OpenCL™ (Open Computing Language) is a low-level API for heterogeneous computing that runs on CUDA-powered GPUs. Using the OpenCL API, developers can launch compute kernels written using a limited subset of the C programming language on a GPU.
NVIDIA is now OpenCL 3.0 conformant and is available on R465 and later drivers. This is supported on x86/x86_64 Linux and Windows only and available at www.nvidia.com/drivers
In addition to OpenCL, NVIDIA supports a variety of GPU-accelerated libraries and high-level programming solutions that enable developers to get started quickly with GPU Computing.
OpenCL is a trademark of Apple Inc., used under license by Khronos.
NVIDIA OpenCL SDK Code Samples
OpenCL-Vulkan Interop Samples
Sinewave and boxfilter simulations demonstrating use of external buffer and image sharing and synchronization through external semaphores between Vulkan and OpenCL.
OpenCL Multi Threads
This sample shows the implementation of multi-threaded heterogeneous computing workloads with tight cooperation between CPU and GPU. The new OpenCL 1.1 features user events, thread-safe API calls and event callbacks are utilized.
Using Inline PTX with OpenCL
A simple test application that demonstrates a new CUDA 4.0 driver ability to embed PTX in a OpenCL kernel.
OpenCL Marching Cubes Isosurfaces
This sample extracts a geometric isosurface from a volume dataset using the marching cubes algorithm. It uses the scan (prefix sum) function from the oclScan SDK sample to perform stream compaction.
OpenCL Tridiagonal
Efficient matrix solvers for large number of small independent tridiagonal linear systems. OpenCL implementation of 3 different solvers: Parallel Cyclic Reduction, Cyclic Reduction, Sweep (Gauss elimination + reordering optimization for full coalescing).
OpenCL Device Query
This sample enumerates the properties of the OpenCL devices present in the system.
OpenCL Bandwidth Test
This is a simple test program to measure the memcopy bandwidth of the GPU. It currently is capable of measuring device to device copy bandwidth, host to device and host to device copy bandwidth for pageable and page-locked memory, memory mapped and direct access.
OpenCL Vector Addition
Element by element addition of two 1-dimensional arrays. Implemented in OpenCL for CUDA GPU’s, with functional comparison against a simple C++ host CPU implementation.
OpenCL Dot Product
Dot Product (scalar product) of set of input vector pairs. Implemented in OpenCL for CUDA GPU’s, with functional comparison against a simple C++ host CPU implementation.
OpenCL Matrix Vector Multiplication
Simple matrix-vector multiplication example showing increasingly optimized implementations.
OpenCL Overlapped Copy/Compute Sample
Element by element hypotenuse for two 1-dimensional arrays. Implemented in OpenCL for CUDA GPU’s, with functional comparison against a simple C++ host CPU implementation. Demonstrates overlapped copy/compute in 2 command queues
OpenCL Simple Multi-GPU
This application demonstrates how to make use of multiple GPUs in OpenCL.
OpenCL Simple OpenGL Interop
Simple program which demonstrates interoperability between OpenCL and OpenGL. The program modifies vertex positions with OpenCL and uses OpenGL to render the geometry.
Simple OpenCL D3D10 Texture
Simple program which demonstrates Direct3D10 texture interoperability with OpenCL. The program creates a number of D3D10 textures (2D, 3D, and CubeMap) which are written to from OpenCL kernels. Direct3D then renders the results on the screen.
Simple OpenCL D3D9 Texture
Simple program which demonstrates Direct3D9 texture interoperability with OpenCL. The program creates a number of D3D9 textures (2D, 3D, and CubeMap) which are written to from OpenCL kernels. Direct3D then renders the results on the screen.
OpenCL Scan
This example demonstrates an efficient OpenCL implementation of parallel prefix sum, also known as «scan». Given an array of numbers, scan computes a new array in which each element is the sum of all the elements before it in the input array.
OpenCL Parallel Reduction
A parallel sum reduction that computes the sum of large arrays of values. This sample demonstrates several important optimization strategies for parallel algorithms like reduction.
OpenCL Matrix Transpose
Efficient matrix transpose.
OpenCL Matrix Multiplication
This sample implements matrix multiplication and is exactly the same as Chapter 6 of the programming guide.
It has been written for clarity of exposition to illustrate various OpenCL programming principles, not with the goal of providing the most performant generic kernel for matrix multiplication.
CUBLAS provides high-performance matrix multiplication.
OpenCL 3D FDTD
This sample applies a finite differences time domain progression stencil on a 3D surface.
OpenCL DCT 8×8
This sample demonstrates how Discrete Cosine Transform (DCT) for 8×8 blocks can be implemented in OpenCL.
OpenCL DirectX Texture Compressor (DXTC)
High Quality DXT Compression using OpenCL.
This example shows how to implement an existing computationally-intensive CPU compression algorithm in parallel on the GPU, and obtain an order of magnitude performance improvement.
OpenCL Radix Sort
This sample demonstrates a very fast and efficient parallel radix sort implemented in OpenCL for CUDA GPUs.
OpenCL Sorting Networks
This sample implements bitonic sort algorithm for batches of short arrays
OpenCL Black-Scholes Option Pricing
This sample evaluates fair call and put prices for a given set of European options by Black-Scholes formula.
OpenCL Hidden Markov Model
This sample implements a Hidden Markov Model in OpenCL for the GPU.
OpenCL Quasirandom Generator
This sample implements Niederreiter quasirandom number generator and Moro’s Inverse Cumulative Normal Distribution generator.
OpenCL Mersenne Twister
This sample implements Mersenne Twister random number generator and Cartesian Box-Muller transformation on the GPU.
OpenCL 64-bin and 256-bin Histogram
This sample demonstrates efficient implementation of 64-bin and 256-bin histograms.
OpenCL Post-Process OpenGL-Rendered Image
This sample shows how to post-process an image rendered in OpenGL using OpenCL.
OpenCL Simple Texture 3D
Simple example that demonstrates use of 3D textures in OpenCL.
OpenCL Box Filter
Linear 2-dimensional variable-width Box Filter of RGBA image. Implemented in OpenCL for CUDA GPU’s, with performance comparison against simple C++ on host CPU. Each of the R, G, B and A channels are treated independently with results computed concurrently for each.
OpenCL Sobel Filter
2-dimensional 3×3 Sobel Magnitude Filter of RGBA image. Implemented in OpenCL for CUDA GPU’s, with performance comparison against simple C++ on host CPU. Gradient magnitude for each of the R, G & B channels is computed concurrently and independently, then combined into a single gradient intensity with linear weighting factors.
OpenCL Median Filter
Multi-GPU enabled, 2-dimensional 3×3 Median Filter of RGBA image. Implemented in OpenCL for CUDA GPU’s, with performance comparison against simple C++ on host CPU. Each of the R, G & B channels are treated independently with results computed concurrently for each.
OpenCL Separable Convolution
This sample implements convolution filter of a 2D image with arbitrary separable kernel.
OpenCL Recursive Gaussian Filter
2-dimensional Gaussian Blur Filter of RGBA image using IRF method. Implemented in OpenCL for CUDA GPU’s, with performance comparison against simple C++ on host CPU. Each of the R, G, B and A channels are treated independently with results computed concurrently for each.
OpenCL Volume rendering
This sample demonstrates basic volume rendering using 3D textures.
OpenCL Particle Collision Simulation
Simulation of elastic collisions of a large # of bodies. Implemented in OpenCL for CUDA GPU’s.
OpenCL N-Body Physics Simulation
Gravitational Simulation of a large # of bodies. Implemented in OpenCL for CUDA GPU’s.

NVIDIA Studio Drivers provide artists, creators and 3D developers the best performance and reliability when working with creative applications. To achieve the highest level of reliability, Studio Drivers undergo extensive testing against multi-app creator workflows and multiple revisions of the top creative applications from Adobe to Autodesk and beyond.
Applications
Provides optimal support and bug fixes for the latest updates to RTX-powered creative applications including Unreal Engine 4.25, OctaneRender 2020, D5 Render, Substance Designer, Substance Painter, Minecraft RTX, and more.
Technology
Provides support for the new GeForce RTX SUPER Max-Q GPUs, including a dozen new RTX Studio laptops.
NVIDIA TITAN RTX, NVIDIA TITAN V, NVIDIA TITAN Xp, NVIDIA TITAN X (Pascal)
GeForce RTX 20 Series:
GeForce RTX 2080 Ti, GeForce RTX 2080 SUPER, GeForce RTX 2080, GeForce RTX 2070 SUPER, GeForce RTX 2070, GeForce RTX 2060 SUPER, GeForce RTX 2060
GeForce GTX 1660 SUPER, GeForce GTX 1650 SUPER, GeForce GTX 1660 Ti, GeForce GTX 1660, GeForce GTX 1650
GeForce GTX 1080 Ti, GeForce GTX 1080, GeForce GTX 1070 Ti, GeForce GTX 1070, GeForce GTX 1060, GeForce GTX 1050 Ti, GeForce GTX 1050
Источник
Как установить и использовать в расчетах OpenCL
OpenCL в клиентском терминале MetaTrader 5
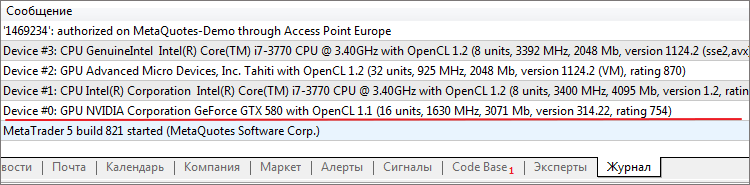
Прошло уже больше года как стало возможным писать программы для OpenCL в MQL5, и теперь при старте терминала MetaTrader 5 в Журнал выводятся сообщения о найденных устройствах с поддержкой OpenCL, как показано на картинке.
Если на вашем компьютере уже есть подходящее устройство с поддержкой OpenCL версии 1.1 и выше, то можете смело пропускать описание и сразу же переходить к разделу Сравнение производительности, чтобы своими глазами увидеть выигрыш в скорости для задач, допускающих распараллеливание.
Однако еще далеко не все пользователи смогли оценить преимущество использования параллельных вычислений в своих советниках, индикаторах или скриптах, так как не знают о новых возможностях или не имеют подходящих знаний.
Все дело в том, что для запуска любой MQL5 программы, использующей OpenCL, необходимо установить соответствующее программное обеспечение. Поэтому многие так и не сумели запустить скрипт расчета фрактала Мандельброта и многие другие программы, представленные на форуме MQL5.community.
Что такое OpenCL
Другими словами OpenCL позволяет задействовать для вычислений одной задачи все ядра центрального процессора или все вычислительные мощности видеокарты, что, в конечном счете, уменьшает время выполнения программы. И поэтому использование OpenCL является очень полезным для задач, связанных с трудоемкими и ресурсозатратными вычислениями.
Например, применительно к MQL5, увеличение быстродействия может быть очень полезно для некоторого скрипта (индикатора или эксперта), который проводит сложный и длительный анализ исторических данных по нескольким символам и таймфреймам (здесь стоит отметить, что MQL5 программа, претендующая на параллельное исполнение, должна быть написана специальным образом при помощи OpenCL API).
Поддержка OpenCL
Поддержка OpenCL в MQL5 начинается с версии стандарта 1.1, который появился в июне 2010 года. Поэтому, для использования параллельных вычислений, необходимо иметь относительно свежее программное и аппаратное обеспечение, соответствующее этому стандарту.
