Содержание
- Перечень основных команд
- Запуск системных утилит
- Работа с файлами и папками
- Работа с текстовыми файлами
- Работа с учетными записями
- Работа с процессами
- Работа в сети
- Другие команды
- Вопросы и ответы
В Windows 7 существуют такие операции, которые невозможно или затруднительно выполнить через обычный графический интерфейс, но их реально осуществить через интерфейс «Командной строки» при помощи интерпретатора CMD.EXE. Рассмотрим основные команды, которые могут применять пользователи при использовании указанного инструмента.
Читайте также:
Основные команды Linux в «Терминале»
Запуск «Командной строки» в Windows 7
Перечень основных команд
С помощью команд в «Командной строке» запускаются различные утилиты и выполняются определенные операции. Зачастую основное командное выражение используется вместе с рядом атрибутов, которые записываются через косую черту (/). Именно эти атрибуты инициируют выполнение конкретных операций.
Мы не ставим перед собой цель описать абсолютно все команды, применяемые при использовании инструмента CMD.EXE. Для этого пришлось бы написать не одну статью. Мы же постараемся уместить на одной странице информацию о наиболее полезных и популярных командных выражениях, разбив их на группы.
Запуск системных утилит
Прежде всего, рассмотрим выражения, которые отвечают за запуск важных системных утилит.
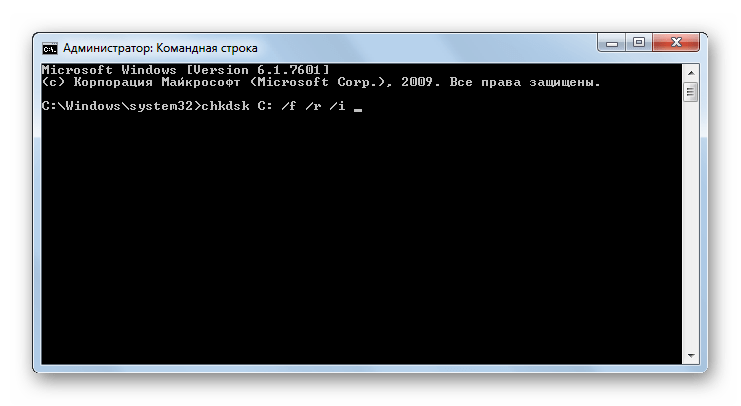
CHKDSK – запускает утилиту Check Disk, которая выполняет проверку жестких дисков компьютера на ошибки. Данное командное выражение можно вводить с дополнительными атрибутами, которые, в свою очередь, запускают выполнение определенных операций:
- /f – восстановление диска в случае обнаружения логических ошибок;
- /r – восстановление секторов накопителя в случае обнаружения физических повреждений;
- /x – отключение указанного жесткого диска;
- /scan – сканирование на упреждение;
- C:, D:, E: … — указание логических дисков для сканирования;
- /? – вызов справки о работе утилиты Check Disk.
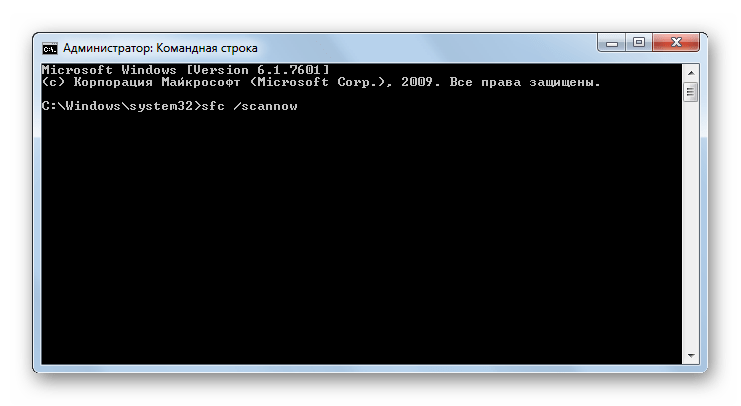
SFC – запуск утилиты проверки целостности системных файлов Windows. Данное командное выражение чаще всего используется с атрибутом /scannow. Оно запускает инструмент, который проверяет файлы ОС на соответствие стандартам. В случае повреждений, при наличии установочного диска существует возможность восстановления целостности системных объектов.
Работа с файлами и папками
Следующая группа выражений предназначена для работы с файлами и папками.
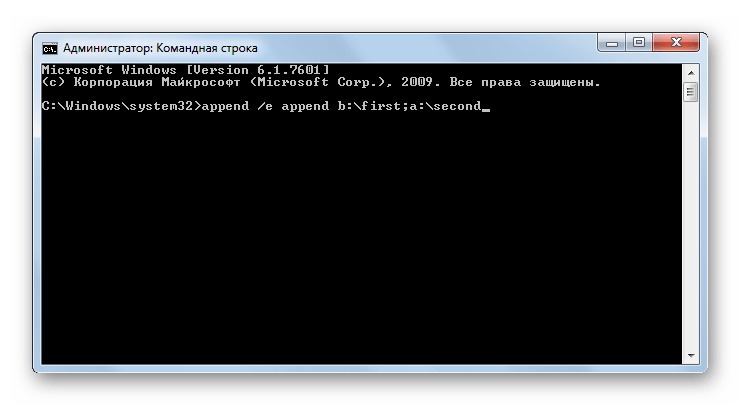
APPEND – открытие файлов в указанной пользователем папке в том виде, как если бы они находились в требуемом каталоге. Обязательным условием является указание пути к папке, к которой будет применено действие. Запись производится по следующему шаблону:
append [;] [[диск компьютера:]путь[;...]]
При использовании данной команды можно применять следующие атрибуты:
- /e – запись полного списка файлов;
- /? – запуск справки.
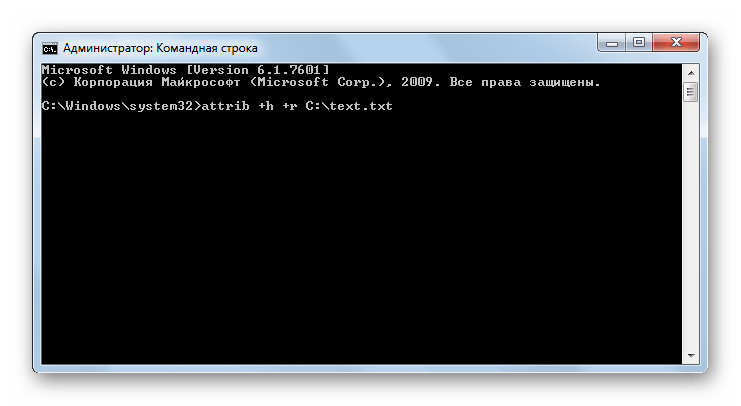
ATTRIB – команда предназначена для изменения атрибутов файлов или папок. Так же, как и в предыдущем случае, обязательным условием является ввод вместе с командным выражением полного пути к обрабатываемому объекту. Для установки атрибутов используются следующие ключи:
- h – скрытый;
- s – системный;
- r – только для чтения;
- a – архивный.
Для того чтобы применить или отключить атрибут, перед ключом соответственно ставится знак «+» или «-».
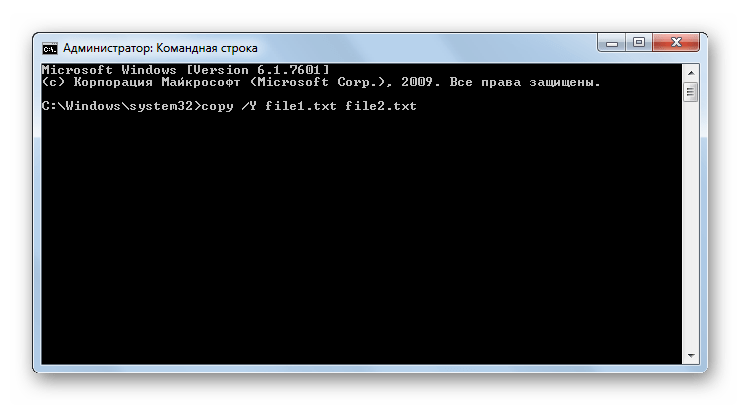
COPY – применяется для копирования файлов и каталогов из одной директории в другую. При использовании команды обязательно указание полного пути объекта копирования и папки, в которую оно будет производиться. С данным командным выражением можно использовать следующие атрибуты:
- /v – проверка корректности копирования;
- /z – копирование объектов из сети;
- /y – перезапись конечного объекта при совпадении имен без подтверждения;
- /? – активация справки.
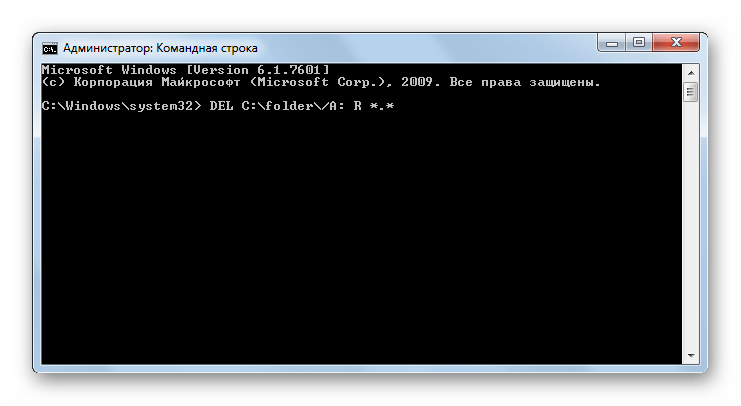
DEL – удаление файлов из указанной директории. Командное выражение предусматривает возможность использования ряда атрибутов:
- /p – включение запроса подтверждения удаления перед манипуляцией с каждым объектом;
- /q – отключение запроса при удалении;
- /s – удаление объектов в каталогах и подкаталогах;
- /a: — удаление объектов с указанными атрибутами, которые назначаются при помощи тех же ключей, что и при использовании команды ATTRIB.
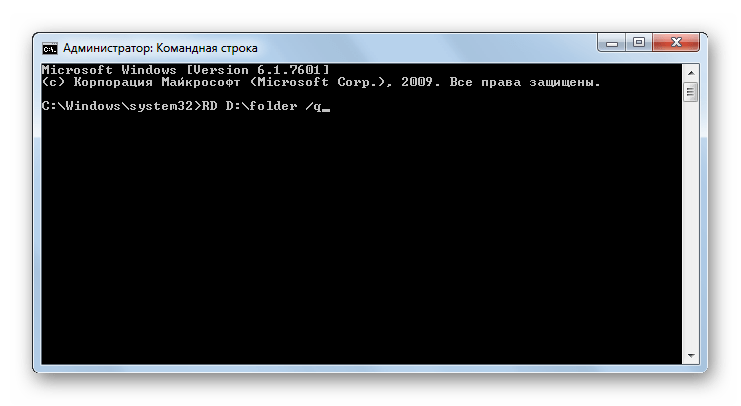
RD – является аналогом предыдущего командного выражения, но удаляет не файлы, а папки в указанной директории. При использовании можно применять те же самые атрибуты.
DIR – выводит список всех подкаталогов и файлов, которые расположены в указанной директории. Вместе с основным выражением применяются такие атрибуты:
- /q – получение информации о владельце файла;
- /s – отображение перечня файлов из указанного каталога;
- /w – вывод списка в несколько колонок;
- /o – сортировка перечня выводимых объектов (e – по расширению; n – по имени; d – по дате; s – по размеру);
- /d – отображение списка в несколько колонок с сортировкой по этим колонкам;
- /b – отображение исключительно имен файлов;
- /a – отображение объектов с определенными атрибутами, для указания которых используются те же ключи, что и при использовании команды ATTRIB.
