Продолжаем знакомиться с новыми возможностями ОС Windows Server 2012 R2. Ранее мы рассказывали о корпоративном аналоге DropBox в Windows Server 2012 R2 под названием Work Folders. Сегодня речь пойдет о еще одном новшестве новой серверной платформы – функции Web Application Proxy. Web Application Proxy – это новая функция роли Remote Access в Windows 2012 R2, позволяющая публиковать HTTP/ HTTPS приложения, расположенные в периметре корпоративной сети на клиентских устройствах (в первую очередь подразумеваются мобильные устройства) за ее периметром. Благодаря возможности интеграции c AD FS (служба может выступать в качестве ADFS-прокси), возможно обеспечить аутентификацию внешних пользователей, пытающихся получить доступ к опубликованным приложениям.
Web Application Proxy предоставляет такие же возможности публикации приложений, как и Forefront Unified Access Gateway (UAG), однако данная служба также позволяет взаимодействовать с другими серверами и сервисами, обеспечивая тем самым более гибкую и рациональную конфигурацию.
Web Application Proxy по сути выполняет функцию обратного прокси сервера (HTTP reverse proxy), организуя ретрансляцию запросов клиентов из внешней сети на внутренний сервер, и является межсетевым экраном на прикладном уровне.
Сервер со службой Web Application Proxy получает внешний HTTP/HTTPS трафик и терминирует его, после чего от своего имени инициирует новое подключение ко внутреннему приложению (веб-серверу). Т.е. внешние пользователи прямого доступа к внутреннему приложению реально не получают. Любой другой трафик, получаемый Web Application Proxy, отклоняется (в том числе отклоняются HTTP/HTTPS запросы, которые могут быть использованы при DoS, SSL и 0-day атаках).
Требования к организации Web Application Proxy и ключевые особенности:
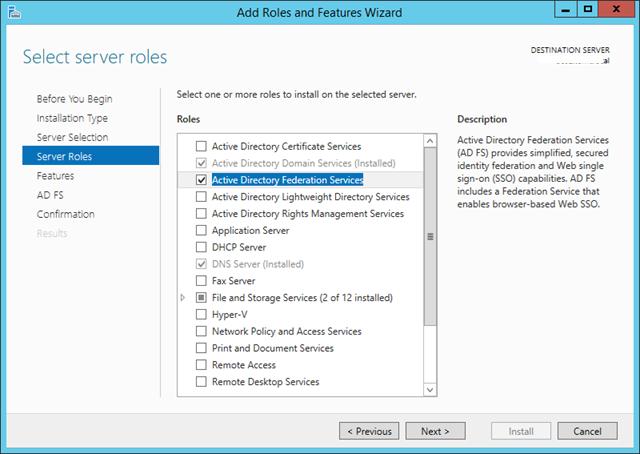
- Систему можно развернуть на серверах с ОС Windows Server 2012 R2, включенных в домен Active Directory, с ролями AD FS и Web Application Proxy. Эти роли должны быть установлены на разных серверах.
- Необходимо обновить схему Active Directory до Windows Server 2012 R2 (обновлять контроллеры домена до Windows Server 2012 R2 не нужно)
- В качестве клиентских устройств поддерживаются устройства с ОС Windows, IOS (iPad и iPhone). Работы над клиентами для Android и Windows Phone пока еще не окончены
- Аутентификация клиентов осуществляется службой Active Directory Federation Services (ADFS), которая также выполняет функции ADFS – проксирования.
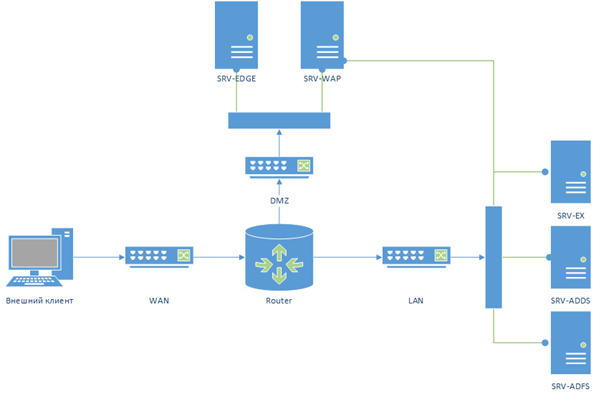
- Типовая схема размещения сервера с ролью Web Application Proxy представлена на рисунке. Данный сервер располагается в выделенной DMZ зоне и отделен от внешней (Интернет) и внутренней сети (Интранет) межсетевыми экранами. В этой конфигурации для работы Web Application Proxy требует наличия двух интерфейсов – внутреннего (Intranet) и внешнего (DMZ)
Установка роли ADFS в Windows Server 2012 R2
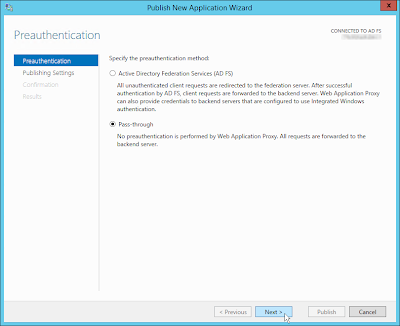
Для обеспечения дополнительной безопасности преаутентифкация внешних клиентов выполняется на сервере ADFS, в противном случае используется pass-through аутентификация на конечном сервере приложения (что менее секьюрно). Поэтому первый шаг при настройке Web Application Proxy – установка на отдельном сервере роли Active Directory Federation Services.
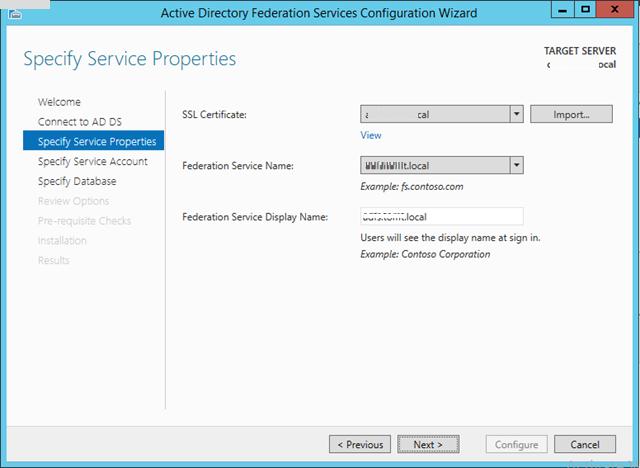
При установке ADFS нужно выбрать SSL сертификат, который будет использоваться для шифрования, а также DNS имена, которые будут использоваться клиентами при подключении (соответствующие записи в DNS зоне придется создать самостоятельно).
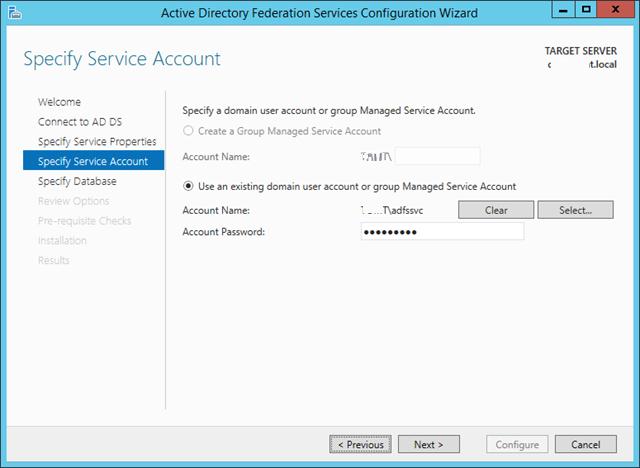
Затем нужно указать сервисную учетную запись для службы ADFS. Необходимо учесть, что имя ADFS должно быть указано в атрибут Service Principal Name аккаунта. Сделать это можно командой:
setspn –F –S host/adfs.winitpro.ru adfssvc
Установка службы Web Application Proxy
Следующий этап, настройка самой службы Web Application Proxy. Напомним, что служба Web Application Proxy в Windows Server 2012 R2 является частью роли “Remote Access”. Установите службу Web Application Proxy и запустите мастер ее настройки.
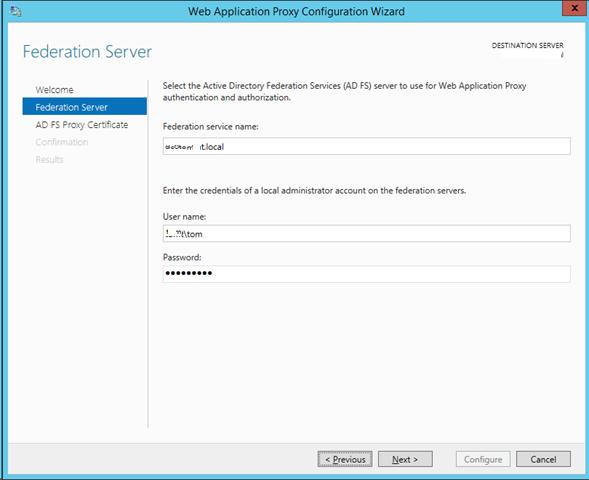
На первом этапе мастер предложит Вам указать имя ADFS сервера и параметры учетной записи, имеющей доступ к данной службе.
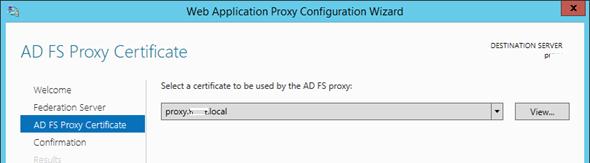
Далее нужно указать сертификат (убедитесь, что в альтернативных именах сертификата содержится имя сервера ADFS).