Конечно, по быстродействию распределенных вычислений центральные процессоры значительно уступают своим соперникам из «графического цеха», однако и хорошего многоядерного центрального процессора Вам будет вполне достаточно для получения значительного увеличения быстродействия. Но мы отвлеклись, идем дальше.
| Производитель | Устройства | Операционные системы |
|---|---|---|
| Intel | Процессоры:
AMD Radeon HD Graphics начиная с серии 6400; Процессоры семейства K8 и старше: Opteron, Athlon 64, Athlon 64 FX, Athlon 64 X2, Sempron, Turion 64, Turion 64 X2, Phenom, Phenom II (подробнее здесь). APU (гибридный процессор, включающий в себя центральный и графический процессоры): Процессоры серий A, C, E, E2, G, R. |
Windows Vista SP2, 7, 8; openSUSE 11.x; Ubuntu 11.04; Red Hat 6.x. |
| NVidia | Видеокарты (использующие архитектуру CUDA):
Tesla, Quadro, GeForce (подробнее здесь). |
Windows XP, Vista, 7, 8 Linux и Mac OS (подробнее здесь) |
Проверьте, установлено ли на вашем персональном компьютере хотя бы одно устройство (CPU или GPU) и операционная система, которые поддерживают OpenCL 1.1. Если таковые имеются, то Вы смело можете переходить к следующему параграфу, который описывает процедуру настройки OpenCL в зависимости от производителя аппаратного обеспечения.
Настройка OpenCL
Ставить для центрального процессора специальный комплект средств разработки (SDK) потребуется только в том случае, если на компьютере не установлена подходящая видеокарта.
Важно: Если уже есть установленная видеокарта с поддержкой OpenCL, то ставить софтверную версию для эмуляции OpenCL на центральном процессоре не нужно!
Ну, разве что для проведения экспериментов, так как видеокарты для использования OpenCL имеют безусловное преимущество.
Следующие параграфы описывают процедуру настройки OpenCL в зависимости от производителя. Вы можете перейти сразу на интересующую Вас инструкцию настройки, нажав на соответствующую ссылку:
1. Intel
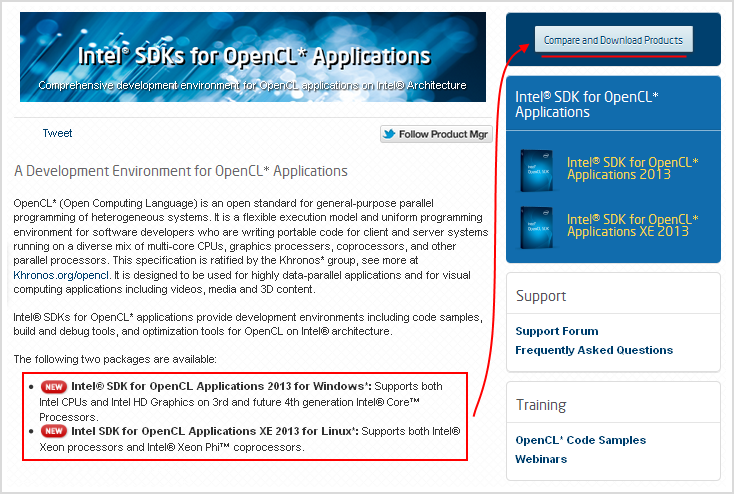
Для использования OpenCL на процессорах Intel необходимо скачать и установить «Intel SDK for OpenCL Applications«. Для этого перейдем на страницу сайта разработчика, с которой это можно сделать.
Рис. 1.1. Страница загрузки Intel SDK для OpenCL.
Здесь представлена общая информация об OpenCL, а также список доступных пакетов для скачивания. Чтобы скачать представленные пакеты нужно нажать на кнопку «Compare and Download Products» в правом верхнем углу страницы.
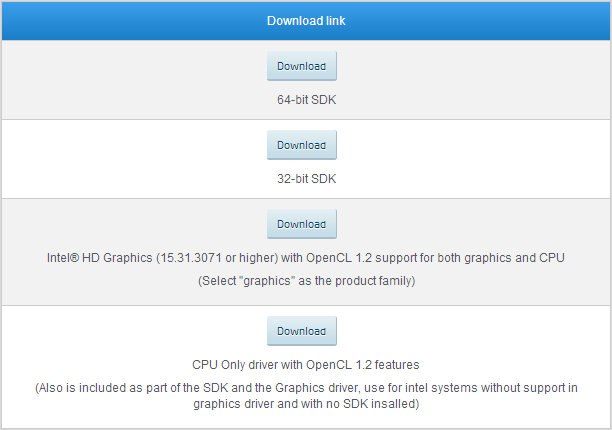
Рис. 1.2. Информация о доступных пакетах и требованиях для установки.
После нажатия на кнопку появится окошко, в котором будет представлена информация о том, для каких типов процессоров и операционных систем подходят указанные пакеты. Выбираем и загружаем подходящий пакет, нажав на кнопку «Download» над его изображением.
Рис. 1.3. Ссылки для скачивания SDK.
Рис. 1.4. Начало установки Intel SDK для OpenCL.
На экране появится окно установки «Intel SDK for OpenCL Applications» с поддержкой OpenCL 1.2. Жмем «Next» и следуем инструкции по установке.
Рис. 1.5. Принятие лицензионного соглашения.
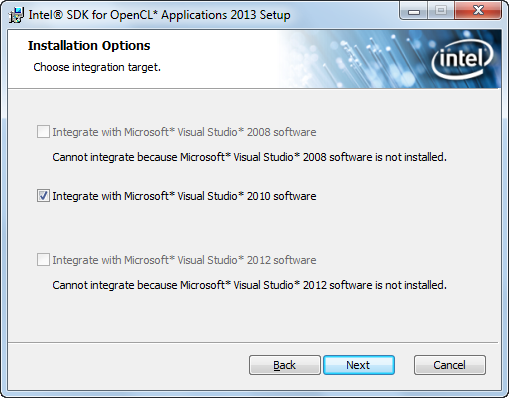
Рис. 1.6. Интеграция SDK c Visual Studio.
Если на Вашем ПК установлена «Microsoft Visual Studio» начиная с 2008 года, то будет предложено провести интеграцию для использования OpenCL также внутри нее. Далее остается лишь выбрать для каких пользователей будут доступны установленные компоненты и путь для установки SDK, после чего нажать «Install«.
Рис. 1.7. Процесс установки.
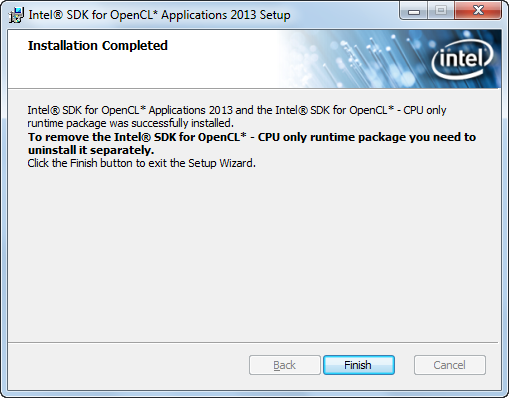
Начнется процесс установки, который займет пару минут, после чего на экране отобразится результат успешного выполнения. Нажимаем «Finish» и заканчиваем установку.
Рис. 1.8. Завершение установки.
2.1. Видеокарты и APU от AMD
Для установки OpenCL на видеокарту от AMD обновим ее драйвер до последней версии. Для этого переходим на страницу загрузки драйверов.
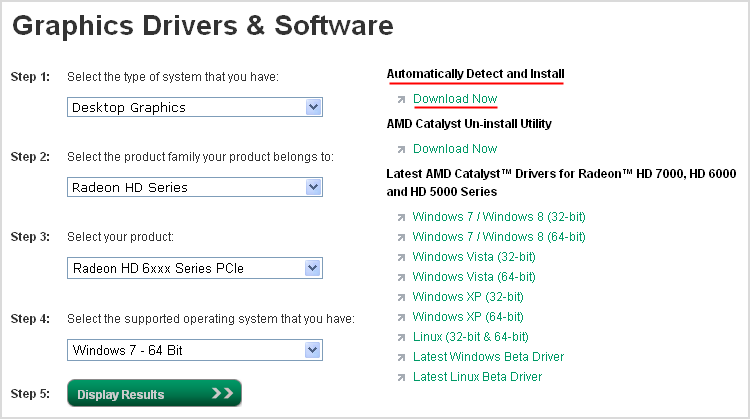
Рис. 2.1.1. Страница загрузки драйвера AMD.
Если вы знаете характеристики Вашей видеокарты, то драйвер можно найти, заполнив форму в левой части страницы. После выбора нужных строк из списков, жмем на «Display Results» для поиска подходящего драйвера.
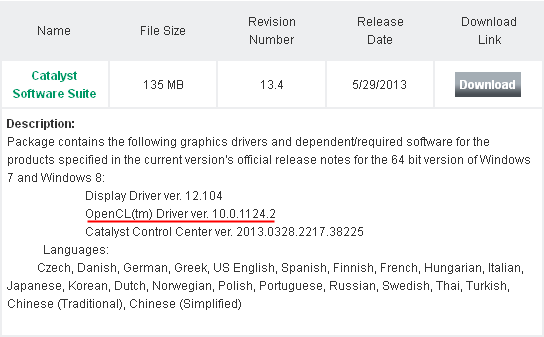
Рис. 2.1.2. Загрузка AMD Catalyst.
Система подберет несколько драйверов в наборе «Catalyst Software Suite«, в том числе и драйвер для OpenCL. Загружаем «Catalyst» и запускаем полученный файл.
Рис. 2.1.3. Страница загрузки приложения для определения типа видеокарты и версии драйвера.
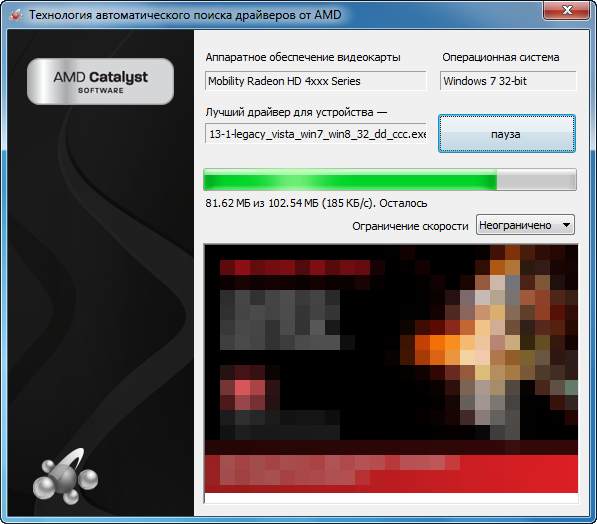
Рис. 2.1.4. Приложение для определения и загрузки подходящего драйвера.
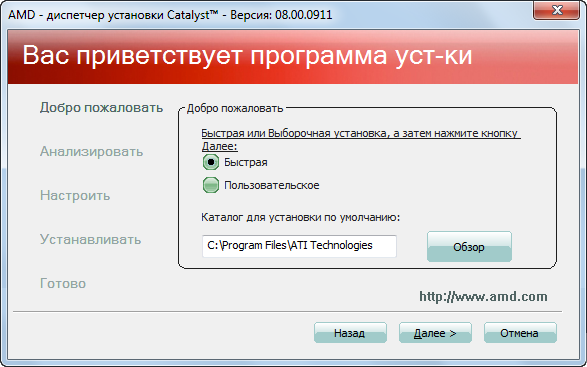
Рис. 2.1.5. Программа установки AMD Catalyst.
Рис. 2.1.6. Процесс установки.
Процесс установки займет пару минут, после чего появится уведомление об успешном завершении.
Рис. 2.1.7. Завершение установки.
2.2. Процессоры от AMD
Для установки OpenCL на процессор от AMD необходимо скачать и установить «AMD APP SDK» последней версии. Для этого переходим на следующую страницу на официальном сайте разработчика.
Рис. 2.2.1. Страница загрузки AMD APP SDK.
Рис. 2.2.2. Таблица доступных для скачивания SDK.
