NV1 SSD (SNVS)
- Resources
- PCN
- Videos
- FAQ
- Contact Us
1:10
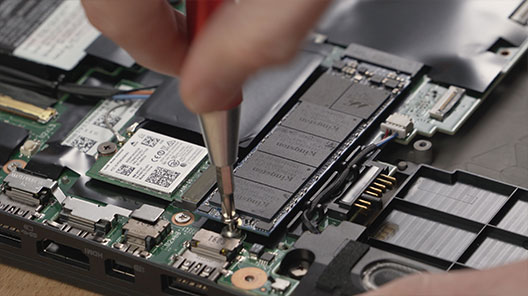
How to install an M.2 SSD in a desktop PC
1:29
How to install an M.2 SSD in a laptop
ElectroStatic Discharge, ESD is simply the discharge of built-up static electricity. ESD should not be taken lightly as this is one of the few things that an individual can do to damage or destroy their computer or hardware components. It is like when you rub your feet on the carpet and you touch something metal. ESD can occur without the user feeling a shock and will occur when only working on the inside of the computer or handling hardware.
How to help prevent ESD
The best method of preventing ESD is to use an ESD wrist strap or an earthing mat or table. However, because most users do not have access to these items, we have included the below steps to help reduce the chance of ESD as much as possible.
- Standing – We recommend that you are standing at all times when working on the computer. Sitting on a chair can generate more electrostatic.
- Cables – Make sure that everything is removed from the back of the computer (power cable, mouse, keyboard, etc).
- Clothes – Do not wear any clothing that conducts a lot of Electrical Charge, such as a wool jumper.
- Accessories – To help reduce ESD and prevent other problems, it is also a good idea to remove all jewellery.
- Weather – Electrical storms can increase the ESD risk; unless absolutely necessary, try not to work on a computer during an electrical storm. In very dry areas, the air itself becomes a part of the electrostatic build-up mechanism every time there is an air flow (wind, air conditioning, blower) passing over an insulated surface. Do not let high humidity levels build false confidence, and beware of corrosion problems with interconnects and other electrical interfaces.
To learn more about ESD and how to protect your electronics, please refer to the below site.
ESD Association
https://www.esda.org
FAQ: KTC-Gen-ESD
Secure Erase User Guide for Linux
This guide will walk you through securely erasing your Kingston SSD using Linux tools
SATA Secure Erase Procedure
Warning
Please make sure to have a full backup of any important data before you proceed!
Prerequisites
• You must have root privileges.
• You must have your SSD connected to the system as a secondary (non-OS) drive.
• You must have lsscsi and hdparm installed. You may need to install them with your distribution’s package manager.
• Your drive must not be in a security freeze.
• Your drive must not be password protected.
Instructions
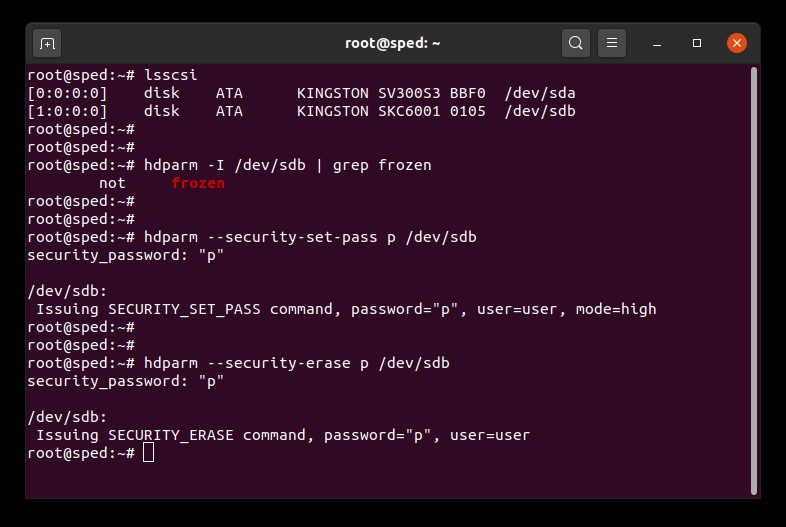
1. Find the device name (/dev/sdX) of the drive you wish to erase:
# lsscsi
2. Make sure drive security is not frozen:
# hdparm -I /dev/sdX | grep frozen
If the output shows «frozen» (instead of «not frozen») then you cannot continue to the next step. You must try to remove the security freeze by trying one of the following methods:
Method 1: Put the system to sleep (suspend to RAM) and wake it up. On most distributions the command to suspend is:
# systemctl suspend
Now issue the hdparm command again. If it worked the output will show “not frozen” (instead of “frozen”).
Method 2: Hot plug the drive. This is done by physically unplugging the SATA power cable from the drive and plugging it back in while the system is powered on. You may need to enable hot plug in BIOS. Not all systems support hot plug.
Now issue the hdparm command again. If it worked the output will show “not frozen” (instead of “frozen”).
3. Set a user password on the drive. The password can be anything. Here we are setting the password to “p”:
# hdparm —security-set-pass p /dev/sdX
4. Issue the secure erase command to the drive using the same password:
# hdparm —security-erase p /dev/sdX
This command may take a few minutes to complete. The drive password is removed upon successful completion.
If the secure erase is interrupted or otherwise fails your drive may become security locked. In this case you can remove the security lock using the command below and then try the secure erase procedure again:
# hdparm —security-disable p /dev/sdX
SATA Secure Erase Example
NVMe Secure Erase Procedure
Warning
Please make sure to have a full backup of any important data before you proceed!
Prerequisites
• You must have root privileges.
• You must have your SSD connected to the system as a secondary (non-OS) drive.
• You must have nvme-cli installed. You may need to install it with your distribution’s package manager.
• Your drive must not be password protected.
Instructions
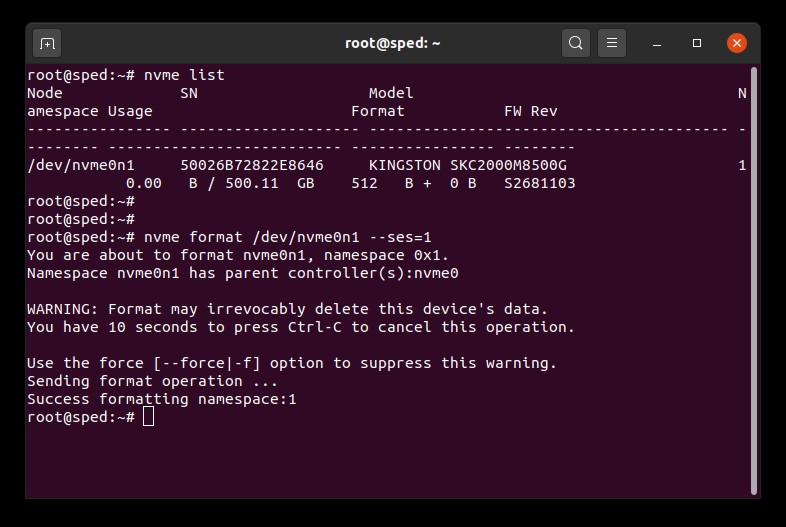
1. Find the device name (/dev/nvmeXn1) of the drive you wish to erase:
# nvme list
2. Issue the format command to the drive. Here we set the secure erase setting to 1 which indicates a user data erase:
# nvme format /dev/nvmeXn1 —ses=1
This command may take a few minutes to complete.
NVMe Secure Erase Example
FAQ: KSM-SE-LIX
Trim and garbage collection are technologies that modern SSDs incorporate to improve both their performance and endurance. When your SSD is fresh out of the box, all of the NAND blocks are empty so the SSD can write new data to the empty blocks in a single operation. Over time, most of the empty blocks will become used blocks that contain user data. In order to write new data to used blocks, the SSD is forced to perform a read-modify-write cycle. The read-modify-write cycle hurts the SSD’s overall performance because it must now do three operations instead of a single operation. The read-modify-write cycle also causes write amplification, which hurts the SSD’s overall endurance.