Совет. Проверьте, что ваши DNSзоны настроены корректно: сервер с ролью WAP должен иметь возможность отрезолвить имя сервера ADFS, а он в свою очередь может разрешить имя прокси сервера. Сертификаты на обоих серверах должны включать имя службы федерации.
Публикация приложения через Web Application Proxy
После того, как установлены роли ADFS и Web Application Proxy (которая работает еще и как ADFS Proxy), можно перейти непосредственно к публикации наружу конкретного приложения. Сделать это можно с помощью консоли Remote Access Management Console.
Запустите мастер публикации и укажите, хотите ли вы использовать для преаутентификации службу ADFS (это именно наш вариант).
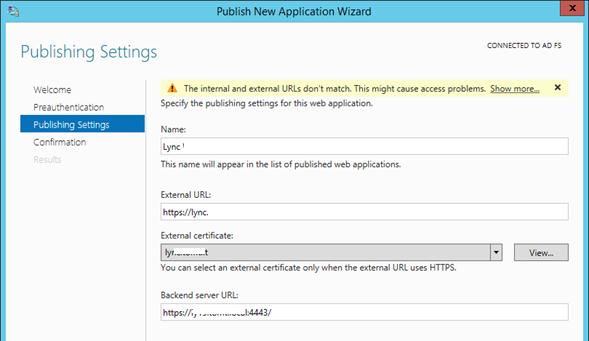
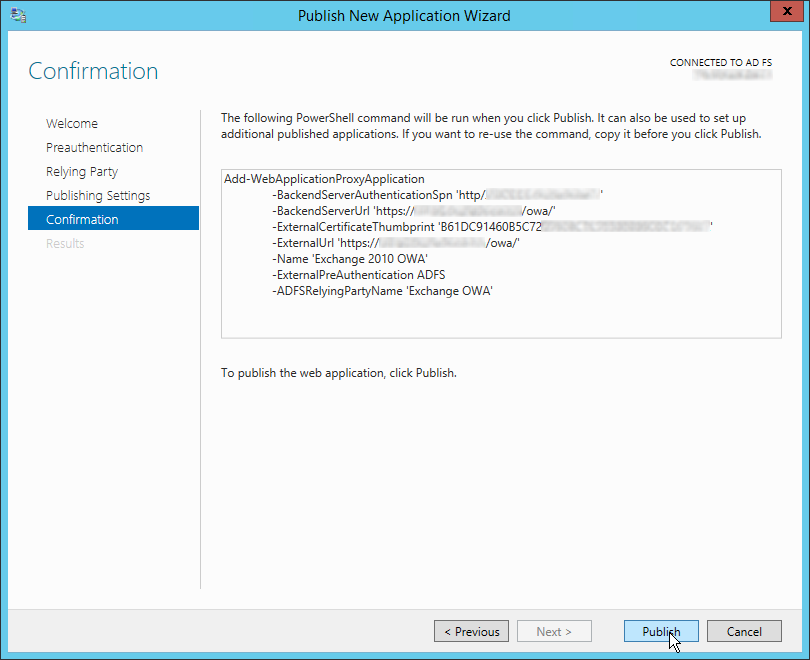
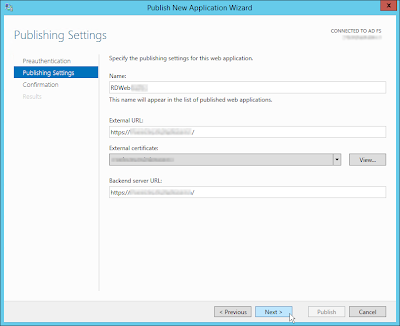
Затем нужно задать имя публикуемого приложения, используемый сертификат, внешний URL (имеенно его для подключения будут использовать внешние пользователи) и внутрений URL-адрес сервера, на который будут пересылаться запросы.
Совет. Если необходимо перенаправить внешнее приложение на альтернативный порт, необходимо задать его в URL, указаывающем на внутренний сервер. Например, если необходимо перенаправить внешние https запросы (443 порт) на 4443 порт, нужно указать:
Backend server URL: lync.winitpro.local:4443
Завершите работу мастера, и на этом публикация приложений окончена. Теперь, если попытаться с помощью браузера зайти на опубликованный внешний URL-адрес, то браузер сначала будет перенаправлен на службу аутентификации (ADFS Proxy), а после успешной аутентификации пользователь будет отправлен непосредственно на внутренний сайт (веб приложение).
Благодаря новой службе Web Application Proxy в Windows Server 2012 R2 возможно реализовать функционал обратного прокси сервера с целью публикации внутренних служб предприятия наружу без необходимости использования задействовать сторонние файерволы и продукты, в том числе такие, как Forefront и пр.
Installing (WAP) Web Application Proxy – Server 2012 R2
This guide shows you how to install WAP (Web Application Proxy) on Server 2012 R2 and also configure it.
First step is to import the certificate into the Personal store on your server.
- Open up MMC, you can click start -> run and type MMC and press enter.
- After the console window has opened then:
- Step 1 -> Click on File.
- Step 2 -> Click on Add/Remove Snap-in
- Step 1 -> Click on Certificates
- Step 2 -> Click on the Add > button
- After you click add button the window above will appear:
- Step 1 -> Select Computer Account
- Step 2 -> Click Next
- Step 1 -> Make sure Local computer is selected.
- Step 2 -> Click Finish.
- Once everything has been selected in the above steps the selected snap-in will show on the right.
- Step 1 -> Click Ok.
- Step 1 -> Right click on Personal and select all tasks.
- Step 2 -> Click on Import.
- Once you have clicked Import the above window appears. Click Next to continue.
- Step 1 -> Click on the Browse button. Locate your certificate.
- Once you have selected your certificate it will show in the box (as above), click Next.
- Leave the selected option as shown above and then click Next.
- Click on Finish.
Installing Remote Access Role.
-
Open up Server Manager.
- Step 1 -> Click Manage.
- Step 2 -> Click on Add Roles and Features.
- Step 1 -> Leave the default as shown above.
- Step 2 -> click Next.
- Step 1 – > Click on Next.
- Step 1 -> Select Remote Access.
- Step 2 -> Click Next.
- Step 1 -> We not selecting any features, click Next.
- Step 1 -> Click Next.
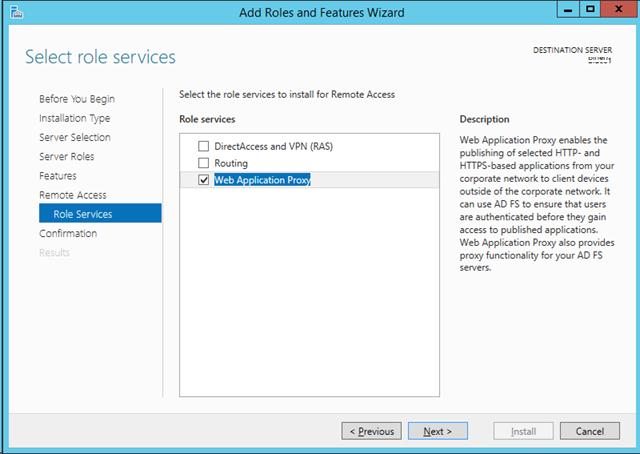
- Step 1 -> Select Web Application Proxy.
- Step 2 -> Click Next.
- Step 1 -> Confirm your selection and then click Install.
- Step 1 -> once the installation is complete, click on the link as shown above to start the Wizard.
- Step 1 -> Click Next.
- Step 1 -> Enter in the Federation Service Name.
- Step 2 & 3 -> Enter in the details of the account you will be using.
- Step 4 – > Click Next.
- Step A -> Click the dropdown arrow and select your certificate.
- Step 1 -> Click Next.
- Step 1 -> Confirm everything and then click Configure.
- Once the configuration is complete, click the close button.
What is Web Application Proxy (WAP)?
WAP is new feature introduced with Server 2012 R2. It was first introduced as ARR( Application Request Routing) in Server 2012.
As you know, Threat Management Gateway (TMG) and Unified Access Gateway (UAG) have a definitive end of life. ARR is a web farm extension meant for publishing web sites, however ARR does not do pre-authentication, there are no PowerShell cmdlets, no high availability, and there is no ongoing investment in ARR. A server role in Windows Server 2012 R2 – the Web Application Proxy or WAP.
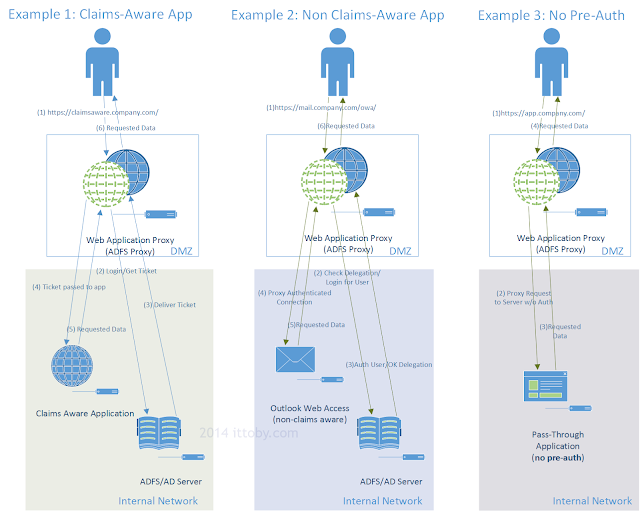
WAP is a reverse proxy solution that relies on ADFS for publication of both claims aware and non-claims aware web applications. WAP is built for current and future web protocols; it understands ADFS, claims, OAUTH, it can also do protocol transition, and Kerberos constrained delegation. Specifically (and applicable to this post) protocol transition and KCD are required for smart card only authentication (authN) into extranet published Kerberos enabled web applications – one of the same functionality sets that TMG and UAG provided. This means that WAP can publish claims aware AND non-claims aware web applications using smart card only authN.
