В Windows 10 имеется два вида переменных сред:
Содержание
- Как изменять, удалять или создавать переменные среды в Windows 10
- Список переменных через командную строку
- Создать переменную со значением
- Переименовать значение переменной
- Два значения в переменной
- Удалить значение в переменной
- Удалить переменную
- Обновить переменную среды
- 3 ответа 3
- Как добавить переменную среды Windows без перезагрузки?
- Изучаем переменные среды в Windows 10
- Переменные среды Windows
- Переменные PATH и PATHEXT
- Создание переменных среды
- Заключение
- Как обновить переменные среды без перезагрузки windows 10
Как изменять, удалять или создавать переменные среды в Windows 10
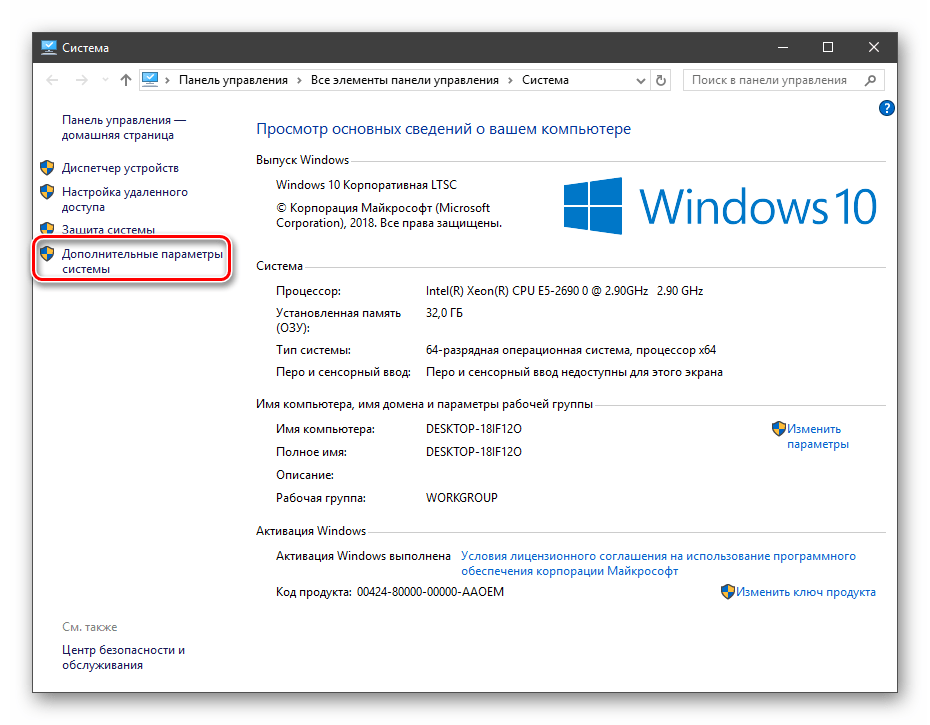
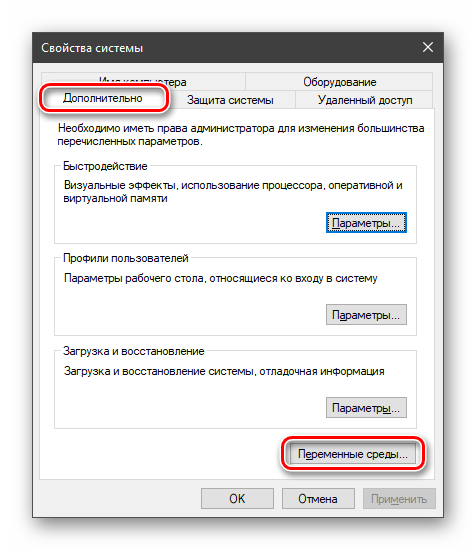
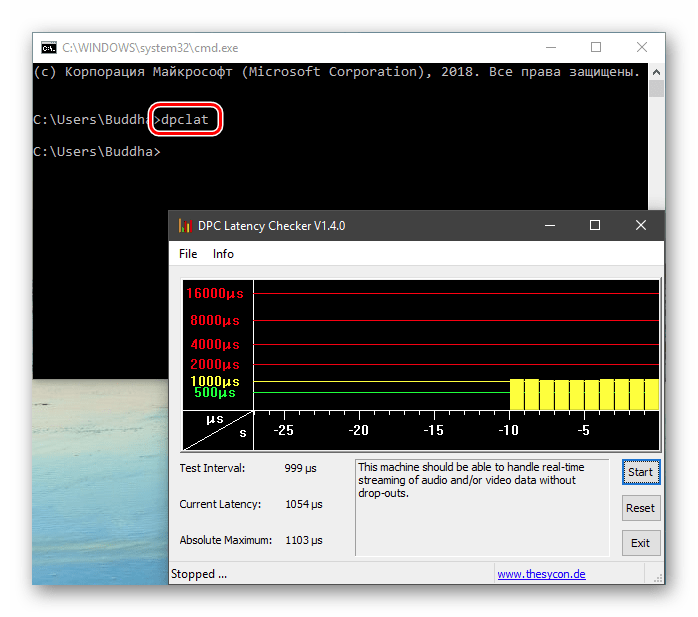
Нажмите Win+R и введите sysdm.cpl, чтобы быстро открыть свойства системы. Перейдите во вкладку «Дополнительно» и снизу нажмите на «Переменные среды«.
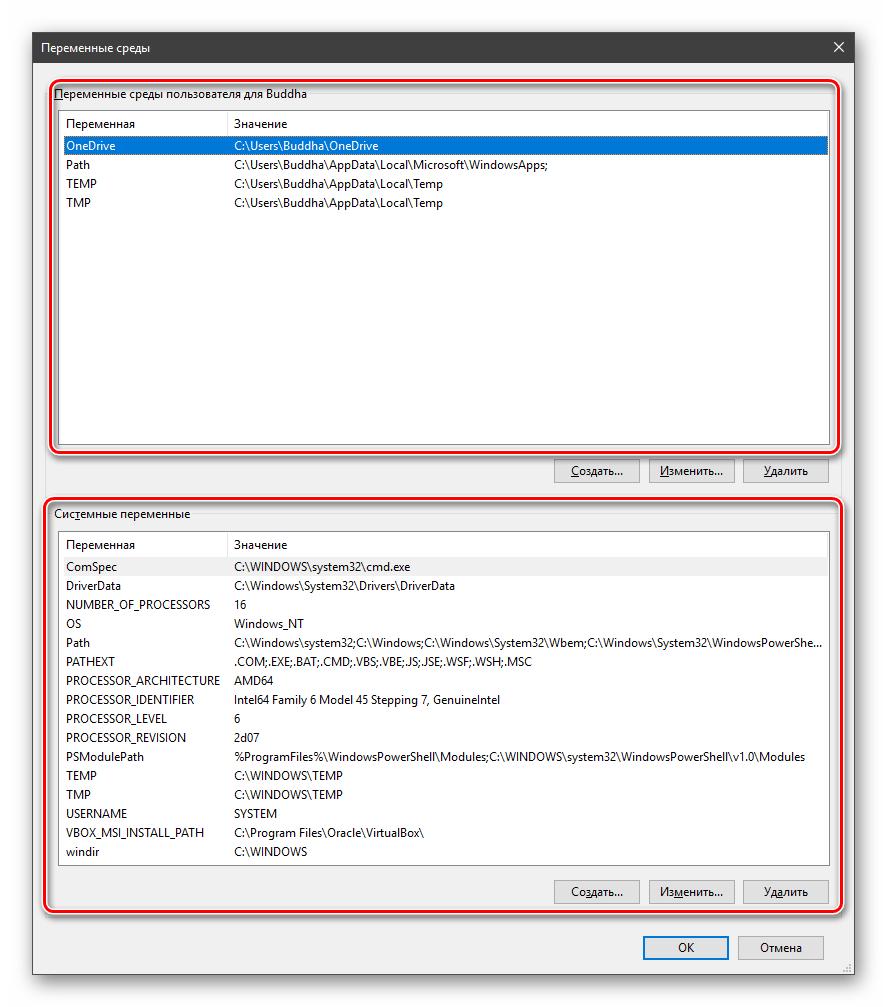
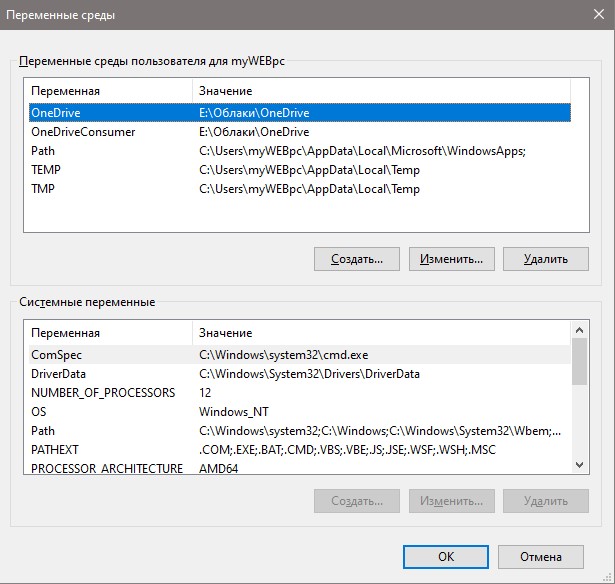
Вы увидите системные и пользовательские переменные среды. Вы можете добавить, удалить или изменить значение для переменных.
Список переменных через командную строку
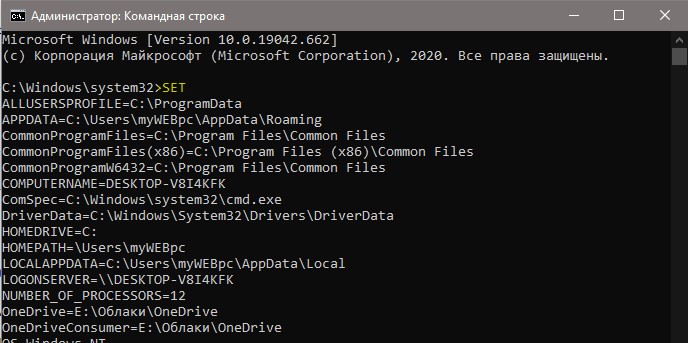
Если вам нужно посмотреть весь список переменных со значением через командную строку, то введите ниже команду:
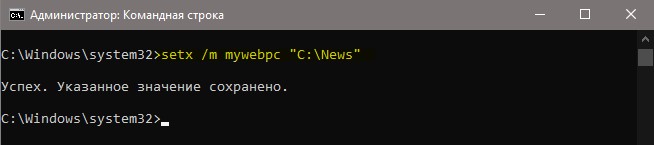
Создать переменную со значением
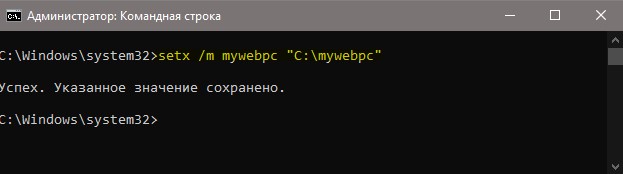
Если нужно создать переменную для пользователя, то команда будет следующая: setx, где MYWEBPC это переменная, а C:mywebpc это значение.
Если нужно создать системную переменную со значением, то:
Переименовать значение переменной
Чтобы изменить значение переменной нужно просто заменить значение на другое. Начнем с пользовательской среды:
Изменить системную системную переменную:
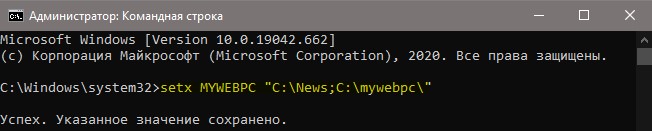
Два значения в переменной
Мы можем добавить два значения и более для одной переменной разделив точкой с запятой. Пользовательская:
Два значения в переменной системной среды:
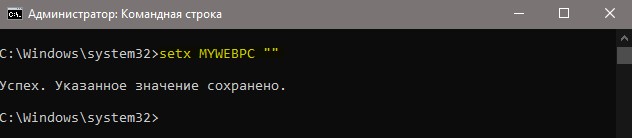
Удалить значение в переменной
Чтобы удалить значение в переменной нужно просто оставить поле в кавычках пустым. Для пользовательской среды:
Удалить значение для системной среды:
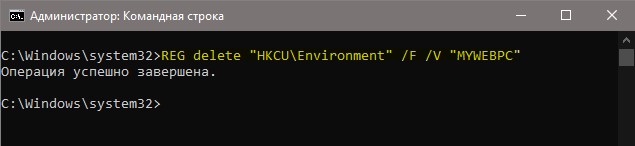
Удалить переменную
Чтобы удалить саму переменную, нужно удалить запись из реестра. Удалить пользовательскую переменную:
Удалить переменную для системной среды:
Источник
Обновить переменную среды
Как обновить командную оболочку Windows после изменения переменных среды?
т.е. в bash я могу просто сделать «source
3 ответа 3
Это действительно зависит от того, как были установлены переменные среды. Если, например, вы использовали команду «SET» в командной строке, это влияет только на текущий экземпляр. С другой стороны, такие команды, как «SETX» будут постоянно корректировать значение переменной среды. SETX гарантирует, что все будущие экземпляры cmd увидят обновление. Это не повлияет на местную среду.
