

Данная статья представляет краткий обзор всех версий операционной системы Windows.
Версия Вашей системы: Windows 7
Версии для настольных компьютеров
| Логотип | Версия | Год | Статус |
|---|---|---|---|
 |
Windows 1 | 1985 | Не поддерживается Не используется |
 |
Windows 2 | 1987 | |
 |
Windows 3 | 1990 | |
 |
Windows NT 3.1 | 1993 | |
 |
Windows NT 3.5 Workstation | 1994 | |
 |
Windows NT 3.51 | 1995 | |
 |
Windows 95 | 1995 | |
 |
Windows NT 4.0 | 1996 | |
 |
Windows 98 | 1998 | |
 |
Windows Millenium | 2000 | |
 |
Windows 2000 (NT 5.0) | 2000 | |
 |
Windows XP (NT 5.1) | 2001 | Не поддерживается Встречается редко |
 |
Windows Vista (NT 6.0) | 2006 | Не поддерживается Почти, не используется |
 |
Windows 7 (NT 6.1) | 2009 | Не поддерживается Пока используется |
 |
Windows 8 (NT 6.2) | 2012 | Не поддерживается Почти, не используется |
 |
Windows 8.1 (NT 6.3) | 2013 | Поддерживается Почти, не используется |
 |
Windows 10 (NT 10) | 2015 | Поддерживается Активно используется |
 |
Windows 11 (NT 10) | 2021 | Поддерживается Начинает применяться |
Серверные Windows
| Логотип | Версия | Год | Статус |
|---|---|---|---|
 |
Windows NT 3.1 Advanced Server | 1993 | Не поддерживается Как правило, не используется |
 |
Windows NT 3.5 Server | 1994 | |
 |
Windows NT 3.51 Server | 1995 | |
 |
Windows NT 4.0 Server | 1996 | |
 |
Windows 2000 Server | 2000 | |
 |
Windows Server 2003 | 2003 | |
 |
Windows Server 2003 R2 | 2005 | |
 |
Windows Server 2008 | 2008 | |
 |
Windows Server 2008 R2 | 2009 | Не поддерживается Пока еще используется |
 |
Windows Server 2012 | 2012 | Поддерживается Активно используется |
 |
Windows Server 2012 R2 | 2013 | |
 |
Windows Server 2016 | 2016 | |
 |
Windows Server 2019 | 2018 | |
 |
Windows Server 2022 | 2021 | Начало использования |
Все версии Windows по линейкам + хронология
| Линейка | Годы | Перечисление версий |
|---|---|---|
| 16 бит | 1985 — 1995 | Windows 1 / 2 / 3 |
| 32 бита (9x) |
1995 — 2001 | Windows 95 / 98 / ME |
| NT (32 и 64 бита) |
с 1993 | Windows NT 3.1 / NT 3.5 / NT 3.51 / NT 4.0 Workstation / 2000 / XP / Vista / 7 / 8 / 8.1 / 10 |
| NT Servers (32 и 64 бита) |
с 1993 | Windows NT 3.1 / NT 3.5 / NT 3.51 / NT 4.0 Server / 2000 Server / 2003 / 2003 R2 / 2008 / 2008 R2 / 2012 / 2012 R2 / 2016 / 2019 / 2022 |
История успеха
Данная история успеха отражает частоту использования системы; количество глюков, с которыми столкнулись пользователи; отзывы.
 |
Windows 1 | Неудача |
 |
Windows 2 | Нейтрально |
 |
Windows 3 | Успех |
 |
Windows 95 | Неудача |
 |
Windows 98 | Успех |
 |
Windows Millenium | Провал |
 |
Windows 2000 | Нейтрально |
 |
Windows XP | Большой успех |
 |
Windows Vista | Провал |
 |
Windows 7 | Успех |
 |
Windows 8 | Провал |
 |
Windows 8.1 | Неудача |
 |
Windows 10 | Успех |
 |
Windows 11 | Нейтрально |
* несмотря на провал некоторых версий операционной системы, они несли новые функции, которые перешли в уже успешные версии. Например, в миллениум появились красивые иконки и окна, которые перешли в Windows 2000. Поэтому провал не стоит оценивать, как неудачную работу.
 Windows 1
Windows 1
Годы поддержки: 1985 — 2001. Ветка: 16 бит.
Издания: —
Что нового
До Windows 1 был MS-DOS, поэтому самое главное новшество — графический интерфейс и возможность управления при помощи мыши.
Системные требования
| Процессор | 8088 |
|---|---|
| Оперативная память | 256 Кбайт |
| Объем жесткого диска | 3 Мб |
 Windows 2
Windows 2
Годы поддержки: 1989 — 2001. Ветка: 16 бит.
Издания: —
Что нового
- Возможность использования сочетания клавиш.
- Появились перекрывающиеся окна.
- Возможность увеличить и уменьшить окно.
Системные требования
| Процессор | 8088 |
|---|---|
| Оперативная память | 256 Кбайт |
| Объем жесткого диска | 3 Мб |
 Windows 3
Windows 3
Годы поддержки: 1990 — 2008. Ветка: 16 бит.
Издания: —
Что нового
- Первый (от Microsoft) удобный для пользователя интерфейс.
- Появление диспетчера программ.
- Появление мультимедийных возможностей.
- Поддержка сети (с 3.1).
Системные требования
| Минимальные | Рекомендуемые | |
|---|---|---|
| Процессор | 8086/8088 | 80486DX 33 МГц |
| Оперативная память | 640 Кбайт | 4 Мб |
| Объем жесткого диска | 6,5 Мб | 60 Мб |
 Windows NT 3.1
Windows NT 3.1
Годы поддержки: 1993 — 2001. Ветка: NT. Разрядность: 16, 32 и 64 бита.
Издания: —
Что нового
- Первая система на базе ядра NT.
- Поддержка файловой системы NTFS.
Системные требования
| Процессор | Intel 80386 |
|---|---|
| Оперативная память | 2 Мб |
| Объем жесткого диска | 8 Мб |
 Windows NT 3.5 Workstation
Windows NT 3.5 Workstation
Годы поддержки: 1994 — 2001. Ветка: NT. Разрядность: 16, 32 и 64 бита.
Издания: —
Что нового
- Встроенная поддержка Winsock и TCP/IP.
- Появление сервера и клиента DHCP и WINS.
- Предоставление общего доступа к файлам и принтерам.
- Поддержка VFAT.
Системные требования
| Процессор | 33 МГц |
|---|---|
| Оперативная память | 12 Мб |
| Объем жесткого диска | 70 Мб |
 Windows NT 3.51 Workstation
Windows NT 3.51 Workstation
Годы поддержки: 1995 — 2001. Ветка: NT. Разрядность: 16, 32 и 64 бита.
Издания: —
Системные требования
| Процессор | 33 МГц |
|---|---|
| Оперативная память | 12 Мб |
| Объем жесткого диска | 70 Мб |
 Windows 95
Windows 95
Годы поддержки: 1995 — 2001. Ветка: 9x (32 бита).
Системные требования
| Минимальные | Рекомендуемые | |
|---|---|---|
| Процессор | 80386 DX | Pentium |
| Оперативная память | 4 Мб | 8 Мб |
| Объем жесткого диска | 50 Мб | 100 Мб |
 Windows NT 4.0 Workstation
Windows NT 4.0 Workstation
Годы поддержки: 1996 — 2004. Ветка: NT. Разрядность: 32 и 64 бита.
Издания: —
Системные требования
| Минимальные | Рекомендуемые | |
|---|---|---|
| Процессор | 486/25 | 486DX2/50 |
| Оперативная память | 12 Мб | 24 Мб |
| Объем жесткого диска | 128 Мб | 1 Гб |
 Windows 98
Windows 98
Годы поддержки: 1998 — 2006. Ветка: 9x (32 бита).
Системные требования
| Минимальные | Рекомендуемые | |
|---|---|---|
| Процессор | 486DX 66 МГц | Pentium |
| Оперативная память | 16 Мб | 24 Мб |
| Объем жесткого диска | 200 Мб | 500 Мб |
 Windows Millenium
Windows Millenium
Годы поддержки: 2000 — 2006. Ветка: 9x (32 бита).
Системные требования
| Минимальные | Рекомендуемые | |
|---|---|---|
| Процессор | 150 МГц | 300 МГц |
| Оперативная память | 32 Мб | 128 Мб |
| Объем жесткого диска | 200 Мб | 500 Мб |
 Windows 2000
Windows 2000
Годы поддержки: 2000 — 2010. Ветка: NT.
Системные требования
| Минимальные | Рекомендуемые | |
|---|---|---|
| Процессор | 133 МГц | 1 ГГц |
| Оперативная память | 32 Мб | 128 Мб |
| Объем жесткого диска | 2 Гб | 20 Гб |
 Windows XP
Windows XP
Годы поддержки: 2000 — 2010. Ветка: NT. Разрядность: 32 и 64 бита.
Редакции: XP, XP Professional
Системные требования
| Минимальные | Рекомендуемые | |
|---|---|---|
| Процессор | 233 МГц | 300 МГц |
| Оперативная память | 64 Мб | 128 Мб |
| Объем жесткого диска | 1,5 Гб | от 1,5 Гб |
 Windows Vista
Windows Vista
Годы поддержки: 2006 — 2017. Ветка: NT. Разрядность: 32 и 64 бита.
Издания: Начальная (Starter), Домашняя базовая (Basic), Домашняя расширенная (Premium), Бизнес (Business), Корпоративная (Enterprise), Максимальная (Ultimate)
Системные требования
| Минимальные | Рекомендуемые | |
|---|---|---|
| Процессор | 800 МГц | 1 ГГц |
| Оперативная память | 512 Мб | 1 Гб |
| Объем жесткого диска | 20 Гб | 40 Гб |
 Windows 7
Windows 7
Годы поддержки: 2009 — 2020. Ветка: NT. Разрядность: 32 и 64 бита.
Издания: Начальная (Starter), Домашняя базовая (Home Basic), Домашняя расширенная (Home Premium), Профессиональная (Professional), Корпоративная (Enterprise), Максимальная (Ultimate)
Системные требования
| Минимальные | Рекомендуемые | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Архитектура | 32-бит | 64-бит | 32-бит | 64-бит |
| Процессор | 1 ГГц | |||
| Оперативная память | 1 Гб | 2 Гб | 4 Гб | |
| Объем жесткого диска | 16 Гб | 20 Гб | 16 Гб | 20 Гб |
 Windows 8
Windows 8
Годы поддержки: 2012 — 2016. Ветка: NT. Разрядность: 32 и 64 бита.
Издания: 8, 8 Профессиональная (Pro), 8 Корпоративная (Enterprise)
Системные требования
| Минимальные | Рекомендуемые | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Архитектура | 32-бит | 64-бит | 32-бит | 64-бит |
| Процессор | 1 ГГц | |||
| Оперативная память | 1 Гб | 2 Гб | 4 Гб | |
| Объем жесткого диска | 16 Гб | 20 Гб | 16 Гб | 20 Гб |
 Windows 8.1
Windows 8.1
Годы поддержки: 2013 — 2023. Ветка: NT. Разрядность: 32 и 64 бита.
Издания: 8, 8 Профессиональная (Pro), 8 Корпоративная (Enterprise)
Системные требования
| Минимальные | Рекомендуемые | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Архитектура | 32-бит | 64-бит | 32-бит | 64-бит |
| Процессор | 1 ГГц | |||
| Оперативная память | 1 Гб | 2 Гб | 4 Гб | |
| Объем жесткого диска | 16 Гб | 20 Гб | 16 Гб | 20 Гб |
 Windows 10
Windows 10
Годы поддержки: 2015 — 2025. Ветка: NT. Разрядность: 32 и 64 бита.
Издания
- Домашняя (Home). Для большинства домашних компьютеров. Нет возможности настроить удаленный рабочий стол для того, чтобы к систему можно было подключиться удаленно; нет возможности использования групповых политик и присоединения к домену.
- Профессиональная (Pro). Содержит все функции домашней версии + возможность присоединения к домену, использования групповых политик, возможность подключения к компьютеру с использованием удаленного рабочего стола.
- Корпоративная (Enterprise). Урезаны некоторые функции домашней версии. Есть все дополнительные функции версии Pro + DirectAccess, AppLocker.
- S. Является урезанной версией; предустановлена на некоторые устройства. Не поддерживает стандартную установку приложений — возможна установка только из магазина Windows.
Что нового
Windows 10 претерпевает сильные изменения с выходом новых билдов. Поэтому нововведения будем рассматривать исходя из этого.
Билд 1507 (ноябрь 2015):
- Улучшенная производительность.
- Новый встроенный браузер Microsoft Edge.
- Автоматическое сжимание соседнего окна, при прижимании активного окна в одной из сторон рабочего стола.
- «Все приложения» в «Пуск» поддерживают отображение в 2048 элементов (раньше только 512).
- Принудительная установка обновлений.
- Использование виртуального голосового помощника Кортана.
- Обновленный меню пуск — представляет из себя гибрид предыдущих версий и Windows 8 (вернулся старый вариант раскрытия, а в правой части появились плитки).
- Возможность создания нескольких рабочих столов.
- Отказ от плиточной системы Windows 8.
1607 (август 2016):
- Возможность рукописного ввода (Windows Ink).
- Идентификация с помощью веб-камеры.
- Синхронизация с мобильного устройства уведомлений.
- Изменение меню параметров системы.
1703 (апрель 2017):
- Встроенная поддержка шлемов виртуальной реальности.
- Игровой режим
- По умолчанию предлагается командная строка в Powershell.
- Доступ к классической панели управления скрыт из контекстного меню. Теперь его можно вызвать командой control.
- Улучшение работы встроенного антивируса.
- Идентификация с помощью веб-камеры для Active Directory.
- Возможность создавать скриншот с выделением области с помощью сочетания клавиш Win + Shaft + S.
- Поддержка шрифта Брайля.
- Увеличенное время работы от батареи.
1709 (октябрь 2017):
- Возможность работы Cortana на одном устройстве и окончание работы на другом.
- Отключение протокола SMBv1. Включить можно вручную.
- Появление панели «Люди».
- Информация о GPU в диспетчере задач.
- Полноэкранный режим Microsoft Edge
- Увеличенное время работы от батареи (функция Power Throttling).
- Появление панели эмодзи.
- Выборочная синхронизация OneDrive.
- Исправление проблемы торможения в играх.
1803 (апрель 2018):
- Возможность восстановить пароль с помощью контрольных вопросов.
1809 (октябрь 2018):
- Темная тема для проводника.
- Возможность получения доступа к сообщениям с телефона (функция «Ваш телефон»).
1903 (май 2019):
- Изолированный рабочий стол для безопасного запуска приложений.
1909 (ноябрь 2019):
- Универсальный поиск в Проводнике.
- Улучшение производительности.
2004 (май 2020):
- Функция «Загрузка из облака» для переустановки Windows 10.
- Регулирование пропускной способности для обновлений Windows.
- Отображение температуры видеоядра в Диспетчере задач.
- Возможность удаления Блокнот, Paint, WordPad.
- Возможность использование Windows без пароля.
* данный список содержит часть нововведений. Полный список на странице в Википедии.
Системные требования
| Минимальные | Рекомендуемые | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Архитектура | 32-бит | 64-бит | 32-бит | 64-бит |
| Процессор | 1 ГГц | |||
| Оперативная память | 1 Гб | 2 Гб | 4 Гб | |
| Объем жесткого диска | 16 Гб | 20 Гб | 16 Гб | 20 Гб |
 Windows 11 (последняя для настольных компьютеров)
Windows 11 (последняя для настольных компьютеров)
Годы поддержки: 2021 — 2031. Ветка: NT. Разрядность: только 64 бита.
Основные издания: Домашняя (Home), Профессиональная (Pro), 8 Корпоративная (Enterprise).
Дополнительные издания: для обучения (Education), для облаков (Cloud).
Системные требования
| Процессор | 2 ядра, 1 ГГц |
|---|---|
| Оперативная память | 4 Гб |
| Объем жесткого диска | 64 Гб |
| БИОС (прошивка) | UEFI |
| Видеоадаптер | Совместимый с DirectX 12 / WDDM 2.x |
| Интернет | Для Home необходим вход под учетной записью Microsoft. |
 Windows NT 3.1 Advanced Server
Windows NT 3.1 Advanced Server
Годы поддержки: 1993 — 2001. Ветка: NT. Разрядность: 16, 32 и 64 бита.
Издания: —
Системные требования
| Процессор | Intel 80386 |
|---|---|
| Оперативная память | 2 Мб |
| Объем жесткого диска | 8 Мб |
 Windows NT 3.5 Server
Windows NT 3.5 Server
Годы поддержки: 1994 — 2001. Ветка: NT. Разрядность: 16, 32 и 64 бита.
Издания: —
Что нового
- Встроенная поддержка Winsock и TCP/IP.
- Появление сервера DHCP и WINS.
- Предоставление общего доступа к файлам и принтерам.
- Поддержка VFAT.
Системные требования
| Процессор | 33 МГц |
|---|---|
| Оперативная память | 16 Мб |
| Объем жесткого диска | 70 Мб |
 Windows NT 3.51 Server
Windows NT 3.51 Server
Годы поддержки: 1995 — 2001. Ветка: NT. Разрядность: 16, 32 и 64 бита.
Издания: —
Системные требования
| Процессор | 33 МГц |
|---|---|
| Оперативная память | 16 Мб |
| Объем жесткого диска | 70 Мб |
 Windows NT 4.0 Server
Windows NT 4.0 Server
Годы поддержки: 1996 — 2004. Ветка: NT. Разрядность: 32 и 64 бита.
Издания: Server, Enterprise Edition, Terminal Server
Системные требования
| Минимальные | Рекомендуемые | |
|---|---|---|
| Процессор | 486/25 | 486DX2/50 |
| Оперативная память | 16 Мб | 24 Мб |
| Объем жесткого диска | 128 Мб | 1 Гб |
 Windows 2000 Server
Windows 2000 Server
Годы поддержки: 2000 — 2010. Ветка: NT. Разрядность: 32 и 64 бита.
Издания: Server, Advanced Server и Datacenter Server
Системные требования
| Минимальные | Рекомендуемые | |
|---|---|---|
| Процессор | 133 МГц | 1 ГГц |
| Оперативная память | 32 Мб | 128 Мб |
| Объем жесткого диска | 2 Гб | 20 Гб |
 Windows Server 2003
Windows Server 2003
Годы поддержки: 2003 — 2015. Ветка: NT. Разрядность: 32 и 64 бита.
Издания: Web, Standard, Enterprise, Datacenter
Системные требования
Web, Standard, Enterprise:
| Минимальные | Рекомендуемые | |
|---|---|---|
| Процессор | 133 МГц | 550 МГц |
| Оперативная память | 128 Мб | 256 Мб |
| Объем жесткого диска | 1,5 Гб | 2 Гб |
Datacenter Edition:
| Минимальные | Рекомендуемые | |
|---|---|---|
| Процессор | 400 МГц | 733 МГц |
| Оперативная память | 512 Мб | 1 Гб |
| Объем жесткого диска | 1,5 Гб | 2 Гб |
 Windows Server 2003 R2
Windows Server 2003 R2
Годы поддержки: 2005 — 2015. Ветка: NT. Разрядность: 32 и 64 бита.
Издания: Standard, Enterprise, Datacenter
Системные требования
Standard, Enterprise:
| Минимальные | Рекомендуемые | |
|---|---|---|
| Процессор | 133 МГц | 550 МГц |
| Оперативная память | 128 Мб | 256 Мб |
| Объем жесткого диска | 1,2 Гб | 2 Гб |
Datacenter Edition:
| Минимальные | Рекомендуемые | |
|---|---|---|
| Процессор | 400 МГц | 733 МГц |
| Оперативная память | 512 Мб | 1 Гб |
| Объем жесткого диска | 1,2 Гб | 2 Гб |
 Windows Server 2008
Windows Server 2008
Годы поддержки: 2008 — 2020. Ветка: NT. Разрядность: 32 и 64 бита.
Издания: Web, Standard, Enterprise, Datacenter, HPC, Storage, Itanium
Системные требования
| Минимальные | Рекомендуемые | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Архитектура | 32-бит | 64-бит | 32-бит | 64-бит |
| Процессор | 1 ГГц | 1.4 ГГц | 2 ГГц | |
| Оперативная память | 512 Мб | 2 Гб | ||
| Объем жесткого диска | 10 Гб | 40 Гб |
 Windows Server 2008 R2
Windows Server 2008 R2
Годы поддержки: 2009 — 2020. Ветка: NT. Разрядность: 64 бита.
Издания: Foundation, Small Business, Web, Standard, Enterprise, Datacenter, HPC, Itanium
Системные требования
| Минимальные | Рекомендуемые | |
|---|---|---|
| Процессор | 1.4 ГГц | 2 ГГц |
| Оперативная память | 512 Мб | 2 Гб |
| Объем жесткого диска | 10 Гб | 40 Гб |
 Windows Server 2012
Windows Server 2012
Годы поддержки: 2012 — 2023. Ветка: NT. Разрядность: 64 бита.
Издания: Foundation, Essentials, Standard, Datacenter
Системные требования
| Минимальные | Рекомендуемые | |
|---|---|---|
| Процессор | 1.4 ГГц | 2 ГГц |
| Оперативная память | 2 Гб | 4 Гб |
| Объем жесткого диска | 32 Гб | 60 Гб |
 Windows Server 2012 R2
Windows Server 2012 R2
Годы поддержки: 2013 — 2023. Ветка: NT. Разрядность: 64 бита.
Издания: Foundation, Essentials, Standard, Datacenter
Системные требования
| Минимальные | Рекомендуемые | |
|---|---|---|
| Процессор | 1.4 ГГц | 2 ГГц |
| Оперативная память | 2 Гб | 4 Гб |
| Объем жесткого диска | 32 Гб | 60 Гб |
 Windows Server 2016
Windows Server 2016
Годы поддержки: 2016 — 2026. Ветка: NT. Разрядность: 64 бита.
Издания: Essentials, Standard, Datacenter
Что нового
- Лицензирование на физические ядра процессора (минимум 16).
- Новый режим установки — Nano.
- Появление контейнерной виртуализации.
- OpenGL и OpenCL для RDP.
- Шифрование виртуальных машин и внутреннего сетевого трафика.
- Блочная репликация файловых хранилищ.
Системные требования
| Минимальные | Рекомендуемые | |
|---|---|---|
| Процессор | 1.4 ГГц | 3.1 ГГц |
| Оперативная память | 2 Гб | 4 Гб |
| Объем жесткого диска | 32 Гб | 60 Гб |
Более подробно в обзоре Windows Server 2016.
 Windows Server 2019
Windows Server 2019
Годы поддержки: 2018 — 2029. Ветка: NT. Разрядность: 64 бита.
Издания: Standard, Datacenter
Что нового
- Улучшенная безопасность — встроенные технологии Defender ATP и Defender Exploit Guard.
- Windows Subsystem Linux (WSL) — контейнеры для поддержки приложений Linux.
- Для построения кластера с четным количеством узлов в качестве диска-свидетеля может выступать USB-диск.
Системные требования
| Минимальные | Рекомендуемые | |
|---|---|---|
| Процессор | 1.4 ГГц | 3.1 ГГц |
| Оперативная память | 512 Мб (Nano) 2 Гб (GUI) |
4 Гб |
| Объем жесткого диска | 32 Гб | 60 Гб |
 Windows Server 2022 (последняя для серверов)
Windows Server 2022 (последняя для серверов)
Годы поддержки: 2021 — 2031. Ветка: NT. Разрядность: 64 бита.
Издания: Standard, Datacenter
Что нового
- Улучшенная безопасность.
- Больше возможностей для работы с облаками, особенно, Microsoft Azure.
Системные требования
| Минимальные | Рекомендуемые | |
|---|---|---|
| Процессор | 1.4 ГГц | 3.1 ГГц |
| Оперативная память | 512 Мб (Nano) 2 Гб (GUI) Поддержка ECC |
4 Гб
Поддержка ECC |
| Объем жесткого диска | 32 Гб | 60 Гб |
| Сетевой адаптер | 1 гигабит в секунду |
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Microsoft Windows is the name of several families of computer software operating systems created by Microsoft. Microsoft first introduced an operating environment named Windows in November 1985 as an add-on to MS-DOS in response to the growing interest in graphical user interfaces (GUIs).
All versions of Microsoft Windows are commercial proprietary software.
General information[edit]
Basic general information about Windows.