Web Application Proxy provides organizations with the ability to provide selective access to applications running on servers inside the organization to end users located outside of the organization. The process to make the application available externally is known as publishing. Web Application Proxy must always be deployed with AD FS. This enables you to leverage the features of AD FS, such as, single sign-on (SSO).
It provides better security to your internal Applications,
- When HTTPS traffic arrives that is directed to an address published by Web Application Proxy, it terminates the traffic and initiates new requests to the published applications. It therefore acts as a session-level buffer between external devices and published applications. That is, when users access published applications, they do not directly access the application, instead, they access the application through Web Application Proxy.
- Any other traffic that arrives at Web Application Proxy is dropped and not forwarded to the published applications. This includes any illegal HTTP or HTTPS requests that might be used as part of denial of service attacks, zero day attacks, SSL attacks, and so on.
- Any authenticated request that arrives at Web Application Proxy containing an authentication token from AD FS will be inspected to make sure that the token received was intended for the client sending the token. This is done by checking that the device (through the Workplace Join certificate) corresponds to the claim within the token that identified the device when authenticated to AD FS. Refer the Technet Article for more information about the WAP.
Now, We will see how to install WAP server in Server 2012 R2. I am so excited!!
Well, I have explained how to install ADFS in few of my earlier Articles,
1. How to install active directory federation services on server 2012
2. ADFS 3.0 Installation and Configuration with SQL Mirroring
After you successfully configured ADFS Server, You need to export the certificate with private keys of your communication certificate( Ideally Wild Card Certificate) and you need to import in the WAP server first and post that follow the below steps to configure.
Normally WAP server required two NIC cards. One is for backbone access and another one is for Internet Access. So you need to configure as mentioned in the diagram below,
in my test lab, I kept in the same way and continued further process,
WAP Feature is the part of Remote Access Role, hence select Remote Access
Select Web Application Proxy
Add ADFS URL and enter service account credentials to configure
So now WAP Installation is successfully completed. Now from the External network, Add how Entry pointing ADFS URL STS.Windowstechpro.com to WAP Server IP Address and try to access the Idp.

You can add multiple servers in the WAP form if you want to highly load balance using HLB or NLB.
Setup of Web Application Proxy Server in Windows 2012 R2
When Microsoft discontinued
Threat
Management Gateway (which once was Proxy
and then ISA server)
I must admit I was disappointed; it was a relatively inexpensive authenticated reverse
proxy that worked with Exchange Server as well as many other complicated
products. In the interim we were told that Unified
Access Gateway would be the replacement, but that product isn’t as
well suited to the task.
Several alternatives are out there, including: Kemp, F5, Nginx, and Squid
but either the price or the relative difficulty of setup isn’t in line with
TMG. Fortunately starting in Windows 2012R2 Microsoft introduced Web
Application Proxy which largely fills the gap.
Web Application Proxy/Server 2012r2 release
party.Trust me, I paid big bucks for this insider photo.
What is Web Application Proxy?
Web Application Proxy
(WAP from henceforth) is based on and replaces Active
Directory Federation Services Proxy 2.0. In addition to the ADFS Proxy
functionality it also introduces the ability to expose internal resources to
external users. These users can be pre-authenticated (and then impersonated
for SSO) against
your Active Directory infrastructure using ADFS prior to being allowed
access to resources.
Wait, This is ADFS Proxy 3.0?
Yup! That and more. Here’s what you can do with it:
- Authorize external users for access to other claims-aware external or
internal resources (Generally SaaS). - Allow access (by «reverse» proxy) to multiple internal applications on
the same port. - Pre-Authenticate users against Active Directory via Kerberos
or NTLM
to facilitate SSO and access to internal applications (if desired) - Expose multiple internal resources on a single IP address/port
(generally 443) differentiated by hostname - Loadbalance using a session affinity based solution in front of WAP
Let’s Go!
This article will cover the following:
- WAP requirements
- Set up
- Forwarding a couple of sample applications
- Troubleshooting
Software Requirements
Web application proxy is available on Windows Server 2012 R2 and higher,
and it requires
ADFS 3.0 to be available on the back end. For assistance in setting
up ADFS 3.0, see my article here.
If you would like to proxy authentication for non-claims aware
applications, I.E. Exchange OWA pre-2013 SP1 (SP1
Claims) or Kerberos/NTLM apps, you will need to have the WAP server
joined to your domain.
Additionally, you’ll need the certificate (private and public key) from
your ADFS server and one certificate (again, private and public) for each
application you intend to proxy. These certificates must be trusted by
your clients, so generally external globally trusted (Digicert for
example) certificate authorities are preferred. The certificates need to
be installed under the «Personal» portion of the «Local Machine» store on
the machine you intend to use as your WAP proxy. If you only intend to
host internal resources to domain-joined computers connecting remotely you
can use an internal PKI provided your clients trust your issuing CA(s).
For information on how to setup an internal CA, see my article here.
If you need help exporting your public and private key from your ADFS
server and other services, see this
article. Note that if these certificates are marked as non-exportable you
will need new certificates for those services, so make sure you plan
accordingly.
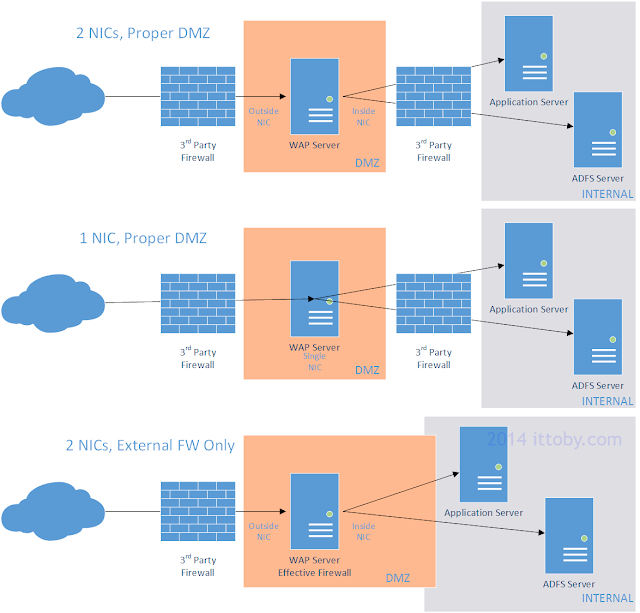
Connectivity and Hardware/VM Requirements
Preferably, your WAP server should be placed in a De-Militarized
Zone with a firewall on either side of it. The machine
can operate with either one or two Network Interface
Cards, but for proper security I recommend two NICs; one
internal and one external. Other connectivity options will work, including
branching into your internal network on the inside interface, but I won’t
be covering those scenarios in detail. For all connectivity options see
the following diagram:
As for the hardware you can use either real hardware or a VM assuming you
have a proper DMZ NIC setup on your Hyper-V/ESX/Xen/whatever host(s). WAP
is not a particularly demanding application and uses very little I/O. It
is also horizontally scalable with a network level load balancer (f5) so I
won’t give direct guidance on specifications since it would likely have
little relevance to your configuration. As in most cases, performance
evaluation and configuration change is the way to go.
After deciding on your hardware and installing the OS, you’ll need to
configure the NICs. We’ll cover that in the next section…
Installation
Now that the hardware and OS are ready to go, let’s configure the NICs:
Network Configuration
- First open the «Network and Sharing Center» and click «Change Adapter
Settings». Re-name the NICs «External» and «Internal» according to how
they are connected to avoid confusion during set up and troubleshooting. - Give each NIC appropriate IP address settings. The subnet for each
will depend on your firewall/switch configuration. Some firewall
configurations may require communication stay on a single subnet but if
given a choice it is generally better to have them on different subnets.
(2 NICs) Leave the default gateway on the internal NIC blank. If your
WAP server is not domain joined because you intend on using only claims
auth or passthrough (not delegation) then leave your DNS servers blank
on the internal NIC as well and be sure to execute step 4. - If the WAP server needs to access resources (ADFS, DC, App) on a
subnet other than that the internal NIC is connected to, you will need
to add a static route to the server so it knows how to get to that
network. For example, if your WAP server is on 192.168.1.10/24, your
ADFS server is 192.168.2.5/24, and your gateway is 192.168.1.1, you
would issue the following command from an elevated command prompt: route
ADD 192.168.2.0 MASK 255.255.255.0 192.168.1.1 IF 192.168.1.10 -p .
For more information, see this
article. - <Only if you haven’t specified DNS servers on the internal
NIC>To look up the ADFS server for claims verification you will need
to add each internal ADFS server address to your
%SYSTEMROOT%system32driversetchosts file. Do this now; if you need
further instructions see this
article. - Now we’ll secure the external NIC. Open the properties of that NIC and
on the «Networking» tab unbind everything except for «QoS Packet
Scheduler» and the protocol you intend on using (IPv4 or IPv6). - If using IPv4, drill into the properties of that protocol and select
«Disable NetBIOS over TCP/IP» under the «WINS» tab. Also ensure you
disable «Register this connection’s address in DNS» on the «DNS» tab. - On your external firewall, open the ports for the services you wish to
forward. (443 would be common) - On your internal firewall, open ports necessary for AD/other
communication. Here
is an excellent guide.
