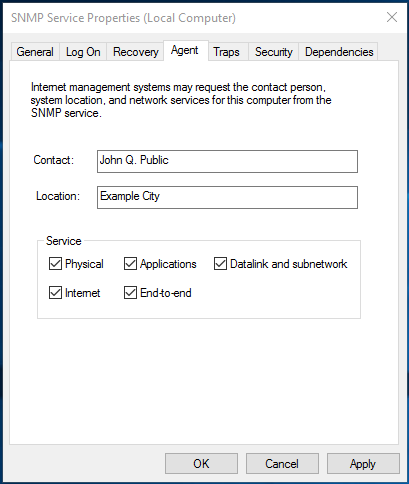
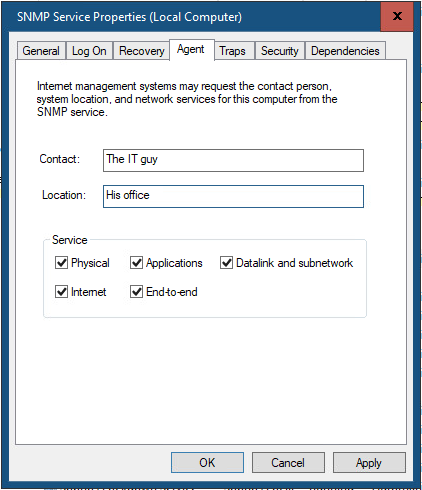
На вкладке Agent указывается базовая информация об устройстве (контакты администратора, местоположение). Здесь же можно указать тип информации, который может отправлять данное устройство при SNMP опросе.
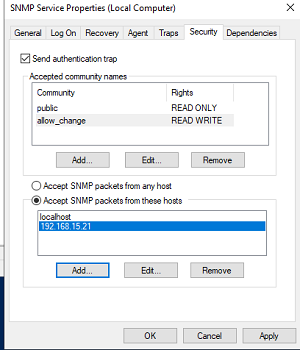
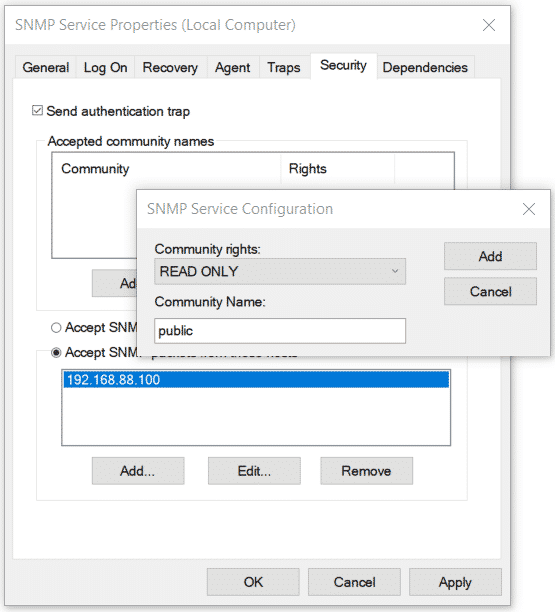
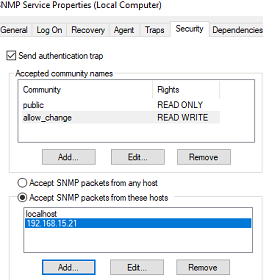
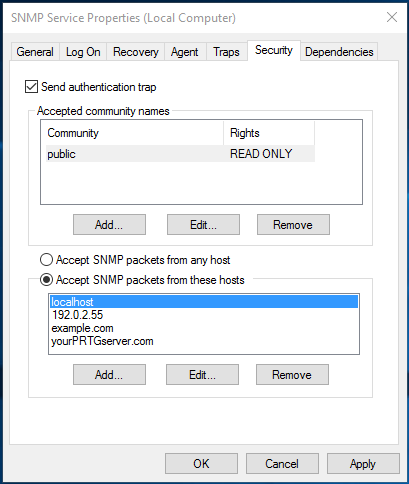
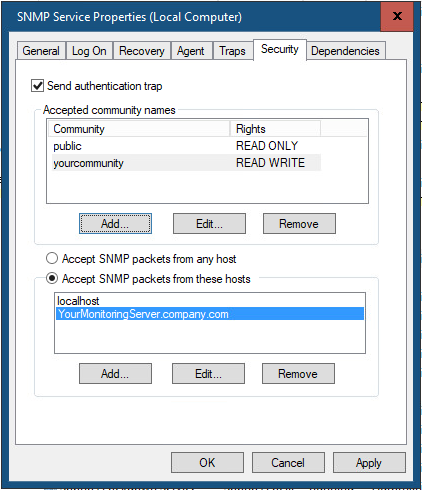
В старых версиях протокола SNMP (SNMP v.1 и SNMP v.2) для авторизации пользователя используется строка сообщества (community string). На вкладке Security можно создать несколько строк подключения.
Можно выбрать один из пяти уровней доступа для сообщества:
- READ ONLY — позволяет получать данные с устройства;
- READ WRITE — позволяет получать данные и изменять конфигурацию устройства;
- NOTIFY — позволяет получать SNMP ловушки;
- READ CREATE – позволяет читать данные, изменять и создавать объекты;
- NONE
Вы можете создать несколько community string. Для этого нужно задать имя и выбрать права/ Для мониторинга состояние сервера достаточно выбрать READ ONLY.
В списке Accept SNMP packets from these hosts можно указать имена/IP адреса серверов, которым разрешено опрашивать данное устройство. Если вы не хотите ограничивать список разрешенных устройств, оставьте здесь Accept SNMP packets from any hosts.