DOS shells[edit]
| Name | Release date | Latest version | Status support | Codename | OS required | Architecture | Editions | Target market |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Windows 1.0 | 1985-11-20 | 1.04 (1987-04-08) | Unsupported (2001-12-31) |
Interface Manager | DOS 2.0 or higher | 16-bit | Desktops | |
| Windows 2.0 | 1987-09-08 | 2.03 (1987-12-09) | Unsupported (2001-12-31) |
DOS 3.0 or higher | 16-bit | Desktops | ||
| Windows 2.1x | 1988-05-27 | 2.11 (1989-03-13) | Unsupported (2001-12-31) |
DOS 3.0 or higher | 16-bit | Desktops | ||
| Windows 3.0 | 1990-05-22 | 3.0a with Multimedia Extensions (1991-10-20) |
Unsupported (2001-12-31) |
DOS 3.1 or higher | 16-bit | Windows 3.0 Windows 3.0a Windows 3.0a with Multimedia Extensions |
Desktops | |
| Windows 3.1x | 1992-04-06 | 3.11 (1993-12-31) | Unsupported (2001-12-31) |
Janus
|
DOS 3.3 or higher | 16-bit* | Windows 3.1 Windows for Workgroups 3.1 Windows 3.11 Windows for Workgroups 3.11 Windows 3.2 (Simplified Chinese only) |
Desktops |
- * Has partial 32-bit compatibility with Win32s
Windows 9x[edit]
| Name | Release date | RTM build | Latest version | Status support | Codename | MS-DOS version | Kernel type | Architecture | Editions | Target market |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Windows 95 | 1995-07-14 | 950 | 4.00.950C OSR2.5 (1997-11-26) | Unsupported (2001-12-31) |
Chicago | MS-DOS 7.0, MS-DOS 7.1 (OSR2.x) | Monolithic | Hybrid 16/32-bit | Retail, OSR1, OSR2, OSR2.1, OSR2.5 | Desktops |
| Windows 98 | 1998-05-15 | 1998 | 4.10.1998 | Unsupported (2006-07-11) |
Memphis | MS-DOS 7.1 | Monolithic | Hybrid 16/32-bit | Desktops | |
| Windows 98 SE | 1999-05-05 | 2222 | 4.10.2222A (2000-02-25) | Unsupported (2006-07-11) |
MS-DOS 7.1 | Monolithic | Hybrid 16/32-bit | Desktops | ||
| Windows Me | 2000-06-19 | 3000 | 4.90.3000 (2000-09-14) | Unsupported (2006-07-11) |
Millennium | MS-DOS 8.0 | Monolithic | Hybrid 16/32-bit | Desktops |
Windows NT[edit]
| Name | Release date | Version | RTM build | Latest build | Status support | Codename, working name | Supported architectures | Editions | OS type | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Windows NT 3.1 | 1993-07-27 | 3.1 | 528 | 528 (SP3) (1994-11-10) |
Unsupported (2000-12-31)[1] |
New Technology OS/2 | IA-32, DEC Alpha, MIPS |
Workstation, Advanced Server |
Workstation, Server |
|
| Windows NT 3.5 | 1994-09-21 | 3.5 | 807 | 807 (SP3) (1995-06-21) |
Unsupported (2001-12-31) |
Daytona | IA-32, DEC Alpha, MIPS, PowerPC[2] |
Workstation, Server |
Workstation, Server |
|
| Windows NT 3.51 | 1995-05-30 | 3.51 | 1057 | 1057 (SP5) (1996-09-19) |
Unsupported (2001-12-31) |
— | IA-32, DEC Alpha, MIPS, PowerPC |
Workstation, Server |
Workstation, Server |
|
| Windows NT 4.0 | 1996-07-31 | 4.0 | 1381 | 1381 (SP6a) (1999-11-30) |
Unsupported (2004-06-30) |
Cairo/Shell Update Release Hydra (Terminal Server) Impala (Embedded) |
IA-32, DEC Alpha, MIPS, PowerPC |
Workstation, Server, Server Enterprise Edition, Terminal Server, Embedded |
Workstation, Server, Embedded PCs |
|
| Windows 2000 | 1999-12-15 | 5.0 | 2195 | SP4 Rollup 1 v2 (2005-09-13) |
Unsupported (2010-07-13) |
N/A
|
IA-32 | Professional, Server, Advanced Server, Datacenter Server, Powered (Embedded) |
Desktop, Workstation, Server, Embedded PCs |
|
| Windows XP | 2001-08-24 | 5.1 | 2600 | 2600 (SP3) (2008-04-21) |
Unsupported (2014-04-08) |
Whistler | IA-32, IA-64, x86-64 | HomeK, ProfessionalKx64, Media Center, Tablet PC, Starter, Embedded |
Desktop, Workstation, Embedded PCs |
|
| Windows Server 2003 | 2003-04-24 | 5.2 | 3790 | 3790 (SP2) (2007-03-13) |
Unsupported (2015-07-14) |
Whistler Server, Windows.NET Server | IA-32, IA-64, x86-64 | Standard, Enterprise, Datacenter, Web, Storage, Small Business Server, Compute Cluster |
Server, Network Appliance, Embedded PCs, HPC |
|
| Windows Server 2003 R2 | 2005 | 5.2 | 3790 | ? | Unsupported (2015-07-14) |
? | IA-32, x86-64 | Server, Network Appliance, Embedded PCs, HPC |
||
| Windows Fundamentals for Legacy PCs | 2006-07-08 | 5.1 | 2600 | — | Unsupported (2014-04-08) |
Eiger, Mönch | IA-32 | Fundamentals for Legacy PCs | Desktop | |
| Windows Vista | 2006-11-30 | 6.0 | 6000 | 6002 (SP2) (2009-04-28) |
Unsupported (2017-04-11) |
Longhorn | IA-32, x86-64 | Starter, Home BasicK, Home PremiumK, BusinessK, EnterpriseK, UltimateK |
Desktop, Workstation |
|
| Windows Home Server | 2007-11-04 | 5.2 | 3790 | — | Unsupported (2013-01-08) |
Q, Quattro | IA-32, x86-64 | Home Server | Server | |
| Windows Server 2008 | 2008-02-04 | 6.0 | 6001 | 6002 (SP2) (2009-04-28) |
Unsupported (2020-01-14) |
Longhorn Server | IA-32, IA-64, x86-64 | WebCore, StandardCorewHVCwHV, EnterpriseCorewHVCwHV, Small Business Server, DatacenterCorewHVCwHV, HPC, HyperV Core, Foundation, Storage |
Server | |
| Windows 7 | 2009-07-22 | 6.1 | 7600 | 7601 (SP1) (2011-02-22) |
Unsupported (2020-01-14) |
7 | IA-32, x86-64 | StarterK, Home BasicK, Home PremiumK, ProfessionalK, UltimateK, EnterpriseK |
Desktop, Workstation, Multi-touch | |
| Windows Server 2008 R2 | 2009-07-22 | 6.1 | 7600 | 7601 (SP1) (2011-02-22) |
Unsupported (2020-01-14) |
7 Server | IA-64, x86-64 | StandardCore, EnterpriseCore, DatacenterCore, WebCore |
Server | |
| Windows Home Server 2011 | 2011-04-06 | 6.1 | 8400 | — | Unsupported (2016-04-12) |
Vail | x86-64 | Home Server | Server | |
| Windows Server 2012 | 2012-08-01 | 6.2 | 9200 | — | Supported (2023-10-10) |
8 Server | x86-64 | Foundation, Essentials, Standard, Datacenter, Storage Standard, Storage Workgroup |
Server | |
| Windows 8 | 2012-08-01 | 6.2 | 9200 | — | (RTM only) Unsupported (2016-01-12) |
8 | IA-32, x86-64, ARMv7 | Windows 8, Pro, EnterpriseK, Windows RT |
Desktop, Workstation, Multi-touch |
|
| Windows 8.1 | 2013-08-27 | 6.3 | 9600 | — | Unsupported (2023-01-10) |
Blue | IA-32, x86-64, ARMv7 | Windows 8.1, Pro, EnterpriseK, Windows RT 8.1 |
Desktop, Workstation, Multi-touch |
|
| Windows Server 2012 R2 | 2013-10-18 | 6.3 | 9600 | — | Supported (2023-10-10) |
Blue Server | x86-64 | Foundation, Essentials, Standard, Datacenter, Storage Essentials, Storage Standard, Storage Workgroup |
Server | |
| Windows 10 | Original Release | 2015-07-29 | 10.0 | 10240 | — | Unsupported (2017-05-09) |
Threshold | IA-32, x86-64, ARMv7 | Home, Pro, Education, Enterprise |
Desktop, Workstation, Multi-touch |
| Supported (2025-10-14) |
Enterprise LTSB | |||||||||
| November Update | 2015-11-12 | 10586 | — | Unsupported (2017-10-10) |
Threshold 2 | Home, Pro | ||||
| Unsupported (2018-04-10) |
Education, Enterprise | |||||||||
| Anniversary Update | 2016-08-02 | 14393 | — | Unsupported (2018-04-10) |
Redstone | Home, Pro, Pro Education |
||||
| Unsupported (2019-04-09) |
Education, Enterprise | |||||||||
| Supported (2026-10-13) |
Enterprise LTSB | |||||||||
| Creators Update | 2017-04-11 | 15063 | — | Unsupported (2018-10-09) |
Redstone 2 | Home, Pro, Pro Education |
||||
| Unsupported (2019-10-08) |
Education, Enterprise | |||||||||
| Fall Creators Update | 2017-10-17 | 16299 | — | Unsupported (2019-04-09) |
Redstone 3 | IA-32, x86-64, ARMv7, ARM64 | Home, Pro, Pro for Workstations, Pro Education |
|||
| Unsupported (2020-10-13) |
Education, Enterprise | |||||||||
| April 2018 Update | 2018-04-30 | 17134 | — | Unsupported (2019-11-12) |
Redstone 4 | Home, Pro, Pro for Workstations, Pro Education |
||||
| Unsupported (2021-05-11) |
Education, Enterprise | |||||||||
| October 2018 Update | 2018-10-02 | 17763 | — | Unsupported (2020-11-10) |
Redstone 5 | Home, Pro, Pro for Workstations, Pro Education |
||||
| Unsupported (2021-05-11) |
Education, Enterprise | |||||||||
| Supported (2029-01-09) |
Enterprise LTSC | |||||||||
| May 2019 Update | 2019-05-21 | 18362 | — | Unsupported (2020-12-08) |
19H1 | Home, Pro, Pro for Workstations, Pro Education, Education, Enterprise |
||||
| November 2019 Update | 2019-11-12 | 18363 | — | Unsupported (2021-05-11) |
19H2 | Home, Pro, Pro for Workstations, Pro Education |
||||
| Unsupported (2022-05-10) |
Education, Enterprise | |||||||||
| May 2020 Update | 2020-05-27 | 19041 | — | Unsupported (2021-12-14) |
20H1 | Home, Pro, Pro for Workstations, Pro Education, Education, Enterprise |
||||
| October 2020 Update | 2020-10-20 | 19042 | — | Unsupported (2022-05-10) |
20H2 | Home, Pro, Pro for Workstations, Pro Education |
||||
| Supported (2023-05-09) |
Education, Enterprise | |||||||||
| May 2021 Update | 2021-05-18 | 19043 | — | Unsupported (2022-12-13) |
21H1 | Home, Pro, Pro for Workstations, Pro Education, Education, Enterprise |
||||
| November 2021 Update | 2021-10-16 | 19044 | — | Supported (2023-06-13) |
21H2 | Home, Pro, Pro for Workstations, Pro Education |
||||
| Supported (2024-06-11) |
Education, Enterprise | |||||||||
| Supported (2027-01-12) |
Enterprise LTSC | |||||||||
| 2022 Update | 2022-10-18 | 19045 | — | Supported (2024-05-14) |
22H2 | Home, Pro, Pro for Workstations, Pro Education |
||||
| Supported (2025-05-13) |
Education, Enterprise | |||||||||
| Windows Server 2016 | 2016-09-26 | 10.0 | 14393 | — | Supported (2027-01-12) |
Redstone Server | x86-64 | Essentials, Standard, Datacenter, MultiPoint Premium, Storage Standard, Storage Workgroup |
Server | |
| Windows Server 2019 | 2018-10-02 | 10.0 | 17763 | — | Supported (2029-01-09) |
Redstone 5 Server | x86-64 | Essentials, Standard, Datacenter |
Server | |
| Windows Server 2022 | 2021-08-18 | 10.0 | 20348 | — | Supported (2031-10-14) |
21H2 Server | x86-64 | Essentials, Standard, Datacenter, Datacenter for Azure |
Server | |
| Windows 11 | Original Release | 2021-10-05 | 10.0 | 22000 | — | Supported (2023-10-10) |
Sunvalley (21H2) | x86-64, ARM64 | Home, Pro, Pro for Workstations, Pro Education, SE |
Desktop, Workstation, Multi-touch |
| Supported (2024-10-08) |
Education, Enterprise | |||||||||
| 2022 Update | 2022-09-20 | 22621 | Supported (2024-10-14) |
22H2 | Home, Pro, Pro for Workstations, Pro Education, SE |
|||||
| Supported (2025-10-14) |
Education, Enterprise | |||||||||
| Name | Release date | Version | RTM build | Latest build | Status support | Codename, working name | Supported architectures | Editions | OS type |
- ^N has also an N-edition
- ^K has also an N-edition
- ^KN has also an N-edition
- ^x64 has a separate x64-edition
- ^Core has also a Core-edition
- ^wHV has also an edition without HyperV
- ^CwHV has also a Core-edition without HyperV
Windows Embedded Compact[edit]
Windows Embedded Compact (Windows CE) is a variation of Microsoft’s Windows operating system for minimalistic computers and embedded systems. Windows CE is a distinctly different kernel, rather than a trimmed-down version of desktop Windows. It is supported on Intel x86 and compatibles, MIPS, ARM, and Hitachi SuperH processors.
| Name | Release date | RTM build | Current version | Status support | Codename | Based on (kernel) | Kernel type | Operating environments | Editions | Purpose | Short description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Windows CE 1.0 | 1996-11-16 | Unsupported | Pegasus, Alder | CE 1.0 | Embedded | First release of Microsoft’s Windows CE line for minimalistic computers and embedded systems | |||||
| Windows CE 2.0 | 1997-11-29 | Unsupported | Mercury, Apollo | CE 2.0 | 2.1, 2.11 | Embedded | |||||
| Windows CE 3.0 | 2000-06-15 | Unsupported (2007-10-09) |
Cedar, Galileo, Rapier, Merlin, Stinger | CE 3.0 | Embedded kernel | Embedded | |||||
| Windows CE 4.0 | 2002-01-07 | Unsupported | Talisker | CE 4.0 | 4.1, 4.2 | Embedded | |||||
| Windows CE 5.0 | 2004-07-09 | 5.0 (2004-07-09) |
Unsupported (2014-10-14) |
Macallan | CE 5.0 | Embedded kernel | Embedded | ||||
| Windows Embedded CE 6.0 | 2006-11-01 | Unsupported (2018-04-10) |
Yamazaki | CE 6.0 | Hybrid kernel | ||||||
| Windows Embedded Compact 7 | 2011-03-01 | ? | ? | Unsupported (2021-04-13) |
Chelan | CE 7.0 | Hybrid | ? Standard, POSReady |
|||
| Windows Embedded Compact 2013 | 2013-08-11 | Update 17 (2017-11-15) |
Supported (2023-10-10) |
— | CE 8.0 | Standard Industry (8.0, 8.1) Handheld |
Embedded |
Windows IoT[edit]
The Windows IoT family is the successor to the now-discontinued Windows Embedded family.
| Name | Release date | Version | RTM build | Editions | License | OS type | Status support | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Windows 10 IoT | Anniversary Update | 2016-08-02 | NT 10.0 | 14393 | Core | OEM | IoT | Unsupported (2018-04-10)[3] |
| Enterprise | Unsupported (2019-04-09)[4] |
|||||||
| Enterprise LTSB | Supported (2026-10-13)[5] |
|||||||
| Creators Update | 2017-04-11 | 15063 | Core | Unsupported (2018-10-09)[3] |
||||
| Enterprise | Unsupported (2019-10-08)[4] |
|||||||
| Fall Creators Update | 2017-10-17 | 16299 | Core | Unsupported (2019-04-09)[3] |
||||
| Enterprise | Unsupported (2020-10-13)[4] |
|||||||
| April 2018 Update | 2018-04-30 | 17134 | Core | Unsupported (2019-11-12)[3] |
||||
| Enterprise | Unsupported (2021-05-11)[4] |
|||||||
| October 2018 Update | 2018-10-02 | 17763 | Core | Unsupported (2020-11-10)[3] |
||||
| Enterprise | Unsupported (2021-05-11)[4] |
|||||||
| Core LTSC, Enterprise LTSC | Supported (2029-01-09)[6][7] |
|||||||
| May 2019 Update | 2019-08-29 | 18362 | Enterprise | Unsupported (2020-12-08)[4] |
||||
| November 2019 Update | 2019-11-12 | 18363 | Unsupported (2022-05-10)[4] |
|||||
| May 2020 Update | 2020-05-27 | 19041 | Unsupported (2021-12-14)[4] |
|||||
| October 2020 Update | 2020-10-20 | 19042 | Supported (2023-05-09)[4] |
|||||
| May 2021 Update | 2021-05-18 | 19043 | Unsupported (2022-12-13)[4] |
|||||
| November 2021 Update | 2021-11-16 | 19044 | Enterprise | Supported (2024-06-11)[4] |
||||
| Enterprise LTSC | Supported (2032-01-13)[8] |
|||||||
| 2022 Update | 2022-10-18 | 19045 | Enterprise | Supported (2025-05-13)[4] |
||||
| Windows Server IoT 2019 | 2019-02-26[9] | NT 10.0 | 17763 | Essentials, Standard, Datacenter, Storage Standard, Storage Workgroup, Telecommunications |
OEM | IoT, Server | Supported (2029-01-09)[10][11] |
|
| Windows Server IoT 2022 | 2021-08-18[12][better source needed][dubious – discuss] | NT 10.0 | 20348 | Standard, Datacenter, Storage Standard, Storage Workgroup, Telecommunications |
OEM | IoT, Server | Supported (2031-10-14)[13] |
|
| Windows 11 IoT | Original Release | 2021-10-04 | NT 10.0 | 22000 | Enterprise | OEM | IoT | Supported (2024-10-08)[14] |
| 2022 Update | 2022-09-20 | 22621 | Supported (2025-10-14)[15] |
|||||
| Name | Release date | Version | RTM build | Editions | License | OS type | Status support |
Windows Mobile[edit]
Windows Mobile is Microsoft’s discontinued line of operating systems for smartphones.
| Name | Release date | RTM build | Current version | Status support | Codename | Based on (kernel) | Supported architectures |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Windows Pocket PC 2000 | 2000-04-19 | Unsupported (2007-10-09) |
Raiper | CE 3.0 | |||
| Windows Pocket PC 2002 | 2001-10-04 | Unsupported (2008-10-14) |
Merlin | CE 3.0 | |||
| Windows Mobile 2003 | 2003-06-23 | Unsupported (2014-07-08) |
Ozone | CE 4.20 | |||
| Windows Mobile 5.0 | 2005-05-9/12 | Unsupported (2015-10-13) |
Magneto | CE 5.0 | |||
| Windows Mobile 6.0 | 2007-02-12 | Unsupported (2013-01-08) |
Crossbow | CE 5.2 | |||
| Windows Mobile 6.1 | 2008-04-01 | ||||||
| Windows Mobile 6.5 | 2009-05-11 |
Windows Phone[edit]
Windows Phone is Microsoft’s discontinued line of operating systems for smartphones.
| Name | Release date | RTM build | Current version | Status support | Codename | Based on (kernel) | Supported architectures |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Windows Phone 7 | 2010-11-08 | 7004 | 7.10.8862 | Unsupported | Photon | CE 6.0 | ARM |
| Windows Phone 7.5 | 2011-09-27 | 7720 | Unsupported | Mango | CE 6.1 | ARM | |
| Windows Phone 7.8 | 2013-02-01 | 8858 | Unsupported (2014-10-14) |
Tango | CE 6.1 | ARM | |
| Windows Phone 8 | 2012-10-29 | 10211 | 10.0.10586 | Unsupported (2014-07-08) |
Apollo, Portico | NT 6.2 | ARM[citation needed] |
| Windows Phone 8.1 | 2014-04-14 | 12359 | Unsupported (2017-07-11) |
Blue | NT 6.3 | ARM | |
| Windows 10 Mobile | 2015-11-08 | 10586–16299 | Unsupported | Threshold, Redstone | NT 10.0 | ARM |
Technical information[edit]
DOS shells[edit]
| Name | Architecture | Integrated firewall | SMP support | USB support | UDMA support | LFN support | Update management | APIs | Safe Mode |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Windows 1.0 | x86 16-bit | No | No | No | No | No | No | Win16 | No |
| Windows 2.0 | x86 16-bit | No | No | No | No | No | No | Win16 | No |
| Windows 2.1x | x86 16-bit | No | No | No | No | No | No | Win16 | No |
| Windows 3.0 | x86 16-bit | No | No | No | No | No | No | Win16 | No |
| Windows 3.1x | x86 16-bit (partial 32-bit compatibility through Win32s) | No | No | No | No | No | No | Win16, Win32s | No |
Windows 9x[edit]
| Name | Kernel | Kernel type | Architecture | Integrated firewall | SMP support | USB support | UDMA support | LFN support | Update management | APIs | DDIs | Safe Mode | DirectX |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Windows 95 | MS-DOS 7.0 (Win95, Win95A), MS-DOS 7.1 (Win95B, Win95C) | Monolithic kernel | x86, hybrid 16/32-bit | No | No | Partial (OSR 2.1/2.5 only)[16] | No | Yes | Windows Update | Win16, Win32 | DOS, DLL, VxD, WDM (USB-only), direct-access | Yes | N/A (RTM/OSR1) 2.0a (OSR2/2.1) 5.0 (OSR2.5) 8.0a (optional) |
| Windows 98 | MS-DOS 7.1 | Monolithic kernel | x86, hybrid 16/32-bit | No | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | Windows Update | Win16, Win32 | DOS, DLL, VxD, WDM (partial), direct-access | Yes | 5.2 9.0c (Oct 2006) (optional) |
| Windows 98 Second Edition | MS-DOS 7.1 | Monolithic kernel | x86, hybrid 16/32-bit | No | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | Windows Update | Win16, Win32 | DOS, DLL, VxD, WDM (partial), direct-access | Yes | 6.1a 9.0c (Oct 2006) (optional) |
| Windows Me | MS-DOS 8.0 | Monolithic kernel | x86, hybrid 16/32-bit | No | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | Windows Update | Win16, Win32 | DLL, VxD, WDM (partial), direct-access | Yes | 7.1 9.0c (Oct 2006) (optional) |
It is possible to install the MS-DOS variants 7.0 and 7.1 without the graphics user interface of Windows. If an independent installation of both, DOS and Windows is desired, DOS ought to be installed prior to Windows, at the start of a small partition. The system must be transferred by the (dangerous) «SYSTEM» DOS-command, while the other files constituting DOS can simply be copied (the files located in the DOS-root and the entire COMMAND directory). Such a stand-alone installation of MS-DOS 8 is not possible, as it is designed to work as real mode for Windows Me and nothing else.
Windows NT[edit]
The Windows NT kernel powers all recent Windows operating systems. It has run on IA-32, x64, DEC Alpha, MIPS architecture, PowerPC, Itanium, ARMv7, and ARM64 processors, but currently supported versions run on IA-32, x64, ARMv7, and ARM64.
| Name | Architecture | Store | Integrated firewall | SMP support | USB support | UDMA support | Long filename support | Package management | Update management | APIs | DDIs | Safe Mode | Data Execution Prevention | DirectX |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Windows NT 3.1 | IA-32, DEC Alpha, MIPS | — | No | Yes | No | ? | Yes (NTFS and HPFS volumes only) | — | Win32, OS/2, POSIX | DLL, KMD | No | No | No | |
| Windows NT 3.5 | IA-32, DEC Alpha, MIPS | — | No | Yes | No | ? | Yes (except on CDFS volumes) | — | Win32, OS/2, POSIX | DLL, KMD | No | No | No | |
| Windows NT 3.51 | IA-32, DEC Alpha, MIPS, PowerPC | — | No | Yes | No | ? | Yes (except on CDFS volumes) | — | Win32, OS/2, POSIX | DLL, KMD | No | No | No | |
| Windows NT 4.0 | IA-32, DEC Alpha, MIPS, PowerPC | — | No | Yes | Yes (if the Ion USB update is installed) | Yes | Yes | — | Windows Update (if Internet Explorer 5 or later is installed) | Win32, OS/2, POSIX | DLL, KMD | No | No | Yes 3.0a, 5.0 (unofficial) |
| Windows 2000 | IA-32 | — | No | Yes | Yes (USB 2.0 with update or SP4)[17] | Yes | Yes | — | Windows Update, WSUS | Win32, OS/2, POSIX | DLL, KMD, WDM, KMDF | Yes | No | Yes 7.0, 9.0c (Feb 2010) (optional) |
| Windows XP | IA-32 (NT5.1), Itanium (NT5.1/5.2), x64 (NT5.2) | — | Yes | Yes (Professional Edition only) | Yes (USB 2.0 with update or SP1+)[18] | Yes | Yes | — | Windows Update, WSUS | Win32, .NET | DLL, KMD, WDM, KMDF, UMDFv1 | Yes | Yes (in SP2) | Yes 9.0c |
| Windows Server 2003 | IA-32, Itanium, x64 | — | Yes | Yes | Yes (USB 2.0)[19] | Yes | Yes | — | Windows Update, WSUS | Win32 | DLL, KMD, WDM, KMDF, UMDFv1 | Yes | Yes (with SP1) | Yes 9.0c |
| Windows Fundamentals for Legacy PCs | IA-32 | — | Yes | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | — | Windows Update, WSUS | Win32 | DLL, KMD, WDM, KMDF, UMDFv1 | Yes | Yes | Yes 9.0c |
| Windows Vista | IA-32, x64 | Windows Marketplace | Yes | Yes | Yes (USB 2.0) | Yes | Yes | — | Windows Update, WSUS | Win32, .NET, POSIX (only Enterprise and Ultimate) | DLL, KMD, WDM, KMDF, UMDFv1 | Yes | Yes | Yes 10.1 11.0 (optional) |
| Windows Server 2008 | IA-32, Itanium, x64 | — | Yes | Yes | Yes (USB 2.0) | Yes | Yes | — | Windows Update, WSUS | Win32 | DLL, KMD, WDM, KMDF, UMDFv1 | Yes | Yes | Yes 10.1 11.0 (optional) |
| Windows Home Server | IA-32 | — | ? | Yes | Yes (USB 2.0) | ? | Yes | — | Windows Update | Win32 | DLL, KMD, WDM, KMDF, UMDFv1 | ? | ? | Yes 9.0c |
| Windows 7 | IA-32, x64 | — | Yes | Yes | Yes (USB 3.0) | Yes | Yes | — | Windows Update, WSUS | Win32, .NET | DLL, KMD, WDM, KMDF, UMDFv1 | Yes | Yes | Yes 11.0 11.1 (optional) |
| Windows Server 2008 R2 | Itanium, x64 | — | Yes | Yes | Yes (USB 3.0) | Yes | Yes | — | Windows Update, WSUS | Win32, .NET | DLL, KMD, WDM, KMDF, UMDFv1 | Yes | Yes | Yes 11.0 11.1 (optional) |
| Windows Home Server 2011 | x64 | — | ? | Yes | Yes (USB 3.0) | ? | Yes | — | Windows Update | Win32 | DLL, KMD, WDM, KMDF, UMDFv1 | ? | ? | Yes 11.0 11.1 (optional) |
| Windows Server 2012 | x64 | Windows Store | Yes | Yes | Yes (USB 3.0) | Yes | Yes | Windows Store | Windows Update, WSUS | Win32, .NET, WinRT | DLL, KMD, WDM, KMDF, UMDFv1 | Yes | Yes | Yes 11.1 |
| Windows 8 | IA-32, x64 | Windows Store | Yes | Yes | Yes (USB 3.0) | Yes | Yes | Windows Store | Windows Update, WSUS | Win32, .NET, WinRT | DLL, KMD, WDM, KMDF, UMDFv1 | Yes | Yes | Yes 11.1 |
| Windows 8.1 | IA-32, x64 | Windows Store | Yes | Yes | Yes (USB 3.0) | Yes | Yes | Windows Store, PowerShell | Windows Update, WSUS, Windows Store | Win32, .NET, WinRT | DLL, KMD, WDM, KMDF, UMDFv1, UMDFv2 | Yes | Yes | Yes 11.2 |
| Windows Server 2012 R2 | x64 | Windows Store | Yes | Yes | Yes (USB 3.0) | Yes | Yes | Windows Store | Windows Update, WSUS, Windows Store | Win32, .NET, WinRT | DLL, KMD, WDM, KMDF, UMDFv1, UMDFv2 | Yes | Yes | Yes 11.2 |
| Windows 10 | IA-32, x64 | Windows Store | Yes | Yes | Yes (USB 3.1 and Thunderbolt 3) | Yes | Yes | Windows Store, PowerShell | Windows Update, WSUS, Windows Store | Win32, .NET, WinRT, Linux | DLL, KMD, WDM, KMDF, UMDFv1, UMDFv2 | Yes | Yes | Yes 12 |
| Windows Server 2016 | x64 | Windows Store | Yes | Yes | Yes (USB 3.1 and Thunderbolt 3) | Yes | Yes | Windows Store | Windows Update, WSUS, Windows Store | Win32, .NET, WinRT | DLL, KMD, WDM, KMDF, UMDFv1, UMDFv2 | Yes | Yes | Yes 12 |
Windows Phone[edit]
| Name | Architecture | Integrated firewall | SMP support | USB support | UDMA support | Package management | APIs |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Windows Phone 8 | ARMv7 | Yes | Yes | Yes (USB 2.0) | Yes | Windows Phone Store | Silverlight |
| Windows Phone 8.1 | ARMv7 | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Windows Phone Store | Silverlight WinRT |
| Windows 10 Mobile | ARMv7 | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Microsoft Store |
Supported file systems[edit]
Various versions of Windows support various file systems, including:FAT12, FAT16, FAT32, HPFS, or NTFS, along with network file systems shared from other computers, and the ISO 9660 and UDF file systems used for CDs, DVDs, and other optical disc drives such as Blu-ray. Each file system is usually limited in application to certain media, for example CDs must use ISO 9660 or UDF, and as of Windows Vista, NTFS is the only file system which the operating system can be installed on. Windows Embedded CE 6.0, Windows Vista Service Pack 1, and Windows Server 2008 onwards support exFAT, a file system more suitable for USB flash drives.
Windows 9x[edit]
| FAT12 | FAT16 | FAT32 | HPFS | ISO 9660 | NTFS | UDF | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Windows 95 | Yes | Yes | Yes (OSR2 or above) | Network Drive | Yes | Network Drive | No |
| Windows 98 | Yes | Yes | Yes | Network Drive | Yes | Network Drive | Yes (1.5, read) |
| Windows Me | Yes | Yes | Yes | Network Drive | Yes | Network Drive | Yes (1.5, read) |
Windows NT[edit]
| FAT12 | FAT16 | FAT32 | HPFS | ISO 9660 | NTFS | exFAT | UDF | ReFS | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Windows NT 3.1, 3.5, 3.51 | Yes | Yes | No | Yes | Yes | Yes v1.0/v1.1 | No | ? | No |
| Windows NT 4.0 | Yes | Yes | No | Partial | Yes | Yes v1.2 | No | ? | No |
| Windows 2000 | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | Yes | Yes v3.0 | No | Yes | No |
| Windows XP | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | Yes | Yes v3.1 | Optional | Yes (2.01) | No |
| Windows Server 2003 | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | Yes | Yes v3.1 | Optional | Yes | No |
| Windows Vista | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | Yes | Yes v5 | Yes | Yes (2.6) | No |
| Windows Server 2008 | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | Yes | Yes v5 | Yes | Yes | No |
| Windows 7 | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | Yes | Yes v5 | Yes | Yes (2.6) | Yes |
| Windows Server 2008 R2 | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | Yes | Yes v5 | Yes | Yes (2.6) | Yes |
| Windows Server 2012 | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | Yes | Yes v5 | Yes | Yes (2.6) | Yes |
| Windows 8 | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | Yes | Yes v5 | Yes | Yes (2.6) | No |
| Windows 8.1 | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | Yes | Yes v5 | Yes | Yes (2.6) | Yes |
| Windows Server 2012 R2 | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | Yes | Yes v5 | Yes | Yes (2.6) | Yes |
| Windows 10 | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | Yes | Yes v5 | Yes | Yes (2.6) | Yes |
| Windows Server 2016 | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | Yes | Yes v5 | Yes | Yes (2.6) | Yes |
Windows Phone[edit]
| FAT12 | FAT16 | FAT32 | HPFS | ISO 9660 | NTFS | UDF (More Info) | ReFS | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Windows Phone 8 | ? | Yes | Yes | No | ? | Yes v5 | ? | No |
| Windows Phone 8.1 | ? | Yes | Yes | No | ? | Yes v5 | ? | No |
| Windows 10 Mobile | ? | Yes | Yes | No | ? | Yes v5 | ? | ? |
Hardware requirements[edit]
Installing Windows requires an internal or external optical drive, or a USB flash drive. A keyboard and mouse are the recommended input devices, though some versions support a touchscreen. For operating systems prior to Vista, an optical drive must be capable of reading CD media, while in Windows Vista onwards, such a drive must be DVD-compatible. The drive may be detached after installing Windows.
