|
|
| Developer | Microsoft |
|---|---|
| Source model |
|
| Initial release | November 20, 1985; 37 years ago |
| Latest release | 22H2 (10.0.22621.1194) (January 26, 2023; 10 days ago[1]) [±] |
| Latest preview |
22H2 (10.0.22621.1194) (January 26, 2023; 10 days ago[2][3]) [±]
22H2 (10.0.22623.1250) (February 2, 2023; 3 days ago[4]) [±]
10.0.25290.1000 (February 1, 2023; 4 days ago[5]) [±] |
| Marketing target | Personal computing |
| Available in | 110 languages |
| Update method |
|
| Package manager | Windows Installer (.msi, .msix, .msp), Microsoft Store (.appx, .appxbundle),[6] Windows Package Manager |
| Platforms | IA-32, x86-64, ARM, ARM64 Previously: 16-bit x86, DEC Alpha, MIPS, PowerPC, Itanium |
| Kernel type |
|
| Default user interface |
Windows shell |
| License | Proprietary commercial software |
| Official website | microsoft.com/windows |
Windows is a group of several proprietary graphical operating system families developed and marketed by Microsoft. Each family caters to a certain sector of the computing industry. For example, Windows NT for consumers, Windows Server for servers, and Windows IoT for embedded systems. Defunct Windows families include Windows 9x, Windows Mobile, and Windows Phone.
The first version of Windows was released on November 20, 1985, as a graphical operating system shell for MS-DOS in response to the growing interest in graphical user interfaces (GUIs).[7]
Windows is the most popular desktop operating system in the world, with 75% market share as of April 2022, according to StatCounter.[8] However, Windows is not the most used operating system when including both mobile and desktop OSes, due to Android’s massive growth.[9]
As of September 2022, the most recent version of Windows is Windows 11 for consumer PCs and tablets, Windows 11 Enterprise for corporations, and Windows Server 2022 for servers.
Genealogy
By marketing role
Microsoft, the developer of Windows, has registered several trademarks, each of which denotes a family of Windows operating systems that target a specific sector of the computing industry. As of 2014, the following Windows families were being actively developed:
- Windows NT: Started as a family of operating systems with Windows NT 3.1, an operating system for server computers and workstations. It now consists of three operating system subfamilies that are released almost at the same time and share the same kernel:
- Windows: The operating system for mainstream personal computers and tablets. The latest version is Windows 11. The main competitor of this family is macOS by Apple for personal computers and iPadOS and Android for tablets (c.f. Usage share of operating systems § Market share by category).
- Windows Server: The operating system for server computers. The latest version is Windows Server 2022. Unlike its client sibling, it has adopted a strong naming scheme. The main competitor of this family is Linux. (c.f. Usage share of operating systems § Market share by category)
- Windows PE: A lightweight version of its Windows sibling, meant to operate as a live operating system, used for installing Windows on bare-metal computers (especially on many computers at once), recovery or troubleshooting purposes. The latest version is Windows PE 10.
- Windows IoT (previously Windows Embedded): Initially, Microsoft developed Windows CE as a general-purpose operating system for every device that was too resource-limited to be called a full-fledged computer. Eventually, however, Windows CE was renamed Windows Embedded Compact and was folded under Windows Compact trademark which also consists of Windows Embedded Industry, Windows Embedded Professional, Windows Embedded Standard, Windows Embedded Handheld and Windows Embedded Automotive.[10]
The following Windows families are no longer being developed:
- Windows 9x: An operating system that targeted the consumer market. Discontinued because of suboptimal performance.[citation needed] (PC World called its last version, Windows Me, one of the worst products of all time.[11]) Microsoft now caters to the consumer market with Windows NT.
- Windows Mobile: The predecessor to Windows Phone, it was a mobile phone operating system. The first version was called Pocket PC 2000; the third version, Windows Mobile 2003 is the first version to adopt the Windows Mobile trademark. The last version is Windows Mobile 6.5.
- Windows Phone: An operating system sold only to manufacturers of smartphones. The first version was Windows Phone 7, followed by Windows Phone 8, and Windows Phone 8.1. It was succeeded by Windows 10 Mobile, which is now also discontinued.
Version history
The term Windows collectively describes any or all of several generations of Microsoft operating system products. These products are generally categorized as follows:
Early versions
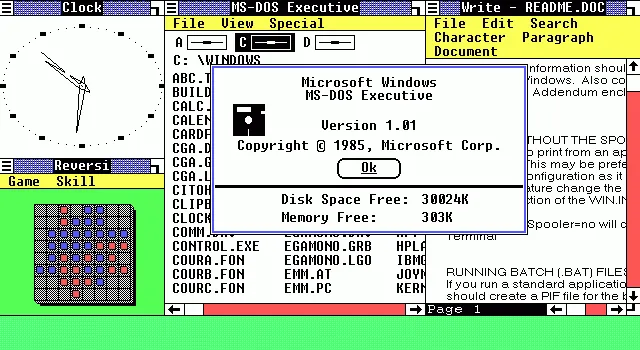
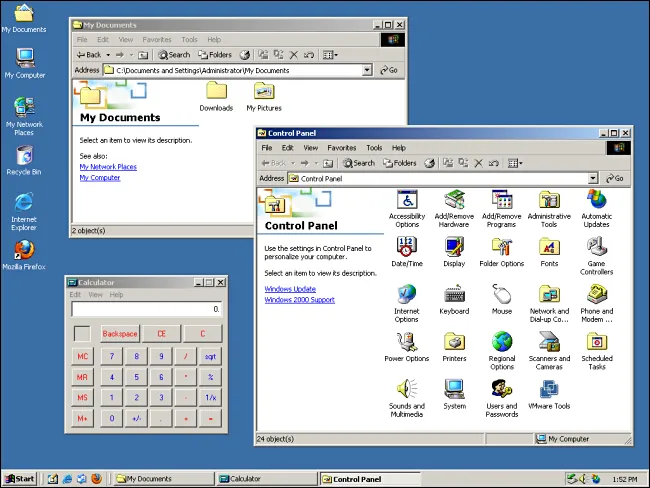
The history of Windows dates back to 1981 when Microsoft started work on a program called «Interface Manager». It was announced in November 1983 (after the Apple Lisa, but before the Macintosh) under the name «Windows», but Windows 1.0 was not released until November 1985.[12] Windows 1.0 was to compete with Apple’s operating system, but achieved little popularity. Windows 1.0 is not a complete operating system; rather, it extends MS-DOS. The shell of Windows 1.0 is a program known as the MS-DOS Executive. Components included Calculator, Calendar, Cardfile, Clipboard Viewer, Clock, Control Panel, Notepad, Paint, Reversi, Terminal and Write. Windows 1.0 does not allow overlapping windows. Instead all windows are tiled. Only modal dialog boxes may appear over other windows. Microsoft sold as included Windows Development libraries with the C development environment, which included numerous windows samples.[13]
Windows 2.0 was released in December 1987, and was more popular than its predecessor. It features several improvements to the user interface and memory management.[14] Windows 2.03 changed the OS from tiled windows to overlapping windows. The result of this change led to Apple Computer filing a suit against Microsoft alleging infringement on Apple’s copyrights (eventually settled in court in Microsoft’s favor in 1993).[15][16] Windows 2.0 also introduced more sophisticated keyboard shortcuts and could make use of expanded memory.
Windows 2.1 was released in two different versions: Windows/286 and Windows/386. Windows/386 uses the virtual 8086 mode of the Intel 80386 to multitask several DOS programs and the paged memory model to emulate expanded memory using available extended memory. Windows/286, in spite of its name, runs on both Intel 8086 and Intel 80286 processors. It runs in real mode but can make use of the high memory area.[citation needed]
In addition to full Windows-packages, there were runtime-only versions that shipped with early Windows software from third parties and made it possible to run their Windows software on MS-DOS and without the full Windows feature set.
The early versions of Windows are often thought of as graphical shells, mostly because they ran on top of MS-DOS and use it for file system services.[17] However, even the earliest Windows versions already assumed many typical operating system functions; notably, having their own executable file format and providing their own device drivers (timer, graphics, printer, mouse, keyboard and sound). Unlike MS-DOS, Windows allowed users to execute multiple graphical applications at the same time, through cooperative multitasking. Windows implemented an elaborate, segment-based, software virtual memory scheme, which allows it to run applications larger than available memory: code segments and resources are swapped in and thrown away when memory became scarce; data segments moved in memory when a given application had relinquished processor control.
Windows 3.x
Windows 3.0, released in 1990, improved the design, mostly because of virtual memory and loadable virtual device drivers (VxDs) that allow Windows to share arbitrary devices between multi-tasked DOS applications.[18] Windows 3.0 applications can run in protected mode, which gives them access to several megabytes of memory without the obligation to participate in the software virtual memory scheme. They run inside the same address space, where the segmented memory provides a degree of protection. Windows 3.0 also featured improvements to the user interface. Microsoft rewrote critical operations from C into assembly. Windows 3.0 was the first version of Windows to achieve broad commercial success, selling 2 million copies in the first six months.[19][20]
Versions before Windows 95 had to be installed from floppy disks by end users (or in professional environments with a network installation), here Windows for Workgroups with nine 3.5-inch-disks to be inserted sequentially.
Windows 3.1, made generally available on March 1, 1992, featured a facelift. In August 1993, Windows for Workgroups, a special version with integrated peer-to-peer networking features and a version number of 3.11, was released. It was sold along with Windows 3.1. Support for Windows 3.1 ended on December 31, 2001.[21]
Windows 3.2, released 1994, is an updated version of the Chinese version of Windows 3.1.[22] The update was limited to this language version, as it fixed only issues related to the complex writing system of the Chinese language.[23] Windows 3.2 was generally sold by computer manufacturers with a ten-disk version of MS-DOS that also had Simplified Chinese characters in basic output and some translated utilities.
Windows 9x
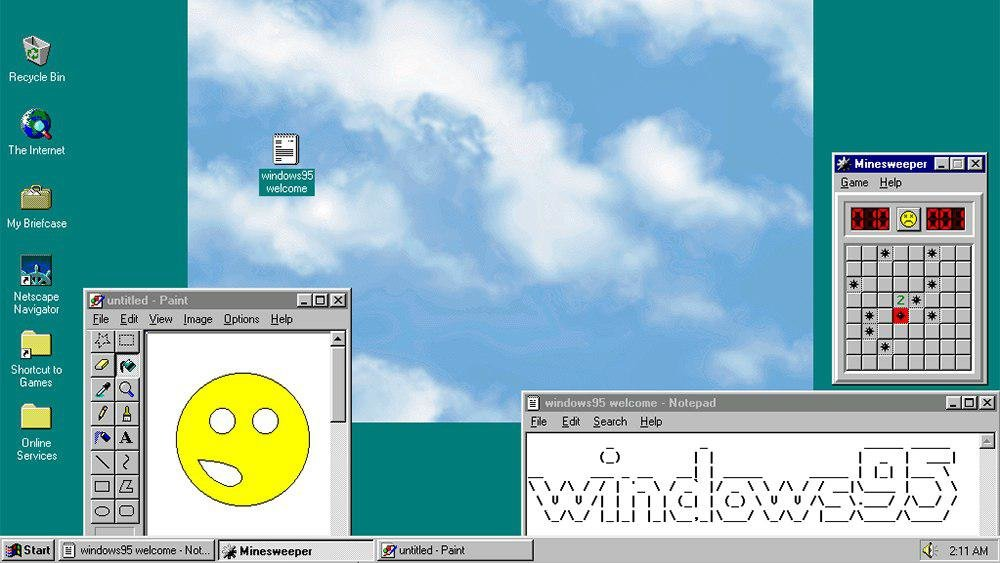
The next major consumer-oriented release of Windows, Windows 95, was released on August 24, 1995. While still remaining MS-DOS-based, Windows 95 introduced support for native 32-bit applications, plug and play hardware, preemptive multitasking, long file names of up to 255 characters, and provided increased stability over its predecessors. Windows 95 also introduced a redesigned, object oriented user interface, replacing the previous Program Manager with the Start menu, taskbar, and Windows Explorer shell. Windows 95 was a major commercial success for Microsoft; Ina Fried of CNET remarked that «by the time Windows 95 was finally ushered off the market in 2001, it had become a fixture on computer desktops around the world.»[24] Microsoft published four OEM Service Releases (OSR) of Windows 95, each of which was roughly equivalent to a service pack. The first OSR of Windows 95 was also the first version of Windows to be bundled with Microsoft’s web browser, Internet Explorer.[25] Mainstream support for Windows 95 ended on December 31, 2000, and extended support for Windows 95 ended on December 31, 2001.[26]
Windows 95 was followed up with the release of Windows 98 on June 25, 1998, which introduced the Windows Driver Model, support for USB composite devices, support for ACPI, hibernation, and support for multi-monitor configurations. Windows 98 also included integration with Internet Explorer 4 through Active Desktop and other aspects of the Windows Desktop Update (a series of enhancements to the Explorer shell which were also made available for Windows 95). In May 1999, Microsoft released Windows 98 Second Edition, an updated version of Windows 98. Windows 98 SE added Internet Explorer 5.0 and Windows Media Player 6.2 amongst other upgrades. Mainstream support for Windows 98 ended on June 30, 2002, and extended support for Windows 98 ended on July 11, 2006.[27]
On September 14, 2000, Microsoft released Windows Me (Millennium Edition), the last DOS-based version of Windows. Windows Me incorporated visual interface enhancements from its Windows NT-based counterpart Windows 2000, had faster boot times than previous versions (which however, required the removal of the ability to access a real mode DOS environment, removing compatibility with some older programs),[28] expanded multimedia functionality (including Windows Media Player 7, Windows Movie Maker, and the Windows Image Acquisition framework for retrieving images from scanners and digital cameras), additional system utilities such as System File Protection and System Restore, and updated home networking tools.[29] However, Windows Me was faced with criticism for its speed and instability, along with hardware compatibility issues and its removal of real mode DOS support. PC World considered Windows Me to be one of the worst operating systems Microsoft had ever released, and the fourth worst tech product of all time.[11]
Windows NT
Version history
Early versions (Windows NT 3.1/3.5/3.51/4.0/2000)
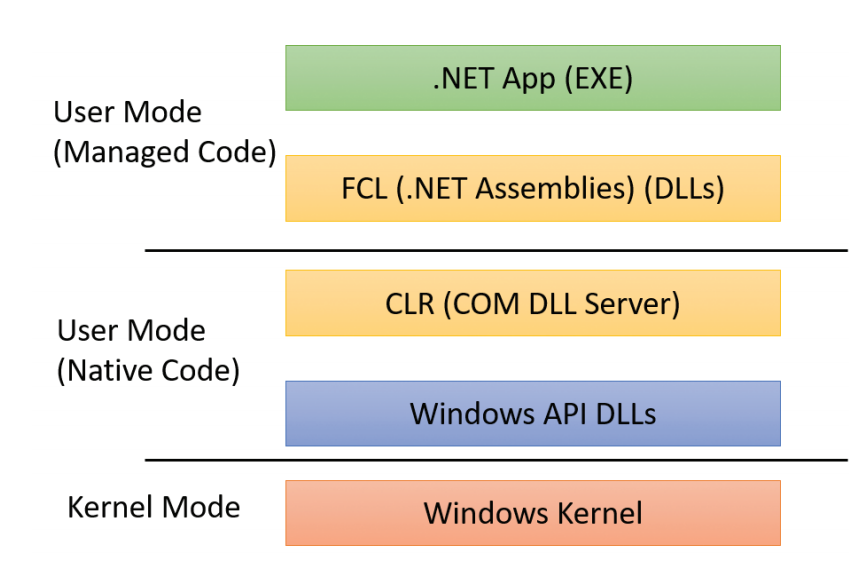
In November 1988, a new development team within Microsoft (which included former Digital Equipment Corporation developers Dave Cutler and Mark Lucovsky) began work on a revamped version of IBM and Microsoft’s OS/2 operating system known as «NT OS/2». NT OS/2 was intended to be a secure, multi-user operating system with POSIX compatibility and a modular, portable kernel with preemptive multitasking and support for multiple processor architectures. However, following the successful release of Windows 3.0, the NT development team decided to rework the project to use an extended 32-bit port of the Windows API known as Win32 instead of those of OS/2. Win32 maintained a similar structure to the Windows APIs (allowing existing Windows applications to easily be ported to the platform), but also supported the capabilities of the existing NT kernel. Following its approval by Microsoft’s staff, development continued on what was now Windows NT, the first 32-bit version of Windows. However, IBM objected to the changes, and ultimately continued OS/2 development on its own.[30][31]
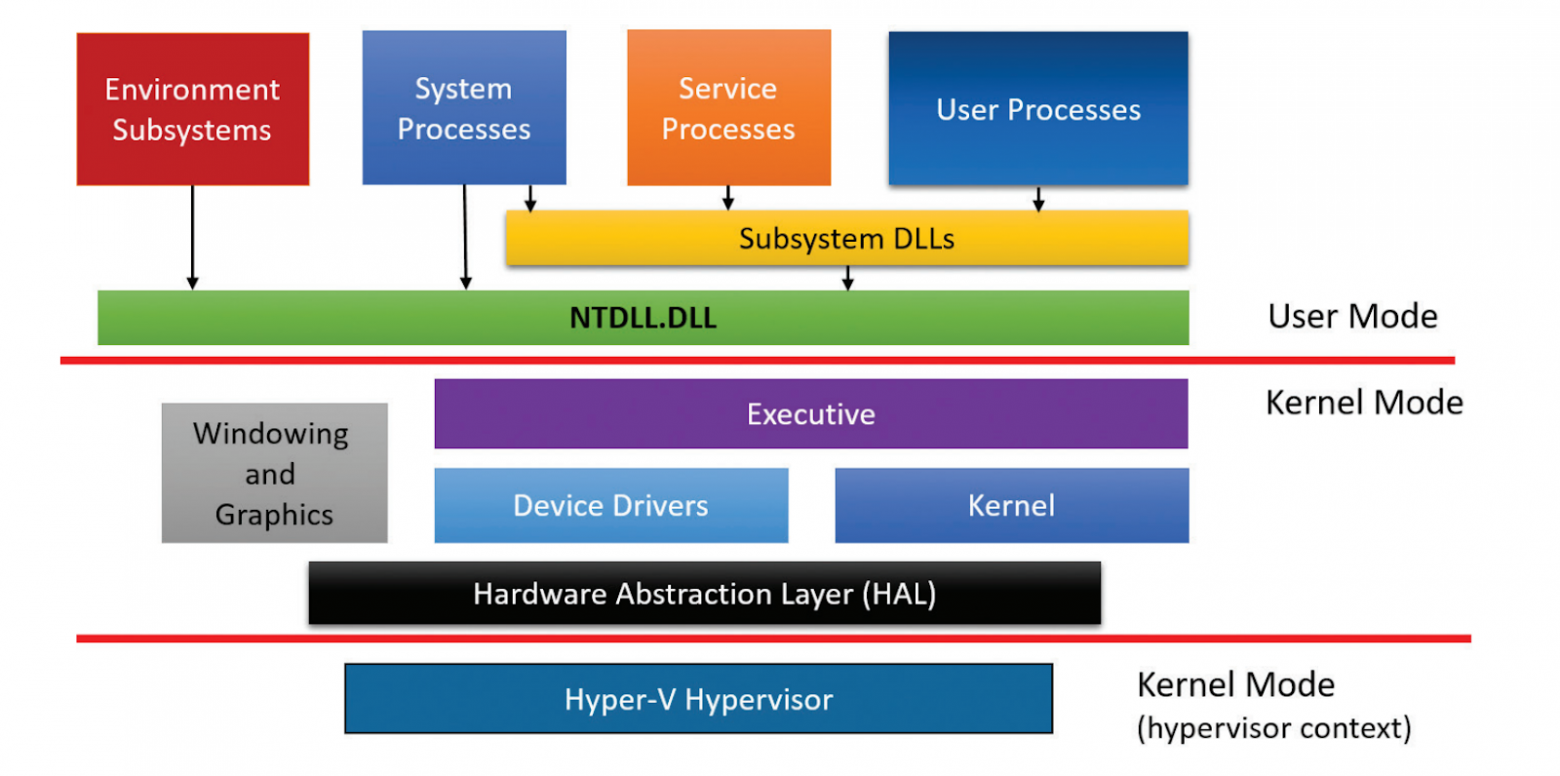
Windows NT was the first Windows operating system based on a hybrid kernel. The hybrid kernel was designed as a modified microkernel, influenced by the Mach microkernel developed by Richard Rashid at Carnegie Mellon University, but without meeting all of the criteria of a pure microkernel.
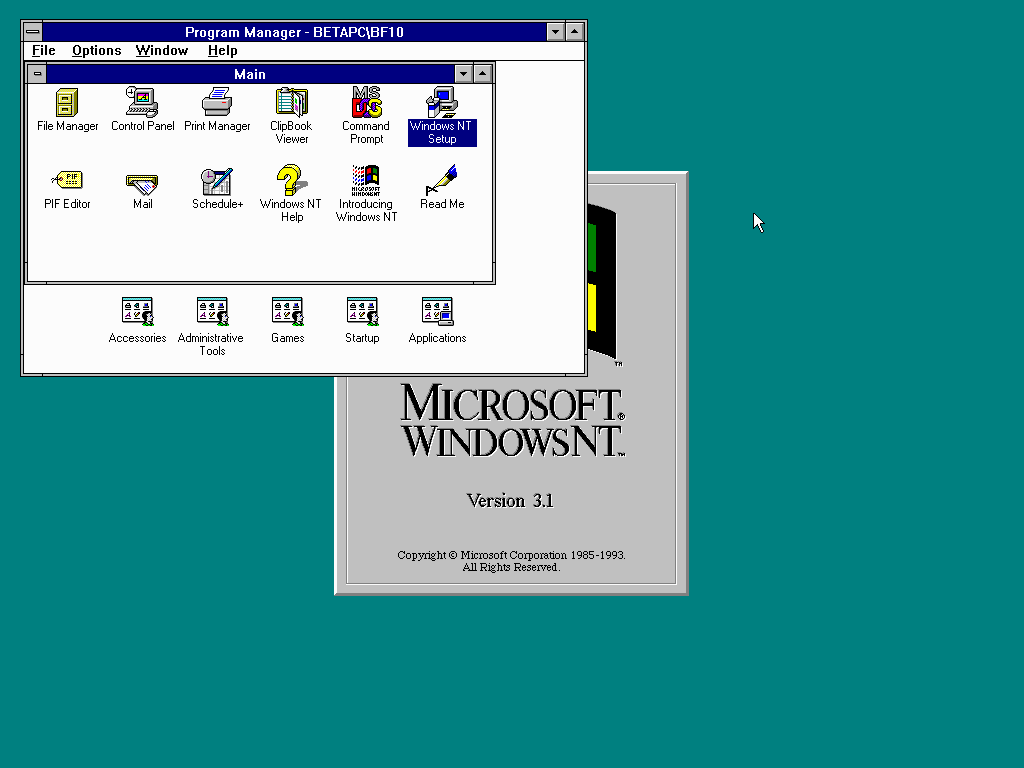
The first release of the resulting operating system, Windows NT 3.1 (named to associate it with Windows 3.1) was released in July 1993, with versions for desktop workstations and servers. Windows NT 3.5 was released in September 1994, focusing on performance improvements and support for Novell’s NetWare, and was followed up by Windows NT 3.51 in May 1995, which included additional improvements and support for the PowerPC architecture. Windows NT 4.0 was released in June 1996, introducing the redesigned interface of Windows 95 to the NT series. On February 17, 2000, Microsoft released Windows 2000, a successor to NT 4.0. The Windows NT name was dropped at this point in order to put a greater focus on the Windows brand.[31]
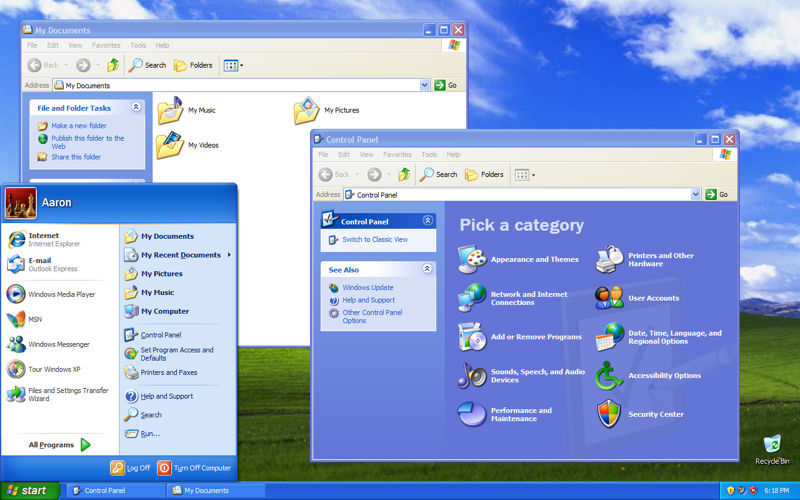
Windows XP
The next major version of Windows NT, Windows XP, was released on October 25, 2001. The introduction of Windows XP aimed to unify the consumer-oriented Windows 9x series with the architecture introduced by Windows NT, a change which Microsoft promised would provide better performance over its DOS-based predecessors. Windows XP would also introduce a redesigned user interface (including an updated Start menu and a «task-oriented» Windows Explorer), streamlined multimedia and networking features, Internet Explorer 6, integration with Microsoft’s .NET Passport services, a «compatibility mode» to help provide backwards compatibility with software designed for previous versions of Windows, and Remote Assistance functionality.[32][33]
At retail, Windows XP was marketed in two main editions: the «Home» edition was targeted towards consumers, while the «Professional» edition was targeted towards business environments and power users, and included additional security and networking features. Home and Professional were later accompanied by the «Media Center» edition (designed for home theater PCs, with an emphasis on support for DVD playback, TV tuner cards, DVR functionality, and remote controls), and the «Tablet PC» edition (designed for mobile devices meeting its specifications for a tablet computer, with support for stylus pen input and additional pen-enabled applications).[34][35][36] Mainstream support for Windows XP ended on April 14, 2009. Extended support ended on April 8, 2014.[37]
After Windows 2000, Microsoft also changed its release schedules for server operating systems; the server counterpart of Windows XP, Windows Server 2003, was released in April 2003.[31] It was followed in December 2005, by Windows Server 2003 R2.