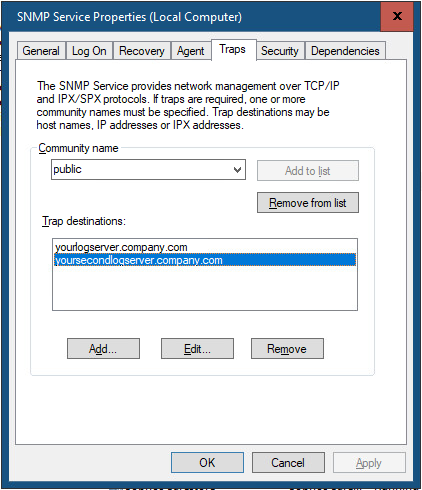
На вкладке Traps указываются адрес серверов, на который SNMP агент должен отправлять SNMP-ловушка (SNMP trap). SNMP Trap это широковещательный USP пакет, используемый для асинхронного уведомления менеджера (например, сообщение о критическом событии).
Не забудьте открыть в Windows Defender Firewall правила, разрешающие входящий и исходящий трафик для SNMP запросов и ловушек (TRAP). Нужные правила фаейрвола можно включить с помощью PowerShell.
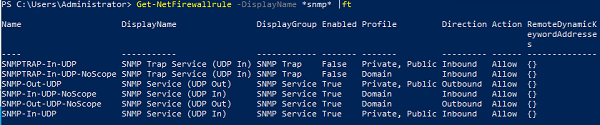
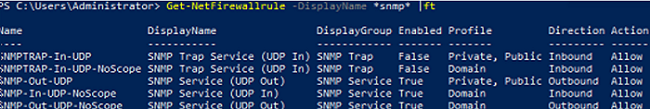
В Windows Firewall есть несколько готовых правил для SNMP трафика:
Get-NetFirewallrule -DisplayName *snmp* |ft
- SNMPTRAP-In-UDP
- SNMPTRAP-In-UDP-NoScope
- SNMP-Out-UDP
- SNMP-In-UDP-NoScope
- SNMP-Out-UDP-NoScope
- SNMP-In-UDP
Можно включить все правила, или только определенное:
Get-NetFirewallrule -DisplayName *snmp* | Enable-NetFirewallRule
Get-NetFirewallrule SNMP-Out-UDP | Disable-NetFirewallRule
В списке служб Windows есть еще одна служба SNMP Trap. Она используется для получения сообщений от других SNMP агентов и пересылки на SNMP сервера (обычно это система мониторинга, опрашивающая устройства по SNMP, например PRTG или Zabbix).
Если вы настраиваете SNMP на Windows Server Core, вы не сможете использовать графический интерфейс службы SNMP для настройки ее параметров. Вместо этого придется вносить изменения в реестр с помощью PowerShell. Настройки службы SNMP хранятся в ветке реестра HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINESYSTEMCurrentControlSetServicesSNMPParameters.
Следующие команды зададут описание агента:
New-ItemProperty -Path "HKLM:SYSTEMCurrentControlSetservicesSNMPParametersRFC1156Agent" -Name "sysContact" -Value "[email protected]" -PropertyType REG_SZ
New-ItemProperty -Path "HKLM:SYSTEMCurrentControlSetservicesSNMPParametersRFC1156Agent" -Name "sysLocation" -Value "MSK_Datacenter1" -PropertyType REG_SZ
Для каждой ловушки SNMP придется создать отдельный ключ в HKLMSYSTEMCurrentControlSetservicesSNMPParametersTrapConfiguration с именем community.
New-Item -Path "HKLM:SYSTEMCurrentControlSetservicesSNMPParametersTrapConfigurationpublic1"
Укажите разрешения для community:
New-ItemProperty -Path "HKLM:SYSTEMCurrentControlSetServicesSNMPParametersValidCommunities" -Name "public1" -Value 4 -PropertyType DWord
Возможные значения:
- 1 — NONE
- 2 — NOTIFY
- 4 — READ ONLY
- 8 — READ WRITE
- 16 — READ CREATE
Для каждого community можно указать список серверов, с которых разрешено принимать запросы:
New-ItemProperty -Path "HKLM:SYSTEMCurrentControlSetServicesSNMPParametersPermittedManagers" -Name "1" -Value "server1.winitpro.ru" -PropertyType REG_SZ
Перезапустите службу SNMP для применения новых настроек из реестра:
Get-Service SNMP|Restart Service
Если нужно распространить эти SNMP настройки на множество компьютеров/серверов Windows в домене, используйте возможности внесения изменений в реестр через GPO.
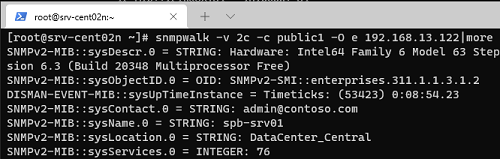
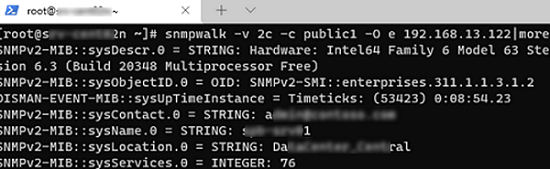
Проверить работу службы SNMP можно с помощью утилиты snmpwalk (доступна в любом Linux дистрибутиве):
# snmpwalk -v 2c -c public1 -O e 192.168.13.122
В этом примере мы опросили наш Windows хост через версию протокола SNMPv2.
Утилита вернула базовыую информацию о хосте (syscontact, sysname, syslocation) и довольно большое количество информации о состоянии сервера Windows.
Introduction
The Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) is a popular protocol for network management. It is used for collecting information from network devices, such as servers, printers, hubs, switches, and routers on an Internet Protocol (IP) network. SNMP protocol is the most common protocol used in monitoring system, usually have ability to connect to any servers and receive performance counters data (such as CPU or RAM usage values).
Let’s Get Started. 🙂
1 – Open the Server Manager, click Add roles and features and proceed installation until you reach the Features page. Check the SNMP Service in the list of features.
2 – Select the SNMP Service then Install the installation process will start.
3 – Once the installation complete, click Close.
4 – Open the Server Manager then click Tools select Services.
5 – Open the Services window, find the SNMP Service, and open Properties.
6 – On the General tab, be sure to select Automatic in the Startup Type section so that it is always available even after a restart of the Server.
7 – On the SNMP Service properties, Click on the Security tab.