Windows 9x[edit]
| CPU | RAM | Free disk space | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Windows 95 | 386 | 4 MB | 120 MB |
| Windows 98 | 486 DX2 66 MHz | 16 MB | 300 MB |
| Windows Me (Millennium Edition) | Pentium 150 MHz | 32 MB | 400 MB |
Windows NT[edit]
| Version | CPU | RAM | Free disk space | Video adapter and monitor | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Minimum | Recommended | ||||
| Windows NT 3.51 Workstation | 386, 25 MHz | 8 MB | 16 MB | 90 MB | VGA (640×480) |
| Windows NT 4.0 Workstation | 486, 33 MHz | 12 MB | ? | 110 MB | |
| Windows 2000 Professional | 133 MHz | 32 MB | 128 MB | 650 MB | |
| Windows XP | 233 MHz | 64 MB | 128 MB | 1.5 GB | Super VGA (800×600) |
| Windows Fundamentals for Legacy PCs | 500 MB | ||||
| Windows XP 64-Bit Edition | 700 MHz Itanium[20] | 1 GB[20] | ? | 6 GB[20] | |
| Windows Server 2003 | 1 GHz (x86) or 1.4 GHz (x64) | 128 MB | 256 MB | 2 GB (x86) 4 GB (x64) |
|
| Windows Vista | 800 MHz | 384 MB (Starter) 512 MB (others)[21][dubious – discuss] |
2 GB | 15 GB (~6.5 GB for OS) |
Super VGA (800×600) WDDM & DirectX 9 for Aero |
| Windows Server 2008 | 1 GHz (x86) or 1.4 GHz (x64) | 2 GB | 10 GB | ||
| Windows 7 | 1 GHz | 1 GB (x86) 2 GB (x64) |
4 GB | 16 GB (x86) 20 GB (x64) (~6.5 GB for OS) |
|
| Windows Server 2012 | 1.4 GHz (x86-64) | 512 MB | 1 GB | 10 GB | Super VGA (800×600), 32-bit color |
| Windows 8 | 1 GHz | 1 GB (x86) 2 GB (x64) |
4 GB | 16 GB (x86) 20 GB (x64) (~6.5 GB for OS) |
Super VGA (800×600), 32-bit color 1024 x 768 for Windows Store apps 1366 x 768 to snap apps |
| Windows 8.1 | |||||
| Windows 10 | 1 GHz or faster processor or SoC | 1 GB (x86) 2 GB (x64) |
4 GB | 16 GB (x86) 20 GB (x64) |
Super VGA (800×600), 32-bit color |
| Windows Server 2016 | 1.4 GHz 64-bit processor | 512 MB ECC memory 2 GB with Desktop Experience installed[22] |
depends on role | 32 GB (~10 GB for OS) |
XGA (1024 x 768) |
| Windows Server 2019 | 1.4 GHz 64-bit processor | 512 MB ECC memory 2 GB with Desktop Experience installed[22] |
depends on role | 32 GB | XGA (1024 x 768) |
| Windows Server 2022 | 1.4 GHz 64-bit processor | 512 MB ECC memory 2 GB with Desktop Experience installed[23] |
depends on role | 32 GB | Super VGA (1024 x 768) |
| Windows 11 | 64-bit 1 GHz or faster processor or SoC with two or more cores | 4 GB | — | 64 GB (~10 GB for OS) |
720p greater than 9″ diagonally, 32-bit color |
Windows Phone[edit]
| Version | CPU | RAM | Free disk space | Video adapter and monitor | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Minimum | Recommended | ||||
| Windows Phone 7 | 0.8 GHz | 256 MB | — | 4 GB | Wide VGA (800 × 480) |
| Windows Phone 8 | 1 GHz | 512 MB | — | 8 GB | Wide VGA (800 × 480) |
| Windows Phone 8.1 | 1 GHz | 512 MB | — | 4 GB | Wide VGA (800 × 480) |
| Windows 10 Mobile | 1 GHz | 1 GB | 2 GB | 8 GB | Wide VGA (800 × 480) |
Physical memory limits[edit]
Maximum limits on physical memory (RAM) that Windows can address vary depending on both the Windows version and between IA-32 and x64 versions.[24][25]
Windows[edit]
| Operating system | Limit on Real Mode | Limit on Standard Mode | Limit on Enhanced Mode |
|---|---|---|---|
| Windows 1.0x | 640 KB | — | — |
| Windows 2.0x | 640 KB | — | 16MB |
| Windows 2.1x | 640 + 64 KB | — | 16MB |
| Windows 3.0x | 640 + 64 KB | 16MB | 16MB |
| Windows 3.1x | — | 256MB[26] | 256MB[26] |
| Windows 95 | — | — | 944MB[27] |
| Windows 98 | — | — | 1GB |
| Windows ME | — | — | 1.5GB |
Windows NT[edit]
| Operating system | Limit on IA-32 | Limit in IA-64 | Limit on x64 | Limit on ARM32 | Limit on ARM64 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Windows NT 3.1 | 4 GB | — | — | — | — |
| Windows NT 3.5 | 4 GB | — | — | — | — |
| Windows NT 3.51 | 4 GB | — | — | — | — |
| Windows NT 4.0 | 4 GB | — | — | — | — |
| Windows 2000 Professional/Server | 4 GB | — | — | — | — |
| Windows 2000 Advanced Server | 8 GB | — | — | — | — |
| Windows 2000 Datacenter | 32 GB | — | — | — | — |
| Windows XP Starter | 512 MB | — | — | — | — |
| Windows XP Home | 4 GB | — | — | — | — |
| Windows XP Professional | 4 GB | 128 GB | 128 GB | — | — |
| Windows Server 2003 RTM Web | 2 GB | — | — | — | — |
| Windows Server 2003 RTM Standard/Small Business | 4 GB | — | — | — | — |
| Windows Server 2003 RTM Enterprise/Datacenter | 64 GB | 512 GB | — | — | — |
| Windows Compute Cluster Server 2003 | — | 32 GB | — | — | — |
| Windows Server 2003 R1/SP1 Standard | 4 GB | — | 32 GB | — | — |
| Windows Server 2003 R1/SP1 Enterprise/Datacenter | 64 GB | 1 TB | 1 TB | — | — |
| Windows Server 2003 R1/SP2 Standard | 4GB | — | 32 GB | — | — |
| Windows Server 2003 R1/SP2 Enterprise/Datacenter | 64 GB | 2 TB | 1 TB | — | — |
| Windows Server 2003 R2/SP1 Standard | 4 GB | — | 32 GB | — | — |
| Windows Server 2003 R2/SP1 Enterprise/Datacenter | 64 GB | — | 1 TB | — | — |
| Windows Vista Starter | 1 GB | — | — | — | — |
| Windows Vista Home Basic | 4 GB | — | 8 GB | — | — |
| Windows Vista Home Premium | 4 GB | — | 16 GB | — | — |
| Windows Vista Business/Enterprise/Ultimate | 4 GB | — | 128 GB | — | — |
| Windows Home Server | 4 GB | — | — | — | — |
| Windows Server 2008 Web Server/Standard/Small Business | 4 GB | — | 32 GB | — | — |
| Windows HPC Server 2008 | — | — | 128 GB | — | — |
| Windows Server 2008 Enterprise/Datacenter | 64 GB | — | 1 TB | — | — |
| Windows Server 2008 for Itanium–Based Systems | — | 2 TB | — | — | — |
| Windows 7 Starter | 2 GB | — | — | — | — |
| Windows 7 Home Basic | 4 GB | — | 8 GB | — | — |
| Windows 7 Home Premium | 4 GB | — | 16 GB | — | — |
| Windows 7 Professional/Enterprise/Ultimate | 4 GB | — | 192 GB | — | — |
| Windows Server 2008 R2 Foundation | — | — | 8 GB | — | — |
| Windows Server 2008 R2 Web Server/Standard | — | — | 32 GB | — | — |
| Windows HPC Server 2008 R2 | — | — | 128 GB | — | — |
| Windows Server 2008 R2 Enterprise/Datacenter | — | — | 2 TB | — | — |
| Windows Server 2008 R2 for Itanium–Based Systems | — | 2 TB | — | — | — |
| Windows 8 (Core) | 4 GB | — | 128 GB | — | — |
| Windows 8 Pro/Enterprise | 4 GB | — | 512 GB | — | — |
| Windows RT | — | — | — | 4 GB | — |
| Windows Server 2012 Standard/Datacenter | — | — | 4 TB | — | — |
| Windows Storage Server 2012 Standard | — | — | 4 TB | — | — |
| Windows Storage Server 2012 Workgroup | — | — | 32 GB | — | — |
| Hyper-V Server 2012 | — | — | 4 TB | — | — |
| Windows 8.1 (Core) | 4 GB | — | 128 GB | — | — |
| Windows 8.1 Pro/Enterprise | 4 GB | — | 512 GB | — | — |
| Windows RT 8.1 | — | — | — | 4 GB | — |
| Windows 10 Mobile | 4 GB | — | — | — | — |
| Windows 10 Home | 4 GB | — | 128 GB | 4 GB | 128 GB |
| Windows 10 Pro | 4 GB | — | 2 TB | 4 GB | 2 TB |
| Windows 10 Pro for Workstations | 4 GB | — | 6 TB | 4 GB | 6 TB |
| Windows 10 Education | 4 GB | — | 2 TB | 4 GB | 2 TB |
| Windows 10 Enterprise | 4 GB | — | 6 TB | 4 GB | 6 TB |
| Windows Server 2016 Essentials | — | — | 64 GB | — | — |
| Windows Server 2016 Standard | — | — | 24 TB | — | — |
| Windows Server 2016 Datacenter | — | — | 24 TB | — | — |
| Windows Server 2019 Essentials | — | — | 64 GB | — | — |
| Windows Server 2019 Standard | — | — | 24 TB | — | — |
| Windows Server 2019 Datacenter | — | — | 24 TB | — | — |
| Windows Server 2022 Essentials | — | — | 64 GB | — | — |
| Windows Server 2022 Standard | — | — | 24 TB | — | — |
| Windows Server 2022 Datacenter | — | — | 24 TB | — | — |
| Windows 11 Home | — | — | 128 GB | — | 128 GB |
| Windows 11 Pro | — | — | 2 TB | — | 2 TB |
| Windows 11 Pro for Workstations | — | — | 6 TB | — | 6 TB |
| Windows 11 Education | — | — | 2 TB | — | 2 TB |
| Windows 11 Enterprise | — | — | 6 TB | — | 6 TB |
Security features[edit]
| Resource access control | Subsystem isolation mechanisms | Integrated firewall | Encrypted file systems | Defender | Windows Hello | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Windows 2000 | ACLs | TCP/IP Filtering, IPSec | Yes (NTFS only) | No | No | |
| Windows XP | ACLs | Win32 WindowStation, Desktop, Job objects | Windows Firewall (from SP2), TCP/IP Filtering, IPSec | Yes (NTFS only) | Optional | No |
| Windows Server 2003 | ACLs, Privileges, RBAC | Win32 WindowStation, Desktop, Job objects | Windows Firewall, TCP/IP Filtering, IPSec | Yes | Optional | No |
| Windows Vista | ACLs, Privileges, RBAC | Win32 WindowStation, Desktop, Job objects | Windows Firewall, TCP/IP Filtering, IPSec | Yes | Yes | No |
| Windows Server 2008 | ACLs, Privileges, RBAC | Win32 WindowStation, Desktop, Job objects | Windows Firewall, TCP/IP Filtering, IPSec | Yes | Yes | No |
| Windows 7 | ACLs, Privileges, RBAC | Win32 WindowStation, Desktop, Job objects | Windows Firewall, TCP/IP Filtering, IPSec | Yes | Yes | No |
| Windows Server 2012 | ACLs, Privileges, RBAC | Win32 WindowStation, Desktop, Job objects | Windows Firewall, TCP/IP Filtering, IPSec | Yes | Yes | No |
| Windows 8 | ACLs, Privileges, RBAC | Win32 WindowStation, Desktop, Job objects | Windows Firewall, TCP/IP Filtering, IPSec | Yes | Yes | No |
| Windows Server 2012 R2 | ACLs, Privileges, RBAC | Win32 WindowStation, Desktop, Job objects | Windows Firewall, TCP/IP Filtering, IPSec | Yes | Yes | No |
| Windows 8.1 | ACLs, Privileges, RBAC | Win32 WindowStation, Desktop, Job objects | Windows Firewall, TCP/IP Filtering, IPSec | Yes | Yes | No |
| Windows 10 | ACLs, Privileges, RBAC | Win32 WindowStation, Desktop, Job objects | Windows Firewall, TCP/IP Filtering, IPSec | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Windows Server 2016 | ACLs, Privileges, RBAC | Win32 WindowStation, Desktop, Job objects | Windows Firewall, TCP/IP Filtering, IPSec | Yes | Yes | Yes |
Features[edit]
| Version | Shell | Visual styles | Browser | Web server | Windows Media Player | Command-line interpreter |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Windows 1.0 | MS-DOS executive | (Unnamed) | — | — | — | — |
| Windows 2.0 | MS-DOS executive | (Unnamed) | — | — | — | — |
| Windows 3.0 | Program Manager | (Unnamed) | — | — | 3.0 (Multimedia Extension edition only) | — |
| Windows 3.1x | Program Manager | (Unnamed) | — | — | 3.1 | — |
| Windows 95 | Windows shell | Classic | Internet Explorer 1 in OEM RTM Internet Explorer 2 in OSR1 Internet Explorer 3 in OSR2 and OSR2.1 Internet Explorer 4 in OSR2.5 |
— | 4.0 | COMMAND.COM |
| Windows NT 4.0 | Windows shell | Classic | Internet Explorer 2 Internet Explorer 3 (in some localized editions) |
PWS | 4.0 | COMMAND.COM, CMD.EXE |
| Windows 98 | Windows shell | Classic | Internet Explorer 4.01 | PWS | 4.0 | COMMAND.COM |
| Windows 98 SE | Windows shell | Classic | Internet Explorer 5 | PWS | 4.0 | COMMAND.COM |
| Windows 2000 | Windows shell | Classic | Internet Explorer 5.01 | IIS 5.0 | 5.0 and 6.4 (side by side) | COMMAND.COM, CMD.EXE |
| Windows Me | Windows shell | Classic | Internet Explorer 5.5 | — | 6.4 and 7.0 (side by side) | COMMAND.COM |
| Windows XP | Windows shell | Luna (default), Classic | Internet Explorer 6 | IIS 5.1 | 5.1, 6.4 and 8 (in RTM) 5.1, 6.4 and 9 (in SP2) |
COMMAND.COM, CMD.EXE, PowerShell (optional) |
| Windows Server 2003 | Windows shell | Classic (default), Luna | Internet Explorer 6 | IIS 6.0 | 9 (in RTM), 10 (in SP1) | COMMAND.COM, CMD.EXE, PowerShell (optional) |
| Windows Vista | Windows shell | Aero (default), Classic | Internet Explorer 7 | IIS 7 | 11 | COMMAND.COM, CMD.EXE, PowerShell (optional) |
| Windows Server 2008 | Windows shell, Server Core | Classic (default), Aero (via «Desktop Experience») | Internet Explorer 7 | IIS 7 | 11 (enabled by installing «Desktop Experience») | COMMAND.COM, CMD.EXE, PowerShell (optional) |
| Windows 7 | Windows shell | Aero (default), Classic | Internet Explorer 8 | IIS 7.5 | 12 | COMMAND.COM, CMD.EXE, PowerShell v2.0 |
| Windows Server 2008 R2 | Windows shell, Server Core | Classic (default), Aero (via «Desktop Experience») | Internet Explorer 8 | IIS 7.5 | 12 (via «Desktop Experience») | CMD.EXE, PowerShell v2.0 |
| Windows Server 2012 | Windows shell, Server Core | Metro | Internet Explorer 10 | IIS 8 | 12 (via «Desktop Experience») | CMD.EXE, PowerShell v3.0 |
| Windows 8 | Windows shell | Metro | Internet Explorer 10 | IIS 8 | 12 | COMMAND.COM, CMD.EXE, PowerShell v3.0 |
| Windows Server 2012 R2 | Windows shell, Windows server core | Metro | Internet Explorer 11 | IIS 8.5 | 12 (via «Desktop Experience») | CMD.EXE, PowerShell v4.0 |
| Windows 8.1 | Windows shell | Metro | Internet Explorer 11 | IIS 8.5 | 12 | COMMAND.COM, CMD.EXE, PowerShell v4.0 |
| Windows 10 | Windows shell | Metro | Internet Explorer 11 Microsoft Edge 12-13 |
IIS 10.0 | 12 | COMMAND.COM, CMD.EXE, PowerShell v5.0 |
| Windows Server 2016 | Windows shell, Windows server core | Metro | Internet Explorer 11 Microsoft Edge 13 |
IIS 10.0 | 12 (via «Desktop Experience») | CMD.EXE, PowerShell v5.0 |
| Windows Server 2019 | Windows shell, Windows server core | Metro | Internet Explorer 11 Microsoft Edge 13 |
IIS 10.0 | 12 (via «Desktop Experience») | CMD.EXE, PowerShell v5.0 |
Timeline[edit]
- view
- talk
- edit
See also[edit]
Other lists[edit]
- List of Microsoft Windows versions
- List of operating systems
- Comparison of operating systems
- Comparison of kernels
- Comparison of Windows Vista and Windows XP
- History of Microsoft Windows
- Comparison of DOS operating systems
- Architecture of the Windows NT operating system line
- Microsoft codenames
Windows clones and emulators[edit]
- Freedows OS–Windows clone
- ReactOS–project to develop an operating system that is binary compatible with application software and device drivers for Microsoft Windows NT version 5.x
- Wine (software)–compatibility layer which allows to execute programs that were originally written for Microsoft Windows
References[edit]
- ^ «Product Lifecycle Dates-Windows Product Family». Microsoft. Archived from the original on 2004-06-11. Retrieved 2021-08-24.
- ^ «Windows NT 3.5 for PowerPC». 9 November 1994. Archived from the original on August 12, 2021.
- ^ a b c d e «Windows 10 IoT Core — Microsoft Lifecycle». Archived from the original on November 18, 2020. Retrieved August 4, 2022.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l «Windows 10 IoT Enterprise — Microsoft Lifecycle». Retrieved August 4, 2022.
- ^ «Windows 10 IoT Enterprise LTSB 2016 — Microsoft Lifecycle». Archived from the original on March 23, 2022. Retrieved August 4, 2022.
- ^ «Windows 10 IoT Core LTSC — Microsoft Lifecycle». Archived from the original on March 10, 2022. Retrieved August 4, 2022.
- ^ «Windows 10 IoT Enterprise LTSC 2019 — Microsoft Lifecycle». Archived from the original on November 16, 2021. Retrieved August 4, 2022.
- ^ «Windows 10 IoT Enterprise LTSC 2021 — Microsoft Lifecycle». Archived from the original on November 16, 2021. Retrieved August 4, 2022.
- ^ «Microsoft announces latest Windows IoT innovations for intelligent edge devices at Embedded World». Archived from the original on February 26, 2019.
- ^ «Windows Server IoT 2019 — Microsoft Lifecycle». Archived from the original on March 23, 2022. Retrieved August 4, 2022.
- ^ «Windows Server IoT 2019 for Storage — Microsoft Lifecycle». Archived from the original on March 23, 2022. Retrieved August 4, 2022.
- ^ «Announcing the GA of Windows Server IoT 2022». Retrieved August 4, 2022.
- ^ «Windows Server IoT 2022 — Microsoft Lifecycle». Archived from the original on October 6, 2021. Retrieved August 4, 2022.
- ^ «Windows 11 IoT Enterprise (Version 21H2) — Microsoft Lifecycle». Archived from the original on October 5, 2021. Retrieved August 4, 2022.
- ^ «Windows 11 IoT Enterprise — Microsoft Lifecycle». Archived from the original on September 22, 2022. Retrieved September 22, 2022.
- ^ «Availability of Universal Serial Bus Support in Windows 95». Microsoft Support. Archived from the original on December 10, 2005.
- ^ «Updated USB 2.0 Drivers Are Available in Windows 2000 Service Pack 4 (SP4)». Microsoft Support. Archived from the original on October 29, 2006. Retrieved February 5, 2012.
- ^ Jones, Don (August 5, 2002). «USB 2.0 Support in Windows XP:High Speed at Last». Microsoft. Archived from the original on December 31, 2004. Retrieved February 5, 2012.
- ^ «USB 2.0 and Windows Operating Systems». Windows Hardware Development. May 11, 2007. Archived from the original on March 3, 2011. Retrieved February 5, 2012.
- ^ a b c «Release Notes for Windows XP 64-Bit Edition Setup». Microsoft. Archived from the original on February 10, 2007. Retrieved September 2, 2014.
- ^ «Windows Vista Starter Fact Sheet». Microsoft. January 2007. Archived from the original on March 7, 2007.
- ^ a b «System Requirements». docs.microsoft.com. Archived from the original on June 27, 2017. Retrieved May 24, 2018.
- ^ «Hardware requirements for Windows Server». docs.microsoft.com. Archived from the original on August 21, 2021. Retrieved August 4, 2022.
- ^ «What is the maximum amount of RAM the Windows operating system can handle?». Crucial. Archived from the original on May 11, 2011. Retrieved February 5, 2012.
- ^ «Memory Limits for Windows and Windows Server Releases». Microsoft. Archived from the original on May 5, 2008. Retrieved February 5, 2012.
- ^ a b «Q84388: Windows 3.1 Memory Limits». December 15, 2022.
- ^ «Windows 95/98 error «Insufficient memory to initialize Windows» — IBM IntelliStation M Pro (Type 6889)». December 15, 2022.
External links[edit]
- Official website
- Time line from Microsoft
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Microsoft Windows is the name of several families of computer software operating systems created by Microsoft. Microsoft first introduced an operating environment named Windows in November 1985 as an add-on to MS-DOS in response to the growing interest in graphical user interfaces (GUIs).
All versions of Microsoft Windows are commercial proprietary software.
General information[edit]
Basic general information about Windows.