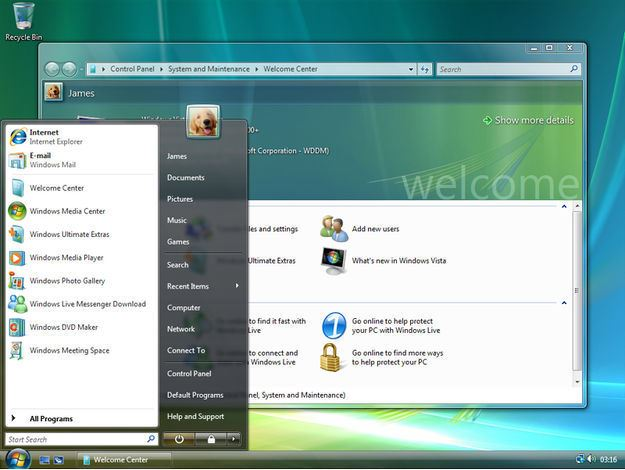
Windows Vista
After a lengthy development process, Windows Vista was released on November 30, 2006, for volume licensing and January 30, 2007, for consumers. It contained a number of new features, from a redesigned shell and user interface to significant technical changes, with a particular focus on security features. It was available in a number of different editions, and has been subject to some criticism, such as drop of performance, longer boot time, criticism of new UAC, and stricter license agreement. Vista’s server counterpart, Windows Server 2008 was released in early 2008.
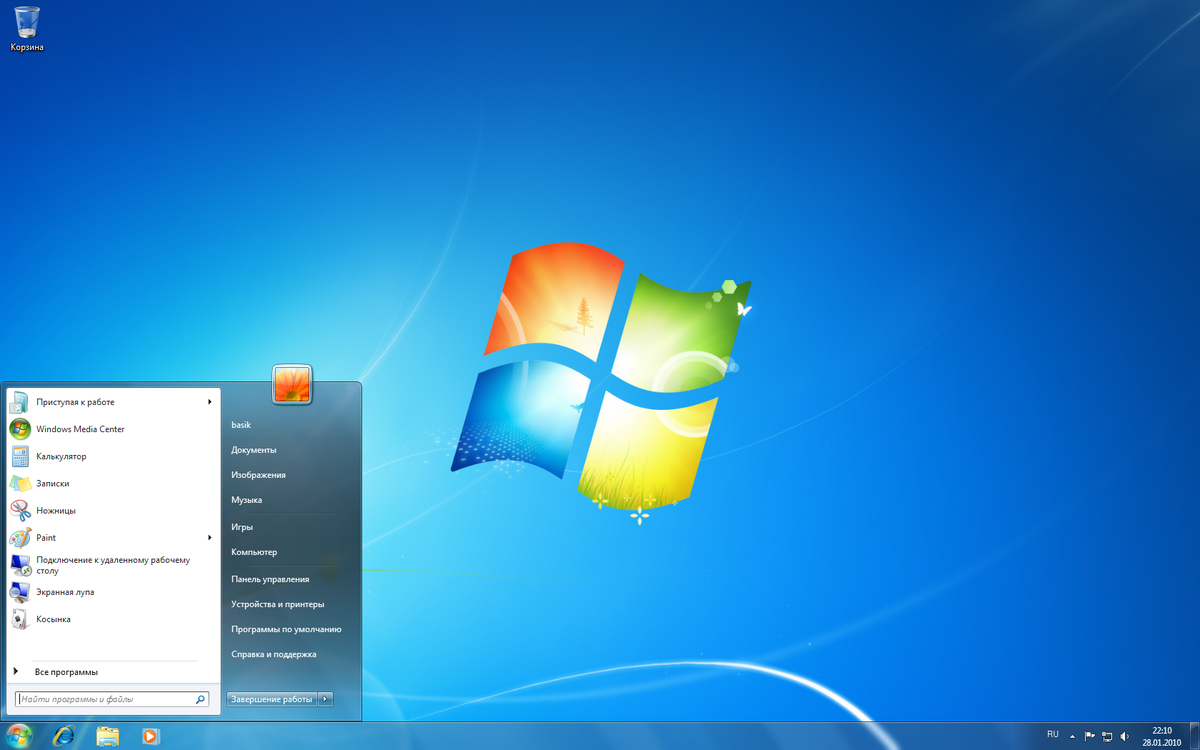
Windows 7
On July 22, 2009, Windows 7 and Windows Server 2008 R2 were released as RTM (release to manufacturing) while the former was released to the public 3 months later on October 22, 2009. Unlike its predecessor, Windows Vista, which introduced a large number of new features, Windows 7 was intended to be a more focused, incremental upgrade to the Windows line, with the goal of being compatible with applications and hardware with which Windows Vista was already compatible.[38] Windows 7 has multi-touch support, a redesigned Windows shell with an updated taskbar with revealable jump lists that contain shortcuts to files frequently used with specific applications and shortcuts to tasks within the application,[39] a home networking system called HomeGroup,[40] and performance improvements.
Windows 8 and 8.1
Windows 8, the successor to Windows 7, was released generally on October 26, 2012. A number of significant changes were made on Windows 8, including the introduction of a user interface based around Microsoft’s Metro design language with optimizations for touch-based devices such as tablets and all-in-one PCs. These changes include the Start screen, which uses large tiles that are more convenient for touch interactions and allow for the display of continually updated information, and a new class of apps which are designed primarily for use on touch-based devices. The new Windows version required a minimum resolution of 1024×768 pixels,[41] effectively making it unfit for netbooks with 800×600-pixel screens.
Other changes include increased integration with cloud services and other online platforms (such as social networks and Microsoft’s own OneDrive (formerly SkyDrive) and Xbox Live services), the Windows Store service for software distribution, and a new variant known as Windows RT for use on devices that utilize the ARM architecture, and a new keyboard shortcut for screenshots.[42][43][44][45][46][47][48] An update to Windows 8, called Windows 8.1,[49] was released on October 17, 2013, and includes features such as new live tile sizes, deeper OneDrive integration, and many other revisions. Windows 8 and Windows 8.1 have been subject to some criticism, such as removal of the Start menu.
Windows 10
On September 30, 2014, Microsoft announced Windows 10 as the successor to Windows 8.1. It was released on July 29, 2015, and addresses shortcomings in the user interface first introduced with Windows 8. Changes on PC include the return of the Start Menu, a virtual desktop system, and the ability to run Windows Store apps within windows on the desktop rather than in full-screen mode. Windows 10 is said to be available to update from qualified Windows 7 with SP1, Windows 8.1 and Windows Phone 8.1 devices from the Get Windows 10 Application (for Windows 7, Windows 8.1) or Windows Update (Windows 7).[50]
In February 2017, Microsoft announced the migration of its Windows source code repository from Perforce to Git. This migration involved 3.5 million separate files in a 300 gigabyte repository.[51] By May 2017, 90 percent of its engineering team was using Git, in about 8500 commits and 1760 Windows builds per day.[51]
In June 2021, shortly before Microsoft’s announcement of Windows 11, Microsoft updated their lifecycle policy pages for Windows 10, revealing that support for their last release of Windows 10 will end on October 14, 2025.[52][53]
Windows 11
On June 24, 2021, Windows 11 was announced as the successor to Windows 10 during a livestream. The new operating system was designed to be more user-friendly and understandable. It was released on October 5, 2021.[54][55] As of May 2022, Windows 11 is a free upgrade to Windows 10 users who meet the system requirements.[56]
Windows 365
In July 2021, Microsoft announced it will start selling subscriptions to virtualized Windows desktops as part of a new Windows 365 service in the following month. It is not a standalone version of Windows, but a web service that provides access to Windows 10 and Windows 11 built on top of Azure Virtual Desktop. The new service will allow for cross-platform usage, aiming to make the operating system available for both Apple and Android users. The subscription service will be accessible through any operating system with a web browser. The new service is an attempt at capitalizing on the growing trend, fostered during the COVID-19 pandemic, for businesses to adopt a hybrid remote work environment, in which «employees split their time between the office and home». As the service will be accessible through web browsers, Microsoft will be able to bypass the need to publish the service through Google Play or the Apple App Store.[57][58][59][60][61]
Microsoft announced Windows 365 availability to business and enterprise customers on August 2, 2021.[62]
Multilingual support
Multilingual support has been built into Windows since Windows 3.0. The language for both the keyboard and the interface can be changed through the Region and Language Control Panel. Components for all supported input languages, such as Input Method Editors, are automatically installed during Windows installation (in Windows XP and earlier, files for East Asian languages, such as Chinese, and right-to-left scripts, such as Arabic, may need to be installed separately, also from the said Control Panel). Third-party IMEs may also be installed if a user feels that the provided one is insufficient for their needs.
Interface languages for the operating system are free for download, but some languages are limited to certain editions of Windows. Language Interface Packs (LIPs) are redistributable and may be downloaded from Microsoft’s Download Center and installed for any edition of Windows (XP or later) – they translate most, but not all, of the Windows interface, and require a certain base language (the language which Windows originally shipped with). This is used for most languages in emerging markets. Full Language Packs, which translates the complete operating system, are only available for specific editions of Windows (Ultimate and Enterprise editions of Windows Vista and 7, and all editions of Windows 8, 8.1 and RT except Single Language). They do not require a specific base language, and are commonly used for more popular languages such as French or Chinese. These languages cannot be downloaded through the Download Center, but available as optional updates through the Windows Update service (except Windows 8).
The interface language of installed applications is not affected by changes in the Windows interface language. The availability of languages depends on the application developers themselves.
Windows 8 and Windows Server 2012 introduces a new Language Control Panel where both the interface and input languages can be simultaneously changed, and language packs, regardless of type, can be downloaded from a central location. The PC Settings app in Windows 8.1 and Windows Server 2012 R2 also includes a counterpart settings page for this. Changing the interface language also changes the language of preinstalled Windows Store apps (such as Mail, Maps and News) and certain other Microsoft-developed apps (such as Remote Desktop). The above limitations for language packs are however still in effect, except that full language packs can be installed for any edition except Single Language, which caters to emerging markets.
Platform support
Windows NT included support for several platforms before the x86-based personal computer became dominant in the professional world. Windows NT 4.0 and its predecessors supported PowerPC, DEC Alpha and MIPS R4000 (although some of the platforms implement 64-bit computing, the OS treated them as 32-bit). Windows 2000 dropped support for all platforms, except the third generation x86 (known as IA-32) or newer in 32-bit mode. The client line of Windows NT family still runs on IA-32 but the Windows Server line ceased supporting this platform with the release of Windows Server 2008 R2.
With the introduction of the Intel Itanium architecture (IA-64), Microsoft released new versions of Windows to support it. Itanium versions of Windows XP and Windows Server 2003 were released at the same time as their mainstream x86 counterparts. Windows XP 64-Bit Edition, released in 2005, is the last Windows client operating systems to support Itanium. Windows Server line continues to support this platform until Windows Server 2012; Windows Server 2008 R2 is the last Windows operating system to support Itanium architecture.
On April 25, 2005, Microsoft released Windows XP Professional x64 Edition and Windows Server 2003 x64 Editions to support x86-64 (or simply x64), the 64-bit version of x86 architecture. Windows Vista was the first client version of Windows NT to be released simultaneously in IA-32 and x64 editions. x64 is still supported.
An edition of Windows 8 known as Windows RT was specifically created for computers with ARM architecture and while ARM is still used for Windows smartphones with Windows 10, tablets with Windows RT will not be updated. Starting from Windows 10 Fall Creators Update (version 1709) and later includes support for ARM-based PCs.[63]
Windows 11 is the first version to drop support for 32-bit hardware.[56]
Windows CE
Windows CE (officially known as Windows Embedded Compact), is an edition of Windows that runs on minimalistic computers, like satellite navigation systems and some mobile phones. Windows Embedded Compact is based on its own dedicated kernel, dubbed Windows CE kernel. Microsoft licenses Windows CE to OEMs and device makers. The OEMs and device makers can modify and create their own user interfaces and experiences, while Windows CE provides the technical foundation to do so.
Windows CE was used in the Dreamcast along with Sega’s own proprietary OS for the console. Windows CE was the core from which Windows Mobile was derived. Its successor, Windows Phone 7, was based on components from both Windows CE 6.0 R3 and Windows CE 7.0. Windows Phone 8 however, is based on the same NT-kernel as Windows 8.
Windows Embedded Compact is not to be confused with Windows XP Embedded or Windows NT 4.0 Embedded, modular editions of Windows based on Windows NT kernel.
Xbox OS
Xbox OS is an unofficial name given to the version of Windows that runs on Xbox consoles.[64] From Xbox One onwards it is an implementation with an emphasis on virtualization (using Hyper-V) as it is three operating systems running at once, consisting of the core operating system, a second implemented for games and a more Windows-like environment for applications.[65]
Microsoft updates Xbox One’s OS every month, and these updates can be downloaded from the Xbox Live service to the Xbox and subsequently installed, or by using offline recovery images downloaded via a PC.[66] It was originally based on NT 6.2 (Windows 
Xbox One and Xbox Series operating systems also allow limited (due to licensing restrictions and testing resources) backward compatibility with previous generation hardware,[69] and the Xbox 360’s system is backwards compatible with the original Xbox.[70]
Version control system
Up to and including every version before Windows 2000, Microsoft used an in-house version control system named Source Library Manager (SLM). Shortly after Windows 2000 was released, Microsoft switched to a fork of Perforce named Source Depot.[71] This system was used up until 2017 once the system couldn’t keep up with the size of Windows. Microsoft had begun to integrate Git into Team Foundation Server in 2013, but Windows continued to rely on Source Depot.[citation needed] The Windows code was divided among 65 different repositories with a kind of virtualization layer to produce unified view of all of the code.
In 2017 Microsoft announced that it would start using Git, an open source version control system created by Linus Torvalds and in May 2017 they reported that has completed migration into the Git repository.[72][73][51]
VFSForGit
Because of its large, decades-long history, however, the Windows codebase is not especially well suited to the decentralized nature of Linux development that Git was originally created to manage.[citation needed] Each Git repository contains a complete history of all the files, which proved unworkable for Windows developers because cloning the whole repository takes several hours.[citation needed] Microsoft has been working on a new project called the Virtual File System for Git (VFSForGit) to address these challenges.[73]
In 2021 the VFS for Git has been superseded by Scalar.[74]
Timeline of releases
Version market share
As a percentage of desktop and laptop systems using Windows,[79] according to StatCounter data from October 2022.[80]
Use of Windows 10 has exceeded Windows 7 globally since early 2018.[81]
For desktop and laptop computers, according to Net Applications and StatCounter, which track the use of operating systems in devices that are active on the Web, Windows was the most used operating-system family in August 2021, with around 91% usage share according to Net Applications[82] and around 76% usage share according to StatCounter.[83]
Including personal computers of all kinds (e.g., desktops, laptops, mobile devices, and game consoles), Windows OSes accounted for 32.67% of usage share in August 2021, compared to Android (highest, at 46.03%), iOS’s 13.76%, iPadOS’s 2.81%, and macOS’s 2.51%, according to Net Applications[84] and 30.73% of usage share in August 2021, compared to Android (highest, at 42.56%), iOS/iPadOS’s 16.53%, and macOS’s 6.51%, according to StatCounter.[85]
Those statistics do not include servers (including so-called cloud computing, where Microsoft is known not to be a leader, with Linux used more than Windows), as Net Applications and StatCounter use web browsing as a proxy for all use.
Security
|
|
This section needs to be updated. Please help update this article to reflect recent events or newly available information. (May 2020) |
Early versions of Windows were designed at a time where malware and networking were less common, and had few built-in security features; they did not provide access privileges to allow a user to prevent other users from accessing their files, and they did not provide memory protection to prevent one process from reading or writing another process’s address space or to prevent a process from code or data used by privileged-mode code.
While the Windows 9x series offered the option of having profiles for multiple users, it had no concept of access privileges, allowing any user to edit others’ files. In addition, while it ran separate 32-bit applications in separate address spaces, protecting an application’s code and data from being read or written by another application, it did not protect the first megabyte of memory from userland applications for compatibility reasons. This area of memory contains code critical to the functioning of the operating system, and by writing into this area of memory an application can crash or freeze the operating system. This was a source of instability as faulty applications could accidentally write into this region, potentially corrupting important operating system memory, which usually resulted in some form of system error and halt.[86]
Windows NT was far more secure, implementing access privileges and full memory protection, and, while 32-bit programs meeting the DoD’s C2 security rating,[87] yet these advantages were nullified by the fact that, prior to Windows Vista, the default user account created during the setup process was an administrator account; the user, and any program the user launched, had full access to the machine. Though Windows XP did offer an option of turning administrator accounts into limited accounts, the majority of home users did not do so, partially due to the number of programs which required administrator rights to function properly. As a result, most home users still ran as administrator all the time. These architectural flaws, combined with Windows’s very high popularity, made Windows a frequent target of computer worm and virus writers.[88][89]
Furthermore, although Windows NT and its successors are designed for security (including on a network) and multi-user PCs, they were not initially designed with Internet security in mind as much, since, when it was first developed in the early 1990s, Internet use was less prevalent.[90]
In a 2002 strategy memo entitled «Trustworthy computing» sent to every Microsoft employee, Bill Gates declared that security should become Microsoft’s highest priority.[91][92]
Windows Vista introduced a privilege elevation system called User Account Control.[93] When logging in as a standard user, a logon session is created and a token containing only the most basic privileges is assigned. In this way, the new logon session is incapable of making changes that would affect the entire system. When logging in as a user in the Administrators group, two separate tokens are assigned. The first token contains all privileges typically awarded to an administrator, and the second is a restricted token similar to what a standard user would receive. User applications, including the Windows shell, are then started with the restricted token, resulting in a reduced privilege environment even under an Administrator account. When an application requests higher privileges or «Run as administrator» is clicked, UAC will prompt for confirmation and, if consent is given (including administrator credentials if the account requesting the elevation is not a member of the administrators group), start the process using the unrestricted token.[94]
Leaked documents published by WikiLeaks, codenamed Vault 7 and dated from 2013 to 2016, detail the capabilities of the CIA to perform electronic surveillance and cyber warfare,[95] such as the ability to compromise operating systems such as Windows.[96]
In August 2019, computer experts reported that the BlueKeep security vulnerability, CVE-2019-0708, that potentially affects older unpatched Windows versions via the program’s Remote Desktop Protocol, allowing for the possibility of remote code execution, may now include related flaws, collectively named DejaBlue, affecting newer Windows versions (i.e., Windows 7 and all recent versions) as well.[97] In addition, experts reported a Microsoft security vulnerability, CVE-2019-1162, based on legacy code involving Microsoft CTF and ctfmon (ctfmon.exe), that affects all Windows versions from Windows XP to the then most recent Windows 10 versions; a patch to correct the flaw is currently available.[98]
Microsoft releases security patches through its Windows Update service approximately once a month (usually the second Tuesday of the month), although critical updates are made available at shorter intervals when necessary.[99] Versions subsequent to Windows 2000 SP3 and Windows XP implemented automatic download and installation of updates, substantially increasing the number of users installing security updates.[100]
Today, Windows integrates the Windows Defender antivirus, which is seen as one of the best available.[101] Windows also implements Secure Boot, Control Flow Guard, ransomware protection, BitLocker disk encryption, a firewall, and Windows SmartScreen.
File permissions
All Windows versions from Windows NT 3 have been based on a file system permission system referred to as AGDLP (Accounts, Global, Domain Local, Permissions) in which file permissions are applied to the file/folder in the form of a ‘local group’ which then has other ‘global groups’ as members. These global groups then hold other groups or users depending on different Windows versions used. This system varies from other vendor products such as Linux and NetWare due to the ‘static’ allocation of permission being applied directly to the file or folder. However using this process of AGLP/AGDLP/AGUDLP allows a small number of static permissions to be applied and allows for easy changes to the account groups without reapplying the file permissions on the files and folders.
Alternative implementations
Owing to the operating system’s popularity, a number of applications have been released that aim to provide compatibility with Windows applications, either as a compatibility layer for another operating system, or as a standalone system that can run software written for Windows out of the box. These include:
- Wine – a free and open-source implementation of the Windows API, allowing one to run many Windows applications on x86-based platforms, including UNIX, Linux and macOS. Wine developers refer to it as a «compatibility layer»[102] and use Windows-style APIs to emulate Windows environment.
- CrossOver – a Wine package with licensed fonts. Its developers are regular contributors to Wine.
- Proton – A fork of Wine by Steam to run Windows games on Linux and other Unix-like OS.
- ReactOS – an open-source OS intended to run the same software as Windows, originally designed to simulate Windows NT 4.0, now aiming at Windows 7 compatibility. It has been in the development stage since 1996.
See also
- Wintel
References
- ^ «January 26, 2023—KB5022360 (OS Build 22621.1194) Preview». Microsoft Support. Microsoft.
- ^ «Releasing Windows 11 Build 22621.1192 to the Release Preview Channel». Windows Insider Blog. January 17, 2023.
- ^ «January 26, 2023—KB5022360 (OS Build 22621.1194) Preview». Microsoft Support. Microsoft.
- ^ «Announcing Windows 11 Insider Preview Build 22621.1250 and 22623.1250». Windows Insider Blog. February 2, 2023.
- ^ «Announcing Windows 11 Insider Preview Build 25290». Windows Insider Blog. February 1, 2023.
- ^ «App packages and deployment (Windows Store apps) (Windows)». Msdn.microsoft.com. Archived from the original on March 30, 2014. Retrieved April 5, 2014.
- ^ Bellis, Mary (October 4, 2019). «The Unusual History of Microsoft Windows». Retrieved January 13, 2023.
- ^ «Desktop Operating System Market Share Worldwide». StatCounter Global Stats.
- ^ Keizer, Gregg (July 14, 2014). «Microsoft gets real, admits its device share is just 14%». Computerworld. IDG. Archived from the original on August 21, 2016.
[Microsoft’s chief operating officer] Turner’s 14% came from a new forecast released last week by Gartner, which estimated Windows’ share of the shipped device market last year was 14%, and would decrease slightly to 13.7% in 2014. Android will dominate, Gartner said, with a 48% share this year
- ^ «RTOS: Embedded Real Time Operating Systems». microsoft.com. Microsoft. Archived from the original on December 15, 2014. Retrieved November 7, 2014.
- ^ a b «The 25 Worst Tech Products of All Time». PC World. IDG. May 26, 2006. Retrieved January 7, 2023.
- ^ «A history of Windows — Microsoft Windows». windows.microsoft.com. Archived from the original on June 11, 2016. Retrieved January 7, 2023.
- ^ Microsoft C 5.0: C Language Reference Guide. Microsoft. 1987. pp. 250–267.
- ^ «A legacy of Windows, part 1: Windows 1-2-3 – TechRepublic». TechRepublic. Archived from the original on March 27, 2017. Retrieved March 26, 2017.
- ^ «The Apple vs. Microsoft GUI Lawsuit». 2006. Archived from the original on March 4, 2008. Retrieved March 12, 2008.
- ^ «Apple Computer, Inc. v. MicroSoft Corp., 35 F.3d 1435 (9th Cir. 1994)». Archived from the original on December 14, 2007. Retrieved March 12, 2008.
- ^ «Windows Evolution». Soft32.com News. Archived from the original on February 8, 2008.
- ^ «Windows 3.0, released in 1990». www.coursehero.com/. Retrieved October 20, 2022.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: url-status (link) - ^ «Chronology of Personal Computer Software». Archived from the original on February 11, 2012.
- ^ «Microsoft Company». Archived from the original on May 14, 2008.
- ^ «Windows 3.1 Standard Edition Support Lifecycle». Archived from the original on January 12, 2012. Retrieved January 3, 2011.
- ^ «Microsoft Windows Simplified Chinese 3.2 Upgrade Is Available». Microsoft Support. Microsoft. Archived from the original on November 8, 2006.
- ^ «Microsoft Windows Simplified Chinese 3.2 Upgrade Is Available». Microsoft. October 30, 2003. Archived from the original on May 24, 2011. Retrieved September 4, 2009.