Trim and garbage collection can work together to improve SSD performance and endurance by freeing up used blocks. Garbage collection is a function built into the SSD controller that consolidates data stored in used blocks in order to free up more empty blocks. This process happens in the background and is completely handled by the SSD itself. However, the SSD may not know which blocks contain user data and which blocks contain stale data that the user has already deleted. This is where the trim function comes in. Trim allows the operating system to inform the SSD that data has been deleted so that the SSD can free up those previously used blocks. For trim to work, both the operating system and the SSD must support it. Most modern operating systems and SSDs support trim, although most RAID configurations do not.
Kingston SSDs take advantage of both garbage collection and trim technologies in order to maintain the highest possible performance and endurance over their lifetime.
Learn More
FAQ: KSD-011411-GEN-13
In Windows — Open the control panel, open administrative tools and then open computer management. Click on Disk Management and see if the SSD drive is seen in the right window pane. If it is, right click on where it is labeled as disk 1, disk 2, etc and select «Initialize disk» (this may come up automatically when you go to Disk Management). Next, right-click on the area to the right of the disk label and choose «New Simple Volume». Continue with the wizard by choosing the size, drive letter and formatting of the partition.
In macOS — A «disk insertion» window will appear. Click on the «initialize» button. This will take you to the disk utility. Select the Kingston drive from the list of drives on the left side of the Window. From the actions available, choose partition. For the «Volume Scheme», choose «1 partition». For the format, choose MacOS extended for a permanent drive. Choose ExFAT for an external drive (available on MacOS 10.6.6 and above). Click Apply. A warning windows will appear stating you will erase all data from the drive. Click on the partition button at the bottom.
FAQ: c
Kingston realises the importance of keeping our customers’ personal data and information confidential and secure.
Kingston takes measures to ensure the security of all of our customers’ personal information when a Solid State Drive (SSD) is returned to our RMA facility for warranty replacement or repair.
When an SSD reaches our repair centre, it will undergo a thorough testing process.
During the first phase of testing, an ATA Secure Erase is performed on the SSD, which erases all data and information.
ATA Secure Erase is federally approved by the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST 800-88) for legal sanitisation of confidential user data.
If the SSD is not in a functional state and not capable of undergoing an ATA Secure Erase, the SSD is dismantled and the NAND Flash Memory is destroyed.
FAQ: KSD-022411-GEN-15
Any of our SSDs can be used in RAID.
However, due to endurance specifications, only certain part numbers should be used in RAID. For servers, please contact Kingston to determine the best Kingston SSD to use for your workload.
FAQ: KSD-052511-GEN-17
Kingston SSD Manager (KSM) is ending support for Microsoft Windows 7. The latest version of KSM with Windows 7 support is v1.1.2.5. If you are using Windows 7 and experience complications with KSM, please make sure you have AHCI mode enabled in BIOS and install the latest Intel RST storage driver provided by your system manufacturer. If you still need assistance, feel free to contact our Kingston Technical Support department.
FAQ: KSM-001125-001-00
Kingston SSD Manager 1.1.2.6 will not offer firmware updates for NVMe SSDs until IEEE 1667 support has been disabled. In order to complete the firmware update you must do the following:
1. First, we recommend you backup your data.
2. Then use a secondary system to complete a REVERT using the PSID on the drive label. Note: Performing a REVERT will securely erase all data on the drive.
3. Disable IEEE 1667 support
4. The firmware update will become available upon refresh or restart of KSM
FAQ: KSM-001125-001-01
Self-Monitoring Analysis and Reporting Technology (SMART) is a built-in monitoring capability in hard drives and SSDs.
It can allow users to monitor the health of a device.
It does this through monitoring software designed specifically for the SMART feature. All of our SSDNow drives support SMART.
FAQ: KSD-011411-GEN-10
Performance decreases have been reported on some SSDNow drives.
If you have an older SSD drive that does not have effective Garbage Collection, SSD drive performance will decrease over time.
This is due to the way the system overwrites data that has been flagged for deletion.
Try using the Secure Erasetool like HDDErase to wipe the drive and restore it to its original condition.
FAQ: KSD-011411-GEN-12
Your system may be loading the Intel RST driver instead of the Microsoft NVMe driver. There is a known compatibility issue with the Intel RST driver that interferes with NVMe firmware update commands. Additionally, KSM is only supported on Windows based systems. Therefore, if you are attempting to run KSM on a macOS or Linux based system, unfortunately these OS are not compatible with KSM.