WAP Installation
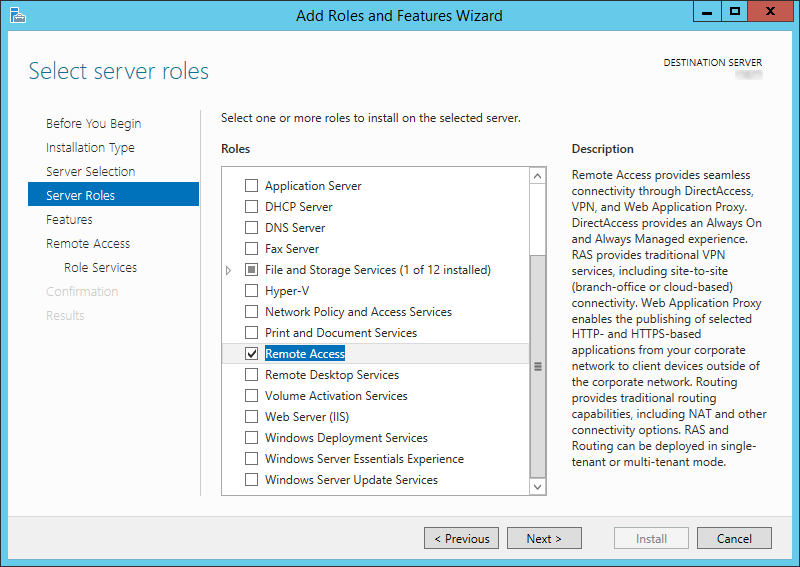
- In server manager, click «Manage->Add Roles and Features».
- Click «Next» on the «Before you begin» screen.
- For «Installation Type» select «Role-based or feature-based
installation» & click «Next». - Select your desired WAP server and click «Next».
- On «Add Roles and Features Wizard», select the «Remote Access» role
and click «Next». - You do not need to select any features; click «Next» on the «Select
features» page. - Read the dialog presented on the «Remote Access» screen and click
«Next». - Leave «Include management tools» checked and click «Add Features».
- On the «Select role services» page select «Web Application Proxy» and
click «Next». - When presented with the confirmation screen, click «Install».
WAP Configuration
Prerequisite Note: For this step you will need the
public and private key for your internal ADFS server(s) installed to the
«Personal» section of the «Local Computer» store on your WAP server. For
more information, refer to «Software Requirements» above.
- After installation, server manager will notify you that configuration
is required. Click the notification flag and select «Open the Web
Application Proxy Wizard». - On the «Welcome» screen of the «Web Application Proxy Wizard» click
«Next». - On the «Federation Server» screen, enter the external
fully qualified domain name of your federation service. This needs to be
registered in external DNS (i.e. resolvable from the internet).
For more information, see my article linked under «Software
Requirements». Insert the username/password of a domain administrator
account to properly register this as a proxy server. This account will not
be used after this point, so a service account is not necessary. Click
«Next». - Select the ADFS certificate you installed earlier from the dropdown
and click «Next». - You’ll be presented with the configuration details. If you intend on
setting up another WAP server for load balancing copy the powershell
command down for later use. Click «Configure» to continue. - You should see the message «Web Application Proxy was configured
successfully».
Setup Verification
To verify basic functionality:
- On the WAP server, open up Tools->Remote Access Management Console
- On the left-hand navigation pane, select «Operations Status»
- The status of the WAP server will be relayed in the middle pane. Do
not be surprised to see the server listed twice, once for the FQDN and
once for netbios. This is normal.
Now that setup is complete, let’s move on to publishing!
Example A: Proxying Exchange 2010 OWA (Pre-auth/Non-Claims/Delegated
Authentication)
Now that we’ve completed the ADFS/WAP setup, let’s walk through the setup
of a non-claims aware application using Kerberos/NTLM delegation. A
popular example would be Exchange Outlook Web Access; I’ll be using
version 2010 SP3.
Prerequisite Note: For this step you will need the
public and private key for the services you wish to host (Exchange OWA in
this case) installed to the «Personal» section of the «Local Computer»
store on your WAP server. Requests destined for your back-end service are
decrypted and re-encrypted at the WAP server. For more information, refer
to «Software Requirements» above.
Trust Setup
First, we must set up the new trust on the ADFS server. On your back-end
ADFS server (not the WAP server) do the following:
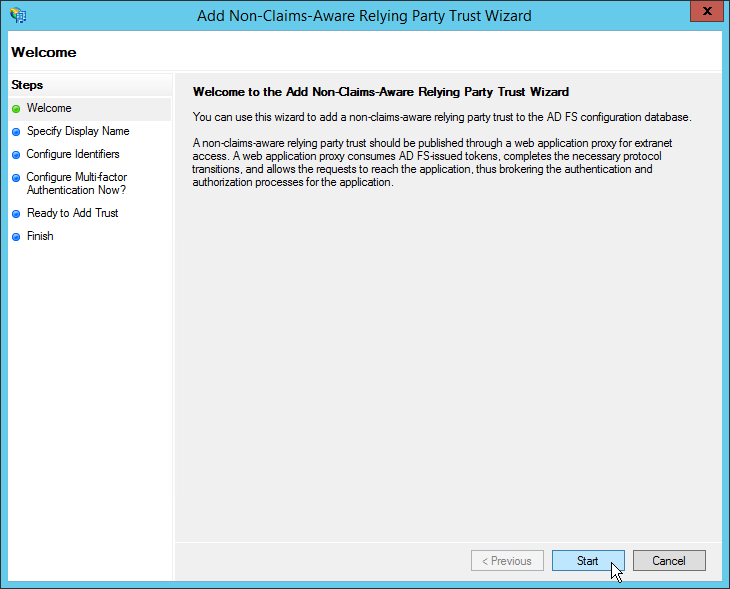
- Open the AD FS management tool and click the «Trust Relationships»
folder on the left hand navigation pane. - In the right hand action pane, click «Add Non-Claims-Aware Relaying
Party Trust». - A wizard will pop up; click «Start» on the welcome screen.
- Give this rule a (human) meaningful name, i.e.» <Servername>
Exchange OWA» along with a description if desired and click «Next». - Now we’ll add the non-claims aware relaying trust party identifier
(which in this case is simply a URL). Enter the external fully qualified
domain name of the server complete with url path ending in a trailing
forward slash, i.e. https://mail.company.com/owa/ and click «Next».
Note: WAP identifiers must end in a trailing slash even though the MSFT
example doesn’t look that way. - On the next screen, «Configure Multi-Factor Authentication Now?», you
can set up multi-factor authentication should you desire. I will not be
configuring multi-factor for this demonstration, but note you can always
set it up later if desired. Leave «I do not want to configure…»
selected and click «Next». - Review your configuration on the «Ready to Add Trust» screen and click
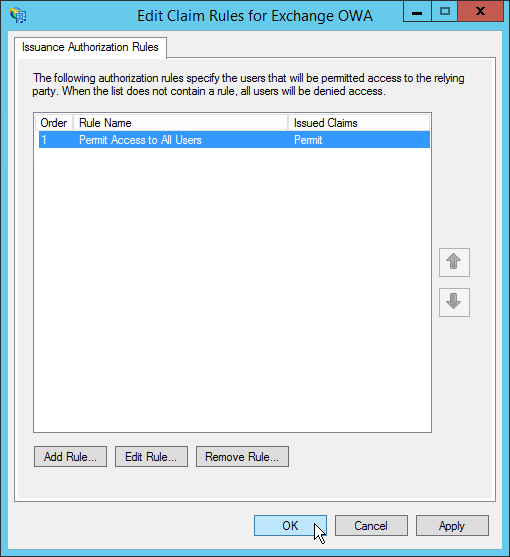
«Next». - The «Finish» screen will have a checkbox starting with «Open the Edit
Authorization Rules dialog…» that is checked by default. Leave it
checked because we will want to specify who is allowed access through to
the back-end via this rule right away. Click «Finish». - A dialog box titled «Edit Claim Rules for <Rule Name>» will come
up allowing us to define who should be allowed access via this rule.
Click «Add Rule’. - You will be asked to select a rule template. What you select here will
depend on what is reasonable for your environment. You should create (a)
rule(s) that correspond with the least access required possible as
anyone getting past this point will be able to attempt to authenticate
directly against the target internal resource. You may, for example,
want to use a specific Active Directory group with only the users that
need access to this resources. For the purposes of testing and this
article, however, I will be using a simple «Permit All Users» rule. This
will allow anyone in AD through and is suitable for testing or in
addition to other rules. Select the rule template and click «Next». - Click «Finish» to close the «Add Issuance Authorization Claim Rule
Wizard» - So long as you do not want any additional rules, click «OK» to close
the Edit Claim Rules dialog box.
Back-end Service Configuration
Now we need to configure our back-end service to accept the
authentication coming from the WAP server. In our case we will need to
change the authentication mechanism allowed by Exchange from forms
based to integrated authentication.Your steps here will differ depending
on what service you are offering up.
- Open the Exchange management console and Click on «Server
Configuration»->»Client Access» - For each server in your Exchange farm, click the «Outlook Web App»
tab, then right click «owa (Default Web Site)» and click «properties». - Select the «Authentication» tab and click «Use one or more standard
authentication methods:» then select only «Integrated Windows
authentication». - Click «OK» on the warning.