- ^ «Windows 95 turns 15: Has Microsoft’s OS peaked?». CNET/CNN Tech. August 25, 2010. Archived from the original on August 26, 2010. Retrieved August 22, 2012.
- ^ «Microsoft Internet Explorer Web Browser Available on All Major Platforms, Offers Broadest International Support». News Center. San Jose, California: Microsoft. April 30, 1996. Archived from the original on January 15, 2008. Retrieved February 14, 2011.
- ^ «Windows 95 Support Lifecycle». Microsoft. Archived from the original on November 22, 2012. Retrieved January 3, 2011.
- ^ «Windows 98 Standard Edition Support Lifecycle». Microsoft. Archived from the original on November 22, 2012. Retrieved January 3, 2011.
- ^ «Improving «Cold Boot» Time for System Manufacturers». Microsoft. December 4, 2001. Archived from the original on February 13, 2010. Retrieved August 26, 2010.
- ^ «Windows Millennium Edition: All About Me». PC World. Archived from the original on August 1, 2013. Retrieved May 21, 2013.
- ^ Custer, Helen (1993). Inside Windows NT. Redmond: Microsoft Press. ISBN 1-55615-481-X.
- ^ a b c Thurrott, Paul (January 24, 2003). «Windows Server 2003: The Road To Gold – Part One: The Early Years». Archived from the original on January 1, 2005. Retrieved May 28, 2012.
- ^ «Windows XP review». CNET. Archived from the original on May 26, 2013. Retrieved May 24, 2013.
- ^ «Windows XP Program Compatibility Wizard». ServerWatch. March 12, 2002. Retrieved November 13, 2021.
- ^ David Coursey (October 25, 2001). «The 10 top things you MUST know about Win XP». ZDNet. Archived from the original on April 3, 2009. Retrieved July 22, 2008.
- ^ David Coursey (August 31, 2001). «Your top Windows XP questions answered! (Part One)». ZDNet. CNET Networks. Archived from the original on December 19, 2007. Retrieved January 3, 2011.
- ^ «A Look at Freestyle and Mira». Paul Thurrott’s SuperSite for Windows. Penton. September 3, 2002. Retrieved January 3, 2011.[permanent dead link]
- ^ «Windows XP Professional Lifecycle Support». Archived from the original on February 27, 2013. Retrieved January 3, 2011.
- ^ Nash, Mike (October 28, 2008). «Windows 7 Unveiled Today at PDC 2008». Windows Experience Blog. Microsoft. Archived from the original on November 1, 2008. Retrieved November 11, 2008.
- ^ Kiriaty, Yochay; Goldshtein, Sasha (2009). «Windows 7 Taskbar APIs». docs.microsoft.com. Retrieved August 21, 2021.
- ^ LeBlanc, Brandon (October 28, 2008). «How Libraries & HomeGroup Work Together in Windows 7». Windows Experience Blog. Microsoft. Archived from the original on November 2, 2008. Retrieved November 11, 2008.
- ^ «New Windows 8 hardware specs hint at 7-inch tablets and a Microsoft Reader». ZDNet. Retrieved March 29, 2013.
- ^ Paul, Ian (July 5, 2021). «How to Take Screenshots in Windows 10, 8, and 7».
- ^ Case, Loyd. «Test Driving Windows 8 RTM». PC World. IDG. Retrieved January 7, 2023.
- ^ Rosoff, Matt. «Here’s Everything You Wanted To Know About Microsoft’s Upcoming iPad Killers». Business Insider. Archived from the original on January 22, 2013. Retrieved February 10, 2012.
- ^ «Announcing the Windows 8 Editions». Microsoft. April 16, 2012. Archived from the original on April 18, 2012. Retrieved April 17, 2012.
- ^ «Building Windows for the ARM processor architecture». Microsoft. Archived from the original on November 26, 2012. Retrieved November 21, 2012.
- ^ «Microsoft talks Windows Store features, Metro app sandboxing for Windows 8 developers». The Verge. Vox Media. May 17, 2012. Archived from the original on September 10, 2012. Retrieved September 8, 2012.
- ^ Miller, Michael. «Build: More Details On Building Windows 8 Metro Apps». PC Magazine. Archived from the original on February 17, 2012. Retrieved February 10, 2012.
- ^ «Windows 8.1 now available!». blogs.windows.com. Archived from the original on October 19, 2013. Retrieved October 31, 2013.
- ^ «Announcing Windows 10 – Windows Blog». September 30, 2014. Archived from the original on September 10, 2015. Retrieved September 30, 2014.
- ^ a b c Bright, Peter (May 24, 2017). «Windows switch to Git almost complete: 8,500 commits and 1,760 builds each day». Ars Technica. Condé Nast. Archived from the original on May 24, 2017.
- ^ a b «Window 10 Home and Pro Lifecycle». Microsoft. Retrieved July 2, 2021.
- ^ a b «Window 10 Enterprise and Education Lifecycle». Microsoft. Retrieved July 2, 2021.
- ^ Cox, George. «Windows 11 release date is October 5». The Spectrum. Retrieved September 18, 2021.
- ^ Warren, Tom (June 24, 2021). «Microsoft announces Windows 11, with a new design, Start menu, and more». The Verge. Retrieved June 24, 2021.
- ^ a b «Windows 11 Specs and System Requirements». Microsoft. Archived from the original on May 31, 2022. Retrieved May 31, 2022.
- ^ Foley, Mary Jo (July 14, 2021). «Microsoft brings Windows to the cloud with Windows 365 and Cloud PC». ZDNet. Retrieved July 14, 2021.
- ^ Tilley, Aaron (July 14, 2021). «Microsoft Aims to Put Windows in Hands of Apple, Android Users Through Hybrid Work». The Wall Street Journal. ISSN 0099-9660.
- ^ Higgins, Tim (June 23, 2021). «Apple’s Fight for Control Over Apps Moves to Congress and EU». The Wall Street Journal. ISSN 0099-9660.
- ^ «Microsoft unveils Windows 365, a Windows 10 PC in the cloud». Engadget. Retrieved July 15, 2021.
- ^ «Windows 365 Cloud PC | Microsoft». www.microsoft.com. Retrieved July 15, 2021.
- ^ Hill, Paul (August 2, 2021). «Microsoft announces the general availability of Windows 365». Neowin. Retrieved August 2, 2021.
- ^ Bott, Ed (October 7, 2019). «Windows 10 on Arm: What you need to know before you buy a Surface Pro X». ZDNet.
- ^ Anand Lal Shimpi. «The Xbox One – Mini Review & Comparison to Xbox 360/PS4». anandtech.com. Archived from the original on October 12, 2014. Retrieved October 21, 2014.
- ^ «Xbox One: Hardware and software specs detailed and analyzed – Three operating systems in one». ExtremeTech. Archived from the original on November 16, 2013. Retrieved December 1, 2013.
- ^ «How to use the Offline System Update Diagnostic Tool on Xbox One». Xbox Official Site. Microsoft. Archived from the original on April 27, 2021. Retrieved November 30, 2013.
- ^ «Xbox One Is «Literally a Windows Device»«. GameSpot. Archived from the original on December 27, 2015.
- ^ «New Xbox One Update Will Make Some Functionality 50 Percent Faster». GameSpot. Archived from the original on February 2, 2016.
- ^ Tom Warren (June 16, 2015). «Xbox One dashboard update includes a huge new design and Cortana». The Verge. Vox Media. Archived from the original on July 8, 2017.
- ^ Eric Qualls. «Xbox 360 and Xbox Games Backwards Compatibility». About.com Tech. Archived from the original on September 28, 2015.
- ^ Chen, Raymond (January 22, 2018). «The history of change-packing tools at Microsoft (so far)». The Old New Thing. Retrieved April 17, 2022.
- ^ «The largest Git repo on the planet». Brian Harry’s Blog. May 24, 2017. Retrieved October 8, 2021.
- ^ a b Bright, Peter (February 6, 2017). «Microsoft hosts the Windows source in a monstrous 300GB Git repository». Ars Technica. Archived from the original on December 26, 2017. Retrieved December 26, 2017.
- ^ Frequently Asked Questions | VFS for Git on GitHub
- ^ «Microsoft Support Lifecycle». Microsoft. Archived from the original on October 11, 2008.
- ^ Chen, Raymond (July 22, 2019). «What was the code name for Windows 7?». The Old New Thing.
- ^ «Products Ending Support in 2024 – Microsoft Build». Microsoft. September 20, 2022.
- ^ «Products Ending Support in 2025 – Microsoft Build». Microsoft. September 20, 2022.
- ^ «Frequently Asked Questions». StatCounter. «Are laptops included in the desktop platform?».
- ^ «Desktop Windows Version Market Share Worldwide». StatCounter.
- ^ «Desktop Windows Version Market Share Worldwide | StatCounter Global Stats». StatCounter Global Stats. Retrieved November 24, 2019.
- ^ «Desktop Operating system market share: August 2021». Net Applications.
- ^ «Desktop Operating System Market Share Worldwide: August 2021». StatCounter.
- ^ «Operating system market share: August 2021». Net Applications.
- ^ «Operating System Market Share Worldwide: August 2021». StatCounter.
- ^ «Transcript: Chat with Ed Bott and Carl Siechert, Co-Authors of Microsoft Windows XP Inside Out». microsoft.com. Microsoft. November 21, 2001. Archived from the original on September 18, 2004. Retrieved April 20, 2019.
- ^ Russinovich, Mark (April 30, 1998). «Windows NT Security, Part 1». ITPro Today: IT News, How-Tos, Trends, Case Studies, Career Tips, More. Retrieved September 29, 2022.
- ^ Bruce Schneier (June 15, 2005). «Crypto-Gram Newsletter». Counterpane Internet Security, Inc. Archived from the original on June 6, 2007. Retrieved April 22, 2007.
- ^ Andy Patrizio (April 27, 2006). «Linux Malware On The Rise». InternetNews. QuinStreet. Archived from the original on February 5, 2012. Retrieved January 3, 2011.
- ^ «Telephones and Internet Users by Country, 1990 and 2005». Information Please Database. Archived from the original on May 22, 2009. Retrieved June 9, 2009.
- ^ Gates, Bill. «Bill Gates: Trustworthy Computing». Wired. ISSN 1059-1028. Retrieved September 29, 2022.
- ^ Verloy, Filip. «20 Years After Bill Gates’ Trustworthy Computing Memo, Cybersecurity Issues Are An Even Harder Problem». nonamesecurity.com. Retrieved September 29, 2022.
- ^ Northrup, Tony (June 1, 2005). «Windows Vista Security and Data Protection Improvements». TechNet. Microsoft Docs. Retrieved October 20, 2021.
In Windows Vista, the User Account Control (UAC) initiative introduces fundamental operating system changes to enhance the experience for the non-administrative user.
- ^ Kenny Kerr (September 29, 2006). «Windows Vista for Developers – Part 4 – User Account Control». Archived from the original on March 29, 2007. Retrieved March 15, 2007.
- ^ Greenberg, Andy (March 7, 2017). «How the CIA Can Hack Your Phone, PC, and TV (Says WikiLeaks)». WIRED.
- ^ «Vault 7: Wikileaks reveals details of CIA’s hacks of Android, iPhone Windows, Linux, MacOS, and even Samsung TVs». Computing. March 7, 2017.
- ^ Greenberg, Andy (August 13, 2019). «DejaBlue: New BlueKeep-Style Bugs Renew The Risk Of A Windows worm». wired. Retrieved August 15, 2019.
- ^ Seals, Tara (August 14, 2019). «20-Year-Old Bug in Legacy Microsoft Code Plagues All Windows Users». ThreatPost.com. Retrieved August 15, 2019.
- ^ Ryan Naraine (June 8, 2005). «Microsoft’s Security Response Center: How Little Patches Are Made». eWeek. Ziff Davis Enterprise. Retrieved January 3, 2011.
- ^ John Foley (October 20, 2004). «Windows XP SP2 Distribution Surpasses 100 Million». InformationWeek. UBM TechWeb. Archived from the original on May 27, 2010. Retrieved January 3, 2011.
- ^ «Test antivirus software for Windows 10 – June 2022». www.av-test.org. Retrieved September 29, 2022.
- ^ «Wine». Winehq.org. Archived from the original on April 4, 2014. Retrieved April 5, 2014.
External links
- Official website
- Official Windows Blog
- Microsoft Developer Network
- Windows Developer Center
- Microsoft Windows History Timeline
- Pearson Education, InformIT – History of Microsoft Windows
- Microsoft Business Software Solutions
- Windows 10 release Information
 |
|
| Developer | Microsoft |
|---|---|
| Source model |
|
| Initial release | November 20, 1985; 37 years ago |
| Latest release | 22H2 (10.0.22621.1194) (January 26, 2023; 10 days ago[1]) [±] |
| Latest preview |
22H2 (10.0.22621.1194) (January 26, 2023; 10 days ago[2][3]) [±]
22H2 (10.0.22623.1250) (February 2, 2023; 3 days ago[4]) [±]
10.0.25290.1000 (February 1, 2023; 4 days ago[5]) [±] |
| Marketing target | Personal computing |
| Available in | 110 languages |
| Update method |
|
| Package manager | Windows Installer (.msi, .msix, .msp), Microsoft Store (.appx, .appxbundle),[6] Windows Package Manager |
| Platforms | IA-32, x86-64, ARM, ARM64 Previously: 16-bit x86, DEC Alpha, MIPS, PowerPC, Itanium |
| Kernel type |
|
| Default user interface |
Windows shell |
| License | Proprietary commercial software |
| Official website | microsoft.com/windows |
Windows is a group of several proprietary graphical operating system families developed and marketed by Microsoft. Each family caters to a certain sector of the computing industry. For example, Windows NT for consumers, Windows Server for servers, and Windows IoT for embedded systems. Defunct Windows families include Windows 9x, Windows Mobile, and Windows Phone.
The first version of Windows was released on November 20, 1985, as a graphical operating system shell for MS-DOS in response to the growing interest in graphical user interfaces (GUIs).[7]
Windows is the most popular desktop operating system in the world, with 75% market share as of April 2022, according to StatCounter.[8] However, Windows is not the most used operating system when including both mobile and desktop OSes, due to Android’s massive growth.[9]
As of September 2022, the most recent version of Windows is Windows 11 for consumer PCs and tablets, Windows 11 Enterprise for corporations, and Windows Server 2022 for servers.
Genealogy
By marketing role
Microsoft, the developer of Windows, has registered several trademarks, each of which denotes a family of Windows operating systems that target a specific sector of the computing industry. As of 2014, the following Windows families were being actively developed:
- Windows NT: Started as a family of operating systems with Windows NT 3.1, an operating system for server computers and workstations. It now consists of three operating system subfamilies that are released almost at the same time and share the same kernel:
- Windows: The operating system for mainstream personal computers and tablets. The latest version is Windows 11. The main competitor of this family is macOS by Apple for personal computers and iPadOS and Android for tablets (c.f. Usage share of operating systems § Market share by category).
- Windows Server: The operating system for server computers. The latest version is Windows Server 2022. Unlike its client sibling, it has adopted a strong naming scheme. The main competitor of this family is Linux. (c.f. Usage share of operating systems § Market share by category)
- Windows PE: A lightweight version of its Windows sibling, meant to operate as a live operating system, used for installing Windows on bare-metal computers (especially on many computers at once), recovery or troubleshooting purposes. The latest version is Windows PE 10.
- Windows IoT (previously Windows Embedded): Initially, Microsoft developed Windows CE as a general-purpose operating system for every device that was too resource-limited to be called a full-fledged computer. Eventually, however, Windows CE was renamed Windows Embedded Compact and was folded under Windows Compact trademark which also consists of Windows Embedded Industry, Windows Embedded Professional, Windows Embedded Standard, Windows Embedded Handheld and Windows Embedded Automotive.[10]
The following Windows families are no longer being developed:
- Windows 9x: An operating system that targeted the consumer market. Discontinued because of suboptimal performance.[citation needed] (PC World called its last version, Windows Me, one of the worst products of all time.[11]) Microsoft now caters to the consumer market with Windows NT.
- Windows Mobile: The predecessor to Windows Phone, it was a mobile phone operating system. The first version was called Pocket PC 2000; the third version, Windows Mobile 2003 is the first version to adopt the Windows Mobile trademark. The last version is Windows Mobile 6.5.
- Windows Phone: An operating system sold only to manufacturers of smartphones. The first version was Windows Phone 7, followed by Windows Phone 8, and Windows Phone 8.1. It was succeeded by Windows 10 Mobile, which is now also discontinued.
Version history
The term Windows collectively describes any or all of several generations of Microsoft operating system products. These products are generally categorized as follows:
Early versions
The history of Windows dates back to 1981 when Microsoft started work on a program called «Interface Manager». It was announced in November 1983 (after the Apple Lisa, but before the Macintosh) under the name «Windows», but Windows 1.0 was not released until November 1985.[12] Windows 1.0 was to compete with Apple’s operating system, but achieved little popularity. Windows 1.0 is not a complete operating system; rather, it extends MS-DOS. The shell of Windows 1.0 is a program known as the MS-DOS Executive. Components included Calculator, Calendar, Cardfile, Clipboard Viewer, Clock, Control Panel, Notepad, Paint, Reversi, Terminal and Write. Windows 1.0 does not allow overlapping windows. Instead all windows are tiled. Only modal dialog boxes may appear over other windows. Microsoft sold as included Windows Development libraries with the C development environment, which included numerous windows samples.[13]
Windows 2.0 was released in December 1987, and was more popular than its predecessor. It features several improvements to the user interface and memory management.[14] Windows 2.03 changed the OS from tiled windows to overlapping windows. The result of this change led to Apple Computer filing a suit against Microsoft alleging infringement on Apple’s copyrights (eventually settled in court in Microsoft’s favor in 1993).[15][16] Windows 2.0 also introduced more sophisticated keyboard shortcuts and could make use of expanded memory.
Windows 2.1 was released in two different versions: Windows/286 and Windows/386. Windows/386 uses the virtual 8086 mode of the Intel 80386 to multitask several DOS programs and the paged memory model to emulate expanded memory using available extended memory. Windows/286, in spite of its name, runs on both Intel 8086 and Intel 80286 processors. It runs in real mode but can make use of the high memory area.[citation needed]
In addition to full Windows-packages, there were runtime-only versions that shipped with early Windows software from third parties and made it possible to run their Windows software on MS-DOS and without the full Windows feature set.
The early versions of Windows are often thought of as graphical shells, mostly because they ran on top of MS-DOS and use it for file system services.[17] However, even the earliest Windows versions already assumed many typical operating system functions; notably, having their own executable file format and providing their own device drivers (timer, graphics, printer, mouse, keyboard and sound). Unlike MS-DOS, Windows allowed users to execute multiple graphical applications at the same time, through cooperative multitasking. Windows implemented an elaborate, segment-based, software virtual memory scheme, which allows it to run applications larger than available memory: code segments and resources are swapped in and thrown away when memory became scarce; data segments moved in memory when a given application had relinquished processor control.
Windows 3.x
Windows 3.0, released in 1990, improved the design, mostly because of virtual memory and loadable virtual device drivers (VxDs) that allow Windows to share arbitrary devices between multi-tasked DOS applications.[18] Windows 3.0 applications can run in protected mode, which gives them access to several megabytes of memory without the obligation to participate in the software virtual memory scheme. They run inside the same address space, where the segmented memory provides a degree of protection. Windows 3.0 also featured improvements to the user interface. Microsoft rewrote critical operations from C into assembly. Windows 3.0 was the first version of Windows to achieve broad commercial success, selling 2 million copies in the first six months.[19][20]
Versions before Windows 95 had to be installed from floppy disks by end users (or in professional environments with a network installation), here Windows for Workgroups with nine 3.5-inch-disks to be inserted sequentially.
Windows 3.1, made generally available on March 1, 1992, featured a facelift. In August 1993, Windows for Workgroups, a special version with integrated peer-to-peer networking features and a version number of 3.11, was released. It was sold along with Windows 3.1. Support for Windows 3.1 ended on December 31, 2001.[21]
Windows 3.2, released 1994, is an updated version of the Chinese version of Windows 3.1.[22] The update was limited to this language version, as it fixed only issues related to the complex writing system of the Chinese language.[23] Windows 3.2 was generally sold by computer manufacturers with a ten-disk version of MS-DOS that also had Simplified Chinese characters in basic output and some translated utilities.
Windows 9x
The next major consumer-oriented release of Windows, Windows 95, was released on August 24, 1995. While still remaining MS-DOS-based, Windows 95 introduced support for native 32-bit applications, plug and play hardware, preemptive multitasking, long file names of up to 255 characters, and provided increased stability over its predecessors. Windows 95 also introduced a redesigned, object oriented user interface, replacing the previous Program Manager with the Start menu, taskbar, and Windows Explorer shell. Windows 95 was a major commercial success for Microsoft; Ina Fried of CNET remarked that «by the time Windows 95 was finally ushered off the market in 2001, it had become a fixture on computer desktops around the world.»[24] Microsoft published four OEM Service Releases (OSR) of Windows 95, each of which was roughly equivalent to a service pack. The first OSR of Windows 95 was also the first version of Windows to be bundled with Microsoft’s web browser, Internet Explorer.[25] Mainstream support for Windows 95 ended on December 31, 2000, and extended support for Windows 95 ended on December 31, 2001.[26]
Windows 95 was followed up with the release of Windows 98 on June 25, 1998, which introduced the Windows Driver Model, support for USB composite devices, support for ACPI, hibernation, and support for multi-monitor configurations. Windows 98 also included integration with Internet Explorer 4 through Active Desktop and other aspects of the Windows Desktop Update (a series of enhancements to the Explorer shell which were also made available for Windows 95). In May 1999, Microsoft released Windows 98 Second Edition, an updated version of Windows 98. Windows 98 SE added Internet Explorer 5.0 and Windows Media Player 6.2 amongst other upgrades. Mainstream support for Windows 98 ended on June 30, 2002, and extended support for Windows 98 ended on July 11, 2006.[27]
On September 14, 2000, Microsoft released Windows Me (Millennium Edition), the last DOS-based version of Windows. Windows Me incorporated visual interface enhancements from its Windows NT-based counterpart Windows 2000, had faster boot times than previous versions (which however, required the removal of the ability to access a real mode DOS environment, removing compatibility with some older programs),[28] expanded multimedia functionality (including Windows Media Player 7, Windows Movie Maker, and the Windows Image Acquisition framework for retrieving images from scanners and digital cameras), additional system utilities such as System File Protection and System Restore, and updated home networking tools.[29] However, Windows Me was faced with criticism for its speed and instability, along with hardware compatibility issues and its removal of real mode DOS support. PC World considered Windows Me to be one of the worst operating systems Microsoft had ever released, and the fourth worst tech product of all time.[11]
Windows NT
Version history
Early versions (Windows NT 3.1/3.5/3.51/4.0/2000)
In November 1988, a new development team within Microsoft (which included former Digital Equipment Corporation developers Dave Cutler and Mark Lucovsky) began work on a revamped version of IBM and Microsoft’s OS/2 operating system known as «NT OS/2». NT OS/2 was intended to be a secure, multi-user operating system with POSIX compatibility and a modular, portable kernel with preemptive multitasking and support for multiple processor architectures. However, following the successful release of Windows 3.0, the NT development team decided to rework the project to use an extended 32-bit port of the Windows API known as Win32 instead of those of OS/2. Win32 maintained a similar structure to the Windows APIs (allowing existing Windows applications to easily be ported to the platform), but also supported the capabilities of the existing NT kernel. Following its approval by Microsoft’s staff, development continued on what was now Windows NT, the first 32-bit version of Windows. However, IBM objected to the changes, and ultimately continued OS/2 development on its own.[30][31]
Windows NT was the first Windows operating system based on a hybrid kernel. The hybrid kernel was designed as a modified microkernel, influenced by the Mach microkernel developed by Richard Rashid at Carnegie Mellon University, but without meeting all of the criteria of a pure microkernel.
The first release of the resulting operating system, Windows NT 3.1 (named to associate it with Windows 3.1) was released in July 1993, with versions for desktop workstations and servers. Windows NT 3.5 was released in September 1994, focusing on performance improvements and support for Novell’s NetWare, and was followed up by Windows NT 3.51 in May 1995, which included additional improvements and support for the PowerPC architecture. Windows NT 4.0 was released in June 1996, introducing the redesigned interface of Windows 95 to the NT series. On February 17, 2000, Microsoft released Windows 2000, a successor to NT 4.0. The Windows NT name was dropped at this point in order to put a greater focus on the Windows brand.[31]
Windows XP
The next major version of Windows NT, Windows XP, was released on October 25, 2001. The introduction of Windows XP aimed to unify the consumer-oriented Windows 9x series with the architecture introduced by Windows NT, a change which Microsoft promised would provide better performance over its DOS-based predecessors. Windows XP would also introduce a redesigned user interface (including an updated Start menu and a «task-oriented» Windows Explorer), streamlined multimedia and networking features, Internet Explorer 6, integration with Microsoft’s .NET Passport services, a «compatibility mode» to help provide backwards compatibility with software designed for previous versions of Windows, and Remote Assistance functionality.[32][33]
At retail, Windows XP was marketed in two main editions: the «Home» edition was targeted towards consumers, while the «Professional» edition was targeted towards business environments and power users, and included additional security and networking features. Home and Professional were later accompanied by the «Media Center» edition (designed for home theater PCs, with an emphasis on support for DVD playback, TV tuner cards, DVR functionality, and remote controls), and the «Tablet PC» edition (designed for mobile devices meeting its specifications for a tablet computer, with support for stylus pen input and additional pen-enabled applications).[34][35][36] Mainstream support for Windows XP ended on April 14, 2009. Extended support ended on April 8, 2014.[37]
After Windows 2000, Microsoft also changed its release schedules for server operating systems; the server counterpart of Windows XP, Windows Server 2003, was released in April 2003.[31] It was followed in December 2005, by Windows Server 2003 R2.