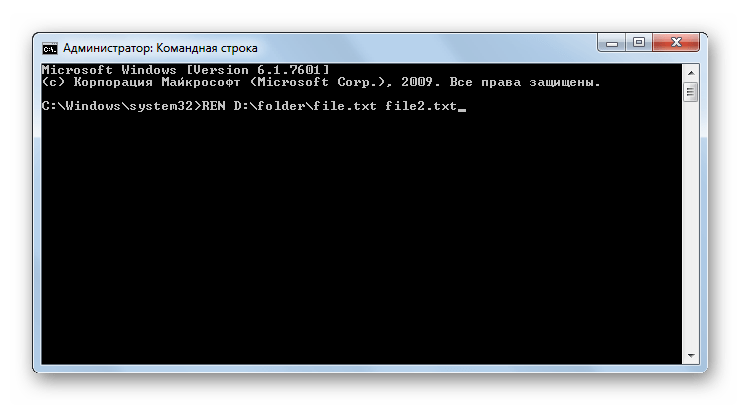
REN – используется для переименования каталогов и файлов. В качестве аргументов к данной команде указывается путь к объекту и его новое название. Например, для переименования файла file.txt, который расположен в папке «Folder», находящейся в корневой директории диска D, в файл file2.txt, нужно ввести следующее выражение:
REN D:folderfile.txt file2.txt
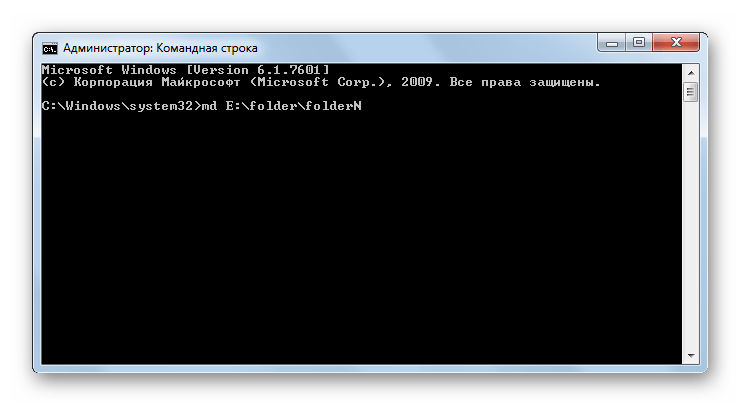
MD – предназначена для создания новой папки. В синтаксисе команды обязательно следует указать диск, на котором будет располагаться новый каталог, и директорию его размещения в том случае, если он является вложенным. Например, для создания каталога folderN, который расположен в директории folder на диске E, следует ввести такое выражение:
md E:folderfolderN
Работа с текстовыми файлами
Следующий блок команд предназначен для работы с текстом.
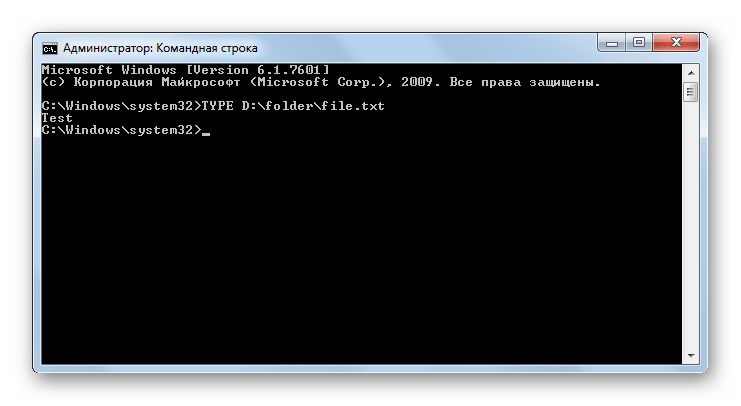
TYPE – отображает на экране содержимое текстовых файлов. Обязательными аргументом данной команды является полный путь к объекту, текст в котором следует просмотреть. Например, для просмотра содержимого файла file.txt, находящегося в папке «Folder» на диске D, требуется ввести следующее командное выражение:
TYPE D:folderfile.txt
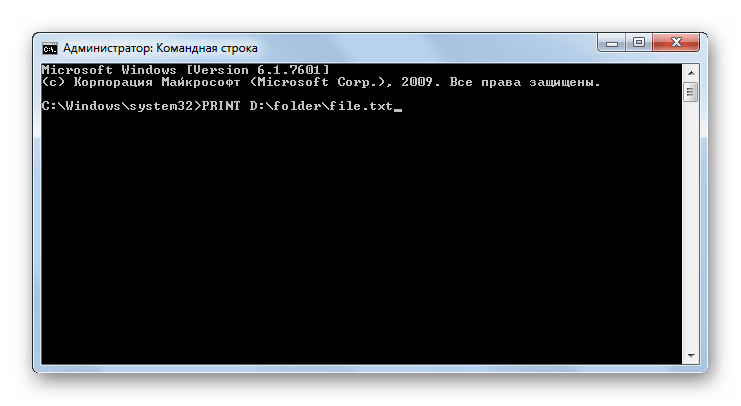
PRINT – распечатка содержимого текстового файла. Синтаксис данной команды аналогичен предыдущему, но вместо вывода текста на экран производится его распечатка.
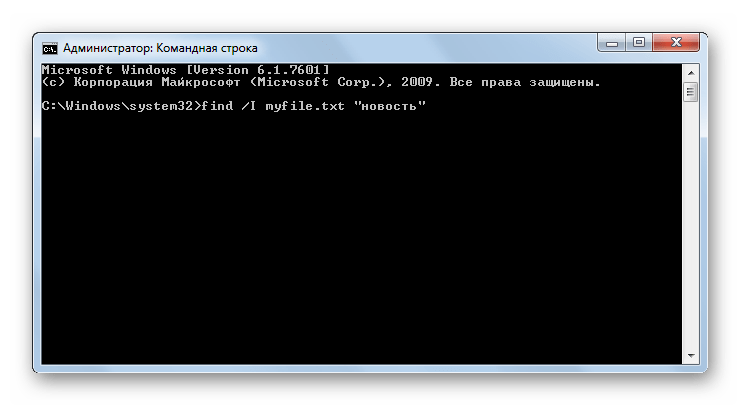
FIND – производит поиск текстовой строки в файлах. Вместе с этой командой обязательно указывается путь к объекту, в котором выполняется поиск, а также название искомой строки, заключенное в кавычки. Кроме того, вместе с данным выражением применяются следующие атрибуты:
- /c – выводится общее количество строк, содержащих искомое выражение;
- /v – вывод строк, которые не содержат искомое выражение;
- /I – поиск без учета регистра.
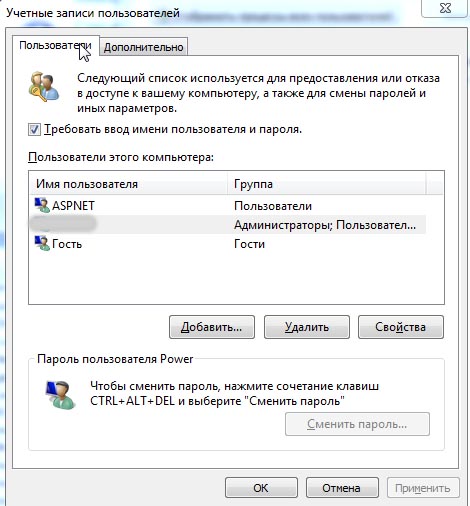
Работа с учетными записями
С помощью командной строки можно просматривать информацию о пользователях системы и управлять ими.
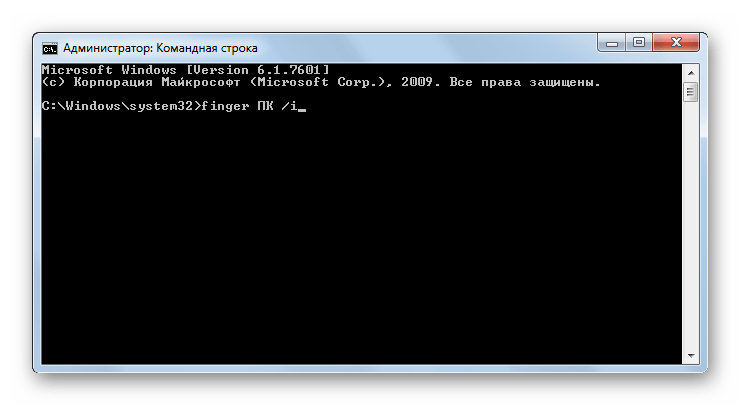
FINGER – отображение информации о зарегистрированных в операционной системе пользователях. Обязательным аргументом данной команды является имя юзера, о котором требуется получить данные. Кроме того, можно использовать атрибут /i. В этом случае вывод информации будет производиться в списочном варианте.
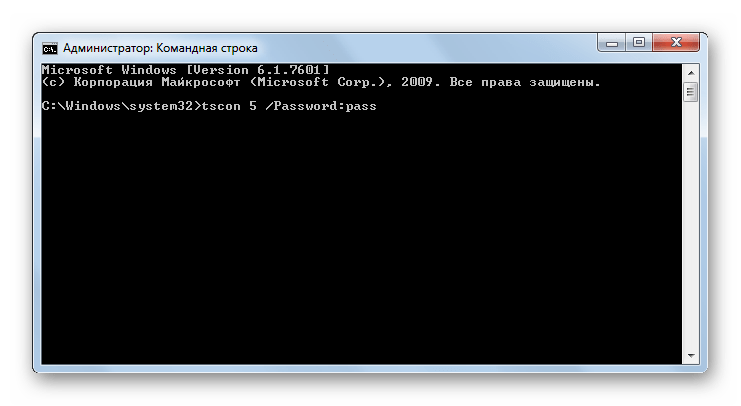
TSCON – выполняет присоединение сеанса пользователя к сеансу терминала. При использовании данной команды обязательно требуется указать ID сеанса или его имя, а также пароль того юзера, которому он принадлежит. Пароль следует указывать после атрибута /PASSWORD.
Работа с процессами
Следующий блок команд предназначен для управления процессами на компьютере.
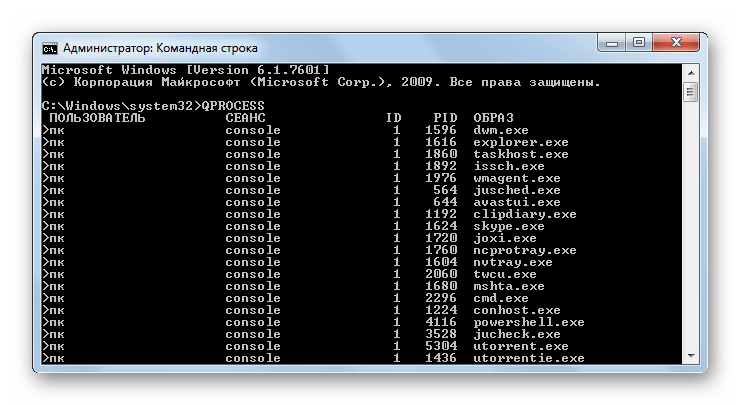
QPROCESS – предоставление данных о запущенных процессах на ПК. Среди выводимой информации будет представлено наименование процесса, имя пользователя, его запустившего, название сеанса, ID и PID.
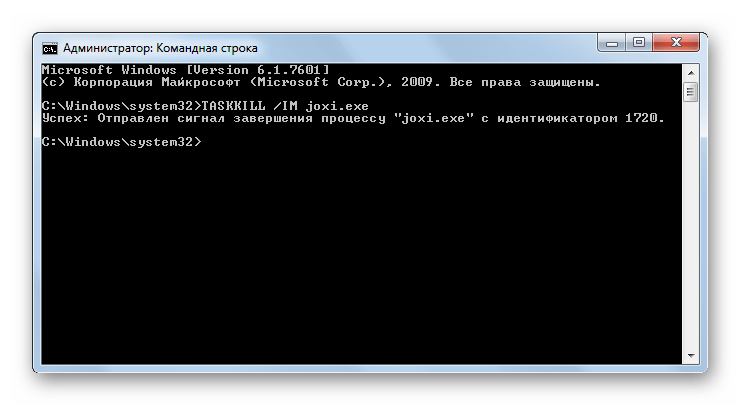
TASKKILL – используется для завершения процессов. Обязательным аргументом является наименование элемента, который нужно остановить. Он указывается после атрибута /IM. Также можно произвести завершение не по имени, а по идентификатору процесса. В этом случае используется атрибут /PID.