DOS shells[edit]
| Name | Release date | Latest version | Status support | Codename | OS required | Architecture | Editions | Target market |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Windows 1.0 | 1985-11-20 | 1.04 (1987-04-08) | Unsupported (2001-12-31) |
Interface Manager | DOS 2.0 or higher | 16-bit | Desktops | |
| Windows 2.0 | 1987-09-08 | 2.03 (1987-12-09) | Unsupported (2001-12-31) |
DOS 3.0 or higher | 16-bit | Desktops | ||
| Windows 2.1x | 1988-05-27 | 2.11 (1989-03-13) | Unsupported (2001-12-31) |
DOS 3.0 or higher | 16-bit | Desktops | ||
| Windows 3.0 | 1990-05-22 | 3.0a with Multimedia Extensions (1991-10-20) |
Unsupported (2001-12-31) |
DOS 3.1 or higher | 16-bit | Windows 3.0 Windows 3.0a Windows 3.0a with Multimedia Extensions |
Desktops | |
| Windows 3.1x | 1992-04-06 | 3.11 (1993-12-31) | Unsupported (2001-12-31) |
Janus
|
DOS 3.3 or higher | 16-bit* | Windows 3.1 Windows for Workgroups 3.1 Windows 3.11 Windows for Workgroups 3.11 Windows 3.2 (Simplified Chinese only) |
Desktops |
- * Has partial 32-bit compatibility with Win32s
Windows 9x[edit]
| Name | Release date | RTM build | Latest version | Status support | Codename | MS-DOS version | Kernel type | Architecture | Editions | Target market |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Windows 95 | 1995-07-14 | 950 | 4.00.950C OSR2.5 (1997-11-26) | Unsupported (2001-12-31) |
Chicago | MS-DOS 7.0, MS-DOS 7.1 (OSR2.x) | Monolithic | Hybrid 16/32-bit | Retail, OSR1, OSR2, OSR2.1, OSR2.5 | Desktops |
| Windows 98 | 1998-05-15 | 1998 | 4.10.1998 | Unsupported (2006-07-11) |
Memphis | MS-DOS 7.1 | Monolithic | Hybrid 16/32-bit | Desktops | |
| Windows 98 SE | 1999-05-05 | 2222 | 4.10.2222A (2000-02-25) | Unsupported (2006-07-11) |
MS-DOS 7.1 | Monolithic | Hybrid 16/32-bit | Desktops | ||
| Windows Me | 2000-06-19 | 3000 | 4.90.3000 (2000-09-14) | Unsupported (2006-07-11) |
Millennium | MS-DOS 8.0 | Monolithic | Hybrid 16/32-bit | Desktops |
Windows NT[edit]
| Name | Release date | Version | RTM build | Latest build | Status support | Codename, working name | Supported architectures | Editions | OS type | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Windows NT 3.1 | 1993-07-27 | 3.1 | 528 | 528 (SP3) (1994-11-10) |
Unsupported (2000-12-31)[1] |
New Technology OS/2 | IA-32, DEC Alpha, MIPS |
Workstation, Advanced Server |
Workstation, Server |
|
| Windows NT 3.5 | 1994-09-21 | 3.5 | 807 | 807 (SP3) (1995-06-21) |
Unsupported (2001-12-31) |
Daytona | IA-32, DEC Alpha, MIPS, PowerPC[2] |
Workstation, Server |
Workstation, Server |
|
| Windows NT 3.51 | 1995-05-30 | 3.51 | 1057 | 1057 (SP5) (1996-09-19) |
Unsupported (2001-12-31) |
— | IA-32, DEC Alpha, MIPS, PowerPC |
Workstation, Server |
Workstation, Server |
|
| Windows NT 4.0 | 1996-07-31 | 4.0 | 1381 | 1381 (SP6a) (1999-11-30) |
Unsupported (2004-06-30) |
Cairo/Shell Update Release Hydra (Terminal Server) Impala (Embedded) |
IA-32, DEC Alpha, MIPS, PowerPC |
Workstation, Server, Server Enterprise Edition, Terminal Server, Embedded |
Workstation, Server, Embedded PCs |
|
| Windows 2000 | 1999-12-15 | 5.0 | 2195 | SP4 Rollup 1 v2 (2005-09-13) |
Unsupported (2010-07-13) |
N/A
|
IA-32 | Professional, Server, Advanced Server, Datacenter Server, Powered (Embedded) |
Desktop, Workstation, Server, Embedded PCs |
|
| Windows XP | 2001-08-24 | 5.1 | 2600 | 2600 (SP3) (2008-04-21) |
Unsupported (2014-04-08) |
Whistler | IA-32, IA-64, x86-64 | HomeK, ProfessionalKx64, Media Center, Tablet PC, Starter, Embedded |
Desktop, Workstation, Embedded PCs |
|
| Windows Server 2003 | 2003-04-24 | 5.2 | 3790 | 3790 (SP2) (2007-03-13) |
Unsupported (2015-07-14) |
Whistler Server, Windows.NET Server | IA-32, IA-64, x86-64 | Standard, Enterprise, Datacenter, Web, Storage, Small Business Server, Compute Cluster |
Server, Network Appliance, Embedded PCs, HPC |
|
| Windows Server 2003 R2 | 2005 | 5.2 | 3790 | ? | Unsupported (2015-07-14) |
? | IA-32, x86-64 | Server, Network Appliance, Embedded PCs, HPC |
||
| Windows Fundamentals for Legacy PCs | 2006-07-08 | 5.1 | 2600 | — | Unsupported (2014-04-08) |
Eiger, Mönch | IA-32 | Fundamentals for Legacy PCs | Desktop | |
| Windows Vista | 2006-11-30 | 6.0 | 6000 | 6002 (SP2) (2009-04-28) |
Unsupported (2017-04-11) |
Longhorn | IA-32, x86-64 | Starter, Home BasicK, Home PremiumK, BusinessK, EnterpriseK, UltimateK |
Desktop, Workstation |
|
| Windows Home Server | 2007-11-04 | 5.2 | 3790 | — | Unsupported (2013-01-08) |
Q, Quattro | IA-32, x86-64 | Home Server | Server | |
| Windows Server 2008 | 2008-02-04 | 6.0 | 6001 | 6002 (SP2) (2009-04-28) |
Unsupported (2020-01-14) |
Longhorn Server | IA-32, IA-64, x86-64 | WebCore, StandardCorewHVCwHV, EnterpriseCorewHVCwHV, Small Business Server, DatacenterCorewHVCwHV, HPC, HyperV Core, Foundation, Storage |
Server | |
| Windows 7 | 2009-07-22 | 6.1 | 7600 | 7601 (SP1) (2011-02-22) |
Unsupported (2020-01-14) |
7 | IA-32, x86-64 | StarterK, Home BasicK, Home PremiumK, ProfessionalK, UltimateK, EnterpriseK |
Desktop, Workstation, Multi-touch | |
| Windows Server 2008 R2 | 2009-07-22 | 6.1 | 7600 | 7601 (SP1) (2011-02-22) |
Unsupported (2020-01-14) |
7 Server | IA-64, x86-64 | StandardCore, EnterpriseCore, DatacenterCore, WebCore |
Server | |
| Windows Home Server 2011 | 2011-04-06 | 6.1 | 8400 | — | Unsupported (2016-04-12) |
Vail | x86-64 | Home Server | Server | |
| Windows Server 2012 | 2012-08-01 | 6.2 | 9200 | — | Supported (2023-10-10) |
8 Server | x86-64 | Foundation, Essentials, Standard, Datacenter, Storage Standard, Storage Workgroup |
Server | |
| Windows 8 | 2012-08-01 | 6.2 | 9200 | — | (RTM only) Unsupported (2016-01-12) |
8 | IA-32, x86-64, ARMv7 | Windows 8, Pro, EnterpriseK, Windows RT |
Desktop, Workstation, Multi-touch |
|
| Windows 8.1 | 2013-08-27 | 6.3 | 9600 | — | Unsupported (2023-01-10) |
Blue | IA-32, x86-64, ARMv7 | Windows 8.1, Pro, EnterpriseK, Windows RT 8.1 |
Desktop, Workstation, Multi-touch |
|
| Windows Server 2012 R2 | 2013-10-18 | 6.3 | 9600 | — | Supported (2023-10-10) |
Blue Server | x86-64 | Foundation, Essentials, Standard, Datacenter, Storage Essentials, Storage Standard, Storage Workgroup |
Server | |
| Windows 10 | Original Release | 2015-07-29 | 10.0 | 10240 | — | Unsupported (2017-05-09) |
Threshold | IA-32, x86-64, ARMv7 | Home, Pro, Education, Enterprise |
Desktop, Workstation, Multi-touch |
| Supported (2025-10-14) |
Enterprise LTSB | |||||||||
| November Update | 2015-11-12 | 10586 | — | Unsupported (2017-10-10) |
Threshold 2 | Home, Pro | ||||
| Unsupported (2018-04-10) |
Education, Enterprise | |||||||||
| Anniversary Update | 2016-08-02 | 14393 | — | Unsupported (2018-04-10) |
Redstone | Home, Pro, Pro Education |
||||
| Unsupported (2019-04-09) |
Education, Enterprise | |||||||||
| Supported (2026-10-13) |
Enterprise LTSB | |||||||||
| Creators Update | 2017-04-11 | 15063 | — | Unsupported (2018-10-09) |
Redstone 2 | Home, Pro, Pro Education |
||||
| Unsupported (2019-10-08) |
Education, Enterprise | |||||||||
| Fall Creators Update | 2017-10-17 | 16299 | — | Unsupported (2019-04-09) |
Redstone 3 | IA-32, x86-64, ARMv7, ARM64 | Home, Pro, Pro for Workstations, Pro Education |
|||
| Unsupported (2020-10-13) |
Education, Enterprise | |||||||||
| April 2018 Update | 2018-04-30 | 17134 | — | Unsupported (2019-11-12) |
Redstone 4 | Home, Pro, Pro for Workstations, Pro Education |
||||
| Unsupported (2021-05-11) |
Education, Enterprise | |||||||||
| October 2018 Update | 2018-10-02 | 17763 | — | Unsupported (2020-11-10) |
Redstone 5 | Home, Pro, Pro for Workstations, Pro Education |
||||
| Unsupported (2021-05-11) |
Education, Enterprise | |||||||||
| Supported (2029-01-09) |
Enterprise LTSC | |||||||||
| May 2019 Update | 2019-05-21 | 18362 | — | Unsupported (2020-12-08) |
19H1 | Home, Pro, Pro for Workstations, Pro Education, Education, Enterprise |
||||
| November 2019 Update | 2019-11-12 | 18363 | — | Unsupported (2021-05-11) |
19H2 | Home, Pro, Pro for Workstations, Pro Education |
||||
| Unsupported (2022-05-10) |
Education, Enterprise | |||||||||
| May 2020 Update | 2020-05-27 | 19041 | — | Unsupported (2021-12-14) |
20H1 | Home, Pro, Pro for Workstations, Pro Education, Education, Enterprise |
||||
| October 2020 Update | 2020-10-20 | 19042 | — | Unsupported (2022-05-10) |
20H2 | Home, Pro, Pro for Workstations, Pro Education |
||||
| Supported (2023-05-09) |
Education, Enterprise | |||||||||
| May 2021 Update | 2021-05-18 | 19043 | — | Unsupported (2022-12-13) |
21H1 | Home, Pro, Pro for Workstations, Pro Education, Education, Enterprise |
||||
| November 2021 Update | 2021-10-16 | 19044 | — | Supported (2023-06-13) |
21H2 | Home, Pro, Pro for Workstations, Pro Education |
||||
| Supported (2024-06-11) |
Education, Enterprise | |||||||||
| Supported (2027-01-12) |
Enterprise LTSC | |||||||||
| 2022 Update | 2022-10-18 | 19045 | — | Supported (2024-05-14) |
22H2 | Home, Pro, Pro for Workstations, Pro Education |
||||
| Supported (2025-05-13) |
Education, Enterprise | |||||||||
| Windows Server 2016 | 2016-09-26 | 10.0 | 14393 | — | Supported (2027-01-12) |
Redstone Server | x86-64 | Essentials, Standard, Datacenter, MultiPoint Premium, Storage Standard, Storage Workgroup |
Server | |
| Windows Server 2019 | 2018-10-02 | 10.0 | 17763 | — | Supported (2029-01-09) |
Redstone 5 Server | x86-64 | Essentials, Standard, Datacenter |
Server | |
| Windows Server 2022 | 2021-08-18 | 10.0 | 20348 | — | Supported (2031-10-14) |
21H2 Server | x86-64 | Essentials, Standard, Datacenter, Datacenter for Azure |
Server | |
| Windows 11 | Original Release | 2021-10-05 | 10.0 | 22000 | — | Supported (2023-10-10) |
Sunvalley (21H2) | x86-64, ARM64 | Home, Pro, Pro for Workstations, Pro Education, SE |
Desktop, Workstation, Multi-touch |
| Supported (2024-10-08) |
Education, Enterprise | |||||||||
| 2022 Update | 2022-09-20 | 22621 | Supported (2024-10-14) |
22H2 | Home, Pro, Pro for Workstations, Pro Education, SE |
|||||
| Supported (2025-10-14) |
Education, Enterprise | |||||||||
| Name | Release date | Version | RTM build | Latest build | Status support | Codename, working name | Supported architectures | Editions | OS type |
- ^N has also an N-edition
- ^K has also an N-edition
- ^KN has also an N-edition
- ^x64 has a separate x64-edition
- ^Core has also a Core-edition
- ^wHV has also an edition without HyperV
- ^CwHV has also a Core-edition without HyperV
Windows Embedded Compact[edit]
Windows Embedded Compact (Windows CE) is a variation of Microsoft’s Windows operating system for minimalistic computers and embedded systems. Windows CE is a distinctly different kernel, rather than a trimmed-down version of desktop Windows. It is supported on Intel x86 and compatibles, MIPS, ARM, and Hitachi SuperH processors.
| Name | Release date | RTM build | Current version | Status support | Codename | Based on (kernel) | Kernel type | Operating environments | Editions | Purpose | Short description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Windows CE 1.0 | 1996-11-16 | Unsupported | Pegasus, Alder | CE 1.0 | Embedded | First release of Microsoft’s Windows CE line for minimalistic computers and embedded systems | |||||
| Windows CE 2.0 | 1997-11-29 | Unsupported | Mercury, Apollo | CE 2.0 | 2.1, 2.11 | Embedded | |||||
| Windows CE 3.0 | 2000-06-15 | Unsupported (2007-10-09) |
Cedar, Galileo, Rapier, Merlin, Stinger | CE 3.0 | Embedded kernel | Embedded | |||||
| Windows CE 4.0 | 2002-01-07 | Unsupported | Talisker | CE 4.0 | 4.1, 4.2 | Embedded | |||||
| Windows CE 5.0 | 2004-07-09 | 5.0 (2004-07-09) |
Unsupported (2014-10-14) |
Macallan | CE 5.0 | Embedded kernel | Embedded | ||||
| Windows Embedded CE 6.0 | 2006-11-01 | Unsupported (2018-04-10) |
Yamazaki | CE 6.0 | Hybrid kernel | ||||||
| Windows Embedded Compact 7 | 2011-03-01 | ? | ? | Unsupported (2021-04-13) |
Chelan | CE 7.0 | Hybrid | ? Standard, POSReady |
|||
| Windows Embedded Compact 2013 | 2013-08-11 | Update 17 (2017-11-15) |
Supported (2023-10-10) |
— | CE 8.0 | Standard Industry (8.0, 8.1) Handheld |
Embedded |
Windows IoT[edit]
The Windows IoT family is the successor to the now-discontinued Windows Embedded family.
| Name | Release date | Version | RTM build | Editions | License | OS type | Status support | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Windows 10 IoT | Anniversary Update | 2016-08-02 | NT 10.0 | 14393 | Core | OEM | IoT | Unsupported (2018-04-10)[3] |
| Enterprise | Unsupported (2019-04-09)[4] |
|||||||
| Enterprise LTSB | Supported (2026-10-13)[5] |
|||||||
| Creators Update | 2017-04-11 | 15063 | Core | Unsupported (2018-10-09)[3] |
||||
| Enterprise | Unsupported (2019-10-08)[4] |
|||||||
| Fall Creators Update | 2017-10-17 | 16299 | Core | Unsupported (2019-04-09)[3] |
||||
| Enterprise | Unsupported (2020-10-13)[4] |
|||||||
| April 2018 Update | 2018-04-30 | 17134 | Core | Unsupported (2019-11-12)[3] |
||||
| Enterprise | Unsupported (2021-05-11)[4] |
|||||||
| October 2018 Update | 2018-10-02 | 17763 | Core | Unsupported (2020-11-10)[3] |
||||
| Enterprise | Unsupported (2021-05-11)[4] |
|||||||
| Core LTSC, Enterprise LTSC | Supported (2029-01-09)[6][7] |
|||||||
| May 2019 Update | 2019-08-29 | 18362 | Enterprise | Unsupported (2020-12-08)[4] |
||||
| November 2019 Update | 2019-11-12 | 18363 | Unsupported (2022-05-10)[4] |
|||||
| May 2020 Update | 2020-05-27 | 19041 | Unsupported (2021-12-14)[4] |
|||||
| October 2020 Update | 2020-10-20 | 19042 | Supported (2023-05-09)[4] |
|||||
| May 2021 Update | 2021-05-18 | 19043 | Unsupported (2022-12-13)[4] |
|||||
| November 2021 Update | 2021-11-16 | 19044 | Enterprise | Supported (2024-06-11)[4] |
||||
| Enterprise LTSC | Supported (2032-01-13)[8] |
|||||||
| 2022 Update | 2022-10-18 | 19045 | Enterprise | Supported (2025-05-13)[4] |
||||
| Windows Server IoT 2019 | 2019-02-26[9] | NT 10.0 | 17763 | Essentials, Standard, Datacenter, Storage Standard, Storage Workgroup, Telecommunications |
OEM | IoT, Server | Supported (2029-01-09)[10][11] |
|
| Windows Server IoT 2022 | 2021-08-18[12][better source needed][dubious – discuss] | NT 10.0 | 20348 | Standard, Datacenter, Storage Standard, Storage Workgroup, Telecommunications |
OEM | IoT, Server | Supported (2031-10-14)[13] |
|
| Windows 11 IoT | Original Release | 2021-10-04 | NT 10.0 | 22000 | Enterprise | OEM | IoT | Supported (2024-10-08)[14] |
| 2022 Update | 2022-09-20 | 22621 | Supported (2025-10-14)[15] |
|||||
| Name | Release date | Version | RTM build | Editions | License | OS type | Status support |
Windows Mobile[edit]
Windows Mobile is Microsoft’s discontinued line of operating systems for smartphones.
| Name | Release date | RTM build | Current version | Status support | Codename | Based on (kernel) | Supported architectures |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Windows Pocket PC 2000 | 2000-04-19 | Unsupported (2007-10-09) |
Raiper | CE 3.0 | |||
| Windows Pocket PC 2002 | 2001-10-04 | Unsupported (2008-10-14) |
Merlin | CE 3.0 | |||
| Windows Mobile 2003 | 2003-06-23 | Unsupported (2014-07-08) |
Ozone | CE 4.20 | |||
| Windows Mobile 5.0 | 2005-05-9/12 | Unsupported (2015-10-13) |
Magneto | CE 5.0 | |||
| Windows Mobile 6.0 | 2007-02-12 | Unsupported (2013-01-08) |
Crossbow | CE 5.2 | |||
| Windows Mobile 6.1 | 2008-04-01 | ||||||
| Windows Mobile 6.5 | 2009-05-11 |
Windows Phone[edit]
Windows Phone is Microsoft’s discontinued line of operating systems for smartphones.
| Name | Release date | RTM build | Current version | Status support | Codename | Based on (kernel) | Supported architectures |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Windows Phone 7 | 2010-11-08 | 7004 | 7.10.8862 | Unsupported | Photon | CE 6.0 | ARM |
| Windows Phone 7.5 | 2011-09-27 | 7720 | Unsupported | Mango | CE 6.1 | ARM | |
| Windows Phone 7.8 | 2013-02-01 | 8858 | Unsupported (2014-10-14) |
Tango | CE 6.1 | ARM | |
| Windows Phone 8 | 2012-10-29 | 10211 | 10.0.10586 | Unsupported (2014-07-08) |
Apollo, Portico | NT 6.2 | ARM[citation needed] |
| Windows Phone 8.1 | 2014-04-14 | 12359 | Unsupported (2017-07-11) |
Blue | NT 6.3 | ARM | |
| Windows 10 Mobile | 2015-11-08 | 10586–16299 | Unsupported | Threshold, Redstone | NT 10.0 | ARM |
Technical information[edit]
DOS shells[edit]
| Name | Architecture | Integrated firewall | SMP support | USB support | UDMA support | LFN support | Update management | APIs | Safe Mode |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Windows 1.0 | x86 16-bit | No | No | No | No | No | No | Win16 | No |
| Windows 2.0 | x86 16-bit | No | No | No | No | No | No | Win16 | No |
| Windows 2.1x | x86 16-bit | No | No | No | No | No | No | Win16 | No |
| Windows 3.0 | x86 16-bit | No | No | No | No | No | No | Win16 | No |
| Windows 3.1x | x86 16-bit (partial 32-bit compatibility through Win32s) | No | No | No | No | No | No | Win16, Win32s | No |
Windows 9x[edit]
| Name | Kernel | Kernel type | Architecture | Integrated firewall | SMP support | USB support | UDMA support | LFN support | Update management | APIs | DDIs | Safe Mode | DirectX |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Windows 95 | MS-DOS 7.0 (Win95, Win95A), MS-DOS 7.1 (Win95B, Win95C) | Monolithic kernel | x86, hybrid 16/32-bit | No | No | Partial (OSR 2.1/2.5 only)[16] | No | Yes | Windows Update | Win16, Win32 | DOS, DLL, VxD, WDM (USB-only), direct-access | Yes | N/A (RTM/OSR1) 2.0a (OSR2/2.1) 5.0 (OSR2.5) 8.0a (optional) |
| Windows 98 | MS-DOS 7.1 | Monolithic kernel | x86, hybrid 16/32-bit | No | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | Windows Update | Win16, Win32 | DOS, DLL, VxD, WDM (partial), direct-access | Yes | 5.2 9.0c (Oct 2006) (optional) |
| Windows 98 Second Edition | MS-DOS 7.1 | Monolithic kernel | x86, hybrid 16/32-bit | No | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | Windows Update | Win16, Win32 | DOS, DLL, VxD, WDM (partial), direct-access | Yes | 6.1a 9.0c (Oct 2006) (optional) |
| Windows Me | MS-DOS 8.0 | Monolithic kernel | x86, hybrid 16/32-bit | No | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | Windows Update | Win16, Win32 | DLL, VxD, WDM (partial), direct-access | Yes | 7.1 9.0c (Oct 2006) (optional) |
It is possible to install the MS-DOS variants 7.0 and 7.1 without the graphics user interface of Windows. If an independent installation of both, DOS and Windows is desired, DOS ought to be installed prior to Windows, at the start of a small partition. The system must be transferred by the (dangerous) «SYSTEM» DOS-command, while the other files constituting DOS can simply be copied (the files located in the DOS-root and the entire COMMAND directory). Such a stand-alone installation of MS-DOS 8 is not possible, as it is designed to work as real mode for Windows Me and nothing else.
Windows NT[edit]
The Windows NT kernel powers all recent Windows operating systems. It has run on IA-32, x64, DEC Alpha, MIPS architecture, PowerPC, Itanium, ARMv7, and ARM64 processors, but currently supported versions run on IA-32, x64, ARMv7, and ARM64.
| Name | Architecture | Store | Integrated firewall | SMP support | USB support | UDMA support | Long filename support | Package management | Update management | APIs | DDIs | Safe Mode | Data Execution Prevention | DirectX |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Windows NT 3.1 | IA-32, DEC Alpha, MIPS | — | No | Yes | No | ? | Yes (NTFS and HPFS volumes only) | — | Win32, OS/2, POSIX | DLL, KMD | No | No | No | |
| Windows NT 3.5 | IA-32, DEC Alpha, MIPS | — | No | Yes | No | ? | Yes (except on CDFS volumes) | — | Win32, OS/2, POSIX | DLL, KMD | No | No | No | |
| Windows NT 3.51 | IA-32, DEC Alpha, MIPS, PowerPC | — | No | Yes | No | ? | Yes (except on CDFS volumes) | — | Win32, OS/2, POSIX | DLL, KMD | No | No | No | |
| Windows NT 4.0 | IA-32, DEC Alpha, MIPS, PowerPC | — | No | Yes | Yes (if the Ion USB update is installed) | Yes | Yes | — | Windows Update (if Internet Explorer 5 or later is installed) | Win32, OS/2, POSIX | DLL, KMD | No | No | Yes 3.0a, 5.0 (unofficial) |
| Windows 2000 | IA-32 | — | No | Yes | Yes (USB 2.0 with update or SP4)[17] | Yes | Yes | — | Windows Update, WSUS | Win32, OS/2, POSIX | DLL, KMD, WDM, KMDF | Yes | No | Yes 7.0, 9.0c (Feb 2010) (optional) |
| Windows XP | IA-32 (NT5.1), Itanium (NT5.1/5.2), x64 (NT5.2) | — | Yes | Yes (Professional Edition only) | Yes (USB 2.0 with update or SP1+)[18] | Yes | Yes | — | Windows Update, WSUS | Win32, .NET | DLL, KMD, WDM, KMDF, UMDFv1 | Yes | Yes (in SP2) | Yes 9.0c |
| Windows Server 2003 | IA-32, Itanium, x64 | — | Yes | Yes | Yes (USB 2.0)[19] | Yes | Yes | — | Windows Update, WSUS | Win32 | DLL, KMD, WDM, KMDF, UMDFv1 | Yes | Yes (with SP1) | Yes 9.0c |
| Windows Fundamentals for Legacy PCs | IA-32 | — | Yes | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | — | Windows Update, WSUS | Win32 | DLL, KMD, WDM, KMDF, UMDFv1 | Yes | Yes | Yes 9.0c |
| Windows Vista | IA-32, x64 | Windows Marketplace | Yes | Yes | Yes (USB 2.0) | Yes | Yes | — | Windows Update, WSUS | Win32, .NET, POSIX (only Enterprise and Ultimate) | DLL, KMD, WDM, KMDF, UMDFv1 | Yes | Yes | Yes 10.1 11.0 (optional) |
| Windows Server 2008 | IA-32, Itanium, x64 | — | Yes | Yes | Yes (USB 2.0) | Yes | Yes | — | Windows Update, WSUS | Win32 | DLL, KMD, WDM, KMDF, UMDFv1 | Yes | Yes | Yes 10.1 11.0 (optional) |
| Windows Home Server | IA-32 | — | ? | Yes | Yes (USB 2.0) | ? | Yes | — | Windows Update | Win32 | DLL, KMD, WDM, KMDF, UMDFv1 | ? | ? | Yes 9.0c |
| Windows 7 | IA-32, x64 | — | Yes | Yes | Yes (USB 3.0) | Yes | Yes | — | Windows Update, WSUS | Win32, .NET | DLL, KMD, WDM, KMDF, UMDFv1 | Yes | Yes | Yes 11.0 11.1 (optional) |
| Windows Server 2008 R2 | Itanium, x64 | — | Yes | Yes | Yes (USB 3.0) | Yes | Yes | — | Windows Update, WSUS | Win32, .NET | DLL, KMD, WDM, KMDF, UMDFv1 | Yes | Yes | Yes 11.0 11.1 (optional) |
| Windows Home Server 2011 | x64 | — | ? | Yes | Yes (USB 3.0) | ? | Yes | — | Windows Update | Win32 | DLL, KMD, WDM, KMDF, UMDFv1 | ? | ? | Yes 11.0 11.1 (optional) |
| Windows Server 2012 | x64 | Windows Store | Yes | Yes | Yes (USB 3.0) | Yes | Yes | Windows Store | Windows Update, WSUS | Win32, .NET, WinRT | DLL, KMD, WDM, KMDF, UMDFv1 | Yes | Yes | Yes 11.1 |
| Windows 8 | IA-32, x64 | Windows Store | Yes | Yes | Yes (USB 3.0) | Yes | Yes | Windows Store | Windows Update, WSUS | Win32, .NET, WinRT | DLL, KMD, WDM, KMDF, UMDFv1 | Yes | Yes | Yes 11.1 |
| Windows 8.1 | IA-32, x64 | Windows Store | Yes | Yes | Yes (USB 3.0) | Yes | Yes | Windows Store, PowerShell | Windows Update, WSUS, Windows Store | Win32, .NET, WinRT | DLL, KMD, WDM, KMDF, UMDFv1, UMDFv2 | Yes | Yes | Yes 11.2 |
| Windows Server 2012 R2 | x64 | Windows Store | Yes | Yes | Yes (USB 3.0) | Yes | Yes | Windows Store | Windows Update, WSUS, Windows Store | Win32, .NET, WinRT | DLL, KMD, WDM, KMDF, UMDFv1, UMDFv2 | Yes | Yes | Yes 11.2 |
| Windows 10 | IA-32, x64 | Windows Store | Yes | Yes | Yes (USB 3.1 and Thunderbolt 3) | Yes | Yes | Windows Store, PowerShell | Windows Update, WSUS, Windows Store | Win32, .NET, WinRT, Linux | DLL, KMD, WDM, KMDF, UMDFv1, UMDFv2 | Yes | Yes | Yes 12 |
| Windows Server 2016 | x64 | Windows Store | Yes | Yes | Yes (USB 3.1 and Thunderbolt 3) | Yes | Yes | Windows Store | Windows Update, WSUS, Windows Store | Win32, .NET, WinRT | DLL, KMD, WDM, KMDF, UMDFv1, UMDFv2 | Yes | Yes | Yes 12 |
Windows Phone[edit]
| Name | Architecture | Integrated firewall | SMP support | USB support | UDMA support | Package management | APIs |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Windows Phone 8 | ARMv7 | Yes | Yes | Yes (USB 2.0) | Yes | Windows Phone Store | Silverlight |
| Windows Phone 8.1 | ARMv7 | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Windows Phone Store | Silverlight WinRT |
| Windows 10 Mobile | ARMv7 | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Microsoft Store |
Supported file systems[edit]
Various versions of Windows support various file systems, including:FAT12, FAT16, FAT32, HPFS, or NTFS, along with network file systems shared from other computers, and the ISO 9660 and UDF file systems used for CDs, DVDs, and other optical disc drives such as Blu-ray. Each file system is usually limited in application to certain media, for example CDs must use ISO 9660 or UDF, and as of Windows Vista, NTFS is the only file system which the operating system can be installed on. Windows Embedded CE 6.0, Windows Vista Service Pack 1, and Windows Server 2008 onwards support exFAT, a file system more suitable for USB flash drives.
Windows 9x[edit]
| FAT12 | FAT16 | FAT32 | HPFS | ISO 9660 | NTFS | UDF | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Windows 95 | Yes | Yes | Yes (OSR2 or above) | Network Drive | Yes | Network Drive | No |
| Windows 98 | Yes | Yes | Yes | Network Drive | Yes | Network Drive | Yes (1.5, read) |
| Windows Me | Yes | Yes | Yes | Network Drive | Yes | Network Drive | Yes (1.5, read) |
Windows NT[edit]
| FAT12 | FAT16 | FAT32 | HPFS | ISO 9660 | NTFS | exFAT | UDF | ReFS | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Windows NT 3.1, 3.5, 3.51 | Yes | Yes | No | Yes | Yes | Yes v1.0/v1.1 | No | ? | No |
| Windows NT 4.0 | Yes | Yes | No | Partial | Yes | Yes v1.2 | No | ? | No |
| Windows 2000 | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | Yes | Yes v3.0 | No | Yes | No |
| Windows XP | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | Yes | Yes v3.1 | Optional | Yes (2.01) | No |
| Windows Server 2003 | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | Yes | Yes v3.1 | Optional | Yes | No |
| Windows Vista | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | Yes | Yes v5 | Yes | Yes (2.6) | No |
| Windows Server 2008 | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | Yes | Yes v5 | Yes | Yes | No |
| Windows 7 | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | Yes | Yes v5 | Yes | Yes (2.6) | Yes |
| Windows Server 2008 R2 | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | Yes | Yes v5 | Yes | Yes (2.6) | Yes |
| Windows Server 2012 | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | Yes | Yes v5 | Yes | Yes (2.6) | Yes |
| Windows 8 | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | Yes | Yes v5 | Yes | Yes (2.6) | No |
| Windows 8.1 | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | Yes | Yes v5 | Yes | Yes (2.6) | Yes |
| Windows Server 2012 R2 | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | Yes | Yes v5 | Yes | Yes (2.6) | Yes |
| Windows 10 | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | Yes | Yes v5 | Yes | Yes (2.6) | Yes |
| Windows Server 2016 | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | Yes | Yes v5 | Yes | Yes (2.6) | Yes |
Windows Phone[edit]
| FAT12 | FAT16 | FAT32 | HPFS | ISO 9660 | NTFS | UDF (More Info) | ReFS | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Windows Phone 8 | ? | Yes | Yes | No | ? | Yes v5 | ? | No |
| Windows Phone 8.1 | ? | Yes | Yes | No | ? | Yes v5 | ? | No |
| Windows 10 Mobile | ? | Yes | Yes | No | ? | Yes v5 | ? | ? |
Hardware requirements[edit]
Installing Windows requires an internal or external optical drive, or a USB flash drive. A keyboard and mouse are the recommended input devices, though some versions support a touchscreen. For operating systems prior to Vista, an optical drive must be capable of reading CD media, while in Windows Vista onwards, such a drive must be DVD-compatible. The drive may be detached after installing Windows.