Это важно, потому что приложения, запущенные другим процессом, наследуют свои переменные среды от своего родителя. Таким образом, если вы запустите cmd из проводника, вы получите переменные так, как их видит проводник.
Основная среда хранится в реестре, но оболочка проводника считывает это по своему адресу. Отсюда он отправляется на каждый сеанс cmd.exe.
SET влияет только на среду cmd. SETX позволяет изменять основную среду, но настройка не отражается в локальной среде.
CONSET и 4NT Фрэнка Вестлейка могут извлекать записи из реестра, но, в частности, без переключателей для основной среды.
это зависит от того, где вы «устанавливаете» переменные окружения. Эквивалент вашего примера Bash будет выглядеть так:
и теперь вы обновляете его
но я думаю, что вы сделали это через диалог windows-system-settings-(или как там его имя). В результате вы действительно изменили реестр. эти параметры реестра отображаются в процессе при запуске нового процесса.
Источник
Как добавить переменную среды Windows без перезагрузки?
Я хотел бы добавить переменную окружения на компьютер Windows (настольный компьютер или сервер) и иметь возможность использовать его без перезагрузки этого компьютера.
Допустим, у вас есть рабочий сервер, на котором размещены различные приложения, а для запуска нового приложения требуется определенная переменная среды. Вы не хотите перезагружать его, когда пользователи подключены к другим вашим приложениям. Какой у вас есть выбор? Мне не нравится опция «ждать, пока наступит хорошее время для перезагрузки». Должен быть лучший способ. Что мне не хватает?
Изменения переменных среды должны вступить в силу немедленно, если вы сделаете это изменение в главном диалоговом окне «Свойства» для рассматриваемого компьютера (перейдите в «Мой компьютер | Свойства | Дополнительно | Переменные среды»). После сохранения изменений проводник передает WM_SETTINGCHANGE сообщение всем окнам, чтобы сообщить им об изменениях. Любые программы, порожденные через Проводник после этого, должны получить обновленную среду, хотя уже запущенные программы не получат, если они не обрабатывают сообщение об изменении настроек.
Я не могу сказать из вашего описания проблемы, какая конкретно у вас проблема с этим. Можете ли вы рассказать нам больше о конкретном сценарии, который не работает?
Теперь, закрыв все командные строки, вы увидите, что PATH переменная действительно обновлена.
Все командные строки должны быть закрыты. Снова откройте новую командную строку, введите путь, и вы увидите новые данные.
Следует иметь в виду, что многие программы получают переменные среды при первом запуске, поэтому, хотя окна могут не нуждаться в перезапуске, некоторые программы могут использовать их, прежде чем они смогут использовать новые переменные. Хорошим примером этого является необходимость открыть новое окно командной строки после добавления PATH (да, я был отключен этим).
Хотя у меня недостаточно репутации, чтобы прокомментировать наиболее высоко оцененный ответ на этот вопрос, я хотел бы заявить, что он не совсем правильный. Я знаю это, потому что независимо от того, какой обходной путь я попробовал в этом посте, на самом деле ничего не получалось.
Тем не менее, обратите внимание, что изменения переменных среды не приводят к немедленному изменению. Например, если вы запустите другую командную строку после внесения изменений, переменные среды будут отражать предыдущие (а не текущие) значения. Изменения не вступят в силу, пока вы не выйдете из системы, а затем снова войдите в систему.
Часть о переменных окружения, сбрасывающих к предыдущим значениям после перезагрузки командной строки, является точно тем, что я испытал в Windows Server 2008.
В статье говорится:
Чтобы внести эти изменения без выхода из системы, передайте сообщение WM_SETTINGCHANGE всем окнам системы, чтобы любые заинтересованные приложения (такие как Windows Explorer, Диспетчер программ, Диспетчер задач, Панель управления и т. Д.) Могли выполнить обновление.
Это не означает, что Explorer транслирует сообщение WM_SETTINGCHANGE после того, как вы изменили системные переменные окружения или что оно действительно работает. Я не уверен, как вы будете делать то, что предложено в статье базы знаний (для немедленного распространения изменений) из командной строки.
Источник
Изучаем переменные среды в Windows 10
Переменные среды Windows
Получить информацию о существующих переменных можно в свойствах системы. Для этого кликаем по ярлыку Компьютера на рабочем столе правой кнопкой мыши и выбираем соответствующий пункт.
Переходим в «Дополнительные параметры».
В открывшемся окне с вкладкой «Дополнительно» нажимаем кнопку, указанную на скриншоте ниже.
Здесь мы видим два блока. Первый содержит пользовательские переменные, а второй системные.
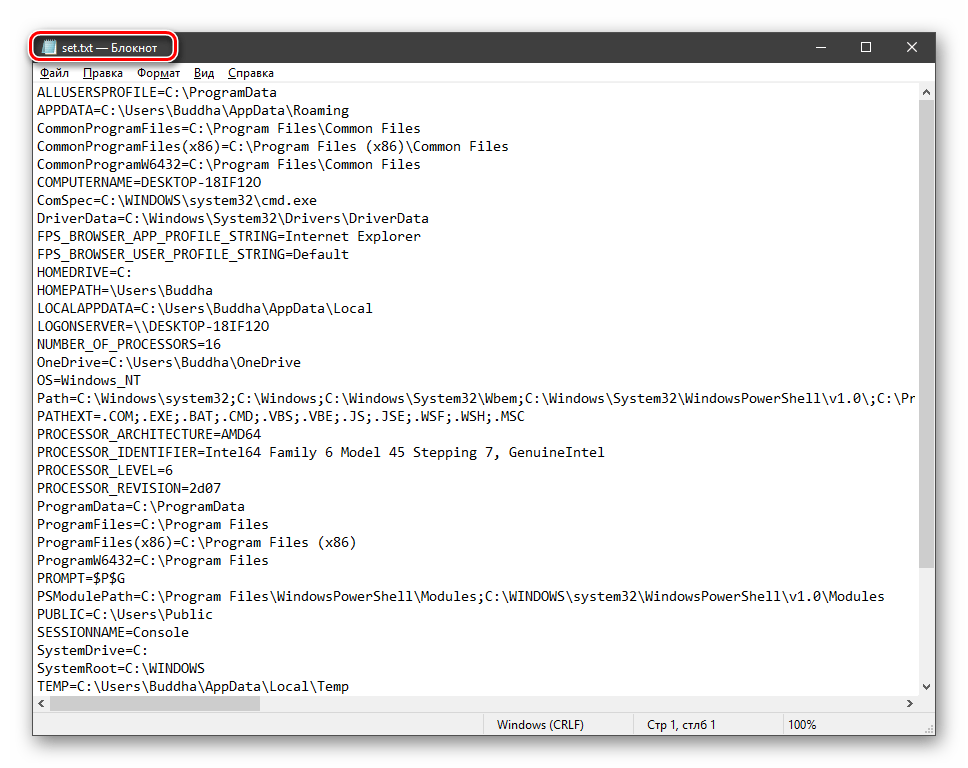
Если требуется просмотреть весь перечень, запускаем «Командную строку» от имени администратора и выполняем команду (вводим и нажимаем ENTER).
На рабочем столе появится файл с названием «set.txt», в котором будут указаны все переменные окружения, имеющиеся в системе.
Все их можно использовать в консоли или скриптах для запуска программ или поиска объектов, заключив имя в знаки процента. Например, в команде выше вместо пути
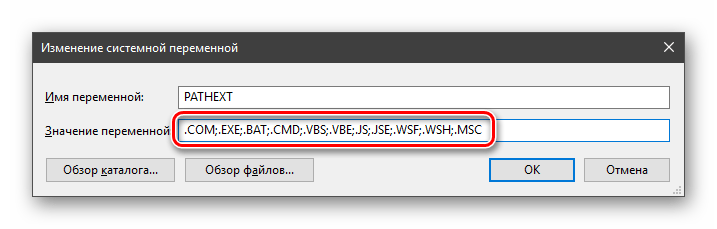
Примечание: регистр при написании переменных не важен. Path=path=PATH
Переменные PATH и PATHEXT
Если с обычными переменными все понятно (одна ссылка – одно значение), то эти две стоят особняком. При детальном рассмотрении видно, что они ссылаются сразу на несколько объектов. Давайте разберемся, как это работает.
«PATH» позволяет запускать исполняемые файлы и скрипты, «лежащие» в определенных каталогах, без указания их точного местоположения. Например, если ввести в «Командную строку»
система осуществит поиск по папкам, указанным в значении переменной, найдет и запустит соответствующую программу. Этим можно воспользоваться в своих целях двумя способами:
%SYSTEMROOT% определяет путь до папки «Windows» независимо от буквы диска.
Затем нажимаем ОК в окнах «Переменные среды» и «Свойства системы».
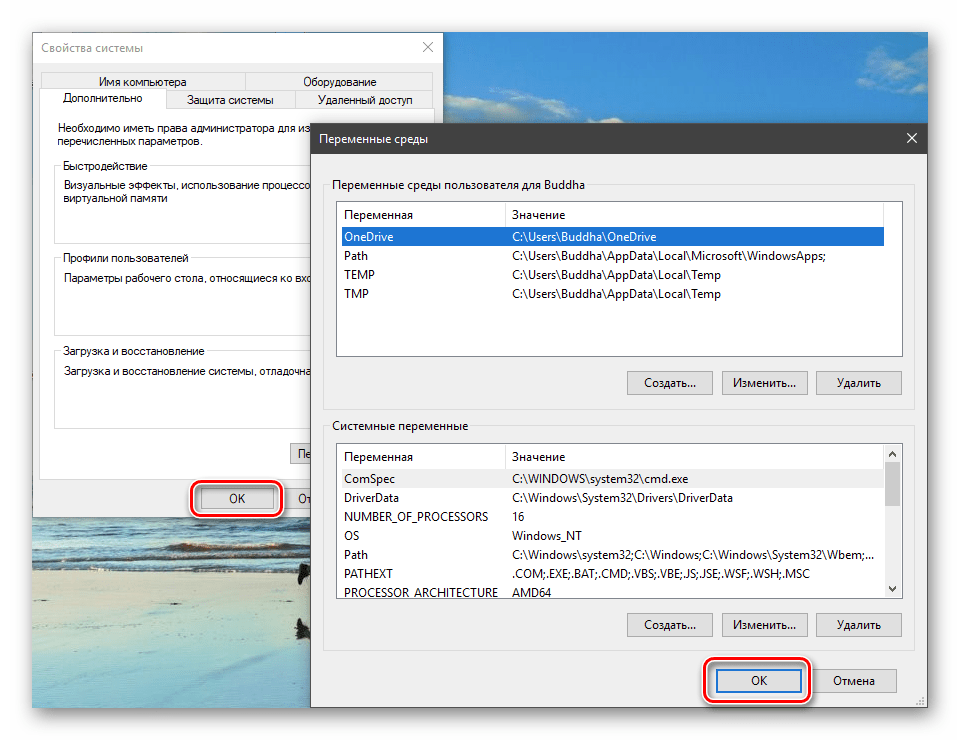
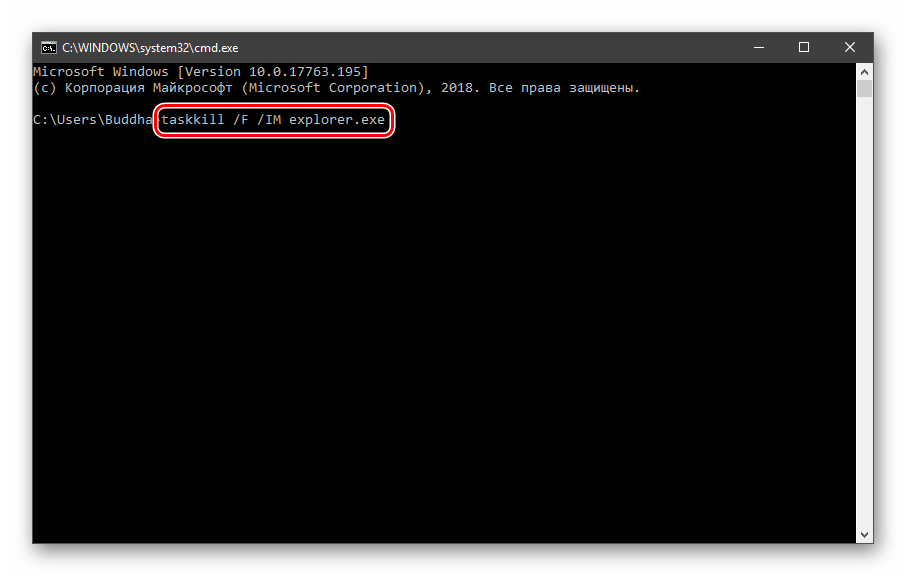
Для применения настроек, возможно, придется перезапустить «Проводник». Сделать это быстро можно так:
Открываем «Командную строку» и пишем команду
taskkill /F /IM explorer.exe
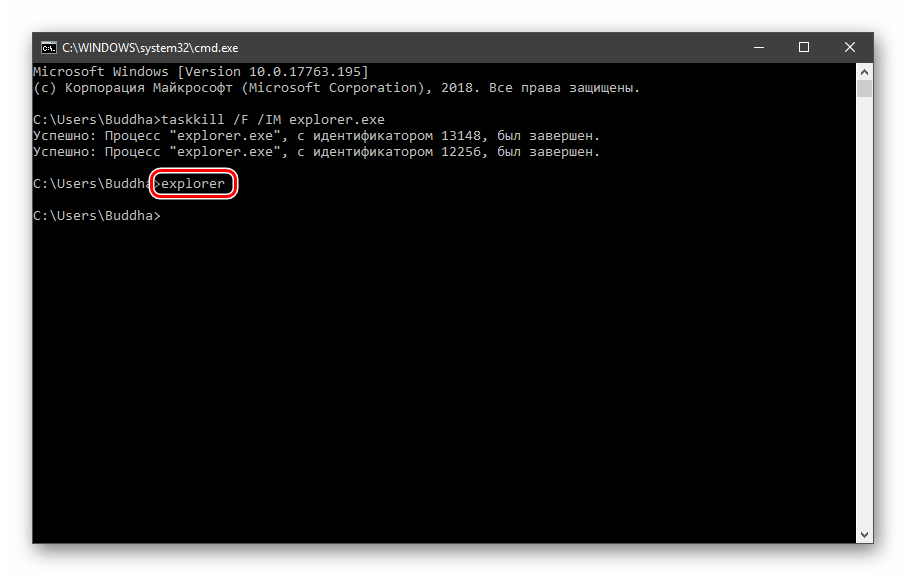
Все папки и «Панель задач» исчезнут. Далее снова запускаем «Проводник».