Работа в сети
С помощью командной строки существует возможность управлять различными действиями в сети.
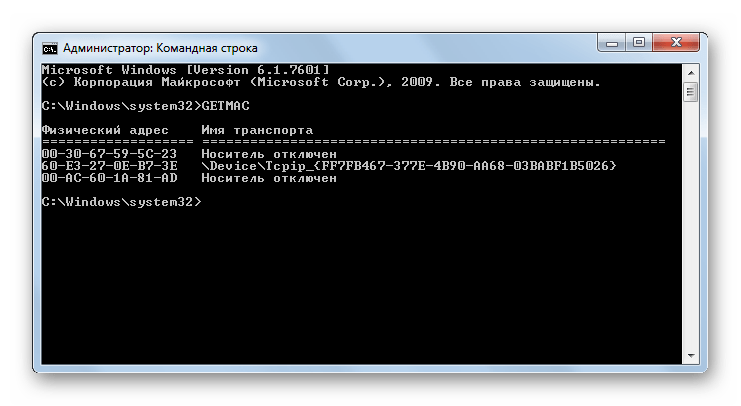
GETMAC – запускает отображение MAC-адреса подключенной к компьютеру сетевой карты. В случае наличия нескольких адаптеров отображаются все их адреса.
NETSH – инициирует запуск одноименной утилиты, с помощью которой производится демонстрация информации о параметрах сети и их изменение. Данная команда, ввиду своей очень широкой функциональности, имеет огромное количество атрибутов, каждый из которых отвечает за выполнение определенной задачи. Для получения подробной информации о них можно воспользоваться справкой, применив следующее командное выражение:
netsh /?
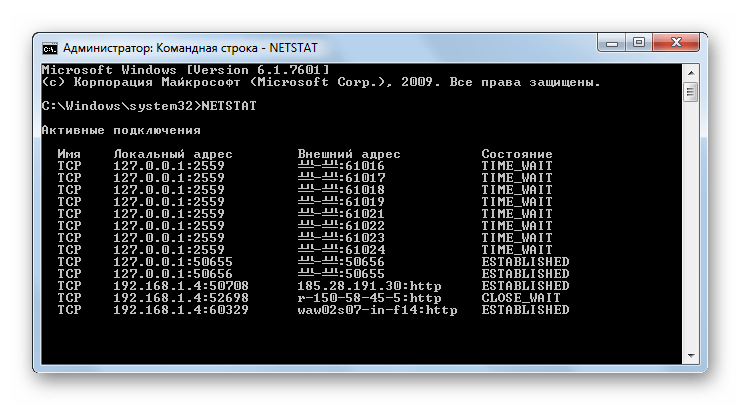
NETSTAT – отображение статистической информации о сетевых подключениях.
Другие команды
Также существует ряд других командных выражений, применяемых при использовании CMD.EXE, которые нельзя выделить в отдельные группы.
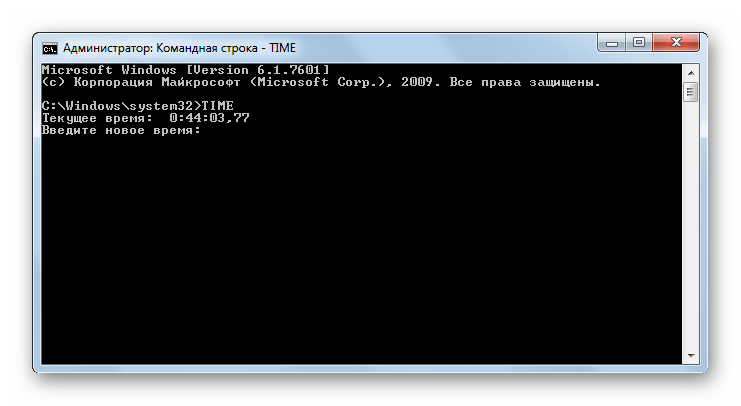
TIME – просмотр и установка системного времени ПК. При вводе данного командного выражения происходит вывод на экран текущего времени, которое в самой нижней строке можно изменить на любое другое.
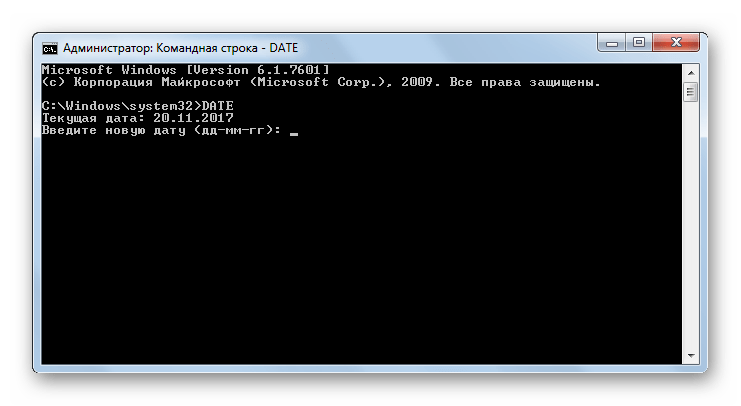
DATE – команда по синтаксису полностью аналогична предыдущей, но применяется не для вывода и изменения времени, а для запуска данных процедур в отношении даты.
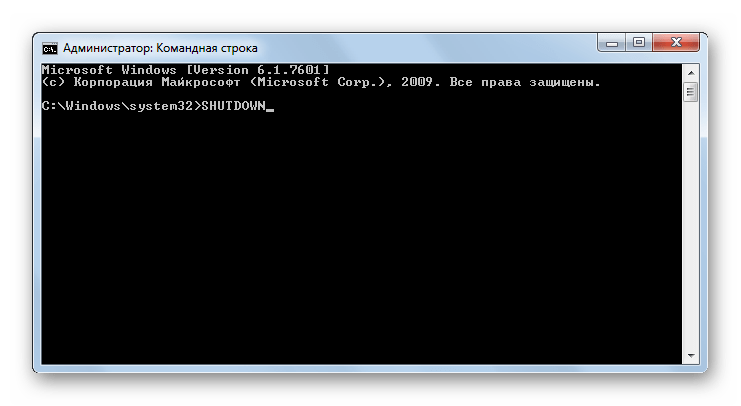
SHUTDOWN – выключает компьютер. Данное выражение можно использовать, как локально, так и удаленно.
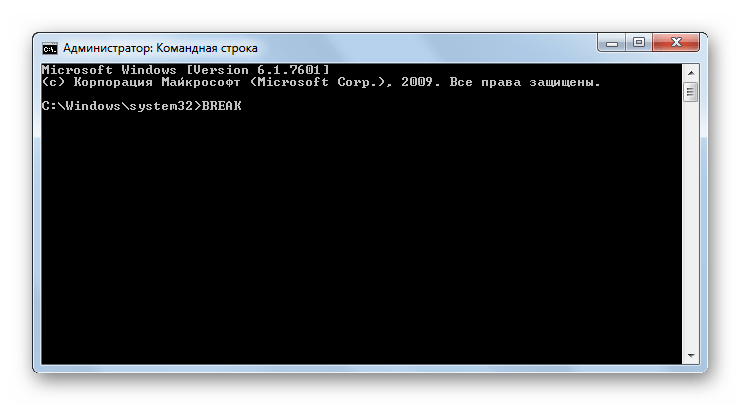
BREAK – отключение или запуск режима обработки сочетания кнопок Ctrl+C.
ECHO – выводит текстовые сообщения и применяется для переключения режимов их отображения.
Это далеко не полный список всех команд, которые применяются при использовании интерфейса CMD.EXE. Тем не менее мы попытались раскрыть наименования, а также вкратце описать синтаксис и основные функции самых востребованных из них, для удобства разбив на группы по назначению.
Командная строка (command line, консоль, терминал) в операционной системе Windows предназначена для работы с системой в текстовом режиме. Программная оболочка служит для связи пользователя с операционной системой посредством ввода текстовых команд с клавиатуры компьютера.
Работа с командной строкой проходит следующим образом: пользователь запускает на компьютере приложение cmd.exe, открывается окно интерфейса командной строки (интерпретатор командной строки), затем пользователь вводит с клавиатуры команду или наборы команд, система их выполняет, иногда выдает запросы или сообщения, отображаемые в окне интерфейса командной строки.
Содержание:
- Как запустить командную строку
- Как выполнить команду в командной строке
- Команды для командной строки Виндовс
- Командная строка Windows: список основных команд
- Выводы статьи
Для выполнения различных задач на компьютере: запуск программ, настройка системы, изменения параметров Windows и т. д., необходимо вводить определенные команды для командной строки.
На заре создания операционных систем, ОС не имели графического интерфейса, все действия выполнялись с помощью команд, набранных на клавиатуре. После появления графического интерфейса командная строка не исчезла из системы.
Большинство пользователей, рано или поздно, сталкиваются с командной строкой, другая часть пользователей, даже не подозревает о ее существовании.
Преимуществом командной строки является то, что командная строка не зависит от графического интерфейса операционной системы. Пользователь вводит команды в окне командной строки, а система их немедленно выполняет. В некоторых случаях этот процесс проходит быстрее, чем подобные действия с использованием графического интерфейса Windows.
Командная строка часто используется при возникновении неполадок на компьютере, когда невозможно выполнить работы по исправлению сбоев системы другим способом.
Начинающим пользователям трудно работать с командной строкой из-за того, что они не знают команд. Поэтому с командную строку чаще используют опытные пользователи и администраторы.
В этой статье вы найдете список команд командной строки. В таблице собраны основные команды командной строки, работающие в операционных системах Windows 10, Windows 8,1, Windows 8, Windows 7.
Как запустить командную строку
В Windows 10 сразу найти командную строку неочевидно, поэтому прочитайте эту статью о разных способах запуска консоли в этой ОС.
В операционной системе Windows имеется несколько способов для запуска командной строки, вот самые простые:
- Из меню «Пуск» войдите в «Программы» («Все программы»), а затем в «Служебные» (в Windows 7 — «Стандартные»), выберите приложение «Командная строка».
- В поле поиска введите «cmd» (без кавычек), среди открывшихся результатов окажется командная строка.
- После нажатия на клавиатуре «Win» + «R», в окне «Выполнить» введите команду запуска командной строки «cmd» (без кавычек).
В обычном режиме командная строка запускается от имени пользователя. Для выполнения некоторых действий в командной строке, требуются повышенные права Администратора компьютера. В этом случае, командную строку необходимо запустить от имени администратора. Прочитайте статью о том, как запустить командную строку от имени администратора в разных версиях операционной системы Windows.
Как выполнить команду в командной строке
Работа в командной строке выполняется очень просто: пользователь вводит текстовую команду, а затем нажимает на клавишу «Enter» (ввод). Если необходимо ввести несколько последовательных команд, повторите данную операцию несколько раз.
После запуска командной строки, в окне интерпретатора командной строки отображается версия операционной системы Windows, и место где сейчас находится пользователь. При запуске в обычном режиме, это адрес профиля пользователя на системном диске.
При запуске командной строки от имени администратора, путь выглядит следующим образом: «C:Windowssystem32».
Команды командной строки Windows необходимо вводить в окне интерпретатора сразу после знака «>», в этом месте мигает курсор.
Для копирования команды с компьютера, а затем вставки команды в командную строку, используется контекстное меню правой кнопки мыши. Скопируйте команду в буфер обмена, вставьте курсор мыши в окно командной строки, нажмите на правую кнопку мыши. В Windows 10 поддерживается копирование и вставка при помощи стандартных клавиш клавиатуры: «Ctrl» + «C» и «Ctrl» + «V».
Некоторые системные приложения запускаются непосредственно после ввода команды, которая состоит из названия приложения, например, если вести команду «calc», то на компьютере запуститься системная программа Калькулятор.
Для других программ потребуется ввести полный путь до исполняемого файла приложения. Если в пути до файла есть пробелы, полный путь заключается в кавычки, например, так выглядит команда для запуска браузера Google Chrome:
"C:Program Files (x86)GoogleChromeApplicationchrome.exe"
После запуска команды из командной строки, реализация выполнения команды не всегда внешне заметна, из-за того, что происходят внутренние изменения в операционной системе.