8 – To configure SNMP Services, first thing is to give a community name. Enter a Community Name and click on the Add button. For example, i’m used NewHelpTech. Community String and Community Name mean the same thing. (Please take note that don’t assign Read Write rights, just assign Read Only rights)
9 – Then Select Accept SNMP packets from these hosts option and then click Add to add Hostname, IP Address of the Monitoring Server.
10 – Just click OK and then restart SNMP Service.
Now you have to configure SNMP Service in order to be useful for polling process that will be started from monitoring tool. Next article will be about configuring SNMP service.
Good luck! Just give it try – I’m sure you’ll love it as well. If you have any comments or questions on feel free to contact me.
That’s all for now. 🙂
In the monitoring world, SNMP is one of the most used protocols to get insights into metrics on target devices. By default, it is not installed in Windows and Windows Server and we will need to enable it manually. In this article, I´ll show you how to install and configure SNMP and SNMP Traps in Windows Server 2019, but the same procedure applies to Windows Servers.
If you are interested in enabling SNMP in Windows 10 1083 and onwards, please check this article How to install deprecated SNMP in Windows 10 1803 and onwards.
INSTALL SNMP SERVICE
- Open Server Manager
- Click Add roles and features
- Under Before you begin click Next
- Under Select installation type click Next
- Under Select destination server click Next
- Under Select server roles click Next
- Under Select features select SNMP Service and click Add Features and then click Next
- Under Confirm installation selection click Install
- Wait until the installation is finished
CONFIGURE SNMP SERVICE
- Open Services applet (click on Start menu and search for services)
- Navigate to the SNMP Service, right click and then click Properties
- Optional: Click on Agent and add Contact and Location and select all services
- Click on Traps and add Community name. In my case it is public.
- Under Trap destinations click Add and add your destination server that is collecting traps.
- Click on Security and then click on Add. Add community name, the default one is public.
- Click on Accept SNMP Packets from these hosts
- Click on Add and then add your NMS (Network Monitoring Solution) that will collect SNMP Traps. You can delete localhost.
- Click Apply and then OK
Thank you for reading this article. In case of any questions, feel free to comment or contact me.
SNMP (Simple Network Management Protocol) is a classic protocol for monitoring and collecting information about network devices (servers, network hardware, workstations, printers, etc.). SNMP is quite a lightweight and fast protocol, it uses UDP ports 161 and 162 to transfer data. In this article, we’ll show how to install and configure SNMP service on Windows Server 2022/2019 and Windows 10/11.
Contents:
- How to Install SNMP Service on Windows Server 2022/2019?
- Installing SNMP Agent on Windows Server Core
- Enabling SNMP Service in Windows 10/11
- How to Configure SNMP Service on Windows?
How to Install SNMP Service on Windows Server 2022/2019?
In Windows Server, you can install the SNMP service using Server Manager. Select Add roles and features -> Features. Click SNMP Service (if needed, also check SNMP WMI Providers).
The SNMP WMI Provider allows you to query an SNMP device via WMI.
Click Next -> Install and wait till the installation is over.
Installing SNMP Agent on Windows Server Core
In Windows Server Core, you can install SNMP using the Windows Admin Center web interface or PowerShell.
If you are using the Windows Admin Center, connect to your Windows Server host, and select Roles and Features -> SNMP Service.
Since there is no graphical interface on Windows Server Core and the Server Core host can be managed from the command prompt, you can install the SNMP service using PowerShell.
You can use the Install-WindowsFeature PowerShell cmdlet to install roles and features on Windows Server.
Check that the SNMP service is not installed:
Get-WindowsFeature SNMP*
Install the SNMP role and WMI provider:
Install-WindowsFeature SNMP-Service,SNMP-WMI-Provider -IncludeManagementTools
Make sure that SNMP services are running:
Get-Service SNMP*
In our example, the SNMP service is running, and SNMPTRAP is stopped.
Enabling SNMP Service in Windows 10/11
You can use the SNMP service not only on Windows Server but also on Windows 10 and 11 desktops. In Windows 10/11, the SNMP service is a part of the Features on Demand (like RSAT or OpenSSH).
You can install SNMP via the Settings panel. Go to Apps -> Optional features -> Add an optional feature -> View features.
Select Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) and WMI SNMP Provider in the list of available components. To start the installation, click Next (you will need an Internet connection to Microsoft servers).
To install the SNMP service using PowerShell, run the command below:
Add-WindowsCapability -Online -Name SNMP.Client~~~~0.0.1.0
To install the SNMP service offline (without an internet connection), download the Windows 10/11 Features on Demand ISO image from your account on the Volume Licensing Service Center (VLSC) website.
To install SNMP from the ISO image offline, use this command:
Add-WindowsCapability -Online -Name SNMP.Client~~~~0.0.1.0 -LimitAccess -Source \munfs01DistrWin11FoD
How to Configure SNMP Service on Windows?
You can configure the SNMP service options with the services.msc console. Find the SNMP Service in the list and open its properties.
Note that the SNMP service has some additional tabs:
- Agent
- Traps
- Security
The Agent tab contains basic information about the device (administrator contact information, location). Here you can also select the type of information that the device can send when polling via SNMP.
In earlier SNMP protocol versions (SNMP 1 and SNMP 2), a community string is used for authentication. In the Security tab, you can create multiple connection strings.
You can select one of five available access levels for the community:
- READ ONLY — allows getting information from a device
- READ WRITE —get information and edit a device configuration
- NOTIFY — allows receiving SNMP traps
- READ CREATE – to read data, change, and create objects
- NONE
You can create multiple community strings. To do it, enter a name and select the permissions. To monitor the server state, the READ ONLY privilege is enough.
In the Accept SNMP packets from these hosts list, you can enter the names or IP addresses of the hosts allowed to query the device. If you don’t want to use the allowed device list, leave Accept SNMP packets from any hosts here.
The Traps tab allows setting the list of the hosts to which the SNMP agent should send SNMP traps. An SNMP Trap is a broadcast UDP packet used for asynchronous notification of the manager (for example, a notification about a critical event).
Remember to create rules allowing inbound and outbound traffic for SNMP queries and traps in your Windows Defender Firewall. You can enable firewall rules with PowerShell.
