Справочный материал к лабораторной работе № 1 (ПК и операционная система Windows)
Основные элементы интерфейса операционной системы
Windows
|
ОСНОВНЫЕ ЭЛЕМЕНТЫ ИНТЕРФЕЙСА…………………………………………………………………………………………. |
1 |
|
РАБОЧИЙ СТОЛ И ПАНЕЛЬ ЗАДАЧ………………………………………………………………………………………………….. |
1 |
|
ПИКТОГРАММЫ И ЯРЛЫКИ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………… |
2 |
|
ОКНА……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… |
2 |
|
ОКНА ПРИЛОЖЕНИЙ ………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………. |
2 |
|
ОКНА ДОКУМЕНТОВ ………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………. |
3 |
|
ВСПОМОГАТЕЛЬНЫЕ (ДИАЛОГОВЫЕ) ОКНА………………………………………………………………………………………………. |
4 |
|
РАСПОЛОЖЕНИЕ ОКОН …………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… |
5 |
Основные элементы интерфейса
Под интерфейсом операционной системы будем понимать совокупность элементов, при помощи которых организуется взаимодействие с пользователем. Операционная система Windows имеет достаточно удобный графический интерфейс, построенный на следующих основных элементах:
1.Рабочий стол
2.Панель задач
3.Окна
4.Диалоговые компоненты (меню, панели инструментов, кнопки, …)
5.Пиктограммы и ярлыки
3
5
4
1
2
Рабочий стол и панель задач
Рабочий стол и панель задач появляются на экране монитора после включения компьютера и окончания загрузки.
Рабочий стол представляет собой всю видимую и доступную часть экрана, которая как бы накрыта красивой скатертью. На рабочем столе и происходит работа пользователя со всеми другими элементами интерфейса.
1

Справочный материал к лабораторной работе № 1 (ПК и операционная система Windows)
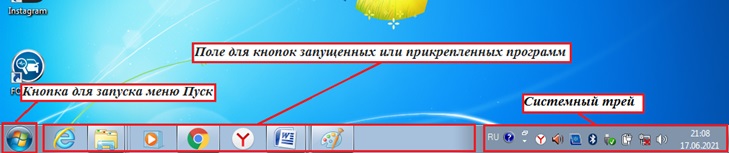
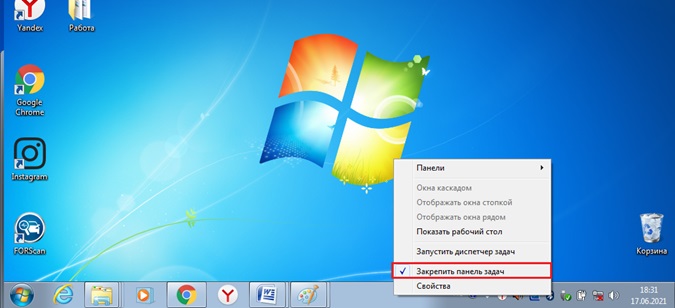
Панель задач – это строка внизу экрана, с помощью которой можно запускать, закрывать, и переключаться между окнами приложений, где решаются пользователем разнообразные задачи. Панель задач может занимать различное положение, может находиться на рабочем столе
или появляться только, когда курсор мыши приближается к соответствующей границе экрана.
Панель задач содержит кнопку 
Справа на панели задач расположены значки системные часы, громкость, индикатор текущей раскладки клавиатуры (буквы RU означают выбор режима раскладки, соответствующего кириллице) и возможно значки ряда других резидентных программ, т.е. запущенных и постоянно находящихся в памяти. Одинарный щелчок или двойной щелчок мышью по одному из этих значков позволяет настроить параметры работы этих программ.
Пиктограммы и ярлыки.
На Рабочем столе располагаются также пиктограммы, ярлыки, а
также окна.
Пиктограмма представляет собой небольшой рисунок с подписью. Они должны отражать назначение того объекта (файла, приложения, документа), который они представляют.
Ярлык представляет собой указатель на объект и помогает быстро обратиться к нему. В левом нижнем углу ярлыка находится стрелка. Ярлык практически не занимает места на диске (всего 1 килобайт), т.к. содержит лишь ссылку на
существующий объект.
Окна.
Окно представляет собой обрамленную область экрана, в которой может отображаться приложение, документ или сообщение.
На поверхности рабочего стола можно увидеть три типа окон: окна приложений,
окна документов, вспомогательные (диалоговые) окна.
Окна приложений
В верхней части каждого окна приложений находится строка заголовка (рис. 3). В ней отображается имя открытого приложения название редактируемого документа —

В левой части строки заголовка находится иконка – это кнопка вызова системного меню. Активизируется системное меню щелчком левой клавиши мыши по кнопке вызова системного меню. Чтобы убрать его, достаточно щелкнуть той же клавишей в любом месте рабочего стола. В правой части строки заголовка расположены три кнопки, причем на двух из них пиктограммы постоянны, а на средней кнопке пиктограммы изменяются в зависимости от состояния окна. Если окно распахнуто на весь экран, то кнопки имеют
|
вид: |
. Если окно занимает часть экрана, то вид кнопок несколько иной: |
. |
|
Левая |
кнопка (со значком подчеркивания — ) сворачивает окно до иконки на |
панели задач. Средняя кнопка (
|
его первоначальные размеры ( |
). Правая кнопка (с крестиком — ) закрывает окно и |
|
прекращает выполнение приложения. |
|
|
Под строкой заголовка |
окна приложений находится строка меню — |

2
Справочный материал к лабораторной работе № 1 (ПК и операционная система Windows)
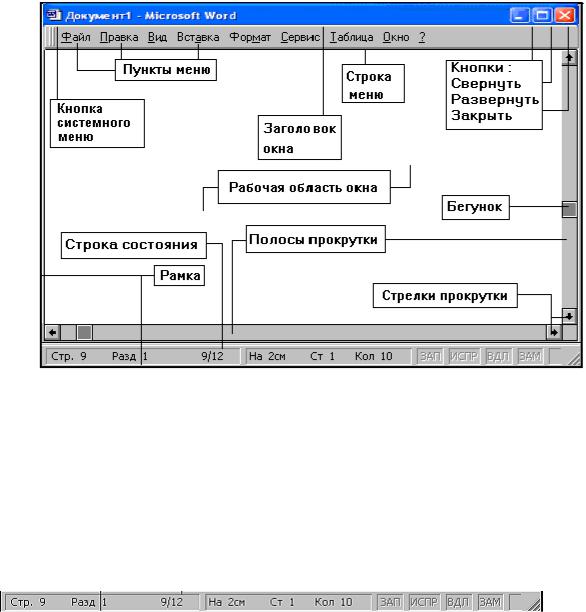
Рис. 3 Основные элементы окна приложений
Добраться до команд меню можно двумя способами. Во-первых, любое меню открывается при щелчке левой клавишей мыши по названию меню. Во-вторых, получить доступ к командам меню можно с помощью клавиатуры. В каждом пункте меню подчеркнута одна из букв. Комбинацией клавиш Alt+буква, подчеркнутая в имени меню, можно сразу открыть нужное меню. Команды меню можно выбрать клавишами, соответствующими подчеркнутым буквам в имени команды. Некоторые команды можно вызвать на выполнение с помощью клавиш или комбинаций клавиш, не открывая меню. Для таких команд справа от их имени указывается соответствующая комбинация.
|
Например, Alt+F4 для команды Закрыть. |
строка |
состояния |
— |
|
|
У |
нижнего |
края |
окна |
находится |
Она содержит информацию о режимах работы приложения.
Размеры окна можно легко изменять. Для этого нужно установить курсор мыши на границу окна, он примет вид двунаправленной стрелки, показывающей направления изменения размеров окна, нажать левую клавишу мыши и установить новые размеры окна.
Полоса прокрутки (вертикальная или горизонтальная 
Окна документов
Окна документов всегда подчинены окнам своих приложений, не выходят за их пределы. Окно документа может быть свернутым (при этом остается на экране лишь заголовок с названием документа), представлено окном нормального размера (не развернутым на все рабочее поле) или полностью развернутым в пределах рабочего поля окном. Для некоторых приложений допустимо располагать на рабочем поле несколько окон документов в различных состояниях. Если окно документа представлено нормальным окном, то оно имеет собственную строку заголовка, содержащую имя документа. При увеличении размеров окна до максимального его имя появляется в строке заголовка приложения после имени приложения. Окна документов, также как и окна
3

Справочный материал к лабораторной работе № 1 (ПК и операционная система Windows)
приложений, имеют кнопки для изменения вида окна, а, установив указатель мыши на границу окна, можно изменить размеры окна.
Вспомогательные (диалоговые) окна
Вспомогательные (диалоговые) окна используются для вывода сообщений, для организации диалога с целью запроса параметров команды или для настройки работы приложения. Как правило, эти окна имеют фиксированный размер и для продолжения работы в приложении необходимо закрыть это окно. В данных окнах в основном и используются диалоговые компоненты. Приведем примеры и особенности использования наиболее распространенных из них:
1.Строка для ввода (однострочный редактор) с подписью –
2.Список
|
а) обыкновенный |
б) раскрывающийся |
Списки используются для просмотра БОЛЬШОГО количества элементов, относящихся к одной категории, и выбора ОДНОГО элемента из представленной совокупности. При этом элементы обыкновенного списка всегда показываются в рамках выделенного окна с полосой прокрутки, а для просмотра и выбора элементов из раскрывающегося списка необходимо нажать на кнопку его раскрытия справа от показанного в строке элемента —
3. Переключатель
В отличии от списков переключатели используются для просмотра НЕБОЛЬШОГО количества элементов, относящихся к одной категории, но также применяются для выбора ОДНОГО элемента из представленной


В отличие от переключателей флаги используются для предоставления возможности выбора НЕСКОЛЬКИХ элементов или ни одного из представленной совокупности.
5.Кнопки
Восновном используются для выбора какого-либо действия (команды) или для вызова другого вспомогательного окна. Краткая характеристика действия, осуществляемого при нажатии кнопки приведена на ней в виде надписи. Многоточие в надписи указывает на вызов другого окна.

Регулятор позволяет установить одно из значений для данной характеристики в диапазоне от некоторого указанного минимального до максимального. Выбранное значение отображается под регулятором.
7. Закладки

4
Справочный материал к лабораторной работе № 1 (ПК и операционная система Windows)
Расположение окон
Одновременно на рабочем столе могут находиться несколько окон. Чтобы упорядочить окна, необходимо щелкнуть правой клавишей мыши на пустом месте панели задач и выбрать один из способов упорядочивания: Окна каскадом (размещает открытые окна “в стопку”), Окна сверху вниз, Окна слева направо. Выбор осуществляется одиночным щелчком левой клавишей мыши.
Чтобы переместить окно, надо установить курсор на строку заголовка окна, нажать левую кнопку мыши и, не отпуская ее, переместить курсор в нужное место, отпустить левую кнопку мыши.
5
Соседние файлы в предмете [НЕСОРТИРОВАННОЕ]
- #
- #
- #
- #
- #
- #
- #
- #
- #
- #
- #
Взаимодействие компьютера с пользователем с каждой новой версией операционной системы становится проще и понятнее. Это означает, что создатели пользовательского интерфейса — набора инструментов, позволяющих пользователю взаимодействовать с компьютером, — создают всё более сложные программы. А сам интерфейс становится более дружественным. Про такой говорят, что он сделан по принципу DWIM (Do What I Mean — «делай то, что я имею в виду»).
Современные операционные системы имеют графический интерфейс. Это значит, что команды управления устройством скрываются за графическими элементами, которыми управляет пользователь. В специальной литературе графический интерфейс иногда называют WIMP — это аббревиатура от Windows, Icons, Menus, Pointer — «окна, иконки, меню, указатель».
WIMP-интерфейс позволяет пользователю управлять программными и аппаратными ресурсами компьютера через окна, иконки, меню и указатели.
Графический интерфейс очень удобен для рядового пользователя, но для профессионального программиста он имеет некоторые недостатки, например, сама графическая оболочка занимает много места и замедляет работу компьютера. Кроме того, графические интерфейсы разных операционных систем затрудняют совместную работу.
Рассмотрим основные элементы графического интерфейса. Иллюстрировать наше исследование будем с помощью примеров операционной системы Windows.
Основными элементами графического интерфейса являются окна и меню.
Окна
Рассмотрим четыре основных вида окон: рабочий стол, диалоговое окно, окно папки и окно документа.
Рабочий стол — ключевое окно графической среды. В нём мы увидим такие элементы управления, как главное меню, значки, ярлыки, панель задач.
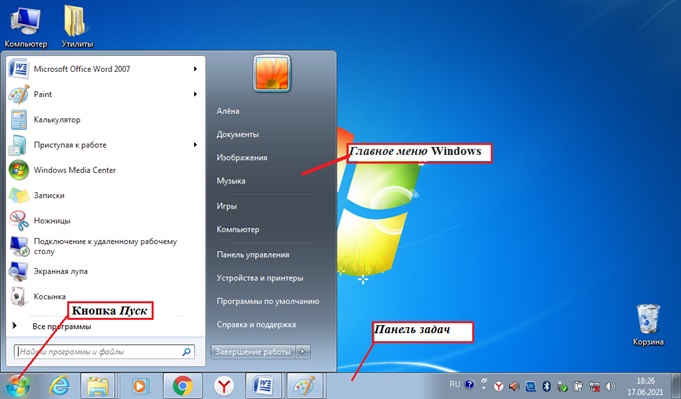
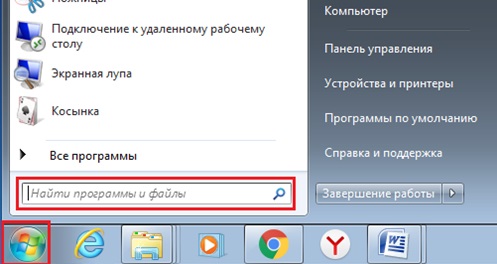
Кнопка Пуск открывает главное меню операционной системы.
Главное меню — это элемент управления рабочего стола, предназначенный для быстрого доступа к программам, документам, средствам настройки и поиска, избранным папкам и объектам. Завершение работы с операционной системой выполняется только с помощью главного меню. Открывается кнопкой «Пуск».
Значки обозначают программы и документы. Для запуска выполняется двойной щелчок мышью.
Ярлыки внешне отличаются от значков стрелкой в левом нижнем углу, но предоставляют быстрый доступ к программе, которая хранится в файловой системе, а на рабочий стол выведен ярлык для её быстрого запуска.
Рис. (1). Рабочий стол
Панель задач — элемент управления, отображает кнопку «Пуск», значки запущенных приложений, индикаторы, время.
Диалоговые окна бывают разными в зависимости от способа взаимодействия с пользователем. Это могут быть окна сообщений, в которых из управляющих элементов присутствуют только кнопки — элемент управления, при нажатии служит для выполнения действия, которое обозначено надписью на кнопке.
Рис. (2). Диалоговое окно
Или это могут быть более сложные окна настройки параметров. В них больше различных элементов управления. Рассмотрим элементы управления на примере окон настройки параметров «Шрифт» и «Табуляция».