К основной команде часто добавляются другие параметры, ключи для выполнения конкретных действий.
При вводе неправильной команды, например, введенной с ошибками, или если операционная система Windows не может по какой-либо причине выполнить команду, об этом появится сообщение в окне интерфейса командной строки.
Команды для командной строки Виндовс
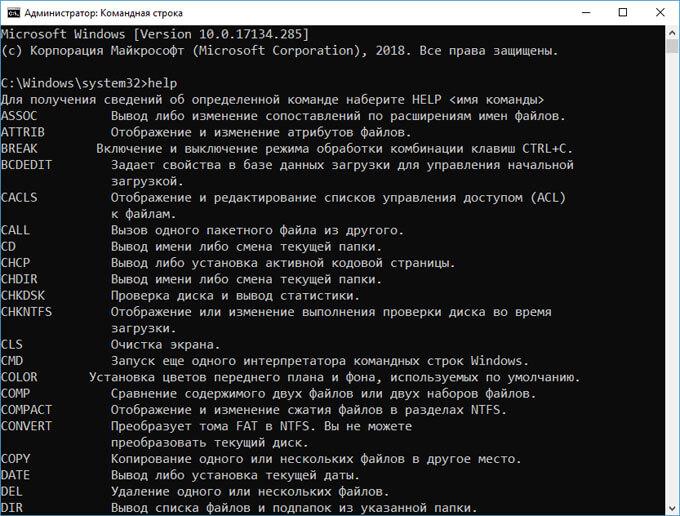
Пользователь может самостоятельно узнать основные команды из самой утилиты Командная строка. Для этого достаточно ввести команду: «help».
В интерфейсе командной строки отобразится список основных команд.
Для получения сведений о параметрах отдельной команды нужно ввести одну из следующих команд, которые выполняются одинаково (не забывайте поставить пробел):
имя_команды /? help имя_команды
В результате вы получите сведения обо всех параметрах данной команды.
Командная строка Windows: список основных команд
Ознакомьтесь с таблицей, в которой собраны команды, используемые в командной строке Windows. Если я пропустил какую-нибудь важную команду, напишите об этом в комментарии к этой статье, я добавляю команду в таблицу.
| Команда | Выполняемое действие |
|---|---|
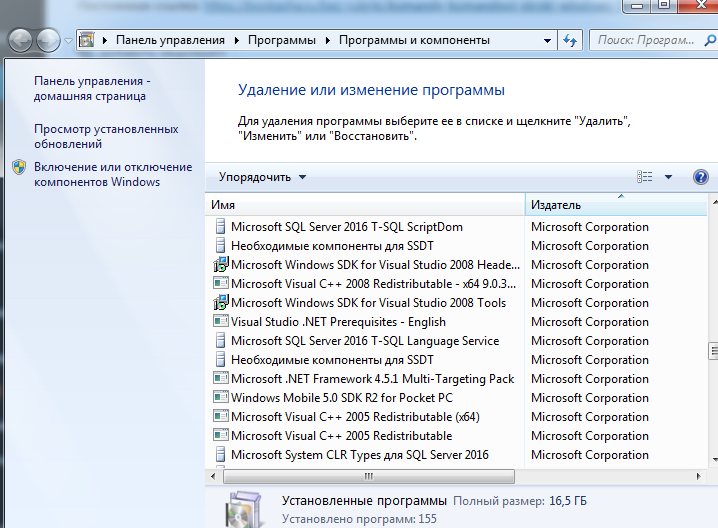
| appwiz.cpl | запуск системного средства для изменения или удаления программ |
| arp | отображение и изменение ARP таблиц преобразования IP-адресов в физические, используемые протоколом разрешения адресов |
| assoc | вывод или изменение сопоставлений по расширениям имен файлов |
| at | запуск программ в указанное время |
| attrib | отображение и изменение атрибутов файлов |
| azman.msc | диспетчер авторизации |
| bcdboot | средство создания и восстановления файлов данных конфигурации загрузки |
| bcdedit | редактирование изменений в базе загрузки начальной загрузки системы |
| break | изменение режима обработки комбинации клавиш «Ctrl» + «C» |
| blastcln | утилита очистки от червей |
| bootcfg | настройка, извлечение, изменение или удаление параметров командной строки в файле Boot.ini в Windows XP |
| call | вызов одного пакетного файла из другого |
| cacls | просмотр и редактирование изменение таблиц управления доступом (ACL) к файлам |
| calc | запуск приложения Калькулятор |
| cd | вывод имени или изменение текущей папки |
| charmap | таблица символов |
| chcp | вывод или изменение активной кодовой страницы |
| chdir | вывод или смена текущей папки |
| copy | копирование одного или нескольких файлов |
| chkdsk | проверка диска на ошибки и вывод статистики |
| chkntfs | вывод или изменение параметров проверки диска во время загрузки |
| ciddaemon | сервис индексации файлов |
| cipher | шифрование файлов и папок в NTFS |
| cleanmgr | утилита Очистка диска |
| cls | очистка экрана |
| cmd | запуск еще одного интерпретатора командной строки Windows |
| compmgmt.msc | открытие консоли Управление компьютером |
| color | установка цветов переднего плана и фона по умолчанию |
| comexp.msc | службы компонентов |
| comp | сравнение содержимого двух файлов или двух наборов файлов |
| compact | просмотр и изменение параметров сжатия файлов в разделах NTFS |
| compmgmt.msc | Управление компьютером |
| computerdefaults | выбор приложений по умолчанию |
| control | Панель управления |
| control admintools | администрирование |
| control desktop | настройка экрана и персонализация |
| control folder | свойства папок в параметрах Проводника |
| control fonts | шрифты |
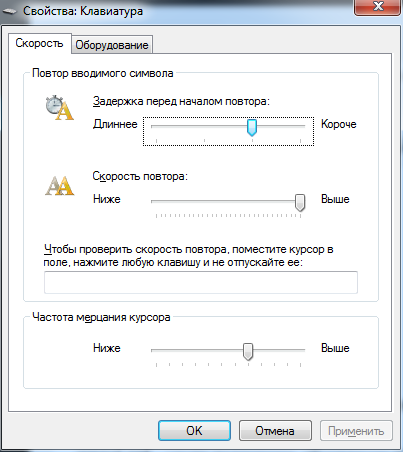
| control keyboard | открытие окна свойства клавиатуры |
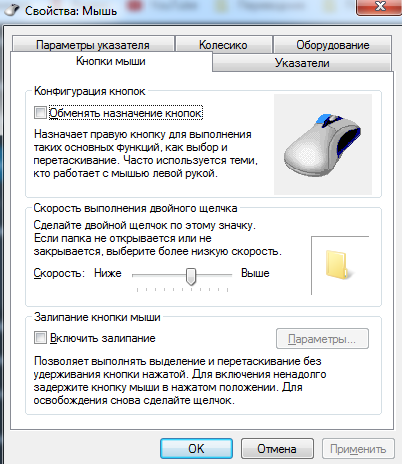
| control mouse | свойства мыши |
| control printer | устройства и принтеры |
| control schedtasks | Планировщик заданий |
| control userpasswords2 | управление учетными записями пользователей |
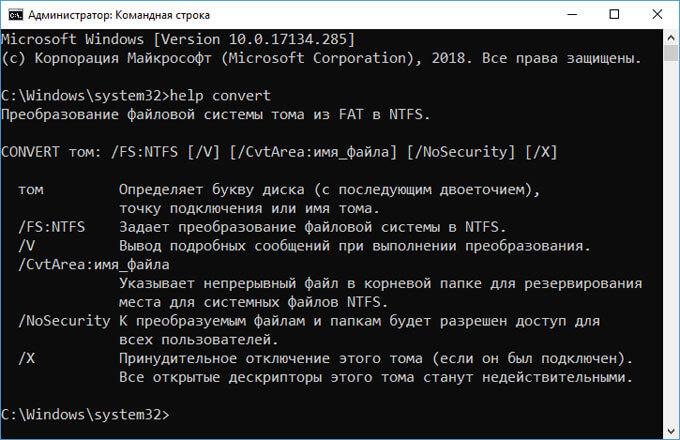
| convert | преобразование файловой системы тома FAT в NTFS (не работает на текущем диске) |
| copy | копирование файлов в другое место |
| credwiz | архивация и восстановление имен пользователей и паролей |
| date | вывод или установка текущей даты |
| debug | средство отладки и редактирования программ |
| defrag | запуск дефрагментации дисков |
| del | удаление одного или нескольких файлов |
| desk.cpl | настройка разрешения экрана |
| devicepairingwizard | добавление нового устройства |
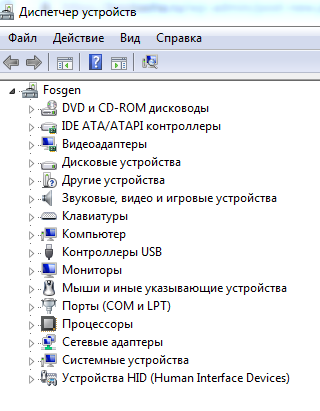
| devmgmt.ms | Диспетчер устройств |
| dfrgui | оптимизация дисков (дефрагментация) |
| dir | вывод списка файлов и подпапок из указанной папки |
| diskmgmt.ms | открытие оснастки Управление дисками |
| diskpart | отображение и настройка свойств раздела диска |
| diskperf | включение или отключение счетчика производительности |
| doskey | редактирование командной строки, повторный вызов команд Windows, создание макросов |
| dpiscaling | настройка параметров дисплея |
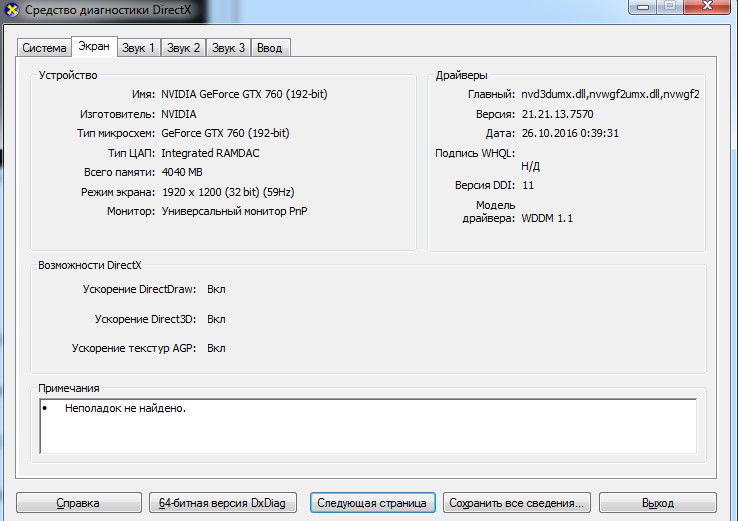
| dxdiag | средство диагностики DirectX |
| echo | вывод сообщений и переключение режима отображения команд на экране |
| endlocal | завершение локальных изменений среды для пакетного файла |
| erase | удаление одного или нескольких файлов (затирание) |
| esentutl | утилиты технического обслуживания баз данных Microsoft Windows |
| eudcedit | редактор личных знаков |
| eventcreate | создание запись об особом событии в указанном журнале событий |
| eventvwr.msc | просмотр событий |
| expand | распаковка сжатых файлов |
| explorer | Проводник Windows |
| fc | сравнение файлов или наборов файлов, вывод различий между ними |
| find | поиск текстовой строки в одном или в нескольких файлах |
| findstr | поиск текстовой строки в файле |
| finger | сведения о пользователях указанной системы, на которой запущена служба Finger |
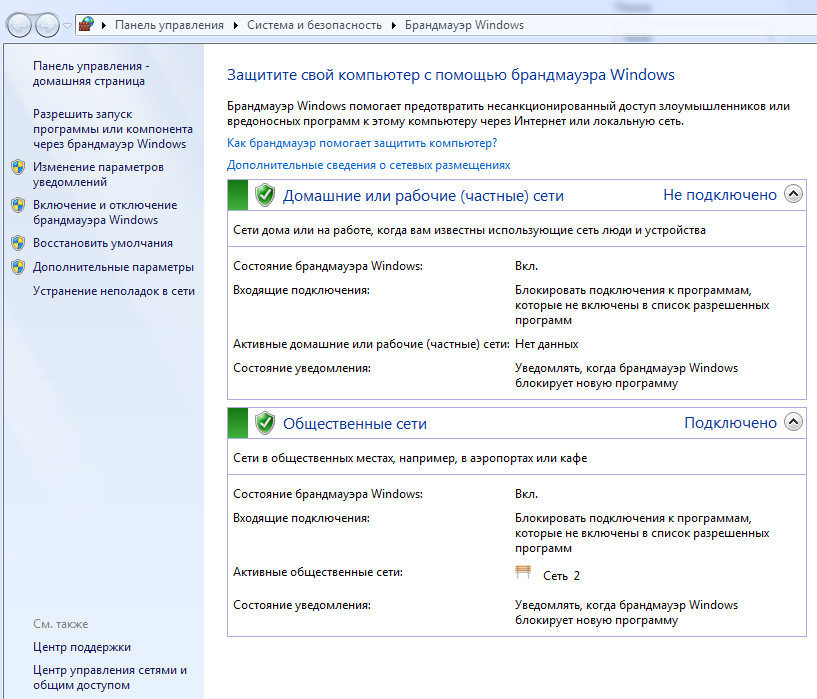
| firewall.cpl | Брандмауэр Защитника Windows |
| for | запуск указанной команды для каждого файла в наборе |
| format | форматирование диска |
| fsmgmt.msc | общие папки |
| fsquirt | передача файлов по Bluetooth |
| fsutil | показ и настройка свойств файловой системы |
| ftype | вывод или изменение типов файлов при сопоставлении имен файлов |
| ftp | обмен файлами по FTP |
| goto | передача управления в указанную строку пакетного файла |
| getmac | отображение MAC-адресов одного или нескольких сетевых адаптеров |
| gpresult | информация о групповой политике для компьютера или пользователя |
| graftabl | отображение расширенного набора символов в графическом режиме Windows |
| gpedit.msc | Редактор локальной групповой политики |
| gpupdate | обновление параметров нескольких групповых политик |
| hdwwiz | мастер установки оборудования |
| icacls | отображение, изменение, архивация, восстановление списков ACL для файлов и каталогов |
| iexpress | создание самораспаковывающегося архива |
| if | условная обработка в пакетных программах (файлах) |
| ipconfig | информация о IP адресе |
| joy.cpl | игровые устройства |