There are several predefined rules for SNMP traffic in Microsoft Defender Firewall:
Get-NetFirewallrule -DisplayName *snmp* |ft
- SNMPTRAP-In-UDP
- SNMPTRAP-In-UDP-NoScope
- SNMP-Out-UDP
- SNMP-In-UDP-NoScope
- SNMP-Out-UDP-NoScope
- SNMP-In-UDP
You can enable all rules or just a specific one:
Get-NetFirewallrule -DisplayName *snmp* | Enable-NetFirewallRule
Get-NetFirewallrule SNMP-Out-UDP | Disable-NetFirewallRule
There is the SNMP Trap in the list of Windows services. It is used to receive messages from other SNMP agents and forward them to SNMP servers (usually it is a monitoring system querying devices using via, for example, PRTG or Zabbix).
If you configure SNMP on Windows Server Core, you won’t be able to use the SNMP service GUI to set its settings. You will have to make changes to the registry using PowerShell instead. SNMP service settings are located under the registry key HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINESYSTEMCurrentControlSetServicesSNMPParameters.
The following commands will set the agent description:
New-ItemProperty -Path "HKLM:SYSTEMCurrentControlSetservicesSNMPParametersRFC1156Agent" -Name "sysContact" -Value "admin@woshub.com" -PropertyType REG_SZ
New-ItemProperty -Path "HKLM:SYSTEMCurrentControlSetservicesSNMPParametersRFC1156Agent" -Name "sysLocation" -Value "MUN_DCn2" -PropertyType REG_SZ
You will have to create a separate key with the community name under HKLMSYSTEMCurrentControlSetservicesSNMPParametersTrapConfiguration for each SNMP trap.
New-Item -Path "HKLM:SYSTEMCurrentControlSetservicesSNMPParametersTrapConfigurationpublic1"
Set the community permissions:
New-ItemProperty -Path "HKLM:SYSTEMCurrentControlSetServicesSNMPParametersValidCommunities" -Name "public1" -Value 4 -PropertyType DWord
Possible values:
- 1 — NONE
- 2 — NOTIFY
- 4 — READ ONLY
- 8 — READ WRITE
- 16 — READ CREATE
For each community, you can set a list of hosts they are allowed to accept queries from:
New-ItemProperty -Path "HKLM:SYSTEMCurrentControlSetServicesSNMPParametersPermittedManagers" -Name "1" -Value "mun-mon1.woshub.com" -PropertyType REG_SZ
Restart your SNMP service to apply new settings from the registry:
Get-Service SNMP|Restart Service
If you want to deploy the SNMP service settings to multiple Windows computers/servers in your domain, use Group Policy Preferences to modify the registry.
To make sure if SNMP is working, use the snmpwalk tool (available in any Linux distro):
# snmpwalk -v 2c -c public1 -O e 192.168.12.200
In this example, we have polled our Windows host using SNMPv2.
The tool has returned basic host information (syscontact, sysname, syslocation) and a lot of data on the Windows server state.
Установка SNMP на Windows Server
Установка SNMP на Windows Server
Хотите узнать, как установить службу SNMP Windows? В этом уроке мы расскажем вам, как установить и настроить SNMP-сервер на сервере Windows.
• Windows 2012 R2
• Windows 2008 R2
Список оборудования:
В следующем разделе представлен список оборудования, используемого для создания этого учебника Windows.
Все перечисленные выше аппаратные средства можно найти на веб-сайте Amazon.
Windows Playlist:
На этой странице мы предлагаем быстрый доступ к списку видеороликов, связанных с установкой Windows.
Не забудьте подписаться на наш канал YouTube, названный FKIT.
Связанный с Windows учебник:
На этой странице мы предлагаем быстрый доступ к списку руководств по установке Windows.
Учебник — Установка SNMP в Windows
Откройте приложение «Диспетчер серверов».
Откройте меню «Управление» и нажмите «Добавить роли и функции».
Откройте экран функций, выберите параметр службы SNMP и завершите установку.
На следующем экране нажмите кнопку «Добавить функции».
Функция SNMP была установлена на вашем компьютере, но нам все равно нужно настроить службу SNMP.
Откройте экран управления службами Windows и получите доступ к свойствам службы SNMP.
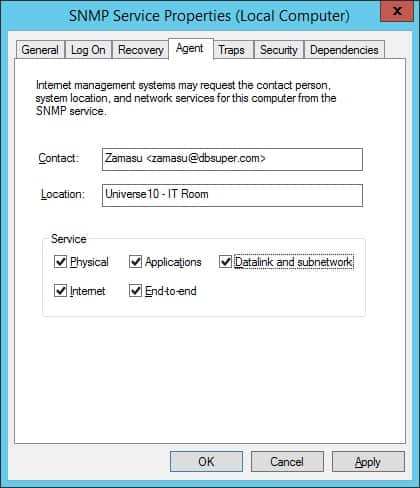
Откройте вкладку «Агент», выберите все параметры и введите контактную информацию устройства.
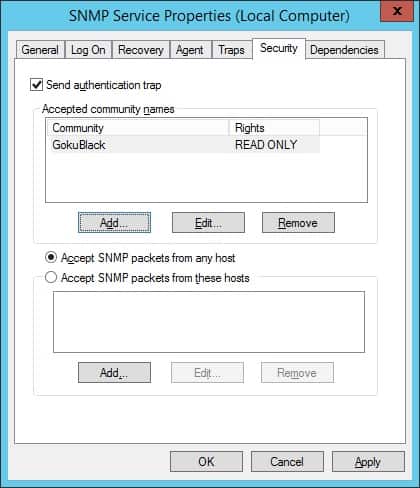
Откройте вкладку «Безопасность» и выберите «Принимать пакеты SNMP с любого хоста».
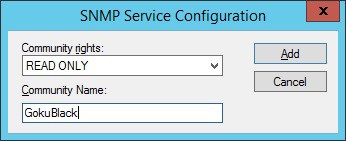
Вам необходимо создать сообщество SNMP для чтения.
Ниже приведен пример нашего примера конфигурации:
Сообщество GokuBlack имеет разрешение на чтение только для Windows-сервера.
Контактное лицо, ответственное за этот компьютер Windows, было настроено как Zamasu.