Рис. (3). Настройки параметров
|
Списки |
Элемент управления, служит для выбора из команд, доступных для выполнения |
|
Раскрывающиеся списки |
То же назначение, что и у списков, но для доступа к командам необходимо раскрыть список с помощью стрелки |
|
Переключатели |
Элемент управления, служит для выбора одного из нескольких вариантов |
|
Флажки |
Элемент управления, служит для выбора нескольких из нескольких вариантов |
|
Кнопки |
Элемент управления, при нажатии служит для выполнения действия, которое обозначено надписью на кнопке |
|
Счётчики |
Элемент управления, который при помощи пары стрелок увеличивает или уменьшает значение в связанном с ним поле |
|
Ползунки |
То же, что и счётчик, но значение в поле меняется плавно |
|
Вкладки |
Элемент управления, служит для отображения нескольких страниц, относящихся к одному диалоговому окну |
Рис. (4). Окно папки
|
Строка меню |
Перечень команд, которые можно выполнить в данном окне |
|
Кнопки управления состоянием окна |
Кнопки, позволяющие управлять окном: закрыть, развернуть/восстановить, свернуть на панель задач |
|
Панель навигации |
Представляет объекты файловой системы для быстрого перехода к ним из текущей папки |
|
Адресная строка |
Указывает путь доступа к текущей папке, содержит раскрывающийся список для удобного перемещения по файловой системе |
|
Рабочая область |
Окна и папки отображаются значками объектов. Могут появляться полосы прокрутки |
|
Полосы прокрутки |
Позволяет прокручивать рабочую область по вертикали или по горизонтали |
|
Границы окна |
Рамка, ограничивающая окно со всех сторон |
|
Строка состояния |
Для дополнительной справочной информации |
|
Область поиска |
Служит для ввода информации о файле, который необходимо найти |
Окно документа — здесь мы увидим все те же элементы графического интерфейса, с которыми уже успели познакомиться.
Рис. (5). Окно документа
|
Значок приложения |
Содержит заголовок активного документа |
|
Строка заголовка |
Указывает активное приложение |
|
Панель инструментов |
Содержит значки инструментов, которые наиболее часто применяет пользователь |
|
Линейка |
Один из специальных инструментов текстового редактора |
Меню
Графический интерфейс применяет два вида меню: главное меню и контекстное. С понятием и назначением главного меню мы уже познакомились, когда обсуждали элементы рабочего стола.
Контекстное меню — список команд, который вызывается пользователем для выбора необходимого действия над выбранным объектом.
Вызывается контекстное меню правой кнопкой мыши. Команды контекстного меню относятся только к тому объекту, для которого это меню вызвано.
Рис. (6). Контекстное меню
На рисунке ты видишь контекстное меню, вызванное к слову «команды». В меню перечислены все возможные действия, которые можно произвести с этим словом.
Источники:
Рис. 1. Рабочий стол. Автор: Операционная система и большая часть программ принадлежит Microsoft Corp. Остальные программы принадлежат G5 Entertainment AB, Gameloft SE, king.com Ltd, MyTona, Playrix Games, и Yandex. — скриншот, Добросовестное использование, https://ru.wikipedia.org/w/index.php?curid=5928961. (Дата обращения: 18.12.2021.)
Рис. 2. Диалоговое окно. © ЯКласс.
Рис. 3. Настройки параметров. © ЯКласс.
Рис. 4. Окно папки. © ЯКласс.
Рис. 5. Окно документа. © ЯКласс.
Рис. 6. Контекстное меню. © ЯКласс.
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
(Redirected from Windows Time)
The following is a list of Microsoft Windows components.
Configuration and maintenance[edit]
| Component | Description | Introduced |
|---|---|---|
| Settings | Allows users to change system settings, similar to the Control Panel, but has less options[1] | Windows 8 |
| Control Panel | ||
| Control Panel | Allows users to view and change basic system settings and controls, such as adding hardware, adding and removing software, controlling user accounts, and changing accessibility options | Windows 1.0 |
| Device Manager | Allows the user to display and control the hardware attached to the computer, and control what device drivers are used | Windows 95 |
| Windows Mobility Center | Centralizes the most relevant information related to mobile computing | Windows Vista |
| Security and Maintenance | Centralizes and reports on the status of anti-virus, Automatic Updates, Windows Firewall, and other security-related components of the operating system | Windows XP SP2 |
| Administrative Tools | ||
| Microsoft Management Console | Provides system administrators and advanced users with a flexible interface through which they may configure and monitor the system | Windows NT 4.0 Option Pack |
| Windows System Assessment Tool | Built-in benchmarking tool that analyzes the different subsystems (graphics, memory, etc.), and uses the results to allow for comparison to other Windows Vista systems, and for software optimizations. It rates the computer’s performance using the Windows Experience Index. | Windows Vista |
| System Restore | Allows for the rolling back of system files, registry keys, installed apps, etc., to a previous state in the event of a system failure | Windows Me |
| Windows Recovery Environment | Helps diagnose and recover from serious errors which may prevent Windows from booting successfully, or restore the computer to a previous state using System Restore or a backup image | Windows Vista |
| Microsoft Drive Optimizer | Rearranges files stored on a hard disk to occupy contiguous storage locations in order to optimize computer performance | Windows 95, Windows 2000 |
| Event Viewer | Lets administrators and users view the event logs on a local or remote machine | Windows NT 3.1 |
| Resource Monitor (previously Reliability and Performance Monitor) |
Lets administrators view current system reliability and performance trends over time | Windows Vista |
| Logical Disk Manager | Logical volume manager developed by Microsoft in conjunction with Veritas Software | Windows NT 4.0 (Separate Tool), Windows 2000 |
| Registry Editor | Allows users to browse and edit the Windows registry | Windows 3.1 |
| Task Scheduler | Allows users to script tasks for running during scheduled intervals | Microsoft Plus! for Windows 95 |
| Software installation and deployment | ||
| Windows Update | An online service providing updates such as service packs, critical updates and device drivers. A variation called Microsoft Update also provides software updates for other Microsoft products. | Windows 98 |
| Windows Installer | An engine for the management of software installation. Includes a GUI framework, automatic generation of the uninstallation sequence and deployment capabilities for corporate networks. | Windows 2000 |
| ClickOnce | Technology for deploying .NET Framework-based software via web pages, with automatic update capabilities. Intended for per-user only applications. | .NET Framework 2.0 |
User interface[edit]
| Component | Description | Introduced |
|---|---|---|
| Action Center | View notifications sent from apps and change common settings | Windows 10 Version 1507 |
| Command Prompt | Text-based shell (command line interpreter) that provides a command line interface to the operating system | Windows NT 3.1 |
| Windows PowerShell | Command-line shell and scripting framework. | Windows XP |
| Windows Shell | The most visible and recognizable aspect of Microsoft Windows. The shell provides the container inside of which the entire graphical user interface is presented, including the taskbar, the desktop, Windows Explorer, as well as many of the dialog boxes and interface controls. In Windows Vista, a new compositing glass-like user interface called Windows Aero has been shown. | Windows 95 |
| File Explorer (previously Windows Explorer) |
Provides an interface for accessing the file systems, launching applications, and performing common tasks such as viewing and printing pictures | Windows 95 |
| Windows Search | Starting with Windows Vista, search is a tightly shell-integrated component of Windows. A downloadable Windows Desktop Search software is available for Windows XP and older versions. | Windows Vista, downloadable for older versions |
| Search Folders | Virtual folders that retrieve items based on queries rather than hierarchical folder trees on disk. | Windows Vista |
| Special Folders | Folders which are presented to the user through an interface as an abstract concept, instead of an absolute path. This makes it possible for an application to locate where certain kinds of files can be found, regardless of what version or language of operating system is being used. See also Windows Shell namespace. | Windows 95 |
| Start menu | Serves as the central launching point for applications. It provides a customizable, nested list of apps for the user to launch, as well as a list of most recently opened documents, a way to find files and get help, and access to the system settings. By default, the Start Button is visible at all times in the lower left-hand corner of the screen. | Windows 95 |
| Taskbar | The application desktop bar which is used to launch and monitor applications | Windows 95 |
| Task View | Displays all open windows and activities (via timeline) at a glance and switch between virtual desktops, starting in version 2004, users can now rename desktops | Windows 10 Version 1507 |
| File associations | Used to open a file with the appropriate app. Users can assign file associations uniquely to specific actions, known as verbs. | Windows 1.0 |
Applications and utilities[edit]
| Component | Description | Introduced |
|---|---|---|
| Easy Transfer | Used to transfer many files at once from one computer to another | Windows Vista |
| Contacts | Keeps a single list of contacts that can be shared by multiple apps | Windows Vista |
| Camera | Allows the user to take pictures or record video[2] | Windows 8 |
| Calculator | Calculation application | Windows 1.0 |
| Calendar | Calendaring application | Windows Vista |
| Character Map | Utility to view and search characters in a font, copy them to the clipboard and view their Windows Alt keycodes and Unicode names | Windows 3.1 |
| Cortana | Digital personal assistant | Windows 10 Version 1507 |
| Edge | Web browser | Windows 10 Version 1507 |
| Feedback Hub | Platform for exchanging communication with Windows Insiders and developers | Windows 10 Version 1607 |
| Groove Music (previously Xbox Music) |
Digital media player and media library application that is used for playing audio. In addition to being a media player, Groove includes the ability to copy music to compact discs, synchronize content with a digital audio player (MP3 player) or other mobile devices, and let users purchase or rent music from the Windows Store. | Windows 8 |
| Movies & TV (previously Xbox Video) |
Digital media player and media library application that is used for playing video. In addition to being a media player, Movies & TV lets users purchase or rent movies and TV episodes from the Windows Store. | Windows 8 |
| OneDrive (previously SkyDrive) |
Freemium cloud storage folder and sync service | Windows 8 |
| OneNote | Integrated note-taking app, based on the Microsoft Office product of the same name | Windows 8 |
| On-Screen Keyboard (osk.exe) | Virtual keyboard | |
| Paint 3D | Simple graphics painting app | Windows 10 Version 1703 |
| Photos | Simple image viewer | Windows 8 |
| Steps Recorder (called Problem Steps Recorder in Windows 7) |
Utility that allows the user to capture steps they took to reproduce a problem | Windows 7 |
| Windows To Go | Utility to create bootable versions of Windows 8 and above | Windows 8 |
| Notepad | Simple text editor | Windows 1.0 |
| Narrator | Screen reader utility that reads dialog boxes and window controls in a number of the more basic applications for Windows | Windows 2000 |
| Sound Recorder | Simple audio recording app that can record from a microphone or headset, and save the results in WAVE format and Windows Media Audio format in some Windows versions | Windows 3.0 Multimedia Extensions |
| Skype | Messaging and calling service | Windows 8.1, downloadable for previous versions |
| Sticky Notes | Tool for jotting notes on the desktop | Windows XP Tablet PC Edition |
| WordPad | Simple word processor that is more advanced than Notepad. It has facilities to format and print text, but lacks intermediate features such as a spell checker and thesaurus. | Windows 95 |
| Private Character Editor | Utility to create private use characters as defined under Unicode and various East Asian encoding schemes | Windows 3.1 East Asian editions |
| Remote Desktop Connection | Client implementation of the Remote Desktop Protocol; allows a user to securely connect to a computer running Terminal Services (Remote Desktop on Windows XP and Server 2003) and interact with a full desktop environment on that machine, including support for remoting of printers, audio, and drives. | Windows XP, downloadable for previous Windows versions |
| Remote Assistance | Allows a user to temporarily take over a remote computer over a network or the internet to offer help with and resolve issues | Windows XP |
| Mobility Center | Allows a user to adjust settings related to mobile computing | Windows Vista |
| Speech Recognition | Allows a user to input voice commands | Windows Vista |
| IExpress | Allows users to create self-extracting, self-installing INF installation-based packages | Internet Explorer 6 |
| Xbox Console Companion (previously Xbox and Xbox Games) |
Account manager for Xbox Live user accounts and a screen recording tool | Windows 8 |
| Xbox Game Bar | Provides a overlay for compatible games allowing for screen capture, chatting over the Xbox network, showing the frame rate of games, and playing music via Spotify[3][4] | Windows 10 May 2019 Update (Version 1903)[5] |
| Magnifier | Screen enlargement app | Windows 98 |
| Fax and Scan | Integrated faxing and image scanning application | Windows Vista, older faxing and scanning applications were present in previous Windows versions |
| Photo Viewer | Simple image viewer that can play a simple slideshow | Windows 7 |
| Email aggregator | Windows 8 | |
| Maps | Map viewer that allows users to look for locations, plan routes, and store offline maps | Windows 8 |
| Media Center | Designed to serve as a home-entertainment hub, to be viewed from a distance up to 3 meters (~10 feet) and controlled by specially designed remote controls. Lets users browse and view pictures, videos, and music from local hard drives, optical drives, and network locations, along with viewing, recording and deferred-playing live TV. Features an interactive TV guide with scheduled recording capabilities. Can also be used for visualization of other information (like sports scores) within the interface. | Windows XP Media Center Edition |
| Task Manager | Provides information about computer performance and displays details about running applications, processes, network activity, logged-in users, and system services | Windows 3.0 |
| Disk Cleanup | Utility for compacting rarely used files and removing files that are no longer required | Windows 98 |
| Snipping Tool | Screen-capture tool that allows for taking screenshots (called snips) | Experience Pack for Windows XP Tablet PC Edition 2005 |
| Microsoft Store (previously Windows Store) |
Initially known as Windows Store, it started as an app store for Windows 8. In Windows 10, it expanded into a broad digital distribution platform for apps, games, music, digital video and e-books. In 2017, it was renamed Microsoft Store and started offering hardware in United States, Canada and United Kingdom. | Windows 8 |
| MSN apps | Provide information from MSN web services | Windows 8 |
| Alarms & Clock(pre Alarms) | App that allows Windows users to set alarms, stopwatches, timers, and view a world clock | Windows 8 |
| Windows Security (previously Windows Defender Security Center) |
Antivirus | Windows 10 Version 1703 |
| Solitaire Collection | Set of solitaire card games | Windows 10 Version 1507, downloadable for Windows 8.x |
Windows Server components[edit]
| Component | Description | Supported by |
|---|---|---|
| Active Directory | A set of technologies introduced with Windows 2000 that allows administrators to assign enterprise-wide policies, deploy apps to many computers, and apply critical updates to an entire organization. Active Directory stores information and settings relating to an organization in a central, organized, accessible database. Networks can vary from a small installation with a few objects, to global-scale directories with millions of objects. Related topics: Domain controller, Flexible single master operation |
Windows 2000 and later server versions |
| Group Policy | Provides centralized management of user and computer settings in an Active Directory environment. Group policy can control a target object’s registry, NTFS security, audit and security policy, software installation, logon/logoff scripts, folder redirection, and Internet Explorer settings. Policy settings are stored in Group Policy Objects (GPOs), and may be linked to one or more sites, domains or organizational units. Related topics: Administrative Templates |
Windows 2000 and later |
| Internet Information Services | Web server | Windows NT family |
File systems[edit]
| Component | Description | Supported by |
|---|---|---|
| FAT12, FAT16 | The original file systems used with MS-DOS. The standard file systems used with Windows 1.0 through Windows 95. | All versions |
| FAT32 | Extensions to FAT supporting larger disk sizes. The standard file system for Windows 98 and Me. | Windows 95 OSR2 and later versions |
| NTFS | Standard file system of Windows NT; supports security via access control lists, as well as file system journaling and file-system metadata. Windows 2000 added support for reparse points (making NTFS junction points and Single instance storage possible), Hard links, file compression, and Sparse files. Encryption of data is provided by Encrypting File System. Symbolic links and transactioning of file operations via Transactional NTFS are features new to Windows Vista.