FAQ: KSM-001125-002-01
To determine which NVMe driver is in use, you can run the AS SSD benchmark tool and select your Kingston NVMe SSD from the drop-down menu. This will report the driver being used for that drive. If the driver is «iaStorAC» then your drive is using the Intel driver. If the driver is «stornvme» then your drive is using the Microsoft driver.
FAQ: KSD-001525-001-00
Caution! The workarounds below will break RST RAID arrays and could lead to data loss. If your system has RST RAID
arrays you should consider an alternate solution.
Workaround 1: Disable RST Control in BIOS
This workaround requires BIOS options to enable or disable RST Control and is not available on all systems.
Note: Please backup all important data before you proceed!
1. Restart and enter the system BIOS
2. Locate the RST Configuration settings in BIOS
3. Change «RST Controlled» to «Not RST Controlled»
4. Save and exit BIOS
5. Open KSM and update the drive firmware
Once these steps are completed you may optionally switch back to «RST Controlled» in BIOS.
Workaround 2: Switch from RAID to AHCI in BIOS
This workaround is to change your system storage mode from RAID to AHCI and should work on all systems.
Note: Please backup all important data before you proceed!
1. Open msconfig
2. Select the Boot tab
3. Check Safe boot (minimal)
4. Click OK and Restart
5. When the system restarts go into the system BIOS
6. Change the storage mode from RAID to AHCI
7. Save and exit BIOS
8. Wait for Windows to boot into safe mode
9. Open msconfig
10. Select the Boot tab
11. Uncheck Safe boot
12. Click OK and Restart
13. Wait for Windows to boot normally
14. Open KSM and update the drive firmware
Once these steps are completed you may optionally switch the storage mode back to RAID in BIOS.
FAQ: KSD-001525-001-01
When the SSD is recognised in the BIOS, but the Windows 7 installation does not detect the drive:
Follow these steps:
Disconnect any other hard drives or SSDs. Boot the Windows 7 installation disk. Choose repair, then advanced, then command prompt. Type: «diskpart» without quotes and press Enter. You will see a prompt labeled «diskpart». Type the following commands and press Enter after each one.
Diskpart > Select Disk 0
Diskpart > Clean
Diskpart > Create Partition Primary Align=1024
Diskpart > Format Quick FS=NTFS
Diskpart > List Partition
Diskpart > Active
Diskpart > Exit
Then, reboot the computer to the Windows 7 installation disk.
KSD-100214-GEN-20
FAQ: KSD-100214-GEN-20
SSDs do not require defragmentation.
Since they do not contain a physical disk, there is no need to organise the data in order to reduce seek time.
Therefore defragmenting an SSD is not effective.
Also, defragmenting an SSD can put undue wear on specific areas of the drive.
SSDs are designed to write data as evenly as possible over the entire drive to reduce undue wear to any one location.
Defragmenting your SSD drive a couple of times will not harm it.
However, if it is done continuously over a long period, it may reduce the life of the drive.
FAQ: KSD-011411-GEN-03
The Windows Experience Index (WEI) merely measures the relative capability of components. The WEI only runs for a short time and does not measure the interactions of components under a software load, but rather characteristics or your hardware.
The WEI does not therefore measure the performance of a system, but merely the relative hardware capabilities when running Windows 7. An article about the WEI can be found here: http://blogs.msdn.com/b/e7/archive/2009/01/19/engineering-the-windows-7-windows-experience-index.aspx
In Vista, the WEI scores ranged from 1.0 to 5.9. In Windows 7, the range has been extended upward to 7.9.
FAQ: KSD-011411-GEN-08
During the OS installation, go to UTILITIES / TERMINAL
In terminal type:
diskutil list
Then press RETURN. Scroll up to top and verify the Kingston SSD disk (i.e. disk0, disk1, etc).
Then type:
diskutil mountDISK disk0 (or whichever ddisk is the Kingston SSD).
Then press RETURN. It should show «mounted successfully».
Then type:
diskutil eraseDISK apfs YOURDRIVENAME disk0 (or whichever disk is the Kingston SSD)
Warning – This step (eraseDISK command) will delete all data on the target drive. Confirm that you have selected the drive you wish to delete and then continue.
Then press RETURN. It should show «successful». Then exit terminal and proceed with the normal installation of the OS.
FAQ: KSD-092917-GEN-21
First, open an Elevated Command Prompt window.
To open an Elevated Command Prompt window: Click on Start Orb > Type «CMD.exe» in Search box > Right click on «CMD» and select «Run as Administrator» (If you receive a prompt confirmation, click YES)
To verify that the TRIM command is enabled, type the following and press enter in the Elevated command:
fsutil behavior query disabledeletenotify
The results will be as follows:
DisableDeleteNotify = 1 (Windows TRIM commands are disabled)
DisableDeleteNotify = 0 (Windows TRIM commands are enabled)
To enable the TRIM command,type the following and press enter in the Elevated command:
fsutil behavior set disabledeletenotify 0
To disable the TRIM command,type the following and press enter in the Elevated command:
fsutil behavior set disabledeletenotify 1
FAQ: KSD-072211-GEN-18