Windows Vista
After a lengthy development process, Windows Vista was released on November 30, 2006, for volume licensing and January 30, 2007, for consumers. It contained a number of new features, from a redesigned shell and user interface to significant technical changes, with a particular focus on security features. It was available in a number of different editions, and has been subject to some criticism, such as drop of performance, longer boot time, criticism of new UAC, and stricter license agreement. Vista’s server counterpart, Windows Server 2008 was released in early 2008.
Windows 7
On July 22, 2009, Windows 7 and Windows Server 2008 R2 were released as RTM (release to manufacturing) while the former was released to the public 3 months later on October 22, 2009. Unlike its predecessor, Windows Vista, which introduced a large number of new features, Windows 7 was intended to be a more focused, incremental upgrade to the Windows line, with the goal of being compatible with applications and hardware with which Windows Vista was already compatible.[38] Windows 7 has multi-touch support, a redesigned Windows shell with an updated taskbar with revealable jump lists that contain shortcuts to files frequently used with specific applications and shortcuts to tasks within the application,[39] a home networking system called HomeGroup,[40] and performance improvements.
Windows 8 and 8.1
Windows 8, the successor to Windows 7, was released generally on October 26, 2012. A number of significant changes were made on Windows 8, including the introduction of a user interface based around Microsoft’s Metro design language with optimizations for touch-based devices such as tablets and all-in-one PCs. These changes include the Start screen, which uses large tiles that are more convenient for touch interactions and allow for the display of continually updated information, and a new class of apps which are designed primarily for use on touch-based devices. The new Windows version required a minimum resolution of 1024×768 pixels,[41] effectively making it unfit for netbooks with 800×600-pixel screens.
Other changes include increased integration with cloud services and other online platforms (such as social networks and Microsoft’s own OneDrive (formerly SkyDrive) and Xbox Live services), the Windows Store service for software distribution, and a new variant known as Windows RT for use on devices that utilize the ARM architecture, and a new keyboard shortcut for screenshots.[42][43][44][45][46][47][48] An update to Windows 8, called Windows 8.1,[49] was released on October 17, 2013, and includes features such as new live tile sizes, deeper OneDrive integration, and many other revisions. Windows 8 and Windows 8.1 have been subject to some criticism, such as removal of the Start menu.
Windows 10
On September 30, 2014, Microsoft announced Windows 10 as the successor to Windows 8.1. It was released on July 29, 2015, and addresses shortcomings in the user interface first introduced with Windows 8. Changes on PC include the return of the Start Menu, a virtual desktop system, and the ability to run Windows Store apps within windows on the desktop rather than in full-screen mode. Windows 10 is said to be available to update from qualified Windows 7 with SP1, Windows 8.1 and Windows Phone 8.1 devices from the Get Windows 10 Application (for Windows 7, Windows 8.1) or Windows Update (Windows 7).[50]
In February 2017, Microsoft announced the migration of its Windows source code repository from Perforce to Git. This migration involved 3.5 million separate files in a 300 gigabyte repository.[51] By May 2017, 90 percent of its engineering team was using Git, in about 8500 commits and 1760 Windows builds per day.[51]
In June 2021, shortly before Microsoft’s announcement of Windows 11, Microsoft updated their lifecycle policy pages for Windows 10, revealing that support for their last release of Windows 10 will end on October 14, 2025.[52][53]
Windows 11
On June 24, 2021, Windows 11 was announced as the successor to Windows 10 during a livestream. The new operating system was designed to be more user-friendly and understandable. It was released on October 5, 2021.[54][55] As of May 2022, Windows 11 is a free upgrade to Windows 10 users who meet the system requirements.[56]
Windows 365
In July 2021, Microsoft announced it will start selling subscriptions to virtualized Windows desktops as part of a new Windows 365 service in the following month. It is not a standalone version of Windows, but a web service that provides access to Windows 10 and Windows 11 built on top of Azure Virtual Desktop. The new service will allow for cross-platform usage, aiming to make the operating system available for both Apple and Android users. The subscription service will be accessible through any operating system with a web browser. The new service is an attempt at capitalizing on the growing trend, fostered during the COVID-19 pandemic, for businesses to adopt a hybrid remote work environment, in which «employees split their time between the office and home». As the service will be accessible through web browsers, Microsoft will be able to bypass the need to publish the service through Google Play or the Apple App Store.[57][58][59][60][61]
Microsoft announced Windows 365 availability to business and enterprise customers on August 2, 2021.[62]
Multilingual support
Multilingual support has been built into Windows since Windows 3.0. The language for both the keyboard and the interface can be changed through the Region and Language Control Panel. Components for all supported input languages, such as Input Method Editors, are automatically installed during Windows installation (in Windows XP and earlier, files for East Asian languages, such as Chinese, and right-to-left scripts, such as Arabic, may need to be installed separately, also from the said Control Panel). Third-party IMEs may also be installed if a user feels that the provided one is insufficient for their needs.
Interface languages for the operating system are free for download, but some languages are limited to certain editions of Windows. Language Interface Packs (LIPs) are redistributable and may be downloaded from Microsoft’s Download Center and installed for any edition of Windows (XP or later) – they translate most, but not all, of the Windows interface, and require a certain base language (the language which Windows originally shipped with). This is used for most languages in emerging markets. Full Language Packs, which translates the complete operating system, are only available for specific editions of Windows (Ultimate and Enterprise editions of Windows Vista and 7, and all editions of Windows 8, 8.1 and RT except Single Language). They do not require a specific base language, and are commonly used for more popular languages such as French or Chinese. These languages cannot be downloaded through the Download Center, but available as optional updates through the Windows Update service (except Windows 8).
The interface language of installed applications is not affected by changes in the Windows interface language. The availability of languages depends on the application developers themselves.
Windows 8 and Windows Server 2012 introduces a new Language Control Panel where both the interface and input languages can be simultaneously changed, and language packs, regardless of type, can be downloaded from a central location. The PC Settings app in Windows 8.1 and Windows Server 2012 R2 also includes a counterpart settings page for this. Changing the interface language also changes the language of preinstalled Windows Store apps (such as Mail, Maps and News) and certain other Microsoft-developed apps (such as Remote Desktop). The above limitations for language packs are however still in effect, except that full language packs can be installed for any edition except Single Language, which caters to emerging markets.
Platform support
Windows NT included support for several platforms before the x86-based personal computer became dominant in the professional world. Windows NT 4.0 and its predecessors supported PowerPC, DEC Alpha and MIPS R4000 (although some of the platforms implement 64-bit computing, the OS treated them as 32-bit). Windows 2000 dropped support for all platforms, except the third generation x86 (known as IA-32) or newer in 32-bit mode. The client line of Windows NT family still runs on IA-32 but the Windows Server line ceased supporting this platform with the release of Windows Server 2008 R2.
With the introduction of the Intel Itanium architecture (IA-64), Microsoft released new versions of Windows to support it. Itanium versions of Windows XP and Windows Server 2003 were released at the same time as their mainstream x86 counterparts. Windows XP 64-Bit Edition, released in 2005, is the last Windows client operating systems to support Itanium. Windows Server line continues to support this platform until Windows Server 2012; Windows Server 2008 R2 is the last Windows operating system to support Itanium architecture.
On April 25, 2005, Microsoft released Windows XP Professional x64 Edition and Windows Server 2003 x64 Editions to support x86-64 (or simply x64), the 64-bit version of x86 architecture. Windows Vista was the first client version of Windows NT to be released simultaneously in IA-32 and x64 editions. x64 is still supported.
An edition of Windows 8 known as Windows RT was specifically created for computers with ARM architecture and while ARM is still used for Windows smartphones with Windows 10, tablets with Windows RT will not be updated. Starting from Windows 10 Fall Creators Update (version 1709) and later includes support for ARM-based PCs.[63]
Windows 11 is the first version to drop support for 32-bit hardware.[56]
Windows CE
Windows CE (officially known as Windows Embedded Compact), is an edition of Windows that runs on minimalistic computers, like satellite navigation systems and some mobile phones. Windows Embedded Compact is based on its own dedicated kernel, dubbed Windows CE kernel. Microsoft licenses Windows CE to OEMs and device makers. The OEMs and device makers can modify and create their own user interfaces and experiences, while Windows CE provides the technical foundation to do so.
Windows CE was used in the Dreamcast along with Sega’s own proprietary OS for the console. Windows CE was the core from which Windows Mobile was derived. Its successor, Windows Phone 7, was based on components from both Windows CE 6.0 R3 and Windows CE 7.0. Windows Phone 8 however, is based on the same NT-kernel as Windows 8.
Windows Embedded Compact is not to be confused with Windows XP Embedded or Windows NT 4.0 Embedded, modular editions of Windows based on Windows NT kernel.
Xbox OS
Xbox OS is an unofficial name given to the version of Windows that runs on Xbox consoles.[64] From Xbox One onwards it is an implementation with an emphasis on virtualization (using Hyper-V) as it is three operating systems running at once, consisting of the core operating system, a second implemented for games and a more Windows-like environment for applications.[65]
Microsoft updates Xbox One’s OS every month, and these updates can be downloaded from the Xbox Live service to the Xbox and subsequently installed, or by using offline recovery images downloaded via a PC.[66] It was originally based on NT 6.2 (Windows 
Xbox One and Xbox Series operating systems also allow limited (due to licensing restrictions and testing resources) backward compatibility with previous generation hardware,[69] and the Xbox 360’s system is backwards compatible with the original Xbox.[70]
Version control system
Up to and including every version before Windows 2000, Microsoft used an in-house version control system named Source Library Manager (SLM). Shortly after Windows 2000 was released, Microsoft switched to a fork of Perforce named Source Depot.[71] This system was used up until 2017 once the system couldn’t keep up with the size of Windows. Microsoft had begun to integrate Git into Team Foundation Server in 2013, but Windows continued to rely on Source Depot.[citation needed] The Windows code was divided among 65 different repositories with a kind of virtualization layer to produce unified view of all of the code.
In 2017 Microsoft announced that it would start using Git, an open source version control system created by Linus Torvalds and in May 2017 they reported that has completed migration into the Git repository.[72][73][51]
VFSForGit
Because of its large, decades-long history, however, the Windows codebase is not especially well suited to the decentralized nature of Linux development that Git was originally created to manage.[citation needed] Each Git repository contains a complete history of all the files, which proved unworkable for Windows developers because cloning the whole repository takes several hours.[citation needed] Microsoft has been working on a new project called the Virtual File System for Git (VFSForGit) to address these challenges.[73]
In 2021 the VFS for Git has been superseded by Scalar.[74]
Timeline of releases
Version market share
As a percentage of desktop and laptop systems using Windows,[79] according to StatCounter data from October 2022.[80]
Use of Windows 10 has exceeded Windows 7 globally since early 2018.[81]
For desktop and laptop computers, according to Net Applications and StatCounter, which track the use of operating systems in devices that are active on the Web, Windows was the most used operating-system family in August 2021, with around 91% usage share according to Net Applications[82] and around 76% usage share according to StatCounter.[83]
Including personal computers of all kinds (e.g., desktops, laptops, mobile devices, and game consoles), Windows OSes accounted for 32.67% of usage share in August 2021, compared to Android (highest, at 46.03%), iOS’s 13.76%, iPadOS’s 2.81%, and macOS’s 2.51%, according to Net Applications[84] and 30.73% of usage share in August 2021, compared to Android (highest, at 42.56%), iOS/iPadOS’s 16.53%, and macOS’s 6.51%, according to StatCounter.[85]
Those statistics do not include servers (including so-called cloud computing, where Microsoft is known not to be a leader, with Linux used more than Windows), as Net Applications and StatCounter use web browsing as a proxy for all use.
Security
|
|
This section needs to be updated. Please help update this article to reflect recent events or newly available information. (May 2020) |
Early versions of Windows were designed at a time where malware and networking were less common, and had few built-in security features; they did not provide access privileges to allow a user to prevent other users from accessing their files, and they did not provide memory protection to prevent one process from reading or writing another process’s address space or to prevent a process from code or data used by privileged-mode code.
While the Windows 9x series offered the option of having profiles for multiple users, it had no concept of access privileges, allowing any user to edit others’ files. In addition, while it ran separate 32-bit applications in separate address spaces, protecting an application’s code and data from being read or written by another application, it did not protect the first megabyte of memory from userland applications for compatibility reasons. This area of memory contains code critical to the functioning of the operating system, and by writing into this area of memory an application can crash or freeze the operating system. This was a source of instability as faulty applications could accidentally write into this region, potentially corrupting important operating system memory, which usually resulted in some form of system error and halt.[86]
Windows NT was far more secure, implementing access privileges and full memory protection, and, while 32-bit programs meeting the DoD’s C2 security rating,[87] yet these advantages were nullified by the fact that, prior to Windows Vista, the default user account created during the setup process was an administrator account; the user, and any program the user launched, had full access to the machine. Though Windows XP did offer an option of turning administrator accounts into limited accounts, the majority of home users did not do so, partially due to the number of programs which required administrator rights to function properly. As a result, most home users still ran as administrator all the time. These architectural flaws, combined with Windows’s very high popularity, made Windows a frequent target of computer worm and virus writers.[88][89]
Furthermore, although Windows NT and its successors are designed for security (including on a network) and multi-user PCs, they were not initially designed with Internet security in mind as much, since, when it was first developed in the early 1990s, Internet use was less prevalent.[90]
In a 2002 strategy memo entitled «Trustworthy computing» sent to every Microsoft employee, Bill Gates declared that security should become Microsoft’s highest priority.[91][92]
Windows Vista introduced a privilege elevation system called User Account Control.[93] When logging in as a standard user, a logon session is created and a token containing only the most basic privileges is assigned. In this way, the new logon session is incapable of making changes that would affect the entire system. When logging in as a user in the Administrators group, two separate tokens are assigned. The first token contains all privileges typically awarded to an administrator, and the second is a restricted token similar to what a standard user would receive. User applications, including the Windows shell, are then started with the restricted token, resulting in a reduced privilege environment even under an Administrator account. When an application requests higher privileges or «Run as administrator» is clicked, UAC will prompt for confirmation and, if consent is given (including administrator credentials if the account requesting the elevation is not a member of the administrators group), start the process using the unrestricted token.[94]
Leaked documents published by WikiLeaks, codenamed Vault 7 and dated from 2013 to 2016, detail the capabilities of the CIA to perform electronic surveillance and cyber warfare,[95] such as the ability to compromise operating systems such as Windows.[96]
In August 2019, computer experts reported that the BlueKeep security vulnerability, CVE-2019-0708, that potentially affects older unpatched Windows versions via the program’s Remote Desktop Protocol, allowing for the possibility of remote code execution, may now include related flaws, collectively named DejaBlue, affecting newer Windows versions (i.e., Windows 7 and all recent versions) as well.[97] In addition, experts reported a Microsoft security vulnerability, CVE-2019-1162, based on legacy code involving Microsoft CTF and ctfmon (ctfmon.exe), that affects all Windows versions from Windows XP to the then most recent Windows 10 versions; a patch to correct the flaw is currently available.[98]
Microsoft releases security patches through its Windows Update service approximately once a month (usually the second Tuesday of the month), although critical updates are made available at shorter intervals when necessary.[99] Versions subsequent to Windows 2000 SP3 and Windows XP implemented automatic download and installation of updates, substantially increasing the number of users installing security updates.[100]
Today, Windows integrates the Windows Defender antivirus, which is seen as one of the best available.[101] Windows also implements Secure Boot, Control Flow Guard, ransomware protection, BitLocker disk encryption, a firewall, and Windows SmartScreen.
File permissions
All Windows versions from Windows NT 3 have been based on a file system permission system referred to as AGDLP (Accounts, Global, Domain Local, Permissions) in which file permissions are applied to the file/folder in the form of a ‘local group’ which then has other ‘global groups’ as members. These global groups then hold other groups or users depending on different Windows versions used. This system varies from other vendor products such as Linux and NetWare due to the ‘static’ allocation of permission being applied directly to the file or folder. However using this process of AGLP/AGDLP/AGUDLP allows a small number of static permissions to be applied and allows for easy changes to the account groups without reapplying the file permissions on the files and folders.
Alternative implementations
Owing to the operating system’s popularity, a number of applications have been released that aim to provide compatibility with Windows applications, either as a compatibility layer for another operating system, or as a standalone system that can run software written for Windows out of the box. These include:
- Wine – a free and open-source implementation of the Windows API, allowing one to run many Windows applications on x86-based platforms, including UNIX, Linux and macOS. Wine developers refer to it as a «compatibility layer»[102] and use Windows-style APIs to emulate Windows environment.
- CrossOver – a Wine package with licensed fonts. Its developers are regular contributors to Wine.
- Proton – A fork of Wine by Steam to run Windows games on Linux and other Unix-like OS.
- ReactOS – an open-source OS intended to run the same software as Windows, originally designed to simulate Windows NT 4.0, now aiming at Windows 7 compatibility. It has been in the development stage since 1996.
See also
- Wintel
References
- ^ «January 26, 2023—KB5022360 (OS Build 22621.1194) Preview». Microsoft Support. Microsoft.
- ^ «Releasing Windows 11 Build 22621.1192 to the Release Preview Channel». Windows Insider Blog. January 17, 2023.
- ^ «January 26, 2023—KB5022360 (OS Build 22621.1194) Preview». Microsoft Support. Microsoft.
- ^ «Announcing Windows 11 Insider Preview Build 22621.1250 and 22623.1250». Windows Insider Blog. February 2, 2023.
- ^ «Announcing Windows 11 Insider Preview Build 25290». Windows Insider Blog. February 1, 2023.
- ^ «App packages and deployment (Windows Store apps) (Windows)». Msdn.microsoft.com. Archived from the original on March 30, 2014. Retrieved April 5, 2014.
- ^ Bellis, Mary (October 4, 2019). «The Unusual History of Microsoft Windows». Retrieved January 13, 2023.
- ^ «Desktop Operating System Market Share Worldwide». StatCounter Global Stats.
- ^ Keizer, Gregg (July 14, 2014). «Microsoft gets real, admits its device share is just 14%». Computerworld. IDG. Archived from the original on August 21, 2016.
[Microsoft’s chief operating officer] Turner’s 14% came from a new forecast released last week by Gartner, which estimated Windows’ share of the shipped device market last year was 14%, and would decrease slightly to 13.7% in 2014. Android will dominate, Gartner said, with a 48% share this year
- ^ «RTOS: Embedded Real Time Operating Systems». microsoft.com. Microsoft. Archived from the original on December 15, 2014. Retrieved November 7, 2014.
- ^ a b «The 25 Worst Tech Products of All Time». PC World. IDG. May 26, 2006. Retrieved January 7, 2023.
- ^ «A history of Windows — Microsoft Windows». windows.microsoft.com. Archived from the original on June 11, 2016. Retrieved January 7, 2023.
- ^ Microsoft C 5.0: C Language Reference Guide. Microsoft. 1987. pp. 250–267.
- ^ «A legacy of Windows, part 1: Windows 1-2-3 – TechRepublic». TechRepublic. Archived from the original on March 27, 2017. Retrieved March 26, 2017.
- ^ «The Apple vs. Microsoft GUI Lawsuit». 2006. Archived from the original on March 4, 2008. Retrieved March 12, 2008.
- ^ «Apple Computer, Inc. v. MicroSoft Corp., 35 F.3d 1435 (9th Cir. 1994)». Archived from the original on December 14, 2007. Retrieved March 12, 2008.
- ^ «Windows Evolution». Soft32.com News. Archived from the original on February 8, 2008.
- ^ «Windows 3.0, released in 1990». www.coursehero.com/. Retrieved October 20, 2022.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: url-status (link) - ^ «Chronology of Personal Computer Software». Archived from the original on February 11, 2012.
- ^ «Microsoft Company». Archived from the original on May 14, 2008.
- ^ «Windows 3.1 Standard Edition Support Lifecycle». Archived from the original on January 12, 2012. Retrieved January 3, 2011.
- ^ «Microsoft Windows Simplified Chinese 3.2 Upgrade Is Available». Microsoft Support. Microsoft. Archived from the original on November 8, 2006.
- ^ «Microsoft Windows Simplified Chinese 3.2 Upgrade Is Available». Microsoft. October 30, 2003. Archived from the original on May 24, 2011. Retrieved September 4, 2009.
- ^ «Windows 95 turns 15: Has Microsoft’s OS peaked?». CNET/CNN Tech. August 25, 2010. Archived from the original on August 26, 2010. Retrieved August 22, 2012.
- ^ «Microsoft Internet Explorer Web Browser Available on All Major Platforms, Offers Broadest International Support». News Center. San Jose, California: Microsoft. April 30, 1996. Archived from the original on January 15, 2008. Retrieved February 14, 2011.
- ^ «Windows 95 Support Lifecycle». Microsoft. Archived from the original on November 22, 2012. Retrieved January 3, 2011.
- ^ «Windows 98 Standard Edition Support Lifecycle». Microsoft. Archived from the original on November 22, 2012. Retrieved January 3, 2011.
- ^ «Improving «Cold Boot» Time for System Manufacturers». Microsoft. December 4, 2001. Archived from the original on February 13, 2010. Retrieved August 26, 2010.
- ^ «Windows Millennium Edition: All About Me». PC World. Archived from the original on August 1, 2013. Retrieved May 21, 2013.
- ^ Custer, Helen (1993). Inside Windows NT. Redmond: Microsoft Press. ISBN 1-55615-481-X.
- ^ a b c Thurrott, Paul (January 24, 2003). «Windows Server 2003: The Road To Gold – Part One: The Early Years». Archived from the original on January 1, 2005. Retrieved May 28, 2012.
- ^ «Windows XP review». CNET. Archived from the original on May 26, 2013. Retrieved May 24, 2013.
- ^ «Windows XP Program Compatibility Wizard». ServerWatch. March 12, 2002. Retrieved November 13, 2021.
- ^ David Coursey (October 25, 2001). «The 10 top things you MUST know about Win XP». ZDNet. Archived from the original on April 3, 2009. Retrieved July 22, 2008.
- ^ David Coursey (August 31, 2001). «Your top Windows XP questions answered! (Part One)». ZDNet. CNET Networks. Archived from the original on December 19, 2007. Retrieved January 3, 2011.
- ^ «A Look at Freestyle and Mira». Paul Thurrott’s SuperSite for Windows. Penton. September 3, 2002. Retrieved January 3, 2011.[permanent dead link]
- ^ «Windows XP Professional Lifecycle Support». Archived from the original on February 27, 2013. Retrieved January 3, 2011.
- ^ Nash, Mike (October 28, 2008). «Windows 7 Unveiled Today at PDC 2008». Windows Experience Blog. Microsoft. Archived from the original on November 1, 2008. Retrieved November 11, 2008.
- ^ Kiriaty, Yochay; Goldshtein, Sasha (2009). «Windows 7 Taskbar APIs». docs.microsoft.com. Retrieved August 21, 2021.
- ^ LeBlanc, Brandon (October 28, 2008). «How Libraries & HomeGroup Work Together in Windows 7». Windows Experience Blog. Microsoft. Archived from the original on November 2, 2008. Retrieved November 11, 2008.
- ^ «New Windows 8 hardware specs hint at 7-inch tablets and a Microsoft Reader». ZDNet. Retrieved March 29, 2013.
- ^ Paul, Ian (July 5, 2021). «How to Take Screenshots in Windows 10, 8, and 7».
- ^ Case, Loyd. «Test Driving Windows 8 RTM». PC World. IDG. Retrieved January 7, 2023.
- ^ Rosoff, Matt. «Here’s Everything You Wanted To Know About Microsoft’s Upcoming iPad Killers». Business Insider. Archived from the original on January 22, 2013. Retrieved February 10, 2012.
- ^ «Announcing the Windows 8 Editions». Microsoft. April 16, 2012. Archived from the original on April 18, 2012. Retrieved April 17, 2012.
- ^ «Building Windows for the ARM processor architecture». Microsoft. Archived from the original on November 26, 2012. Retrieved November 21, 2012.
- ^ «Microsoft talks Windows Store features, Metro app sandboxing for Windows 8 developers». The Verge. Vox Media. May 17, 2012. Archived from the original on September 10, 2012. Retrieved September 8, 2012.
- ^ Miller, Michael. «Build: More Details On Building Windows 8 Metro Apps». PC Magazine. Archived from the original on February 17, 2012. Retrieved February 10, 2012.
- ^ «Windows 8.1 now available!». blogs.windows.com. Archived from the original on October 19, 2013. Retrieved October 31, 2013.