Еще один момент: если вы работали с «Командной строкой», ее также следует перезапустить, то есть консоль не будет «знать», что настройки изменились. Это же касается и фреймворков, в которых вы отлаживаете свой код. Также можно перезагрузить компьютер или выйти и снова зайти в систему.
Теперь все файлы, помещенные в «C:Script» можно будет открывать (запускать), введя только их название.
«PATHEXT», в свою очередь, дает возможность не указывать даже расширение файла, если оно прописано в ее значениях.
Принцип работы следующий: система перебирает расширения по очереди, пока не будет найден соответствующий объект, причем делает это в директориях, указанных в «PATH».
Создание переменных среды
Создаются переменные просто:
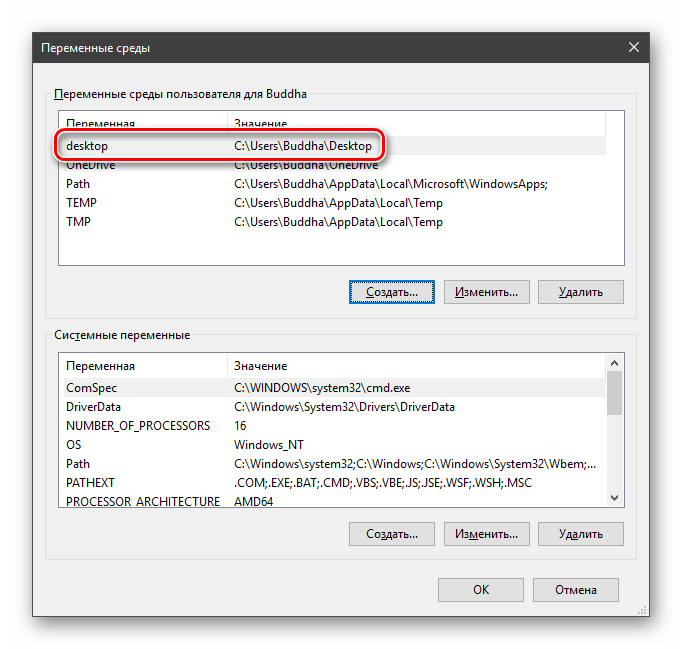
Для примера переделаем команду, которую мы использовали для получения списка (самая первая в статье). Теперь нам вместо
потребуется ввести только
Заключение
Использование переменных окружения позволяет значительно сэкономить время при написании скриптов или взаимодействии с системной консолью. Еще одним плюсом является оптимизация создаваемого кода. Имейте в виду, что созданные вами переменные отсутствуют на других компьютерах, и сценарии (скрипты, приложения) с их использованием работать не будут, поэтому перед тем, как передавать файлы другому пользователю, необходимо уведомить его об этом и предложить создать соответствующий элемент в своей системе.
Помимо этой статьи, на сайте еще 12372 инструкций.
Добавьте сайт Lumpics.ru в закладки (CTRL+D) и мы точно еще пригодимся вам.
Отблагодарите автора, поделитесь статьей в социальных сетях.
Источник
Как обновить переменные среды без перезагрузки windows 10
Возможно ли в Win менять значения переменных окружения буз перезагрузки?
Да и вообще, существует ли удобный инструментарий для работы с ними. Стандартный похож на издевательство ибо:
— если переменная длинная и является перечислением (типа PATH), то фиг в ней что найдешь в этом маленьком окошке, который предлагается для ее редактирования
— чтобы ввести новую переменную нужно нажать Добавить, нужно что-то написать в очень маленьком окошке и нажать ОК
IMHO обычный текстовый файл был бы и то удобнее, и не было бы очередной проблемы
— резервного копирования эих переменных
Кстати, почему после изменения переменной окрыжения нужно обязательно перезагружаться иначе она не вступит в силу? Что за такие важные структуры инициализуруются в windows internals, что я не могу прописать путь где ОС будет искать файлы без ее перезагрузки? Бред? Или я что-то не понимаю?
Кроме того надоели такие вещи:
После установки компилятора необходимо проверить, что в переменной окружения PATH прописан путь:
bini386-win32;
Причём, он должен там быть раньше, чем пути к остальным FPC, если их в системе несколько. Кроме того, если в системе установлен, например, MinGW, то, если, в PATH путь к нему прописан раньше, чем к FPC, то будет использован не ld из FPC, а ld из MinGW и ничего собрать не удастся.
В общем, может кто-то нашел что-то удобное, чтобы сосуществовать рядом с этим безобразием?
p.s. Linux не предлагать
| |
От: | Sergeant_BY |
| Дата: | 04.12.07 07:07 | |
| Оценка: | 4 (1) |
DAS> После установки компилятора необходимо проверить, что в переменной окружения PATH прописан путь:
DAS> bini386-win32;
DAS>Причём, он должен там быть раньше, чем пути к остальным FPC, если их в системе несколько. Кроме того, если в системе установлен, например, MinGW, то, если, в PATH путь к нему прописан раньше, чем к FPC, то будет использован не ld из FPC, а ld из MinGW и ничего собрать не удастся.
| |
От: | DOOM |
| Дата: | 04.12.07 07:11 | |
| Оценка: | 2 (1) |
Здравствуйте, DemAS, Вы писали:
DAS>Возможно ли в Win менять значения переменных окружения буз перезагрузки?
Конечно.
DAS> Да и вообще, существует ли удобный инструментарий для работы с ними. Стандартный похож на издевательство ибо:
DAS> — если переменная длинная и является перечислением (типа PATH), то фиг в ней что найдешь в этом маленьком окошке, который предлагается для ее редактирования
DAS> — чтобы ввести новую переменную нужно нажать Добавить, нужно что-то написать в очень маленьком окошке и нажать ОК
DAS> IMHO обычный текстовый файл был бы и то удобнее, и не было бы очередной проблемы
DAS> — резервного копирования эих переменных
Ну тут да. Косяк. Можно напрямую через реестр, если этот способ можно назвать удобным.
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINESYSTEMCurrentControlSetControlSession ManagerEnvironment — это системные переменные
HKEY_CURRENT_USEREnvironment — пользовательские
Кроме того, в Support Tools’ах есть утилита setx, которая, в отличие от set позволяет делать постоянные изменения в переменных окружения.
DAS> Кстати, почему после изменения переменной окрыжения нужно обязательно перезагружаться иначе она не вступит в силу? Что за такие важные структуры инициализуруются в windows internals, что я не могу прописать путь где ОС будет искать файлы без ее перезагрузки? Бред? Или я что-то не понимаю?
Видать что-то не понимаешь. В винде, как и во многих других ОС, окружение привязано к процессу — поэтому, чтобы отразить изменения в окружении надо перезапустить процесс. Т.е. поменял PATH, перезапусти cmd.exe и он уже будет с новыми путями.
DAS> Кроме того надоели такие вещи:
DAS>
DAS> После установки компилятора необходимо проверить, что в переменной окружения PATH прописан путь:
DAS> bini386-win32;
DAS>Причём, он должен там быть раньше, чем пути к остальным FPC, если их в системе несколько. Кроме того, если в системе установлен, например, MinGW, то, если, в PATH путь к нему прописан раньше, чем к FPC, то будет использован не ld из FPC, а ld из MinGW и ничего собрать не удастся.
Не вижу проблемы. Сделай себе 2 скрипта — один при запуске cmd добавляет в PATH пути к MinGW, другой к чему-нибудь еще. Запускай нужный и не засоряй общесистемные переменные.
DAS> В общем, может кто-то нашел что-то удобное, чтобы сосуществовать рядом с этим безобразием?
Ну что знал, то предложил.
DAS> p.s. Linux не предлагать 
А там по сути также. Переменные окружения вещь очень старая и ведет себя так, как это было придумано десятилетия назад.
| |
От: | DemAS | http://demas.me |
| Дата: | 04.12.07 07:18 | ||
| Оценка: |
Здравствуйте, Sergeant_BY, Вы писали:
S_B>setx path «%PATH%;C:New Folder»
S_B>setx — из ресурскита к XP, например.
А обратно как? 
Понимаю, что можно написать скрипт, который сформирует набор команд для setx, но может есть что-то готовое.
S_B>Оккрываю System properties->Advanced->Environment, добавляю какую-нибудь лабуду в конце %PATH%, нажимаю ОК.
S_B>Запускаю cmd, пишу set и вижу в %PATH% ту самую лабуду.
S_B>Что я делаю не так?
Я тоже вижу. Но если я пытаюсь запустить exe-к из каталога, находящегося в добавленной директории — система говорит, что не знает такого.
Хотя возможно это я ступил — наверное надо было перезапустить cmd.
DAS>> p.s. Linux не предлагать 
S_B>А в Linux’е разве по другому?
Не знаю. Но на всякий случай предупредил. 
Источник
I made a better alternative to the Chocolatey refreshenv for cmd and cygwin which solves a lot of problems like:
-
The Chocolatey refreshenv is so bad if the variable have some
cmd meta-characters, see this test:add this to the path in HKCUEnvironment:
test & echo baaaaaaaaaad,
and run the chocolateyrefreshenvyou will see that it prints
baaaaaaaaaadwhich is very bad, and the new path is not added to
your path variable.This script solve this and you can test it with any meta-character, even something so bad like:
; & % ' ( ) ~ + @ # $ { } [ ] , ` ! ^ | > < / " : ? * = . - _ & echo baaaad -
refreshenv adds only system and user
environment variables, but CMD adds volatile variables too
(HKCUVolatile Environment). This script will merge all the three and
remove any duplicates. -
refreshenv reset your PATH. This script append the new path to the
old path of the parent script which called this script. It is better
than overwriting the old path, otherwise it will delete any newly
added path by the parent script. -
This script solve this problem described in a comment here by @Gene
Mayevsky: refreshenv modifies env variables TEMP and TMP replacing
them with values stored in HKCUEnvironment. In my case I run the
script to update env variables modified by Jenkins job on a slave
that’s running under SYSTEM account, so TEMP and TMP get substituted
by %USERPROFILE%AppDataLocalTemp instead of C:WindowsTemp. This
breaks build because linker cannot open system profile’s Temp folder.
I made one script for cmd and another for cygwin/bash,
you can found them here: https://github.com/badrelmers/RefrEnv
For cmd
This script uses vbscript so it works in all windows versions xp+
to use it save it as refrenv.bat and call it with call refrenv.bat
<!-- : Begin batch script
@echo off
REM PUSHD "%~dp0"
REM author: Badr Elmers 2021
REM description: refrenv = refresh environment. this is a better alternative to the chocolatey refreshenv for cmd
REM https://github.com/badrelmers/RefrEnv
REM https://stackoverflow.com/questions/171588/is-there-a-command-to-refresh-environment-variables-from-the-command-prompt-in-w
REM ___USAGE_____________________________________________________________
REM usage:
REM call refrenv.bat full refresh. refresh all non critical variables*, and refresh the PATH
REM debug:
REM to debug what this script do create this variable in your parent script like that
REM set debugme=yes
REM then the folder containing the files used to set the variables will be open. Then see
REM _NewEnv.cmd this is the file which run inside your script to setup the new variables, you
REM can also revise the intermediate files _NewEnv.cmd_temp_.cmd and _NewEnv.cmd_temp2_.cmd
REM (those two contains all the variables before removing the duplicates and the unwanted variables)
REM you can also put this script in windowssystems32 or another place in your %PATH% then call it from an interactive console by writing refrenv
REM *critical variables: are variables which belong to cmd/windows and should not be refreshed normally like:
REM - windows vars:
REM ALLUSERSPROFILE APPDATA CommonProgramFiles CommonProgramFiles(x86) CommonProgramW6432 COMPUTERNAME ComSpec HOMEDRIVE HOMEPATH LOCALAPPDATA LOGONSERVER NUMBER_OF_PROCESSORS OS PATHEXT PROCESSOR_ARCHITECTURE PROCESSOR_ARCHITEW6432 PROCESSOR_IDENTIFIER PROCESSOR_LEVEL PROCESSOR_REVISION ProgramData ProgramFiles ProgramFiles(x86) ProgramW6432 PUBLIC SystemDrive SystemRoot TEMP TMP USERDOMAIN USERDOMAIN_ROAMINGPROFILE USERNAME USERPROFILE windir SESSIONNAME
REM ___INFO_____________________________________________________________
REM :: this script reload environment variables inside cmd every time you want environment changes to propagate, so you do not need to restart cmd after setting a new variable with setx or when installing new apps which add new variables ...etc
REM This is a better alternative to the chocolatey refreshenv for cmd, which solves a lot of problems like:
REM The Chocolatey refreshenv is so bad if the variable have some cmd meta-characters, see this test:
REM add this to the path in HKCUEnvironment: test & echo baaaaaaaaaad, and run the chocolatey refreshenv you will see that it prints baaaaaaaaaad which is very bad, and the new path is not added to your path variable.