Although Windows 9x operating systems cannot read or write NTFS formatted disks, they can access the data over a network if it is shared by a computer running Windows NT. |
Windows NT (all versions) |
| ISO 9660 (CDFS) | The predominant file system for CD-ROM and DVD-ROM media. Windows includes support for Joliet extensions and the ISO 9660:1999 standard. ISO 9660:1999 is supported since Windows XP. | MS-DOS and Windows 9x via extensions, such as MSCDEX.EXE (Microsoft CDROM Extension), natively in Windows NT |
| Universal Disk Format (UDF) | A file system for storing files on optical media. It is an implementation of the ISO/IEC 13346 standard (also known as ECMA-167). It is considered to be a replacement of ISO 9660. Successive versions of Windows have supported newer versions of UDF. | Windows 98, Windows 2000, Windows XP, Windows Server 2003, Windows Vista |
| HPFS | High-Performance File system, used on OS/2 computers. Read and write capability in Windows 95 (where it also listed network computer NTFS-formatted drives as «HPFS», even though it had no direct NTFS capabilities). HPFS write support was dropped in Windows NT 4.0 and Windows 98, and dropped altogether shortly before the release of Windows 2000. | Windows 95 (Read/write), Windows 98, Windows NT (read), 3.1/3.51 (read/write/boot) |
| ReFS | A newer file system, based on NTFS. This system adds built-in integrity checking and removes the need for chkdsk, among other features. The maximum partition size is 1 YB. | Windows Server 2012, Windows 8.1 |
Core components[edit]
| Component | Acronym | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Windows kernel (Windows NT)
Main article: Architecture of the Windows NT operating system line |
||
| Ntoskrnl.exe | The Windows kernel image. Provides the kernel and executive layers of the kernel architecture, and is responsible for services such as hardware virtualization, process and memory management, etc. | |
| hal.dll | HAL | Provides and handles the interaction between software and hardware via the Hardware Abstraction Layer. |
| kernel32.dll | This application provides kernel operations to apps in the Win32 mode, like memory management, I/Os, process creation, etc. | |
| Core processes (Windows NT) | ||
| System idle process | SIP | A counter which measures how much idle capacity the CPU has at any given time. The process runs in the background and monitors processing bandwidth, occupied memory and the Windows virtual paging file. |
| Session Manager Subsystem | SMSS | Performs several critical boot-time operations, such as the creation of environment variables, starting CSRSS, and performing file-copy operations that were queued up from before the system was booted (pending file rename operations). During system operation, it handles Windows File Protection and the creation of logon sessions via Winlogon. |
| Client/Server Runtime Subsystem | CSRSS | User-mode side of the Win32 subsystem. Provides the capability for applications to use the Windows API. |
| Local Security Authority Subsystem Service | LSASS | Responsible for enforcing the security policy on the system. Verifies users logging on to the computer and creates security tokens. |
| Winlogon | Responsible for handling the secure attention key, loading the user profile on logon, and optionally locking the computer when a screensaver is running. On Windows NT systems prior to Windows Vista, Winlogon is also responsible for loading GINA libraries which are responsible collecting logon credentials from the user. | |
| Svchost.exe | A generic host process name for services that run from dynamic-link libraries (DLLs). Several Svchost processes are typically present on a Windows machine, each running in a different security context, depending on what privileges the contained services require. | |
| Windows on Windows and WOW64 | WoW | An abstraction layer that allows legacy code to operate on more modern versions of Windows; typically this means running 16-bit Windows applications on 32-bit Windows, and 32-bit applications on 64-bit Windows. |
| Virtual DOS machine | NTVDM | Allows MS-DOS apps to run on Intel 80386 or higher computers when there is already another operating system running and controlling the hardware. Introduced in Windows 2.1; not available in any 64-bit edition of Windows. |
| System startup (Windows NT)
Main articles: Windows NT Startup Process and Windows Vista Startup Process |
||
| NTLDR, IA64ldr, Winload | The boot loader; performs basic system initialization options such as loading the hardware abstraction layer and boot-time device drivers, prior to passing control to the Windows kernel. In versions prior to Vista, NTLDR and IA64ldr also display menus to the user if multiple operating systems are defined in boot.ini, or if F8 is pressed. | |
| Recovery Console | Provides the means for administrators to perform a limited range of tasks using a command line interface, primarily to aid in recovering from situations where Windows does not boot successfully. | |
| ntdetect.com | Used during the boot process to detect basic hardware components that may be required during the boot process | |
| Windows Boot Manager | In Windows Vista and later operating systems, displays boot menus to the user if multiple operating systems are configured in the system’s Boot Configuration Data. | |
| Graphical subsystem | ||
| Desktop Window Manager | DWM | The compositing manager introduced in Windows Vista that handles compositing and manages special effects on screen objects in a graphical user interface |
| Graphics Device Interface | GDI/GDI+ | The kernel graphics component for representing graphical objects and transmitting them to output devices such as monitors and printers |
| Windows USER | The Windows USER component provides core user interface, messaging and visual elements |
Services[edit]
This list is not all-inclusive.
| Display name | Service key name | Description | Introduced |
|---|---|---|---|
| Active Directory Service | NTDS | Network Authentication Management | Windows 2000 Server |
| Alerter service | Alerter | Sends administrative alerts over the network to client computers, administrators and users | Windows NT |
| Application Layer Gateway service |
ALG | Provides support for plugins that allow network protocols to pass through Windows Firewall and work behind Internet Connection Sharing | Windows 2000 |
| Application Experience service | Processes application compatibility cache requests for applications as they launch[6] | ||
| Application Management | AppMgmt | Processes requests to enumerate, install, and remove applications that are installed on the computer or deployed through an organization’s network | Windows 2000 |
| Background Intelligent Transfer Service |
BITS | Transfers files between machines using idle network bandwidth. Used by Windows Update, Windows Server Update Services, and Systems Management Server to deliver software updates to clients, as well as by Windows Messenger. | Windows XP |
| Computer Browser | Browser | Crawls neighboring computers on the network and locates shared resources. One of the computers acts as the Master Browser and supplies this information to other computers designated as browsers.[7] | Windows for Workgroups |
| Delivery Optimization | DoSvc | A peer-to-peer distribution service that downloads Windows updates and Microsoft Store apps from the local network or Internet peers, and redistributes them to others. Can be configured using either the Settings app or Group Policy. The Settings app can turn it on or off, and specify whether the service operates on the local network only, downloads from and uploads to the Internet peers as well. Group Policy allows finer control.[8][9] Delivery Optimization relies on a centralized web service that does not index contents under 10 MB. Computers without Internet access cannot use Delivery Optimization.[10] | Windows 10 Anniversary Update[8] |
| Distributed Link Tracking | TrkWks, TrkSrv | Used to track links to files on NTFS volumes. Windows uses these services to find linked files if they are renamed or moved (locally or to another machine).[11] | Windows 2000 |
| Distributed Transaction Coordinator |
MSDTC | Allows transactional components to be configured through COM+ by coordinating transactions that are distributed across multiple computers and/or resource managers, such as databases, message queues, file systems, and other transaction–based resource managers.[12] | Windows 2000 and later NT-based |
| DNS Client | DNSCache | Resolves and caches domain names (e.g. “en.wikipedia.org”) to IP addresses | Windows 2000 |
| Event Log | EventLog | Stores and retrieves events that can be viewed in the event viewer. Part of services.exe.[13] | Windows NT |
| Extensible Authentication Protocol | EAPHost | Provides EAP authentication to connecting clients | Windows 2000 |
| Indexing Service | CISVC | Indexes contents and properties of files on local and remote computers; provides rapid access to files through flexible querying language.[14] | Windows 2000 and later NT-based |
| Interactive Services Detection | UI0Detect | For compatibility; when a service-displayed user interface is detected, it gives the user an option to switch to Session0 to see it | Windows Vista |
| Internet Connection Sharing (ICS) | SharedAccess | When enabled, it allows other computers on the local network to access an internet connection that is available to the host computer | Windows 2000;[15] Windows Vista onward[16] |
| Network Location Awareness | NLA | Manages network configurations and information, and notifies applications of changes | Windows XP |
| Network Store Interface Service | NSIS | Collects routing information of active network interfaces, shares this with other services and notifies applications of changes | Windows XP |
| NTLM Security Support Provider | NTLMSSP | Uses the NTLM MS-CHAP protocol to encapsulate and negotiate options in order to provide signed and sealed communication. Deprecated now in favor of Kerberos authentication. | Windows NT |
| Peer Name Resolution Protocol | PNRPSvc | Resolves domain names using Peer Name Resolution Protocol | Windows XP |
| Plug and Play | PlugPlay | Enables autodetection and configuration of hardware | Windows 2000 |
| Windows Print spooler [fr] | Spooler | Manages printer devices and moves files into memory for printing | Windows 95, Windows NT |
| Remote Procedure Call (RPC) | RpcSs | Provides Remote Procedure Call features via remotely accessible Named Pipes | Windows NT family |
| Routing and Remote Access Service | RRAS | API and server software that enables applications to administer the routing and remote-access service capabilities of the operating system, to function as a network router. | Windows 2000 |
| Secondary Logon | SecLogon | Allows users to run apps with a different account than the one they logged in with. Allows non-administrative accounts to perform administrative tasks.[17] | |
| Security Accounts Manager | SamSs | Manages user account security information | Windows NT family |
| System Event Notification Service | SENS | Monitors system events, such as network, power, logon, logoff, terminal services session connection and disconnection, and delivers these to applications and other system components.[18] | Windows 2000 |
| Superfetch | SysMain | Monitors file usage patterns and boosts system speed by caching frequently accessed files to RAM[19] | Windows Vista |
| Task Scheduler | Schedule | Lets users setup and schedule automated tasks | Microsoft Plus! for Windows 95 |
| TCP/IP NetBIOS Helper | LmHosts | Enables support for NetBIOS over TCP/IP (NetBT) service and NetBIOS name resolution | Windows NT family |
| Volume Shadow Copy | VSS | Creates multiple versions of files that change. The ability to store persistent snapshots was added in Windows Server 2003.[20] | Windows XP |
| Windows Audio | AudioSrv | Manages audio devices for Windows-based apps. Controls all audio functions. | Windows XP |
| Windows Error Reporting | WERSvc | Generates error logs and reports errors. On Windows Vista and later, it notifies of solutions. | Windows XP |
| Windows Firewall | MpsSvc | Blocks unauthorized network connections to and from the computer | Windows Vista |
| Windows Firewall(née Internet Connection Sharing) | SharedAccess | Provides a simple firewall feature which was introduced in Windows XP. It also shares the internet on the local network, if the internet connection sharing feature is turned on.[21] | Windows XP only[22][23] |
| Windows Image Acquisition (WIA) | STISvc | Handles scanner and camera inputs | Windows Me |
| Windows Time | W32Time | Synchronizes the system time with external time servers. From Windows Server 2003 forward, full and compliant NTP support is provided.[24] | Windows 2000 |
| Windows Update | WUAUServ | Provides updates for the operating system and its installed components | Windows XP |
| Wireless Zero Configuration | WZCSvc (XP), WLANSvc | Configures and manages 802.11 wireless adapters | Windows XP, Server 2003 only |
| Windows Messenger service | Messenger | Allows users to send pop-up messages to other computers over the network | Windows NT family |
| WebClient[25] | Enables Windows-based apps to create and interact with Internet-based files | Windows XP |
DirectX[edit]
- Direct3D
- DirectDraw
- DirectInput
- DirectMusic
- DirectPlay
- DirectShow
- DirectSound
- DirectX Media Objects
- DirectX plugin
- DirectX Video Acceleration
Networking[edit]
- Administrative share
- Distributed File System
- My Network Places (formerly Network Neighborhood)
- Network Access Protection
- Remote Installation Services
- Server Message Block
- Windows Rights Management Services
Scripting and command-line[edit]
- Batch file
- CHKDSK
- Cmd.exe
- ComSpec
- Ipconfig
- Net / Net Send
- Netdom.exe: Windows Domain Manager
- Netsh
- Netstat
- QBasic
- Regsvr32
- Robocopy
- Win32 console
- Windows Script Host
- Windows PowerShell
- XCOPY
Kernel[edit]
- Commit charge
- Kernel Transaction Manager
- Win32 Thread Information Block
.NET Framework[edit]
- Assembly
- CLI Languages
- Metadata
- .NET Remoting
- ADO.NET
- ASP.NET
- Base Class Library
- Common Intermediate Language
- Common Language Infrastructure
- Common Language Runtime
- Common Type System
- Virtual Execution System
- Windows CardSpace
- Windows Communication Foundation
- Windows Forms
- Windows Presentation Foundation
- Windows Workflow Foundation
Security[edit]
| Component | Description | Introduced |
|---|---|---|
| AppLocker | Policy-based component that enables or disables execution of software based on rules such as location, properties and digital signature | Windows 7 Professional, Enterprise and Ultimate editions Windows Server 2008 R2 |
| BitLocker Drive Encryption | Disk encryption software, designed to protect data by providing encryption for entire volumes | Windows Vista Enterprise and Ultimate editions, Windows Server 2008 |
| Credential Guard | Virtualization-based isolation of stored credentials to prevent theft and pass-the-hash attacks. | Windows 10 Enterprise, Education, IoT Enterprise, or , Windows Server 2016 |
