7
Операционная система– это
совокупность программ для организации
диалога пользователя с компьютером,
для управления аппаратными средствами
и ресурсами, для запуска программ и
выполнения некоторых других функций.
В настоящее время наибольшее распространение
в нашей стране получили различные версии
графической операционной системы
WindowsфирмыMicrosoft – Windows – 95,Windows – 98,Windows – NT,Windows –2000,Windows – XP.
Во всех версиях интерфейс пользователя
и приемы работы с дисками, папками и
файлами практически не отличаются.
ОС Windows загружается
автоматическипри включениипитаниякомпьютера.
При работе в операционной системе
Windows широко применяется манипулятор
мышь. Указатель мыши в зависимости
от конкретной ситуации может иметь
различный вид.
Основные приемы управления с помощью
мыши:
-
однократныйщелчоклевойкнопкой мыши — выделение объектов,
выбор команды меню, кнопки панели
инструментов, установка и снятие флажка; -
однократный щелчокправойкнопкой мыши – вызов контекстного
меню; -
двойнойщелчоклевойкнопкой мыши по объекту – открытие
объекта (запуск приложений, открытие
документов, папок); -
задержкауказателя мыши на
объекте — вызов всплывающих
подсказок; -
протягивание при нажатой левой
кнопке мыши — изменение размеров
объектов, выделение фрагментов
документов.
Пользовательский интерфейс ос Windows
Пользовательский интерфейс-это методы
и средства, предоставляемые ОС пользователю
для взаимодействия с ней.
ОС Windows
имеет удобный графический
интерфейс пользователя.
Ниже перечислены основные
элементы пользовательского интерфейса
Windows:
-
рабочий стол;
-
меню;
-
панели инструментов;
-
программные окна;
-
диалоговые окна;
-
вторичные окна.
Р
стол— это экран, появляющийся после
загрузки Windows. (рис. 1).
Рис. 1. Рабочий стол.
Ниже содержится обзор объектов, являющихся
составными частями рабочего стола.
Папкав Windows— этосредствоорганизации и представления системных
ресурсов ПК (каталогов, файлов, дисковых
накопителей и т. д.).
Папка может содержать другие папки
(вложенные папки), а также такие объекты,
как, например, файлы, принтеры, диски.
Объекты в папке представляются значками,
и каждый значок имеет название,
расположенное ниже него. Для того чтобы
открыть папку, запустить программу,
открыть документ или активизировать и
открыть объект любого другого типа в
папке, достаточно дважды щелкнуть
на соответствующем значке.
По умолчанию рабочий стол содержит
следующие специальные папки:
-
Мой компьютер,
-
Сетевое окружение,
-
Корзина.
Значок Мой компьютерпредставляет
наРабочем столепапку, как бы
содержащую весь компьютер целиком.
ПапкаМой компьютерсодержит
значки всех дисковых накопителей ПК,
включая жесткие диски, накопители на
гибких и компакт-дисках и подсоединенные
сетевые диски.
Значок Сетевое окружениеобеспечивает быстрый доступ к сетевым
ресурсам, если данный ПК подсоединен к
сети. Эти сетевые ресурсы включают диски
и принтеры, общие для всех компьютеров
в сети. Чтобы просмотреть список
компьютеров, входящих в рабочую группу,
или структуру сети в целом, необходимо
дважды щелкнуть этот значок.
Корзинапредназначена для
временного хранения удаленных файлов,
папок и ярлыков. Она позволяет восстановить
объекты, удаленные по ошибке. При
переполнении корзины объекты, находящиеся
в ней дольше всех, удаляются безвозвратно.
По внешнему виду корзины видно — пуста
она или нет. Конкретную информацию о
перенесенных в корзину объектах можно
получить, перейдя в режим просмотра
корзины (двойной щелчок левой кнопкой
мыши или щелчок правой кнопкой и в
контекстном меню выбрать команду
Открыть).
Ярлык – ссылка на другой объект
Windows. Таким объектом может быть файл,
папка, устройство (диск, принтер). Это
файл специального вида, в котором
хранится путь к объекту. В отличие от
файлов, ярлыки имеют на своем значке в
левом нижнем углуизогнутую стрелку.
Используется ярлык для быстрого доступа
к объекту (быстрого открытия объекта).
Для этого достаточно дваждыщелкнуть
левой кнопкой на ярлыке.
Соседние файлы в предмете [НЕСОРТИРОВАННОЕ]
- #
- #
- #
- #
- #
- #
- #
- #
- #
- #
- #
Содержание
- Компоненты операционной системы Windows 7. Окна и основные элементы интерфейса
- Основные функции, обеспечиваемые операционной системой
- Компоненты операционной системы Windows 7
- Окна Windows
- Элементы интерфейса. Ярлыки
- Элементы интерфейса. Панель задач
- Элементы интерфейса. Кнопка «Пуск»
- Основные элементы интерфейса операционной системы Windows
- Структура интерфейса Windows
Компоненты операционной системы Windows 7. Окна и основные элементы интерфейса
В самом простом случае пользователь может выполнять на ПК только одну задачу, например, смотреть фильм, печатать текст, рисовать или слушать музыку. Ещё несколько лет назад так оно и было – персональный компьютер обеспечивал выполнение только какой-то одной функции или действия. Но техническое развитие не стоит на месте и сегодня, благодаря постоянному повышению своего быстродействия, аппаратных ресурсов современного ПК вполне хватает на то, чтобы одновременно пользователь смог выполнять сразу несколько действий одновременно: печатать текст, слушать музыку, разговаривать через интернет с другими пользователями, находящимися на другом конце земного шара.
Современные возможности ПК стали действительно впечатляющими. Но чтобы осуществить эту возможность необходимо правильно распределить технические ресурсы компьютера между всеми одновременно выполняющимися на нём программами.
Осуществляет данную функцию специальное программное обеспечение, которое называется «операционная система». Представляет собой совокупность различных программ, составляющих единое целое и обеспечивающих правильное функционирование всех технических узлов персонального компьютера, а также удобное взаимодействие с пользователем ПК и запуск стороннего ПО различного назначения.
Основные функции, обеспечиваемые операционной системой
По своей функциональности, операционные системы делятся на однозадачные, т. е. выполняющие одновременно не более одной задачи, и многозадачные, способные обеспечивать выполнение нескольких программ одновременно.
Современные операционные системы в большинстве своём обеспечивают многозадачную возможность работы.
Компоненты операционной системы Windows 7
После запуска ПК и загрузки ОС пользователь видит на экране так называемый рабочий стол, на котором расположены ярлыки наиболее часто запускаемых программ пользователя.
Вся основная «навигация», то есть управление интерфейсом осуществляется при помощи манипулятора «мышь», указатель которой при нормальной работе операционной системы всегда присутствует на экране. Для вызова меню на «мышке» есть кнопки, нажимая на которые можно осуществлять ряд дополнительных функций или действий (в зависимости от нахождения).
Окна Windows
Прикладное программное обеспечение при своём запуске, как правило, имеет рабочее окно – графический элемент изменяемого размера.
Справедливости ради следует заметить, что существуют программы, выполняемые без таких «видимых» окон – они не взаимодействуют напрямую с пользователем и работают по заранее отлаженному, чёткому алгоритму, поэтому в оконном отображении их действий нет какой-либо необходимости. К такому ПО, например, относятся ряд вспомогательных программ самой системы: программы ядра ОС, драйвера и утилиты, обслуживающие оборудование (видеокарты, звуковые карты) и т. п. Но в большинстве случаев запуск программного обеспечения в Windows сопровождается выводом «окна» (кстати, именно по этой причине данная ОС и носит название Windows, что с английского и переводится, как «окна»).
После запуска прикладной программы, к примеру, текстового редактора, пользователь видит её «окно» — своеобразное рабочее пространство, в котором он может выполнять определённые действия, в этом случае – набирать текст.
Благодаря мультизадачности Windows можно запустить сразу несколько разных программ (теоретически – сколько позволят ресурсы ПК) и выполнять их одновременно, переключаясь от окна к окну, когда это нужно.
Окна в ОС Windows имеют стандартный интерфейс, за редким исключением, когда программист разрабатывает свой стиль окна. Но и в этом случае управление даже такими окнами стараются сделать «стандартным» или близким к нему.
После запуска классическое окно можно перемещать по экрану. Для этого достаточно установить указатель мышки на верхнюю часть окна (там, где расположено название), щёлкнуть правой кнопкой мыши и, не отпуская её, начать перетаскивать окно в нужное место. По окончании операции перемещения кнопку можно отпустить.
В правом верхнем углу «классического» окна имеются кнопки быстрого управления. Кнопка с крестиком: 


Следует иметь в виду, что не всегда все три кнопки могут присутствовать в интерфейсе, и не всегда они выполняют стандартные «функции», все зависит от «фантазии» разработчика программы. Кроме этого, есть ещё один скрытый элемент управления – меню окна, пункты которого повторяют вышеуказанные опции кнопок. Для его вызова следует переместить указатель в левый верхний угол и нажать правую кнопку.