| label | создание, изменение и удаление меток тома для дисков |
| lodctr | обновление параметров реестра, относящееся к производительности счетчиков |
| logman | управление службой «Оповещения и журналы производительности» |
| logoff | завершение сеанса |
| lpksetup | установка или удаление языков интерфейса Windows |
| lusrmgr.msc | локальные пользователи и группы |
| magnify | запуск приложения Лупа |
| main.cpl | свойства мыши |
| makecab | архивация файлов в CAB архив |
| md | создание каталога (папки) |
| mdsched | средство проверки оперативной памяти на ошибки |
| mkdir | создать каталог (папку) |
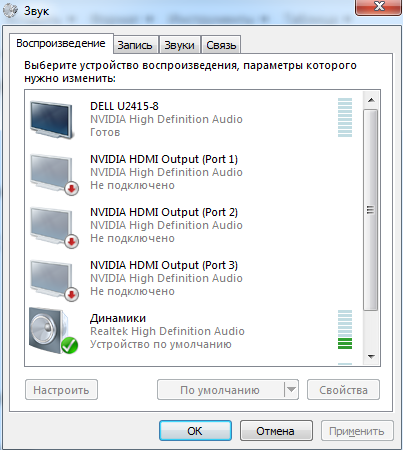
| mmsys.cpl | свойства звука |
| mode | конфигурирование системных устройств |
| mofcomp | 32-разрядный компилятор |
| more | последовательный вывод данных по частям размером в один экран |
| mountvol | создание, просмотр и удаление точек подключения |
| move | перемещение одного или нескольких файлов из одной папки в другую |
| mrinfo | работа с многоадресными сообщениями |
| mrt | запуск средства удаления вредоносных программ Malicious Software Removal Tool |
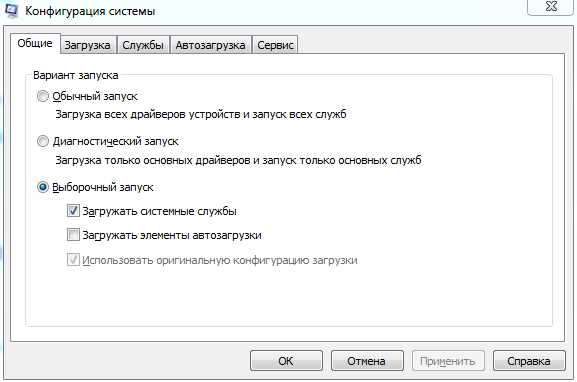
| msconfig | конфигурация системы |
| msg | отправка сообщений пользователю |
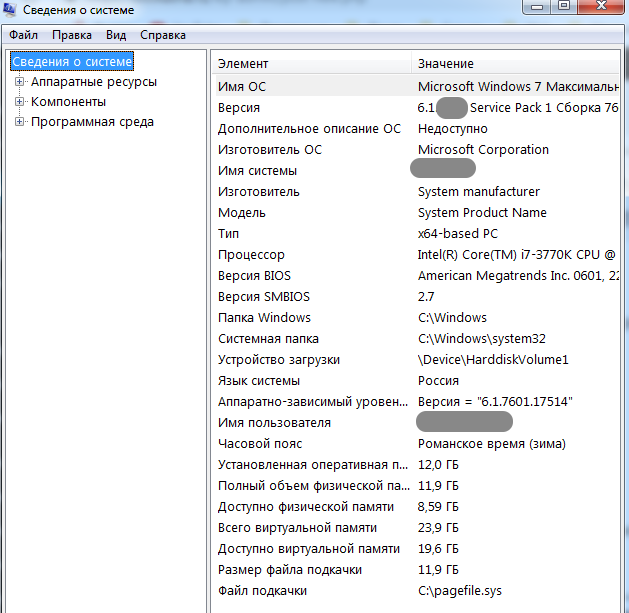
| msinfo32 | сведения о системе |
| mspaint | запуск графического редактора Paint |
| msra | удаленный помощник Windows |
| net | управление сетевыми ресурсами |
| ncpa.cpl | сетевые подключения |
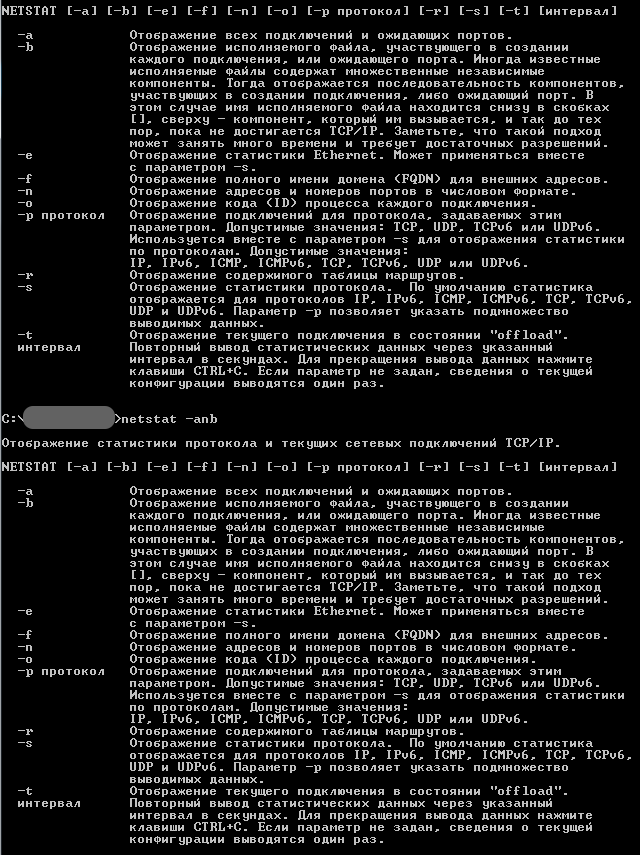
| netstat | отображение статистики протоколов и текущих сетевых подключений TCP/IP |
| netplwiz | управление учетными записями пользователей |
| notepad | запуск программы Блокнот |
| odbcconf | настройка драйвера ODBC |
| openfiles | вывод списка открытых файлов и папок, открытых в системе |
| optionalfeatures | включение или отключение компонентов Windows |
| osk | запуск экранной клавиатуры |
| path | вывод или установка пути поиска исполняемых файлов |
| pause | приостановка выполнения пакетного файла, вывод сообщения |
| perfmon | системный монитор |
| resmon | монитор ресурсов |
| popd | восстановление предыдущего значения текущей папки, сохраненное командой pushd |
| prompt | изменение командной строки Windows |
| pushd | сохранение текущего каталога, а затем изменение каталога |
| ping | отправка пакетов на указанный адрес |
| powercfg | управление параметрами электропитания системы |
| печать текстового файла | |
| qprocess | отображение информации о процессах |
| qwinsta | отображение информации о сеансах служб удаленных рабочих столов |
| rd | удаление каталога |
| recover | восстановление сохранившихся данных на повреждённом диске |
| recdisc | создание диска восстановления Windows |
| reg | команда для работы с реестром |
| regedit | Редактор реестра |
| rem | помещение комментария в пакетный файл или в файл config.sys |
| ren | переименование файлов и папок |
| rename | переименование файлов и папок |
| rmdir | удаление каталога |
| replace | замена файлов |
| rstrui | восстановление Windows из точек восстановления системы |
| runas | для использования приложений от имени другого пользователя |
| rwinsta | сброс значений подсистем оборудования и программ сеанса в начальное состояние |
| secpol.msc | локальная политика безопасности |
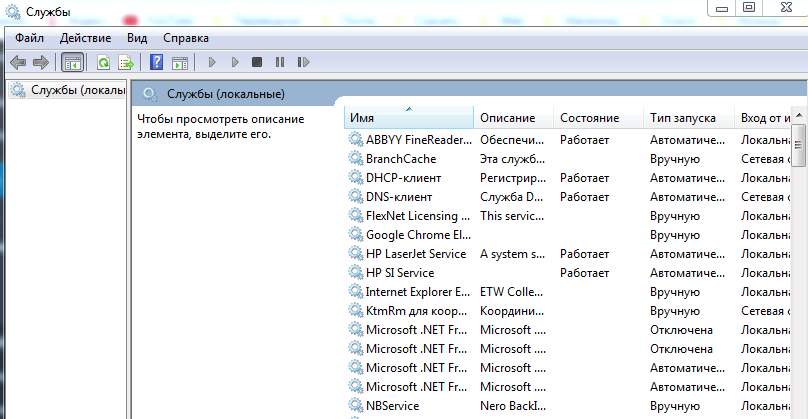
| services.msc | службы |
| set | вывод, установка и удаление переменных среды Windows |
| setlocal | начало локальных изменений среды в пакетном файле |
| sc | отображение и настройка служб (фоновых процессов) |
| sfc | проверка целостности всех защищенных системных файлов и замена неправильных |
| sigverif | проверка подписи файла |
| shift | изменение содержимого заменяемых параметров для пакетного файла |
| slui | активация Windows |
| sndvol | микшер громкости |
| start | запуск указанной программы или команды в отдельном окне |
| schtasks | запуск программ и выполнение команд на ПК по расписанию |
| sdbinst | установщик базы данных совместимости |
| shutdown | перезагрузка или выключения компьютера |
| sort | программа сортировки |
| subst | сопоставление имени диска указанному пути |
| sysdm.cpl | свойства системы |
| systeminfo | информация о конфигурации операционной системы |
| taskkill | принудительное завершение процесса или приложения |
| tasklist | показ всех задач, выполняемых в данный момент, включая службы |
| taskmgr | Диспетчер задач |
| tcmsetup | установка клиента телефонии |
| time | просмотр и изменение текущего времени |
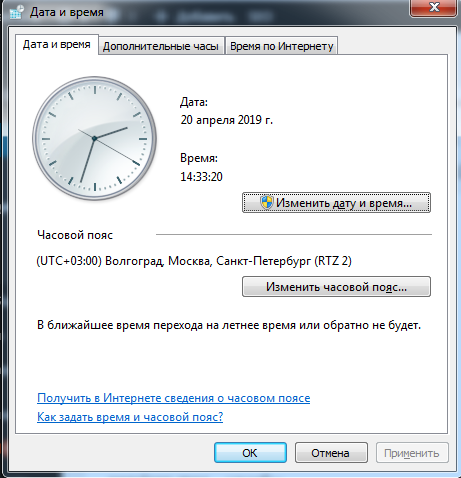
| timedate.cpl | настройка времени и даты |
| title | назначение заголовка текущего окна интерпретатора командной строки |
| tracert | трассировка маршрута к указанному узлу |
| tree | графическое отображение структуры заданного диска или папки |
| tscon | присоединение сеанса пользователя к сеансу удаленного рабочего стола |
| tsdiscon | отключение сеанса служб удаленных рабочих столов |
| tskill | прекращение процесса |
| type | вывод содержимого текстовых файлов |
| typeperf | вывод сведений о производительности на экран или в журнал |
| utilman | центр специальных возможностей |
| ver | вывод сведений о версии Windows |
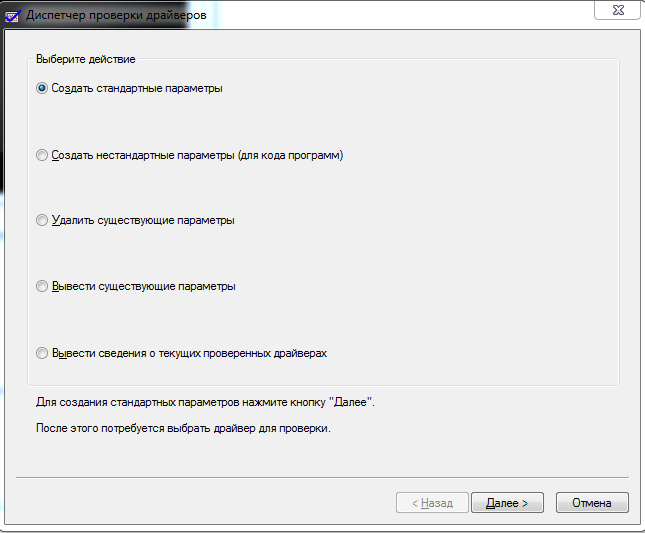
| verifier | диспетчер проверки драйверов |
| verify | установка режима проверки в Windows правильности записи файлов на диск |
| vol | вывод метки и серийного номера тома для диска |
| vssadmin | программа командной строки для администрирования службы теневого копирования тома |
| w32tm | показ текущих параметров для отображения часового пояса |
| winver | информация о версии Windows на экране |
| wmic | сведения об инструментарии WMI в интерактивной командной оболочке |
| write | текстовый редактор WordPad |
| wscui.cpl | центр безопасности и обслуживания |
| wusa | автономный установщик обновлений |
| xcopy | копирование файлов и дерева папок |
Выводы статьи
Командная строка в операционной системе Windows позволяет пользователю управлять компьютером без использования графического интерфейса. Для выполнения определенных действий на ПК, необходимо ввести в интерпретатор командной строки специальные команды. В этой статье опубликована таблица со списком самых востребованных команд для командной строки Windows.
Похожие публикации:
- Восстановление Windows через командную строку
- Сравнение версий Windows 10: таблица
- Как перейти с 32 битной на 64 битную версию Windows
- Как узнать версию Windows
- Как отключить обновления в Windows 10 — 5 способов
- Как открыть командную строку Windows?
- Параметры команд и получение помощи
- Запуск системных компонентов и программ из командной строки
- Работа с файлами и папками из командной строки
- Востребованные сетевые команды командной строки
- Редко используемые, но очень полезные команды