Расположение оборудования было настроено как IT-комната Вселенной 10.
Вы успешно установили службу SNMP Windows.
Вы успешно настроили службу SNMP Windows.
Чтобы проверить конфигурацию SNMP, используйте следующие команды на компьютере под управлением Ubuntu Linux.
# apt-get install snmp
# snmpwalk -v2c -c GokuBlack 192.168.0.50
Вот небольшой пример вывода SNMPWALK.
iso.3.6.1.2.1.1.1.0 = STRING: «Hardware: Intel64 — Software: Windows Version 6.3
iso.3.6.1.2.1.1.2.0 = OID: iso.3.6.1.4.1.311.1.1.3.1.3
iso.3.6.1.2.1.1.3.0 = Timeticks: (614928) 1:42:29.28
iso.3.6.1.2.1.1.4.0 = STRING: «Zamasu <zamasu@dbsuper.com>»
iso.3.6.1.2.1.1.5.0 = STRING: «TECH-DC01.TECH.LOCAL»
iso.3.6.1.2.1.1.6.0 = STRING: «Universe10 — IT Room»
Поздравляем! вы установили службу SNMP на компьютер под управлением Windows.
Брандмауэр Windows должен принимать сетевые пакеты на порте UDP: 161
VirtualCoin CISSP, PMP, CCNP, MCSE, LPIC22018-08-17T12:03:03-03:00
Related Posts
Page load link
Join Our Newsletter

Ok
Originally published on March 13, 2017 by
Last updated on April 28, 2022
•
12 minute read
The Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP), that has accompanied IT professionals for decades, is available on a large number of devices and solutions. This is great because it’s one of the most basic technologies for monitoring and other network management tasks. Although SNMP won’t fix the internet for you, you won’t come across SNMP if you are a system administrator and responsible for IT infrastructure.
There are several things to consider when configuring SNMP for monitoring. The first and most important step is: Enable SNMP! How to do this depends on your specific piece of hardware (read the friendly manual if you need help). How enabling SNMP works on computers and servers with Windows, Linux, and macOS operating systems is something we’ll show you in this article.
Enabling SNMP on Windows
Installing and configuring the SNMP service on the different Windows client and server versions mostly works the same way. On Windows versions older than Windows 8 and Windows Server 2012, it is already installed. For Windows 8, Windows 10, Windows Server 2012, Windows Server 2016, and Windows Server 2019 you will have to install the SNMP service first. (Yes, that’s correct. Although you might have read contrary statements on some boards, SNMP is still available on Windows Server 2012, 2016 and even 2019!)
If you use Windows 10 Version 1809 or later, scroll down to the next paragraph.
What you have to do is to open the Control Panel on your Windows machine. Open the Programs and Features section where you can Turn Windows features on or off.
On Windows workstations select Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) and install it.
On Windows Server you’ll have to click Next in the Add Roles and Features Wizard until you reach the Features sections where you can install the SNMP Service.
After installing the SNMP service, configure it appropriately. So, run services.msc as administrator and navigate to the properties of the SNMP service. Choose Automatic as startup type to have the service always running, even after turning your computer off and on again.
For monitoring purposes, you should also check all services on the Agent tab to have all SNMP values available.
Don’t forget to adjust security parameters like the community string and the IP/host filter list to your security compliances! For example, add the community name public with READ ONLY rights and accept SNMP packets from at least the address of your monitoring server.
That’s it! You have successfully configured SNMP on your Windows machine.
Enabling SNMP on Windows 10 Version 1809 and Later
With Windows 10 version 1809, the process of enabling SNMP changed. SNMP is an optional feature as of this Windows 10 version. You can enable it as follows.
- Open the Settings on your Windows machine.
- Click Apps.
- Choose Manage optional features under Apps & features.
- Click Add a feature.
- Select Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) from the list.
- Click Install to enable SNMP on your computer.
Enabling SNMP on Linux
Now look at how you can enable SNMP on Linux. We describe the setup process for Ubuntu, Debian, CentOS and OpenSuse.
In the first step you need to install the SNMP deamon
| Ubuntu/Debian | sudo apt-get install snmp snmpd snmp-mibs-downloader |
| CentOS | Sudo dnf install net-snmp |
| OpenSuse | Zypper install net-snmp snmp-mibs |
You will now find the SNMP configuration in /etc/snmp/snmpd.config. Make a backup of the original configuration file and open snmpd.config with an editor. Now set the community string.
| Ubuntu/Debian | rocommunity public |
| CentOS | com2sec default public |
| OpenSuse | rocommunity public |
public is the default community string that most SNMP devices listen to. Of course you can also choose a string individually. The only important thing is that the string is also the same on the devices to be queried.
If you are using OpenSuse, the snmpd service may not be activated and started by default. In this case, activate the snmpd service so it will start on system boot with the command: systemctl enable snmpd. Then start the service with the command systemctl start snmpd.
For other Linux distributions you might have to adjust the steps mentioned above slightly.
Enabling SNMP on macOS
Current macOS versions include SNMP by default. You can use the basic setup assistant to appropriately configure SNMP on your Mac:
- Open a new terminal and use this command:
- sudo snmpconf -g basic_setup
Configure read-only community access for SNMP v1/v2c by answering the setup questions and start the SNMP daemon:
- sudo launchctl load -w /System/Library/LaunchDaemons/org.net-snmp.snmpd.plist
Best practice is to add your SNMP daemon to automatic startup to manage the macOS machine via SNMP in a comfortable way.
What’s Next?
Enabling SNMP on your operating system wasn’t so hard, was it? Configuring access from other servers to useful system parameters via SNMP might be harder. We will cover this topic in the next articles about SNMP on our blog. Stay tuned!
In my previous articles on monitoring Windows server and the Windows SNMP MIB files, I covered the basic capabilities of using SNMP protocol to monitor Windows servers in your LAN. During my further investigations, I discovered a better way to perform this task.
Any Windows platform (at least from Windows 2000) supports the SNMP V1 and SNMP V2c protocols. The SNMP V2c is the improved version of V1 protocol with the same community based strings. Even better, this version supports the bulk requests with the new GetBulk command.
