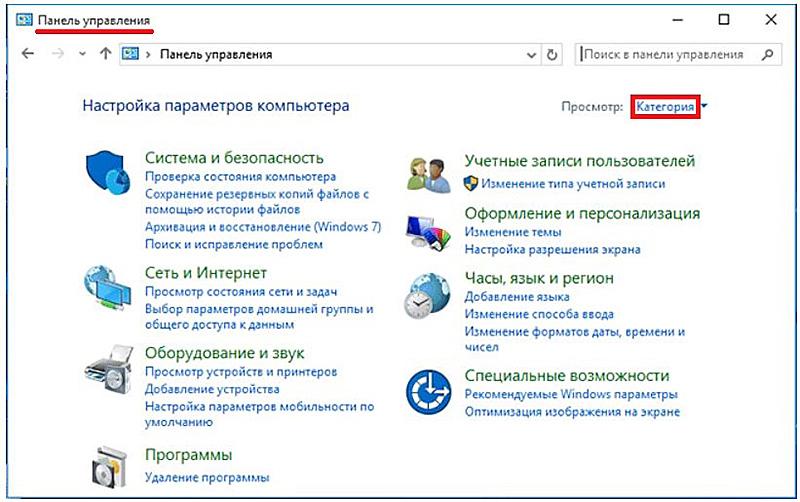
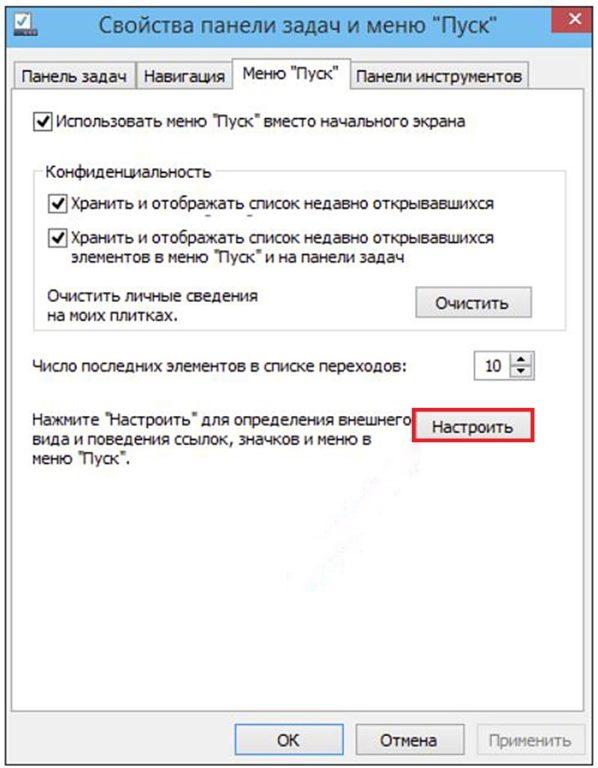
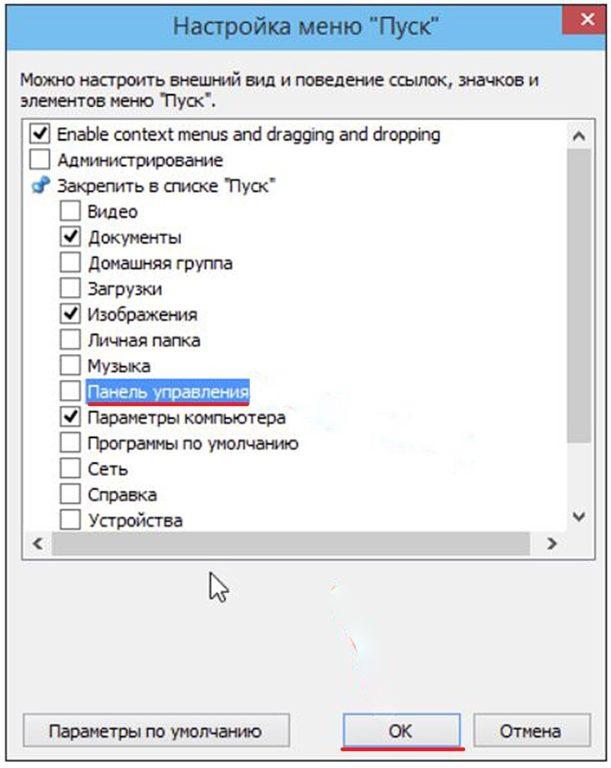
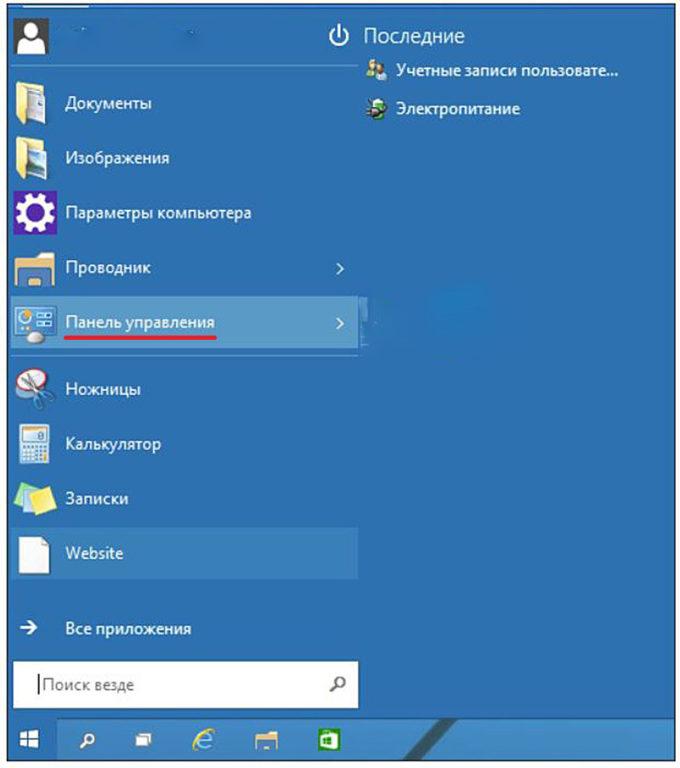
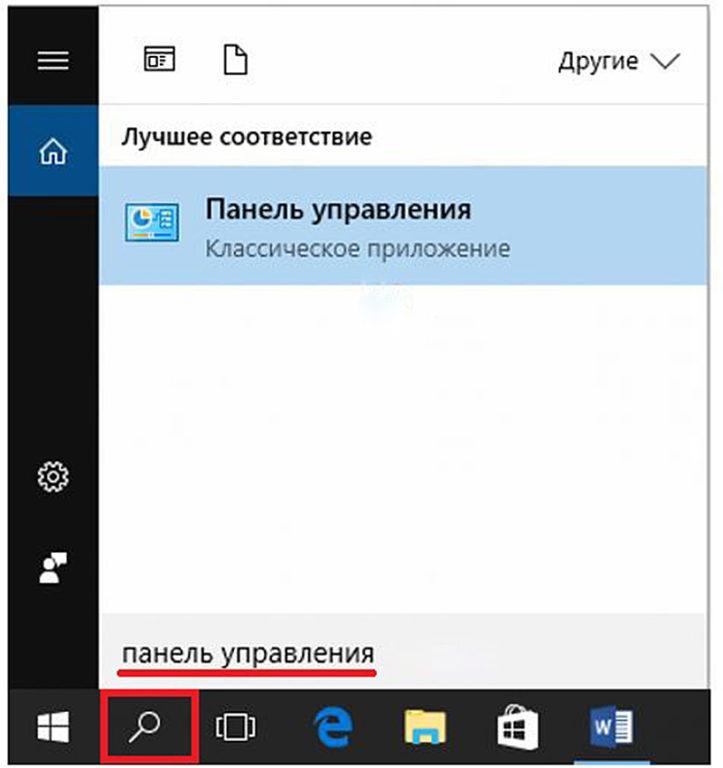
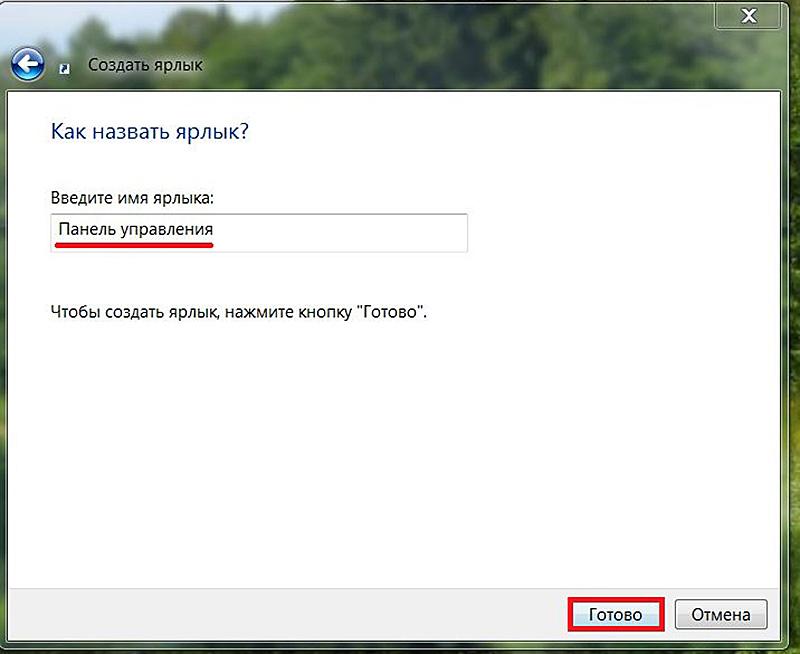
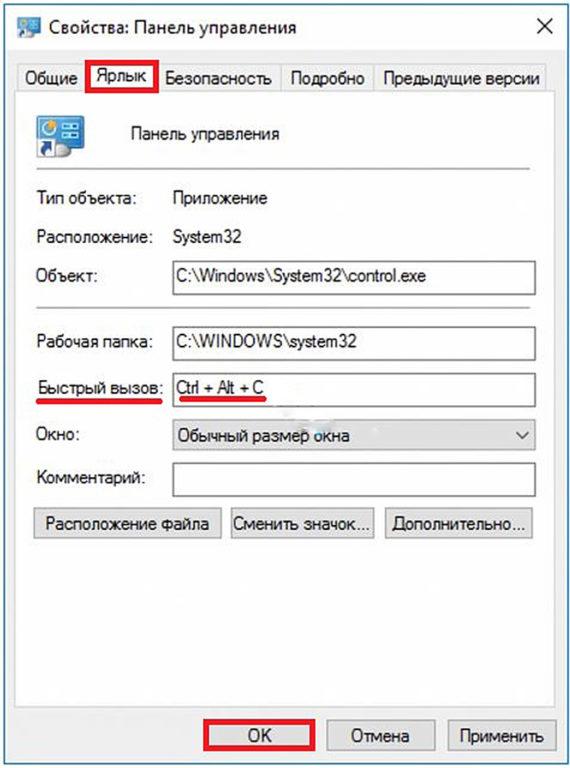
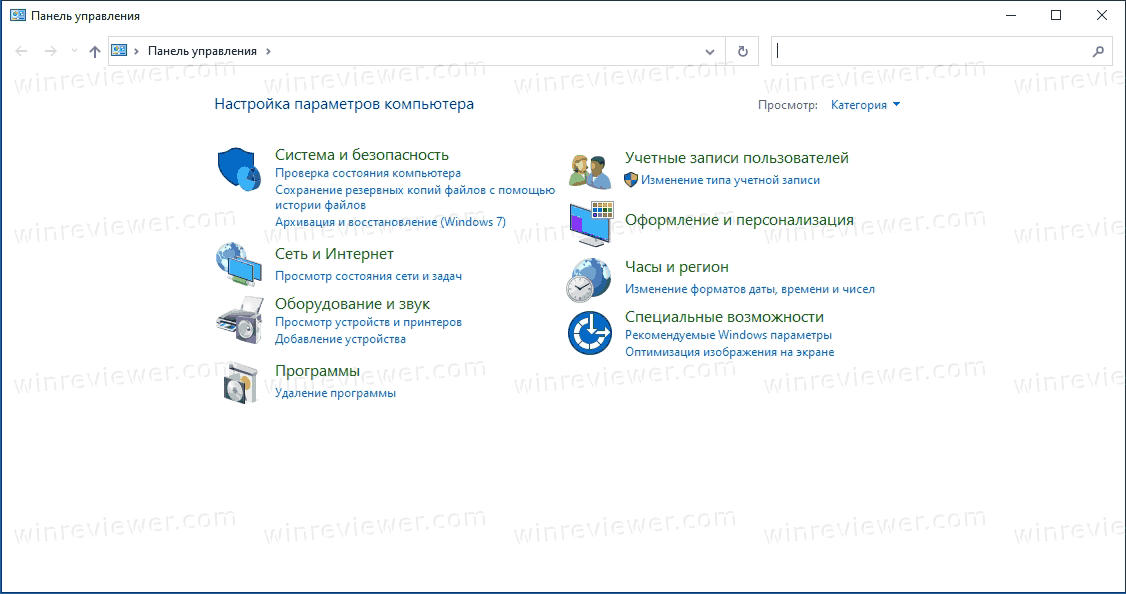
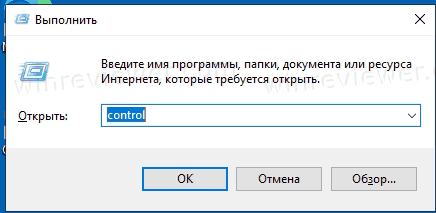
Многие пользователи windows 10 задаются вопросом, где находится панель управления в данной системе и если раньше ее можно было запустить через контекстное меню кнопки пуск, то после выхода последнего обновления Windows 10 v.1703 (Creators Update), разработчики компании Microsoft решили убрать данный пункт меню даже от туда.
Но расстраиваться сразу не стоит, потому что, существует куча способов попасть в панель управления windows 10, о которых мы поговорим в данной статье. Так же расскажу как вернуть панель управления на свое привычное место, а именно в контекстное меню кнопки пуск. И еще советую прочитать статью Как добавить новый пункт в контекстное меню рабочего стола Windows, где описывается пример добавления именно панели управления. Инструкция открытия панели в других версиях windows, читаем в стаье Как открыть панель управления в Windows.
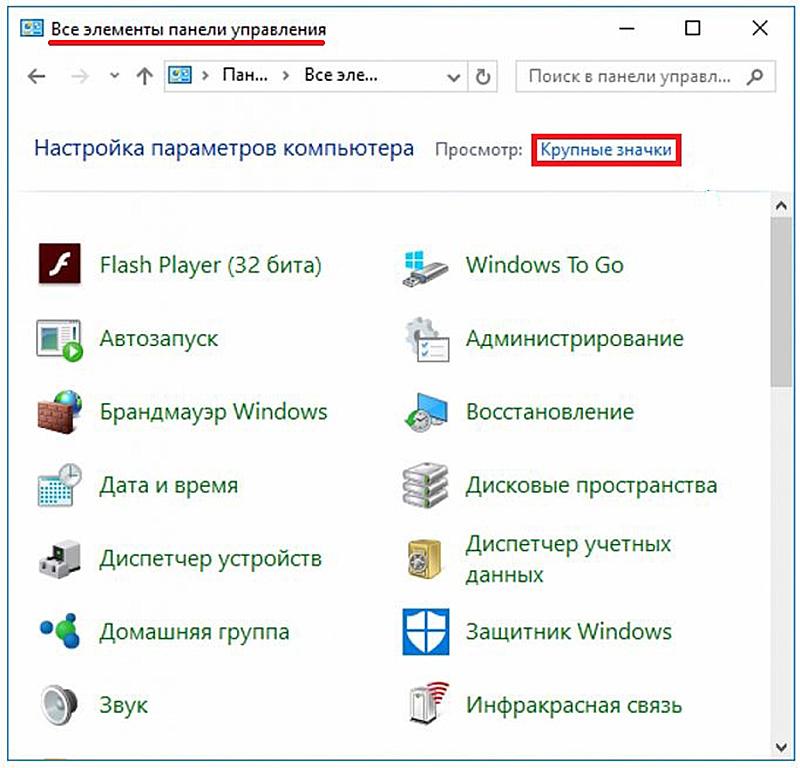
Где панель управления в windows 10
Первое, что приходит на ум при задаче вопроса где находится панель управления в windows 10, это обращение к системному поиску. Для этого жмем по значку лупы, находящемуся рядом с кнопкой пуск, где в строке поиска вводим название искомого файл, в нашем случае это панель управления. Далее запускаем найденное приложение.