Windows 9x[edit]
| CPU | RAM | Free disk space | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Windows 95 | 386 | 4 MB | 120 MB |
| Windows 98 | 486 DX2 66 MHz | 16 MB | 300 MB |
| Windows Me (Millennium Edition) | Pentium 150 MHz | 32 MB | 400 MB |
Windows NT[edit]
| Version | CPU | RAM | Free disk space | Video adapter and monitor | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Minimum | Recommended | ||||
| Windows NT 3.51 Workstation | 386, 25 MHz | 8 MB | 16 MB | 90 MB | VGA (640×480) |
| Windows NT 4.0 Workstation | 486, 33 MHz | 12 MB | ? | 110 MB | |
| Windows 2000 Professional | 133 MHz | 32 MB | 128 MB | 650 MB | |
| Windows XP | 233 MHz | 64 MB | 128 MB | 1.5 GB | Super VGA (800×600) |
| Windows Fundamentals for Legacy PCs | 500 MB | ||||
| Windows XP 64-Bit Edition | 700 MHz Itanium[20] | 1 GB[20] | ? | 6 GB[20] | |
| Windows Server 2003 | 1 GHz (x86) or 1.4 GHz (x64) | 128 MB | 256 MB | 2 GB (x86) 4 GB (x64) |
|
| Windows Vista | 800 MHz | 384 MB (Starter) 512 MB (others)[21][dubious – discuss] |
2 GB | 15 GB (~6.5 GB for OS) |
Super VGA (800×600) WDDM & DirectX 9 for Aero |
| Windows Server 2008 | 1 GHz (x86) or 1.4 GHz (x64) | 2 GB | 10 GB | ||
| Windows 7 | 1 GHz | 1 GB (x86) 2 GB (x64) |
4 GB | 16 GB (x86) 20 GB (x64) (~6.5 GB for OS) |
|
| Windows Server 2012 | 1.4 GHz (x86-64) | 512 MB | 1 GB | 10 GB | Super VGA (800×600), 32-bit color |
| Windows 8 | 1 GHz | 1 GB (x86) 2 GB (x64) |
4 GB | 16 GB (x86) 20 GB (x64) (~6.5 GB for OS) |
Super VGA (800×600), 32-bit color 1024 x 768 for Windows Store apps 1366 x 768 to snap apps |
| Windows 8.1 | |||||
| Windows 10 | 1 GHz or faster processor or SoC | 1 GB (x86) 2 GB (x64) |
4 GB | 16 GB (x86) 20 GB (x64) |
Super VGA (800×600), 32-bit color |
| Windows Server 2016 | 1.4 GHz 64-bit processor | 512 MB ECC memory 2 GB with Desktop Experience installed[22] |
depends on role | 32 GB (~10 GB for OS) |
XGA (1024 x 768) |
| Windows Server 2019 | 1.4 GHz 64-bit processor | 512 MB ECC memory 2 GB with Desktop Experience installed[22] |
depends on role | 32 GB | XGA (1024 x 768) |
| Windows Server 2022 | 1.4 GHz 64-bit processor | 512 MB ECC memory 2 GB with Desktop Experience installed[23] |
depends on role | 32 GB | Super VGA (1024 x 768) |
| Windows 11 | 64-bit 1 GHz or faster processor or SoC with two or more cores | 4 GB | — | 64 GB (~10 GB for OS) |
720p greater than 9″ diagonally, 32-bit color |
Windows Phone[edit]
| Version | CPU | RAM | Free disk space | Video adapter and monitor | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Minimum | Recommended | ||||
| Windows Phone 7 | 0.8 GHz | 256 MB | — | 4 GB | Wide VGA (800 × 480) |
| Windows Phone 8 | 1 GHz | 512 MB | — | 8 GB | Wide VGA (800 × 480) |
| Windows Phone 8.1 | 1 GHz | 512 MB | — | 4 GB | Wide VGA (800 × 480) |
| Windows 10 Mobile | 1 GHz | 1 GB | 2 GB | 8 GB | Wide VGA (800 × 480) |
Physical memory limits[edit]
Maximum limits on physical memory (RAM) that Windows can address vary depending on both the Windows version and between IA-32 and x64 versions.[24][25]
Windows[edit]
| Operating system | Limit on Real Mode | Limit on Standard Mode | Limit on Enhanced Mode |
|---|---|---|---|
| Windows 1.0x | 640 KB | — | — |
| Windows 2.0x | 640 KB | — | 16MB |
| Windows 2.1x | 640 + 64 KB | — | 16MB |
| Windows 3.0x | 640 + 64 KB | 16MB | 16MB |
| Windows 3.1x | — | 256MB[26] | 256MB[26] |
| Windows 95 | — | — | 944MB[27] |
| Windows 98 | — | — | 1GB |
| Windows ME | — | — | 1.5GB |
Windows NT[edit]
| Operating system | Limit on IA-32 | Limit in IA-64 | Limit on x64 | Limit on ARM32 | Limit on ARM64 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Windows NT 3.1 | 4 GB | — | — | — | — |
| Windows NT 3.5 | 4 GB | — | — | — | — |
| Windows NT 3.51 | 4 GB | — | — | — | — |
| Windows NT 4.0 | 4 GB | — | — | — | — |
| Windows 2000 Professional/Server | 4 GB | — | — | — | — |
| Windows 2000 Advanced Server | 8 GB | — | — | — | — |
| Windows 2000 Datacenter | 32 GB | — | — | — | — |
| Windows XP Starter | 512 MB | — | — | — | — |
| Windows XP Home | 4 GB | — | — | — | — |
| Windows XP Professional | 4 GB | 128 GB | 128 GB | — | — |
| Windows Server 2003 RTM Web | 2 GB | — | — | — | — |
| Windows Server 2003 RTM Standard/Small Business | 4 GB | — | — | — | — |
| Windows Server 2003 RTM Enterprise/Datacenter | 64 GB | 512 GB | — | — | — |
| Windows Compute Cluster Server 2003 | — | 32 GB | — | — | — |
| Windows Server 2003 R1/SP1 Standard | 4 GB | — | 32 GB | — | — |
| Windows Server 2003 R1/SP1 Enterprise/Datacenter | 64 GB | 1 TB | 1 TB | — | — |
| Windows Server 2003 R1/SP2 Standard | 4GB | — | 32 GB | — | — |
| Windows Server 2003 R1/SP2 Enterprise/Datacenter | 64 GB | 2 TB | 1 TB | — | — |
| Windows Server 2003 R2/SP1 Standard | 4 GB | — | 32 GB | — | — |
| Windows Server 2003 R2/SP1 Enterprise/Datacenter | 64 GB | — | 1 TB | — | — |
| Windows Vista Starter | 1 GB | — | — | — | — |
| Windows Vista Home Basic | 4 GB | — | 8 GB | — | — |
| Windows Vista Home Premium | 4 GB | — | 16 GB | — | — |
| Windows Vista Business/Enterprise/Ultimate | 4 GB | — | 128 GB | — | — |
| Windows Home Server | 4 GB | — | — | — | — |
| Windows Server 2008 Web Server/Standard/Small Business | 4 GB | — | 32 GB | — | — |
| Windows HPC Server 2008 | — | — | 128 GB | — | — |
| Windows Server 2008 Enterprise/Datacenter | 64 GB | — | 1 TB | — | — |
| Windows Server 2008 for Itanium–Based Systems | — | 2 TB | — | — | — |
| Windows 7 Starter | 2 GB | — | — | — | — |
| Windows 7 Home Basic | 4 GB | — | 8 GB | — | — |
| Windows 7 Home Premium | 4 GB | — | 16 GB | — | — |
| Windows 7 Professional/Enterprise/Ultimate | 4 GB | — | 192 GB | — | — |
| Windows Server 2008 R2 Foundation | — | — | 8 GB | — | — |
| Windows Server 2008 R2 Web Server/Standard | — | — | 32 GB | — | — |
| Windows HPC Server 2008 R2 | — | — | 128 GB | — | — |
| Windows Server 2008 R2 Enterprise/Datacenter | — | — | 2 TB | — | — |
| Windows Server 2008 R2 for Itanium–Based Systems | — | 2 TB | — | — | — |
| Windows 8 (Core) | 4 GB | — | 128 GB | — | — |
| Windows 8 Pro/Enterprise | 4 GB | — | 512 GB | — | — |
| Windows RT | — | — | — | 4 GB | — |
| Windows Server 2012 Standard/Datacenter | — | — | 4 TB | — | — |
| Windows Storage Server 2012 Standard | — | — | 4 TB | — | — |
| Windows Storage Server 2012 Workgroup | — | — | 32 GB | — | — |
| Hyper-V Server 2012 | — | — | 4 TB | — | — |
| Windows 8.1 (Core) | 4 GB | — | 128 GB | — | — |
| Windows 8.1 Pro/Enterprise | 4 GB | — | 512 GB | — | — |
| Windows RT 8.1 | — | — | — | 4 GB | — |
| Windows 10 Mobile | 4 GB | — | — | — | — |
| Windows 10 Home | 4 GB | — | 128 GB | 4 GB | 128 GB |
| Windows 10 Pro | 4 GB | — | 2 TB | 4 GB | 2 TB |
| Windows 10 Pro for Workstations | 4 GB | — | 6 TB | 4 GB | 6 TB |
| Windows 10 Education | 4 GB | — | 2 TB | 4 GB | 2 TB |
| Windows 10 Enterprise | 4 GB | — | 6 TB | 4 GB | 6 TB |
| Windows Server 2016 Essentials | — | — | 64 GB | — | — |
| Windows Server 2016 Standard | — | — | 24 TB | — | — |
| Windows Server 2016 Datacenter | — | — | 24 TB | — | — |
| Windows Server 2019 Essentials | — | — | 64 GB | — | — |
| Windows Server 2019 Standard | — | — | 24 TB | — | — |
| Windows Server 2019 Datacenter | — | — | 24 TB | — | — |
| Windows Server 2022 Essentials | — | — | 64 GB | — | — |
| Windows Server 2022 Standard | — | — | 24 TB | — | — |
| Windows Server 2022 Datacenter | — | — | 24 TB | — | — |
| Windows 11 Home | — | — | 128 GB | — | 128 GB |
| Windows 11 Pro | — | — | 2 TB | — | 2 TB |
| Windows 11 Pro for Workstations | — | — | 6 TB | — | 6 TB |
| Windows 11 Education | — | — | 2 TB | — | 2 TB |
| Windows 11 Enterprise | — | — | 6 TB | — | 6 TB |
Security features[edit]
| Resource access control | Subsystem isolation mechanisms | Integrated firewall | Encrypted file systems | Defender | Windows Hello | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Windows 2000 | ACLs | TCP/IP Filtering, IPSec | Yes (NTFS only) | No | No | |
| Windows XP | ACLs | Win32 WindowStation, Desktop, Job objects | Windows Firewall (from SP2), TCP/IP Filtering, IPSec | Yes (NTFS only) | Optional | No |
| Windows Server 2003 | ACLs, Privileges, RBAC | Win32 WindowStation, Desktop, Job objects | Windows Firewall, TCP/IP Filtering, IPSec | Yes | Optional | No |
| Windows Vista | ACLs, Privileges, RBAC | Win32 WindowStation, Desktop, Job objects | Windows Firewall, TCP/IP Filtering, IPSec | Yes | Yes | No |
| Windows Server 2008 | ACLs, Privileges, RBAC | Win32 WindowStation, Desktop, Job objects | Windows Firewall, TCP/IP Filtering, IPSec | Yes | Yes | No |
| Windows 7 | ACLs, Privileges, RBAC | Win32 WindowStation, Desktop, Job objects | Windows Firewall, TCP/IP Filtering, IPSec | Yes | Yes | No |
| Windows Server 2012 | ACLs, Privileges, RBAC | Win32 WindowStation, Desktop, Job objects | Windows Firewall, TCP/IP Filtering, IPSec | Yes | Yes | No |
| Windows 8 | ACLs, Privileges, RBAC | Win32 WindowStation, Desktop, Job objects | Windows Firewall, TCP/IP Filtering, IPSec | Yes | Yes | No |
| Windows Server 2012 R2 | ACLs, Privileges, RBAC | Win32 WindowStation, Desktop, Job objects | Windows Firewall, TCP/IP Filtering, IPSec | Yes | Yes | No |
| Windows 8.1 | ACLs, Privileges, RBAC | Win32 WindowStation, Desktop, Job objects | Windows Firewall, TCP/IP Filtering, IPSec | Yes | Yes | No |
| Windows 10 | ACLs, Privileges, RBAC | Win32 WindowStation, Desktop, Job objects | Windows Firewall, TCP/IP Filtering, IPSec | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Windows Server 2016 | ACLs, Privileges, RBAC | Win32 WindowStation, Desktop, Job objects | Windows Firewall, TCP/IP Filtering, IPSec | Yes | Yes | Yes |
Features[edit]
| Version | Shell | Visual styles | Browser | Web server | Windows Media Player | Command-line interpreter |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Windows 1.0 | MS-DOS executive | (Unnamed) | — | — | — | — |
| Windows 2.0 | MS-DOS executive | (Unnamed) | — | — | — | — |
| Windows 3.0 | Program Manager | (Unnamed) | — | — | 3.0 (Multimedia Extension edition only) | — |
| Windows 3.1x | Program Manager | (Unnamed) | — | — | 3.1 | — |
| Windows 95 | Windows shell | Classic | Internet Explorer 1 in OEM RTM Internet Explorer 2 in OSR1 Internet Explorer 3 in OSR2 and OSR2.1 Internet Explorer 4 in OSR2.5 |
— | 4.0 | COMMAND.COM |
| Windows NT 4.0 | Windows shell | Classic | Internet Explorer 2 Internet Explorer 3 (in some localized editions) |
PWS | 4.0 | COMMAND.COM, CMD.EXE |
| Windows 98 | Windows shell | Classic | Internet Explorer 4.01 | PWS | 4.0 | COMMAND.COM |
| Windows 98 SE | Windows shell | Classic | Internet Explorer 5 | PWS | 4.0 | COMMAND.COM |
| Windows 2000 | Windows shell | Classic | Internet Explorer 5.01 | IIS 5.0 | 5.0 and 6.4 (side by side) | COMMAND.COM, CMD.EXE |
| Windows Me | Windows shell | Classic | Internet Explorer 5.5 | — | 6.4 and 7.0 (side by side) | COMMAND.COM |
| Windows XP | Windows shell | Luna (default), Classic | Internet Explorer 6 | IIS 5.1 | 5.1, 6.4 and 8 (in RTM) 5.1, 6.4 and 9 (in SP2) |
COMMAND.COM, CMD.EXE, PowerShell (optional) |
| Windows Server 2003 | Windows shell | Classic (default), Luna | Internet Explorer 6 | IIS 6.0 | 9 (in RTM), 10 (in SP1) | COMMAND.COM, CMD.EXE, PowerShell (optional) |
| Windows Vista | Windows shell | Aero (default), Classic | Internet Explorer 7 | IIS 7 | 11 | COMMAND.COM, CMD.EXE, PowerShell (optional) |
| Windows Server 2008 | Windows shell, Server Core | Classic (default), Aero (via «Desktop Experience») | Internet Explorer 7 | IIS 7 | 11 (enabled by installing «Desktop Experience») | COMMAND.COM, CMD.EXE, PowerShell (optional) |
| Windows 7 | Windows shell | Aero (default), Classic | Internet Explorer 8 | IIS 7.5 | 12 | COMMAND.COM, CMD.EXE, PowerShell v2.0 |
| Windows Server 2008 R2 | Windows shell, Server Core | Classic (default), Aero (via «Desktop Experience») | Internet Explorer 8 | IIS 7.5 | 12 (via «Desktop Experience») | CMD.EXE, PowerShell v2.0 |
| Windows Server 2012 | Windows shell, Server Core | Metro | Internet Explorer 10 | IIS 8 | 12 (via «Desktop Experience») | CMD.EXE, PowerShell v3.0 |
| Windows 8 | Windows shell | Metro | Internet Explorer 10 | IIS 8 | 12 | COMMAND.COM, CMD.EXE, PowerShell v3.0 |
| Windows Server 2012 R2 | Windows shell, Windows server core | Metro | Internet Explorer 11 | IIS 8.5 | 12 (via «Desktop Experience») | CMD.EXE, PowerShell v4.0 |
| Windows 8.1 | Windows shell | Metro | Internet Explorer 11 | IIS 8.5 | 12 | COMMAND.COM, CMD.EXE, PowerShell v4.0 |
| Windows 10 | Windows shell | Metro | Internet Explorer 11 Microsoft Edge 12-13 |
IIS 10.0 | 12 | COMMAND.COM, CMD.EXE, PowerShell v5.0 |
| Windows Server 2016 | Windows shell, Windows server core | Metro | Internet Explorer 11 Microsoft Edge 13 |
IIS 10.0 | 12 (via «Desktop Experience») | CMD.EXE, PowerShell v5.0 |
| Windows Server 2019 | Windows shell, Windows server core | Metro | Internet Explorer 11 Microsoft Edge 13 |
IIS 10.0 | 12 (via «Desktop Experience») | CMD.EXE, PowerShell v5.0 |
Timeline[edit]
- view
- talk
- edit
See also[edit]
Other lists[edit]
- List of Microsoft Windows versions
- List of operating systems
- Comparison of operating systems
- Comparison of kernels
- Comparison of Windows Vista and Windows XP
- History of Microsoft Windows
- Comparison of DOS operating systems
- Architecture of the Windows NT operating system line
- Microsoft codenames
Windows clones and emulators[edit]
- Freedows OS–Windows clone
- ReactOS–project to develop an operating system that is binary compatible with application software and device drivers for Microsoft Windows NT version 5.x
- Wine (software)–compatibility layer which allows to execute programs that were originally written for Microsoft Windows
References[edit]
- ^ «Product Lifecycle Dates-Windows Product Family». Microsoft. Archived from the original on 2004-06-11. Retrieved 2021-08-24.
- ^ «Windows NT 3.5 for PowerPC». 9 November 1994. Archived from the original on August 12, 2021.
- ^ a b c d e «Windows 10 IoT Core — Microsoft Lifecycle». Archived from the original on November 18, 2020. Retrieved August 4, 2022.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l «Windows 10 IoT Enterprise — Microsoft Lifecycle». Retrieved August 4, 2022.
- ^ «Windows 10 IoT Enterprise LTSB 2016 — Microsoft Lifecycle». Archived from the original on March 23, 2022. Retrieved August 4, 2022.
- ^ «Windows 10 IoT Core LTSC — Microsoft Lifecycle». Archived from the original on March 10, 2022. Retrieved August 4, 2022.
- ^ «Windows 10 IoT Enterprise LTSC 2019 — Microsoft Lifecycle». Archived from the original on November 16, 2021. Retrieved August 4, 2022.
- ^ «Windows 10 IoT Enterprise LTSC 2021 — Microsoft Lifecycle». Archived from the original on November 16, 2021. Retrieved August 4, 2022.
- ^ «Microsoft announces latest Windows IoT innovations for intelligent edge devices at Embedded World». Archived from the original on February 26, 2019.
- ^ «Windows Server IoT 2019 — Microsoft Lifecycle». Archived from the original on March 23, 2022. Retrieved August 4, 2022.
- ^ «Windows Server IoT 2019 for Storage — Microsoft Lifecycle». Archived from the original on March 23, 2022. Retrieved August 4, 2022.
- ^ «Announcing the GA of Windows Server IoT 2022». Retrieved August 4, 2022.
- ^ «Windows Server IoT 2022 — Microsoft Lifecycle». Archived from the original on October 6, 2021. Retrieved August 4, 2022.
- ^ «Windows 11 IoT Enterprise (Version 21H2) — Microsoft Lifecycle». Archived from the original on October 5, 2021. Retrieved August 4, 2022.
- ^ «Windows 11 IoT Enterprise — Microsoft Lifecycle». Archived from the original on September 22, 2022. Retrieved September 22, 2022.
- ^ «Availability of Universal Serial Bus Support in Windows 95». Microsoft Support. Archived from the original on December 10, 2005.
- ^ «Updated USB 2.0 Drivers Are Available in Windows 2000 Service Pack 4 (SP4)». Microsoft Support. Archived from the original on October 29, 2006. Retrieved February 5, 2012.
- ^ Jones, Don (August 5, 2002). «USB 2.0 Support in Windows XP:High Speed at Last». Microsoft. Archived from the original on December 31, 2004. Retrieved February 5, 2012.
- ^ «USB 2.0 and Windows Operating Systems». Windows Hardware Development. May 11, 2007. Archived from the original on March 3, 2011. Retrieved February 5, 2012.
- ^ a b c «Release Notes for Windows XP 64-Bit Edition Setup». Microsoft. Archived from the original on February 10, 2007. Retrieved September 2, 2014.
- ^ «Windows Vista Starter Fact Sheet». Microsoft. January 2007. Archived from the original on March 7, 2007.
- ^ a b «System Requirements». docs.microsoft.com. Archived from the original on June 27, 2017. Retrieved May 24, 2018.
- ^ «Hardware requirements for Windows Server». docs.microsoft.com. Archived from the original on August 21, 2021. Retrieved August 4, 2022.
- ^ «What is the maximum amount of RAM the Windows operating system can handle?». Crucial. Archived from the original on May 11, 2011. Retrieved February 5, 2012.
- ^ «Memory Limits for Windows and Windows Server Releases». Microsoft. Archived from the original on May 5, 2008. Retrieved February 5, 2012.
- ^ a b «Q84388: Windows 3.1 Memory Limits». December 15, 2022.
- ^ «Windows 95/98 error «Insufficient memory to initialize Windows» — IBM IntelliStation M Pro (Type 6889)». December 15, 2022.
External links[edit]
- Official website
- Time line from Microsoft
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Original Windows logo from 1985
Current Windows logo (introduced in 2021)
Timeline of Windows releases
Microsoft Windows is a computer operating system developed by Microsoft. It was first launched in 1985 as a graphical operating system built on MS-DOS. The initial version was followed by several subsequent releases, and by the early 1990s, the Windows line had split into two separate lines of releases: Windows 9x for consumers and Windows NT for businesses and enterprises. In the following years, several further variants of Windows would be released: Windows CE in 1996 for embedded systems; Pocket PC in 2000 (renamed to Windows Mobile in 2003 and Windows Phone in 2010) for personal digital assistants and, later, smartphones; Windows Holographic in 2016 for AR/VR headsets; and several other editions.
Personal computer versions[edit]
A «personal computer» version of Windows is considered to be a version that end-users or OEMs can install on personal computers, including desktop computers, laptops, and workstations.
The first five versions of Windows–Windows 1.0, Windows 2.0, Windows 2.1, Windows 3.0, and Windows 3.1–were all based on MS-DOS, and were aimed at both consumers and businesses. However, Windows 3.1 had two separate successors, splitting the Windows line in two: the consumer-focused «Windows 9x» line, consisting of Windows 95, Windows 98, and Windows Me; and the professional Windows NT line, comprising Windows NT 3.1, Windows NT 3.5, Windows NT 3.51, Windows NT 4.0, and Windows 2000. These two lines were reunited into a single line with the NT-based Windows XP; this Windows release succeeded both Windows Me and Windows 2000 and had separate editions for consumer and professional use. Since Windows XP, multiple further versions of Windows have been released, the most recent of which is Windows 11.
| Name | Codename | Release date | Version | Editions | Build number | Architecture | End of support | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Windows 1.01 | Interface Manager | 1985-11-20 | 1.01 | — | — | x86-16 | 2001-12-31 | |
| Windows 1.02 | — | 1986-05-14 | 1.02 | — | — | |||
| Windows 1.03 | — | 1986-08-21 | 1.03 | — | — | |||
| Windows 1.04 | — | 1987-04-10 | 1.04 | — | — | |||
| Windows 2.01 | — | 1987-12-09 | 2.01 | — | — | x86-16, IA-32 | ||
| Windows 2.03 | — | 1987-12-09 | 2.03 | — | — | |||
| Windows 2.1 | — | 1988-05-27 | 2.10 | — | — | |||
| Windows 2.11 | — | 1989-03-13 | 2.11 | — | — | |||
| Windows 3.0 | — | 1990-05-22 | 3.00 |
|
— | |||
| Windows 3.1 | — | 1992-04-06 | 3.10 |
|
103 | |||
| Sparta[a] | 1992-10 |
|
102 | IA-32 | ||||
| Windows NT 3.1 | Razzle[1] | 1993-07-27 | NT 3.1 |
|
528 | IA-32, Alpha, MIPS | 2000-12-31 | |
| Windows 3.11 | — | 1993-11-08 | 3.11 |
|
? | x86-16, IA-32 | 2001-12-31 | |
| Snowball |
|
300 | IA-32 | |||||
| Windows 3.2 | — | 1993-11-22 | 3.2 |
|
153 | x86-16, IA-32 | ||
| Windows NT 3.5 | Daytona | 1994-09-21 | NT 3.5 |
|
807 | IA-32, Alpha, MIPS, PowerPC | ||
| Windows NT 3.51 | 1995-05-30 | NT 3.51 |
|
1057 | ||||
| Windows 95 | Chicago | 1995-08-24 | 4.00 |
|
950 | IA-32 | ||
| Windows NT 4.0 | Shell Update Release | 1996-08-24 | NT 4.0 |
|
1381 | IA-32, Alpha, MIPS, PowerPC | 2004-06-30 | |
| Windows 98 | Memphis[b] | 1998-06-25 | 4.10 |
|
1998 | IA-32 | 2006-07-11 | |
| Windows 98 Second Edition | — | 1999-05-05 |
|
2222A | ||||
| Windows 2000 | Windows NT 5.0 | 2000-02-17 | NT 5.0 |
|
2195 | IA-32 | 2010-07-13 | |
| Windows Me | Millennium | 2000-09-14 | 4.90 |
|
3000 | IA-32 | 2006-07-11 | |
| Windows XP | Whistler | 2001-10-25 | NT 5.1 |
|
2600 | IA-32 | 2014-04-08 | |
|
Itanium | |||||||
| Freestyle | 2002-10-29 |
|
IA-32 | |||||
| Harmony | 2003-09-30 |
|
||||||
| Symphony | 2004-10-12 |
|
2700 | |||||
| Emerald | 2005-10-14 |
|
2710 | |||||
| Anvil | 2005-04-25 | NT 5.2 |
|
3790 | x86-64 | |||
| Windows Vista | Longhorn[3] | 2007-01-30 | NT 6.0 |
|
6002[c] | IA-32, x86-64 | 2017-04-11 | |
| Windows 7 | Windows 7[4] | 2009-10-22 | NT 6.1 |
|
7601[d] | IA-32, x86-64 | 2020-01-14 | |
| Windows 8 | Windows 8 | 2012-10-26 | NT 6.2 |
|
9200 | IA-32, x86-64 | 2016-01-12 | 2023-07-11 (Embedded) |
| Windows 8.1 | Blue | 2013-10-17 | NT 6.3 |
|
9600 | IA-32, x86-64 | 2023-01-10 | 2023-07-11 (Embedded) |
| 2014-05-23[e] |
|
|||||||
| Windows 10 version 1507 | Threshold[5][f] | 2015-07-29 | NT 10.0[g][h] |
|
10240 | IA-32, x86-64 | 2025-10-14[7][m] | |
| Windows 10 version 1511 | Threshold 2 | 2015-11-10 | 1511 | 10586 | ||||
| Windows 10 version 1607 | Redstone 1 | 2016-08-02 | 1607 | 14393 | ||||
| Windows 10 version 1703 | Redstone 2[8] | 2017-04-05 | 1703 | 15063 | ||||
| Windows 10 version 1709 | Redstone 3[9] | 2017-10-17 | 1709 | 16299 | IA-32, x86-64, ARM64 | |||
| Windows 10 version 1803 | Redstone 4 | 2018-04-30 | 1803 | 17134 | ||||
| Windows 10 version 1809 | Redstone 5[10] | 2018-11-13 | 1809 | 17763 | ||||
| Windows 10 version 1903 | 19H1[11] | 2019-05-21 | 1903 | 18362 | ||||
| Windows 10 version 1909 | Vanadium[n][13] | 2019-11-12 | 1909 | 18363 | ||||
| Windows 10 version 2004 | Vibranium[13][14][o] | 2020-05-27 | 2004 | 19041 | ||||
| Windows 10 version 20H2 | 2020-10-20 | 20H2 | 19042 | |||||
| Windows 10 version 21H1 | 2021-05-18 | 21H1 | 19043 | |||||
| Windows 10 version 21H2 | 2021-11-16 | 21H2 | 19044 | |||||
| Windows 10 version 22H2 | 2022-10-18 | 22H2 | 19045 | |||||
| Windows 11 version 21H2 | Sun Valley[p] | 2021-10-05 | 21H2 |
|
22000 | x86-64, ARM64 | 2023-10-10[q] | |
| Windows 11 version 22H2 | Sun Valley 2 | 2022-09-20 | 22H2 | 22621 | 2024-10-14[q] |
Mobile versions[edit]
Mobile versions refer to versions of Windows that can run on smartphones or personal digital assistants.
