From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
A taskbar is an element of a graphical user interface which has various purposes. It typically shows which programs are currently running.
The specific design and layout of the taskbar varies between individual operating systems, but generally assumes the form of a strip located along one edge of the screen. On this strip are various icons which correspond to the windows open within a program. Clicking these icons allow the user to easily switch between programs or windows, with the currently active program or window usually appearing differently from the rest. In more recent versions of operating systems, users can also «pin» programs or files so that they can be accessed quickly, often with a single click. Due to its prominence on the screen, the taskbar usually also has a notification area, which uses interactive icons to display real-time information about the state of the computer system and some of the programs active on it.
With the rapid development of operating systems and graphical user interfaces in general, more OS-specific elements have become integrated into and become key elements of the taskbar.
Early implementations[edit]
Windows 1.0[edit]
Windows 1.0, released in 1985, features a horizontal bar located at the bottom of the screen where running programs reside when minimized (referred to as «iconization» at the time), represented by icons. A window can be minimized by double-clicking its title bar, dragging it onto an empty spot on the bar, or by issuing a command from one of its menus. A minimized window is restored by double-clicking its icon or dragging the icon out of the bar.
The bar features multiple slots for icons and expands vertically to provide the user with more rows as more slots are needed. Its color is the same as that of the screen background, which can be customized. Minimized windows can be freely placed in any of the empty slots. Program windows cannot overlap the bar unless maximized.
The Start button did not make an appearance in these early implementations of the taskbar, and would be introduced at a much later date with the release of Windows 95.
Appearance of the bar used for holding minimized windows in Windows 1.0
Arthur[edit]
Another early implementation can be seen in the Arthur operating system from Acorn Computers. It is called the icon bar[1] and remains an essential part of Arthur’s succeeding RISC OS operating system. The icon bar holds icons which represent mounted disc drives and RAM discs, running applications and system utilities. These icons have their own context-sensitive menus and support drag and drop behaviour.
Appearance of Acorn’s icon bar in 1987 under Arthur, after launching a number of devices and applications
Amiga[edit]
AmigaOS featured various third party implementations of the taskbar concept, and this inheritance is present also in its successors. For example, AmiDock, born as third-party utility, has then been integrated into AmigaOS 3.9 and AmigaOS 4.0.[2] The AROS operating system has its version of Amistart that is provided with the OS and free to be installed by users, while MorphOS has been equipped with a dock utility just like in AmigaOS or Mac OS X.
Microsoft Windows[edit]
The default settings for the taskbar in Microsoft Windows place it at the bottom of the screen and includes from left to right the Start menu button, Quick Launch bar, taskbar buttons, and notification area. The Quick Launch toolbar was added with the Windows Desktop Update and is not enabled by default in Windows XP. Windows 7 removed the Quick Launch feature in favor of pinning applications to the taskbar itself. On Windows 8 and Windows Server 2012, a hotspot located in the bottom-left corner of the screen replaced the Start button, although this change was reverted in Windows 8.1 and Windows Server 2012 R2.
The taskbar was originally developed as a feature of Windows 95, but it was based on a similar user interface feature called the tray that was developed as part of Microsoft’s Cairo project.[3][4][5]
With the release of Windows XP, Microsoft changed the behavior of the taskbar to take advantage of Fitts’s law by removing a border of pixels surrounding the Start button which did not activate the menu, allowing the menu to be activated by clicking directly in the corner of the screen.[6]
A standard Windows XP taskbar with multiple tasks running. Note the Quick Launch toolbar, introduced in Windows 95 OSR 2.5. When the notification area is full, it can be expanded.
The taskbar in Windows Vista. The design is quite similar to Windows XP, but with a whole new Start button, Windows Aero, transparency on the taskbar, and more updated icons added to it.
The taskbar in Windows 7 hides application names in favor of large icons that can be «pinned» to the taskbar even when not running.
The taskbar in Windows 8. Note that the Start button is missing in this version of Windows (in favor of the Charms menu) and the Metro apps that are running are not shown in the taskbar.
The taskbar in Windows 8.1. The Start button has returned to this version of Windows, and Metro apps that are running are now shown by default on the taskbar.
The taskbar in Windows 10, in Desktop mode, on the RTM version (1507). The next major revision to the taskbar came in Windows 10, where icons for Search and Task View have been added. Also, the shortcut to Action Center is visible (the icon for Action Center has been moved to the right when the Windows Anniversary Update came along).
The taskbar in Windows 10, in tablet mode, on the RTM version (1507). The next major revision to the taskbar came in Windows 10, where icons for Search and Task View have been added. Also, the shortcut to Action Center is visible (the icon for Action Center has been moved to the right when the Windows Anniversary Update came along).
The taskbar in Windows 10, in Desktop mode, on version 22H2. New features got added to the taskbar like News and Interests, and Search spotlight and are shown by default on a clean install.
The taskbar in Windows 10, in Tablet (handheld) mode, on version 22H2.
The taskbar in Windows 11, in version 22H2, with the icons at the center by default.
The taskbar in Windows 11, in version 22H2, with the icons at the left.
Taskbar elements[edit]
- The Start button, a button that invokes the Start menu (or the Start screen in Windows 8.1). It appears in Windows 9x, Windows NT 4.0 and all its successors, except Windows 8 and Windows Server 2012.
- The Quick Launch bar, introduced on Windows 95 and Windows NT 4.0 through the Windows Desktop Update for Internet Explorer 4 and bundled with Windows 95 OSR 2.5 Windows 98, contains shortcuts to applications. Windows provides default entries, such as Launch Internet Explorer Browser, and the user or third-party software may add any further shortcuts that they choose. A single click on the application’s icon in this area launches the application. This section may not always be present: for example it is turned off by default in Windows XP and Windows 7.
- The Windows shell places a taskbar button on the taskbar whenever an application creates an unowned window: that is, a window that does not have a parent and that is created according to normal Windows user interface guidelines. Typically all Single Document Interface applications have a single taskbar button for each open window, although modal windows may also appear there.
- Windows 98 and Windows Desktop Update for Windows 95 introduced the ability to minimize foreground windows by clicking their button on the taskbar. They also introduced DeskBands (band objects).[7][8]
- Windows 2000 introduced balloon notifications.
- Windows Me added an option to disable moving or resizing the taskbar.
- Windows XP introduced taskbar grouping, which can group the taskbar buttons of several windows from the same application into a single button. This button pops up a menu listing all the grouped windows when clicked. This keeps the taskbar from being overcrowded when many windows are open at once.
- Windows Vista introduced window previews which show thumbnail views of the application in real-time. This capability is provided by the Desktop Window Manager. The Start menu tooltip no longer says «Click here to begin» but now says simply «Start».
- Windows 7 introduced jumplists which are menus that provide shortcuts to recently opened documents, frequently opened documents, folders paths (in case of Windows Explorer), or various options (called Tasks) which apply to that specific program or pinned website shortcut. Jump lists appear when the user right-clicks on an icon in the taskbar or drags the icon upwards with the mouse left click. Recent and frequent files and folders can be pinned inside the jump list.
- Windows 7 introduced the ability to pin applications to the taskbar so that buttons for launching them appear when they are not running. Previously, the Quick Launch was used to pin applications to the taskbar; however, running programs appeared as a separate button.
- Windows 7 removed several classic taskbar features.
- Deskbands are minimized functional, long-running programs, such as Windows Media Player. Programs that minimize to deskbands are not displayed in the taskbar.[9]
- The notification area is the portion of the taskbar that displays icons for system and program features that have no presence on the desktop as well as the time and the volume icon. It contains mainly icons that show status information, though some programs, such as Winamp, use it for minimized windows. By default, this is located in the bottom-right of the primary monitor (or bottom-left on languages of Windows that use right-to-left reading order), or at the bottom of the taskbar if docked vertically. The clock appears here, and applications can put icons in the notification area to indicate the status of an operation or to notify the user about an event. For example, an application might put a printer icon in the status area to show that a print job is under way, or a display driver application may provide quick access to various screen resolutions. The notification area is commonly referred to as the system tray, which Microsoft states is wrong,[10][11][12] although the term is sometimes used in Microsoft documentation,[13][14][15] articles,[16] software descriptions,[17] and even applications from Microsoft such as Bing Desktop. Raymond Chen suggests the confusion originated with systray.exe, a small application that controlled some icons within the notification area in Windows 95.[5] The notification area is also referred to as the status area by Microsoft.[18][19][20]
- In older versions of Windows the notification area icons were limited to 16 colors. Windows Me added support for high color notification area icons.
- Starting with Windows XP, the user can choose to always show or hide some icons, or hide them if inactive for some time. A button allows the user to reveal all the icons.
- Starting with Windows Vista, the taskbar notification area is split into two areas: one reserved for system icons including clock, volume, network and power; the other for applications.
- Since the Windows 95 Desktop Update, the Quick Launch bar featured Show desktop as one of its default shortcuts which automatically minimizes all opened applications, redundant with the Winkey-D key combination. On Windows 7, a dedicated Show desktop button was placed to the right of the notification area and could not be removed. With the «Peek» option enabled, hovering over the button hides all opened windows to expose the desktop (leaving outlines of them on-screen). On Windows 10, the «Show desktop» widget changed yet again, being reduced to a narrow iconless strip at the far right of the taskbar.
Customization[edit]
The Windows taskbar can be modified by users in several ways. The position of the taskbar can be changed to appear on any edge of the primary display (except in Windows 11, where the taskbar is permanently fixed at the bottom of the screen and cannot be moved to the top, left, or right side). Up to and including Windows Server 2008, the taskbar is constrained to single display, although third-party utilities such as UltraMon allow it to span multiple displays. When the taskbar is displayed vertically on versions of Windows prior to Windows Vista, the Start menu button will only display the text «Start» or translated equivalent if the taskbar is wide enough to show the full text.[21] However, the edge of the taskbar (in any position) can be dragged to control its height (width for a vertical taskbar); this is especially useful for a vertical taskbar to show window titles next to the window icons.
Users can resize the height (or width when displayed vertically) of the taskbar up to half of the display area. To avoid inadvertent resizing or repositioning of the taskbar, Windows XP and later lock the taskbar by default.[22][23] When unlocked, «grips» are displayed next to the movable elements which allow grabbing with the mouse to move and size. These grips slightly decrease amount of available space in the taskbar.
The taskbar as a whole can be hidden until the mouse pointer is moved to the display edge, or has keyboard focus. The Windows 7+ taskbar does not allow pinning any arbitrary folder to the taskbar, it gets pinned instead to the jumplist of a pinned Explorer shortcut, however third party utilities such as Winaero’s Taskbar Pinner can be used to pin any type of shortcut to the Taskbar.[24]
Desktop toolbars[edit]
Other toolbars, known as «Deskbands», may be added to the taskbar.[25] This feature, along with many other taskbar features is currently absent in Windows 11. Windows includes the following deskbands but does not display them by default (except the Quick Launch toolbar in certain versions and configurations).
- Address. Contains an address bar similar to that found in Internet Explorer. (not available in Windows XP SP3, due to legal restrictions).
- Windows Media Player. Optionally shown when the Windows Media Player is minimized.(Windows XP, Windows Vista)
- Links. Shortcuts to items located in the user’s Links folder. Usually shortcuts to internet sites.
- Tablet PC Input Panel. Contains a button to show the Tablet PC input panel for ink text entry.
- Desktop. Contains shortcuts to items contained on the user’s desktop. Since the taskbar is always shown, this provides easy access to desktop items without having to minimize applications.
- Quick Launch. Contains shortcuts to Internet Explorer, email applications and a link to display the desktop. Windows Vista adds a link to the Flip 3D feature.
- Language. Contains shortcuts to quickly change the desired language for the keyboard to follow.
In addition to deskbands, Windows supports «Application Desktop Toolbars» (also called «appbands») that supports creating additional toolbars that can dock to any side of the screen, and cannot be overlaid by other applications.[26]
Users can add additional toolbars that display the contents of folders. The display for toolbars that represent folder items (such as Links, Desktop and Quick Launch) can be changed to show large icons and the text for each item. Prior to Windows Vista, the Desktop Toolbars could be dragged off the taskbar and float independently, or docked to a display edge. Windows Vista greatly limited, but did not eliminate the ability to have desktop toolbar not attached to the taskbar.[27] Windows 7 has deprecated the use of Floating Deskbands altogether; they only appear pinned into the Taskbar.