| Data Execution Prevention | Security feature that is intended to prevent an application or service from executing code from a non-executable memory region | Windows XP Service Pack 2 |
| Encrypting File System | File system driver that provides file system-level encryption | Windows 2000 |
| Security Account Manager | Database stored as a registry file | Windows NT 3.1 |
| SYSKEY | Utility that encrypts the hashed password information in a SAM database using a 128-bit encryption key | Windows NT 4.0 Service Pack 3 |
| User Account Control | Technology and security infrastructure utility that aims to improve the security of Microsoft Windows by limiting application software to standard user privileges until an administrator authorizes an increase | Windows Vista, Windows Server 2008 |
| Windows Firewall | Utility designed to block unauthorized access while permitting authorized communications. An earlier edition known as Internet Connection Firewall that was disabled by default was included with the original Windows XP release. | Windows XP Service Pack 2 |
| Windows Defender | Security utility to prevent, remove and quarantine malware (viruses, Trojan horses, etc.) | Downloadable for Windows XP and Windows Server 2003 |
| Windows Resource Protection | Protects Registry keys and folders in addition to critical system files | Windows Vista |
Deprecated components and apps[edit]
| Component | Description | Category | Introduced | Last OS included | Superseded by |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3D Pinball | Pinball game | Game | Plus! 95 for Windows 95 | Windows XP | — |
| ActiveMovie | Streaming media technology | API | Windows 95 | Windows Me | DirectShow |
| Cardfile | Personal information manager | Personal organizer | Windows 1.0 | Windows Me | Outlook Express, Windows Mail, or Windows Live Mail |
| Chess Titans | Chess game | Game | Windows Vista | Windows 7 | Microsoft Chess |
| DriveSpace | Disk compression utility | Data compression | MS-DOS | Windows Me | — |
| Windows DVD Maker | DVD authoring software | Video | Windows Vista | Windows 7 | — |
| File Manager | File manager app | File manager | Windows 3.0 | Windows Me | Windows Explorer |
| FreeCell | FreeCell game | Game | Win32s | Windows 7 | Microsoft Solitaire Collection |
| Hearts | Version of the Hearts game using Black Lady scoring | Game | Windows for Workgroups 3.11 | Windows 7 | Microsoft Hearts |
| Insider Hub | Windows 10 Version 1507 | Windows 10 Version 1511 | Feedback Hub | ||
| Windows Help and Support | Online and offline reference manual for troubleshooting. | Utility | Windows Me | Windows 8.1 | Microsoft Tips or Get Started |
| HyperTerminal | Communication utility based on a low end version of HyperACCESS | Communication | Windows 95 | Windows XP | — |
| Hold ‘Em | Version of the Texas hold ’em game | Game | Windows Vista | Windows Vista | — |
| Hover! | Video game in a combination of bumper cars and capture the flag | Game | Windows 95 | Windows 95 | — |
| InkBall | Game where the user tries to get colored balls into the correct holes | Game | Windows XP Tablet PC Edition | Windows Vista | — |
| Internet Explorer | Web browser | Web browser and FTP client. See also: Internet Explorer versions, Features, History, Removal, Browser Helper Objects | Microsoft Plus! for Windows 95 | Windows 10 | Microsoft Edge |
| Mahjong Titans | Version of the Mahjong solitaire game | Game | Windows Vista | Windows 7 | Microsoft Mahjong |
| Windows Mail | E-mail client | Windows Vista | Windows Vista | Mail (Windows) | |
| Internet Mail and News | E-mail and news client | Windows 95 | Windows 95 | Outlook Express, Windows Mail, or Windows Live Mail | |
| Minesweeper | Version of the minesweeper game | Game | Microsoft Entertainment Pack, Windows 3.1 | Windows 7 | Microsoft Minesweeper |
| Media Control Interface | An app that can play media files and record sound by passing commands as strings. | API | Windows 3.0 | Windows Me | — |
| Windows Media Player | Digital media player app | Media player | Windows 3.0 Multimedia Extensions | Windows 10 | Windows Media Player, Movies & TV, or Groove Music |
| Microsoft Calendar | Calendaring app | Personal organizer | Windows 1.0 | Windows 3.1 | Windows Calendar, Windows Live Mail, or the Calendar app for Windows |
| Microsoft Diagnostics | Tool that provides detailed technical information about user’s software and hardware | Diagnostics | MS-DOS | Plus! 95 for Windows 95 | Microsoft System Information |
| Microsoft Fax | Faxing app | Fax | Windows 95 | Windows XP | Windows Fax and Scan |
| Microsoft Private Folder | Tool to protect private data | Personal organizer | Windows XP | Windows XP | |
| Windows Help | Documentation browser that used a proprietary format | Online help | Windows 3.0 | Windows XP | Microsoft Help |
| Windows Feedback | Windows 10 Version 1507 | Windows 10 Version 1511 | Feedback Hub | ||
| NTBackup | Built-in backup app | Backup | Downloadable for Windows NT 4.0 | Windows XP, Windows Server 2003 | Backup and Restore, Windows Server Backup |
| Outlook Express | E-mail client | Internet Explorer 4 | Windows XP | Windows Mail or Windows Live Mail | |
| Paint | Simple graphics painting app | Application | Windows 1.0 | — | — |
| Program Manager | Shell composed of a task-oriented graphical user interface, consisting of icons (shortcuts for apps) arranged into app groups. | GUI | Windows 3.0 | Windows XP | Windows Explorer |
| Purble Place | Educational game for children, teaching pattern recognition, shapes, and colors | Game | Windows Vista | Windows 7 | — |
| Reader | e-book reader | e-book reader | Windows 8 | Windows 10 Creators Update | Microsoft Edge (PDF), XPS Viewer (XPS), Photos (TIFF)[26] |
| Reversi | Version of Reversi. | Game | Windows 1.0 | Windows 3.0 | Internet Reversi only on Windows Me and Windows XP |
| Solitaire | Klondike Solitaire game | Game | Windows 3.0 | Windows 7 | Microsoft Solitaire Collection |
| Spider Solitaire | Spider Solitaire game | Game | Microsoft Plus! 98 | Windows 7 | Microsoft Solitaire Collection |
| System File Checker | Utility that allows users to scan for and restore corruptions in Windows system files | Security | Windows 98 | Windows Server 2003 | Windows Resource Protection |
| Tinker | Puzzle game in which the player controls a robot through various mazes and obstacle courses | Game | Windows Vista | Windows Vista | — |
| Video for Windows | Multimedia framework | API | Windows 3.1 | Windows 95 | DirectShow |
| Windows Address Book | List of contacts that can be shared by multiple apps | Contact manager | Internet Explorer 3 | Windows XP | Windows Contacts, People, or Windows Live Mail |
| Windows Desktop Gadgets | Widget engine for Microsoft Gadgets | User interface | Windows Vista | Windows 7 | Live tiles |
| Windows File Protection | Sub-system in the operating system, aims to prevent apps from replacing critical Windows system files. | Security | Windows Me as System File Protection | Windows XP | Windows Resource Protection |
| Windows Journal | Notetaking application that allows for the creation of handwritten notes | Accessories | Windows XP Tablet PC Edition | Windows 10 Threshold 2 | General improvements in Ink API |
| Windows Messaging | E-mail client | Windows 95 | Windows 95 | Internet Mail and News, Windows Mail, or Windows Live Mail | |
| Windows Messenger | Instant messaging client | Internet messaging | Windows XP | Windows XP, Windows Server 2003 | Windows Live Messenger or Skype |
| Windows Movie Maker | Non-linear video editing software | Video | Windows Me | Windows Vista | Windows Live Movie Maker or Microsoft Photos |
| Windows NetMeeting | Video conferencing client | Web conference | Windows 95 OSR2 | Windows XP | Windows Meeting Space |
| Windows Photo Gallery | Image organizer | Photo | Windows Vista | Windows Vista | Windows Live Photo Gallery or Microsoft Photos |
| Windows Picture and Fax Viewer | Image viewer | Photo | Windows XP | Windows XP | Windows Photo Gallery, Windows Fax and Scan, Windows Live Photo Gallery, Windows Photo Viewer, or Microsoft Photos |
| Windows Write | Simple word processor | Word processor | Windows 1.0 | Windows NT 3.51 | WordPad |
APIs[edit]
- ClearType
- Media Foundation
- Windows Driver Foundation
- Windows Imaging Component
- Windows Management Instrumentation
Miscellaneous (to be categorized)[edit]
- ActiveSync
- Compatibility Appraiser collects telemetry information.[27]
- DMRC (Device Metadata Retrieval Client) interfaces to metadata about devices from Windows 7 onwards.[28]
- I/O technologies
- Macro Recorder
- Microsoft Agent
- Prefetcher
- ReadyBoost
- Sync Center
- Text Services Framework
- Universal Audio Architecture
- Windows Color System
- Windows Diagnostic Infrastructure (WDI)[29]
- Windows Mobile Device Center
- Windows Rally
- Windows Registry
- Windows Speech Recognition
- XML Paper Specification
See also[edit]
- Outline of Microsoft
- List of Unix daemons
- List of games included with Windows
References[edit]
- ^ Shultz, Greg (February 28, 2015). «Control Panel and Settings: Why are both still UI options in Windows 10?». TechRepublic. Retrieved October 7, 2022.
- ^ «Get $Windows Camera from the Microsoft Store». apps.microsoft.com. Retrieved October 7, 2022.
- ^ «Xbox Support». support.xbox.com. Retrieved October 7, 2022.
- ^ Hoffman, Chris. «How to See FPS in Any Windows 10 Game (Without Extra Software)». How-To Geek. Retrieved October 7, 2022.
- ^ The Xbox Game Bar Team (May 22, 2019). «Introducing the New Xbox Game Bar». Xbox Wire. Microsoft. Archived from the original on September 21, 2019. Retrieved August 21, 2019.
- ^ «System Services». technet.microsoft.com. Microsoft. 2014. Archived from the original on November 5, 2017. Retrieved September 2, 2014.
The Application Experience service (AELookupSvc) is a part of the Application Compatibility Administrator. It processes application compatibility lookup requests for applications as they are started, provides support for Windows Server 2008 and Windows Vista–based computers running apps in compatibility mode, reports on compatibility issues, and automatically applies software updates to apps.
- ^ «Description of the Microsoft Computer Browser Service». Microsoft. Archived from the original on January 1, 2015. Retrieved November 3, 2017.
- ^ a b Mackie, Kurt (August 16, 2016). «Microsoft Clarifies Windows 10 ‘Delivery Optimization’«. Redmond Magazine. 1105 Enterprise Computing Group. Archived from the original on February 13, 2020. Retrieved January 27, 2018.
- ^ Hachman, Mark (March 29, 2017). «How Delivery Optimization in Windows 10 Creators Update helps avoid data overage fees». PCWorld. IDG. Archived from the original on August 25, 2017. Retrieved January 27, 2018.
- ^ Halfin, Dani; Poggemeyer, Liza; Lich, Brian; Kieselbach, Oliver; Childs, Andrew (April 30, 2018). «Configure Delivery Optimization for Windows 10 updates». docs.microsoft.com. Microsoft. Archived from the original on July 23, 2018. Retrieved July 23, 2018.
- ^ «Distributed Link Tracking on Windows-based domain controllers». Microsoft. Archived from the original on February 25, 2015. Retrieved October 28, 2008.
- ^ «Distributed Transaction Coordinator (MSDTC)». Microsoft. Archived from the original on September 10, 2016. Retrieved June 27, 2008.
- ^ «Event Log». Microsoft. Archived from the original on September 10, 2016. Retrieved June 27, 2008.
- ^ «What is Indexing Service?». Microsoft. Archived from the original on January 1, 2011. Retrieved June 27, 2008.
- ^ «Windows 2000 Professional and Server Service Pack 4 Services Configuration by Black Viper» Archived December 17, 2019, at the Wayback Machine, notice that the service is listed on this page. Retrieved April 2013
- ^ «Windows Firewall» Archived February 13, 2020, at the Wayback Machine. Retrieved April 2013
- ^ «Secondary Logon (Run As): Starting Programs and Tools in Local Administrative Context». Microsoft Corporation. Archived from the original on March 6, 2015. Retrieved October 28, 2008.
- ^ «System Event Notification Service». The Elder Geek. Archived from the original on October 26, 2008. Retrieved June 27, 2008.
- ^ «Myth Busted: Why Disabling SuperFetch on Vista and Windows 7 Is a Bad Idea», retrieved April 2013
- ^ «What Is Volume Shadow Copy Service?: Data Recovery». Microsoft Corporation. Archived from the original on August 26, 2017. Retrieved October 28, 2008.
- ^ «Windows Firewall/Internet Connection Sharing (ICS)» Archived September 10, 2016, at the Wayback Machine, Retrieved April 2013
- ^ «Windows 2000 Professional and Server Service Pack 4 Services Configuration by Black Viper» Archived December 17, 2019, at the Wayback Machine, Notice the absence of the service on this page. Retrieved April 2013
- ^ «Windows Firewall/Internet Connection Sharing (ICS)» Archived February 13, 2020, at the Wayback Machine, Notice that XP is the operating system listed. Retrieved April 2013
- ^ «How Windows Time Service Works: Windows Time Service». Microsoft Corporation. Archived from the original on April 22, 2016. Retrieved October 28, 2008.
- ^ Minasi, Mark; Layfield, Rhonda; Justice, Lisa (2006). Mastering Windows Server 2003: upgrade edition for SP1 and R2 (12 ed.). John Wiley & Sons. p. 56. ISBN 978-0-470-05645-5. Archived from the original on September 21, 2019. Retrieved July 21, 2010.
There is also a client piece for WebDAV built into XP, 2003, R2, and Vista, called the WebClient Service.
- ^ «Microsoft replaces standalone PDF reader app with Edge». MSPoweruser. November 26, 2017. Archived from the original on August 19, 2019. Retrieved August 19, 2019.
- ^ Leonhard, Woody (April 20, 2015). «KB 2952664 triggers daily telemetry run in Windows 7 — and may be snooping on users: Microsoft bills the ‘compatibility update’ as way to ease the upgrade process to Windows 10 — but it’s collecting data daily». Operating Systems. InfoWorld. InfoWorld, Inc. Archived from the original on June 2, 2017. Retrieved August 23, 2016.
The Microsoft Compatibility Appraiser task runs %windir%system32rundll32.exe appraiser.dll,DoScheduledTelemetryRun with the description ‘Collects program telemetry information if opted-in to the Microsoft Customer Experience Improvement Program.’
- ^ Compare: Tulloch, Mitch; Northrup, Tony; Honeycutt, Jerry; Wilson, Ed (2010). Windows 7 Resource Kit. Windows 7 Resource Kit, Microsoft Corporation. Vol. 1. Microsoft Press. p. 708. ISBN 9780735627000. Archived from the original on January 11, 2022. Retrieved August 18, 2016.
The DMRC [(Device Metadata Retrieval Client)] checks the computer’s local metadata cache and metadata store for metadata that applies to the device.
- ^ Solomon, David A.; Russinovich, Mark E.; Ionescu, Alex (June 17, 2009). Windows Internals. Developer Reference (5 ed.). Microsoft Press (published 2009). ISBN 9780735637962. Archived from the original on September 21, 2019. Retrieved October 24, 2016.
The Windows Diagnostic Infrastructure (WDI) helps to detect, diagnose, and resolve common problem scenarios with minimal user intervention.
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
(Redirected from Windows Time)
The following is a list of Microsoft Windows components.