- ^ «Announcing Windows 10 – Windows Blog». September 30, 2014. Archived from the original on September 10, 2015. Retrieved September 30, 2014.
- ^ a b c Bright, Peter (May 24, 2017). «Windows switch to Git almost complete: 8,500 commits and 1,760 builds each day». Ars Technica. Condé Nast. Archived from the original on May 24, 2017.
- ^ a b «Window 10 Home and Pro Lifecycle». Microsoft. Retrieved July 2, 2021.
- ^ a b «Window 10 Enterprise and Education Lifecycle». Microsoft. Retrieved July 2, 2021.
- ^ Cox, George. «Windows 11 release date is October 5». The Spectrum. Retrieved September 18, 2021.
- ^ Warren, Tom (June 24, 2021). «Microsoft announces Windows 11, with a new design, Start menu, and more». The Verge. Retrieved June 24, 2021.
- ^ a b «Windows 11 Specs and System Requirements». Microsoft. Archived from the original on May 31, 2022. Retrieved May 31, 2022.
- ^ Foley, Mary Jo (July 14, 2021). «Microsoft brings Windows to the cloud with Windows 365 and Cloud PC». ZDNet. Retrieved July 14, 2021.
- ^ Tilley, Aaron (July 14, 2021). «Microsoft Aims to Put Windows in Hands of Apple, Android Users Through Hybrid Work». The Wall Street Journal. ISSN 0099-9660.
- ^ Higgins, Tim (June 23, 2021). «Apple’s Fight for Control Over Apps Moves to Congress and EU». The Wall Street Journal. ISSN 0099-9660.
- ^ «Microsoft unveils Windows 365, a Windows 10 PC in the cloud». Engadget. Retrieved July 15, 2021.
- ^ «Windows 365 Cloud PC | Microsoft». www.microsoft.com. Retrieved July 15, 2021.
- ^ Hill, Paul (August 2, 2021). «Microsoft announces the general availability of Windows 365». Neowin. Retrieved August 2, 2021.
- ^ Bott, Ed (October 7, 2019). «Windows 10 on Arm: What you need to know before you buy a Surface Pro X». ZDNet.
- ^ Anand Lal Shimpi. «The Xbox One – Mini Review & Comparison to Xbox 360/PS4». anandtech.com. Archived from the original on October 12, 2014. Retrieved October 21, 2014.
- ^ «Xbox One: Hardware and software specs detailed and analyzed – Three operating systems in one». ExtremeTech. Archived from the original on November 16, 2013. Retrieved December 1, 2013.
- ^ «How to use the Offline System Update Diagnostic Tool on Xbox One». Xbox Official Site. Microsoft. Archived from the original on April 27, 2021. Retrieved November 30, 2013.
- ^ «Xbox One Is «Literally a Windows Device»«. GameSpot. Archived from the original on December 27, 2015.
- ^ «New Xbox One Update Will Make Some Functionality 50 Percent Faster». GameSpot. Archived from the original on February 2, 2016.
- ^ Tom Warren (June 16, 2015). «Xbox One dashboard update includes a huge new design and Cortana». The Verge. Vox Media. Archived from the original on July 8, 2017.
- ^ Eric Qualls. «Xbox 360 and Xbox Games Backwards Compatibility». About.com Tech. Archived from the original on September 28, 2015.
- ^ Chen, Raymond (January 22, 2018). «The history of change-packing tools at Microsoft (so far)». The Old New Thing. Retrieved April 17, 2022.
- ^ «The largest Git repo on the planet». Brian Harry’s Blog. May 24, 2017. Retrieved October 8, 2021.
- ^ a b Bright, Peter (February 6, 2017). «Microsoft hosts the Windows source in a monstrous 300GB Git repository». Ars Technica. Archived from the original on December 26, 2017. Retrieved December 26, 2017.
- ^ Frequently Asked Questions | VFS for Git on GitHub
- ^ «Microsoft Support Lifecycle». Microsoft. Archived from the original on October 11, 2008.
- ^ Chen, Raymond (July 22, 2019). «What was the code name for Windows 7?». The Old New Thing.
- ^ «Products Ending Support in 2024 – Microsoft Build». Microsoft. September 20, 2022.
- ^ «Products Ending Support in 2025 – Microsoft Build». Microsoft. September 20, 2022.
- ^ «Frequently Asked Questions». StatCounter. «Are laptops included in the desktop platform?».
- ^ «Desktop Windows Version Market Share Worldwide». StatCounter.
- ^ «Desktop Windows Version Market Share Worldwide | StatCounter Global Stats». StatCounter Global Stats. Retrieved November 24, 2019.
- ^ «Desktop Operating system market share: August 2021». Net Applications.
- ^ «Desktop Operating System Market Share Worldwide: August 2021». StatCounter.
- ^ «Operating system market share: August 2021». Net Applications.
- ^ «Operating System Market Share Worldwide: August 2021». StatCounter.
- ^ «Transcript: Chat with Ed Bott and Carl Siechert, Co-Authors of Microsoft Windows XP Inside Out». microsoft.com. Microsoft. November 21, 2001. Archived from the original on September 18, 2004. Retrieved April 20, 2019.
- ^ Russinovich, Mark (April 30, 1998). «Windows NT Security, Part 1». ITPro Today: IT News, How-Tos, Trends, Case Studies, Career Tips, More. Retrieved September 29, 2022.
- ^ Bruce Schneier (June 15, 2005). «Crypto-Gram Newsletter». Counterpane Internet Security, Inc. Archived from the original on June 6, 2007. Retrieved April 22, 2007.
- ^ Andy Patrizio (April 27, 2006). «Linux Malware On The Rise». InternetNews. QuinStreet. Archived from the original on February 5, 2012. Retrieved January 3, 2011.
- ^ «Telephones and Internet Users by Country, 1990 and 2005». Information Please Database. Archived from the original on May 22, 2009. Retrieved June 9, 2009.
- ^ Gates, Bill. «Bill Gates: Trustworthy Computing». Wired. ISSN 1059-1028. Retrieved September 29, 2022.
- ^ Verloy, Filip. «20 Years After Bill Gates’ Trustworthy Computing Memo, Cybersecurity Issues Are An Even Harder Problem». nonamesecurity.com. Retrieved September 29, 2022.
- ^ Northrup, Tony (June 1, 2005). «Windows Vista Security and Data Protection Improvements». TechNet. Microsoft Docs. Retrieved October 20, 2021.
In Windows Vista, the User Account Control (UAC) initiative introduces fundamental operating system changes to enhance the experience for the non-administrative user.
- ^ Kenny Kerr (September 29, 2006). «Windows Vista for Developers – Part 4 – User Account Control». Archived from the original on March 29, 2007. Retrieved March 15, 2007.
- ^ Greenberg, Andy (March 7, 2017). «How the CIA Can Hack Your Phone, PC, and TV (Says WikiLeaks)». WIRED.
- ^ «Vault 7: Wikileaks reveals details of CIA’s hacks of Android, iPhone Windows, Linux, MacOS, and even Samsung TVs». Computing. March 7, 2017.
- ^ Greenberg, Andy (August 13, 2019). «DejaBlue: New BlueKeep-Style Bugs Renew The Risk Of A Windows worm». wired. Retrieved August 15, 2019.
- ^ Seals, Tara (August 14, 2019). «20-Year-Old Bug in Legacy Microsoft Code Plagues All Windows Users». ThreatPost.com. Retrieved August 15, 2019.
- ^ Ryan Naraine (June 8, 2005). «Microsoft’s Security Response Center: How Little Patches Are Made». eWeek. Ziff Davis Enterprise. Retrieved January 3, 2011.
- ^ John Foley (October 20, 2004). «Windows XP SP2 Distribution Surpasses 100 Million». InformationWeek. UBM TechWeb. Archived from the original on May 27, 2010. Retrieved January 3, 2011.
- ^ «Test antivirus software for Windows 10 – June 2022». www.av-test.org. Retrieved September 29, 2022.
- ^ «Wine». Winehq.org. Archived from the original on April 4, 2014. Retrieved April 5, 2014.
External links
- Official website
- Official Windows Blog
- Microsoft Developer Network
- Windows Developer Center
- Microsoft Windows History Timeline
- Pearson Education, InformIT – History of Microsoft Windows
- Microsoft Business Software Solutions
- Windows 10 release Information
Здравствуйте, начинающие пользователи компьютера! Вместе с вами постараемся разобраться в том, что такое Windows и зачем оно нам нужно.
Windows — это операционная система, сделанная корпорацией Microsoft (Майкрософт). Операционная система (ОС) — это главная программа, которая запускается при включении компьютера. Она позволяет пользователям компьютера работать с файлами, пользоваться Интернетом и запускать в окошках другие программы, игры, фильмы, музыку. Windows переводится как «окна».
Операционная система Windows платная. Если вы покупаете компьютер с уже установленной Windows, то часть денег вы платите за операционную систему. Для подтверждения того, что вы являетесь владельцем Windows, может потребоваться лицензионный ключ. Такое бывает, например, если вы переустановили Windows. Лицензионный ключ это набор символов вида «XXXXX-XXXXX-YYYYY-YYYYY-ZZZZZ». Он может быть указан в наклейке на корпусе вашего компьютера или на диске с Windows. Перепишите лицензионный ключ на листок и сохраните, может пригодиться. Наклейка выглядит примерно так:
Вместе с Windows на компьютер устанавливается набор программ, необходимых для повседневного использования:
- Калькулятор.
- Редактор Notepad (блокнот) для работы с текстовыми файлами.
- Редактор WordPad для работы с документами.
- Редактор картинок Paint.
- Браузер Edge или Internet Explorer для работы в Интернет.
- Проигрыватель видео и музыки.
- Антивирус от Microsoft (защитник).
- другие программы и даже игры.
Можно устанавливать другие программы и игры из Интернета или с дисков. Такие программы также могут быть платные.
История и разновидности Windows
Даты выхода ОС Windows для персональных компьютеров (ПК):
- Windows 1.0 (1985)
- Windows 2.0 — 2.1 (1987-1988)
- Windows 3.0 — 3.2 (1990-1994)
- Windows NT 3.1 — 3.51 (1993-1995)
- Windows 95 — Windows 4.0 (1995)
- Windows NT 4.0 (1996)
- Windows 98 — Windows 4.1 (1998)
- Windows 2000 — Windows NT 5.0 (1999)
- Windows ME — Windows 4.9 (2000)
- Windows XP — Windows NT 5.1 — 5.2 (2001-2005)
- Windows Vista — Windows NT 6.0 (2006)
- Windows 7 — Windows NT 6.1 (2009)
- Windows 8 — Windows NT 6.2 (2012)
- Windows 8.1 — Windows NT 6.3 (2013)
- Windows 10 — Windows NT 10.0 (2015)
- Windows 11 — Windows NT 10.0 (2021)
В последних версиях Windows есть сборки, отличающиеся функционалом и ценой:
- Home Edition — сборка для домашнего использования с простой конфигурацией.
- Professional — сборка с дополнительным функционалом для более продвинутых пользователей.
- Enterprise — корпоративная версия для организаций.
Интерфейс Windows
Интерфейс — это внешний вид операционной системы. У отдельных частей интерфейса есть свои названия.
- Рабочий стол — основное место, занимает большую часть экрана. Здесь можно располагать ярлыки.
- Панель задач — здесь можно закреплять программы, с которыми вы чаще всего работаете. Здесь же показываются открытые в данный момент программы, выбранный язык, дата и время.
- Кнопка ПУСК — при нажатии открывается меню для быстрого доступа к программам.
- Ярлык — картинка, при нажатии на которые открывается соответствующая программа или документ.
Кнопка ПУСК может также находиться на вашей клавиатуре.
Внешний вид меню ПУСК:
Ссылки
Linux — что это такое?
Разновидности операционных систем
Рассмотрим какие ещё бывают операционные системы, кроме Windows. Речь пойдёт об операционных системах для персональных компьютеров. Не будем акцентировать внимание на операционных системах для серверов, мобильных телефонов и специализированной техники.
- MacOS — операционная система от компании Apple. Установлена как основная операционная система на продуктах компании. Платная.
- Linux — операционная система распространяется бесплатно. Сложна в освоении, поэтому мало распространена. Имеет несколько разновидностей (модификаций), которые поддерживаются различными компаниями и сообществами, например:
- Ubuntu
- Fedora
- Elementary OS
- Chrome OS
- OpenSuse
- Linux Mint
- Mageia
- PCLinuxOS
- Manjaro
- Arch
- Puppy
- и ещё много других
- FreeBSD — современная операционная система семейства UNIX, распространяется свободно.
Интересные факты об операционных системах
На одном компьютере может быть установлено одновременно несколько операционных систем. В этом случае при включении компьютера вас спросят, какую операционную систему нужно загрузить.
Microsoft Windows и ядро Linux могут быть запущены одновременно на одной и той же машине с помощью специального программного обеспечения CoLinux. В windows 10 уже появилась встроенная подсистема linux.
Для обучения пользователей обращению с мышкой в Microsoft разработали и внедрили в Windows компьютерную версию игры Reversi. Таким образом пользователи привыкали использовать мышь, кликая с её помощью на фишки. Задумайтесь, для чего сделана игра «сапёр»?
На рекламу Windows 95 было потрачено более 300 миллионов долларов.
В Windows нельзя создать папку с названиями con, prn, aux, nul. Это ограничение восходит относят к временам операционной системы MS-DOS. Некоторые слова были зарезервированы для обозначения устройств ввода-вывода, поэтому нельзя создать папки с такими именами.
Линус Торвальдс использовал операционную систему Minix, однако был недоволен многими ограничениями в ней и решил написать свою систему. Когда была выпущена более-менее стабильная версия, интерес Торвальдса к проекту угас, и он был готов его забросить. Но в тот же период он случайно испортил раздел на жёстком диске, где стояла Minix, и вместо её переустановки Торвальдс решил всё-таки закончить начатое. Так благодаря случайности появилось ядро Linux и впоследствии ОС GNU/Linux.
На данный момент более 75% серверов обеспечивающие надежную работу Интернет работают под управлением Linux.
MenuetOS — самая маленькая операционная система. Написана на ассемблере и помещается на дискету.
Операцио́нная
систе́ма, сокр. ОС (англ. operating
system, OS) – комплекс управляющих и
обрабатывающих программ,
которые, с одной стороны, выступают
как интерфейс между
устройствами вычислительной
системы и прикладными
программами,
а с другой стороны – предназначены
для управления устройствами,
управления вычислительными
процессами,
эффективного распределения вычислительных
ресурсов между
вычислительными процессами и организации
надёжных вычислений. Это определение
применимо к большинству современных
операционных систем общего назначения.
В логической структуре типичной вычислительной
системы операционная
система занимает положение
между устройствами с
их микроархитектурой, машинным
языком и,
возможно, собственными
встроенными микропрограммами –
с одной стороны – и прикладными
программами с
другой. Разработчикам программного
обеспечения операционная
система позволяет абстрагироваться от
деталей реализации и функционирования
устройств, предоставляя минимально
необходимый набор функций. В большинстве
вычислительных систем операционная
система является основной, наиболее
важной (а иногда и единственной)
частью системного
программного обеспечения.
С 1990-х годов наиболее распространёнными
операционными системами являются
системы семейства Windows и
системы класса UNIX (особенно Linux и Mac
OS).
Операционная
система (ОС)
— это комплекс программного обеспечения,
предназначенный для снижения стоимости
программирования, упрощения доступа к
системе, повышения эффективности работы.
Назначение операционной системы можно
разделить на четыре основные составляющие:
1.
Организация (обеспечение) удобного
интерфейса между приложениями и
пользователями, с одной стороны, и
аппаратурой компьютера – с другой.
Вместо реальной аппаратуры компьютера
ОС представляет пользователю расширенную
виртуальную машину, с которой удобнее
работать и которую легче программировать.
2.
Организация эффективного использования
ресурсов компьютера. ОС не только
представляет пользователям и программистам
удобный интерфейс к аппаратным средствам
компьютера, но и является своеобразным
диспетчером ресурсов компьютера. К
числу основных ресурсов современных
вычислительных систем относятся
процессоры, основная память, таймеры,
наборы данных, диски, накопители,
принтеры, сетевые устройства, и др. Эти
ресурсы определяются операционной
системой между выполняемыми программами.
В отличие от программы, которая является
статическим объектом, выполняемая
программа – это динамический объект,
он называется процессом и является
базовым понятием современных ОС.
3.
Облегчение процессов эксплуатации
аппаратных и программных средств
вычислительной системы. Ряд операционных
систем имеет в своем составе наборы
служебных программ, обеспечивающие
резервное копирование, архивацию данных,
проверку, очистку и дефрагментацию
дисковых устройств и др. Кроме того,
современные ОС имеют достаточно большой
набор средств и способов диагностики
и восстановления работоспособности
системы.
Сюда
относятся:
—
диагностические программы для выявления
ошибок в конфигурации ОС;
—
средства восстановления последней
работоспособной конфигурации;
—
средства восстановления поврежденных
и пропавших системных файлов и др.
4.
Возможность развития. Современные ОС
организуются таким образом, что допускают
эффективную разработку, тестирование
и внедрение новых системных функций,
не прерывая процесса нормального
функционирования вычислительной
системы. Большинство операционных
систем постоянно развиваются (нагляден
пример Windows).
Функции
операционной системы:
—
связь с пользователем в реальном времени
для подготовки устройств к работе,
переопределение конфигурации и изменения
состояния системы.
—
выполнение операций ввода-вывода; в
частности, в состав операционной системы
входят программы обработки прерываний
от устройств ввода-вывода, обработки
запросов к устройствам ввода-вывода и
распределения этих запросов между
устройствами.
—
управление памятью, связанное с
распределением оперативной памяти
между прикладными программами.
—
управление файлами; основными задачами
при этом являются обеспечение защиты,
управление выборкой и сохранение
секретности хранимой информации.
—
обработка исключительных условий во
время выполнения задачи
—
появление арифметической или машинной
ошибки, прерываний, связанных с
неправильной адресацией или выполнением
привилегированных команд.
—
вспомогательные, обеспечивающие
организацию сетей, использование
служебных программ и языков высокого
уровня.
Операционные
системы разные, но их назначение и
функции одинаковые. Операционная система
является базовой и необходимой
составляющей программного обеспечения
компьютера, без нее компьютер не может
работать в принципе.
Назначение
операционной системы
Операционная
система (ОС) — это комплекс программного
обеспечения, предназначенный для
снижения стоимости программирования,
упрощения доступа к системе, повышения
эффективности работы. Цель создания
операционной системы — получить
экономический выигрыш при использовании
системы, путем увеличения производительности
труда программистов и эффективности
работы оборудования.
Функции
операционной системы:
– связь
с пользователем в реальном времени для
подготовки устройств к работе,
переопределение конфигурации и изменения
состояния системы.
– выполнение
операций ввода-вывода; в частности, в
состав операционной системы входят
программы обработки прерываний от
устройств ввода-вывода, обработки
запросов к устройствам ввода-вывода и
распределения этих запросов между
устройствами.
– управление
памятью, связанное с распределением
оперативной памяти между прикладными
программами.
– управление
файлами; основными задачами при этом
являются обеспечение защиты, управление
выборкой и сохранение секретности
хранимой информации.
– обработка
исключительных условий во время
выполнения задачи, появление арифметической
или машинной ошибки, прерываний, связанных
с неправильной адресацией или выполнением
привилегированных команд.
– вспомогательные,
обеспечивающие организацию сетей,
использование служебных программ и
языков высокого уровня.
Основные
функции
-
Исполнение
запросов программ (ввод и вывод данных,
запуск и остановка других программ,
выделение и освобождение дополнительной
памяти и др.). -
Загрузка
программ в
оперативную память и их выполнение. -
Стандартизованный
доступ к периферийным устройствам
(устройства
ввода-вывода). -
Управление
оперативной памятью (распределение
между процессами, организация виртуальной
памяти). -
Управление
доступом к данным на энергонезависимых
носителях (таких как жёсткий
диск, оптические
диски и
др.), организованным в той или иной файловой
системе. -
Обеспечение пользовательского
интерфейса. -
Сохранение
информации об ошибках системы.
Дополнительные
функции:
-
Параллельное
или псевдопараллельное выполнение
задач (многозадачность). -
Эффективное
распределение ресурсов вычислительной
системы между процессами. -
Разграничение
доступа различных процессов к ресурсам. -
Организация
надёжных вычислений (невозможности
одного вычислительного процесса
намеренно или по ошибке повлиять на
вычисления в другом процессе), основана
на разграничении доступа к ресурсам. -
Взаимодействие
между процессами:
обмен данными, взаимная синхронизация. -
Защита
самой системы, а также пользовательских
данных и программ от действий пользователей
(злонамеренных или по незнанию) или
приложений. -
Многопользовательский
режим работы и разграничение прав
доступа.
Компоненты
операционной системы:
– Загрузчик;
– Ядро;
– Командный
процессор (Интерфейс);
– Драйверы устройств;
– Встроенное
программное обеспечение;
–Прилагаемое
программное обеспечение;
Понятие
Существуют
две группы определений операционной
системы: «набор программ, управляющих
оборудованием» и «набор программ,
управляющих другими программами». Обе
они имеют свой точный технический смысл,
который связан с вопросом, в каких
случаях требуется операционная система.
Есть приложения вычислительной техники,
для которых операционные системы
излишни. Например, встроенные микрокомпьютеры,
содержащиеся во многих бытовых приборах,
автомобилях (иногда по десятку в каждом),
простейших сотовых телефонах, постоянно
исполняют лишь одну программу,
запускающуюся по включении. Многие
простые игровые приставки – также
представляющие собой специализированные
микрокомпьютеры – могут обходиться
без операционной системы, запуская при
включении программу, записанную на
вставленном в устройство «картридже»
иликомпакт-диске.
Операционные
системы нужны, если:
-
вычислительная
система используется для различных
задач, причём программы, решающие эти
задачи, нуждаются в сохранении данных
и обмене ими. Из этого следует необходимость
универсального механизма сохранения
данных; в подавляющем большинстве
случаев операционная система отвечает
на неё реализацией файловой системы.
Современные системы, кроме того,
предоставляют возможность непосредственно
«связать» вывод одной программы со
вводом другой, минуя относительно
медленные дисковые операции; -
различные
программы нуждаются в выполнении одних
и тех же рутинных действий. Например,
простой ввод символа с клавиатуры и
отображение его на экране может
потребовать исполнения сотен машинных
команд, а дисковая операция – тысяч.
Чтобы не программировать их каждый раз
заново, операционные системы
предоставляют системные
библиотеки часто
используемых подпрограмм (функций); -
между
программами и пользователями системы
необходимо распределять полномочия,
чтобы пользователи могли защищать свои
данные от несанкционированного доступа,
а возможная ошибка в программе не
вызывала тотальных неприятностей; -
необходима
возможность имитации «одновременного»
исполнения нескольких программ на
одном компьютере (даже содержащем лишь
один процессор), осуществляемой с
помощью приёма, известного как «разделение
времени». При этом специальный
компонент, называемый планировщиком,
делит процессорное время на короткие
отрезки и предоставляет их поочерёдно
различным исполняющимся программам
(процессам); -
оператор
должен иметь возможность так или иначе
управлять процессами выполнения
отдельных программ. Для этого служат
операционные среды – оболочка и
наборы утилит – они могут являться
частью операционной системы.
Таким
образом, современные универсальные
операционные системы можно охарактеризовать,
прежде всего, как: – использующие
файловые системы (с универсальным
механизмом доступа к данным); –
многопользовательские (с разделением
полномочий); – многозадачные (с разделением
времени).
Многозадачность
и распределение полномочий требуют
определённой иерархии привилегий
компонентов самой операционной системе.
В составе операционной системы различают
три группы компонентов:
а.)
– ядро,
содержащее планировщик; – драйверы
устройств, непосредственно управляющие
оборудованием; – сетевая подсистема,
файловая система;
б.)
– системные
библиотеки;
в.)
– оболочкасутилитами.
Большинство
программ, как системных (входящих в
операционную систему), так и прикладных,
исполняются в непривилегированном
(«пользовательском») режиме работы процессораи получают доступ к оборудованию (и, при
необходимости, к другим ресурсам ядра,
а также ресурсам иных программ) только
посредством системных
вызовов. Ядро исполняется в
привилегированном режиме: именно в этом
смысле говорят, что система (точнее, её
ядро) управляет оборудованием.
В
определении состава операционной
системы значение имеет критерий
операциональной целостности (замкнутости):
система должна позволять полноценно
использовать (включая модификацию) свои
компоненты. Поэтому в полный состав
операционной системы включают и набор
инструментальных средств (от текстовых
редакторов до компиляторов, отладчиков
и компоновщиков).
Ядро
операционной системы
Ядро –
центральная часть операционной системы,
управляющая выполнением процессов,
ресурсами вычислительной
системы и
предоставляющая процессам координированный
доступ к этим ресурсам. Основными
ресурсами являются процессорное
время, памятьиустройства
ввода-вывода.