- Upon opening the Taskbar properties on Windows 95 and Windows 98 whilst holding down the CTRL key, an extra tab for DeskBar Options is shown, but no part of it can be used. The DeskBar option was a feature that was never included within these versions of Windows.[28]
macOS[edit]
Classic Mac OS did not display a taskbar onscreen by default. Application switching prior to Mac OS 8.5 was done by clicking on an application’s window or via a pull-down menu at the right end of the menu bar. Prior to version 8.5 the menu’s title was the icon of the foreground application. Version 8.5 introduced the ability to optionally also display the application name and to «tear off» the menu by dragging the title with the mouse. The torn off menu was displayed as a palette. The palette window could be configured using AppleScript to appear much like a taskbar, with no title bar and fixed to one edge of the screen. No control panel was provided by Apple to access this functionality, but third-party developers quickly wrote applications that allowed users unfamiliar with AppleScript to customize their application palettes. Third party taskbars such as DragThing were a popular category of shareware on these systems.
The Dock, as featured in macOS and its predecessor NeXTSTEP, is also a kind of taskbar. The macOS Dock is application-oriented instead of window-oriented. Each running application is represented by one icon in the Dock regardless of how many windows it has on screen. A textual menu can be opened by right-clicking on the dock icon that gives access to an application’s windows. Mac OS X 10.2 added the ability for an application to add items of its own to this menu. Minimized windows also appear in the dock, in the rightmost section, represented by a real-time graphical thumbnail of the window’s contents. The trash can is also represented in the Dock, as a universal metaphor for deletion. For example, dragging selected text to the trash should remove the text from the document and create a clipping file in the trash.
The right side of macOS’s Menu bar also typically contains several notification widgets and quick access functions, called Menu extras.
Unix-like operating systems[edit]
KDE Plasma[edit]
In KDE Plasma 5, taskbar uses Widgets, called «Plasmoids», as elements in taskbar. In the update 5.20 (November 2020) they updated the taskbar to look more like Windows 10 by only displaying icons by default and grouping application windows together. [29]
The new taskbar of Plasma 5.20
GNOME[edit]
GNOME 2 used its own type of taskbar, known as panels (the program responsible for them is therefore called gnome-panel). By default, GNOME 2 usually contains two full-width panels at the top and bottom of the screen. The top panel usually contains navigation menus labeled Applications, Places, and System in that order. These menus hold links to common applications, areas of the file system, and system preferences and administration utilities, respectively.
Default top panel appearance from Ubuntu 6.10 to 8.04
Default bottom panel from Ubuntu 6.10 to 8.04
The top panel usually contains a clock and notification area, while the bottom panel contains buttons for navigating between virtual desktops, the window list proper, and a button which minimizes all windows (similarly to Windows’ Show desktop button). The contents of panels are handled by widgets called panel applets, which can consist of application shortcuts, search tools, or other tools. The contents of the panels can be moved, removed, or configured in other ways.
GNOME Shell Activities Overview which showcases the Dash
In GNOME 3, panels are replaced by GNOME Shell, which consists of a bar across the top of the screen with an Activities button on the left, a clock in the centre, and a notification area on the right. GNOME Shell does not contain a traditional taskbar; users can manage windows, virtual desktops, and launch applications from either a «Dash» on the side of the screen, or by searching from Activities Overview, which is displayed by clicking on the Activities button. GNOME 3.8 introduces Classic Mode, which re-implements certain aspects of GNOME 2’s desktop as an alternate desktop environment that can be selected at the login screen. [30]
Other Unix environments[edit]
These desktop environments provide their own implementation of a taskbar:
- Cinnamon
- MATE
- LXDE
- Xfce
- Trinity Desktop (based on KDE3’s Kicker)
Standalone window managers that provide an integrated taskbar include:
- Fluxbox
- FVWM95
- IceWM
- JWM
- qvwm
- WindowLab
- Window Maker
Programs that offer standalone taskbars for desktop environments or window managers without one include Avant Window Navigator, pypanel, fbpanel, perlpanel, tint2, and others.
References[edit]
- ^ Dan Ryan (13 April 2011). History of Computer Graphics: DLR Associates Series. AuthorHouse. p. 358. ISBN 978-1-4567-5115-9. Retrieved 13 June 2013.
- ^ Amiga Amidock Homepage
- ^ US patent 5825357, Malamud, Marceau, Grauman, Levien, Oran, Bolnick, Barnes, Johnson, Scott, «Continuously accessible computer system interface», issued 1998-10-20, assigned to Microsoft Corporation
- ^ Kent Sullivan (April 17, 1996). «The Windows 95 User Interface: A Case Study in Usability Engineering». CHI 96 Design Briefs. Archived from the original on October 22, 2008. Retrieved 2008-10-22.
- ^ a b Chen, Raymond (September 10, 2003). «Why do some people call the taskbar the «tray»?». The Old New Thing. Microsoft. Retrieved 2021-08-12.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: url-status (link) - ^ Harris, Jensen (August 22, 2006). «Giving You Fitts». Jensen Harris: An Office User Interface Blog. Microsoft. Retrieved 2008-01-14.
- ^ Creating Custom Explorer Bars, Tool Bands, and Desk Bands
- ^ The Next Windows: Windows 98
- ^ «Windows Vista Developer Center — The Windows desktop». Archived from the original on 2010-01-27. Retrieved 2008-05-27.
- ^ «How to remove items from the notification area in Windows 2000». November 1, 2006. Retrieved 2008-10-21.
- ^ «Microsoft Style Guide: System Tray». Retrieved 2020-02-10.
- ^ «Notification Area». Microsoft Developer Network. Archived from the original on 2010-01-27. Retrieved 2008-05-27.
- ^ «How To Manipulate Icons in the System Tray with Visual Basic». 2004-07-15. Retrieved 2009-01-23.
- ^ «How to use the System Tray directly from Visual Basic». 2006-09-26. Retrieved 2009-01-23.
- ^ «System Tray Icon Sample». Retrieved 2009-01-23.
- ^ «System Tray Balloon Tips and Freeing Resources Quickly in .NET». November 2002. Retrieved 2009-01-23.
- ^ «Microsoft Time Zone». Microsoft. 2004-10-20. Retrieved 2009-01-23.
- ^ «The Taskbar». Retrieved 2011-06-09.
- ^ «Shell_NotifyIcon Function». Retrieved 2011-06-09.
- ^ «How To Manipulate Icons in the System Tray with Visual Basic». Retrieved 2011-06-09.
- ^ Chen, Raymond (September 20, 2003). «When I dock my taskbar vertically, why does the word «Start» disappear?». The Old New Thing. Microsoft. Retrieved 2008-04-20.
- ^ «Differences with Windows XP Home Edition». Windows XP Resource Kit. Microsoft. November 3, 2005. Retrieved 2008-04-20.
- ^ «Cannot Move or Resize the Taskbar or Any Toolbars on the Taskbar (MSKB279774)». Knowledge Base. Microsoft. January 25, 2006. Retrieved 2008-04-20.
- ^ Taskbar Pinner
- ^ «Notification Area». Windows Vista User Experience Guidelines. Microsoft. Archived from the original on 2008-10-15. Retrieved 2008-04-20.
- ^ «Using Application Desktop Toolbars». Microsoft.
- ^ Create a shortcut toolbar on the desktop
- ^ DeskBar Options Tab in Taskbar Properties Is Not Functional
- ^ «Plasma 5.20: One absolutely massive release». KDE Community. 2020-10-13. Retrieved 2022-05-20.
- ^ «GNOME 3.8 Release Notes». help.gnome.org. Retrieved 2022-05-20.
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
A taskbar is an element of a graphical user interface which has various purposes. It typically shows which programs are currently running.
The specific design and layout of the taskbar varies between individual operating systems, but generally assumes the form of a strip located along one edge of the screen. On this strip are various icons which correspond to the windows open within a program. Clicking these icons allow the user to easily switch between programs or windows, with the currently active program or window usually appearing differently from the rest. In more recent versions of operating systems, users can also «pin» programs or files so that they can be accessed quickly, often with a single click. Due to its prominence on the screen, the taskbar usually also has a notification area, which uses interactive icons to display real-time information about the state of the computer system and some of the programs active on it.
With the rapid development of operating systems and graphical user interfaces in general, more OS-specific elements have become integrated into and become key elements of the taskbar.
Early implementations[edit]
Windows 1.0[edit]
Windows 1.0, released in 1985, features a horizontal bar located at the bottom of the screen where running programs reside when minimized (referred to as «iconization» at the time), represented by icons. A window can be minimized by double-clicking its title bar, dragging it onto an empty spot on the bar, or by issuing a command from one of its menus. A minimized window is restored by double-clicking its icon or dragging the icon out of the bar.
The bar features multiple slots for icons and expands vertically to provide the user with more rows as more slots are needed. Its color is the same as that of the screen background, which can be customized. Minimized windows can be freely placed in any of the empty slots. Program windows cannot overlap the bar unless maximized.
The Start button did not make an appearance in these early implementations of the taskbar, and would be introduced at a much later date with the release of Windows 95.
Appearance of the bar used for holding minimized windows in Windows 1.0
Arthur[edit]
Another early implementation can be seen in the Arthur operating system from Acorn Computers. It is called the icon bar[1] and remains an essential part of Arthur’s succeeding RISC OS operating system. The icon bar holds icons which represent mounted disc drives and RAM discs, running applications and system utilities. These icons have their own context-sensitive menus and support drag and drop behaviour.
Appearance of Acorn’s icon bar in 1987 under Arthur, after launching a number of devices and applications
Amiga[edit]
AmigaOS featured various third party implementations of the taskbar concept, and this inheritance is present also in its successors. For example, AmiDock, born as third-party utility, has then been integrated into AmigaOS 3.9 and AmigaOS 4.0.[2] The AROS operating system has its version of Amistart that is provided with the OS and free to be installed by users, while MorphOS has been equipped with a dock utility just like in AmigaOS or Mac OS X.
Microsoft Windows[edit]
The default settings for the taskbar in Microsoft Windows place it at the bottom of the screen and includes from left to right the Start menu button, Quick Launch bar, taskbar buttons, and notification area. The Quick Launch toolbar was added with the Windows Desktop Update and is not enabled by default in Windows XP. Windows 7 removed the Quick Launch feature in favor of pinning applications to the taskbar itself. On Windows 8 and Windows Server 2012, a hotspot located in the bottom-left corner of the screen replaced the Start button, although this change was reverted in Windows 8.1 and Windows Server 2012 R2.
The taskbar was originally developed as a feature of Windows 95, but it was based on a similar user interface feature called the tray that was developed as part of Microsoft’s Cairo project.[3][4][5]
With the release of Windows XP, Microsoft changed the behavior of the taskbar to take advantage of Fitts’s law by removing a border of pixels surrounding the Start button which did not activate the menu, allowing the menu to be activated by clicking directly in the corner of the screen.[6]
A standard Windows XP taskbar with multiple tasks running. Note the Quick Launch toolbar, introduced in Windows 95 OSR 2.5. When the notification area is full, it can be expanded.
The taskbar in Windows Vista. The design is quite similar to Windows XP, but with a whole new Start button, Windows Aero, transparency on the taskbar, and more updated icons added to it.
The taskbar in Windows 7 hides application names in favor of large icons that can be «pinned» to the taskbar even when not running.
The taskbar in Windows 8. Note that the Start button is missing in this version of Windows (in favor of the Charms menu) and the Metro apps that are running are not shown in the taskbar.
The taskbar in Windows 8.1. The Start button has returned to this version of Windows, and Metro apps that are running are now shown by default on the taskbar.
The taskbar in Windows 10, in Desktop mode, on the RTM version (1507). The next major revision to the taskbar came in Windows 10, where icons for Search and Task View have been added. Also, the shortcut to Action Center is visible (the icon for Action Center has been moved to the right when the Windows Anniversary Update came along).
The taskbar in Windows 10, in tablet mode, on the RTM version (1507). The next major revision to the taskbar came in Windows 10, where icons for Search and Task View have been added. Also, the shortcut to Action Center is visible (the icon for Action Center has been moved to the right when the Windows Anniversary Update came along).