Запуск панели управления windows 10 через вкладку параметры
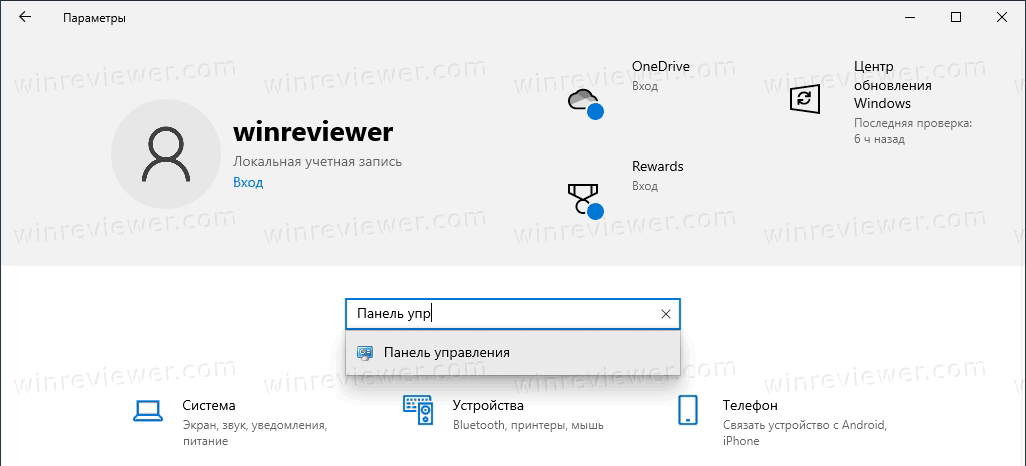
Хоть разработчики и пытаются навязать нам работать через вкладку параметры, но через нее тоже можно попасть в панель управления. Для этого переходим в пуск -> параметры.
Где так же в строке поиске вводим «панель управления» и открываем найденный пункт.
Открываем панель управления через командную строку
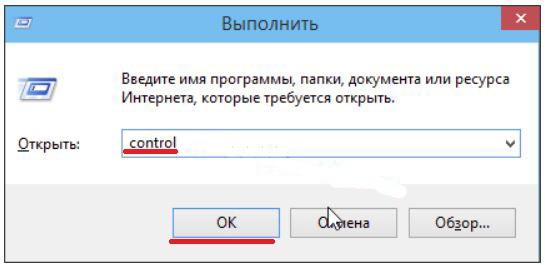
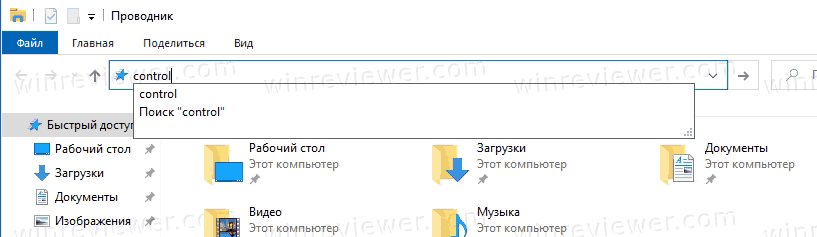
Конечно всегда есть вариант воспользоваться определенной командой, для запуска различных системных программ и приложений. Для открытия панели управления, тоже существует определенная команда, это команда «control». Ее можно ввести в диалоговом окне «выполнить«, которое запускается нажатием сочетания клавиш 
Windows powershell желательно запускать от имени администратора.
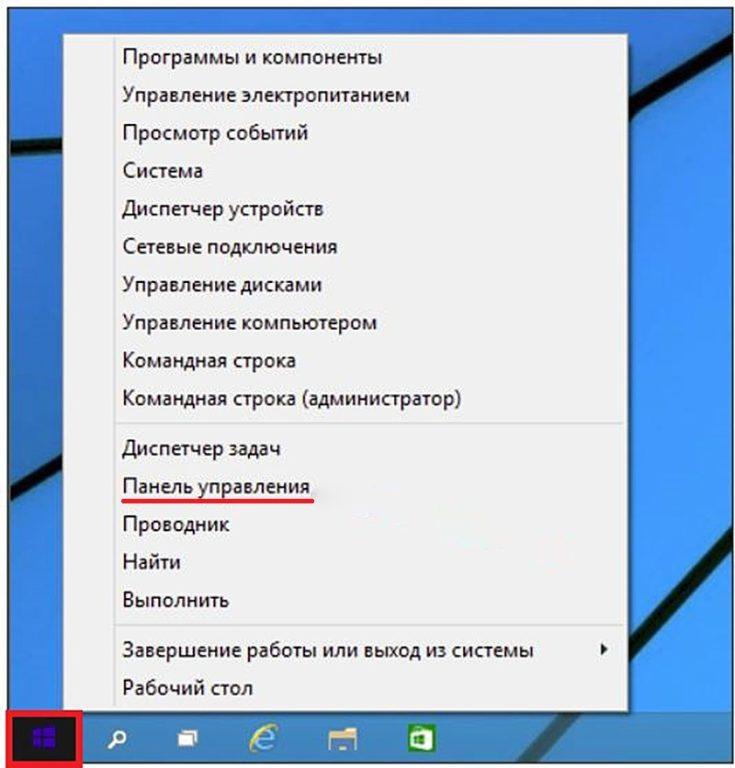
Ну и конечно в самом пуске, перейдя в папку служебные можно запустить панель управления.
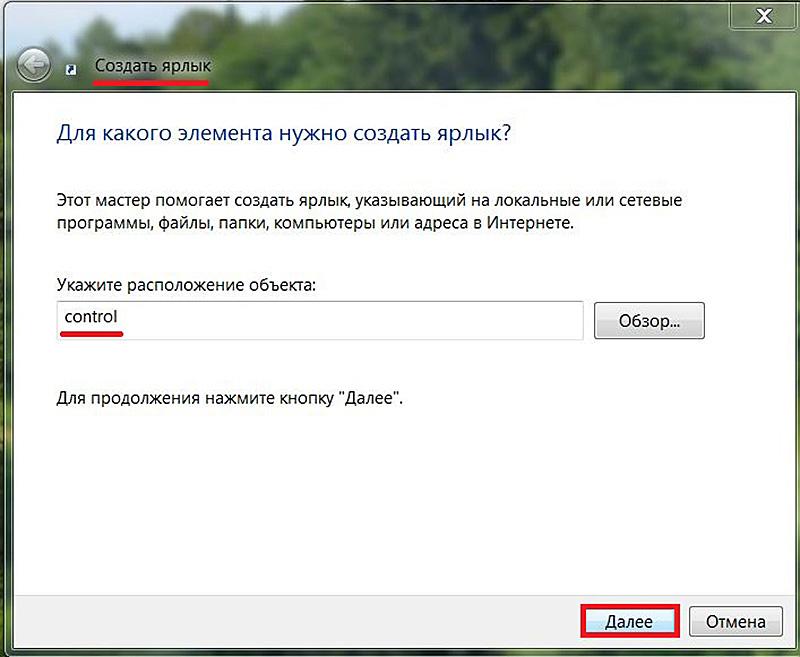
Так же вы можете упростит себе задачу и просто скопировать файл отвечающий за запуск панели управления на рабочий стол. Для этого переходим в системную папку по пути C:windowssystem32, находим файл под названием control.exe и копируем его на рабочий стол, запускаем и радуемся.
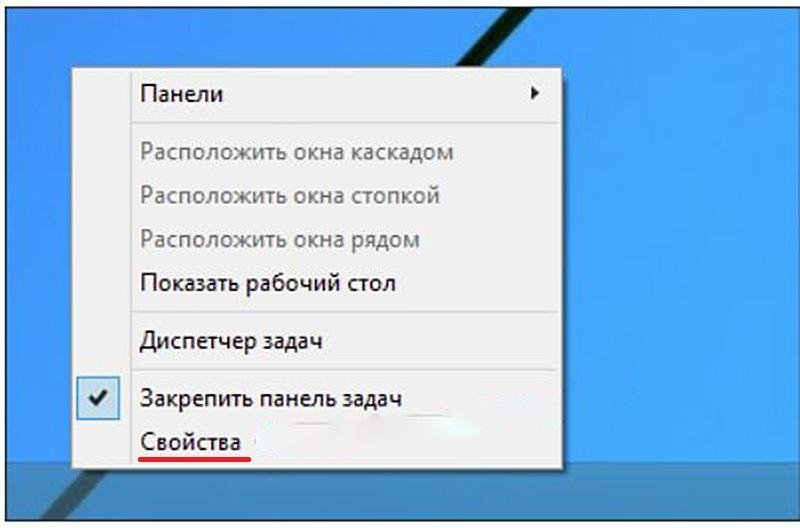
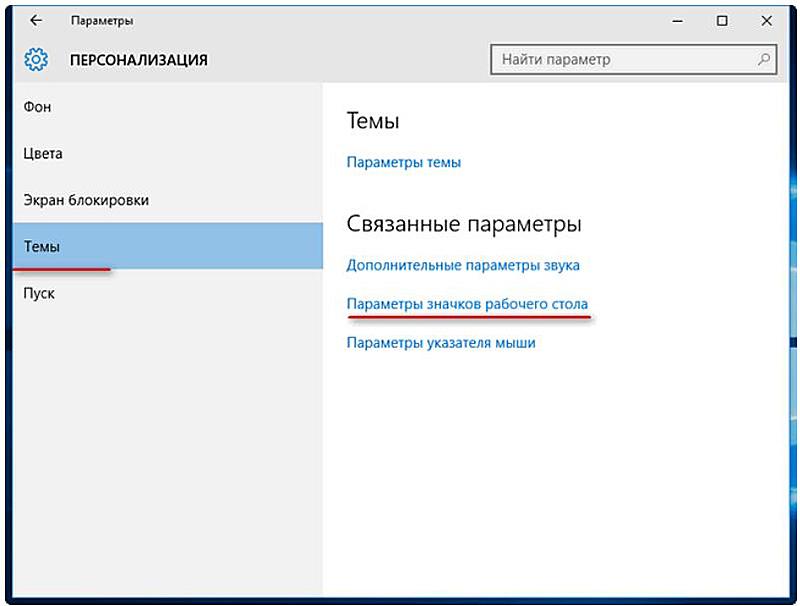
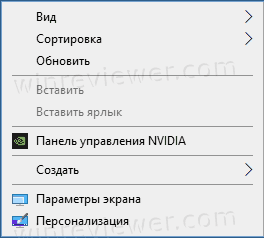
Возвращаем панель управления в контекстное меню кнопки пуск
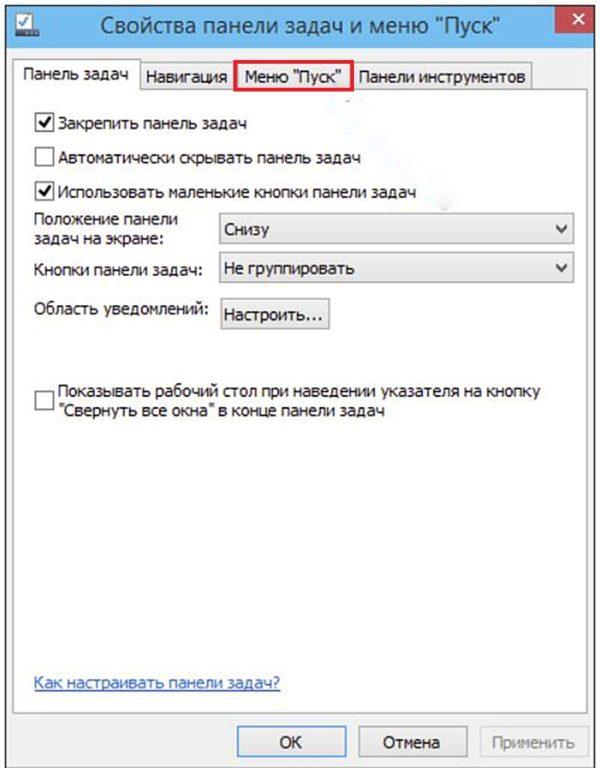
На скриншоте ниже, вы можете наблюдать картину до и после обновления windows 10. Где панель управления сменилось на вкладку параметры. Сейчас попробуем вернуть панель на свое законное место с сохранением вкладки параметры. Для этого нам понадобится скачать небольшую программку под названием Win+X Menu Editor.
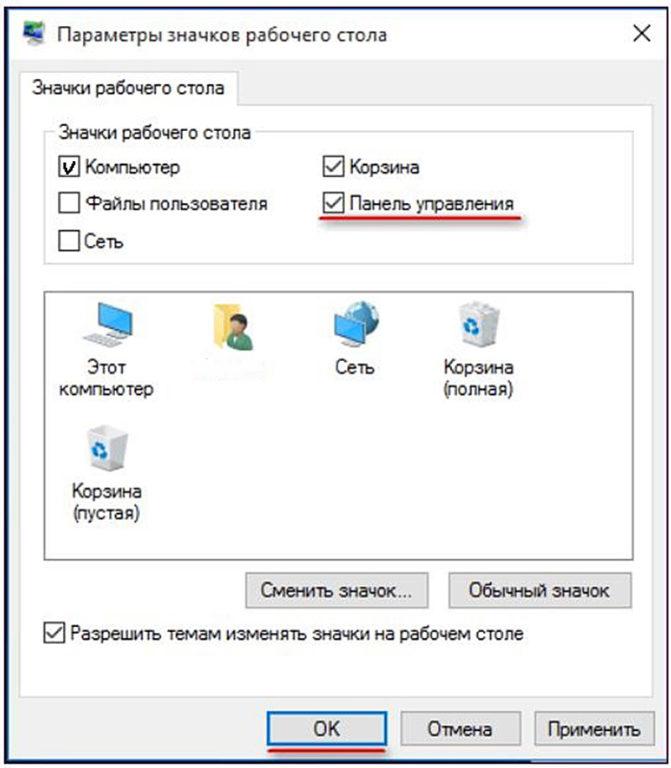
Переходим на сайт разработчика, по ссылке http://winaero.com/download.php?view.21, где скачиваем данное приложение. Распаковываем из архива и запускаем. В главном окне программы выбираем вкладку group2, далее жмем add a program -> add a control panel item.
Находим панель управления и жмем кнопку select.
После необходимо нажать на кнопку Restart Explorer, для перезагрузки проводника windows и применения внесенных изменений.