Выполнение множества задач в операционных системах Windows возможно не только при использовании привычного графического пользовательского интерфейса, но и при помощи интерпретатора командной строки (командной строки, консоли). Через него можно изменять различные системные параметры, управлять файлами и папками, запускать системные компоненты и любые программы, выполнять иные операции. Рассмотрим наиболее важные команды командной строки Windows, которые могут пригодиться любому пользователю.
Как открыть командную строку Windows?
Некоторые из консольных команд можно выполнить лишь из учетной записи администратора. Потому лучше сразу запомнить, как запускать интерпретатор с максимальным количеством прав доступа к системе. В ОС Windows 7/8/10 делается это просто:
- Откройте «Поиск» в/около меню «Пуск».
- Впишите поле поиска «Командная строка».
- В результатах поиска отобразится нужная нам программа. Кликните по ней правой кнопкой мыши, затем выберите из выпадающего меню пункт «Запустить от имени администратора».
Но для выполнения простых команд консоль Windows можно запускать и без прав администратора. Проще всего это сделать следующим образом:
- Нажмите на клавиатуре клавиши «Win» и «R».
- Откроется окно «Выполнить».
- Впишите в него команду cmd и нажмите «ОК».
Так или иначе, системное приложение «Командная строка Windows» будет запущена и готова выполнению пользовательских команд:
Параметры команд и получение помощи
Прежде чем приступать к изучению команд, следует понимать два важных момента:
- У многих команд существуют изменяемые параметры, уточняющие выполнение командой той или иной функции.
- По любой команде можно получить помощь прямо в окне интерпретатора. Для этого следует сразу после команды вписать «/?«, что также является параметром.
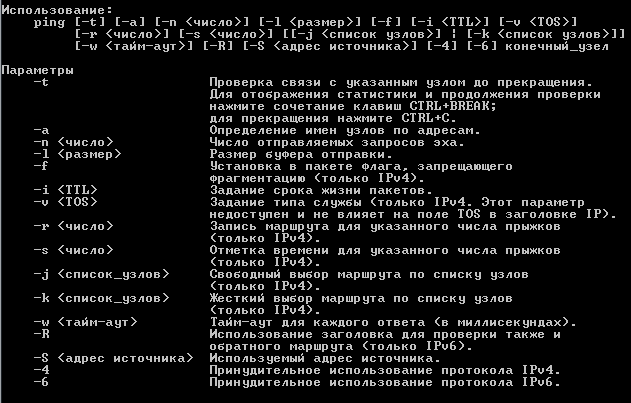
Возьмем, к примеру, одну из наиболее востребованных команд ping. Впишите в консоль следующую строку:
ping /?
Подобным способом можно получить справку по большинству команд (в основном по тем, у которых имеются атрибуты).
Запуск системных компонентов и программ из командной строки
Здесь стоит отметить, что запускать системные компоненты и программы все же проще не напрямую из командной строки, а из ранее упомянутого приложения «Выполнить». Но разницы в синтаксисе (написании) самих команд никакой нет. В обоих случаях после ввода команды достаточно нажать «Enter».
Вот список наиболее востребованных команд для запуска системных приложений и компонентов:
- control — запуск «Панели управления Windows».
- regedit — запуск «Редактора реестра».
- devmgmt.msc — запуск «Диспетчера устройств».
- taskmgr — запуск «Диспетчера задач».
- services.msc — запуск приложения «Службы».
- appwiz.cpl — «Программы и компоненты» («Установка и удаление программ»).
И это далеко не полный список команд запуска системных приложений и компонентов, а лишь самые востребованные у нас — обычных пользователей.
А вот 4 команды для запуска предустановленных (стандартных) в Windows программ:
- calc — запуск «Калькулятора».
- mspaint — запуск графического редактора «Paint».
- notepad — запуск текстового редактора «Блокнот».
- wordpad — запуск текстового редактора «WordPad»
Вообще, из командной строки можно запустить любую другую программу или файл. Рассмотрим, как это сделать, а заодно познакомимся с некоторыми командами по управлению файлами и папками.
Работа с файлами и папками из командной строки
Бывают ситуации, когда невозможно запустить стандартный файловый менеджер «Проводник Windows». Например, из-за действия вирусов-блокировщиков или при системных сбоях. В любом случае все, что можно сделать при помощи «Проводника», можно сделать и при помощи командной строки. Начнем с самого простого — просмотра содержимого папок.
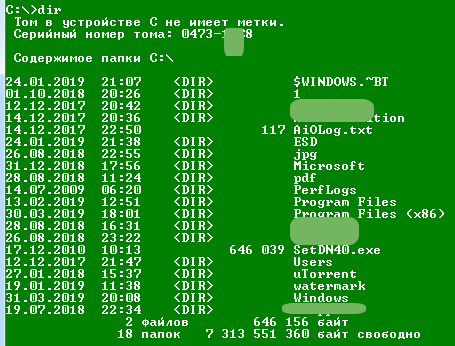
Просмотр содержимого папки. При запуске командной строки перед мигающим курсором можно увидеть адрес расположения папки учетной записи на жестком диске. В нашем случае — это «C:Usersvzgn»:
Давайте, выведем на экран список все других объектов (файлов и папок), содержащихся в данной папке. Для этого используйте команду dir:
Объекты, напротив которых написано <DIR> — это папки, все остальное — файлы (напротив них указан размер в байтах).
Команду dir можно применять вообще папкам, расположенным в вообще любом месте на жестком диске. Для этого после команды следует указать путь до каталога. К примеру, для просмотра содержимого папки «Windows» на диске «C:» следует ввести команду:
dir c:windows
Запомните одно простое правило. Если в именах папок/файлов присутствуют пробелы, их следует писать в двойных («имя папки или файла») кавычках.
Открытие файла из командной строки. Для открытия файла достаточно вписать его полное название вместе с расширением в командную строку. Что не вводить имя файла целиком, используйте клавишу «Tab» (с ее помощью можно поочередно перебирать имена всех объектов в текущей папке).
В нашем случае был открыт файл .pgAdmin4.startup.log при помощи «Блокнота». Если бы это был музыкальный файл, запустился бы аудиопроигрыватель, если DOC/DOCX-файл — редактор «MS Word» и т.д. Таким образом, открытие файла в командной строке равнозначно двойному клику по файлу в «Проводнике Windows».
Переход в другую папку. Для перехода в папку используется команда cd, после которой следует прописать путь к открываемой папке либо просто ее имя (если она расположена в нашем текущем местоположении на жестком диске).
Перейдем в папку «Music». Т.к. она находится в текущем каталоге, достаточно ввести в консоль:
cd music
Теперь наше местоположение изменилось на «C:UsersvzgnMusic».
Давайте, перейдем в какую-нибудь папку, расположенную на другом локальном диске. Это можно сделать несколькими способами, но воспользуемся самым легким для запоминания.
- Для начала перейдем в сам локальный диск (изменим наше местоположение). Для этого достаточно использовать (независимо от текущего местоположения) команду e:. Вместо e можно использовать любую другую букву локального диска (или даже флешки, например):
- Допустим, нам известно, что на диске «E» существует папка «Install«, а в ней — пака «Web«. Перейти в нее можно одной командой:
cd e:installweb
Запуск/открытие программы/файлы в другой папке или на другом диске. Запустим программу, расположенную где-нибудь глубоко на диске. Для запуска файла или программы можно просто указать полный путь до него. Текущее местоположение в этом случае не имеет значения. Запустим, например, текстовый редактор «Notepad++» одной командой:
C:»Program Files»Notepad++notepad++.exe
Обратите внимание, что имя папки «Program Files» взято в кавычки, т.к. в нем присутствует пробел.
Создание, удаление и переименование файлов и папок. Из командной строки можно выполнить все эти операции над файлами и папками.
- Создание простого текстового файла — copy nul простой_текстовый_файл.txt. Перед названием файла можно указать путь до конечной папки, в которой тот будет создан (если не указать, файл создастся в текущей папке).