The taskbar in Windows 10, in Desktop mode, on version 22H2. New features got added to the taskbar like News and Interests, and Search spotlight and are shown by default on a clean install.
The taskbar in Windows 10, in Tablet (handheld) mode, on version 22H2.
The taskbar in Windows 11, in version 22H2, with the icons at the center by default.
The taskbar in Windows 11, in version 22H2, with the icons at the left.
Taskbar elements[edit]
- The Start button, a button that invokes the Start menu (or the Start screen in Windows 8.1). It appears in Windows 9x, Windows NT 4.0 and all its successors, except Windows 8 and Windows Server 2012.
- The Quick Launch bar, introduced on Windows 95 and Windows NT 4.0 through the Windows Desktop Update for Internet Explorer 4 and bundled with Windows 95 OSR 2.5 Windows 98, contains shortcuts to applications. Windows provides default entries, such as Launch Internet Explorer Browser, and the user or third-party software may add any further shortcuts that they choose. A single click on the application’s icon in this area launches the application. This section may not always be present: for example it is turned off by default in Windows XP and Windows 7.
- The Windows shell places a taskbar button on the taskbar whenever an application creates an unowned window: that is, a window that does not have a parent and that is created according to normal Windows user interface guidelines. Typically all Single Document Interface applications have a single taskbar button for each open window, although modal windows may also appear there.
- Windows 98 and Windows Desktop Update for Windows 95 introduced the ability to minimize foreground windows by clicking their button on the taskbar. They also introduced DeskBands (band objects).[7][8]
- Windows 2000 introduced balloon notifications.
- Windows Me added an option to disable moving or resizing the taskbar.
- Windows XP introduced taskbar grouping, which can group the taskbar buttons of several windows from the same application into a single button. This button pops up a menu listing all the grouped windows when clicked. This keeps the taskbar from being overcrowded when many windows are open at once.
- Windows Vista introduced window previews which show thumbnail views of the application in real-time. This capability is provided by the Desktop Window Manager. The Start menu tooltip no longer says «Click here to begin» but now says simply «Start».
- Windows 7 introduced jumplists which are menus that provide shortcuts to recently opened documents, frequently opened documents, folders paths (in case of Windows Explorer), or various options (called Tasks) which apply to that specific program or pinned website shortcut. Jump lists appear when the user right-clicks on an icon in the taskbar or drags the icon upwards with the mouse left click. Recent and frequent files and folders can be pinned inside the jump list.
- Windows 7 introduced the ability to pin applications to the taskbar so that buttons for launching them appear when they are not running. Previously, the Quick Launch was used to pin applications to the taskbar; however, running programs appeared as a separate button.
- Windows 7 removed several classic taskbar features.
- Deskbands are minimized functional, long-running programs, such as Windows Media Player. Programs that minimize to deskbands are not displayed in the taskbar.[9]
- The notification area is the portion of the taskbar that displays icons for system and program features that have no presence on the desktop as well as the time and the volume icon. It contains mainly icons that show status information, though some programs, such as Winamp, use it for minimized windows. By default, this is located in the bottom-right of the primary monitor (or bottom-left on languages of Windows that use right-to-left reading order), or at the bottom of the taskbar if docked vertically. The clock appears here, and applications can put icons in the notification area to indicate the status of an operation or to notify the user about an event. For example, an application might put a printer icon in the status area to show that a print job is under way, or a display driver application may provide quick access to various screen resolutions. The notification area is commonly referred to as the system tray, which Microsoft states is wrong,[10][11][12] although the term is sometimes used in Microsoft documentation,[13][14][15] articles,[16] software descriptions,[17] and even applications from Microsoft such as Bing Desktop. Raymond Chen suggests the confusion originated with systray.exe, a small application that controlled some icons within the notification area in Windows 95.[5] The notification area is also referred to as the status area by Microsoft.[18][19][20]
- In older versions of Windows the notification area icons were limited to 16 colors. Windows Me added support for high color notification area icons.
- Starting with Windows XP, the user can choose to always show or hide some icons, or hide them if inactive for some time. A button allows the user to reveal all the icons.
- Starting with Windows Vista, the taskbar notification area is split into two areas: one reserved for system icons including clock, volume, network and power; the other for applications.
- Since the Windows 95 Desktop Update, the Quick Launch bar featured Show desktop as one of its default shortcuts which automatically minimizes all opened applications, redundant with the Winkey-D key combination. On Windows 7, a dedicated Show desktop button was placed to the right of the notification area and could not be removed. With the «Peek» option enabled, hovering over the button hides all opened windows to expose the desktop (leaving outlines of them on-screen). On Windows 10, the «Show desktop» widget changed yet again, being reduced to a narrow iconless strip at the far right of the taskbar.
Customization[edit]
The Windows taskbar can be modified by users in several ways. The position of the taskbar can be changed to appear on any edge of the primary display (except in Windows 11, where the taskbar is permanently fixed at the bottom of the screen and cannot be moved to the top, left, or right side). Up to and including Windows Server 2008, the taskbar is constrained to single display, although third-party utilities such as UltraMon allow it to span multiple displays. When the taskbar is displayed vertically on versions of Windows prior to Windows Vista, the Start menu button will only display the text «Start» or translated equivalent if the taskbar is wide enough to show the full text.[21] However, the edge of the taskbar (in any position) can be dragged to control its height (width for a vertical taskbar); this is especially useful for a vertical taskbar to show window titles next to the window icons.
Users can resize the height (or width when displayed vertically) of the taskbar up to half of the display area. To avoid inadvertent resizing or repositioning of the taskbar, Windows XP and later lock the taskbar by default.[22][23] When unlocked, «grips» are displayed next to the movable elements which allow grabbing with the mouse to move and size. These grips slightly decrease amount of available space in the taskbar.
The taskbar as a whole can be hidden until the mouse pointer is moved to the display edge, or has keyboard focus. The Windows 7+ taskbar does not allow pinning any arbitrary folder to the taskbar, it gets pinned instead to the jumplist of a pinned Explorer shortcut, however third party utilities such as Winaero’s Taskbar Pinner can be used to pin any type of shortcut to the Taskbar.[24]
Desktop toolbars[edit]
Other toolbars, known as «Deskbands», may be added to the taskbar.[25] This feature, along with many other taskbar features is currently absent in Windows 11. Windows includes the following deskbands but does not display them by default (except the Quick Launch toolbar in certain versions and configurations).
- Address. Contains an address bar similar to that found in Internet Explorer. (not available in Windows XP SP3, due to legal restrictions).
- Windows Media Player. Optionally shown when the Windows Media Player is minimized.(Windows XP, Windows Vista)
- Links. Shortcuts to items located in the user’s Links folder. Usually shortcuts to internet sites.
- Tablet PC Input Panel. Contains a button to show the Tablet PC input panel for ink text entry.
- Desktop. Contains shortcuts to items contained on the user’s desktop. Since the taskbar is always shown, this provides easy access to desktop items without having to minimize applications.
- Quick Launch. Contains shortcuts to Internet Explorer, email applications and a link to display the desktop. Windows Vista adds a link to the Flip 3D feature.
- Language. Contains shortcuts to quickly change the desired language for the keyboard to follow.
In addition to deskbands, Windows supports «Application Desktop Toolbars» (also called «appbands») that supports creating additional toolbars that can dock to any side of the screen, and cannot be overlaid by other applications.[26]
Users can add additional toolbars that display the contents of folders. The display for toolbars that represent folder items (such as Links, Desktop and Quick Launch) can be changed to show large icons and the text for each item. Prior to Windows Vista, the Desktop Toolbars could be dragged off the taskbar and float independently, or docked to a display edge. Windows Vista greatly limited, but did not eliminate the ability to have desktop toolbar not attached to the taskbar.[27] Windows 7 has deprecated the use of Floating Deskbands altogether; they only appear pinned into the Taskbar.
- Upon opening the Taskbar properties on Windows 95 and Windows 98 whilst holding down the CTRL key, an extra tab for DeskBar Options is shown, but no part of it can be used. The DeskBar option was a feature that was never included within these versions of Windows.[28]
macOS[edit]
Classic Mac OS did not display a taskbar onscreen by default. Application switching prior to Mac OS 8.5 was done by clicking on an application’s window or via a pull-down menu at the right end of the menu bar. Prior to version 8.5 the menu’s title was the icon of the foreground application. Version 8.5 introduced the ability to optionally also display the application name and to «tear off» the menu by dragging the title with the mouse. The torn off menu was displayed as a palette. The palette window could be configured using AppleScript to appear much like a taskbar, with no title bar and fixed to one edge of the screen. No control panel was provided by Apple to access this functionality, but third-party developers quickly wrote applications that allowed users unfamiliar with AppleScript to customize their application palettes. Third party taskbars such as DragThing were a popular category of shareware on these systems.
The Dock, as featured in macOS and its predecessor NeXTSTEP, is also a kind of taskbar. The macOS Dock is application-oriented instead of window-oriented. Each running application is represented by one icon in the Dock regardless of how many windows it has on screen. A textual menu can be opened by right-clicking on the dock icon that gives access to an application’s windows. Mac OS X 10.2 added the ability for an application to add items of its own to this menu. Minimized windows also appear in the dock, in the rightmost section, represented by a real-time graphical thumbnail of the window’s contents. The trash can is also represented in the Dock, as a universal metaphor for deletion. For example, dragging selected text to the trash should remove the text from the document and create a clipping file in the trash.
The right side of macOS’s Menu bar also typically contains several notification widgets and quick access functions, called Menu extras.
Unix-like operating systems[edit]
KDE Plasma[edit]
In KDE Plasma 5, taskbar uses Widgets, called «Plasmoids», as elements in taskbar. In the update 5.20 (November 2020) they updated the taskbar to look more like Windows 10 by only displaying icons by default and grouping application windows together. [29]
The new taskbar of Plasma 5.20
GNOME[edit]
GNOME 2 used its own type of taskbar, known as panels (the program responsible for them is therefore called gnome-panel). By default, GNOME 2 usually contains two full-width panels at the top and bottom of the screen. The top panel usually contains navigation menus labeled Applications, Places, and System in that order. These menus hold links to common applications, areas of the file system, and system preferences and administration utilities, respectively.
Default top panel appearance from Ubuntu 6.10 to 8.04
Default bottom panel from Ubuntu 6.10 to 8.04
The top panel usually contains a clock and notification area, while the bottom panel contains buttons for navigating between virtual desktops, the window list proper, and a button which minimizes all windows (similarly to Windows’ Show desktop button). The contents of panels are handled by widgets called panel applets, which can consist of application shortcuts, search tools, or other tools. The contents of the panels can be moved, removed, or configured in other ways.
GNOME Shell Activities Overview which showcases the Dash
In GNOME 3, panels are replaced by GNOME Shell, which consists of a bar across the top of the screen with an Activities button on the left, a clock in the centre, and a notification area on the right. GNOME Shell does not contain a traditional taskbar; users can manage windows, virtual desktops, and launch applications from either a «Dash» on the side of the screen, or by searching from Activities Overview, which is displayed by clicking on the Activities button. GNOME 3.8 introduces Classic Mode, which re-implements certain aspects of GNOME 2’s desktop as an alternate desktop environment that can be selected at the login screen. [30]
Other Unix environments[edit]
These desktop environments provide their own implementation of a taskbar:
- Cinnamon
- MATE
- LXDE
- Xfce
- Trinity Desktop (based on KDE3’s Kicker)
Standalone window managers that provide an integrated taskbar include:
- Fluxbox
- FVWM95
- IceWM
- JWM
- qvwm
- WindowLab
- Window Maker
Programs that offer standalone taskbars for desktop environments or window managers without one include Avant Window Navigator, pypanel, fbpanel, perlpanel, tint2, and others.
References[edit]
- ^ Dan Ryan (13 April 2011). History of Computer Graphics: DLR Associates Series. AuthorHouse. p. 358. ISBN 978-1-4567-5115-9. Retrieved 13 June 2013.