Теперь открываем контекстное меню пуска и видим появившийся пункт. Если данный пункт не появился, попробуйте перезагрузить компьютер.
Надеюсь вопрос где панель управления в windows 10, у вас уже не возникнет.
Оставляйте своё мнение о данной статье, ну и конечно же задавайте свои вопросы, если у вас что-то вдруг пошло не так.
Спасибо за внимание!
Статьи рекомендуемые к прочтению:
-
Как активировать Windows 10 бесплатно
(36222)
-
Секунды в трее windows 10
(7684)
-
Как удалить учетную запись Майкрософт в Windows 10
(8613)
-
Как войти в безопасный режим windows 10
(11640)
-
Как скачать официальный ISO-образ Windows 10, содержащий в себе 32-х и 64-х битные системы
(6243)
-
Где панель управления в windows 10
(27259)
-
Как отключить автоматическое обновление в Windows 10
(3773)
You can use Control Panel to change settings for Windows. These settings control nearly everything about how Windows looks and works, and you can use them to set up Windows so that it’s just right for you.
Open Control Panel
|
For Windows 10 |
In the search box on the taskbar, type control panel, and then select Control Panel. |
|
For Windows 8.1 / Windows RT 8.1 |
Swipe in from the right edge of the screen, tap Search (or if you’re using a mouse, point to the upper-right corner of the screen, move the mouse pointer down, and then click Search), enter Control Panel in the search box, and then tap or click Control Panel. |
|
For Windows 7 |
Click the Start button, and then click Control Panel. |
Find Control Panel items
When you’re in Control Panel:
-
Use search. To find a setting you’re interested in or a task you want to perform, type a word or phrase in the search box. For example, type «sound» to find specific settings for your sound card, system sounds, and the volume icon on the taskbar.
-
Browse. You can explore Control Panel by selecting different categories (for example, System and Security, Programs, or Ease of Access), and viewing common tasks listed under each category. Or, under View by, click either Large icons or Small icons to view a list of all Control Panel items.
Tips:
-
If you browse Control Panel by icons, you can quickly find an item in the list by typing the first letter of the item’s name. For example, to find Keyboard, type K, and the first Control Panel item beginning with the letter K—in this case, Keyboard—is selected in the list.
-
You can also use the arrow keys (Up Arrow, Down Arrow, Left Arrow, and Right Arrow) to scroll through the list of icons in Control Panel.
-
If you can’t find a setting in Control Panel, select the Start button > Settings . Many Control Panel features are now available in Settings .
Need more help?
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
The Control Panel is a component of Microsoft Windows that provides the ability to view and change system settings. It consists of a set of applets that include adding or removing hardware and software, controlling user accounts, changing accessibility options, and accessing networking settings. Additional applets are provided by third parties, such as audio and video drivers, VPN tools, input devices, and networking tools.

Control Panel in Windows 11 |
|
| Developer(s) | Microsoft |
|---|---|
| Initial release | 1985; 38 years ago |
| Operating system | Microsoft Windows |
| Type | Control panel |
Overview[edit]
The Control Panel has been part of Microsoft Windows since Windows 1.0,[1] with each successive version introducing new applets. Beginning with Windows 95, the Control Panel is implemented as a special folder, i.e. the folder does not physically exist, but only contains shortcuts to various applets such as Add or Remove Programs and Internet Options. Physically, these applets are stored as .cpl files. For example, the Add or Remove Programs applet is stored under the name appwiz.cpl in the SYSTEM32 folder. ==
In Windows XP, the Control Panel home screen was changed to present a categorized navigation structure reminiscent of navigating a web page. Users can switch between this Category View and the grid-based Classic View through an option that appears on either the left side or top of the window. In Windows Vista and Windows 7, additional layers of navigation were introduced, and the Control Panel window itself became the main interface for editing settings, as opposed to launching separate dialogs.
Many of the individual Control Panel applets can be accessed in other ways. For instance, Display Properties can be accessed by right-clicking on an empty area of the desktop and choosing Properties. The Control Panel can be accessed from a command prompt by typing control; optional parameters are available to open specific control panels.[2]
On Windows 10, Control Panel is deprecated in favor of Settings app, which was originally introduced on Windows 8 as «PC settings» to provide a touchscreen-optimized settings area using its Metro-style app platform. Some functions, particularly the ability to add and remove user accounts, were moved exclusively to this app on Windows 8 and cannot be performed from Control Panel.[3][4]
As of the October 2020 update to Windows 10, opening up the System applet in Control Panel will now redirect users to the About section of the Windows 10 Settings application. The page for the applet in Control Panel still exists even in current versions of Windows 10, however Microsoft is actively trying to block shortcuts and third party applications that could have been used to get into the old System page, which could potentially lead to a permanent removal of said page from Control Panel in future versions of Windows.[citation needed]
List of Control Panel applets[edit]
The applets listed below are components of the Microsoft Windows control panel, which allows users to define a range of settings for their computer, monitor the status of devices such as printers and modems, and set up new hardware, programs and network connections. Each applet is stored individually as a separate file (usually a .cpl file), folder or DLL, the locations of which are stored in the registry under the following keys:
- HKLMSOFTWAREMicrosoftWindowsCurrentVersionControl PanelCpls
This contains the string format locations of all .cpl files on the hard drive used within the control panel. - HKLMSOFTWAREMicrosoftWindowsCurrentVersionExplorerControlPanelNamespace
This contains the location of the CLSID variables for all the panels not included as cpl files. These are commonly folders or shell applets, though Windows Vista allows physical programs themselves to be registered as well. The CLSID then allows items such as the icon, infobox and category to be set and gives the location of the file to be used.
The control panel then uses these lists to locate the applets and load them into the control panel program (control.exe) when started by the user. In addition to using the control panel, a user can also invoke the applets manually via the command processor. For instance, the syntax «Control.exe inetcpl.cpl» or «control.exe /name Microsoft.InternetOptions» will run the internet properties applet in Windows XP or Vista respectively. While both syntax examples are accepted on Windows Vista, only the former one is accepted on Windows XP.[5]
Standard applets[edit]
| Accessibility options (Access.cpl) (control /name microsoft.easeofaccesscenter) (Renamed «Ease of Access Center» in Windows Vista and later) |
|---|
Allows users to configure the accessibility of their PC. It comprises various settings primarily aimed at users with disabilities or hardware problems.
Note that in Windows Vista onwards, the Ease of Access control panel superseded the old access.cpl control panel applet found in previous versions. |
| Add New Hardware (hdwwiz.cpl) |
| Launches a wizard which allows users to add new hardware devices to the system. This can be done by selecting from a list of devices or by specifying the location of the driver installation files. |
| Add or Remove Programs (appwiz.cpl) (Renamed «Programs and Features» in Windows Vista and later) |
The Add/Remove Programs dialog allows the user to manipulate software installed on the system in a number of ways;
|
| Administrative Tools (control admintools) |
| Contains tools for system administration, including security, performance and service configuration. These are links to various configurations of the Microsoft Management Console such as the local services list and the Event Viewer. |
| Automatic Updates (wuaucpl.cpl) |
| This is used to specify how the Automatic Updates client (wuauclt.exe) should download updates from the Microsoft Update Website, by default this is set to download and install daily, however this can be changed to a more suitable frequency. This also allows the user to specify whether to ask permission before downloading and/or installing updates or to simply switch off Automatic Updates altogether.
Removed in Windows 10, and moved to the Settings App. |
| Date and Time (timedate.cpl) |
| Allows user to change the date and time stored in the machine’s BIOS, change the time zone and specify whether to synchronize the date and time with an Internet Time Server and which server to use. |
| Display (control desktop) (desk.cpl)
(Renamed «Personalization» in Windows Vista, 7 and 8.1) |
Allows the user to change the display characteristics of their computer;
Removed in Windows 10 and moved to the Settings App. |
| Folder Options (control folders) (rundll32.exe shell32.dll, Options_RunDLL 0) |
| This item allows for configuration of how folders and files are presented in Windows Explorer. More specifically it allows the user to specify general settings like whether folders open in a new window or the existing window and whether the common tasks pane is shown, as well as more advanced tasks such as whether windows should hide critical system files and whether to show file extensions. It is also used to modify file type associations in Windows; i.e., which program opens which type of file and other settings like actions for each file type and the file extension. |
| Fonts (control fonts) |
| Displays all fonts installed on the computer. Users can remove fonts, install new fonts or search for fonts using font characteristics. Note that «explorer WindowsFonts» has the same effect. This still exists on Windows 10, but there is a similar page in Settings starting from the Windows 10 April 2018 Update. |
| Internet Options (inetcpl.cpl) |
Allows the user to change the way the computer manages internet connections and browser settings for Internet Explorer, it has several tags specifying different attributes;
|
| Game controllers (joy.cpl) (control /name microsoft.gamecontrollers) |
| Allows one to add, display, troubleshoot, and use advanced settings on joysticks and game controllers and connect to other type of game controllers.
Moved to the Settings app on Windows 10 Anniversary Update. |
| Keyboard (control keyboard) (main.cpl) |
| Lets the user change and test keyboard settings, including cursor blink rate and key repeat rate. |
| Mail (mlcfg32.cpl) (mlcfg.cpl) |
| Mail allows for configuration of the mail client in Windows. Microsoft Outlook Express cannot be configured with this item; it is configured through its own interface. mlcfg.cpl is used for 64 bit office applications first available with the Office 2010 release. |
| Mouse (control mouse) (main.cpl) |
| Mouse allows the configuration of pointer options, such as the double click and scroll speed, and includes visibility options such as whether to use pointer trails and whether the pointer should disappear when typing. This also allows the user to specify the pointer appearance for each task, such as resize and busy. |
| Network Connections (control netconnections) (ncpa.cpl) |
| Displays and allows the user to edit or create network connections such as Local Area Networks (LAN) and internet connections. It also offers troubleshooting functions in case the computer has to be reconnected to the network. |
| Phone and Modem Options (telephon.cpl) |
| Manages telephone and modem connections. |
| Power Options (powercfg.cpl) |
Includes options to manage energy consumption such as;
|
| Printers and Faxes (control printers) (control /name microsoft.devicesandprinters) |
Displays all the printers and faxes currently installed on the computer, and has two main uses;
|
| Regional and Language Settings (intl.cpl) aka Regional and Language Options |
Various regional settings can be altered, for instance:
Removed in the Windows 10 April 2018 Update and moved to Settings App. |
| Security Center or Action Center (Windows 7 & 8.x) (wscui.cpl) Renamed «Security & Maintenance» in Windows 10 |
| First added in Windows XP with Service Pack 2, Security Center gives the user access to the inbuilt Windows security components, as well as providing information about any existing antivirus software such as McAfee or Zone Alarm. It includes access to Windows Update, where users can specify whether the computer should check for updates regularly (also available through the Windows Update panel), and options for managing internet security settings. It also includes links to internet articles about PC security and current virus threats and notifies the user when the PC’s security is compromised. |
| Sounds and Audio Devices (mmsys.cpl) |
This panel contains various audio-related functions;
|
| Speech (Sapi.cpl) |
This applet has two main functions, the first is specify settings for Speech synthesis, allowing the user to select the voice the computer should use to narrate text and how fast it should read. The second is to specify settings for Speech recognition, allowing the user to set up different profiles detailing how the computer should deal with an individual’s dialect, for instance;
This also allows the user to access the voice recognition training wizard, in which an individual ‘teaches’ the computer to recognize a person voice interactively using the microphone. |
| Stored User Names and Passwords (keymgr.dll) (control.exe /name microsoft.credentialmanager) (Renamed «Credential Manager» in Windows 7 and later) |
| This is used to view and edit logon credentials for servers, websites and programs. |
| System (Sysdm.cpl) |
This is used to view and change core system settings, a user can for instance:
Moved to the Settings App on Windows 10, but the shortcut still exists. Clicking on it goes to the Settings App. |
| Taskbar and Start Menu (rundll32.exe shell32.dll, Options_RunDLL 1) |
Allows the user to change the behavior and appearance of the task bar and Start Menu;
Moved to the Settings App on Windows 10, but the shortcut still exists. Clicking on it goes to the Settings App. |
| User Accounts (control userpasswords) (nusrmgr.cpl) |
| This allows the user to configure their account and other accounts used in the system, should they have sufficient privileges. They can change their username, password, their account picture (if enabled), and their .NET Passport (in versions of Windows prior to Vista). If the current user has an administrator account they can also add, delete, and modify other user accounts as well as make changes to core system settings. This panel also specifies whether or not the guest account should be active and (in Windows XP only) whether or not to use the Welcome screen when Windows loads.
This panel is not available in Windows Server 2003, where the syntax «control userpasswords» will instead run the Local Users and Groups utility. |
| Users and Passwords (control userpasswords2) (rundll32.exe netplwiz.dll, UsersRunDll) |
| This is the legacy user account utility that was first introduced in Windows 2000 Professional. This allows the user to configure their account and other accounts used in the system, change their .NET Passports (in versions of Windows prior to Vista), as well as configuring autologin settings. This panel also specifies whether or not to press Ctrl+Alt+Del before login.
This panel is not available in the Windows 2000 Server family, where it will instead run the Local Users and Groups utility. |
Peripheral devices[edit]
These are options in the control panel that show devices connected to the computer. They do not actually offer a direct interface to control these devices, but rather offer basic tasks such as removal procedures and links to wizards (Printers & Faxes is an exception). Such applets include Scanners and Cameras, Game Controllers, and Portable Media Devices.
Other Microsoft-distributed applets[edit]
| Biometric Devices (biocpl.dll) |
|---|
Available with Fingerprint enabled systems running 7 or later, this enables users to configure a Fingerprint reader, showing a list of all Biometric devices interacting with the system, in addition to the following items;
Moved to Settings on Windows 10. |
| Bluetooth Devices (bthprops.cpl) |
Available with Bluetooth enabled systems running XP SP2 or later, this enables users to configure a Bluetooth connection, showing a list of all Bluetooth devices interacting with the system, in addition to the following items;
Moved to Settings on Windows 10. |
| Color (color.cpl) |
| Enables a more advanced control of color settings within Windows than is available in ‘display’, suitable for developers and visual specialists it allows users to create and load International Color Consortium compliant color profiles, associate screen color with printers and cameras and view a 3D graphics plot of the color gamut. By default this applet is not installed, however it can be installed for free from the Microsoft Website. |
| Infrared (irprops.cpl) |
| Similar to the Bluetooth applet, this is used to configure how the computer manages any wireless infrared ports installed, including options such as connectivity and security. |
| Location and Other Sensors (SensorsCpl.dll) |
| Manages Location based data like addresses and other location based sensors. Available in Windows 7 & 8.x only. |
| CSNW (nwc.cpl) |
| The Client Service for NetWare applet is used to select a default tree and context in a Novell Directory Services (NDS) environment, or the NetWare server used most frequently in a non-NDS environment.
Requirement: Installing the Client Service for NetWare. |
| Software Explorers |
| Part of Windows Defender, allows users to view detailed information about software that is currently running on the computer that can affect the users’ privacy or the security of the computer.