Доступ к файловой
системе и
сетевое взаимодействие также могут
быть реализованы на уровне ядра. Как
основополагающий элемент операционной
системы, ядро представляет собой наиболее
низкий уровень абстракции для доступа
приложений к ресурсам вычислительной
системы, необходимым для их работы. Как
правило, ядро предоставляет такой доступ
исполняемым процессам соответствующих
приложений за счёт использования
механизмов межпроцессного
взаимодействияи обращения
приложений к системным вызовам ОС.
Описанная задача может различаться в
зависимости от типа архитектуры ядра
и способа её реализации.
Объекты
ядра ОС:
– Процессы;
–Файлы; –
События; –Потоки;
–Семафоры;
–Мьютексы;
–Каналы;
–Файлы,
проецируемые в память;
Пакетный
режим
Необходимость
оптимального использования дорогостоящих
вычислительных ресурсов привела к
появлению концепции «пакетного режима»
исполнения программ. Пакетный режим
предполагает наличие очереди программ
на исполнение, причём система может
обеспечивать загрузку программы с
внешних носителей данных в оперативную
память, не дожидаясь завершения исполнения
предыдущей программы, что позволяет
избежать простоя процессора.
Разделение
времени и многозадачность
Уже
пакетный режим в своём развитом варианте
требует разделения процессорного
времени между выполнением нескольких
программ. Необходимость в разделении
времени (многозадачности,
мультипрограммировании) проявилась
ещё сильнее при распространении в
качестве устройств ввода-вывода
телетайпов (а позднее, терминалов с
электронно-лучевыми дисплеями) (1960-е
годы). Поскольку скорость клавиатурного
ввода (и даже чтения с экрана) данных
оператором много ниже, чем скорость
обработки этих данных компьютером,
использование компьютера в «монопольном»
режиме (с одним оператором) могло привести
к простою дорогостоящих вычислительных
ресурсов. Разделение времени позволило
создать «многопользовательские»
системы, в которых один (как
правило) центральный
процессор и
блок оперативной памяти соединялся с
многочисленными терминалами. При этом
часть задач (таких как ввод или
редактирование данных оператором) могла
исполняться в режиме диалога, а другие
задачи (такие как массивные вычисления) –
в пакетном режиме.
Разделение
полномочий
Распространение
многопользовательских систем потребовало
решения задачи разделения полномочий,
позволяющей избежать возможности
изменения исполняемой программы или
данных одной программы в памяти компьютера
другой программой (намеренно или по
ошибке), а также изменения самой системы
прикладной программой. Реализация
разделения полномочий в операционных
системах была поддержана разработчиками
процессоров, предложивших архитектуры
с двумя режимами работы процессора –
«реальным» (в котором исполняемой
программе доступно всё адресное
пространствокомпьютера) и
«защищённым» (в котором доступность
адресного пространства ограничена
диапазоном, выделенным при запуске
программы на исполнение).
Масштаб
реального времени
Применение
универсальных компьютеров для управления
производственными процессами потребовало
реализации «масштаба реального времени»
(«реального времени») — синхронизации
исполнения программ с внешними физическими
процессами.
Включение
функции масштаба реального времени
позволило создавать решения, одновременно
обслуживающие производственные процессы
и решающие другие задачи (в пакетном
режиме и/или в режиме разделения времени).
Файловые
системы и структуры
Постепенная
замена носителей с последовательным
доступом (перфолент,перфокарт,магнитных
лент) накопителями произвольного
доступа (намагнитных
дисках).
Файловая
система –
способ хранения данных на внешних
запоминающих устройствах.
Основные
характеристики операционной системы
UNIX
Операционная
система UNIX разработана в 70-х годах Кеном
Томпсоном и Деннисом Ритчи в Bell Laboratory
и первоначально предназначалась для
проведения исследовательских работ.
Однако концептуальная целостность
системы и целый ряд новых нетрадиционных
и прогрессивных решений, заложенных в
нее при создании, показали преимущества
UNIX по сравнению с другими операционными
системами этого класса. Система UNIX
быстро распространилась и сейчас активно
используется на многих вычислительных
установках. В нашей стране аналогом
операционной системы UNIX является ИНМОС.
Сначала эта система была ориентирована
на СМ ЭВМ, а затем перенесена и в сферу
ЕС ЭВМ. К несомненным достоинствам UNIX
следует отнести:– концептуальное
единство; – простоту; – инструментальность;
– мобильность; – эффективность.
Концептуальное единство заключается
в том, что система UNIX «обозрима», и
пользователь, работающий с ней, как
правило, не только использует ее
возможности, но и хорошо представляет,
как они реализуются. Простота системы
проистекает из того условия, что средства
системы выразительны и имеют удобную
мнемонику. Допускается изучение по
частям, что дает возможность пользователю
ограничиться изучением только того
набора средств, который ему в данный
момент необходим. Инструментальность
проявляется в насыщении различными
инструментальными средствами, облегчающими
процесс конструирования программного
обеспечения. Их можно разделить на
следующие группы: – утилиты различного
назначения; – средства работы с текстами;
– средства поддержки разработок
программного обеспечения; – средства
генерации программ анализа; – интерпретатор
shell, являющийся важным инструментальным
средством, позволяющий на уровне
командного языка строить новые
инструментальные средства проблемной
направленности. Мобильность означает
возможность переноса системы с одной
машинной архитектуры на другую с
минимальными затратами. Эффективность
заключается в конструктивных особенностях,
реализованных в системе, освобождающих
пользователя от решения многих проблем,
свойственных другим системам, и
значительно повышают продуктивность
практического использования системы
для решения самых разнообразных задач.
Недостатки
системы:
— не
поддерживается режим реального времени
— слабая
устойчивость к аппаратным сбоям
— снижение
эффективности при решении однотипных
задач
— слабо
развиты средства взаимодействия и
синхронизации процессов
Основные
характеристики операционной системы
MS-DOS
Операционная
система MS-DOS (дисковая операционная
система фирмы Microsoft), была разработана
в 1981 г. Билом Гейтсом — президентом фирмы
Microsoft, одновременно с машинами типа IBM
PC и стала для них доминирующей. К
настоящему времени разработано несколько
версий системы. MS-DOS во многом напоминает
по своим возможностям ОС UNIX. Предоставляемые
MS DOS возможности обеспечивают, с одной
стороны, удобный доступ к имеющимся
прикладным пакетам и программам для
непрофессиональных пользователей, с
другой стороны, создают хорошую среду
для разработки программного обеспечения.
MS DOS является стандартом для 16-разрядных
микро ЭВМ. В отличие от СР/М MS-DOS обеспечивает
организацию многоуровневых каталогов,
имеет более развитый командный язык.
Структура
MS-DOS.
Операционная
система MS-DOS состоит из трех основных
подсистем:
— модуль
взаимодействия с базовой системой
ввода-вывода (файл IO.SYS)
— собственно
операционная система, обеспечивающая
взаимодействие с программами пользователя.
Она состоит из программы файловой
системы, программ блочного обмена с
дисками и других встроенных операций
доступных программ пользователей
(MSDOS.SYS)
— командный
процессор (файл command.com) Все подсистемы
должны располагаться на диске, с которого
происходит загрузка операционной
системы. При запуске системы (любая
операция перезагрузки, либо при включении
питания) в память считывается и получает
управление специальная программа — так
называемая программа начальной загрузки.
Она помещается на все дискеты, чтобы
напечатать сообщение об ошибке при
попытке запустить систему с дискетой
в формате отличном от формата MS-DOS. При
получении управления программой
начальной загрузки просматривается
оглавление диска — проверяется, что
первые два файла — это IO.SYS и MSDOS.SYS. Если
они не обнаружены, на экран выдается
сообщение об ошибке, если обнаружены,
оба файла считываются в оперативную
память и управление передается в модуль
взаимодействия с базовой системой
ввода-вывода (IO.SYS). Подпрограмма
инициализации (начала работы) в IO.SYS
определяет состояние оборудования,
приводит в действие дисковую систему
и подключенные устройства, загружает
драйверы устройств и устанавливает
значения специальных управляющих
блоков, связанных с обработкой прерываний.
Затем она выполняет настройку адресов
в ядре MS DOS и передает ему управление.
Ядро MS DOS инициализирует свои внутренние
рабочие таблицы, создает управляющие
таблицы и возвращает управление модулю
взаимодействия с BIOS. Последнее действие
IO.SYS — загрузка командного процессора
по адресу, установленному подпрограммой
инициализации ядра MS DOS. Затем управление
передается COMMAND. COM. Модуль взаимодействия
с базовой системой ввода/вывода реализует
набор операций работы с дисками и
устройствами ввода/вывода. Только эта
часть MS DOS непосредственно взаимодействует
с внешними устройствами, только она
зависит от особенностей и характеристик
внешних устройств, используемых в
конкретных компьютерах. В ней определена
логика взаимодействия с устройствами
ввода-вывода адресов подключения, набор
команд контроллера дисков и т. д. Все
другие компоненты MS DOS общаются с внешним
миром только через модуль взаимодействия
с BIOS. Пользователь из своих прикладных
программ может обращаться к некоторым
MS DOS командам. Имеются программы для
ввода с клавиатуры, для вывода на терминал
и на печать, для формирования блоков
управления файлами, управления памятью,
обработки даты и времени, операций над
дисками, каталогами и файлами. Ядро MS
DOS реализует все функции, связанные с
файловой организацией информации на
дисках, управлением дисководами,
распределением пространства и работой
с их справочниками. MS DOS размещает
(форматирует) все диски и дискеты с
размером сектора 512 байт. Область для
MS DOS (вся дискета или раздел на твердом
диске) распределена следующим образом:
— блок
начальной загрузки
— таблица
размещения файлов
— копия
таблицы размещения файлов
— корневой
каталог
— область
данных
Файлам
выделяется пространство в области
данных по мере необходимости, когда
происходит фактическая запись;
предварительного распределения не
производится. Пространство выделяется
порциями, называемыми кластерами. На
односторонних дискетах кластер равен
одному блоку; на двухсторонних каждый
кластер состоит из двух блоков. Размер
кластера для твердого диска определяется
при разметке командой FORMAT и зависит от
размера раздела MS DOS. Таблица размещения
файлов (File Allocation Table — FAT) связывает
кластеры одного файла в цепочку. Кластеры
устроены так, что минимизированы
перемещения головок при работе с
многосторонними носителями. Все
пространство одной дорожки или одного
цилиндра заполняется информацией, после
чего происходит переход к следующий
дорожке или цилиндру. При этом сначала
используются последовательные секторы
для головки с наименьшим сектором, после
чего секторы следующей головки и так
далее до последней головки, затем
происходит переход к следующему цилиндру.
Файлы пишутся на диск в область данных
обязательно последовательно. Пространство
области данных распределяется по одному
кластеру, при этом уже занятые кластеры
пропускаются. Выделяется первый найденный
свободный кластер вне зависимости от
его физического расположения на диске.
Это обеспечивает наиболее эффективное
использование дискового пространства,
так как кластеры, освобожденные при
удалении файла, становятся доступными
для размещения новых файлов. Командный
процессор организует взаимодействие
системы с пользователем на языке команд
MS DOS. Он читает команды, введенные с
пульта оператора, анализирует их и
выполняет либо непосредственно
(встроенные команды), либо загрузив в
оперативную память программу,
соответствующую этой команде (загружаемые
команды), и передав ей управление.
Windows
3. 1 и Windows
3. 11
По
сути дела Windows 3.1 и 3.11 является всего-навсего
надстройкой над DOS, однако между ними
существуют серьёзные различия — именно
они позволяют называть Windows операционной
системой. Графический интерфейс, как
оказывается здесь не главное. В Windows вы
можете последовательно запустить
несколько (а не строго одно, как в DOS)
приложений и переключаться между ними
в процессе работы. Некоторые приложения,
в зависимости от задачи, могут продолжать
работать, находясь в запущенном, но
неактивном состоянии. В Windows используется
неактивный режим работы процессора
(protected mode), и программа пользователя уже
не может влезть в какую ей угодно область
памяти и делать там что вздумается.
Большим преимуществом Windows 3.11 стала
возможность работы в одно-ранговой сети
или с выделенным сервером. Теоретически,
можно забыть про приобретение специального
сетевого программного обеспечения и
обойтись только средствами Windows 3.11.
Однако на практике в локальной сети
всё-таки лучше ставить специальное
сетевое ПО, а уже поверх него — Windows 3.11.
Тем более что в Windows предусмотрена
поддержка не только своей сети, но и
других сетевых протоколов. Возможность
использования в программах виртуальной
памяти — (иными словами, выделение
программе шести мегабайт памяти на
машине с физическими четырьмя) также
весьма удобна. И хотя в таком режиме
компьютер заметно замедляет свою работу,
бывает очень важно, чтобы “требовательная”
программа работала уж как-нибудь, чем
никак. Windows распахивает перед пользователями
фантастический мир мультимедиа, измерения
которого системе DOS и не снились. DOS могла
позволить воспроизведение максимум
небольших мультфильмов — способности
Windows трудно перечислить: это компьютерные
игры, электронные энциклопедии,
интерактивная графика и многое другое.
По своим возможностям Windows значительно
превосходит DOS, но и требования к
аппаратным ресурсам компьютера
предъявляет немалые. Так, для работы в
защищённом режиме компьютер должен
быть оснащён как минимум 386-м процессором,
а уж памяти Windows потребляет исходя из
принципа “чем больше, тем лучше”. И
если DOS на “двушке” с мегабайтом памяти
работала быстро и уверенно, то Windows, даже
версии 3.0, на такой машине работает
крайне медленно. Сегодня совмещение
DOS + Windows на персональных компьютерах
встречается наиболее часто; для Windows
разработано несметное количество
приложений, игр и инструментария.
Windows
95
Windows
95 выделяется среди других систем по
совокупности своих характеристик:
удобства, совместимости, функциональных
возможностей и быстродействия. Создавая
Windows 95, корпорация Microsoft, по-видимому,
задумала такую систему, работать с
которой мог бы человек, не окончивший
даже среднюю школу. Инсталлировать
Windows 95 не сложнее, чем хлеба к обеду
нарезать. Правда преемственность
предыдущих версий Windows только этим не
ограничивается: Windows 95 имеет много общего
со своими предшественницами. Она
устанавливается, по сути дела, поверх
MS-DOS, и, честно говоря безразлично, что
она пишет в ответ на команду “ver” в
режиме DOS:MS-DOS version x.xx или Windows 95. Несмотря
на то что Windows 95 разрекламирована как
полноценная 32-разрядная операционная
система, в действительности же она имеет
16-разрядное ядро. Как это ни прискорбно,
для разработки 32-разрядных приложений
необходимо запускать специальные
утилиты — аналогично тому, как в Windows
3.11 ставился модуль Win32S. (Кстати, это и
есть тот же Win32S, только видоизменённый
для Windows 95). Из всех усовершенствований,
реализованных в Windows 95, для повышения
производительности работы пользователя,
вероятно, важнее всего значительные
усовершенствования в интерфейсе.
Изменения в нём, по сравнению с Windows 3.x
в самом деле поразительны, но не меньше
бросается в глаза то, как много в нем
заимствований из Mac OS и OS/2.
Например:
— при
нажатии правой кнопки мыши появляется
контекстно-зависимое меню (OS/2).
— корзина
“ Recicle Bin “, аналог Мусорного Ведра (“
Trasch “ Mac OS) и т. д.
— программы,
документы и ярлыки (указатели на другие
файлы могут размещаться на “Рабочем
столе “ (OS/2)). Поддержка сетевых протоколов
в Windows 95 немного расширилась по сравнению
с предыдущими версиями Windows: например,
появилась поддержка протокола TCP/IP; по
отношению к локальным сетям политика
не претерпела изменений. Сохранился
свой протокол обмена между компьютерами
и возможность поддержки других сетевых
протоколов. Новая ОС не только выполняет
подавляющее большинство существующих
программ для Windows 3.х и DOS, но и совместима
с драйверами реального режима для этих
систем. Использование таких драйверов
может ослабить устойчивость работы
32-разрядной системы, зато устраняет
сложности, возникающие из-за отсутствия
нужного драйвера для того или иного
периферийного устройства. Эту проблему
никак не удаётся решить ни в Windows NT ни в
OS/2 Warp. Требования Windows 95 к аппаратному
обеспечению несколько выросли по
сравнению с Windows 3.11. В первую очередь
они коснулись объёма оперативной памяти,
необходимой для нормальной работы.
Windows 95 вышла на рынок сравнительно
недавно, однако под неё написано уже
много приложений: ведущие производители
ПО связывают с ней большие надежды и
переводят свои популярные продукты на
рельсы Windows 95.
OS/2
Операционная
система OS/2, разработанная фирмой IBM,
даже в ранних версиях зарекомендовала
себя как весьма мощная ОС. Думаю, что не
ошибусь, сказав, что OS/2 стала первой
реально многозадачной операционной
системой на персоналках, к тому же в
своей основе она является
объектно-ориентированной. В общем-то,
складывается такое впечатление, что
если Windows разрабатывалась начиная с
интерфейса, то OS/2 создавалась, как и
положено операционным системам, начиная
с ядра. OS/2 является действительно
32-разрядной операционной системой, и
ей не требуется никаких дополнений для
работы с 32- разрядными приложениями.
Апологеты Windows довольно долго обвиняли
OS/2 в том, что она не “понимает” программ,
написанных для Windows, — что и говорить, их
число огромно, а некоторые из них
уникальны. Уже в версии 2.0 программисты
IBM исправили свою ошибку и включили в
OS/2 сессию Windows. И сделали они это, надо
отдать должное, весьма неплохо:
Windows-приложения стали работать на порядок
быстрее (кстати, DOS приложения под OS/2
тоже работают быстрее, нежели под DOS).
Первая версия OS/2 вообще не имела
графического интерфейса (presentation manager)
— он появился относительно недавно.
Правда, у ранних версий этой ОС и запросы
к аппаратному обеспечению сравнительно
невысоки. Так что если вам нужна реальная
многозадачность, но денег на мощный
компьютер не хватает, то ранние версии
OS/2 — это неплохой вариант решения данной
проблемы. Более поздние версии OS/2
получили графический интерфейс. И хотя
интерфейс OS/2 иногда обвиняют в том, что
с ним не возможно работать, многие не
склонны разделять это мнение; некоторые
пользователи, напротив, устанавливают
в Windows программу, реализующую интерфейс
от OS/2. Основное достоинство OS/2 — это,
несомненно, возможность работать в
режиме разделения времени. Она позволяет
выполнять вам несколько задач одновременно:
например, форматировать дискету и
одновременно компилировать программу.
При этом выполнение задач почти не
замедляется. Работа с сетями в OS/2
ориентирована в первую очередь на
поддержку протокола TCP/IP, однако система
неплохо работает и с другими протоколами,
например IPX. Нельзя не упомянуть и о том,
что недавно была выпущена локализованная
версия OS/2 Warp 3.0. Теперь стало проще
разбираться в многочисленных настройках
самой OS/2, а так же сеансов DOS и Windows. Само
собой разумеется, что широкие возможности
OS/2 обходятся пользователю недёшево. И
хотя IBM объявила, что OS/2 Warp работает на
386-м компьютере с четырьмя мегабайтами
оперативной памяти, специалисты замечают:
если вы хотите, чтобы OS/2 работала без
проблем, помножьте все аппаратные
требования, которые указаны в руководстве,
на два. В целом же, кто имел раньше дело
с Win 95, NT и Mac OS сочли OS/2 наименее удобной
в работе среди рассматриваемых ОС. Одним
из очень больших недостатков является
например то, что Warp позволяет удалять
файлы простым перемещением их на
пиктограмму Shredder (“Дробилка”), однако
по умолчанию она не может восстановить
файл, который был стёрт ошибочно. Она
не выдаёт предупреждений при попытке
удаления жизненно важных системных
файлов. OS/2 Warp 3.0 остаётся привлекательной
для тех, кто любит настраивать интерфейс
по своему вкусу и кому не требуется
очень много готовых прикладных пакетов.
Высококачественные средства
программирования, имеющиеся в данной
ОС, обеспечивают этой системе успех у
фирм, разрабатывающих собственное
программное обеспечение для внутреннего
пользования. Иными словами, имеет смысл
устанавливать в том случае, если вам
действительно необходим режим разделения
времени между задачами, а также
возможности, которые другие операционные
системы предоставить не могут.
Windows 98
Windows
98 позиционируется компанией Microsoft как
обновление для Windows 95. Сама Microsoft настаивает
на том, что, не будучи «революционно
новой», очередная ОС обеспечивает
прирост производительности системы и
большую стабильность в работе. Кроме
того, в Windows 98 реализован ряд новых
возможностей, позволяющих, к примеру,
работать с USB-устройствами, DVD-дисководами
и т.д. В Windows 98
значительно богаче набор средств для
диагностики и разрешения конфликтов,
чем в Windows 95,
включая Version Conflict Manager и Maintenance Wizard.
Microsoft предполагает, что благодаря этим
средствам уменьшение числа обращений
пользователей к службам технической
поддержки. Добавлена версия Internet
Explorer
4.0. Windows
98 улучшает качество воспроизведения
графики, звука и мультимедийных
приложений, созданных по новейшим
технологиям. Через некоторое время
появилась на свет вторая редакция
популярной операционной системы Windows
98 (полное название версии 4.10.2222). Windows 98
Second Edition – скорее, сборник апдейтов и
мелких дополнений, чем что-то революционно
новое. Во-первых, это новый Explorer версии
5.0. Во-вторых, в новой редакции системы
появился прокси-сервер ICS (Internet Connection
Sharing — совместное использование Internet),
который позволяет в небольшой локальной
сети организовать совместный доступ в
Интернет при помощи одного модема.
В-третьих, это новая версия NetMeeting — 3.0.
Последняя версия NetMeeting расширяет
возможности проведения сетевых
конференций, повышает быстродействие
и обеспечивает безопасность и поддержку
стандартов Интернета. В четвертых это
Service Pack, то есть сборник апдейтов и
устранений ошибок предыдущей версии
Windows. В-пятых, в систему введена поддержка
IEEE 1394 и ACPI, а также улучшена поддержка
USB.
Преимущества:
Простота
использования и доступа в Интернет.
Динамическая справочная система на
основе веб-технологии и 15 программ-мастеров
упрощают использование компьютера.
Веб-совместимый интерфейс пользователя
Windows 98 облегчает поиск, унифицируя
представление информации в компьютере,
локальной сети и Вебе. Второе издание
Windows 98 обеспечивает возможность
одновременного доступа в Интернет с
нескольких сетевых компьютеров через
одно общее подключение. Высокая
производительность и надежность.
Сокращение времени запуска приложений,
новые средства очистки диска и повышения
эффективности его работы. Все это стало
возможным благодаря новшествам,
превращающим Windows 98 в мощную и надежную
операционную систему. Поддержка
аппаратных средств нового поколения.
Использование преимуществ новейших
стандартов и технологий, таких как шина
USB, DVD и IEEE 1394, расширение возможностей
за счет подключения к одному компьютеру
нескольких мониторов, поддержка
технологий Digital Imaging и Microsoft WebTV для
Windows.
Windows
NT
С
такими операционными системами, как
Windows NT, рядовому пользователю приходится
сталкиваться довольно редко: разве что
где-нибудь на работе или на выставке.
Несмотря на то что Windows NT названием и
интерфейсом похожа на другие ОС корпорации
Microsoft, она значительно от них отличается
— Windows NT предназначена в первую очередь
для крупных сетей. Windows NT, в отличие от
Windows 3.11, является полноценной 32-разрядной
операционной системой с широкими
возможностями; благодаря развитым
сетевым возможностям она может
использоваться при интеграции нескольких
сетей. Система не поддерживает идеологию
Plug&Play. Однако, по целому ряду причин
для некоторых пользователей именно эта
ОС является наилучшей. Если характер
вашей работы таков, что любая порча
данных может обойтись очень дорого, то
серьёзные меры по обеспечению устойчивости
и безопасности, реализованные в Windows NT
могут быть спасением. Windows NT — система
скорее для корпоративных, чем для
домашних пользователей. В этой промышленной
версии Windows фирмы Microsoft основной упор
сделан на безопасность и надёжность в
ущерб всему остальному, в том числе и
удобству пользователя.
Windows 2000
В
феврале 2000 г. в Москве прошла презентация
новой системы Windows 2000.
Платформа Windows 2000 представляет собой
операционную систему нового поколения
для делового использования на самых
разнообразных компьютерах – от переносных
компьютеров до высококлассных серверов.
Данная операционная система основывается
на технологии NT и является наилучшей
операционной системой для ведения
коммерческой деятельности в Интернете.
Система является надежной: настольные
компьютеры, портативные компьютеры и
серверы, на которых используется
операционная система Windows 2000, работают
безотказно. Применение Windows 2000 снижает
затраты, так как упрощается управление
системой. Кроме того, это наилучшая
операционная система, которая позволяет
применять любое новейшее оборудование
— от самых маленьких мобильных устройств
и до самых больших серверов для электронной
коммерции. Операционная система Windows
2000 Professional объединяет присущую Windows 98
простоту использования в Интернете, на
работе, в пути, с присущими Windows
NT управляемостью,
надежностью и безопасностью. Семейство
Windows 2000 Server является новым поколением
удостоенной наград и пользующейся
коммерческим успехом операционной
системы Windows NT Server. Данное семейство
состоит из многоцелевых масштабируемых
сетевых операционных систем. Windows 2000
предоставит удобную в управлении
систему, обеспечивающую большую
работоспособность оборудования, а также
платформу для наиболее ответственных
приложений электронной коммерции и
ведения бизнеса в определенной области.