That command will retrieve a larger number of SNMP values at once. The old GetNext command in V1 will read them one by one. Consequently, our monitoring software will read faster any device’s status. Having that in mind, we should generally use V2c over V1 whenever it’s possible. Unfortunately, not all devices will support this new standard.
Configuring the Windows side
There’s no special setup on the Windows side. Once installed and configured, the SNMP service will support both V1 and V2c protocols.
You should add all Windows MIBs into the repository of your NMS system, like MikroTik Dude. That’s it. A very simple task.
In addition, we can even configure the SNMP parameters through the Group Policy and every Windows machine will be automatically configured for our system.
Changing the SNMP profile in Dude
We could switch from SNMP V1 to SNMP V2c in Dude in two ways:
- changing the SNMP profile for any device, or
- making that change on the global level.
Let’s check those options in details.
Changing the SNMP profile for device
To choose SNMP V2c for any specific device, you should:
1. Locate the device icon on the map
2. Right-click on the icon and choose Settings
3. In the newly opened window, select the tab named General
4. Locate the option named Snmp Profile on the right side of this dialog and click to open its drop down menu.
5. Change the version from default to v2-public in the drop down list and then click on the button [ OK ].
6. This window will close and your new settings are saved.
That’s it! The Dude will now use SNMP V2c to communicate with your device.
Changing the global SNMP profile settings
If you have a lot of monitored devices, it will be faster to change the default profile in the Dude server.
1. Click on the [ Settings ] button. The new window will pop up.
2. Choose the SNMP tab.
3. You can see here all defined SNMP profiles and the settings for the default profile. By default, The Dude will use SNMP V1 with the public community string.
4. Click on the drop down list named Default and choose v2-public.
5. Click on the button [ OK ] to apply these changes and to close this dialog.
That’s it! All devices will be polled with SNMP V2C.
Checking all devices
This simple trick will improve both monitoring capabilities and network bandwidth. Instead to issue multiple separate requests, our NMS will in one request acquire more information from any monitored host. That means that we will release the network bandwidth and CPU time for other processes.
In case you have any device which is not V2c capable, it will very soon change its icon colour to orange or red. In such situation you can simply change the SNMP profile of that particular device back to V1.
In my experience, only small number of devices isn’t V2C compatible. Therefore, it’s a good practice to start with V2c as the default option and only tune a few incompatible devices.
Stay tuned.
This article teaches you how to install SNMP on your Windows Servers and how to configure it.
What is SNMP and why use it on Windows Server?
SNMP might look like an old-school protocol nowadays. But it fast, lightweight and reliable. For servers and switches SNMP is THE monitoring protocol and can even be used to configure your hardware.
Windows Servers on the other side are often queried and managed with WMI. WMI offers a lot of functionalities and can be used for almost any task you want to perform on a server or client.
The downside of WMI is that it is not as fast as SNMP. Also is consumes more resources. Just to visualize the difference: The monitoring software PRTG recommends that you do not run more than 5.000 sensors on one server. For WMI sensors, the number should not exceed 200 per monitoring server.
How to install SNMP on Windows servers
Using the GUI
Open the Server Manager. Click on Manage and select Add Roles and Features.
Server manager: Add Roles and Features
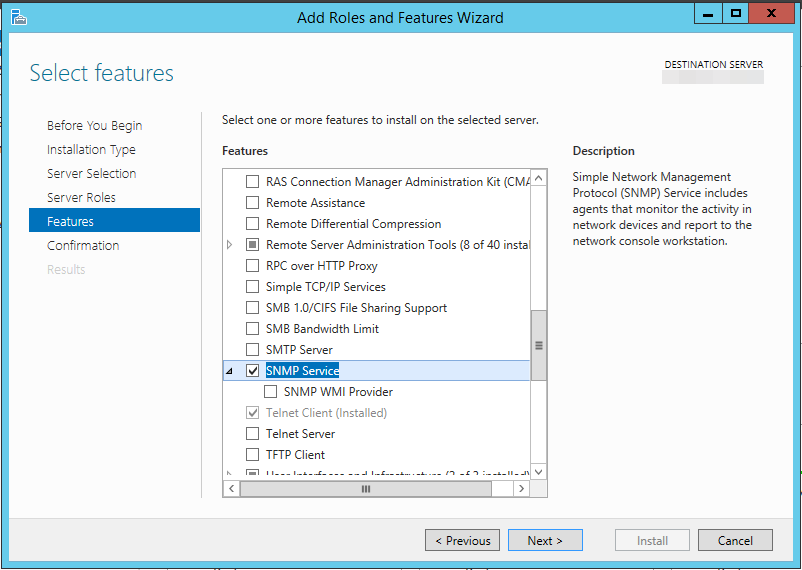
Click through the assistant until you can select the features to be installed. Check SNMP Service. SNMP WMI Provider allows to query other SNMP devices with WMI. But this is not required to monitor your server via SNMP.
Server manager: Select the SNMP feature
Click next until the wizard is completed. Then wait for the installation to complete. You will find a new service SNMP Service (SNMP) running on your server.
Using Windows Admin Center
Log on to your Windows Admin Center and select to server you want to add SNMP to. On the left side, select Roles & features. Here scroll down to the features and select SNMP Service. SNMP WMI Provider allows to query other SNMP devices with WMI. But this is not required to monitor your server via SNMP.
WAC: Select feature
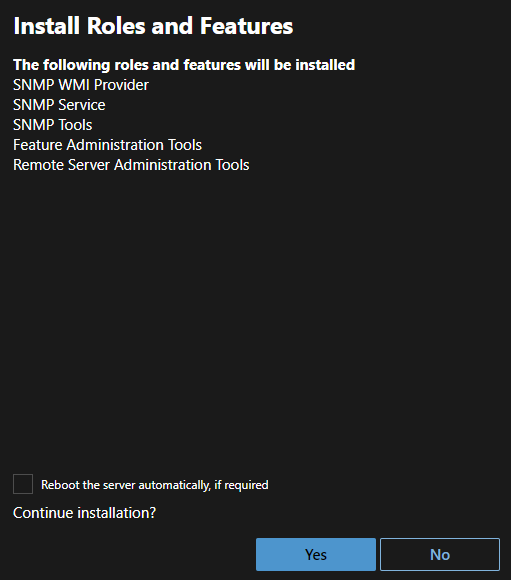
click Install on top of the list. A new window will appear which summarizes the roles and features to be installed.