Элементы интерфейса. Ярлыки
Запускать программное обеспечение в Windows можно разными способами. Для запуска часто используемых программ в ОС сделана возможность создания ярлыков на «рабочем столе».
«Ярлык» (его ещё называют «иконкой») представляет собой небольшую картинку (графическое изображение, как правило, отражающую назначение программы) с определёнными свойствами. Щёлкнув по этой картинке мышкой, пользователь осуществляет запуск программы, поэтому свойства, которые хранит эта картинка – это на самом деле путь к папке, в которой лежит файл этой программы.
Таким образом, «рабочий стол» — это не что иное, как удобное отображение в графическом виде того набора программ, которые наиболее часто использует пользователь в своей работе.
Для удобства пользователя Майкрософт позаботилось и о том, чтобы ярлыки служили не только, как средство для запуска ПО, но и для быстрой навигации по файловой системе. Таким образом, ярлык может служить ещё и для обозначения папки с файлами, а также являться ссылкой на какой-то конкретный документ, например, текстовый или звуковой файл, видеофильм, рисунок и т. п. Это действительно очень удобно – не нужно каждый раз вспоминать и искать, где находится часто используемый файл, достаточно создать его ярлык на рабочем столе и, щёлкая по нему, быстро открывать нужный файл.
Назначение ярлыка можно посмотреть и изменить при необходимости в его свойствах или сразу указать при создании. Технически, ярлык представляет собой тоже файл небольшого размера, внутри которого содержится ссылка — полный путь к нужному файлу. Располагаться он может в любом каталоге и необязательно отображаться на рабочем столе. При этом, графическое изображение созданного ярлыка запуска файла отличается от оригинального ярлыка программы наличием небольшой стрелочки в левом нижнем углу картинки.
Чтобы создать ярлык на рабочем столе, наведите курсор мыши на свободное место и щёлкните правой кнопкой. Из выпадающего меню выберите соответствующий пункт – «Создать», а затем – «Ярлык».
После того как на экране откроется окно поиска необходимого файла:
необходимо будет, нажав кнопку «Обзор», найти нужный файл и выбрать его для создания ярлыка.
При необходимости, ярлык вы можете назвать так, как вам необходимо, изменив его название в поле:
Если менять наименование файла вам не нужно, просто нажмите на кнопку «Готово» и ярлык будет создан на рабочем столе.
Для удаления необходимо навести курсор мыши на нужный ярлык, и нажать правую кнопку. Из появившегося меню выбрать пункт – «Удалить».
Для того, чтобы просмотреть или изменить свойства ярлыка, необходимо навести курсор на нужный ярлык и правой кнопкой вызвать меню, в котором необходимо выбрать пункт – «Свойства».
Элементы интерфейса. Панель задач
Кроме ярлыков «рабочий стол» содержит такой важный элемент интерфейса, как «панель задач». Основное назначение этой панели – отображать запущенные и выполняемые на текущий момент программы пользователя и давать возможность быстро переключаться между ними без сворачивания окон.
Такая возможность интерфейса обеспечивает комфортную работу, например, когда требуется работать в разных программах, но сворачивать (или изменять) размер окна крайне нежелательно.
В левом углу панели задач возле кнопки пуск, расположена панель быстрого запуска.
Сюда пользователь может перетащить ярлыки с рабочего стола. Дело в том, что в процессе работы может потребоваться запуск той или иной программы, но сворачивать открытые окна не совсем удобно. Панель же задач, практически всегда видна на экране и запуск нужного ПО с панели быстрого запуска придётся в этом случае весьма кстати.
Кроме этого, в правом углу «панели задач» отображается и область «системных значков» — небольших графических «ярлычков» от программ, постоянно работающих в так называемом «фоновом режиме»: сеть, раскладка клавиатуры, время, антивирусное и другое, специализированное ПО. Это делает общий интерфейс более функциональным и наглядным. При желании, отображение этих значков можно отключить в режиме настройки. Иногда, встречается ещё одно название этой области – «систем трей».
«Фоновый режим» — режим работы программного обеспечения, при котором ПО выполняется в большинстве случаев незаметно для пользователя, привлекая его внимание только при необходимости, какими-либо сообщениями. Хорошим примером подобных программ могут служить антивирусы. Их работа незаметна для пользователя, и лишь в момент возникновения неотложных проблем они могут предупредить об этом своего владельца. Соответственно и вирусное ПО работает также незаметно от пользователя в «фоновом режиме».
«Вирусное ПО» — программное обеспечение, в большинстве случаев работающее в фоновом режиме и предназначенное для совершения злонамеренных действий на ПК пользователя: кражи личных данных, повреждения файловой системы, удалённого управления компьютером и похожих действий.
После первой установки ОС панель задач отображается внизу, в горизонтальной плоскости. Но пользователь может по своему усмотрению располагать её, например, горизонтально вверху, вертикально – слева или справа.
Изменить расположение панели задач очень просто. Для этого вначале необходимо произвести её «открепление». Поместите указатель мышки на свободное место панели задачи и щёлкните правой кнопкой мышки. В появившемся меню кликните по пункту «Закрепить панель задач», если на нём стоит галочка, чтобы она исчезла.
Если галочки нет, то ваша панель задач не закреплена, и с ней можно производить манипуляции по «перетягиванию». Для этого снова установите курсор мыши на свободное место панели задач, нажмите и удерживайте левую кнопку мышки, затем, не отпуская кнопки, ведите мышью в то место, куда вы хотите установить панель задач. Как только она переместится, кнопку мышки можно отпустить. После перемещения не забудьте снова закрепить панель задач. Эта функция как раз и служит для того, чтобы избежать случайного перемещения панели.
Для удобства использования, «панель задач» имеет ряд дополнительных настроек, позволяющих установить её параметры «под себя». Чтобы вызвать меню дополнительных настроек, необходимо, как и в случае с перемещением панели задач, установить указатель мышки на свободное место и щёлкнуть правую кнопку мышки. В полученном меню можно воспользоваться настройкой дополнительных панелей (если они нужны):
либо, кликнув по пункту «Свойства» перейти к дополнительной настройке панели задач.
В настройке «области уведомлений» (а это как раз системные уведомления в правом нижнем углу) рекомендуется всегда включать пункт – «Всегда отображать все значки и уведомления на панели задач».
Таким образом, вы всегда будете «иметь перед глазами» картинку всех запущенных системных задач.
Элементы интерфейса. Кнопка «Пуск»
Ещё одним немаловажным элементом интерфейса ОС Windows является кнопка «Пуск». При её нажатии система отображает графическое меню содержащее как список установленных в операционной системе программ, так и пункты, позволяющие произвести настройку системных параметров и открывать содержимое ваших накопителей (жёстких дисков, «флешек», SD-карт и прочее).
Первоначально, данное меню содержит в верхней строке имя пользователя, слева список наиболее часто используемых (запускаемых) в ОС программ, а справа – список системных программ — «Панель управления» и каталогов — «Компьютер».
Для поиска и ручного запуска программного обеспечения (непосредственным указанием имени фала) или выполнения системных команд существует специальное поле. По мере ввода команды или имени файла, система производит одновременный поиск, результат которого отображается непосредственно в этом же окне.
Раздел «Все программы» открывает дополнительное меню со списком всего, установленного на данном ПК, программного обеспечения. Для того, чтобы этот список был «удобочитаемым» разработчики позаботились о делении его на программные группы, так как при установке какого-либо ПО практически всегда его разработчики создают и файлы автоматической деинсталляции (удаления), помощи, описания, вспомогательных программ и т. п. Для того, чтобы программу и все, что с ней связано можно было легко найти, система Windows создаёт для неё свой раздел, в который и помещает все, что с ней связанно.
Раздел «Документы» отражает папку, в которой по умолчанию сохраняются, как правило, текстовые файлы пользователя, которые он создаёт на ПК. То же самое касается разделов «Музыка» и «Изображения», с той лишь разницей, что в них хранится соответствующий тип файлов.
Для быстрого доступа и управления печатающими устройствами (принтерами), а также другим, подключённым к ПК оборудованием, существует пункт «Устройства и принтеры».
Раздел «Программы по умолчанию» позволяет задать программное обеспечение, при помощи которого будут на ПК открываться файлы определённого типа.
Например, если пользователь предпочитает воспроизводить музыкальные файлы при помощи проигрывателя AIMP, а не стандартного, встроенного в Windows, то открыв этот раздел можно задать эту программу в качестве «умолчательной» для открытия любых музыкальных файлов или музыкального файла конкретного типа.
Ниже в примере, в качестве программы по умолчанию для воспроизведения музыкальных файлов, имеющих расширение *.mp3 выбирается проигрыватель AIMP.
Выбирая программу по умолчанию, следует иметь в виду, что она должна быть установлена на вашем ПК, в противном случае её не будет в списке.
Источник
Основные элементы интерфейса операционной системы Windows



Элементы интерфейса ОС Windows
Интерфейс ОС Windows — графический. Он позволяет осуществлять взаимодействие человека с компьютером в форме диалога с использованием окон, меню и элементов управления.
Перечислим основные элементы интерфейса.