- Repeat steps 2 and 3 for the «ecp (Default Web Site)» under «Exchange
Control Panel» on each server. - Using an elevated command prompt or PowerShell, execute «iisreset
-noforce» to restart IIS. (This should be done in a maintenance
window)
Configure Delegation
Now we’ll configure the WAP server AD computer object so that it can pass
authentication to your back-end server(s). Note the SPNs referenced to not
need to be manually registered at a domain level.
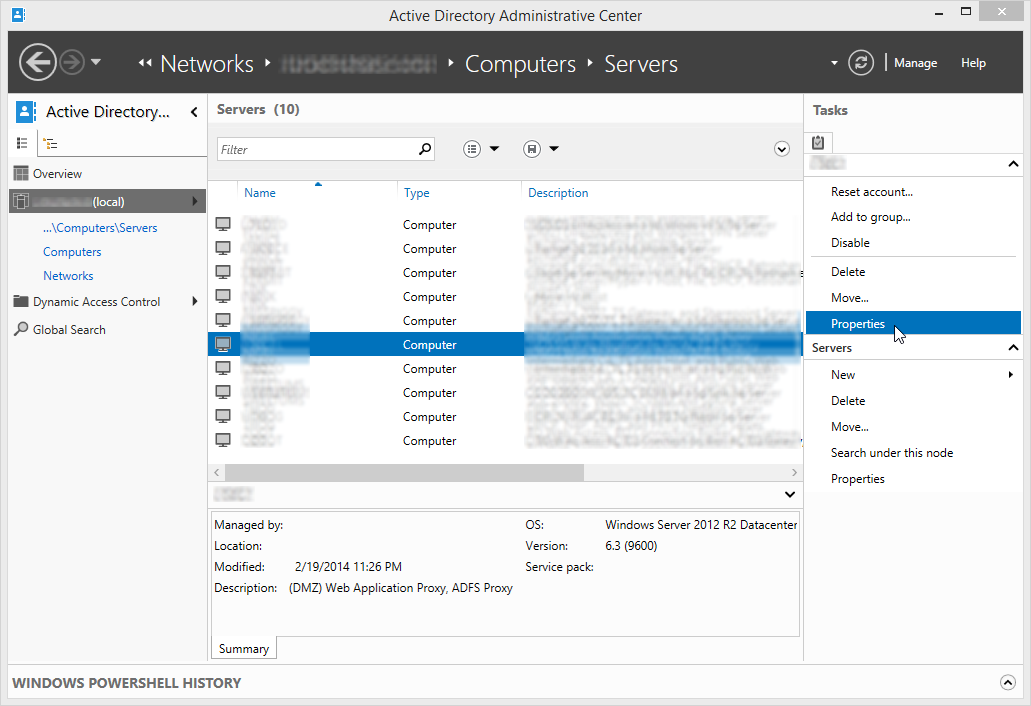
- With domain administrator privileges, open the Active Directory
Administrative Center. (Active Directory Users and Computers if you
prefer) - Navigate to and open the properties of the WAP server computer object.
- Click or scroll down to the «Delegation» section of the object.
- Select «Trust this computer for delegation to specified servers only»
and «Use any authentication protocol» (since we’ll be using NTLM here;
select Kerberos only for applications that support it) then click
«Add…» - When presented with the «Add Services» dialog, click «Add Users or
Computers…». - Type the name of the back-end Exchange server(s) and click «Check
Names» and then «OK» - Scroll to the http/SERVERNAME.domain.ext (since we’re serving up the
HTTP protocol; change if your app differs) and select it, then click
«OK». Note: If using Active Directory Administrative
Center you need to add the FQDN
name and the NETBIOS name; if using Active Directory Users
Computers you need only add the FQDN and both will be added.
Configure Application Publishing on WAP Server
Finally we’ll configure WAP publishing for this application.
- On the WAP server, open the Remote Access Management Console (can be
found in admin tools or tools from Server Manager) - In the left hand navigation plane, select «Configuration»->»Web
Application Proxy» - On the right hand action pane, click «Publish»
- A wizard will come up. Click «Next» on the welcome screen.
- When prompted for preauthentication type, select «Active Directory
Federation Services (AD FS)». This ensures requests are authenticated by
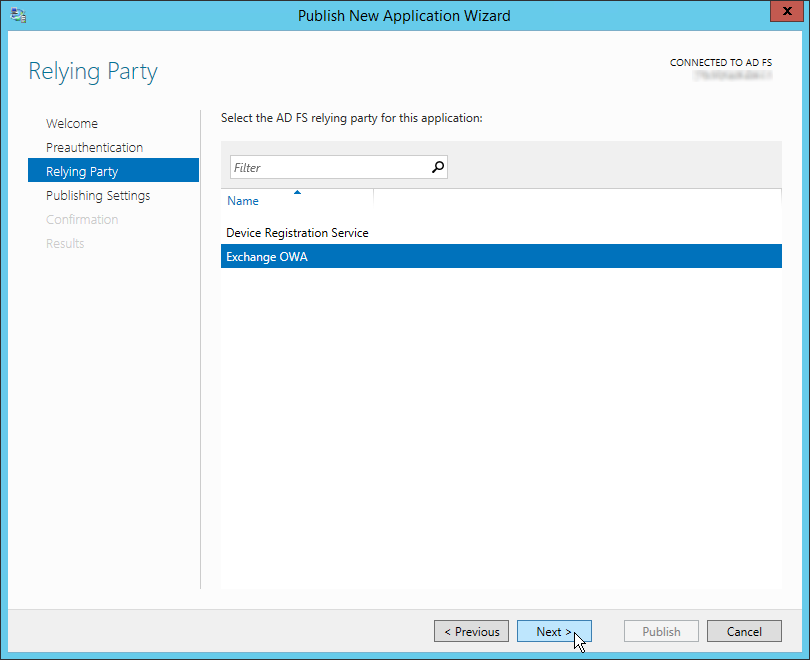
ADFS prior to being passed onto the back-end server. Click «Next». - For «Relying Party», select the trust rule we created earlier under
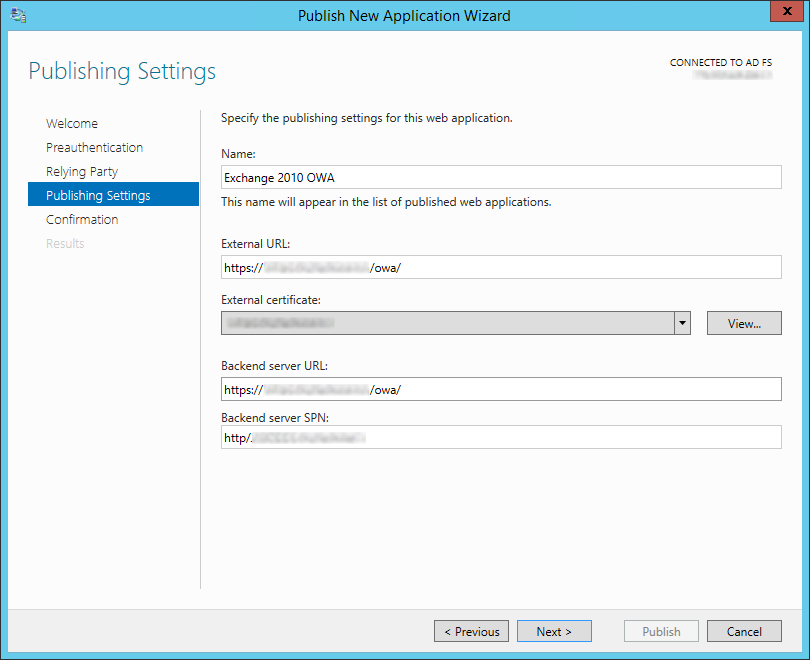
the «Trust Setup» section above and click «Next». - Now the meat of the settings; on the «Publishing Settings» step enter
a meaningful name for this connection (i.e. Exchange 2010 OWA), the
external URL it will be accessed by (i.e.
https://mail.company.com/owa/), select the external certificate for that
service (see «Software Requirements» above), the internal URL
(preferably should match the external but doesn’t have to in all cases),
and the server SPN that we specified on the step above, then click
«Next». - You will be shown the confirmation screen with the appropriate
PowerShell command line for the options you have configured. Should you
want to repeat a similar publishing step, copy and retain this command
line for use later. Click «Publish». - The results screen will display the publishing status. Assuming all is
well, click «Close» to close the wizard.
Example B: RDP Proxy (No Pre-auth/Passthrough)
Passthrough applications are substantially easier (and less secure)
because they do not require any set up in ADFS and do not subject the user
connection attempt to any authentication before passing it on. This isn’t
to say the back-end service won’t require authentication, however, but it
is still less secure since you are opening your back-end service up to
processing logon requests directly from the internet.
Publish RDP Proxy on WAP Server
In this example I will publish RDP proxy direct to the internet proxied
through the WAP server. This allows me to serve up this application on the
same IP address and port as other services assuming the hostname requested
is unique. Again, this section assumes the public and private keys
associated with the URL you intend to use installed in the WAP server’s
«personal» store. In my example I use a hostname of «rdp.company.com»
- On the WAP server, open the Remote Access Management Console (can be
found in admin tools or tools from Server Manager) - In the left hand navigation plane, select «Configuration»->»Web
Application Proxy» - On the right hand action pane, click «Publish»
- A wizard will come up. Click «Next» on the welcome screen.
- When prompted for preauthentication type, select «Pass-through» and
click «Next». - On the «Publishing Settings» step enter a meaningful name for this
connection (i.e. RDProxy), the external URL it will be accessed by (i.e.
https://rdp.company.com/), select the external certificate for that
service (see «Software Requirements» above), and the internal URL
(preferably should match the external but doesn’t have to in all cases).