Configuration and maintenance[edit]
| Component | Description | Introduced |
|---|---|---|
| Settings | Allows users to change system settings, similar to the Control Panel, but has less options[1] | Windows 8 |
| Control Panel | ||
| Control Panel | Allows users to view and change basic system settings and controls, such as adding hardware, adding and removing software, controlling user accounts, and changing accessibility options | Windows 1.0 |
| Device Manager | Allows the user to display and control the hardware attached to the computer, and control what device drivers are used | Windows 95 |
| Windows Mobility Center | Centralizes the most relevant information related to mobile computing | Windows Vista |
| Security and Maintenance | Centralizes and reports on the status of anti-virus, Automatic Updates, Windows Firewall, and other security-related components of the operating system | Windows XP SP2 |
| Administrative Tools | ||
| Microsoft Management Console | Provides system administrators and advanced users with a flexible interface through which they may configure and monitor the system | Windows NT 4.0 Option Pack |
| Windows System Assessment Tool | Built-in benchmarking tool that analyzes the different subsystems (graphics, memory, etc.), and uses the results to allow for comparison to other Windows Vista systems, and for software optimizations. It rates the computer’s performance using the Windows Experience Index. | Windows Vista |
| System Restore | Allows for the rolling back of system files, registry keys, installed apps, etc., to a previous state in the event of a system failure | Windows Me |
| Windows Recovery Environment | Helps diagnose and recover from serious errors which may prevent Windows from booting successfully, or restore the computer to a previous state using System Restore or a backup image | Windows Vista |
| Microsoft Drive Optimizer | Rearranges files stored on a hard disk to occupy contiguous storage locations in order to optimize computer performance | Windows 95, Windows 2000 |
| Event Viewer | Lets administrators and users view the event logs on a local or remote machine | Windows NT 3.1 |
| Resource Monitor (previously Reliability and Performance Monitor) |
Lets administrators view current system reliability and performance trends over time | Windows Vista |
| Logical Disk Manager | Logical volume manager developed by Microsoft in conjunction with Veritas Software | Windows NT 4.0 (Separate Tool), Windows 2000 |
| Registry Editor | Allows users to browse and edit the Windows registry | Windows 3.1 |
| Task Scheduler | Allows users to script tasks for running during scheduled intervals | Microsoft Plus! for Windows 95 |
| Software installation and deployment | ||
| Windows Update | An online service providing updates such as service packs, critical updates and device drivers. A variation called Microsoft Update also provides software updates for other Microsoft products. | Windows 98 |
| Windows Installer | An engine for the management of software installation. Includes a GUI framework, automatic generation of the uninstallation sequence and deployment capabilities for corporate networks. | Windows 2000 |
| ClickOnce | Technology for deploying .NET Framework-based software via web pages, with automatic update capabilities. Intended for per-user only applications. | .NET Framework 2.0 |
User interface[edit]
| Component | Description | Introduced |
|---|---|---|
| Action Center | View notifications sent from apps and change common settings | Windows 10 Version 1507 |
| Command Prompt | Text-based shell (command line interpreter) that provides a command line interface to the operating system | Windows NT 3.1 |
| Windows PowerShell | Command-line shell and scripting framework. | Windows XP |
| Windows Shell | The most visible and recognizable aspect of Microsoft Windows. The shell provides the container inside of which the entire graphical user interface is presented, including the taskbar, the desktop, Windows Explorer, as well as many of the dialog boxes and interface controls. In Windows Vista, a new compositing glass-like user interface called Windows Aero has been shown. | Windows 95 |
| File Explorer (previously Windows Explorer) |
Provides an interface for accessing the file systems, launching applications, and performing common tasks such as viewing and printing pictures | Windows 95 |
| Windows Search | Starting with Windows Vista, search is a tightly shell-integrated component of Windows. A downloadable Windows Desktop Search software is available for Windows XP and older versions. | Windows Vista, downloadable for older versions |
| Search Folders | Virtual folders that retrieve items based on queries rather than hierarchical folder trees on disk. | Windows Vista |
| Special Folders | Folders which are presented to the user through an interface as an abstract concept, instead of an absolute path. This makes it possible for an application to locate where certain kinds of files can be found, regardless of what version or language of operating system is being used. See also Windows Shell namespace. | Windows 95 |
| Start menu | Serves as the central launching point for applications. It provides a customizable, nested list of apps for the user to launch, as well as a list of most recently opened documents, a way to find files and get help, and access to the system settings. By default, the Start Button is visible at all times in the lower left-hand corner of the screen. | Windows 95 |
| Taskbar | The application desktop bar which is used to launch and monitor applications | Windows 95 |
| Task View | Displays all open windows and activities (via timeline) at a glance and switch between virtual desktops, starting in version 2004, users can now rename desktops | Windows 10 Version 1507 |
| File associations | Used to open a file with the appropriate app. Users can assign file associations uniquely to specific actions, known as verbs. | Windows 1.0 |
Applications and utilities[edit]
| Component | Description | Introduced |
|---|---|---|
| Easy Transfer | Used to transfer many files at once from one computer to another | Windows Vista |
| Contacts | Keeps a single list of contacts that can be shared by multiple apps | Windows Vista |
| Camera | Allows the user to take pictures or record video[2] | Windows 8 |
| Calculator | Calculation application | Windows 1.0 |
| Calendar | Calendaring application | Windows Vista |
| Character Map | Utility to view and search characters in a font, copy them to the clipboard and view their Windows Alt keycodes and Unicode names | Windows 3.1 |
| Cortana | Digital personal assistant | Windows 10 Version 1507 |
| Edge | Web browser | Windows 10 Version 1507 |
| Feedback Hub | Platform for exchanging communication with Windows Insiders and developers | Windows 10 Version 1607 |
| Groove Music (previously Xbox Music) |
Digital media player and media library application that is used for playing audio. In addition to being a media player, Groove includes the ability to copy music to compact discs, synchronize content with a digital audio player (MP3 player) or other mobile devices, and let users purchase or rent music from the Windows Store. | Windows 8 |
| Movies & TV (previously Xbox Video) |
Digital media player and media library application that is used for playing video. In addition to being a media player, Movies & TV lets users purchase or rent movies and TV episodes from the Windows Store. | Windows 8 |
| OneDrive (previously SkyDrive) |
Freemium cloud storage folder and sync service | Windows 8 |
| OneNote | Integrated note-taking app, based on the Microsoft Office product of the same name | Windows 8 |
| On-Screen Keyboard (osk.exe) | Virtual keyboard | |
| Paint 3D | Simple graphics painting app | Windows 10 Version 1703 |
| Photos | Simple image viewer | Windows 8 |
| Steps Recorder (called Problem Steps Recorder in Windows 7) |
Utility that allows the user to capture steps they took to reproduce a problem | Windows 7 |
| Windows To Go | Utility to create bootable versions of Windows 8 and above | Windows 8 |
| Notepad | Simple text editor | Windows 1.0 |
| Narrator | Screen reader utility that reads dialog boxes and window controls in a number of the more basic applications for Windows | Windows 2000 |
| Sound Recorder | Simple audio recording app that can record from a microphone or headset, and save the results in WAVE format and Windows Media Audio format in some Windows versions | Windows 3.0 Multimedia Extensions |
| Skype | Messaging and calling service | Windows 8.1, downloadable for previous versions |
| Sticky Notes | Tool for jotting notes on the desktop | Windows XP Tablet PC Edition |
| WordPad | Simple word processor that is more advanced than Notepad. It has facilities to format and print text, but lacks intermediate features such as a spell checker and thesaurus. | Windows 95 |
| Private Character Editor | Utility to create private use characters as defined under Unicode and various East Asian encoding schemes | Windows 3.1 East Asian editions |
| Remote Desktop Connection | Client implementation of the Remote Desktop Protocol; allows a user to securely connect to a computer running Terminal Services (Remote Desktop on Windows XP and Server 2003) and interact with a full desktop environment on that machine, including support for remoting of printers, audio, and drives. | Windows XP, downloadable for previous Windows versions |
| Remote Assistance | Allows a user to temporarily take over a remote computer over a network or the internet to offer help with and resolve issues | Windows XP |
| Mobility Center | Allows a user to adjust settings related to mobile computing | Windows Vista |
| Speech Recognition | Allows a user to input voice commands | Windows Vista |
| IExpress | Allows users to create self-extracting, self-installing INF installation-based packages | Internet Explorer 6 |
| Xbox Console Companion (previously Xbox and Xbox Games) |
Account manager for Xbox Live user accounts and a screen recording tool | Windows 8 |
| Xbox Game Bar | Provides a overlay for compatible games allowing for screen capture, chatting over the Xbox network, showing the frame rate of games, and playing music via Spotify[3][4] | Windows 10 May 2019 Update (Version 1903)[5] |
| Magnifier | Screen enlargement app | Windows 98 |
| Fax and Scan | Integrated faxing and image scanning application | Windows Vista, older faxing and scanning applications were present in previous Windows versions |
| Photo Viewer | Simple image viewer that can play a simple slideshow | Windows 7 |
| Email aggregator | Windows 8 | |
| Maps | Map viewer that allows users to look for locations, plan routes, and store offline maps | Windows 8 |
| Media Center | Designed to serve as a home-entertainment hub, to be viewed from a distance up to 3 meters (~10 feet) and controlled by specially designed remote controls. Lets users browse and view pictures, videos, and music from local hard drives, optical drives, and network locations, along with viewing, recording and deferred-playing live TV. Features an interactive TV guide with scheduled recording capabilities. Can also be used for visualization of other information (like sports scores) within the interface. | Windows XP Media Center Edition |
| Task Manager | Provides information about computer performance and displays details about running applications, processes, network activity, logged-in users, and system services | Windows 3.0 |
| Disk Cleanup | Utility for compacting rarely used files and removing files that are no longer required | Windows 98 |
| Snipping Tool | Screen-capture tool that allows for taking screenshots (called snips) | Experience Pack for Windows XP Tablet PC Edition 2005 |
| Microsoft Store (previously Windows Store) |
Initially known as Windows Store, it started as an app store for Windows 8. In Windows 10, it expanded into a broad digital distribution platform for apps, games, music, digital video and e-books. In 2017, it was renamed Microsoft Store and started offering hardware in United States, Canada and United Kingdom. | Windows 8 |
| MSN apps | Provide information from MSN web services | Windows 8 |
| Alarms & Clock(pre Alarms) | App that allows Windows users to set alarms, stopwatches, timers, and view a world clock | Windows 8 |
| Windows Security (previously Windows Defender Security Center) |
Antivirus | Windows 10 Version 1703 |
| Solitaire Collection | Set of solitaire card games | Windows 10 Version 1507, downloadable for Windows 8.x |
Windows Server components[edit]
| Component | Description | Supported by |
|---|---|---|
| Active Directory | A set of technologies introduced with Windows 2000 that allows administrators to assign enterprise-wide policies, deploy apps to many computers, and apply critical updates to an entire organization. Active Directory stores information and settings relating to an organization in a central, organized, accessible database. Networks can vary from a small installation with a few objects, to global-scale directories with millions of objects. Related topics: Domain controller, Flexible single master operation |
Windows 2000 and later server versions |
| Group Policy | Provides centralized management of user and computer settings in an Active Directory environment. Group policy can control a target object’s registry, NTFS security, audit and security policy, software installation, logon/logoff scripts, folder redirection, and Internet Explorer settings. Policy settings are stored in Group Policy Objects (GPOs), and may be linked to one or more sites, domains or organizational units. Related topics: Administrative Templates |
Windows 2000 and later |
| Internet Information Services | Web server | Windows NT family |
File systems[edit]
| Component | Description | Supported by |
|---|---|---|
| FAT12, FAT16 | The original file systems used with MS-DOS. The standard file systems used with Windows 1.0 through Windows 95. | All versions |
| FAT32 | Extensions to FAT supporting larger disk sizes. The standard file system for Windows 98 and Me. | Windows 95 OSR2 and later versions |
| NTFS | Standard file system of Windows NT; supports security via access control lists, as well as file system journaling and file-system metadata. Windows 2000 added support for reparse points (making NTFS junction points and Single instance storage possible), Hard links, file compression, and Sparse files. Encryption of data is provided by Encrypting File System. Symbolic links and transactioning of file operations via Transactional NTFS are features new to Windows Vista.
Although Windows 9x operating systems cannot read or write NTFS formatted disks, they can access the data over a network if it is shared by a computer running Windows NT. |
Windows NT (all versions) |
| ISO 9660 (CDFS) | The predominant file system for CD-ROM and DVD-ROM media. Windows includes support for Joliet extensions and the ISO 9660:1999 standard. ISO 9660:1999 is supported since Windows XP. | MS-DOS and Windows 9x via extensions, such as MSCDEX.EXE (Microsoft CDROM Extension), natively in Windows NT |
| Universal Disk Format (UDF) | A file system for storing files on optical media. It is an implementation of the ISO/IEC 13346 standard (also known as ECMA-167). It is considered to be a replacement of ISO 9660. Successive versions of Windows have supported newer versions of UDF. | Windows 98, Windows 2000, Windows XP, Windows Server 2003, Windows Vista |
| HPFS | High-Performance File system, used on OS/2 computers. Read and write capability in Windows 95 (where it also listed network computer NTFS-formatted drives as «HPFS», even though it had no direct NTFS capabilities). HPFS write support was dropped in Windows NT 4.0 and Windows 98, and dropped altogether shortly before the release of Windows 2000. | Windows 95 (Read/write), Windows 98, Windows NT (read), 3.1/3.51 (read/write/boot) |
| ReFS | A newer file system, based on NTFS. This system adds built-in integrity checking and removes the need for chkdsk, among other features. The maximum partition size is 1 YB. | Windows Server 2012, Windows 8.1 |
Core components[edit]
| Component | Acronym | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Windows kernel (Windows NT)
Main article: Architecture of the Windows NT operating system line |
||
| Ntoskrnl.exe | The Windows kernel image. Provides the kernel and executive layers of the kernel architecture, and is responsible for services such as hardware virtualization, process and memory management, etc. | |
| hal.dll | HAL | Provides and handles the interaction between software and hardware via the Hardware Abstraction Layer. |
| kernel32.dll | This application provides kernel operations to apps in the Win32 mode, like memory management, I/Os, process creation, etc. | |
| Core processes (Windows NT) | ||
| System idle process | SIP | A counter which measures how much idle capacity the CPU has at any given time. The process runs in the background and monitors processing bandwidth, occupied memory and the Windows virtual paging file. |
| Session Manager Subsystem | SMSS | Performs several critical boot-time operations, such as the creation of environment variables, starting CSRSS, and performing file-copy operations that were queued up from before the system was booted (pending file rename operations). During system operation, it handles Windows File Protection and the creation of logon sessions via Winlogon. |
| Client/Server Runtime Subsystem | CSRSS | User-mode side of the Win32 subsystem. Provides the capability for applications to use the Windows API. |
| Local Security Authority Subsystem Service | LSASS | Responsible for enforcing the security policy on the system. Verifies users logging on to the computer and creates security tokens. |
| Winlogon | Responsible for handling the secure attention key, loading the user profile on logon, and optionally locking the computer when a screensaver is running. On Windows NT systems prior to Windows Vista, Winlogon is also responsible for loading GINA libraries which are responsible collecting logon credentials from the user. | |
| Svchost.exe | A generic host process name for services that run from dynamic-link libraries (DLLs). Several Svchost processes are typically present on a Windows machine, each running in a different security context, depending on what privileges the contained services require. | |
| Windows on Windows and WOW64 | WoW | An abstraction layer that allows legacy code to operate on more modern versions of Windows; typically this means running 16-bit Windows applications on 32-bit Windows, and 32-bit applications on 64-bit Windows. |
| Virtual DOS machine | NTVDM | Allows MS-DOS apps to run on Intel 80386 or higher computers when there is already another operating system running and controlling the hardware. Introduced in Windows 2.1; not available in any 64-bit edition of Windows. |
| System startup (Windows NT)
Main articles: Windows NT Startup Process and Windows Vista Startup Process |
||
| NTLDR, IA64ldr, Winload | The boot loader; performs basic system initialization options such as loading the hardware abstraction layer and boot-time device drivers, prior to passing control to the Windows kernel. In versions prior to Vista, NTLDR and IA64ldr also display menus to the user if multiple operating systems are defined in boot.ini, or if F8 is pressed. | |
| Recovery Console | Provides the means for administrators to perform a limited range of tasks using a command line interface, primarily to aid in recovering from situations where Windows does not boot successfully. | |
| ntdetect.com | Used during the boot process to detect basic hardware components that may be required during the boot process | |
| Windows Boot Manager | In Windows Vista and later operating systems, displays boot menus to the user if multiple operating systems are configured in the system’s Boot Configuration Data. | |
| Graphical subsystem | ||
| Desktop Window Manager | DWM | The compositing manager introduced in Windows Vista that handles compositing and manages special effects on screen objects in a graphical user interface |
| Graphics Device Interface | GDI/GDI+ | The kernel graphics component for representing graphical objects and transmitting them to output devices such as monitors and printers |
| Windows USER | The Windows USER component provides core user interface, messaging and visual elements |
Services[edit]
This list is not all-inclusive.