- Создание папки — mkdir папка. Папка также создается в текущем местоположении.
- Удаление файла (или нескольких) — del простой_текстовый_файл.txt (если требуется удалить несколько файлов, просто вписываем их имена друг за другом через пробел). Удаляем созданный ранее файл.
- Удаление папки — rmdir папка. Удаляем созданную ранее папку.
- Переименование папки/файла — ren простой_текстовый_файл.txt новое_имя_файла.txt или ren папка новое_имя_папки. Переименуем созданный файл и папку.
Через командную строку можно выполнить и ряд других операций над файлами и папками, включая копирование, перемещение, применение/изменение атрибутов (скрытый, системный, только для чтения и т.д.), слияние и т.д.
Востребованные сетевые команды командной строки
Из командной строки Windows можно взаимодействовать с сетевыми подключениями, изменять их настройки, просматривать различную информацию и многое другое. Рассмотрим наиболее востребованные сетевые команды.
Команда ping
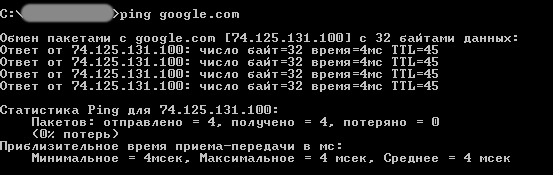
Наверное, это самая популярная команда среди пользователей ОС Windows (как, впрочем, и других операционных систем). Предназначена она для проверки доступности и качества связи между компьютером и целевым IP-адресом. Также команда может применяться для определения IP-адреса сайта по доменному имени сайта и для выполнения других задач.
Определим, есть ли связь с каким-нибудь IP-адресом. Пусть это будет — 173.194.73.139 (IP-адрес поисковой системы Google). Вводим следующую команду:
ping 173.194.73.139
Как видим, обмен пакетами с указанным IP-адресом осуществляется, значит, связь есть. Если бы ее не было, картина была бы следующая (уберем из IP Google последнюю цифру):
«100% потерь» означает, что связь установить не удалось.
А теперь определим IP-адрес сайта по его доменному имени. Возьмем адрес softsalad.ru:
ping softsalad.ru
На изображении выше можно увидеть IP-адрес сайта, определенный по его доменному имени.
Команда tracert
А эта команда применяется для отслеживания сетевого маршрута от компьютера до целевого IP-адреса (можно использовать и доменное имя сайта):
tracert softsalad.ru
Видите, чтобы «достучаться» до сайта компьютеру в данном случае потребовалось обратиться к 12 промежуточным IP-адресам (ваш провайдер, сервер сайта и т.д.).
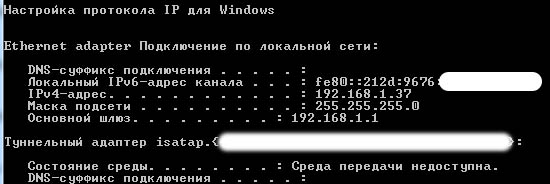
Команда ipconfig
С помощью этой команды можно получить информацию о настройках IP-протокола компьютера (или, грубо говоря — настройки сетевых карт). Воспользуемся данной командой с атрибутом /all, который позволит вывести более подробную информацию:
ipconfig /all
Команда getmac
Если требуется определить только MAC-адрес сетевой карты, используем эту команду без всяких атрибутов:
getmac
Редко используемые, но очень полезные команды
При помощи командной строки можно выполнять различные интересные функции (большинство приведенных ниже команд работает только с правами администратора):
Превращаем ноутбук в Wi-Fi-роутер (включение раздачи интернета с ноутбука или настольного компьютера с Wi-Fi-адаптером)
Для реализации этой затеи нужно поочередно выполнить три несложные команды:
- netsh wlan set hostednetwork mode=allow
- netsh wlan set hostednetwork mode=allow ssid= MiWiFi key= MiWiFipassword keyUsage=persistent. Вместо MiWiFi и MiWiFipassword можно использовать свои фразы. Первый параметр задает имя беспроводной сети, второй — пароль (должен состоять из 8 символов или более).
- netsh wlan start hostednetwork.
Если после выполнения каждой команды вы видите сообщения, аналогичные тем, что приведены на изображении выше, значит, все прошло успешно. Теперь к ноутбуку можно подключиться, например, с телефона так же, как и к обычному Wi-Fi-роутеру.
Удалениям службу Windows (или любую другую) через командную строку
Если попробовать удалить службу через штатное приложение «Службы», то ничего не получится (в нем попросту не предусмотрено такой функции). Однако это бывает необходимым, особенно после установки различных программ, которые устанавливают службы, но «забывают» их удалять при деинсталляции. Это легко реализуется через командную строку. Однако для начала необходимо узнать имя службы, и это можно сделать через стандартное Windows-приложение:
- Запустите программу «Службы», используя команду msc.
- Найдите в отобразившемся списке службу, которую необходимо удалить, и кликните по ней два раза мышкой:
- Нас интересует текст в блоке «Имя службы».
- Теперь вернитесь в окно командной строки и впишите в него команду:
sc delete имя_службы
- Подставьте вместо фразы «имя_службы» имя удаляемой службы. Если оно содержит пробелы, как в нашем случае, заключите имя службы в кавычки.
- Служба удалена.
Выключаем/перезагружаем/отправляем в сон/гибернацию компьютер с задержкой. Если необходимо выключить, перезагрузить или отправить в сон компьютер с задержкой по времени, не обязательно использовать какие-либо сторонние программы — все можно сделать при помощи командной строки. Для этого достаточно использовать команду:
shutdown /s /t 60 /f
В данном случае компьютер будет выключен (параметр «/s«) через 60 секунд (параметр «/t 60«) с принудительным завершением работы всех приложений без предупреждения пользователя (параметр «/f» — обязательный при использовании таймера «/t«).
Вместо выключения компьютера «/s» использовать:
- /l — завершение сеанса (выход из учетной записи пользователя с блокировкой, если для входа требуется пароль).
- /r — перезагрузка компьютера.
- /hybrid /s — «отправка» компьютера в сон (параметр «/s» использовать обязательно).
- /h — режим гибернации (или режим максимального энергосбережения, при котором ключевые компоненты компьютера остаются включенными).
Для выключения компьютера, например, через 2 часа следует указывать в параметре «/t» число 7200 (1 час равен 3600 секундам).
Сразу после выполнения команды на экран будет выведено уведомление:
Выполнение команды всегда можно отменить (если была использована задержка), воспользовавшись:
shutdown /a
Просмотр списка запущенных процессов и завершение работы любого из них. Если по каким-то причинам не удается запустить «Диспетчер задач», но имеется доступ к командной строке, запущенный процесс может быть снят при помощи специальных команд:
- Сначала выведем на экран список всех запущенных процессов при помощи команды tasklist:
- Нас интересует идентификатор «PID» завершаемого процесса. Возьмем для примера PID процесс «NVDisplay.Container.exe» — 1100.
- Для завершения его работы используем команду taskkill /pid 1100 /f (параметр «/f» необходим для принудительного завершения работы процесса).
Чиним интернет при помощи командной строки. Разнообразные неполадки с сетевыми подключениями можно устранить «одним махом» через командную строку путем сброса настроек TCP/IP (не будем вдаваться в подробности, но если вам интересно, об это можно почитать тут — Netsh Winsock — что это и зачем нужно?.
Для выполнения этой задачи нужно поочередно ввести две команды:
netsh int ip reset
netsh winsock reset
Перезагружаем компьютер для применения изменений.
Команды Windows для работы с сетью
ipconfig – информация об ip адресах (локальная сеть, DNS, маска, шлюз)
ipconfig /displaydns – очистить кэш DNS
ipconfig /flushdns – показывает содержание кэш DNS
inetcpl.cpl — настройка и свойства интернета
ping — проверяет связь с указанным узлом
Например,
ping google.com
ping google.com -t
ping 127.0.0.1
arp -a — выводит содержание таблицы ARP хоста
arp -d — сброс всей таблицы ARP хоста
getmac — получить MAC-адрес сетевой карты XX-XX-XX-XX-XX-XX
ncpa.cpl – сетевые подключения
netstat -rn – показывает таблицу маршрутизации хоста
netstat – открытые IP адреса с портами
net stop was /y — отключение портов
netsh winhttp show proxy — отображает текущее состояния прокси
netsh winhttp set proxy 127.0.0.1 — установка прокси
netsh winhttp reset proxy — сбор настроек proxy
mstsc — подключение к удалённому рабочему столу
shutdown.exe -r -t 30 -f -m \192.168.111.132 – перезагрузка удаленного компьютера
ftp – команда, для работы с ftp протоколом
shutdown -s – выключить компьютер
shutdown -r – перезагрузка компьютера
tskill chrome — закрывает процессы из cmd
%systemroot%system32shutdown.exe -r -t 30 – создание ярлыка
Команды для работы с дисками и файловой системой
cd .. – выйти из текущей директории;
cd %systemroot% — перейти к папке C:WINDOWS
cd /d C: — перейти на диск C:
G: — перейти на другой диск, например на флешку
md file.txt – создание в текущей директории файла file.txt
mkdir — команда создаёт каталог, аналог команды md
RENAME [hdd:][path]old_file new_file — переименование файла
del file.txt – удаление файла или папки, в данном случае удаление файла file.txt
RMDIR [/S] [/Q] [hdd:]path — удаление дерева каталога или директории
dir – выводит информацию о файлах и папках (размер файла, названия файлов и папок, дата)
diskmgmt.msc – управление дисками
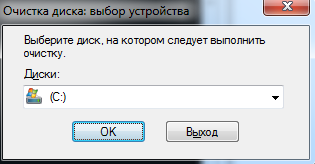
cleanmgr – очистка диска, выбор устройства для очистки
sfc /scannow – проверка и восстановления системных файлов ОС
CHKDSK F — стандартная утилита windows для проверки диска, ключ F проверяет и исправляет ошибки на hdd или флешки, ключ R — поиск и исправление повреждённых секторов
chkdsk c: /f — этой командой можно воспользоваться, если нет доступа к файлу или папки на флешки, при этом, если ещё появляется сообщение «файл или папка повреждены чтение невозможно»
RECOVER [имя_диска:][путь_к_файлу]имя_файла — восстановление данных на повреждённом диске
reagentc /disable — при загрузке windows 7, отключает средства восстановления системы (для выполнения команды нужны дополнительные привилегии)
Iexpress — утилита IExpress Wizard для сжатия файлов в exe-файл
copy /b old_capture.jpg+Doc.rar new_capture.jpg — спрятать информацию внутри файла jpg old_capture.jpg и Doc.rar в новый файл new_capture.jpg
Базовые команды cmd
winver – версия ОС Windows
msconfig — конфигурация ОС windows
msinfo32 – отображает сведения об ОС и компьютере
prompt $t – отображает системное время в формате 20:12:12,18
date — установка новой даты, также отображает текущую дату
timedate.cpl – дата и время, дополнительные часы, время по интернету
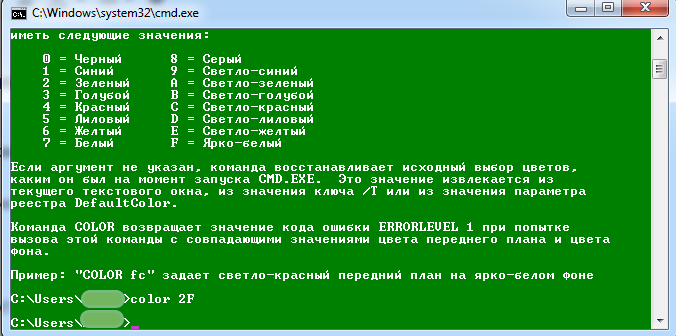
color 2F – параметры цвета фона и шрифтов (в данном примере фон зелёный, шрифт — белый);
regedit – редактор реестра ОС
taskmgr – диспетчер задач
control userpasswords2 — учетные записи пользователей
control – панель управления
services.msc – службы
devmgmt.msc – диспетчер устройств
dxdiag -средство диагностики DirectX, драйверы
verifier – диспетчер проверки драйверов
mmsys.cpl – звук, запись, воспроизведение, динамики
appwiz.cpl – программы и компоненты, установка и удаление программ
control printers – устройства и принтеры
desk.cpl – свойство и разрешение экрана
control folders – параметры папок, вид, поиск
powercfg.cpl – электропитание (выбор плана электропитания)
control fonts – установленные шрифты
control mouse – свойство мышки, скорость