Click «Next». - You will be given a summary of the publishing rule about to be created
and a Powershell command of it’s equivalent. If you are satisfied with
the details click «Publish».
Troubleshooting
Something not working? Check out the following locations:
Event Logs
Applications and Services Logs->AD FS/Admin
Applications and Services
Logs->Microsoft->Windows->WebApplicationProxy/Admin
Other
Should you need to enable debug logging, there is an excellent article here
demonstrating how to do so. One word of caution, however; should you edit
the C:WindowsADFSConfigmicrosoft.identityServer.proxyservice.exe.config
referenced therein I recommend backing it up first. If not formatted
correctly WAP will start up successfully with the values listed in the file,
but when it comes time to rotate the ADFS Proxy Trust certificate (an
automatic action that happens once every 3 weeks) the configuration of the
new cert will fail. In that case you would see an Event ID 422 logged to AD
FS/Admin stating «Unable to retrieve proxy configuration data from the
Federation Service.».
(Excellent!) References
Want more? Here are some wonderful resources!
Technet:
Web Application Proxy Overview
Technet:
Install and Configure the Web Application Proxy Server
Technet:
Installing and Configuring Web Application Proxy for Publishing Internal
Applications
Technet
Overview Guide: Connect to Applications and Services from Anywhere with
Web Application Proxy
Technet
Social: On WAP and IPv6
Technet Social: ADFS, WAP, and Logging
Technet
Blog: How to support non-SNI capable Clients with Web Application Proxy
and AD FS 2012 R2 (Needed to support Android clients for
Exchange ActiveSync or other clients that don’t support SNI hosted through
WAP)
Technet
Ask PFE: FAQ on ADFS Part 1, Excellent coverage of SQL vs. Internal DB and
certificates for AD FS (Not WAP per se)
Marc
Terblanche: Windows 2012 R2 Preview Web Application Proxy — Exchange 2013
Publishing Tests
Ask
the DS Team: Understanding the ADFS 2.0 Proxy (Not about WAP but
excellent coverage of AD FS proxy functionality)
Rob
Sanders: Troubleshooting ADFS 2.0 (Not about 3.0/WAP but too good not
to be mentioned)
Technet: Configure Event Logging on a Federation Server Proxy (Still
partially relevant)
Technet:
Things to check before troubleshooting ADFS 2.0 (Still partially
relevant)
Technet:
Configuring Computers for Troubleshooting AD FS 2.0 (Still partially
relevant)
Thanks for reading, if you have questions or comments leave them below!
Понадобилось мне как-то раз настроить на IIS 7 прозрачное проксирование запросов из интернета на другой web-сервер, расположенный во внутренней сети. По сути, нужно было настроить IIS 7 как обратный прокси-сервер (reverse proxy). Потом сделал то же самое на IIS 10.
Обратный прокси-сервер (reverse proxy) — тип прокси-сервера, который ретранслирует запросы клиентов из внешней сети на один или несколько серверов, логически расположенных во внутренней сети. При этом для клиента это выглядит так, будто запрашиваемые ресурсы находятся непосредственно на прокси-сервере.
Из коробки эта штука не заработала. Будем настраивать. Нам понадобится модуль для IIS 7 под названием URL Rewrite. У меня он установлен, но этого, как показала практика, недостаточно.
На IIS 10 всё поставилось таким же образом, только проблем было меньше.
Ссылки
ARR — Application Request Routing:
https://www.iis.net/downloads/microsoft/application-request-routing
Настраиваем reverse proxy
Итак, задача. Есть сайт http://setpizza.com, кстати, он продаётся. Сайт делегирован на наш web-сервер IIS 7. Нужно настроить обратное проксирование на другой сервер в локальной сети с IP адресом 192.168.1.11 на 81 порт. Не важно что там крутится, IIS, apache, nginx — мы не знаем. Допустим, мы решили проблемы с доступами и прорубили дырку по 81 порту на этот сервер с нашего IIS.
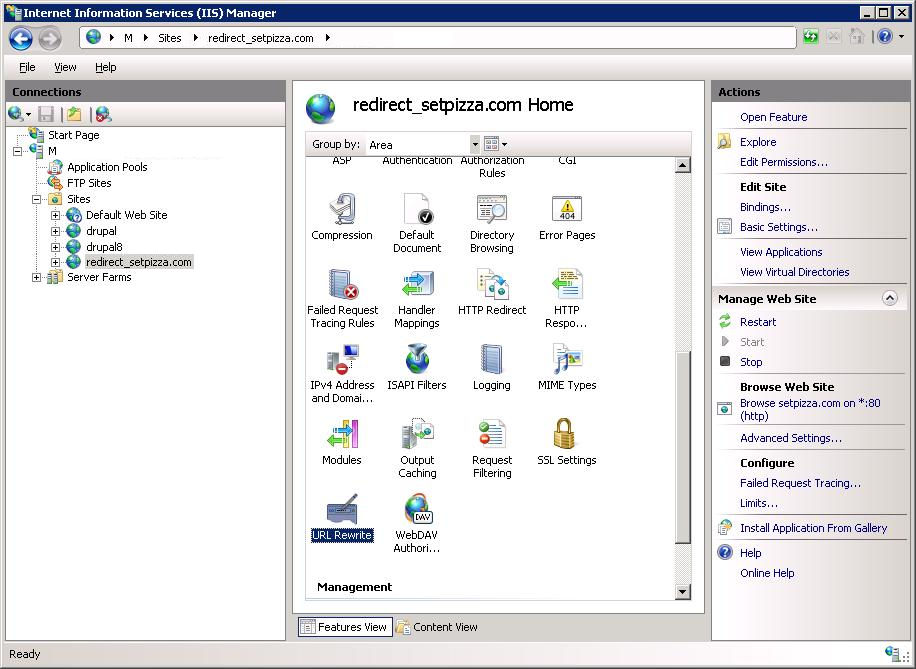
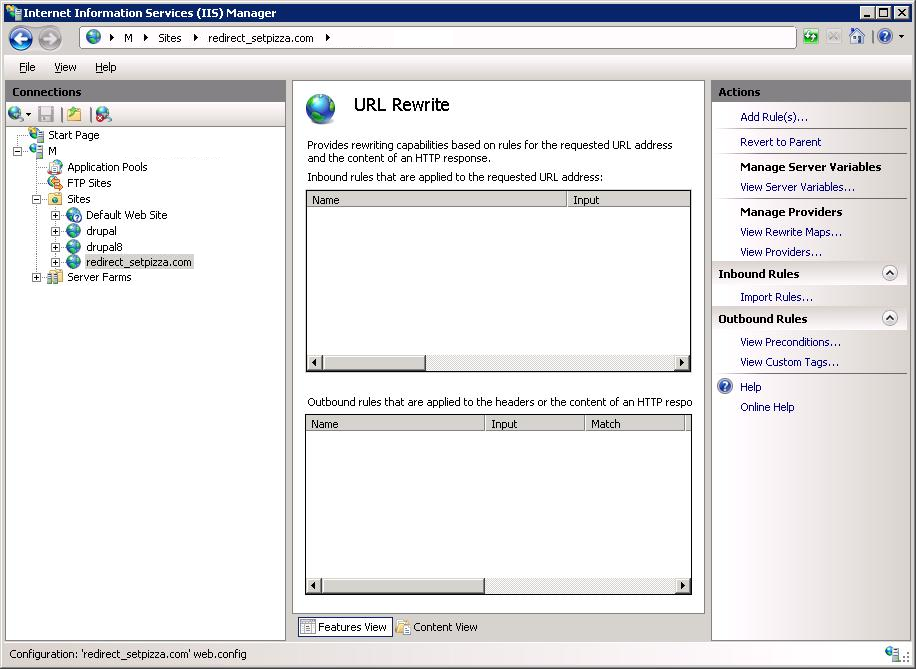
Открываем IIS там, где будем настраивать проксирование, создаём там пустую директорию, C:redirect_setpizza.com. Создаём сайт redirect_setpizza.com, который привязан к этой директории. Выбираем сайт мышкой.
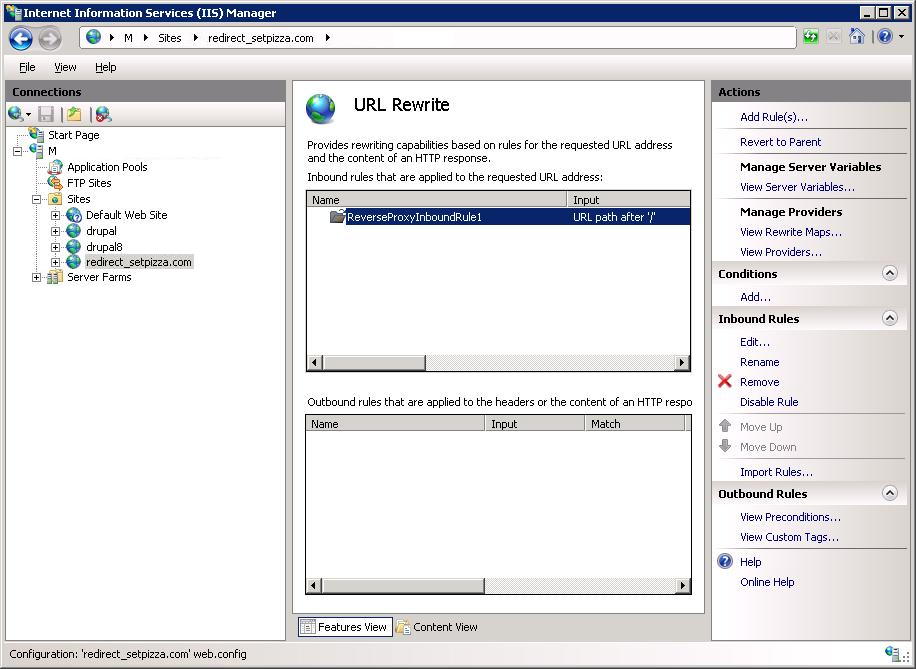
Находим URL Rewrite — тыкаем.