Replaced by Windows Defender Security Center on Windows 10. |
Third-party applets[edit]
Third-party software vendors have released many applets. Although it is impossible to mention all of them, some of them are listed here:
| Icon | File name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| AC3 Filter | ac3filter.cpl | Configures speaker configuration and other parameters of the AC3 decoder filter. |
| Adobe Gamma | Adobe Gamma.cpl | For altering the screen display with Adobe Systems Imaging Software such as Photoshop. |
| Adobe Version Cue CS2 | VersionCueCS2.cpl | To configure Adobe Version Cue. |
| Application paths | apppaths.cpl | Sets application paths, start-up commands and system services, coded by Gregory Braun. |
| ATI DVD Player | QISWCINE.CPL | Changes setings for your DVD decoding. |
| AudioHQ | AudHQ.cpl | Creative Labs Soundblaster Audio HQ. |
| Autodesk Plotter Manager | plotman.cpl | Adds, remove and changes plotters properties for AutoCAD products. |
| AvantGo Connect | agcpl.cpl | Synchronizes mobile versions (called «channels») of websites to a smartphone or PDA, see AvantGo. |
| Avira AntiVir PersonalEdition | avconfig.cpl | Configures Avira Antivirus program. |
| BACKPACK Finder | bpcpl.cpl | To configure the Micro Solutions BackPack CD driver. |
| BDE Administrator | bdeadmin.cpl | To configure the Borland Database Engine. |
| Boot Camp Control Panel | Setting for Mac OS X based computers. | |
| Broadcom Advanced Control Suite | BACSCPL.cpl | Enables Broadcom network cards testing and diagnostics. |
| CD/DVD Drive Acoustic Silencer | TOSCDSPD.cpl | Configures the rotation speed of CD/DVD drive. (Toshiba ) |
| ClearCase | cc.cpl | To configure IBM Rational ClearCase. |
| Color Settings | 3dcc.cpl | Changes the look and feel of Windows. |
| Compaq Diagnostics | cpqdiag.cpl | To view information a computer’s hardware and software configuration, legacy application. |
| Control Panel | controlp.cpl | Control Panel Customization Toy, coded by Ali Lokhandwala. |
| Control Version System | cvsnt.cpl | Control Panel Customization Toy, by Brian Berliner. david d ‘zoo’ zuhn, Jeff Polk, Tony Hoyle |
| Creative Element Power Tools | To configure Creative Element Power Tools, a free-to-try program providing access to additional Windows tools. | |
| Corel Versions | verscpl.cpl | Configures Corel versions. |
| DANS | danetsvc.cpl | Configures the Shaffer Solutions DiskAccess Network Services, NFS client for Windows. |
| Diagnostics for Windows | cpqdiag.cpl | HP Diagnostics for Windows 4.15 replaces Compaq |
| Digidesign ElevenRack | DigidesignElevenRackControlPanelApplet.cpl | Launch Eleven Rack Control Panel |
| DiskAccess | dacfg.cpl | Configures how the Shaffer Solutions DiskAccess makes connections to remote NFS servers. |
| DS18x Applet | DS18xCPL.cpl | MR Soft DS18x Temperature Logging Service. |
| Flash Player | FlashPlayerCPLApp.cpl | For changing settings for the Flash Player. |
| Folder size | FolderSize.cpl | Folder Size for Windows shows the size of folders in Windows Explorer. |
| FirebirdSQL Service Manager | fmmgr.cpl | Configures Firebird (database server) service options. |
| HP Jetadmin | jetadmin.cpl | HP Jetadmin configures and monitors HP printers. |
| HP Lock | Hplock.cpl | A Windows 95 utility to lock the PC keyboard, mouse and on/off switch in one click on legacy HP Vectra. |
| IconPackager | ipcpl.cpl | To customize Windows icons and cursors, see IconPackager. |
| ImDisk Virtual Disk Driver | imdisk.cpl | Administration of ImDisk Virtual Disk Driver. |
| InstallShield Update Manager | isuspm.cpl | The InstallShield Update Manager allows users to receive program updates and messages from software makers who use the service. |
| Intel Extreme Graphics | igfxcpl.cpl | To change advanced settings on systems using Intel GPUs. |
| Intel Product Improvement Program | executable | Installed with Intel Driver Update Utility version 2.4 (on Vista and up) |
| IP Office Voicemail Pro | ims.cpl | To configure Avaya IP Office Voicemail Pro. |
| Java | jpicpl32.cpl | For changing settings with Java Runtime Console. |
| JInitiator 1.x.y.z | plugincpl1xyz.cpl | To configure Oracle’s JInitiator, note x.y.z are version numbers. |
| MLCFG32.cpl | Launches the Microsoft Outlook Profile Manager. | |
| MSConfig | MSConfig.cpl | Launches the Microsoft System Configuration Utility. |
| Multi-finger | ETDUI.cpl | Customize the Smart-Pad Multi-finger Setting. |
| MultiSite | ms.cpl | To configure IBM Rational ClearCase Multisite. |
| Nero BurnRights | NeroBurnRights.cpl | For specifying who is allowed to use the CD burner with Nero. |
| nVIDIA Control panel | nvidia.cpl | To change advanced settings on systems using nVIDIA GPUs. |
| Panda Media Booster | PMB.cpl | Panda Media Booster cache and network settings. |
| Parallel Port Joysticks | PPjoy.cpl | Configures Joysticks connected on the Parallel Port. |
| Pointer Devices | tbctlpnl.cpl | To configure the Touch-Base Universal Pointer Device Driver (UPDD). |
| QuickTime | quicktime.cpl | For specifying settings of the Apple QuickTime Player. |
| RealPlayer | prefscpl.cpl | To configure the RealPlayer preferences, older versions. |
| Realtek AC97 Audio Control Panel | alsndmgr.cpl | To configure the Realtek audio controller. |
| Realtek HD-Audio Manager | RTSnMg64.cpl | To launch the Realtek HD-Audio Manager |
| RESTrick Control Panel | rest2.cpl | Windows Tuning and system restrictions setup, by Rtsecurity. |
| Safarp | safarp.cpl | Safarp is a small and fast alternative to the Add or Remove Programs applet. |
| ScrewDrivers Client | sdclient.cpl | From Tricerat, remote desktop print management solution. |
| Send To Toys | sendtotoys.cpl | To configure the Send To right click system menu in Microsoft Windows. |
| Services and Devices | pserv.cpl | From p-nand-q to manage Windows services and devices and uninstall applications. |
| Softex OmniPass | scurecpl.cpl | Softex OmniPass provides password management capabilities to MS Windows. |
| SNTP Service | sntpserv.cpl | From Dillobits Software, to manage the SNTP client service. |
| Soundscape | scurecpl.cpl | Adds, removes or changes settings of Soundscape devices. |
| Startup | startup.cpl | Control programs that run at system start-up, coded by Mike Lin. |
| Startup Disk | Startup Disk.cpl | Boot Camp drivers, when Windows runs on a Mac OS virtual machine. |
| Symantec LiveUpdate | s32lucp2.cpl | Configures the Symantec LiveUpdate update service. |
| System Change Log | scl.cpl | From Greyware Automation Products, monitors disks for changes and records a detailed log. |
| System Information | Sancpl.cpl | Launches SiSoftware Sandra utility. |
| System Info for Windows | siw.cpl | Launches the SIW application. |
| Trust-No-Exe | trustnoexe.cpl | Configures the Beyond Logic Trust-No-Exe executable filter. |
| VMware Tools | VMControlPanel.cpl | To configure VMware Tools. |
| WIBU-KEY | wibuke32.cpl | To configure the WIBU-KEY Software Protection. |
| Winlogos | wnlgo.cpl | To change the Windows start-up and shutdown screens in Windows 98 or ME, coded by Ali Lokhandwala. |
| X-Setup Pro | xqdcXSPApplet.cpl | Launches X-Setup Pro, a Windows tweaker application. |
References[edit]
- ^ «A history of Windows». Windows. Microsoft. Archived from the original on November 17, 2010.
- ^ «Accessing the Control Panel via the Commandline». Microsoft. August 29, 2011.
- ^ Bradley, Tony (July 6, 2012). «Adding and Managing Users in Windows 8». PC World. IDG. Retrieved September 20, 2015.
- ^ Bright, Peter (March 25, 2013). «Windows Blue leaks: More Metro, more multitasking». Ars Technica. Condé Nast. Retrieved January 20, 2014.
- ^ «How to run Control Panel tools by typing a command». Support. Microsoft. Retrieved February 26, 2014.
External links[edit]
- How to run Control Panel tools by typing a command at Microsoft.com
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
The Control Panel is a component of Microsoft Windows that provides the ability to view and change system settings. It consists of a set of applets that include adding or removing hardware and software, controlling user accounts, changing accessibility options, and accessing networking settings. Additional applets are provided by third parties, such as audio and video drivers, VPN tools, input devices, and networking tools.

Control Panel in Windows 11 |
|
| Developer(s) | Microsoft |
|---|---|
| Initial release | 1985; 38 years ago |
| Operating system | Microsoft Windows |
| Type | Control panel |
Overview[edit]
The Control Panel has been part of Microsoft Windows since Windows 1.0,[1] with each successive version introducing new applets. Beginning with Windows 95, the Control Panel is implemented as a special folder, i.e. the folder does not physically exist, but only contains shortcuts to various applets such as Add or Remove Programs and Internet Options. Physically, these applets are stored as .cpl files. For example, the Add or Remove Programs applet is stored under the name appwiz.cpl in the SYSTEM32 folder. ==
In Windows XP, the Control Panel home screen was changed to present a categorized navigation structure reminiscent of navigating a web page. Users can switch between this Category View and the grid-based Classic View through an option that appears on either the left side or top of the window. In Windows Vista and Windows 7, additional layers of navigation were introduced, and the Control Panel window itself became the main interface for editing settings, as opposed to launching separate dialogs.
Many of the individual Control Panel applets can be accessed in other ways. For instance, Display Properties can be accessed by right-clicking on an empty area of the desktop and choosing Properties. The Control Panel can be accessed from a command prompt by typing control; optional parameters are available to open specific control panels.[2]
On Windows 10, Control Panel is deprecated in favor of Settings app, which was originally introduced on Windows 8 as «PC settings» to provide a touchscreen-optimized settings area using its Metro-style app platform. Some functions, particularly the ability to add and remove user accounts, were moved exclusively to this app on Windows 8 and cannot be performed from Control Panel.[3][4]
As of the October 2020 update to Windows 10, opening up the System applet in Control Panel will now redirect users to the About section of the Windows 10 Settings application. The page for the applet in Control Panel still exists even in current versions of Windows 10, however Microsoft is actively trying to block shortcuts and third party applications that could have been used to get into the old System page, which could potentially lead to a permanent removal of said page from Control Panel in future versions of Windows.[citation needed]
List of Control Panel applets[edit]
The applets listed below are components of the Microsoft Windows control panel, which allows users to define a range of settings for their computer, monitor the status of devices such as printers and modems, and set up new hardware, programs and network connections. Each applet is stored individually as a separate file (usually a .cpl file), folder or DLL, the locations of which are stored in the registry under the following keys:
- HKLMSOFTWAREMicrosoftWindowsCurrentVersionControl PanelCpls
This contains the string format locations of all .cpl files on the hard drive used within the control panel. - HKLMSOFTWAREMicrosoftWindowsCurrentVersionExplorerControlPanelNamespace
This contains the location of the CLSID variables for all the panels not included as cpl files. These are commonly folders or shell applets, though Windows Vista allows physical programs themselves to be registered as well. The CLSID then allows items such as the icon, infobox and category to be set and gives the location of the file to be used.
The control panel then uses these lists to locate the applets and load them into the control panel program (control.exe) when started by the user. In addition to using the control panel, a user can also invoke the applets manually via the command processor. For instance, the syntax «Control.exe inetcpl.cpl» or «control.exe /name Microsoft.InternetOptions» will run the internet properties applet in Windows XP or Vista respectively. While both syntax examples are accepted on Windows Vista, only the former one is accepted on Windows XP.[5]
Standard applets[edit]
| Accessibility options (Access.cpl) (control /name microsoft.easeofaccesscenter) (Renamed «Ease of Access Center» in Windows Vista and later) |
|---|
Allows users to configure the accessibility of their PC. It comprises various settings primarily aimed at users with disabilities or hardware problems.
Note that in Windows Vista onwards, the Ease of Access control panel superseded the old access.cpl control panel applet found in previous versions. |
| Add New Hardware (hdwwiz.cpl) |
| Launches a wizard which allows users to add new hardware devices to the system. This can be done by selecting from a list of devices or by specifying the location of the driver installation files. |
| Add or Remove Programs (appwiz.cpl) (Renamed «Programs and Features» in Windows Vista and later) |
The Add/Remove Programs dialog allows the user to manipulate software installed on the system in a number of ways;
|
| Administrative Tools (control admintools) |
| Contains tools for system administration, including security, performance and service configuration. These are links to various configurations of the Microsoft Management Console such as the local services list and the Event Viewer. |
| Automatic Updates (wuaucpl.cpl) |
| This is used to specify how the Automatic Updates client (wuauclt.exe) should download updates from the Microsoft Update Website, by default this is set to download and install daily, however this can be changed to a more suitable frequency. This also allows the user to specify whether to ask permission before downloading and/or installing updates or to simply switch off Automatic Updates altogether.
Removed in Windows 10, and moved to the Settings App. |
| Date and Time (timedate.cpl) |
| Allows user to change the date and time stored in the machine’s BIOS, change the time zone and specify whether to synchronize the date and time with an Internet Time Server and which server to use. |
| Display (control desktop) (desk.cpl)
(Renamed «Personalization» in Windows Vista, 7 and 8.1) |
Allows the user to change the display characteristics of their computer;
Removed in Windows 10 and moved to the Settings App. |
| Folder Options (control folders) (rundll32.exe shell32.dll, Options_RunDLL 0) |
| This item allows for configuration of how folders and files are presented in Windows Explorer. More specifically it allows the user to specify general settings like whether folders open in a new window or the existing window and whether the common tasks pane is shown, as well as more advanced tasks such as whether windows should hide critical system files and whether to show file extensions. It is also used to modify file type associations in Windows; i.e., which program opens which type of file and other settings like actions for each file type and the file extension. |
| Fonts (control fonts) |
| Displays all fonts installed on the computer. Users can remove fonts, install new fonts or search for fonts using font characteristics. Note that «explorer WindowsFonts» has the same effect. This still exists on Windows 10, but there is a similar page in Settings starting from the Windows 10 April 2018 Update. |
| Internet Options (inetcpl.cpl) |
Allows the user to change the way the computer manages internet connections and browser settings for Internet Explorer, it has several tags specifying different attributes;
|
| Game controllers (joy.cpl) (control /name microsoft.gamecontrollers) |
| Allows one to add, display, troubleshoot, and use advanced settings on joysticks and game controllers and connect to other type of game controllers.