WAC: Confirm installation
Click yes if you want to start the installation.
Wait for the installation to complete.
WAC: Installation completed
You will find a new service SNMP Service (SNMP) running on your server.
On Windows Server core / Powershell
Log on to your system or enter a Powershell session on your server.
First check if SNMP is available and has not been installed already
Get-WindowsFeature SNMP*
Powershell: Check SNMP status
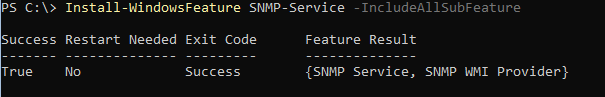
Now you can install SNMP.
Install-WindowsFeature SNMP-Service
If you need the SNMP WMI Provider, just add -IncludeAllSubFeature to your command.
Powershell: Install Windows feature
You will find a new service SNMP Service (SNMP) running on your server. You can check the status with this command:
Get-Service SNMP
Configure the SNMP service
Using the GUI
Please note that you might have to restart your server in order to display the tabs for that service.
Open the services management (services.msc). Search for SNMP Service, right click and select Properties.
The new window shows additional tabs for configuring SNMP.
Agent tab
SNMP Agent tab
These are general settings for your endpoint. Contact and location are information which can be displayed in your monitoring software to easily determine where that server is and who is managing it.
Below Service you can specify which information you want to retrieve from the server.
Traps tab
SNMP Traps tab
Setting up traps, requires one or more communities to be used. For each community you need to define one or more destination server for the trap to be sent to.
Security tab
SNMP Security tab
The first setting is called Send authentication trap. This checkbox specifies if your server will send a trap if an unknown community is used to query the system (Which could hint to an attacker probing for communities.
The first list contains the accepted community names. For each community you have to specify which rights are assigned to it.
The last option is whether you like to accept SNMP packets from any host or you want to restrict to certain hosts only.
Using Powershell / Group Policies
Unfortunately Powershell does not offer dedicated cmdlets for SNMP and the SNMP administrative templates are for Server 2003 and do not offer all options the GUI has.
Therefore configuration has to be done using the registry keys.
The registry path for the SNMP service is HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINESYSTEMCurrentControlSetServicesSNMPParameters
Agent settings
Contact and Location are both simple string (REG_SZ) values:
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINESYSTEMCurrentControlSetServicesSNMPParametersRFC1156AgentsysContact is the lontact
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINESYSTEMCurrentControlSetServicesSNMPParametersRFC1156AgentsysContact is the location
New-ItemProperty -Path "HKLM:SYSTEMCurrentControlSetservicesSNMPParametersRFC1156Agent" -Name "sysContact" -Value "Contact" -PropertyType REG_SZ New-ItemProperty -Path "HKLM:SYSTEMCurrentControlSetservicesSNMPParametersRFC1156Agent" -Name "sysLocation" -Value "Location" -PropertyType REG_SZ
The services each have a value assigned:
| Service | Value |
|---|---|
| None | 0 |
| Physical | 1 |
| Applications | 64 |
| Datalink and subnetwork | 2 |
| Internet | 4 |
| End-To-End | 8 |
If you are not using a GUI to configure the service, use sum the values of the services. Example: Applications and Physical has the value 65 (64 for Applications + 1 for Physical).
Allowing every service requires the value to be 79 (decimal)
New-ItemProperty -Path "HKLM:SYSTEMCurrentControlSetservicesSNMPParametersRFC1156Agent" -Name "sysServices" -Value 79 -PropertyType DWord
Traps settings
For each community you need to create a new key (Or subfolder) in HKLM:SYSTEMCurrentControlSetservicesSNMPParametersTrapConfiguration with the name of the community.
New-Item -Path "HKLM:SYSTEMCurrentControlSetservicesSNMPParametersTrapConfigurationpublic"
Within this key, you need to enter each trap destination as a separate value and the name start from 1 and counting up:
New-ItemProperty -Path "HKLM:SYSTEMCurrentControlSetservicesSNMPParametersTrapConfigurationpublic" -Name "1" -Value "yourlogserver.company.com" -PropertyType REG_SZ New-ItemProperty -Path "HKLM:SYSTEMCurrentControlSetservicesSNMPParametersTrapConfigurationpublic" -Name "2" -Value "yoursecondlogserver.company.com" -PropertyType REG_SZ
Security settings
The first option are the authentication traps. This is a simple 0 or 1 value where 0 is disabled and 1 is enabled.
New-ItemProperty -Path "HKLM:SYSTEMCurrentControlSetservicesSNMPParameters" -Name "EnableAuthenticationTraps" -Value 1 -PropertyType DWord
Your accepted communities are added to HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINESYSTEMCurrentControlSetServicesSNMPParametersValidCommunities as DWORD with the value indicating the permission:
| Value | Permission |
|---|---|
| 1 | None |
| 2 | notify |
| 4 | read only |
| 8 | read write |
| 16 | read create |
New-ItemProperty -Path "HKLM:SYSTEMCurrentControlSetServicesSNMPParametersValidCommunities" -Name "public" -Value 4 -PropertyType DWord New-ItemProperty -Path "HKLM:SYSTEMCurrentControlSetServicesSNMPParametersValidCommunities" -Name "yourwritingcommunity" -Value 8 -PropertyType DWord
And finally the accepted SNMP sending hosts:
These are added to HKLM:SYSTEMCurrentControlSetServicesSNMPParametersPermittedManagers as sub values with the name starting at 1 and counting up.
New-ItemProperty -Path "HKLM:SYSTEMCurrentControlSetServicesSNMPParametersPermittedManagers" -Name "1" -Value "yourmonitoringserver.company.com" -PropertyType REG_SZ New-ItemProperty -Path "HKLM:SYSTEMCurrentControlSetServicesSNMPParametersPermittedManagers" -Name "2" -Value "localhost" -PropertyType REG_SZ
На первый взгляд задача «включение SNMP на Windows» не должна быть сложной.