1. Основную часть экрана системы занимает РАБОЧИЙ СТОЛ, на котором располагаются ЯРЛЫКИ.
2. В нижней части экрана системы располагается ПАНЕЛЬ ЗАДАЧ, на которой находится кнопка ПУСК, кнопки выполняемых задач и открытых папок, индикаторы и часы. Кнопка ПУСК позволяет вызывать ГЛАВНОЕ МЕНЮ, которое обеспечивает доступ практически ко всем ресурсам системы и содержит команды запуска приложений, настройки системы, поиска файлов и документов, доступа к справочной системе и др. Поскольку ОС Windows является многозадачной операционной системой, то есть параллельно могут выполняться несколько приложений, то каждое запущенное приложение отображается на ПАНЕЛИ ЗАДАЧ кнопкой.
3. Важнейшим элементом интерфейса являются ОКНА. Основными элементами ОКНА приложения являются:
— рабочая область (внутренняя часть окна, содержащая вложенные папки или окна документов);
— границы (рамка, ограничивающая окно с 4-х сторон);
— заголовок (строка непосредственно под верхней границей окна, название окна);
— значок системного меню (кнопка слева в строке заголовка, меню перемещения и изменения размеров);
— строка горизонтального меню (непосредственно под заголовком, обеспечивает доступ к командам);
— панель инструментов (под строкой горизонтального меню, набор кнопок для быстрого доступа к некоторым командам);
— кнопки («свернуть», «развернуть/восстановить», «закрыть», в верхней правой части окна).
4. МЕНЮ является одним из основных элементов интерфейса и представляет собой перечень команд, из которых необходимо сделать выбор. Выбор пункта меню приводит к выполнению определенной команды.
5. ДИАЛОГОВЫЕ ОКНА могут включать в себя разнообразные элементы:
ВКЛАДКИ (несколько страниц в одном окне);
СПИСКИ (набор предлагаемых на выбор значений, раскрывающийся список — текстовое поле, снабженное кнопкой со стрелкой вниз);
СЧЕТЧИКИ (пара стрелок, которые позволяют увеличивать или уменьшать значение в связанном с ними поле);
ПОЛЗУНКИ (элементы, позволяющие плавно изменять значение какого-либо параметра, например, громкости).
Источник
Структура интерфейса Windows
ОПЕРАЦИОННЫЕ СИСТЕМЫ
(материалы для выполнения лабораторных, практических, самостоятельных работ)
«Операционная система MS Windows»
Содержание
| Тема 1. Интерфейс |
| · Роль и назначение операционной оболочки Windows. · Основные элементы интерфейса (диалога) Windows, их назначение. · Основные элементы окна. · Основные элементы Главного меню. · Буфер обмена. · Поиск файлов. · Приемы работы с манипулятором мышь. |
| Тема 2. Справочная система |
| · Способы получения справки. |
| Тема 3. Управление файловой системой |
| · Назначение папки Мой компьютер, программы Проводник. · Создание, сохранение, переименование, копирование, перемещение, удаление файлов, папок и ярлыков. · Восстановление удаленных объектов из папки Корзина. |
| Тема 4. Стандартные программы · Назначение и основные возможности стандартных программ. |
| · Простейшие приемы редактирования текста в редакторе Блокнот. · Выполнять простейшие рисунки в графическом редакторе Paint. · Обзор программ папки Служебные. Тема 5. Настройки Windows · Настройки операционной системы Windows. · Настройки элементов оформления. |
Тема 1. ИНТЕРФЕЙС WINDOWS
Операционная система Windows
Особенности ОС:
· Повышенная производительность, обусловленная многозадачностью т.е. компьютер может работать одновременно с несколькими программами.
· Совместимость с программами ОС MS DOS.
· Устойчивость к сбоям.
· Допустимость длинных имен файлов (до 256 символов).
· Высокое качество мультимедиа (звук, видео, графика).
Основные понятия ОС Windows
& Стартовый экран Windows представляет собой системный объект, называемый Рабочим столом.
Рабочий стол- это графическая среда, на которой отображаются объекты Windows и элементы управления Windows.
Все, с чем мы имеем дело, работая с компьютером в данной системе, можно отнести либо к объектам, либо к элементам управления. В исходном состоянии на Рабочем столе можно наблюдать несколько экранных значков и Панель задач.
Значкам соответствуют папки, приложения (программы), документы, сетевые устройства.
Окно – структурный и управляющий элемент пользовательского интерфейса, представляющий собой обрамленную часть экрана, в которой может отображаться объект (приложение, документ или сообщение).
Результаты работы большинства приложений (программ) сохраняются в их рабочих файлах, называемых также документами.
Документ – любой файл, обрабатываемый с помощью приложений (программ).
В Windows документ может содержать текстовую, графическую, звуковую и видеоинформацию.
Структура интерфейса Windows
Основные элементы интерфейса (диалога): Рабочий стол, Панель задач, Главное меню, папка Мой компьютер, программа Проводник, Панель управления, Корзина.
Дадим краткую характеристику данным элементам.
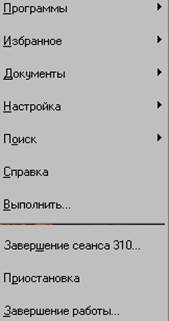
На панели задач расположены кнопка «Пуск», кнопки открытых окон, индикатор клавиатуры, системные часы. Кнопки открытых окон на панели задач можно использовать для переключения между окнами т.е. щелкнув мышью на данной кнопке, окно соответствующее данной кнопке становится активным. При нажатии кнопки Пуск раскрывается Главное меню рис.1

Команда Поиск — позволяет осуществить поиск файлов и папок.
Команда Выполнить…— предназначен для непосредственного запуска программ из командной строки указав полный путь к файлу.
С помощью папки Мой компьютер можно выполнить все операции с файлами и папками, обратиться к различным дискам и устройствам.
Программа Проводник более мощное средство для работы с файловой системой. Проводник отображает содержимое компьютера в виде «дерева» папок.
Корзина предназначена для временного хранения удаленных объектов. Она позволяет восстанавливать объекты удаленные по ошибке. Корзина занимает часть дискового пространства. Если Вы удалили файл, то он помещается из папки, где был прописан, в Корзину. Файл с диска удаляется только при очистке Корзины.
Панель Управления служит для изменения режима работы ОС, для установки программного и аппаратного обеспечения, для настройки параметров клавиатуры, мыши, экрана и т.д. Открыть панель Управления можно через Главное меню команда Настройка- Панель управления.
Приемы работы с мышью
Инструментом управления в ОС WINDOWS становится указатель мыши передвигаемый по экрану с помощью манипулятора мышь.
Основными приемами управления являются:
Щелчок (быстрое нажатие и отпускание левой кнопки мыши). Используется при выделении объекта, выборе пункта меню, нажатии кнопки;
Вызов контекстного меню – указать курсором на объект и нажать правую кнопку мыши.
Работа с окнами
Рассмотрим структуру окна папки Windows:











Диалоговые окна
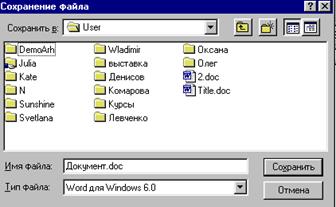
Если после команды подменю стоит многоточие (…), то после выбора данной команды появиться диалоговое окно. Диалоговые окна позволяют вести диалог с ОС, например в какой папке сохранить файл и дать имя файлу, найти нужный файл по имени просмотрев все папки диска С: и т.д.
Поле ввода со спускающимся списком





Выделим элементы диалогового окна:
Поле ввода текста предоставляет вам место, где вы указываете необходимую информацию, например имя файла, который нужно сохранить, или путь (содержащий название диска и папок), который вы используете для того, чтобы найти определенный файл. В поле ввода со списком представлен перечень элементов, из которых можно выбрать тот, который вам нужен. В поле ввода со списком часто есть линейки прокрутки, позволяющие просматривать очень длинные списки.
Поле ввода со спускающимся списком представляет из себя поле, в котором первоначально видна только одна строчка. Справа от него находится стрелка, направленная вниз. Если щелкнуть на стрелке, то развернется «спускающийся» список, и вы увидите элементы, из которых можно сделать выбор.
Кнопки опций (зависимые переключатели) представляют группу взаимосвязанных элементов, из которых можно выбрать («включить») только один. Просто щелкните на кнопке той опции, которую вы хотите выделить. При этом все другие кнопки «отключаются».
Поля меток (независимые переключатели) могут представлять собой как отдельную опцию, так и группу взаимосвязанных опций. Метка (обычно «крестик» или «галочка») появляется после щелчка в поле рядом с опцией, чтобы показать, что она активна.
Командные кнопки выполняют команды, название которых написано на данной кнопке (например, Сохранить, Открыть, Выход, Отмена, и т.д.). Если на кнопке после названия стоит многоточие, (например, как на кнопке Параметры. ), то при ее выборе появится другое диалоговое окно.
Вкладки представляют собой составные части сложных диалоговых окон. В одно и то же время можно видеть только одну вкладку, которая содержит логически связанные опции. При щелчке на названии вкладки изменяется содержание диалогового окна.