Moved to the Settings app on Windows 10 Anniversary Update. |
| Keyboard (control keyboard) (main.cpl) |
| Lets the user change and test keyboard settings, including cursor blink rate and key repeat rate. |
| Mail (mlcfg32.cpl) (mlcfg.cpl) |
| Mail allows for configuration of the mail client in Windows. Microsoft Outlook Express cannot be configured with this item; it is configured through its own interface. mlcfg.cpl is used for 64 bit office applications first available with the Office 2010 release. |
| Mouse (control mouse) (main.cpl) |
| Mouse allows the configuration of pointer options, such as the double click and scroll speed, and includes visibility options such as whether to use pointer trails and whether the pointer should disappear when typing. This also allows the user to specify the pointer appearance for each task, such as resize and busy. |
| Network Connections (control netconnections) (ncpa.cpl) |
| Displays and allows the user to edit or create network connections such as Local Area Networks (LAN) and internet connections. It also offers troubleshooting functions in case the computer has to be reconnected to the network. |
| Phone and Modem Options (telephon.cpl) |
| Manages telephone and modem connections. |
| Power Options (powercfg.cpl) |
Includes options to manage energy consumption such as;
|
| Printers and Faxes (control printers) (control /name microsoft.devicesandprinters) |
Displays all the printers and faxes currently installed on the computer, and has two main uses;
|
| Regional and Language Settings (intl.cpl) aka Regional and Language Options |
Various regional settings can be altered, for instance:
Removed in the Windows 10 April 2018 Update and moved to Settings App. |
| Security Center or Action Center (Windows 7 & 8.x) (wscui.cpl) Renamed «Security & Maintenance» in Windows 10 |
| First added in Windows XP with Service Pack 2, Security Center gives the user access to the inbuilt Windows security components, as well as providing information about any existing antivirus software such as McAfee or Zone Alarm. It includes access to Windows Update, where users can specify whether the computer should check for updates regularly (also available through the Windows Update panel), and options for managing internet security settings. It also includes links to internet articles about PC security and current virus threats and notifies the user when the PC’s security is compromised. |
| Sounds and Audio Devices (mmsys.cpl) |
This panel contains various audio-related functions;
|
| Speech (Sapi.cpl) |
This applet has two main functions, the first is specify settings for Speech synthesis, allowing the user to select the voice the computer should use to narrate text and how fast it should read. The second is to specify settings for Speech recognition, allowing the user to set up different profiles detailing how the computer should deal with an individual’s dialect, for instance;
This also allows the user to access the voice recognition training wizard, in which an individual ‘teaches’ the computer to recognize a person voice interactively using the microphone. |
| Stored User Names and Passwords (keymgr.dll) (control.exe /name microsoft.credentialmanager) (Renamed «Credential Manager» in Windows 7 and later) |
| This is used to view and edit logon credentials for servers, websites and programs. |
| System (Sysdm.cpl) |
This is used to view and change core system settings, a user can for instance:
Moved to the Settings App on Windows 10, but the shortcut still exists. Clicking on it goes to the Settings App. |
| Taskbar and Start Menu (rundll32.exe shell32.dll, Options_RunDLL 1) |
Allows the user to change the behavior and appearance of the task bar and Start Menu;
Moved to the Settings App on Windows 10, but the shortcut still exists. Clicking on it goes to the Settings App. |
| User Accounts (control userpasswords) (nusrmgr.cpl) |
| This allows the user to configure their account and other accounts used in the system, should they have sufficient privileges. They can change their username, password, their account picture (if enabled), and their .NET Passport (in versions of Windows prior to Vista). If the current user has an administrator account they can also add, delete, and modify other user accounts as well as make changes to core system settings. This panel also specifies whether or not the guest account should be active and (in Windows XP only) whether or not to use the Welcome screen when Windows loads.
This panel is not available in Windows Server 2003, where the syntax «control userpasswords» will instead run the Local Users and Groups utility. |
| Users and Passwords (control userpasswords2) (rundll32.exe netplwiz.dll, UsersRunDll) |
| This is the legacy user account utility that was first introduced in Windows 2000 Professional. This allows the user to configure their account and other accounts used in the system, change their .NET Passports (in versions of Windows prior to Vista), as well as configuring autologin settings. This panel also specifies whether or not to press Ctrl+Alt+Del before login.
This panel is not available in the Windows 2000 Server family, where it will instead run the Local Users and Groups utility. |
Peripheral devices[edit]
These are options in the control panel that show devices connected to the computer. They do not actually offer a direct interface to control these devices, but rather offer basic tasks such as removal procedures and links to wizards (Printers & Faxes is an exception). Such applets include Scanners and Cameras, Game Controllers, and Portable Media Devices.
Other Microsoft-distributed applets[edit]
| Biometric Devices (biocpl.dll) |
|---|
Available with Fingerprint enabled systems running 7 or later, this enables users to configure a Fingerprint reader, showing a list of all Biometric devices interacting with the system, in addition to the following items;
Moved to Settings on Windows 10. |
| Bluetooth Devices (bthprops.cpl) |
Available with Bluetooth enabled systems running XP SP2 or later, this enables users to configure a Bluetooth connection, showing a list of all Bluetooth devices interacting with the system, in addition to the following items;
Moved to Settings on Windows 10. |
| Color (color.cpl) |
| Enables a more advanced control of color settings within Windows than is available in ‘display’, suitable for developers and visual specialists it allows users to create and load International Color Consortium compliant color profiles, associate screen color with printers and cameras and view a 3D graphics plot of the color gamut. By default this applet is not installed, however it can be installed for free from the Microsoft Website. |
| Infrared (irprops.cpl) |
| Similar to the Bluetooth applet, this is used to configure how the computer manages any wireless infrared ports installed, including options such as connectivity and security. |
| Location and Other Sensors (SensorsCpl.dll) |
| Manages Location based data like addresses and other location based sensors. Available in Windows 7 & 8.x only. |
| CSNW (nwc.cpl) |
| The Client Service for NetWare applet is used to select a default tree and context in a Novell Directory Services (NDS) environment, or the NetWare server used most frequently in a non-NDS environment.
Requirement: Installing the Client Service for NetWare. |
| Software Explorers |
| Part of Windows Defender, allows users to view detailed information about software that is currently running on the computer that can affect the users’ privacy or the security of the computer.
Replaced by Windows Defender Security Center on Windows 10. |
Third-party applets[edit]
Third-party software vendors have released many applets. Although it is impossible to mention all of them, some of them are listed here:
| Icon | File name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| AC3 Filter | ac3filter.cpl | Configures speaker configuration and other parameters of the AC3 decoder filter. |
| Adobe Gamma | Adobe Gamma.cpl | For altering the screen display with Adobe Systems Imaging Software such as Photoshop. |
| Adobe Version Cue CS2 | VersionCueCS2.cpl | To configure Adobe Version Cue. |
| Application paths | apppaths.cpl | Sets application paths, start-up commands and system services, coded by Gregory Braun. |
| ATI DVD Player | QISWCINE.CPL | Changes setings for your DVD decoding. |
| AudioHQ | AudHQ.cpl | Creative Labs Soundblaster Audio HQ. |
| Autodesk Plotter Manager | plotman.cpl | Adds, remove and changes plotters properties for AutoCAD products. |
| AvantGo Connect | agcpl.cpl | Synchronizes mobile versions (called «channels») of websites to a smartphone or PDA, see AvantGo. |
| Avira AntiVir PersonalEdition | avconfig.cpl | Configures Avira Antivirus program. |
| BACKPACK Finder | bpcpl.cpl | To configure the Micro Solutions BackPack CD driver. |
| BDE Administrator | bdeadmin.cpl | To configure the Borland Database Engine. |
| Boot Camp Control Panel | Setting for Mac OS X based computers. | |
| Broadcom Advanced Control Suite | BACSCPL.cpl | Enables Broadcom network cards testing and diagnostics. |
| CD/DVD Drive Acoustic Silencer | TOSCDSPD.cpl | Configures the rotation speed of CD/DVD drive. (Toshiba ) |
| ClearCase | cc.cpl | To configure IBM Rational ClearCase. |
| Color Settings | 3dcc.cpl | Changes the look and feel of Windows. |
| Compaq Diagnostics | cpqdiag.cpl | To view information a computer’s hardware and software configuration, legacy application. |
| Control Panel | controlp.cpl | Control Panel Customization Toy, coded by Ali Lokhandwala. |
| Control Version System | cvsnt.cpl | Control Panel Customization Toy, by Brian Berliner. david d ‘zoo’ zuhn, Jeff Polk, Tony Hoyle |
| Creative Element Power Tools | To configure Creative Element Power Tools, a free-to-try program providing access to additional Windows tools. | |
| Corel Versions | verscpl.cpl | Configures Corel versions. |
| DANS | danetsvc.cpl | Configures the Shaffer Solutions DiskAccess Network Services, NFS client for Windows. |
| Diagnostics for Windows | cpqdiag.cpl | HP Diagnostics for Windows 4.15 replaces Compaq |
| Digidesign ElevenRack | DigidesignElevenRackControlPanelApplet.cpl | Launch Eleven Rack Control Panel |
| DiskAccess | dacfg.cpl | Configures how the Shaffer Solutions DiskAccess makes connections to remote NFS servers. |
| DS18x Applet | DS18xCPL.cpl | MR Soft DS18x Temperature Logging Service. |
| Flash Player | FlashPlayerCPLApp.cpl | For changing settings for the Flash Player. |
| Folder size | FolderSize.cpl | Folder Size for Windows shows the size of folders in Windows Explorer. |
| FirebirdSQL Service Manager | fmmgr.cpl | Configures Firebird (database server) service options. |
| HP Jetadmin | jetadmin.cpl | HP Jetadmin configures and monitors HP printers. |
| HP Lock | Hplock.cpl | A Windows 95 utility to lock the PC keyboard, mouse and on/off switch in one click on legacy HP Vectra. |
| IconPackager | ipcpl.cpl | To customize Windows icons and cursors, see IconPackager. |
| ImDisk Virtual Disk Driver | imdisk.cpl | Administration of ImDisk Virtual Disk Driver. |
| InstallShield Update Manager | isuspm.cpl | The InstallShield Update Manager allows users to receive program updates and messages from software makers who use the service. |
| Intel Extreme Graphics | igfxcpl.cpl | To change advanced settings on systems using Intel GPUs. |
| Intel Product Improvement Program | executable | Installed with Intel Driver Update Utility version 2.4 (on Vista and up) |
| IP Office Voicemail Pro | ims.cpl | To configure Avaya IP Office Voicemail Pro. |
| Java | jpicpl32.cpl | For changing settings with Java Runtime Console. |
| JInitiator 1.x.y.z | plugincpl1xyz.cpl | To configure Oracle’s JInitiator, note x.y.z are version numbers. |
| MLCFG32.cpl | Launches the Microsoft Outlook Profile Manager. | |
| MSConfig | MSConfig.cpl | Launches the Microsoft System Configuration Utility. |
| Multi-finger | ETDUI.cpl | Customize the Smart-Pad Multi-finger Setting. |
| MultiSite | ms.cpl | To configure IBM Rational ClearCase Multisite. |
| Nero BurnRights | NeroBurnRights.cpl | For specifying who is allowed to use the CD burner with Nero. |
| nVIDIA Control panel | nvidia.cpl | To change advanced settings on systems using nVIDIA GPUs. |
| Panda Media Booster | PMB.cpl | Panda Media Booster cache and network settings. |
| Parallel Port Joysticks | PPjoy.cpl | Configures Joysticks connected on the Parallel Port. |
| Pointer Devices | tbctlpnl.cpl | To configure the Touch-Base Universal Pointer Device Driver (UPDD). |
| QuickTime | quicktime.cpl | For specifying settings of the Apple QuickTime Player. |
| RealPlayer | prefscpl.cpl | To configure the RealPlayer preferences, older versions. |
| Realtek AC97 Audio Control Panel | alsndmgr.cpl | To configure the Realtek audio controller. |
| Realtek HD-Audio Manager | RTSnMg64.cpl | To launch the Realtek HD-Audio Manager |
| RESTrick Control Panel | rest2.cpl | Windows Tuning and system restrictions setup, by Rtsecurity. |
| Safarp | safarp.cpl | Safarp is a small and fast alternative to the Add or Remove Programs applet. |
| ScrewDrivers Client | sdclient.cpl | From Tricerat, remote desktop print management solution. |
| Send To Toys | sendtotoys.cpl | To configure the Send To right click system menu in Microsoft Windows. |
| Services and Devices | pserv.cpl | From p-nand-q to manage Windows services and devices and uninstall applications. |
| Softex OmniPass | scurecpl.cpl | Softex OmniPass provides password management capabilities to MS Windows. |
| SNTP Service | sntpserv.cpl | From Dillobits Software, to manage the SNTP client service. |
| Soundscape | scurecpl.cpl | Adds, removes or changes settings of Soundscape devices. |
| Startup | startup.cpl | Control programs that run at system start-up, coded by Mike Lin. |
| Startup Disk | Startup Disk.cpl | Boot Camp drivers, when Windows runs on a Mac OS virtual machine. |
| Symantec LiveUpdate | s32lucp2.cpl | Configures the Symantec LiveUpdate update service. |
| System Change Log | scl.cpl | From Greyware Automation Products, monitors disks for changes and records a detailed log. |
| System Information | Sancpl.cpl | Launches SiSoftware Sandra utility. |
| System Info for Windows | siw.cpl | Launches the SIW application. |
| Trust-No-Exe | trustnoexe.cpl | Configures the Beyond Logic Trust-No-Exe executable filter. |
| VMware Tools | VMControlPanel.cpl | To configure VMware Tools. |
| WIBU-KEY | wibuke32.cpl | To configure the WIBU-KEY Software Protection. |
| Winlogos | wnlgo.cpl | To change the Windows start-up and shutdown screens in Windows 98 or ME, coded by Ali Lokhandwala. |
| X-Setup Pro | xqdcXSPApplet.cpl | Launches X-Setup Pro, a Windows tweaker application. |
References[edit]
- ^ «A history of Windows». Windows. Microsoft. Archived from the original on November 17, 2010.
- ^ «Accessing the Control Panel via the Commandline». Microsoft. August 29, 2011.
- ^ Bradley, Tony (July 6, 2012). «Adding and Managing Users in Windows 8». PC World. IDG. Retrieved September 20, 2015.
- ^ Bright, Peter (March 25, 2013). «Windows Blue leaks: More Metro, more multitasking». Ars Technica. Condé Nast. Retrieved January 20, 2014.
- ^ «How to run Control Panel tools by typing a command». Support. Microsoft. Retrieved February 26, 2014.
External links[edit]
- How to run Control Panel tools by typing a command at Microsoft.com
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
The Control Panel is a component of Microsoft Windows that provides the ability to view and change system settings. It consists of a set of applets that include adding or removing hardware and software, controlling user accounts, changing accessibility options, and accessing networking settings. Additional applets are provided by third parties, such as audio and video drivers, VPN tools, input devices, and networking tools.

Control Panel in Windows 11 |
|
| Developer(s) | Microsoft |
|---|---|
| Initial release | 1985; 38 years ago |
| Operating system | Microsoft Windows |
| Type | Control panel |
Overview[edit]
The Control Panel has been part of Microsoft Windows since Windows 1.0,[1] with each successive version introducing new applets. Beginning with Windows 95, the Control Panel is implemented as a special folder, i.e. the folder does not physically exist, but only contains shortcuts to various applets such as Add or Remove Programs and Internet Options. Physically, these applets are stored as .cpl files. For example, the Add or Remove Programs applet is stored under the name appwiz.cpl in the SYSTEM32 folder. ==
In Windows XP, the Control Panel home screen was changed to present a categorized navigation structure reminiscent of navigating a web page. Users can switch between this Category View and the grid-based Classic View through an option that appears on either the left side or top of the window. In Windows Vista and Windows 7, additional layers of navigation were introduced, and the Control Panel window itself became the main interface for editing settings, as opposed to launching separate dialogs.