Pocket PC 2000 logo
Windows Phone 7 logo
Windows Phone 8 logo
Windows Phone 8.1 logo
Logo used for Windows 10 and Windows 10 Mobile
| Name | Codename | Architecture | Release date |
Version Number |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pocket PC 2000 | Rapier | ARMv4, MIPS, SH-3 | 2000-04-19 | CE 3.0 |
| Pocket PC 2002 | Merlin | ARMv4 | 2001-10-04 | |
| Windows Mobile 2003 | Ozone | ARMv5 | 2003-06-23 | CE 4.x |
| Windows Mobile 2003 SE | — | 2004-03-24 | ||
| Windows Mobile 5.0 | Magneto | 2005-05-09 | CE 5.0 | |
| Windows Mobile 6.0 | Crossbow | 2007-02-12 | ||
| Windows Mobile 6.1 | — | 2008-04-01 | CE 5.2 | |
| Windows Mobile 6.1.4 | 6 on 6 | 2008-11-11[16] | ||
| Windows Mobile 6.5 | Titanium | 2009-05-11 | CE 6.0 | |
| Windows Phone 7[r] | — | ARMv7 | 2010-10-29 | |
| Windows Phone 7.5 | Mango | 2011-09-27 | ||
| Windows Phone 7.8 | — | 2013-02-01 | ||
| Windows Phone 8 | Apollo | 2012-10-29 | NT 6.2 | |
| Windows Phone 8.1 | Blue | 2014-04-14 | NT 6.3 | |
| Windows 10 Mobile, version 1511 | Threshold 2 | 2015-11-12 | 1511 | |
| Windows 10 Mobile, version 1607 | Redstone 1 | 2016-08-16 | 1607 | |
| Windows 10 Mobile, version 1703 | Redstone 2 | 2017-04-24 | 1703 | |
| Windows 10 Mobile, version 1709 | feature2[17] | 2017-10-24 | 1709 |
Server versions[edit]
| Name | Release date | Version number | Editions | Build number | Architecture | End of support |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Windows NT 3.1 | 1993-07-27 | NT 3.1 |
|
528 | IA-32, Alpha, MIPS | 2000-12-31 |
| Windows NT 3.5 | 1994-09-20 | NT 3.5 |
|
807 | IA-32, Alpha, MIPS, PowerPC | 2001-12-31 |
| Windows NT 3.51 | 1995-05-29 | NT 3.51 |
|
1057 | 2001-12-31 | |
| Windows NT 4.0 | 1996-07-29 | NT 4.0 |
|
1381 | 2004-12-31 | |
| Windows 2000 | 2000-02-17 | NT 5.0 |
|
2195 | IA-32 | 2010-07-13 |
| Windows Server 2003 | 2003-04-24 | NT 5.2 |
|
3790 | IA-32, x86-64, Itanium | 2015-07-14 |
| Windows Server 2003 R2 | 2005-12-06 | 2015-07-14 | ||||
| Windows Server 2008 | 2008-02-27 | NT 6.0 |
|
6002[c] | IA-32, x86-64, Itanium | 2020-01-14 |
| Windows Server 2008 R2 | 2009-10-22 | NT 6.1 | 7601[d] | x86-64, Itanium | 2020-01-14 | |
| Windows Server 2012 | 2012-09-04 | NT 6.2 |
|
9200 | x86-64 | 2023-10-10 |
| Windows Server 2012 R2 | 2013-10-17 | NT 6.3 | 9600 | 2023-10-10 | ||
| Windows Server 2016 | 2016-10-12 | 1607[18] |
|
14393 | 2027-01-12 | |
| Windows Server, version 1709[19] | 2017-10-17 | 1709 | 16299 | 2019-04-09 | ||
| Windows Server, version 1803[20] | 2018-04-30 | 1803 | 17134 | 2019-11-12 | ||
| Windows Server, version 1809 | 2018-11-13[21] | 1809 | 17763 | 2020-11-10 | ||
| Windows Server 2019[18] | 2029-01-09[18] | |||||
| Windows Server, version 1903[18] | 2019-05-21 | 1903 | 18362 | 2020-12-08[18] | ||
| Windows Server, version 1909[18] | 2019-11-12 | 1909 | 18363 | 2021-05-11[18] | ||
| Windows Server, version 2004[22] | 2020-06-26 | 2004 | 19041 | 2021-12-14[18] | ||
| Windows Server, version 20H2[22] | 2020-10-20 | 20H2 | 19042 | 2022-08-09[18] | ||
| Windows Server 2022 | 2021-08-18 | 21H2[23] | 20348 | 2031-10-14[18] |
High-performance computing (HPC) servers[edit]
| Name | Codename | Release date | Based on |
|---|---|---|---|
| Windows Compute Cluster Server 2003 | — | 2006-06-09 | Windows Server 2003 R2 |
| Windows HPC Server 2008 | Socrates | 2008-09-22 | Windows Server 2008 |
| Windows HPC Server 2008 R2 | — | 2010-09-20 | Windows Server 2008 R2 |
Windows Essential Business Server[edit]
| Name | Codename | Release date | End-of-support date | Build number | Based on |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Windows Essential Business Server 2008 | Centro | 2008-09-15 | 2020-01-14 | 5700 | Windows Server 2008 |
Windows Home Server[edit]
| Name | Codename | Release date | End-of-support date | Based on |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Windows Home Server | Quattro | 2007-11-04 | 2013-01-08 | Windows Server 2003 R2 |
| Windows Home Server 2011 | Vail | 2011-04-06 | 2016-04-12 | Windows Server 2008 R2 |
Windows MultiPoint Server[edit]
Windows MultiPoint Server was an operating system based on Windows Server. It was succeeded by the MultiPoint Services role in Windows Server 2016 and Windows Server version 1709. It was no longer being developed in Windows Server version 1803 and later versions.
| Name | Codename | Release date | End-of-support date | Version number | Build number | Based on |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Windows MultiPoint Server 2010 | Solution Server | 2010-02-24 | 2020-07-14 | NT 6.1 | 537 | Windows Server 2008 R2 |
| Windows MultiPoint Server 2011 | WMS 2 | 2011-05-12 | 2021-07-13 | 1600 | Windows Server 2008 R2 Service Pack 1 | |
| Windows MultiPoint Server 2012 | WMS 3 | 2012-10-30 | 2023-10-10 | NT 6.2 | 2506 | Windows Server 2012 |
Windows Small Business Server[edit]
| Name | Codename | Release date | End-of-support date | Build number | Based on |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Small Business Server 2000 | — | 2001-02-21 | 2010-07-13 | 1343 | Windows 2000 Server |
| Windows Small Business Server 2003 | Bobcat | 2003-10-09 | 2015-07-14 | 2893 | Windows Server 2003 |
| Windows Small Business Server 2008 | Cougar | 2008-08-21 | 2020-01-14 | 5601 | Windows Server 2008 |
| Windows Small Business Server 2011 Standard | Windows Small Business Server 7 | 2010-12-13 | 2020-01-14 | 7900 | Windows Server 2008 R2 |
| Windows Small Business Server 2011 Essentials | Colorado | 2011-06-28 | 2013-01-05 | 8800 |
Device versions[edit]
ARM-based tablets[edit]
Windows RT logo
The Surface RT (shown with keyboard cover attached) was the flagship Windows RT device upon its release.
In 2012 and 2013, Microsoft released versions of Windows specially designed to run on ARM-based tablets; these versions of Windows were based on Windows 8 and Windows 8.1, respectively, although the standard versions could run on x86-based tablets without modification. Upon the release of Windows 10 in 2015, the ARM-specific version for large tablets was discontinued; large tablets (such as the Surface Pro 4) were only released with x86 processors and could run the full version of Windows 10. Windows 10 Mobile had the ability to be installed on smaller tablets (up to nine inches);[24] however, very few such tablets were released, and Windows 10 Mobile primarily ended up only running on smartphones until its discontinuation. In 2017, the full version of Windows 10 gained the ability to run on ARM, which rendered a specific version of Windows for ARM-based tablets unnecessary.
| Name | Release date | Version number | Build number | Based on |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Windows RT | 2012-10-26 | NT 6.2 | 9200 | Windows 8 |
| Windows RT 8.1 | 2013-10-18 | NT 6.3 | 9600 | Windows 8.1 |
Mixed reality and virtual reality headsets[edit]
| Name | Build number |
|---|---|
| Windows 10 Holographic, version 1607[25] | 14393 |
| Windows 10 Holographic, version 1803[25] | 17134 |
| Windows 10 Holographic, version 1809[25] | 17763 |
| Windows Holographic, version 1903[26] | 18362 |
| Windows Holographic, version 2004[26] | 19041 |
| Windows Holographic, version 20H2[26] | 19041 |
| Windows Holographic, version 21H1[26] | 20346 |
| Windows Holographic, version 21H2[26] | 20348 |
| Windows Holographic, version 22H1[26] | 20348 |
Surface Hub[edit]
Microsoft originally announced the Surface Hub, an interactive whiteboard, in January 2015. The Surface Hub family of devices runs a custom variant of Windows 10 known as Windows 10 Team.
| Name | Build number |
|---|---|
| Windows 10 Team, version 1511[27] | 10586 |
| Windows 10 Team, version 1607[27] | 14393 |
| Windows 10 Team, version 1703[27] | 15063 |
| Windows 10 Team, version 20H2[27] | 19042 |
Windows XP-based tablets[edit]
Tablet computer running a «Tablet PC Edition» of Windows XP
Two versions of Windows XP were released that were optimized for tablets. Beginning with Windows Vista, all tablet-specific components were included in the main version of the operating system.
| Name | Codename | Release date | Version number | Build number | Based on |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Windows XP Tablet PC Edition | — | 2002-11-07 | NT 5.1 | 2600 | Windows XP |
| Windows XP Tablet PC Edition 2005 | Lonestar | 2004-08 | NT 5.1 | 2600 | Windows XP |
Embedded versions[edit]
Windows Embedded Compact[edit]
| Name | Codename(s) | Release date |
|---|---|---|
| Windows CE 1.0 | Pegasus; Alder | 1996-11-16 |
| Windows CE 2.0 | Jupiter; Birch | 1997-09-29 |
| Windows CE 2.1 | — | 1998-07 |
| Windows CE 2.11 | — | 1998-10 |
| Windows CE 2.12 | — | 1999 |
| Windows CE 3.0 | Cedar; Galileo | 2000 |
| Windows CE 4.0 | Talisker | 2002-01-07 |
| Windows CE 4.1 | Jameson | 2002-07-30 |
| Windows CE 4.2 | McKendric | 2003-04-23 |
| Windows CE 5.0 | Macallan | 2004-07-09 |
| Windows Embedded CE 6.0 | Yamakazi | 2006-11-01 |
| Windows Embedded Compact 7 | Chelan | 2011-03-01 |
| Windows Embedded Compact 2013 | — | 2013-06-13 |
Windows Embedded Standard[edit]
| Name | Codename | Release date | Based on |
|---|---|---|---|
| Windows NT Embedded 4.0 | Impala | 1999-08-30 | Windows NT 4.0 Workstation |
| Windows XP Embedded | Mantis | 2001-11-28 | Windows XP Professional |
| Windows Embedded Standard 2009 | — | 2008-12-14 | Windows XP Service Pack 3 |
| Windows Embedded Standard 7 | Quebec | 2010 | Windows 7 |
| Windows Embedded 8 | — | 2013 | Windows 8 |
| Windows Embedded 8.1 | — | 2013 | Windows 8.1 |
Other embedded versions[edit]
- Windows Embedded Industry
- Windows Embedded Automotive
Cancelled versions[edit]
Cancelled personal computer versions[edit]
| Codename | Intended name | Discontinuation | Version | Latest known build number | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cairo | — | 1996 | NT 4.0 | 1175 | Originally announced in 1991 |
| Nashville[t] | Windows 96 | — | 4.1 | 999 | Planned to be released between Windows 95 and Windows 98 |
| Neptune | — | Early 2000 | NT 5.50 | 5111 | The first planned version of Microsoft Windows NT to have a consumer edition variant, based on the Windows 2000 codebase. A version was sent out to testers but was never released.[28] The teams working on Neptune and Odyssey combined to work on Windows XP. |
| Odyssey | — | Early 2000 | NT 6.0[29] | — | Planned to be the successor of Windows 2000. The teams working on Neptune and Odyssey combined to work on Windows XP. |
| Triton | — | — | — | — | Planned to be the successor of Windows Neptune and had been scheduled to be released in March 2001 |
| Blackcomb | — | 2006-01 | — | — | Blackcomb was originally planned to be a release of Windows following Windows XP. However, due to the large feature scope planned for Blackcomb, a smaller release codenamed «Longhorn» was planned first, and Blackcomb was delayed to 2003/2004. Both projects faced delays; Longhorn would go on to be released to consumers as «Windows Vista» in January 2007, while development on Blackcomb continued until the Blackcomb project was renamed «Vienna» in early 2006. |
| Vienna | — | 2007-07[u] | — | — | Vienna replaced Blackcomb and was intended as Windows Vista’s successor. Vienna was eventually cancelled in favor of a new project codenamed «Windows 7» (which went on to be released in 2009 with the same name). |
| Polaris | — | 2018 | — | 16299 | Cancelled in favor of Santorini |
| Santorini[v] | Windows 10X | 2021-05-18[w][31] | 21H1 | 20279 | Microsoft had been reported as working on a new «lite» version of Windows as early as December 2018.[32] Such a version was officially announced under the name «Windows 10X» at an event in October 2019; the operating system was intended to first launch on dual-screen devices. In May 2020, Microsoft announced that Windows 10X would instead be launching on single-screen PCs, such as laptops and 2-in-1 devices, first.[33] However, on May 18, 2021, Microsoft announced that Windows 10X would not be launching (at least not in 2021); many of its features were rolled into Windows 11 instead. |
Cancelled mobile versions[edit]
| Codename | Intended name | Discontinuation | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Photon | Windows Mobile 7 | September 2008[34] | Originally a successor of Windows Mobile, it had been scrapped for Windows Phone 7[35][36] |
| Phoenix | — | Early 2017 | Cancelled when Microsoft «wound down» its phone efforts.[37] |
| Andromeda | — | Mid-2018 | Much of the work that was put into Andromeda was migrated into Santorini. The Surface Duo, a dual-screen Android-powered smartphone launched by Microsoft in 2020, was loosely based on the prototype hardware that had been used to test Andromeda.[38] |
Cancelled server versions[edit]
| Codename | Intended name | Discontinuation | Latest known build number |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cascades | Windows Essential Business Server 2008 R2 | April 7, 2010[w] | 7224 |
See also[edit]
- List of Microsoft operating systems
- Microsoft Windows version history
- Windows 10 version history
- Windows 11 version history
- Comparison of Microsoft Windows versions
- List of Microsoft codenames
Notes[edit]
- ^ Originally codenamed Winball
- ^ Has also been called ChiCairo and London.[2]
- ^ a b Windows Vista and Windows Server 2008 originally had the build number 6000 when they were first released; the build number was increased by one with each of the two subsequent Service Packs.
- ^ a b Windows 7 and Windows Server 2008 R2 originally had the build number 7600 when they were first released; the build number was increased to 7601 with the release of Service Pack 1.
- ^ Announcement date
- ^ Retroactively referred to as Threshold 1
- ^ Early preview builds of Windows 10 had the version number NT 6.4.[6]
- ^ Retroactively referred to as version 1507
- ^ Windows 10 Pro for Workstations became a Windows 10 edition starting with version 1709. Prior versions of Windows 10 do not include this as an edition.
- ^ Windows 10 versions 1507 and 1511 do not include a «Windows 10 Pro Education» edition; that edition was only added with version 1607.
- ^ Windows 10 S is only available in version 1703 and 1709.
- ^ Windows 10 Enterprise LTSC is only available for versions 1507, 1607, 1809, and 21H2. It had originally been named Windows 10 Enterprise LTSB in version 1507.
- ^ October 14, 2025 is the general end-of-support date for Windows 10. Specific versions and editions of Windows 10 have different end of support dates; see Windows 10 version history for a breakdown of dates by version and edition.
- ^ Originally codenamed 19H2[12]
- ^ Vibranium was the codename for Windows 10 version 2004. During the 20H2, 21H1, and 21H2 development cycles, builds were compiled under the codenames Manganese, Iron, and Cobalt, respectively. However, the versions of 20H2 and 21H1 that were released were built on top of version 2004 instead of these new builds. Windows 10 version 21H2 was similarly built on top of the Vibranium/2004 codebase instead of the Cobalt codebase; Cobalt builds were instead used as the base for the first version of Windows 11 (which had a core based on Cobalt in addition to a UI codenamed Sun Valley, and which also carries the version 21H2).
- ^ The core of Windows 11 version 21H2 is codenamed Cobalt;[15] the «Sun Valley» codename refers to the UI layer of Windows 11 version 21H2 and is commonly used to address Windows 11 version 21H2 as a whole.
- ^ a b The end-of-support date listed in the table refers to Home and Pro editions. The date for other editions, such as Education and Enterprise, may differ.
- ^ Originally named «Windows Phone 7 Series»
- ^ Between versions 1709 and 20H2 of Windows Server, the «Windows Server Essentials» edition of Windows Server was only included in Windows Server 2019.
- ^ Nashville was originally codenamed Cleveland.
- ^ July 2007 is when it was reported that the Vista’s successor was codenamed «7,» rather than «Vienna,» indicating that Vienna’s discontinuation had occurred by then. However, Vienna may have been cancelled prior to then.
- ^ While Santorini was the general codename for Windows 10X, Centaurus was the specific codename for Windows 10X on foldable PCs and Pegasus was the codename for Windows 10X on «traditional» PCs (such as laptops or 2-in-1 computers).[30]
- ^ a b Date refers to when the cancellation of the operating system was announced. The decision for the operating system to be cancelled may have occurred prior to then.
References[edit]
- ^ «Random internal Windows terminology:IDW, Razzle, and their forgotten partners IDS and Dazzle». The Old New Thing. 2018-12-24. Retrieved 2020-04-09.
- ^ «Systems Release Strategy — Draft:10/10/93» (PDF). Slated Antitrust. November 10, 1993.
- ^ Martens, China (July 22, 2005). «Update:Microsoft’s Longhorn becomes Windows Vista». IDG Communications, Inc. Retrieved 13 June 2021.
Microsoft Corp. has announced the official name for its upcoming operating system, previously known under the code name Longhorn. The operating system, now due out in 2006, will be called Windows Vista
- ^ «What was the code name for Windows 7?». The Old New Thing. 2019-07-22. Retrieved 2021-05-09.
- ^ Foley, Mary Jo. «Microsoft to share Windows Threshold plans at Build 2014 show: Report». ZDNet. ZDNET. Retrieved 7 April 2022.
- ^ Warren, Tom. «Windows 10 won’t be Windows 6.4». The Verge. Vox Media, LLC. Retrieved 3 January 2022.
Windows 10 Technical Preview builds are currently identified as Windows NT 6.4, but future builds will include the change
- ^ Warren, Tom. «Microsoft to end Windows 10 support on October 14th, 2025». The Verge. Vox Media, LLC. Retrieved 5 January 2022.
- ^ Bowden, Zac (August 4, 2016). «Microsoft confirms two major updates planned for Windows 10 in 2017». Windows Central. Future US, Inc. Retrieved 13 June 2021.
Windows Central understands that the first major update for 2017 (codenamed Redstone 2) will release in the early part of 2017.
- ^ Bowden, Zac (August 4, 2016). «Microsoft confirms two major updates planned for Windows 10 in 2017». Windows Central. Future US, Inc. Retrieved 13 June 2021.
The second major update scheduled for 2017 is codenamed «Redstone 3»
- ^ Woods, Rich. «Windows 10 Redstone 5 is officially version 1809». Neowin. Neowin LLC. Retrieved 13 June 2021.
Redstone 5 is now officially Windows 10 version 1809.
- ^ Hassan, Mehedi (October 31, 2018). «Windows 10’s Next Major Updates Will Be Codenamed Vanadium, Vibranium». Thurrott. BWW Media Group. Retrieved 13 June 2021.
Windows 10’s next major update is codenamed 19H1.
- ^ Hassan, Mehedi (October 31, 2018). «Windows 10’s Next Major Updates Will Be Codenamed Vanadium, Vibranium». Thurrott. BWW Media Group. Retrieved 13 June 2021.
This means the next Windows 10 update, previously codenamed 19H2, will be called Vanadium (comes after Titanium/19H1).
- ^ a b Brown, Matt (October 31, 2018). «Next Windows 10 updates reportedly codenamed ‘Vanadium’ and ‘Vibranium’«. Windows Central. Future US, Inc. Retrieved 13 June 2021.
- ^ Hassan, Mehedi (October 31, 2018). «Windows 10’s Next Major Updates Will Be Codenamed Vanadium, Vibranium». Thurrott. BWW Media Group. Retrieved 13 June 2021.
- ^ Parmar, Mayank (3 September 2021). «Windows 11 Build 22449 is now available with new loading animation». Windows Latest. Retrieved 4 September 2021.
Windows 11 version 21H2 (shipping on October 5)=Cobalt (Co).
- ^ Foley, Mary Jo. «Microsoft starts rolling out IE 6 for Windows Mobile». ZDNET. ZDNET. Retrieved 23 September 2022.
The new IE 6 bits were released on November 11 as part of the Windows Mobile 6.1.4 release from Microsoft’s Download Center Web site.
- ^ Woods, Rich. «It’s finally dead: Windows 10 Mobile is no longer supported after today». Neowin. Neowin LLC. Retrieved 23 December 2021.
Windows 10 feature2 ended up being version 1709, and it was the final feature update for Windows 10 Mobile.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j Gerend, Jason. «Windows Server release information». docs.microsoft.com. Retrieved 2020-09-09.
- ^ «What’s New in Windows Server version 1709». Microsoft Docs. Microsoft. Retrieved 2 January 2022.
- ^ «Windows Server, version 1803 end of servicing on November 12, 2019». Microsoft Docs. Microsoft. Retrieved 2 January 2022.
- ^ Woods, Rich. «Microsoft re-releases Windows Server 2019 and Windows Server, version 1809». Neowin. Neowin LLC. Retrieved 2 January 2022.
- ^ a b Gerend, Jason. «Windows Server servicing channels». docs.microsoft.com. Retrieved 2020-09-09.
- ^ Sharma, Mayank. «Microsoft has snuck out its Windows Server 2022 release». TechRadar. Future US, Inc. Retrieved 3 January 2022.
Windows Server 2022 identifies itself as version 21H2
- ^ Foley, Mary Jo. «Microsoft ups allowable Windows 10 Mobile screen size to nearly nine inches». ZDNET. ZDNET. Retrieved 11 September 2022.
- ^ a b c «HoloLens 1st (gen) release notes». Retrieved 18 July 2021.
- ^ a b c d e f «HoloLens 2 release notes». Retrieved 18 July 2021.
- ^ a b c d «Surface Hub update history». Retrieved 18 July 2021.
- ^ «Microsoft combines Neptune, Odyssey into Whistler». CNN. January 27, 2000. Archived from the original on September 1, 2008. Retrieved January 6, 2010.
- ^ «Windows Odyssey». Retrieved 16 July 2021.
Knowing that Neptune is 5.50, it’s only logical to conclude Odyssey was to be 6.0
- ^ Bowden, Zac (October 30, 2019). «Windows Core OS:The complete guide». Windows Central. Future US, Inc. Retrieved 14 June 2021.
- ^ Warren, Tom (May 18, 2021). «Microsoft confirms Windows 10X is dead». The Verge. Vox Media, LLC. Retrieved 14 June 2021.
- ^ Sams, Brad (December 3, 2018). «What is Windows Lite? It’s Microsoft’s Chrome OS Killer». Petri. BWW Media Group. Retrieved 16 July 2021.
- ^ Bowden, Zac (May 4, 2020). «Windows 10X will now launch first on single-screen PCs». Windows Central. Future US, Inc. Retrieved 16 July 2021.
- ^ Litvinenko, Yuri. «Microsoft’s Project Photon:A Stunted Effort to Rebuild Windows Mobile». Retrieved 16 July 2021.
Checking reports against each other provides the grounds to assume Microsoft kept working on Photon till September 2008.
- ^ «Windows Mobile 7 vs Windows Phone 7». Popular Pages at brighthub.com. May 20, 2011. Retrieved December 15, 2016.
- ^ «Revealed:Original Windows Mobile 7 UI». neowin.net. February 20, 2010. Retrieved December 15, 2016.
- ^ Bowden, Zac (September 18, 2020). «Project Andromeda:The secret history of Windows on Surface Duo». Windows Central. Future US, Inc. Retrieved 16 July 2021.
Microsoft had originally planned to ship CShell on Windows 10 Mobile under the codename Pheonix [sic], but that plan very quickly went away once the company decided to wind down its existing phone efforts in early 2017.
- ^ Bowden, Zac (September 18, 2020). «Project Andromeda:The secret history of Windows on Surface Duo». Windows Central. Future US, Inc. Retrieved 16 July 2021.
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Original Windows logo from 1985
Current Windows logo (introduced in 2021)
Timeline of Windows releases
Microsoft Windows is a computer operating system developed by Microsoft. It was first launched in 1985 as a graphical operating system built on MS-DOS. The initial version was followed by several subsequent releases, and by the early 1990s, the Windows line had split into two separate lines of releases: Windows 9x for consumers and Windows NT for businesses and enterprises. In the following years, several further variants of Windows would be released: Windows CE in 1996 for embedded systems; Pocket PC in 2000 (renamed to Windows Mobile in 2003 and Windows Phone in 2010) for personal digital assistants and, later, smartphones; Windows Holographic in 2016 for AR/VR headsets; and several other editions.
Personal computer versions[edit]
A «personal computer» version of Windows is considered to be a version that end-users or OEMs can install on personal computers, including desktop computers, laptops, and workstations.
The first five versions of Windows–Windows 1.0, Windows 2.0, Windows 2.1, Windows 3.0, and Windows 3.1–were all based on MS-DOS, and were aimed at both consumers and businesses. However, Windows 3.1 had two separate successors, splitting the Windows line in two: the consumer-focused «Windows 9x» line, consisting of Windows 95, Windows 98, and Windows Me; and the professional Windows NT line, comprising Windows NT 3.1, Windows NT 3.5, Windows NT 3.51, Windows NT 4.0, and Windows 2000. These two lines were reunited into a single line with the NT-based Windows XP; this Windows release succeeded both Windows Me and Windows 2000 and had separate editions for consumer and professional use. Since Windows XP, multiple further versions of Windows have been released, the most recent of which is Windows 11.
| Name | Codename | Release date | Version | Editions | Build number | Architecture | End of support | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Windows 1.01 | Interface Manager | 1985-11-20 | 1.01 | — | — | x86-16 | 2001-12-31 | |
| Windows 1.02 | — | 1986-05-14 | 1.02 | — | — | |||
| Windows 1.03 | — | 1986-08-21 | 1.03 | — | — | |||
| Windows 1.04 | — | 1987-04-10 | 1.04 | — | — | |||
| Windows 2.01 | — | 1987-12-09 | 2.01 | — | — | x86-16, IA-32 | ||
| Windows 2.03 | — | 1987-12-09 | 2.03 | — | — | |||
| Windows 2.1 | — | 1988-05-27 | 2.10 | — | — | |||
| Windows 2.11 | — | 1989-03-13 | 2.11 | — | — | |||
| Windows 3.0 | — | 1990-05-22 | 3.00 |
|
— | |||
| Windows 3.1 | — | 1992-04-06 | 3.10 |
|
103 | |||
| Sparta[a] | 1992-10 |
|
102 | IA-32 | ||||
| Windows NT 3.1 | Razzle[1] | 1993-07-27 | NT 3.1 |
|
528 | IA-32, Alpha, MIPS | 2000-12-31 | |
| Windows 3.11 | — | 1993-11-08 | 3.11 |
|
? | x86-16, IA-32 | 2001-12-31 | |
| Snowball |
|
300 | IA-32 | |||||
| Windows 3.2 | — | 1993-11-22 | 3.2 |
|
153 | x86-16, IA-32 | ||
| Windows NT 3.5 | Daytona | 1994-09-21 | NT 3.5 |
|
807 | IA-32, Alpha, MIPS, PowerPC | ||
| Windows NT 3.51 | 1995-05-30 | NT 3.51 |
|
1057 | ||||
| Windows 95 | Chicago | 1995-08-24 | 4.00 |
|
950 | IA-32 | ||
| Windows NT 4.0 | Shell Update Release | 1996-08-24 | NT 4.0 |
|
1381 | IA-32, Alpha, MIPS, PowerPC | 2004-06-30 | |
| Windows 98 | Memphis[b] | 1998-06-25 | 4.10 |
|
1998 | IA-32 | 2006-07-11 | |
| Windows 98 Second Edition | — | 1999-05-05 |
|
2222A | ||||
| Windows 2000 | Windows NT 5.0 | 2000-02-17 | NT 5.0 |
|
2195 | IA-32 | 2010-07-13 | |
| Windows Me | Millennium | 2000-09-14 | 4.90 |
|
3000 | IA-32 | 2006-07-11 | |
| Windows XP | Whistler | 2001-10-25 | NT 5.1 |
|
2600 | IA-32 | 2014-04-08 | |
|
Itanium | |||||||
| Freestyle | 2002-10-29 |
|
IA-32 | |||||
| Harmony | 2003-09-30 |
|
||||||
| Symphony | 2004-10-12 |
|
2700 | |||||
| Emerald | 2005-10-14 |
|
2710 | |||||
| Anvil | 2005-04-25 | NT 5.2 |
|
3790 | x86-64 | |||
| Windows Vista | Longhorn[3] | 2007-01-30 | NT 6.0 |
|
6002[c] | IA-32, x86-64 | 2017-04-11 | |
| Windows 7 | Windows 7[4] | 2009-10-22 | NT 6.1 |
|
7601[d] | IA-32, x86-64 | 2020-01-14 | |
| Windows 8 | Windows 8 | 2012-10-26 | NT 6.2 |
|
9200 | IA-32, x86-64 | 2016-01-12 | 2023-07-11 (Embedded) |
| Windows 8.1 | Blue | 2013-10-17 | NT 6.3 |
|
9600 | IA-32, x86-64 | 2023-01-10 | 2023-07-11 (Embedded) |
| 2014-05-23[e] |
|
|||||||
| Windows 10 version 1507 | Threshold[5][f] | 2015-07-29 | NT 10.0[g][h] |
|
10240 | IA-32, x86-64 | 2025-10-14[7][m] | |
| Windows 10 version 1511 | Threshold 2 | 2015-11-10 | 1511 | 10586 | ||||
| Windows 10 version 1607 | Redstone 1 | 2016-08-02 | 1607 | 14393 | ||||
| Windows 10 version 1703 | Redstone 2[8] | 2017-04-05 | 1703 | 15063 | ||||
| Windows 10 version 1709 | Redstone 3[9] | 2017-10-17 | 1709 | 16299 | IA-32, x86-64, ARM64 | |||
| Windows 10 version 1803 | Redstone 4 | 2018-04-30 | 1803 | 17134 | ||||
| Windows 10 version 1809 | Redstone 5[10] | 2018-11-13 | 1809 | 17763 | ||||
| Windows 10 version 1903 | 19H1[11] | 2019-05-21 | 1903 | 18362 | ||||
| Windows 10 version 1909 | Vanadium[n][13] | 2019-11-12 | 1909 | 18363 | ||||
| Windows 10 version 2004 | Vibranium[13][14][o] | 2020-05-27 | 2004 | 19041 | ||||
| Windows 10 version 20H2 | 2020-10-20 | 20H2 | 19042 | |||||
| Windows 10 version 21H1 | 2021-05-18 | 21H1 | 19043 | |||||
| Windows 10 version 21H2 | 2021-11-16 | 21H2 | 19044 | |||||
| Windows 10 version 22H2 | 2022-10-18 | 22H2 | 19045 | |||||
| Windows 11 version 21H2 | Sun Valley[p] | 2021-10-05 | 21H2 |
|
22000 | x86-64, ARM64 | 2023-10-10[q] | |
| Windows 11 version 22H2 | Sun Valley 2 | 2022-09-20 | 22H2 | 22621 | 2024-10-14[q] |
Mobile versions[edit]
Mobile versions refer to versions of Windows that can run on smartphones or personal digital assistants.