Иногда Вы не можете найти нужный файл, папку. В организации поиска вам поможет команда Главного меню Поиск— Искать файлы и папки.
Рассмотрим работу по поиску файла, используя вкладку Имя и размещение. В поле со списком введите Имя файла (можно первые буквы), в текстовое поле Содержащий можно ввести (не обязательно) фразу из текста искомого файла, для указания места поиска воспользуйтесь текстовым полем со списком, где и выберите диск, папку (для выбора другой папки воспользуйтесь командной кнопкой Обзор), нажмите командную кнопку Найти.
Контрольные вопросы:
1 Назначение и особенности ОС Windows.
2 Перечислите основные элементы Рабочего стола.
3 Какие объекты соответствуют значкам?
4 Перечислите основные элементы окна. Чем отличается команда закрыть и свернуть?
5 Перечислите основные элементы диалогового окна.
6 Для чего служат ярлыки? Повлияет ли на зарегистрированные программы удаление ярлыка?
7 Назначение Корзины, Главного меню, Панели задач.
Упражнения для приобретения простейших умений работы с окнами:
1. Найти на рабочем столе Windows значок Мой компьютер. Установить на него указатель мыши и щелкнуть два раза левой клавишей мыши (откроется окно).
2. Найти на экране все элементы окна.
3. Переместить окно в правый угол экрана. Для того, чтобы переместить окно:
· поместите курсор в строку заголовка
· нажмите левую кнопку мыши и, не отпуская ее, перетащите окно
· отпустите кнопку мыши.
4. Измените размер окна. Чтобы изменить размер окна:
· поставьте курсор на одну из границ окна
· нажмите левую кнопку мыши и, не отпуская ее, перетащите границу в нужное место
· отпустите кнопку мыши.
5. Измените размер окна до минимума.
6. Используя линейки прокрутки, просмотрите содержимое окна.
7. Распахните окно во весь экран. Для этого найдите в строке заголовка кнопку 
8. Восстановите исходный размер окна, нажав на кнопку 
9. Сверните окно Мой компьютер, нажав на кнопку 
10. Восстановите окно, щелкнув по значку Мой компьютер в панели задач.
11. Измените вид представления содержимого окна с помощью пункта меню Вид:
· щелкните по пункту меню Вид и выберите Мелкие значки
· щелкните по пункту меню Вид и выберите Таблица
· щелкните по пункту меню Вид и выберите Список
· самостоятельно вернитесь к исходной форме представления данных в окне.
12. Закройте окно Мой компьютер, щелкнув по кнопке 
Упражнения для приобретения дополнительных умений работы с окнами:
· текстовый процессор Microsoft Word,
· графический редактор Paint,
· текстовый редактор Блокнот,
2. Измените размеры каждого окна, размер окна установите приблизительно равным 1/4 размера экрана.
3. Расположите окна так, чтобы они не перекрывали друг друга.
4. Расположите окна каскадом, мозаикой.
(Для этого используйте контекстно-зависимое меню, вызываемое нажатием правой кнопкой мыши на системных часах Панели задач).
5. Закройте все окна.
6. Перенесите Панель задач (влево, вправо, вверх), затем верните на место.
(Эта операция выполняется как с обычным окном)
7. Измените размеры Панели задач, восстановите прежние размеры.
(Эта операция выполняется как с обычным окном)
Упражнения по настройке окна и поиску компьютеров, папок и файлов:
1. Раскройте окно папки Мой компьютер.
2. Используя команду меню Вид измените представление значков (крупные, мелкие, список, таблица).
3. Скройте панель инструментов и строку состояния, выбрав данные команды в меню Вид. Повторным выбором данных команд восстановите панель инструментов и строку состояния.
4. Найдите, используя команду Поиск главного меню:
5. Запустите программу Word на выполнение.
6. Сверните окно документа, затем окно программы.
7. Используя вкладку Дата диалогового окна «Найти: Все файлы», найдите все файлы, измененные за два последних дня.
8. Используя команду Главного меню Документы, откройте любой файл из списка имеющихся.
Источник
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
(Redirected from Windows Time)
The following is a list of Microsoft Windows components.
Configuration and maintenance[edit]
| Component | Description | Introduced |
|---|---|---|
| Settings | Allows users to change system settings, similar to the Control Panel, but has less options[1] | Windows 8 |
| Control Panel | ||
| Control Panel | Allows users to view and change basic system settings and controls, such as adding hardware, adding and removing software, controlling user accounts, and changing accessibility options | Windows 1.0 |
| Device Manager | Allows the user to display and control the hardware attached to the computer, and control what device drivers are used | Windows 95 |
| Windows Mobility Center | Centralizes the most relevant information related to mobile computing | Windows Vista |
| Security and Maintenance | Centralizes and reports on the status of anti-virus, Automatic Updates, Windows Firewall, and other security-related components of the operating system | Windows XP SP2 |
| Administrative Tools | ||
| Microsoft Management Console | Provides system administrators and advanced users with a flexible interface through which they may configure and monitor the system | Windows NT 4.0 Option Pack |
| Windows System Assessment Tool | Built-in benchmarking tool that analyzes the different subsystems (graphics, memory, etc.), and uses the results to allow for comparison to other Windows Vista systems, and for software optimizations. It rates the computer’s performance using the Windows Experience Index. | Windows Vista |
| System Restore | Allows for the rolling back of system files, registry keys, installed apps, etc., to a previous state in the event of a system failure | Windows Me |
| Windows Recovery Environment | Helps diagnose and recover from serious errors which may prevent Windows from booting successfully, or restore the computer to a previous state using System Restore or a backup image | Windows Vista |
| Microsoft Drive Optimizer | Rearranges files stored on a hard disk to occupy contiguous storage locations in order to optimize computer performance | Windows 95, Windows 2000 |
| Event Viewer | Lets administrators and users view the event logs on a local or remote machine | Windows NT 3.1 |
| Resource Monitor (previously Reliability and Performance Monitor) |
Lets administrators view current system reliability and performance trends over time | Windows Vista |
| Logical Disk Manager | Logical volume manager developed by Microsoft in conjunction with Veritas Software | Windows NT 4.0 (Separate Tool), Windows 2000 |
| Registry Editor | Allows users to browse and edit the Windows registry | Windows 3.1 |
| Task Scheduler | Allows users to script tasks for running during scheduled intervals | Microsoft Plus! for Windows 95 |
| Software installation and deployment | ||
| Windows Update | An online service providing updates such as service packs, critical updates and device drivers. A variation called Microsoft Update also provides software updates for other Microsoft products. | Windows 98 |
| Windows Installer | An engine for the management of software installation. Includes a GUI framework, automatic generation of the uninstallation sequence and deployment capabilities for corporate networks. | Windows 2000 |
| ClickOnce | Technology for deploying .NET Framework-based software via web pages, with automatic update capabilities. Intended for per-user only applications. | .NET Framework 2.0 |
User interface[edit]
| Component | Description | Introduced |
|---|---|---|
| Action Center | View notifications sent from apps and change common settings | Windows 10 Version 1507 |
| Command Prompt | Text-based shell (command line interpreter) that provides a command line interface to the operating system | Windows NT 3.1 |
| Windows PowerShell | Command-line shell and scripting framework. | Windows XP |
| Windows Shell | The most visible and recognizable aspect of Microsoft Windows. The shell provides the container inside of which the entire graphical user interface is presented, including the taskbar, the desktop, Windows Explorer, as well as many of the dialog boxes and interface controls. In Windows Vista, a new compositing glass-like user interface called Windows Aero has been shown. | Windows 95 |
| File Explorer (previously Windows Explorer) |
Provides an interface for accessing the file systems, launching applications, and performing common tasks such as viewing and printing pictures | Windows 95 |
| Windows Search | Starting with Windows Vista, search is a tightly shell-integrated component of Windows. A downloadable Windows Desktop Search software is available for Windows XP and older versions. | Windows Vista, downloadable for older versions |
| Search Folders | Virtual folders that retrieve items based on queries rather than hierarchical folder trees on disk. | Windows Vista |
| Special Folders | Folders which are presented to the user through an interface as an abstract concept, instead of an absolute path. This makes it possible for an application to locate where certain kinds of files can be found, regardless of what version or language of operating system is being used. See also Windows Shell namespace. | Windows 95 |
| Start menu | Serves as the central launching point for applications. It provides a customizable, nested list of apps for the user to launch, as well as a list of most recently opened documents, a way to find files and get help, and access to the system settings. By default, the Start Button is visible at all times in the lower left-hand corner of the screen. | Windows 95 |