Many of the individual Control Panel applets can be accessed in other ways. For instance, Display Properties can be accessed by right-clicking on an empty area of the desktop and choosing Properties. The Control Panel can be accessed from a command prompt by typing control; optional parameters are available to open specific control panels.[2]
On Windows 10, Control Panel is deprecated in favor of Settings app, which was originally introduced on Windows 8 as «PC settings» to provide a touchscreen-optimized settings area using its Metro-style app platform. Some functions, particularly the ability to add and remove user accounts, were moved exclusively to this app on Windows 8 and cannot be performed from Control Panel.[3][4]
As of the October 2020 update to Windows 10, opening up the System applet in Control Panel will now redirect users to the About section of the Windows 10 Settings application. The page for the applet in Control Panel still exists even in current versions of Windows 10, however Microsoft is actively trying to block shortcuts and third party applications that could have been used to get into the old System page, which could potentially lead to a permanent removal of said page from Control Panel in future versions of Windows.[citation needed]
List of Control Panel applets[edit]
The applets listed below are components of the Microsoft Windows control panel, which allows users to define a range of settings for their computer, monitor the status of devices such as printers and modems, and set up new hardware, programs and network connections. Each applet is stored individually as a separate file (usually a .cpl file), folder or DLL, the locations of which are stored in the registry under the following keys:
- HKLMSOFTWAREMicrosoftWindowsCurrentVersionControl PanelCpls
This contains the string format locations of all .cpl files on the hard drive used within the control panel. - HKLMSOFTWAREMicrosoftWindowsCurrentVersionExplorerControlPanelNamespace
This contains the location of the CLSID variables for all the panels not included as cpl files. These are commonly folders or shell applets, though Windows Vista allows physical programs themselves to be registered as well. The CLSID then allows items such as the icon, infobox and category to be set and gives the location of the file to be used.
The control panel then uses these lists to locate the applets and load them into the control panel program (control.exe) when started by the user. In addition to using the control panel, a user can also invoke the applets manually via the command processor. For instance, the syntax «Control.exe inetcpl.cpl» or «control.exe /name Microsoft.InternetOptions» will run the internet properties applet in Windows XP or Vista respectively. While both syntax examples are accepted on Windows Vista, only the former one is accepted on Windows XP.[5]
Standard applets[edit]
| Accessibility options (Access.cpl) (control /name microsoft.easeofaccesscenter) (Renamed «Ease of Access Center» in Windows Vista and later) |
|---|
Allows users to configure the accessibility of their PC. It comprises various settings primarily aimed at users with disabilities or hardware problems.
Note that in Windows Vista onwards, the Ease of Access control panel superseded the old access.cpl control panel applet found in previous versions. |
| Add New Hardware (hdwwiz.cpl) |
| Launches a wizard which allows users to add new hardware devices to the system. This can be done by selecting from a list of devices or by specifying the location of the driver installation files. |
| Add or Remove Programs (appwiz.cpl) (Renamed «Programs and Features» in Windows Vista and later) |
The Add/Remove Programs dialog allows the user to manipulate software installed on the system in a number of ways;
|
| Administrative Tools (control admintools) |
| Contains tools for system administration, including security, performance and service configuration. These are links to various configurations of the Microsoft Management Console such as the local services list and the Event Viewer. |
| Automatic Updates (wuaucpl.cpl) |
| This is used to specify how the Automatic Updates client (wuauclt.exe) should download updates from the Microsoft Update Website, by default this is set to download and install daily, however this can be changed to a more suitable frequency. This also allows the user to specify whether to ask permission before downloading and/or installing updates or to simply switch off Automatic Updates altogether.
Removed in Windows 10, and moved to the Settings App. |
| Date and Time (timedate.cpl) |
| Allows user to change the date and time stored in the machine’s BIOS, change the time zone and specify whether to synchronize the date and time with an Internet Time Server and which server to use. |
| Display (control desktop) (desk.cpl)
(Renamed «Personalization» in Windows Vista, 7 and 8.1) |
Allows the user to change the display characteristics of their computer;
Removed in Windows 10 and moved to the Settings App. |
| Folder Options (control folders) (rundll32.exe shell32.dll, Options_RunDLL 0) |
| This item allows for configuration of how folders and files are presented in Windows Explorer. More specifically it allows the user to specify general settings like whether folders open in a new window or the existing window and whether the common tasks pane is shown, as well as more advanced tasks such as whether windows should hide critical system files and whether to show file extensions. It is also used to modify file type associations in Windows; i.e., which program opens which type of file and other settings like actions for each file type and the file extension. |
| Fonts (control fonts) |
| Displays all fonts installed on the computer. Users can remove fonts, install new fonts or search for fonts using font characteristics. Note that «explorer WindowsFonts» has the same effect. This still exists on Windows 10, but there is a similar page in Settings starting from the Windows 10 April 2018 Update. |
| Internet Options (inetcpl.cpl) |
Allows the user to change the way the computer manages internet connections and browser settings for Internet Explorer, it has several tags specifying different attributes;
|
| Game controllers (joy.cpl) (control /name microsoft.gamecontrollers) |
| Allows one to add, display, troubleshoot, and use advanced settings on joysticks and game controllers and connect to other type of game controllers.
Moved to the Settings app on Windows 10 Anniversary Update. |
| Keyboard (control keyboard) (main.cpl) |
| Lets the user change and test keyboard settings, including cursor blink rate and key repeat rate. |
| Mail (mlcfg32.cpl) (mlcfg.cpl) |
| Mail allows for configuration of the mail client in Windows. Microsoft Outlook Express cannot be configured with this item; it is configured through its own interface. mlcfg.cpl is used for 64 bit office applications first available with the Office 2010 release. |
| Mouse (control mouse) (main.cpl) |
| Mouse allows the configuration of pointer options, such as the double click and scroll speed, and includes visibility options such as whether to use pointer trails and whether the pointer should disappear when typing. This also allows the user to specify the pointer appearance for each task, such as resize and busy. |
| Network Connections (control netconnections) (ncpa.cpl) |
| Displays and allows the user to edit or create network connections such as Local Area Networks (LAN) and internet connections. It also offers troubleshooting functions in case the computer has to be reconnected to the network. |
| Phone and Modem Options (telephon.cpl) |
| Manages telephone and modem connections. |
| Power Options (powercfg.cpl) |
Includes options to manage energy consumption such as;
|
| Printers and Faxes (control printers) (control /name microsoft.devicesandprinters) |
Displays all the printers and faxes currently installed on the computer, and has two main uses;
|
| Regional and Language Settings (intl.cpl) aka Regional and Language Options |
Various regional settings can be altered, for instance:
Removed in the Windows 10 April 2018 Update and moved to Settings App. |
| Security Center or Action Center (Windows 7 & 8.x) (wscui.cpl) Renamed «Security & Maintenance» in Windows 10 |
| First added in Windows XP with Service Pack 2, Security Center gives the user access to the inbuilt Windows security components, as well as providing information about any existing antivirus software such as McAfee or Zone Alarm. It includes access to Windows Update, where users can specify whether the computer should check for updates regularly (also available through the Windows Update panel), and options for managing internet security settings. It also includes links to internet articles about PC security and current virus threats and notifies the user when the PC’s security is compromised. |
| Sounds and Audio Devices (mmsys.cpl) |
This panel contains various audio-related functions;
|
| Speech (Sapi.cpl) |
This applet has two main functions, the first is specify settings for Speech synthesis, allowing the user to select the voice the computer should use to narrate text and how fast it should read. The second is to specify settings for Speech recognition, allowing the user to set up different profiles detailing how the computer should deal with an individual’s dialect, for instance;
This also allows the user to access the voice recognition training wizard, in which an individual ‘teaches’ the computer to recognize a person voice interactively using the microphone. |
| Stored User Names and Passwords (keymgr.dll) (control.exe /name microsoft.credentialmanager) (Renamed «Credential Manager» in Windows 7 and later) |
| This is used to view and edit logon credentials for servers, websites and programs. |
| System (Sysdm.cpl) |
This is used to view and change core system settings, a user can for instance:
Moved to the Settings App on Windows 10, but the shortcut still exists. Clicking on it goes to the Settings App. |
| Taskbar and Start Menu (rundll32.exe shell32.dll, Options_RunDLL 1) |
Allows the user to change the behavior and appearance of the task bar and Start Menu;
Moved to the Settings App on Windows 10, but the shortcut still exists. Clicking on it goes to the Settings App. |
| User Accounts (control userpasswords) (nusrmgr.cpl) |
| This allows the user to configure their account and other accounts used in the system, should they have sufficient privileges. They can change their username, password, their account picture (if enabled), and their .NET Passport (in versions of Windows prior to Vista). If the current user has an administrator account they can also add, delete, and modify other user accounts as well as make changes to core system settings. This panel also specifies whether or not the guest account should be active and (in Windows XP only) whether or not to use the Welcome screen when Windows loads.
This panel is not available in Windows Server 2003, where the syntax «control userpasswords» will instead run the Local Users and Groups utility. |
| Users and Passwords (control userpasswords2) (rundll32.exe netplwiz.dll, UsersRunDll) |
| This is the legacy user account utility that was first introduced in Windows 2000 Professional. This allows the user to configure their account and other accounts used in the system, change their .NET Passports (in versions of Windows prior to Vista), as well as configuring autologin settings. This panel also specifies whether or not to press Ctrl+Alt+Del before login.
This panel is not available in the Windows 2000 Server family, where it will instead run the Local Users and Groups utility. |
Peripheral devices[edit]
These are options in the control panel that show devices connected to the computer. They do not actually offer a direct interface to control these devices, but rather offer basic tasks such as removal procedures and links to wizards (Printers & Faxes is an exception). Such applets include Scanners and Cameras, Game Controllers, and Portable Media Devices.
Other Microsoft-distributed applets[edit]
| Biometric Devices (biocpl.dll) |
|---|
Available with Fingerprint enabled systems running 7 or later, this enables users to configure a Fingerprint reader, showing a list of all Biometric devices interacting with the system, in addition to the following items;
Moved to Settings on Windows 10. |
| Bluetooth Devices (bthprops.cpl) |
Available with Bluetooth enabled systems running XP SP2 or later, this enables users to configure a Bluetooth connection, showing a list of all Bluetooth devices interacting with the system, in addition to the following items;
Moved to Settings on Windows 10. |
| Color (color.cpl) |
| Enables a more advanced control of color settings within Windows than is available in ‘display’, suitable for developers and visual specialists it allows users to create and load International Color Consortium compliant color profiles, associate screen color with printers and cameras and view a 3D graphics plot of the color gamut. By default this applet is not installed, however it can be installed for free from the Microsoft Website. |
| Infrared (irprops.cpl) |
| Similar to the Bluetooth applet, this is used to configure how the computer manages any wireless infrared ports installed, including options such as connectivity and security. |
| Location and Other Sensors (SensorsCpl.dll) |
| Manages Location based data like addresses and other location based sensors. Available in Windows 7 & 8.x only. |
| CSNW (nwc.cpl) |
| The Client Service for NetWare applet is used to select a default tree and context in a Novell Directory Services (NDS) environment, or the NetWare server used most frequently in a non-NDS environment.
Requirement: Installing the Client Service for NetWare. |
| Software Explorers |
| Part of Windows Defender, allows users to view detailed information about software that is currently running on the computer that can affect the users’ privacy or the security of the computer.
Replaced by Windows Defender Security Center on Windows 10. |
Third-party applets[edit]
Third-party software vendors have released many applets. Although it is impossible to mention all of them, some of them are listed here:
| Icon | File name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| AC3 Filter | ac3filter.cpl | Configures speaker configuration and other parameters of the AC3 decoder filter. |
| Adobe Gamma | Adobe Gamma.cpl | For altering the screen display with Adobe Systems Imaging Software such as Photoshop. |
| Adobe Version Cue CS2 | VersionCueCS2.cpl | To configure Adobe Version Cue. |
| Application paths | apppaths.cpl | Sets application paths, start-up commands and system services, coded by Gregory Braun. |
| ATI DVD Player | QISWCINE.CPL | Changes setings for your DVD decoding. |
| AudioHQ | AudHQ.cpl | Creative Labs Soundblaster Audio HQ. |
| Autodesk Plotter Manager | plotman.cpl | Adds, remove and changes plotters properties for AutoCAD products. |
| AvantGo Connect | agcpl.cpl | Synchronizes mobile versions (called «channels») of websites to a smartphone or PDA, see AvantGo. |
| Avira AntiVir PersonalEdition | avconfig.cpl | Configures Avira Antivirus program. |
| BACKPACK Finder | bpcpl.cpl | To configure the Micro Solutions BackPack CD driver. |
| BDE Administrator | bdeadmin.cpl | To configure the Borland Database Engine. |
| Boot Camp Control Panel | Setting for Mac OS X based computers. | |
| Broadcom Advanced Control Suite | BACSCPL.cpl | Enables Broadcom network cards testing and diagnostics. |
| CD/DVD Drive Acoustic Silencer | TOSCDSPD.cpl | Configures the rotation speed of CD/DVD drive. (Toshiba ) |
| ClearCase | cc.cpl | To configure IBM Rational ClearCase. |
| Color Settings | 3dcc.cpl | Changes the look and feel of Windows. |
| Compaq Diagnostics | cpqdiag.cpl | To view information a computer’s hardware and software configuration, legacy application. |
| Control Panel | controlp.cpl | Control Panel Customization Toy, coded by Ali Lokhandwala. |
| Control Version System | cvsnt.cpl | Control Panel Customization Toy, by Brian Berliner. david d ‘zoo’ zuhn, Jeff Polk, Tony Hoyle |
| Creative Element Power Tools | To configure Creative Element Power Tools, a free-to-try program providing access to additional Windows tools. | |
| Corel Versions | verscpl.cpl | Configures Corel versions. |
| DANS | danetsvc.cpl | Configures the Shaffer Solutions DiskAccess Network Services, NFS client for Windows. |
| Diagnostics for Windows | cpqdiag.cpl | HP Diagnostics for Windows 4.15 replaces Compaq |
| Digidesign ElevenRack | DigidesignElevenRackControlPanelApplet.cpl | Launch Eleven Rack Control Panel |
| DiskAccess | dacfg.cpl | Configures how the Shaffer Solutions DiskAccess makes connections to remote NFS servers. |
| DS18x Applet | DS18xCPL.cpl | MR Soft DS18x Temperature Logging Service. |
| Flash Player | FlashPlayerCPLApp.cpl | For changing settings for the Flash Player. |
| Folder size | FolderSize.cpl | Folder Size for Windows shows the size of folders in Windows Explorer. |
| FirebirdSQL Service Manager | fmmgr.cpl | Configures Firebird (database server) service options. |
| HP Jetadmin | jetadmin.cpl | HP Jetadmin configures and monitors HP printers. |
| HP Lock | Hplock.cpl | A Windows 95 utility to lock the PC keyboard, mouse and on/off switch in one click on legacy HP Vectra. |
| IconPackager | ipcpl.cpl | To customize Windows icons and cursors, see IconPackager. |
| ImDisk Virtual Disk Driver | imdisk.cpl | Administration of ImDisk Virtual Disk Driver. |
| InstallShield Update Manager | isuspm.cpl | The InstallShield Update Manager allows users to receive program updates and messages from software makers who use the service. |
| Intel Extreme Graphics | igfxcpl.cpl | To change advanced settings on systems using Intel GPUs. |
| Intel Product Improvement Program | executable | Installed with Intel Driver Update Utility version 2.4 (on Vista and up) |
| IP Office Voicemail Pro | ims.cpl | To configure Avaya IP Office Voicemail Pro. |
| Java | jpicpl32.cpl | For changing settings with Java Runtime Console. |
| JInitiator 1.x.y.z | plugincpl1xyz.cpl | To configure Oracle’s JInitiator, note x.y.z are version numbers. |
| MLCFG32.cpl | Launches the Microsoft Outlook Profile Manager. | |
| MSConfig | MSConfig.cpl | Launches the Microsoft System Configuration Utility. |
| Multi-finger | ETDUI.cpl | Customize the Smart-Pad Multi-finger Setting. |
| MultiSite | ms.cpl | To configure IBM Rational ClearCase Multisite. |
| Nero BurnRights | NeroBurnRights.cpl | For specifying who is allowed to use the CD burner with Nero. |
| nVIDIA Control panel | nvidia.cpl | To change advanced settings on systems using nVIDIA GPUs. |
| Panda Media Booster | PMB.cpl | Panda Media Booster cache and network settings. |
| Parallel Port Joysticks | PPjoy.cpl | Configures Joysticks connected on the Parallel Port. |
| Pointer Devices | tbctlpnl.cpl | To configure the Touch-Base Universal Pointer Device Driver (UPDD). |
| QuickTime | quicktime.cpl | For specifying settings of the Apple QuickTime Player. |
| RealPlayer | prefscpl.cpl | To configure the RealPlayer preferences, older versions. |
| Realtek AC97 Audio Control Panel | alsndmgr.cpl | To configure the Realtek audio controller. |
| Realtek HD-Audio Manager | RTSnMg64.cpl | To launch the Realtek HD-Audio Manager |
| RESTrick Control Panel | rest2.cpl | Windows Tuning and system restrictions setup, by Rtsecurity. |
| Safarp | safarp.cpl | Safarp is a small and fast alternative to the Add or Remove Programs applet. |
| ScrewDrivers Client | sdclient.cpl | From Tricerat, remote desktop print management solution. |
| Send To Toys | sendtotoys.cpl | To configure the Send To right click system menu in Microsoft Windows. |
| Services and Devices | pserv.cpl | From p-nand-q to manage Windows services and devices and uninstall applications. |
| Softex OmniPass | scurecpl.cpl | Softex OmniPass provides password management capabilities to MS Windows. |
| SNTP Service | sntpserv.cpl | From Dillobits Software, to manage the SNTP client service. |
| Soundscape | scurecpl.cpl | Adds, removes or changes settings of Soundscape devices. |
| Startup | startup.cpl | Control programs that run at system start-up, coded by Mike Lin. |
| Startup Disk | Startup Disk.cpl | Boot Camp drivers, when Windows runs on a Mac OS virtual machine. |
| Symantec LiveUpdate | s32lucp2.cpl | Configures the Symantec LiveUpdate update service. |
| System Change Log | scl.cpl | From Greyware Automation Products, monitors disks for changes and records a detailed log. |
| System Information | Sancpl.cpl | Launches SiSoftware Sandra utility. |
| System Info for Windows | siw.cpl | Launches the SIW application. |
| Trust-No-Exe | trustnoexe.cpl | Configures the Beyond Logic Trust-No-Exe executable filter. |
| VMware Tools | VMControlPanel.cpl | To configure VMware Tools. |
| WIBU-KEY | wibuke32.cpl | To configure the WIBU-KEY Software Protection. |
| Winlogos | wnlgo.cpl | To change the Windows start-up and shutdown screens in Windows 98 or ME, coded by Ali Lokhandwala. |
| X-Setup Pro | xqdcXSPApplet.cpl | Launches X-Setup Pro, a Windows tweaker application. |
References[edit]
- ^ «A history of Windows». Windows. Microsoft. Archived from the original on November 17, 2010.