3. NVidia
Если у Вас имеется видеокарта от NVidia, то для установки OpenCL также необходимо обновить ее драйвер до последней версии. Для этого откроем страницу загрузки драйверов на сайте разработчика.
Рис. 3.1. Страница загрузки драйвера NVidia.
На странице расположено меню, которое позволит найти интересующий драйвер либо вручную, либо в автоматическом режиме. В ручном режиме необходимо ввести тип видеокарты, серию, тип операционной системы и нажать на «Поиск«. После этого система подберет самый свежий драйвер подходящий для Вашей видеокарты, и предложит скачать его.
Рис. 3.2. Загрузка выбранного драйвера.
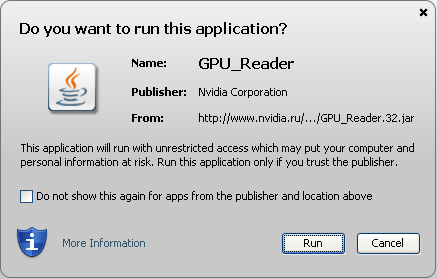
В автоматическом режиме нужно нажать на «Графические драйверы«, после чего вам будет предложено выполнить сканирование вашей системы при помощи java-приложения «GPU_Reader«.
Рис. 3.3. Запуск приложения для определения типа видеокарты и версии драйвера.
Запускаем приложение, нажав на «Run«. Ждем несколько секунд, после чего на странице появится информация о Вашей видеокарте, текущей версии установленного драйвера и версии самого свежего, рекомендованного для установки драйвера. Жмем на «Download» и попадаем на страницу загрузки, показанную на рисунке 3.2.
Рис. 3.4. Результат автоматического определения типа видеокарты и версии драйвера.
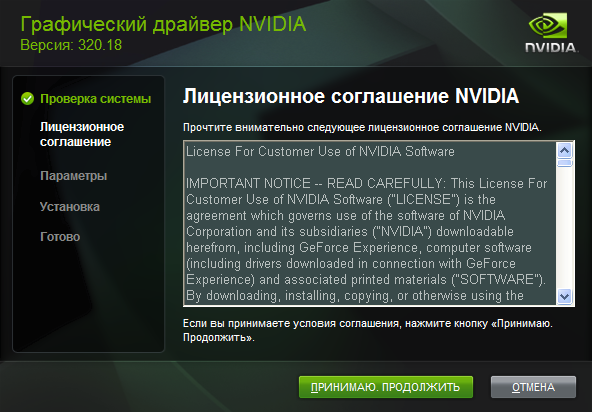
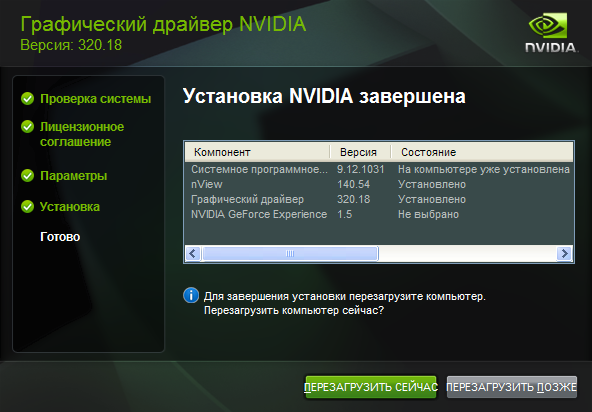
Нажимаем «Загрузить сейчас» и соглашаемся с лицензионным соглашением, нажав на «Принять и скачать«.
Рис. 3.5. Принятие лицензионного соглашения и скачивание драйвера.
Рис. 3.6. Принятие лицензионного соглашения на первом этапе установки.
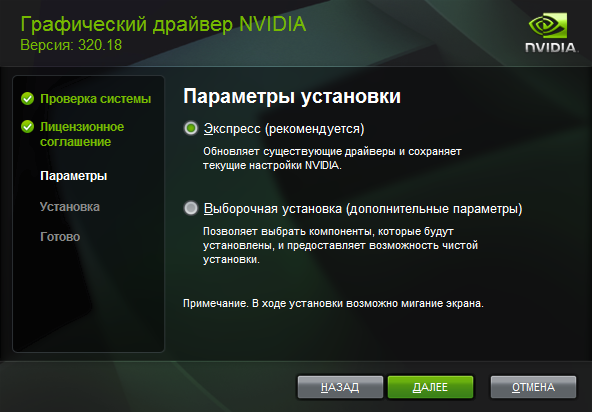
Рис. 3.7. Выбор режима установки.
Рис. 3.8. Процесс установки.
И всё, драйвер установлен, осталось лишь перезагрузить систему, и Вы сможете использовать OpenCL внутри терминала MetaTrader 5.
Рис. 3.9. Завершение установки.
Сравнение производительности
После выполнения скрипта, в окне графика на несколько секунд появится раскрашенное множество значений функции. Каждому из них сопоставляется один из тонов цвета, выбранного во входных параметрах (красный, зеленый или синий).
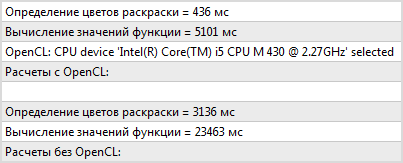
Помимо самой картинки в журнал «Эксперты» выводится время расчета функций каждым из способов, что позволяет легко убедиться в преимуществе и целесообразности использования OpenCL в MQL5. Увеличим значение шага и получим результаты работы скрипта:
Расчет значений функции и их раскраска двумя способами.
Суммарное время расчета функций на CPU с OpenCL уменьшилось более чем в 5 раз, а ведь это еще далеко не предел! Хорошо известно, что расчеты на современных видеокартах с поддержкой OpenCL выполняются на порядок быстрее, чем на процессорах. Этот факт хорошо отражают результаты выполнения скрипта на разных устройствах с OpenCL, представленные в следующей таблице:
| Устройство с OpenCL | Время выполнения без OpenCL в миллисекундах | Время выполнения с OpenCL в миллисекундах | Выигрыш |
|---|---|---|---|
| AMD Radeon HD 7970 | 20 361 мс | 171 мс | 119.07 раз |
| NVidia GeForce GT 630 | 24 742 мс | 578 мс | 42.8 раз |
| Intel Core i5 430M | 27 222 мс | 5 428 мс | 5.01 раз |
| AMD Athlon X2 Dual-Core QL-65 | 45 723 мс | 9 516 мс | 4.8 раз |
Источник
StreamHPC communications

Before we start, a few notes:
If you want to know more about OpenCL and you are looking for simple examples to get started, check the Tutorials section on this webpage.
Running an OpenCL application
If you only need to run an OpenCL application without getting into development stuff then most probably everything already works.
If OpenCL applications fail to launch, then you need to have a closer look to the drivers and hardware installed on your machine:
Here is where you can download drivers manually:
In addition, it is always a good idea to check for any other special requirements that the OpenCL application may have. Look for device type and OpenCL version in particular. For example, the application may run only on OpenCL CPUs, or conversely, on OpenCL GPUs. Or it may require a certain OpenCL version that your device does not support.
Developing OpenCL applications
Now it’s time to put the pedal to the metal and start developing some proper OpenCL applications.
The basic steps would be the following:
Ok, so let’s have a look into each of these.
OpenCL SDKs
For OpenCL headers and libraries the main options you can choose from are:
As long as you pay attention to the OpenCL version and the OpenCL features supported by your device, you can use the OpenCL headers and libraries from any of these three vendors.
OpenCL headers
Let’s assume that we are developing a 64bit C/C++ application using Visual Studio 2013. To begin with, we need to check how many OpenCL platforms are available in the system:
We need to specify where the OpenCL headers are located by adding the path to the OpenCL “CL” is in the same location as the other CUDA include files, that is, CUDA_INC_PATH. On a x64 Windows 8.1 machine with CUDA 6.5 the environment variable CUDA_INC_PATH is defined as “C:Program FilesNVIDIA GPU Computing ToolkitCUDAv6.5include”
If you’re using the AMD SDK, you need to replace “$(CUDA_INC_PATH)” with “$(AMDAPPSDKROOT)/include” or, for Intel SDK, with “$(INTELOCLSDKROOT)/include“.
OpenCL libraries
Similarly, we need to let the linker know about the OpenCL libraries. Firstly, add OpenCL.lib to the list of Additional Dependencies:
Secondly, specify the OpenCL.lib location in Additional Library Directories:
And you’re good to go! The application should now build and run. Now, just how difficult was it? Happy OpenCL-coding on Windows!
If you have any question or suggestion, just leave a comment.
Related Posts
An example of real-world, end-user OpenCL usage
OpenCL basics: Multiple OpenCL devices with the ICD.
Overview of OpenCL 2.0 hardware support, samples, blogs and drivers
Using OpenCL 1.2 with 1.1 devices
Anca Hamuraru joined StreamComputing in 2014, a collective of performance engineering experts.
Источник
OpenCL™ Runtimes for Intel® Processors
Last Updated: 10/05/2022
Deploy OpenCL™ Runtimes
Obtain runtimes to execute or develop OpenCL™ applications on Intel® Processors
Important Change
There is a change in OpenCL™ CPU runtime for Windows* distribution in the 2020 February release to be consistent with Linux* distribution. The OpenCL CPU runtime is removed from the OpenCL driver for Windows starting in the 2020 February release version «igfx_win10_100.7870.exe».
Intel® Graphics Technology Runtimes
Execute OpenCL™ applications on Intel® Processors with Intel® Graphics Technology.
Check release notes to ensure supported targets include your target device. For Intel® processors older than supported targets, please see the legacy deployment page.
Linux* OS
Note: The latest OpenCL runtime for CPU requires GNU* gcc version 7.3 or newer.
Intel® Graphics Compute Runtime for OpenCL™ Driver is deployed with package managers for multiple distributions. Please see the documentation on the GitHub* portal for deployment instructions.
Considerations for deployment:
Windows* OS
Intel® Xeon® Processor OR Intel® Core™ Processor (CPU) Runtimes
Execute OpenCL™ kernels directly on Intel® CPUs as OpenCL™ target devices.
Check release notes to ensure supported targets include your target device. For Intel® processors older than supported targets, see the legacy deployment page.
Intel® CPU Runtime for OpenCL™ Applications 18.1 for Linux* OS (64bit only)
Intel® CPU Runtime for OpenCL™ Applications 18.1 for Windows* OS (64bit or 32bit)
Intel® CPU Runtime for OpenCL™ Applications with SYCL support
Please visit the Intel® CPU Runtime for OpenCL™ Applications with SYCL support to download and install the runtime for Windows or Linux.
Develop OpenCL™ Applications
Tools to develop OpenCL™ applications for Intel® Processors
Intel® oneAPI: DPC++ Compiler
Intel® System Studio
Intel® SDK for OpenCL™ Applications
Intel® Distribution of OpenVINO™ toolkit
Intercept Layer for Debugging and Analyzing OpenCL™ Applications
Additional resources
*OpenCL and the OpenCL logo are trademarks of Apple Inc. used by permission by Khronos.
Источник
Adblock
detector
GeForce 382.33
Драйвер для видеокарт семейства GeForce 400 и выше, поддержка CUDA и ION/ION LE. Включает в себя драйвер контроллера 3D Vision, HD Audio, NVIDIA Surround и PhysX System Software. Обеспечивает поддержку дисплеев 4K (4kx2k @ 60 Hz). Поддержка технологий GeForce ShadowPlay, NVIDIA GameStream, NVIDIA FXAA, TXAA, Adaptive Vertical Sync, Frame Rate Target, а также функции ShadowPlay Twitch Streaming. Добавлены и обновлены ряд SLI и 3D Vision профилей. Драйверы Game Ready оптимизированы для Tekken 7 и Star Trek Bridge Crew. Включают оптимизации для ряда популярных игр, обеспечивающие увеличение производительности для видеокарт семейств GeForce 800/900/10.