Windows 2000 Datacenter Server является самой
производительной и полнофункциональной
серверной операционной системой из
всех, когда-либо предлагавшихся
корпорацией Microsoft.
Эта система поддерживает до 64 ГБ
физической памяти, а также симметричную
мультипроцессорную обработку с
использованием до 32 процессоров. Ее
стандартные компоненты обеспечивают
4-узловую кластеризацию и балансировку
нагрузки. Она оптимизирована для работы
с большими хранилищами данных,
эконометрического анализа, моделирования
крупномасштабных процессов в науке и
технике, оперативной обработки транзакций
и объединения серверов. Служба каталогов
Microsoft Windows 2000 Active Directory является одним
из самых важных новшеств операционной
системы Windows 2000. Служба Active Directory
значительно упрощает управление
системой, усиливает систему безопасности
и расширяет возможности интеграции с
другими платформами. Ключевой особенностью,
обеспечивающей интеграцию, является
возможность синхронизации информации,
хранимой в каталоге Active Directory, с другими
хранилищами информации, в том числе со
службой каталогов Novell Directory Services (NDS) и
системными базами данных. Русскоязычные
версии Windows 2000 помимо полной поддержки
русского языка имеют поддержку
украинского, белорусского, казахского,
армянского, грузинского, азербайджанского,
узбекского, а также татарского языков.
Это значит, что пользователи локализованной
версии смогут создавать и редактировать
документы на перечисленных языках, при
том что интерфейс пользователя и
справочная система будут оставаться
на русском языке. Кроме того, в Windows 2000
локализованы и утилиты командной строки.
В Windows 2000 разработчики не только
постарались учесть опыт создания
NT-систем предыдущего поколения, сохранив
все их традиционные достоинства, но и
включили в нее много полезных наработок
из привычной в своей доступности и
простоте Windows 9x, как бы сблизив эти две
разные системы. Главное же и важнейшее
ее достоинство для нас с вами – это
совместимость с большинством программ
Windows 9x. При
этом надежность Windows 2000 на порядки выше,
чем у Windows 9x. Устойчивость работы Windows
2000 объясняется не только тем, что DOS в
ней отсутствует – система полностью
32-х разрядная, но и тем, что в ней, в
отличие от Windows 9x, применена так называемая
вытесняющая многозадачность. При таком
способе реализации многозадачности,
ни один процесс не сможет полностью
завладеть центральным процессором, а
получит в свое распоряжение лишь
небольшой кусочек времени работы CPU,
после чего процессор благополучно
перейдет к обслуживанию следующего
процесса – и так по кругу. Таким образом,
каждый процесс обрабатывается по очереди
под управлением специального диспетчера,
и зависшая программа принудительно
освобождает процессор, когда время, ей
отведенное на работу, истекает. При
появлении же сбоя достаточно снять
“повисшую” задачу, что никак не
отражается на деятельности всей системы
и других программ, так как друг на друга
они никак не влияют. По сравнению с
Windows NT, новая операционная система не
только значительно облагорожена приятным
внешним видом пользовательского
интерфейса, который не вызовет никаких
проблем у тех, кто видел Windows 9x, но и
заметно улучшена поддержка широкого
спектра нового оборудования. Система
воспринимает без проблем и Plug and Play, USB,
IEEE, ACPI, AGP, MMX, и даже FAT32. Таким образом,
наконец-то появилась операционная
система, которая хоть как-то может
заменить нам “капризного” монополиста
Windows 9x, позволив при этом не расстаться
с любимыми программами. В большинстве
случаев программы под Windows 2000 работают
даже быстрее, чем под Windows 9x.
Главный
недостаток Windows 2000 – большая требовательность
к аппаратной конфигурации персонального
компьютера, значительно превышающая
запросы Windows 9x. И хотя Microsoft и заявляет,
что минимум для нее – Pentium 133, 32Mb RAM,
2Гб HDD,
на деле же — это характеристики машины,
на которую Windows 2000 можно установить, но
не работать. В жизни же, рекомендуется
как минимум 96Mb ОЗУ, при которых уже можно
более-менее комфортно работать, лучше
128Мб и выше. Процессор необходим не хуже
Pentium 233МГц. 650 свободных мегабайт на
жестком диске, как написано в руководстве
Microsoft, также едва-едва хватит под саму
операционную систему – под раздел с ОС
надо отвести минимум 2-4Гб, иначе системные
программы придется ставить в другие
разделы.
Время прочтения
11 мин
Просмотры 59K
Несколько дней назад в сеть просочился образ ранней версии Windows 11. Различные издательства провели тесты по производительности и пришли к неутешительному выводу: Windows 11 в среднем работает хуже, чем Windows 10. Но расстраиваться рано! Проблемы производительности могут быть связаны с «сыростью» слитого образа и нюансами совместимости с текущими программами. Так или иначе, 24 июня состоится официальная презентация нового поколения операционных систем Windows, которая, возможно, даст ответы на многие вопросы. Если сегодня у вас есть настроение для ностальгии, предлагаем вам окунуться в мир Windows: познакомиться с историей, как менялась ось и что у нее внутри.
История Windows
В начале 80 годов прошлого века компания IBM работала над персональным компьютером на базе процессора Intel 8088. С середины 70 годов компания Microsoft была основным поставщиком Basic для восьмибитных микрокомпьютеров. Когда IBM обратилась к Microsoft для лицензирования Basic для их нового компьютера IBM PC, Microsoft согласилась, а также посоветовала обратиться к компании Digital Research для лицензирования операционной системы CP/M. Но, получилось так, что глава Digital Research не нашел в своем графике времени для встречи для IBM, и IBM снова обратилась к Microsoft, теперь уже с просьбой решить вопрос операционной системы для IBM PC. Microsoft купила клон ОС CP/M у компании Seattle Computer Products и перенесла её на IBM PC. Итоговым названием получившейся ОС стало MS-DOS 1.0.
IBM PC
Первые продукты с названием «Windows» от Microsoft не были операционными системами. Это были графические среды для MS-DOS. На фоне успеха, в том числе и коммерческого, пользовательского интерфейса на Apple Lisa, компания решила реализовать графический интерфейс на IBM PC с MS-DOS. В отличии от относительно дешевых IBM PC, Apple Lisa стоили дорого (почти 10 тысяч долларов), и немногие покупатели могли позволить купить их. Microsoft решила занять нишу дешевых компьютеров с графическим интерфейсом. При этом низкая стоимость достигалась экономией на комплектующих и более низкая производительность, по сравнению с Lisa, избежать не получилось. Так, в 1985, 1987 и в 1990 выходят первые три версии Windows — 1.0, 2.0 и 3.0. Причем за первые шесть месяцев после релиза Windows 3.0 было продано более 1 миллиона экземпляров. Дальнейшее развитие Windows можно разделить на два направления — Windows на базе MS-DOS и Windows на базе NT.
Windows 1.01
Windows 9x
Windows на базе MS-DOS или Windows 9x не были первыми ОС от Microsoft, но они продолжали «старые традиции» и были построены на основе 16-битного кода MS-DOS. В августе 1995 года была выпущена Windows 95 — первая система семейства Windows 9x. Она уже была полноценной операционной системой с соответствующими возможностями. Однако у системы были проблемы с безопасностью (например, не было «администратора») и с изоляцией приложений. Зависание 16-битного приложения приводило к блокировке всей системы. Проблемы со стабильностью достались и Windows 98 и Windows ME, которые отличались от выпуска 95 года рядом небольших обновлений.
Windows 95
Windows NT
В целом, к концу 80-х годов в Microsoft появилось понимание о необходимости разработки операционной системы не на базе MS-DOS. Параллельно с разработкой софта, связанного с MS-DOS, Microsoft наняла команду инженеров из компании DEC для разработки новой 32-битной операционной системы. Главой группы стал Дэйв Катлер — один из главных разработчиков ОС VMS. Новая система была названа NT — от сокращения New Technology. Основной упор при разработке NT делался на безопасность и надежность системы, а также на совместимость с Windows на MS-DOS. Так получилось, что опыт при разработке VMS повлиял на NT и сходство между ними стало причиной спора между DEC и Microsoft. По итогу спор был решен во внесудебном порядке.
Дэйв Катлер
Первая система Windows называлась Windows NT 3.1 и была выпущена в 1993 году. Это была первая ОС от Microsoft. Индекс 3.1 был выбран для соответствия Windows 3.1 на MS-DOS. Эта версия не имела особого успеха. Для NT требовалось больше памяти, 32-разрядных приложений на рынке было мало, возникали проблемы с совместимостью драйвером. Достичь поставленных целей смогли в NT 3.5. А первым серьезным обновлением для NT стала версия 4.0 в 96 году. Теперь эта система была мощна, надежна и безопасна, а также обеспечивала тот же интерфейс, что и Windows 95 (которая к тому моменту была чрезвычайно популярной).
Windows NT 3.1
В 2000 году вышла новая версия Windows — Windows 2000. Она развивала идеи, заложенные в системы NT. Был добавлена технология Plug-and-Play, управление электропитанием и улучшен интерфейс пользователя.
Windows 2000
Успех Windows 2000 задал вектор развития для следующего поколения — Windows XP. В «хрюшке» Microsoft улучшила совместимость, интерфейс стал более дружелюбным. Стратегия Microsoft завоевывать аудиторию уже знакомыми системами дала плоды — за несколько лет Windows XP была установлена на сотнях миллионах ПК. Эпоха MS-DOS подошла к концу.
Windows XP
Следующий проект Microsoft пал жертвой собственных амбиций. Через пять лет после Windows XP, в 2006 году на свет вышла Windows Vista. В ней был переделан графический интерфейс, переработаны и добавлены функциональные возможности в плане безопасности. Была улучшена производительность, надежность.
Первоначальные планы Microsoft по поводу Vista были настолько обширны, что через несколько лет после начала разработки проект пришлось сильно ограничить. Vista включала в себе 70 миллионов строк кода, часть которого составлял «причесанный» код XP. Неудача Vista отчасти с тем, что она вышла не в то время. На 2006 год пришелся бум недорогих компьютеров, которые не могли обеспечить достаточную для Vista производительность.
Windows Vista
Проблемы Vista были учтены при разработке Windows 7. Microsoft уделила большее внимание тестированию и производительности новой системы. Windows 7 быстро вытеснила Vista, а затем и XP, став самой популярной версией Windows до появления Windows 10 (сейчас Windows 7 на втором месте по популярности).
Windows 7
Бум смартфонов в начале 2010-х подтолкнул Microsoft к созданию операционной системы, которую можно было бы развернуть на разных устройствах: на телефонах, планшетах, приставках и т. д. В результате этой работы мир узрел Windows 8. «Восьмерка» построена на модульном подходе MinWin для получения небольшого ядра ОС, которое можно было бы расширить на линейку других типов устройств. Но аудитория встретила холодно такой подход. Многие люди критиковали «смартфоноподобный» интерфейс на ПК, отсутствие кнопки пуск. Для решения многих проблем Microsoft выпустила обновление под названием Windows 8.1, которая, помимо исправления имеющихся ошибок, добавила новые функции.
Windows 8.1
И вот, к 2015 году Microsoft выпускает Windows 10. При разработке Microsoft продолжала развитие идеи единой системы для разных устройств. В «десятке» появилась голосовая помощница Кортана, вернули меню «Пуск», улучшена системная безопасность.
Технические аспекты
Чтобы осветить все технические аспекты и тонкости операционной системы Windows понадобится не менее 1000 страниц. Для особо любопытных советуем 7-е издание «Внутреннего устройства Windows« Марка Руссиновича, специалиста по внутреннему устройству Windows. Также можно почитать «Современные операционные системы« Эндрю Таненбаума и «Operating System Concepts«: в обеих книгах есть главы, посвященные Windows. Здесь же ограничимся рассмотрением инструментов взаимодействия приложений пользователя с операционной системой (Windows API) и архитектуры «оси».
Архитектура
Во многих многопользовательских операционных системах сама ОС отделяется от приложений. Код ядра ОС выполняется в привилегированном режиме процессора (режим ядра). Для него доступны системные данные и оборудование. В непривилегированном режиме (пользовательский режим) выполняется код приложений. Ему предоставляется ограниченный набор интерфейсов и ограниченный доступ к системным данным. Прямой доступ к оборудованию заблокирован. При вызове программой пользовательского режима системной функции процессор выполняет специальную команду, переключающую вызывающий поток (последовательность команд внутри процесса, планируемая Windows для исполнения) в режим ядра. Когда системная функция завершается, операционная система переключает контекст потока обратно в пользовательский режим и дает возможность вызывающей стороне продолжить работу.
Windows считается операционной системой с гибридным ядром. С одной стороны компоненты ядра Windows располагаются в вытесняемой памяти и взаимодействуют друг с другом путем передачи сообщений, как в микроядерных системах. С другой стороны ядро слишком велико (более 1 Мбайт), а большая часть кода ОС и кода драйверов устройств использует одно защищенное пространство памяти защищенного режима, что свойственно монолитным ОС. Это означает, что в теории любой компонент ОС или драйвер устройства может повредить данные, используемые другими системными компонентами. В Windows эта проблема решается за счет повышения качества и контроля происхождения сторонних драйверов через такие программы, как WHQL или KMCS. Одновременно применяются дополнительные технологии защиты ядра, такие как безопасность на базе виртуализации, функции Device Guard.
Рассмотрим ключевые системные компоненты, формирующие архитектуру системы. На рисунке ниже представлена упрощенная схема, на которой опущены некоторые элементы, например, сетевые компоненты и различные уровни драйверов. Первое, на что стоит обратить внимание — это линия, разделяющая части пользовательского режима и режима ядра. Как упоминалось выше, потоки пользовательского режима выполняются в закрытом адресном пространстве процессов. На время выполнения в режиме ядра они получают доступ к системному пространству. Таким образом, системные процессы, пользовательские процессы, процессы служб и подсистемы среды обладают собственным закрытыми адресными пространствами.
Упрощенная схема архитектуры Windows
Вторая линия разделяет компоненты режима ядра и гипервизор (Hyper-V). Гипервизор перехватывает многие привилегированные операции, выполняемые ядром, и эмулирует их таким образом, чтобы позволить на одной и той же машине одновременно работать нескольким операционными системам. Гипервизор работает на том же уровне привилегий процессора (0), что и ядро. Но из-за использования специализированных команд процессора (VT-x у процессоров Intel, SVM у АMD) он может изолироваться от ядра с сохранением контроля над ним и приложениями. Поэтому некоторые иногда применяют термин «кольцо -1».
Четыре базовых типа процессов пользовательского режима:
- Пользовательские процессы. Эти процессы относятся к одному из следующих типов: 32- или 64-разрядные приложения Windows (приложения Windows Apps, работающие на базе среды Windows Runtime в Windows 8 и выше, включаются в эту категорию), 16-разрядные приложения Windows 3.1, 16-разрядные приложения MS-DOS, 32- и 64-разрядные приложения POSIX. Заметим, что 16-разрядные приложения могут выполняться только в 32-разрядных версиях Windows, а приложения POSIX в Windows 8 уже не поддерживаются.
- Процессы служб. В эту категорию входят процессы, являющиеся хостами для служб Windows (например, службы планировщика задач и диспетчер печати). Обычно к службам предъявляется требование независимости выполнения от входа пользователя. Многие серверные приложения Windows (например, Microsoft SQL Server и Microsoft Exchange Server) также включают компоненты, выполняемые как службы.
- Системные процессы. Фиксированные процессы, такие как процесс входа или диспетчер сеансов, не являются службами Windows. Другими словами, они не запускаются диспетчером служб.
- Серверные процессы подсистем среды. Такие процессы реализуют часть поддержки среды ОС, предоставляемой пользователю и программисту. Изначально в Windows NT было три подсистемы среды: Windows, POSIX и OS/2. Подсистема OS/2 включалась только до Windows 2000, подсистема POSIX в последний раз была включена в Windows XP.Ultimate- и Enterprise-выпуски клиента Windows 7. Все серверные версии Windows 2008 R2 включают поддержку расширенной подсистемы POSIX, называемой SUA (Subsystem for UNIX-based Applications). Сейчас подсистема SUA не поддерживается и уже не включается как необязательное часть в версии Windows (Windows 10 версии 1607 включает подсистему Windows для Linux — WSL, Windows Subsystem for Linux).
Обратим внимание на блок DLL подсистем под блоками Процессы служб и Пользовательские процессы. В Windows пользовательские приложения не вызывают низкоуровневые сервисные функции операционной системы напрямую. Вместо этого они проходят через одну или несколько динамических библиотек (DLL) подсистем. Их роль состоит в том, чтобы преобразовывать документированные функции в соответствующие внутренние (недокументированные) вызовы системных функций, реализованных в основном в Ntdll.dll. Преобразование может включать (а может не включать) отправку сообщения процессу, обслуживающему пользовательский процесс.
Компоненты режима ядра:
- Исполнительная система. Она содержит базовые сервисные функции ОС: управление памятью, управление процессами и потоками, безопасность, ввод/вывод, сетевая поддержка и межпроцессные коммуникации.
- Ядро Windows. Низкоуровневые функции ОС: планирование потоков, диспетчеризация прерываний и исключений и многопроцессорная синхронизация. Также ядро предоставляет набор функций и базовых объектов, которые используются исполнительной системой для реализации высокоуровневых конструкций.
- Драйверы устройств. Сюда входят как драйверы физических устройств, преобразующие вызовы пользовательских функций ввода/вывода в конкретные запросы ввода/вывода к устройству, так и драйверы устройств, не относящихся к физическому оборудованию, например драйверы файловой системы или сетевые драйверы.
- Слой абстрагирования оборудования (HAL). Прослойка кода, изолирующее ядро, драйверы устройств и прочий исполняемый код Windows от платформенно-зависимых различий в работе оборудования, например различий между системными платами.
- Оконная и графическая система. Реализация функций графического интерфейса (GUI), также известных как функции GDI: работа с окнами, элементы пользовательского интерфейса и графический вывод.
- Уровень гипервизора. Включает всего-навсего один компонент: сам гипервизор. В этой среде нет ни драйверов, ни других модулей. При этом сам гипервизор состоит из нескольких внутренних уровней и служб: собственный диспетчер памяти, планировщик виртуальных процессов, управление прерываниями и таймером, функции синхронизации, разделы (экземпляры виртуальных машин) и внутрипроцессные коммуникации (IPC, Inter-Process Communication) и многие другие.
В таблице ниже представлены некоторые файлы некоторых базовых компонентов Windows:
Windows API
Windows API (Application Programming Interface) — это программный интерфейс пользовательского режима для Windows. До появления 64-разрядной версии операционной системы программный интерфейс 32-разрядных версий Windows назывался Win32 API в отличие от исходного 16-разрядного Windows API (программный интерфейс для исходных 16-разрядных версий Windows). На данный момент термин Windows API или Win32 API относят как к 32-разрядным, так и к 64-разрядным версиям.
В «доисторические времена» Windows API состоял только из функций в стиле C. Выбор языка C был обусловлен тем, что написанный на нем код также мог использоваться из других языков. Он являлся достаточно низкоуровневым для предоставления сервиса ОС. Но огромное количество функций в сочетании с недостаточной последовательностью выбора имен и отсутствием логических группировок (вроде пространств имен C++) привели к тому, что в некоторых новых API используется другой механизм — модель COM.
COM базируется на двух основных принципах. Во-первых, клиенты взаимодействуют с объектами (серверные объекты COM) через интерфейсы — четко определенные контракты с набором логически связанных методов, сгруппированных посредством механизма диспетчеризации по виртуальным таблицам. Такой же механизм, к слову, обычно применяется компиляторами C++ для реализации диспетчеризации виртуальных функций. Таким образом обеспечивается двоичная совместимость и снимаются проблемы с декорированием имен компилятором. Поэтому, такие методы могут вызываться из многих других языков и компиляторов, включая C, C++, VB, языки .NET, Delphi и т. д. Вторым принципом является динамическая загрузка компонентов (вместо статической компоновки с клиентом).
WinRT
В Windows 8 появился новый API и исполнительная среда поддержки Windows Runtime (WinRT). WinRT состоит из платформенных сервисов, предназначенных для разработчиков приложений Windows Apps (приложения Windows Apps подходят для устройств, начиная от миниатюрных IoT-устройств до телефонов, планшетов, десктопных систем, ноутбуков и даже Xbox One и Microsoft HoloLens).
С точки зрения API платформа WinRT строится на базе COM, добавляя в базовую инфраструктуру COM различные расширения. С архитектурной точки зрения она обладает намного большей целостностью: в ней реализованы иерархии пространств имен, последовательная схема назначения имен и паттерны программирования. На базовом двоичном уровне WinRT API все равно строится на основе унаследованных двоичных файлов и API Windows. Это не новый «машинный» API для системы: ситуация немного напоминает то, как .NET строится на основе традиционного Windows API.
.NET Framework
.NET Framework является частью Windows. Он состоит из двух основных компонентов:
- CLR (Common Language Runtime). Исполнительная среда .NET, включает JIT-компилятор для преобразования инструкций языка CIL в низкоуровневый язык машинных команд процессора, сборщик мусора, систему проверки типов, безопасность обращения к коду и т. д. Среда реализована в виде внутрипроцессного сервера COM (DLL) и использует различные средства, предоставляемые Windows API.
- .NET Framework Class Library (FCL). Обширная подборка типов, реализующих функциональность, часто используемую в клиентских и серверных приложениях, — средства пользовательского интерфейса, поддержка сети, работа с базами данных и т. д.
На схеме представлены отношения между .NET Framework и ОС Windows:
Отношение между .NET и ОС Windows. Термин «сервер COM» обычно относится к DLL библиотеке или исполняемому файлу (EXE), в котором реализованы классы COM.

«Windows» переводится с Английского языка, как «окна», но ничего общего с окнами, предназначенными для домов эта операционная система не имеет. Она была придумана компанией Microsoft, которая также является разработчиком браузера Internet Explorer.
А как мы все знаем, этой компанией до 2008-го года руководил один из самых богатых людей в мире, по имени «Билл Гейтс». На протяжении 11-ти лет он занимал первое место в списке Forbes. И как вы думаете он так разбогател? Конечно же, тем, что вместе со своим другом основал компанию Майкрософт.
[adsense1]Но не будем больше о нем, так как сегодняшняя статья посвящена не ему, а если вы хотите узнать о Билле Гейтсе подробнее, просто перейдите по ссылке на Википедию.
Зачем нужна операционная система?
Она нужна для того чтобы компьютер работал исправно, иначе говоря, без него на экране монитора включался бы чёрный экран. Ведь для того, чтобы компьютеру понимать нас, ему нужно думать, а делать это ему помогает операционная система.
Благодаря ей, вы без проблем можете играть в любимые игры, смотреть фильмы и пользоваться соц. сетями, типа Вконтакте и Фэйсбука. Надеюсь, вы поняли для чего она нужна. А если вам что-то непонятно вы всегда можете спросить у меня.
Список операционных систем
Хоть операционная система windows, использующаяся на большинстве компьютеров во всём мире и является на данный момент самой популярной и на мой взгляд, самой лучшей ОС, но она далеко не единственная в своем роде, так как кроме неё ещё существуют:
- Linux;
- Mac OS;
- Unix.
Выше я перечислил три наиболее популярные операционные системы. Они, конечно же, популярны, но до самого Виндовса им далеко. Ведь по данным NetMarketShare, операционная система windows занимает около 91% рынка, что говорит о его значительном превосходстве над своими конкурентами.
Версии ОС windows
- старые версии: 95, 98, 2000;
- версии поновее: XP, Vista;
- новые версии: 7, 8, 8.1;
- И недавно вышедшая Виндовс 10 (о настройке интерфейса которой я писал в одном из выпусков).
Хоть и самой новой из них является 10-я версия, но наиболее распространённой на данный момент считается 7-ая.
Так что я лично советую 7-ю версию windows, так как она для меня наиболее интуитивно понятная чем 10 и более современная чем XP.
Кстати, может быть и не по теме, но продолжая о седьмой версии windows, хотелось бы ещё добавить, что если вы только недавно установили её на свой компьютер и не знаете где активировать, то об этом можно узнать в статье, как активировать windows 7 максимальная за три минуты.
Теперь, пожалуй, можно завершать статью. Надеюсь, вы поняли что такое операционная система windows и зачем она нужна, а также какую операционную систему лучше всего ставить на компьютер. А на этом я с вами прощаюсь, всем удачи и до скорого!
| Windows | |
 |
|
 Стартовый экран Windows 8 |
|
| Разработчик |
Microsoft Corporation |
|---|---|
| Семейство ОС |
MS-DOS/9x-based |
| Поддерживаемые платформы |
x86, x86-64, IA-64 (только серверный вариант), ARM |
| Лицензия |
Microsoft EULA |
| Состояние |
Актуально |
| Веб-сайт |
windows.microsoft.com |
Microsoft Windows (МФА: [ˈmaɪkɹəˌsɔft ˈwɪn.doʊz], произносится [ма́йкрософт ви́ндоус]) — семейство проприетарных операционных систем корпорации Майкрософт (Microsoft), ориентированных на применение графического интерфейса при управлении. Изначально были всего лишь графическими надстройками для MS-DOS.