- ^ «Accessing the Control Panel via the Commandline». Microsoft. August 29, 2011.
- ^ Bradley, Tony (July 6, 2012). «Adding and Managing Users in Windows 8». PC World. IDG. Retrieved September 20, 2015.
- ^ Bright, Peter (March 25, 2013). «Windows Blue leaks: More Metro, more multitasking». Ars Technica. Condé Nast. Retrieved January 20, 2014.
- ^ «How to run Control Panel tools by typing a command». Support. Microsoft. Retrieved February 26, 2014.
External links[edit]
- How to run Control Panel tools by typing a command at Microsoft.com
Содержание
- Переключение языков с помощью языковой панели
- Использование языковой панели для переключения раскладок клавиатуры
- Я не вижу языковую панели
- Смена языка интерфейса Windows 10 через Параметры или Панель управления
- В окне Параметры
- Скачивание языка в магазине Майкрософт
- Использование кнопки Добавление языка
- Через Панель управления
- Как изменить язык в Windows 10: включаем русский интерфейс
- Изменение языка системы в Windows 10: английский на русский
- Как загрузить языковой пакет для Windows 10 и изменить язык интерфейса
- Для чего нужен языковой пакет
- Установка ЯП
- Установка ЯП при помощи настроек параметров Windows
- Установка ЯП из панели управления Windows
- Добавление языка из cab-файла
- Изменение языка интерфейса
- Видео: работа с языковыми пакетами в Windows 10
- Изменения языка приветствия
- Установка ЯП на Single Language версию
- Изменения языка программ
- Как изменить язык интерфейса Windows 10 на английский
- Изменить язык интерфейса Windows 10
- Установить языковой пакет Windows 10
Переключение языков с помощью языковой панели
После включения раскладки клавиатуры для нескольких языков в операционной системе Windows можно выбирать нужные языки с помощью языковой панели.
Примечание: Если вы просто хотите добавить несколько иностранных символов и вводите текст только на языках с кириллическим алфавитом, таких как русский или украинский, вы можете вставлять символы, не переключаясь на другую раскладку клавиатуры.
Дополнительные сведения о добавлении дополнительных языков редактирования и раскладок клавиатуры см. в меню и средствах проверки.
Использование языковой панели для переключения раскладок клавиатуры
При переключении на другой язык с помощью языковой панели раскладка клавиатуры меняется на раскладку для выбранного языка.
Используйте языковую панель в следующих случаях:
для переключения между языками с латинским алфавитом, например английским, испанским или французским, и прочими языками, такими как арабский или китайский;
для переключения между языками с нелатинскими алфавитами, например греческим и русским;
для использования стандартных раскладок клавиатуры при вводе на разных языках с латинским алфавитом.
Включив нужный язык клавиатуры, откройте документ и установите курсор в то место, куда требуется ввести текст на другом языке.
Щелкните значок 
Сочетание клавиш: Чтобы переключиться на другую раскладку клавиатуры, нажмите клавиши ALT+SHIFT.
Примечание: В 
Если для одного языка установлено несколько раскладок клавиатуры, для переключения между ними щелкните значок раскладки клавиатуры на языковой панели и выберите нужную раскладку. Буквы на индикаторе изменятся в соответствии с активной раскладкой клавиатуры.
Для переключения между различными языками повторяйте действия 1 и 2.
Я не вижу языковую панели
Обычно языковая панель автоматически появляется на рабочем столе или на панели задач после включения в операционной системе Windows двух и более раскладок клавиатуры. Языковая панель не отображается, если она скрыта или в операционной системе включена только одна раскладка клавиатуры.
Если языковая панель не отображается, выполните следующие действия, чтобы проверить, скрыта ли языковая панель.
В Windows 10 и Windows 8
Выберите пункт Панель управления.
В разделе Часы, язык и регион нажмите Изменение способа ввода.
Нажмите кнопку Дополнительные параметры.
В разделе Переключение методов ввода установите флажок Использовать языковую панель, если она доступна и выберите элемент Параметры.
В диалоговом окне Языки и службы текстового ввода откройте вкладку Языковая панель и убедитесь, что выбран параметр Располагается в произвольном месте рабочего стола или Закреплена в панели задач.
Нажмите кнопку Пуск и выберите команду Панель управления.
В разделе Часы, язык и регион нажмите кнопку Смена клавиатуры или других способов ввода.
В диалоговом окне Язык и региональные стандарты нажмите кнопку Изменить клавиатуру.
В диалоговом окне Языки и службы текстового ввода откройте вкладку Языковая панель.
Проверьте, не выбрано ли в разделе Языковая панель значение Скрыта. Если это так, выберите Располагается в произвольном месте рабочего стола или Закреплена в панели задач.
Нажмите кнопку Пуск и выберите команду Панель управления.
В разделе Часы, язык и регион нажмите кнопку Смена клавиатуры или других способов ввода.
В диалоговом окне Язык и региональные стандарты нажмите кнопку Изменить клавиатуру.
В диалоговом окне Языки и службы текстового ввода откройте вкладку Языковая панель.
Проверьте, не выбрано ли в разделе Языковая панель значение Скрыта. Если это так, выберите Располагается в произвольном месте рабочего стола или Закреплена в панели задач.
Источник
Смена языка интерфейса Windows 10 через Параметры или Панель управления
Во время установки Windows вы сами выбираете язык интерфейса, на котором в дальнейшем будут отображаться все контекстные меню, магазин Microsoft, проводник и прочее. Но как быть, если вы захотели поменять язык системы, или купили ноутбук с предустановленной Windows на английском или китайском?
Ответ достаточно прост: нужно изменить язык интерфейса Windows 10. Для этого придется скачать подходящий языковой пакет и установить его для отображения интерфейса. В последних версиях Windows (начиная с 1803) все можно сделать через окно Параметров, а тем, у кого установлена версия 1709 или более ранняя, придется воспользоваться Панелью управления.
Еще обратите внимание, что если на ноутбуке или компьютере установлена Windows 10 Домашняя для одного языка (single language), то описанные в статье способы применить не получится.
В окне Параметры
Для того, чтобы сменить язык интерфейса в Windows 10, версия которой 1803 или новее, можно воспользоваться окном Параметров. В примере все пункты будут на английском и украинском, если у вас по-другому, то ориентируйтесь на иконки и смотрите, каким по счету будет нужный пункт.
Скачивание языка в магазине Майкрософт
В открывшемся окне «Settings» ( «Параметры» ) выберите пункт «Time & Language» ( «Время и язык» ).
Затем нужно перейти на третью вкладку «Language» ( «Язык» ). В самом верху будет выпадающий список. Разверните его и посмотрите, нет ли в нем нужного. Если есть – выберите его и перезагрузите устройство.
Дальше может потребоваться авторизация в личном аккаунте. Введите логин и пароль для входа.
Если у вас нет аккаунта и вы пользуетесь компьютером из-под локальной учетной записи, можете прочесть статью: как создать учетную запись Майкрософт.
Из открывшегося списка выберите подходящий язык и нажмите по названию, которое выделено жирным.
Дождитесь завершения процесса установки.
Использование кнопки Добавление языка
Откроется знакомое окно дополнительных параметров. В нем должны стоять птички на первом и втором пункте. После этого нажимайте левую кнопку внизу и начнется установка.
Дождитесь окончания процесса и выполните перезагрузку компьютера.
После смены языка интерфейса на привычный, многих интересуют другие популярные вопросы.
Затем поставьте птичку «Экран приветствия и системные учетные записи» и сохраните изменения. Теперь язык ввода на экране приветствия у вас будет английский.
Если у вас приложения и страницы в Интернете отображаются не на нужном языке, то просто из списка установленных выделите нужный и с помощью стрелочки переместите его вверх списка.
Через Панель управления
Если в списке под кнопкой есть интересующий вас язык, то этот и следующий пункт нужно пропустить.
О том, как добрать к этому окну по-другому описано в 3 пункте статьи: добавление языка в Windows 10.
Дальше возвращаемся к знакомому окну и напротив нужного языка нажмите на кнопку «Параметры» ( «Options» ).
В окне параметров жмите на кнопку «Скачать и установить языковой пакет» ( «Download and install language pack» ). Для этого потребуются права администратора и подключение к Интернету.
Если у вас получилось изменить язык интерфейса Windows 10, но при входе в Microsoft Store все на другом языке, то проверьте, чтобы был выбран подходящий регион. Также обращайте внимание, какой язык установлен в самом верху списка.
Источник
Как изменить язык в Windows 10: включаем русский интерфейс
Изменение основного языка системы может быть необходимым, например, если на компьютере установлена англоязычная версия системы, а вам нужен русский интерфейс. Вы можете скачать и установить дополнительные языковые пакеты для Windows 10 и Windows 10 Enterprise 1903 / LTSC 2019, чтобы получить интерфейс операционной системы на требуемым языке.
Изменение языка системы в Windows 10: английский на русский
Прежде всего, войдите в учетную запись администратора устройства. Нажмите сочетание клавиша Windows + I для запуска приложения Settings (Параметры), а затем перейдите в раздел Time & Language (Время и язык).
В разделе Windows display language (Язык интерфейса Windows) нажмите ссылку Add a Windows display language in Microsoft Store (Добавьте язык интерфейса Windows в Microsoft Store).
Откроется страница Microsoft Store со всеми доступными для установки языковыми пакетами. Найдите и выберите язык, который нужно установить – например, русский (пакет локализованного интерфейса на русском).
На следующей странице нажмите Get (Получить).
Затем нажмите Install (Установить).
Дождитесь загрузки и установки выбранного языкового пакета. Выберите Yes, sign out now (Да, выйти сейчас), чтобы выйти из учетной записи для применений изменений или No, sign out later (Нет, выйти из системы позже).
Система будет доступна на выбранном языке после выхода из учетной записи или перезагрузки.
Источник
Как загрузить языковой пакет для Windows 10 и изменить язык интерфейса
Язык интерфейса в Windows 10 выбирается при установке операционной системы. Но после того как процедура установки закончена, его можно изменить. Для этого понадобится языковой пакет.
Для чего нужен языковой пакет
Языковой пакет (далее «ЯП» для краткости) – набор слов и предложений, обеспечивающий перевод системы на определённый язык. Например, установив русский ЯП, вы переведёте все системные сообщения, приложения и настройки на русский язык. Соответственно, выбрав ЯП другого языка, вы сможете пользоваться Windows на наиболее удобном для вас языке.
Установка ЯП
В Windows 10 встроено несколько методов, позволяющих работать с ЯП. Благодаря им можно выбирать язык из уже скачанных пакетов, а также устанавливать новые ЯП.
Установка ЯП при помощи настроек параметров Windows
В Windows 10 есть встроенная утилита «Параметры», позволяющая управлять настройками системы. Если ОС на вашем компьютере уже обновлена до версии 1803 April Update, то с помощью этой утилиты можно загрузить дополнительный ЯП. Если у вас установлена более старая версия Windows, то воспользуйтесь любым из описанных ниже методов — результат будет тот же. Для загрузки ЯП с помощью утилиты «Параметры» сделайте следующее:
Как только загрузка закончится, в списке языков появится новый ЯП — выберите его, чтобы осуществить перевод системы на нужный язык.
Установка ЯП из панели управления Windows
Пользователи, не обновившие ещё свою Windows до версии 1803 или более поздней, могут выполнить смену ЯП через панель управления. Для этого сделайте следующее:
Готово. Новый ЯП загружен и применён. Возможно, вас попросят выйти из системы, чтобы применить изменённые параметры. Дайте согласие, затем снова войдите в свою учётную запись и проверьте результат.
Добавление языка из cab-файла
Если у вас есть отдельно загруженный ЯП в формате cab, то для его установки выполните следующие шаги:
Изменение языка интерфейса
Установка нового ЯП не гарантирует того, что язык системы изменится. Обычно для этого нужно ввести соответствующую команду, которая изменит язык интерфейса. Выполните следующие шаги:
Видео: работа с языковыми пакетами в Windows 10
Изменения языка приветствия
Если вы хотите при входе в систему видеть тот же язык, который назначили языком интерфейса, то выполните дополнительные шаги:
Установка ЯП на Single Language версию
Есть специальная редакция Windows — Single Language. Она включает в себя только один язык и не позволяет загрузить дополнительные ЯП через панель управления или утилиту «Параметры». Сделано это для того, чтобы неопытный пользователь случайно не перевёл систему не непонятный ему язык.