GeForce 359.06
Драйвер для видеокарт семейства GeForce 8 и выше, поддержка CUDA и ION/ION LE. Включает в себя драйвер контроллера 3D Vision, HD Audio, NVIDIA Surround и PhysX System Software. Обеспечивает поддержку дисплеев 4K (4kx2k @ 60 Hz). Поддержка технологий GeForce ShadowPlay, NVIDIA GameStream, NVIDIA FXAA, TXAA, Adaptive Vertical Sync, Frame Rate Target, а также функции ShadowPlay Twitch Streaming. Добавлены и обновлены ряд SLI и 3D Vision профилей. Включают оптимизации для ряда популярных игр, обеспечивающие увеличение производительности для видеокарт семейств GeForce 400/500/600/700/900.
GeForce 334.89
Драйвер для видеокарт семейства GeForce 8 и выше, поддержка CUDA и ION/ION LE. Включает в себя драйвер контроллера 3D Vision, HD Audio, NVIDIA Surround и PhysX System Software. Обеспечивает поддержку дисплеев 4K (4kx2k @ 60 Hz). Поддержка технологий GeForce ShadowPlay, NVIDIA GameStream, NVIDIA FXAA, TXAA, Adaptive Vertical Sync, Frame Rate Target, а также функции ShadowPlay Twitch Streaming. Добавлены и обновлены ряд SLI и 3D Vision профилей. Включают оптимизации для ряда популярных игр, обеспечивающие увеличение производительности для видеокарт семейств GeForce 400/500/600/700.
GeForce 327.23 (R326)
Драйвер для видеокарт GeForce 6 и выше, поддержка CUDA. Включает в себя драйвер контроллера 3D Vision, HD Audio, NVIDIA Surround и PhysX System Software. Обеспечивает поддержку дисплеев 4K (4kx2k @ 60 Hz). Поддержка технологий NVIDIA FXAA, TXAA, Adaptive Vertical Sync, Frame Rate Target. Добавлено и обновлено множество SLI профилей и профилей 3D Vision. Включают оптимизации для ряда популярных игр, обеспечивающие увеличение производительности для видеокарт семейств GeForce 400/500/600/700. Рекомендован для использования с ОС Windows 8.1 Preview.
GeForce 314.07 (R313)
Драйвер для видеокарт GeForce серии 8 и выше, поддержка CUDA. Включает в себя драйвер контроллера 3D Vision, HD Audio, NVIDIA Surround и PhysX System Software. Обеспечивает поддержку DisplayPort 1.2 для серии GeForce GTX 600. Поддержка технологий NVIDIA FXAA, TXAA, Adaptive Vertical Sync, Frame Rate Target. Добавлено и обновлено множество SLI профилей, а также профилей 3D Vision. Включают оптимизации для ряда популярных игр, обеспечивающие увеличение производительности.
GeForce 310.90 (R310)
Драйвер для видеокарт GeForce 6 и выше, поддержка CUDA. Включает в себя драйвер контроллера 3D Vision, HD Audio, NVIDIA Surround и PhysX System Software. Поддержка технологий NVIDIA FXAA, TXAA, Adaptive Vertical Sync, Frame Rate Target. Добавлено и обновлено множество SLI профилей, а также профилей 3D Vision. Включают оптимизации для ряда популярных игр, обеспечивающие увеличение производительности.
GeForce 306.81 (R304)
Драйвер для видеокарт GeForce 6 и выше, поддержка CUDA. Включает в себя драйвер контроллера 3D Vision, HD Audio и PhysX System Software. Поддержка GPU серии GeForce GTX 6Х0. Добавлено и обновлено множество SLI профилей.
GeForce 306.97 (R304)
Драйвер для видеокарт GeForce 6 и выше, поддержка CUDA. Включает в себя драйвер контроллера 3D Vision, HD Audio, NVIDIA Surround и PhysX System Software. Поддержка GPU серии GeForce GTX 6Х0. Поддержка технологий NVIDIA FXAA, TXAA, Adaptive Vertical Sync, Frame Rate Target. Добавлено и обновлено множество SLI профилей. Рекомендованный драйвер для запуска ОС Windows 8.
GeForce 306.23 (R304)
Драйвер для видеокарт GeForce 6 и выше, поддержка CUDA. Включает в себя драйвер контроллера 3D Vision, HD Audio и PhysX System Software. Поддержка новых GPU серии GeForce GT 600, введена поддержка GeForce GTX 660 и GeForce GTX 650. Поддержка технологий NVIDIA FXAA, TXAA, Adaptive Vertical Sync, Frame Rate Target.
GeForce 305.68 (R304)
Драйвер для видеокарт GeForce 6 и выше, поддержка CUDA. Включает в себя драйвер контроллера 3D Vision. Поддержка новых GPU серии GeForce GT 600, введена поддержка GeForce GTX 660 Ti. Поддержка технологий NVIDIA FXAA, TXAA, Adaptive Vertical Sync, Frame Rate Target.
GeForce 301.42 (R300)
Драйвер для видеокарт GeForce 6 и выше, поддержка CUDA. Включает в себя драйвер контроллера 3D Vision. Поддержка новых GPU серии GeForce GT 600. Поддержка технологий NVIDIA FXAA, Adaptive Vertical Sync, Frame Rate Target.
GeForce 296.10
Драйвер для видеокарт GeForce 6 и выше, поддержка ION. Включает в себя драйвер контроллера 3D Vision.
Всем привет!
Подскажите, как установить OpenCL (Windows 10 x64 / Intel Core i5)?
Откуда скачать драйвер для запуска прог, использующих OpenCL?
Гуглю, находится сайт https://software.intel.com/en-… cl-drivers
Там есть ссылки «Intel® Processor Graphics» (видеокарта у меня интегрированная Intel HD Graphics 3000 (Gen6) и «Intel® Xeon™ Processor or Intel® Core™ Processor»
Тыкаю на одну ссылку, на другую, в итоге попадаю:
• либо на Page not found (https://software.intel.com/sdk/opencl),
• либо на скачку «Intel Driver & Support Assistant» — ставлю, запускаю, получаю сообщение «К сожалению, нет доступных обновлений ПО»,
• либо на страницу скачки драйверов, скачиваю драйвер (2 варианта) для 6-го поколения Intel Graphics, выводится сообщение, что система не удовлетворяет минимальным требованиям.
При запуске прог, работающих с OpenCL выводятся сообщения вида:
Код
Cannot find an OpenCL ICD loader library. You are probably missing the native OpenCL runtime or driver for your platform. * AMD GPUs on Windows require this runtime and/or driver: "AMD Radeon Software Crimson Edition" (15.12 or later) * Intel CPUs require this runtime and/or driver: "OpenCL Runtime for Intel Core and Intel Xeon Processors" (16.1.1 or later) * Intel GPUs on Windows require this runtime and/or driver: "OpenCL Driver for Intel Iris and Intel HD Graphics" * NVIDIA GPUs require this runtime and/or driver: "NVIDIA Driver" (367.x or later)
• Гуглю «OpenCL Runtime for Intel Core and Intel Xeon Processors», выхожу на страницу скачки «Intel SDK for OpenCL». При запуске пишет «Intel HD graphics driver is installed. Uninstall it before installing Intel SDK for OpenCL — CPU only runtime package for Intel Core and Intel Xeon Processors«. Видимо, этот пак только для CPU без задействования GPU.
• Гуглю «OpenCL Driver for Intel Iris and Intel HD Graphics», попадаю на страницу, которую я описывал в самом начале.
Где-то на сайте проскальзывают сообщения о том, что дрова OpenCL идут вместе с дровами видеокарты. Но почему у меня тогда не запускаются проги с OpenCL ?!!!
Другая прога выдаёт «Error: no opencl platforms found».
С сайта https://www.khronos.org/opencl/ тоже непонятно что скачивать, там вообще исходники сплошные…

Before we start, a few notes:
- The steps described herein have been tested on Windows 8.1 only, but should also apply for Windows 7 and Windows 8.
- We will not discuss how to write an actual OpenCL program or kernel, but focus on how to get everything installed and ready for OpenCL on a Windows machine. This is because writing efficient OpenCL kernels is almost entirely OS independent.
If you want to know more about OpenCL and you are looking for simple examples to get started, check the Tutorials section on this webpage.
Running an OpenCL application
If you only need to run an OpenCL application without getting into development stuff then most probably everything already works.
If OpenCL applications fail to launch, then you need to have a closer look to the drivers and hardware installed on your machine:
- Check that you have a device that supports OpenCL. All graphics cards and CPUs from 2011 and later support OpenCL. If your computer is from 2010 or before, check this page. You can also find a list with OpenCL conformant products on Khronos webpage.
- Make sure your OpenCL device driver is up to date, especially if you’re not using the latest and greatest hardware. With certain older devices OpenCL support wasn’t initially included in the drivers.
Here is where you can download drivers manually:
- Intel has hidden them a bit, but you can find them here with support for OpenCL 2.0.
- AMD’s GPU-drivers include the OpenCL-drivers for CPUs, APUs and GPUs, version 2.0.
- NVIDIA’s GPU-drivers mention mostly CUDA, but the drivers for OpenCL 1.1 1.2 are there too.
In addition, it is always a good idea to check for any other special requirements that the OpenCL application may have. Look for device type and OpenCL version in particular. For example, the application may run only on OpenCL CPUs, or conversely, on OpenCL GPUs. Or it may require a certain OpenCL version that your device does not support.
A great tool that will allow you to retrieve the details for the OpenCL devices in your system is Caps Viewer.
Developing OpenCL applications
Now it’s time to put the pedal to the metal and start developing some proper OpenCL applications.
The basic steps would be the following:
- Make sure you have a machine which supports OpenCL, as described above.
- Get the OpenCL headers and libraries included in the OpenCL SDK from your favourite vendor.
- Start writing OpenCL code. That’s the difficult part.
- Tell the compiler where the OpenCL headers are located.
- Tell the linker where to find the OpenCL .lib files.
- Build the fabulous application.
- Run and prepare to be awed in amazement.
Ok, so let’s have a look into each of these.
OpenCL SDKs
For OpenCL headers and libraries the main options you can choose from are:
- NVIDIA – CUDA Toolkit. You can grab the OpenCL samples here.
- AMD – AMD APP SDK. Also works with Intel’s CPUs.
- Headers and OpenCL.lib are here: https://github.com/GPUOpen-LibrariesAndSDKs/OCL-SDK/releases
- Samples are here: https://github.com/OpenCL/AMD_APP_samples
- Math libraries are here: https://github.com/clMathLibraries
- Intel – the previous Intel SDK for OpenCL is now integrated into Intel’s new tools, such as Intel INDE (which has a free starters edition) or Intel Media Server Studio. Grab any of these in order to have everything ready for building OpenCL code.
As long as you pay attention to the OpenCL version and the OpenCL features supported by your device, you can use the OpenCL headers and libraries from any of these three vendors.
OpenCL headers
Let’s assume that we are developing a 64bit C/C++ application using Visual Studio 2013. To begin with, we need to check how many OpenCL platforms are available in the system:
[raw]
#include<stdio.h>
#include<CL/cl.h>
int main(void)
{
cl_int err;
cl_uint numPlatforms;
err = clGetPlatformIDs(0, NULL, &numPlatforms);
if (CL_SUCCESS == err)
printf("nDetected OpenCL platforms: %d", numPlatforms);
else
printf("nError calling clGetPlatformIDs. Error code: %d", err);
return 0;
}
[/raw]
We need to specify where the OpenCL headers are located by adding the path to the OpenCL “CL” is in the same location as the other CUDA include files, that is, CUDA_INC_PATH. On a x64 Windows 8.1 machine with CUDA 6.5 the environment variable CUDA_INC_PATH is defined as “C:Program FilesNVIDIA GPU Computing ToolkitCUDAv6.5include”
If you’re using the AMD SDK, you need to replace “$(CUDA_INC_PATH)” with “$(AMDAPPSDKROOT)/include” or, for Intel SDK, with “$(INTELOCLSDKROOT)/include“.