Encrypted solid state drives utilise the hard drive security command available on most business-class computers and motherboards.It is accessed through the BIOS.
This will allow you to create a password for multiple HDDs and SSDs and securely erase the drives if needed.
Some computers will not have this feature.
If this is the case, the drive can still be used, just without these security features.
Be sure not to confuse the BIOS password with the hard drive security password.
KSD-011411-ENC-01
FAQ: KSD-011411-ENC-01
You can, but you must first disable the security for the drive in the original computer.
Then you can enable it again in the new computer.
KSD-011411-ENC-02
FAQ: KSD-011411-ENC-02
No. If you forget the password for this drive, it cannot be accessed. Be aware that forgetting your password is not covered under Kingston’s warranty.
The only exception to this is using a master or administrative password for the drive in addition to the user password. The BIOS would have to support this and it would have to be enabled at the time you initiated the ATA security for this drive. Using a master password would allow an administrator to reset the drive.
FAQ: KSD-011411-ENC-03
Полный размер
Картинка с hothardware.com/reviews/adata-sx8200-m2-nvme-ssd-review
Пару лет назад обзавёлся я SSD диском и вещь оказалась такая шустрая и удобная, только маленькая. Очень быстро забил я всякими IDEшками игрушками и прочими андроид-эмуляторами. А на обычный диск записывать и ждать каждый раз когда загрузится — уже не то.
Поэтому решил обзавестись ещё одним SSD, только на это раз взял планку повыше — решил поставить тот, который втыкается в PCIx (т.н. NVMe), чтобы не полгига в секунду, а все три.
Прикупил соответствующий адаптер, воткнул всё, а Windows 7 PCI устройство видит, но, говорит, драйверов нету.
Оказалось нужно специальный патч ставить для винды чтобы она его видела. Вот только микрософтовцы оказались нехорошими людьми, и с сайта этот патчик убрали. При загрузке там написано мол «выкусите и идите покупать виндовс 10».
Так дела не делаются. Я немного погуглил и нашёл вот тут решение:
Нужно скачать архивчик с драйверами от гигабайтовского устройства, вот этот: www.gigabyte.com/us/Mothe…rev-10#support-dl-utility
Сам он не нужен, но внутри в нём в WindowsImageTool/HOTFIX прячутся как раз тот самый патчик и ещё один патч с исправлениями.
(UPD: архивчик удалили вот копия патча)
После их установки и перезагрузки устройство определилось как диск, осталось отформатировать и можно записывать.
-
Standard NVM Express Controller
Производитель:
Advanced Micro Devices Inc
Версия:
9.4.0.00059
(05 янв 2022)
Файл *.inf:
rcbottom.inf
Windows Vista x64, 7 x64, 8 x64, 8.1 x64, 10 x64
-
Standard NVM Express Controller
Производитель:
Broadcom Limited
Версия:
3.00.71.90
(07 ноя 2020)
Файл *.inf:
mpi3drvi.inf
Windows Vista, 7, 8, 8.1, 10
В каталоге нет драйверов для Standard NVM Express Controller под Windows.
Скачайте DriverHub для автоматического подбора драйвера.
Драйверы для Standard NVM Express Controller собраны с официальных сайтов компаний-производителей и других проверенных источников.
Официальные пакеты драйверов помогут исправить ошибки и неполадки в работе Standard NVM Express Controller (контроллеры).
Скачать последние версии драйверов на Standard NVM Express Controller для компьютеров и ноутбуков на Windows.
Kingston A400 Driver Download
Here you will find the Kingston A400 SSD Drivers, Software, Firmware and Installation Guide. This package contains the files needed for installing the Western Digital NVMe (non-volatile memory express) driver.
If you install this package, your device will be properly recognized by compatible systems, and might even benefit from new features or various bug fixes. The driver, which is now available, includes a compatibility fix for Windows.
Instructions
- Download the Western Digital Dashboard to your hard drive
- Run the downloaded installer by double clicking DashboardSetup.exe
- Follow the onscreen prompts to complete the installation
- When the installation has completed successfully, click on the Finish button
- The Dashboard will automatically launch and load the Status section
Details Drivers:
- Producer: Kingston
- Model: Kingston A400
- Language: English
- License: Free
Supported Operating Systems
Refer to the table below for Kingston® SSD Manager operating system requirements.
| Software Version | Supported Operating Systems |
|---|---|
| Kingston® SSD Manager x64 v1.5.X.X | Windows 10, 11 x64 |
| Kingston® SSD Manager v1.1.X.X | Windows 8, 8.1, 10 x86, x64 |
Download Kingston SSD Manager x64 v1.5.1.5 Driver & Software (Recommended) for Windows
» File version: 1.5.1.5
» File Size: 4.18 MB
Download
Download Kingston SSD Manager
» File version: v1.1.2.6
» File Size: 25.0 MB
Download
Download Files (PDF)
- User Manual Kingston A400 SSD- Download
See also : WD Black SN750 SSD Driver Download
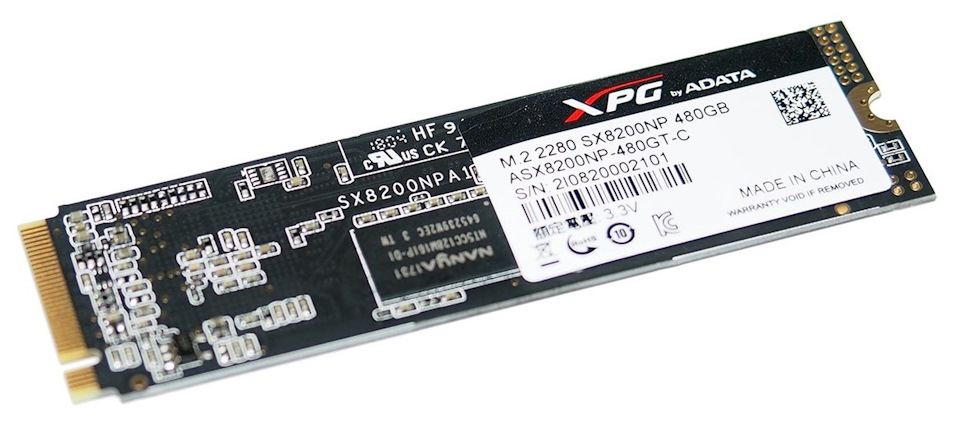
Мы рассмотрим преимущества логического интерфейса NVMe новой спецификации 1.3 на примере твердотельного накопителя формата M.2 из обновлённой серии WD Black SN750. Заодно покажем, как сделать «невозможное» и использовать современные SSD на старых компьютерах.
Над контроллером и чипами памяти этой серии трудились инженеры одной команды, так что модель обещает быть интересной сама по себе. Для чистоты эксперимента тесты выполнялись параллельно в Windows 10 Enterprise v.1803 и Windows 7 SP1 x64.
Справка «Компьютерры»