В настоящее время под управлением операционных систем семейства Windows, по данным ресурса Netmarketshare (Net Applications) по состоянию на декабрь 2011 года, работает около 92 % персональных компьютеров[1].
Операционные системы Windows работают на платформах x86, x86-64, IA-64, ARM. Существовали также версии для DEC Alpha, MIPS, PowerPC и SPARC[2].
Содержание
- 1 Версии Microsoft Windows
- 1.1 Графические интерфейсы и расширения для DOS
- 1.2 Семейство Windows 9x
- 1.3 Семейство Windows NT
- 1.4 Семейство ОС для карманных компьютеров
- 1.5 Семейство встраиваемых ОС Windows Embedded
- 1.6 Microsoft Windows N
- 2 История выпусков версий Microsoft Windows
- 3 Интегрированные программные продукты
- 4 Популярность
- 5 См. также
- 6 Примечания
- 7 Литература
- 8 Ссылки
Версии Microsoft Windows
Версии Windows делят на несколько «групп».
| Список версий | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Дата выхода | Название | Последняя версия | Дата прекращения поддержки[3] | Последняя совместимая версия Internet Explorer |
| 20 ноября 1985 | Windows 1.0 | 1.04 (апрель 1987) | 31 декабря 2001 | |
| 1 ноября 1987 | Windows 2.0 | 2.11 (13 марта 1989) | 31 декабря 2001 | |
| 22 мая 1990 | Windows 3.0 | 3.00a (31 октября 1990) | 31 декабря 2001[4] | |
| 18 марта 1992 | Windows 3.1 | 3.1 | 31 декабря 2001[5] | 5 |
| октябрь 1992 | Windows for Workgroups 3.1 | 3.11 (31 декабря 1993) | 31 декабря 2001[6] | 5 |
| 27 июля 1993 | Windows NT 3.1 | 3.10.528 SP3 (10 ноября 1994) | 31 декабря 2000 | 2 |
| 21 сентября 1994 | Windows NT 3.5 | 3.50.807 SP3 (21 июня 1995) | 31 декабря 2001 | 3 |
| 30 мая 1995 | Windows NT 3.51 | 3.51.1057 SP5 (19 сентября 1996) | 31 декабря 2001 | 5 |
| 24 августа 1995 | Windows 95 | 4.00.950C (4.03.1214) (26 ноября 1997) | 31 декабря 2000 (осн.); 31 декабря 2001 (ext) | 5.5 |
| 29 июля 1996 | Windows NT 4.0 | 4.00.1381 / SP6a SRP (26 июля 2001) | 20 июня 2002 (осн.); 30 июня 2003 (SBL); 31 декабря 2004 (ext) | 6 |
| 25 июня 1998 | Windows 98 | 4.10.1998 (25 июня 1998) | 30 июня 2002 (осн.); 30 ноября 2003 (SBL); 11 июля 2006 (ext) | 6 |
| 5 мая 1999 | Windows 98 SE | 4.10.2222A (5 мая 1999) | 30 июня 2002 (осн.); 31 марта 2004 (SBL); 11 июля 2006 (ext) | 6 |
| 17 февраля 2000 | Windows 2000 | 5.0.2195 / 5.0 SP4 Rollup 1 v2 (13 сентября 2005) | 31 марта 2004 (retail); 31 марта 2005 (SBL); 30 июня 2005 (осн); 13 июля 2010 (ext) | 6 |
| 14 сентября 2000 | Windows Me | 4.90.9000 (14 сентября 2000) | 31 декабря 2003 (осн.); 30 июня 2004 (SBL); 11 июля 2006 (ext) | 6 |
| 24 августа 2001(RTM) 25 октября 2001 (продажи) |
Windows XP | 5.1.2600.5512 SP3 (21 апреля 2008) | 30 сентября 2004 (RTM); 10 сентября 2006 (SP1/SP1a); 30 июня 2008 (retail); 14 апреля 2009 (SP2/SP3 осн.); 13 июля 2010 (SP2); 22 октября 2010 (SBL); 8 апреля 2014 (ext) | 8[7] |
| 28 марта 2003 | Windows XP 64-bit Edition | 5.2.3790 | 25 июля 2006 | 8[7] |
| 24 апреля 2003 | Windows Server 2003 | 5.2.3790.3959 SP2 (13 марта 2007) | 30 июня 2009 (RTM); 13 июля 2010 (осн.); 14 июля 2015 (ext); | 8[7] |
| 25 апреля 2005 | Windows XP Professional x64 Edition | 5.2.3790.3959 SP2 (13 марта 2007) | 30 июня 2008 (retail); 31 января 2009 (SBL) | 8[7] |
| 8 июля 2006 | Windows Fundamentals for Legacy PCs | 5.1.2600 RTM (8 июля 2006) | 8 июля 2008(retail), 12 июля 2010(Service Pack) | 8[7] |
| 8 ноября 2006 (RTM) 30 января 2007 (продажи) |
Windows Vista | 6.0.6001 / SP2 Build 6002 (25 мая 2009) | 13 апреля 2010(RTM); 22 октября 2010(retail); 12 июля 2011(SP1); 22 октября 2011(SBL); 10 апреля 2012(осн.); 11 апреля 2017(ext) | 9[8] |
| 16 июля 2007 | Windows Home Server | 5.2.1500 (16 июля 2007) | 8 января 2013(осн.) | |
| 27 февраля 2008 | Windows Server 2008 | 6.0.6002 / SP2 build 6002 (25 мая 2009) | 9 июля 2015(осн.),10 июля 2018(ext), 12 июля 2011(SP1) | 9[8] |
| 13 июля 2009 (RTM) 22 октября 2009 (продажи) |
Windows 7 | 6.1.7601 / SP1 Build 7601 (22 февраля 2011) | 9 апреля 2013(RTM),13 января 2015(осн),14 января 2020(ext) | 9[8] |
| 13 июля 2009 (RTM) 22 октября 2009 (продажи) |
Windows Server 2008 R2 (ранее известна как Windows Server 7) | 6.1.7601 / SP1 Build 7601 (22 февраля 2011) | 9 июля 2015(осн.),10 июля 2018(ext) | 9[8] |
| 6 апреля 2011 | Windows Home Server 2011 | 6.1.8400 | 12 апреля 2016(осн.) | 9[8] |
| 1 августа 2012 (RTM) 4 сентября 2012 (продажи) |
Windows Server 2012 | 6.2.9200 | 9 января 2018(осн),10 января 2023(ext) | 10 |
| 1 августа 2012 (RTM) 26 октября 2012 (продажи) |
Windows 8 | 6.2.9200 | 9 января 2018(осн),10 января 2023(ext) | 10 |
Графические интерфейсы и расширения для DOS
Эти версии Windows не были полноценными операционными системами, а являлись надстройками к операционной системе MS-DOS и были по сути многофункциональным расширением, добавляя поддержку новых режимов работы процессора, поддержку многозадачности, обеспечивая стандартизацию интерфейсов аппаратного обеспечения и единообразие для пользовательских интерфейсов программ. Предоставляли встроенные средства (GDI и USER, первые версии Windows вообще состояли из трех модулей — KERNEL, GDI и USER, первый из них предоставлял вызовы управления памятью, запуском EXE-файлов и загрузкой DLL-файлов, второй — графику, третий — окна) для создания графического интерфейса пользователя. Они работали с процессорами начиная с Intel 8086.
- Windows 1.0 (1985)
- Windows 2.0 (1987)
- Windows 2.1 (Windows 386) (1987) — в системе появилась возможность запуска DOS-приложений в графических окнах, причём каждому приложению предоставлялись полные 640 Кб памяти. Полная поддержка процессора 80286. Появилась поддержка процессоров 80386.
- Windows 3.0 (1990) — улучшена поддержка процессоров 80386 и защищённого режима.
- Windows 3.1 (1992) — серьёзно переработанная Windows 3.0; устранены UAE (Unrecoverable Application Errors — фатальные ошибки прикладных программ), добавлен механизм OLE, печать в режиме WYSIWYG («что видите, то и получите»), шрифты TrueType, изменён Проводник (диспетчер файлов), добавлены мультимедийные функции.
- Windows для рабочих групп (Windows for Workgroups) 3.1/3.11 — первая версия ОС семейства с поддержкой локальных сетей. В WFWG 3.11 также испытывались отдельные усовершенствования ядра, применённые позднее в Windows 95.
Семейство Windows 9x
Включает в себя Windows 95, Windows 98 и Windows Me.
Windows 95 была выпущена в 1995 году. Её отличительными особенностями являются: новый пользовательский интерфейс, поддержка длинных имён файлов, автоматическое определение и конфигурация периферийных устройств Plug and Play, способность исполнять 32-битные приложения и наличие поддержки TCP/IP прямо в системе. Windows 95 использует вытесняющую многозадачность и выполняет каждое 32-битное приложение в своём адресном пространстве.
Операционные системы этого семейства не являлись безопасными многопользовательскими системами как Windows NT, поскольку из соображений совместимости вся подсистема пользовательского интерфейса и графики оставалась 16-битной и мало отличалась от той, что в Windows 3.x. Так как этот код не был thread-safe, все вызовы в подсистему оборачивались в мьютекс по имени Win16Lock, который, кроме того, еще и находился всегда в захваченном состоянии во время исполнения 16-битного приложения. Таким образом, «повисание» 16-битного приложения немедленно блокировало всю ОС.
Программный интерфейс был подмножеством Win32 API, поддерживаемым Windows NT, но имел поддержку юникода в очень ограниченном объёме[9]. Также в нём не было должного обеспечения безопасности (списков доступа к объектам и понятия «администратор»).
В составе Windows 95 присутствовал MS-DOS 7.0, однако его роль сводилась к обеспечению процесса загрузки и исполнению 16-битных DOS приложений. Исследователи заметили, что ядро Windows 95 — VMM — обращается к DOS под собой, но таких обращений довольно мало, главнейшая функция ядра DOS — файловая система FAT — не использовалась. В целом же интерфейс между VMM и нижележащей DOS никогда не публиковался, и DOS была замечена (тем же Эндрю Шульманом) в наличии недокументированных вызовов только для поддержки VMM.
Семейство Windows NT
Текстовый логотип Windows® XP (обычно используется вместе с графическим)
Операционные системы этого семейства в настоящее время работают на процессорах с архитектурами x86, x64, и Itanium,ARM. Ранние версии (до 4.0 включительно) также поддерживали некоторые RISC-процессоры: Alpha, MIPS, и Power PC. Все операционные системы этого семейства являются полностью 32- или 64- битными операционными системами, и не нуждаются в MS-DOS даже для загрузки.
Только в этом семействе представлены операционные системы для серверов. До версии Windows 2000 включительно они выпускались под тем же названием, что и аналогичная версия для рабочих станций, но с добавлением суффикса, например, «Windows NT 4.0 Server» и «Windows 2000 Datacenter Server». Начиная с Windows Server 2003 серверные операционные системы называются по-другому.
- Windows NT 3.1 (1993)
- Windows NT 3.5 (1994)
- Windows NT 3.51 (1995)
- Windows NT 4.0 (1996)
- Windows 2000 (2000) — Windows NT 5.0
- Windows XP (2001) — Windows NT 5.1
- Windows XP 64-bit Edition (2003) — Windows NT 5.2
- Windows Server 2003 (2003) — Windows NT 5.2
- Windows Vista (2006) — Windows NT 6.0
- Windows Home Server (2007) — Windows NT 5.2
- Windows Server 2008 (2008) — Windows NT 6.0
- Windows Small Business Server (2008) — Windows NT 6.0
- Windows 7 — Windows NT 6.1 (2009)
- Windows Server 2008 R2 — Windows NT 6.1 (2009)
- Windows Home Server 2011 — Windows NT 6.1 (2011)
- Windows 8 — Windows NT 6.2 (2012)
- Windows Server 2012 — Windows NT 6.2 (2012)
В основу семейства Windows NT положено разделение адресных пространств между процессами. Каждый процесс имеет возможность работать с выделенной ему памятью. Однако он не имеет прав для записи в память других процессов, драйверов и системного кода.
Семейство Windows NT относится к операционным системам с вытесняющей многозадачностью. Разделение процессорного времени между потоками происходит по принципу «карусели». Ядро операционной системы выделяет квант времени (в Windows 2000 квант равен примерно 20 мс) каждому из потоков по очереди при условии, что все потоки имеют одинаковый приоритет. Поток может отказаться от выделенного ему кванта времени. В этом случае система перехватывает у него управление (даже если выделенный квант времени не закончен) и передаёт управление другому потоку. При передаче управления другому потоку система сохраняет состояние всех регистров процессора в особой структуре в оперативной памяти. Эта структура называется контекстом потока. Сохранение контекста потока достаточно для последующего возобновления его работы.
Семейство ОС для карманных компьютеров
Логотип Windows® CE
Это семейство операционных систем реального времени было специально разработано для мобильных устройств. Поддерживаются процессоры ARM, MIPS, SuperH и x86. В отличие от остальных операционных систем Windows, операционные системы этого семейства продаются только в составе готовых устройств, таких как смартфоны, карманные компьютеры, GPS-навигаторы, MP3-проигрыватели и другие.
В настоящее время под термином «Windows CE» понимают только ядро операционной системы. Например, Windows Mobile 5.0 включает в себя ядро Windows CE 5.0, хотя в некоторых устройствах ядро Windows CE используется и без Windows Mobile.
- Windows CE
- Windows Mobile
- Windows Phone
Семейство встраиваемых ОС Windows Embedded
Windows Embedded — это семейство операционных систем реального времени, было специально разработано для применения в различных встраиваемых системах. Ядро системы имеет общее с семейством ОС Windows CE и поддерживает процессоры ARM, MIPS, SuperH и x86. Windows Embedded включает дополнительные функции по встраиванию, среди которых фильтр защиты от записи (EWF и FBWF), загрузка с флеш-памяти, CD-ROM, сети, использование собственной оболочки системы и т. п.
В отличие от операционных систем Windows, операционные системы этого семейства продаются только в составе готовых устройств, таких как: банкоматы, медицинские приборы, навигационное оборудование, «тонкие» клиенты, VoIP-терминалы, медиапроигрыватели, цифровые рамки (альбомы), кассовые терминалы, платёжные терминалы, роботы, игровые автоматы, музыкальные автоматы и другие.
В настоящее время выпускаются следующие варианты ОС Windows Embedded[10]:
- Windows Embedded CE,
- Windows Embedded Standard,
- Windows Embedded POSReady,
- Windows Embedded Enterprise,
- Windows Embedded NavReady,
- Windows Embedded Server.
Microsoft Windows N
Microsoft Windows N — версии Microsoft Windows, из которых корпорацией Microsoft были удалены компоненты, не совместимые с законодательством стран Европейского союза.
История выпусков версий Microsoft Windows
График выхода и поддержки Windows
Интегрированные программные продукты
|
|
В этом разделе не хватает ссылок на источники информации.
Информация должна быть проверяема, иначе она может быть поставлена под сомнение и удалена. |
Пакет Microsoft Windows включает в себя «стандартные» приложения, такие как браузер (Internet Explorer), почтовый клиент (Outlook Express или Windows Mail), музыкальный и видеопроигрыватель (Windows Media Player). С помощью технологий COM и OLE их компоненты могут быть использованы в приложениях сторонних производителей. Эти продукты бесплатны и могут быть свободно скачаны с официального сайта Microsoft, однако для установки некоторых из них необходимо иметь лицензионную версию Microsoft Windows (верно только для ранних версий до windows, начиная с windows 98 являются неотъемлемой частью системы). Запуск этих программ под другими операционными системами возможен только с помощью эмуляторов среды Windows (Wine).
Вокруг факта включения таких «стандартных» продуктов в ОС Windows разгорается много дискуссий и юридических споров, по мнению сторонних разработчиков, это ведёт к отсутствию конкуренции и создает препятствия для распространения конкурирующих продуктов, они же часто ставят под сомнение качество браузера Internet Explorer, объясняя его популярность вхождением в пакет Windows и плохой осведомленностью пользователей о наличии альтернатив.
В 1997 компания Sun Microsystems подала в суд на компанию за нарушение лицензии на использование технологий Java. В 2001 Microsoft выплатила штраф и исключила не совместимую с лицензированной виртуальную машину Java из состава своих продуктов.
Популярность
В настоящее время Microsoft Windows установлена более чем на 89 % персональных компьютеров и рабочих станций. По данным компании Net Applications, на июль 2011 года рыночная доля Windows составляла 87,60 %[11] . Стоит отметить, что одним из основных клиентов NetApplications является корпорация Microsoft.
Среди различных версий Microsoft Windows по данным W3Schools с августа 2011 наиболее популярна Windows 7[12].
| Источник | NetApplications | NetApplications | NetApplications | [NetApplications] | GoStats | GoStats |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Дата | январь 2011 | июнь 2011 | сентябрь 2011 | февраль 2012 | январь 2012 | сентябрь 2012 |
| Все версии | 89,67 % | 88,29 % | 86,57 % | 91,92 % | 94,07 % | 92,84 % |
| Windows XP | 55,27 % | 51,14 % | 47,29 % | 45,39 % | 60,17 % | 48,08 % |
| Windows 7 | 22,31 % | 27,14 % | 30,36 % | 38,12 % | 20,79 % | 38,31 % |
| Windows Vista | 11,66 % | 9,52 % | 8,51 % | 8,10 % | 12,28 % | 6,17 % |
| Windows 2000 | 0,27 % | 0,19 % | 0,16 % | 0,15 % | 0,57 % | 0,26 % |
| Windows Server 2003 | — | — | — | — | 0,21 % | 0,02 % |
| Windows 98 | 0,03 % | 0,03 % | 0,03 % | 0,05 % | — | — |
| Windows ME | — | — | — | 0,01 % | — | — |
| Windows NT | 0,13 % | 0,27 % | 0,22 % | 0,06 % | — | — |
| Windows CE | — | — | — | — | — | — |
См. также
- Список операционных систем;
- Windows API;
- Проводник Windows;
- Windows Script Host
- Многозадачность;
Примечания
- ↑ Operating system market share
- ↑ http://ftp.lanet.lv/ftp/sun-info/sunflash/1993/Jul/55.11-Sun-Intergraph:-SPARC-and-Windows-NT
- ↑ В столбце «Дата прекращения поддержки» словом «retail» помечается дата окончания продаж конечному пользователю; аббревиатурой «SBL» помечена дата окончания выдачи System Builder лицензии; «ext» — окончание срока продления поддержки
- ↑ Эра Windows 3.x завершилась
- ↑ Please Verify your Location
- ↑ Please Verify your Location
- ↑ 1 2 3 4 5 IE8: System requirements
- ↑ 1 2 3 4 5 IE9: system requirements
- ↑ Unicode support in Windows 95 and Windows 98
- ↑ http://www.microsoft.com/windowsembedded/en-us/about/what.mspx
- ↑ Operating System Market Share, April 2010. Net Applications. Архивировано из первоисточника 22 августа 2011.
- ↑ OS Statistics
Литература
- Брайан Ливингстон, Пол Таррот. Секреты Microsoft Windows Vista = Windows Vista Secrets. — М.: «Диалектика», 2007. — С. 456. — ISBN 0-7645-7704-2
- Пол Мак-Федрис. Microsoft Windows XP SP2. Полное руководство = Microsoft Windows XP Unleashed. — М.: «Вильямс», 2006. — С. 880. — ISBN 0-672-32833-X
Ссылки
- Home page for the Windows family of products and technologies.
- Microsoft Windows Update
- Центр загрузки Майкрософт: Windows
- Как вернуть деньги за OEM-Windows, 3dnews.ru, 28 сентября 2009 г.
| |
|
|---|---|
| Основные |
Aero • ClearType • Диспетчер рабочего стола • DirectX • Панель задач (Пуск • Область уведомлений) • Проводник (Пространство имён • Специальные папки • Ассоциации файлов) • Windows Search (Smart folders • iFilters) • GDI • WIM • SMB • .NET Framework • XPS • Active Scripting (WSH • VBScript • JScript) • COM (OLE • DCOM • ActiveX • Структурированное хранилище • Сервер транзакций) • Теневая копия • WDDM • UAA • Консоль Win32 |
| Службы управления |
Архивация и восстановление • COMMAND.COM • cmd.exe • Средство переноса данных • Просмотр событий • Установщик • netsh.exe • PowerShell • Отчёты о проблемах • rundll32.exe • Программа подготовки системы (Sysprep) • Настройка системы (MSConfig) • Проверка системных файлов • Индекс производительности • Центр обновления • Восстановление системы • Дефрагментация диска • Диспетчер задач • Диспетчер устройств • Консоль управления • Очистка диска • Панель управления (элементы) |
| Приложения |
Контакты • DVD Maker • Факсы и сканирование • Internet Explorer • Журнал • Экранная лупа • Media Center • Проигрыватель Windows Media • Программа совместной работы • Центр устройств Windows Mobile • Центр мобильности • Экранный диктор • Paint • Редактор личных символов • Удалённый помощник • Распознавание речи • WordPad • Блокнот • Боковая панель • Звукозапись • Календарь • Калькулятор • Ножницы • Почта • Таблица символов • Исторические: Movie Maker • NetMeeting • Outlook Express • Диспетчер программ • Диспетчер файлов • Фотоальбом |
| Игры |
Chess Titans • Mahjong Titans • Purble Place • Пасьянсы (Косынка • Паук • Солитер) • Сапёр • Пинбол • Червы |
| Ядро ОС |
Ntoskrnl.exe • Слой аппаратных абстракций (hal.dll) • Бездействие системы • svchost.exe • Реестр • Службы • Диспетчер управления сервисами • DLL (формат модулей) • PE • NTLDR • Диспетчер загрузки • Программа входа в систему (winlogon.exe) • Консоль восстановления • Windows RE • Windows PE • Защита ядра от изменений |
| Службы |
Autorun.inf • Фоновая интеллектуальная служба передачи • Файловая система стандартного журналирования • Отчёты об ошибках • Планировщик классов мультимедиа • Теневая копия • Планировщик задач • Беспроводная настройка |
| Файловые системы |
Protogon • NTFS (Жёсткая ссылка • Точка соединения • Точка монтирования • Точка повторной обработки • Символьная ссылка • TxF • EFS) • WinFS • FAT • exFAT • CDFS • UDF • DFS • IFS |
| Сервер |
Active Directory • Службы развёртывания • Служба репликации файлов • DNS • Домены • Перенаправление папок • Hyper-V • IIS • Media Services • MSMQ • Защита доступа к сети (NAP) • Службы печати для UNIX • Удалённое разностное сжатие • Службы удаленной установки • Служба управления правами • Перемещаемые профили пользователей • SharePoint • Диспетчер системных ресурсов • Удаленный рабочий стол • WSUS • Групповая политика • Координатор распределённых транзакций |
| Архитектура |
NT • Диспетчер объектов • Пакеты запроса ввода/вывода • Диспетчер транзакций ядра • Диспетчер логических дисков • Диспетчер учетных записей безопасности • Защита ресурсов • lsass.exe • csrss.exe • smss.exe • spoolsv.exe • Запуск |
| Безопасность |
BitLocker • Защитник • Предотвращение выполнения данных • Обязательный контроль целостности • Защищенный канал данных • UAC • UIPI • Брандмауэр • Центр обеспечения безопасности • Защита файлов |
| Совместимость |
Подсистема UNIX (Interix) • Виртуальная машина DOS • Windows on Windows • WOW64 |
| |
||
|---|---|---|
|
Оболочки над MS-DOS: 1.0 • 2.x • 3.x • Windows 9x: 95 • 98 • ME • Windows NT: NT 3.1 • NT 3.5 • NT 3.51 • NT 4.0 • 2000 • XP • Vista • 7 • 8 |
||
| Windows Server |
2003 • Home (2011) • 2008 (HPC 2008 • R2) • Essential Business • MultiPoint • Small Business • 2012 |
 |
| Специализированные |
Embedded (Automotive • POSReady) • PE • FLP |
|
| Мобильные |
Windows CE (1.0 • 2.0 • 3.0 • 4.0 • 5.0 • 6.0 • 7.0) • Mobile • Phone • RT |
|
| Другие проекты |
Xenix • OS/2 • Singularity • Midori • Закрытые: Neptune • Nashville • Odyssey • Cairo |
|
| Альтернативные реализации |
ReactOS • Wine |
| |
|
|---|---|
| Ядро |
Гибридное • Микро • Модульное • Монолитное • Нано • Экзо • Драйвер • Пространство пользователя • Область пользователя |
| Управление процессами |
Режимы (супервизора • реальный • защищённый) • Прерывание • Кольца защиты • Переключение контекста • Многозадачность (вытесняющая • кооперативная • мультипрограммирование) • Процесс • Управление процессом • Планировщик задач • Многопоточность |
| Управление памятью |
Защита памяти • Сегментная адресация памяти • Страничная память • Менеджер виртуальной памяти • Ошибка сегментации • Общая ошибка защиты |
| Прочее |
Загрузчик ОС • API • VFS • Компьютерная сеть • GUI • Слой аппаратных абстракций (HAL) |