Добавляем правило — Add Rule(s)…
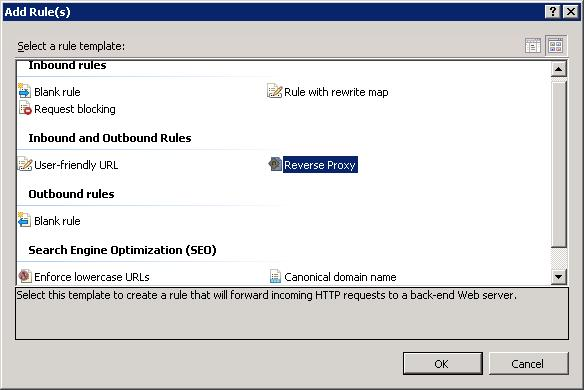
Выбираем правило Reverse Proxy. OK.
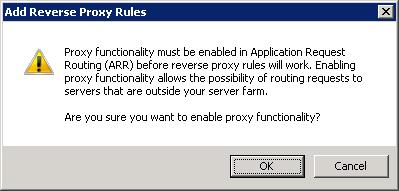
Первая проблема. О как, хочешь пирожок? А нету! Для Reverse Proxy требуется фича для IIS под названием Application Request Routing (ARR). Тыкаем OK. Открывается сайт:
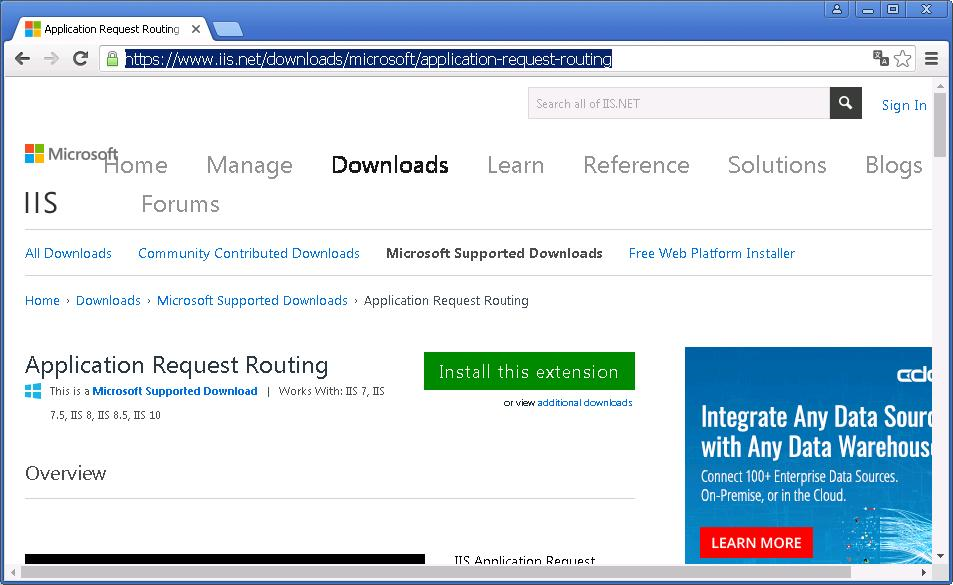
https://www.iis.net/downloads/microsoft/application-request-routing
Install this extension. Качаем ARRv3_0.exe.
Запускаем.
Ждём.
Начинается запуск инсталлятора Microsoft Web Platform Installer 5.1.
Ждём.
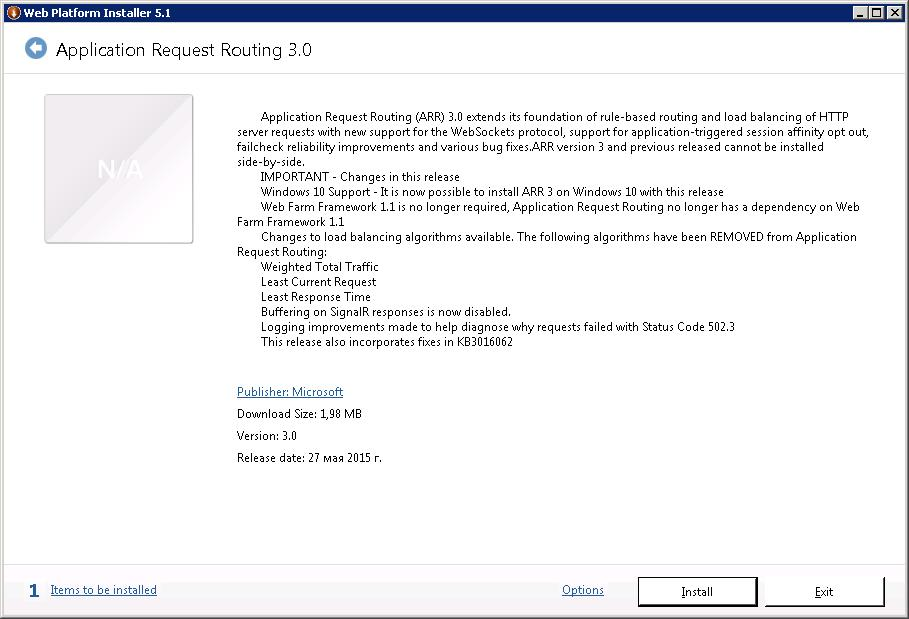
Читаем описание того, что мы ставим. На самом деле ARR позволяет не только делать обратное проксирование на один сервер. С помощью ARR можно настраивать фермы веб-серверов и выступать в качестве балансировщика, но в моей задаче всё проще. Install.
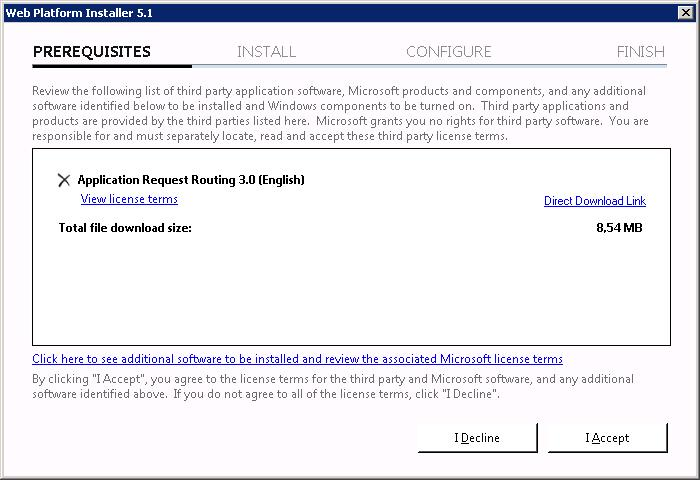
Нам говорят, что надо скачать файлы на 8,54 мегабайт. I Accept.
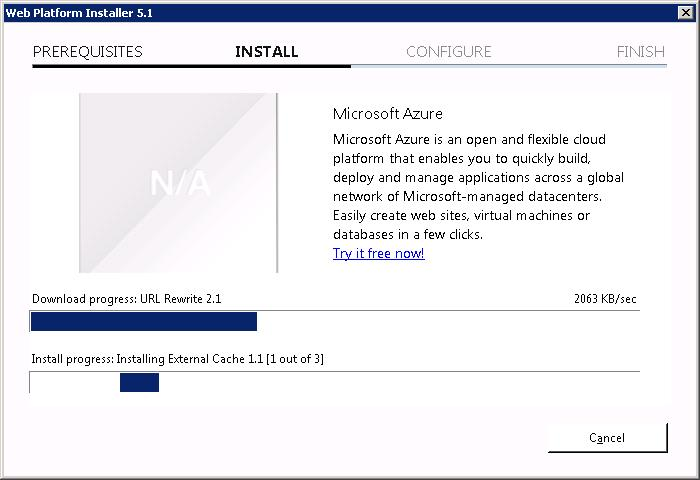
ARR состоит из нескольких модулей, в него входит External Cache 1.1, URL Rewrite 2.1, сам ARR 3.0.
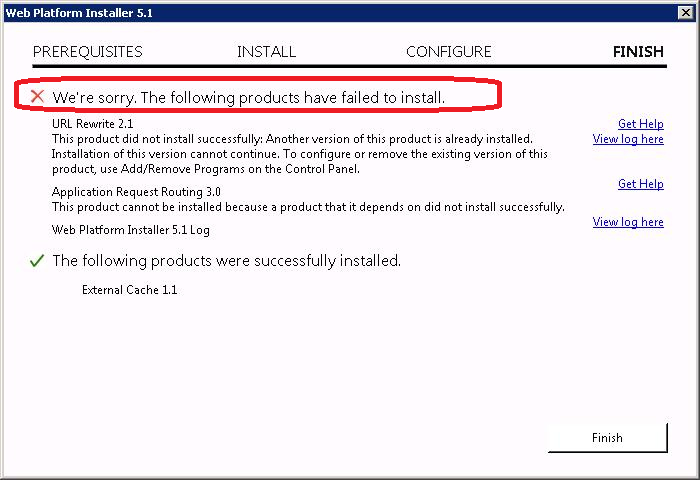
Вторая проблема. URL Rewrite 2.1 не установился — установка прервалась. Говорят. что URL Rewrite уже установлен более старой версии. Требуется сначала его удалить вручную.