Pocket PC 2000 logo
Windows Phone 7 logo
Windows Phone 8 logo
Windows Phone 8.1 logo
Logo used for Windows 10 and Windows 10 Mobile
| Name | Codename | Architecture | Release date |
Version Number |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pocket PC 2000 | Rapier | ARMv4, MIPS, SH-3 | 2000-04-19 | CE 3.0 |
| Pocket PC 2002 | Merlin | ARMv4 | 2001-10-04 | |
| Windows Mobile 2003 | Ozone | ARMv5 | 2003-06-23 | CE 4.x |
| Windows Mobile 2003 SE | — | 2004-03-24 | ||
| Windows Mobile 5.0 | Magneto | 2005-05-09 | CE 5.0 | |
| Windows Mobile 6.0 | Crossbow | 2007-02-12 | ||
| Windows Mobile 6.1 | — | 2008-04-01 | CE 5.2 | |
| Windows Mobile 6.1.4 | 6 on 6 | 2008-11-11[16] | ||
| Windows Mobile 6.5 | Titanium | 2009-05-11 | CE 6.0 | |
| Windows Phone 7[r] | — | ARMv7 | 2010-10-29 | |
| Windows Phone 7.5 | Mango | 2011-09-27 | ||
| Windows Phone 7.8 | — | 2013-02-01 | ||
| Windows Phone 8 | Apollo | 2012-10-29 | NT 6.2 | |
| Windows Phone 8.1 | Blue | 2014-04-14 | NT 6.3 | |
| Windows 10 Mobile, version 1511 | Threshold 2 | 2015-11-12 | 1511 | |
| Windows 10 Mobile, version 1607 | Redstone 1 | 2016-08-16 | 1607 | |
| Windows 10 Mobile, version 1703 | Redstone 2 | 2017-04-24 | 1703 | |
| Windows 10 Mobile, version 1709 | feature2[17] | 2017-10-24 | 1709 |
Server versions[edit]
| Name | Release date | Version number | Editions | Build number | Architecture | End of support |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Windows NT 3.1 | 1993-07-27 | NT 3.1 |
|
528 | IA-32, Alpha, MIPS | 2000-12-31 |
| Windows NT 3.5 | 1994-09-20 | NT 3.5 |
|
807 | IA-32, Alpha, MIPS, PowerPC | 2001-12-31 |
| Windows NT 3.51 | 1995-05-29 | NT 3.51 |
|
1057 | 2001-12-31 | |
| Windows NT 4.0 | 1996-07-29 | NT 4.0 |
|
1381 | 2004-12-31 | |
| Windows 2000 | 2000-02-17 | NT 5.0 |
|
2195 | IA-32 | 2010-07-13 |
| Windows Server 2003 | 2003-04-24 | NT 5.2 |
|
3790 | IA-32, x86-64, Itanium | 2015-07-14 |
| Windows Server 2003 R2 | 2005-12-06 | 2015-07-14 | ||||
| Windows Server 2008 | 2008-02-27 | NT 6.0 |
|
6002[c] | IA-32, x86-64, Itanium | 2020-01-14 |
| Windows Server 2008 R2 | 2009-10-22 | NT 6.1 | 7601[d] | x86-64, Itanium | 2020-01-14 | |
| Windows Server 2012 | 2012-09-04 | NT 6.2 |
|
9200 | x86-64 | 2023-10-10 |
| Windows Server 2012 R2 | 2013-10-17 | NT 6.3 | 9600 | 2023-10-10 | ||
| Windows Server 2016 | 2016-10-12 | 1607[18] |
|
14393 | 2027-01-12 | |
| Windows Server, version 1709[19] | 2017-10-17 | 1709 | 16299 | 2019-04-09 | ||
| Windows Server, version 1803[20] | 2018-04-30 | 1803 | 17134 | 2019-11-12 | ||
| Windows Server, version 1809 | 2018-11-13[21] | 1809 | 17763 | 2020-11-10 | ||
| Windows Server 2019[18] | 2029-01-09[18] | |||||
| Windows Server, version 1903[18] | 2019-05-21 | 1903 | 18362 | 2020-12-08[18] | ||
| Windows Server, version 1909[18] | 2019-11-12 | 1909 | 18363 | 2021-05-11[18] | ||
| Windows Server, version 2004[22] | 2020-06-26 | 2004 | 19041 | 2021-12-14[18] | ||
| Windows Server, version 20H2[22] | 2020-10-20 | 20H2 | 19042 | 2022-08-09[18] | ||
| Windows Server 2022 | 2021-08-18 | 21H2[23] | 20348 | 2031-10-14[18] |
High-performance computing (HPC) servers[edit]
| Name | Codename | Release date | Based on |
|---|---|---|---|
| Windows Compute Cluster Server 2003 | — | 2006-06-09 | Windows Server 2003 R2 |
| Windows HPC Server 2008 | Socrates | 2008-09-22 | Windows Server 2008 |
| Windows HPC Server 2008 R2 | — | 2010-09-20 | Windows Server 2008 R2 |
Windows Essential Business Server[edit]
| Name | Codename | Release date | End-of-support date | Build number | Based on |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Windows Essential Business Server 2008 | Centro | 2008-09-15 | 2020-01-14 | 5700 | Windows Server 2008 |
Windows Home Server[edit]
| Name | Codename | Release date | End-of-support date | Based on |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Windows Home Server | Quattro | 2007-11-04 | 2013-01-08 | Windows Server 2003 R2 |
| Windows Home Server 2011 | Vail | 2011-04-06 | 2016-04-12 | Windows Server 2008 R2 |
Windows MultiPoint Server[edit]
Windows MultiPoint Server was an operating system based on Windows Server. It was succeeded by the MultiPoint Services role in Windows Server 2016 and Windows Server version 1709. It was no longer being developed in Windows Server version 1803 and later versions.
| Name | Codename | Release date | End-of-support date | Version number | Build number | Based on |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Windows MultiPoint Server 2010 | Solution Server | 2010-02-24 | 2020-07-14 | NT 6.1 | 537 | Windows Server 2008 R2 |
| Windows MultiPoint Server 2011 | WMS 2 | 2011-05-12 | 2021-07-13 | 1600 | Windows Server 2008 R2 Service Pack 1 | |
| Windows MultiPoint Server 2012 | WMS 3 | 2012-10-30 | 2023-10-10 | NT 6.2 | 2506 | Windows Server 2012 |
Windows Small Business Server[edit]
| Name | Codename | Release date | End-of-support date | Build number | Based on |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Small Business Server 2000 | — | 2001-02-21 | 2010-07-13 | 1343 | Windows 2000 Server |
| Windows Small Business Server 2003 | Bobcat | 2003-10-09 | 2015-07-14 | 2893 | Windows Server 2003 |
| Windows Small Business Server 2008 | Cougar | 2008-08-21 | 2020-01-14 | 5601 | Windows Server 2008 |
| Windows Small Business Server 2011 Standard | Windows Small Business Server 7 | 2010-12-13 | 2020-01-14 | 7900 | Windows Server 2008 R2 |
| Windows Small Business Server 2011 Essentials | Colorado | 2011-06-28 | 2013-01-05 | 8800 |
Device versions[edit]
ARM-based tablets[edit]
Windows RT logo
The Surface RT (shown with keyboard cover attached) was the flagship Windows RT device upon its release.
In 2012 and 2013, Microsoft released versions of Windows specially designed to run on ARM-based tablets; these versions of Windows were based on Windows 8 and Windows 8.1, respectively, although the standard versions could run on x86-based tablets without modification. Upon the release of Windows 10 in 2015, the ARM-specific version for large tablets was discontinued; large tablets (such as the Surface Pro 4) were only released with x86 processors and could run the full version of Windows 10. Windows 10 Mobile had the ability to be installed on smaller tablets (up to nine inches);[24] however, very few such tablets were released, and Windows 10 Mobile primarily ended up only running on smartphones until its discontinuation. In 2017, the full version of Windows 10 gained the ability to run on ARM, which rendered a specific version of Windows for ARM-based tablets unnecessary.
| Name | Release date | Version number | Build number | Based on |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Windows RT | 2012-10-26 | NT 6.2 | 9200 | Windows 8 |
| Windows RT 8.1 | 2013-10-18 | NT 6.3 | 9600 | Windows 8.1 |
Mixed reality and virtual reality headsets[edit]
| Name | Build number |
|---|---|
| Windows 10 Holographic, version 1607[25] | 14393 |
| Windows 10 Holographic, version 1803[25] | 17134 |
| Windows 10 Holographic, version 1809[25] | 17763 |
| Windows Holographic, version 1903[26] | 18362 |
| Windows Holographic, version 2004[26] | 19041 |
| Windows Holographic, version 20H2[26] | 19041 |
| Windows Holographic, version 21H1[26] | 20346 |
| Windows Holographic, version 21H2[26] | 20348 |
| Windows Holographic, version 22H1[26] | 20348 |
Surface Hub[edit]
Microsoft originally announced the Surface Hub, an interactive whiteboard, in January 2015. The Surface Hub family of devices runs a custom variant of Windows 10 known as Windows 10 Team.
| Name | Build number |
|---|---|
| Windows 10 Team, version 1511[27] | 10586 |
| Windows 10 Team, version 1607[27] | 14393 |
| Windows 10 Team, version 1703[27] | 15063 |
| Windows 10 Team, version 20H2[27] | 19042 |
Windows XP-based tablets[edit]
Tablet computer running a «Tablet PC Edition» of Windows XP
Two versions of Windows XP were released that were optimized for tablets. Beginning with Windows Vista, all tablet-specific components were included in the main version of the operating system.
| Name | Codename | Release date | Version number | Build number | Based on |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Windows XP Tablet PC Edition | — | 2002-11-07 | NT 5.1 | 2600 | Windows XP |
| Windows XP Tablet PC Edition 2005 | Lonestar | 2004-08 | NT 5.1 | 2600 | Windows XP |
Embedded versions[edit]
Windows Embedded Compact[edit]
| Name | Codename(s) | Release date |
|---|---|---|
| Windows CE 1.0 | Pegasus; Alder | 1996-11-16 |
| Windows CE 2.0 | Jupiter; Birch | 1997-09-29 |
| Windows CE 2.1 | — | 1998-07 |
| Windows CE 2.11 | — | 1998-10 |
| Windows CE 2.12 | — | 1999 |
| Windows CE 3.0 | Cedar; Galileo | 2000 |
| Windows CE 4.0 | Talisker | 2002-01-07 |
| Windows CE 4.1 | Jameson | 2002-07-30 |
| Windows CE 4.2 | McKendric | 2003-04-23 |
| Windows CE 5.0 | Macallan | 2004-07-09 |
| Windows Embedded CE 6.0 | Yamakazi | 2006-11-01 |
| Windows Embedded Compact 7 | Chelan | 2011-03-01 |
| Windows Embedded Compact 2013 | — | 2013-06-13 |
Windows Embedded Standard[edit]
| Name | Codename | Release date | Based on |
|---|---|---|---|
| Windows NT Embedded 4.0 | Impala | 1999-08-30 | Windows NT 4.0 Workstation |
| Windows XP Embedded | Mantis | 2001-11-28 | Windows XP Professional |
| Windows Embedded Standard 2009 | — | 2008-12-14 | Windows XP Service Pack 3 |
| Windows Embedded Standard 7 | Quebec | 2010 | Windows 7 |
| Windows Embedded 8 | — | 2013 | Windows 8 |
| Windows Embedded 8.1 | — | 2013 | Windows 8.1 |
Other embedded versions[edit]
- Windows Embedded Industry
- Windows Embedded Automotive
Cancelled versions[edit]
Cancelled personal computer versions[edit]
| Codename | Intended name | Discontinuation | Version | Latest known build number | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cairo | — | 1996 | NT 4.0 | 1175 | Originally announced in 1991 |
| Nashville[t] | Windows 96 | — | 4.1 | 999 | Planned to be released between Windows 95 and Windows 98 |
| Neptune | — | Early 2000 | NT 5.50 | 5111 | The first planned version of Microsoft Windows NT to have a consumer edition variant, based on the Windows 2000 codebase. A version was sent out to testers but was never released.[28] The teams working on Neptune and Odyssey combined to work on Windows XP. |
| Odyssey | — | Early 2000 | NT 6.0[29] | — | Planned to be the successor of Windows 2000. The teams working on Neptune and Odyssey combined to work on Windows XP. |
| Triton | — | — | — | — | Planned to be the successor of Windows Neptune and had been scheduled to be released in March 2001 |
| Blackcomb | — | 2006-01 | — | — | Blackcomb was originally planned to be a release of Windows following Windows XP. However, due to the large feature scope planned for Blackcomb, a smaller release codenamed «Longhorn» was planned first, and Blackcomb was delayed to 2003/2004. Both projects faced delays; Longhorn would go on to be released to consumers as «Windows Vista» in January 2007, while development on Blackcomb continued until the Blackcomb project was renamed «Vienna» in early 2006. |
| Vienna | — | 2007-07[u] | — | — | Vienna replaced Blackcomb and was intended as Windows Vista’s successor. Vienna was eventually cancelled in favor of a new project codenamed «Windows 7» (which went on to be released in 2009 with the same name). |
| Polaris | — | 2018 | — | 16299 | Cancelled in favor of Santorini |
| Santorini[v] | Windows 10X | 2021-05-18[w][31] | 21H1 | 20279 | Microsoft had been reported as working on a new «lite» version of Windows as early as December 2018.[32] Such a version was officially announced under the name «Windows 10X» at an event in October 2019; the operating system was intended to first launch on dual-screen devices. In May 2020, Microsoft announced that Windows 10X would instead be launching on single-screen PCs, such as laptops and 2-in-1 devices, first.[33] However, on May 18, 2021, Microsoft announced that Windows 10X would not be launching (at least not in 2021); many of its features were rolled into Windows 11 instead. |
Cancelled mobile versions[edit]
| Codename | Intended name | Discontinuation | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Photon | Windows Mobile 7 | September 2008[34] | Originally a successor of Windows Mobile, it had been scrapped for Windows Phone 7[35][36] |
| Phoenix | — | Early 2017 | Cancelled when Microsoft «wound down» its phone efforts.[37] |
| Andromeda | — | Mid-2018 | Much of the work that was put into Andromeda was migrated into Santorini. The Surface Duo, a dual-screen Android-powered smartphone launched by Microsoft in 2020, was loosely based on the prototype hardware that had been used to test Andromeda.[38] |
Cancelled server versions[edit]
| Codename | Intended name | Discontinuation | Latest known build number |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cascades | Windows Essential Business Server 2008 R2 | April 7, 2010[w] | 7224 |
See also[edit]
- List of Microsoft operating systems
- Microsoft Windows version history
- Windows 10 version history
- Windows 11 version history
- Comparison of Microsoft Windows versions
- List of Microsoft codenames
Notes[edit]
- ^ Originally codenamed Winball
- ^ Has also been called ChiCairo and London.[2]
- ^ a b Windows Vista and Windows Server 2008 originally had the build number 6000 when they were first released; the build number was increased by one with each of the two subsequent Service Packs.
- ^ a b Windows 7 and Windows Server 2008 R2 originally had the build number 7600 when they were first released; the build number was increased to 7601 with the release of Service Pack 1.
- ^ Announcement date
- ^ Retroactively referred to as Threshold 1
- ^ Early preview builds of Windows 10 had the version number NT 6.4.[6]
- ^ Retroactively referred to as version 1507
- ^ Windows 10 Pro for Workstations became a Windows 10 edition starting with version 1709. Prior versions of Windows 10 do not include this as an edition.
- ^ Windows 10 versions 1507 and 1511 do not include a «Windows 10 Pro Education» edition; that edition was only added with version 1607.
- ^ Windows 10 S is only available in version 1703 and 1709.
- ^ Windows 10 Enterprise LTSC is only available for versions 1507, 1607, 1809, and 21H2. It had originally been named Windows 10 Enterprise LTSB in version 1507.
- ^ October 14, 2025 is the general end-of-support date for Windows 10. Specific versions and editions of Windows 10 have different end of support dates; see Windows 10 version history for a breakdown of dates by version and edition.
- ^ Originally codenamed 19H2[12]
- ^ Vibranium was the codename for Windows 10 version 2004. During the 20H2, 21H1, and 21H2 development cycles, builds were compiled under the codenames Manganese, Iron, and Cobalt, respectively. However, the versions of 20H2 and 21H1 that were released were built on top of version 2004 instead of these new builds. Windows 10 version 21H2 was similarly built on top of the Vibranium/2004 codebase instead of the Cobalt codebase; Cobalt builds were instead used as the base for the first version of Windows 11 (which had a core based on Cobalt in addition to a UI codenamed Sun Valley, and which also carries the version 21H2).
- ^ The core of Windows 11 version 21H2 is codenamed Cobalt;[15] the «Sun Valley» codename refers to the UI layer of Windows 11 version 21H2 and is commonly used to address Windows 11 version 21H2 as a whole.
- ^ a b The end-of-support date listed in the table refers to Home and Pro editions. The date for other editions, such as Education and Enterprise, may differ.
- ^ Originally named «Windows Phone 7 Series»
- ^ Between versions 1709 and 20H2 of Windows Server, the «Windows Server Essentials» edition of Windows Server was only included in Windows Server 2019.
- ^ Nashville was originally codenamed Cleveland.
- ^ July 2007 is when it was reported that the Vista’s successor was codenamed «7,» rather than «Vienna,» indicating that Vienna’s discontinuation had occurred by then. However, Vienna may have been cancelled prior to then.
- ^ While Santorini was the general codename for Windows 10X, Centaurus was the specific codename for Windows 10X on foldable PCs and Pegasus was the codename for Windows 10X on «traditional» PCs (such as laptops or 2-in-1 computers).[30]
- ^ a b Date refers to when the cancellation of the operating system was announced. The decision for the operating system to be cancelled may have occurred prior to then.
References[edit]
- ^ «Random internal Windows terminology:IDW, Razzle, and their forgotten partners IDS and Dazzle». The Old New Thing. 2018-12-24. Retrieved 2020-04-09.
- ^ «Systems Release Strategy — Draft:10/10/93» (PDF). Slated Antitrust. November 10, 1993.
- ^ Martens, China (July 22, 2005). «Update:Microsoft’s Longhorn becomes Windows Vista». IDG Communications, Inc. Retrieved 13 June 2021.
Microsoft Corp. has announced the official name for its upcoming operating system, previously known under the code name Longhorn. The operating system, now due out in 2006, will be called Windows Vista
- ^ «What was the code name for Windows 7?». The Old New Thing. 2019-07-22. Retrieved 2021-05-09.
- ^ Foley, Mary Jo. «Microsoft to share Windows Threshold plans at Build 2014 show: Report». ZDNet. ZDNET. Retrieved 7 April 2022.
- ^ Warren, Tom. «Windows 10 won’t be Windows 6.4». The Verge. Vox Media, LLC. Retrieved 3 January 2022.
Windows 10 Technical Preview builds are currently identified as Windows NT 6.4, but future builds will include the change
- ^ Warren, Tom. «Microsoft to end Windows 10 support on October 14th, 2025». The Verge. Vox Media, LLC. Retrieved 5 January 2022.
- ^ Bowden, Zac (August 4, 2016). «Microsoft confirms two major updates planned for Windows 10 in 2017». Windows Central. Future US, Inc. Retrieved 13 June 2021.
Windows Central understands that the first major update for 2017 (codenamed Redstone 2) will release in the early part of 2017.
- ^ Bowden, Zac (August 4, 2016). «Microsoft confirms two major updates planned for Windows 10 in 2017». Windows Central. Future US, Inc. Retrieved 13 June 2021.
The second major update scheduled for 2017 is codenamed «Redstone 3»
- ^ Woods, Rich. «Windows 10 Redstone 5 is officially version 1809». Neowin. Neowin LLC. Retrieved 13 June 2021.
Redstone 5 is now officially Windows 10 version 1809.
- ^ Hassan, Mehedi (October 31, 2018). «Windows 10’s Next Major Updates Will Be Codenamed Vanadium, Vibranium». Thurrott. BWW Media Group. Retrieved 13 June 2021.
Windows 10’s next major update is codenamed 19H1.
- ^ Hassan, Mehedi (October 31, 2018). «Windows 10’s Next Major Updates Will Be Codenamed Vanadium, Vibranium». Thurrott. BWW Media Group. Retrieved 13 June 2021.
This means the next Windows 10 update, previously codenamed 19H2, will be called Vanadium (comes after Titanium/19H1).
- ^ a b Brown, Matt (October 31, 2018). «Next Windows 10 updates reportedly codenamed ‘Vanadium’ and ‘Vibranium’«. Windows Central. Future US, Inc. Retrieved 13 June 2021.
- ^ Hassan, Mehedi (October 31, 2018). «Windows 10’s Next Major Updates Will Be Codenamed Vanadium, Vibranium». Thurrott. BWW Media Group. Retrieved 13 June 2021.
- ^ Parmar, Mayank (3 September 2021). «Windows 11 Build 22449 is now available with new loading animation». Windows Latest. Retrieved 4 September 2021.
Windows 11 version 21H2 (shipping on October 5)=Cobalt (Co).
- ^ Foley, Mary Jo. «Microsoft starts rolling out IE 6 for Windows Mobile». ZDNET. ZDNET. Retrieved 23 September 2022.
The new IE 6 bits were released on November 11 as part of the Windows Mobile 6.1.4 release from Microsoft’s Download Center Web site.
- ^ Woods, Rich. «It’s finally dead: Windows 10 Mobile is no longer supported after today». Neowin. Neowin LLC. Retrieved 23 December 2021.
Windows 10 feature2 ended up being version 1709, and it was the final feature update for Windows 10 Mobile.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j Gerend, Jason. «Windows Server release information». docs.microsoft.com. Retrieved 2020-09-09.
- ^ «What’s New in Windows Server version 1709». Microsoft Docs. Microsoft. Retrieved 2 January 2022.
- ^ «Windows Server, version 1803 end of servicing on November 12, 2019». Microsoft Docs. Microsoft. Retrieved 2 January 2022.
- ^ Woods, Rich. «Microsoft re-releases Windows Server 2019 and Windows Server, version 1809». Neowin. Neowin LLC. Retrieved 2 January 2022.
- ^ a b Gerend, Jason. «Windows Server servicing channels». docs.microsoft.com. Retrieved 2020-09-09.
- ^ Sharma, Mayank. «Microsoft has snuck out its Windows Server 2022 release». TechRadar. Future US, Inc. Retrieved 3 January 2022.
Windows Server 2022 identifies itself as version 21H2
- ^ Foley, Mary Jo. «Microsoft ups allowable Windows 10 Mobile screen size to nearly nine inches». ZDNET. ZDNET. Retrieved 11 September 2022.
- ^ a b c «HoloLens 1st (gen) release notes». Retrieved 18 July 2021.
- ^ a b c d e f «HoloLens 2 release notes». Retrieved 18 July 2021.
- ^ a b c d «Surface Hub update history». Retrieved 18 July 2021.
- ^ «Microsoft combines Neptune, Odyssey into Whistler». CNN. January 27, 2000. Archived from the original on September 1, 2008. Retrieved January 6, 2010.
- ^ «Windows Odyssey». Retrieved 16 July 2021.
Knowing that Neptune is 5.50, it’s only logical to conclude Odyssey was to be 6.0
- ^ Bowden, Zac (October 30, 2019). «Windows Core OS:The complete guide». Windows Central. Future US, Inc. Retrieved 14 June 2021.
- ^ Warren, Tom (May 18, 2021). «Microsoft confirms Windows 10X is dead». The Verge. Vox Media, LLC. Retrieved 14 June 2021.
- ^ Sams, Brad (December 3, 2018). «What is Windows Lite? It’s Microsoft’s Chrome OS Killer». Petri. BWW Media Group. Retrieved 16 July 2021.
- ^ Bowden, Zac (May 4, 2020). «Windows 10X will now launch first on single-screen PCs». Windows Central. Future US, Inc. Retrieved 16 July 2021.
- ^ Litvinenko, Yuri. «Microsoft’s Project Photon:A Stunted Effort to Rebuild Windows Mobile». Retrieved 16 July 2021.
Checking reports against each other provides the grounds to assume Microsoft kept working on Photon till September 2008.
- ^ «Windows Mobile 7 vs Windows Phone 7». Popular Pages at brighthub.com. May 20, 2011. Retrieved December 15, 2016.
- ^ «Revealed:Original Windows Mobile 7 UI». neowin.net. February 20, 2010. Retrieved December 15, 2016.
- ^ Bowden, Zac (September 18, 2020). «Project Andromeda:The secret history of Windows on Surface Duo». Windows Central. Future US, Inc. Retrieved 16 July 2021.
Microsoft had originally planned to ship CShell on Windows 10 Mobile under the codename Pheonix [sic], but that plan very quickly went away once the company decided to wind down its existing phone efforts in early 2017.
- ^ Bowden, Zac (September 18, 2020). «Project Andromeda:The secret history of Windows on Surface Duo». Windows Central. Future US, Inc. Retrieved 16 July 2021.

Introducing Microsoft Surface Studio 2

Windows 8
Microsoft Windows — семейство проприетарных операционных систем корпорации Microsoft, ориентированных на применение графического интерфейса при управлении. Изначально Windows была всего лишь графической надстройкой для MS-DOS. По состоянию на август 2014 года под управлением операционных систем семейства Windows по данным ресурса NetMarketShare работает более 91% персональных компьютеров. Windows работает на платформах x86, x86-64, IA-64 и ARM. Существовали также версии для DEC Alpha, MIPS, PowerPC и SPARC.