| Taskbar | The application desktop bar which is used to launch and monitor applications | Windows 95 |
| Task View | Displays all open windows and activities (via timeline) at a glance and switch between virtual desktops, starting in version 2004, users can now rename desktops | Windows 10 Version 1507 |
| File associations | Used to open a file with the appropriate app. Users can assign file associations uniquely to specific actions, known as verbs. | Windows 1.0 |
Applications and utilities[edit]
| Component | Description | Introduced |
|---|---|---|
| Easy Transfer | Used to transfer many files at once from one computer to another | Windows Vista |
| Contacts | Keeps a single list of contacts that can be shared by multiple apps | Windows Vista |
| Camera | Allows the user to take pictures or record video[2] | Windows 8 |
| Calculator | Calculation application | Windows 1.0 |
| Calendar | Calendaring application | Windows Vista |
| Character Map | Utility to view and search characters in a font, copy them to the clipboard and view their Windows Alt keycodes and Unicode names | Windows 3.1 |
| Cortana | Digital personal assistant | Windows 10 Version 1507 |
| Edge | Web browser | Windows 10 Version 1507 |
| Feedback Hub | Platform for exchanging communication with Windows Insiders and developers | Windows 10 Version 1607 |
| Groove Music (previously Xbox Music) |
Digital media player and media library application that is used for playing audio. In addition to being a media player, Groove includes the ability to copy music to compact discs, synchronize content with a digital audio player (MP3 player) or other mobile devices, and let users purchase or rent music from the Windows Store. | Windows 8 |
| Movies & TV (previously Xbox Video) |
Digital media player and media library application that is used for playing video. In addition to being a media player, Movies & TV lets users purchase or rent movies and TV episodes from the Windows Store. | Windows 8 |
| OneDrive (previously SkyDrive) |
Freemium cloud storage folder and sync service | Windows 8 |
| OneNote | Integrated note-taking app, based on the Microsoft Office product of the same name | Windows 8 |
| On-Screen Keyboard (osk.exe) | Virtual keyboard | |
| Paint 3D | Simple graphics painting app | Windows 10 Version 1703 |
| Photos | Simple image viewer | Windows 8 |
| Steps Recorder (called Problem Steps Recorder in Windows 7) |
Utility that allows the user to capture steps they took to reproduce a problem | Windows 7 |
| Windows To Go | Utility to create bootable versions of Windows 8 and above | Windows 8 |
| Notepad | Simple text editor | Windows 1.0 |
| Narrator | Screen reader utility that reads dialog boxes and window controls in a number of the more basic applications for Windows | Windows 2000 |
| Sound Recorder | Simple audio recording app that can record from a microphone or headset, and save the results in WAVE format and Windows Media Audio format in some Windows versions | Windows 3.0 Multimedia Extensions |
| Skype | Messaging and calling service | Windows 8.1, downloadable for previous versions |
| Sticky Notes | Tool for jotting notes on the desktop | Windows XP Tablet PC Edition |
| WordPad | Simple word processor that is more advanced than Notepad. It has facilities to format and print text, but lacks intermediate features such as a spell checker and thesaurus. | Windows 95 |
| Private Character Editor | Utility to create private use characters as defined under Unicode and various East Asian encoding schemes | Windows 3.1 East Asian editions |
| Remote Desktop Connection | Client implementation of the Remote Desktop Protocol; allows a user to securely connect to a computer running Terminal Services (Remote Desktop on Windows XP and Server 2003) and interact with a full desktop environment on that machine, including support for remoting of printers, audio, and drives. | Windows XP, downloadable for previous Windows versions |
| Remote Assistance | Allows a user to temporarily take over a remote computer over a network or the internet to offer help with and resolve issues | Windows XP |
| Mobility Center | Allows a user to adjust settings related to mobile computing | Windows Vista |
| Speech Recognition | Allows a user to input voice commands | Windows Vista |
| IExpress | Allows users to create self-extracting, self-installing INF installation-based packages | Internet Explorer 6 |
| Xbox Console Companion (previously Xbox and Xbox Games) |
Account manager for Xbox Live user accounts and a screen recording tool | Windows 8 |
| Xbox Game Bar | Provides a overlay for compatible games allowing for screen capture, chatting over the Xbox network, showing the frame rate of games, and playing music via Spotify[3][4] | Windows 10 May 2019 Update (Version 1903)[5] |
| Magnifier | Screen enlargement app | Windows 98 |
| Fax and Scan | Integrated faxing and image scanning application | Windows Vista, older faxing and scanning applications were present in previous Windows versions |
| Photo Viewer | Simple image viewer that can play a simple slideshow | Windows 7 |
| Email aggregator | Windows 8 | |
| Maps | Map viewer that allows users to look for locations, plan routes, and store offline maps | Windows 8 |
| Media Center | Designed to serve as a home-entertainment hub, to be viewed from a distance up to 3 meters (~10 feet) and controlled by specially designed remote controls. Lets users browse and view pictures, videos, and music from local hard drives, optical drives, and network locations, along with viewing, recording and deferred-playing live TV. Features an interactive TV guide with scheduled recording capabilities. Can also be used for visualization of other information (like sports scores) within the interface. | Windows XP Media Center Edition |
| Task Manager | Provides information about computer performance and displays details about running applications, processes, network activity, logged-in users, and system services | Windows 3.0 |
| Disk Cleanup | Utility for compacting rarely used files and removing files that are no longer required | Windows 98 |
| Snipping Tool | Screen-capture tool that allows for taking screenshots (called snips) | Experience Pack for Windows XP Tablet PC Edition 2005 |
| Microsoft Store (previously Windows Store) |
Initially known as Windows Store, it started as an app store for Windows 8. In Windows 10, it expanded into a broad digital distribution platform for apps, games, music, digital video and e-books. In 2017, it was renamed Microsoft Store and started offering hardware in United States, Canada and United Kingdom. | Windows 8 |
| MSN apps | Provide information from MSN web services | Windows 8 |
| Alarms & Clock(pre Alarms) | App that allows Windows users to set alarms, stopwatches, timers, and view a world clock | Windows 8 |
| Windows Security (previously Windows Defender Security Center) |
Antivirus | Windows 10 Version 1703 |
| Solitaire Collection | Set of solitaire card games | Windows 10 Version 1507, downloadable for Windows 8.x |
Windows Server components[edit]
| Component | Description | Supported by |
|---|---|---|
| Active Directory | A set of technologies introduced with Windows 2000 that allows administrators to assign enterprise-wide policies, deploy apps to many computers, and apply critical updates to an entire organization. Active Directory stores information and settings relating to an organization in a central, organized, accessible database. Networks can vary from a small installation with a few objects, to global-scale directories with millions of objects. Related topics: Domain controller, Flexible single master operation |
Windows 2000 and later server versions |
| Group Policy | Provides centralized management of user and computer settings in an Active Directory environment. Group policy can control a target object’s registry, NTFS security, audit and security policy, software installation, logon/logoff scripts, folder redirection, and Internet Explorer settings. Policy settings are stored in Group Policy Objects (GPOs), and may be linked to one or more sites, domains or organizational units. Related topics: Administrative Templates |
Windows 2000 and later |
| Internet Information Services | Web server | Windows NT family |
File systems[edit]
| Component | Description | Supported by |
|---|---|---|
| FAT12, FAT16 | The original file systems used with MS-DOS. The standard file systems used with Windows 1.0 through Windows 95. | All versions |
| FAT32 | Extensions to FAT supporting larger disk sizes. The standard file system for Windows 98 and Me. | Windows 95 OSR2 and later versions |
| NTFS | Standard file system of Windows NT; supports security via access control lists, as well as file system journaling and file-system metadata. Windows 2000 added support for reparse points (making NTFS junction points and Single instance storage possible), Hard links, file compression, and Sparse files. Encryption of data is provided by Encrypting File System. Symbolic links and transactioning of file operations via Transactional NTFS are features new to Windows Vista.