Тысяча чертей! Находим установленный старый URL Rewrite Module 2 и удаляем его. Он с 2011 года тут болтается.
Запускаем инсталлятор ARR заново.
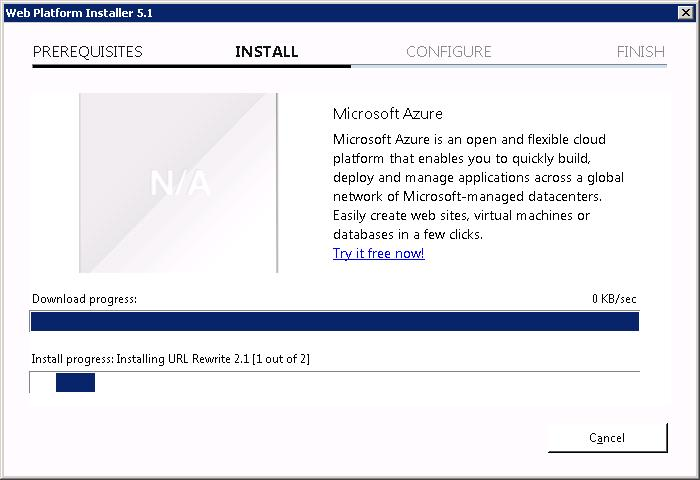
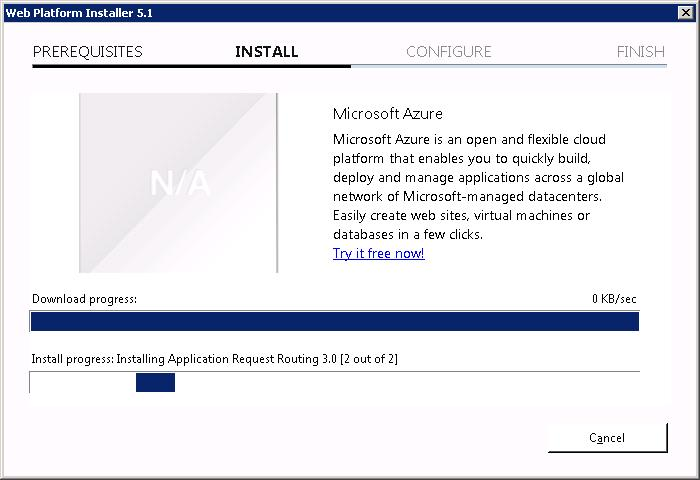
Теперь URL Rewrite 2.1 устанавливается.
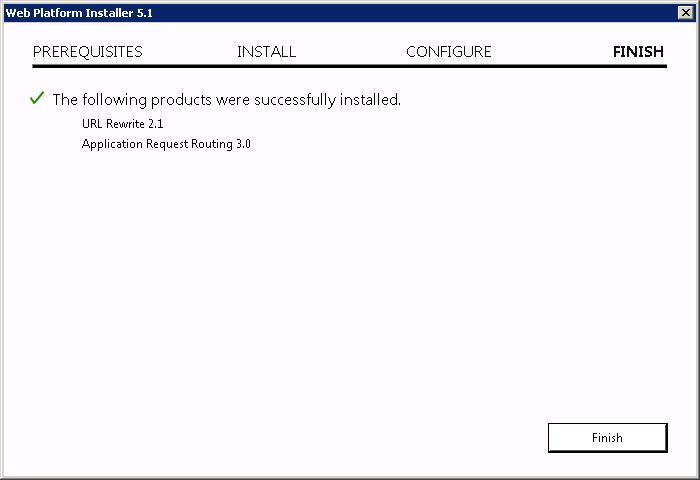
За ним ставится Application Request Routing 3.0.
ARR установлен. Возвращаемся к нашему IIS. Добавляем правило — Add Rule(s)… Выбираем правило Reverse Proxy. OK.
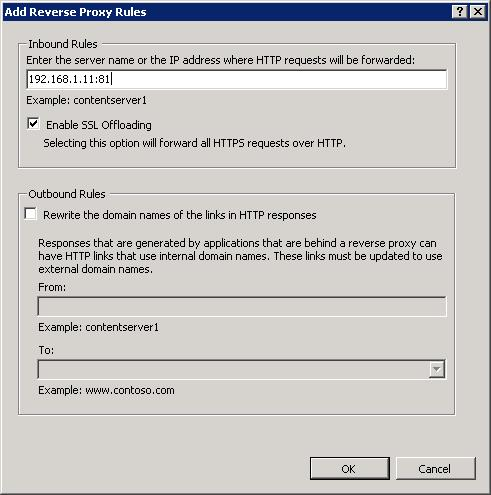
На этот раз правило создаётся. Пишем. «192.168.1.11:81». Ставим галку Enable SSL Offloading — терминируем SSL на этом прокси-сервере. OK.
Всё, собственно. В пустой папке сайта создался файлик web.config. В нём:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<configuration>
<system.webServer>
<rewrite>
<rules>
<rule name="ReverseProxyInboundRule1" stopProcessing="true">
<match url="(.*)" />
<action type="Rewrite" url="http://192.168.1.11:81/{R:1}" />
</rule>
</rules>
</rewrite>
</system.webServer>
</configuration>«http://» и {R:1} дописываются автоматически. Проверяем работу сайта — всё отлично.
Web Application Proxy в Server 2012 R2, функционал и использование на примере публикации приложений Exchange 2013 (часть 1)
Операционная система Windows Server 2012 R2 предоставила в руки системных администраторов интересные изменения и дополнения к существовавшим ранее возможностям. Этим сообщением в своем блоге я открываю цикл из 5 статьей, которые ознакомят читателей с некоторыми из нововведений. Сегодняшняя речь пойдет о Web Application Proxy.
Web Application Proxy (далее просто WAP) используется как средство публикации внутрикорпоративных приложений, таких как Exchange, Lync и др. для внешних клиентов. Технология основывается на «реверс-проксировании» краткие сведения о котором будут изложены далее.
Для иллюстрации описываемого будет использован демо-стенд, на котором произойдет публикация Exchange 2013 с последующей настройкой его служб для аутентификации средствами, собственно, самого WAP. Данный инструмент позволяет гибко настраивать критерии доступа к конкретному приложению, например, по наличию нужных групп.
В результате тестирования на лабораторном стенде была успешно проделана публикация приложений OWA, ECP, PowerShell, OAB, RPC, EWS, Autodiscover, ActiveSync Отображение всего процесса будет показано в последующих статьях.
Содержание
- Немного теории
- Обзор Web Application Proxy
- Требования к развертыванию Web Application Proxy
- Описание лабораторного стенда
Немного теории
Web Application Proxy (WAP) – это reverse proxy server (сервер обратного проксирования). Если кратко, суть сводится к следующему:
Приложение публикуется на этом специально выделенном сервере-посреднике и внешний клиент сначала устанавливает соединение с посредником, а тот, в свою очередь, инициализирует подключение к публикуемому приложению от своего имени.
Такой подход позволяет решить проблемы:
- Предварительная аутентификация клиентов для подключения к приложению;
- Фильтрация подключений и проверка трафика;
- Публикации нескольких приложений под одним доменным именем;
- Гибких сценариев балансировки нагрузки и отказоустойчивости.
Обзор Web Application Proxy
На прикладном уровне, Web Application Proxy (WAP) является дополнительной службой роли Remote Access в Server 2012 R2. Для реализации WAP за основу была взята служба роли ADFS Federation Service Proxy в Windows Server 2012, решавшая задачу Front-end сервера при развертывании служб федерации Active Directory.
WAP расширил возможности публикации. Теперь помимо публикации самих служб ADFSстало возможным публиковать другие HTTPS приложения такие как Exchange, Lync и др.
В Windows Server 2012 R2 существует два типа предварительной аутентификации клиентов посредством WAP:
- Active Directory Federation Services (ADFS) – В этом случае используются либо ADFS Claim, либо встроенная проверка подлинности Windows по протоколу Kerberos.
- Pass-through, сквозная аутентификация. В данном варианте WAP не будет самостоятельно производить аутентификация клиентов, а пропускать через себя запросы далее, в том виде в каком они есть.
В практических демонстрация будут использоваться оба типа, так как пока не все публикуемые приложения Exchange поддерживают ADFS аутентификацию.
Требования к развертыванию Web Application Proxy
- Для развертывания WAP необходимо иметь минимум 2 сервера с ОС Windows Server 2012 R2, включенные в домен Active Directory. На первом сервере должна быть установлена роль ADFS, на втором – служба роли Remote Access, Web Application Proxy.
- Схема леса Active Directory должна быть расширена до уровня Sevrer 2012 R2. В тоже время, можно использовать домен-контроллеры, работающие под управлением предыдущей версий операционной системы Windows Server 2012.
Описание лабораторного стенда
Исследование WAP будет выполнено на лабораторном стенде, работающем под управлением Windows Server 2012 R2 Datacenter с установленной ролью Hyper-V. На сервере создано 3 виртуальных коммутатора: WAN, LAN и DMZ.
Ниже представлена упрощенная топология стенда – WAP Network
В качестве маршрутизатора использовался Endian Firewall community, основанный на Linux. Маршрутизатор реализует «трехногую» конфигурацию, образовывая 2 частных сети DMZ и LAN.
Адресное пространство DMZ — 192.168.1.0/24, а для LAN — 172.16.20.0/24.