| Display name | Service key name | Description | Introduced |
|---|---|---|---|
| Active Directory Service | NTDS | Network Authentication Management | Windows 2000 Server |
| Alerter service | Alerter | Sends administrative alerts over the network to client computers, administrators and users | Windows NT |
| Application Layer Gateway service |
ALG | Provides support for plugins that allow network protocols to pass through Windows Firewall and work behind Internet Connection Sharing | Windows 2000 |
| Application Experience service | Processes application compatibility cache requests for applications as they launch[6] | ||
| Application Management | AppMgmt | Processes requests to enumerate, install, and remove applications that are installed on the computer or deployed through an organization’s network | Windows 2000 |
| Background Intelligent Transfer Service |
BITS | Transfers files between machines using idle network bandwidth. Used by Windows Update, Windows Server Update Services, and Systems Management Server to deliver software updates to clients, as well as by Windows Messenger. | Windows XP |
| Computer Browser | Browser | Crawls neighboring computers on the network and locates shared resources. One of the computers acts as the Master Browser and supplies this information to other computers designated as browsers.[7] | Windows for Workgroups |
| Delivery Optimization | DoSvc | A peer-to-peer distribution service that downloads Windows updates and Microsoft Store apps from the local network or Internet peers, and redistributes them to others. Can be configured using either the Settings app or Group Policy. The Settings app can turn it on or off, and specify whether the service operates on the local network only, downloads from and uploads to the Internet peers as well. Group Policy allows finer control.[8][9] Delivery Optimization relies on a centralized web service that does not index contents under 10 MB. Computers without Internet access cannot use Delivery Optimization.[10] | Windows 10 Anniversary Update[8] |
| Distributed Link Tracking | TrkWks, TrkSrv | Used to track links to files on NTFS volumes. Windows uses these services to find linked files if they are renamed or moved (locally or to another machine).[11] | Windows 2000 |
| Distributed Transaction Coordinator |
MSDTC | Allows transactional components to be configured through COM+ by coordinating transactions that are distributed across multiple computers and/or resource managers, such as databases, message queues, file systems, and other transaction–based resource managers.[12] | Windows 2000 and later NT-based |
| DNS Client | DNSCache | Resolves and caches domain names (e.g. “en.wikipedia.org”) to IP addresses | Windows 2000 |
| Event Log | EventLog | Stores and retrieves events that can be viewed in the event viewer. Part of services.exe.[13] | Windows NT |
| Extensible Authentication Protocol | EAPHost | Provides EAP authentication to connecting clients | Windows 2000 |
| Indexing Service | CISVC | Indexes contents and properties of files on local and remote computers; provides rapid access to files through flexible querying language.[14] | Windows 2000 and later NT-based |
| Interactive Services Detection | UI0Detect | For compatibility; when a service-displayed user interface is detected, it gives the user an option to switch to Session0 to see it | Windows Vista |
| Internet Connection Sharing (ICS) | SharedAccess | When enabled, it allows other computers on the local network to access an internet connection that is available to the host computer | Windows 2000;[15] Windows Vista onward[16] |
| Network Location Awareness | NLA | Manages network configurations and information, and notifies applications of changes | Windows XP |
| Network Store Interface Service | NSIS | Collects routing information of active network interfaces, shares this with other services and notifies applications of changes | Windows XP |
| NTLM Security Support Provider | NTLMSSP | Uses the NTLM MS-CHAP protocol to encapsulate and negotiate options in order to provide signed and sealed communication. Deprecated now in favor of Kerberos authentication. | Windows NT |
| Peer Name Resolution Protocol | PNRPSvc | Resolves domain names using Peer Name Resolution Protocol | Windows XP |
| Plug and Play | PlugPlay | Enables autodetection and configuration of hardware | Windows 2000 |
| Windows Print spooler [fr] | Spooler | Manages printer devices and moves files into memory for printing | Windows 95, Windows NT |
| Remote Procedure Call (RPC) | RpcSs | Provides Remote Procedure Call features via remotely accessible Named Pipes | Windows NT family |
| Routing and Remote Access Service | RRAS | API and server software that enables applications to administer the routing and remote-access service capabilities of the operating system, to function as a network router. | Windows 2000 |
| Secondary Logon | SecLogon | Allows users to run apps with a different account than the one they logged in with. Allows non-administrative accounts to perform administrative tasks.[17] | |
| Security Accounts Manager | SamSs | Manages user account security information | Windows NT family |
| System Event Notification Service | SENS | Monitors system events, such as network, power, logon, logoff, terminal services session connection and disconnection, and delivers these to applications and other system components.[18] | Windows 2000 |
| Superfetch | SysMain | Monitors file usage patterns and boosts system speed by caching frequently accessed files to RAM[19] | Windows Vista |
| Task Scheduler | Schedule | Lets users setup and schedule automated tasks | Microsoft Plus! for Windows 95 |
| TCP/IP NetBIOS Helper | LmHosts | Enables support for NetBIOS over TCP/IP (NetBT) service and NetBIOS name resolution | Windows NT family |
| Volume Shadow Copy | VSS | Creates multiple versions of files that change. The ability to store persistent snapshots was added in Windows Server 2003.[20] | Windows XP |
| Windows Audio | AudioSrv | Manages audio devices for Windows-based apps. Controls all audio functions. | Windows XP |
| Windows Error Reporting | WERSvc | Generates error logs and reports errors. On Windows Vista and later, it notifies of solutions. | Windows XP |
| Windows Firewall | MpsSvc | Blocks unauthorized network connections to and from the computer | Windows Vista |
| Windows Firewall(née Internet Connection Sharing) | SharedAccess | Provides a simple firewall feature which was introduced in Windows XP. It also shares the internet on the local network, if the internet connection sharing feature is turned on.[21] | Windows XP only[22][23] |
| Windows Image Acquisition (WIA) | STISvc | Handles scanner and camera inputs | Windows Me |
| Windows Time | W32Time | Synchronizes the system time with external time servers. From Windows Server 2003 forward, full and compliant NTP support is provided.[24] | Windows 2000 |
| Windows Update | WUAUServ | Provides updates for the operating system and its installed components | Windows XP |
| Wireless Zero Configuration | WZCSvc (XP), WLANSvc | Configures and manages 802.11 wireless adapters | Windows XP, Server 2003 only |
| Windows Messenger service | Messenger | Allows users to send pop-up messages to other computers over the network | Windows NT family |
| WebClient[25] | Enables Windows-based apps to create and interact with Internet-based files | Windows XP |
DirectX[edit]
- Direct3D
- DirectDraw
- DirectInput
- DirectMusic
- DirectPlay
- DirectShow
- DirectSound
- DirectX Media Objects
- DirectX plugin
- DirectX Video Acceleration
Networking[edit]
- Administrative share
- Distributed File System
- My Network Places (formerly Network Neighborhood)
- Network Access Protection
- Remote Installation Services
- Server Message Block
- Windows Rights Management Services
Scripting and command-line[edit]
- Batch file
- CHKDSK
- Cmd.exe
- ComSpec
- Ipconfig
- Net / Net Send
- Netdom.exe: Windows Domain Manager
- Netsh
- Netstat
- QBasic
- Regsvr32
- Robocopy
- Win32 console
- Windows Script Host
- Windows PowerShell
- XCOPY
Kernel[edit]
- Commit charge
- Kernel Transaction Manager
- Win32 Thread Information Block
.NET Framework[edit]
- Assembly
- CLI Languages
- Metadata
- .NET Remoting
- ADO.NET
- ASP.NET
- Base Class Library
- Common Intermediate Language
- Common Language Infrastructure
- Common Language Runtime
- Common Type System
- Virtual Execution System
- Windows CardSpace
- Windows Communication Foundation
- Windows Forms
- Windows Presentation Foundation
- Windows Workflow Foundation
Security[edit]
| Component | Description | Introduced |
|---|---|---|
| AppLocker | Policy-based component that enables or disables execution of software based on rules such as location, properties and digital signature | Windows 7 Professional, Enterprise and Ultimate editions Windows Server 2008 R2 |
| BitLocker Drive Encryption | Disk encryption software, designed to protect data by providing encryption for entire volumes | Windows Vista Enterprise and Ultimate editions, Windows Server 2008 |
| Credential Guard | Virtualization-based isolation of stored credentials to prevent theft and pass-the-hash attacks. | Windows 10 Enterprise, Education, IoT Enterprise, or , Windows Server 2016 |
| Data Execution Prevention | Security feature that is intended to prevent an application or service from executing code from a non-executable memory region | Windows XP Service Pack 2 |
| Encrypting File System | File system driver that provides file system-level encryption | Windows 2000 |
| Security Account Manager | Database stored as a registry file | Windows NT 3.1 |
| SYSKEY | Utility that encrypts the hashed password information in a SAM database using a 128-bit encryption key | Windows NT 4.0 Service Pack 3 |
| User Account Control | Technology and security infrastructure utility that aims to improve the security of Microsoft Windows by limiting application software to standard user privileges until an administrator authorizes an increase | Windows Vista, Windows Server 2008 |
| Windows Firewall | Utility designed to block unauthorized access while permitting authorized communications. An earlier edition known as Internet Connection Firewall that was disabled by default was included with the original Windows XP release. | Windows XP Service Pack 2 |
| Windows Defender | Security utility to prevent, remove and quarantine malware (viruses, Trojan horses, etc.) | Downloadable for Windows XP and Windows Server 2003 |
| Windows Resource Protection | Protects Registry keys and folders in addition to critical system files | Windows Vista |
Deprecated components and apps[edit]
| Component | Description | Category | Introduced | Last OS included | Superseded by |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3D Pinball | Pinball game | Game | Plus! 95 for Windows 95 | Windows XP | — |
| ActiveMovie | Streaming media technology | API | Windows 95 | Windows Me | DirectShow |
| Cardfile | Personal information manager | Personal organizer | Windows 1.0 | Windows Me | Outlook Express, Windows Mail, or Windows Live Mail |
| Chess Titans | Chess game | Game | Windows Vista | Windows 7 | Microsoft Chess |
| DriveSpace | Disk compression utility | Data compression | MS-DOS | Windows Me | — |
| Windows DVD Maker | DVD authoring software | Video | Windows Vista | Windows 7 | — |
| File Manager | File manager app | File manager | Windows 3.0 | Windows Me | Windows Explorer |
| FreeCell | FreeCell game | Game | Win32s | Windows 7 | Microsoft Solitaire Collection |
| Hearts | Version of the Hearts game using Black Lady scoring | Game | Windows for Workgroups 3.11 | Windows 7 | Microsoft Hearts |
| Insider Hub | Windows 10 Version 1507 | Windows 10 Version 1511 | Feedback Hub | ||
| Windows Help and Support | Online and offline reference manual for troubleshooting. | Utility | Windows Me | Windows 8.1 | Microsoft Tips or Get Started |
| HyperTerminal | Communication utility based on a low end version of HyperACCESS | Communication | Windows 95 | Windows XP | — |
| Hold ‘Em | Version of the Texas hold ’em game | Game | Windows Vista | Windows Vista | — |
| Hover! | Video game in a combination of bumper cars and capture the flag | Game | Windows 95 | Windows 95 | — |
| InkBall | Game where the user tries to get colored balls into the correct holes | Game | Windows XP Tablet PC Edition | Windows Vista | — |
| Internet Explorer | Web browser | Web browser and FTP client. See also: Internet Explorer versions, Features, History, Removal, Browser Helper Objects | Microsoft Plus! for Windows 95 | Windows 10 | Microsoft Edge |
| Mahjong Titans | Version of the Mahjong solitaire game | Game | Windows Vista | Windows 7 | Microsoft Mahjong |
| Windows Mail | E-mail client | Windows Vista | Windows Vista | Mail (Windows) | |
| Internet Mail and News | E-mail and news client | Windows 95 | Windows 95 | Outlook Express, Windows Mail, or Windows Live Mail | |
| Minesweeper | Version of the minesweeper game | Game | Microsoft Entertainment Pack, Windows 3.1 | Windows 7 | Microsoft Minesweeper |
| Media Control Interface | An app that can play media files and record sound by passing commands as strings. | API | Windows 3.0 | Windows Me | — |
| Windows Media Player | Digital media player app | Media player | Windows 3.0 Multimedia Extensions | Windows 10 | Windows Media Player, Movies & TV, or Groove Music |
| Microsoft Calendar | Calendaring app | Personal organizer | Windows 1.0 | Windows 3.1 | Windows Calendar, Windows Live Mail, or the Calendar app for Windows |
| Microsoft Diagnostics | Tool that provides detailed technical information about user’s software and hardware | Diagnostics | MS-DOS | Plus! 95 for Windows 95 | Microsoft System Information |
| Microsoft Fax | Faxing app | Fax | Windows 95 | Windows XP | Windows Fax and Scan |
| Microsoft Private Folder | Tool to protect private data | Personal organizer | Windows XP | Windows XP | |
| Windows Help | Documentation browser that used a proprietary format | Online help | Windows 3.0 | Windows XP | Microsoft Help |
| Windows Feedback | Windows 10 Version 1507 | Windows 10 Version 1511 | Feedback Hub | ||
| NTBackup | Built-in backup app | Backup | Downloadable for Windows NT 4.0 | Windows XP, Windows Server 2003 | Backup and Restore, Windows Server Backup |
| Outlook Express | E-mail client | Internet Explorer 4 | Windows XP | Windows Mail or Windows Live Mail | |
| Paint | Simple graphics painting app | Application | Windows 1.0 | — | — |
| Program Manager | Shell composed of a task-oriented graphical user interface, consisting of icons (shortcuts for apps) arranged into app groups. | GUI | Windows 3.0 | Windows XP | Windows Explorer |
| Purble Place | Educational game for children, teaching pattern recognition, shapes, and colors | Game | Windows Vista | Windows 7 | — |
| Reader | e-book reader | e-book reader | Windows 8 | Windows 10 Creators Update | Microsoft Edge (PDF), XPS Viewer (XPS), Photos (TIFF)[26] |
| Reversi | Version of Reversi. | Game | Windows 1.0 | Windows 3.0 | Internet Reversi only on Windows Me and Windows XP |
| Solitaire | Klondike Solitaire game | Game | Windows 3.0 | Windows 7 | Microsoft Solitaire Collection |
| Spider Solitaire | Spider Solitaire game | Game | Microsoft Plus! 98 | Windows 7 | Microsoft Solitaire Collection |
| System File Checker | Utility that allows users to scan for and restore corruptions in Windows system files | Security | Windows 98 | Windows Server 2003 | Windows Resource Protection |
| Tinker | Puzzle game in which the player controls a robot through various mazes and obstacle courses | Game | Windows Vista | Windows Vista | — |
| Video for Windows | Multimedia framework | API | Windows 3.1 | Windows 95 | DirectShow |
| Windows Address Book | List of contacts that can be shared by multiple apps | Contact manager | Internet Explorer 3 | Windows XP | Windows Contacts, People, or Windows Live Mail |
| Windows Desktop Gadgets | Widget engine for Microsoft Gadgets | User interface | Windows Vista | Windows 7 | Live tiles |
| Windows File Protection | Sub-system in the operating system, aims to prevent apps from replacing critical Windows system files. | Security | Windows Me as System File Protection | Windows XP | Windows Resource Protection |
| Windows Journal | Notetaking application that allows for the creation of handwritten notes | Accessories | Windows XP Tablet PC Edition | Windows 10 Threshold 2 | General improvements in Ink API |
| Windows Messaging | E-mail client | Windows 95 | Windows 95 | Internet Mail and News, Windows Mail, or Windows Live Mail | |
| Windows Messenger | Instant messaging client | Internet messaging | Windows XP | Windows XP, Windows Server 2003 | Windows Live Messenger or Skype |
| Windows Movie Maker | Non-linear video editing software | Video | Windows Me | Windows Vista | Windows Live Movie Maker or Microsoft Photos |
| Windows NetMeeting | Video conferencing client | Web conference | Windows 95 OSR2 | Windows XP | Windows Meeting Space |
| Windows Photo Gallery | Image organizer | Photo | Windows Vista | Windows Vista | Windows Live Photo Gallery or Microsoft Photos |
| Windows Picture and Fax Viewer | Image viewer | Photo | Windows XP | Windows XP | Windows Photo Gallery, Windows Fax and Scan, Windows Live Photo Gallery, Windows Photo Viewer, or Microsoft Photos |
| Windows Write | Simple word processor | Word processor | Windows 1.0 | Windows NT 3.51 | WordPad |
APIs[edit]
- ClearType
- Media Foundation
- Windows Driver Foundation
- Windows Imaging Component
- Windows Management Instrumentation
Miscellaneous (to be categorized)[edit]
- ActiveSync
- Compatibility Appraiser collects telemetry information.[27]
- DMRC (Device Metadata Retrieval Client) interfaces to metadata about devices from Windows 7 onwards.[28]
- I/O technologies
- Macro Recorder
- Microsoft Agent
- Prefetcher
- ReadyBoost
- Sync Center
- Text Services Framework
- Universal Audio Architecture
- Windows Color System
- Windows Diagnostic Infrastructure (WDI)[29]
- Windows Mobile Device Center
- Windows Rally
- Windows Registry
- Windows Speech Recognition
- XML Paper Specification
See also[edit]
- Outline of Microsoft
- List of Unix daemons
- List of games included with Windows
References[edit]
- ^ Shultz, Greg (February 28, 2015). «Control Panel and Settings: Why are both still UI options in Windows 10?». TechRepublic. Retrieved October 7, 2022.