Although Windows 9x operating systems cannot read or write NTFS formatted disks, they can access the data over a network if it is shared by a computer running Windows NT. |
Windows NT (all versions) |
| ISO 9660 (CDFS) | The predominant file system for CD-ROM and DVD-ROM media. Windows includes support for Joliet extensions and the ISO 9660:1999 standard. ISO 9660:1999 is supported since Windows XP. | MS-DOS and Windows 9x via extensions, such as MSCDEX.EXE (Microsoft CDROM Extension), natively in Windows NT |
| Universal Disk Format (UDF) | A file system for storing files on optical media. It is an implementation of the ISO/IEC 13346 standard (also known as ECMA-167). It is considered to be a replacement of ISO 9660. Successive versions of Windows have supported newer versions of UDF. | Windows 98, Windows 2000, Windows XP, Windows Server 2003, Windows Vista |
| HPFS | High-Performance File system, used on OS/2 computers. Read and write capability in Windows 95 (where it also listed network computer NTFS-formatted drives as «HPFS», even though it had no direct NTFS capabilities). HPFS write support was dropped in Windows NT 4.0 and Windows 98, and dropped altogether shortly before the release of Windows 2000. | Windows 95 (Read/write), Windows 98, Windows NT (read), 3.1/3.51 (read/write/boot) |
| ReFS | A newer file system, based on NTFS. This system adds built-in integrity checking and removes the need for chkdsk, among other features. The maximum partition size is 1 YB. | Windows Server 2012, Windows 8.1 |
Core components[edit]
| Component | Acronym | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Windows kernel (Windows NT)
Main article: Architecture of the Windows NT operating system line |
||
| Ntoskrnl.exe | The Windows kernel image. Provides the kernel and executive layers of the kernel architecture, and is responsible for services such as hardware virtualization, process and memory management, etc. | |
| hal.dll | HAL | Provides and handles the interaction between software and hardware via the Hardware Abstraction Layer. |
| kernel32.dll | This application provides kernel operations to apps in the Win32 mode, like memory management, I/Os, process creation, etc. | |
| Core processes (Windows NT) | ||
| System idle process | SIP | A counter which measures how much idle capacity the CPU has at any given time. The process runs in the background and monitors processing bandwidth, occupied memory and the Windows virtual paging file. |
| Session Manager Subsystem | SMSS | Performs several critical boot-time operations, such as the creation of environment variables, starting CSRSS, and performing file-copy operations that were queued up from before the system was booted (pending file rename operations). During system operation, it handles Windows File Protection and the creation of logon sessions via Winlogon. |
| Client/Server Runtime Subsystem | CSRSS | User-mode side of the Win32 subsystem. Provides the capability for applications to use the Windows API. |
| Local Security Authority Subsystem Service | LSASS | Responsible for enforcing the security policy on the system. Verifies users logging on to the computer and creates security tokens. |
| Winlogon | Responsible for handling the secure attention key, loading the user profile on logon, and optionally locking the computer when a screensaver is running. On Windows NT systems prior to Windows Vista, Winlogon is also responsible for loading GINA libraries which are responsible collecting logon credentials from the user. | |
| Svchost.exe | A generic host process name for services that run from dynamic-link libraries (DLLs). Several Svchost processes are typically present on a Windows machine, each running in a different security context, depending on what privileges the contained services require. | |
| Windows on Windows and WOW64 | WoW | An abstraction layer that allows legacy code to operate on more modern versions of Windows; typically this means running 16-bit Windows applications on 32-bit Windows, and 32-bit applications on 64-bit Windows. |
| Virtual DOS machine | NTVDM | Allows MS-DOS apps to run on Intel 80386 or higher computers when there is already another operating system running and controlling the hardware. Introduced in Windows 2.1; not available in any 64-bit edition of Windows. |
| System startup (Windows NT)
Main articles: Windows NT Startup Process and Windows Vista Startup Process |
||
| NTLDR, IA64ldr, Winload | The boot loader; performs basic system initialization options such as loading the hardware abstraction layer and boot-time device drivers, prior to passing control to the Windows kernel. In versions prior to Vista, NTLDR and IA64ldr also display menus to the user if multiple operating systems are defined in boot.ini, or if F8 is pressed. | |
| Recovery Console | Provides the means for administrators to perform a limited range of tasks using a command line interface, primarily to aid in recovering from situations where Windows does not boot successfully. | |
| ntdetect.com | Used during the boot process to detect basic hardware components that may be required during the boot process | |
| Windows Boot Manager | In Windows Vista and later operating systems, displays boot menus to the user if multiple operating systems are configured in the system’s Boot Configuration Data. | |
| Graphical subsystem | ||
| Desktop Window Manager | DWM | The compositing manager introduced in Windows Vista that handles compositing and manages special effects on screen objects in a graphical user interface |
| Graphics Device Interface | GDI/GDI+ | The kernel graphics component for representing graphical objects and transmitting them to output devices such as monitors and printers |
| Windows USER | The Windows USER component provides core user interface, messaging and visual elements |
Services[edit]
This list is not all-inclusive.
| Display name | Service key name | Description | Introduced |
|---|---|---|---|
| Active Directory Service | NTDS | Network Authentication Management | Windows 2000 Server |
| Alerter service | Alerter | Sends administrative alerts over the network to client computers, administrators and users | Windows NT |
| Application Layer Gateway service |
ALG | Provides support for plugins that allow network protocols to pass through Windows Firewall and work behind Internet Connection Sharing | Windows 2000 |
| Application Experience service | Processes application compatibility cache requests for applications as they launch[6] | ||
| Application Management | AppMgmt | Processes requests to enumerate, install, and remove applications that are installed on the computer or deployed through an organization’s network | Windows 2000 |
| Background Intelligent Transfer Service |
BITS | Transfers files between machines using idle network bandwidth. Used by Windows Update, Windows Server Update Services, and Systems Management Server to deliver software updates to clients, as well as by Windows Messenger. | Windows XP |
| Computer Browser | Browser | Crawls neighboring computers on the network and locates shared resources. One of the computers acts as the Master Browser and supplies this information to other computers designated as browsers.[7] | Windows for Workgroups |
| Delivery Optimization | DoSvc | A peer-to-peer distribution service that downloads Windows updates and Microsoft Store apps from the local network or Internet peers, and redistributes them to others. Can be configured using either the Settings app or Group Policy. The Settings app can turn it on or off, and specify whether the service operates on the local network only, downloads from and uploads to the Internet peers as well. Group Policy allows finer control.[8][9] Delivery Optimization relies on a centralized web service that does not index contents under 10 MB. Computers without Internet access cannot use Delivery Optimization.[10] | Windows 10 Anniversary Update[8] |
| Distributed Link Tracking | TrkWks, TrkSrv | Used to track links to files on NTFS volumes. Windows uses these services to find linked files if they are renamed or moved (locally or to another machine).[11] | Windows 2000 |
| Distributed Transaction Coordinator |
MSDTC | Allows transactional components to be configured through COM+ by coordinating transactions that are distributed across multiple computers and/or resource managers, such as databases, message queues, file systems, and other transaction–based resource managers.[12] | Windows 2000 and later NT-based |
| DNS Client | DNSCache | Resolves and caches domain names (e.g. “en.wikipedia.org”) to IP addresses | Windows 2000 |
| Event Log | EventLog | Stores and retrieves events that can be viewed in the event viewer. Part of services.exe.[13] | Windows NT |
| Extensible Authentication Protocol | EAPHost | Provides EAP authentication to connecting clients | Windows 2000 |
| Indexing Service | CISVC | Indexes contents and properties of files on local and remote computers; provides rapid access to files through flexible querying language.[14] | Windows 2000 and later NT-based |
| Interactive Services Detection | UI0Detect | For compatibility; when a service-displayed user interface is detected, it gives the user an option to switch to Session0 to see it | Windows Vista |
| Internet Connection Sharing (ICS) | SharedAccess | When enabled, it allows other computers on the local network to access an internet connection that is available to the host computer | Windows 2000;[15] Windows Vista onward[16] |
| Network Location Awareness | NLA | Manages network configurations and information, and notifies applications of changes | Windows XP |
| Network Store Interface Service | NSIS | Collects routing information of active network interfaces, shares this with other services and notifies applications of changes | Windows XP |
| NTLM Security Support Provider | NTLMSSP | Uses the NTLM MS-CHAP protocol to encapsulate and negotiate options in order to provide signed and sealed communication. Deprecated now in favor of Kerberos authentication. | Windows NT |