- ^ Amiga Amidock Homepage
- ^ US patent 5825357, Malamud, Marceau, Grauman, Levien, Oran, Bolnick, Barnes, Johnson, Scott, «Continuously accessible computer system interface», issued 1998-10-20, assigned to Microsoft Corporation
- ^ Kent Sullivan (April 17, 1996). «The Windows 95 User Interface: A Case Study in Usability Engineering». CHI 96 Design Briefs. Archived from the original on October 22, 2008. Retrieved 2008-10-22.
- ^ a b Chen, Raymond (September 10, 2003). «Why do some people call the taskbar the «tray»?». The Old New Thing. Microsoft. Retrieved 2021-08-12.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: url-status (link) - ^ Harris, Jensen (August 22, 2006). «Giving You Fitts». Jensen Harris: An Office User Interface Blog. Microsoft. Retrieved 2008-01-14.
- ^ Creating Custom Explorer Bars, Tool Bands, and Desk Bands
- ^ The Next Windows: Windows 98
- ^ «Windows Vista Developer Center — The Windows desktop». Archived from the original on 2010-01-27. Retrieved 2008-05-27.
- ^ «How to remove items from the notification area in Windows 2000». November 1, 2006. Retrieved 2008-10-21.
- ^ «Microsoft Style Guide: System Tray». Retrieved 2020-02-10.
- ^ «Notification Area». Microsoft Developer Network. Archived from the original on 2010-01-27. Retrieved 2008-05-27.
- ^ «How To Manipulate Icons in the System Tray with Visual Basic». 2004-07-15. Retrieved 2009-01-23.
- ^ «How to use the System Tray directly from Visual Basic». 2006-09-26. Retrieved 2009-01-23.
- ^ «System Tray Icon Sample». Retrieved 2009-01-23.
- ^ «System Tray Balloon Tips and Freeing Resources Quickly in .NET». November 2002. Retrieved 2009-01-23.
- ^ «Microsoft Time Zone». Microsoft. 2004-10-20. Retrieved 2009-01-23.
- ^ «The Taskbar». Retrieved 2011-06-09.
- ^ «Shell_NotifyIcon Function». Retrieved 2011-06-09.
- ^ «How To Manipulate Icons in the System Tray with Visual Basic». Retrieved 2011-06-09.
- ^ Chen, Raymond (September 20, 2003). «When I dock my taskbar vertically, why does the word «Start» disappear?». The Old New Thing. Microsoft. Retrieved 2008-04-20.
- ^ «Differences with Windows XP Home Edition». Windows XP Resource Kit. Microsoft. November 3, 2005. Retrieved 2008-04-20.
- ^ «Cannot Move or Resize the Taskbar or Any Toolbars on the Taskbar (MSKB279774)». Knowledge Base. Microsoft. January 25, 2006. Retrieved 2008-04-20.
- ^ Taskbar Pinner
- ^ «Notification Area». Windows Vista User Experience Guidelines. Microsoft. Archived from the original on 2008-10-15. Retrieved 2008-04-20.
- ^ «Using Application Desktop Toolbars». Microsoft.
- ^ Create a shortcut toolbar on the desktop
- ^ DeskBar Options Tab in Taskbar Properties Is Not Functional
- ^ «Plasma 5.20: One absolutely massive release». KDE Community. 2020-10-13. Retrieved 2022-05-20.
- ^ «GNOME 3.8 Release Notes». help.gnome.org. Retrieved 2022-05-20.
Опубликовано 26.05.2022
Содержание:
- 1 Что делает панель задач
- 2 Как добавить значки на панель задач
- 3 Как убрать значки с панели задач Windows 10
- 4 Почему не получается удалить значки с панели задач
- 5 Как вернуть панель задач, когда она совсем пропала
- 5.1 Панель скрыта пользователем
- 5.2 Как переместить панель задач обратно
- 5.3 Полностью пропала панель задач — что делать
- 5.4 Почему пропала панель задач Windows — иные причины
- 6 Пропала панель задач «Виндовс» — анализируем посредством командной строки
- 7 Заключение
Что делает панель задач
Панель задач — встроенная функция всех версий Windows. Обычно эта полоса со значками программ расположена внизу рабочего стола. Здесь размещены самые нужные пользователю приложения, добавленные им самим либо системой. Главное назначение элемента — удобный и быстрый доступ к наиболее популярным программам, значки которых легко добавить и удалить. Ниже мы подробнее рассмотрим, как работать в панели задач, а также, что делать, если она исчезла с экрана.
Как добавить значки на панель задач
Для добавления значков пользователь применяет следующие способы:
- Захватывает ярлык программы с рабочего стола ЛКМ (обязательно удерживая ее), перетаскивает и сбрасывает иконку на панель. На рабочем столе ярлык останется.
- Находит нужную программу в «Пуск». Кликает по ней ПКМ и среди дополнительных действий выбирает закрепление на панели задач (не все приложения закрепляются подобным образом).
- Персонализирует элемент под свои интересы в настройках, которые вызывает win+I. Нужен отдел персонализации, но он доступен, если только Windows активирована. В противном случае система не даст внести изменения, блокируя все кнопки.
Если ваша операционная система Windows активирована, то пролистывайте перечень настроек вниз и персонализируйте панель задач под свои запросы.
Как убрать значки с панели задач Windows 10
Убрать значок программы еще проще. Кликаем ПКМ по более ненужному элементу и выбираем из списка опцию открепления.
Также персонализируем системный элемент из меню настроек, вызываемого через win+I.
Почему не получается удалить значки с панели задач
В определенный момент система может не ответить пользователю, который решил удалить ненужные значки. Причиной этому могут быть различные сбои в работе элемента. Рассмотрим другие способы удаления значков.
- Воспользуемся тем же методом через меню «Пуск». Кликаем ПКМ по названию программы и в дополнительных действиях выбираем открепление.
- Если не помогает, пробуем полностью удалить программу. Желательно использовать сторонний софт, чтобы ликвидировать все ненужные «хвосты». Но можно применить и штатные средства ОС. Нажимаем win+I и переходим в «Система». Здесь производим нужные действия.
После удаления приложения значок тоже должен исчезнуть с панели задач, а ярлык — с рабочего стола. Если этого не произошло, удаляем их вручную через ПКМ. По завершении всех манипуляций заново инсталлируем программу.
- Удаляем ярлыки из каталога TaskBar на диске C. Предварительно включаем отображение скрытых элементов.
Проходим путь Users→«Имя пользователя»→AppData→Roaming→Microsoft→Internet Explorer→Quick Launch→User Pinned→TaskBar. Здесь удаляем ненужный ярлык через ПКМ и проверяем, исчез ли он с панели задач. В противном случае снова пробуем убрать его вручную с помощью правой кнопки мыши.
Как вернуть панель задач, когда она совсем пропала
Исчезновение панели задач с рабочего стола обусловлено множеством причин — от сбоя в системе до вирусных атак. Рассмотрим несколько способов возврата элемента на прежнее место. Первым делом перезагрузите свой компьютер и, если это не решило проблему, читайте далее.
Панель скрыта пользователем
Проверим, возможно, панель задач была скрыта пользователем. Наведите курсор туда, где элемент был ранее, а также проведите по всем краям рабочего стола. Если системный элемент при этих манипуляциях появляется в каком-либо месте, отключим в настройках опцию, которая отвечает за ее сокрытие.
- Кликаем win+r и применяем control.
- В блоке «Оформление и …» находим раздел «Панель задач и…».
- Если ваша Windows активирована, настройте ее параметры под свои желания.
После проведенных манипуляций панель задач должна появиться на прежнем месте.
Как переместить панель задач обратно
Если ваша панель задач «убежала» в другое место и теперь отображается слева, справа или сверху рабочего стола, то при желании ее легко вернуть на привычную позицию. Делаем это через свойства системы, как описано в предыдущем блоке.
Как переместить панель задач обратно
Или кликаем ПКМ по панели задач и снимаем отметку с «Закрепить…».
Теперь захватываем панель задач на свободном поле ЛКМ и перетаскиваем ее в удобное место, где снова закрепляем.
Полностью пропала панель задач — что делать
Если панель задач пропала совсем и ее никак нельзя обнаружить, то попробуем перезапустить работу проводника. Не дало результата? Тогда перезапустим сам процесс Explorer.exe, отвечающий за функционирование панели задач, проводника, кнопки «Пуск» и т. д. Возможно, сбой в его работе явился причиной неполадок. Используем win+r и Explorer.exe. Откроется окно «Проводника». Перезагружаем компьютер и проверяем, наладило ли это работу.
Также воспользуемся настройками. Снова применим win+r и control, как было описано выше, и проверим, не скрыт ли элемент автоматически.
Все установлено корректно, но элемент не отображается? Попробуем изменить его параметры (к примеру, месторасположение) и убедиться, что он появился в соответствии с заданными настройками. После этого элемент можно вернуть на начальные позиции.
Почему пропала панель задач Windows — иные причины
Причиной пропажи элемента с рабочего стола также могут быть:
- Комбинирование нескольких мониторов. Если вы используете в «Виндовс» 10 два монитора либо подключаете к ТВ ноутбук, то системный элемент отобразится только на одном экране. Проверьте, действительно ли проблема в этом. Нажмите win+p и укажите другой режим (но не «Расширить»).
- Стороннее программное обеспечение. Некоторые приложения влияют на корректное отображение панели задач. Чтобы выявить причину неполадок, выполните загрузку ОС в безопасном режиме. Если все функционирует нормально, поищите проблемное приложение. Возможно, это одна из недавно установленных программ. Также проверьте автозагрузку. Комбинирование нескольких мониторов. Если вы используете в «Виндовс» 10 два монитора либо подключаете к ТВ ноутбук, то системный элемент отобразится только на одном экране. Проверьте, действительно ли проблема в этом. Нажмите win+p и укажите другой режим (но не «Расширить»).
- Некорректные системные файлы. Возможно, их целостность была повреждена, особенно, если недавно ваша система обновлялась. Скорее всего, здесь поможет только чистая переустановка Windows.
- Неполадки в работе видеоадаптера. Удалите драйвера и проверьте, видно ли теперь панель задач. Инсталлируйте актуальные официальные драйвера.
- Настройки системы. Снова зайдите в меню персонализации (в блок «Цвета») и деактивируйте параметр прозрачности.
Также необходимо проверить настройки режима планшета. Некоторые пользователи по незнанию включают его случайно. Применим win+I и перейдем в блок «Система», а затем в параметры режима планшета. Установите настройки, соответствующие вашим запросам.
Пропала панель задач «Виндовс» — анализируем посредством командной строки
Чтобы система нашла поврежденные файлы, проанализируем ситуацию с помощью командной строки, открытой от имени админа. Используем sfc /scannow и «Энтер». Система проанализирует файлы и, если найдет среди них проблемные, предложит способы устранения ошибок.
Заключение
Мы с вами рассмотрели множество способов, позволяющих вернуть или убрать значки с панели задач, а также найти сам элемент, который иногда пропадает с рабочего стола. Есть и более сложные методы, но непрофессионалам лучше их не применять. Ведь любые изменения (внесенные, например, в редактор реестра) или сброс панели задач посредством создания специальных файлов могут навредить работе операционной системы, и здесь понадобится помощь специалиста. В любых затруднительных ситуациях обращайтесь к сотрудникам компании «АйТи Спектр». Мы проведем тщательную диагностику оборудования и решим проблемы.
- Панель задач Microsoft Windows
-
Пане́ль зада́ч (англ. taskbar) — приложение, которое используется для запуска других программ или управления уже запущенными, и представляет собой панель инструментов. В частности используется для управления окнами приложений. Панель задач может быть компонентом операционной системы (например, она присутствует в операционных системах Microsoft Windows начиная с версии Windows 95), элементом среды рабочего стола (например, в GNOME) или отдельной сторонней программой.
Microsoft Windows
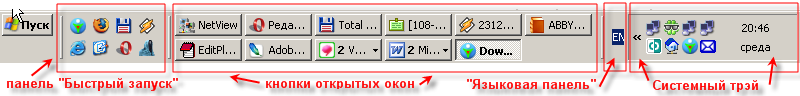
Панель задач Windows XP
Составные части панели задач:
- Кнопка «Пуск» для вызова меню «Пуск»;
- Область для отображения кнопок открытых окон, для быстрого переключения между окнами;
- Область уведомлений (часто ошибочно называют «системным треем»), где находятся значки, помещенные туда некоторыми программами;
- «Быстрый запуск» (появилась вместе с Internet Explorer 4), на которую можно поместить ярлыки для запуска часто используемых программ;
- Другие элементы панели от сторонних программ.