Как подружить любой NVMe SSD c Windows 7 SP1 x64? Для этого нужно установить два патча, которые добавляют в «семёрку» поддержку современных твердотельных накопителей с логическим интерфейсом NVMe. Microsoft внезапно™ убрала их со своего сайта, стимулируя переход на «десятку». Поэтому вот [копии KB3087873 + KB2990941] и контрольные суммы (хеши MD5) для проверки их целостности. Вдохни новую жизнь в древнее железо!
KB3087873: 86DB9E6A7667ACD09C091CCE02C23586
KB2990941: AFFFE9C2CC56FA6565839D9CA44E21DB
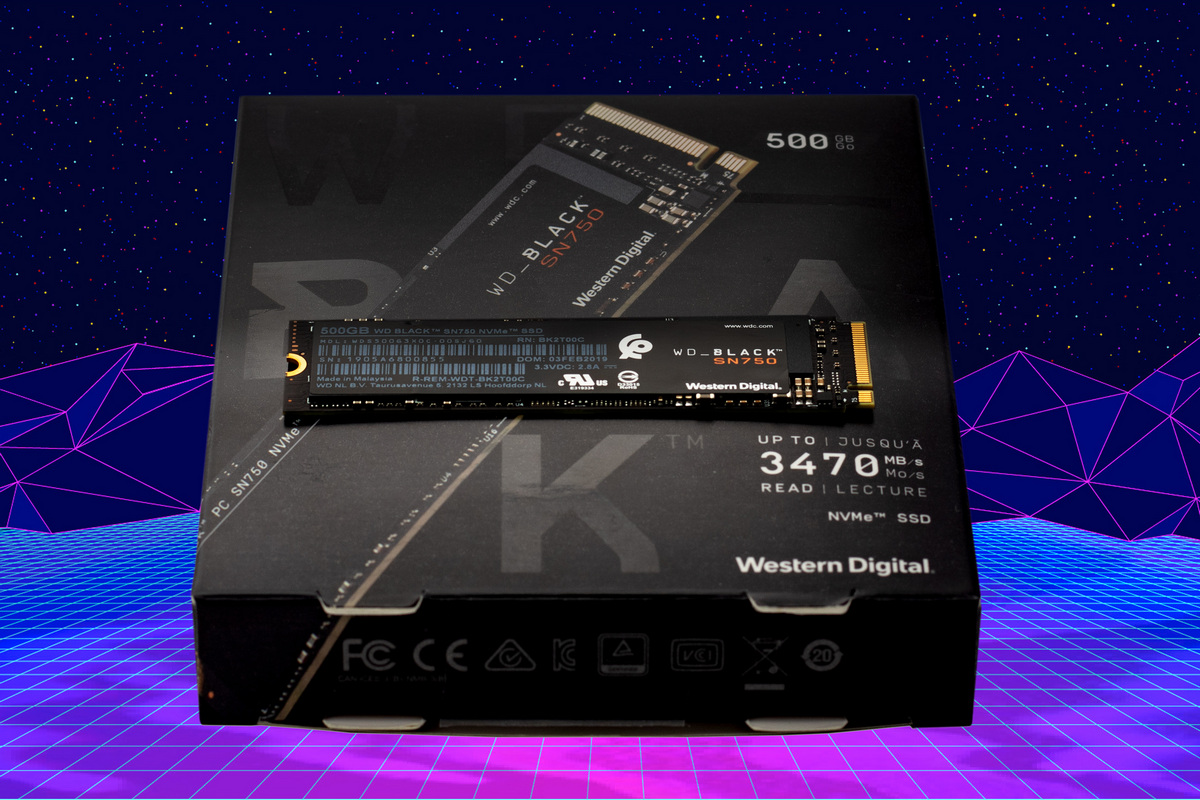
Пропатченная Windows 7 SP1 x64 может использовать NVMe SSD как обычные накопители, но неспособна считывать их расширенные атрибуты через API. Поэтому возникают сложности с оценкой атрибутов SMART. На повседневной работе это никак не сказывается. Забегая вперёд, отмечу, что даже скорости в седьмой винде получаются практически такими же, как в «десятке», если накопителю не требуется специфический драйвер (как раз наш случай). Если на вашей материнке нет разъёма M.2 (NGFF), то установите SSD в переходник M.2 – PCI-E x4. Он выглядит примерно так.
# Технические характеристики
В серии SN750 присутствуют модели объёмом от 250 Гб до 2 Тб. Самые шустрые – терабайтные накопители WDS100T3X0C и WDS100T3XHC (бука «H» расшифровывается heatsink и указывает на наличие радиатора). Именно их характеристики указываются на коробке любого экземпляра.
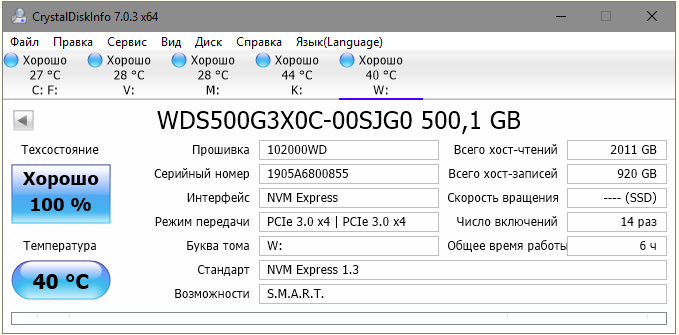
Вот краткие спецификации предоставленной на обзор модели WDS500G3X0C без радиатора:
- форм-фактор: M.2 2280;
- логический интерфейс: NVMe 1.3;
- расположение чипов: одностороннее (легче установить в компактные системы);
- буфер SDRAM: DDR4-2400, 512 Мб;
- ресурс записи: 300 Тб (600 P/E циклов на ячейку)
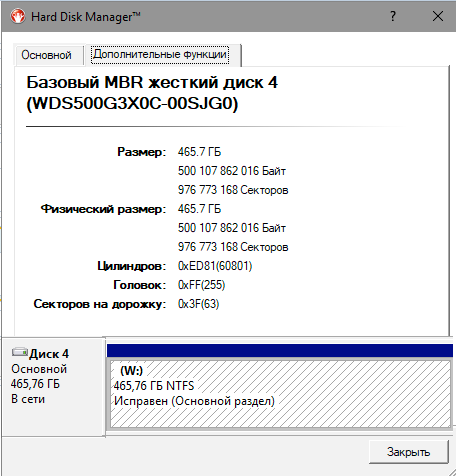
- неформатированная ёмкость: 500 107 862 016 байт
- среднее время наработки на отказ: 1,75 млн. часов
- размеры: 80 х 22 х 2,4 мм
- масса: 7,5 г.
После создания одного раздела NTFS доступный пользователю объём составляет 465,76 Гб. Около 2% занимает служебная область (over-provisioning), ещё немного теряется при форматировании, а остальное «съедает» разница между двоичной и десятичной системой счисления. В итоге полезный объём оказывается на 18 гигабайт больше по сравнению с другими SSD, выпускаемыми с паспортной ёмкостью 480 Гб.
Наиболее полные характеристики можно посмотреть в программе AIDA64.
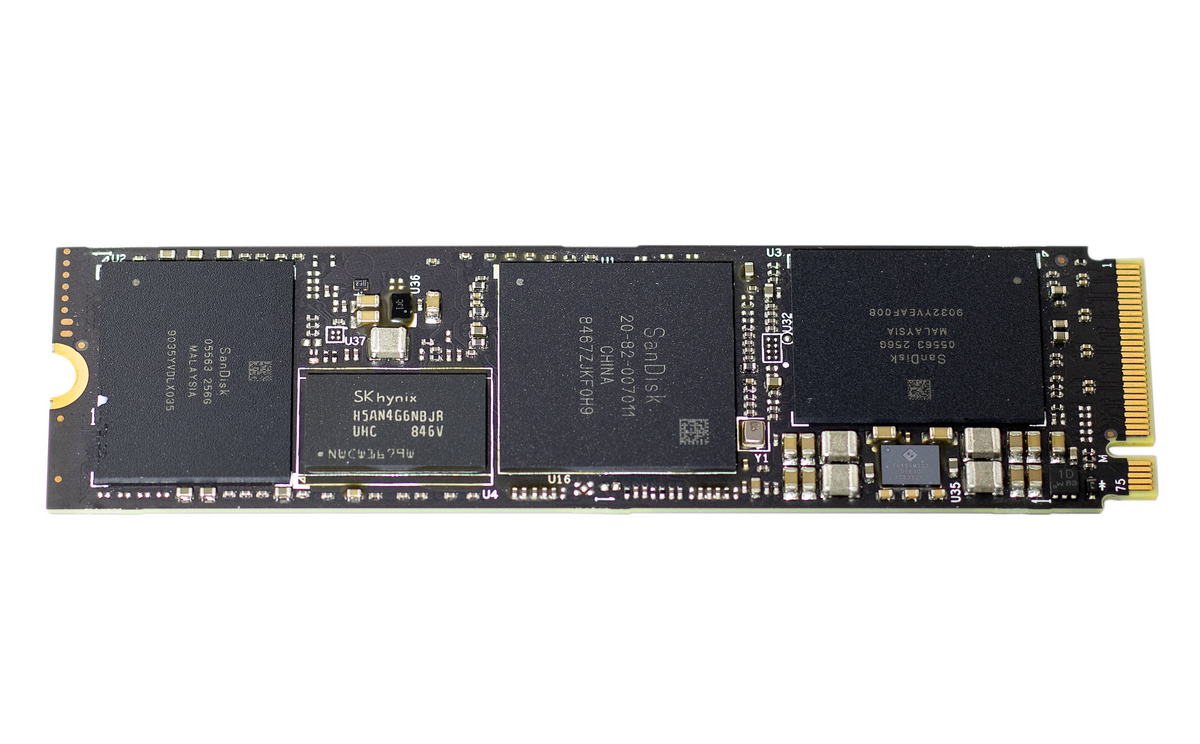
# WD Black SN750 под микроскопом
По привычке хотел написать «проведём вскрытие», но в данном случае вскрывать нечего – разве что снять наклейку и посмотреть маркировку чипов под ней с небольшим увеличением. Так и сделаем!
Посередине платы находится фирменный контроллер SanDisk 20-82-007011. Как вы наверняка помните, в 2016 году Western Digital купила SanDisk. Поэтому не удивительно, что на WD Black SN750 мы видим 28-нм восьмиканальный чип «дочки» концерна WD. Правда, в тестируемой нами 500-гигабайтной модели задействовано всего два канала.
Зато контроллер помимо трёх процессорных ядер архитектуры ARM Cortex-R содержит дополнительные модули, реализующие на аппаратном уровне те функции ускорения, которые у других выполняются драйверами. За чтение флэш-памяти и начальную коррекцию ошибок в контроллере отвечают отдельные вычислительные блоки, разгружая ядра ARM для более ресурсоёмких операций. Поэтому специфичного драйвера для WD Black SN750 не требуется, он работает с универсальным.
Слева и справа от контроллера находятся две микросхемы флэш-памяти SanDisk 05563 256G. Это сборки по восемь 256-гигабитных 64-слойных чипов TLC 3D NAND третьего поколения (BiSC3). Они были крайне популярны в 2018 году, а сейчас производители массово внедряют микросхемы памяти четвёртого поколения (BiSC4, 96 слоёв) и одновременно анонсируют скорый выход BiSC5 (128 слоёв).
Многослойные чипы хороши с точки зрения более высокой плотности хранения данных и удешевления массового производства, однако наращивание слоёв негативно влияет на стабильность показателей ячеек и ресурс их перезаписи.
Так или иначе, WD даёт на этот накопитель пятилетнюю гарантию, а морально устаревшие BiSC3 сейчас выглядят разумным компромиссом. Каких-то проблем с компактным размещением больших объёмов с ними тоже не наблюдается. В серии WD Black SN750 есть даже двухтерабайтные модели!
Между контроллером и одним из модулей памяти находится микросхема H5AN4G6NBJR производства SK Hynix. Это SDRAM-буфер стандарта DDR4, имеющий объём 512 Мб и работающей на частоте 2400 МГц с таймингами 17-17-17.
Основная роль этого буфера – ускорить трансляцию адресов, поэтому его объём подбирается исходя из ёмкости самого SSD. Дополнительные мегабайты погоды не сделают, а вот за высокую частоту производителю большое спасибо! Обычно с ростом тактовой частоты повышается и нагрев, но здесь беспокоиться не о чем. Допустимая работа модуля DDR4 составляет 95°С. Это на 10 градусов ниже критической температуры контроллера и на 25°С выше той, на которой SSD начинает сбрасывать частоты во избежание перегрева.
Кстати говоря, контроллер SanDisk 20-82-007011 применяет двухуровневый троттлинг согласно спецификациям NVMe 1.3. При температуре выше 70°С он сначала пропускает единичные такты, а затем снижает эффективную частоту сильнее, и только если температура продолжает расти.
На практике ни того, ни другого обычно не происходит. В наших тестах максимально зарегистрированная температура WD Black SN750 составила 48°С при 22°C за бортом. Никакого дополнительного охлаждения не использовалось, просто рядом со слотом M.2 не было дискретной видюхи, которая обычно нагревает всё вокруг.