REM This script solve this and you can test it with any meta-character, even something so bad like:
REM ; & % ' ( ) ~ + @ # $ { } [ ] , ` ! ^ | > < / " : ? * = . - _ & echo baaaad
REM refreshenv adds only system and user environment variables, but CMD adds volatile variables too (HKCUVolatile Environment). This script will merge all the three and remove any duplicates.
REM refreshenv reset your PATH. This script append the new path to the old path of the parent script which called this script. It is better than overwriting the old path, otherwise it will delete any newly added path by the parent script.
REM This script solve this problem described in a comment by @Gene Mayevsky: refreshenv modifies env variables TEMP and TMP replacing them with values stored in HKCUEnvironment. In my case I run the script to update env variables modified by Jenkins job on a slave that's running under SYSTEM account, so TEMP and TMP get substituted by %USERPROFILE%AppDataLocalTemp instead of C:WindowsTemp. This breaks build because linker cannot open system profile's Temp folder.
REM ________
REM this script solve things like that too:
REM The confusing thing might be that there are a few places to start the cmd from. In my case I run cmd from windows explorer and the environment variables did not change while when starting cmd from the "run" (windows key + r) the environment variables were changed.
REM In my case I just had to kill the windows explorer process from the task manager and then restart it again from the task manager.
REM Once I did this I had access to the new environment variable from a cmd that was spawned from windows explorer.
REM my conclusion:
REM if I add a new variable with setx, i can access it in cmd only if i run cmd as admin, without admin right i have to restart explorer to see that new variable. but running this script inside my script (who sets the variable with setx) solve this problem and i do not have to restart explorer
REM ________
REM windows recreate the path using three places at less:
REM the User namespace: HKCUEnvironment
REM the System namespace: HKLMSYSTEMCurrentControlSetControlSession ManagerEnvironment
REM the Session namespace: HKCUVolatile Environment
REM but the original chocolatey script did not add the volatile path. This script will merge all the three and remove any duplicates. this is what windows do by default too
REM there is this too which cmd seems to read when first running, but it contains only TEMP and TMP,so i will not use it
REM HKEY_USERS.DEFAULTEnvironment
REM ___TESTING_____________________________________________________________
REM to test this script with extreme cases do
REM :: Set a bad variable
REM add a var in reg HKCUEnvironment as the following, and see that echo is not executed. if you use refreshenv of chocolatey you will see that echo is executed which is so bad!
REM so save this in reg:
REM all 32 characters: & % ' ( ) ~ + @ # $ { } [ ] ; , ` ! ^ | > < / " : ? * = . - _ & echo baaaad
REM and this:
REM (^.*)(Form Product=")([^"]*") FormType="[^"]*" FormID="([0-9][0-9]*)".*$
REM and use set to print those variables and see if they are saved without change ; refreshenv fail dramatically with those variables
REM invalid characters (illegal characters in file names) in Windows using NTFS
REM / : * ? " < > | and ^ in FAT
REM __________________________________________________________________________________________
REM __________________________________________________________________________________________
REM __________________________________________________________________________________________
REM this is a hybrid script which call vbs from cmd directly
REM :: The only restriction is the batch code cannot contain - - > (without space between - - > of course)
REM :: The only restriction is the VBS code cannot contain </script>.
REM :: The only risk is the undocumented use of "%~f0?.wsf" as the script to load. Somehow the parser properly finds and loads the running .BAT script "%~f0", and the ?.wsf suffix mysteriously instructs CSCRIPT to interpret the script as WSF. Hopefully MicroSoft will never disable that "feature".
REM :: https://stackoverflow.com/questions/9074476/is-it-possible-to-embed-and-execute-vbscript-within-a-batch-file-without-using-a
if "%debugme%"=="yes" (
echo RefrEnv - Refresh the Environment for CMD - ^(Debug enabled^)
) else (
echo RefrEnv - Refresh the Environment for CMD
)
set "TEMPDir=%TEMP%refrenv"
IF NOT EXIST "%TEMPDir%" mkdir "%TEMPDir%"
set "outputfile=%TEMPDir%_NewEnv.cmd"
REM detect if DelayedExpansion is enabled
REM It relies on the fact, that the last caret will be removed only in delayed mode.
REM https://www.dostips.com/forum/viewtopic.php?t=6496
set "DelayedExpansionState=IsDisabled"
IF "^!" == "^!^" (
REM echo DelayedExpansion is enabled
set "DelayedExpansionState=IsEnabled"
)
REM :: generate %outputfile% which contain all the new variables
REM cscript //nologo "%~f0?.wsf" %1
cscript //nologo "%~f0?.wsf" "%outputfile%" %DelayedExpansionState%
REM ::set the new variables generated with vbscript script above
REM for this to work always it is necessary to use DisableDelayedExpansion or escape ! and ^ when using EnableDelayedExpansion, but this script already solve this, so no worry about that now, thanks to God
REM test it with some bad var like:
REM all 32 characters: ; & % ' ( ) ~ + @ # $ { } [ ] , ` ! ^ | > < / " : ? * = . - _ & echo baaaad
REM For /f delims^=^ eol^= %%a in (%outputfile%) do %%a
REM for /f "delims== tokens=1,2" %%G in (%outputfile%) do set "%%G=%%H"
For /f delims^=^ eol^= %%a in (%outputfile%) do set %%a
REM for safely print a variable with bad charachters do:
REM SETLOCAL EnableDelayedExpansion
REM echo "!z9!"
REM or
REM set z9
REM but generally paths and environment variables should not have bad metacharacters, but it is not a rule!
if "%debugme%"=="yes" (
explorer "%TEMPDir%"
) else (
rmdir /Q /S "%TEMPDir%"
)
REM cleanup
set "TEMPDir="
set "outputfile="
set "DelayedExpansionState="
set "debugme="
REM pause
exit /b
REM #############################################################################
REM :: to run jscript you have to put <script language="JScript"> directly after ----- Begin wsf script --->
----- Begin wsf script --->
<job><script language="VBScript">
REM #############################################################################
REM ### put you code here #######################################################
REM #############################################################################
REM based on itsadok script from here
REM https://stackoverflow.com/questions/171588/is-there-a-command-to-refresh-environment-variables-from-the-command-prompt-in-w
REM and it is faster as stated by this comment
REM While I prefer the Chocolatey code-wise for being pure batch code, overall I decided to use this one, since it's faster. (~0.3 seconds instead of ~1 second -- which is nice, since I use it frequently in my Explorer "start cmd here" entry) –
REM and it is safer based on my tests, the Chocolatey refreshenv is so bad if the variable have some cmd metacharacters
Const ForReading = 1
Const ForWriting = 2
Const ForAppending = 8
Set WshShell = WScript.CreateObject("WScript.Shell")
filename=WScript.Arguments.Item(0)
DelayedExpansionState=WScript.Arguments.Item(1)
TMPfilename=filename & "_temp_.cmd"
Set fso = CreateObject("Scripting.fileSystemObject")
Set tmpF = fso.CreateTextFile(TMPfilename, TRUE)
set oEnvS=WshShell.Environment("System")
for each sitem in oEnvS
tmpF.WriteLine(sitem)
next
SystemPath = oEnvS("PATH")
set oEnvU=WshShell.Environment("User")
for each sitem in oEnvU
tmpF.WriteLine(sitem)
next
UserPath = oEnvU("PATH")
set oEnvV=WshShell.Environment("Volatile")
for each sitem in oEnvV
tmpF.WriteLine(sitem)
next
VolatilePath = oEnvV("PATH")
set oEnvP=WshShell.Environment("Process")
REM i will not save the process env but only its path, because it have strange variables like =::=:: and =F:=.... which seems to be added by vbscript
REM for each sitem in oEnvP
REM tmpF.WriteLine(sitem)
REM next
REM here we add the actual session path, so we do not reset the original path, because maybe the parent script added some folders to the path, If we need to reset the path then comment the following line
ProcessPath = oEnvP("PATH")
REM merge System, User, Volatile, and process PATHs
NewPath = SystemPath & ";" & UserPath & ";" & VolatilePath & ";" & ProcessPath
REM ________________________________________________________________
REM :: remove duplicates from path
REM :: expand variables so they become like windows do when he read reg and create path, then Remove duplicates without sorting
REM why i will clean the path from duplicates? because:
REM the maximum string length in cmd is 8191 characters. But string length doesnt mean that you can save 8191 characters in a variable because also the assignment belongs to the string. you can save 8189 characters because the remaining 2 characters are needed for "a="
REM based on my tests:
REM when i open cmd as user , windows does not remove any duplicates from the path, and merge system+user+volatil path
REM when i open cmd as admin, windows do: system+user path (here windows do not remove duplicates which is stupid!) , then it adds volatil path after removing from it any duplicates
REM ' https://www.rosettacode.org/wiki/Remove_duplicate_elements#VBScript
Function remove_duplicates(list)
arr = Split(list,";")
Set dict = CreateObject("Scripting.Dictionary")
REM ' force dictionary compare to be case-insensitive , uncomment to force case-sensitive
dict.CompareMode = 1
For i = 0 To UBound(arr)
If dict.Exists(arr(i)) = False Then
dict.Add arr(i),""
End If
Next
For Each key In dict.Keys
tmp = tmp & key & ";"
Next
remove_duplicates = Left(tmp,Len(tmp)-1)
End Function
REM expand variables
NewPath = WshShell.ExpandEnvironmentStrings(NewPath)
REM remove duplicates
NewPath=remove_duplicates(NewPath)
REM remove_duplicates() will add a ; to the end so lets remove it if the last letter is ;
If Right(NewPath, 1) = ";" Then
NewPath = Left(NewPath, Len(NewPath) - 1)
End If
tmpF.WriteLine("PATH=" & NewPath)
tmpF.Close
REM ________________________________________________________________
REM :: exclude setting variables which may be dangerous to change
REM when i run a script from task scheduler using SYSTEM user the following variables are the differences between the scheduler env and a normal cmd script, so i will not override those variables
REM APPDATA=D:UsersLLED2AppDataRoaming
REM APPDATA=D:Windowssystem32configsystemprofileAppDataRoaming
REM LOCALAPPDATA=D:UsersLLED2AppDataLocal
REM LOCALAPPDATA=D:Windowssystem32configsystemprofileAppDataLocal
REM TEMP=D:UsersLLED2AppDataLocalTemp
REM TEMP=D:WindowsTEMP
REM TMP=D:UsersLLED2AppDataLocalTemp
REM TMP=D:WindowsTEMP
REM USERDOMAIN=LLED2-PC
REM USERDOMAIN=WORKGROUP
REM USERNAME=LLED2
REM USERNAME=LLED2-PC$
REM USERPROFILE=D:UsersLLED2
REM USERPROFILE=D:Windowssystem32configsystemprofile
REM i know this thanks to this comment
REM The solution is good but it modifies env variables TEMP and TMP replacing them with values stored in HKCUEnvironment. In my case I run the script to update env variables modified by Jenkins job on a slave that's running under SYSTEM account, so TEMP and TMP get substituted by %USERPROFILE%AppDataLocalTemp instead of C:WindowsTemp. This breaks build because linker cannot open system profile's Temp folder. – Gene Mayevsky Sep 26 '19 at 20:51
REM Delete Lines of a Text File Beginning with a Specified String
REM those are the variables which should not be changed by this script
arrBlackList = Array("ALLUSERSPROFILE=", "APPDATA=", "CommonProgramFiles=", "CommonProgramFiles(x86)=", "CommonProgramW6432=", "COMPUTERNAME=", "ComSpec=", "HOMEDRIVE=", "HOMEPATH=", "LOCALAPPDATA=", "LOGONSERVER=", "NUMBER_OF_PROCESSORS=", "OS=", "PATHEXT=", "PROCESSOR_ARCHITECTURE=", "PROCESSOR_ARCHITEW6432=", "PROCESSOR_IDENTIFIER=", "PROCESSOR_LEVEL=", "PROCESSOR_REVISION=", "ProgramData=", "ProgramFiles=", "ProgramFiles(x86)=", "ProgramW6432=", "PUBLIC=", "SystemDrive=", "SystemRoot=", "TEMP=", "TMP=", "USERDOMAIN=", "USERDOMAIN_ROAMINGPROFILE=", "USERNAME=", "USERPROFILE=", "windir=", "SESSIONNAME=")
Set objFS = CreateObject("Scripting.FileSystemObject")
Set objTS = objFS.OpenTextFile(TMPfilename, ForReading)
strContents = objTS.ReadAll
objTS.Close
TMPfilename2= filename & "_temp2_.cmd"
arrLines = Split(strContents, vbNewLine)
Set objTS = objFS.OpenTextFile(TMPfilename2, ForWriting, True)
REM this is the equivalent of findstr /V /I /L or grep -i -v , i don t know a better way to do it, but it works fine
For Each strLine In arrLines
bypassThisLine=False
For Each BlackWord In arrBlackList
If Left(UCase(LTrim(strLine)),Len(BlackWord)) = UCase(BlackWord) Then
bypassThisLine=True
End If
Next
If bypassThisLine=False Then
objTS.WriteLine strLine
End If
Next
REM ____________________________________________________________
REM :: expand variables because registry save some variables as unexpanded %....%
REM :: and escape ! and ^ for cmd EnableDelayedExpansion mode
set f=fso.OpenTextFile(TMPfilename2,ForReading)
REM Write file: ForAppending = 8 ForReading = 1 ForWriting = 2 , True=create file if not exist
set fW=fso.OpenTextFile(filename,ForWriting,True)
Do Until f.AtEndOfStream
LineContent = f.ReadLine
REM expand variables
LineContent = WshShell.ExpandEnvironmentStrings(LineContent)
REM _____this part is so important_____
REM if cmd delayedexpansion is enabled in the parent script which calls this script then bad thing happen to variables saved in the registry if they contain ! . if var have ! then ! and ^ are removed; if var do not have ! then ^ is not removed . to understand what happens read this :
REM how cmd delayed expansion parse things
REM https://stackoverflow.com/questions/4094699/how-does-the-windows-command-interpreter-cmd-exe-parse-scripts/7970912#7970912
REM For each parsed token, first check if it contains any !. If not, then the token is not parsed - important for ^ characters. If the token does contain !, then scan each character from left to right:
REM - If it is a caret (^) the next character has no special meaning, the caret itself is removed
REM - If it is an exclamation mark, search for the next exclamation mark (carets are not observed anymore), expand to the value of the variable.