Если панель задач не закреплена, можно её «прилепить» к любой из границ рабочего стола, просто перетягивая её мышкой, а также изменить размер (количество строк).
Unix и Unix-подобные
Apple Macintosh
Компоненты Microsoft Windows
Основные Aero • Desktop Window Manager • Проводник (Explorer) • Панель задач • Меню «Пуск» • Shell (namespace • Special Folders • File associations) • Search (Saved search • iFilters) • Graphics Device Interface • WIM • Next Generation TCP/IP stack () • .NET Framework • Audio • Printing (XML Paper Specification) • Active Scripting (WSH • VBScript • COM (OLE • OLE Automation • DCOM • ActiveX • ActiveX Document • Structured storage • Transaction Server) • Previous Versions • WDDM • UAA • Win32 console
Службы
управленияBackup and Restore Center • Панель управления (Applets) • Диспетчер устройств • Очистка диска • Дефрагментация диска • Event Viewer • Management Console • Problem Reports and Solutions • Sysprep • • Диспетчер задач • System File Checker • Восстановление системы • Windows Installer • Windows PowerShell • Windows Update • WinSAT • Windows Easy Transfer
Приложения Калькулятор • Calendar • Таблица символов • Contacts • DVD Maker • Fax and Scan • Internet Explorer • Journal • Outlook Express • Почта Windows • Magnifier • Media Center • Meeting Space • Mobile Device Center • Mobility Center • Movie Maker • Narrator • Notepad • Paint • Фотоальбом • Private Character Editor • Remote Assistance • Sidebar • Snipping Tool • Звукозапись • Windows Media Player • Windows Speech Recognition • Игры
Chess Titans • Hold ‘Em • InkBall • Mahjong Titans • Purble Place • Пасьянс «Косынка» • Пасьянс «Паук» • Сапёр • Пасьянс «Свободная ячейка» • Пинбол • Червы
Ядро ОС hal.dll • System Idle Process • Registry (реестр) • Windows service • Service Control Manager • EXE • Boot Manager • Recovery Console • I/O • WinRE • WinPE • Kernel Patch Protection
Службы Autorun • BITS • Task Scheduler • Wireless Zero Configuration • Shadow Copy • Windows Error Reporting • Multimedia Class Scheduler • CLFS
Файловые
системыHard link • Junction point • Mount Point • Reparse point • Symbolic link • TxF • FAT • CDFS • UDF • DFS • IFS
Сервер Domains • Active Directory • DNS • Групповая политика • Roaming user profiles • Folder redirection • Координатор распределённых транзакций • MSMQ • Windows SharePoint Services • Windows Media Services • Rights Management Services • IIS • Terminal Services • WSUS • Network Access Protection • DFS Replication • Remote Differential Compression • Print Services for UNIX • Remote Installation Services • Windows Deployment Services • Windows System Resource Manager • Hyper-V
Архитектура NT series architecture • Object Manager • Startup process (Vista) • I/O request packets • Kernel Transaction Manager • Logical Disk Manager • Security Accounts Manager • Windows Resource Protection • LSASS • CSRSS • SMSS
Безопасность UAC • BitLocker • Defender • DEP • Protected Media Path • Mandatory Integrity Control • UIPI • Windows Firewall • Security Center
Совместимость Unix subsystem (Interix) • Virtual DOS Machine • Windows on Windows • WOW64
Wikimedia Foundation.
2010.
Полезное
Смотреть что такое «Панель задач Microsoft Windows» в других словарях:
-
Диспетчер задач Microsoft Windows — Эта статья о Диспетчере задач в Microsoft Windows. О других подобных программах читайте в статье Диспетчер задач. Task manager из Windows 4.x под Windows XP (NT 5.1) … Википедия
-
Панель задач — У этого термина существуют и другие значения, см. Панель. Панель задач (англ. taskbar) приложение, которое используется для запуска других программ или управления уже запущенными, и представляет собой … Википедия
-
Microsoft Windows — Эту страницу предлагается переименовать в Windows. Пояснение причин и обсуждение на странице Википедия:К переименованию/2 апреля 2012. Возможно, её текущее название не соответствует нормам современного русского языка и/или правилам… … Википедия
-
Панель задач Windows — Панель задач (англ. taskbar) приложение, которое используется для запуска других программ или управления уже запущенными, и представляет собой панель инструментов. В частности используется для управления окнами приложений. Панель задач может… … Википедия
-
Меню «Пуск» (Microsoft Windows) — Меню «Пуск» Компонент Microsoft Windows … Википедия
-
Диспетчер рабочего стола (Microsoft Windows) — Про аналогичные программы см. Менеджер окон Desktop Window Manager Компонент Microsoft Windows Детали Другие названия Диспетчер рабочего стола[1] Поставляется с Windows Vista Windows 7 Windows 8 … Википедия
-
Сервисы Microsoft Windows для UNIX — (англ. Microsoft Windows Services for UNIX, SFU) программный пакет, разработанный компанией Microsoft, обеспечивающий подсистему UNIX на системах класса Windows NT (в том числе и более поздних). Данная подсистема называется Interix.… … Википедия
-
Панель GNOME — gnome panel Скриншот рабочего стола GNOME с двумя панелями сверху и снизу Тип … Википедия
-
Windows 7 — Windows 7 … Википедия
-
Windows PowerShell — Windows PowerShell … Википедия
72.
Операционная система Windows отличается
от системы MS DOS следующим:
C.
все ответы верны;
73.
Основные элементы рабочего стола
(Desktop)
системы Windows 98: кнопка ПУСК (Start),
значки МОЙ КОМПЬЮТЕР (My
Computer)
и КОРЗИНА (Recycler).
Что еще?
B.панель
задач (Task
Bar);
74.
Панель задач (Task
Bar)
рабочего стола (Desktop)
системы Windows 98 используется:
D.
для переключения между открытыми
окнами;
75.
Что обычно происходит на рабочем столе
Windows 98 пpи запуске какой-либо программы?
C.
открывается окно программы, а в панели
задач появляется соответствующая
кнопка;
76.
Для перехода от одной работающей
программы к другой необходимо:
A.
все ответы верны;
77.
Основные элементы управления окнами
в системе Windows: заголовок, рамка, кнопка
закрытия окна. Что еще?
C.
кнопки сворачивания и разворачивания
окна;
78.
Что НЕ относится к основным элементам
управления окнами в Windows:
D.
кнопка ПУСК (Start
;
79.
Щелчок на кнопке сворачивания окна
приводит:
A.
к удалению окна с рабочего стола с
сохранением в панели задач соответствующей
кнопки;
80.
Основные операции с окнами в системе
Windows: открытие, закрытие. Что еще?
C.
все ответы верны;
81.
Значок МОЙ КОМПЬЮТЕР (My
Computer)
на рабочем столе системы Windows 98
используется
B.
все ответы верны;
82.
Перемещение значка файла или папки на
значок КОРЗИНА (Recycler)
на рабочем столе системы Windows 98 приводит:
E.
к
сохранению файлов в специальном каталоге
без удаления с диска;
83.
Имена файлов и каталогов (папок) в
системе Windows 98 могут:
A.
все ответы верны;
84.
Пpогpамма ПРОВОДНИК (Explorer)
в системе Windows 98 используется:
B.
все ответы пpавильные;
85.
Для запуска программы в системе Windows
98 необходимо:
A.
все ответы верны;
86.
Для окончания работы с Windows необходимо:
B.
выбрать команду «Завершение работы»
в основном меню;
87.
Назовите программу, впервые включенную
в состав Microsoft
Office
для Windows
98:
C.
Microsoft
Schedule+;
88. Какая программа осуществляет
поиск файла, копирование файла,
перетаскивание файла?
B.
программа “Проводник”;
89. Какой редактор называется
графическим редактором?
D.
“PAINT”;
90.
Команда “Проверка диска” находится
в папке:
C.
“Служебные”;
91. Файл сохранить на дискету
можно:
D.
в программе “Проводник”;
92. Проверка диска осуществляется:
E.
в программе “Служебные”.
93. Для создания конспектов
доклада и для раздачи материала
слушателям используется:
D.
Power Point;
94.
Анимация находится в программе:
D.
Power
Point;
95.
Заметки для выступления создаются в
программе:
D.
Power
Point;
96.
К справочной системе Windows
можно обратиться из:
D.
Главного меню;
97. Дефрагментацию диска можно
произвести в:
C.
Программы – Стандартные — Служебные;
98. Очистку диска можно
произвести в:
C.
Программы – Стандартные — Служебные;
99. Проверку диска можно
произвести в:
C.
Программы – Стандартные — Служебные;
100. Сведения о системе можно
получить в:
C.
Программы – Стандартные — Служебные;
Соседние файлы в предмете [НЕСОРТИРОВАННОЕ]
- #
- #
- #
- #
- #
- #
- #
- #
- #
- #
- #
Элемент интерфейса, отображающийся на его краю, и использующийся для быстрого запуска программ или слежения за изменениями уже запущенных программ.

Приложение, которое используется для запуска других программ или управления уже запущенными.
По сути — панель задач является панелью инструментов.
В Windows это полоска внизу экрана («трей» от английского слова «tray») с кнопкой главного меню «Пуск», иконками часто используемых программ и значками программ, выполняемых компьютером в данный момент.
С выходом Windows 7, панель задач заметно изменилась, по сравнению с предыдущими версиями этой операционной системы. И все эти изменения заметно упрощают работу.
В Macintosh функции строки задач выполняет строка главного меню в верхней части экрана.
Первейшей задачей разума является сведение неизвестного к известному.
(Эмманюэль Мун)

ВОЗМОЖНО, ВАМ ПОНРАВИТСЯ!
Случайная статья
Поделитесь с друзьями в социальных сетях!
Нажмите на иконку, чтобы опубликовать на своей странице
-
Вы здесь:
- КОМПЬЮТЕР
- Компьютерные термины
- Панель задач (taskbar)
Новое на сайте
Все материалы

Популярные статьи
Во многих рекомендациях, касающихся компьютера, можно услышать или прочесть: «Посмотрите на панели задач», «Сверните в панель задач» и подобное. Вот только что делать, если понятия не имеешь, где она находится, и что это такое?! В этой статье я постараюсь подробно рассмотреть эту тему, чтобы вы знали, как настроить панель задач и сделать ее максимально удобной для себя.
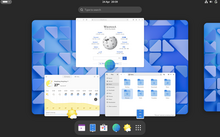
Панель задач – это область на рабочем столе компьютера, где отображаются запущенные (будут выделены или подчеркнуты) и закрепленные (значки отображаются всегда и не подчеркнуты) приложения, системные значки (часы, кнопка смены языка, громкость) и кнопка Пуск. По умолчанию она закреплена в нижней части экрана.
С ней можно выполнять много различных действий, так что давайте рассмотрим все по порядку. Показывать буду на компьютере с ОС Windows 10, но в конце статьи есть скриншоты, которые относятся к Windows 7. Внимательно прочитав статью вы поймете, что пункты те же, отличается только их расположение.
Закрепление ярлыков
Значки всех запущенных вами программ появляются на панели задач. Когда вы закрываете утилиту, он оттуда пропадает. Чтобы этого не произошло, и можно было получить быстрый доступ к нужной программке, достаточно закрепить его.
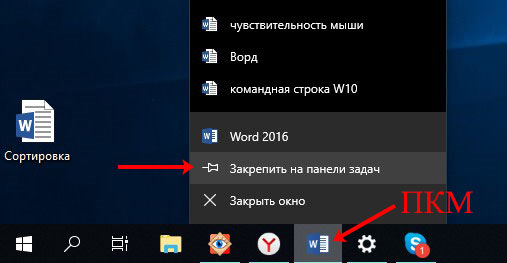
Для этого нажмите правой кнопкой мыши по нужному значку и выберите в контекстном меню
«Закрепить на панели задач».
Если они у вас пропали и нужно восстановить на панели задач значки важных для вас программ, то запустите утилиту, кликните по ее значку правой кнопкой и выберите пункт закрепить.