OpenCL libraries
Similarly, we need to let the linker know about the OpenCL libraries. Firstly, add OpenCL.lib to the list of Additional Dependencies:
Secondly, specify the OpenCL.lib location in Additional Library Directories:
As in the case of the includes, If you’re using the AMD SDK, replace “$(CUDA_LIB_PATH)” with “$(AMDAPPSDKROOT)/lib/x86_64” , or in the case of Intel with “$(INTELOCLSDKROOT)/lib/x64“.
And you’re good to go! The application should now build and run. Now, just how difficult was it? Happy OpenCL-coding on Windows!
If you have any question or suggestion, just leave a comment.
Related Posts

NVIDIA has released a new driver belonging to the R465 family (from version 460.xx to 469.xx). The GeForce 465 family supports the following GPU architectures: Ampere, Turing, Volta, Pascal, Kepler and Maxwell.
The GeForce 465 family brings the support of OpenCL 3.0 to Kepler and later GPUs and the new Resizable BAR (Base Address Register) technology that should improve gaming framerates like AMD SAM (Smart Access Memory).
Game Ready for Outriders
This new Game Ready Driver provides support for the launch of Outriders, which features NVIDIA
DLSS technology. Additionally, this release also provides optimal day-1 support for:
– DIRT 5’s new ray tracing update
– The launch of Evil Genius 2: World Domination
– The launch of the KINGDOM HEARTS Series on the Epic Games StoreGaming Technology
– Includes support for Resizable BAR across the GeForce RTX 30 Series of Desktop and
Notebook GPUs
– Includes beta support for virtualization on GeForce GPUsOpenCL 3.0
Added support for OpenCL 3.02, the latest major version of OpenCL maintaining backward
compatibility with OpenCL 1.2. NVIDIA OpenCL 3.0 continues to support existing OpenCL 1.2
functionality as well as Khronos and vendor extensions that are already supported with NVIDIA OpenCL 1.2 drivers.Fixed Issues in this Release
– [Rainbow Six Siege][Vulkan]: Smoke appears pixelated. [3266916]
– [Vulkan][X4: Foundations 4.00/X4: Cradle of Humanity] The game may crash on GeForce RTX 30 Series. [200701230]
– [GeForce RTX 3090]: Blue-screen crash occurs when Samsung Odyssey G9 is paired with HDMI TV. [3240366]
– [GeForce RTX 2060]: Blue-screen crash (DPC_WATCHDOGS_VIOLATION) occurs when playing a game and watching YouTube video simultaneously. [3196272]
– [Sunset Overdrive]: The application may display random green corruption if Depth of Field is enabled from in-game settings [2750770]
– Realtek Displayport-to-HDMI 2.1 protocol converter clock limited to 600MHz pixel clock [3202060]
– [G-SYNC][NVIDIA Ampere/Turing GPU architecture]: GPU power consumption may increase in idle mode on systems using certain higher refresh-rate G-SYNC monitors. [200667566].
– [GFE Screenshot/HDR]: Application screenshots are washed out when HDR is enabled [3229781]
GeForce 466.11
Game Ready for Mortal Shell
This new Game Ready Driver provides support for Mortal Shell’s RTX update, which introduces NVIDIA DLSS, boosting performance by up to 130% at 4K. Additionally, this release also provides optimal support for Valorant’s NVIDIA Reflex update, NVIDIA Broadcast Noise Reduction support in OBS, 6 new G-SYNC Compatible gaming monitors and TVs, and more.Fixed Issues in this Release
– [Supreme Commander/Supreme Commander 2]: The games experience low FPS. [3231218/3230880]
– [Adobe Camera RAW 12.x]: RAW files may show up black in Adobe Lightroom. [3266883/200717265]
– [VR]: Microsoft Flight Simulator 2020 VR may stutter if Hardware-accelerated GPU scheduling is disabled. [3246674]
– Some displays may show incorrect color levels after booting into Windows. [3285148/3287063]
More information: Mortal Shell Game Ready Driver Released: Experience RTX Goodness With Ray Tracing And DLSS @ NVIDIA.
GeForce 466.27
Game Ready for the Metro Exodus PC Enhanced Edition
This new Game Ready Driver provides support for the Metro Exodus PC Enhanced Edition, which adds additional ray-traced effects and NVIDIA DLSS 2.0 for greater performance and improved image quality. Additionally, this release also provides optimal support for Mass Effect Legendary Edition and Resident Evil Village, along with support for 5 new G-SYNC Compatible displays.New Features and Other Changes
– Added support for DirectX 12 Agility SDK.
– This driver updates the hash limiter for the GeForce RTX 3060 12GB and is required for product shipped starting mid-May.
GeForce 466.47
Game Ready for Days Gone
This new Game Ready Driver provides support for the launch of Days Gone on PC with increased levels of detail, higher foliage draw distances, native 4K rendering, a configurable field of view, ultra-wide monitor support, unlocked frame rates, and more. Additionally, this release also provides optimal support for Knockout City.New Features and Other Changes
– This driver version is required for GeForce RTX 3080, RTX 3070, and RTX 3060 TI graphics cards with LHR, which ship starting late May, 2021.
More information: Days Gone GeForce Game Ready Driver @ NVIDIA.
Downloads
- latest version for win10 64-bit (desktop+notebook) @ Geeks3D
- 466.47 win10 64-bit @ NVIDIA
- 466.27 win10 64-bit @ NVIDIA
- 466.27 win7 64-bit @ NVIDIA
- 466.11 win10 64-bit @ NVIDIA
- 466.11 win7 64-bit @ NVIDIA
- 465.89 win10 64-bit @ NVIDIA
- 465.89 win7 64-bit @ NVIDIA
GeForce 465.89
GeForce 466.11
GeForce 466.27
GeForce 466.47
OpenGL support
GeForce 465.89
GeForce 465.89 exposes OpenGL 4.6 and 433 extensions for a GeForce RTX 3060 Ti on Windows 10 (v20H2).
- GL_VENDOR: NVIDIA Corporation - GL_RENDERER: NVIDIA GeForce RTX 3060 Ti/PCIe/SSE2 - GL_VERSION: 4.6.0 NVIDIA 465.89 - GL_SHADING_LANGUAGE_VERSION: 4.60 NVIDIA - OpenGL Extensions: 433 extensions (GL=401 and WGL=32) - GL_AMD_multi_draw_indirect - GL_AMD_seamless_cubemap_per_texture - GL_AMD_vertex_shader_viewport_index - GL_AMD_vertex_shader_layer - GL_ARB_arrays_of_arrays - GL_ARB_base_instance - GL_ARB_bindless_texture - GL_ARB_blend_func_extended - GL_ARB_buffer_storage - GL_ARB_clear_buffer_object - GL_ARB_clear_texture - GL_ARB_clip_control - GL_ARB_color_buffer_float - GL_ARB_compatibility - GL_ARB_compressed_texture_pixel_storage - GL_ARB_conservative_depth - GL_ARB_compute_shader - GL_ARB_compute_variable_group_size - GL_ARB_conditional_render_inverted - GL_ARB_copy_buffer - GL_ARB_copy_image - GL_ARB_cull_distance - GL_ARB_debug_output - GL_ARB_depth_buffer_float - GL_ARB_depth_clamp - GL_ARB_depth_texture - GL_ARB_derivative_control - GL_ARB_direct_state_access - GL_ARB_draw_buffers - GL_ARB_draw_buffers_blend - GL_ARB_draw_indirect - GL_ARB_draw_elements_base_vertex - GL_ARB_draw_instanced - GL_ARB_enhanced_layouts - GL_ARB_ES2_compatibility - GL_ARB_ES3_compatibility - GL_ARB_ES3_1_compatibility - GL_ARB_ES3_2_compatibility - GL_ARB_explicit_attrib_location - GL_ARB_explicit_uniform_location - GL_ARB_fragment_coord_conventions - GL_ARB_fragment_layer_viewport - GL_ARB_fragment_program - GL_ARB_fragment_program_shadow - GL_ARB_fragment_shader - GL_ARB_fragment_shader_interlock - GL_ARB_framebuffer_no_attachments - GL_ARB_framebuffer_object - GL_ARB_framebuffer_sRGB - GL_ARB_geometry_shader4 - GL_ARB_get_program_binary - GL_ARB_get_texture_sub_image - GL_ARB_gl_spirv - GL_ARB_gpu_shader5 - GL_ARB_gpu_shader_fp64 - GL_ARB_gpu_shader_int64 - GL_ARB_half_float_pixel - GL_ARB_half_float_vertex - GL_ARB_imaging - GL_ARB_indirect_parameters - GL_ARB_instanced_arrays - GL_ARB_internalformat_query - GL_ARB_internalformat_query2 - GL_ARB_invalidate_subdata - GL_ARB_map_buffer_alignment - GL_ARB_map_buffer_range - GL_ARB_multi_bind - GL_ARB_multi_draw_indirect - GL_ARB_multisample - GL_ARB_multitexture - GL_ARB_occlusion_query - GL_ARB_occlusion_query2 - GL_ARB_parallel_shader_compile - GL_ARB_pipeline_statistics_query - GL_ARB_pixel_buffer_object - GL_ARB_point_parameters - GL_ARB_point_sprite - GL_ARB_polygon_offset_clamp - GL_ARB_post_depth_coverage - GL_ARB_program_interface_query - GL_ARB_provoking_vertex - GL_ARB_query_buffer_object - GL_ARB_robust_buffer_access_behavior - GL_ARB_robustness - GL_ARB_sample_locations - GL_ARB_sample_shading - GL_ARB_sampler_objects - GL_ARB_seamless_cube_map - GL_ARB_seamless_cubemap_per_texture - GL_ARB_separate_shader_objects - GL_ARB_shader_atomic_counter_ops - GL_ARB_shader_atomic_counters - GL_ARB_shader_ballot - GL_ARB_shader_bit_encoding - GL_ARB_shader_clock - GL_ARB_shader_draw_parameters - GL_ARB_shader_group_vote - GL_ARB_shader_image_load_store - GL_ARB_shader_image_size - GL_ARB_shader_objects - GL_ARB_shader_precision - GL_ARB_shader_storage_buffer_object - GL_ARB_shader_subroutine - GL_ARB_shader_texture_image_samples - GL_ARB_shader_texture_lod - GL_ARB_shading_language_100 - GL_ARB_shader_viewport_layer_array - GL_ARB_shading_language_420pack - GL_ARB_shading_language_include - GL_ARB_shading_language_packing - GL_ARB_shadow - GL_ARB_sparse_buffer - GL_ARB_sparse_texture - GL_ARB_sparse_texture2 - GL_ARB_sparse_texture_clamp - GL_ARB_spirv_extensions - GL_ARB_stencil_texturing - GL_ARB_sync - GL_ARB_tessellation_shader - GL_ARB_texture_barrier - GL_ARB_texture_border_clamp - GL_ARB_texture_buffer_object - GL_ARB_texture_buffer_object_rgb32 - GL_ARB_texture_buffer_range - GL_ARB_texture_compression - GL_ARB_texture_compression_bptc - GL_ARB_texture_compression_rgtc - GL_ARB_texture_cube_map - GL_ARB_texture_cube_map_array - GL_ARB_texture_env_add - GL_ARB_texture_env_combine - GL_ARB_texture_env_crossbar - GL_ARB_texture_env_dot3 - GL_ARB_texture_filter_anisotropic - GL_ARB_texture_filter_minmax - GL_ARB_texture_float - GL_ARB_texture_gather - GL_ARB_texture_mirror_clamp_to_edge - GL_ARB_texture_mirrored_repeat - GL_ARB_texture_multisample - GL_ARB_texture_non_power_of_two - GL_ARB_texture_query_levels - GL_ARB_texture_query_lod - GL_ARB_texture_rectangle - GL_ARB_texture_rg - GL_ARB_texture_rgb10_a2ui - GL_ARB_texture_stencil8 - GL_ARB_texture_storage - GL_ARB_texture_storage_multisample - GL_ARB_texture_swizzle - GL_ARB_texture_view - GL_ARB_timer_query - GL_ARB_transform_feedback2 - GL_ARB_transform_feedback3 - GL_ARB_transform_feedback_instanced - GL_ARB_transform_feedback_overflow_query - GL_ARB_transpose_matrix - GL_ARB_uniform_buffer_object - GL_ARB_vertex_array_bgra - GL_ARB_vertex_array_object - GL_ARB_vertex_attrib_64bit - GL_ARB_vertex_attrib_binding - GL_ARB_vertex_buffer_object - GL_ARB_vertex_program - GL_ARB_vertex_shader - GL_ARB_vertex_type_10f_11f_11f_rev - GL_ARB_vertex_type_2_10_10_10_rev - GL_ARB_viewport_array - GL_ARB_window_pos - GL_ATI_draw_buffers - GL_ATI_texture_float - GL_ATI_texture_mirror_once - GL_S3_s3tc - GL_EXT_texture_env_add - GL_EXT_abgr - GL_EXT_bgra - GL_EXT_bindable_uniform - GL_EXT_blend_color - GL_EXT_blend_equation_separate - GL_EXT_blend_func_separate - GL_EXT_blend_minmax - GL_EXT_blend_subtract - GL_EXT_compiled_vertex_array - GL_EXT_Cg_shader - GL_EXT_depth_bounds_test - GL_EXT_direct_state_access - GL_EXT_draw_buffers2 - GL_EXT_draw_instanced - GL_EXT_draw_range_elements - GL_EXT_fog_coord - GL_EXT_framebuffer_blit - GL_EXT_framebuffer_multisample - GL_EXTX_framebuffer_mixed_formats - GL_EXT_framebuffer_multisample_blit_scaled - GL_EXT_framebuffer_object - GL_EXT_framebuffer_sRGB - GL_EXT_geometry_shader4 - GL_EXT_gpu_program_parameters - GL_EXT_gpu_shader4 - GL_EXT_multi_draw_arrays - GL_EXT_multiview_texture_multisample - GL_EXT_multiview_timer_query - GL_EXT_packed_depth_stencil - GL_EXT_packed_float - GL_EXT_packed_pixels - GL_EXT_pixel_buffer_object - GL_EXT_point_parameters - GL_EXT_polygon_offset_clamp - GL_EXT_post_depth_coverage - GL_EXT_provoking_vertex - GL_EXT_raster_multisample - GL_EXT_rescale_normal - GL_EXT_secondary_color - GL_EXT_separate_shader_objects - GL_EXT_separate_specular_color - GL_EXT_shader_image_load_formatted - GL_EXT_shader_image_load_store - GL_EXT_shader_integer_mix - GL_EXT_shadow_funcs - GL_EXT_sparse_texture2 - GL_EXT_stencil_two_side - GL_EXT_stencil_wrap - GL_EXT_texture3D - GL_EXT_texture_array - GL_EXT_texture_buffer_object - GL_EXT_texture_compression_dxt1 - GL_EXT_texture_compression_latc - GL_EXT_texture_compression_rgtc - GL_EXT_texture_compression_s3tc - GL_EXT_texture_cube_map - GL_EXT_texture_edge_clamp - GL_EXT_texture_env_combine - GL_EXT_texture_env_dot3 - GL_EXT_texture_filter_anisotropic - GL_EXT_texture_filter_minmax - GL_EXT_texture_integer - GL_EXT_texture_lod - GL_EXT_texture_lod_bias - GL_EXT_texture_mirror_clamp - GL_EXT_texture_object - GL_EXT_texture_shadow_lod - GL_EXT_texture_shared_exponent - GL_EXT_texture_sRGB - GL_EXT_texture_sRGB_R8 - GL_EXT_texture_sRGB_decode - GL_EXT_texture_storage - GL_EXT_texture_swizzle - GL_EXT_timer_query - GL_EXT_transform_feedback2 - GL_EXT_vertex_array - GL_EXT_vertex_array_bgra - GL_EXT_vertex_attrib_64bit - GL_EXT_window_rectangles - GL_EXT_import_sync_object - GL_IBM_rasterpos_clip - GL_IBM_texture_mirrored_repeat - GL_KHR_context_flush_control - GL_KHR_debug - GL_EXT_memory_object - GL_EXT_memory_object_win32 - GL_NV_memory_object_sparse - GL_EXT_win32_keyed_mutex - GL_KHR_parallel_shader_compile - GL_KHR_no_error - GL_KHR_robust_buffer_access_behavior - GL_KHR_robustness - GL_EXT_semaphore - GL_EXT_semaphore_win32 - GL_NV_timeline_semaphore - GL_KHR_shader_subgroup - GL_KTX_buffer_region - GL_NV_alpha_to_coverage_dither_control - GL_NV_bindless_multi_draw_indirect - GL_NV_bindless_multi_draw_indirect_count - GL_NV_bindless_texture - GL_NV_blend_equation_advanced - GL_NV_blend_equation_advanced_coherent - GL_NVX_blend_equation_advanced_multi_draw_buffers - GL_NV_blend_minmax_factor - GL_NV_blend_square - GL_NV_clip_space_w_scaling - GL_NV_command_list - GL_NV_compute_program5 - GL_NV_compute_shader_derivatives - GL_NV_conditional_render - GL_NV_conservative_raster - GL_NV_conservative_raster_dilate - GL_NV_conservative_raster_pre_snap - GL_NV_conservative_raster_pre_snap_triangles - GL_NV_conservative_raster_underestimation - GL_NV_copy_depth_to_color - GL_NV_copy_image - GL_NV_depth_buffer_float - GL_NV_depth_clamp - GL_NV_draw_texture - GL_NV_draw_vulkan_image - GL_NV_ES1_1_compatibility - GL_NV_ES3_1_compatibility - GL_NV_explicit_multisample - GL_NV_feature_query - GL_NV_fence - GL_NV_fill_rectangle - GL_NV_float_buffer - GL_NV_fog_distance - GL_NV_fragment_coverage_to_color - GL_NV_fragment_program - GL_NV_fragment_program_option - GL_NV_fragment_program2 - GL_NV_fragment_shader_barycentric - GL_NV_fragment_shader_interlock - GL_NV_framebuffer_mixed_samples - GL_NV_framebuffer_multisample_coverage - GL_NV_geometry_shader4 - GL_NV_geometry_shader_passthrough - GL_NV_gpu_program4 - GL_NV_internalformat_sample_query - GL_NV_gpu_program4_1 - GL_NV_gpu_program5 - GL_NV_gpu_program5_mem_extended - GL_NV_gpu_program_fp64 - GL_NV_gpu_shader5 - GL_NV_half_float - GL_NV_light_max_exponent - GL_NV_memory_attachment - GL_NV_mesh_shader - GL_NV_multisample_coverage - GL_NV_multisample_filter_hint - GL_NV_occlusion_query - GL_NV_packed_depth_stencil - GL_NV_parameter_buffer_object - GL_NV_parameter_buffer_object2 - GL_NV_path_rendering - GL_NV_path_rendering_shared_edge - GL_NV_pixel_data_range - GL_NV_point_sprite - GL_NV_primitive_restart - GL_NV_primitive_shading_rate - GL_NV_query_resource - GL_NV_query_resource_tag - GL_NV_register_combiners - GL_NV_register_combiners2 - GL_NV_representative_fragment_test - GL_NV_sample_locations - GL_NV_sample_mask_override_coverage - GL_NV_scissor_exclusive - GL_NV_shader_atomic_counters - GL_NV_shader_atomic_float - GL_NV_shader_atomic_float64 - GL_NV_shader_atomic_fp16_vector - GL_NV_shader_atomic_int64 - GL_NV_shader_buffer_load - GL_NV_shader_storage_buffer_object - GL_NV_shader_subgroup_partitioned - GL_NV_shader_texture_footprint - GL_NV_shading_rate_image - GL_NV_stereo_view_rendering - GL_NV_texgen_reflection - GL_NV_texture_barrier - GL_NV_texture_compression_vtc - GL_NV_texture_dirty_tile_map - GL_NV_texture_env_combine4 - GL_NV_texture_multisample - GL_NV_texture_rectangle - GL_NV_texture_rectangle_compressed - GL_NV_texture_shader - GL_NV_texture_shader2 - GL_NV_texture_shader3 - GL_NV_transform_feedback - GL_NV_transform_feedback2 - GL_NV_uniform_buffer_unified_memory - GL_NV_vertex_array_range - GL_NV_vertex_array_range2 - GL_NV_vertex_attrib_integer_64bit - GL_NV_vertex_buffer_unified_memory - GL_NV_vertex_program - GL_NV_vertex_program1_1 - GL_NV_vertex_program2 - GL_NV_vertex_program2_option - GL_NV_vertex_program3 - GL_NV_viewport_array2 - GL_NV_viewport_swizzle - GL_NVX_conditional_render - GL_NVX_linked_gpu_multicast - GL_NV_gpu_multicast - GL_NVX_gpu_multicast2 - GL_NVX_progress_fence - GL_NVX_gpu_memory_info - GL_NVX_multigpu_info - GL_NVX_nvenc_interop - GL_NV_shader_thread_group - GL_NV_shader_thread_shuffle - GL_KHR_blend_equation_advanced - GL_KHR_blend_equation_advanced_coherent - GL_OVR_multiview - GL_OVR_multiview2 - GL_SGIS_generate_mipmap - GL_SGIS_texture_lod - GL_SGIX_depth_texture - GL_SGIX_shadow - GL_SUN_slice_accum - GL_WIN_swap_hint - WGL_EXT_swap_control - WGL_ARB_buffer_region - WGL_ARB_create_context - WGL_ARB_create_context_no_error - WGL_ARB_create_context_profile - WGL_ARB_create_context_robustness - WGL_ARB_context_flush_control - WGL_ARB_extensions_string - WGL_ARB_make_current_read - WGL_ARB_multisample - WGL_ARB_pbuffer - WGL_ARB_pixel_format - WGL_ARB_pixel_format_float - WGL_ARB_render_texture - WGL_ATI_pixel_format_float - WGL_EXT_colorspace - WGL_EXT_create_context_es_profile - WGL_EXT_create_context_es2_profile - WGL_EXT_extensions_string - WGL_EXT_framebuffer_sRGB - WGL_EXT_pixel_format_packed_float - WGL_EXT_swap_control_tear - WGL_NVX_DX_interop - WGL_NV_DX_interop - WGL_NV_DX_interop2 - WGL_NV_copy_image - WGL_NV_delay_before_swap - WGL_NV_float_buffer - WGL_NV_multisample_coverage - WGL_NV_multigpu_context - WGL_NV_render_depth_texture - WGL_NV_render_texture_rectangle - OpenGL SPIR-V Extensions: 11 - SPV_KHR_post_depth_coverage - SPV_KHR_shader_atomic_counter_ops - SPV_KHR_shader_ballot - SPV_KHR_shader_draw_parameters - SPV_KHR_storage_buffer_storage_class - SPV_KHR_subgroup_vote - SPV_NV_geometry_shader_passthrough - SPV_NV_sample_mask_override_coverage - SPV_NV_shader_subgroup_partitioned - SPV_NV_stereo_view_rendering - SPV_NV_viewport_array2