REM - Consecutive opening ! are collapsed into a single !
REM - Any remaining unpaired ! is removed
REM ...
REM Look at next string of characters, breaking before !, :, or <LF>, and call them VAR
REM conclusion:
REM when delayedexpansion is enabled and var have ! then i have to escape ^ and ! ,BUT IF VAR DO NOT HAVE ! THEN DO NOT ESCAPE ^ .this made me crazy to discover
REM when delayedexpansion is disabled then i do not have to escape anything
If DelayedExpansionState="IsEnabled" Then
If InStr(LineContent, "!") > 0 Then
LineContent=Replace(LineContent,"^","^^")
LineContent=Replace(LineContent,"!","^!")
End If
End If
REM __________
fW.WriteLine(LineContent)
Loop
f.Close
fW.Close
REM #############################################################################
REM ### end of vbscript code ####################################################
REM #############################################################################
REM this must be at the end for the hybrid trick, do not remove it
</script></job>
For cygwin/bash:
I cannot post it here I reached the post limit, so download it from here
call it from bash with: source refrenv.sh
For Powershell:
download it from here
Call it from Powershell with: . .refrenv.ps1
I made a better alternative to the Chocolatey refreshenv for cmd and cygwin which solves a lot of problems like:
-
The Chocolatey refreshenv is so bad if the variable have some
cmd meta-characters, see this test:add this to the path in HKCUEnvironment:
test & echo baaaaaaaaaad,
and run the chocolateyrefreshenvyou will see that it prints
baaaaaaaaaadwhich is very bad, and the new path is not added to
your path variable.This script solve this and you can test it with any meta-character, even something so bad like:
; & % ' ( ) ~ + @ # $ { } [ ] , ` ! ^ | > < / " : ? * = . - _ & echo baaaad -
refreshenv adds only system and user
environment variables, but CMD adds volatile variables too
(HKCUVolatile Environment). This script will merge all the three and
remove any duplicates. -
refreshenv reset your PATH. This script append the new path to the
old path of the parent script which called this script. It is better
than overwriting the old path, otherwise it will delete any newly
added path by the parent script. -
This script solve this problem described in a comment here by @Gene
Mayevsky: refreshenv modifies env variables TEMP and TMP replacing
them with values stored in HKCUEnvironment. In my case I run the
script to update env variables modified by Jenkins job on a slave
that’s running under SYSTEM account, so TEMP and TMP get substituted
by %USERPROFILE%AppDataLocalTemp instead of C:WindowsTemp. This
breaks build because linker cannot open system profile’s Temp folder.
I made one script for cmd and another for cygwin/bash,
you can found them here: https://github.com/badrelmers/RefrEnv
For cmd
This script uses vbscript so it works in all windows versions xp+
to use it save it as refrenv.bat and call it with call refrenv.bat
<!-- : Begin batch script
@echo off
REM PUSHD "%~dp0"
REM author: Badr Elmers 2021
REM description: refrenv = refresh environment. this is a better alternative to the chocolatey refreshenv for cmd
REM https://github.com/badrelmers/RefrEnv
REM https://stackoverflow.com/questions/171588/is-there-a-command-to-refresh-environment-variables-from-the-command-prompt-in-w
REM ___USAGE_____________________________________________________________
REM usage:
REM call refrenv.bat full refresh. refresh all non critical variables*, and refresh the PATH
REM debug:
REM to debug what this script do create this variable in your parent script like that
REM set debugme=yes
REM then the folder containing the files used to set the variables will be open. Then see
REM _NewEnv.cmd this is the file which run inside your script to setup the new variables, you
REM can also revise the intermediate files _NewEnv.cmd_temp_.cmd and _NewEnv.cmd_temp2_.cmd
REM (those two contains all the variables before removing the duplicates and the unwanted variables)
REM you can also put this script in windowssystems32 or another place in your %PATH% then call it from an interactive console by writing refrenv
REM *critical variables: are variables which belong to cmd/windows and should not be refreshed normally like:
REM - windows vars:
REM ALLUSERSPROFILE APPDATA CommonProgramFiles CommonProgramFiles(x86) CommonProgramW6432 COMPUTERNAME ComSpec HOMEDRIVE HOMEPATH LOCALAPPDATA LOGONSERVER NUMBER_OF_PROCESSORS OS PATHEXT PROCESSOR_ARCHITECTURE PROCESSOR_ARCHITEW6432 PROCESSOR_IDENTIFIER PROCESSOR_LEVEL PROCESSOR_REVISION ProgramData ProgramFiles ProgramFiles(x86) ProgramW6432 PUBLIC SystemDrive SystemRoot TEMP TMP USERDOMAIN USERDOMAIN_ROAMINGPROFILE USERNAME USERPROFILE windir SESSIONNAME
REM ___INFO_____________________________________________________________
REM :: this script reload environment variables inside cmd every time you want environment changes to propagate, so you do not need to restart cmd after setting a new variable with setx or when installing new apps which add new variables ...etc
REM This is a better alternative to the chocolatey refreshenv for cmd, which solves a lot of problems like:
REM The Chocolatey refreshenv is so bad if the variable have some cmd meta-characters, see this test:
REM add this to the path in HKCUEnvironment: test & echo baaaaaaaaaad, and run the chocolatey refreshenv you will see that it prints baaaaaaaaaad which is very bad, and the new path is not added to your path variable.
REM This script solve this and you can test it with any meta-character, even something so bad like:
REM ; & % ' ( ) ~ + @ # $ { } [ ] , ` ! ^ | > < / " : ? * = . - _ & echo baaaad
REM refreshenv adds only system and user environment variables, but CMD adds volatile variables too (HKCUVolatile Environment). This script will merge all the three and remove any duplicates.
REM refreshenv reset your PATH. This script append the new path to the old path of the parent script which called this script. It is better than overwriting the old path, otherwise it will delete any newly added path by the parent script.
REM This script solve this problem described in a comment by @Gene Mayevsky: refreshenv modifies env variables TEMP and TMP replacing them with values stored in HKCUEnvironment. In my case I run the script to update env variables modified by Jenkins job on a slave that's running under SYSTEM account, so TEMP and TMP get substituted by %USERPROFILE%AppDataLocalTemp instead of C:WindowsTemp. This breaks build because linker cannot open system profile's Temp folder.
REM ________
REM this script solve things like that too:
REM The confusing thing might be that there are a few places to start the cmd from. In my case I run cmd from windows explorer and the environment variables did not change while when starting cmd from the "run" (windows key + r) the environment variables were changed.
REM In my case I just had to kill the windows explorer process from the task manager and then restart it again from the task manager.
REM Once I did this I had access to the new environment variable from a cmd that was spawned from windows explorer.
REM my conclusion:
REM if I add a new variable with setx, i can access it in cmd only if i run cmd as admin, without admin right i have to restart explorer to see that new variable. but running this script inside my script (who sets the variable with setx) solve this problem and i do not have to restart explorer
REM ________
REM windows recreate the path using three places at less:
REM the User namespace: HKCUEnvironment
REM the System namespace: HKLMSYSTEMCurrentControlSetControlSession ManagerEnvironment
REM the Session namespace: HKCUVolatile Environment
REM but the original chocolatey script did not add the volatile path. This script will merge all the three and remove any duplicates. this is what windows do by default too
REM there is this too which cmd seems to read when first running, but it contains only TEMP and TMP,so i will not use it
REM HKEY_USERS.DEFAULTEnvironment
REM ___TESTING_____________________________________________________________
REM to test this script with extreme cases do
REM :: Set a bad variable
REM add a var in reg HKCUEnvironment as the following, and see that echo is not executed. if you use refreshenv of chocolatey you will see that echo is executed which is so bad!
REM so save this in reg:
REM all 32 characters: & % ' ( ) ~ + @ # $ { } [ ] ; , ` ! ^ | > < / " : ? * = . - _ & echo baaaad
REM and this:
REM (^.*)(Form Product=")([^"]*") FormType="[^"]*" FormID="([0-9][0-9]*)".*$
REM and use set to print those variables and see if they are saved without change ; refreshenv fail dramatically with those variables
REM invalid characters (illegal characters in file names) in Windows using NTFS
REM / : * ? " < > | and ^ in FAT
REM __________________________________________________________________________________________
REM __________________________________________________________________________________________
REM __________________________________________________________________________________________
REM this is a hybrid script which call vbs from cmd directly
REM :: The only restriction is the batch code cannot contain - - > (without space between - - > of course)
REM :: The only restriction is the VBS code cannot contain </script>.
REM :: The only risk is the undocumented use of "%~f0?.wsf" as the script to load. Somehow the parser properly finds and loads the running .BAT script "%~f0", and the ?.wsf suffix mysteriously instructs CSCRIPT to interpret the script as WSF. Hopefully MicroSoft will never disable that "feature".
REM :: https://stackoverflow.com/questions/9074476/is-it-possible-to-embed-and-execute-vbscript-within-a-batch-file-without-using-a
if "%debugme%"=="yes" (
echo RefrEnv - Refresh the Environment for CMD - ^(Debug enabled^)
) else (
echo RefrEnv - Refresh the Environment for CMD
)
set "TEMPDir=%TEMP%refrenv"
IF NOT EXIST "%TEMPDir%" mkdir "%TEMPDir%"
set "outputfile=%TEMPDir%_NewEnv.cmd"
REM detect if DelayedExpansion is enabled
REM It relies on the fact, that the last caret will be removed only in delayed mode.
REM https://www.dostips.com/forum/viewtopic.php?t=6496
set "DelayedExpansionState=IsDisabled"
IF "^!" == "^!^" (
REM echo DelayedExpansion is enabled
set "DelayedExpansionState=IsEnabled"
)
REM :: generate %outputfile% which contain all the new variables
REM cscript //nologo "%~f0?.wsf" %1
cscript //nologo "%~f0?.wsf" "%outputfile%" %DelayedExpansionState%
REM ::set the new variables generated with vbscript script above
REM for this to work always it is necessary to use DisableDelayedExpansion or escape ! and ^ when using EnableDelayedExpansion, but this script already solve this, so no worry about that now, thanks to God
REM test it with some bad var like:
REM all 32 characters: ; & % ' ( ) ~ + @ # $ { } [ ] , ` ! ^ | > < / " : ? * = . - _ & echo baaaad
REM For /f delims^=^ eol^= %%a in (%outputfile%) do %%a
REM for /f "delims== tokens=1,2" %%G in (%outputfile%) do set "%%G=%%H"
For /f delims^=^ eol^= %%a in (%outputfile%) do set %%a
REM for safely print a variable with bad charachters do:
REM SETLOCAL EnableDelayedExpansion
REM echo "!z9!"