Основные статьи: История логотипов Windows, История логотипов Windows 1985-2015
Версии[]
| Версии Microsoft Windows | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Дата выхода | Название | Последняя версия | Дата прекращения поддержки | Последняя версия встроенного браузера |
| 20 ноября 1985 | Windows 1.0x | 1.04 (апрель 1987) | 31 декабря 2001 | Нет браузеров |
| 1 ноября 1987 | Windows 2.x Windows 2.1x |
2.11 (13 марта 1989) | 31 декабря 2001 | |
| 22 мая 1990 | Windows 3.x | 3.00a (31 октября 1990) | 31 декабря 2001 [1] | |
| 18 марта 1992 | Windows 3.1 | 3.1 | 31 декабря 2001 | Internet Explorer 5 |
| 1 октября 1992 | Windows для рабочих групп 3.1 | 3.11 (31 декабря 1993) | 31 декабря 2001 | |
| 27 июля 1993 | Windows NT 3.1 | 3.10.528 SP3 (10 ноября 1994) | 31 декабря 2000 | |
| 21 сентября 1994 | Windows NT 3.5 | 3.50.807 SP3 (21 июня 1995) | 31 декабря 2001 | |
| 30 мая 1995 | Windows NT 3.51 | 3.51.1057 SP5 (19 сентября 1996) | 31 декабря 2001 | |
| 24 августа 1995 | Windows 95 | 4.00.950C (4.03.1214) (26 ноября 1997) | 31 декабря 2000 (осн.) (Retail); 31 декабря 2001 (SBL) (ext) | Internet Explorer 5.5 |
| 29 июля 1996 | Windows NT 4.0 | 4.00.1381 / SP6a SRP (26 июля 2001) | 20 июня 2002 (осн.); 30 июня 2003 (SBL); 31 декабря 2004 (ext) | Internet Explorer 6 |
| 25 июня 1998 | Windows 98 | 4.10.2222A (SE) (5 мая 1999) | 30 июня 2002 (осн.); 31 марта 2004 (SBL); 11 июля 2006 (ext) | |
| 20 апреля 2000 | Windows 2000 | 5.0.2195 / 5.0 SP4 Rollup 1 v2 (13 сентября 2005) | 31 марта 2004 (retail); 31 марта 2005 (SBL); 30 июня 2005 (осн); 13 июля 2010 (ext) | |
| 14 сентября 2000 | Windows ME | 4.90.9000 (14 сентября 2000) | 31 декабря 2003 (осн.); 30 июня 2004 (SBL) (Retail); 11 июля 2006 (ext) | |
| 24 августа 2001 (RTM) 25 октября 2001 (продажи) |
Windows XP | 5.1.2600.5512 SP3 (21 апреля 2008) | 30 сентября 2004 (RTM); 10 сентября 2006 (SP1/SP1a); 30 июня 2008 (retail); 14 апреля 2009 (SP2/SP3 осн.); 13 июля 2010 (SP2); 22 октября 2010 (SBL); 8 апреля 2014 (ext) | Internet Explorer 8 |
| 28 марта 2003 | Windows XP 64-bit Edition | 5.2.3790 | 25 июля 2006 | |
| 24 апреля 2003 | Windows Server 2003 | 5.2.3790.3959 SP2 (13 марта 2007) | 30 июня 2009 (RTM); 13 июля 2010 (осн.); 14 июля 2015 (ext) | |
| 25 апреля 2005 | Windows XP Professional x64 Edition | 5.2.3790.3959 SP2 (13 марта 2007) | 30 июня 2008 (retail); 31 января 2009 (SBL) | |
| 8 ноября 2006 (RTM) 30 января 2007 (продажи) |
Windows Vista | 6.0.6001 / SP2 Build 6002 (25 мая 2009) | 13 апреля 2010 (RTM); 22 октября 2010 (retail); 12 июля 2011 (SP1); 22 октября 2011 (SBL); 10 апреля 2012 (осн.); 11 апреля 2017 (ext) | Internet Explorer 9 |
| 16 июля 2007 | Windows Home Server | 5.2.4500 (16 июля 2007) | 8 января 2013 (осн.) | |
| 27 февраля 2008 | Windows Server 2008 | 6.0.6002 / SP2 build 6002 (25 мая 2009) | 12 июля 2011 (SP1), 9 июля 2015 (осн.), 10 июля 2018 (ext) | |
| 13 июля 2009 (RTM) 22 октября 2009 (продажи) |
Windows 7 | 6.1.7601 / SP1 Build 7601 (22 февраля 2011) | 9 апреля 2013 (RTM), 13 января 2015 (осн), 14 января 2020 (ext) | Internet Explorer 11 |
| 13 июля 2009 (RTM) 22 октября 2009 (продажи) |
Windows Server 2008 R2 или Windows Server 7 | 6.1.7601 / SP1 Build 7601 (22 февраля 2011) | 9 июля 2015 (осн.), 10 июля 2018 (ext) | |
| 6 апреля 2011 | Windows Home Server 2011 | 6.1.8400 | 12 апреля 2016 (осн.) | |
| 1 августа 2012 (RTM) 4 сентября 2012 (продажи) |
Windows Server 2012 | 6.2.9200 (26 октября 2012) | 12 января 2016(осн), 10 января 2018 (ext) | |
| 1 августа 2012 (RTM) 26 октября 2012 (продажи) |
Windows 8 | 6.2.9200 (26 октября 2012) | 12 января 2016 (осн) 10 января 2018 (ext) | |
| 21 августа 2013 (RTM) 17 октября 2013 (продажи) |
Windows Server 2012 R2 | 6.3.9600 (17 октября 2013) | 9 января 2018 (осн) 10 января 2023 (ext) | |
| 21 августа 2013 (RTM) 17 октября 2013 (продажи) |
Windows 8.1 | 6.3.9600 (17 октября 2013) | 9 января 2018 (осн) 10 января 2023 (ext) | |
| 15 июля 2015 (RTM) 29 июля 2015 (продажи) |
Windows 10 | 10.0.10586 (12 ноября 2015) | 13 октября 2020 (осн.), 14 октября 2025 (ext.) | Microsoft Edge / Internet Explorer 11(оставлен для совместимости) |
| 5 октября 2021 | Windows 11 | 10.0.22000.778 | не анонсирована | |
| Условные обозначения: | ||||
| Оболочка для MS-DOS | Windows 9x | Windows NT | Windows Server | |
| Поддержка прекращена | ||||
| осн. — окончание действия лицензии для первого (основного) релиза | SBL — окончание срока лицензии для производителей[2] | retail — окончание срока лицензии для розничных покупателей | SPx — окончание срока лицензии для различных дополнений (сервис-паков) к системе | ext — полное окончание поддержки системы |
Графические интерфейсы и расширения для DOS[]
Логотип первых Windows
Первые версии Windows не были полноценными операционными системами, а являлись надстройками к операционной системе DOS и были по сути многофункциональным расширением, добавляя поддержку новых режимов работы процессора, поддержку многозадачности, обеспечивая стандартизациюинтерфейсов аппаратного обеспечения и единообразие для пользовательских интерфейсов программ. Предоставляли встроенные средства GDI и USER для создания графического интерфейса. Первые версии Windows вообще состояли из трёх модулей — KERNEL, GDI и USER. Первый из них предоставлял вызовы управления памятью, запуском .EXE-файлов и загрузкой .DLL-файлов, второй — графику, третий — окна. Они работали с процессорами начиная с Intel 8086.
- Windows 1.0 (1985)
- Windows 2.0 (1987)
- Windows 2.1 (Windows 386, 1987) — в системе появилась возможность запуска DOS-приложений в графических окнах, причём каждому приложению предоставлялись полные 640 Кб памяти. Полная поддержка процессора 80286. Появилась поддержка процессоров 80386.
- Windows 3.0 (1990) — улучшена поддержка процессоров 80386 и защищённого режима.
- Windows 3.1 (1992) — серьёзно переработанная Windows 3.0; устранены UAE (фатальные ошибки прикладных программ), добавлен механизм OLE, печать в режиме WYSIWYG («что видите, то и получите»), шрифты TrueType, изменён диспетчер файлов, добавлены мультимедийные функции.
- Windows для рабочих групп (Windows for Workgroups) 3.1/3.11 — первая версия ОС семейства с поддержкой локальных сетей. В системе также испытывались отдельные усовершенствования ядра, применённые позднее в Windows 95.
Семейство Windows 9x[]
Основная статья: Windows 9x
Логотип первой системы семейства Windows 95
Первая система данного семейства Windows 95 была выпущена в 1995 году. Её отличительными особенностями являлись: новый пользовательский интерфейс, поддержка длинных имён файлов, автоматическое определение и конфигурация периферийных устройств Plug and Play, способность исполнять 32-битные приложения и наличие поддержки TCP/IP прямо в системе. Windows 95 использовала вытесняющую многозадачность и выполняла каждое 32-битное приложение в своём адресном пространстве. К данному семейству относятся также Windows 98 и Windows ME.
Логотип второй системы семейства Windows 98
Операционные системы этого семейства не являлись безопасными многопользовательскими системами как Windows NT, поскольку из соображений совместимости вся подсистема пользовательского интерфейса и графики оставалась 16-битной и мало отличалась от той, что в Windows 3.x. Так как этот код не был потокобезопасным, все вызовы в подсистему оборачивались в мьютекс по имени Win16Lock, который, кроме того, ещё и находился всегда в захваченном состоянии во время исполнения 16-битного приложения. Таким образом, «повисание» 16-битного приложения немедленно блокировало всю ОС. Но уже в 1999 году вышло второе исправленное издание. Программный интерфейс был подмножеством Win32 API, поддерживаемым Windows NT, но имел поддержку юникода в очень ограниченном объёме[3]. Также в нём не было должного обеспечения безопасности (списков доступа к объектам и понятия «администратор»). В составе Windows 95 присутствовал MS-DOS 7.0, однако его роль сводилась к обеспечению процесса загрузки и исполнению 16-битных DOS приложений. Исследователи заметили, что ядро Windows 95 — VMM — обращается к DOS под собой, но таких обращений довольно мало, главнейшая функция ядра DOS — файловая система FAT — не использовалась. В целом же интерфейс между VMM и нижележащей DOS никогда не публиковался, и DOS была замечена Эндрю Шульманом (книга Недокументированный Windows 95) в наличии недокументированных вызовов только для поддержки VMM.
Семейство Windows NT[]
Основная статья: Windows NT
Логотип семейства Windows NT
Операционные системы этого семейства в настоящее время работают на процессорах с архитектурами x86, x86-64, и Itanium, ARM. Ранние версии (до 4.0 включительно) также поддерживали некоторые RISC-процессоры: Alpha, MIPS, и Power PC. Все операционные системы этого семейства являются полностью 32- или 64- битными операционными системами, и не нуждаются в MS-DOS даже для загрузки.
Только в этом семействе представлены операционные системы для серверов. До версии Windows 2000 включительно они выпускались под тем же названием, что и аналогичная версия для рабочих станций, но с добавлением суффикса, например, «Windows NT 4.0 Server» и «Windows 2000 Datacenter Server». Начиная с Windows Server 2003 серверные операционные системы называются добавлением суффикса «Server» и года выпуска.
Логотип Windows 7 Логотип Windows 8
- Windows NT 3.1 (1993)
- Windows NT 3.5 (1994)
- Windows NT 3.51 (1995)
- Windows NT 4.0 (1996)
- Windows 2000 — Windows NT 5.0 (2000)
- Windows XP — Windows NT 5.1 (2001)
- Windows XP 64-bit Edition — Windows NT 5.2 (2003)
- Windows Server 2003 — Windows NT 5.2 (2003)
- Windows XP Professional x64 Edition — Windows NT 5.2 (2005)
- Windows Vista — Windows NT 6.0 (2006)
- Windows Home Server — Windows NT 5.2 (2007)
- Windows Server 2008 — Windows NT 6.0 (2008)
- Windows Small Business Server — Windows NT 6.0 (2008)
- Windows 7 — Windows NT 6.1 (2009)
- Windows Server 2008 R2 — Windows NT 6.1 (2009)
- Windows Home Server 2011 — Windows NT 6.1 (2011)
- Windows 8 — Windows NT 6.2 (2012)
- Windows Server 2012 — Windows NT 6.2 (2012)
- Windows 8.1 — Windows NT 6.3 (2013)
- Windows Server 2012 R2 — Windows NT 6.3 (2013)
- Windows 9 — Windows NT 6.4 (2015)
В основу семейства Windows NT положено разделение адресных пространств между процессами. Каждый процесс имеет возможность работать с выделенной ему памятью. Однако он не имеет прав для записи в память других процессов, драйверов и системного кода.
Семейство Windows NT относится к операционным системам с вытесняющей многозадачностью. Разделение процессорного времени между потоками происходит по принципу «карусели». Ядро операционной системы выделяет квант времени (в Windows 2000 квант равен примерно 20 мс) каждому из потоков по очереди при условии, что все потоки имеют одинаковый приоритет. Поток может отказаться от выделенного ему кванта времени. В этом случае система перехватывает у него управление (даже если выделенный квант времени не закончен) и передаёт управление другому потоку. При передаче управления другому потоку система сохраняет состояние всех регистров процессора в особой структуре в оперативной памяти. Эта структура называется контекстом потока. Сохранения контекста потока достаточно для последующего возобновления его работы.
Семейство ОС для смартфонов[]
Основная статья: Windows Phone
Логотип Windows Phone
Это семейство операционных систем реального времени было специально разработано для мобильных устройств. Поддерживаются процессоры ARM, MIPS, SuperH и x86. В отличие от остальных операционных систем Windows, операционные системы этого семейства продаются только в составе готовых устройств, таких как смартфоны, карманные компьютеры, GPS-навигаторы, MP3-проигрыватели и другие. В настоящее время под термином «Windows CE» понимают только ядро операционной системы. Например, Windows Mobile 5.0 включает в себя ядро Windows CE 5.0.
- Windows CE
- Windows Mobile
- Windows Phone
- Windows 10 Mobile
Семейство встраиваемых ОС Windows Embedded[]
Основная статья: Windows Embedded
Логотип Windows Embedded
Windows Embedded — это семейство операционных систем реального времени, было специально разработано для применения в различных встраиваемых системах. Ядро системы имеет общее с семейством ОС Windows CE и поддерживает процессоры ARM, MIPS, SuperH и x86.
Windows Embedded включает дополнительные функции по встраиванию, среди которых фильтр защиты от записи (EWF и FBWF), загрузка с флеш-памяти,CD-ROM, сети, использование собственной оболочки системы и т. п.
В отличие от операционных систем Windows, операционные системы этого семейства продаются только в составе готовых устройств, таких как: банкоматы,медицинские приборы, навигационное оборудование, «тонкие» клиенты, VoIP-терминалы, медиапроигрыватели, цифровые рамки (альбомы), кассовые терминалы, платёжные терминалы, роботы, игровые автоматы, музыкальные автоматы и другие.
В настоящее время выпускаются следующие варианты ОС Windows Embedded[4]:
- Windows Embedded CE,
- Windows Embedded Standard,
- Windows Embedded POSReady,
- Windows Embedded Enterprise,
- Windows Embedded NavReady,
- Windows Embedded Server.
Интегрированные программные продукты[]
Пакет Windows включает в себя «стандартные» приложения[5], такие как браузер (Internet Explorer), почтовый клиент (Outlook Express или Почта Windows), музыкальный и видеопроигрыватель (Проигрыватель Windows Media). С помощью технологий COM и OLE их компоненты могут быть использованы в приложениях сторонних производителей. Эти продукты бесплатны и могут быть свободно скачаны с официального сайта Microsoft, однако для установки некоторых из них необходимо иметь лицензионную версию Windows (верно только для ранних версий до Windows, начиная с Windows 98 являются неотъемлемой частью системы). Запуск этих программ под другими операционными системами возможен только с помощью эмуляторов среды Windows (Wine).
Вокруг факта включения таких «стандартных» продуктов в ОС Windows разгорается много дискуссий и юридических споров, по мнению сторонних разработчиков, это ведёт к отсутствию конкуренции и создает препятствия для распространения конкурирующих продуктов, они же часто ставят под сомнение качество браузера Internet Explorer, объясняя его популярность вхождением в пакет Windows и плохой осведомленностью пользователей о наличии альтернатив.
В 1997 году компания Sun Microsystems подала в суд на компанию за нарушение лицензии на использование технологий Java. В 2001 году Microsoft выплатила штраф и исключила не совместимую с лицензированной виртуальную машину Java из состава своих продуктов[6].
Распространённость[]
В настоящее время Windows установлена на 91% персональных компьютеров и рабочих станций. По данным компании Net Applications, на август 2014 года рыночная доля Windows составила ▲91,68%.
Среди различных версий Windows по данным W3Schools с августа 2011 года наиболее популярна Windows 7[7] (около 50%).
| «GoStats.ru»,
июнь 2011[8] |
«Net Market Share»,
июнь 2011[9] |
«GoStats.ru»,
август 2014[10] |
«Net Market Share»,
август 2014[11] |
«GoStats.ru»,
август 2015[12] |
|
| Все версии | 94.70 % | 93.32 % | 90.46% | 91.68% | 84.76% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Windows 10 | — | — | — | — | 2.87% |
| Windows 8 | — | — | 2,4% | 12,48% | 33,67% |
| Windows 7 | 25.89 % | 28.68 % | 76.72% | 51.22% | 40.63% |
| Windows XP | 55.44 % | 54.04 % | — | 23.89% | 6.55% |
<nowiki>
Комментарии[]
Windows 7 — умершая легенда (Ghast88)
| Хронология ОС Windows | |
|---|---|
| Основные версии | MS-DOS: Windows 1.0x • Windows 2.x (Windows 2.1x) • Windows 3.x Windows 9x: Windows 95 • Windows 98 • Windows ME Windows NT: Windows NT 3.1 • Windows NT 3.5 • Windows NT 3.51 • Windows NT 4.0 • Windows 2000 • Windows XP • Windows Vista • Windows 7 • Windows 8 • Windows 8.1 • Windows 10 |
| Windows Server | Windows Server 2003 • Windows Home Server (Windows Home Server 2011) • Windows Server 2008 (Windows HPC Server 2008 • Windows Server 2008 R2) • Windows Essential Business Server • Windows MultiPoint Server • Windows Small Business Server • Windows Server 2012 (Windows Server 2012 R2) • Windows Server 2016 |
| Специализированные | Windows Embedded (Windows Embedded Automotive • Windows Embedded POSReady) • Среда предустановки Windows • Windows Fundamentals for Legacy PCs |
| Мобильные | Windows CE (Windows CE 1.0 • Windows CE 2.0 • Windows CE 3.0 • Windows CE 4.0 • Windows CE 5.0 • Windows CE 6.0 • Windows Embedded Compact 7 • Windows Embedded Compact 2013) • Windows Mobile • Windows Phone • Windows RT • Windows 10 Mobile |
| Другие проекты | Открытые: Xenix • OS/2 • Microsoft Singularity • Midori Закрытые: Windows Neptune • Windows Nashville • Windows Odyssey • Windows Cairo • Windows Longhorn • Windows 10x |
| Альтернативные реализации | ReactOS • Wine |
| |
|
|---|---|
| Основные |
Aero • |
| Службы управления |
Архивация и восстановление • |
| Приложения |
Контакты • |
| Игры |
Chess Titans • |
| Ядро ОС |
Ntoskrnl.exe • |
| Службы |
Autorun.inf • |
| Файловые системы |
ReFS • |
| Сервер |
Active Directory • |
| Архитектура |
NT • |
| Безопасность |
BitLocker • |
| Совместимость |
Подсистема UNIX (Interix) • |
- ↑ Microsoft Support Lifecycle Шаблон:Ref-en
- ↑ Лицензирование для сборщиков систем OEM
13 версий за 35 лет — не так уж и много
Ровно 35 лет назад в этот день, 20 ноября 1985 года, Microsoft выпустила первую версию операционной системы Windows, которой впоследствии было суждено стать самой популярной ОС в мире. Windows 1.0 пришла на смену MS-DOS и принесла с собой много всего нового – элементов, которые в ней используются до сих пор. Это полосы прокрутки, диалоговые окна и такие приложения, как Блокнот и Paint. В Windows 1.0 появилась поддержка мышки. Парадоксально, но поначалу многие жаловались, что в своей работе ОС слишком уж сильно опирается на манипулятор, вместо ввода команд с клавиатуры. Критикуют операционную систему и сейчас, но уже за другие вещи.
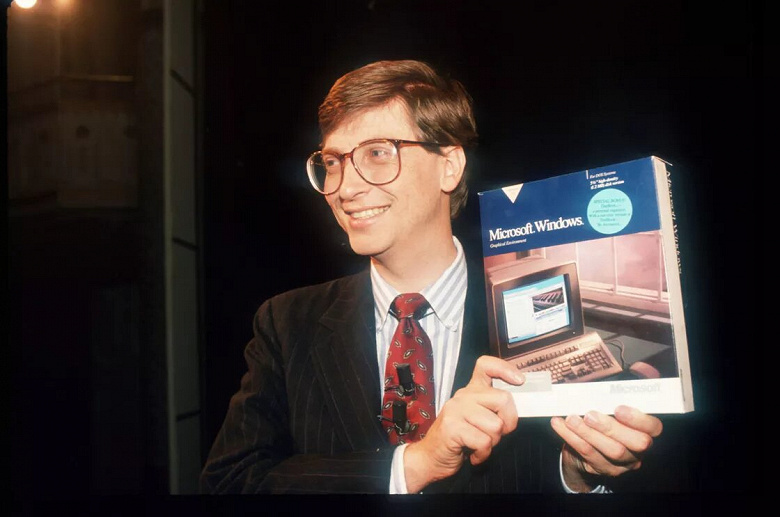

Для работы Windows 1.0 требовалось две дискеты, 256 КБ ОЗУ и графическая карта. Если была потребность в запуске нескольких программ, то требования повышались – жесткий диск и 512 КБ ОЗУ.
В то время на рынке ОС Microsoft конкурировала с Apple, но именно Windows было суждено стать самой популярной операционной системой. В нашей фотогалерее мы вспоминаем все основные версии Windows, от 1.0 до 10. Какая из них нравится вам больше всего и почему? Делитесь своими мнениями в комментариях.
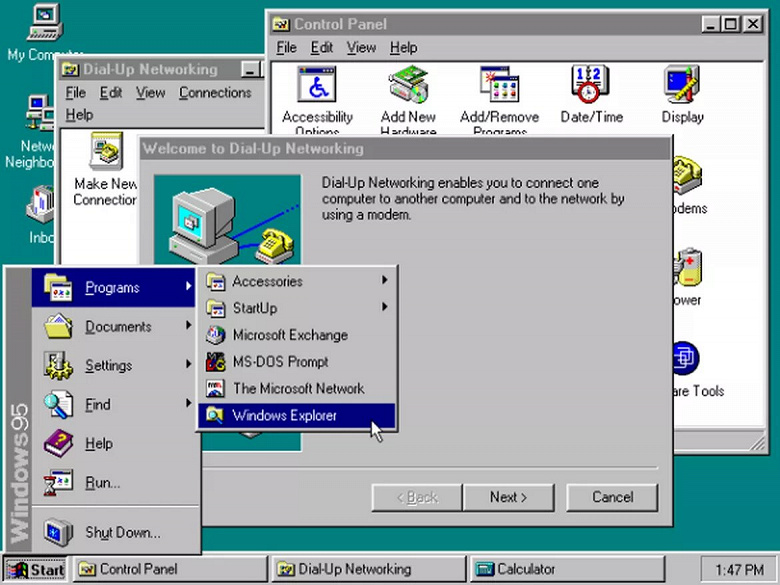
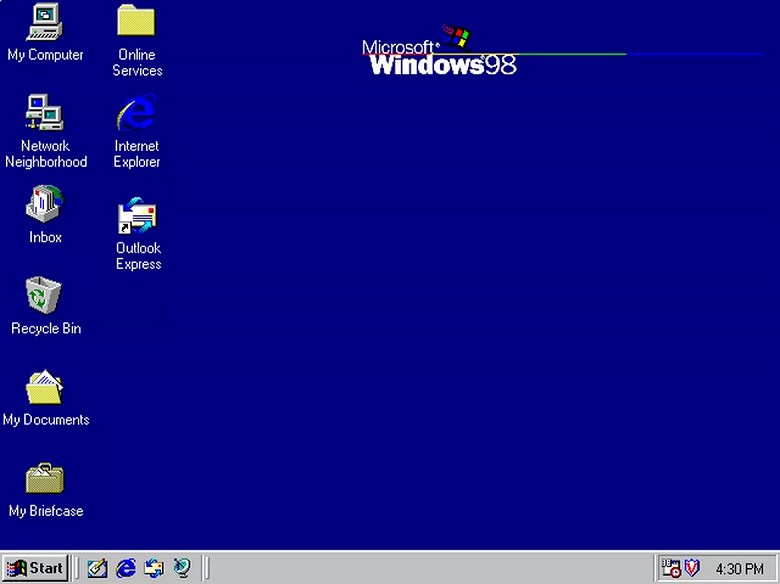
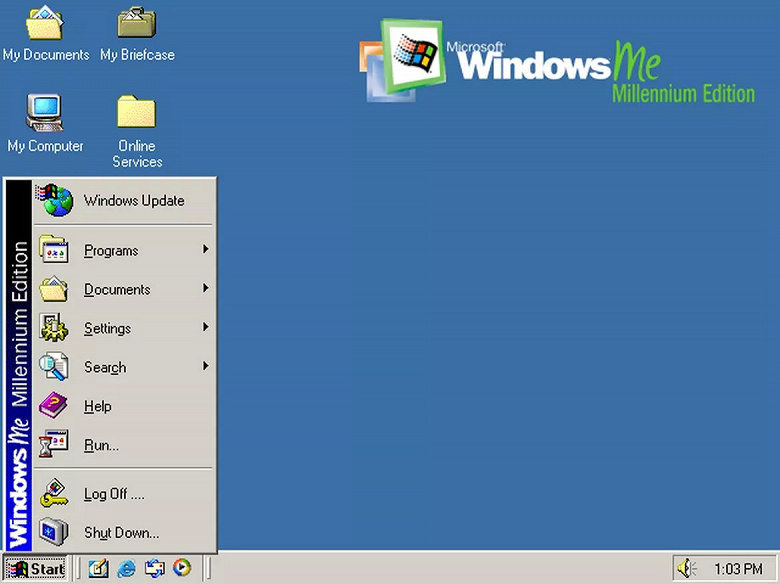
Итого 13 крупных релизов за эти 35 лет. В следующем году должна выйти Windows 10X, адаптированная для использования в ноутбуках, двухэкранных ПК и ноутбуках с гибкими дисплеями. Что же касается версии Windows для настольных ПК, то это по-прежнему будет Windows 10. По крайней мере, в ближайшие пару лет.
20 ноября 2020 в 23:19
| Теги: Microsoft, Windows
| Источник: The Verge
Ровно 35 лет назад в этот день, 20 ноября 1985 года, Microsoft выпустила первую версию операционной системы Windows, которой впоследствии было суждено стать самой популярной ОС в мире. Windows 1.0 пришла на смену MS-DOS и принесла с собой много всего нового – элементов, которые в ней используются до сих пор. Это полосы прокрутки, диалоговые окна и такие приложения, такие Блокнот и Paint. В Windows 1.0 появилась поддержка мышки. Парадоксально, но поначалу многие жаловались, что в своей работе ОС слишком уж сильно опирается на манипулятор, вместо ввода команд с клавиатуры. Критикуют операционную систему и сейчас, но уже за другие вещи.
Для работы Windows 1.0 требовалось две дискеты, 256 КБ ОЗУ и графическая карта. Если была потребность в запуске нескольких программ, но требования повышались – жесткий диск и 512 КБ ОЗУ.
В то время на рынке ОС Microsoft конкурировала с Apple, но именно Windows было суждено стать самой популярной операционной системой. В нашей фотогалерее мы вспоминаем все основные версии Windows, от 1.0 до 10. Какая из них нравится вам больше всего и почему? Делитесь своими мнениями в комментариях.
Windows 1.0, 1985 год
Windows 2.0, 1987 год
Windows 3.0, 1990 год
Windows NT 3.5, 1994 год
Windows 95, 1995 год
Windows 98, 1998 год
Windows ME, 2000 год
Windows 2000 (она же Win2K или NT 5.0), 2000 год
Windows XP, 2001 год
Windows Vista, 2007 год
Windows 7, 2009 год
Windows 8, 2012 год
Windows 10, 2015 год
Windows 10, 2020 год
Итого 13 крупных релизов за эти 35 лет. В следующем году должна выйти Windows 10X, адаптированная для использования в ноутбуках, двухэкранных ПК и ноутбуках с гибкими дисплеями. Что же касается версии Windows для настольных ПК, то это по-прежнему будет Windows 10. По крайней мере, в ближайшие пару лет.





