| Peer Name Resolution Protocol | PNRPSvc | Resolves domain names using Peer Name Resolution Protocol | Windows XP |
| Plug and Play | PlugPlay | Enables autodetection and configuration of hardware | Windows 2000 |
| Windows Print spooler [fr] | Spooler | Manages printer devices and moves files into memory for printing | Windows 95, Windows NT |
| Remote Procedure Call (RPC) | RpcSs | Provides Remote Procedure Call features via remotely accessible Named Pipes | Windows NT family |
| Routing and Remote Access Service | RRAS | API and server software that enables applications to administer the routing and remote-access service capabilities of the operating system, to function as a network router. | Windows 2000 |
| Secondary Logon | SecLogon | Allows users to run apps with a different account than the one they logged in with. Allows non-administrative accounts to perform administrative tasks.[17] | |
| Security Accounts Manager | SamSs | Manages user account security information | Windows NT family |
| System Event Notification Service | SENS | Monitors system events, such as network, power, logon, logoff, terminal services session connection and disconnection, and delivers these to applications and other system components.[18] | Windows 2000 |
| Superfetch | SysMain | Monitors file usage patterns and boosts system speed by caching frequently accessed files to RAM[19] | Windows Vista |
| Task Scheduler | Schedule | Lets users setup and schedule automated tasks | Microsoft Plus! for Windows 95 |
| TCP/IP NetBIOS Helper | LmHosts | Enables support for NetBIOS over TCP/IP (NetBT) service and NetBIOS name resolution | Windows NT family |
| Volume Shadow Copy | VSS | Creates multiple versions of files that change. The ability to store persistent snapshots was added in Windows Server 2003.[20] | Windows XP |
| Windows Audio | AudioSrv | Manages audio devices for Windows-based apps. Controls all audio functions. | Windows XP |
| Windows Error Reporting | WERSvc | Generates error logs and reports errors. On Windows Vista and later, it notifies of solutions. | Windows XP |
| Windows Firewall | MpsSvc | Blocks unauthorized network connections to and from the computer | Windows Vista |
| Windows Firewall(née Internet Connection Sharing) | SharedAccess | Provides a simple firewall feature which was introduced in Windows XP. It also shares the internet on the local network, if the internet connection sharing feature is turned on.[21] | Windows XP only[22][23] |
| Windows Image Acquisition (WIA) | STISvc | Handles scanner and camera inputs | Windows Me |
| Windows Time | W32Time | Synchronizes the system time with external time servers. From Windows Server 2003 forward, full and compliant NTP support is provided.[24] | Windows 2000 |
| Windows Update | WUAUServ | Provides updates for the operating system and its installed components | Windows XP |
| Wireless Zero Configuration | WZCSvc (XP), WLANSvc | Configures and manages 802.11 wireless adapters | Windows XP, Server 2003 only |
| Windows Messenger service | Messenger | Allows users to send pop-up messages to other computers over the network | Windows NT family |
| WebClient[25] | Enables Windows-based apps to create and interact with Internet-based files | Windows XP |
DirectX[edit]
- Direct3D
- DirectDraw
- DirectInput
- DirectMusic
- DirectPlay
- DirectShow
- DirectSound
- DirectX Media Objects
- DirectX plugin
- DirectX Video Acceleration
Networking[edit]
- Administrative share
- Distributed File System
- My Network Places (formerly Network Neighborhood)
- Network Access Protection
- Remote Installation Services
- Server Message Block
- Windows Rights Management Services
Scripting and command-line[edit]
- Batch file
- CHKDSK
- Cmd.exe
- ComSpec
- Ipconfig
- Net / Net Send
- Netdom.exe: Windows Domain Manager
- Netsh
- Netstat
- QBasic
- Regsvr32
- Robocopy
- Win32 console
- Windows Script Host
- Windows PowerShell
- XCOPY
Kernel[edit]
- Commit charge
- Kernel Transaction Manager
- Win32 Thread Information Block
.NET Framework[edit]
- Assembly
- CLI Languages
- Metadata
- .NET Remoting
- ADO.NET
- ASP.NET
- Base Class Library
- Common Intermediate Language
- Common Language Infrastructure
- Common Language Runtime
- Common Type System
- Virtual Execution System
- Windows CardSpace
- Windows Communication Foundation
- Windows Forms
- Windows Presentation Foundation
- Windows Workflow Foundation
Security[edit]
| Component | Description | Introduced |
|---|---|---|
| AppLocker | Policy-based component that enables or disables execution of software based on rules such as location, properties and digital signature | Windows 7 Professional, Enterprise and Ultimate editions Windows Server 2008 R2 |
| BitLocker Drive Encryption | Disk encryption software, designed to protect data by providing encryption for entire volumes | Windows Vista Enterprise and Ultimate editions, Windows Server 2008 |
| Credential Guard | Virtualization-based isolation of stored credentials to prevent theft and pass-the-hash attacks. | Windows 10 Enterprise, Education, IoT Enterprise, or , Windows Server 2016 |
| Data Execution Prevention | Security feature that is intended to prevent an application or service from executing code from a non-executable memory region | Windows XP Service Pack 2 |
| Encrypting File System | File system driver that provides file system-level encryption | Windows 2000 |
| Security Account Manager | Database stored as a registry file | Windows NT 3.1 |
| SYSKEY | Utility that encrypts the hashed password information in a SAM database using a 128-bit encryption key | Windows NT 4.0 Service Pack 3 |
| User Account Control | Technology and security infrastructure utility that aims to improve the security of Microsoft Windows by limiting application software to standard user privileges until an administrator authorizes an increase | Windows Vista, Windows Server 2008 |
| Windows Firewall | Utility designed to block unauthorized access while permitting authorized communications. An earlier edition known as Internet Connection Firewall that was disabled by default was included with the original Windows XP release. | Windows XP Service Pack 2 |
| Windows Defender | Security utility to prevent, remove and quarantine malware (viruses, Trojan horses, etc.) | Downloadable for Windows XP and Windows Server 2003 |
| Windows Resource Protection | Protects Registry keys and folders in addition to critical system files | Windows Vista |
Deprecated components and apps[edit]
| Component | Description | Category | Introduced | Last OS included | Superseded by |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3D Pinball | Pinball game | Game | Plus! 95 for Windows 95 | Windows XP | — |
| ActiveMovie | Streaming media technology | API | Windows 95 | Windows Me | DirectShow |
| Cardfile | Personal information manager | Personal organizer | Windows 1.0 | Windows Me | Outlook Express, Windows Mail, or Windows Live Mail |
| Chess Titans | Chess game | Game | Windows Vista | Windows 7 | Microsoft Chess |
| DriveSpace | Disk compression utility | Data compression | MS-DOS | Windows Me | — |
| Windows DVD Maker | DVD authoring software | Video | Windows Vista | Windows 7 | — |
| File Manager | File manager app | File manager | Windows 3.0 | Windows Me | Windows Explorer |
| FreeCell | FreeCell game | Game | Win32s | Windows 7 | Microsoft Solitaire Collection |
| Hearts | Version of the Hearts game using Black Lady scoring | Game | Windows for Workgroups 3.11 | Windows 7 | Microsoft Hearts |
| Insider Hub | Windows 10 Version 1507 | Windows 10 Version 1511 | Feedback Hub | ||
| Windows Help and Support | Online and offline reference manual for troubleshooting. | Utility | Windows Me | Windows 8.1 | Microsoft Tips or Get Started |
| HyperTerminal | Communication utility based on a low end version of HyperACCESS | Communication | Windows 95 | Windows XP | — |
| Hold ‘Em | Version of the Texas hold ’em game | Game | Windows Vista | Windows Vista | — |
| Hover! | Video game in a combination of bumper cars and capture the flag | Game | Windows 95 | Windows 95 | — |
| InkBall | Game where the user tries to get colored balls into the correct holes | Game | Windows XP Tablet PC Edition | Windows Vista | — |
| Internet Explorer | Web browser | Web browser and FTP client. See also: Internet Explorer versions, Features, History, Removal, Browser Helper Objects | Microsoft Plus! for Windows 95 | Windows 10 | Microsoft Edge |
| Mahjong Titans | Version of the Mahjong solitaire game | Game | Windows Vista | Windows 7 | Microsoft Mahjong |
| Windows Mail | E-mail client | Windows Vista | Windows Vista | Mail (Windows) | |
| Internet Mail and News | E-mail and news client | Windows 95 | Windows 95 | Outlook Express, Windows Mail, or Windows Live Mail | |
| Minesweeper | Version of the minesweeper game | Game | Microsoft Entertainment Pack, Windows 3.1 | Windows 7 | Microsoft Minesweeper |
| Media Control Interface | An app that can play media files and record sound by passing commands as strings. | API | Windows 3.0 | Windows Me | — |
| Windows Media Player | Digital media player app | Media player | Windows 3.0 Multimedia Extensions | Windows 10 | Windows Media Player, Movies & TV, or Groove Music |
| Microsoft Calendar | Calendaring app | Personal organizer | Windows 1.0 | Windows 3.1 | Windows Calendar, Windows Live Mail, or the Calendar app for Windows |
| Microsoft Diagnostics | Tool that provides detailed technical information about user’s software and hardware | Diagnostics | MS-DOS | Plus! 95 for Windows 95 | Microsoft System Information |
| Microsoft Fax | Faxing app | Fax | Windows 95 | Windows XP | Windows Fax and Scan |
| Microsoft Private Folder | Tool to protect private data | Personal organizer | Windows XP | Windows XP | |
| Windows Help | Documentation browser that used a proprietary format | Online help | Windows 3.0 | Windows XP | Microsoft Help |
| Windows Feedback | Windows 10 Version 1507 | Windows 10 Version 1511 | Feedback Hub | ||