GeForce 466.11
GeForce 466.11 exposes the same OpenGL 4.6 support than 465.89:
GL_RENDERER: NVIDIA GeForce RTX 3060 Ti/PCIe/SSE2 GL_VENDOR: NVIDIA Corporation GL_VERSION: 4.6.0 NVIDIA 466.11 OpenGL extensions: 433
GeForce 466.27
GeForce 466.27 exposes the same OpenGL 4.6 support than 465.89:
- GL_VENDOR: NVIDIA Corporation - GL_RENDERER: NVIDIA GeForce RTX 3060 Ti/PCIe/SSE2 - GL_VERSION: 4.6.0 NVIDIA 466.27 - GL_SHADING_LANGUAGE_VERSION: 4.60 NVIDIA OpenGL extensions: 433
Vulkan support
GeForce 465.89
GeForce 465.89 exposes Vulkan 1.2.168 and 137 device extensions for a GeForce RTX 3060 Ti on Windows 10 (v20H2). Compared to family 460, this driver brings the following new NVIDIA extensions:
– VK_NVX_binary_import
– VK_NVX_image_view_handle
– VK_NVX_multiview_per_view_attributes
- Device 1
- name: NVIDIA GeForce RTX 3060 Ti
- device type: VK_PHYSICAL_DEVICE_TYPE_DISCRETE_GPU
- device ID: 10DE-2486
- API version: 1.2.168
- NVIDIA driver version: 465.89.0.0
- VK_KHR_driver_properties information:
- driverName: NVIDIA
- driverID_str: VK_DRIVER_ID_NVIDIA_PROPRIETARY_KHR
- driverID: 4
- conformanceVersion: 1.2.2.5
- driverInfo: 465.89
- # of extensions => 137
- 001/ VK_KHR_16bit_storage
- 002/ VK_KHR_8bit_storage
- 003/ VK_KHR_acceleration_structure
- 004/ VK_KHR_bind_memory2
- 005/ VK_KHR_buffer_device_address
- 006/ VK_KHR_copy_commands2
- 007/ VK_KHR_create_renderpass2
- 008/ VK_KHR_dedicated_allocation
- 009/ VK_KHR_deferred_host_operations
- 010/ VK_KHR_depth_stencil_resolve
- 011/ VK_KHR_descriptor_update_template
- 012/ VK_KHR_device_group
- 013/ VK_KHR_draw_indirect_count
- 014/ VK_KHR_driver_properties
- 015/ VK_KHR_external_fence
- 016/ VK_KHR_external_fence_win32
- 017/ VK_KHR_external_memory
- 018/ VK_KHR_external_memory_win32
- 019/ VK_KHR_external_semaphore
- 020/ VK_KHR_external_semaphore_win32
- 021/ VK_KHR_fragment_shading_rate
- 022/ VK_KHR_get_memory_requirements2
- 023/ VK_KHR_image_format_list
- 024/ VK_KHR_imageless_framebuffer
- 025/ VK_KHR_maintenance1
- 026/ VK_KHR_maintenance2
- 027/ VK_KHR_maintenance3
- 028/ VK_KHR_multiview
- 029/ VK_KHR_pipeline_executable_properties
- 030/ VK_KHR_pipeline_library
- 031/ VK_KHR_push_descriptor
- 032/ VK_KHR_ray_query
- 033/ VK_KHR_ray_tracing_pipeline
- 034/ VK_KHR_relaxed_block_layout
- 035/ VK_KHR_sampler_mirror_clamp_to_edge
- 036/ VK_KHR_sampler_ycbcr_conversion
- 037/ VK_KHR_separate_depth_stencil_layouts
- 038/ VK_KHR_shader_atomic_int64
- 039/ VK_KHR_shader_clock
- 040/ VK_KHR_shader_draw_parameters
- 041/ VK_KHR_shader_float16_int8
- 042/ VK_KHR_shader_float_controls
- 043/ VK_KHR_shader_non_semantic_info
- 044/ VK_KHR_shader_subgroup_extended_types
- 045/ VK_KHR_shader_terminate_invocation
- 046/ VK_KHR_spirv_1_4
- 047/ VK_KHR_storage_buffer_storage_class
- 048/ VK_KHR_swapchain
- 049/ VK_KHR_swapchain_mutable_format
- 050/ VK_KHR_synchronization2
- 051/ VK_KHR_timeline_semaphore
- 052/ VK_KHR_uniform_buffer_standard_layout
- 053/ VK_KHR_variable_pointers
- 054/ VK_KHR_vulkan_memory_model
- 055/ VK_KHR_win32_keyed_mutex
- 056/ VK_KHR_workgroup_memory_explicit_layout
- 057/ VK_KHR_zero_initialize_workgroup_memory
- 058/ VK_EXT_4444_formats
- 059/ VK_EXT_blend_operation_advanced
- 060/ VK_EXT_buffer_device_address
- 061/ VK_EXT_calibrated_timestamps
- 062/ VK_EXT_conditional_rendering
- 063/ VK_EXT_conservative_rasterization
- 064/ VK_EXT_custom_border_color
- 065/ VK_EXT_depth_clip_enable
- 066/ VK_EXT_depth_range_unrestricted
- 067/ VK_EXT_descriptor_indexing
- 068/ VK_EXT_discard_rectangles
- 069/ VK_EXT_extended_dynamic_state
- 070/ VK_EXT_external_memory_host
- 071/ VK_EXT_fragment_shader_interlock
- 072/ VK_EXT_full_screen_exclusive
- 073/ VK_EXT_hdr_metadata
- 074/ VK_EXT_host_query_reset
- 075/ VK_EXT_image_robustness
- 076/ VK_EXT_index_type_uint8
- 077/ VK_EXT_inline_uniform_block
- 078/ VK_EXT_line_rasterization
- 079/ VK_EXT_memory_budget
- 080/ VK_EXT_memory_priority
- 081/ VK_EXT_pci_bus_info
- 082/ VK_EXT_pipeline_creation_cache_control
- 083/ VK_EXT_pipeline_creation_feedback
- 084/ VK_EXT_post_depth_coverage
- 085/ VK_EXT_private_data
- 086/ VK_EXT_robustness2
- 087/ VK_EXT_sample_locations
- 088/ VK_EXT_sampler_filter_minmax
- 089/ VK_EXT_scalar_block_layout
- 090/ VK_EXT_separate_stencil_usage
- 091/ VK_EXT_shader_atomic_float
- 092/ VK_EXT_shader_demote_to_helper_invocation
- 093/ VK_EXT_shader_image_atomic_int64
- 094/ VK_EXT_shader_subgroup_ballot
- 095/ VK_EXT_shader_subgroup_vote
- 096/ VK_EXT_shader_viewport_index_layer
- 097/ VK_EXT_subgroup_size_control
- 098/ VK_EXT_texel_buffer_alignment
- 099/ VK_EXT_tooling_info
- 100/ VK_EXT_transform_feedback
- 101/ VK_EXT_vertex_attribute_divisor
- 102/ VK_EXT_ycbcr_image_arrays
- 103/ VK_NV_acquire_winrt_display
- 104/ VK_NV_clip_space_w_scaling
- 105/ VK_NV_compute_shader_derivatives
- 106/ VK_NV_cooperative_matrix
- 107/ VK_NV_corner_sampled_image
- 108/ VK_NV_coverage_reduction_mode
- 109/ VK_NV_cuda_kernel_launch
- 110/ VK_NV_dedicated_allocation
- 111/ VK_NV_dedicated_allocation_image_aliasing
- 112/ VK_NV_device_diagnostic_checkpoints
- 113/ VK_NV_device_diagnostics_config
- 114/ VK_NV_device_generated_commands
- 115/ VK_NV_external_memory
- 116/ VK_NV_external_memory_win32
- 117/ VK_NV_fill_rectangle
- 118/ VK_NV_fragment_coverage_to_color
- 119/ VK_NV_fragment_shader_barycentric
- 120/ VK_NV_fragment_shading_rate_enums
- 121/ VK_NV_framebuffer_mixed_samples
- 122/ VK_NV_geometry_shader_passthrough
- 123/ VK_NV_mesh_shader
- 124/ VK_NV_ray_tracing
- 125/ VK_NV_representative_fragment_test
- 126/ VK_NV_sample_mask_override_coverage
- 127/ VK_NV_scissor_exclusive
- 128/ VK_NV_shader_image_footprint
- 129/ VK_NV_shader_sm_builtins
- 130/ VK_NV_shader_subgroup_partitioned
- 131/ VK_NV_shading_rate_image
- 132/ VK_NV_viewport_array2
- 133/ VK_NV_viewport_swizzle
- 134/ VK_NV_win32_keyed_mutex
- 135/ VK_NVX_binary_import
- 136/ VK_NVX_image_view_handle
- 137/ VK_NVX_multiview_per_view_attributes
- # of layers => 1
- 001/ VK_LAYER_NV_optimus
- # of memory heaps => 3
- heap 1 => 8050 MB
- heap 2 => 8149 MB
- heap 3 => 214 MB
- # of features => 55
- 001/ robustBufferAccess => 1
- 002/ fullDrawIndexUint32 => 1
- 003/ imageCubeArray => 1
- 004/ independentBlend => 1
- 005/ geometryShader => 1
- 006/ tessellationShader => 1
- 007/ sampleRateShading => 1
- 008/ dualSrcBlend => 1
- 009/ logicOp => 1
- 010/ multiDrawIndirect => 1
- 011/ drawIndirectFirstInstance => 1
- 012/ depthClamp => 1
- 013/ depthBiasClamp => 1
- 014/ fillModeNonSolid => 1
- 015/ depthBounds => 1
- 016/ wideLines => 1
- 017/ largePoints => 1
- 018/ alphaToOne => 1
- 019/ multiViewport => 1
- 020/ samplerAnisotropy => 1
- 021/ textureCompressionETC2 => 0
- 022/ textureCompressionASTC_LDR => 0
- 023/ textureCompressionBC => 1
- 024/ occlusionQueryPrecise => 1
- 025/ pipelineStatisticsQuery => 1
- 026/ vertexPipelineStoresAndAtomics => 1
- 027/ fragmentStoresAndAtomics => 1
- 028/ shaderTessellationAndGeometryPointSize => 1
- 029/ shaderImageGatherExtended => 1
- 030/ shaderStorageImageExtendedFormats => 1
- 031/ shaderStorageImageMultisample => 1
- 032/ shaderStorageImageReadWithoutFormat => 1
- 033/ shaderStorageImageWriteWithoutFormat => 1
- 034/ shaderUniformBufferArrayDynamicIndexing => 1
- 035/ shaderSampledImageArrayDynamicIndexing => 1
- 036/ shaderStorageBufferArrayDynamicIndexing => 1
- 037/ shaderStorageImageArrayDynamicIndexing => 1
- 038/ shaderClipDistance => 1
- 039/ shaderCullDistance => 1
- 040/ shaderFloat64 => 1