Все закрепленные ярлыки остаются на панели независимо от того, запущена программа или нет. На скриншоте под некоторыми значками есть голубая полоска – это значит, что приложение запущено. Если вы закрыли утилиту, а значок остался, и полоска под ним пропала – это значит, что он закреплен. Чтобы убрать значок, кликните по нему правой кнопкой мыши и выберите «Изъять программу».
Как закрепить или удалить значок с панели задач
Перемещение ярлыков
Отображаемые ярлыки программ на панели задач можно перемещать. Для этого кликните по нужному значку мышкой и, не отпуская кнопки, переместите его в другое место.
Ярлыки появляются здесь по мере запуска утилиты. Значок нового приложения всегда будет отображен правее остальных. Поэтому, если вы привыкли к их определенному расположению, просто запускайте программы по очереди.
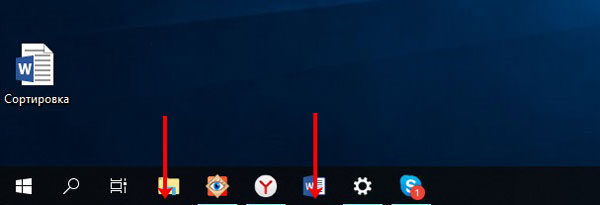
Закрепление панели задач
Частенько пользователи не могут обнаружить ее на привычном месте. Нечаянный клик мышкой и панель задач можно найти сверху или справа. Это происходит потому, что она не закреплена. Исправить это просто: кликните правой кнопкой мыши по пустому месту на ней и нажмите на строку «Закрепить панель задач».
Галочка в данном поле значит, что панель закреплена, ее отсутствие – что не закреплена.
Как вернуть пропавшую панель задач в Windows?
Нахождение на рабочем столе
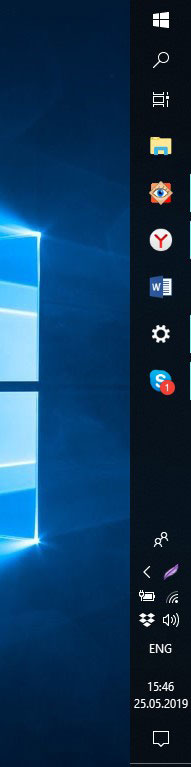
Как я уже заметила, местоположение панели задач может быть возле любой границы экрана. Если у вас она переместилась случайно, то нужно вернуть и закрепить панель задач внизу. Или можно поэкспериментировать с ее расположением на рабочем столе самостоятельно.
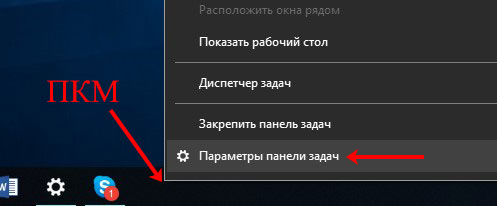
Для этого кликайте по пустой области правой кнопкой и выбирайте «Параметры панели задач».
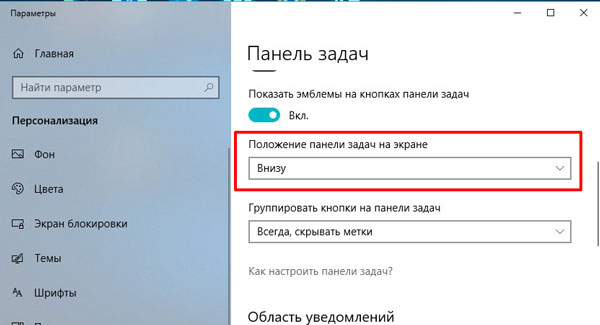
Здесь нас будет интересовать пункт «Положение … на экране». Из выпадающего списка можете выбрать подходящий вариант и разместить ее вверху, справа или слева.
При выборе любого варианта из списка, панель сразу переместится, а вы уже решайте – удобно вам или нет.
Отображение уведомлений на кнопках
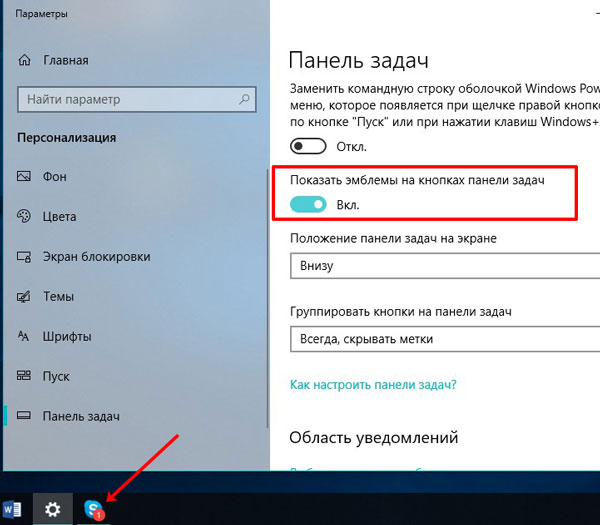
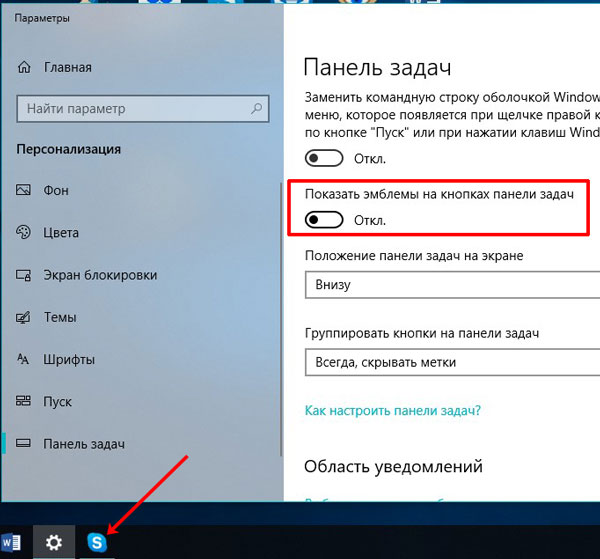
Если вы активируете показ уведомлений, то никогда не пропустите важное сообщение, даже если звук на компьютере выключен. Для этого в окне «Параметры» найдите пункт «Показать эмблемы на кнопках панели задач» и передвиньте ползунок в положение «Вкл.».
Если ползунок будет находиться в положении «Откл.», то на ярлыках запущенных программ не будет эмблем-оповещений о новых событиях.
Обратите внимание, что, если вы захотите использовать маленькие кнопки, значок оповещений отображаться на ярлычках не будет.
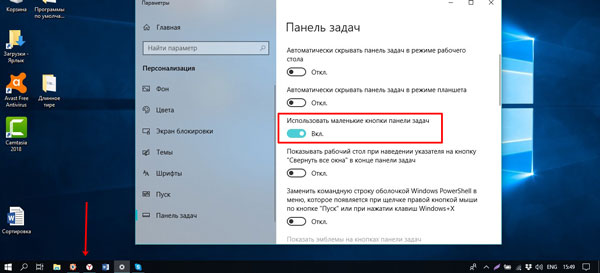
Уменьшение или увеличение кнопок на панели
По ширине данная строчка тоже может быть разной. Все значки на ней могут быть маленькие или большие. Уменьшить панель задач очень просто: в «Параметрах» найдите пункт «Использовать маленькие кнопки…» и включите данную функцию.
Если ситуация у вас обратная и строчка выглядит маленькой и незаметной, то в этом же пункте нужно передвинуть ползунок в положение «Откл.».
Быстрый просмотр рабочего стола
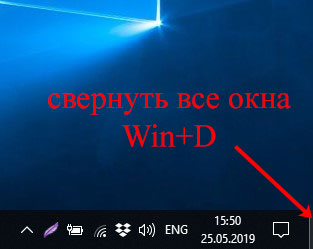
Когда открыто много окон и нужно запустить какую-нибудь программу с рабочего стола, то закрывать каждое в отдельности долго. Для этого используется еле заметная кнопка на панели задач справа или комбинация Win+D – нажали на нее и все сразу свернулось. Нажали на кнопку еще раз и окна опять развернулись.
Как вернуть ярлык свернуть все окна
Как свернуть все окна в Windows 7
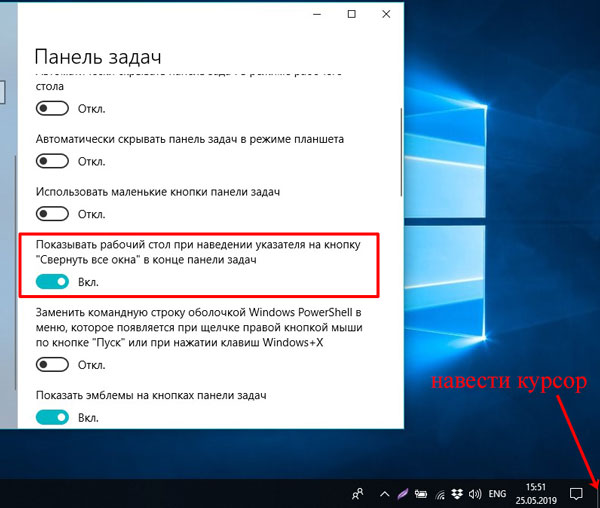
Но если вам достаточно просто взглянуть на рабочий стол, то в параметрах активируйте пункт «Показывать рабочий стол при наведении указателя на кнопку…». После этого просто наведите курсор в конец панели и окна пропадут, а как только уберете курсор они снова появятся.
Автоматическое скрытие
Если данная область вам мешает работать в программе, смотреть фильмы и прочее, перекрывая часть активного окна, то можно скрыть панель задач. Для этого в параметрах активируйте пункт «Автоматически скрывать…». После этого панель пропадет, а чтобы она снова стала видимой, нужно подвести курсив к той части экрана, где она закреплена.
Настроить скрытие панели можно и с помощью программы Taskbar Hider. Скачайте ее с нашего сайта, выберите комбинацию и используйте е, чтобы убрать панель.
Группировка кнопок
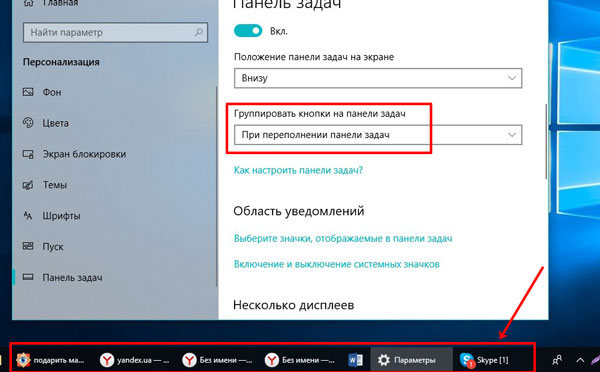
Как скрыть значки, мы разобрались – достаточно их открепить, а теперь давайте разберемся, какой вид они могут иметь. В параметрах пролистывайте до пункта «Группировать кнопки…». Если из списка выбрать «Всегда, скрывать метки» – то запущенные и закрепленные утилиты будут отображаться в виде ярлыков. Причем если у меня открыто три окна Яндекс Браузера, ярлык будет всего один.
Второй вариант группировки – «При переполнении…». В данном случае рядом со значком программы или файла отображается еще и название. А когда места в строке становится недостаточно, значки группируются.
Последний вариант – «Не группировать». Значки отображаются вмести с названием и, по мере заполнения строки, появляется стрелка для прокручивания всех запущенных программ.
Отображение значков в области уведомлений
Справа находится область уведомлений. Здесь мы привыкли видеть часы и различные значки программ. Последние там появляются в том случае, когда в настройках утилиты вместо полного закрытия указано «Свернуть в трей».