| NTBackup | Built-in backup app | Backup | Downloadable for Windows NT 4.0 | Windows XP, Windows Server 2003 | Backup and Restore, Windows Server Backup |
| Outlook Express | E-mail client | Internet Explorer 4 | Windows XP | Windows Mail or Windows Live Mail | |
| Paint | Simple graphics painting app | Application | Windows 1.0 | — | — |
| Program Manager | Shell composed of a task-oriented graphical user interface, consisting of icons (shortcuts for apps) arranged into app groups. | GUI | Windows 3.0 | Windows XP | Windows Explorer |
| Purble Place | Educational game for children, teaching pattern recognition, shapes, and colors | Game | Windows Vista | Windows 7 | — |
| Reader | e-book reader | e-book reader | Windows 8 | Windows 10 Creators Update | Microsoft Edge (PDF), XPS Viewer (XPS), Photos (TIFF)[26] |
| Reversi | Version of Reversi. | Game | Windows 1.0 | Windows 3.0 | Internet Reversi only on Windows Me and Windows XP |
| Solitaire | Klondike Solitaire game | Game | Windows 3.0 | Windows 7 | Microsoft Solitaire Collection |
| Spider Solitaire | Spider Solitaire game | Game | Microsoft Plus! 98 | Windows 7 | Microsoft Solitaire Collection |
| System File Checker | Utility that allows users to scan for and restore corruptions in Windows system files | Security | Windows 98 | Windows Server 2003 | Windows Resource Protection |
| Tinker | Puzzle game in which the player controls a robot through various mazes and obstacle courses | Game | Windows Vista | Windows Vista | — |
| Video for Windows | Multimedia framework | API | Windows 3.1 | Windows 95 | DirectShow |
| Windows Address Book | List of contacts that can be shared by multiple apps | Contact manager | Internet Explorer 3 | Windows XP | Windows Contacts, People, or Windows Live Mail |
| Windows Desktop Gadgets | Widget engine for Microsoft Gadgets | User interface | Windows Vista | Windows 7 | Live tiles |
| Windows File Protection | Sub-system in the operating system, aims to prevent apps from replacing critical Windows system files. | Security | Windows Me as System File Protection | Windows XP | Windows Resource Protection |
| Windows Journal | Notetaking application that allows for the creation of handwritten notes | Accessories | Windows XP Tablet PC Edition | Windows 10 Threshold 2 | General improvements in Ink API |
| Windows Messaging | E-mail client | Windows 95 | Windows 95 | Internet Mail and News, Windows Mail, or Windows Live Mail | |
| Windows Messenger | Instant messaging client | Internet messaging | Windows XP | Windows XP, Windows Server 2003 | Windows Live Messenger or Skype |
| Windows Movie Maker | Non-linear video editing software | Video | Windows Me | Windows Vista | Windows Live Movie Maker or Microsoft Photos |
| Windows NetMeeting | Video conferencing client | Web conference | Windows 95 OSR2 | Windows XP | Windows Meeting Space |
| Windows Photo Gallery | Image organizer | Photo | Windows Vista | Windows Vista | Windows Live Photo Gallery or Microsoft Photos |
| Windows Picture and Fax Viewer | Image viewer | Photo | Windows XP | Windows XP | Windows Photo Gallery, Windows Fax and Scan, Windows Live Photo Gallery, Windows Photo Viewer, or Microsoft Photos |
| Windows Write | Simple word processor | Word processor | Windows 1.0 | Windows NT 3.51 | WordPad |
APIs[edit]
- ClearType
- Media Foundation
- Windows Driver Foundation
- Windows Imaging Component
- Windows Management Instrumentation
Miscellaneous (to be categorized)[edit]
- ActiveSync
- Compatibility Appraiser collects telemetry information.[27]
- DMRC (Device Metadata Retrieval Client) interfaces to metadata about devices from Windows 7 onwards.[28]
- I/O technologies
- Macro Recorder
- Microsoft Agent
- Prefetcher
- ReadyBoost
- Sync Center
- Text Services Framework
- Universal Audio Architecture
- Windows Color System
- Windows Diagnostic Infrastructure (WDI)[29]
- Windows Mobile Device Center
- Windows Rally
- Windows Registry
- Windows Speech Recognition
- XML Paper Specification
See also[edit]
- Outline of Microsoft
- List of Unix daemons
- List of games included with Windows
References[edit]
- ^ Shultz, Greg (February 28, 2015). «Control Panel and Settings: Why are both still UI options in Windows 10?». TechRepublic. Retrieved October 7, 2022.
- ^ «Get $Windows Camera from the Microsoft Store». apps.microsoft.com. Retrieved October 7, 2022.
- ^ «Xbox Support». support.xbox.com. Retrieved October 7, 2022.
- ^ Hoffman, Chris. «How to See FPS in Any Windows 10 Game (Without Extra Software)». How-To Geek. Retrieved October 7, 2022.
- ^ The Xbox Game Bar Team (May 22, 2019). «Introducing the New Xbox Game Bar». Xbox Wire. Microsoft. Archived from the original on September 21, 2019. Retrieved August 21, 2019.
- ^ «System Services». technet.microsoft.com. Microsoft. 2014. Archived from the original on November 5, 2017. Retrieved September 2, 2014.
The Application Experience service (AELookupSvc) is a part of the Application Compatibility Administrator. It processes application compatibility lookup requests for applications as they are started, provides support for Windows Server 2008 and Windows Vista–based computers running apps in compatibility mode, reports on compatibility issues, and automatically applies software updates to apps.
- ^ «Description of the Microsoft Computer Browser Service». Microsoft. Archived from the original on January 1, 2015. Retrieved November 3, 2017.
- ^ a b Mackie, Kurt (August 16, 2016). «Microsoft Clarifies Windows 10 ‘Delivery Optimization’«. Redmond Magazine. 1105 Enterprise Computing Group. Archived from the original on February 13, 2020. Retrieved January 27, 2018.
- ^ Hachman, Mark (March 29, 2017). «How Delivery Optimization in Windows 10 Creators Update helps avoid data overage fees». PCWorld. IDG. Archived from the original on August 25, 2017. Retrieved January 27, 2018.
- ^ Halfin, Dani; Poggemeyer, Liza; Lich, Brian; Kieselbach, Oliver; Childs, Andrew (April 30, 2018). «Configure Delivery Optimization for Windows 10 updates». docs.microsoft.com. Microsoft. Archived from the original on July 23, 2018. Retrieved July 23, 2018.
- ^ «Distributed Link Tracking on Windows-based domain controllers». Microsoft. Archived from the original on February 25, 2015. Retrieved October 28, 2008.
- ^ «Distributed Transaction Coordinator (MSDTC)». Microsoft. Archived from the original on September 10, 2016. Retrieved June 27, 2008.
- ^ «Event Log». Microsoft. Archived from the original on September 10, 2016. Retrieved June 27, 2008.
- ^ «What is Indexing Service?». Microsoft. Archived from the original on January 1, 2011. Retrieved June 27, 2008.
- ^ «Windows 2000 Professional and Server Service Pack 4 Services Configuration by Black Viper» Archived December 17, 2019, at the Wayback Machine, notice that the service is listed on this page. Retrieved April 2013
- ^ «Windows Firewall» Archived February 13, 2020, at the Wayback Machine. Retrieved April 2013
- ^ «Secondary Logon (Run As): Starting Programs and Tools in Local Administrative Context». Microsoft Corporation. Archived from the original on March 6, 2015. Retrieved October 28, 2008.
- ^ «System Event Notification Service». The Elder Geek. Archived from the original on October 26, 2008. Retrieved June 27, 2008.
- ^ «Myth Busted: Why Disabling SuperFetch on Vista and Windows 7 Is a Bad Idea», retrieved April 2013
- ^ «What Is Volume Shadow Copy Service?: Data Recovery». Microsoft Corporation. Archived from the original on August 26, 2017. Retrieved October 28, 2008.
- ^ «Windows Firewall/Internet Connection Sharing (ICS)» Archived September 10, 2016, at the Wayback Machine, Retrieved April 2013
- ^ «Windows 2000 Professional and Server Service Pack 4 Services Configuration by Black Viper» Archived December 17, 2019, at the Wayback Machine, Notice the absence of the service on this page. Retrieved April 2013
- ^ «Windows Firewall/Internet Connection Sharing (ICS)» Archived February 13, 2020, at the Wayback Machine, Notice that XP is the operating system listed. Retrieved April 2013
- ^ «How Windows Time Service Works: Windows Time Service». Microsoft Corporation. Archived from the original on April 22, 2016. Retrieved October 28, 2008.
- ^ Minasi, Mark; Layfield, Rhonda; Justice, Lisa (2006). Mastering Windows Server 2003: upgrade edition for SP1 and R2 (12 ed.). John Wiley & Sons. p. 56. ISBN 978-0-470-05645-5. Archived from the original on September 21, 2019. Retrieved July 21, 2010.
There is also a client piece for WebDAV built into XP, 2003, R2, and Vista, called the WebClient Service.
- ^ «Microsoft replaces standalone PDF reader app with Edge». MSPoweruser. November 26, 2017. Archived from the original on August 19, 2019. Retrieved August 19, 2019.
- ^ Leonhard, Woody (April 20, 2015). «KB 2952664 triggers daily telemetry run in Windows 7 — and may be snooping on users: Microsoft bills the ‘compatibility update’ as way to ease the upgrade process to Windows 10 — but it’s collecting data daily». Operating Systems. InfoWorld. InfoWorld, Inc. Archived from the original on June 2, 2017. Retrieved August 23, 2016.
The Microsoft Compatibility Appraiser task runs %windir%system32rundll32.exe appraiser.dll,DoScheduledTelemetryRun with the description ‘Collects program telemetry information if opted-in to the Microsoft Customer Experience Improvement Program.’
- ^ Compare: Tulloch, Mitch; Northrup, Tony; Honeycutt, Jerry; Wilson, Ed (2010). Windows 7 Resource Kit. Windows 7 Resource Kit, Microsoft Corporation. Vol. 1. Microsoft Press. p. 708. ISBN 9780735627000. Archived from the original on January 11, 2022. Retrieved August 18, 2016.
The DMRC [(Device Metadata Retrieval Client)] checks the computer’s local metadata cache and metadata store for metadata that applies to the device.
- ^ Solomon, David A.; Russinovich, Mark E.; Ionescu, Alex (June 17, 2009). Windows Internals. Developer Reference (5 ed.). Microsoft Press (published 2009). ISBN 9780735637962. Archived from the original on September 21, 2019. Retrieved October 24, 2016.
The Windows Diagnostic Infrastructure (WDI) helps to detect, diagnose, and resolve common problem scenarios with minimal user intervention.