Едва заметный чип под вторым модулем памяти – схема управления питанием со встроенным стабилизатором. Опознать её по маркировке у нас не получилось, но результат её работы великолепен. Накопитель моментально переключается между состоянием простоя и максимальным быстродействием, радует скоростями и практически не греется. Возможно, благодарить за это стоит и новые спецификации NVMe, предусматривающие продвинутые режимы управления питанием.
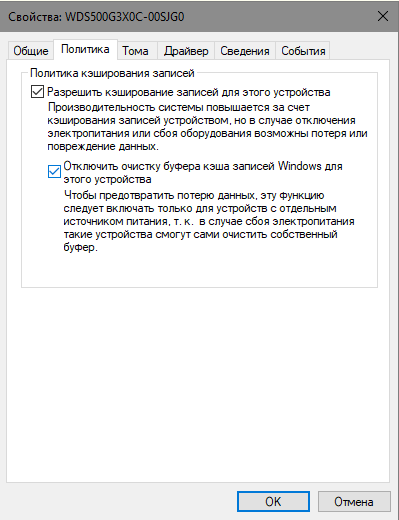
Если у вас ноутбук или компьютер, подключённый через ИБП, то для максимальной производительности SSD компания Western Digital рекомендует отключить очистку буфера кэша записей Windows и функции энергосбережения в свойствах накопителя.
Последнее также можно выполнить, включив режим Gaming Mode в фирменной утилите SSD Dashboard. Помимо этого она предоставит информацию о текущем состоянии накопителя, обновит прошивку и покажет степень его износа. Также в ней есть функция мониторинга текущей производительности SSD, чем мы и воспользуемся в тестах.
# Тесты реальные и синтетические
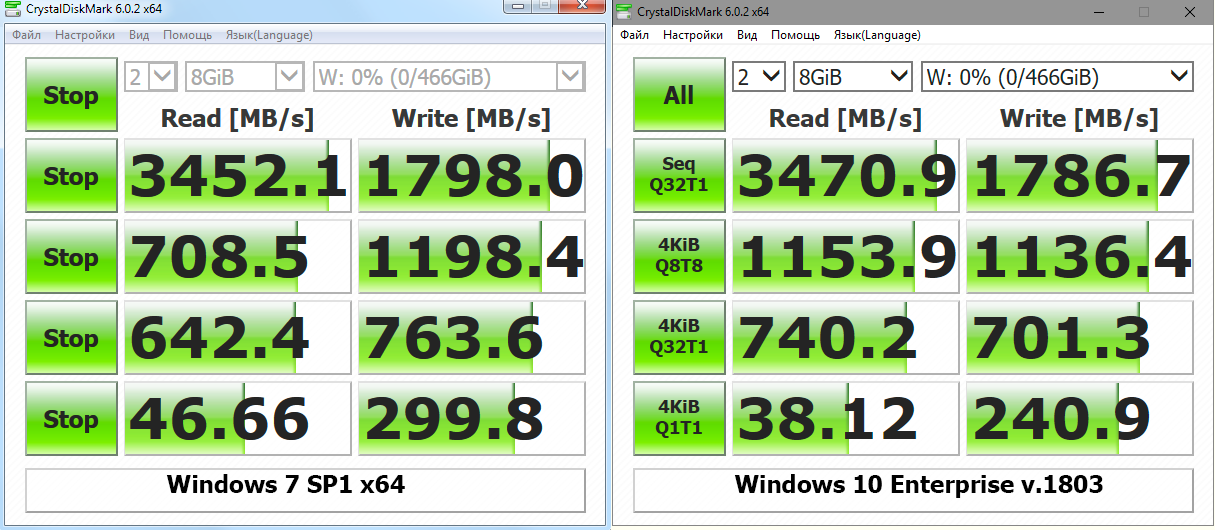
По негласной традиции начнём со скриншотов Crystal Disk Benchmark. Большие (во всех смыслах) цифры этого бенчмарка очень радуют обозревателей и покупателей.
Внушительные значения полностью соответствуют заявлению производителя о скоростных характеристиках SSD. Действительно, он демонстрирует «до 3470 Мб/с» и даже чуть выше. При этом не стоит забывать, что CrystalDiskMark – хитрая программа. Она фиксирует максимальный результат чтения из SLC-кэша, которому в реальной жизни соответствует начало операций с файлами, превышающими его размер.
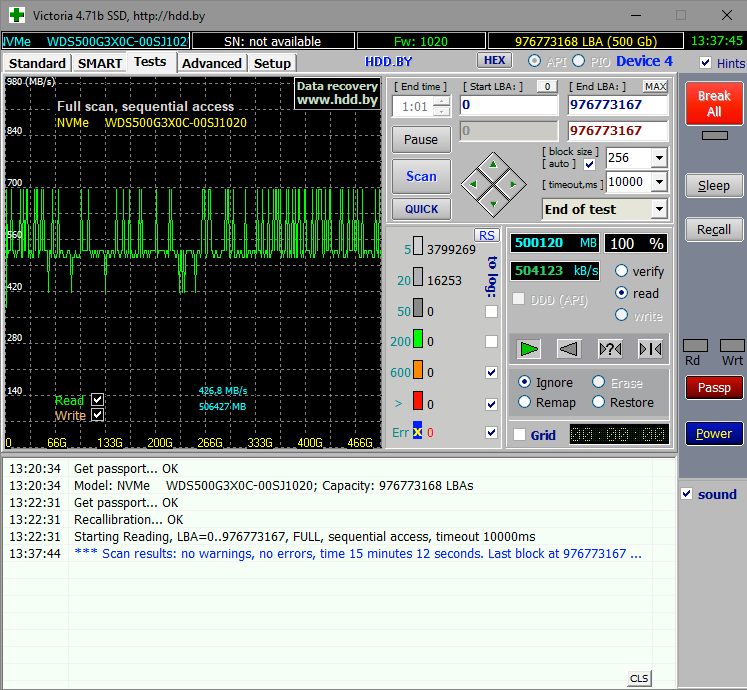
Чтение из основной памяти TLC 3D NAND хорошо показывает другая программа – обновлённая в 2019 году Victoria, в которую её бессменный разработчик Сергей Казанский добавил поддержку SSD.
Утилита выполняет прямое посекторное чтение, и на графике мы видим характерную для многоуровневых ячеек флэш-памяти «гребёнку». Максимальная скорость составляет около 700 Мб/с, минимальная – 420 Мб/с, а устоявшаяся средняя – 500 Мб/с. То есть, это примерно как у накопителей с интерфейсом SATA 3. Вполне ожидаемый результат – сама флэш-память ведь не стала быстрее, изменилась лишь логика работы с ней.
Следует отметить, что режим посекторного чтения характеризует физические возможности массива TLC 3D NAND. Файловые операции на SSD ускоряются как программно, так и самим контроллером. Поэтому в большинстве пользовательских сценариев WD Black NVMe SN750 оказывается гораздо быстрее.
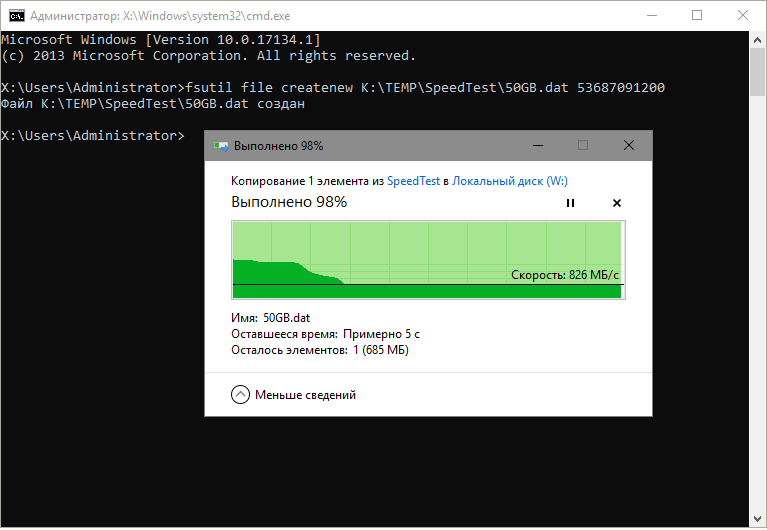
Для проверки создадим файл с размером, заведомо превышающим объём SLC-кэша. Скажем, 50 гигабайт. Теперь скопируем его с другого SSD на наш тестовый WDS500G3X0C.
Запись начинается очень бодро – около 2,5 Гб/с, но как только SLC-кэш заканчивается, происходит падение скорости. На графике мы видим плавное снижение, а не резкий провал. Причиной тому технология nCache 3.0, аппаратно реализованная в контроллере. Она позволяет организовать работу со статическим SLC-кэшем параллельно прямой записи в TLC-массив. Поэтому скорость записи после опустошения кэша получается выше, чем у большинства аналогов – 826 Мб/с.
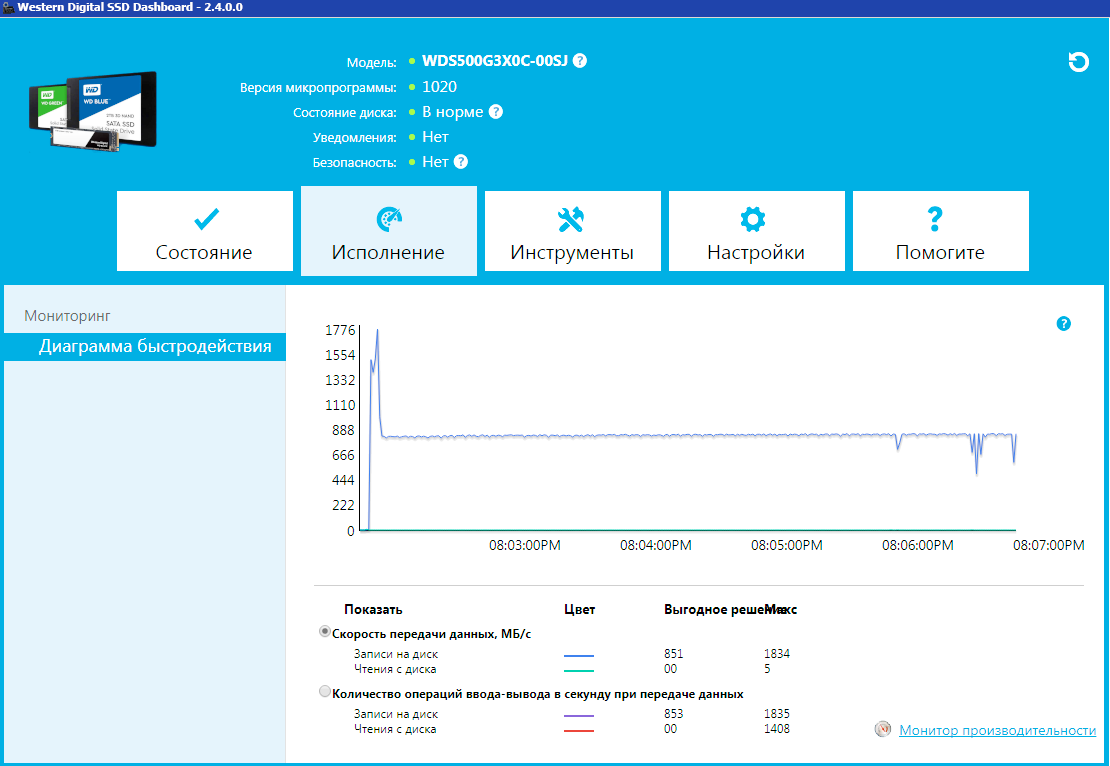
Практически такой же результат показывает мониторинг активности SSD в режиме реального времени через фирменную утилиту WD SSD Dashboard.
Пик вначале, а затем спад до изолинии на уровне около 830 Мб/с. Весьма неплохо для TLC 3D NAND! Разделение потоков для повышения скорости записи также стало возможным благодаря поддержке WD Black SN750 спецификации NVMe 1.3.
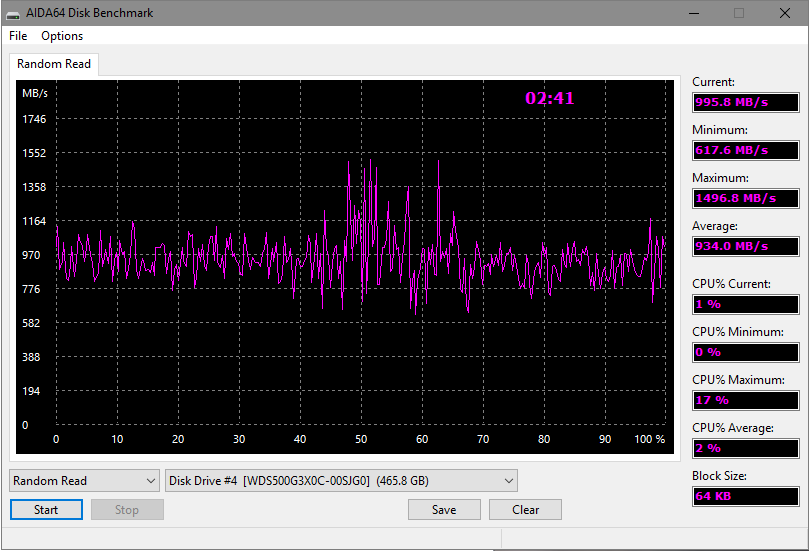
Тест чтения случайных блоков хорошо имитирует одновременное обращение к накопителю нескольких процессов.
Здесь с учётом SLC-кэша (всплески до 1,5 Гб/с) наблюдается даже ещё более высокая средняя скорость на уровне 934 Мб/с. Запуск часто используемых программ и открытие недавних документов должны происходить практически мгновенно.
# Выводы
WD Black SN750 – это ремейк довольно удачной серии SN720 на уровне прошивки и вариантов компоновки. Она имеет расширенный до 2 Тб модельный ряд, накопители с радиатором и без, а сами SSD стали чуть умнее, быстрее и холоднее.
По сравнению с подобными SSD, использующими интерфейс SATA 3 (6 Гбит/с), новые NVMe-накопители серии WD Black SN750 демонстрируют многократный прирост скорости для ключевых операций. Случайное чтение и запись стали быстрее в 2-2,5 раза, а линейная запись в пределах SLC-кэша – в 3,3 раза. Последовательное чтение из SLC-кэша ускорилось в 4,5 раза и фактически лимитируется пропускной способностью PCI Express 3.0 x4, которая пару лет назад казалась запредельной.
Напомним, что линии PCI Express 3.0 имеют скоростной лимит на уровне 8 млрд транзакций в секунду, а для кодирования каждых 128 бит приходится использовать ещё 2 служебных. Таким образом, для четырёх линий PCI Express 3.0 получаем теоретическую планку 3,93 Гб/с. На отдельных операциях SSD WDS500G3X0C очень близко подошёл к теоретическому пределу внешнего интерфейса.
Если компания Western Digital увеличит объём SLC-кэша, или сделает его динамически настраиваемым в широких пределах, то обновлённые твердотельные накопители станут ещё более интересным решением.
Устройство для обзора предоставлено компанией Western Digital.
- Главная
- Форум
- Мануалы