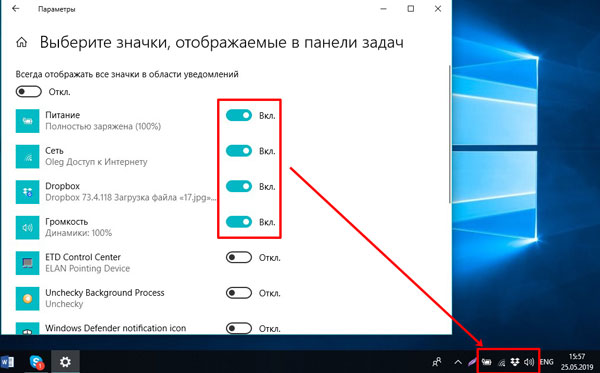
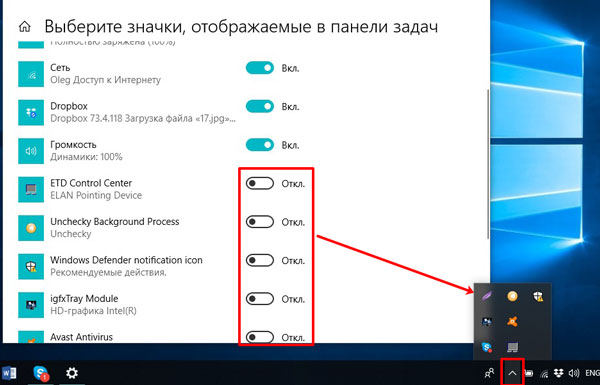
Для начала нажмите кнопку «Выберите значки, отображаемые в….». Это позволит указать, что должно быть на виду, а что для вас не так важно.
Откроется страница со списком доступных значков. Те, напротив которых указано «Вкл.», отображаются прямо на панели задач.
Если же напротив значков стоит «Откл.», то они там тоже есть, но находятся в отдельном списке, который появляется после нажатия на стрелочку.
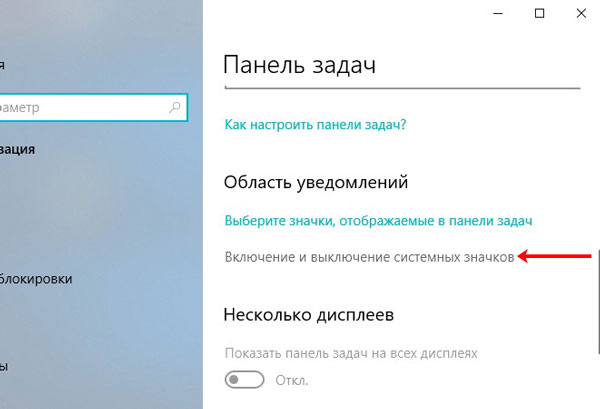
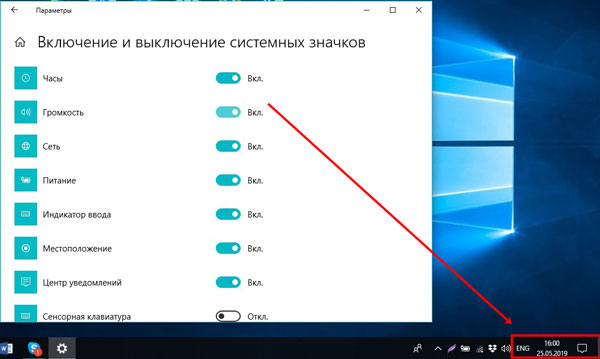
Вторая кнопка «Включение и выключение системных значков». Ею следует воспользоваться, если у вас пропал язык или часы.
Если у вас пропал язык на панели задач в Windows 7, прочтите статью, как его вернуть. Еще есть отдельная статья: как вернуть языковую панель в Windows XP. Если у вас установлена самая новая ОС, прочтите: что делать, если в Windows 10 пропала языковая панель.
Жмите на нее и в списке активируйте нужные пункты.
Если у вас пропал значок батареи на ноутбуке, то можете прочесть отдельную статью о том, как его вернуть.
Изменение цвета
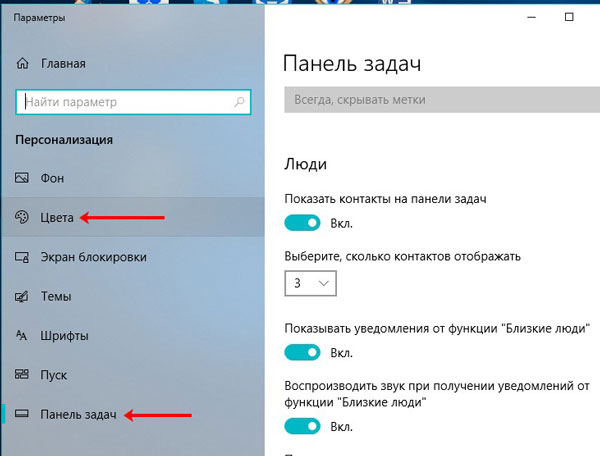
Теперь перейдем к цвету. Чтобы его изменить, перейдите со вкладки «Панель задач» на вкладку «Цвета».
Дальше найдите пункт «Отображать цвет элементов на следующих поверхностях» и в строке «В меню Пуск, на панели задач и в центре уведомлений» поставьте птичку.
Прозрачной она не станет, но ее цвет изменится, в зависимости от выбранной темы. Если же вам важно, чтобы панель стала прозрачная, настройте для нее автоматическое скрытие.
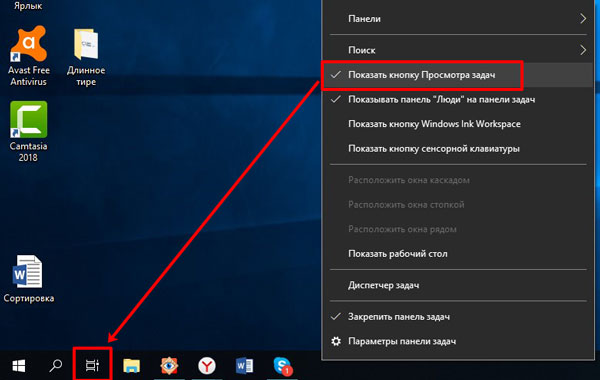
Значки рядом с Пуск
Рядом с кнопкой «Пуск» есть еще две. Одна из них – это «Просмотр задач». В контекстном меню панели есть отдельный пункт, который к ней относится – «Показать кнопку Просмотра задач». Если напротив него стоит птичка, кнопка будет отображаться. Если вы ей не пользуетесь, то скройте ее.
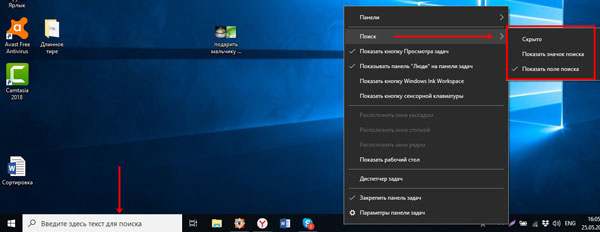
Еще одна кнопка – это «Поиск». Ее можно вообще убрать, оставить только значок лупы или сделать так, чтобы отображалось поле для поиска.
Добавление панелей
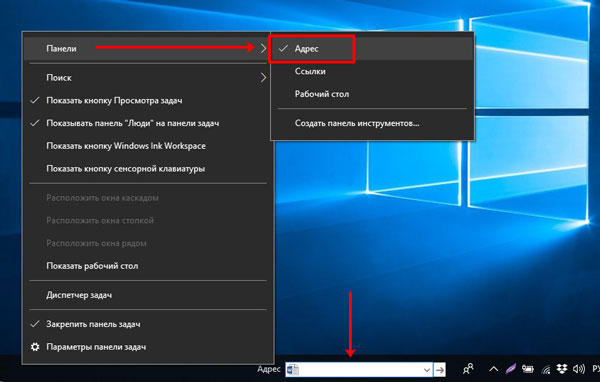
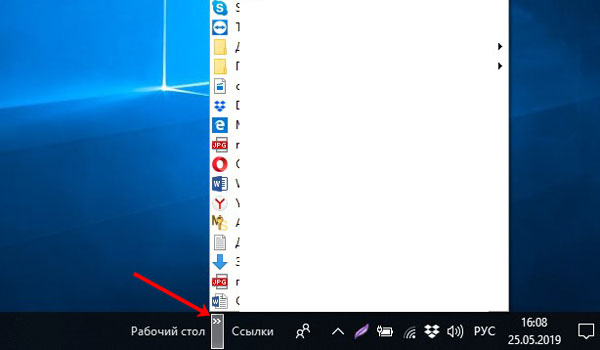
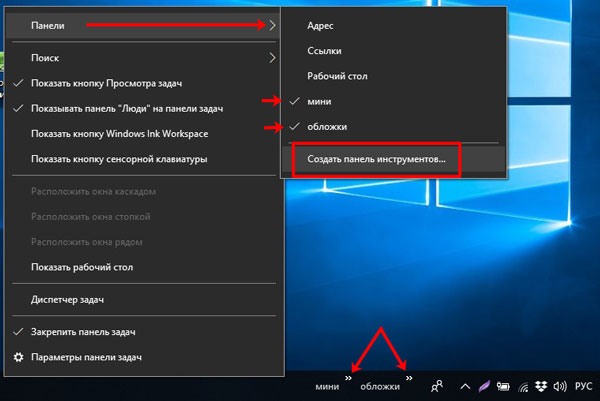
В контекстном меню есть такой пункт, как «Панели». Активировав строчку «Адрес» на панели задач появится соответствующее поле. В него можно вводить адрес как страницы из Интернета, например, comp-profi.com, так и название любой папки или программы на компьютере (очень похоже на обычный поиск).
Следующие два пункта: «Ссылки» и «Рабочий стол». Возле них будут маленькие стрелочки, после клика по которым откроется список. Для ссылок вы его формируете сами – это могут быть программы, папки, документы, музыка, видео и другое. В списке рабочего стола будет показано все то, что у вас на нем находится.
Если вы часто пользуетесь какой-то папкой, можно выбрать пункт «Создать панель инструментов». Дальше через Проводник найдите и выберите нужную папку. Ее название появится на панели, а после клика по стрелочкам в виде списка отобразится ее содержимое. Когда необходимость в быстром доступе к папке пропадет, в раскрывающемся списке «Панели» просто снимите напротив ее названия галочку.
Создание панели быстрого запуска в Windows 7
Настройка панели быстрого запуска в Windows XP
В Windows 7
Настройка панели задач в Windows 7, или 8, и ее элементы, очень похожи на десятку. Кликом по свободному месту на строке открывается контекстное меню. В нем есть все пункты, которые мы уже рассмотрели.
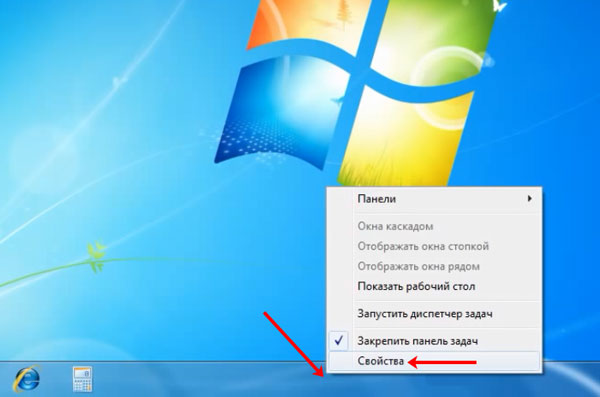
Если же вас интересует больше настроек, например, нужно закрепить или убрать панель задач с экрана, то вместо кнопки «Параметры» заходите в «Свойства».
Как скрыть панель задач в Windows 7
Откроется отдельное окошко, в котором, собственно, все это и можно сделать: выбрать вид кнопок, положение самой панели на экране и прочее. Если пропали часы или значок громкости, то воспользуйтесь кнопкой «Настроить».
Теперь, вы точно знаете, где находится панель задач в Windows, и как ее можно настраивать. Недооценивать ее не стоит, поскольку она позволяет не только переключаться между открытыми утилитами, но и может помочь в быстром доступе к нужной папке. А благодаря правильной настройке отображения системных значков, на виду всегда будет нужная информация.
Смотрите видео по теме:
Загрузка…
Панель задач в Windows 10
Ранние вариации[]
Windows 1.0[]
Windows примонтированные диски, запущенные приложения и системные приложения. Иконки имели всплывающие подсказки и могли менять своё местоположение.