control keyboard – свойство клавиатуры, частота мерцания курсора
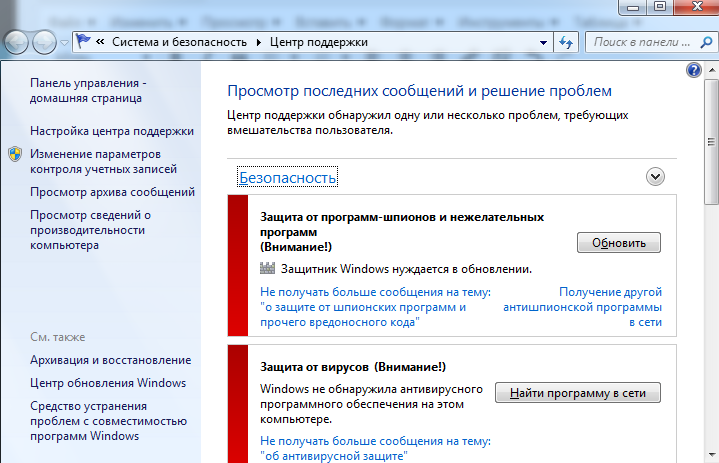
wscui.cpl – центр поддержки, обновление Windows
firewall.cpl – брандмауэр ОС Windows
explorer – проводник ОС Windows
logoff –выйти из ОС Windows
CLS — очистить экран
exit — выйти из cmd
Дополнительные команды для вызова стандартных программ Windows
notepad – блокнот
mspaint.exe – paint (рисование)
magnify – экранная лупа (увеличение масштаба экрана)
charmap – таблица символов
eudcedit – редактор личных знаков и символов
Narrator – экранный диктор
joy.cpl – игровые устройства
Команды Windows для администрирования
rstrui.exe — восстановление системы
control admintools — администрирование системы (инструменты)
odbcad32 — администратор источников данных ODBC в windows
gpedit.msc — редактор локальной групповой политики
secpol.msc — локальная политика безопасности в ОС windows
lusrmgr.msc — локальные пользователи и группы
sigverif — проверка цифровой подписи файлов
certmgr.msc — зарегистрированные сертификаты текущего пользователя в системе
mmc — корень консоли управления windows
compmgmt.msc — управление компьютером
wmimgmt.msc — корень консоли элемент управления WMIWindows
rsop.msc — результирующая политика windows
cliconfg — программа сетевого клиента SQL Server
shrpubw — мастер создания общих ресурсов ОС windows
syskey — защита базы данных учетных записей Windows
wscript — параметры сервера сценариев ОС Windows на языках JScript или VBScript
control schedtasks — планировщик заданий windows
eventvwr.msc — просмотр событий (журнал событий)
fsmgmt.msc — общие папки
perfmon.msc — системный монитор
dcomcnfg — службы компонентов, установленных в ОС
Определить кодировку cmd:
chcp
Например, чтобы поменять кодировку в windows на UTF-8 (по умолчанию стоит кодировка 866)
chcp 65001
Историю открывавшихся файлов в Windows 7
%APPDATA%/Microsoft/Windows/Recent
Путь к временным файлам (temp) на windows 7,8,10
C:Usersимя учётной записиAppDataLocalTemp
C:Usersимя учётной записиAppDataLocalTemporary Internet Files
Путь к временным файлам (temp) для браузера Google Chrome
C:Documents and SettingsИмя пользователяLocal SettingsApplication DataGoogleChromeUser DataDefaultCache
Путь к закладкам в браузере Google Chrome (Bookmarks)
C:UsersИмя пользователяAppDataLocalGoogleChromeUser DataDefault
Путь к временным файлам (temp) для браузера Internet Explorer
C:Documents and SettingsИмя пользователяLocal SettingsTemporary Internet Files
Путь к файлам Telegram
C:UsersUserAppDataRoamingTelegram Desktop
Принудительно удалить файл, пример
Del /F /Q /S d:/temp.exe
Нередко неопытные пользователи воспринимают командную строку Windows как нечто совершенно ненужное и отжившее свой век. Думать так — это большая ошибка. Значение командной строки или иначе консоли CMD трудно переоценить даже после того как она потеряла большую часть своих команд доступных в MSDOS. Достоинство командной строки заключается, прежде всего, в обеспечении прямого доступа к операционной системе и её скрытым возможностям, кроме того консоль CMD имеет в себе несколько полезнейших встроенных утилит предназначенных для работы с программными и аппаратными компонентами компьютера.
Быть асом командной строки совершенно не обязательно, тем не менее, есть команды, которые должен знать каждый уважающий себя пользователь Windows. Вот они.
Assoc
Большинство пользовательских файлов в операционной систем связаны с определёнными программами, которые обрабатывает их по умолчанию. Такая связь называется ассоциацией. Для её просмотра как раз и существует команда assoc. При её выполнении выводится список сопоставлений расширений и типов файлов. А ещё команда assoc позволяет изменять ассоциации.
Например командой assoc .html = txtfile для файлов с расширением HTML устанавливается тип файла txtfile (текстовый). Если же вам нужно узнать какой именно программой открываются файлы с таким расширением, используйте команду ftype txtfile.
Cipher
Эта команда предназначается для шифрования и дешифрования данных на дисках с файловой системой NTFS, но с таким же успехом она может использоваться для зачистки свободного дискового пространства. Пользоваться ей очень просто. Если вам нужно гарантированно удалить остатки всех ранее удалённых файлов на диске D, выполните в консоли команду cipher /w:D.
Driverquery
Полезная команда позволяющая просмотреть список всех установленных в операционной системе драйверов. При выполнении команды без параметров данные выводятся в виде отсортированного списка. Колонка «Модуль» содержит имена драйверов без расширения, колонка «Название» включает краткое описание драйвера, «Тип драйвера» — соответственно тип, «Дата ссылки» указывает на дату установки или последней модификации драйвера.
FC (File Compare)
Команда FC пригодится в основном кодерам, также она может использоваться теми юзерами, которым приходится работать с текстовыми файлами. Эта команда позволяет сравнивать содержимое двух файлов, отыскивая между ними несоответствия. Допустим, у вас имеются два файла file1.docx и file2.docx и вы хотите их сравнить. Выполните в консоли следующую команду:
fc /U «D:file1.docx» «D:file2.docx»
В данном примере мы сравнили два простых текстовых документа. Интерпретатор командной строки нашел несоответствие в одном из предложений и указал конкретное место. Команда FC также позволяет сравнивать бинарные файлы, файлы в кодировке юникод, определять число несоответствий и т.п. Если сравниваемые файлы окажутся идентичными, при выполнении команды FC будет выведено соответствующее сообщение.
Ipconfig
Полезная команда позволяющая определить текущие настройки протокола TCP/IP или попросту IP-адрес. Однако показывает она только внутренний IP-адрес, если же вы используете роутер и хотите узнать тот IP, с которым вы выходите в глобальную Сеть, лучше обратиться к помощи специальных онлайновых сервисов типа 2ip.ru.
Netstat
Эта команда выводит список всех текущих интернет-соединений. Используется она в основном администраторами для отображения TCP и UDP-соединений, прослушиваемых портов, таблиц маршрутизации и статистических данных для различных протоколов. Также может использоваться для поиска следов, оставляемых вирусами и прочими вредоносными объектами. Выполненная без параметров команда Netstat отображает тип соединения, локальный адрес, внешний адрес и текущее состояние.
Ping
Как и Netstat команда ping используется в основном системными администраторами. Служит она для диагностики компьютерных сетей. С её помощью можно определять доступность тех или иных ресурсов. Допустим вам нужно проверить доступность Google. Поскольку DNS сервер Google имеет адрес 8.8.8.8, в консоли CMD нужно выполнить команду ping 8.8.8.8.
Цифровой IP-адрес также может быть заменён текстовым URL-адресом — ping google.com. Если узел окажется недоступен будет выведено сообщение «превышен лимит ожидания», а количество потерь при этом составит 100 процентов.
Tracert
Ещё одна «сетевая» команда, предназначенная для диагностики сети (трассировки). Команда позволяет получить цепочку узлов, через которые проходит IP-пакет, адресованный конечному узлу. Используется системными администраторами для выявления неполадки, препятствующей доставке пакетов конечному узлу. Примером использования команды может послужить трассировка к узлу того же Google: tracert google.com.
Pathping
Работает эта команда примерно так же как и tracert, но в отличие от последней является более функциональной. Команда выполняет трассировку плюс отправку запросов на промежуточные узлы маршрута для сбора информации о задержках и потерях пакетов на каждом из них.
Powercfg
Мощная утилита командной строки, предназначенная для управления параметрами электропитания Windows. Выполняется только с параметрами. Выполненная с ключом /Q команда Powercfg выводит текущую конфигурацию схемы электропитания, с ключом /a выводит отчет об использовании электроэнергии в ноутбуках, с ключом –energy генерирует детальный текстовый лог о состоянии компонентов компьютера, включая аккумуляторные батареи. Также команда Powercfg может использоваться для создания резервных копий настроек электропитания и развёртывания их на новом оборудовании.
Shutdown
Эта команда используется для завершения сеанса пользователя, выключения, перезагрузки и перевода компьютера в режим гибернации. Поддерживает удалённое управление. Выполняется shutdown всегда с параметрами. Например, команда вида shutdown /s /t 0 приведёт к завершению работы открытых приложений и немедленному выключению компьютера. Посмотреть список доступных ключей можно выполнив в консоли shutdown /?.
Sfc (System File Checker)
Одна из самых полезных и нужных команд. Предназначается для обнаружения и восстановления повреждённых или модифицированных системных файлов Windows. Восстановление производится из резервных копий создаваемых самой операционной системой. Чтобы запустить сканирование системы с последующим восстановлением файлов выполните команду sfc с параметром /scannow. После завершения проверки потребуется перезагрузка компьютера. Выполнять эту команду нужно в консоли, запущенной от имени администратора.
Tasklist
Команда Tasklist делает ту же работу, что и Диспетчер задач. Выполненная без параметров она выводит список всех запущенных процессов выполняющихся на локальном или удалённом компьютере. При этом для каждого процесса отображается его название, идентификатор (PID), имя сессии, номер сеанса и выделенный объём оперативной памяти. Команда Tasklist поддерживает использование ключей и фильтров. Например, Tasklist /SVC выводит список процессов вместе со службами для каждого процесса в отдельности.
Taskkill
Если Tasklist просто выводит список запущенных процессов, то Taskkill завершает их работу в принудительном режиме. Правда для этого вам потребуется знать идентификатор завершаемого процесса или название исполняемого файла. Допустим, вам нужно принудительно закрыть Блокнот. Выполняем для начала команду Tasklist и смотрим PID процесса notepad.exe. В нашем случае он имеет значение 2580. Зная PID процесса его легко можно «убить». Сама же команда будет выглядеть так: Taskkill /PID 2580. Примерно так же сработает команда Taskkill /IM notepad.exe, только в этом примере будут завершены все экземпляры процесса notepad.exe.
Итог
На этом пока всё. Есть и другие полезные команды CMD, с которыми пользователям желательно было бы познакомиться, но о них мы расскажем в следующий раз. К таковым в частности относится Diskpart — мощный инструмент управления дисками и разделами не уступающий возможностями коммерческим программным продуктам типа Acronis Disk Director.
Имеет ли смысл изучать командную строку профессионально? Вряд ли, если только вы не собираетесь становиться программистом или системным администратором.
Впрочем, желающим освоить консоль CMD не мешало бы также обратить внимание на её продвинутый аналог — встроенную утилиту PowerShell.