REM or
REM set z9
REM but generally paths and environment variables should not have bad metacharacters, but it is not a rule!
if "%debugme%"=="yes" (
explorer "%TEMPDir%"
) else (
rmdir /Q /S "%TEMPDir%"
)
REM cleanup
set "TEMPDir="
set "outputfile="
set "DelayedExpansionState="
set "debugme="
REM pause
exit /b
REM #############################################################################
REM :: to run jscript you have to put <script language="JScript"> directly after ----- Begin wsf script --->
----- Begin wsf script --->
<job><script language="VBScript">
REM #############################################################################
REM ### put you code here #######################################################
REM #############################################################################
REM based on itsadok script from here
REM https://stackoverflow.com/questions/171588/is-there-a-command-to-refresh-environment-variables-from-the-command-prompt-in-w
REM and it is faster as stated by this comment
REM While I prefer the Chocolatey code-wise for being pure batch code, overall I decided to use this one, since it's faster. (~0.3 seconds instead of ~1 second -- which is nice, since I use it frequently in my Explorer "start cmd here" entry) –
REM and it is safer based on my tests, the Chocolatey refreshenv is so bad if the variable have some cmd metacharacters
Const ForReading = 1
Const ForWriting = 2
Const ForAppending = 8
Set WshShell = WScript.CreateObject("WScript.Shell")
filename=WScript.Arguments.Item(0)
DelayedExpansionState=WScript.Arguments.Item(1)
TMPfilename=filename & "_temp_.cmd"
Set fso = CreateObject("Scripting.fileSystemObject")
Set tmpF = fso.CreateTextFile(TMPfilename, TRUE)
set oEnvS=WshShell.Environment("System")
for each sitem in oEnvS
tmpF.WriteLine(sitem)
next
SystemPath = oEnvS("PATH")
set oEnvU=WshShell.Environment("User")
for each sitem in oEnvU
tmpF.WriteLine(sitem)
next
UserPath = oEnvU("PATH")
set oEnvV=WshShell.Environment("Volatile")
for each sitem in oEnvV
tmpF.WriteLine(sitem)
next
VolatilePath = oEnvV("PATH")
set oEnvP=WshShell.Environment("Process")
REM i will not save the process env but only its path, because it have strange variables like =::=:: and =F:=.... which seems to be added by vbscript
REM for each sitem in oEnvP
REM tmpF.WriteLine(sitem)
REM next
REM here we add the actual session path, so we do not reset the original path, because maybe the parent script added some folders to the path, If we need to reset the path then comment the following line
ProcessPath = oEnvP("PATH")
REM merge System, User, Volatile, and process PATHs
NewPath = SystemPath & ";" & UserPath & ";" & VolatilePath & ";" & ProcessPath
REM ________________________________________________________________
REM :: remove duplicates from path
REM :: expand variables so they become like windows do when he read reg and create path, then Remove duplicates without sorting
REM why i will clean the path from duplicates? because:
REM the maximum string length in cmd is 8191 characters. But string length doesnt mean that you can save 8191 characters in a variable because also the assignment belongs to the string. you can save 8189 characters because the remaining 2 characters are needed for "a="
REM based on my tests:
REM when i open cmd as user , windows does not remove any duplicates from the path, and merge system+user+volatil path
REM when i open cmd as admin, windows do: system+user path (here windows do not remove duplicates which is stupid!) , then it adds volatil path after removing from it any duplicates
REM ' https://www.rosettacode.org/wiki/Remove_duplicate_elements#VBScript
Function remove_duplicates(list)
arr = Split(list,";")
Set dict = CreateObject("Scripting.Dictionary")
REM ' force dictionary compare to be case-insensitive , uncomment to force case-sensitive
dict.CompareMode = 1
For i = 0 To UBound(arr)
If dict.Exists(arr(i)) = False Then
dict.Add arr(i),""
End If
Next
For Each key In dict.Keys
tmp = tmp & key & ";"
Next
remove_duplicates = Left(tmp,Len(tmp)-1)
End Function
REM expand variables
NewPath = WshShell.ExpandEnvironmentStrings(NewPath)
REM remove duplicates
NewPath=remove_duplicates(NewPath)
REM remove_duplicates() will add a ; to the end so lets remove it if the last letter is ;
If Right(NewPath, 1) = ";" Then
NewPath = Left(NewPath, Len(NewPath) - 1)
End If
tmpF.WriteLine("PATH=" & NewPath)
tmpF.Close
REM ________________________________________________________________
REM :: exclude setting variables which may be dangerous to change
REM when i run a script from task scheduler using SYSTEM user the following variables are the differences between the scheduler env and a normal cmd script, so i will not override those variables
REM APPDATA=D:UsersLLED2AppDataRoaming
REM APPDATA=D:Windowssystem32configsystemprofileAppDataRoaming
REM LOCALAPPDATA=D:UsersLLED2AppDataLocal
REM LOCALAPPDATA=D:Windowssystem32configsystemprofileAppDataLocal
REM TEMP=D:UsersLLED2AppDataLocalTemp
REM TEMP=D:WindowsTEMP
REM TMP=D:UsersLLED2AppDataLocalTemp
REM TMP=D:WindowsTEMP
REM USERDOMAIN=LLED2-PC
REM USERDOMAIN=WORKGROUP
REM USERNAME=LLED2
REM USERNAME=LLED2-PC$
REM USERPROFILE=D:UsersLLED2
REM USERPROFILE=D:Windowssystem32configsystemprofile
REM i know this thanks to this comment
REM The solution is good but it modifies env variables TEMP and TMP replacing them with values stored in HKCUEnvironment. In my case I run the script to update env variables modified by Jenkins job on a slave that's running under SYSTEM account, so TEMP and TMP get substituted by %USERPROFILE%AppDataLocalTemp instead of C:WindowsTemp. This breaks build because linker cannot open system profile's Temp folder. – Gene Mayevsky Sep 26 '19 at 20:51
REM Delete Lines of a Text File Beginning with a Specified String
REM those are the variables which should not be changed by this script
arrBlackList = Array("ALLUSERSPROFILE=", "APPDATA=", "CommonProgramFiles=", "CommonProgramFiles(x86)=", "CommonProgramW6432=", "COMPUTERNAME=", "ComSpec=", "HOMEDRIVE=", "HOMEPATH=", "LOCALAPPDATA=", "LOGONSERVER=", "NUMBER_OF_PROCESSORS=", "OS=", "PATHEXT=", "PROCESSOR_ARCHITECTURE=", "PROCESSOR_ARCHITEW6432=", "PROCESSOR_IDENTIFIER=", "PROCESSOR_LEVEL=", "PROCESSOR_REVISION=", "ProgramData=", "ProgramFiles=", "ProgramFiles(x86)=", "ProgramW6432=", "PUBLIC=", "SystemDrive=", "SystemRoot=", "TEMP=", "TMP=", "USERDOMAIN=", "USERDOMAIN_ROAMINGPROFILE=", "USERNAME=", "USERPROFILE=", "windir=", "SESSIONNAME=")
Set objFS = CreateObject("Scripting.FileSystemObject")
Set objTS = objFS.OpenTextFile(TMPfilename, ForReading)
strContents = objTS.ReadAll
objTS.Close
TMPfilename2= filename & "_temp2_.cmd"
arrLines = Split(strContents, vbNewLine)
Set objTS = objFS.OpenTextFile(TMPfilename2, ForWriting, True)
REM this is the equivalent of findstr /V /I /L or grep -i -v , i don t know a better way to do it, but it works fine
For Each strLine In arrLines
bypassThisLine=False
For Each BlackWord In arrBlackList
If Left(UCase(LTrim(strLine)),Len(BlackWord)) = UCase(BlackWord) Then
bypassThisLine=True
End If
Next
If bypassThisLine=False Then
objTS.WriteLine strLine
End If
Next
REM ____________________________________________________________
REM :: expand variables because registry save some variables as unexpanded %....%
REM :: and escape ! and ^ for cmd EnableDelayedExpansion mode
set f=fso.OpenTextFile(TMPfilename2,ForReading)
REM Write file: ForAppending = 8 ForReading = 1 ForWriting = 2 , True=create file if not exist
set fW=fso.OpenTextFile(filename,ForWriting,True)
Do Until f.AtEndOfStream
LineContent = f.ReadLine
REM expand variables
LineContent = WshShell.ExpandEnvironmentStrings(LineContent)
REM _____this part is so important_____
REM if cmd delayedexpansion is enabled in the parent script which calls this script then bad thing happen to variables saved in the registry if they contain ! . if var have ! then ! and ^ are removed; if var do not have ! then ^ is not removed . to understand what happens read this :
REM how cmd delayed expansion parse things
REM https://stackoverflow.com/questions/4094699/how-does-the-windows-command-interpreter-cmd-exe-parse-scripts/7970912#7970912
REM For each parsed token, first check if it contains any !. If not, then the token is not parsed - important for ^ characters. If the token does contain !, then scan each character from left to right:
REM - If it is a caret (^) the next character has no special meaning, the caret itself is removed
REM - If it is an exclamation mark, search for the next exclamation mark (carets are not observed anymore), expand to the value of the variable.
REM - Consecutive opening ! are collapsed into a single !
REM - Any remaining unpaired ! is removed
REM ...
REM Look at next string of characters, breaking before !, :, or <LF>, and call them VAR
REM conclusion:
REM when delayedexpansion is enabled and var have ! then i have to escape ^ and ! ,BUT IF VAR DO NOT HAVE ! THEN DO NOT ESCAPE ^ .this made me crazy to discover
REM when delayedexpansion is disabled then i do not have to escape anything
If DelayedExpansionState="IsEnabled" Then
If InStr(LineContent, "!") > 0 Then
LineContent=Replace(LineContent,"^","^^")
LineContent=Replace(LineContent,"!","^!")
End If
End If
REM __________
fW.WriteLine(LineContent)
Loop
f.Close
fW.Close
REM #############################################################################
REM ### end of vbscript code ####################################################
REM #############################################################################
REM this must be at the end for the hybrid trick, do not remove it
</script></job>
For cygwin/bash:
I cannot post it here I reached the post limit, so download it from here
call it from bash with: source refrenv.sh
For Powershell:
download it from here
Call it from Powershell with: . .refrenv.ps1
We can use setx as discussed here.
setx PATH "%PATH%;C:Somethingbin"
But this command can just make changed to user PATH variable not the system one.
How can we make a similar system wide command?
asked Jun 14, 2014 at 11:51
1
Type setx /? to get basic command help. You’ll easily discover:
/M Specifies that the variable should be set in
the system wide (HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE)
environment. The default is to set the
variable under the HKEY_CURRENT_USER
environment.
You need to run this from an elevated command prompt. Right-click the cmd shortcut and select Run as Administrator.
E.g.
setx /M PATH "%PATH%;C:Somethingbin"
Caution:
We may destroy the current system’s PATH variable. Make sure you backup its value before you modify it.
answered Jun 14, 2014 at 12:10
Hans PassantHans Passant
913k145 gold badges1671 silver badges2507 bronze badges
6
From powershell
setx /M PATH "$($env:path);c:program filesmynewprogram"
answered Nov 21, 2017 at 17:45
Solution when dealing with a >1024 char path:
None of the other answers worked in my case, but using pathed did the trick. You can append to path as simply as this:
pathed /append C:PathToBeAdded /machine
You can check if the edit happened correctly by running
pathed
PS: if you want to change the user’s path instead use:
pathed /append C:PathToBeAdded /user
and pathed /user to check if it went through correctly.
PPS: In order to be able to run pathed from terminal, you need to put the exe in a directory already on your path (or add a new directory to path, but then you you might need to open a new instance of cmd.exe in order for the new path to be recognized)
answered Nov 6, 2021 at 19:22
jlojlo
2,0572 gold badges15 silver badges20 bronze badges
One problem with %PATH%, is it includes the user’s path. If you don’t mind Powershell, you can run the following
$p = [Environment]::GetEnvironmentVariable("PATH", [EnvironmentVariableTarget]::Machine);
[Environment]::SetEnvironmentVariable("PATH", $p + ";C:MyPath", [EnvironmentVariableTarget]::Machine);
answered Sep 30, 2020 at 23:20
Clay LenhartClay Lenhart
1,59715 silver badges17 bronze badges
If you want to add some location to the PATH environment variable on user level, use the following on the command line:
setx PATH ^%PATH^%;"C:Program FilesSomethingbin"
Why the strange syntax?
First, you do not want to expand the system PATH variable but keep it as a symbol, otherwise you will not participate in future additions to the system PATH variable. Therefore, you have to quote the % characters with ^.
If you use this in a command script, you have to use double %% instead of ^%.
The » encloses a string that contains spaces. If you do not have spaces, you can omit the quotes.
The added string has to follow directly without space so the whole thing forms a single argument to the setx command.
answered Jan 5, 2021 at 16:33
AchimAchim
513 bronze badges
1
Содержание
- Каким образом я могу изменить переменные среды Windows 10?
- Откройте окно переменных среды
- Как редактировать переменную среды в Windows
- Как редактировать переменную среды из командной строки
- Как редактировать переменную среды из PowerShell
- Как очистить значение переменной среды в Windows (из командной строки)
- Как удалить переменную среды в Windows
- Как удалить переменную среды из командной строки
- Как удалить переменную среды из PowerShell
- Переменные среды в Windows 10 — Как редактировать?
- Как изменять, удалять или создавать переменные среды в Windows 10
- Список переменных через командную строку
- Создать переменную со значением
- Переименовать значение переменной
- Два значения в переменной
- Удалить значение в переменной
- Удалить переменную
- Как обновить переменные среды без перезагрузки windows 10
Каким образом я могу изменить переменные среды Windows 10?
Программистам, системным администраторам и опытным пользователям может потребоваться в какой-то момент поработать с переменными среды. Некоторые могут захотеть удалить переменную среды; другие захотят изменить его значение и так далее. В этом руководстве рассказывается, как редактировать или удалять переменные среды, а также как отключить переменные среды в Windows:
Откройте окно переменных среды
Чтобы внести многие изменения, показанные в этой статье, вам сначала нужно открыть окно переменных среды. В этом руководстве объясняется, как это сделать, и показаны основы работы с переменными среды.