Amiga[]
AmigaOS представила третью реализацию панели задач и сохранила эту реализацию поныне. Например, AmiDOCK, возникший как сторонняя утилита, был интегрирован в AmigaOS с версии 3.9[1]. Операционная система AROS имела свою версию Amistart, что обеспечивает пользователю бесплатную установку системы. Также MorphOS обеспеgaOS или OS X.
Microsoft Windows[]
По умолчанию в Windows находится внизу экрана и включает в себя: меню «Пуск», панель быстрого запуска, иконки приложений, область уведомлений. Панель быстрого запуска была добавлена с Шаблон:Нп4 и не была включена по умолчанию в Windows XP. В Windows 7 эта панель была убрана в пользу прикрепления иконок приложений в панели задач. В Windows 8 кнопка «Пуск» была удалена в пользу Шаблон:Нп4, которая находится слева.
Панель управления изначально была предназначена для Windows 95, но была основана на функции системы под названием трей, как часть проекта Windows Cairo
[2][3].
С выпуском Windows XP разработчики изменили поведение панели в соответствии с законом Фиттса и убрали ненужные пиксели, окружающие кнопку «Пуск», пока кнопка не активирована, и появляющиеся, когда кнопка активируется[4].
Элементы панели задач[]
- Кнопка «Пуск», главный элемент в Windows, кнопка, показывающая Меню «Пуск». Отсутствует в Windows 8 и Windows Server 2012.
- Панель быстрого запуска, представленная Windows 95 и Windows NT 4.0 благодаря Шаблон:Нп4 для Internet Explorer 4 и Windows 98, содержащему ссылки на приложения. Windows предоставляет такие записи по умолчанию, как Запустить Internet Explorer, и даёт пользователю возможность добавлять несистемные приложения. Простой клик по иконке вызывает запуск программы. Данная панель не всегда включена: например, в Windows XP и Windows 7 она отключена по умолчанию.
- Поле поиска позволяет производить поиск по локальным приложениям, файлам, настройкам и веб-сайтам. Также используется для вызова голосового помощника Cortana(только на поддерживаемых языках). Может быть отключено, или отображаться в сокращённом виде используя контекстное меню панели задач. Присутствует, начиная с Windows 10.
- Кнопка «Представление задач» — при нажатии показывает выполняемые приложения, а также рабочие столы. Кнопка может быть отключена используя контекстное меню панели задач. Присутствует, начиная с Windows 10.
- Кнопки программ: каждое окно создаёт свою иконку на панели задач. На панели также могут появиться всплывающие окна приложения.
- В Windows 98 и Шаблон:Нп4 для Windows 95 была представлена возможность скрыть окно, нажав на его иконку в панели задач.
- В Windows 2000 были представлены всплывающие уведомления.
- В Windows ME была добавлена настройка перемещения и изменения размера панели задач.
- В Windows XP было представлено группирование в панели задач, позволяющее не заполнять полностью панель задач, группируя окна по запущенным приложениям. Нажатие на группу иконок позволяет увидеть все окна приложения.
- В Windows Vista был представлен быстрый просмотр (Aero Peak). Эта способность обеспечивается диспетчером рабочего стола. Подсказка для кнопки «Пуск» больше не подсказывает «Нажмите для старта». Сейчас там написано «Пуск».
- В Windows 7 был представлен Шаблон:Нп4, открывающий специальное меню, в котором можно открыть недавние документы, папки (в проводнике Windows), разные настройки (так называемые задачи), которые позволяют закреплять приложения или сайты. Быстрый переход открывается нажатием правой кнопкой мыши на иконку. Также файлы или папки могут быть туда прикреплены.
- В Windows 7 была представлена возможность прикреплять приложения к панели задач, чтобы быстрее запускать их. Ранее это реализовывалось с помощью быстрого запуска.
- В Windows 7 был удалены Шаблон:Нп4.
- Область уведомлений — часть панели управления, которая показывает иконки для различных приложений, в том числе управление громкостью. Содержит главным образом системные иконки, иконки некоторых программ, например, Winamp использует эту функцию. По умолчанию панель расположена справа снизу на панели на основном мониторе (или слева сверху для некоторых языков) или сверху, если панель расположена вертикально. Часы также расположены рядом. Например, приложение Принтеры отображает очередь документов на печать, или приложение драйвера экрана отображает иконку изменения разрешения экрана. По-другому область уведомлений называется системным треем, но это название не является официальным[5][6], однако используется в документации[7][8][9], статьях[10], описаниях приложений[11] и в приложении Шаблон:Нп4. Реймонд Чен (Шаблон:Lang-en) предполагает, что возникнет недопонимание с приложением systray.exe, маленьким приложением, управляющим иконками в трее в Windows 95.[3] Также есть название область статусов, созданное Microsoft.[12][13][7]
- В старых версиях Windows область уведомлений могла иметь только 16 цветов. В Windows ME было добавлена поддержка Шаблон:Нп4.
- Начиная с Windows XP может выбрать настройку показа панели. При прекращении использования панели она скрывается.
- Начиная с Windows Vista область уведомлений была поделена на две части; первая включала в себя часы, системные приложения, громкость, сеть и энергопотребление. Вторая часть включает в себя остальные приложения.
- В Windows 10 был добавлен центр уведомлений.
- Начиная с Windows 95 Desktop Update, в панели появилась кнопка Показать рабочий стол как стандартный ярлык, автоматически скрывающий все открытые окна. В Windows 7 кнопка Показать рабочий стол перешла на правую сторону. Если функция «Aero Peek» активирована, то подведение к кнопке вызывает простой показ рабочего стола и отведение скрывает показ.
Персонализация[]
Панель задач Windows может быть изменён по разным причинам. Позиция панели может быть изменена. Начиная с Windows Server 2008 панель расположена на одном экране, программа Шаблон:Нп4 позволяет располагать панель на всех экранах, если их несколько. Когда панель расположена вертикально в системах версии ниже Windows Vista, кнопка «Пуск» показывает слово «Пуск», в отличие от полной фразы[14]. Когда панель изменяет высоту (или ширину, если панель расположена вертикально), то под иконками появляются названия окон и приложений.
Пользователь может изменить высоту (или ширину, если панель расположена вертикально) до половины экрана. Чтобы избежать случайного изменения размера, в Windows XP была встроена блокировка от изменения панели[15][16]. Когда панель разблокирована, появляются «бегунки», позволяющие с помощью мыши изменять размер панели или её частей. Эти бегунки могут быть перемещены по всей панели или экрану.
Когда панель управления скрыта, то её можно отобразить простым наведением на тот край, куда скрылась панель. В Windows 7 панель задач не позволяет закреплять папки, за неё это делает ярлыки в приложении проводника Windows. Также это возможно с помощью сторонних программ, например, утилита Шаблон:Нп4 Taskbar Pinner может дать возможность прикреплять к панели задач любой ярлык.[17]
Панель инструментов[]
Другие панели, называемые «Инструментами», могут быть добавлены на панель инструментов[18]. Windows включает представленные инструменты, но не показывает их по умолчанию (за исключением панели быстрого запуска в некоторых версиях).
- Адреса. Включает адрес-бар, похожий на адрес-бар в Internet Explorer.
- Проигрыватель Windows Media. Опционально показывает уменьшенный Проигрыватель Windows Media.
- Ссылки. Ссылки из папки Ссылки. Обычно показывает ссылки на сайты.
- Сенсорная панель. Включает кнопку для показа панели для планшетного компьютера.
- Рабочий стол. Включает ярлыки с рабочего стола. Позволяет быстро получать ярлыки, не выходя на рабочий стол.
- Быстрый запуск. Включает ярлыки Internet Explorer, приложения для электронной почты и ссылки на рабочий стол. В Windows Vista добавлена ссылка на Windows Aero.
- Языковая панель. Включает в себя переключатель языков для клавиатуры.
В дополнение Windows поддерживает функцию «Application Desktop Toolbars» (или «appbands»), позволяющую создавать дополнительные панели и не дающую накладывать другие приложения[19].
- Настройки панели в Windows 95 и Windows 98 могут быть открыты с помощью зажатия Шаблон:Клавиша и клика на панель, однако появившаяся панель не отвечает на запросы. Настройка может быть найдена и в последних версиях[20].
OS X[]
Dock — это панель задач для OS X и её предшественника NeXTSTEP. Панель в OS X является ориентированной на приложения. Запуск приложения можно сделать с помощью одного клика по иконке. Также существует меню, активируемое правым кликом на иконку и вызывающее окно приложения и другие функции приложения. Свёрнутое приложение может быть скрыто в Dock-панель, в секции справа. Корзина также находится на Dock-панели, и используется для удаления файлов и приложений. Например, перемещение части текста в корзину перемещает удалённую часть текста в корзину.
Справа экрана в OS X расположена Шаблон:Нп4, содержащая виджеты и другие возможности, названные Шаблон:Нп4.
Android[]
Стиль Windows 8 в несистемных приложениях для Android реализуют панель задач[21].
Unix-like[]
KDE[]
В KDE 3 и ранее панель задач запускалась с помощью программы Шаблон:Нп4, которая показывала панели, содержащие апплеты. Апплеты могли быть свободно перемещены, например, панель уведомлений может быть убрана с панели. Панель может быть перемещена наверх и другие стороны экрана. Существует возможность изменять высоту или ширину от 24 до 256 пикселей. Также могут быть добавлены дополнительные панели, могущие располагаться в другом месте, например, одна панель слева, а другая — справа (одна закреплённая, а другая скрывающаяся).
Начиная с Plasma (KDE), панель реализована с помощью виджетов.
Шаблон:Wide image
Шаблон:Wide image
GNOME[]
Подобным образом в GNOME 2 используется собственный тип панели (панель GNOME). По умолчанию GNOME 2 обычно содержит две широких панели сверху и снизу. Панель сверху содержит меню Приложения, Переходы и Система. Также там есть запущенные приложения, место для файловой системы, настройки системы и административные утилиты.
Панель снизу обычно используется для вывода на экран часов и области уведомлений, панель сверху позволяет переключаться между Шаблон:Нп4, окнами и кнопка скрытия всех приложений. Панель также может содержать виджеты, названные апплетами. Также там могут располагаться ярлыки приложений, поиск и прочее. Это всё может быть перемещено, удалено или настроено.
Файл:GNOME Shell.png GNOME 3.0, апрель 2011
В GNOME 3 панель была перемещена в GNOME Shell, который состоит из панели сверху, содержащей кнопку Активность слева, часов в центре и панель уведомлений справа. GNOME Shell не содержит традиционную панель управления и окно не может быть скрыто; пользователь может управлять окнами, рабочими столами и запускать приложения (либо с помощью панели на краю экрана, либо с помощью поиска) из Главного меню. В GNOME 3.8 был представлен Классический режим, где были представлены элементы из GNOME 2 в GNOME Shell с помощью расширений.
Другие среды Unix[]
Эти среды рабочего стола имеют собственную панель задач:
- Xfce
- LXDE
- Cinnamon
- MATE
Автономные менеджеры окон позволяют запускать панель задач:
- Fluxbox
- Шаблон:Нп4
- IceWM
- JWM
- Шаблон:Нп4
- Шаблон:Нп4
- Window Maker
Программы, позволяющие запускать панели задач, обычно используют Шаблон:Нп4, pypanel, fbpanel, perlpanel, tint2 и проч.
Примечания[]
- ↑ Сайт Amiga Amidock
- ↑ Шаблон:Ссылка
- ↑ 3,0 3,1 Шаблон:Ссылка
- ↑ Шаблон:Ссылка
- ↑ Шаблон:Ссылка
- ↑ Content Moved (Windows)
- ↑ 7,0 7,1 Шаблон:Ссылка
- ↑ Шаблон:Ссылка
- ↑ Шаблон:Ссылка
- ↑ Шаблон:Ссылка
- ↑ Шаблон:Ссылка
- ↑ Шаблон:Ссылка
- ↑ Шаблон:Ссылка
- ↑ Шаблон:Ссылка
- ↑ Шаблон:Ссылка
- ↑ Шаблон:Ссылка
- ↑ Taskbar Pinner
- ↑ Шаблон:Ссылка
- ↑ Шаблон:Ссылка
- ↑ Настройка панели задач не работает
- ↑ Пример панели задач для Android
Шаблон:Компоненты Windows