Как включить SNMP на Windows и как ее настроить будем разбираться по пунктам.
Способ №1 Включение SNMP в Windows.
Стандартным, идеальным для пользователя считается следующий способ, он работает в Windows 7 и некоторых сборках Windows 10:
1. Заходим в Панель Управления.
2. Находим меню «Установка и удаление программ» или «Программы и компоненты».
3. В открывшемся окне слева в списке переходим по ссылке «Включение или отключение компонентов Windows».
4. В списке «Компоненты Windows» ищем строчку «Компонент SNMP» и отмечаем галочкой — Нажимаем «ОК».
5. Осталось перейти в Службы (Панель управления — Администрирование — Службы) где выбираем среди всех служб «Служба SNMP» и запускаем.
Способ №2 Включение и настройка SNMP в Windows 10.
Если первый способ не увенчался успехом, то второй нам поможет:
1. Для начала нам нужно будет в меню Пуск найти и запустить WindowsPowerShell «ЗАПУСК ОТ ИМЕНИ АДМИНИСТРАТОРА»!!!.
2. Вводим команду для проверки доступности SNMP — службы :
Get-WindowsCapability -Online -Name "SNMP*"
Вывод команды будет следующим:
Name: SNMP.Client~~~~0.0.1.0 State: NotPresent DisplayName: SNMP-протокол.
Как видим в строке состояния указано, что SNMP-протокол не представлен.
P.S. Бывали случае, когда в строке состояния указано Installed, но все равно службы SNMP нет. В этом случае все равно переходим к следующему 3 пункту.
3. Устанавливаем службу SNMP командой:
Add-WindowsCapability -Online -Name "SNMP.Client~~~~0.0.1.0"
Видим процесс установки и получаем ответ:
Path: Online: True RestartNeeded: False
4. Снова проверим состояние службы SNMP командой из пункта 2:
Get-WindowsCapability -Online -Name "SNMP*"
Вывод команды:
Name: SNMP.Client~~~~0.0.1.0 State: Installed DisplayName: SNMP-протокол.
5. Обязательно перезагружаем компьютер.
После запуска переходим в Службы и находим «Служба SNMP».
Заходим в свойства службы SNMP. Если состояние службы остановлена, нужно запустить ее кнопкой «Запустить» и в меню «Тип запуска» выбираем «Автоматически».
Способ 3. Как установить SNMP на Windows Server.
1. Включить SNMP можно в «Параметры» — раздел «Приложения и возможности»- ссылка «Дополнительные возможности».
2. В окне «Дополнительные возможности» нажимаем «Добавить компонент» и выбираем в списке «SNMP-протокол» — Установить.
3. Перезагружаем систему.
Как настроить SNMP в Windows.
Необходимо найти службу «Служба SNMP» и открыть свойства службы.
— На вкладке «Безопасность» установим флажок «Посылать ловушку проверки подлинности».
— Нажмем кнопку «Добавить» для настройки «SNMP Community».
— Выбираем уровень доступа (None, Notify, READ ONLY, READ WRITE, READ CREATE). Для мониторинга состояния сервера достаточно выбрать Read Only.
— По-умолчанию community чаще всего указывается public для уровня READ ONLY или private для Read Write.
— Ниже есть пункт «Принимать пакеты SNMP от любого узла» и «Принимать пакеты SNMP от следующих узлов». Здесь вы можете указать конкретный адрес вашего сервера мониторинга, который будет собирать данные или оставить 1 вариант, если вы хотите, что бы не было ограничений по ip-адресу.
— Сохраняем изменения и перезапускаем службу SNMP.
If you run Windows Server as Core Installation, like Windows Server 2016 Core or any Microsoft Hyper-V Server edition and you want to use SNMP (Simple Network Management Protocol) on that system, you first have to install the SNMP feature on that Core Server. After that you can use the MMC to remotely connect to the services list on the Core Server.
Install SNMP on Windows Server Core
First lets see if the SNMP feature is installed, using PowerShell:
Get-WindowsFeature *SNMP*
By default the SNMP feature is not installed. To install the SNMP feature on Windows Server Core, you can run the following command:
Install-WindowsFeature SNMP-Service -IncludeAllSubFeature -Verbose
Configure SNMP on Windows Server Core
After you have installed the SNMP feature, you and you have enabled Remote Management you can mange and configure smtp via remote MMC.
Simply open up MMC click on File and then on Add/Remove Snap-in. Now you can select the Services snap-in and enter the name or IP address of the Windows Server Core you want to configure the SNMP services.
Important: If you need to configure the SNMP Service on a remote machine using the MMC, you have to install the RSAT-SNMP feature on the local administrative computer. Otherwise, you will not see the SNMP specific tabs. In older versions of Windows and Windows Server, you needed to install the SNMP feature instead of the RSAT-SNMP feature.
Install-WindowsFeature RSAT-SNMP -verbose
I hope this blog post was helpful. And it helps you to install and configure the SNMP feature on Windows Server. Especially you should have a look at the remote management part for the SNMP service. It works with all the latest Windows Server versions like 2008 R2, 2012, 2016 and event Windows Server 2019. If you have any question, feel free to comment on this post.
Tags: Core Server, Hyper-V, Install SNMP, Microsoft, mmc, Monitoring, PowerShell, Remote SNMP, RSAT SNMP, snmp, SNMP Feature, SNMP Trap, Windows Server, Windows Server 2012 R2, Windows Server 2016, Windows Server 2019, Windows Server Core Last modified: March 10, 2021
About the Author / Thomas Maurer
Thomas works as a Senior Cloud Advocate at Microsoft. He engages with the community and customers around the world to share his knowledge and collect feedback to improve the Azure cloud platform. Prior joining the Azure engineering team, Thomas was a Lead Architect and Microsoft MVP, to help architect, implement and promote Microsoft cloud technology.
If you want to know more about Thomas, check out his blog: www.thomasmaurer.ch and Twitter: www.twitter.com/thomasmaurer