Если вы хотите пропустить его чтение, один путь, который работает одинаково во всех версиях Windows, — это открыть окно «Выполнить» (Win + R), командную строку или PowerShell и выполнить команду: rundll32.exe sysdm.cpl,EditEnvironmentVariables .
Как редактировать переменную среды в Windows
Если вы хотите изменить значение существующей переменной среды, сначала выберите ее в окне «Переменные среды». Затем щелкните или коснитесь «Изменить».
Вам будет показано окно, в котором вы можете редактировать как имя, так и значение переменной. Внесите желаемые изменения и нажмите ОК . Затем еще раз нажмите OK в окне переменных среды .
Как редактировать переменную среды из командной строки
Вы также можете создать новую переменную среды или изменить значение существующей переменной среды (но не ее имя) из командной строки . Вам нужно ввести следующую команду:
- setx variable_name «value» , если вы хотите создать переменную среды пользователя
- setx variable_name «value» /m , если вы собираетесь создать системную переменную среды
Например, мы набрали setx TEST «C:digitalcitizen» и создали пользовательскую переменную TEST со значением C:digitalcitizen.
Если мы хотим изменить значение переменной среды, мы можем запустить ту же команду setx, но указать новое значение для переменной. Например, выполнение setx TEST «C:DC» изменяет значение переменной среды TEST на C:DC.
Это работает, потому что команда setx перезаписывает существующее значение последним введенным вами. Следовательно, если вы используете эту команду несколько раз для одной и той же переменной, переменная сохранит последнее введенное вами значение.
Если вы хотите, чтобы переменная имела несколько путей в своем значении, вы должны записать их все, разделяя их точкой с запятой, без пробелов, как на скриншоте ниже.
ПРИМЕЧАНИЕ. Вы можете получить список всех доступных переменных среды, выполнив команду set в командной строке (не setx и без каких-либо параметров). Однако, если вы только что создали или отредактировали переменную среды, необходимо закрыть и снова открыть командную строку, чтобы изменения отобразились.
Как редактировать переменную среды из PowerShell
Вы также можете создать или изменить значение существующей переменной среды из PowerShell . Команда PowerShell для этого:
- [Environment]::SetEnvironmentVariable(«variable_name»,»variable_value»,»User») , если вы хотите создать переменную среды пользователя.
- [Environment]::SetEnvironmentVariable(“variable_name”,”variable_value”,”Machine”) , если вы хотите создать системную переменную среды.
Например, мы набрали [Environment]::SetEnvironmentVariable(“TEST”,”digitalcitizen.life”,”User”) , чтобы создать переменную пользовательской среды под названием TEST со значением digitalcitizen.life. Чтобы изменить значение переменной позже, мы можем запустить ту же команду с другим значением. Как и setx в командной строке, эта команда переписывает значение указанной переменной каждый раз, когда вы ее запускаете.
Если вы хотите присвоить переменной несколько значений, введите их все в команду, разделяя их точками с запятой, как показано ниже.
ПРИМЕЧАНИЕ. В PowerShell вы можете получить список всех переменных среды, выполнив команду Get-ChildItem Env: . Однако, если вы только что создали или отредактировали переменную среды, вам необходимо закрыть и снова открыть PowerShell, чтобы изменения отобразились.
Как очистить значение переменной среды в Windows (из командной строки)
Если вы хотите удалить значение переменной среды (сохранив ее имя), вы не можете сделать это с помощью мыши и клавиатуры из окна переменных среды . Если вы выберете переменную и нажмете «Изменить», вы можете удалить значение, но не можете нажать «ОК», так как эта кнопка становится серой. Поэтому вы не можете сохранить свои изменения.
Однако вы можете очистить значение переменной среды с помощью командной строки. Чтобы отменить установку переменной среды из командной строки , введите команду setx variable_name «» . Например, мы набрали setx TEST «» , и эта переменная среды теперь имела пустое значение.
Далее давайте посмотрим, как удалить переменную среды.
Как удалить переменную среды в Windows
Если вы больше не хотите использовать конкретную переменную среды, выберите ее в окне «Переменные среды». Затем нажмите Удалить. Windows не запрашивает подтверждения этого действия. Поэтому, если вы передумали, необходимо нажать Отмена, чтобы удаление не применялось. Если вы хотите, чтобы удаление продолжилось, нажмите ОК .
Как удалить переменную среды из командной строки
Чтобы удалить переменную среды из командной строки , введите одну из этих двух команд в зависимости от типа этой переменной:
- REG delete «HKCUEnvironment» /F /V «variable_name» , если это переменная среды пользователя, или
- REG delete «HKLMSYSTEMCurrentControlSetControlSession ManagerEnvironment» /F /V «variable_name» , если это системная переменная среды.
Например, мы набрали REG delete «HKCUEnvironment» /F /V «TEST» , и наша переменная среды TEST исчезла из профиля пользователя.
Как удалить переменную среды из PowerShell
Чтобы отменить установку и удалить переменную среды из PowerShell , введите команду:
- [Environment]::SetEnvironmentVariable(«variable_name», $null ,»User») , если это переменная профиля пользователя, или
- [Environment]::SetEnvironmentVariable(«variable_name», $null ,»Machine») , если это общесистемная переменная.
Например, мы набрали [Environment]::SetEnvironmentVariable(«TEST», $null ,»User») , и эта переменная среды исчезла из профиля пользователя.
Переменные среды в Windows 10 — Как редактировать?
Переменные среды в Windows 10 — Это динамические пути, которые указывают на привязку какой-либо папки или другие данные о настройках операционной системе. К примеру, если мы начнем устанавливать игру, то установщику нужна будет информация, где папка Program Files, чтобы установить по умолчанию в этот каталог игру. Также, мы можем быстро перейти в папку TEMP, командой %Temp%, не переходя по имени пользователя, которое может отличаться.
В Windows 10 имеется два вида переменных сред:
- Переменные среды пользователя — Содержат информацию для конкретной учетной записи. К примеру, папка OneDrive, расположение профиля и данные о нем, временная папка учетной записи и т.п.
- Системные переменные — Содержат информацию, которая относится к системным ресурсам и устанавливаются операционной системой или драйверами при установке. К примеру, если набрать %windir%, то нас перекинет в системную папку в C:Windows, где установлена ОС.
Как изменять, удалять или создавать переменные среды в Windows 10
Нажмите Win+R и введите sysdm.cpl, чтобы быстро открыть свойства системы. Перейдите во вкладку «Дополнительно» и снизу нажмите на «Переменные среды«.
Вы увидите системные и пользовательские переменные среды. Вы можете добавить, удалить или изменить значение для переменных.
Список переменных через командную строку
Если вам нужно посмотреть весь список переменных со значением через командную строку, то введите ниже команду:
Создать переменную со значением
Если нужно создать переменную для пользователя, то команда будет следующая: setx, где MYWEBPC это переменная, а C:mywebpc это значение.
Если нужно создать системную переменную со значением, то:
Переименовать значение переменной
Чтобы изменить значение переменной нужно просто заменить значение на другое. Начнем с пользовательской среды:
Изменить системную системную переменную:
Два значения в переменной
Мы можем добавить два значения и более для одной переменной разделив точкой с запятой. Пользовательская:
Два значения в переменной системной среды:
Удалить значение в переменной
Чтобы удалить значение в переменной нужно просто оставить поле в кавычках пустым. Для пользовательской среды:
Удалить значение для системной среды:
Удалить переменную
Чтобы удалить саму переменную, нужно удалить запись из реестра. Удалить пользовательскую переменную:
- REG delete «HKCUEnvironment» /F /V «MYWEBPC»
Удалить переменную для системной среды:
- REG delete «HKLMSYSTEMCurrentControlSetControlSession ManagerEnvironment» /F /V «MYWEBPC»
Как обновить переменные среды без перезагрузки windows 10
Возможно ли в Win менять значения переменных окружения буз перезагрузки?
Да и вообще, существует ли удобный инструментарий для работы с ними. Стандартный похож на издевательство ибо:
— если переменная длинная и является перечислением (типа PATH), то фиг в ней что найдешь в этом маленьком окошке, который предлагается для ее редактирования
— чтобы ввести новую переменную нужно нажать Добавить, нужно что-то написать в очень маленьком окошке и нажать ОК
IMHO обычный текстовый файл был бы и то удобнее, и не было бы очередной проблемы
— резервного копирования эих переменных
Кстати, почему после изменения переменной окрыжения нужно обязательно перезагружаться иначе она не вступит в силу? Что за такие важные структуры инициализуруются в windows internals, что я не могу прописать путь где ОС будет искать файлы без ее перезагрузки? Бред? Или я что-то не понимаю?
Кроме того надоели такие вещи:
После установки компилятора необходимо проверить, что в переменной окружения PATH прописан путь:
bini386-win32;
Причём, он должен там быть раньше, чем пути к остальным FPC, если их в системе несколько. Кроме того, если в системе установлен, например, MinGW, то, если, в PATH путь к нему прописан раньше, чем к FPC, то будет использован не ld из FPC, а ld из MinGW и ничего собрать не удастся.
В общем, может кто-то нашел что-то удобное, чтобы сосуществовать рядом с этим безобразием?
p.s. Linux не предлагать
| |
От: | Sergeant_BY |
| Дата: | 04.12.07 07:07 | |
| Оценка: | 4 (1) |
DAS> После установки компилятора необходимо проверить, что в переменной окружения PATH прописан путь:
DAS> bini386-win32;
DAS>Причём, он должен там быть раньше, чем пути к остальным FPC, если их в системе несколько. Кроме того, если в системе установлен, например, MinGW, то, если, в PATH путь к нему прописан раньше, чем к FPC, то будет использован не ld из FPC, а ld из MinGW и ничего собрать не удастся.
| |
От: | DOOM |
| Дата: | 04.12.07 07:11 | |
| Оценка: | 2 (1) |
Здравствуйте, DemAS, Вы писали:
DAS>Возможно ли в Win менять значения переменных окружения буз перезагрузки?
Конечно.
DAS> Да и вообще, существует ли удобный инструментарий для работы с ними. Стандартный похож на издевательство ибо:
DAS> — если переменная длинная и является перечислением (типа PATH), то фиг в ней что найдешь в этом маленьком окошке, который предлагается для ее редактирования
DAS> — чтобы ввести новую переменную нужно нажать Добавить, нужно что-то написать в очень маленьком окошке и нажать ОК
DAS> IMHO обычный текстовый файл был бы и то удобнее, и не было бы очередной проблемы
DAS> — резервного копирования эих переменных
Ну тут да. Косяк. Можно напрямую через реестр, если этот способ можно назвать удобным.
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINESYSTEMCurrentControlSetControlSession ManagerEnvironment — это системные переменные
HKEY_CURRENT_USEREnvironment — пользовательские
Кроме того, в Support Tools’ах есть утилита setx, которая, в отличие от set позволяет делать постоянные изменения в переменных окружения.
DAS> Кстати, почему после изменения переменной окрыжения нужно обязательно перезагружаться иначе она не вступит в силу? Что за такие важные структуры инициализуруются в windows internals, что я не могу прописать путь где ОС будет искать файлы без ее перезагрузки? Бред? Или я что-то не понимаю?
Видать что-то не понимаешь. В винде, как и во многих других ОС, окружение привязано к процессу — поэтому, чтобы отразить изменения в окружении надо перезапустить процесс. Т.е. поменял PATH, перезапусти cmd.exe и он уже будет с новыми путями.
DAS> Кроме того надоели такие вещи:
DAS>
DAS> После установки компилятора необходимо проверить, что в переменной окружения PATH прописан путь:
DAS> bini386-win32;
DAS>Причём, он должен там быть раньше, чем пути к остальным FPC, если их в системе несколько. Кроме того, если в системе установлен, например, MinGW, то, если, в PATH путь к нему прописан раньше, чем к FPC, то будет использован не ld из FPC, а ld из MinGW и ничего собрать не удастся.
Не вижу проблемы. Сделай себе 2 скрипта — один при запуске cmd добавляет в PATH пути к MinGW, другой к чему-нибудь еще. Запускай нужный и не засоряй общесистемные переменные.
DAS> В общем, может кто-то нашел что-то удобное, чтобы сосуществовать рядом с этим безобразием?
Ну что знал, то предложил.
DAS> p.s. Linux не предлагать 
А там по сути также. Переменные окружения вещь очень старая и ведет себя так, как это было придумано десятилетия назад.
| |
От: | DemAS | http://demas.me |
| Дата: | 04.12.07 07:18 | ||
| Оценка: |
Здравствуйте, Sergeant_BY, Вы писали:
S_B>setx path «%PATH%;C:New Folder»
S_B>setx — из ресурскита к XP, например.
Спасибо, гораздо удобнее.
DAS>> — резервного копирования эих переменных
S_B>set > backup_env.txt ?
А обратно как? 
Понимаю, что можно написать скрипт, который сформирует набор команд для setx, но может есть что-то готовое.
S_B>Оккрываю System properties->Advanced->Environment, добавляю какую-нибудь лабуду в конце %PATH%, нажимаю ОК.
S_B>Запускаю cmd, пишу set и вижу в %PATH% ту самую лабуду.
S_B>Что я делаю не так?
Я тоже вижу. Но если я пытаюсь запустить exe-к из каталога, находящегося в добавленной директории — система говорит, что не знает такого.
Хотя возможно это я ступил — наверное надо было перезапустить cmd.