|
|
![Ответить с цитатой [Цитировать]](data:image/svg+xml,%3Csvg%20xmlns='http://www.w3.org/2000/svg'%20viewBox='0%200%200%200'%3E%3C/svg%3E)
 Отправлено: 06-Фев-2017 13:36
Отправлено: 06-Фев-2017 13:36
(спустя 12 дней)

(спустя 12 дней)
darkalexx4 |
dism /Mount-Image /ImageFile:c:tempsrcsourcesboot.wim /Index:1 /MountDir:c:tempmount и dism /Mount-Image /ImageFile:c:tempsrcsourcesinstall.wim /Index:1 /MountDir:c:tempmount И любой ssd m2 nvme будет работать. |
![Ответить с цитатой [Цитировать]](data:image/svg+xml,%3Csvg%20xmlns='http://www.w3.org/2000/svg'%20viewBox='0%200%200%200'%3E%3C/svg%3E)
 Отправлено: 03-Сен-2017 18:32
Отправлено: 03-Сен-2017 18:32
(спустя 6 месяцев 25 дней)

(спустя 6 месяцев 25 дней)
ANDREISM |
|
![Ответить с цитатой [Цитировать]](data:image/svg+xml,%3Csvg%20xmlns='http://www.w3.org/2000/svg'%20viewBox='0%200%200%200'%3E%3C/svg%3E)
 Отправлено: 03-Сен-2017 20:50
Отправлено: 03-Сен-2017 20:50
(спустя 2 часа 17 минут)