- ^ «Get $Windows Camera from the Microsoft Store». apps.microsoft.com. Retrieved October 7, 2022.
- ^ «Xbox Support». support.xbox.com. Retrieved October 7, 2022.
- ^ Hoffman, Chris. «How to See FPS in Any Windows 10 Game (Without Extra Software)». How-To Geek. Retrieved October 7, 2022.
- ^ The Xbox Game Bar Team (May 22, 2019). «Introducing the New Xbox Game Bar». Xbox Wire. Microsoft. Archived from the original on September 21, 2019. Retrieved August 21, 2019.
- ^ «System Services». technet.microsoft.com. Microsoft. 2014. Archived from the original on November 5, 2017. Retrieved September 2, 2014.
The Application Experience service (AELookupSvc) is a part of the Application Compatibility Administrator. It processes application compatibility lookup requests for applications as they are started, provides support for Windows Server 2008 and Windows Vista–based computers running apps in compatibility mode, reports on compatibility issues, and automatically applies software updates to apps.
- ^ «Description of the Microsoft Computer Browser Service». Microsoft. Archived from the original on January 1, 2015. Retrieved November 3, 2017.
- ^ a b Mackie, Kurt (August 16, 2016). «Microsoft Clarifies Windows 10 ‘Delivery Optimization’«. Redmond Magazine. 1105 Enterprise Computing Group. Archived from the original on February 13, 2020. Retrieved January 27, 2018.
- ^ Hachman, Mark (March 29, 2017). «How Delivery Optimization in Windows 10 Creators Update helps avoid data overage fees». PCWorld. IDG. Archived from the original on August 25, 2017. Retrieved January 27, 2018.
- ^ Halfin, Dani; Poggemeyer, Liza; Lich, Brian; Kieselbach, Oliver; Childs, Andrew (April 30, 2018). «Configure Delivery Optimization for Windows 10 updates». docs.microsoft.com. Microsoft. Archived from the original on July 23, 2018. Retrieved July 23, 2018.
- ^ «Distributed Link Tracking on Windows-based domain controllers». Microsoft. Archived from the original on February 25, 2015. Retrieved October 28, 2008.
- ^ «Distributed Transaction Coordinator (MSDTC)». Microsoft. Archived from the original on September 10, 2016. Retrieved June 27, 2008.
- ^ «Event Log». Microsoft. Archived from the original on September 10, 2016. Retrieved June 27, 2008.
- ^ «What is Indexing Service?». Microsoft. Archived from the original on January 1, 2011. Retrieved June 27, 2008.
- ^ «Windows 2000 Professional and Server Service Pack 4 Services Configuration by Black Viper» Archived December 17, 2019, at the Wayback Machine, notice that the service is listed on this page. Retrieved April 2013
- ^ «Windows Firewall» Archived February 13, 2020, at the Wayback Machine. Retrieved April 2013
- ^ «Secondary Logon (Run As): Starting Programs and Tools in Local Administrative Context». Microsoft Corporation. Archived from the original on March 6, 2015. Retrieved October 28, 2008.
- ^ «System Event Notification Service». The Elder Geek. Archived from the original on October 26, 2008. Retrieved June 27, 2008.
- ^ «Myth Busted: Why Disabling SuperFetch on Vista and Windows 7 Is a Bad Idea», retrieved April 2013
- ^ «What Is Volume Shadow Copy Service?: Data Recovery». Microsoft Corporation. Archived from the original on August 26, 2017. Retrieved October 28, 2008.
- ^ «Windows Firewall/Internet Connection Sharing (ICS)» Archived September 10, 2016, at the Wayback Machine, Retrieved April 2013
- ^ «Windows 2000 Professional and Server Service Pack 4 Services Configuration by Black Viper» Archived December 17, 2019, at the Wayback Machine, Notice the absence of the service on this page. Retrieved April 2013
- ^ «Windows Firewall/Internet Connection Sharing (ICS)» Archived February 13, 2020, at the Wayback Machine, Notice that XP is the operating system listed. Retrieved April 2013
- ^ «How Windows Time Service Works: Windows Time Service». Microsoft Corporation. Archived from the original on April 22, 2016. Retrieved October 28, 2008.
- ^ Minasi, Mark; Layfield, Rhonda; Justice, Lisa (2006). Mastering Windows Server 2003: upgrade edition for SP1 and R2 (12 ed.). John Wiley & Sons. p. 56. ISBN 978-0-470-05645-5. Archived from the original on September 21, 2019. Retrieved July 21, 2010.
There is also a client piece for WebDAV built into XP, 2003, R2, and Vista, called the WebClient Service.
- ^ «Microsoft replaces standalone PDF reader app with Edge». MSPoweruser. November 26, 2017. Archived from the original on August 19, 2019. Retrieved August 19, 2019.
- ^ Leonhard, Woody (April 20, 2015). «KB 2952664 triggers daily telemetry run in Windows 7 — and may be snooping on users: Microsoft bills the ‘compatibility update’ as way to ease the upgrade process to Windows 10 — but it’s collecting data daily». Operating Systems. InfoWorld. InfoWorld, Inc. Archived from the original on June 2, 2017. Retrieved August 23, 2016.
The Microsoft Compatibility Appraiser task runs %windir%system32rundll32.exe appraiser.dll,DoScheduledTelemetryRun with the description ‘Collects program telemetry information if opted-in to the Microsoft Customer Experience Improvement Program.’
- ^ Compare: Tulloch, Mitch; Northrup, Tony; Honeycutt, Jerry; Wilson, Ed (2010). Windows 7 Resource Kit. Windows 7 Resource Kit, Microsoft Corporation. Vol. 1. Microsoft Press. p. 708. ISBN 9780735627000. Archived from the original on January 11, 2022. Retrieved August 18, 2016.
The DMRC [(Device Metadata Retrieval Client)] checks the computer’s local metadata cache and metadata store for metadata that applies to the device.
- ^ Solomon, David A.; Russinovich, Mark E.; Ionescu, Alex (June 17, 2009). Windows Internals. Developer Reference (5 ed.). Microsoft Press (published 2009). ISBN 9780735637962. Archived from the original on September 21, 2019. Retrieved October 24, 2016.
The Windows Diagnostic Infrastructure (WDI) helps to detect, diagnose, and resolve common problem scenarios with minimal user intervention.
Практическая работа № 1.
Тема: Операционная система. Графический интерфейс пользователя.
Цель: ознакомиться с основными элементами интерфейса Windows, освоить стандартные способы работы с приложениями Windows, а также некоторые общепринятые элементы настройки пользовательского интерфейса.
Ход работы
1. Изучить основные сведения.
2. Выполнить задания, описывая каждый пункт в тетради.
3. Ответить на контрольные вопросы.
1. Изучите основные сведения.
Краткие теоретические сведения
Операционные системы семейства Windows – это графические операционные системы для компьютеров платформы IBM PC. Ее основные средства управления – графический манипулятор мышь и клавиатура.
Интерфейс Windows является оконным, точнее, многооконным. Windows в переводе с английского означает «окна».
Окном называется ограниченный фрагмент экрана прямоугольной формы, в котором находятся элементы управления.
Основные элементы графического интерфейса Windows:
- кнопка (button)
- значок, иконка (icon)
- список (list box)
- раскрывающийся список (combo box, drop-down list)
- метка (label)
- поле редактирования (textbox, edit field)
- меню (menu)
- главное меню (main menu или menu bar)
- контекстное меню (popup menu)
- ниспадающее меню (pull down menu)
- окно (window)
- диалоговое окно (dialog box)
- модальное окно (modal window)
- панель (panel)
- вкладка (tab)
- панель инструментов (toolbar)
- полоса прокрутки (scrollbar)
- ползунок (slider)
- строка состояния (status bar)
- всплывающая подсказка (tooltip, hint)
В Windows большую часть команд можно выполнять с помощью мыши. С мышью связан активный элемент управления – указатель мыши. При перемещении мыши по плоской поверхности указатель перемещается по Рабочему столу, и его можно позиционировать на значках объектов или на пассивных элементах управления приложений.
Общепринятое обозначение:
- ПКМ – правая кнопка мыши
- ЛКМ – левая кнопка мыши
Стартовый экран Windows представляет собой системный объект, называемый Рабочим столом.
Рабочий стол – это графическая среда, на которой отображаются объекты Windows и элементы управления Windows. Рабочий стол – элемент интерфейса, который обеспечивает эффективный доступ пользователя ко всем ресурсам компьютера, а также к наиболее часто используемым программам.
В исходном состоянии на Рабочем столе располагаются несколько экранных значков, ярлыков и Панель задач.
Значки – это графическое представление объектов Windows
Ярлыки – это значки (пиктограммы) с маленькими стрелочками в нижнем левом углу.
Значки и ярлыки обеспечивают (с помощью двойного щелчка ЛКМ) быстрый доступ к дискам, папкам, документам, приложениям и устройствам.
Панель задач — один из основных элементов интерфейса, отображающийся на краю рабочего стола и использующийся для быстрого запуска программ или слежения за изменениями уже запущенных программ.
Панель задач имеет вид не широкой полосы с кнопкой для запуска меню Пуск, полем для кнопок запущенных или прикрепленных программ, и системным треем, в котором отображаются значки часов, календаря, динамиков, индикатор ввода (или языковая панель), и всплывающее окошко со значками постоянно работающих программ.
Системный трей (или область состояния, область уведомлений)— это часть пользовательского интерфейса, в которой отображаются значки функций системы и программ, которые отсутствуют на рабочем столе, а также время и значок громкости. По умолчанию он расположен в правом нижнем углу или в нижней части панели задач, если закреплен вертикально. Здесь отображаются часы, и приложения могут отображать значки в область уведомлений, чтобы указывать состояние операции или уведомлять пользователя о событии. Например, приложение может отобразить значок принтера в область состояния, чтобы показать, что задание печати выполняется.
Меню – элемент интерфейса, горизонтальный или вертикальный список альтернативных вариантов команд, из которых пользователь должен выбрать один вариант
Кнопка Пуск позволяет вызывать Главное меню, которое обеспечивает доступ практически ко всем ресурсам системы и содержит команды запуска приложений, настройки системы, поиска файлов и документов, доступа к справочной системе и др.
Главное меню системы Windows (меню Пуск) — меню Windows, запускаемое нажатием кнопки Пуск на панели задач или нажатием клавиши Win на клавиатуре, оно является центральной отправной точкой для запуска программ, а также открытия недавних документов и доступа к свойствам системы.

Контекстное меню — элемент графического интерфейса операционной системы, представляющий собой список команд, вызываемый пользователем для выбора необходимого действия над выбранным объектом. Команды контекстного меню относятся к тому объекту, над которым это меню было вызвано.
Некоторые способы вызова контекстного меню:
- Нажатием правой кнопки мыши (для правшей).
- Специальной клавишей Menu.
- Сочетанием клавиш — Shift+F10 (если специальной клавиши Menu нет на клавиатуре)
Открытие объекта, расположенного па Рабочем столе:
1-й способ: двойной щелчок ЛКМ по значку объекта;
2-й способ: щелчком ПКМ по значку объекта вызвать контекстное меню объекта и ЛКМ выбрать команду Открыть.
При составлении отчета по практическим работам вам часто придется делать снимок экрана – скриншот.
Скриншот (или снимок экрана, скрин) — изображение, полученное устройством и показывающее в точности то, что видит пользователь на экране монитора или другого визуального устройства вывода.
Простейший способ получения снимка экрана для операционных систем Microsoft Windows — использование клавиши Print Screen (для изображения, отображаемого у пользователя на экране) или сочетания клавиш Alt+PrtScr (для текущего активного окна) на клавиатуре.
При этом снимок копируется в буфер обмена операционной системы и может быть затем вставлен в любой документ, а при необходимости отредактирован в любом графическом редакторе.
Как сделать скриншот:
1. Нажмите на клавиатуре кнопку Print Screen (иногда она называется PrntScrn, PrtScn, PrtScr или PrtSc) — в буфер обмена будет скопирован снимок всего экрана;
2. Откройте документ, в который надо поместить скриншот. Если снимок экрана надо сначала отредактировать, то откройте любой из установленных графических редакторов, например, Paint.
3. Нажмите кнопку Вставить в верхнем меню программы. Вы также можете воспользоваться универсальным сочетанием клавиш Ctrl + V
4. Сохраните документ со скриншотом на вашем компьютере, выполнив команду меню Файл → Сохранить как; или нажав кнопку 
2. Выполните задания.
Задание № 1. Загрузка Windows, создание папок и файлов.
1. Включите компьютер, дождитесь окончания загрузки операционной системы.
2. На диске Х: и создайте папку с именем ПР1.
Для этого откройте диск Х:, на свободной поверхности окна диска вызовите контекстное меню и выберите команду Создать—>Папку.
Наберите на клавиатуре имя папки, например ПР1 и нажмите клавишу Enter .
Откройте свою папку. Вы ее только что создали.
3. В папке ПР1 создайте документ Microsoft Word под именем Отчет_ПР1.
Для этого на свободной поверхности внутри папки вызовите контекстное меню и выберите команду Создать —> Документ Microsoft Word, дальше наберите на клавиатуре имя документа (файла), например Отчет_ПР1, и обязательно нажмите клавишу Enter .
4. В папке ПР1 создайте еще один текстовый документ под именем Картинка.
Задание № 2. Элементы Рабочего стола и работа с ними.
1. Рассмотрите значки, расположенные на Рабочем столе.
2. Откройте документ с именем Отчет_ПР1. Обратите внимание: документ пуст; напечатайте названия всех объектов, находящихся на Рабочем столевашего компьютера.
Сохраните изменения в документе, для этого выберите команду меню Файл—>Сохранить.
3. Разместите значки на Рабочем столе, расположив их по своему усмотрению. Для этого наведите указатель мыши на значок, нажмите ЛКМ и, не отпуская её, перетащите значок в нужном направлении.
Сделайте Скриншот экрана и поместите его в документ Отчет_ПР1. Сохраните изменения в документе
4. Выполните обратное действие, выстроив значки автоматически по левому краю Рабочего стола. Для этого вызовите контекстное меню щелчком ПКМ на свободном месте Рабочего стола, выберите команду Вид—>Упорядочить значки автоматически.
Сделайте Скриншот экрана и поместите его в документ Отчет_ПР1. Сохраните изменения в документе
5. Рассмотрите Панель задач. Закройте и откройте Главное меню Windows, используя кнопку Пуск.