- 041/ shaderInt64 => 1
- 042/ shaderInt16 => 1
- 043/ shaderResourceResidency => 1
- 044/ shaderResourceMinLod => 1
- 045/ sparseBinding => 1
- 046/ sparseResidencyBuffer => 1
- 047/ sparseResidencyImage2D => 1
- 048/ sparseResidencyImage3D => 1
- 049/ sparseResidency2Samples => 1
- 050/ sparseResidency4Samples => 1
- 051/ sparseResidency8Samples => 1
- 052/ sparseResidency16Samples => 1
- 053/ sparseResidencyAliased => 1
- 054/ variableMultisampleRate => 1
- 055/ inheritedQueries => 1
- # of hardware limits => 106
- 001/ maxImageDimension1D => 32768
- 002/ maxImageDimension2D => 32768
- 003/ maxImageDimension3D => 16384
- 004/ maxImageDimensionCube => 32768
- 005/ maxImageArrayLayers => 2048
- 006/ maxTexelBufferElements => 134217728
- 007/ maxUniformBufferRange => 65536
- 008/ maxStorageBufferRange => 4294967295
- 009/ maxPushConstantsSize => 256
- 010/ maxMemoryAllocationCount => 4096
- 011/ maxSamplerAllocationCount => 4000
- 012/ bufferImageGranularity => 1024
- 013/ sparseAddressSpaceSize => 1099511627775
- 014/ maxBoundDescriptorSets => 32
- 015/ maxPerStageDescriptorSamplers => 1048576
- 016/ maxSamplerAllocationCount => 1048576
- 017/ maxPerStageDescriptorStorageBuffers => 1048576
- 018/ maxPerStageDescriptorSampledImages => 1048576
- 019/ maxPerStageDescriptorStorageImages => 1048576
- 020/ maxPerStageDescriptorInputAttachments => 1048576
- 021/ maxPerStageResources => 4294967295
- 022/ maxDescriptorSetSamplers => 1048576
- 023/ maxDescriptorSetUniformBuffers => 1048576
- 024/ maxDescriptorSetUniformBuffersDynamic => 15
- 025/ maxDescriptorSetStorageBuffers => 1048576
- 026/ maxDescriptorSetStorageBuffersDynamic => 16
- 027/ maxDescriptorSetSampledImages => 1048576
- 028/ maxDescriptorSetStorageImages => 1048576
- 029/ maxDescriptorSetInputAttachments => 1048576
- 030/ maxVertexInputAttributes => 32
- 031/ maxVertexInputBindings => 32
- 032/ maxVertexInputAttributeOffset => 2047
- 033/ maxVertexInputBindingStride => 2048
- 034/ maxVertexOutputComponents => 128
- 035/ maxTessellationGenerationLevel => 64
- 036/ maxTessellationPatchSize => 32
- 037/ maxTessellationControlPerVertexInputComponents => 128
- 038/ maxTessellationControlPerVertexOutputComponents => 128
- 039/ maxTessellationControlPerPatchOutputComponents => 120
- 040/ maxTessellationControlTotalOutputComponents => 4216
- 041/ maxTessellationEvaluationInputComponents => 128
- 042/ maxTessellationEvaluationOutputComponents => 128
- 043/ maxGeometryShaderInvocations => 32
- 044/ maxGeometryInputComponents => 128
- 045/ maxGeometryOutputComponents => 128
- 046/ maxGeometryOutputVertices => 1024
- 047/ maxGeometryTotalOutputComponents => 1024
- 048/ maxFragmentInputComponents => 128
- 049/ maxFragmentOutputAttachments => 8
- 050/ maxFragmentDualSrcAttachments => 1
- 051/ maxFragmentCombinedOutputResources => 16
- 052/ maxComputeSharedMemorySize => 49152
- 053/ maxComputeSharedMemorySize => 2147483647 x 65535 x 65535
- 054/ maxComputeWorkGroupInvocations => 1024
- 055/ maxComputeWorkGroupSize => 1024 x 1024 x 64
- 056/ subPixelPrecisionBits => 8
- 057/ subTexelPrecisionBits => 8
- 058/ mipmapPrecisionBits => 8
- 059/ maxDrawIndexedIndexValue => 4294967295
- 060/ maxDrawIndirectCount => 4294967295
- 061/ maxSamplerLodBias => 15.000000
- 062/ maxSamplerAnisotropy => 16.000000
- 063/ maxViewports => 16
- 064/ maxViewportDimensions => 32768 x 32768
- 065/ viewportBoundsRange => -65536.000000 x 65536.000000
- 066/ viewportSubPixelBits => 8
- 067/ minMemoryMapAlignment => 64
- 068/ minTexelBufferOffsetAlignment => 16
- 069/ minUniformBufferOffsetAlignment => 64
- 070/ minStorageBufferOffsetAlignment => 16
- 071/ minTexelOffset => -8
- 072/ maxTexelOffset => 7
- 073/ minTexelGatherOffset => -32
- 074/ maxTexelGatherOffset => 31
- 075/ minInterpolationOffset => -0.500000
- 076/ maxInterpolationOffset => 0.437500
- 077/ subPixelInterpolationOffsetBits => 4
- 078/ maxFramebufferWidth => 32768
- 079/ maxFramebufferHeight => 32768
- 080/ maxFramebufferLayers => 2048
- 081/ framebufferColorSampleCounts => 15
- 082/ framebufferDepthSampleCounts => 15
- 083/ framebufferStencilSampleCounts => 31
- 084/ framebufferNoAttachmentsSampleCounts => 31
- 085/ maxColorAttachments => 8
- 086/ sampledImageColorSampleCounts => 15
- 087/ sampledImageIntegerSampleCounts => 15
- 088/ sampledImageDepthSampleCounts => 15
- 089/ sampledImageStencilSampleCounts => 31
- 090/ storageImageSampleCounts => 15
- 091/ maxSampleMaskWords => 1
- 092/ timestampComputeAndGraphics => 1
- 093/ timestampPeriod => 1.000000
- 094/ maxClipDistances => 8
- 095/ maxCullDistances => 8
- 096/ maxCombinedClipAndCullDistances => 8
- 097/ discreteQueuePriorities => 2
- 098/ pointSizeRange => 1.000000 x 2047.937500
- 099/ lineWidthRange => 1.000000 x 64.000000
- 100/ pointSizeGranularity => 0.062500
- 101/ lineWidthGranularity => 0.062500
- 102/ strictLines => 1
- 103/ standardSampleLocations => 1
- 104/ optimalBufferCopyOffsetAlignment => 1
- 105/ optimalBufferCopyRowPitchAlignment => 1
- 106/ nonCoherentAtomSize => 64
GeForce 466.11
GeForce 466.11 exposes Vulkan 1.2.168 and 137 device extensions. It’s the same support than previous 465.89.
- Device 1
- name: NVIDIA GeForce RTX 3060 Ti
- device type: VK_PHYSICAL_DEVICE_TYPE_DISCRETE_GPU
- device ID: 10DE-2486
- API version: 1.2.168
- NVIDIA driver version: 466.11.0.0
- VK_KHR_driver_properties information:
- driverName: NVIDIA
- driverID_str: VK_DRIVER_ID_NVIDIA_PROPRIETARY_KHR
- driverID: 4
- conformanceVersion: 1.2.2.5
- driverInfo: 466.11
- # of extensions => 137
GeForce 466.27
GeForce 466.11 exposes Vulkan 1.2.168 and 137 device extensions. It’s the same support than previous 465.89.
- Device 1
- name: NVIDIA GeForce RTX 3060 Ti
- device type: VK_PHYSICAL_DEVICE_TYPE_DISCRETE_GPU
- device ID: 10DE-2486
- API version: 1.2.168
- NVIDIA driver version: 466.27.0.0
- VK_KHR_driver_properties information:
- driverName: NVIDIA
- driverID_str: VK_DRIVER_ID_NVIDIA_PROPRIETARY_KHR
- driverID: 4
- conformanceVersion: 1.2.2.5
- driverInfo: 466.27
- # of extensions => 137
OpenCL support
The driver 465.89 brings the OpenCL 3.0 support:
- Num OpenCL platforms: 1
- CL_PLATFORM_NAME: NVIDIA CUDA
- CL_PLATFORM_VENDOR: NVIDIA Corporation
- CL_PLATFORM_VERSION: OpenCL 3.0 CUDA 11.3.55
- CL_PLATFORM_PROFILE: FULL_PROFILE
- Num devices: 1
- CL_DEVICE_NAME: NVIDIA GeForce RTX 3060 Ti
- CL_DEVICE_VENDOR: NVIDIA Corporation
- CL_DRIVER_VERSION: 465.89
- CL_DEVICE_PROFILE: FULL_PROFILE
- CL_DEVICE_VERSION: OpenCL 3.0 CUDA
- CL_DEVICE_TYPE: GPU
- CL_DEVICE_VENDOR_ID: 0x10DE
- CL_DEVICE_MAX_COMPUTE_UNITS: 38
- CL_DEVICE_MAX_CLOCK_FREQUENCY: 1740MHz
- CL_NV_DEVICE_COMPUTE_CAPABILITY_MAJOR: 8
- CL_NV_DEVICE_COMPUTE_CAPABILITY_MINOR: 6
- CL_NV_DEVICE_REGISTERS_PER_BLOCK: 65536
- CL_NV_DEVICE_WARP_SIZE: 32
- CL_NV_DEVICE_GPU_OVERLAP: 1
- CL_NV_DEVICE_KERNEL_EXEC_TIMEOUT: 1
- CL_NV_DEVICE_INTEGRATED_MEMORY: 0
- CL_DEVICE_ADDRESS_BITS: 32
- CL_DEVICE_MAX_MEM_ALLOC_SIZE: 2097152KB
- CL_DEVICE_GLOBAL_MEM_SIZE: 8192MB
- CL_DEVICE_MAX_PARAMETER_SIZE: 4352
- CL_DEVICE_GLOBAL_MEM_CACHELINE_SIZE: 128 Bytes
- CL_DEVICE_GLOBAL_MEM_CACHE_SIZE: 1064KB
- CL_DEVICE_ERROR_CORRECTION_SUPPORT: NO
- CL_DEVICE_LOCAL_MEM_TYPE: Local (scratchpad)
- CL_DEVICE_LOCAL_MEM_SIZE: 48KB
- CL_DEVICE_MAX_CONSTANT_BUFFER_SIZE: 64KB
- CL_DEVICE_MAX_WORK_ITEM_DIMENSIONS: 3
- CL_DEVICE_MAX_WORK_ITEM_SIZES: [1024 ; 1024 ; 64]
- CL_DEVICE_MAX_WORK_GROUP_SIZE: 1024
- CL_EXEC_NATIVE_KERNEL: 4236012
- CL_DEVICE_IMAGE_SUPPORT: YES
- CL_DEVICE_MAX_READ_IMAGE_ARGS: 256
- CL_DEVICE_MAX_WRITE_IMAGE_ARGS: 32
- CL_DEVICE_IMAGE2D_MAX_WIDTH: 32768
- CL_DEVICE_IMAGE2D_MAX_HEIGHT: 32768
- CL_DEVICE_IMAGE3D_MAX_WIDTH: 16384
- CL_DEVICE_IMAGE3D_MAX_HEIGHT: 16384
- CL_DEVICE_IMAGE3D_MAX_DEPTH: 16384
- CL_DEVICE_MAX_SAMPLERS: 32
- CL_DEVICE_PREFERRED_VECTOR_WIDTH_CHAR: 1
- CL_DEVICE_PREFERRED_VECTOR_WIDTH_SHORT: 1
- CL_DEVICE_PREFERRED_VECTOR_WIDTH_INT: 1
- CL_DEVICE_PREFERRED_VECTOR_WIDTH_LONG: 1
- CL_DEVICE_PREFERRED_VECTOR_WIDTH_FLOAT: 1
- CL_DEVICE_PREFERRED_VECTOR_WIDTH_DOUBLE: 1
- CL_DEVICE_EXTENSIONS: 19
- Extensions:
- cl_khr_global_int32_base_atomics
- cl_khr_global_int32_extended_atomics
- cl_khr_local_int32_base_atomics
- cl_khr_local_int32_extended_atomics
- cl_khr_fp64
- cl_khr_3d_image_writes
- cl_khr_byte_addressable_store
- cl_khr_icd
- cl_khr_gl_sharing
- cl_nv_compiler_options
- cl_nv_device_attribute_query
- cl_nv_pragma_unroll
- cl_nv_d3d10_sharing
- cl_khr_d3d10_sharing
- cl_nv_d3d11_sharing
- cl_nv_copy_opts
- cl_nv_create_buffer
- cl_khr_int64_base_atomics
- cl_khr_int64_extended_atomics