(спустя 2 часа 17 минут)
SunOK |
|
![Ответить с цитатой [Цитировать]](data:image/svg+xml,%3Csvg%20xmlns='http://www.w3.org/2000/svg'%20viewBox='0%200%200%200'%3E%3C/svg%3E)
 Отправлено: 03-Сен-2017 21:45
Отправлено: 03-Сен-2017 21:45
(спустя 55 минут)

(спустя 55 минут)
Adler |
|
![Ответить с цитатой [Цитировать]](data:image/svg+xml,%3Csvg%20xmlns='http://www.w3.org/2000/svg'%20viewBox='0%200%200%200'%3E%3C/svg%3E)
 Отправлено: 03-Сен-2017 22:02
Отправлено: 03-Сен-2017 22:02
(спустя 17 минут)

(спустя 17 минут)
ANDREISM |
|
![Ответить с цитатой [Цитировать]](data:image/svg+xml,%3Csvg%20xmlns='http://www.w3.org/2000/svg'%20viewBox='0%200%200%200'%3E%3C/svg%3E)
 Отправлено: 04-Сен-2017 00:11
Отправлено: 04-Сен-2017 00:11
(спустя 2 часа 9 минут)

(спустя 2 часа 9 минут)
SunOK |
|
![Ответить с цитатой [Цитировать]](data:image/svg+xml,%3Csvg%20xmlns='http://www.w3.org/2000/svg'%20viewBox='0%200%200%200'%3E%3C/svg%3E)
 Отправлено: 09-Мар-2018 08:51
Отправлено: 09-Мар-2018 08:51
(спустя 6 месяцев 5 дней)

(спустя 6 месяцев 5 дней)
Policai |
|
![Ответить с цитатой [Цитировать]](data:image/svg+xml,%3Csvg%20xmlns='http://www.w3.org/2000/svg'%20viewBox='0%200%200%200'%3E%3C/svg%3E)
 Отправлено: 09-Мар-2018 09:37
Отправлено: 09-Мар-2018 09:37
(спустя 46 минут)

(спустя 46 минут)
Adler |
![Ответить с цитатой [Цитировать]](data:image/svg+xml,%3Csvg%20xmlns='http://www.w3.org/2000/svg'%20viewBox='0%200%200%200'%3E%3C/svg%3E)
 Отправлено: 09-Мар-2018 12:06
Отправлено: 09-Мар-2018 12:06
(спустя 2 часа 29 минут)

(спустя 2 часа 29 минут)
naifle |
|
![Ответить с цитатой [Цитировать]](data:image/svg+xml,%3Csvg%20xmlns='http://www.w3.org/2000/svg'%20viewBox='0%200%200%200'%3E%3C/svg%3E)
 Отправлено: 09-Мар-2018 16:06
Отправлено: 09-Мар-2018 16:06
(спустя 3 часа)

(спустя 3 часа)
Policai |
|
![Ответить с цитатой [Цитировать]](data:image/svg+xml,%3Csvg%20xmlns='http://www.w3.org/2000/svg'%20viewBox='0%200%200%200'%3E%3C/svg%3E)
 Отправлено: 09-Мар-2018 16:22
Отправлено: 09-Мар-2018 16:22
(спустя 16 минут)

(спустя 16 минут)
Adler |
|
![Ответить с цитатой [Цитировать]](data:image/svg+xml,%3Csvg%20xmlns='http://www.w3.org/2000/svg'%20viewBox='0%200%200%200'%3E%3C/svg%3E)
 Отправлено: 09-Мар-2018 16:31
Отправлено: 09-Мар-2018 16:31
(спустя 8 минут)

(спустя 8 минут)
Policai |
|
![Ответить с цитатой [Цитировать]](data:image/svg+xml,%3Csvg%20xmlns='http://www.w3.org/2000/svg'%20viewBox='0%200%200%200'%3E%3C/svg%3E)
 Отправлено: 09-Мар-2018 16:48
Отправлено: 09-Мар-2018 16:48
(спустя 17 минут)

(спустя 17 минут)
sergeysvirid |
ЧТО НОВОГО:Драйверы NVMe в boot.wim и install.esd |
![Ответить с цитатой [Цитировать]](data:image/svg+xml,%3Csvg%20xmlns='http://www.w3.org/2000/svg'%20viewBox='0%200%200%200'%3E%3C/svg%3E)
 Отправлено: 09-Мар-2018 18:48
Отправлено: 09-Мар-2018 18:48
(спустя 2 часа)

(спустя 2 часа)
naifle |
|
Страница 1 из 2
Текущее время: 04-Фев 20:43
Часовой пояс: UTC + 3
Вы не можете начинать темы
Вы не можете отвечать на сообщения
Вы не можете редактировать свои сообщения
Вы не можете удалять свои сообщения
Вы не можете голосовать в опросах
Вы не можете прикреплять файлы к сообщениям
Вы можете скачивать файлы
 Drivers KingSpec NVMe PCIe SSD NE 10.4.31.0
Drivers KingSpec NVMe PCIe SSD NE 10.4.31.0

KingSpec (Shenzhen KingSpec Electronics Technology)

NVMe PCIe SSD NE










Drivers

10.4.31.0

Yes

Official

WinDrv226x_1043100_20170713.zip

810 KB


10/28/2020

10/27/2020


Drivers pour les Solid-State Drives (SSD) KingSpec.

- Correction d’un écran bleu (BSOD) lors de l’exécution de la commande Sanitize lorsque la commande formatNVM est en cours.

- NVMe PCIe SSD NE 22x42mm 64 Go (NE-64 2242)
- NVMe PCIe SSD NE 22x42mm 128 Go (NE-128 2242)
- NVMe PCIe SSD NE 22x42mm 256 Go (NE-256 2242)
- NVMe PCIe SSD NE 22x42mm 512 Go (NE-512 2242)
- NVMe PCIe SSD NE 22x80mm 128 Go (NE-128 2280)
- NVMe PCIe SSD NE 22x80mm 256 Go (NE-256 2280
- NVMe PCIe SSD NE 22x80mm 512 Go (NE-512 2280)
- NVMe PCIe SSD NE 22x80mm 1 To (NE-1TB 2280)
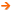
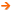







 .
. .
. .
. .
. .
. .
. .
. .
. .
. .
.