Сделайте Скриншот экрана с открытым Главным меню и поместите его в документ Отчет_ПР1. Сохраните изменения в документе
6. Ознакомьтесь с контекстным меню Панели задач, вызвав его щелчком ПКМ по Панели задач. Перетащите Панель задач, разместив ее по вертикали в правой части Рабочего стола. (данное действие можно выполнить только если команда контекстного меню Закрепить панель задач не активирована – не стоит флаг (галочка) перед командой).
Сделайте Скриншот экрана и поместите его в документ Отчет_ЛР1. Сохраните изменения в документе
Верните Панель задач на место.
Задание № 3. Удалить и восстановить объекты.
1. Скопируйте документ Картинка из папки ПР1 на Рабочий стол.
2. Удалите документ Картинка с Рабочего стола.
Для этого вызовите контекстное меню (щелчком ПКМ по значку документа) и выберите команду Удалить. В открывшемся Диалоговом окне подтвердите намерения удаления.
3. Восстановите удаленный объект.
Для этого откройте папку Корзина, выделите нужный объект и восстановите его с помощью контекстного меню.
4. Удалите документ Картинка из папки ПР1.
Для этого выделите объект и нажмите комбинацию клавиш Delete + Shift, подтвердите удаление объекта. Попробуйте его восстановить. Возможно ли восстановление? Если нет — почему?
Задание № 4. Используя быстрый поиск объектов, найти объект calc.exe (стандартное приложение Калькулятор).
1. Из Главного меню запустите программу пуска (Пуск —>Найти программы и файлы).
2. В диалоговое окно Что искать введите критерий поиска: calc.exe.
3. Запустите найденное стандартное приложение Калькулятор.
Сделайте Скриншот экрана и поместите его в документ Отчет_ПР1. Сохраните изменения в документе
4. Закройте все окна на Рабочем столе.
3. Ответьте на контрольные вопросы (в тетради).
Контрольные вопросы:
- Операционные системы семейства Windows – это?
- Графический интерфейс пользователя — это?
- Стартовый экран Windows представляет собой …?
- Что такое Рабочий стол?
- Значки — это?
- Чем отличается Значок от Ярлыка?
- Как выделить объект?
- Как открыть Главное меню?
- Как произвести вызов контекстного меню?
- Для чего служат полосы прокруток?
- Как создать папку?
- Как удалить объект?
- Как восстановить объект?
- Как произвести быстрый поиск объектов?
Современный Windows — это операционная
система, управляющая работой персонального
компьютера. Windows имеет удобный графический
пользовательский интерфейс. В отличие от
старой операционной системы DOS с текстовым
интерфейсом, Windows не требует знания команд
операционной системы и их точного ввода с
клавиатуры. Подавляющее большинство
операций по управлению работой
персонального компьютера выполняются
манипулятором мышь над графическими
объектами Windows, либо короткими комбинациями
клавиш (горячими клавишами) на клавиатуре.
Пользовательский интерфейс – это методы и средства взаимодействия человека с аппаратными и программными средствами компьютера.
Стартовый экран Windows представляет собой системный объект, называемый рабочим столом.
Рабочий стол — это графическая среда, на которой
отображаются объекты и элементы управления Windows. На рабочем столе
можно видеть значки (пиктограммы),
ярлыки и панель задач (основной элемент управления).
При запуске Windows на рабочем столе присутствуют, как минимум , три
значка:
Мой компьютер, Сетевое окружение, Корзина.
На рабочем столе могут быть расположены и другие значки. Его можно
использовать и как временное хранилище своих файлов, но по окончании
работы в учебном классе они должны быть либо удалены, либо перемещены в
собственные папки.
Значки являются графическим изображением объектов и позволяют управлять ими.
Значок — это графическое представление объекта в свернутом виде,
соответствующее папке, программе, документу, сетевому устройству или
компьютеру.
Значки, как правило имеют метки — надписи, которые располагаются под
ними. Щелчок левой кнопкой мыши по значку позволяет выделить
его, а двойной щелчок – открыть (запустить) соответствующее этому значку
приложение.
Ярлык является указателем на объект. Ярлык – это специальный
файл, в котором содержится ссылка на представленный им объект
(информация о месте расположения объекта на жестком диске). Двойной
щелчок мыши по ярлыку позволяет запустить (открыть) представляемый им
объект. При его удалении сам объект не стирается, в отличие от удаления
значка. Достоинство ярлыков в том, что они обеспечивают быстрый доступ к
объекту из любой папки, не расходуя на это памяти.
Отличить ярлык от значка можно по маленькой
стрелке в левом нижнем углу пиктограммы.
Панель задач является инструментом для переключения между
открытыми папками или приложениями.
В левой части панели задач расположена кнопка «Пуск»; в правой — панель
индикации. На самой панели изображаются все открытые в данный момент
объекты.
Кнопка «Пуск» открывает Главное меню. С его помощью
можно запустить все программы, зарегистрированные в операционной
системе, получить доступ ко всем средствам настройки
операционной системы, к поисковой и справочной системам и другим
функциям.
Центральным понятием Windows является окно. Окно – структурный
и управляющий элемент пользовательского интерфейса, представляющий
собой ограниченную рамкой прямоугольную область экрана, в которой может
отображаться приложение, документ или сообщение.
Выше на рисунке показан рабочий стол Windows
с открытым Главным меню, окном текстового
процессора Word, значками и ярлыками и
некоторыми свернутыми на панели задач
документами.
Из других понятий Windows следует отметить
понятия каталога и папки.
Каталог – поименованная группа файлов, объединенных по какому-либо признаку.
Папка – понятие, которое используется в Windows вместо понятия
каталог в более ранних операционных системах. Понятие папка имеет
расширенное толкование, так как наряду с обычными каталогами папки
представляют и такие объекты, как Мой компьютер, Проводник, Принтер,
Модем и др.
Структура окна папки
Типовое окно папки показано на рисунке.
Окно содержит следующие обязательные элементы.
- Строка заголовка — в ней написано название папки. Служит для перетаскивания окна.
- Системный значок. Открывает служебное меню, с помощью которого можно управлять размером и расположением окна.
- Кнопки управления размером:
разворачивающая (восстанавливающая), сворачивающая, закрывающая. - Строка меню (ниспадающее меню). Гарантированно предоставляет доступ ко всем командам данного окна.
- Панель инструментов. Содержит командные кнопки для
выполнения наиболее часто встречающихся операций. Часто пользователь
может сам настраивать эту панель размещая на ней необходимые кнопки. - Адресная строка. В ней указан путь доступа к текущей папке. Позволяет быстро перейти к другим разделам файловой структуры.
- Рабочая область. Отображает значки объектов, хранящихся в папке, причем способом отображения можно управлять.
- Полосы прокрутки – позволяют прокручивать содержимое окна в горизонтальном или вертикальном направлении если информация не умещается в окне.
- Строка состояния. Выводит дополнительную информацию об объектах в окне.
Файловая система персонального
компьютера
Файловая система обеспечивает хранение и доступ к файлам на диске.
Принцип организации файловой системы — табличный. Поверхность диска
рассматривается как трехмерная матрица, измерениями которой являются
номера поверхности, цилиндра и сектора. Под
цилиндром подразумевается совокупность всех дорожек,
принадлежащих разным поверхностям и равноудаленных от оси вращения.
Данные о том, в каком месте записан тот или иной файл, хранятся в
системной области диска в специальной таблице размещения файлов
(FAT-таблица). FAT-таблица хранится в двух экземплярах, идентичность которых контролируется операционной системой.
ОС MS-DOS, OS/2, Windows-95/NT реализуют 16-разрядные поля в
FAT-таблицах. Такая система
называлась FAT-16. Такая система позволяет разместить не более 65536
записей о местоположении единиц хранения данных. Наименьшей единицей
хранения данных является
сектор. Размер сектора равен 512 байтам. Группы секторов условно объединяют в
кластеры, которые являются наименьшей единицей адресации к
данным. Размер кластера зависит от емкости диска:
в Fat-16 для дисков от 1 до 2 Гбайт 1 кластер занимает 64 сектора или 32
Кбайта. Это нерационально, поскольку даже маленький файл занимает 1
кластер. У больших файлов, занимающих несколько кластеров, в конце
образуется незаполненный кластер. Поэтому потери емкости для дисков в
системе FAT-16 могут быть очень велики. С дисками свыше 2,1 Гбайт FAT-16
вообще не работает.
В Windows 98 и старших версиях реализована более совершенная файловая
система — FAT-32 с 32-разрядными полями в таблице размещения файлов.
Она обеспечивает маленький размер кластера для дисков большой емкости.
Например, для диска до 8 Гбайт 1 кластер занимает 8 секторов (4 Кбайта).
Файл — это именованная последовательность байтов произвольной
длины. До появления Windows-95 общепринятой схемой именования файлов
была схема 8.3 (короткое имя)
– 8 символов собственно имя файла, 3 символа – расширение его имени.
Недостаток коротких имен — их низкая содержательность. Начиная с
Windows-95 введено понятие длинного имени (до 256 символов). Оно может
содержать любые символы, кроме девяти специальных: / : * ? » < >
|.
Расширением имени считаются все символы после последней
точки. В современных
операционных ситемах расширение имени несет для системы важную
информацию о типе файла. Типы файлов регистрируются и связывают файл с
открывающей его программой. Например файл MyText.doc будет открыт
текстовым процессором Word, поскольку расширение .doc обычно связывается
именно с этим приложением. Обычно, если файл не связан ни с какой
открывающей программой, то на его значке обозначен флаг
— логотип Microsoft Windows, а открывающую программу пользователь может
указать сам, выбрав ее из предоставленного ОС списка.
Логически структура файлов организована по иерархическому принципу:
папки более низких уровней вкладываются в папки более высоких уровней.
Верхним уровнем вложенности является корневой каталог диска. Термины
«папка» и «каталог» равнозначны. Каждому каталогу файлов на диске
соответствует одноименная папка операционной системы. Однако, понятие
папки несколько шире. Так в Windows-95 существуют специальные папки,
осуществляющие удобный доступ к программам, но которым не соответствует
ни один каталог диска.
Атрибуты файлов — это параметры, определяющие некоторые
свойства файлов. Для получения доступа к атрибутам файла, следует
щелкнуть правой кнопкой мыши по его значку и выбрать меню Свойства.
Основных атрибутов 4: «Только для чтения», «Скрытый», «Системный»,
Архивный». Атрибут «Только для чтения» предполагает, что файл не
предназначен для внесения изменений. Атрибут «Скрытый» говорит о том,
что данный файл не следует отображать на экране при проведении файловых
операций. Атрибутом «Системный» помечаются наиболее важные файлы ОС (как
правило они имеют и атрибут «Скрытый»). Атрибут «Архивный» связан с
резервным копированием файлов и особого значения не имеет.
Операции с файлами и папками
Копирование и перемещение
1 способ. Разместить на рабочем столе два окна: источник и
приемник копирования. Выделить в окне-источнике необходимые значки.
Несколько значков выделяются при нажатой клавише Ctrl. Перетащить мышью
выделенные значки в окно-приемник, указав на любой из выделенных
значков. При одновременно нажатой клавише Ctrl происходит копирование,
без нее — перемещение элементов (при условии, что папки находятся на
одном диске).
2 способ. Выделить копируемые элементы. Выбрать меню
Правка/Копировать (Вырезать). При выборе «Вырезать» произойдет
перемещение. Открыть папку-приемник. Выбрать меню Правка/Вставить.
Удаление файлов и папок
Удаление файлов выполняется выбором элементов и нажатием клавиши
Delete. При этом отмеченные элементы перемещаются в специальную папку —
Корзину. При очистке корзины происходит уничтожение файлов. Существует
еще операция стирания файлов, когда специальными служебными программами
кластеры, в которых содержались стираемые файлы, заполняются случайными
данными.
Групповые операции с файлами
Если требуется выполнить операцию копирования или удаления с большим
количеством файлов одновременно, то выделять их удерживая Ctrl не очень
удобно. Можно выделить целую группу подряд идущих значков, щелкнув по
первому их них и при нажатой клавише Shift — по последнему. Однако, в
этом случае требуется определенным образом упорядочить значки. Для этого
следует открыть папку с файлами и обратиться к меню Вид/Упорядочить
значки. Существует 4 способа упорядочивания значков в папке: по имени,
по типу, по размеру, по дате. Например, необходимо скопировать все
файлы с расширением .txt. В этом случае следует упорядочить значки по
типу, после чего все файлы типа .txt будут сгруппированы вместе и
использовать клавишу Shift для их выделения. Аналогичный прием
применяется для выделения «старых» файлов (упорядочение по дате),
«маленьких» (упорядочение по размеру) и в других стандартных ситуациях.
Если в окне не показана полная информация о файлах (расширение, объем
и дата создания), следует обратиться к меню окна папки Вид/Таблица и в
окне будут выведены все характеристики файлов.
Переименование файлов и папок.
Переименование файла или папки выполняется либо через меню
Переименовать, вызываемого щелчком правой кнопки мыши на соответствующем
значке, либо щелчком по имени выделенного значка.
Замечание. Удаление или переименование невозможно, если указанный файл уже открыт каким-либо приложением.
Работа с буфером обмена
ОС Windows создает и обслуживает специальную область памяти,
называемую буфером обмена. Буфер обмена служит для обмена данными между
приложениями Windows. Описанный выше второй способ копирования
предполагает использование буфера обмена.
В меню Правка для операций с буфером обмена используются пункты
Копировать, Вырезать и Вставить. Первые два помещают в буфер обмена
объект, последний — копирует из буфера обмена. Если объект (часть
текста, рисунок и т.д.) не выделен, то первые два пункта будут не
активны. Если буфер обмена пуст, то не будет активен и третий пункт.
Операции с буфером обмена выполняются очень часто, поэтому на панель инструментов окна помещаются кнопки быстрого доступа.
Самый быстрый способ работы с буфером обмена — использование
комбинаций клавиш: Ctrl+C — копировать; Ctrl+X — вырезать; Ctrl + V —
вставить.

Контрольные вопросы
- Что такое пользовательский интерфейс
Windows? - Перечислите основные элементы пользовательского интерфейса. Каково их назначение?
- Что представляет собой объект Windows Рабочий стол?
- Что такое панель задач? Для чего она предназначена?
- Что такое значок и каково его назначение?
- Что такое ярлык? Каково его назначение? В чем его отличие от значка?
- Какие операции с соответствующим объектом позволяют выполнять значок и ярлык? Как они выполняются?
- Что собой представляет объект Мой компьютер? Каковы его возможности?
- Каково назначение кнопки Пуск?
- Как получить доступ к Главному меню Windows? Какие возможности предоставляет Главное меню?
- Какова структура окна папки? Каково назначение элементов этого окна?
- Каково назначение файловой системы?
- Каков принцип организации файловой системы?
- Что такое таблица размещения файлов (FAT)? Для чего она предназначена? Охарактеризуйте способы реализации
FAT. - Что такое сектор?
- Что представляет собой кластер? От чего зависит его размер?
Сравните 16-разрядную и 32-разрядную FAT. - Что называется файлом?
- Как записывается короткое имя файла? Каков недостаток такой записи?
- По каким правилам записывается длинное имя файла?
- Что такое расширение имени файла? Как оно используется ОС?
- Опишите логическую структуру файла.
- Какие свойства задают атрибуты файлов? Как получить к ним доступ?
- Перечислите основные операции с файлами и папками и опишите способы их реализации.
- Что называется буфером обмена? Для чего он используется?
- Как получить доступ к буферу обмена? Какие команды меню предназначены для работы с буфером? Опишите их.
- Каков самый быстрый способ работы с буфером обмена?