Если вы столкнулись с тем, что на вашем компьютере установлена версия Single Language, а новый ЯП вам нужен, то воспользуйтесь методом, описанным в пункте «Добавление языка из cab-файла». Установить пакет и начать пользоваться им можно, предварительно загрузив cab-файл со стороннего ресурса.
Изменения языка программ
Сторонние программы работают на том языке, который вы выбрали при установке, но встроенные в Windows приложения и утилиты, загруженные из официального магазина Microsoft, при определении языка интерфейса опираются на настройки системы. Используемый в них язык выбирается на основе данных о местоположении.
В более ранних версиях Windows 10 языковые пакеты устанавливаются через панель управления, а в последних — через параметры системы. Универсальный способ — установить ЯП при помощи cab-файла. После того как пакет будет установлен, перейдите в настройки региональных стандартов и измените язык интерфейса, приветствия и стандартных программ.
Источник
Как изменить язык интерфейса Windows 10 на английский
Все языковые настройки были перенесены в новые параметры Windows 10. Майкрософт пытается избавиться от устаревшей панели управления. В параметрах системы можно изменить язык. Хотя в процессе установки сразу указывается подходящий язык и регион.
Эта статья расскажет, как изменить язык интерфейса Windows 10 на английский. Вы можете выбрать любой с поддерживаемых языков. Начиная от русской и вплоть до китайской локализации. Изредка бывает нужно загрузить и установить необходимый языковый пакет.
Изменить язык интерфейса Windows 10
В разделе Параметры > Время и язык > Язык найдите Язык интерфейса Windows. В списке выберите собственно английский язык English (United States). Этот язык интерфейса будет использоваться, когда Вы в следующий раз войдёте в систему. Например, после перезагрузки.
Чтобы полностью применить новый язык, необходимо выйти из Windows. В окошке сразу предлагается выйти, просто подтвердите нажав Да, выйти сейчас или отклоните выбрав Нет, выйти позже. Конечно же, лучше закрыть все важные документы и самостоятельно выйти.
На выбранном языке будут показываться такие компоненты Windows, как приложение параметров и проводник. В подразделе Предпочитаемый язык указывается приоритетный. Все приложения и веб-сайты будут отображаться на первом поддерживаемом языке из списка.
В приложениях Фотографии или Кино и ТВ мгновенно переключаются язык интерфейса. Здесь уже не нужно перезагружать компьютер. Необязательно использовать один язык интерфейса и приложений. Например, с русским можно использовать английский, выбрав приоритетный.
Установить языковой пакет Windows 10
Сейчас в параметрах системы всё стало значительно проще. В большинства пользователей английский язык уже добавлен. Ну давайте на примере китайского разберёмся, как установить и выбрать язык интерфейса. Нажмите Добавление языка и введите его название в поиске.
Например, выделив Китайский (традиционное письмо, Гонконг, САР) нажмите Далее. Ставим отметку Установить языковый пакет > Назначить языком интерфейса Windows. Нажав Установить дождитесь завершения его скачивания языкового пакета и его установки.
Корпорация Майкрософт доводит свои обновлённые параметры до ума. Вспомните, какие они были в системе Windows 8.1. Сейчас в классической панели управления почти ничего не осталось. Все языковые настройки (интерфейса и раскладки) легко доступны в Windows 10.
Ранее рассматривался процесс добавления русского языка в Windows 10. Бывает полезно изменить язык интерфейса на английский. Особенно если Вы его только начинаете учить. Отдельно выставлением приоритетного указывается язык UWP-приложений и веб-страниц.
Источник
Для чего нужна панель управления
Начинающий пользователь персонального компьютера пользуется его возможностями, данными по умолчанию. По мере набора опыта и перехода в разряд продвинутого пользователя у него возникает потребность в более удобной и комфортной работе. Операционная система Windows предусмотрела возможность настройки ряда некритичных параметров компьютера под вкусы и предпочтения пользователя. Эти настройки сведены в компонент интерфейса, называемый панелью управления. Такое название очевидно и чётко определяет её назначение.
После вызова (способы которого будут рассмотрены ниже) окно панели управления по умолчанию имеет следующий вид.
Как видно, настраиваемые параметры компьютера разделены на восемь категорий и снабжены соответствующими значками. Рядом с ними и названием приведена краткая информация о возможностях данной настройки. Поясним эту информацию с тем, чтобы сделать её более понятной начинающему пользователю. Начнём с более простых категорий.
«Специальные возможности»
Абсолютное большинство пользователей может не обращать внимания на категорию «Специальные возможности». Она предназначена для людей, имеющих проблемы со зрением, слухом или двигательными функциями. Такие пользователи смогут внутри неё, например, сделать изображение более контрастным, сильно увеличить отображаемый на экране курсор мыши, заменить звуковые сигналы визуальными подсказками. Есть также возможность проще работать с сочетаниями клавиш: например, пользователь с дрожащей рукой сможет нажимать Ctrl+Alt+Del не одновременно, а по очереди.
«Часы, язык и регион»
Правильная настройка компьютера предполагает выбор форматов отображения на экране даты и времени, принятой для того региона, в котором эксплуатируется компьютер. Вряд ли можно считать удобным, если на работающем в России компьютере отображаются принятые в США форматы даты – 04/25/2017 (дата начинается с месяца) или 6:53 PM. Для их точного отображения нужно выбрать правильный часовой пояс. Можно также указать, происходит ли в данном регионе переход на летнее и зимнее время с тем, чтобы компьютер автоматически корректировал время.
В этой же категории пользователь выбирает, на каких языках ему придётся набирать текст в редакторе. К стандартным EN и RU можно добавить, например, DE для немецкого, что будет нужно переводчику на этот язык.
«Оформление и персонализация»
В этой категории настраивается оптимальное для используемого монитора разрешение экрана с тем, чтобы изображение на нём было комфортным для пользователя. Здесь же выбирается заставка экрана и размер текста и значков рабочего стола. Можно также добавлять значки и ярлыки в меню «Пуск» и на панель задач, примеры чего будут рассмотрены ниже.
«Учётные записи пользователей»
Единственному рядовому пользователю компьютера вряд ли пригодится эта категория. Но если компьютер находится в пользовании нескольких человек, то каждый из них сможет входить в систему под автономной учётной записью (т. е. аккаунтом), настроенным под его предпочтения и вкусы. Аккаунты могут иметь разные права в системе: в частности, опытным пользователям будут доступны расширенные возможности настройки.
Другие категории
Категории в левой части окна панели управления ориентированы на продвинутых пользователей.
Категория «Программы» предназначена для корректного удаления и добавления на компьютер внешних программ и компонентов Windows. В категории «Оборудование и звук» можно подключать к компьютеру внешние устройства, например, принтер или сканер. «Сеть и Интернет» позволяют, в частности, настраивать «домашнюю сеть», объединяющую, например, стационарный компьютер, ноутбук и смартфон с общим выходом в Интернет. С категорией «Система и безопасность» работают опытные пользователи. Ведь она позволяет устранять неполадки компьютера, например, возвратом к состоянию недельной давности или восстановлением повреждённых файлов из резервных (архивных).
Степень детализации возможностей панели управления может быть изменена, если в верхнем выпадающем списке «Просмотр» поменять «Категория» на «Крупные значки» или «Мелкие значки». В этом случае каждый инструмент отображается автономно (см. ниже).
Вызов панели управления
Пользователь Windows 7, привыкший вызывать панель управления через меню «Пуск», в Windows 10 не найдёт соответствующего пункта. Но перейти к ней нетрудно, и сделать это можно несколькими способами.
С помощью контекстного меню «Пуск»
Самый простой из них так же происходит через меню «Пуск», только не обычное, а контекстное (вызываемое нажатием правой клавиши на кнопке «Пуск»).
Представленное на скриншоте контекстное меню может быть открыто и другим способом – сочетанием клавиш Win+X.
Добавление в обычное меню «Пуск»
Пользователи Windows 7, предпочитающие открывать панель управления привычным способом – через обычное меню «Пуск», смогут делать это после выполнения следующей последовательности действий.
- На панели задач (нижней строке с кнопкой «Пуск») щёлкаемна свободном месте правой клавишей мыши. В появившемся окне выбираем пункт «Свойства».
- В окне «Свойства панели задач и меню «Пуск» переходим на вкладку Меню «Пуск».
- На этой вкладке нажимаем кнопку «Настроить».
- В окне «Настройка» меню «Пуск» ставим галочку рядом со словосочетанием «Панель управления» и жмем OK.
- После этого в стандартном меню «Пуск» появится новая, но привычная строка «Панель управления».
Встроенной функцией поиска
Панель управления может быть вызвана посредством поисковой системы, обозначаемой значком лупы в левой части панели задач. После нажатия на этом значке в появившейся строке следует ввести «панель управления». Как правило, искомый результат появляется ещё до полного ввода этого словосочетания.
Поисковая строка может быть вызвана не только через значок лупы, но сочетанием клавиш Win+S. Более того, указанное словосочетание можно набирать и без предварительного вызова поисковой строки. По мере набора система «соображает», что хочет пользователь, и автоматически предоставляет ему поисковую строку.
Поиск посредством функции поиска, разумеется, применим при поиске не только панели управления, но и произвольного приложения, место расположения которого неизвестно пользователю.
С помощью команды в строке «Выполнить»
К панели управления можно перейти и с помощью строки «Выполнить». Она возникает при нажатии сочетания клавиш Win+R. В появившейся строке «Открыть» нужно набрать команду control.
Добавление значка на рабочем столе
После инсталляции Windows 10 на рабочем столе системы по умолчанию появляются значки «Этот компьютер» и «Корзина». Пользователь, однако, имеет возможность добавить на него и некоторые другие значки, включая «Панель управления». Для этого следует выполнить приводимую последовательность действий:
- В свободном месте рабочего стола кликаем правой клавишей мыши.
- В появившемся контекстном меню щёлкаем пункт «Персонализация».
- В новом окне «Параметры» следует щёлкнуть пункт «Темы», а затем – «Параметры значков рабочего стола»;
- В появившемся одноимённом окне необходимо поставить галочку рядом со словосочетанием «Панель управления» и подтвердить намерение, щёлкнув OK.
В результате панель управления будет постоянно отображаться на рабочем столе.
В скобках отметим, что для внимательного читателя будет очевидно, что при открытой панели управления окно «Персонализация» может вызвано через категорию «Оформление и персонализация» (см. первый скриншот).
Добавление ярлыка на рабочем столе
Элементы управления, обычно находящиеся на рабочем столе, подразделяются на значки и ярлыки. Последние легко отличить по стрелке рядом со значком (указывающей, что само приложение находится в другом месте). Для добавления ярлыка на рабочий стол должна быть выполнена следующая последовательность действий.
- В контекстном меню рабочего стола в выпадающем списке «Создать» выбираем пункт «Ярлык».
- В появившемся окне в поле «Укажите расположение объекта» вводим control и жмем кнопку «Далее».
- В новом окне вводим желаемое имя и жмем «Готово».
Вызов панели управления с помощью «горячих клавиш»
После создания ярлыка на рабочем столе его можно связать с комбинацией «горячих клавиш». Для этого следует вызвать контекстное меню ярлыка «Панель управления», щёлкнуть пункт «Свойства», и в поле «Быстрый вызов» набрать комбинацию клавиш, разделяя их знаком +. Первые две клавиши – Ctrl+Alt, а третья – на усмотрение пользователя.
Post Views: 3 525
Как открыть классическую Панель управления в Windows 10
Начиная с Windows 8, Microsoft планомерно переносит апплеты классической Панели управления в новое приложение «Параметры». В Windows 10 это приложение не только включает в себя большинство настроек и опций, доступных в классической панели управления, но и также получило немало новшеств, для которых нет в традиционного аналога.
Несмотря на то, что многие из настроек классической Панели управления были перемещены в новое приложение Параметры, в ней ещё немало функций, которыми приходиться пользоваться; как пример тому — тонкая настройка режима высокого контраста. Поэтому я предлагаю рассмотреть основные способы, которыми можно открыть классическую Панель управления в Windows 10.
Существует несколько способов открыть классическую Панель управления в Windows 10. Я начну не с самого простого, но с самого любимого. Ниже я поясню, чем он мне так нравится.
- Нажмите сочетание
Win+R. - В открывшемся диалоговом окне «Выполнить» введите control в поле «Открыть».
- Нажмите
Enterна клавиатуре, или щелкните кнопку ОК, чтобы открыть Проводник.
Несмотря на то, что это способ немного «хакерский», он очень удобный. Все действия выполняются с клавиатуры, не открывая рук от клавиш и никуда не целясь мышкой. К тому же, в Windows 10 всё очень быстро меняется, сегодня есть некий пункт меню, а в следующей сборке его уже нет. А этот способ всегда работает.
Для новичка может быть удобнее
Открыть Панель управления с помощью Поиска
- В поле Поиска Windows на панели задач или в открытом меню Пуск и начните набирать
Панель управления. - В результатах поиска выберите Панель управления.
- Там же вы её можете закрепить к панели задач, и открывать её в дальнейшем ещё быстрее.
А ещё, можно
Открыть Панель управления с помощью значка Рабочего стола
- Щелкните правой кнопкой мыши на пустой области рабочего стола.
- Выберите в контекстном меню
Персонализация. - Перейдите слева в раздел
Темы(или же откройте приложениеПараметрыи перейдите вПерсонализация > Темы. - В разделе «Сопутствующие параметры» нажмите на ссылку
Параметры значков рабочего стола. - В окне настройки значков, установите флажок напротив пункта «Панель управления», чтобы разместить ярлык классической панели управления на рабочем столе и нажмите кнопку
ОК.
Теперь на рабочем столе есть удобный значок.
Как открыть Панель управления с помощью приложения Параметры
Было бы удобно, если бы в Параметрах была ссылка, позволяющая открыть классическую Панель управления. Однако, простой способ открыть классическую Панель управления оттуда всё же есть. Вы можете использовать строку поиска в Параметрах Windows, чтобы открыть Панель управления.
Чтобы открыть панель управления из приложения Параметры, все, что вам нужно сделать, это набрать в строке поиска Параметров Панель управления и нажать клавишу Enter.
Кроме того, вы можете использовать строку поиска в Параметрах для быстрого доступа и к другим разделам Панели управления. Например, вы можете ввести Диспетчер устройств, чтобы быстро открыть Диспетчер устройств. Это работает и для других апплетов
Как открыть Панель управления с помощью Проводника Windows 10
- Откройте окно Проводника в Windows 10.
- В его адресной строке наберите или скопируйте и вставьте: Панель управления и нажмите клавишу
Enter. - Классическая панель управления тут же откроется.
- Вместо
Панель управленияможно напечататьcontrolи нажатьEnter. Это тоже сработает.
Способов предостаточно. Но кроме этого, вы можете вернуть классическую Панель управления в меню Win + X!
💡Узнавайте о новых статьях быстрее. Подпишитесь на наши каналы в Telegram и Twitter.
Судя по тому, что вы читаете этот текст, вы дочитали эту статью до конца. Если она вам понравилась, поделитесь, пожалуйста, с помощью кнопок ниже. Спасибо за вашу поддержку!