DAS>> p.s. Linux не предлагать 
S_B>А в Linux’е разве по другому?
Не знаю. Но на всякий случай предупредил. 
6 ответы
- В Windows 10 перейдите в Пуск> Настройки> Обновление и безопасность> Восстановление.
- В разделе «Расширенный запуск» нажмите «Перезагрузить сейчас».
- После перезагрузки компьютера в режиме расширенного запуска щелкните Устранение неполадок.
- Щелкните Обновить компьютер.
30 юл. 2017 г.
Как восстановить переменную пути?
- В меню «Пуск» откройте «Выполнить» (или нажмите ⊞ Win + R).
- Введите regedit. Найдите папку HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE. Зайдите в папку SYSTEM. Перейдите в папку ControlSet002. Перейдите в папку управления. Зайдите в Session Manager. Перейдите в папку Environment. Затем в папке Environment дважды щелкните Путь.
Нужно ли мне перезагружать после изменения переменной PATH?
Применение изменения
Из-за того, как Windows применяет переменные среды, вам, скорее всего, потребуется перезапустить приложения, чтобы они приняли изменение, включая explorer.exe. Перезагрузка компьютера рекомендуется (но не обязательна) и обеспечивает запуск всех приложений с изменением PATH.
Какая переменная пути по умолчанию в Windows 10?
Типичный путь — C: ProgramDataMicrosoftWindowsStart MenuPrograms. Каталог файловой системы, содержащий программы и папки, которые отображаются в меню «Пуск» для всех пользователей. Типичный путь в Windows — C: ProgramDataMicrosoftWindowsStart Menu.
Как установить переменную PATH в Windows 10?
Добавить в ПУТЬ в Windows 10
- Откройте «Начать поиск», введите «env» и выберите «Изменить системные переменные среды»:
- Нажмите кнопку «Переменные среды…».
- В разделе «Системные переменные» (нижняя половина) найдите строку с «Путь» в первом столбце и нажмите «Изменить».
- Появится пользовательский интерфейс «Изменить переменную среды».
17 мар. 2018 г.
Какие у меня окна пути?
PATH — это системная переменная, которую ваша операционная система использует для поиска необходимых исполняемых файлов из командной строки или окна Терминала. Системную переменную PATH можно установить с помощью системной утилиты на панели управления в Windows или в файле запуска вашей оболочки в Linux и Solaris.
Что должно быть в переменной PATH?
Переменная PATH избавляет нас от необходимости записывать полный путь к программе в CLI каждый раз, когда мы ее запускаем. По сути, это просто переменная, в которой хранится множество ярлыков. Когда вы вводите команду в CLI без использования абсолютного пути, операционная система проверяет переменную PATH.
Как мне найти свой путь в CMD?
2. Windows 10
- Перейдите в папку назначения и щелкните путь (выделен синим).
- введите cmd.
- Командная строка открывается с указанием пути к вашей текущей папке.
Какое значение по умолчанию для переменной среды PATH?
Переменная среды Path пользователя по умолчанию отсутствует (т. Е. Такая переменная не была установлена).
Как изменить путь без перезагрузки?
Обновить путь Windows без перезагрузки
- Откройте окно свойств вашей системы. …
- Откройте окно переменных среды.
- Дважды щелкните свой путь (если вы хотите просто изменить свой путь для входа в систему, используйте верхний, если вы хотите изменить его для всех входов, используйте нижний)
- Добавьте путь, который вы хотите добавить, через точку с запятой.
19 июн. 2008 г.
Как обновить переменные среды?
процесс обновления переменных среды без перезагрузки окон
- открыть окно командной строки cmd commend.
- входной набор PATH = C -> это обновит переменные среды.
- закройте и перезапустите окно cmd.
- введите эхо% PATH% для проверки.
22 сред. 2018 г.
Как установить переменные среды?
Инструкции для Windows
- Откройте панель управления.
- Щелкните Система и безопасность, затем Система.
- Щелкните Дополнительные параметры системы слева.
- В окне «Свойства системы» щелкните «Переменные среды…»
- Щелкните свойство, которое вы хотите изменить, затем нажмите кнопку Изменить…
Каков путь к системной переменной по умолчанию?
Эта переменная указывает на каталог Common Files. По умолчанию это «C: Program FilesCommon Files» в английской версии Windows. … Его значение — это расположение системного каталога, включая диск и путь.
Как установить путь по умолчанию?
Примечание:
- Перейдите в Windows Пуск> Открыть «Компьютер».
- Щелкните треугольник рядом с надписью «Документы».
- Щелкните правой кнопкой мыши папку «Мои документы».
- Щелкните «Свойства»> выберите вкладку «Местоположение».
- Введите «H: docs» на панели> щелкните [Применить].
- В окне сообщения может появиться вопрос, хотите ли вы переместить содержимое папки в новую папку.
Как изменить путь в командной строке?
Установка временного пути
- Откройте командную строку в Windows.
- Скопируйте путь к каталогу jdk / bin, в котором находится java (C: Program FilesJavajdk_versionbin)
- Напишите в командной строке: SET PATH = C: Program FilesJavajdk_versionbin и нажмите Enter command.
Я внес некоторые изменения в %PATH% в реестре. Теперь я хотел бы, чтобы эти изменения были применены без необходимости выхода из системы, перезагрузки или перезагрузки проводника. Есть ли способ сделать это?
Я бы предпочел сделать это с помощью некоторой команды, которая может быть помещена в конец .BAT файл, и я не хочу использовать какие-либо инструменты, кроме тех, которые поставляются с ОС в новой установке. Это должно быть минимально совместимо с Windows XP SP3 и должно работать вплоть до Windows 7 x64 и Server 2008 R2.
- Измените пользовательский или системный путь в свойствах системы.
- Запуск этого пакетного файла извлекает новые переменные PATH с помощью запроса REG.
- Команды FOR анализируют переменные PATH из результатов REG.
- Текущий PATH обновляется до значений реестра.
- Я использую ConEmu для своих консолей, и он запускает этот пакетный файл на каждой новой консоли, чтобы обновить PATH, поэтому перезагрузка не требуется.
@echo off
echo.
echo Refreshing PATH from registry
:: Get System PATH
for /f "tokens=2*" %%A in ('reg query "HKLMSYSTEMCurrentControlSetControlSession ManagerEnvironment" /v Path') do set syspath=%%B
:: Get User Path
for /f "tokens=2*" %%A in ('reg query "HKCUEnvironment" /v Path') do set userpath=%%B
:: Set Refreshed Path
set PATH=%userpath%;%syspath%
echo Refreshed PATH
echo %PATH%
« `
Параметр Commands задачи в ConEmu запускает C:WindowsSystem32cmd.exe с ключом /k, чтобы запустить вышеупомянутый файл refreshpath.cmd, а затем остается. Это обновляет путь и оставляет консоль открытой.
C:WindowsSystem32cmd.exe /k refreshpath.cmd
Если вы пытаетесь использовать новое значение переменной пути из командной оболочки Windows, все, что вам нужно сделать, это закрыть окно командной оболочки и открыть новое. Новая командная оболочка загрузит обновленную переменную пути.
Поэтому я думаю, что ответ на ваш первоначальный вопрос в некоторой степени зависит от того, где именно вы пытаетесь увидеть, как изменения вступят в силу … Есть ли что-то конкретное, что не работает для вас?
ответ дан Shannon Wagner863
- Измените переменную PATH из пользовательского интерфейса в переменных среды.
- Добавьте новую переменную окружения, назовите ее случайной. Может быть, что-то вроде CHANGE_TO_UPDATE и положить случайное значение, как х в нем.
- Не забудьте перезапустить cmd.exe или любую другую программу, которая должна увидеть новую переменную пути.
Это фактически приведет к обновлению настроек при запуске нового приложения.
Самый простой способ добавить переменную в путь без перезагрузки — это открыть командную строку и ввести: PATH =(VARIABLE);% path% и нажать ввод. Чтобы проверить, загружена ли ваша переменная, введите PATH и нажмите ввод.
ответ дан Richard Woodruff1
Всё ещё ищете ответ? Посмотрите другие вопросы с метками windows windows-registry environment-variables batch-file.
I’ve made some changes to the %PATH% variable in the registry. Now, I’d like to see those changes applied without having to go so far as a logoff, reboot, or reload of Explorer. Is there a way this can be done?
I’d rather do this via some sort of command that can be put at the end of a .BAT file, and don’t want to use any tools other than those that come with the OS in a fresh install. This needs to be minimally compatible with Windows XP SP3, and should work all the way up to Windows 7 x64 and Server 2008 R2.
asked Feb 16, 2012 at 21:36
5
- Change either User or System PATH in System Properties.
- Running this batch file pulls the new PATH variables with a REG query.
- The FOR commands parse the PATH variables from the REG results.
- The current PATH is updated to the registry values.
- I use ConEmu for my consoles and it runs this batch file on each new console to refresh the PATH so a reboot isn’t necessary.
@echo off
echo.
echo Refreshing PATH from registry
:: Get System PATH
for /f "tokens=2*" %%A in ('reg query "HKLMSYSTEMCurrentControlSetControlSession ManagerEnvironment" /v Path') do set syspath=%%B
:: Get User Path
for /f "tokens=2*" %%A in ('reg query "HKCUEnvironment" /v Path') do set userpath=%%B
:: Set Refreshed Path
set PATH=%userpath%;%syspath%
echo Refreshed PATH
echo %PATH%
«`
The task Commands parameter in ConEmu launches C:WindowsSystem32cmd.exe with the /k switch to run the refreshpath.cmd above and then remain. That updates the path and leaves the console open.
C:WindowsSystem32cmd.exe /k refreshpath.cmd
answered Dec 25, 2015 at 15:57
DaveDave
811 silver badge5 bronze badges
3
If you are trying to use the new value of the path variable from within a Windows command shell, all you should need to do is close your command shell window and open a new one. The new command shell will load the updated path variable.
So I think the answer to your original question sort of depends on where exactly you are trying to see the change take effect… Is there something specific that is not working for you?
answered Feb 16, 2012 at 22:29
Shannon WagnerShannon Wagner
1,0331 gold badge10 silver badges20 bronze badges
6
The easiest way to add a variable to the path without rebooting is to open the command prompt and type: PATH=(VARIABLE);%path% and press enter. To check if your variable loaded, type PATH and press enter.
answered Jun 28, 2016 at 22:25
1
- Change the PATH variable from the UI in environment variables.
- Add a new environment variable, call it something random. Maybe something like CHANGE_TO_UPDATE and put a random value like x in it.
- Remember to restart cmd.exe or whatever program that needs to see the new path variable.
This will actually trigger the settings to update when you launch a new application.
answered Mar 26, 2015 at 3:17
iopqiopq
993 bronze badges
I’ve made some changes to the %PATH% variable in the registry. Now, I’d like to see those changes applied without having to go so far as a logoff, reboot, or reload of Explorer. Is there a way this can be done?
I’d rather do this via some sort of command that can be put at the end of a .BAT file, and don’t want to use any tools other than those that come with the OS in a fresh install. This needs to be minimally compatible with Windows XP SP3, and should work all the way up to Windows 7 x64 and Server 2008 R2.
asked Feb 16, 2012 at 21:36
5
- Change either User or System PATH in System Properties.
- Running this batch file pulls the new PATH variables with a REG query.
- The FOR commands parse the PATH variables from the REG results.
- The current PATH is updated to the registry values.
- I use ConEmu for my consoles and it runs this batch file on each new console to refresh the PATH so a reboot isn’t necessary.
@echo off
echo.
echo Refreshing PATH from registry
:: Get System PATH
for /f "tokens=2*" %%A in ('reg query "HKLMSYSTEMCurrentControlSetControlSession ManagerEnvironment" /v Path') do set syspath=%%B
:: Get User Path
for /f "tokens=2*" %%A in ('reg query "HKCUEnvironment" /v Path') do set userpath=%%B
:: Set Refreshed Path
set PATH=%userpath%;%syspath%
echo Refreshed PATH
echo %PATH%
«`
The task Commands parameter in ConEmu launches C:WindowsSystem32cmd.exe with the /k switch to run the refreshpath.cmd above and then remain. That updates the path and leaves the console open.
C:WindowsSystem32cmd.exe /k refreshpath.cmd
answered Dec 25, 2015 at 15:57
DaveDave
811 silver badge5 bronze badges
3
If you are trying to use the new value of the path variable from within a Windows command shell, all you should need to do is close your command shell window and open a new one. The new command shell will load the updated path variable.
So I think the answer to your original question sort of depends on where exactly you are trying to see the change take effect… Is there something specific that is not working for you?
answered Feb 16, 2012 at 22:29
Shannon WagnerShannon Wagner
1,0331 gold badge10 silver badges20 bronze badges
6
The easiest way to add a variable to the path without rebooting is to open the command prompt and type: PATH=(VARIABLE);%path% and press enter. To check if your variable loaded, type PATH and press enter.
answered Jun 28, 2016 at 22:25
1
- Change the PATH variable from the UI in environment variables.
- Add a new environment variable, call it something random. Maybe something like CHANGE_TO_UPDATE and put a random value like x in it.
- Remember to restart cmd.exe or whatever program that needs to see the new path variable.
This will actually trigger the settings to update when you launch a new application.
answered Mar 26, 2015 at 3:17
iopqiopq
993 bronze badges